Deploying the orchestrator
The orchestrator requires the following components:
- Redis.
- Redis Sentinel.
- MongoDB.
- KNBE (backend service of the orchestrator, included with the solution).
As cluster nodes, you can use hosts that are already in use (virtual machines (VMs) or physical servers) or dedicated hosts. Hosts must be running Linux with Docker Engine installed.
Hardware and software requirements
The orchestrator components require the following software and its dependencies to be installed on the nodes:
- pacemaker.
- pcs.
- docker.io.
- openjdk-17-jre-headless.
You can use the table below to calculate the required resources on an individual node depending on the deployment scheme and the number of managed devices.
Table for calculating the computing resource requirement on nodes
Solution component |
Virtual CPU (vCPU) |
RAM, GB |
Disk, GB |
IOPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
50 managed devices |
||||
Redis |
2 |
1 |
100 |
1000 |
Redis Sentinel |
2 |
1 |
||
MongoDB |
2 |
2 |
||
KNBE |
4 |
4 |
||
100 managed devices |
||||
Redis |
2 |
1 |
100 |
1000 |
Redis Sentinel |
2 |
1 |
||
MongoDB |
4 |
4 |
||
KNBE |
4 |
4 |
||
250 managed devices |
||||
Redis |
2 |
2 |
100 |
1000 |
Redis Sentinel |
2 |
2 |
||
MongoDB |
4 |
4 |
||
KNBE |
6 |
4 |
||
500 managed devices |
||||
Redis |
2 |
2 |
100 |
1000 |
Redis Sentinel |
2 |
2 |
||
MongoDB |
6 |
4 |
||
KNBE |
6 |
6 |
||
1000 managed devices |
||||
Redis |
4 |
2 |
100 |
1000 |
Redis Sentinel |
2 |
2 |
||
MongoDB |
6 |
6 |
||
KNBE |
6 |
8 |
||
2000 managed devices |
||||
Redis |
4 |
4 |
200 |
2000 |
Redis Sentinel |
2 |
4 |
||
MongoDB |
6 |
8 |
||
KNBE |
6 |
10 |
||
Calculation example:
All components are deployed on node 1 and node 2, and only MongoDB and Redis Sentinel are deployed on node 3. Therefore, if you want to connect up to 50 devices, then on node 1 and node 2, you will need 10 vCPUs, 8 GB of RAM, 100 GB of disk space, and 1000 IOPS (on each node), and on node 3, you will need 4 vCPUs, 3 GB of RAM, 100 GB of disk space, and 1000 IOPS.
This article describes a scenario for deploying the orchestrator as a minimal high-availability cluster with three nodes: Node_1, Node_2, and Node_3. Nodes are created as virtual machines. The deployment is described below.
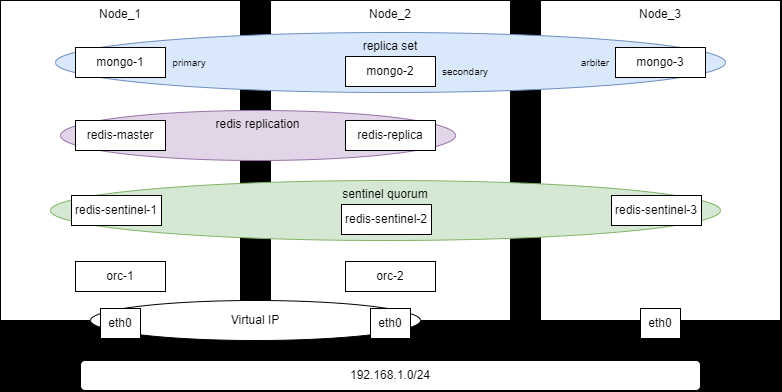
Deploying the orchestrator on three nodes
The high availability of the orchestrator is achieved by configuring a virtual IP address (Virtual IP, VIP), which means connecting nodes Node_1 and Node_2 to the same L2 network segment. If you must place Node_1 and Node_2 in different subnets, then high availability must be achieved using the means of the client application or other technologies (DNS Health Checking, BGP Anycast).
- Prepare the files necessary for deployment.
