Contents
- Administrator guides
- Managing Kaspersky CyberTrace Web
- Working with default credentials
- Service settings
- Feeds settings
- Importing a certificate for Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds
- Specifying the feeds update period
- Enabling and disabling feeds
- Selecting available fields for a feed
- Adding actionable fields to a feed
- Specifying filtering rules for a feed
- Truncating a feed
- Launching a feeds update manually
- About custom, third-party, and Kaspersky feeds
- Adding a custom or third-party feed
- Configuring a custom or third-party feed
- Managing false positives
- Matching process settings
- Event format settings
- User settings
- Logging settings
- Licensing settings
- Tenants settings
- Indicators export settings
- Retrospective scan settings
- Feed Service Guide
- About Feed Service
- Managing Feed Service
- Feed Service configuration reference
- Feed Service logging
- About resending detection events
- Feed Service in ReplyBack mode
- Features of event processing by Feed Service
- Limitations on Feed Service incoming events
- Feed Utility guide
- Using Password Utility
- Choosing the best feeds for your environment
- Upgrading and managing the installation
- Managing the installation on Linux systems
- Managing the installation on Windows systems
- Upgrading Kaspersky CyberTrace from a previous version
- About the upgrade process
- Upgrading automatically from 3.1 to 4.0 (Linux)
- Upgrading automatically from 3.1 to 4.0 (Windows)
- Upgrading Kaspersky CyberTrace integration (QRadar)
- Upgrading Kaspersky CyberTrace integration (Splunk)
- Upgrading Kaspersky CyberTrace integration (ArcSight)
- Upgrading Kaspersky CyberTrace integration (RSA)
- Upgrading Kaspersky CyberTrace integration (LogRhythm)
- Uninstalling Kaspersky CyberTrace
- Adding self-signed SSL certificates for CyberTrace Web
- Watchdog module workflow
- Testing the connection with Feed Service and the availability of feeds
- Managing Kaspersky CyberTrace Web
Administrator guides
This chapter provides information about using the Kaspersky CyberTrace web interface, command-line tools, and applications for SIEM solutions.
Managing Kaspersky CyberTrace Web
This section describes how Administrator users can manage Kaspersky CyberTrace from the web user interface (web interface).
All web interface pages described in this section are available only for user accounts that have the Administrator role. Users with Analyst role cannot access these pages.
Working with default credentials
This section explains how to work with default credentials and passwords for other users.
Default credentials
After Kaspersky CyberTrace is installed, the following default credentials are set for Kaspersky CyberTrace Web:
- User name:
admin - Password:
CyberTrace!1
To avoid possible security risks, change this password as soon as possible. For more information, see Logging in to Kaspersky CyberTrace Web.
Resetting the password for the default user
Use the kl_access_util utility to reset the credentials for the default user (admin).
Changing passwords for other users
To create user accounts and change passwords for other users, use the User Settings page.
Page topService settings
This section explains how to manage different service settings that are available when you select the General tenant or a particular settings tenant in the drop-down list with all available tenants in the upper-left area of the window.
Service settings (General tenant)
You can manage the general service settings in the CyberTrace web user interface by selecting the Settings tab, and then the Service tab. Make sure that the General item is selected from the drop-down list that has all available tenants, in the upper-left area of the window.
The Service tab allows you to edit settings stored in the kl_feed_util.conf and kl_feed_service_log.conf configuration files. You can perform the following actions by clicking the following links below the tab:
- Restart Feed Service
- Export the configuration file
You can export the kl_feed_service.conf and kl_feed_util.conf configuration files to a directory that you choose.
- Run self-test
Verifies that the Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds that you use work correctly.
Please make sure you run the self-test before editing any filtering rules on the Settings > Feeds tab, in the Filtering rules for feeds section.
If the verification test (self-test) yields incorrect results (that is, if a feed that is expected to produce detections produces none), see possible solutions for this problem in the general troubleshooting section. If the problem persists, contact your technical account manager (TAM).
- Reset statistics
Clears the Dashboard of all the detection statistics. When you select the General tenant, Kaspersky CyberTrace clears the detection statistics for all tenants.
It is recommended to perform this operation after successfully integrating CyberTrace with a SIEM solution: this way, the dashboard will not display any detection events generated during the verification test and will only contain real detection events, if there are any.
The Settings tab displays the Feed Service status, which can be one of the following:
- Feed Service is running
- Feed Service is starting
- Feed Service has stopped
- Feed Service is updating feeds
This status specifies that indicators are loading into the database and indexing. Until all indicators processed, the Indicators tab may contain partially outdated information, and a search for data that is being updated may not be performed correctly. However, the process of matching incoming events is performed based on the actual data and the Kaspersky CyberTrace Web page with detailed information about indicators displays up-to-date data.
Connection settings
In the Connection settings section of the Service tab, you can specify the following settings:
- IP address and port (on Linux, it can be also a UNIX socket) that Feed Service listens on for incoming events
These settings are stored in the
InputSettings > ConnectionStringelement of the kl_feed_service.conf file. - IP address and port (on Linux, it can also be a UNIX socket) to which Feed Service sends detection events and alert events
These settings are stored in the
OutputSettings > ConnectionStringelement of the kl_feed_service.conf file. - IP address or hostname, and port (on Linux, it can also be a UNIX socket) to which Feed Service sends alert events that inform the event target software of the state of the service
These settings are stored in the
OutputSettings > AlertConnectionStringelement of the kl_feed_service.conf file.You can enable or disable this setting by using Kaspersky CyberTrace Web. When this setting is enabled, Kaspersky CyberTrace does not send alert events to the IP address and port that are stored in the
OutputSettings > ConnectionStringelement of the kl_feed_service.conf file. - IP address or hostname of the proxy server for updating feeds
This setting is stored in the
Hostelement of the kl_feed_util.conf file. - Port of the proxy server for updating feeds
This setting is stored in the
Portelement of the kl_feed_util.conf file.The preset value is
0. If you do not want to use a proxy server, leave this value unchanged. - Proxy user name
This setting is stored encrypted in the
Userelement of the kl_feed_util.conf file. - Proxy password
This setting is stored encrypted in the
Passwordelement of the kl_feed_util.conf file.
External address of the web interface
In the Web interface section of the Service tab, you can specify the IP address or hostname to be used in Kaspersky CyberTrace events.
This setting is stored in the ResourcesIP element of the kl_feed_service.conf file.
The preset value is 127.0.0.1.
Using a proxy server
To configure CyberTrace to use a proxy server:
Specify proxy settings in the IP address or hostname, Port, User name, and Password fields.
To configure CyberTrace not to use a proxy server:
- Enter
0in the Port text field. - Clear the IP address or hostname, User name, and Password text fields.
About the disk space notification
When Kaspersky CyberTrace updates feeds, it checks the amount of remaining disk space. If the remaining disk space is low, Kaspersky CyberTrace displays a notification. The notification states how many MB of disk space is still available for the indicator database.
In addition, Kaspersky CyberTrace sends a KL_ALERT_FreeSpaceEnds event.
Page topService settings (custom tenant)
You can manage the service settings for a particular settings tenant in the CyberTrace web user interface by selecting the Settings tab, and then the Service tab. Make sure that a tenant for which you want to display service settings is selected from the drop-down list that has all available tenants, in the upper-left area of the window.
The Service tab allows you to do the following:
- Edit settings stored in the kl_feed_util.conf and kl_feed_service_log.conf configuration files.
- Reset statistics by clicking the Reset statistics link below the tab.
This action clears the Dashboard of all the detection statistics related to this tenant.
We recommend performing this operation after successfully integrating CyberTrace with a SIEM solution. This means the dashboard will not display any detection events generated during the verification test and will only contain real detection events, if there are any.
Connection settings
In the Connection settings section of the Service tab, you can specify the following settings:
- IP address and port (on Linux, it can be also a UNIX socket) that Feed Service listens on for incoming events
These settings are stored in the
InputSettings > ConnectionStringelement of the kl_feed_service.conf file. - IP address and port (on Linux, it can also be a UNIX socket) to which Feed Service sends detection events and alert events
These settings are stored in the
OutputSettings > ConnectionStringelement of the kl_feed_service.conf file.
