Contents
Mic security model
The Mic security model lets you implement mandatory integrity control. In other words, this security model provides the capability to manage data streams between different processes and between processes and the KasperskyOS kernel by controlling the integrity levels of processes, the kernel, and resources that are used via IPC.
In Mic security model terminology, processes and the kernel are called subjects while resources are called objects. However, the information provided in this section slightly deviates from the terminology of the Mic security model. In this section, the term "object" is not used to refer to a "resource".
Data streams are generated between subjects when the subjects interact via IPC.
The integrity level of a subject/resource is the level of trust afforded to the subject/resource. The degree of trust in a subject depends on whether the subject interacts with untrusted external software/hardware systems or whether the subject has a proven quality level, for example. (The kernel has a high level of integrity.) The degree of trust in a resource depends on whether this resource was created by a trusted subject within a software/hardware system running KasperskyOS or if it was received from an untrusted external software/hardware system, for example.
The Mic security model is characterized by the following provisions:
- By default, data streams from subjects with less integrity to subjects with higher integrity are prohibited. You have the option of permitting such data streams if you can guarantee that the subjects with higher integrity will not be compromised.
- A resource consumer is prohibited from writing data to a resource if the integrity level of the resource is higher than the integrity level of the resource consumer.
- By default, a resource consumer is prohibited from reading data from a resource if the integrity level of the resource is lower than the integrity level of the resource consumer. You have the option to allow the resource consumer to perform such an operation if you can guarantee that the resource consumer will not be compromised.
Methods of the Mic security model let you assign integrity levels to subjects and resources, check the permissibility of data streams based on a comparison of integrity levels, and elevate the integrity levels of resources.
A PSL file containing a description of the Mic security model is located in the KasperskyOS SDK at the following path:
toolchain/include/nk/mic.psl
For an example of using the Mic security model, we can examine a secure software update for a software/hardware system running KasperskyOS. Four processes are involved in the update:
Downloaderis a low-integrity process that downloads a low-integrity update image from a remote server on the Internet.Verifieris a high-integrity process that verifies the digital signature of the low-integrity update image (high-integrity process that can read data from a low-integrity resource).FileSystemis a high-integrity process that manages the file system.Updateris a high-integrity process that applies an update.
A software update is performed according to the following scenario:
- The
Downloaderdownloads an update image and saves it to a file by transferring the contents of the image to theFileSystem. A low integrity level is assigned to this file. - The
Verifierreceives the update image from theFileSystemby reading the high-integrity file, and verifies its digital signature. If the signature is correct, theVerifierqueries theFileSystemso that theFileSystemcreates a copy of the file containing the update image. A high integrity level is assigned to the new file. - The
Updaterreceives the update image from theFileSystemby reading the high-integrity file, and applies the update.
In this example, the Mic security model ensures that the high-integrity Updater process can read data only from a high-integrity update image. As a result, the update can be applied only after the digital signature of the update image is verified.
Mic security model object
To use the Mic security model, you need to create an object or objects of this model. You also need to assign a set of integrity levels for subjects and resources.
A Mic security model object has the following parameters:
configrefers to a set of integrity levels or configuration of a set of integrity levels:degreesrefers to a set of gradations for generating a set of integrity levels.categoriesrefers to a set of categories for generating a set of integrity levels.
Examples:
policy object mic : Mic {
config = ["LOW", "MEDIUM", "HIGH"]
}
policy object mic_po : Mic {
config =
{ degrees : ["low", "high"]
, categories : ["net", "log"]
}
}
A set of integrity levels is a partially ordered set that is linearly ordered or contains incomparable elements. The set {LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH} is linearly ordered because all of its elements are comparable to each other. Incomparable elements arise when a set of integrity levels is defined through a set of gradations and a set of categories. In this case, the set of integrity levels L is a Cartesian product of the Boolean set of categories C multiplied by the set of gradations D:
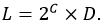
The degrees and categories parameters in this example define the following set:
{
{}/low, {}/high,
{net}/low, {net}/high,
{log}/low, {log}/high,
{net,log}/low, {net,log}/high
}
In this set, {} means an empty set.