- Download the OS image that you want to use on the nodes:
When using Astra Linux, install the required packages from the following repository: https://download.astralinux.ru/astra/frozen/1.8_x86-64/1.8.2/main-repository 1.8_x86-64.
- For Astra Linux 1.8.3, install packages your personal account https://lk.astra.ru/
When using Astra Linux, install the required packages from the Astra Linux 1.8.3 repository.
- Ubuntu 22.04 from the
https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/jammy/currentrepository (for example, thejammy-server-cloudimg-amd64.imgdistribution kit).
- Download the images of containers that you will use to deploy the corresponding orchestrator components:
mongo:5.0.7, built using executable files from the Kaspersky NGFW distribution kitastra/ubi18-redis7015:1.8.2from the Astra Container Registry for Astra Linux 1.8 orredis:6.2.20from Docker Hub for Ubuntu 22.04knbe-1.0.0.release.*.cis.amd64_en-US_ru-RU.tgzfrom the Kaspersky NGFW distribution kit
- Create three VMs for each node.
- Set up environment variables.
On each node, set the environment variables listed below. Use different values of the variables if necessary.
Environment variables are set for the duration of a user session. If the session is interrupted, the variables must be set again.
export HACLUSTER_PASS="SmplPss"export ORC_KEY_PASS="SmplPss"export NODE_1="192.168.1.101"export NODE_1_HOSTNAME="knbe-orc-1"export NODE_2="192.168.1.102"export NODE_2_HOSTNAME="knbe-orc-2"export NODE_3="192.168.1.103"export NODES_VIP="192.168.1.100"export NODES_NET_MASK="24"export NODES_VIP_ETH="eth0"export MONGO_ADMIN_PASS="SmplPss"export MONGO_KNAAS_PASS="SmplPss"The value of the
ORC_ENC_PASSvariable must be at least 32 characters long.export ORC_ENC_PASS="SmplPssSmplPssSmplPssSmplSmplPss"export ORC_CONTAINER_NAME="knaas-orc:2.25.03.release.39.cis.amd64_en-US_ru-RU"Installation must be performed as the
sdwanuser. - Install the required packages.
Install docker on each node:
sudo apt install docker.io -ysudo usermod -aG docker $USEROn Node_1 and Node_2, install pacemaker:
sudo apt install pacemaker corosync pcs -yOn Node_1, install OpenJDK to be able to use keytool:
sudo apt install openjdk-17-jre-headless -y - Configure a cluster using Corosync/Pacemaker.
Configuration is performed on Node_1 and Node_2. Node_3 is the arbiter and does not participate in processing requests.
- Clear the contents of the
hostsfile on Node_1 and Node_2:sudo sed -i "/^127\.0\.1\.1\s.*$HOSTNAME/d" /etc/hosts - On Node_1 and Node_2, add A records of hosts to
/etc/hosts:echo "$NODE_1 $NODE_1_HOSTNAME" | sudo tee -a /etc/hostsecho "$NODE_2 $NODE_2_HOSTNAME" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts - Set a password for hacluster user on Node_1 and Node_2:
echo "hacluster:$HACLUSTER_PASS" | sudo chpasswd - Start services on Node_1 and Node_2:
sudo systemctl enable --now pcsd corosync pacemaker - Delete the default cluster on Node_1:
sudo pcs cluster destroy --force - Authenticate the cluster on Node_1:
sudo pcs host auth $NODE_1_HOSTNAME $NODE_2_HOSTNAME -u hacluster -p $HACLUSTER_PASS - Initialize the cluster on Node_1:
sudo pcs cluster setup orc-ha $NODE_1_HOSTNAME $NODE_2_HOSTNAME --force - Start the cluster on Node_1:
sudo pcs cluster start --allsudo pcs cluster enable --all - Configure the cluster on Node_1 and Node_2:
sudo pcs property set stonith-enabled=falsesudo pcs property set no-quorum-policy=stopsudo pcs property set symmetric-cluster=true - Check the cluster status on any of the nodes:
sudo pcs status
The list must consist of two nodes, which must be online:
Node List:* Online: [ knbe-orc-1 knbe-orc-2 ]- Create a resource with a virtual IP address on Node_1:
sudo pcs resource create VirtualIP ocf:heartbeat:IPaddr2 ip=$NODES_VIP cidr_netmask=$NODES_NET_MASK nic=$NODES_VIP_ETH op monitor interval=2s meta target-role="Started" - Configure resource usage priorities for nodes on Node_1:
sudo pcs constraint location VirtualIP prefers $NODE_1_HOSTNAME=200sudo pcs constraint location VirtualIP prefers $NODE_2_HOSTNAME=0
- Clear the contents of the
- Create and install certificates
All actions with certificates must be performed on Node_1.
