Operating principle of the application
Kaspersky Web Traffic Security scans user HTTP, HTTPS and FTP traffic that passes through the proxy server.
The same Kaspersky Web Traffic Security package is installed on all servers; it includes the traffic processing functionality and the user interface for managing application settings. Traffic is then transmitted from users' computers through a proxy server to the Kaspersky Web Traffic Security node for scanning. If the scan result allows access to the requested web resource and the traffic does not contain viruses or other threats, the request is transmitted through the proxy server to the web server. The response of the web server is processed in a similar way. The traffic processing scheme is presented in the figure below.
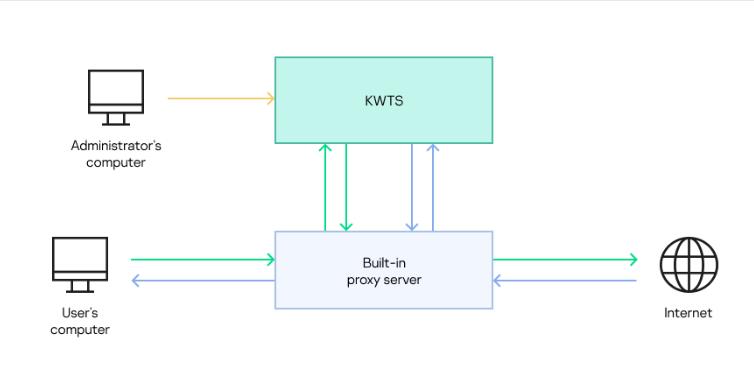
How Kaspersky Web Traffic Security processes traffic
When processing traffic, the application can use information about user accounts and their membership in domain groups. To do so, you need to configure integration of Kaspersky Web Traffic Security with Active Directory. Integration with Active Directory allows you to use user account autocompletion when managing user roles in the application, and to recognize user accounts when creating workspaces and traffic processing rules. Primary user authentication will be performed on the proxy server. The proxy server passes the information received from Active Directory to the application along with the user's original request. The proxy server and application nodes interact with the Active Directory server independently of each other. The principle of operation of the application when Active Directory integration is configured is shown in the figure below.
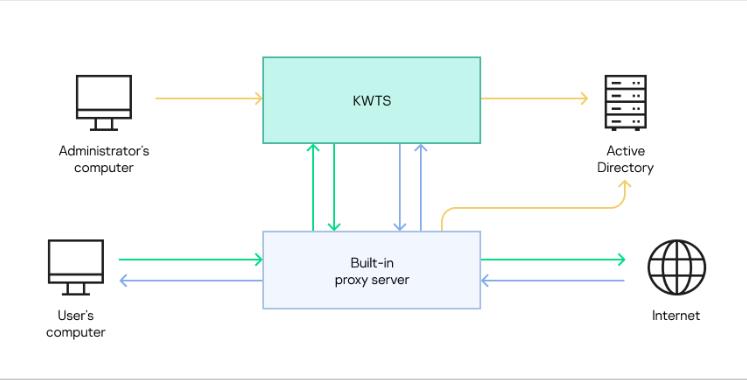
Principle of operation of the application when integrated with Active Directory
If traffic processing requires two or more application servers, all servers are combined into a cluster. One of the servers in the cluster should be assigned the Node with role Control role. The other servers in the cluster will be assigned the Node with role Secondary role. You can configure traffic processing on all nodes, including on the node with role Control. You can use the Control node, but not Secondary nodes to manage application settings. They are distributed from the node with role Control to all nodes with role Secondary in the cluster. Then each cluster node exchanges data with the Active Directory server independently of the node with role Control and other nodes with role Secondary. The interactions of components are presented in the figure below.
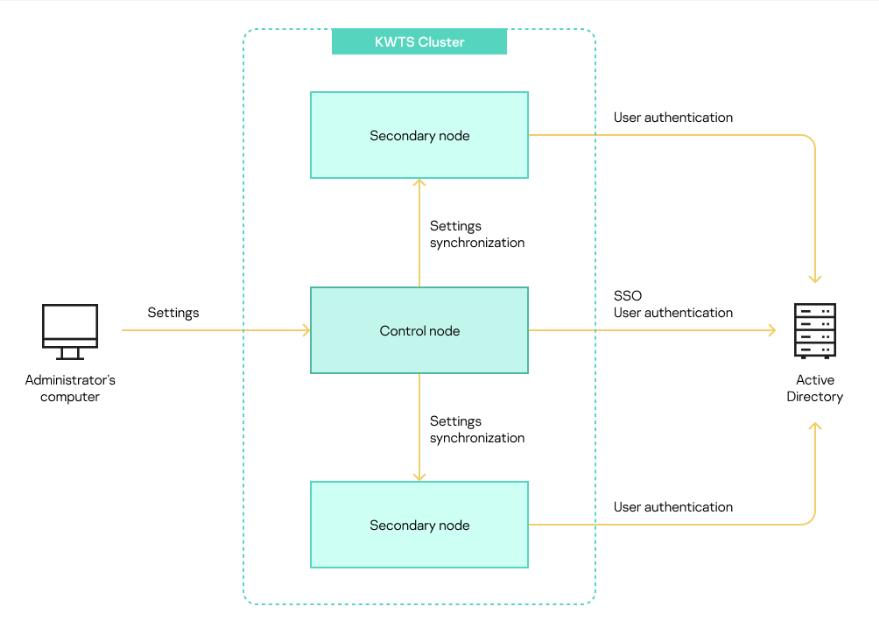
Interaction diagram of application components
If the Control node fails, the application goes into emergency mode. In this case, the administrator must assign the Control node role to one of the nodes with role Secondary. Traffic processing will not be interrupted during this procedure. All nodes continue to process network traffic using the latest settings received from the Control node before the application switched to emergency mode. Subsequent configuration of settings is done on the new node with role Control. The diagram of role changes that take place when the application goes into emergency mode is shown in the figure below.
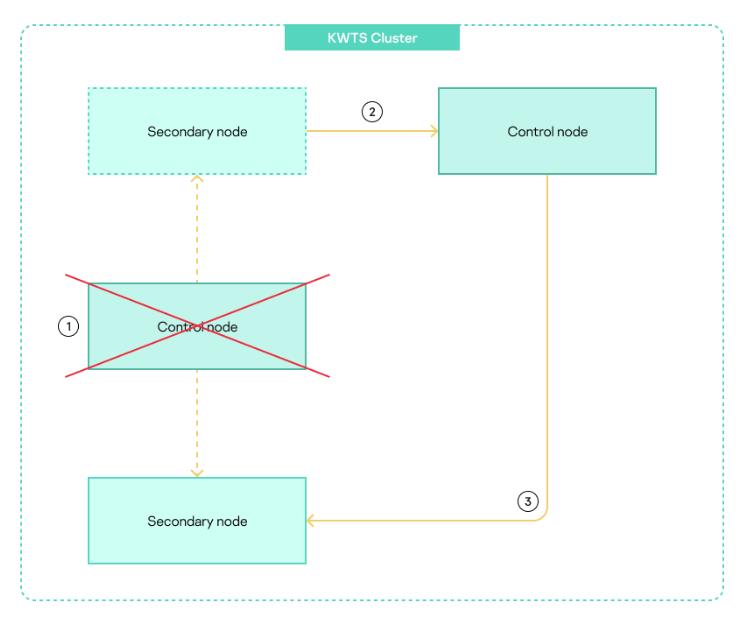
Diagram of role changes that take place when the application goes into emergency mode
If the volume of processed traffic involves a large number of cluster nodes, it is recommended to use load balancing.