Contents
- Distributed integration scheme (Splunk)
- About the distributed integration scheme
- Step 1. Installing Forwarder and Search Head apps
- Step 2. Configuring Forwarder and Search Head apps (distributed deployment)
- Step 3 (optional). Configuring the lookup script (distributed deployment)
- Step 4. Performing the verification test (Splunk, distributed integration)
Distributed integration scheme (Splunk)
This section contains instructions for integrating Kaspersky CyberTrace and Splunk in the distributed integration scheme.
For a description of the integration process, see Integration guide (Splunk).
For a description of distributed integration scheme, see About the distributed integration scheme.
About the distributed integration scheme
Kaspersky CyberTrace supports distributed Splunk environments. The integration scheme for distributed Splunk environments is called the distributed integration scheme.
About the apps and services used in the distributed integration scheme
In the distributed integration scheme, Kaspersky CyberTrace is divided into two apps and one service:
- Feed Service
This service matches Splunk events against Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds.
Feed Service sends the resulting events to a single indexer that keeps the index with events from Kaspersky CyberTrace.
This service can be installed on a separate computer.
- Kaspersky CyberTrace App Search Head (or Search Head App)
This app contains Kaspersky CyberTrace App dashboards, alert templates, and the lookup script.
This app is intended for installation on a Splunk instance that acts as a search head and sends search requests to the indexer that keeps the index with events from Kaspersky CyberTrace.
- Kaspersky CyberTrace App Forwarder (or Forwarder App)
This app contains rules for forwarding events from Splunk to Feed Service. It also receives events from Feed Service.
This app is intended for installation on Splunk instances that must forward events to Feed Service.
About the integration scheme variants
The following variants of the distributed integration scheme demonstrate a general approach to integrating Kaspersky CyberTrace with your distributed Splunk environment. Depending on how your distributed Splunk environment is organized, you may have to change or combine these variants.
One indexer, multiple forwarders variant
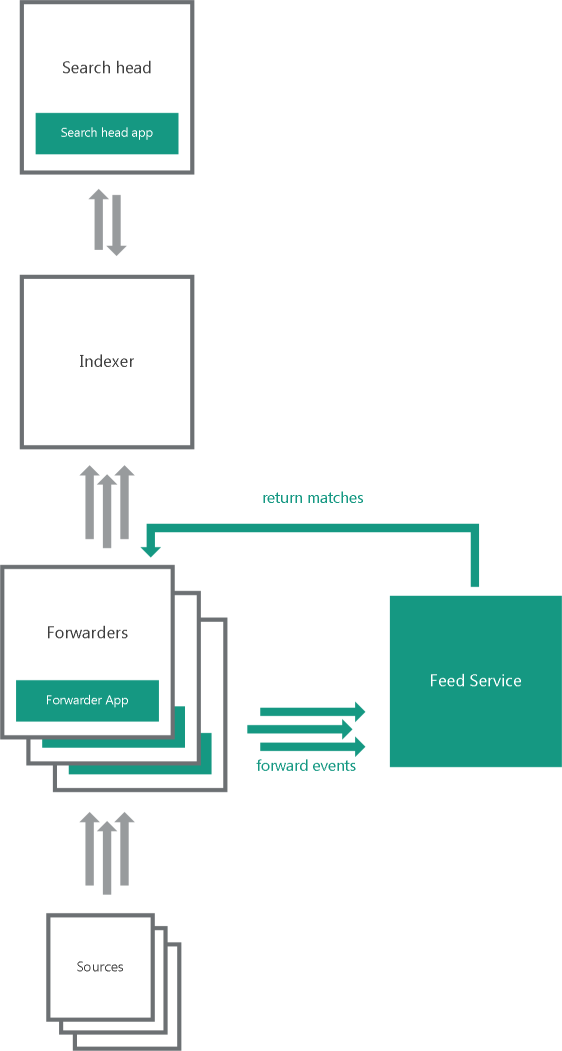
One indexer, multiple forwarders
In the one indexer, multiple forwarders variant, several heavy forwarders parse and send events directly to Feed Service. These forwarders must use Forwarder App. One of the forwarders receives matches from Feed Service. The forwarders send the matches to the indexers that store them in the index used by Kaspersky CyberTrace for Splunk Search Head App.
Multiple indexers, multiple forwarders variant
In the multiple indexers, multiple forwarders variant, several heavy forwarders parse and send events directly to Feed Service. These forwarders must use Forwarder App. One of the forwarders receives matches from Feed Service. The forwarders send the matches to the indexers that store them in the index used by Kaspersky CyberTrace App.
Default ports and addresses
By default, Forwarder App and Feed Service are configured to use certain addresses and ports for forwarding events and receiving matches. You must change these addresses and ports based on the organization of your distributed Splunk environment.
You must change the default addresses and ports that are used by Forwarder App and Feed Service.
By default, Forwarder App:
- Receives events at
:3000port. - Receives events from Kaspersky CyberTrace at
:9998port. These events are stored in themainindex. - Forwards events to
127.0.0.1:9999.