- Create a directory structure to store the certificates of installation components on Node_1:
mkdir -p -m 0755 $HOME/ssl/camkdir -p -m 0755 $HOME/ssl/mongomkdir -p -m 0755 $HOME/ssl/redismkdir -p -m 0755 $HOME/ssl/redis-sentinelmkdir -p -m 0755 $HOME/ssl/orc - Create a self-signed root certificate.
To do this, create a private key:
openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -out $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.key -pkeyopt rsa_keygen_bits:4096Then create the root certificate:
openssl req -x509 -new -key $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.key \-subj "/C=RU/ST=Moscow/O=Kaspersky/CN=*" \-addext "basicConstraints=critical,CA:TRUE" \-addext "keyUsage=critical,keyCertSign" \-days 3650 -out $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem - Create the certificates of installation components:
- MongoDB
Create a private key:
openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -out $HOME/ssl/mongo/cert.key -pkeyopt rsa_keygen_bits:4096Create a certificate:
openssl req -x509 -new -key $HOME/ssl/mongo/cert.key \-subj "/C=RU/ST=Moscow/L=Moscow/O=LK/OU=LK/CN=mongo" \-addext "subjectAltName=DNS:mongo,IP:127.0.0.1,IP:$NODE_1,IP:$NODE_2,IP:$NODE_3,IP:$NODES_VIP" \-CA $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem \-CAkey $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.key \-out $HOME/ssl/mongo/cert.pem \-days 365Combine the generated key and certificate into one file:
cat $HOME/ssl/mongo/cert.key $HOME/ssl/mongo/cert.pem > $HOME/ssl/mongo/combined.pem - Redis
Create a private key:
openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -out $HOME/ssl/redis/cert.key -pkeyopt rsa_keygen_bits:4096Create a certificate:
openssl req -x509 -new -key $HOME/ssl/redis/cert.key \-subj "/C=RU/ST=Moscow/L=Moscow/O=LK/OU=LK/CN=redis" \-addext "subjectAltName=DNS:redis,IP:127.0.0.1,IP:$NODE_1,IP:$NODE_2,IP:$NODE_3,IP:$NODES_VIP" \-CA $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem \-CAkey $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.key \-out $HOME/ssl/redis/cert.pem \-days 365Convert the key:
openssl pkcs8 -topk8 -in $HOME/ssl/redis/cert.key -out $HOME/ssl/redis/key.pem -nocrypt - Redis Sentinel
Create a private key:
openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -out $HOME/ssl/redis-sentinel/cert.key -pkeyopt rsa_keygen_bits:4096Create a certificate:
openssl req -x509 -new -key $HOME/ssl/redis-sentinel/cert.key \-subj "/C=RU/ST=Moscow/L=Moscow/O=LK/OU=LK/CN=redis-sentinel" \-addext "subjectAltName=DNS:redis-sentinel,IP:127.0.0.1,IP:$NODE_1,IP:$NODE_2,IP:$NODE_3,IP:$NODES_VIP" \-CA $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem \-CAkey $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.key \-out $HOME/ssl/redis-sentinel/cert.pem \-days 365Convert the key:
openssl pkcs8 -topk8 -in $HOME/ssl/redis-sentinel/cert.key -out $HOME/ssl/redis-sentinel/key.pem -nocrypt - Backend service of the orchestrator
Create a private key:
openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -out $HOME/ssl/orc/cert.key -pkeyopt rsa_keygen_bits:4096Convert the key:
openssl pkcs8 -topk8 -in $HOME/ssl/orc/cert.key -out $HOME/ssl/orc/key.pem -nocryptCreate a certificate:
