Contents
InputSettings
Contains input settings for the General tenant.
This element defines the IP address and port that Feed Service will listen on for incoming events, normalizing rules for processing the events, and regular expressions for parsing the events.
Path
InputSettings
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- RegExps
Contains Boost regular expressions that are used to parse incoming events originating from different sources.
- ConnectionString
Specifies the IP address and port (or the Windows-named pipe) that the service will listen on for incoming events.
- EventDelimiter
Specifies the rule for the splitting of incoming events,
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<InputSettings> <RegExps> ... </RegExps> <ConnectionString>0.0.0.0:9999</ConnectionString> </InputSettings> |
RegExps
Contains Boost regular expressions that are used to parse incoming events originating from different sources.
Path
InputSettings > RegExps
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested element:
- Source
Contains parameters for a specific event source.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<RegExps> <Source id="default"> ... </Source> <Source id="ExampleSource1"> ... </Source> <Source id="ExampleSource2"> ... </Source> </RegExps> |
Source
Contains parameters for a specific event source.
The regular expressions and event normalizing rules specified in the configuration file are grouped by event sources that are represented by Source elements. Usually these event sources are devices that issue events, which afterward are checked by Feed Service. Every Source element contains a set of rules. There can be one or more Source elements in the InputSettings > RegExps element.
Rules workflow
The way Feed Service chooses rules from different Source elements is described in the following flow chart.
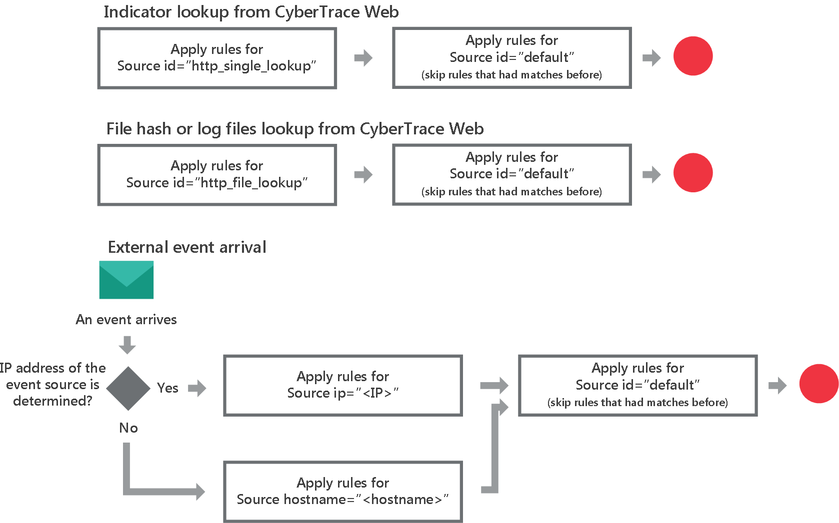
Choosing a rule
Note that event normalizing rules are applied first and regular expressions are applied afterwards.
The regular expressions of the default event source for finding URLs, IP addresses, and hashes are universal; that is, they can be used for parsing events issued by most devices. They can be used for parsing events that contain multiple URLs, but cannot be used, for example, for parsing events that contain URLs with no protocol specified. The use of universal regular expressions lowers the performance of Feed Service, compared to using device-specific regular expressions. Also, the universal regular expressions do not handle the dispersal, in an event, of different parts of a URL (for example, the host and the path). The universal regular expressions for finding hashes can extract symbol sequences that actually are not hashes.
Special event sources
There must be an event source with the default identifier (<Source id="default">). Rules of the default event source have lower priority than rules specific to the event source. Rules specific to the event source are applied first. Rules of the default event source are applied next. If a rule specific to the event source and a rule of the default event source have the same name, the rule of the default event source is applied only if the rule specific to the event source had no matches.
There are two special event sources that you can use: http_single_lookup (<Source id="http_single_lookup">) and http_file_lookup (<Source id="http_file_lookup">).
The rules of the http_single_lookup event source are used when single values are searched for by using CyberTrace Web.
The rules of the http_file_lookup event source are used when hashes of specified files or indicators in log files are searched for by using CyberTrace Web. Therefore, if you have to search for values contained in a log file that has a special format, we recommend specifying rules for the http_file_lookup event source.
If the configuration file contains the http_single_lookup event source or the http_file_lookup event source, we strongly recommend that you do not remove the regular expressions specified in these special event sources by default and, instead, edit them as needed.
Path
InputSettings > RegExps > Source
Attributes
This element has the following attributes.