By default, Feed Service does the following:
- Receives events at
127.0.0.1:9999. - Sends its own events to
127.0.0.1:9998.
Event format
By default, Kaspersky CyberTrace App and Feed Service are configured to receive events in a certain format:
- Feed Service parses events with regular expressions defined in its configuration file (the regular expressions are also displayed in Kaspersky CyberTrace Web). These regular expressions are created for a specific format of inbound data. For example, the default regular expression for URLs will match a URL containing the protocol (for example, HTTP, HTTPS). If the URLs in the events generated by your devices do not contain the procotol, change the regular expression accordingly.
- The lookup script that comes with Kaspersky CyberTrace App (or Search Head App in the case of the distributed integration scheme) sends events to Feed Service in a format that matches the regular expressions used by Feed Service.
Step 1. Installing Forwarder and Search Head apps
In the distributed deployment scheme, you must install Forwarder App and Search Head App on the basis of the organization of your distributed Splunk environment. For more information about how to choose the computers where the apps must be installed, see the section about the distributed integration scheme.
Forwarder App is installed from the %service_dir%/integration/splunk/Kaspersky-CyberTrace-App-for-Splunk_Forwarder.tar.gz file. Search Head App is installed from the %service_dir%/integration/splunk/Kaspersky-CyberTrace-App-for-Splunk_Search-Head.tar.gz file.
Installing the apps
Forwarder App and Search Head App are installed from Splunk Web. The only difference in the installation process is the application file name.
To install Forwarder App or Search Head App:
- Open Splunk Web for the Splunk instance where you want to install the app.
- In Splunk Web, go to the home page.
- On the home page, click the Manage Apps button.
Manage Apps button
- On the Apps page, click the Install app from file button.

Install app from file button
- In the Upload an app window, click Choose File and select the application file mentioned above in this section.
Choose File button
- In the Upload an app window, click the Upload button.
![Upload an app (Upload) [Search Head]](install_35_upload_form_upload.png)
Upload button
- In the Restart required window, click the Restart Splunk button.
This step can be skipped, depending on the Splunk version. If Splunk does not display the Restart required window, skip this step.
Restart Splunk button
- When Splunk starts again, the Forwarder App will be displayed in the list of installed apps. When Kaspersky Search Head App is installed, the Apps page will open with information about the successful installation of Kaspersky Search Head App. Kaspersky Search Head App will appear in the list of apps on the Splunk home page.

Kaspersky Search Head App for Splunk in the list of apps
Step 2. Configuring Forwarder and Search Head apps (distributed deployment)
In the distributed deployment scheme, you must configure Forwarder App on the basis of the organization of your distributed Splunk environment. For example, the configuration changes may include changing the Feed Service address used by the apps, or adding new event sources for Forwarder App. For Search Head App, you may have to configure the email addresses for alerts.
Configuration actions for Forwarder App and Search Head App
For Forwarder App, you may have to do the following:
- Change the address and port for forwarding events to Feed Service. See subsection "Changing the address and port for forwarding data to Feed Service" below.
- Configure Forwarder App to send events to the Indexer (or multiple Indexers). By default, events that are sent from Forwarder App to Feed Service are not registered in the indexes. See subsection "Configuring Forwarder App to send events to indexes" below.
- If several Forwarder Apps are used, only one Forwarder App must receive events from Kaspersky CyberTrace at port
9998. For all other Forwarder Apps, disable this rule by specifyingtruein thedisabledparameter for this rule in the Forwarder App configuration file. The IP address and port of the Forwarder App that will receive events from Kaspersky CyberTrace must be specified on the Settings > Service tab in Kaspersky CyberTrace Web. - Add new event sources. See subsection "Adding new event sources" below.
For Search Head App, you may have to do the following:
- Add email addresses to alert templates. See "Adding email addresses to alert templates" below.
Restart Splunk after you make changes to the configuration files.
Edit only those Forwarder App and Search Head App configuration files that are described in this section. Editing other configuration files may result in unpredictable behavior.
Configuration files (distributed deployment)
The following table summarizes configuration files used by Forwarder App and Search Head App in the following distributed deployment scheme variants:
- One indexer, multiple forwarders
- Multiple indexers, multiple forwarders
Configuration files of Forwarder App and Search Head App
Application
Configuration file
Default rules
Forwarder App
\default\inputs.confReceives data from sources at port
3000and forwards it as configured inoutputs.conf.Receives events from Kaspersky CyberTrace at
:9998port.Forwarder App
\default\outputs.confForwards data to
127.0.0.1:9999(Feed Service address).Forwarder App
\default\props.confParse data received at
:3000. For a description of default data parsing rules, see "Default data parsing rules" below.Search Head App
\default\savedsearches.confRules for alert templates.
Default data parsing rules
The way in which Forwarder App parses incoming data is defined in the props.conf file. By default, Forwarder App does the following:
- Defines how time stamps are extracted from incoming data.