openssl req -x509 -new -key $HOME/ssl/orc/cert.key \-subj "/C=RU/ST=Moscow/L=Moscow/O=LK/OU=LK/CN=orc" \-addext "subjectAltName=DNS:orc,IP:127.0.0.1,IP:$NODE_1,IP:$NODE_2,IP:$NODE_3,IP:$NODES_VIP" \-CA $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem \-CAkey $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.key \-out $HOME/ssl/orc/cert.pem \-days 365Create a key store (PKCS12 KeyStore):
openssl pkcs12 -export \-in $HOME/ssl/orc/cert.pem \-inkey $HOME/ssl/orc/cert.key \-certfile $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem \-out $HOME/ssl/orc/keyStore.p12 \-name "orc" \-passout env:ORC_KEY_PASS && \chmod 644 $HOME/ssl/orc/keyStore.p12Add the CA certificate to the store:
keytool -importcert -alias ca \-file $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem \-keystore $HOME/ssl/orc/keyStore.p12 \-storetype PKCS12 \-storepass $ORC_KEY_PASS \-trustcacerts -nopromptCreate a trust store (PKCS12 TrustStore):
openssl pkcs12 -export \-name "orc" \-inkey $HOME/ssl/orc/cert.key \-in $HOME/ssl/orc/cert.pem \-certfile $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem \-out $HOME/ssl/orc/trustStore.p12 \-passout env:ORC_KEY_PASS && \chmod 644 $HOME/ssl/orc/trustStore.p12Add the CA certificate to the store:
keytool -importcert -alias ca \-file $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem \-keystore $HOME/ssl/orc/trustStore.p12 \-storetype PKCS12 \-storepass $ORC_KEY_PASS \-trustcacerts -nopromptDistribute certificates to nodes:
Run the following commands on Node_1:
scp -r ssl $NODE_2:/tmpscp -r ssl $NODE_3:/tmpRun the following commands on Node_2 and Node_3:
cp -r /tmp/ssl $HOME
- MongoDB
- Create a directory structure to store the certificates of installation components on Node_1:
- Create a Docker network on all nodes:
docker network create \--driver=bridge \--subnet=10.11.11.0/24 \--gateway=10.11.11.1 \--opt com.docker.network.bridge.name=knaas_aio_int \knaas_aio_int - Install and configure the components:
- MongoDB
To use MongoDB, the AVX instruction set extensions must be enabled on the CPU. To do this, when deploying the VM, set the CPU
host-passthroughmode if you are using KVM.- Start the containers:
Create a Docker volume on all nodes:
docker volume create --name orc_dbs_dataCreate and run a container on Node_1:
docker run -d --name=mongo-1 \--hostname=mongo-1 \--volume orc_dbs_data:/data/db \--volume $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem:/ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/mongo/combined.pem:/ssl/certs/mongo/combined.pem:ro \--volume /data/configdb \--env=TZ=Europe/Moscow \--network=knaas_aio_int \-p 27017:27017 \--restart=unless-stopped \--runtime=runc \mongo:5.0.7 \mongod --bind_ip_all --replSet knaas --tlsMode requireTLS --tlsCertificateKeyFile /ssl/certs/mongo/combined.pem --tlsCAFile /ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem --tlsDisabledProtocols TLS1_0,TLS1_1Create and run a container on Node_2:
docker run -d --name=mongo-2 \--hostname=mongo-2 \--volume orc_dbs_data:/data/db \--volume $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem:/ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/mongo/combined.pem:/ssl/certs/mongo/combined.pem:ro \--volume /data/configdb \--env=TZ=Europe/Moscow \--network=knaas_aio_int \-p 27017:27017 \--restart=unless-stopped \--runtime=runc \mongo:5.0.7 \mongod --bind_ip_all --replSet knaas --tlsMode requireTLS --tlsCertificateKeyFile /ssl/certs/mongo/combined.pem --tlsCAFile /ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem --tlsDisabledProtocols TLS1_0,TLS1_1Create and run a container on Node_3:
