Memory states
Each page of virtual memory can be free, reserved, or committed.
The transition from a free state to a reserved state is called allocation. Pre-reserving memory (without committing physical pages) enables an application to mark its address space in advance. The transition from a reserved state back to a free state is referred to as freeing memory.
The assignment of physical memory for a previously reserved page of virtual memory is referred to as committing memory, and the inverse transition from the committed state to the reserved state is called returning memory.
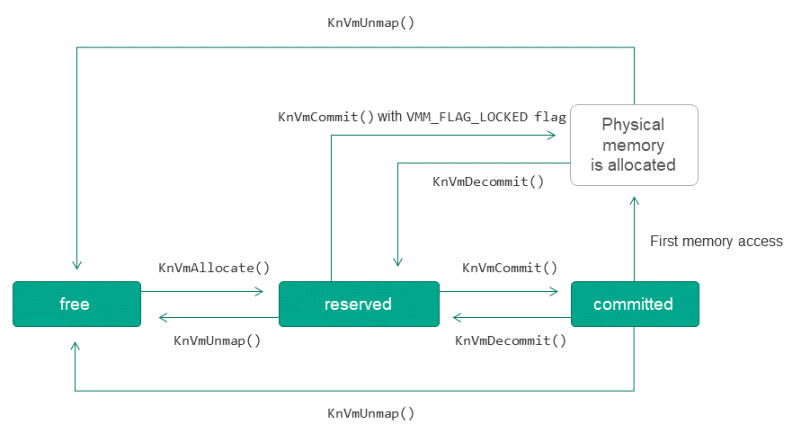
Transitions between memory page states
Page topKnVmAllocate()
This function is declared in the coresrv/vmm/vmm_api.h file.
void *KnVmAllocate(void *addr, rtl_size_t size, int flags);
Reserves a range of physical pages defined by the addr and size parameters. If the VMM_FLAG_COMMIT flag is indicated, the function reserves and commits pages for one call.
Parameters:
addris the page-aligned base physical address; ifaddris set equal to 0, the system chooses a free area of physical memory.sizeis the size of the memory area in bytes (must be a multiple of the page size).flagsrefers to allocation flags.
Returns the base virtual address of the reserved area. If it is not possible to reserve a memory area, the function returns RTL_NULL.
Allocation flags
In the flags parameter, you can use the following flags (vmm/flags.h):
- VMM_FLAG_RESERVE is a required flag.
- VMM_FLAG_COMMIT lets you reserve and commit memory pages to one
KnVmAllocate()call in so-called "lazy" mode. - VMM_FLAG_LOCKED is used together with VMM_FLAG_COMMIT and lets you immediately commit physical memory pages instead of "lazy" commitment.
- VMM_FLAG_WRITE_BACK, VMM_FLAG_WRITE_THROUGH, VMM_FLAG_WRITE_COMBINE, VMM_FLAG_CACHE_DISABLE and VMM_FLAG_CACHE_MASK manage caching of memory pages.
- VMM_FLAG_READ, VMM_FLAG_WRITE, VMM_FLAG_EXECUTE and VMM_FLAG_RWX_MASK are memory protection attributes.
- VMM_FLAG_LOW_GUARD and VMM_FLAG_HIGH_GUARD add a protective page before and after the allocated memory, respectively.
- VMM_FLAG_GROW_DOWN defines the direction of memory access (from older addresses to newer addresses).
Permissible combinations of memory protection attributes:
- VMM_FLAG_READ allows reading page contents.
- VMM_FLAG_READ | VMM_FLAG_WRITE allows reading and modifying page contents.
- VMM_FLAG_READ | VMM_FLAG_EXECUTE allows reading and executing page contents.
- VMM_FLAG_RWX_MASK or VMM_FLAG_READ | VMM_FLAG_WRITE | VMM_FLAG_EXECUTE refers to full access to page contents (these entries are equivalent).
Example
coredump->base = KnVmAllocate(RTL_NULL, vmaSize,
VMM_FLAG_READ | VMM_FLAG_RESERVE |
VMM_FLAG_WRITE | VMM_FLAG_COMMIT |
VMM_FLAG_LOCKED).
The KnVmProtect() function can be used to modify the defined memory area protection attributes if necessary.
KnVmCommit()
This function is declared in the coresrv/vmm/vmm_api.h file.
Retcode KnVmCommit(void *addr, rtl_size_t size, int flags);
Commits a range of physical pages defined by the "addr" and "size" parameters.
All committed pages must be reserved in advance.
Parameters:
addris the page-aligned base virtual address of the memory area.sizeis the size of the memory area in bytes (must be a multiple of the page size).flagsis an unused parameter (indicate the VMM_FLAG_LOCKED flag in this parameter value to ensure compatibility).
If pages are successfully committed, the function returns rcOk.
Page topKnVmDecommit()
This function is declared in the coresrv/vmm/vmm_api.h file.
Retcode KnVmDecommit(void *addr, rtl_size_t size);
Frees a range of pages (switches them to the reserved state).
Parameters:
addris the page-aligned base virtual address of the memory area.sizeis the size of the memory area in bytes (must be a multiple of the page size).
If pages are successfully freed, the function returns rcOk.
Page topKnVmProtect()
This function is declared in the coresrv/vmm/vmm_api.h file.
Retcode KnVmProtect(void *addr, rtl_size_t size, int newFlags);
Modifies the protection attributes of reserved or committed memory pages.
Parameters:
addris the page-aligned base virtual address of the memory area.sizeis the size of the memory area in bytes (must be a multiple of the page size).newFlagsrefers to new protection attributes.
If the protection attributes are successfully changed, the function returns rcOk.
Permissible combinations of memory protection attributes:
- VMM_FLAG_READ allows reading page contents.
- VMM_FLAG_READ | VMM_FLAG_WRITE allows reading and modifying page contents.
- VMM_FLAG_READ | VMM_FLAG_EXECUTE allows reading and executing page contents.
- VMM_FLAG_RWX_MASK or VMM_FLAG_READ | VMM_FLAG_WRITE | VMM_FLAG_EXECUTE refers to full access to page contents (these entries are equivalent).
KnVmUnmap()
This function is declared in the coresrv/vmm/vmm_api.h file.
Retcode KnVmUnmap(void *addr, rtl_size_t size);
Frees the memory area.
Parameters:
addrrefers to the page-aligned address of the memory area.sizerefers to the memory area size.
If pages are successfully freed, the function returns rcOk.
Page top