Secure Logger example
The Secure Logger example demonstrates use of the Distrustful Decomposition pattern for separating event log read/write functionality.
Example architecture
The security goal of the Secure Logger example is to prevent any possibility of distortion or deletion of information from the event log. This example utilizes the capabilities provided by KasperskyOS to achieve this security goal.
A logging system can be examined by distinguishing the following functional steps:
- Generate information to be written to the log.
- Save information to the log.
- Read entries from the log.
- Provide entries in a convenient format for the consumer.
Accordingly, the logging subsystem can be divided into four processes depending on the required functional capabilities of each process.
For this purpose, the Secure Logger example contains the following four entities: Application, Logger, Reader and LogViewer.
- The
Applicationentity initiates the creation of entries in the event log maintained by theLoggerentity. - The
Loggerentity creates entries in the log and writes them to the disk. - The
Readerentity reads entries from the disk to send them to theLogViewerentity. - The
LogViewerentity sends entries to the user.
The IPC interface provided by the Logger entity is intended only for writing to storage. The IPC interface of the Reader entity is intended only for reading from storage. The example architecture looks as follows:
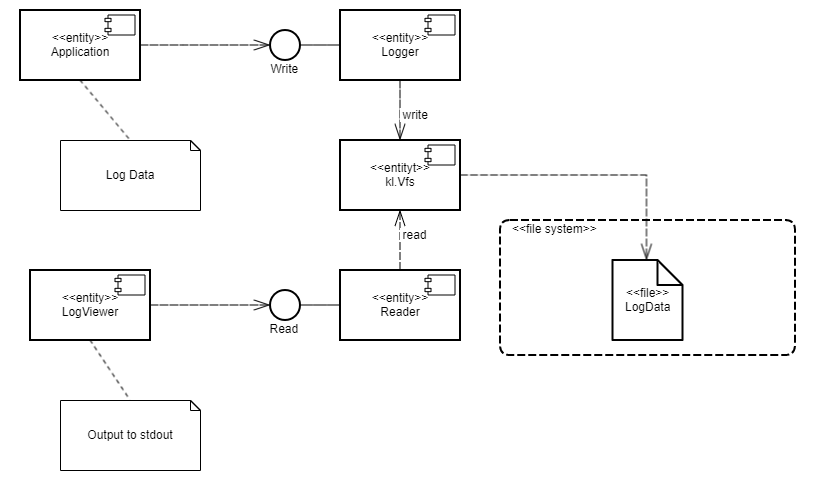
- The
Applicationentity uses the interface of theLoggerentity to save log entries. - The
LogViewerentity uses the interface of theReaderentity to read the log entries and present them to a user.
The LogViewer entity normally has external channels for interacting with a user (for example, to receive data write commands and to provide data to a user). Naturally, this entity is an untrusted component of the system, and therefore could potentially be used to conduct an attack. However, even if a successful attack results in the infiltration of unauthorized executable code into the LogViewer entity, information in the log cannot be distorted through this entity. This is because the entity can only utilize the data read interface, which cannot actually be used to distort or delete data. Moreover, the LogViewer entity does not have the capability to gain access to other IPC interfaces because this access is controlled by the security module.
A security policy in the Secure Logger example has the following characteristics:
- The
Applicationentity has the capability to query theLoggerentity to create a new entry in the event log. - The
LogViewerentity has the capability to query theReaderentity to read entries from the event log. - The
Applicationentity does not have the capability to query theReaderentity to read entries from the event log. - The
LogViewerentity does not have the capability to query theLoggerentity to create a new entry in the event log.
Example files
The code of the example and build scripts are available at the following path:
/opt/KasperskyOS-Community-Edition-<version>/examples/secure_logger
Building and running example
See the Building and running examples section.
Page top