Considerations for working with file systems
Entities in KasperskyOS can use standard POSIX functions for working with files, for example, read() and write(). To do so, you only need to add a few additional steps when building the solution.
Working with file systems in KasperskyOS
Just like when interfacing with a network, you work with file systems in KasperskyOS through vfs_entity:
- Calls to standard POSIX functions are converted into calls to
vfs_remotelibrary functions. - The
vfs_remotelibrary makes IPC requests tovfs_entity. - The
vfs_serverserver library receives the IPC request and calls the implementation of the utilized file system. - The file system implementation makes an IPC request to the
atadriver-entity.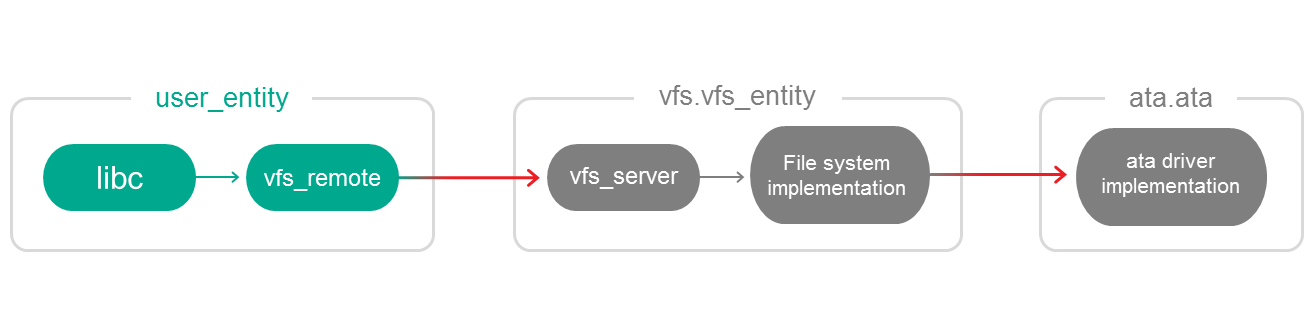
The vfs_entity included in KasperskyOS Starter Kit contains implementations of the FAT32 and RAMFS file systems. If necessary, you can add other file systems to the VFS.
Special features of building a solution
To enable user_entity to use file systems, it should be linked to the vfs_remote library. In addition, in the init.yaml file you need to indicate the vfs_entity and ata entities and describe two connections:
init.yaml
entities:
# Start user_entity.
- name: user_entity
connections:
# Connect user_entity to the vfs_entity (located in the folder vfs).
- target: vfs.vfs_entity
# For correct operation, the connection must be named "VFS".
id: VFS
# Start the vfs_entity (located in the folder vfs).
- name: vfs.vfs_entity
connections:
# Connect vfs_entity to the ata entity (located in the folder ata).
- target: ata.ata
# For correct operation, the connection must be named "ata".
id: ata
# Start the ata entity (located in the folder ata).
- name: ata.ata
Please note that the connection of entities has a "direction". The user_entity calls methods of vfs_entity, which, in turn, calls methods of the ata entity. Therefore, the vfs_entity is the server entity (- target) for user_entity, and ata is the server entity for vfs_entity. The vfs_entity is a client entity and server entity simultaneously.
The second part of the Guide examines client-server interactions between entities in more detail.
See also the fat example.
Page top