Contents
About Kaspersky CyberTrace
Welcome to Kaspersky CyberTrace documentation.
What is Kaspersky CyberTrace
Kaspersky CyberTrace is a threat intelligence fusion and analysis tool that integrates threat data feeds with SIEM solutions so that users can immediately leverage threat intelligence for security monitoring and IR activities in their existing security operations workflow.
Kaspersky CyberTrace uses continuously updated threat data feeds to identify existing breaches or newly launched attacks, and to inform your business or clients about the risks and implications associated with the threat.
Kaspersky CyberTrace integrates with threat intelligence sources (threat intelligence feeds from Kaspersky, other vendors, OSINT, or even custom sources), SIEM solutions, and log sources. As indicators of compromise (IoC) from the threat intelligence feeds are found in your environment, Kaspersky CyberTrace automatically sends alerts to SIEM solutions for ongoing monitoring, validation, and discovery of additional contextual evidence for ongoing security incidents. Kaspersky CyberTrace provides analysts with a set of instruments for conducting alert triage and response through categorization and assessment of identified matches.
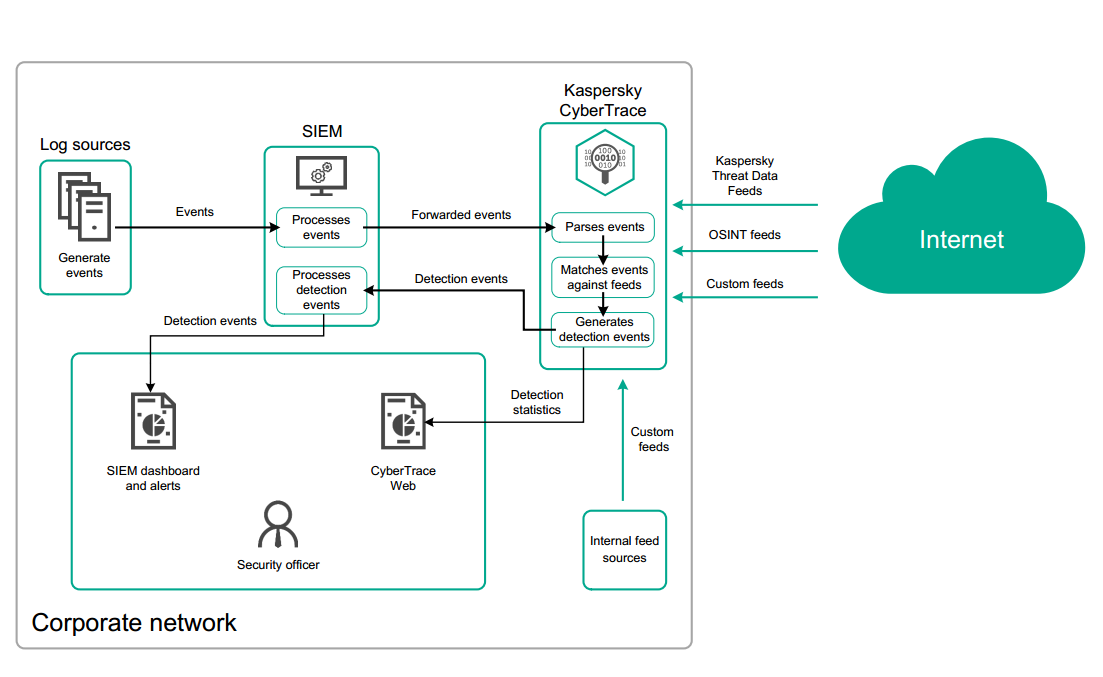
Kaspersky CyberTrace inside a corporate network
Features of Kaspersky CyberTrace:
- Automatic high-performance matching of incoming logs and events with Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds, OSINT feeds, or any other custom feeds in the most popular formats (JSON, STIX, XML, CSV, MISP). Demo feeds from Kaspersky and OSINT are available out of the box.
- Internalized process of parsing and matching incoming data significantly reduces SIEM solution load. Kaspersky CyberTrace parses incoming logs and events, matches the resulting data to feeds, and generates its own alerts on threat detection. Consequently, a SIEM solution has to process less data.