Feeds settings
You can manage the settings of feeds in the Kaspersky CyberTrace web user interface by selecting the Settings tab, and then the Feeds tab. When you change the settings, you will be asked whether to update the feeds. Depending on the item selected in the drop-down list with all available tenants in the upper-left area of the window, the changes will affect either the general feeds settings (if General is selected) or the feeds settings for a specific tenant (if a specific tenant is selected).
For all tenants, Kaspersky CyberTrace displays only the feeds that are enabled in the General tenant.
For the General tenant, the form allows you to:
- Import a certificate for Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds
- Specify the feeds update period
- Enable and disable feeds
- Select available fields for a feed
- Add actionable fields to a feed
- Specify filtering rules for a feed
- Truncate a feed
- Launch a feeds update manually
- Add custom or third-party feeds
- Configure a custom or third-party feed
- Manage false positives
For a specific tenant, the form allows you to:
Feed tabs
Feeds are listed on the following tabs:
- Kaspersky
This tab contains Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds.
- <Vendor name>
Custom and third-party threat data feeds are grouped into tabs by vendor.
If no vendor name is provided for a feed, it is listed on the Custom feeds tab.
If there are no custom and third-party feeds, these tabs are not displayed.
- OSINT
This tab contains OSINT feeds.
- Internal TI
This tab contains the Internal TI supplier, with indicators added to the database by users.
About the feed update notifications
If any feeds have become available or unavailable with your certificate during an update, a window opens and lists all newly available and unavailable feeds.
In each list of feeds:
- If a currently used feed becomes unavailable, the toggle button remains On but a warning appears next to the feed. The warning states that this feed is no longer supported by your certificate and will not be updated anymore. You can either continue using the last available copy of the unsupported feed, or set the toggle button to Off and stop using the feed.
- For all feeds that become available, the toggle button becomes enabled.
By default, the toggle button next to all newly available feeds is set to Off. You have to manually set it to On for the feeds that you want to start using.
Importing a certificate for Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds
This section explains how to import a certificate for Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds. Make sure that the General tenant is selected from the drop-down list that has all available tenants, in the upper-left area of the window.
About the feeds certificate
Kaspersky CyberTrace downloads and updates Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds if they are available with the current certificate.
Importing a feeds certificate for Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds
To import a new feeds certificate for Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds:
- Navigate to the Settings page.
- Open the Feeds tab.
- In the Feeds update period section, select the Import certificate link.
The Import certificate window opens.
- In the Import certificate window, select the Browse link.
- In the opened browser window, select the certificate file in the .pem format and open it.
- In the Import certificate window, click the Save button.
After you import a new certificate, Feed Service checks for and displays all the feeds that are available with it.
Page topSpecifying the feeds update period
This section explains what is feeds update period and how to change it. Make sure that the General tenant is selected from the drop-down list that has all available tenants, in the upper-left area of the window.
About the feeds update period
The feeds update period specifies how often Kaspersky CyberTrace updates all enabled feeds. The default update frequency is 30 minutes. The date and time of the last feeds update is displayed.
Feeds can be rolled back after an update if Kaspersky CyberTrace fails to upload new indicators into the Matching engine (for more information, see the description of the FeedsRollbackEnabled parameter in ServiceSettings).
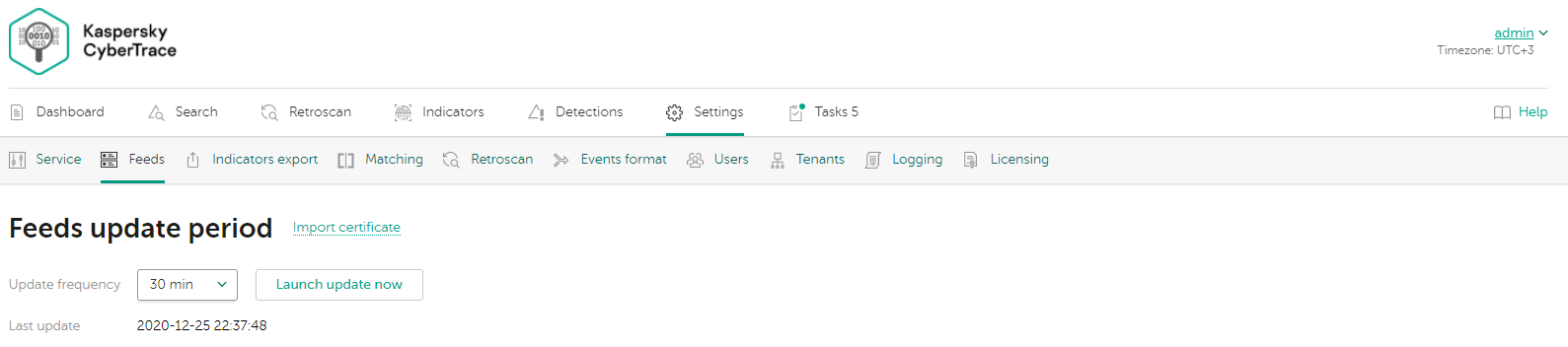
Feeds update period section
Specifying the feeds update period
To specify the feeds update period:
- Navigate to the Settings page.
- Open the Feeds tab.
- In the Feeds update period section, select a value in the Update frequency drop-down list.
- Scroll to the bottom of the Feeds tab and click the Save button.
Enabling and disabling feeds
This section describes how to enable and disable feeds.
When you enable a feed, it is automatically added and enabled in all tenants. When you disable a feed, it is automatically removed from all tenants.
Enabling and disabling feeds
You can enable or disable feeds, except for the InternalTI supplier on the Internal TI tab, by using the Feed is off or Feed is on toggle button. For the InternalTI supplier on the Internal TI tab, you can only specify actionable fileds.
If you disable a feed, its indicators will not be removed from the indicator database. These indicators will not be displayed on the Indicators tab, but will be taken into consideration regarding the limit on the number of indicators. To avoid that, you must remove the indicators manually before disabling the feed.
When only demo feeds are used, there is a notification at the top of the Feeds tab. Use the Request access to all feeds link in that notification to send your request by email. Alternatively, you can use the Request Kaspersky Threat Intelligence form to subscribe to Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal and get commercial feeds, which have a higher level of protection.
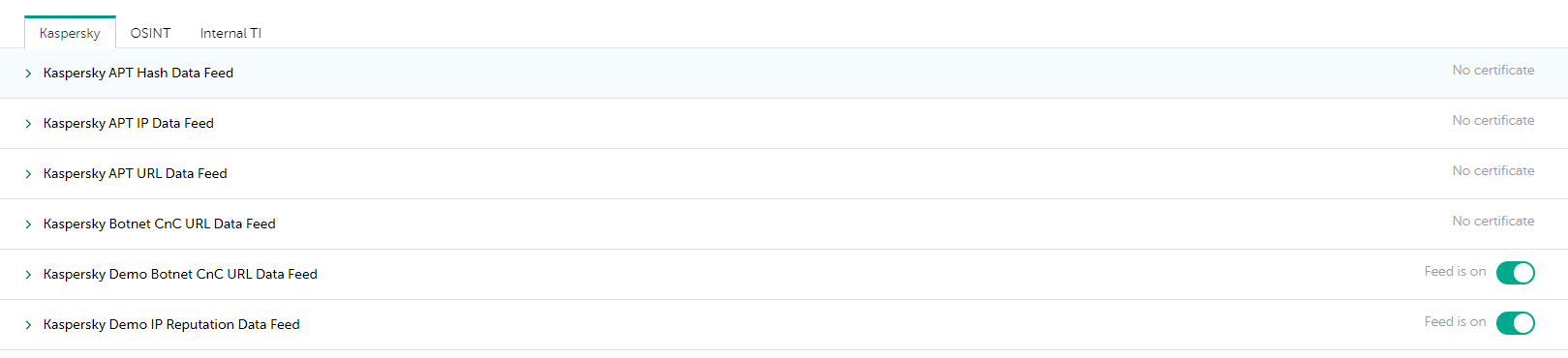
Enabling or disabling a feed
Page topSelecting available fields for a feed
This section explains how to specify which fields must be included in a feed. Make sure that the General tenant is selected from the drop-down list that has all available tenants, in the upper-left area of the window.