The order relation between elements of the set of integrity levels L is defined as follows:
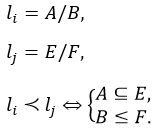
According to this order relation, the jth element exceeds the ith element if the subset of categories E includes the subset of categories A, and gradation F is greater than or equal to gradation A. Examples of comparing elements of the set of integrity levels L:
- The {net,log}/high element exceeds the {log}/low element because the "high" gradation is greater than the "low" gradation, and the subset of categories {net,log} includes the subset of categories {log}.
- The {net,log}/low element exceeds the {log}/low element because the levels of gradations for these elements are equal, and the subset of categories {net,log} includes the subset of categories {log}.
- The {net,log}/high element is the highest because it exceeds all other elements.
- The {}/low element is the lowest because all other elements exceed this element.
- The {net}/low and {log}/high elements are incomparable because the "high" gradation is greater than the "low" gradation but the subset of categories {log} does not include the subset of categories {net}.
- The {net,log}/low and {log}/high elements are incomparable because the "high" gradation is greater than the "low" gradation but the subset of categories {log} does not include the subset of categories {net,log}.
For subjects and resources that have incomparable integrity levels, the Mic security model provides conditions that are analogous to the conditions that the security model provides for subjects and resources that have comparable integrity levels.
By default, data streams between subjects that have incomparable integrity levels are prohibited. However, you have the option to allow such data streams if you can guarantee that the subjects receiving data will not be compromised. A resource consumer is prohibited from writing data to a resource and read data from a resource if the integrity level of the resource is incomparable to the integrity level of the resource consumer. You have the option to allow the resource consumer to read data from a resource if you can guarantee that the resource consumer will not be compromised.
A Mic security model object can be covered by a security audit. There are no audit conditions specific to the Mic security model.
It is necessary to create multiple objects of the Mic security model in the following cases:
- You need to configure a security audit differently for different objects of the Mic security model (for example, you can apply different audit profiles or different audit configurations of the same profile for different objects).
- You need to distinguish between calls of methods provided by different objects of the Mic security model (audit data includes the name of the security model method and the name of the object that provides this method, so you can verify that the method of a specific object was called).
- You need to use multiple variants of mandatory integrity control that may have different sets of integrity levels for subjects and resources, for example.
Mic security model create rule
create { source : <Sid>
, target : <Sid>
, container : <Sid | ()>
, driver : <Sid>
, level : <Level | ... | ()>
}
Assign the specified integrity level to the target resource in the following situation:
- The
sourceprocess initiates creation of thetargetresource. - The
targetresource is managed by thedriversubject, which is the resource provider or the KasperskyOS kernel. - The
containerresource is a container for thetargetresource (for example, a directory is a container for files and/or other directories).
If the container value is not defined (container : ()), the target resource is considered to be the root resource, which means that it has no container.
To define the integrity level, values of the Level type are used:
type Level = LevelFull | LevelNoCategory
type LevelFull =
{ degree : Text | ()
, categories : List<Text> | ()
}
type LevelNoCategory = Text
The rule returns the "granted" result if a specific integrity level was assigned to the target resource.
The rule returns the "denied" result in the following cases:
- The
levelvalue exceeds the integrity level of thesourceprocess,driversubject orcontainerresource. - The
levelvalue is incomparable to the integrity level of thesourceprocess,driversubject orcontainerresource. - An integrity level was not assigned to the
sourceprocess,driversubject, orcontainerresource. - The value of
source,target,containerordriveris outside of the permissible range.
Example:
/* A server of the updater.Realmserv class will be allowed to respond to
* queries of any client in the solution calling the resolve method
* of the realm.Reader endpoint if the resource whose creation is requested
* by the client will be assigned the LOW integrity level during response initiation.
* Otherwise a server of the updater.Realmserv class will be prohibited from responding to
* queries of any client calling the resolve method of the realm.Reader endpoint. */
response src=updater.Realmserv,
endpoint=realm.Reader {
match method=resolve {
mic.create { source : dst_sid
, target : message.handle.handle
, container : ()
, driver : src_sid
, level : "LOW"
}
}
}
Mic security model execute rule
execute <ExecuteImage | ExecuteLevel>
type ExecuteImage =
{ image : Sid
, target : Sid
, level : Level | ... | ()
, levelR : Level | ... | ()
}
type ExecuteLevel =
{ image : Sid | ()
, target : Sid
, level : Level | ...