Source element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
A unique identifier of the event source. In detection events, the identifier of the event source can be referred to by the %SourceId% pattern. |
|
The IP address of the event source. If an event has arrived from an event source that has the specified IP address, the event is processed by using the rules contained in this The |
|
The host name of the event source. The value of the host name is extracted from the event. In syslog events, the host name follows the timestamp (https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5424). For example, in the event If an event has arrived from an event source that has the specified host name and the IP address of the event source is not among those specified in the The hostname attribute cannot be set for the default, |
|
The regular expression that is used to determine if an event comes from the source. The specified regular expression is applied to an event. If the regular expression matches the event one or more times, the event is considered to be from the source. In this case, the event is processed by using the rules contained in this The hostname attribute cannot be set for the |
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- Regular expressions
Regular expressions that are used to parse incoming events originating from this source.
Each regular expression is a separate element with the name of the regular expression.
- NormalizingRules
Rules for modifying incoming events.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<Source id="CustomSource" ip="192.0.2.15"> <RE_MD5 type="MD5" extract="all">([\da-fA-F]{32})</RE_MD5> <RE_SHA1 type="SHA1" extract="all">([\da-fA-F]{40})</RE_SHA1> <RE_SHA256 type="SHA256" extract="all">([\da-fA-F]{64})</RE_SHA256> <NormalizingRules> ... </NormalizingRules> </Source> |
Source > Regular expression
Defines a regular expression for an event source.
Path
InputSettings > RegExps > Source > %RegexpName%
This element has the name of the regular expression.
Attributes
This element has the following attributes.
%RegexpName% element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Sets a rule for creating a compound value from data extracted from an event. For more information, see section "About regular expressions". |
|
The Possible values are The The |
|
Specifies the type of value that is extracted by this regular expression. Possible values:
|
|
Specifies if the extracted value that matched a specified regular expression must be used for a retrospective scan. If the extracted value must be used for the retrospective scan, the value of this attribute is If the extracted value must not be used for the retrospective scan, the value of this attribute is This attribute cannot be used within elements where the |
Value
This element contains a Boost regular expression.
For more information about specifying values for this parameter, see section "About regular expressions".
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<RE_MD5 type="MD5" use_for_retroscan="true" extract="all">([\da-fA-F]{32})</RE_MD5> |
Source > NormalizingRules
Defines rules for modifying incoming events.
For more information about normalizing rules, see Adding normalizing rules.
Path
InputSettings > RegExps > Source > NormalizingRules
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- Replace
These elements specify replacing rules.
- Ignore
These elements specify ignoring rules.
NormalizingRules > Replace
Defines a replacing rule.
This element has the following attributes.
Replace element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies a regular expression for the rule. |
|
Specifies the replacement sequence. |
NormalizingRules > Ignore
Defines an ignoring rule
This element has the following attributes.
Ignore element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies a regular expression for the rule. |
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<NormalizingRules> <Replace input="^\<(\d+)\>" output="NEW_EVENT\:\1\s" /> <Ignore input="Device0002" /> </NormalizingRules> |
ConnectionString
Specifies the IP address and port (or the Windows-named pipe) that the service will listen on for incoming events.
This element is mandatory.
Path
InputSettings > ConnectionString
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Value
The value is formatted as <ip_address>:<port> (if an IP address and port are used) or as \\.\pipe\<pipe_name> (if a Windows-named pipe is used).
The IP address must consist of four decimal octets, each separated by a dot. The value in each octet must be less than 256.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<ConnectionString>0.0.0.0:9999</ConnectionString> |
EventDelimiter
Specifies the rule for the splitting of incoming events.
Path
InputSettings > EventDelimiter
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Value
The value rule must have the following format:
<EventDelimiter>%START_EVENT_SYMBOLS%</EventDelimiter>
The %START_EVENT_SYMBOLS% value contains the regular expression that corresponds to the beginning of the substring of the incoming event.
The rule processes all occurrences of the %START_EVENT_SYMBOLS% value. If the %START_EVENT_SYMBOLS% value is found in the string of the incoming event, this string will be split into multiple events by the addition of the newline character (\n) before every matched substring.
If the %START_EVENT_SYMBOLS% value does not match any substring of the incoming string, the incoming string is considered a single event.
If an event contains newline characters (\n), such an event will be split by using both the %START_EVENT_SYMBOLS% value and newline characters as event delimiters.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<EventDelimiter><![CDATA[;]]></EventDelimiter> |