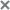Configuring SIEM integration settings
To reduce the load on low-performance devices and to reduce the risk of system degradation as a result of increased application log sizes, you can configure the publication of audit events and task performance events to the syslog server via the Syslog protocol.
A syslog server is an external server for aggregating events (SIEM). It stores and analyzes received events and performs other log management actions.
You can use SIEM integration in two modes:
- Duplicate events on the syslog server: in this mode, all task performance events whose publication is configured in log settings, as well as all system audit events, continue to be stored on the protected device even after they are sent to the SIEM server.
We recommend that you use this mode to reduce the load on the protected device as much as possible.
- Delete local copies of events: in this mode, all events that are registered during application operation and published to the SIEM server will be deleted from the protected device.
The application never deletes local versions of the security log.
Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows can convert events in application logs into formats supported by the syslog server so that those events can be transmitted and successfully recognized by the SIEM server. The application supports conversion into structured data format and into JSON format.
You can reduce the risk that events will be relayed to the SIEM server unsuccessfully by defining the settings for connecting to a mirror syslog server.
A mirror syslog server is an additional syslog server to which the application switches automatically if the connection to the main syslog server is unavailable or if the main server cannot be used.
By default, SIEM integration is not used. You can enable and disable SIEM integration, and configure relevant settings (see the table below).
SIEM integration settings
Setting |
Default value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Send events to a remote syslog server via syslog protocol |
Not applied |
You can enable or disable SIEM integration by selecting or clearing the check box, respectively. |
Remove local copies for events that have been sent to a remote syslog server |
Not applied |
You can configure the settings for storing local copies of logs after they are sent to the SIEM server by selecting or clearing the check box. |
Events format |
Structured data |
You can select one of two formats to which the application converts its events prior to sending them to the syslog server for better recognition of these events by the SIEM server. |
Connection protocol |
TCP |
You can use the drop-down list to configure the connection to the main syslog server via the UDP or TCP protocols, and to the mirror syslog server via the TCP protocol. |
Main syslog server connection settings |
IP address: 127.0.0.1 Port: 514 |
You can use the appropriate fields to configure the IP address and port used to connect to the main syslog server. You can specify the IP address only in IPv4 format. |
Use mirror syslog server if the main server is not accessible |
Not applied |
You can use the check box to enable or disable the use of a mirror syslog server. |
Mirror syslog server connection settings |
IP address: 127.0.0.1 Port: 514 |
You can use the appropriate fields to configure the IP address and port used to connect to the mirror syslog server. You can specify the IP address only in IPv4 format. |
To configure the settings for integration with SIEM:
- Expand the Managed devices node in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console tree.
- Select the administration group for which you want to configure application settings.
- Perform one of the following actions in the details pane of the selected administration group:
- To configure log settings for a group of protected devices, select the Policies tab and open the Properties: <Policy name> window.
- To configure the application for an individual protected device, select the Devices tab and go to the application settings.
- In the Logs and notifications section, click the Task logs button in the Settings subsection.
The Logs and notifications settings window opens.
- Select the SIEM integration tab.
- In the Integration settings block, select the Send events to a remote syslog server via syslog protocol check box.
- If necessary, in the Integration settings block, select the Remove local copies for events that have been sent to a remote syslog server check box.
The status of the Remove local copies for events that have been sent to a remote syslog server check box does not affect the settings for storing events of the security log: the application never automatically deletes security log events.
- In the Events format block, specify the format to which you want to convert application events so that they can be sent to the SIEM server.
By default, the application converts them into a structured data format.
- In the Connection settings block:
- Specify the SIEM connection protocol.
- In the fields of the same name, specify the IPv4 address and port for connecting to the main syslog server.
- Select the Use mirror syslog server if the main server is not accessible check box if you want the application to use other connection settings when unable to send events to the main syslog server.
- In the fields of the same name, specify the IPv4 address and port for connecting to an additional syslog server.
- Click the OK button.
The configured SIEM integration settings will be applied.
Page top