- Generates feed usage statistics for measuring the effectiveness of feeds.
- In-depth threat investigation by using on-demand search of indicators (hashes, IP addresses, domains, URLs). Bulk scanning of logs and files is also supported.
- Universal approach to integration of threat matching capabilities with SIEM solutions and other security controls. SIEM connectors for a wide range of SIEM solutions can be used to visualize and manage data about threat detections.
- IoC and related context are efficiently stored in RAM for rapid access and filtering.
- Kaspersky CyberTrace Web, a web user interface for Kaspersky CyberTrace, provides data visualization, on-demand IoC search functionality, and access to Kaspersky CyberTrace configuration. Kaspersky CyberTrace Web also supports the management of feeds, log parsing rules, Internal TI and false positives lists, and event sources.
- Command-line interface for Windows and Linux platforms.
- Advanced filtering for feeds and log events. Feeds can be converted and filtered based on a broad set of criteria such as time, popularity, geographical location, and threat type. Log events can be filtered based on custom conditions.
- DMZ integration support. The computer on which event data is matched against feeds can be located in DMZ and isolated from the Internet.
- In standalone mode, where Kaspersky CyberTrace is not integrated with a SIEM solution, Kaspersky CyberTrace receives logs from various sources such as networking devices, processes these logs according to the defined normalizing rules, and parses the logs according to the defined regular expressions.
- Export lookup results that match feeds to CSV format for integration with other systems (firewalls, network and host IDS, custom tools).
- Exposes obfuscation techniques used by some threats to hide malicious activities in logs.
The main parts of Kaspersky CyberTrace are Feed Service, Feed Utility, Log Scanner, and Kaspersky CyberTrace Web.
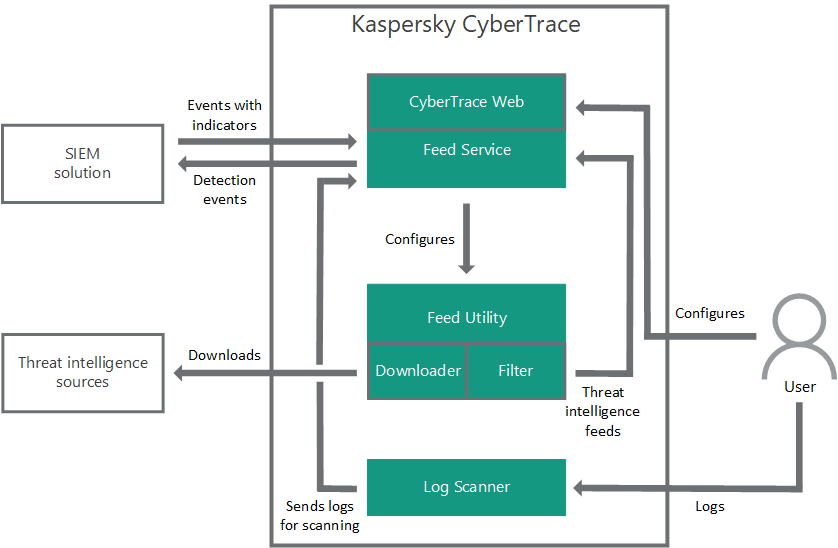
Main components of Kaspersky CyberTrace
Documentation contents
This documentation is divided into several chapters:
- Installation and integration guides
This chapter provides guides about installing Kaspersky CyberTrace, integrating it with SIEM solutions and event sources, and configuring Kaspersky CyberTrace after the integration is completed.
For a starting point of the installation and integration process, see Getting started.
- User guides
This chapter provides information about Kaspersky CyberTrace Web, which is a web interface of Kaspersky CyberTrace, and about apps and dashboards that provide access to Kaspersky CyberTrace from a SIEM solution.
- Administrator guides
This chapter provides information about managing Kaspersky CyberTrace and covers advanced topics of Kaspersky CyberTrace usage. Descriptions of Kaspersky CyberTrace components and workflow of these components can also be found in this chapter.
- Troubleshooting
This section provides solutions to common problems encountered while using Kaspersky CyberTrace.
- Risk mitigation
This section provides guidelines for mitigating potential security risks when working with Kaspersky CyberTrace.
