Creating a scan exclusion
A scan exclusion is a set of conditions that must be fulfilled so that Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not scan a particular object for viruses and other threats.
Scan exclusions make it possible to safely use legitimate software that can be exploited by criminals to damage the computer or user data. Although they do not have any malicious functions, such applications can be exploited by intruders. For details on legitimate software that could be used by criminals to harm the computer or personal data of a user, please refer to the Kaspersky IT Encyclopedia website.
Such applications may be blocked by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. To prevent them from being blocked, you can configure scan exclusions for the applications in use. To do so, add the name or name mask that is listed in the Kaspersky IT Encyclopedia to the trusted zone. For example, you often use the Radmin application for remote administration of computers. Kaspersky Endpoint Security regards this activity as suspicious and may block it. To prevent the application from being blocked, create a scan exclusion with the name or name mask that is listed in the Kaspersky IT Encyclopedia.
If an application that collects information and sends it to be processed is installed on your computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may classify this application as malware. To avoid this, you can exclude the application from scanning by configuring Kaspersky Endpoint Security as described in this document.
Scan exclusions can be used by the following application components and tasks that are configured by the system administrator:
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan an object if the drive or folder containing this object is included in the scan scope at the start of one of the scan tasks. However, the scan exclusion is not applied when a custom scan task is started for this particular object.
How to create a scan exclusion in the Administration Console (MMC)
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select General settings → Exclusions.
- In the Scan exclusions and trusted applications block, click the Settings button.
- In the window that opens, select the Scan exclusions tab.
This opens a window containing a list of exclusions.
- Select the Merge values when inheriting check box if you want to create a consolidated list of exclusions for all computers in the company. The lists of exclusions in the parent and child policies will be merged. The lists will be merged provided that merging values when inheriting is enabled. Exclusions from the parent policy are displayed in child policies in a read-only view. Changing or deleting exclusions of the parent policy is not possible.
- Select the Allow use of local exclusions check box if you want to enable the user to create a local list of exclusions. This way, a user can create their own local list of exclusions in addition to the general list of exclusions generated in the policy. An administrator can use Kaspersky Security Center to view, add, edit, or delete list items in the computer properties.
If the check box is cleared, the user can access only the general list of exclusions generated in the policy.
- Click Add.
- To exclude a file or folder from scanning:
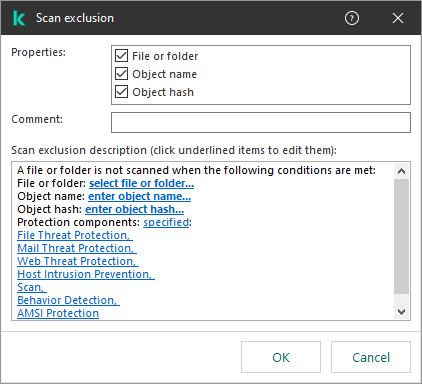
Exclusion settings
- In the Properties block, select the File or folder check box.
- Click the select file or folder link in the Scan exclusion description (click underlined items to edit them) block to open the Name of file or folder window.
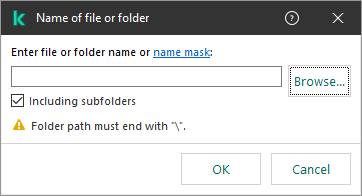
Select file or folder
- Enter the file or folder name or the mask of the file or folder name, or select the file or folder in the folder tree by clicking Browse.
Use masks:
- The
* (asterisk) character, which takes the place of any set of characters, except the \ and / characters (delimiters of the names of files and folders in paths to files and folders). For example, the mask C:\*\*.txt will include all paths to files with the TXT extension located in folders on the C: drive, but not in subfolders. - Two consecutive
* characters take the place of any set of characters (including an empty set) in the file or folder name, including the \ and / characters (delimiters of the names of files and folders in paths to files and folders). For example, the mask C:\Folder\**\*.txt will include all paths to files with the TXT extension located in folders nested within the Folder, except the Folder itself. The mask must include at least one nesting level. The mask C:\**\*.txt is not a valid mask. - The
? (question mark) character, which takes the place of any single character, except the \ and / characters (delimiters of the names of files and folders in paths to files and folders). For example, the mask C:\Folder\???.txt will include paths to all files residing in the folder named Folder that have the TXT extension and a name consisting of three characters.