About the available fields
Available fields for a feed define which fields from an original feed Kaspersky CyberTrace must include in the resulting feed. For example, if you specify that all but one of the fields in a feed must be ignored, the resulting feed will have only one field for each record.
A feed must have at least one available field that is used for matching. This field must contains IPs, hashes, or URLs.
In the original feed files, some records can have extra fields or can lack some fields; one record can have less or more fields than another record.
If a record has an extra field and this field is selected for a feed, the record will have this field in the resulting feed. If a record has an extra field and this field is not selected for a feed, the record will not have this field in the resulting feed.
If a record lacks a field and this field is selected for a feed, the record will not have this field. If a record lacks a field and this field is not selected for a feed, the record will not have this field.
If you want to exclude records with missing fields from the output, you must create filtering rules for all required fields. You can specify criteria for field values. For more information about filtering rules, see Specifying filtering rules for a feed.
Selecting available fields for a feed
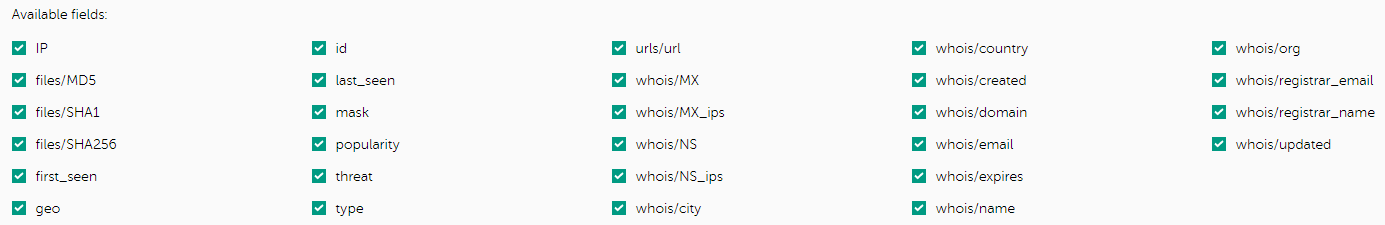
Selecting available feed fields
To select available fields for a feed:
- Navigate to the Settings page.
- Open the Feeds tab.
- In the Filtering rules for feeds section select the tab that contains the feed you need to configure.
You cannot include or exclude available fields for the Internal TI supplier.
- Locate the feed that you want to configure, and then expand its section.
- In the settings section for the individual feed, locate the Available fields section.
- Select the fields that you want to include and remove the selection for fields that you want to exclude.
- Scroll to the bottom of the Feeds tab, and then click the Save button.
Adding actionable fields to a feed
This section explains how to add extra fields to the outgoing events sent by Kaspersky CyberTrace. These settings are applied to the tenant that is selected in the drop-down list with all available tenants, in the upper-left area of the window.
About the actionable fields
Actionable fields are extra fields that you can insert into outgoing events apart from the context of feed records. You can use actionable fields to extract specific information from the context and pass it in separate fields.
Adding actionable fields
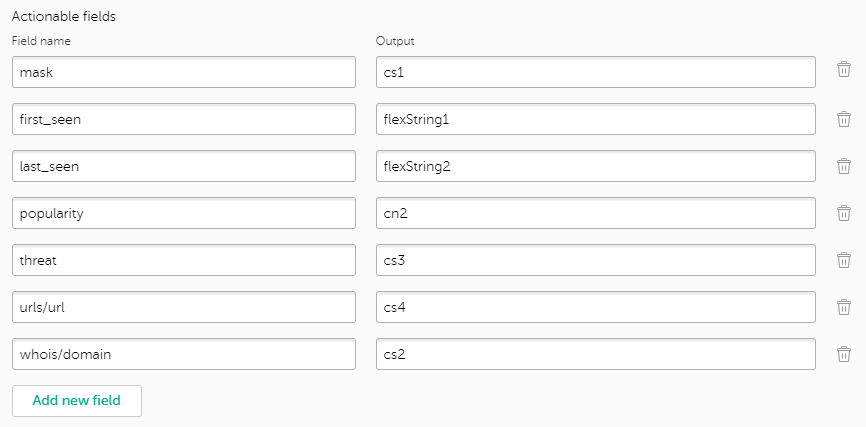
Managing actionable fields
To add actionable fields for a feed:
- Navigate to the Settings page.
- Open the Feeds tab.
- In the Filtering rules for feeds section select the tab that contains the feed you need to configure.
- Locate a feed that you want to configure, and then expand its section.
- In the settings section for the individual feed, locate the Actionable fields section.
- Click the Add new field button to add a new actionable field.
- In the Field name text box, specify the name of a field in the original feed.
If a feed record contains several equally named fields, and their name is mentioned in the actionable fields list, the outgoing event will contain all of the values delimited by a semicolon in one field.
- In the Output text box, specify the name of the field, as it will be inserted into outgoing events.
If the Output text box is empty, the field name in the outgoing event will be the same as the field name specified in the feed.
- Scroll to the bottom of the Feeds tab, and then click the Save button.
Specifying filtering rules for a feed
This section explains what filtering rules are and how to configure them. Make sure that the General tenant is selected from the drop-down list that has all available tenants, in the upper-left area of the window.
About the filtering rules
Filtering rules are criteria for a feed and they let you exclude specific records from a feed.
Kaspersky CyberTrace uses filtering rules to filter the downloaded feed files during the update.The filtering rules that you specify are applied to feeds after they are updated, not to the current feeds.
Only those records that match all the specified criteria are included in the output file. If a filtering criterion is specified for a field and the field is missing from a record, this record will not be included in the output file.
Specifying filtering rules for a feed

Filtering rules section
To specify a filtering rule for a feed:
- Navigate to the Settings page.
- Open the Feeds tab.
- In the Filtering rules for feeds section, select the tab that contains the feed you need to configure.
You cannot specify filtering rules for the InternalTI supplier.
- Locate the feed that you want to configure, and then expand its section.
- In the settings section for the individual feed, locate the Filtering rules section.
- Click the Add new rule button.
- In the Field name drop-down list, select the name of one of the fields available for the feed.
Each field in a feed can have only one filtering rule associated with it. You cannot have two filtering rules specified for one field.
- In the Condition drop-down list, select the filtering condition.
For the list of possible filtering conditions, see section "Possible filtering conditions" below.
- In the Value text box, specify a filtering criterion for the field.
For more information on how to define specific filtering criteria, see subsections "Defining filtering criteria for numeric values", "Defining filtering criteria for strings", and "Defining filtering criteria for dates" below.
- Scroll to the bottom of the Feeds tab, and then click the Save button.
Possible filtering conditions
The table below lists filtering conditions that can be applied to feeds:
Possible filtering conditions
Filtering condition |
Description |
Match an exact value |
The field in a feed is exactly equal to the specified value. To apply this condition, select value is equal to in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a single value in the Value text box. |
Match at least one of several possible values |
The field in a feed must contain one or more of the specified values. To apply this condition, select value is one of (separated by a new line) in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify several values in the Value text box. Do not specify empty values. Each new value must be separated by a new line. |
Belonging to a range of numeric values |
The field in a feed must contain the value in the specified range. To apply this condition, select value is in range (inclusive) in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a range of values in the Value text boxes. Notice that the range boundaries are included. The values must be integers. |
Belonging to a range of numeric values that are equal to or greater than the specified value |
The field in a feed must contain a value that is equal to or greater than the specified value. To apply this condition, select value is more than (inclusive) in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a single value in the Value text box. The value must be integer. |
Belonging to a range of numeric values that are equal to or less than the specified value |
The field in a feed must contain a value that is equal to or less than the specified value. To apply this condition, select value is less than (inclusive) in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a single value in the Value text box. The value must be integer. |
Belonging to a range of dates |
The field in a feed must contain a date in the specified range. To apply this condition, select date is in range (inclusive) in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a range of dates in the Value text boxes.
|
Belonging to a range of dates that are equal to or greater than the specified value |
The field in a feed must contain a date that is equal to or greater than the specified value. To apply this condition, select date is more than (inclusive) in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a date in the Value text box.
|
Belonging to a range of dates that are equal to or less than the specified value |
The field in a feed must contain a date that is equal to or less than the specified value. To apply this condition, select date is less than (inclusive) in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a date in the Value text box.
|
Match a non-empty value |
The field in a feed must contain any non-empty value. To apply this condition, select value is non-empty in the Condition drop-down list. |
Truncating a feed
This section explains how to limit a feed to a certain maximum number of records. Make sure that the General tenant is selected from the drop-down list that has all available tenants, in the upper-left area of the window.