docker run -d --name=mongo-3 \--hostname=mongo-3 \--volume orc_dbs_data:/data/db \--volume $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem:/ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/mongo/combined.pem:/ssl/certs/mongo/combined.pem:ro \--volume /data/configdb \--env=TZ=Europe/Moscow \--network=knaas_aio_int \-p 27017:27017 \--restart=unless-stopped \--runtime=runc \mongo:5.0.7 \mongod --bind_ip_all --replSet knaas --tlsMode requireTLS --tlsCertificateKeyFile /ssl/certs/mongo/combined.pem --tlsCAFile /ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem --tlsDisabledProtocols TLS1_0,TLS1_1 - Configure a replica set:
Initiate a replica set on Node_1:
docker exec -i mongo-1 mongosh --tls \--tlsCertificateKeyFile /ssl/certs/mongo/combined.pem \--tlsCAFile /ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem <<EOFrs.initiate({_id: 'knaas',version: 1,members: [{_id: 0, host: '$NODE_1:27017', priority: 2},{_id: 1, host: '$NODE_2:27017', priority: 1},{_id: 2, host: '$NODE_3:27017', arbiterOnly: true}]})EOFOn Node_1, add the admin user to the database:
docker exec -i mongo-1 mongosh --tls \--tlsCertificateKeyFile /ssl/certs/mongo/combined.pem \--tlsCAFile /ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem <<EOFdb.getSiblingDB("admin").createUser({user:"admin",pwd:"$MONGO_ADMIN_PASS",roles:[{role:"userAdminAnyDatabase",db:"admin"}]})EOFOn Node_1, add the knaas user to the database:
docker exec -i mongo-1 mongosh --tls \--tlsCertificateKeyFile /ssl/certs/mongo/combined.pem \--tlsCAFile /ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem <<EOFdb.getSiblingDB("admin").auth("admin","$MONGO_ADMIN_PASS");db.getSiblingDB("knaas").createUser({user:"knaas",pwd:"$MONGO_KNAAS_PASS",roles:["readWrite"]})EOF
- Start the containers:
- Redis
For Ubuntu 22.04, use the
redis:6.2.20image instead ofregistry.astralinux.ru/library/astra/ubi18-redis7015:1.8.2.- Create a Docker volume on all nodes:
docker volume create --name redis_data - Create and run a container on Node_1:
docker run -d \--name redis-master \-p 6379:6379 \-v redis_data:/data \--volume $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem:/ssl/certs/ca/ca.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/redis/cert.pem:/ssl/certs/redis/cert.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/redis/cert.key:/ssl/keys/redis/key.pem:ro \registry.astralinux.ru/library/astra/ubi18-redis7015:1.8.2 \redis-server \--port 0 \--bind 0.0.0.0 \--protected-mode no \--tls-port 6379 \--tls-replication yes \--tls-cert-file /ssl/certs/redis/cert.pem \--tls-key-file /ssl/keys/redis/key.pem \--tls-ca-cert-file /ssl/certs/ca/ca.pem - Create and run a container on Node_2:
docker run -d \--name redis-replica \-p 6379:6379 \-v redis_data:/data \--volume $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem:/ssl/certs/ca/ca.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/redis/cert.pem:/ssl/certs/redis/cert.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/redis/cert.key:/ssl/keys/redis/key.pem:ro \registry.astralinux.ru/library/astra/ubi18-redis7015:1.8.2 \redis-server \--port 0 \--bind 0.0.0.0 \--protected-mode no \--tls-port 6379 \--tls-replication yes \--tls-cert-file /ssl/certs/redis/cert.pem \--tls-key-file /ssl/keys/redis/key.pem \--tls-ca-cert-file /ssl/certs/ca/ca.pem \--replicaof $NODE_1 6379
- Create a Docker volume on all nodes:
- Redis Sentinel