You can use masks at the beginning, in the middle or at the end of the file path. For example, if you want to add a folder for all users to exclusions, enter the C:\Users\*\Folder\ mask.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports environment variables
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support the %userprofile% environment variable when generating a list of exclusions using the Kaspersky Security Center console. To apply the entry to all user accounts, you can use the * character (for example, C:\Users\*\Documents\File.exe). Whenever you add a new environment variable, you need to restart the application.
- Save your changes.
- To exclude objects with a specific name from scanning:
- In the Properties block, select the Object name check box.
- Click the enter object name link in the Scan exclusion description (click underlined items to edit them) block to open the Object name window.
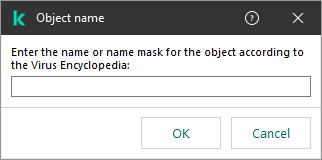
Select object
- Enter the name of the object type according to the classification of the Kaspersky Encyclopedia (for example,
Email-Worm, Rootkit or RemoteAdmin).You can use masks with the ? character (replaces any single character) and the * character (replaces any number of characters). For example, if the Client* mask is specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security excludes Client-IRC, Client-P2P and Client-SMTP objects from scans.
- Save your changes.
- If you want to exclude an individual file from scans:
- In the Properties block, select the Object hash check box.
- Click enter object hash link to open the Object hash window.
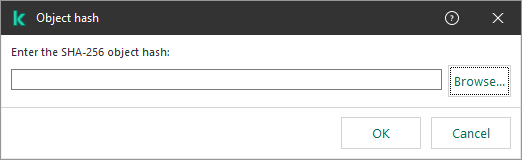
Select file
- Enter the file hash or select the file by clicking the Browse button.
If the file is modified, the file hash will also be modified. If this happens, the modified file will not be added to exclusions.
- Save your changes.
- If necessary, in the Comment field, enter a brief comment on the scan exclusion that you are creating.
- Specify the Kaspersky Endpoint Security components that should use the scan exclusion:
- Click the any link in the Scan exclusion description (click underlined items to edit them) block to activate the select components link.
- Click the select components link to open the Protection components window.
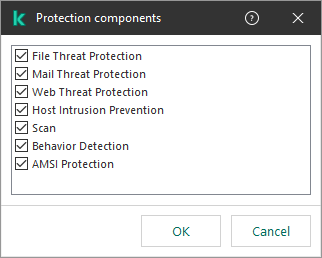