About the maximum number of records in a feed
By default, Kaspersky CyberTrace imports all records that match the filtering criteria for a feed. This behavior can be changed. You can set the maximum number of records that must be imported. Kaspersky CyberTrace will import the records in the order they are arranged in the original feed up to the specified maximum of records.
Truncating a feed
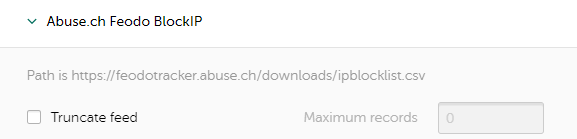
Managing the number of records in a feed
To specify the maximum number of records in a feed:
- Navigate to the Settings page.
- Open the Feeds tab.
- In the Filtering rules for feeds section, select the tab that contains the feed you need to configure.
You cannot specify the maximum number of records for the Internal TI supplier.
- Locate a feed that you want to configure, and then expand its section.
- In the settings section for the individual feed, select the Truncate feed check box.
- In the Maximum records text box, specify the maximum number of records for a feed.
- Scroll to the bottom of the Feeds tab, and then click the Save button.
Launching a feeds update manually
This section explains how to launch a feed update manually. Make sure that the General tenant is selected from the drop-down list that has all available tenants, in the upper-left area of the window.
About the manual feed updates
Kaspersky CyberTrace updates all enabled feeds automatically with a configured feeds update period. In addition, you can perform a manual feeds update at any time.
If another user has started an update, you will not be able to launch an update until the feeds are updated.
Launching a manual feeds update
To specify the feeds update period:
- Navigate to the Settings page.
- Open the Feeds tab.
- In the Feeds update period section, click the Launch update now button.
About custom, third-party, and Kaspersky feeds
This section describes the feeds available in Kaspersky CyberTrace.
About Kaspersky feeds
For more information about Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds, see About Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds.
About custom and third-party feeds
Custom and third-party feeds are feeds that you can add to Kaspersky CyberTrace.
The addition or deletion of third-party feeds, or turning on the use of OSINT feeds, can be disabled due to restrictions imposed by the licensing level. In this case, the form for adding a custom or third-party feed can be disabled.
Encoding of custom and third-party feeds
All custom or third-party feeds that you add to Kaspersky CyberTrace must be in UTF-8 encoding. If your custom or third-party feeds have a different encoding, make sure to convert them to UTF-8. You can add custom feeds that contain subnet masks of Class C networks. These feeds can be used in the matching process, by marking the feed field as IP.
Certificates and demo feeds
Kaspersky CyberTrace downloads and updates Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds that are available with the current certificate. With the default certificate, only demo feeds are available.
If you use demo feeds, a notification pops up when you select the Settings > Feeds tab. This notification states that you use Kaspersky demo feeds and provides information on how to purchase commercial feeds that have a higher level of protection. The Request access to all feeds link in the notification redirects you to the Request Kaspersky Threat Intelligence form, where you can subscribe to Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal and get commercial feeds.
Page topAdding a custom or third-party feed
This section explains how to add a custom or third-party feed and change its settings. Make sure that the General tenant is selected from the drop-down list that has all available tenants, in the upper-left area of the window.
You can add feeds through only one field of the URL or DOMAIN type. That is, if you mark one field in a feed as URL or DOMAIN, do not mark another field in the feed as URL or DOMAIN. The URL and DOMAIN types are counted as the same field type.
When you add a feed, it is automatically added and enabled in all settings tenants.
Adding a custom feed
To add a feed:
- In the Filtering rules for feeds section, click Add custom feed.
The Custom feed window opens:
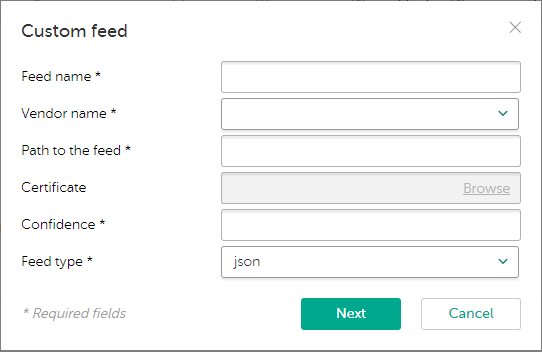
Adding a custom or third-party feed
- For any custom or third-party feed, specify the following information:
- Feed name
In the feed name, you can use Latin letters, numbers, underscores, and hyphens. The name must differ from other feed names that are already used.
Do not use FalsePositive or InternalTI as the feed name, since they are reserved for the built-in supplier names of Kaspersky CyberTrace.
Do not use the
@character in the feed name if basic authentication is used, and the username or password contains@. - Vendor name
From the drop-down list, select the name of the feed vendor or add a new one.
- Path to the feed
You can specify the path in one of the following forms:
- Full path on the computer where Kaspersky CyberTrace is installed
- Network path
The specified network path is available for the active user account, while Feed Service and Feed Utility run under the LocalService account. Therefore, if you need to download custom and third-party feeds from a network directory, give the LocalService user account access to this network directory.
The network directory must be mapped.
You can only specify the network path in Windows.
- HTTP(S) address
Starting from Kaspersky CyberTrace version 4.0, you can download Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds from https://wlinfo.kaspersky.com which were not added at the moment of the product release.
- FTP address
- Certificate
Path to the certificate that gives access to the feed. The full path must be specified.
You can only specify the certificate path if the feed will be downloaded over an HTTPS connection.
If you download Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds from https://wlinfo.kaspersky.com, the field contains the preset value
Kaspersky Lab certificate. You cannot change this value. - Feed type
This type can be one of the following:
- json
If a feed in JSON format contains a field with a subnet mask value, Kaspersky CyberTrace discloses data only if it is a first-level field. If this field is nested, Kaspersky CyberTrace cannot disclose data.
If you download Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds from https://wlinfo.kaspersky.com, JSON format is used. You cannot change this value.
- stix
Kaspersky CyberTrace currently supports STIX versions 1.0 and 1.1.
- csv
- xml
- misp
- json
- Confidence
The level of confidence of the feed. This field cannot be empty. The range of possible values is from 1 to 100.
The preset values are
100for feeds from Kaspersky,50for OSINT feeds,50for third-party feeds. You can change these values.Level of confidence is provided in the
Feeds > Feed > confidenceattribute of the Feed Service configuration file. - Authentication type
The authentication type can be Basic or None.
The basic authentication scheme is available if the path to the feed is an HTTP(S) or FTP address. For this type of authentication, enter the following settings:
- User name
This field cannot be empty.
- Password
Authentication type is provided in the
Settings > Feeds > Feedparameter of the Feed Utility configuration file. - User name
- Feed name
- For a STIX feed, also specify the following information:
- Get from a TAXII server
If this check box is selected, the STIX feed must be downloaded from the TAXII server.
When a STIX feed is downloaded from the TAXII server, Kaspersky CyberTrace parses this feed and counts the number of indicators.
- Collection name
The name of the collection that must be downloaded from the TAXII server. Note that you can specify only one collection name at a time.
Kaspersky CyberTrace does not support TAXII feeds that have information about the reputation of one object. IBM feeds like xfe.ipr and xfe.url are not supported.
- Get from a TAXII server
- For CSV and XML feeds, specify the following information:
- For a CSV feed, specify a delimiter. After that, the rule will be appllied immediately, and the columns will be split. By default, a semicolon (;) is used as a delimiter.
- For an XML feed, specify the root element. This allows you to use the names of feed elements relative to the root element. Which element to specify as the root depends on the level of nesting in a given feed.
In the following example, the root element is
root:<root><url>http</url><ip>1</ip></root><root><url>https</url><ip>2</ip></root>In the following example, the root element is
root/element*:<root><element1><url>http</url><ip>1</ip></element1></root><root><element2><url>https</url><ip>2</ip></element2></root>You cannot use wildcard characters (the asterisk (
*) or question mark (?)) to specify the path, only the root element.