- Defines a delimiter (line breaker) between events for incoming data.
For example, if the incoming data has the sequence
"%data_1%\n\n%data_2%"and the line breaker is one or more\nsymbols, Splunk splits this sequence into two events (%data_1%and%data_2%).
The following are the default rules used by Forwarder App to parse incoming data.
TIME_PREFIX = ^ MAX_TIMESTAMP_LOOKAHEAD = 17 TIME_FORMAT = %b %d %H:%M:%S LINE_BREAKER = ([\n]+) SHOULD_LINEMERGE = false |
Changing the address and port for forwarding data to Feed Service
By default, Forwarder App is configured to forward data to Feed Service at 127.0.0.1:9999.
To change the address and port for forwarding data to Feed Service,
In the outputs.conf configuration file, in the [tcpout:service9999] section, specify the new address and port for the server parameter that will be used by Feed Service.
In the following example, 192.0.2.100:9999 is specified as the Feed Service address.
[tcpout:service9999] disabled=false server = 192.0.2.100:9999 sendCookedData = false |
Adding new event sources
To add new event sources, edit the inputs.conf and props.conf configuration files of the app.
To add a new event source:
- In inputs.conf, specify a new event source that uses the
service9999TCP routing rule.All data from this input will be forwarded to Feed Service.
- In props.conf, specify how data from this source must be processed.
- Restart Splunk.
Make sure that data from the new event source matches the regular expressions used by Kaspersky CyberTrace.
Below is an example of adding the address :3001 as the event source; it specifies that data from the address :3001 must be processed as other input data in the default integration scheme (in this scheme, the forwarder, indexer, and search head are installed on a single computer).
# to inputs.conf [tcp://:3001] _TCP_ROUTING = service9999
# to props.conf [source::tcp:3001] TIME_PREFIX = ^ MAX_TIMESTAMP_LOOKAHEAD = 17 TIME_FORMAT = %b %d %H:%M:%S LINE_BREAKER = ([\n]+) SHOULD_LINEMERGE = false |
If Splunk Forwarder is already configured for receiving events from different event sources and you want to send events to Feed Service, perform the following procedure. This can be done if the server field of the outputs.conf configuration file of Forwarder App contains the IP address and port that are specified in the InputSettings > ConnectionString element of the Feed Service configuration file.
To forward events to Feed Service:
- In the outputs.conf file that is used for forwarding events from Splunk (it can be either the outputs.conf file of a custom Splunk application or the
%SPLUNK_DIR%/etc/system/local/inputs.conffile), in thedefaultGroupfield, add a comma and a stringservice9999.In this case, check the event forwarding logic and make sure that events that arrived from Feed Service are not sent again to Feed Service by Splunk.
If the inputs.conf configuratioin file contains the
_TCP_ROUTINGparameter for those event sources, the events from which are sent to Feed Service, add a comma and theservice9999string to the_TCP_ROUTINGparameter. - Restart Splunk.
Configuring Forwarder App to send events to indexes
By default, events that are sent from Forwarder App to Feed Service are not registered in the indexes. You can change this behavior by configuring Forwarder App.
To configure Forwarder App to send events to the main index:
- Locate the Forwarder that you want to configure. This Forwarder is typically a machine with Forwarder App installed. You must configure all Forwarders that are used in your distributed integration scheme.
- On the Forwarder, in the
%SPLUNK_HOME%\etc\system\local\outputs.conffile, locate the name of the target group that is used for sending events to the Indexer (or multiple Indexers). Here%SPLUNK_HOME%is the Splunk installation directory.By default, the name of this group is default-autogroup-lb:
[tcpout: default-autogroup-lb] - In the
inputs.conffile used by the Forwarder App, locate the section withservice9999TCP routing rule:_TCP_ROUTING = service9999 - Add the name of the target group to this rule.
For example, if the name of the target group is default-autogroup-lb, the rule must be changed in the following way:
_TCP_ROUTING=service9999, default-autogroup-lb - Restart Splunk on the Forwarder.
Configuring alert templates
For more information about configuring alert templates, see "Configuring alert templates" in Step 2 (optional). Configuring Kaspersky CyberTrace App.
Page topStep 3 (optional). Configuring the lookup script (distributed deployment)
The lookup script is used to match individual URLs, IP addresses, and hashes to Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds. It can be invoked from the Indicators lookup tab in Kaspersky CyberTrace App for Search Head.
To configure the lookup script:
- In Kaspersky CyberTrace App, go to the Indicators lookup tab.
- Specify Kaspersky CyberTrace connection strings:
- In the Kaspersky CyberTrace address field, specify the IP address of Kaspersky CyberTrace
- In the Kaspersky CyberTrace port field, specify the port that Kaspersky CyberTrace uses
The script is ready for use.
Page topStep 4. Performing the verification test (Splunk, distributed integration)
The verification test for the distributed integration of Kaspersky CyberTrace with Splunk is performed in the same way as the verification test for the single-instance integration.
Page top