Select protection components
- Select the check boxes opposite the components to which the scan exclusion must be applied.
- Save your changes.
If the components are specified in the settings of the scan exclusion, this exclusion is applied only during scanning by these components of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
If the components are not specified in the settings of the scan exclusion, this exclusion is applied during scanning by all components of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- You can stop the exclusion at any time using the check box.
- Save your changes.
How to create a scan exclusion in the Web Console and Cloud Console
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Policies & Profiles.
- Click the name of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
The policy properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- Go to General settings → Exclusions and types of detected objects.
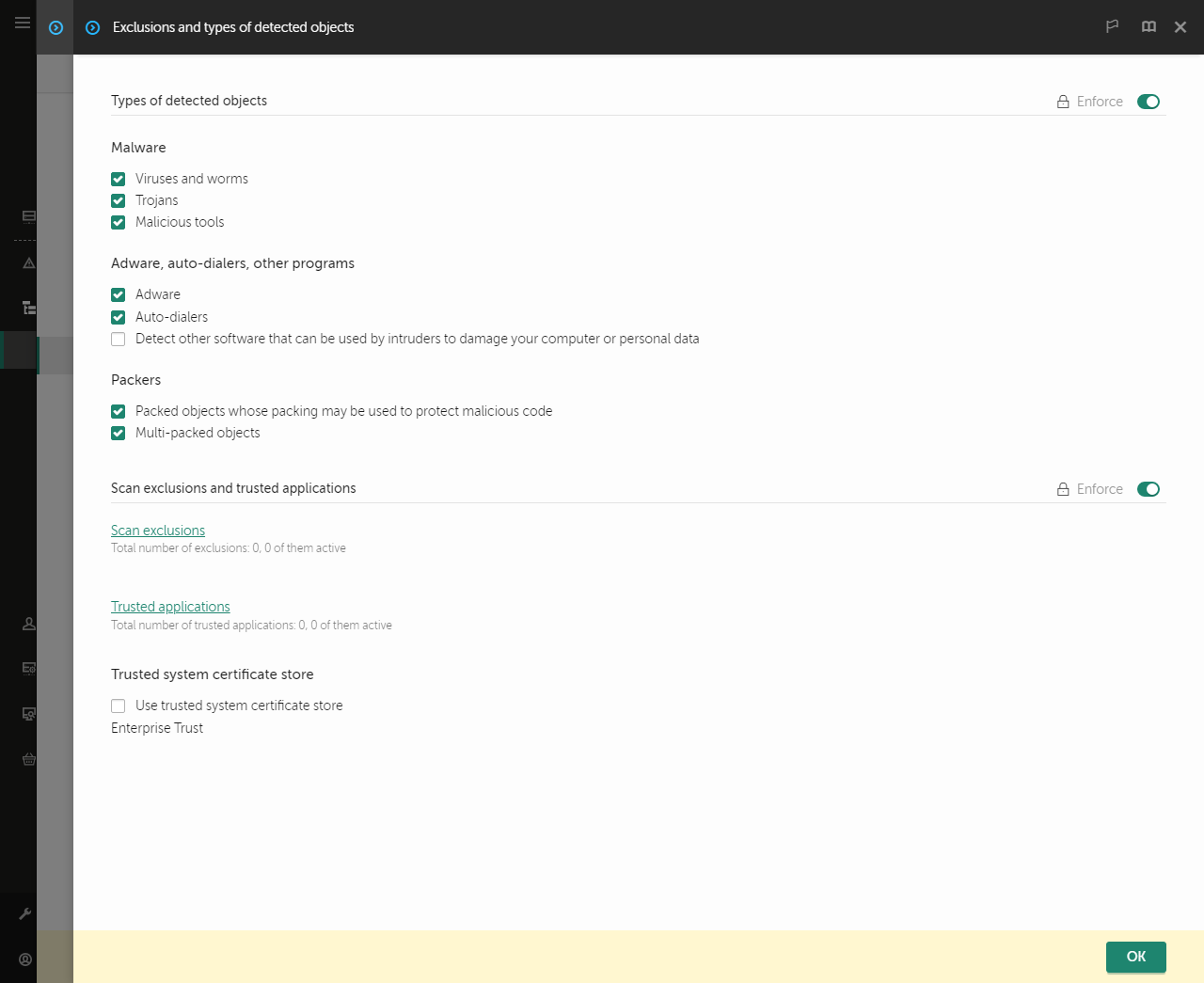
Settings of exclusions
- In the Scan exclusions and trusted applications block, click the Scan exclusions link.
- Select the Merge values when inheriting check box if you want to create a consolidated list of exclusions for all computers in the company. The lists of exclusions in the parent and child policies will be merged. The lists will be merged provided that merging values when inheriting is enabled. Exclusions from the parent policy are displayed in child policies in a read-only view. Changing or deleting exclusions of the parent policy is not possible.
- Select the Allow use of local exclusions check box if you want to enable the user to create a local list of exclusions. This way, a user can create their own local list of exclusions in addition to the general list of exclusions generated in the policy. An administrator can use Kaspersky Security Center to view, add, edit, or delete list items in the computer properties.
If the check box is cleared, the user can access only the general list of exclusions generated in the policy.
- Click the Add button.
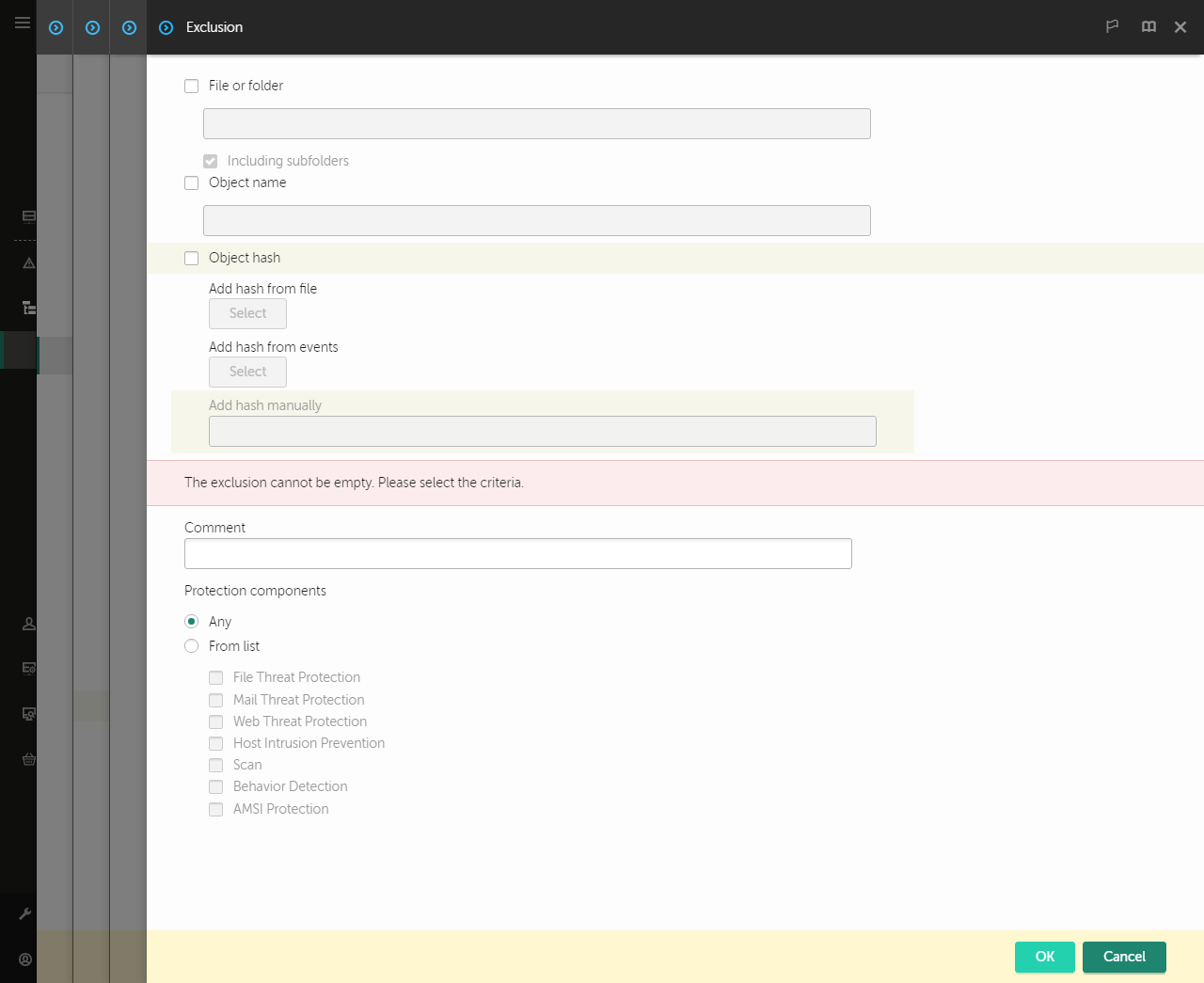
Exclusion settings
- Select how you want to add the exclusion: File or folder, Object name or Object hash.
- To exclude a file or folder from scan, enter the path manually. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports environment variables and the
