Administration Server in DMZ, managed devices on internet
The figure below shows data traffic if the Administration Server is in the demilitarized zone (DMZ) and the managed devices are on the internet.
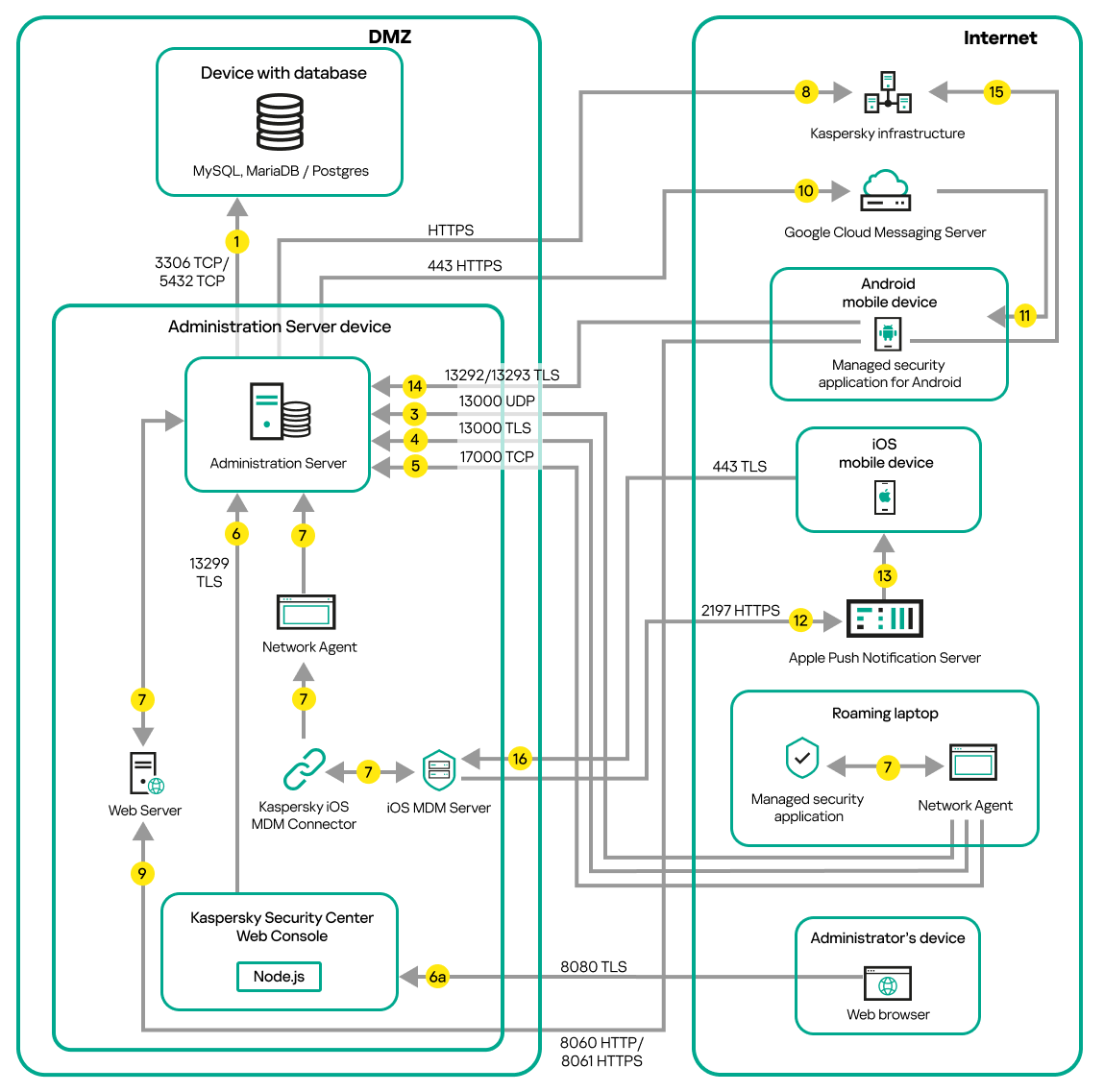
Administration Server in DMZ, managed mobile devices on the internet
In this figure, a connection gateway is not in use: the mobile devices connect to the Administration Server directly.