After you specify a custom or third-party feed and the settings for it, the feed is fully loaded and a part of it is displayed so that you can choose the fields of the feed to be used in the matching process (see section "Configuring feed fields to be used for matching (CSV, JSON, XML feeds)" below).
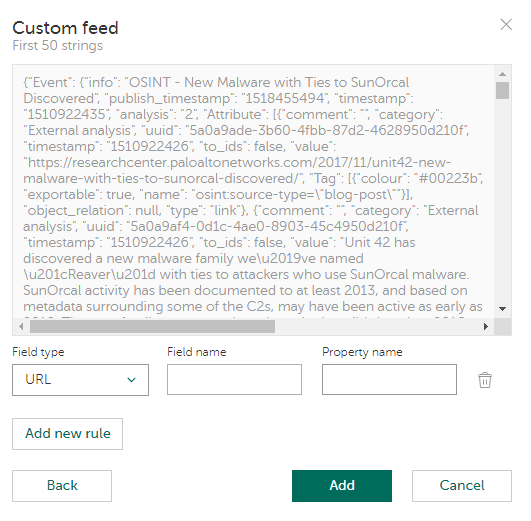
Selecting feed fields for matching
This is relevant for feeds in the following formats: CSV, JSON, XML. After a STIX or MISP feed is added, Kaspersky CyberTrace fully loads it for use.
In some cases (when a STIX feed is too large or the TAXII server used for downloading the feed is too slow, or both), it may take Kaspersky CyberTrace up to an hour to load a STIX feed.
Configuring feed fields to be used for matching (CSV, JSON, XML feeds)
To choose feed fields to be used for matching, specify the following information for each field:
- Field type
One of the following values can be used as the field type:
- URL
- MD5
- SHA1
- SHA256
- IP
- DOMAIN
- CONTEXT
Note that there must be at least one field with a type other than CONTEXT. Such fields are used for matching. When such a field is involved in the detection process, a detection event is generated with the
%FEEDNAME%_%FIELDTYPE%category, where%FEEDNAME%is the feed name and%FIELDTYPE%is the field type.A feed can have one field of the CONTEXT type, at most one field of the URL or DOMAIN type, and several fields of other types. The URL and DOMAIN types are considered the same field type.
- Field name
This name will be referred to in the matching process.
In the field name, you can use Latin letters, numbers, underscores, and hyphens. The name must contain at least one Latin letter.
- Reference to the data in the feed:
- For a CSV feed, specify the column number.
- For a JSON feed, specify the property name.
For JSON feeds, the name of the property is case-sensitive. Specify property names in the same case as they are in a JSON feed.
To specify a nested field, use a slash (
/): for example,mainField/subField. - For an XML feed, specify the element.
Specify the full path to the element relative to the root element. You cannot use wildcard characters (the asterisk (
*) or question mark (?)) to specify the path, only the root element. The path is case sensitive.In the following example, if you specified
root/element*as the root element, then the full path to the elements relative to the root element isurlandip, notroot/element1/urlorroot/element2/ip:
<root>
<element1>
<url>http</url>
<ip>1</ip>
</element1>
</root>
<root>
<element2>
<url>https</url>
<ip>2</ip>
</element2>
</root>
When adding a custom or third-party feed, feeds updating can be performed. In this case, you will see a notification about it, and a new feed will not be added. We recommend that you wait awhile and then try again to add a feed.
Page topConfiguring a custom or third-party feed
This section explains how to configure a custom or a third-party feed. Make sure that the General tenant is selected from the drop-down list that has all available tenants, in the upper-left area of the window.
Changing the settings of a custom or third-party feed
To change the settings of a custom or third-party feed:
- In the Filtering rules for feeds section, select the tab that contains the feed you need to configure.
You cannot change the settings for the Internal TI supplier.
- Click the name of the feed that you want to modify, and then click Edit.

Editing a custom or third-party feed
- In the Edit custom feed window that opens, make any necessary changes.
- Click Save.
You can change all the settings of a custom or third-party feed, except the feed type. For example, you cannot change a CSV feed to JSON.
Adding new fields to a custom or third-party feed
If a new field or fields have been added to your custom or third-party feed being used, and you want Kaspersky CyberTrace to start using these new fields, do the following:
- For a CSV, JSON, or XML feed, follow the procedure outlined in subsection "Changing the settings of a custom or third-party feed" above, to open the Edit custom feed window. Then add each new field by clicking the Add new rule button and specifying the values described above in "Step 2. Choosing feed fields to be used for matching".
If you do not specify any new fields for a feed, the feed will contain them, but they will not be displayed in the Available fields subsection and will not be used in the matching process.
- For a STIX feed, in the Filtering rules for feeds section, click the feed name and, in the Available fields subsection, select any new field or fields that must be used by CyberTrace, and then click Save.
For more information, see section Specifying filtering rules for a feed.
Deleting a custom or third-party feed
To delete a custom or third-party feed:
- In the Filtering rules for feeds section, select the tab that contains the feed you need to delete.
You cannot delete the Internal TI supplier.
- Click the name of the feed that you want to delete, and then click Delete.
Managing false positives
This section explains how to manage the False Positives supplier on the Feeds tab. Make sure that the General tenant is selected from the drop-down list that has all available tenants, in the upper-left area of the window.
You can access the false positives list by clicking the Manage False Positives button in the Filtering rules for feeds section.
Managing the false positives list
To access the false positives list, click the Manage False Positives button.
The False Positives window opens:
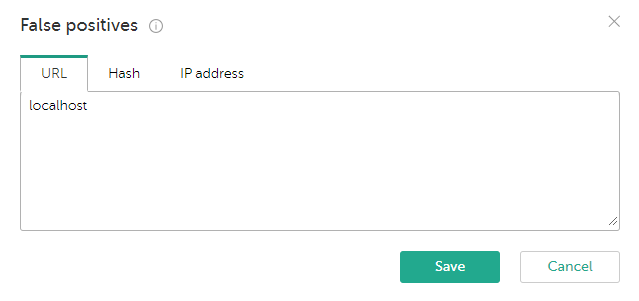
False Positives list
You can edit the false positives list of indicators as follows:
- Select the URL, Hash, or IP address tab to manage the group you want.
On the URL tab, you can specify a URL containing a wildcard symbol
*(for example,example.com/testpage/*, which will match URLs such asexample.com/testpage/test1andexample.com/testpage/test/long_url).Starting from Kaspersky CyberTrace version 4.0, the
*symbol in the URL is not used as a wildcard. The*just means the "asterisk."Kaspersky CyberTrace will apply normalization rules to any URL that you add on the URL tab and which is not yet contained in the indicator database. Thus, the representation of these URLs may change. For example, if you add a URL that contains a port, this port value will be removed. For instructions on how Kaspersky CyberTrace normalizes a URL, see subsection "URL normalization rules" below.
- Every indicator must be on a separate line in the text box.
The false positives list is checked only after all events from a thread have been matched against all the suppliers. The main purpose of the false positives list is to enable Kaspersky CyberTrace to ignore detections for trusted indicators. If any feed produces a detection, but a given indicator is found in the false positives list, Kaspersky CyberTrace does not generate a detection event. In this case, on the Dashboard tab, in the Supplier statistics table, the value in the False positives column corresponding to the supplier that produced the detection is incremented by one. The values in the False positives column show how many false detections were produced by each supplier. For more information about the Dashboard, see section "Kaspersky CyberTrace Dashboard".
URL normalization rules
Any URLs added to the false positives list on the URL tab will be normalized according to the following URL normalization rules:
- Remove dot segments ("
." and "..") according to the algorithm described in RFC 3986, section 5.2.4 Remove Dot Segments (https://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3986.txt):http://www.example.com/../a/b/../c/./d.html => http://www.example.com/a/c/d.html - Remove the protocol:
http://example.com => example.com - Convert internationalized domain names according to the Punycode algorithm described in RFC 3492 (https://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3492.txt):
тест.рф => xn--e1aybc.xn--p1ai - Remove the
wwwprefix:www.example.com => example.com - Remove repeated slashes:
example.com//dir/test.html => example.com/dir/test.html - Remove the trailing slash at the end of the URL:
example.com/ => example.com - Remove the authorization information:
login:password@example.com => example.com - Remove the port number:
example.com:80/index => example.com/index - Remove the
#fragmentreference:example.com#fragment => example.com - Remove dots at the end of the host name:
example.com./index.html => example.com/index.html - Convert percent-encoded symbols to UTF-8 according to RFC 3986 (https://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3986.txt) and RFC 2279 (https://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2279.txt).