* and ? characters when entering a mask:- The
* (asterisk) character, which takes the place of any set of characters, except the \ and / characters (delimiters of the names of files and folders in paths to files and folders). For example, the mask C:\*\*.txt will include all paths to files with the TXT extension located in folders on the C: drive, but not in subfolders. - Two consecutive
* characters take the place of any set of characters (including an empty set) in the file or folder name, including the \ and / characters (delimiters of the names of files and folders in paths to files and folders). For example, the mask C:\Folder\**\*.txt will include all paths to files with the TXT extension located in folders nested within the Folder, except the Folder itself. The mask must include at least one nesting level. The mask C:\**\*.txt is not a valid mask. - The
? (question mark) character, which takes the place of any single character, except the \ and / characters (delimiters of the names of files and folders in paths to files and folders). For example, the mask C:\Folder\???.txt will include paths to all files residing in the folder named Folder that have the TXT extension and a name consisting of three characters.You can use masks at the beginning, in the middle or at the end of the file path. For example, if you want to add a folder for all users to exclusions, enter the C:\Users\*\Folder\ mask.
- If you want to exclude a specific type of object from scans, in the Object name field enter the name of the object type according to the classification of the Kaspersky Encyclopedia (for example,
Email-Worm, Rootkit or RemoteAdmin).You can use masks with the ? character (replaces any single character) and the * character (replaces any number of characters). For example, if the Client* mask is specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security excludes Client-IRC, Client-P2P and Client-SMTP objects from scans.
- If you want to exclude an individual file from scans, enter the file hash in the Object hash field.
If the file is modified, the file hash will also be modified. If this happens, the modified file will not be added to exclusions.
- In the Protection components block, select the components that you want the scan exclusion to apply to.