What's new
Kaspersky CyberTrace offers the following new features and improvements:
What's new in version 4.0
- A database of indicators with full text search capability and the ability to search by using advanced search queries was added to enable complex searches across all indicator fields, including the context fields. The ability to filter results by Intelligence supplier simplifies the process of analyzing threat intelligence data.
- Pages with detailed information about each indicator were added for deeper analysis. Each page presents all information about an indicator from all threat intelligence suppliers (deduplication) and allows analysts to discuss threats in comments, as well as add internal threat intelligence about the indicator. If the indicator was detected, information about detection dates and links to the detections list will be available.
- Storage for detections was added to simplify the security monitoring and alerts triage processes. The raw event from the source and full information about the detection are saved to the database, for future analysis. The detection list supports searching saved data, to find all detections by threat, source IP address, user name, or any other field.
- An indicators export feature was added to support exporting indicator sets to security controls such as policies lists (block lists) and to support the sharing of threat data between Kaspersky CyberTrace instances or with other TI Platforms.
- A historical correlation feature (retroscan) was added to allow analyzing observables from previously checked events by using the latest feeds to find previously uncovered threats. All historical detections will be included in the report, for future investigations.
- Filter for sending detection events to SIEM solutions was added to reduce the load on the solutions and on the Analyst (fighting with alerts fatigue). It allows sending SIEM solutions only the most dangerous and confident detections that must be treated as incidents. All other detections will be saved to the internal database, and can be used during root cause analysis or in threat hunting.
- Multitenancy feature was added to support MSSP or Large Enterprise use cases when a service provider (central office) needs to handle events from different branches (tenants) separately. The feature allows connecting a single Kaspersky CyberTrace instance with different SIEM solutions from different tenants and configuring what feeds must be used for each tenant.
- HTTP REST API for looking up and managing threat intelligence was added. By using the REST API, Kaspersky CyberTrace can be easily integrated into complex environments for automation and orchestration. The API supports observables lookup, as well as TI indicators and TI suppliers managing scenarios.
- Integration with Kaspersky Unified Monitoring and Analysis Platform (KUMA) was added, including Web UI integration (single UI).
- New components were added to the Dashboard:
- Table with last feed update statuses was added to inform the user about the updating of statistics for feeds.
- Graph with checked events count was added to inform the user about the current and historical load on the system (in Event Per Second – EPS).
- Feeds intersection matrix was added to help with choosing the most valuable threat intelligence suppliers.
- Scenario for auto-updatable dashboard on TV was added, to allow displaying key metrics on a TV screen in the user's office.
- Authentication with LDAP (MS Active Directory) was added.
- Ability to load feeds from Kaspersky as custom feeds was added, to simplify the process of adding new Kaspersky feeds to Kaspersky CyberTrace.
- UI style was updated in accordance with the Kaspersky rebranding guidelines.
- Process of creating format strings for events that will be sent to SIEM solutions was simplified. A wizard that automatically composes event format strings based on the selected set of event fields has been added.
- Installers for Windows and Linux were updated:
- Kaspersky CyberTrace will be delivered as a single package for all SIEM solutions. The LogRhythm SIEM solution is supported out of the box.
- Initial configuration was moved from installers to CyberTrace Web and must be performed after the first launch in Web UI.
- In Linux packages, init.d management scripts were replaced with systemd unit files.
- URL normalization for third-party intelligence sources was added to simplify the process of integrating third-party intelligence into Kaspersky CyberTrace.
- New X-KF-SaveStatistic flag was added to support saving detection statistics when X-KF-ReplyBack mode is used.
- Integration with RSA was updated (“:rfc3164” mode for forwarding from SIEM solutions is recommended instead of using EventDelimiter on the Kaspersky CyberTrace side).
- Windows Server 2019 is now supported; and support for Windows Server 2008 and Desktop versions of Windows was limited.
- Feed Service can send alerts to a specific IP address or hostname separately from detection events. The connection settings for alert events can be specified in Kaspersky CyberTrace Web.
- If an error occurs while sending a detection event, Feed Service will try to resend it after a specific period of time. The number of attempts and the time interval between them is specified in the configuration file of Feed Service.