The arrows indicate the initiation of traffic: each arrow points from a device that initiates the connection to the device that "answers" the call. The number of the port and the name of the protocol used for data transfer are provided. Each arrow has a number label, and details about the corresponding data traffic are as follows:
- Administration Server sends data to the database. If you install the Administration Server and the database on different devices, you must make available the necessary ports on the device where the database is located (for example, port 3306 for MySQL Server and MariaDB Server, or port 5432 for PostgreSQL Server or Postgres Pro Server). Please refer to the DBMS documentation for the relevant information.
- Requests for communication from the Administration Server are transferred to all non-mobile managed devices through UDP port 15000.
Network Agents send requests to each other within one broadcasting domain. The data is then sent to the Administration Server and is used for defining the limits of the broadcasting domain and for automatic assignment of distribution points (if this option is enabled).
If Administration Server does not have direct access to the managed devices, communication requests from Administration Server to these devices are not sent directly.
- Information about shutdown of the managed devices is transferred from Network Agent to the Administration Server through UDP port 13000.
- The Administration Server receives connection from Network Agents and from secondary Administration Servers through TLS port 13000.
If you used an earlier version of Kaspersky Security Center, the Administration Server on your network can receive connection from Network Agents through non-TLS port 14000. Kaspersky Security Center Linux also supports connection of Network Agents through port 14000, although using TLS port 13000 is recommended.
- The managed devices (except for mobile devices) request activation through TCP port 17000. This is not necessary if the device has its own access to the internet; in this case, the device sends the data to Kaspersky servers over the internet directly.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server sends data to the Administration Server, which may be installed on the same or on a different device, through TLS port 13299.
6a. Data from the browser, which is installed on a separate device of the administrator, is transferred to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server through TLS port 8080. The Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server can be installed either on the Administration Server or on another device.
- Applications on a single device exchange local traffic (either on the Administration Server or on a managed device). No external ports have to be opened.
- Data from the Administration Server to the Kaspersky servers (such as KSN data or information about licenses) and data from the Kaspersky servers to the Administration Server (such as application updates and anti-virus database updates) are transferred using the HTTPS protocol.
If you do not want your Administration Server to have access to the internet, you must manage this data manually.
- Requests for packages from managed devices are transferred to the Web Server, which is on the same device as the Administration Server.
- For Android mobile devices only: data from the Administration Server is transferred to Google servers. This connection is used to notify Android mobile devices that they are required to connect to the Administration Server. Then push notifications are sent to the mobile devices. FCM service also runs on 443 HTTPS port.
- For Android mobile devices only: push notifications from Google servers are sent to the mobile device. This connection is used to notify mobile devices that they are required to connect to the Administration Server.
- For iOS mobile devices only: data from the iOS MDM Server is transferred to Apple Push Notification servers. Then push notifications are sent to the mobile devices.
- For iOS mobile devices only: push notifications are sent from Apple servers to the mobile device. This connection is used to notify iOS mobile devices that they are required to connect to the iOS MDM Server.
- For mobile devices only: data from the managed application is transferred to the Administration Server (or to the connection gateway) through TLS port 13292 / 13293—directly or through a reverse proxy.
- For mobile devices only: data from the mobile device is transferred to the Kaspersky infrastructure.
If a mobile device does not have internet access, the data is transferred to Administration Server through port 17100, and the Administration Server sends it to the Kaspersky infrastructure; however, this scenario applies very rarely.
- For iOS mobile devices only: data from the mobile device is transferred through TLS port 443 to the iOS MDM Server, which is on the same device as the Administration Server or on the connection gateway.