- If necessary, in the Comment field, enter a brief comment on the scan exclusion that you are creating.
- You can use the toggle to stop an exclusion at any time.
- Save your changes.
How to create a scan exclusion in the application interface
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Exclusions and types of detected objects.
- In the Exclusions block, click the Manage exclusions link.
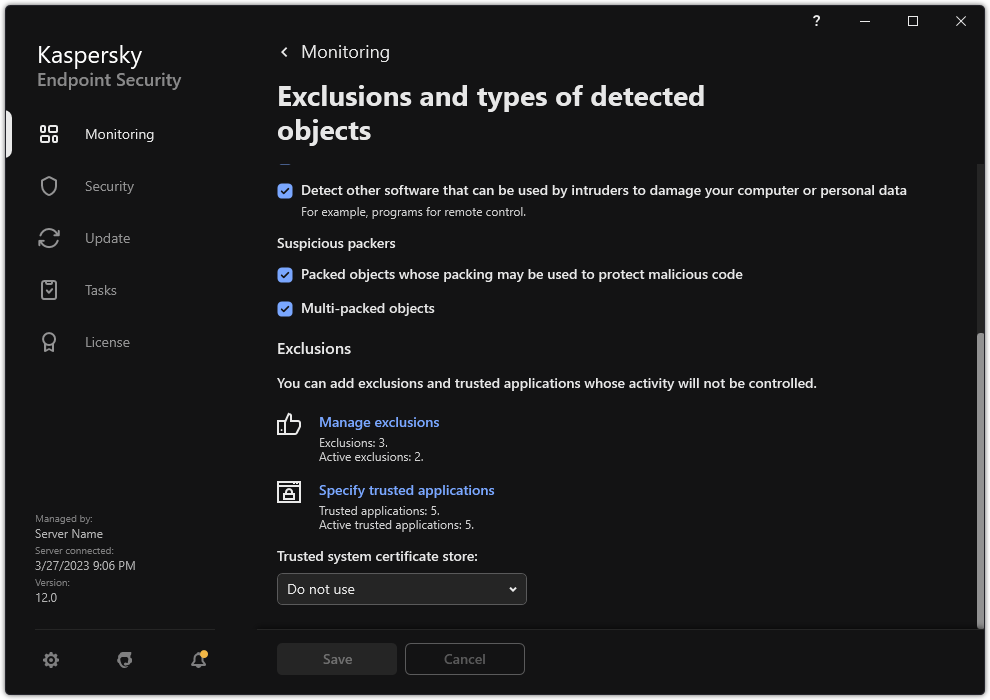
Settings of exclusions
- Click Add.
- If you want to exclude a file or folder from scans, select the file or folder by clicking the Browse button.
You can also enter the path manually. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports environment variables and the * and ? characters when entering a mask:
- The
* (asterisk) character, which takes the place of any set of characters, except the \ and / characters (delimiters of the names of files and folders in paths to files and folders). For example, the mask C:\*\*.txt will include all paths to files with the TXT extension located in folders on the C: drive, but not in subfolders. - Two consecutive
* characters take the place of any set of characters (including an empty set) in the file or folder name, including the \ and / characters (delimiters of the names of files and folders in paths to files and folders). For example, the mask C:\Folder\**\*.txt will include all paths to files with the TXT extension located in folders nested within the Folder, except the Folder itself. The mask must include at least one nesting level. The mask C:\**\*.txt is not a valid mask. - The
? (question mark) character, which takes the place of any single character, except the \ and / characters (delimiters of the names of files and folders in paths to files and folders). For example, the mask C:\Folder\???.txt will include paths to all files residing in the folder named Folder that have the TXT extension and a name consisting of three characters.You can use masks at the beginning, in the middle or at the end of the file path. For example, if you want to add a folder for all users to exclusions, enter the C:\Users\*\Folder\ mask.
- If you want to exclude a specific type of object from scans, in the Object field enter the name of the object type according to the classification of the Kaspersky Encyclopedia (for example,
Email-Worm, Rootkit or RemoteAdmin).You can use masks with the ? character (replaces any single character) and the * character (replaces any number of characters). For example, if the Client* mask is specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security excludes Client-IRC, Client-P2P and Client-SMTP objects from scans.
- If you want to exclude an individual file from scans, enter the file hash in the File hash field.
If the file is modified, the file hash will also be modified. If this happens, the modified file will not be added to exclusions.
- In the Protection components block, select the components that you want the scan exclusion to apply to.
