TLS Terminator component
The TLS Terminator component supplied as part of KasperskyOS Community Edition ensures secure data transmission over the network between the client and the server using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol.
The TLS Terminator component is built into the network interaction between the client and the network VFS backend. When a client uses network functions from the libc library, calls of these functions are redirected to the TLS Terminator component. The TLS Terminator component implements wrapper functions for standard calls of the network VFS backend. These wrappers ensure that TLS connections are established, outbound data is encrypted before it is sent to the network VFS backend, and inbound data is decrypted before being returned to the client. This implementation of the component ensures data protection during transmission over the network without the need to modify the client code.
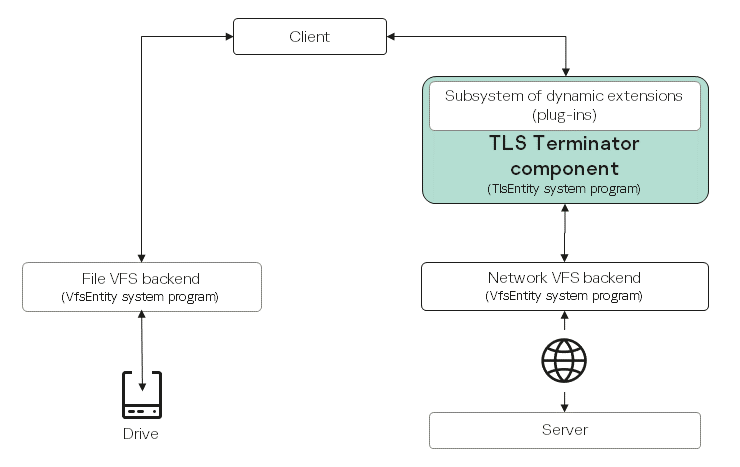
How the TLS Terminator component works
- Client
Calls functions from the
libclibrary (see the table below for a complete list of supported functions) as if it were working directly with the network VFS backend. - TLS Terminator
Intercepts function calls from the client to the
libclibrary and replaces them with wrapper functions implementing TLS. TLS connections are managed by using the Mbed TLS and OpenSSL libraries, which implement TLS protocols and cryptographic algorithms.A subsystem of dynamic extensions (plug-ins) lets you extend the functionality of the TLS Terminator component without changing its source code by using dynamic libraries developed by the user.
- Network VFS backend
Implements the network stack.
- File VFS backend
Implements file systems.
API of the libc library supported by the TLS Terminator component
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Functions marked with * in the table have standard POSIX behavior. The behavior of the rest of the functions is modified by the TLS Terminator component as indicated in the table below.
Modification of the behavior of libc functions by the TLS Terminator component
libc function |
POSIX behavior of the function |
Behavior of the function when using TLS Terminator |
|---|---|---|
|
Accepts a connection request from the pending connection queue and creates a new socket handle for interaction |
|
|
Closes the socket |
|
|
Initiates a connection on the socket |
|
|
Gets socket options |
|
|
Receives data from the server |
|
|
Sends data to the server |
|
|
Sets the parameters of a socket. |
|
|
Terminates data transfer over the socket |
|
|
Creates a socket for network communication |
|
|
Tracks the state of file handles. |
|
|
Sends data to the server |
|
The IPPROTO_TLS value, which is not available in POSIX, has been implemented for the level parameter for the getsockopt() and setsockopt() functions. This value is defined in the /opt/KasperskyOS-Community-Edition-<platform>-<version>/sysroot-*-kos/include/netinet/in.h file from KasperskyOS Community Edition. Syntax of functions:
int setsockopt(int socket, int level, int option_name, const void *option_value, socklen_t option_len);
int getsockopt(int socket, int level, int option_name, void *restrict option_value, socklen_t *restrict option_len);
The level parameter specifies the level at which the option_name socket parameter name is defined. If the level parameter is equal to IPPROTO_TLS when calling the getsockopt() and setsockopt() functions, the TLS Terminator component processes the option_name socket parameter names that are available for this level from the table below.
Socket parameter names and their corresponding function behavior
Socket parameter name |
Behavior of the setsockopt() function |
Behavior of the getsockopt() function |
|---|---|---|
|
Sets the name of the server to which the TLS connection is being established. This name will be used in the Server Name Indication (SNI) extension when performing the TLS handshake. |
Gets the name of the server to which the TLS connection is being established. |
|
Enables an OCSP Stapling check (confirmation that the certificate is valid) for the specified client socket. |
This parameter is not processed. |
|
This parameter is not processed. |
Gets the ID of the TLS session. |
|
This parameter is not processed. |
Returns the server certificate validation result as a combination of error flags. |
If the default functionality of the TLS Terminator component is insufficient, it can be extended by using a plug-in mechanism. For more details, refer to Extending TLS Terminator functionality.
Contents of the TLS Terminator component
The component consists of the following files:
- Executable file
/opt/KasperskyOS-Community-Edition-<platform>-<version>/sysroot-*-kos/bin/tls - Formal specification file
/opt/KasperskyOS-Community-Edition-<platform>-<version>/sysroot-*-kos/include/kl/TlsEntity.edland the header file generated from it - Solution security policy description file
/opt/KasperskyOS-Community-Edition-<platform>-<version>/sysroot-*-kos/include/kl/TlsEntity.psl