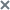Creating the Security Audit task with the default settings
This section provides information related to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows. This information may be partially or completely inapplicable to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Linux. For complete information about Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Linux, please refer to the Help of the solution that includes the application: Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform or Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response.
The task can be run only if you have an active Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Node license key with an ICS Audit licensed object.
To create and configure a Standard Security Audit task:
- In the main Kaspersky Security Center Web Console window select Devices → Tasks.
- Click the Add button.
The task creation wizard will start.
- In the Application drop-down list, select Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- In the Task type drop-down list, select Security Audit.
- Enter a task name or leave the default name.
- Select devices to which the task will be assigned.
- Click Next.
- On the Source of rules tab, Custom rule database from file is selected by default.
- Click the Import rule base from file.
- In the window that opens, specify the file with the rule database.
You can load only one archive containing an XML file with OVAL rules and XCCDF rules.
The total archive size must not exceed 2 MB.
- Click ОК.
The Source of rules section displays information about the loaded rules. Follow the Details links in the Platforms and Products fields to open windows with lists of the operating systems and products mentioned in the rules of the selected source.
- If necessary, load the file with external variables:
You cannot use external variables if the selected source contains XCCDF rules.
- Select the Use external variables data with custom database check box.
- Click the Import external variables from file.
- In the window that opens, specify the path to the file with the external variables.
- Click OK.
- In the Scope section, if necessary, change the vulnerability scan mode:
The Scope section is unavailable if the selected rule source contains XCCDF rules.
- Select one of the modes:
- Scan all vulnerabilities.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent scans the devices to which the task is assigned in order to detect all vulnerabilities described in the rules of the Kaspersky ICS CERT vulnerabilities database for SCADA.
- Scan all vulnerabilities except added to the list.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent scans the devices to which the task is assigned in order to detect all vulnerabilities described in the rules of of the Kaspersky ICS CERT vulnerabilities database for SCADA except for those added to the list below.
- Scan vulnerabilities added to the list.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent scans the devices to which the task is assigned in order to detect vulnerabilities added to the list below.
- Scan all vulnerabilities.
- If you selected Scan all vulnerabilities except added to the list or Scan vulnerabilities added to the list, create a list of vulnerabilities using the Add or Add according to conditions.
- Select one of the modes:
- In the Advanced section, if necessary, determine the statuses of directive-based scans that will be included in the security audit task report:
Directives cannot be applied if the selected rule source contains XCCDF rules.
- Select the Use Directives check box.
- Using the switch next to each directive, determine the statuses of directive-based scans that will be displayed in the security audit task report.
If the switch next to a directive status is on, results of scans based on the directive's rules that have this status will be displayed in the security audit task report.
By default, the check boxes next to the True and False scan result are selected for all directives.
- In the Advanced section, if necessary, configure settings for logging task completion events:
- Select the Enable logging check box.
- Select the desired Logging level from the list.
- Click Next.
- In the Selecting an account to run the task window that opens, do one of the following:
- Select the default account.
- Enter the name and password of the user whose account permissions will be used to start the task.
- Click Next.
- In the Finish task creation window, click the Finish button.
The task with the default settings will be created and displayed in the list of tasks. You can change the task settings later.
You can start the created task manually or configure a scheduled task start.
Page top