- Convert all characters to lower case:
EXAMPLE.COM => example.com - Convert the IP address (if any) leading to the requested host to dot-decimal notation:
0112.0175.0117.0150 => 74.125.79.104
Matching process settings
You can manage the matching process settings by selecting the Settings tab and then the Matching tab.
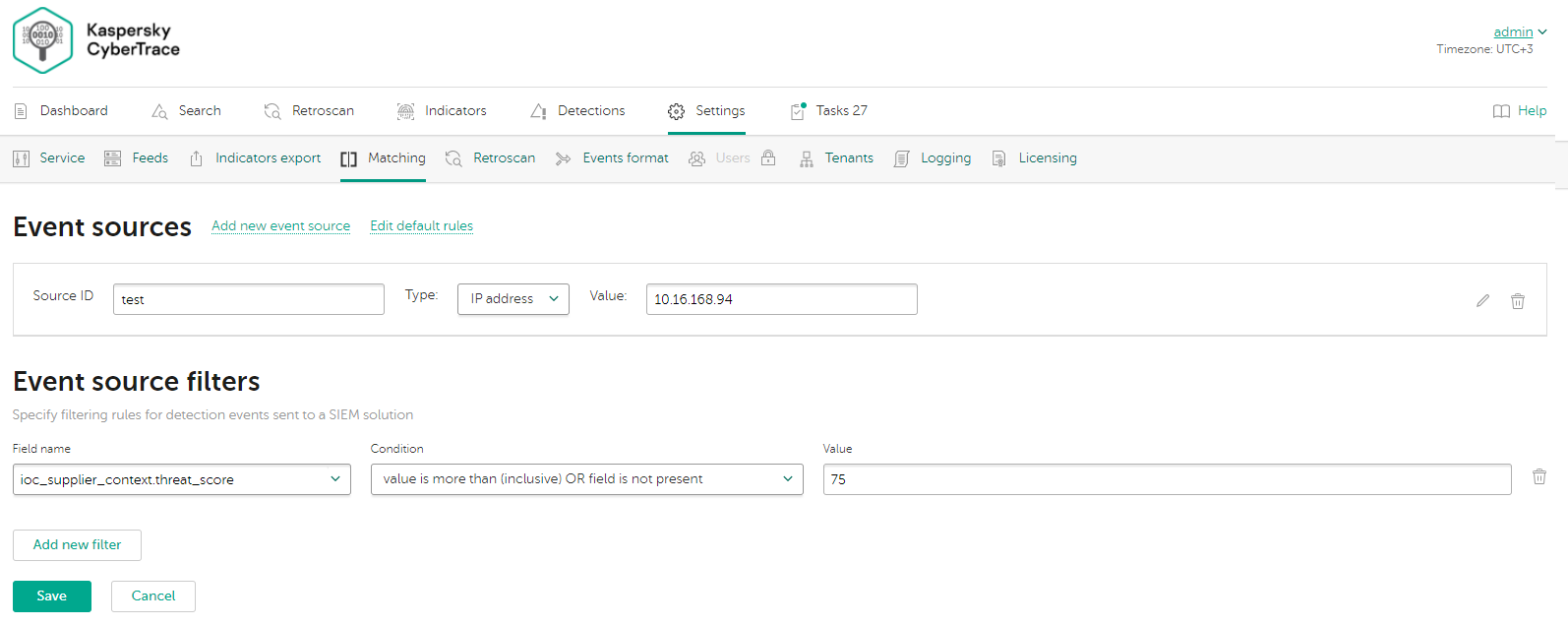
Event sources
In Kaspersky CyberTrace, regular expressions and event normalizing rules are grouped by event source. Regular expressions and event normalizing rules that are not related to a specific event source are grouped under the default event source. Each event source must have at least one regular expression. You can add or remove event sources other than default or edit their properties.
The Event sources page displays all event sources defined in the Feed Service configuration file, except the default event source. You can edit the following properties of the displayed event sources directly in the Event sources page:
- Source ID
The name of the event source. It must be unique among the event source names used. In the name the following symbols are allowed: Latin letters, numbers, a hyphen (
-), and a period (.). - IP address or Host name or Regular expression
The IP address of a device that issues events for which you want to add parsing rules. The host name of a device that issues events. The regular expression that will match the source in the events received by Kaspersky CyberTrace.
The value in the Host name box must be the same as the value in the
HOSTNAMEfield of the incoming syslog messages from this event source.The value in the Regular expression box must be optimized. For more information on how to optimize regular expressions, see the "Optimization of regular expressions" subsection of the "About regular expressions" section.
To edit the event normalizing rules and regular expressions defined for a displayed event source, select the corresponding Properties link. For the default event source, you must select the Edit default rules link. In both cases, the form for editing event source properties opens (see subsection "Form for editing event source properties" below).
For more information on event sources and regular expressions used for parsing events that are issued by various devices, see section "About regular expressions".
Adding event sources
To add an event source:
- Select the Add new event source link.
The Add New Event Source Wizard starts.
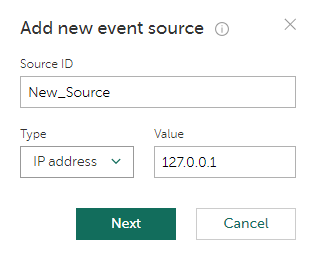
Adding a new event source (step 1)
- Specify the name and the IP address or host name or the regular expression of a new event source.
- Click Next.
If the data entered at the previous step is correct, the form for specifying regular expressions and event normalizing rules opens (see subsection "Form for editing event source properties" below).
Kaspersky CyberTrace will attempt to obtain data from received events by using the default regular expressions. We recommend that you keep collecting events for at least five seconds.
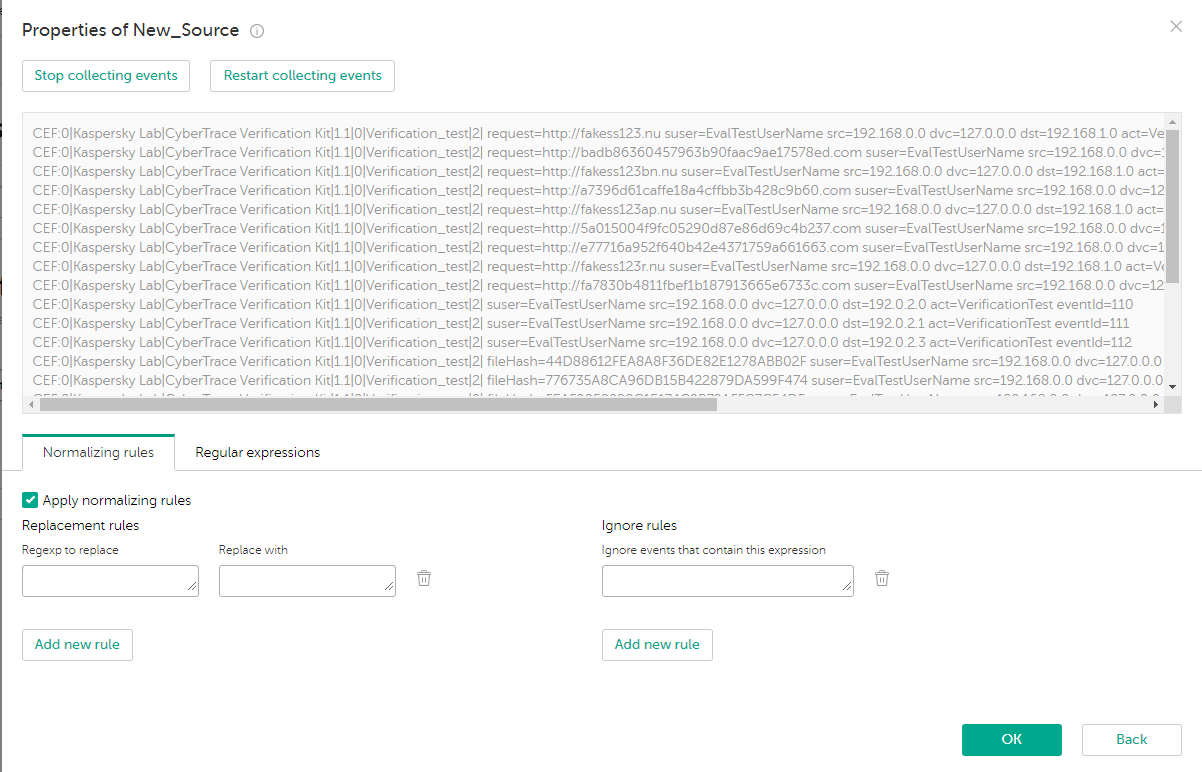
Specifying the event source properties
- Specify the event source properties and click OK.