- If necessary, in the Comment field, enter a brief comment on the scan exclusion that you are creating.
- Select the Active status for the exclusion.
You can stop the exclusion at any time using the toggle.
- Save your changes.
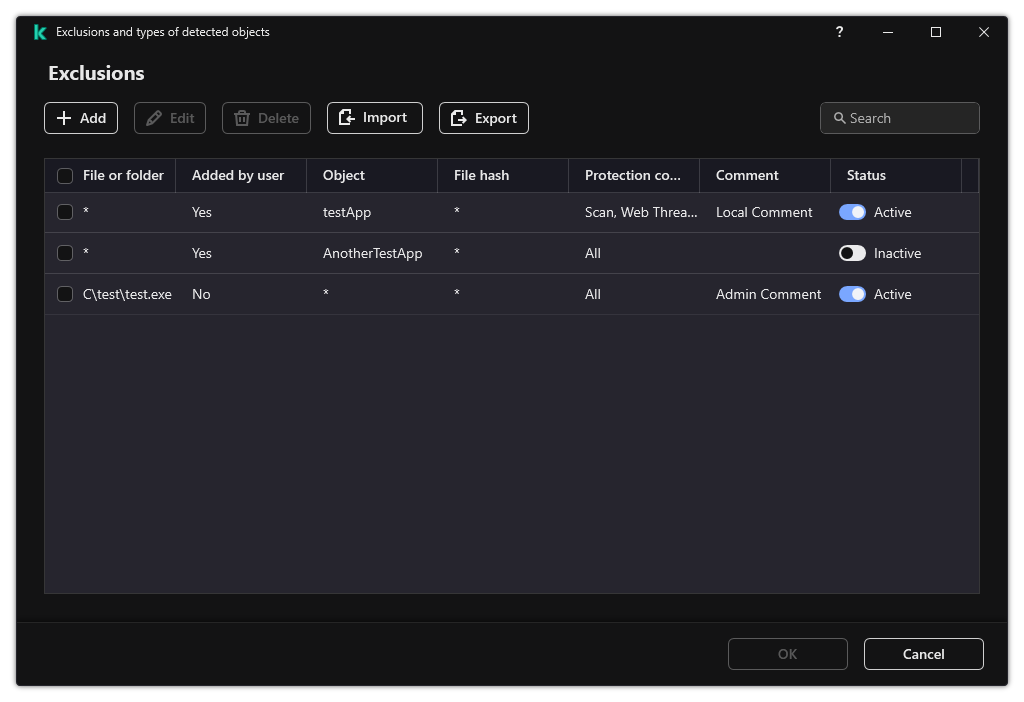
List of exclusions
Path mask examples:
Paths to files located in any folder:
- The mask
*.exe will include all paths to files that have the exe extension. - The mask
example* will include all paths to files named EXAMPLE.
Paths to files located in a specified folder:
- The
C:\dir\*.* mask will include all paths to files located in the C:\dir\ folder, but not in the subfolders of C:\dir\. - The mask
C:\dir\* will include all paths to files located in the C:\dir\ folder, including subfolders. - The mask
C:\dir\ will include all paths to files located in the C:\dir\ folder, including subfolders. - The mask
C:\dir\*.exe will include all paths to files with the EXE extension located in the C:\dir\ folder, but not in the subfolders of C:\dir\. - The mask
C:\dir\test will include all paths to files named "test" located in the C:\dir\ folder, but not in the subfolders of C:\dir\. - The mask
C:\dir\*\test will include all paths to files named "test" located in the C:\dir\ folder and in the subfolders of C:\dir\. - The mask
C:\dir1\*\dir3\ will include all paths to files in dir3 subfolders one level into the C:\dir1\ folder. - The mask
C:\dir1\**\dirN\ will include all paths to files in dirN subfolders in the C:\dir1\ folder at any level.
Paths to files located in all folders with a specified name:
- The mask
dir\*.* will include all paths to files in folders named "dir", but not in the subfolders of those folders. - The mask
dir\* will include all paths to files in folders named "dir", but not in the subfolders of those folders. - The mask
dir\ will include all paths to files in folders named "dir", but not in the subfolders of those folders. - The mask
dir\*.exe will include all paths to files with the EXE extension in folders named "dir", but not in the subfolders of those folders. - The mask
dir\test will include all paths to files named "test" in folders named "dir", but not in the subfolders of those folders.
|
Page top








