Kaspersky Security System
Controlling interactions between entities
Interactions between entities in KasperskyOS are controlled by a separate subsystem called Kaspersky Security System. This system is provided by a security module that is executed in privileged mode.
Kaspersky Security System verifies each message (the request and the response) sent by entities. The kernel delivers a message only if Kaspersky Security System allows its delivery.
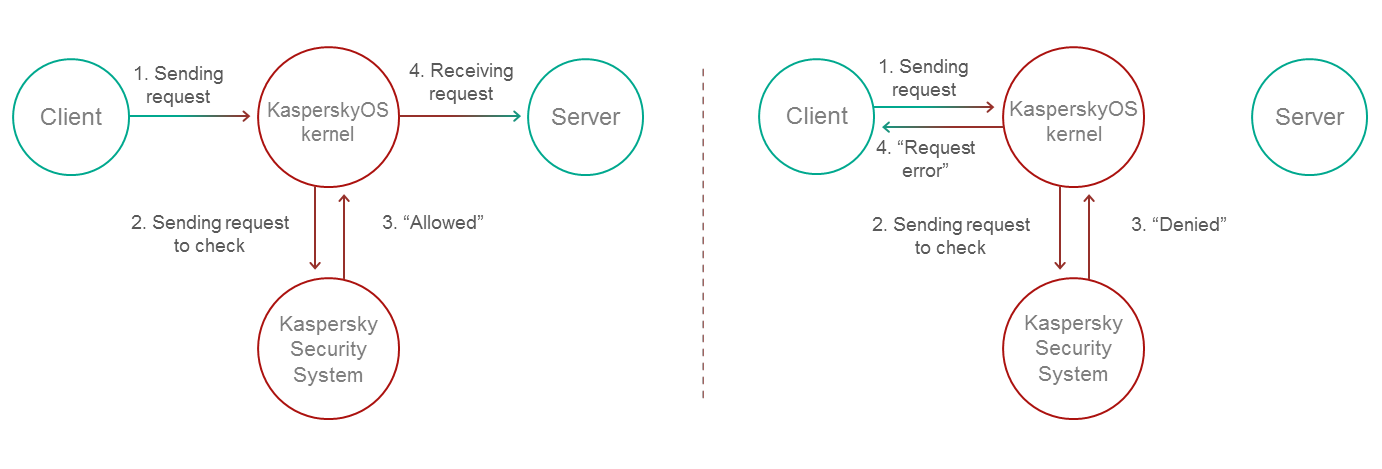
On the left: Kaspersky Security System allows the delivery of a request. On the right: delivery of a request is denied.
Other types of monitored events
In addition to the interactions of entities, Kaspersky Security System monitors the following events:
- Entity startup
Using Kaspersky Security System, you can allow or deny the startup of an entity depending on specific conditions and initialize the security context of an entity. For example, when using a role-based access model, you can start an entity with a defined role.
- Query via the security interface
The security interface allows an entity to directly query Kaspersky Security System. While the kernel informs Kaspersky Security System about each query to an entity, you can use the security interface to notify Kaspersky Security System about queries to any other resources.
Solution security policy
The rules governing interactions between entities, startup of entities and their queries via the security interface are statically defined in a separate file named security.psl (the solution security policy). When building the solution image, security.psl is used to build the security module. You can also combine different security models, such as role-based access (RBAC), finite-state machine models, and many others.
The solution security policy is completely separate from the business logic. This helps simplify development and lets you change the solution security policy and code of entities independently of each other.
For more details, refer to Part 3. Solution security policy.
Page top