For Ubuntu 22.04, use the
redis:6.2.20image instead ofregistry.astralinux.ru/library/astra/ubi18-redis7015:1.8.2.- Create a Docker volume on all nodes:
docker volume create --name redis_sentinel_data - Create and run a container on Node_1:
docker run -d \--name redis-sentinel-1 \--volume $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem:/ssl/certs/ca/ca.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/redis-sentinel/cert.pem:/ssl/certs/redis/cert.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/redis-sentinel/cert.key:/ssl/keys/redis/key.pem:ro \-p 26379:26379 \registry.astralinux.ru/library/astra/ubi18-redis7015:1.8.2 \sh -c "cat > /sentinel.conf <<EOFport 0bind 0.0.0.0protected-mode notls-port 26379tls-cert-file /ssl/certs/redis/cert.pemtls-key-file /ssl/keys/redis/key.pemtls-ca-cert-file /ssl/certs/ca/ca.pemtls-auth-clients optionaltls-replication yestls-cluster yessentinel monitor mymaster $NODE_1 6379 2sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 5000sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 60000sentinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1sentinel announce-ip $NODE_1sentinel announce-port 26379EOFredis-server /sentinel.conf --sentinel" - Create and run a container on Node_2:
docker run -d \--name redis-sentinel-2 \--volume $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem:/ssl/certs/ca/ca.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/redis-sentinel/cert.pem:/ssl/certs/redis/cert.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/redis-sentinel/cert.key:/ssl/keys/redis/key.pem:ro \-p 26379:26379 \registry.astralinux.ru/library/astra/ubi18-redis7015:1.8.2 \sh -c "cat > /sentinel.conf <<EOFport 0bind 0.0.0.0protected-mode notls-port 26379tls-cert-file /ssl/certs/redis/cert.pemtls-key-file /ssl/keys/redis/key.pemtls-ca-cert-file /ssl/certs/ca/ca.pemtls-auth-clients optionaltls-replication yestls-cluster yessentinel monitor mymaster $NODE_1 6379 2sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 5000sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 60000sentinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1sentinel announce-ip $NODE_2sentinel announce-port 26379EOFredis-server /sentinel.conf --sentinel" - Create and run a container on Node_3:
docker run -d \--name redis-sentinel-3 \--volume $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem:/ssl/certs/ca/ca.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/redis-sentinel/cert.pem:/ssl/certs/redis/cert.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/redis-sentinel/cert.key:/ssl/keys/redis/key.pem:ro \-p 26379:26379 \registry.astralinux.ru/library/astra/ubi18-redis7015:1.8.2 \sh -c "cat > /sentinel.conf <<EOFport 0bind 0.0.0.0protected-mode notls-port 26379tls-cert-file /ssl/certs/redis/cert.pemtls-key-file /ssl/keys/redis/key.pemtls-ca-cert-file /ssl/certs/ca/ca.pemtls-auth-clients optionaltls-replication yestls-cluster yessentinel monitor mymaster $NODE_1 6379 2sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 5000sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 60000sentinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1sentinel announce-ip $NODE_3sentinel announce-port 26379EOFredis-server /sentinel.conf --sentinel"
- Create a Docker volume on all nodes:
- Orchestrator web service
- Transfer the image of the orchestrator container from the distribution kit to Node_1 and Node_2.