, levelR : Level | ... | ()
}
This assigns the specified integrity level to the target subject and defines the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which this subject can receive data (levelR). The code of the target subject is in the image executable file.
If the level value is not defined (level : ()), the integrity level of the image executable file is assigned to the target subject. If the image value is not defined (image : ()), the level value must be defined.
If the levelR value is not defined (levelR : ()), the value of levelR is equal to level.
To define the integrity level and levelR, values of the Level type are used. For the definition of the Level type, see "Mic security model create rule".
The rule returns the "granted" result if it assigned the specified integrity level to the target subject and defined the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which this subject can receive data (levelR).
The rule returns the "denied" result in the following cases:
- The
levelvalue exceeds the integrity level of theimageexecutable file. - The
levelvalue is incomparable to the integrity level of theimageexecutable file. - The value of
levelRexceeds the value oflevel. - The
levelandlevelRvalues are incomparable. - An integrity level was not assigned to the
imageexecutable file. - The
imageortargetvalue is outside of the permissible range.
Example:
/* A process of the updater.Manager class will be allowed to start
* if, at startup initiation, this process will be assigned
* the integrity level LOW, and the minimum
* integrity level will be defined for the processes and resources from which this
* process can received data (LOW). Otherwise the startup of a process
* of the updater.Manager class will be denied. */
execute src=Einit, dst=updater.Manager, method=main {
mic.execute { target : dst_sid
, image : ()
, level : "LOW"
, levelR : "LOW"
}
}
Mic security model upgrade rule
upgrade { source : <Sid>
, target : <Sid>
, container : <Sid | ()>
, driver : <Sid>
, level : <Level | ...>
}
This elevates the previously assigned integrity level of the target resource to the specified level in the following situation:
- The
sourceprocess initiates elevation of the integrity level of thetargetresource. - The
targetresource is managed by thedriversubject, which is the resource provider or the KasperskyOS kernel. - The
containerresource is a container for thetargetresource (for example, a directory is a container for files and/or other directories).
If the container value is not defined (container : ()), the target resource is considered to be the root resource, which means that it has no container.
To define the integrity level, values of the Level type are used. For the definition of the Level type, see "Mic security model create rule".
The rule returns the "granted" result if it elevated the previously assigned integrity level of the target resource to the level value.
The rule returns the "denied" result in the following cases:
- The
levelvalue does not exceed the integrity level of thetargetresource. - The
levelvalue exceeds the integrity level of thesourceprocess,driversubject orcontainerresource. - The integrity level of the
targetresource exceeds the integrity level of thesourceprocess. - An integrity level was not assigned to the
sourceprocess,driversubject, orcontainerresource. - The value of
source,target,containerordriveris outside of the permissible range.
Mic security model call rule
call {source : <Sid>, target : <Sid>}
This verifies the permissibility of data streams from the target subject to the source subject.
It returns the "allowed" result in the following cases:
- The integrity level of the
sourcesubject does not exceed the integrity level of thetargetsubject. - The integrity level of the
sourcesubject exceeds the integrity level of thetargetsubject, but the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which thesourcesubject can receive data does not exceed the integrity level of thetargetsubject. - The integrity level of the
sourcesubject is incomparable to the integrity level of thetargetsubject, but the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which thesourcesubject can receive data does not exceed the integrity level of thetargetsubject.
It returns the "denied" result in the following cases:
- The integrity level of the
sourcesubject exceeds the integrity level of thetargetsubject, and the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which thesourcesubject can receive data exceeds the integrity level of thetargetsubject. - The integrity level of the
sourcesubject exceeds the integrity level of thetargetsubject, and the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which thesourcesubject can read data is incomparable to the integrity level of thetargetsubject. - The integrity level of the
sourcesubject is incomparable to the integrity level of thetargetsubject, and the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which thesourcesubject can receive data exceeds the integrity level of thetargetsubject. - The integrity level of the
sourcesubject is incomparable to the integrity level of thetargetsubject, and the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which thesourcesubject can receive data is incomparable to the integrity level of thetargetsubject. - An integrity level was not assigned to the
sourcesubject or to thetargetsubject. - The
sourceortargetvalue is outside of the permissible range.
