About the distributed integration scheme
Kaspersky CyberTrace supports distributed Splunk environments. The integration scheme for distributed Splunk environments is called the distributed integration scheme.
About the apps and services used in the distributed integration scheme
In the distributed integration scheme, Kaspersky CyberTrace is divided into two apps and one service:
- Feed Service
This service matches Splunk events against Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds.
Feed Service sends the resulting events to a single indexer that keeps the index with events from Kaspersky CyberTrace.
This service can be installed on a separate computer.
- Kaspersky CyberTrace App Search Head (or Search Head App)
This app contains Kaspersky CyberTrace App dashboards, alert templates, and the lookup script.
This app is intended for installation on a Splunk instance that acts as a search head and sends search requests to the indexer that keeps the index with events from Kaspersky CyberTrace.
- Kaspersky CyberTrace App Forwarder (or Forwarder App)
This app contains rules for forwarding events from Splunk to Feed Service. It also receives events from Feed Service.
This app is intended for installation on Splunk instances that must forward events to Feed Service.
About the integration scheme variants
The following variants of the distributed integration scheme demonstrate a general approach to integrating Kaspersky CyberTrace with your distributed Splunk environment. Depending on how your distributed Splunk environment is organized, you may have to change or combine these variants.
One indexer, multiple forwarders variant
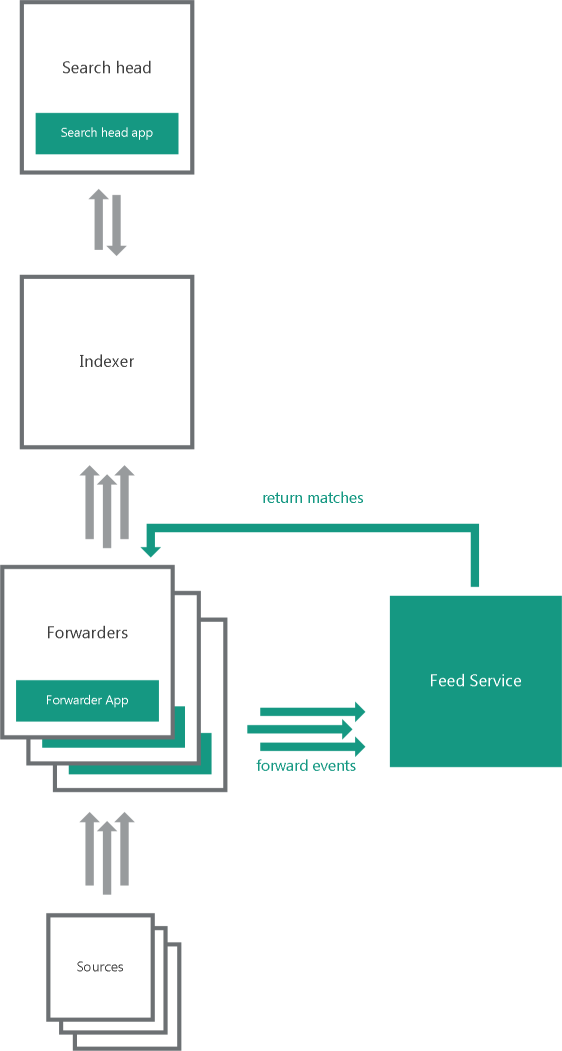
One indexer, multiple forwarders
In the one indexer, multiple forwarders variant, several heavy forwarders parse and send events directly to Feed Service. These forwarders must use Forwarder App. One of the forwarders receives matches from Feed Service. The forwarders send the matches to the indexers that store them in the index used by Kaspersky CyberTrace for Splunk Search Head App.
Multiple indexers, multiple forwarders variant
In the multiple indexers, multiple forwarders variant, several heavy forwarders parse and send events directly to Feed Service. These forwarders must use Forwarder App. One of the forwarders receives matches from Feed Service. The forwarders send the matches to the indexers that store them in the index used by Kaspersky CyberTrace App.
Default ports and addresses
By default, Forwarder App and Feed Service are configured to use certain addresses and ports for forwarding events and receiving matches. You must change these addresses and ports based on the organization of your distributed Splunk environment.
You must change the default addresses and ports that are used by Forwarder App and Feed Service.
By default, Forwarder App:
- Receives events at
:3000port. - Receives events from Kaspersky CyberTrace at
:9998port. These events are stored in themainindex. - Forwards events to
127.0.0.1:9999.
By default, Feed Service does the following:
- Receives events at
127.0.0.1:9999. - Sends its own events to
127.0.0.1:9998.
Event format
By default, Kaspersky CyberTrace App and Feed Service are configured to receive events in a certain format:
- Feed Service parses events with regular expressions defined in its configuration file (the regular expressions are also displayed in Kaspersky CyberTrace Web). These regular expressions are created for a specific format of inbound data. For example, the default regular expression for URLs will match a URL containing the protocol (for example, HTTP, HTTPS). If the URLs in the events generated by your devices do not contain the procotol, change the regular expression accordingly.
- The lookup script that comes with Kaspersky CyberTrace App (or Search Head App in the case of the distributed integration scheme) sends events to Feed Service in a format that matches the regular expressions used by Feed Service.