If the entered event source properties are correct, a new event source is created.
Form for editing event source properties
The form for editing event source properties has an upper area and the lower area. The upper area displays events and highlights substrings that are extracted by a selected regular expression. The lower area has two tabs: the Normalizing rules tab and the Regular expressions tab.
When the form for editing event source properties opens, it starts collecting events that are issued by the event source. These events are processed according to the normalizing rules and the result is displayed in the upper area of the form.
If you have specified the host name of the event source, but the HOSTNAME field of incoming events cannot be extracted, no event is displayed. To fix this problem, either specify the IP address or regular expression of the event source, or change the format of events.
You can pause (or resume), or restart collecting the arriving events in real time. If you restart collecting the incoming events, the text box for displaying events is cleared. This text box can contain up to 50 lines. If more data arrives, older data is removed.
Specifying event normalizing rules
In the lower area of the form for editing event source properties, select the Normalizing rules tab to add, remove, or edit normalizing rules that will be applied to incoming events that meet the conditions of the event source. You can specify which character sequences must be replaced with others (replacing rules) and which character sequences must be used for identifying events to ignore (ignoring rules). If you clear the Apply normalizing rules check box, all the controls for specifying normalizing rules will be disabled, and no normalizing rule will be saved for the event source being edited.
Do not specify the newline character (\n) in replacing rules. Use the InputSettings > EventDelimiter element of the Feed Service configuration file to separate compound incoming events into individual events.
For an event source that is being created, initially the form under the Normalizing rules tab is filled with the normalizing rules specified for the default event source.
Specifying regular expressions
In the lower area of the form for editing event source properties, select the Regular expressions tab to add, remove, or edit regular expressions that will be applied to incoming events that meet the conditions of the event source. For an event source that is being created, initially the form under the Regular expressions tab is filled with the regular expressions that are specified for the default event source and that extract at least some data from the events that are displayed.
Regular expressions have the following properties:
- Indicator type
The type of data to be extracted from an event. You can set one of the following indicator types:
- URL
- MD5
- SHA1
- SHA256
- HASH
- IP
- DOMAIN
- CONTEXT
- Regular expression name
The regular expression name must be unique among the names of the regular expressions that relate to the same event source.
- Regular expression itself
The regular expression used for extracting the required value from an event. For more information on regular expressions, see section "About regular expressions".
- Extract all check box
If this check box is cleared, the regular expression will extract only the first matched value. If this check box is selected, the regular expression will extract all of the matched values.
- Concatenation rules
You can specify how to concatenate different parts of extracted data to a single value. For information about concatenation of extracted data, see section "About regular expressions", subsection "Compound values".
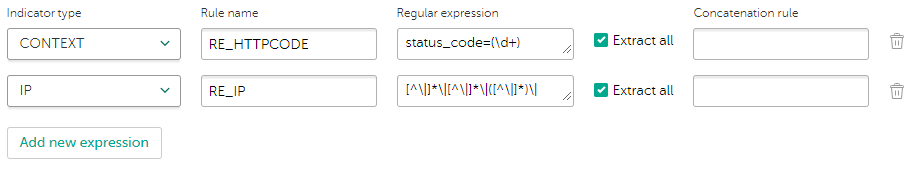
Setting regular expressions and their properties
You can highlight values that match the regular expressions that you specified for the event source. Click inside the text box that contains the regular expression that you want to highlight.
Specifying event filters
You can specify filtering rules for detection events sent to a SIEM solution from Kaspersky CyberTrace. Kaspersky CyberTrace will send detection events only if the flag for sending detection events to the SIEM solution (the ioc_supplier_send_match event attribute from the indicator database) is set to true and all fields of a feed record that matched the indicator meet the filtering criteria. Note that if the detected indicator does not have the attribute specified in the filtering rule, this indicator is considered to meet the filter. However, all detection events will be included in statistics and displayed on the Dashboard and Detections tabs.
To specify filters for detection events:
- In the Field name drop-down list, select the value corresponds to the indicator attribute name from the indicator database to which filtering rules are applied.
To learn more about possible values for
%FIELD_NAME%, see section "Working with indicators". - In the Condition drop-down list, select a filtering condition.
For the list of possible filtering conditions, see section "About filtering criteria for sending events to SIEM".
- In the Value text box, specify a filtering value.
- Click the Add new filter button if you want to add new event filter.
If necessary, you can edit or delete any filtering rules.
Page topAdding normalizing rules
This section explains how to add normalizing rules to an event source.
About normalizing rules
Normalizing rules are used for transforming events. After Kaspersky CyberTrace applies normalizing rules to an incoming event, the event is processed using regular expressions.
There are two types of normalizing rules:
- Replacing rules
Rules for replacing one character sequence with another.
- Ignoring rules
Rules for ignoring events that contain a character sequence.
If the replacing rules and ignoring rules are set, replacing rules are applied first and ignoring rules are applied second.
In the specified regular expressions, the asterisk (*) and question mark (?) are not treated as wildcard characters.
Adding normalizing rules
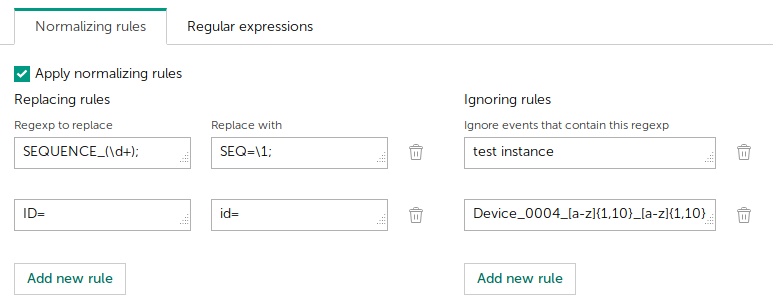
Adding normalizing rules
To add a normalizing rule:
- Navigate to the Settings page.
- Open the Matching tab.
- Locate an event source that must use the new normalizing rule. Click
 to open source properties.
to open source properties.The window with the properties of the selected event source opens.
- Locate the Normalizing rules tab.
- Select the Apply normalizing rules check box.
- If normalizing rules are already specified for the event source, add a new entry. Click Add new rule to add extra text boxes for new rule parameters.
- Specify rule parameters:
- For a replacing rule, specify a regular expression in the Regexp to replace text box and a replacement in the Replace with text box.
- For an ignoring rule, specify a regular expression in the Ignore events that contain this expression text box.
- Click the OK button.
About regular expressions
This section describes regular expressions and provides information about using them.
About regular expressions
Regular expressions are used to parse incoming events processed by normalizing rules. They extract information to be checked in feeds and to be used in outgoing events.
The preset regular expressions correspond to the format of the events used in the verification test.
After the verification test is performed, you may have to add some new regular expressions or change existing ones for use with specific event source software. For examples of regular expressions to be used for parsing events issued by popular devices, see section "Regular expressions for popular devices".
We recommend that you set regular expressions for extracting data such as the IP address and port of the event source, and of the event target, user name, and date. Use these regular expressions to define the format of the outgoing events.
About regular expression names
You can use any name for a regular expression except the following ones:
SourceIdMatchedIndicatorRecordContextCategoryActionableFieldsConfidenceIndicatorInfo
Compound values
The concatenate attribute is used to set a rule for creating a compound value from data extracted from an event. A rule refers to groups of extracted data by using #N symbols, where N is the number of a group (starting from 1). If a backslash (\) precedes the hash symbol (#), the latter is not used in the number of a group; instead, the # is treated merely as a number sign.