- When adding a custom or third-party feed, the level of confidence is specified.This information is further included in detection events.
- When adding a custom or third-party feed, the vendor name must be specified. Such feeds and suppliers are listed separately from OSINT feeds.
- Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds now include ICS Hash Data Feed for protection against malicious applications that are aimed at Industrial Control Systems.
- Adding custom feeds in the MISP format is supported. Such feeds can be loaded from a local folder or via HTTP(S).
- The basic authentication scheme is available for each custom feed that is loaded via HTTP(S) or FTP(S).
- Information about the running and finished tasks is now available on the Tasks tab.
- The following OSINT feeds are no longer supported:
- Abuse.ch_Ransomware_Common
- Abuse.ch_Ransomware_BlockUrl
- Abuse.ch_Ransomware_BlockDomain
- Abuse.ch_Ransomware_BlockIP
- Abuse.ch_Feodo_MalwareHash
About feeds and certificates
This chapter describes feeds and certificates used with Kaspersky CyberTrace.
About Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds
This section describes Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds available for Kaspersky CyberTrace.
Basics of Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds
First-tier security vendors and enterprises use time-tested and authoritative Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds to produce premium security solutions or to protect their business.
Cyber attacks happen every day. Cyber threats are constantly growing in frequency, complexity, and obfuscation, as they try to compromise your defenses. Adversaries currently use complicated intrusion kill chains, campaigns, and customized Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) to disrupt business or damage clients.
Kaspersky offers continuously updated Threat Data Feeds to inform your business or clients about risks and implications associated with cyber threats, helping you to mitigate threats more effectively and defend against attacks even before they are launched.
Information contained in Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds
Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds contain thoroughly vetted threat indicator data sourced from the real world in real time.
Every record in each feed is enriched with actionable context (threat names, time stamps, geolocation, resolved IPs, addresses of infected web resources, hashes, popularity, and so on). Contextual data helps to reveal the "big picture", further validating and supporting wide-ranging use of the data.
Set in context, the data can more readily be used to answer the who, what, where, and when questions that lead to the identification of adversaries, helping you make timely decisions and actions specific to your organization.
Available feed groups
Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds available for Kaspersky CyberTrace can be divided into the following major groups:
- Commercial feeds
This group contains regular commercial feeds that can be accessed with a commercial certificate. Feeds from this group cover a wide variety of cyberthreats.
- APT feeds
APT feeds are commercial feeds that contain information about cyber threats related to advanced persistent threat (APT) campaigns.
- Demo feeds
Demo feeds can be used for evaluation purposes. These feeds do not require a commercial certificate. Demo feeds provide lower detection rates in comparison with their corresponding commercial versions.
Commercial feeds
The following feeds are available in this group:
- Botnet CnC URL Data Feed
A set of URLs and hashes with context that cover desktop botnet C&C servers and related malicious objects. Masked and non-masked records are available.
- IP Reputation Data Feed
A set of IP addresses with context that cover different categories of suspicious and malicious hosts.
- Malicious Hash Data Feed
A set of file hashes with context that cover the most dangerous, prevalent, or emerging malware.
- Malicious URL Data Feed
A set of URLs with context that cover malicious websites and web pages. Masked and non-masked records are available.
- Mobile Botnet CnC URL Data Feed
A set of URLs with context that cover mobile botnet C&C servers.
- Mobile Malicious Hash Data Feed
A set of file hashes with context for detecting malicious objects that infect mobile Google Android and Apple iPhone devices.
- Phishing URL Data Feed
A set of URLs with context that cover phishing websites and web pages. Masked and non-masked records are available.
- Ransomware URL Data Feed
A set of URLs, domains, and hosts with context that cover ransomware links and websites.
- Vulnerability Data Feed
A set of file hashes with context that cover vulnerabilities in applications and cover exploits that use those vulnerabilities.
Kaspersky CyberTrace does not support the
cpesfield of the Vulnerability Data Feed. - IoT URL Data Feed
A set of URLs with context that cover malicious links used to download malware targeting Internet of Things-enabled devices.
- ICS Hash Data Feed
A set of hashes of malicious applications that are used to attack the ICS (Industrial Control Systems) infrastructure.