Example:
/* Any client in the solution is allowed to query
* any server (kernel) if data streams from
* the server (kernel) to the client are permitted by the
* Mic security model. Otherwise any client in the solution
* is prohibited from querying any server (kernel). */
request {
mic.call { source : src_sid
, target : dst_sid
}
}
Mic security model invoke rule
invoke {source : <Sid>, target : <Sid>}
This verifies the permissibility of data streams from the source subject to the target subject.
It returns the "granted" result if the integrity level of the target subject does not exceed the integrity level of the source subject.
It returns the "denied" result in the following cases:
- The integrity level of the
targetsubject exceeds the integrity level of thesourcesubject. - The integrity level of the
targetsubject is incomparable to the integrity level of thesourcesubject. - An integrity level was not assigned to the
sourcesubject or to thetargetsubject. - The
sourceortargetvalue is outside of the permissible range.
Mic security model read rule
read {source : <Sid>, target : <Sid>}
This verifies that the source resource consumer is allowed to read data from the target resource.
It returns the "allowed" result in the following cases:
- The integrity level of the
sourceresource consumer does not exceed the integrity level of thetargetresource. - The integrity level of the
sourceresource consumer exceeds the integrity level of thetargetresource, but the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which thesourceresource consumer can receive data does not exceed the integrity level of thetargetresource. - The integrity level of the
sourceresource consumer is incomparable to the integrity level of thetargetresource, but the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which thesourceresource consumer can receive data does not exceed the integrity level of thetargetresource.
It returns the "denied" result in the following cases:
- The integrity level of the
sourceresource consumer exceeds the integrity level of thetargetresource, and the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which thesourceresource consumer can receive data exceeds the integrity level of thetargetresource. - The integrity level of the
sourceresource consumer exceeds the integrity level of thetargetresource, and the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which thesourceresource consumer can receive data is incomparable to the integrity level of thetargetresource. - The integrity level of the
sourceresource consumer is incomparable to the integrity level of thetargetresource, and the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which thesourceresource consumer can receive data exceeds the integrity level of thetargetresource. - The integrity level of the
sourceresource consumer is incomparable to the integrity level of thetargetresource, and the minimum integrity level of subjects and resources from which thesourceresource consumer can receive data is incomparable to the integrity level of thetargetresource. - An integrity level was not assigned to the
sourceresource consumer or to thetargetresource. - The
sourceortargetvalue is outside of the permissible range.
Example:
/* Any client in the solution is allowed to query a server of
* the updater.Realmserv class by calling the read method of the
* realm.Reader service if the Mic security model permits
* this client to read data from the resource needed by
* this client. Otherwise any client in the solution is prohibited from
* querying a server of the updater.Realmserv class by calling
* the read method of the realm.Reader endpoint. */
request dst=updater.Realmserv,
endpoint=realm.Reader {
match method=read {
mic.read { source : src_sid,
, target : message.handle.handle
}
}
}
Mic security model write rule
write {source : <Sid>, target : <Sid>}
This verifies that the source resource consumer is allowed to write data to the target resource.
It returns the "granted" result if the integrity level of the target resource does not exceed the integrity level of the source resource consumer.
It returns the "denied" result in the following cases:
- The integrity level of the
targetresource exceeds the integrity level of thesourceresource consumer. - The integrity level of the
targetresource is incomparable to the integrity level of thesourceresource consumer. - An integrity level was not assigned to the
sourceresource consumer or to thetargetresource. - The
sourceortargetvalue is outside of the permissible range.
Mic security model query_level expression
query_level {source : <Sid>}
It is intended to be used as an expression that verifies fulfillment of the conditions in the choice construct (for details on the choice construct, see "Binding methods of security models to security events"). It checks the integrity level of the source resource or subject. Depending on the results of this check, various options for security event handling can be performed.
It runs incorrectly in the following cases:
- An integrity level was not assigned to the subject or
sourceresource. - The
sourcevalue is outside of the permissible range.
When the expression runs incorrectly, the Kaspersky Security Module returns the "denied" decision.
Page top