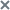Data exchange mechanism in Kaspersky Neuromorphic Platform
When working with the source code, consider the characteristics of the platform data exchange mechanism.
Kaspersky Neuromorphic Platform ensures data exchange between populations and projections, and between the platform objects and the external environment objects. Populations and projections share data via messages.
Data exchange between populations and projections
The population's neurons generate messages containing spikes to which more than one projection can be subscribed. Population spikes are sent to the synapse projections.
After receiving spikes, the backend calculates synaptic impacts. Projections send messages with the values of the synaptic impacts to the postsynaptic populations of neurons.
Data exchange between the backend and the external environment
The backend receives data from the external environment in the form of spikes. Spikes can be sent to the backend synchronously (upon the user's request). To receive spikes the method that blocks the data source is called.
Messages from the backend to the external environment can be sent to the subscribers upon a signal from the backend or in synchronous mode upon the user's request.
If needed, you can implement and use asynchronous mode for data sharing between the backend and the external environment.
Data exchange between the neural network and the external environment
Data from the external environment gets into the neural network through the input channels, which convert this data to spikes.
The neural network transmits data to the external environment through the output channels connected to the specified populations that convert spikes into data. Transmission of data, such as the membrane potential, is also possible through a monitoring subsystem.
If needed, you can implement and use custom platform objects for data sharing between the neural network and the external environment.
Page top