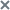Viewing the table of events
The events table is displayed in the Threat Hunting section of the application web interface window after completion of Threat Hunting in the events database. You can sort events in the table by the Event time, Event type, Host, and User name columns.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, events in the table are grouped by hosts of the selected servers and tenants.
The table of events contains the following information:
- Event time—Date and time when the event was detected.
- Event type, for example, Process started.
- Host name—Name of the host on which the alert was generated.
- Details—Information about the event.
- User name—Name of the user on the computer with the Endpoint Agent component whose user account was used to detect the event.
In the events table, the Details column displays the set of data for each type of event in the Event type column (see the table below).
Set of data in the Details column for each event type in the Event type column
Event type |
Details |
|---|---|
Process started |
Name of the process file that was started. SHA256 and MD5 hashes. |
Module loaded |
Name of the dynamic library that was loaded. SHA256 and MD5 hashes. |
Connection to remote host |
URL to which a remote connection attempt was made. Name of the file that attempted to establish a remote connection. |
Blocked application (prevention rule) |
Name of the file of the application that was blocked from starting. SHA256 and MD5 hashes. |
Document blocked |
Name of the document that was blocked from starting. SHA256 and MD5 hashes. |
File changed |
Name of the created file. SHA256 and MD5 hashes. |
System event log |
Channel for recording events in the system log. Event type ID. |
Registry modified |
Name of key in registry. |
Port listened |
Server address and port. Name of the file of the process that listens to the port. |
Driver loaded |
File name of the driver that has been loaded. SHA256 and MD5 hashes. |
Detection |
Name of the file in which the object was detected. Name of the detected object. SHA256 and MD5 hashes. |
Detection processing result |
Name of the file in which the object was detected. Name of the detected object. SHA256 and MD5 hashes. |
AMSI scan |
Name of the scanned object. Type of the script. Text of the script sent to be scanned. |
Process: interpreted file run |
Name of the file that was run. SHA256 and MD5 hashes. |
Process: console interactive input |
Command text. |
Process terminated |
File name of the stopped process. SHA256 and MD5 hashes. |
DNS |
Name of the domain being looked up. Resource record type ID. |
LDAP |
Search scope and filter. |
Named pipe |
Pipe name. Pipe operation type. |
WMI |
WMI operation type. Event consumer source code. |
Code injection |
File name of the target process or name of the dynamic-link library that contains the hook procedure and the name of the function to which control is passed after injection. Method of access to the target process file. SHA256 and MD5 hashes of the target process file. |
Process access |
Name of the recipient process file. Importance of the event. Type of operation performed on the process file. Process access permissions. |
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent as the Endpoint Agent component, information about the AMSI scan event is available when Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows 3.10 or later and when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows 11.5 or later. If Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows is not installed on the computer and is not integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, information about the AMSI scan event is not logged in the event database and is not displayed in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface.
If Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is used in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, the Central Node server generates Detection and Detection processing result events based on data received from EPP applications. If EPP applications are not installed on the computer and are not integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, information about these events is not logged in the event database and is not displayed in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface.
Clicking the link with the name of the event type, data, additional information and user name opens a list in which you can select the action to perform on the object. Depending on the value in the cell, you can do one of the following:
- For all values in the cell:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Host name:
- File name:
- MD5 hash:
- SHA256 hash:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Create prevention rule.
- Find in Storage.