APT Feeds
The following demo feeds are available in this group:
- APT Hash Data Feed
A set of hashes that cover malicious artifacts used by APT actors to conduct APT campaigns.
- APT IP Data Feed
A set of IP addresses that belong to the infrastructure used in APT campaigns.
- APT URL Data Feed
A set of domains that belong to the infrastructure used in APT campaigns.
Demo feeds
The following demo feeds are available in this group:
- Demo Botnet CnC URL Data Feed
Provides lower detection rates in comparison with Botnet CnC URL Data Feed.
- Demo IP Reputation Data Feed
Provides lower detection rates in comparison with IP Reputation Data Feed.
- Demo Malicious Hash Data Feed
Provides lower detection rates in comparison with Malicious Hash Data Feed.
Sorting order for records in feeds
Feed records are sorted as follows:
- Records in IP Reputation Data Feed are sorted by threat score in descending order.
- Records in all other feeds are sorted by popularity in descending order.
About OSINT feeds
This section describes OSINT feeds supported by Kaspersky CyberTrace.
OSINT feeds are publicly available threat intelligence data sources provided by organizations and individuals.
OSINT feeds supported by Kaspersky CyberTrace
Kaspersky Feed Utility supports OSINT feeds from the following sources:
- Abuse.ch
This source has several associated sources of information:
- Feodo Tracker is an abuse.ch project that has the goal of sharing botnet C&C servers associated with the Feodo malware family (Dridex, Emotet/Heodo).
- SSLBL is an abuse.ch project that has the goal of detecting malicious SSL connections by identifying the SSL certificates used by botnet C&C servers and adding them to a denylist.
- Proofpoint ET intelligence
This source provides information about emerging threats.
- BlockList.de
This is a free and voluntary service provided by a Fraud/Abuse specialist, whose servers are often attacked on SSH, Mail Login, FTP, Webserver, and other services.
BlockList.de has reported more than 70,000 attacks in twelve hours in real time and uses the Whois (abuse-mailbox, abuse@, security@, email, remarks), the RIPE Abuse Finder, and the contact-database from abusix.org to find the abuse address assigned to the attacking host.
- Cyber Crime Tracker
Cyber Crime Tracker monitors and tracks various malware families that are used to perpetrate cyber crimes, such as banking trojans and ransomware. It lists mainly malware C&Cs, and file hashes of Zeus and Zeus-originated malware families.
The following table lists supported OSINT feeds:
OSINT feeds
Identifier |
Description |
Link |
Abuse.ch_Feodo_BlockIP |
Feodo IP Blocklist |
|
Abuse.ch_SSL_Certificate_BlockIP |
Botnet C2 IP Denylist |
|
Abuse.ch_SSL_Certificate_BlockHash |
SSL Certificate Denylist |
|
Blocklist.de_BlockIP |
Blocklist.de IP Blocklist |
|
CyberCrime_Tracker_BlockUrl |
Cyber Crime Tracker URL Blocklist |
|
EmergingThreats_BlockIP |
Raw IPs for the firewall block lists |
https://rules.emergingthreats.net/fwrules/emerging-Block-IPs.txt |
EmergingThreats_CompromisedIP |
Compromised IP addresses |
https://rules.emergingthreats.net/blockrules/compromised-ips.txt |
The OSINT feeds in the table above are maintained by third parties only. Some URLs in the table may, for various reasons, become obsolete over time.
Page topAbout the certificates
Kaspersky CyberTrace uses a certificate to download feeds. The certificate determines which feeds can be downloaded from the update servers.
Certificate types
Kaspersky CyberTrace can use two types of certificates:
- Demo certificate
This certificate is shipped in the distribution kit. It allows access to the demo Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds.
- Commercial certificate
This certificate allows access to one or more Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds.
To obtain a commercial certificate, contact Kaspersky Cybersecurity Service team at intelligence@kaspersky.com.
Certificates and security
When Kaspersky CyberTrace establishes a connection with Kaspersky servers, it passes the certificate in encrypted form to Kaspersky. The connection between Kaspersky CyberTrace and Kaspersky servers is encrypted to ensure that all data is protected.
Page top