- Load the container image to the Docker engine:
docker load -i "${ORC_CONTAINER_NAME//:/_}.tar" - Create a Docker volume on all nodes:
docker volume create --name orc_data - Create and run a container on Node_1:
docker run -d --name=orc-1 \--hostname=orc-1 \--volume $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem:/ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.key:/ssl/keys/ca/key.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/orc/trustStore.p12:/ssl/certs/orc/trustStore.p12:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/orc/keyStore.p12:/ssl/certs/orc/keyStore.p12:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/orc/cert.pem:/ssl/certs/orc/cert.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/orc/key.pem:/ssl/keys/orc/key.pem:ro \--volume orc_data:/data \-p 8080:8080 \--env=TZ=Europe/Moscow \--env=KNAAS_EULA_AGREED=yes \--env="JAVA_OPTS=-Xms2048m -Xmx3560m -Dspring.data.mongodb.database=knaas -Dorc.security.encryption.password=$ORC_ENC_PASS -Dspring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://knaas:$MONGO_KNAAS_PASS@$NODE_1:27017,$NODE_2:27017,$NODE_3:27017/knaas?replicaSet=knaas&tls=true -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.subscription-mode=master -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.master-name=mymaster -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.add-sentinel-address=rediss://$NODE_1:26379,rediss://$NODE_2:26379,rediss://$NODE_3:26379 -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.ssl-truststore=file:///ssl/certs/orc/trustStore.p12 -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.ssl-truststore-password=$ORC_KEY_PASS -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.ssl-keystore=file:///ssl/certs/orc/keyStore.p12 -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.ssl-keystore-password=$ORC_KEY_PASS -Dorc.openflow.tls.ca-private.certificate.path=/ssl/keys/ca/key.pem -Dorc.openflow.tls.ca-public.certificate.path=/ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem -Dgrpc.tls.certificate.path=/ssl/certs/orc/cert.pem -Dgrpc.tls.private.key.path=/ssl/keys/orc/key.pem -Dgrpc.tls.ca.certificate.path=/ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem -Dserver.ssl.enabled=true -Dserver.ssl.trust-store=/ssl/certs/orc/trustStore.p12 -Dserver.ssl.trust-store-password=$ORC_KEY_PASS -Dserver.ssl.trust-store-type=pkcs12 -Dserver.ssl.key-store=/ssl/certs/orc/keyStore.p12 -Dserver.ssl.key-store-password=$ORC_KEY_PASS -Dserver.ssl.key-store-type=pkcs12 -Dorc.sdn.grpc.timeout=60s" \--network=knaas_aio_int \--workdir=/opt/b4n/orc \--restart=unless-stopped \hub.brain4net.com/$ORC_CONTAINER_NAME - Create and run a container on Node_2:
docker run -d --name=orc-2 \--hostname=orc-2 \--volume $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.pem:/ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/ca/certificate.key:/ssl/keys/ca/key.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/orc/trustStore.p12:/ssl/certs/orc/trustStore.p12:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/orc/keyStore.p12:/ssl/certs/orc/keyStore.p12:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/orc/cert.pem:/ssl/certs/orc/cert.pem:ro \--volume $HOME/ssl/orc/key.pem:/ssl/keys/orc/key.pem:ro \--volume orc_data:/data \-p 8080:8080 \--env=TZ=Europe/Moscow \--env=KNAAS_EULA_AGREED=yes \--env="JAVA_OPTS=-Xms2048m -Xmx3560m -Dspring.data.mongodb.database=knaas -Dorc.security.encryption.password=$ORC_ENC_PASS -Dspring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://knaas:$MONGO_KNAAS_PASS@$NODE_1:27017,$NODE_2:27017,$NODE_3:27017/knaas?replicaSet=knaas&tls=true -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.subscription-mode=master -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.master-name=mymaster -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.add-sentinel-address=rediss://$NODE_1:26379,rediss://$NODE_2:26379,rediss://$NODE_3:26379 -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.ssl-truststore=file:///ssl/certs/orc/trustStore.p12 -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.ssl-truststore-password=$ORC_KEY_PASS -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.ssl-keystore=file:///ssl/certs/orc/keyStore.p12 -Dspring.redis.redisson.sentinel-servers-config.ssl-keystore-password=$ORC_KEY_PASS -Dorc.openflow.tls.ca-private.certificate.path=/ssl/keys/ca/key.pem -Dorc.openflow.tls.ca-public.certificate.path=/ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem -Dgrpc.tls.certificate.path=/ssl/certs/orc/cert.pem -Dgrpc.tls.private.key.path=/ssl/keys/orc/key.pem -Dgrpc.tls.ca.certificate.path=/ssl/certs/ca/cert.pem -Dserver.ssl.enabled=true -Dserver.ssl.trust-store=/ssl/certs/orc/trustStore.p12 -Dserver.ssl.trust-store-password=$ORC_KEY_PASS -Dserver.ssl.trust-store-type=pkcs12 -Dserver.ssl.key-store=/ssl/certs/orc/keyStore.p12 -Dserver.ssl.key-store-password=$ORC_KEY_PASS -Dserver.ssl.key-store-type=pkcs12 -Dorc.sdn.grpc.timeout=60s" \--network=knaas_aio_int \--workdir=/opt/b4n/orc \--restart=unless-stopped \hub.brain4net.com/$ORC_CONTAINER_NAME
- MongoDB
- Test the orchestrator.
