The send and receive statements (<iface-method-policy-binding>)
The send and receive statements are for configuring method call events for the specified interface. The send statement lets you configure message forwarding events when all method instances for the specified interface are called. The receive statement lets you configure events for delivery of these messages.
Syntax
<iface-method-policy-binding> ::=
<event-type> [<direction>] [<iface-method>] "="
<policy-list> ";"
<event-type> ::= "send"|"receive"
<direction> ::= "in"|"out"
<iface-method> ::= <interface-method-name>
["(" <arg-name> {"," <arg-name> "}"]
["[" <src-sid> "," <dst-sid> "]"]
Elements
|
Type of event that is checked when the method is called. Permissible values:
|
|
Specifies the direction of a message. Permissible values:
|
|
Full name of the method and optional list of arguments. The names of arguments must be consistent with the names from the IDL description of the method. If the method is not specified, the |
|
Full name of the method in the interface. The interface can be any interface, including the interface that the entity is not implementing. It has the following format:
|
|
Name of the argument. |
|
Name of the argument containing the identifier of the security context of the message sender-entity. This argument is implicitly defined and is passed in each interaction event of the entity. The argument name is arbitrarily defined. By this name, the argument can be passed to security policies in the list of arguments. |
|
Name of the argument containing the identifier of the security context of the message recipient-entity. This argument is implicitly defined and is passed in each interaction event of the entity. The argument name is arbitrarily defined. By this name, the argument can be passed to security policies in the list of arguments. |
|
List of security policies that will be applied to an event. |
Example
/* Policies applied to calls of all methods of the entity. They are computed each time an entity receives a request-message (regardless of the interface or method by which the request is passed).
*/
receive in = tl.control["request"];
/* Policies applied each time an entity returns a response-message.
*/
send out = tl.control["response"];
Configuring of the events using the send and receive statements is shown in the example of interaction between two entities (see the figure below).
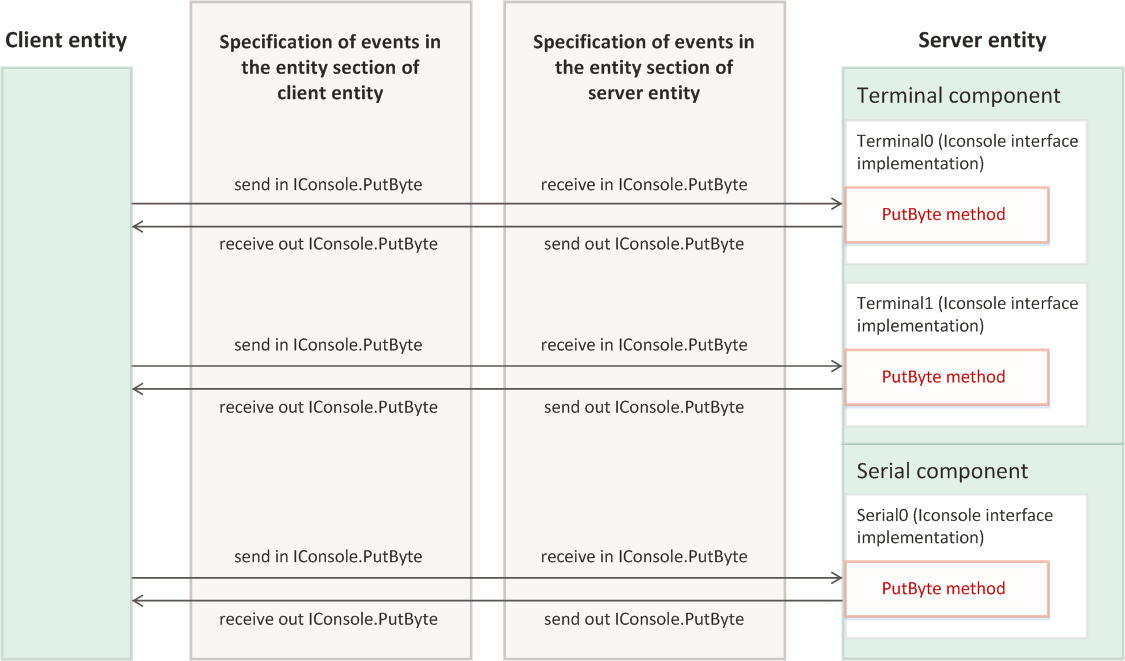
Configuring of the messages delivery and forwarding events using the send and receive statements
Page top