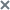Viewing the alert table
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform uses a table of alerts to display the detected signs of targeted attacks and intrusions into the corporate IT infrastructure.
The table of alerts does not display information on objects which satisfy at least one of the following conditions:
- The object has reputation Trusted in the KSN database.
- The object is digitally signed by a trusted vendor:
- Kaspersky.
- Google.
- Apple.
- Microsoft.
Information about these alerts is saved to the application log. You can view this information.
Information about alerts in the application log is rotated every night when the maximum allowed number of alerts is reached:
- Alerts generated by the (IDS) Intrusion Detection System and (URL) URL Reputation components have a maximum of 100,000 alerts for each component.
- All other alerts have a maximum of 20,000 alerts for each module or component.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, rotation is performed on all SCNs and then synchronization with the PCN is performed. After synchronization, all deleted alerts are automatically deleted from the PCN.
The alerts table is in the Alerts section.
By default, this section displays information only on alerts that were not processed by users. To also display information on processed alerts, turn on the Processed switch in the upper-right corner of the window.
You can sort alerts in the table by Created or Updated, Importance, Source, and State columns.
The table of alerts contains the following information:
- VIP specifies if the alert has a status with special access rights. For example, alerts with the VIP status cannot be viewed by program users with the Security officer role.
- Created is the time when the program generated the alert, and Updated is the time when the alert was updated.
 —Alert importance for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user depending on the impact this alert may have on computer or corporate LAN security based on Kaspersky experience.
—Alert importance for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user depending on the impact this alert may have on computer or corporate LAN security based on Kaspersky experience.Alerts can have one of the following importance levels:
- High, marked with the
 symbol—the alert has a high level of importance.
symbol—the alert has a high level of importance. - Medium, marked with the
 symbol—the alert has a medium level of importance.
symbol—the alert has a medium level of importance. - Low, marked with the
 symbol—the alert has a low level of importance.
symbol—the alert has a low level of importance.
- High, marked with the
- Detected—One or multiple categories of detected objects. For example, when the application detects a file infected with the Trojan-Downloader.JS.Cryptoload.ad virus, the Detected field shows the Trojan-Downloader.JS.Cryptoload.ad category for this alert.
- Details—Brief summary of the alert. For example: the name of a detected file or URL address of a malicious link.
- Source—Address of the source of the detected object. For example, this can be the email address from which a malicious file was sent, or the URL from which a malicious file was downloaded.
- Destination—Destination address of a detected object. For example, this can be the email address of your organization's mail domain to which a malicious file was sent, or the IP address of a computer on your corporate LAN to which a malicious file was downloaded.
- Technologies are names of application modules or components that generated the alert.
The Technologies column may indicate the following application modules and components:
- (YARA) YARA.
- (SB) Sandbox.
- (URL) URL Reputation.
- (IDS) Intrusion Detection System.
- (AM) Anti-Malware Engine.
- (TAA) Targeted Attack Analyzer.
- (IOC) IOC.
- State—Alert status depending on whether or not this alert has been processed by the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user.
Alerts can have one of the following states:
- New for new alerts.
- In process for alerts that are already being processed by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user.
- Rescan for alerts resulting from a rescan of an object.
- Assigned to is the name of the user to which the alert is assigned.
- Servers is the list of names of servers which created the alert. Servers belong to the tenant that you are managing in the application web interface. This column is displayed if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
If information in table columns is displayed as a link, you can click the link to open a list in which you can select the action to perform on the object. Depending on the type of value of the cell, you can perform one of the following actions:
- Any type of cell value:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- MD5 hash:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Find events.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- SHA256 hash:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Find events.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Destination IP address:
- Find events.
- Alert state:
- Assign to me.
- Close alert.
Special considerations involved in updating detections and consolidating events in them
The Targeted Attack Analyzer module updates the list of hosts and the number of events in detections if events with the same ID of the triggered TAA (IOA) rule are found during processing. The update is performed within the current calendar day: from 00:00 of the current day to 00:00 of the following day. If the detection is already closed at the time of the update, the system automatically reopens it.
The Intrusion Detection System module consolidates information about processed network events in one alert when the following conditions are simultaneously met:
- The name of the triggered rule, version of application databases, and source all match for network events.
- No more than 24 hours elapsed between the events.
One alert is displayed for all network events that meet these conditions. The alert notification contains information only about the first network event.
Page top