After running all commands, containers should be started and should not be restarting. The orchestrator responds on port 8080 on the configured virtual IP address. You can check whether the orchestrator is running and available at the specified virtual IP address by performing a check that must return an empty response:
curl -k https://$NODES_VIP:8080To test authentication on the orchestrator, you can run the following python script:
test_auth.py
import requestsimport sysfrom requests.packages.urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarningrequests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings(InsecureRequestWarning)ip = sys.argv[1]sess = requests.Session()sess.verify = Falsetry:response=sess.get(f'https://{ip}:8080/api/core/users/current')response=sess.post((f'https://{ip}:8080/api/authentication'), data={'j_username': 'admin', 'j_password': 'admin'},headers={'X-CSRF-TOKEN': sess.cookies['CSRF-TOKEN']})response=sess.get(f'https://{ip}:8080/api/core/users/current')print(response.status_code)print(response.content)except Exception as e:print(f"Error - {e}")Run the script:
python3 test_auth.py $NODES_VIPExample of a response indicating success:
200b'{"id":"9cb4bba3-6b82-472d-8347-4e217dac00cb","login":"admin","firstName":"Administrator","lastName":"Administrator","email":"admin@example.com","rbacPermission":{"id":"permission-0","name":"Full access"},"role":"ROLE_PLATFORM_ADMIN","requiredRequestConfirmation":false,"state":"ONLINE","currentTenants":[],"type":"LOCAL","groups":[],"enabled2fa":false,"initialized2fa":false}' - Change the default administrator password
To change the administrator password, run the change_password.py script:
python3 change_password.py 192.168.200.100:8080Contents of the change_password.py script:
import requestsimport sysimport getpassimport jsonfrom requests.packages.urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarningrequests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings(InsecureRequestWarning)ip = sys.argv[1]sess = requests.Session()sess.verify = Falseusername = input("Enter the orchestrator user login: ")password = getpass.getpass(f"Enter the current password for the user {username}: ")try:response=sess.get('https://'+ ip +'/api/core/users/current')response=sess.post(('https://'+ ip +'/api/authentication'), data={'j_username': username, 'j_password': password},headers={'X-CSRF-TOKEN': sess.cookies['CSRF-TOKEN']})if response.status_code != 200:if response.status_code == 403 and response.json()[0]['code'] == "required_2fa_code":secFA_code = getpass.getpass(f"Enter the two-factor authentication code: ")response=sess.post(('https://'+ ip +'/api/authentication'), data={'j_username': username, 'j_password': password, 'code': secFA_code},headers={'X-CSRF-TOKEN': sess.cookies['CSRF-TOKEN']})if response.status_code != 200:print(f"Authentication failed.")sys.exit(1)else:print(f"Authentication failed.")sys.exit(1)except Exception as e:print(f"Authentication failed. Error: {e}")sys.exit(1)sess.get('https://'+ ip +'/api/core/users/current')sess.headers.update({'Accept': 'application/json','content-type': 'application/json','X-CSRF-TOKEN': sess.cookies['CSRF-TOKEN']})response.status_code = 400while response.status_code != 200:new_password = getpass.getpass(f"Enter a new password for the user {username}: ")new_password2 = getpass.getpass(f"Repeat the new password for the user {username}: ")if new_password != new_password2:print()print("The new password you entered does not match")print()else:payload = {"password": new_password}response=sess.post(('https://'+ ip +'/api/core/users/password/validate'), data=json.dumps(payload),headers={'X-CSRF-TOKEN': sess.cookies['CSRF-TOKEN']})if response.status_code != 200:print()print("Weak password!")print()payload = {"password": new_password}try:response=sess.put(('https://'+ ip +'/api/core/users/current/password'), data=json.dumps(payload),headers={'X-CSRF-TOKEN': sess.cookies['CSRF-TOKEN']})if response.status_code != 200:print("Failed to change password!")elif response.status_code == 200:print()print("Password successfully changed!")print()except Exception as e:print("Failed to change password", e)