The following example event is parsed:
url_1=http://domain test_event url_2=/page/mypage test
The regular expressions used and the results of parsing of the example event are provided in the table below.
Examples of applying regular expressions
Regular expression |
Result of parsing |
|
http://domain/page/mypage |
|
/page/mypagehttp://domain |
|
/page/mypage_/_http://domain |
If no concatenation rule is set or the value of the concatenate attribute is empty, and the regular expression contains more than one group, the values of the groups are concatenated in the order in which they appear in the regular expression.
If the concatenate attribute contains more groups than the regular expression contains, the extra groups will be ignored and will be substituted with the corresponding #N text.
Event being parsed: url_1=http://domain test_event url_2=/page/my_page test Regular expression used: <RE_URL concatenate="#1#2#3">url_1=(.*?)\stest_event\surl_2=(.*?)\stest</RE_URL> Result of parsing: http://domain/page/my_page#3 |
Multiple matching
When parsing an event by using a regular expression, it is possible to extract all values that match the regular expression. For this purpose, set the value of the extract attribute to "all". If this value is set to "first" or the attribute is not specified, only the first value that matches the regular expression will be extracted.
For every matched value a separate detection event is generated. If the detection process does not affect a certain event field, the value of this field in the output event is set to a hyphen (-).
Event being parsed: ip1=12.12.12.12 ip2=23.23.23.23 hash1=abc hash2=cde user1=N1 user2=N2 Configuration file elements: <RegExps> <Source id="default"> <RE_IP extract="all">...</RE_IP> <RE_HASH extract="all">...</RE_HASH> <RE_USER extract="first">...</RE_USER> </Source> </RegExps> <EventFormat>ip=%RE_IP% hash=%RE_HASH% user=%RE_USER% %FeedContext%</EventFormat> Available feed records: IP = 12.12.12.12 IP = 23.23.23.23 hash = cde Detection events generated: ip=12.12.12.12 hash=- user= N1 <context for 12.12.12.12> ip=23.23.23.23 hash=- user= N1 <context for 23.23.23.23> ip=- hash=cde user=N1 <context for cde> |
Specifying characters by their hexadecimal code
Feed Service uses regular expressions that conform to PCRE syntax. This syntax allows specifying a character by its code in several ways.
Feed Service does not support specifying a character in \x{hhh..} format. Instead, specify a character by its code in the following way: \uhhhh, where hhhh is the hexadecimal code of the character. For example, you cannot use a ([\x{00a1}-\x{ffff}]) expression, but you can use a ([\u00a1-\uffff]) expression.
Optimization of regular expressions
You can optimize regular expressions to prevent backtracking that interfere with matching a string.
To optimize regular expressions, use the following rules:
- Use possessive quantifiers
(++, *+). - If possible, use non-matching group
(?:)with outer brackets. - Try to use alternation as little as possible and find matches at the end of the string. The alternation operator has the lowest precedence of all regular expression operators.
- Use the anchors
(^, $)that match the starting and the ending position within the string. - Use an atomic group. Atomic groups automatically discard all backtracking positions remembered by any tokens inside the group. The syntax is
(?> ...). - In long regular expressions, try to avoid exponentially increasing the amount of backtracking. An example such as
(qwerty.*)*is not recommended.
About filtering criteria for sending events to SIEM
You can specify filtering rules for detection events by using Kaspersky CyberTrace. Each filtering rule is set in the Matching > Event source filters section. The indicator attribute name is set from the indicator database, and filtering conditions and filtering values are specified in the Field name drop-down list, the Condition drop-down list, and the Value text box, respectively. Note that if the detected indicator does not have the attribute specified in the filtering rule, this indicator is considered as meeting the filtering criteria.
Kaspersky CyberTrace will send detection events only if the flag for sending detection events to the SIEM solution (the ioc_supplier_send_match_event attribute from the indicator database) is set to true and all fields of a feed record that matched the indicator meet the filtering criteria.
The table below lists filtering conditions that can be applied to detection events:
Possible filtering conditions
Filtering condition |
Description |
Equal to a specific value |
The indicator attribute is equal to the specified value. To apply this condition, select value is equal to OR field is not present in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a single value in the Value text box. |
Equal to at least one of several values |
The indicator attribute must contain one or more of the specified values. To apply this condition, select value is one of (separated by a new line) OR field is not present in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify several values in the Value text box. Do not specify empty values. Each new value must be separated from the previous value by a new line. |
Belonging to a range of numeric values |
The indicator attribute must contain a value in the specified range. To apply this condition, select value is in range (inclusive) OR field is not present in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a range of values in the Value text boxes. Notice that the range boundaries are included. The values must be integers. |
Belonging to a range of numeric values that are greater than or equal to the specified value |
The indicator attribute must contain a value that is greater than or equal to the specified value. To apply this condition, select value is more than (inclusive) OR field is not present in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a single value in the Value text box. The value must be an integer. |
Belonging to a range of numeric values that are less than or equal to the specified value |
The indicator attribute must contain a value that is less than or equal to the specified value. To apply this condition, select value is less than (inclusive) OR field is not present in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a single value in the Value text box. The value must be an integer. |
Belonging to a range of dates |
The indicator attribute must contain a date in the specified range. To apply this condition, select date is in range (inclusive) OR field is not present in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a range of dates in the Value text boxes. You can use a In addition, you can choose an arbitrary number of days or one of the following preset values for boundaries as the relative values to
|
Belonging to a range of dates that are greater than or equal to the specified value |
The indicator attribute must contain a date that is equal to or greater than the specified value. To apply this condition, select date is more than (inclusive) OR field is not present in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a date in the Value text box. You can use a In addition, you can choose one of the following preset values for the boundary (this value is relative to
|
Belonging to a range of dates that are less than or equal to the specified value |
The indicator attribute must contain a date that is less than or equal to the specified value. To apply this condition, select date is less than (inclusive) OR field is not present in the Condition drop-down list, and then specify a date in the Value text box. You can use a In addition, you can choose one of the following preset values for the boundary (this value is relative to
|
Equal to a non-empty value |
The indicator attribute must contain any non-empty value. To apply this condition, select value is non-empty in the Condition drop-down list. |
Configuring event sources with custom regular expressions
This section explains how to use the web interface to add and configure event sources with custom regular expressions.
Kaspersky CyberTrace sends information about a detection to a SIEM as a single event. To reduce dwell time, all context information that is required for triage and investigation should be included into this event. This can be accomplished by configuring event sources and custom regular expressions.
Repeat the steps below for every unique source of events that you have.
To configure an event source with custom regular expressions:
- Create an event source as described in section "Matching process settings".
- In addition to regular expressions for indicators (
URL,IP,MD5and other indicator types), add regular expressions ofCONTEXTtype. Regular expressions ofCONTEXTtype must match any information that will be relevant for the response, such as event identifiers, request identifiers, and time stamps. This context information will also help to search for raw events in the SIEM software, if required. - We recommend replacing universal regular expressions for indicators with the ones that match the event source event format. Regular expressions for many popular devices are described in section "Regular expressions for popular devices".
- Add all
CONTEXTregular expressions to the Detection events format field. To do so, specify the names of all regular expressions in the detection events format by using the%RegexpName%pattern.
Example
The event source for this example is a McAfee Web Gateway source.
The event source with custom regular expressions is configured as follows:
- Create a new event source.
This event source sends logs through the SIEM software, so adding this event source by IP is not possible because all such event sources will have the IP address of the SIEM software. Instead, specify a regular expression that will identify this event source based on the data contained in the events. For example, the expression can match a device name or a device version that are contained in the events. Note that If your event source sends the events directly to Kaspersky CyberTrace, specify such source by its IP instead.
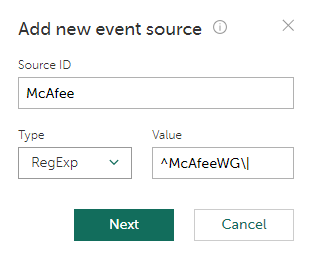
Creating a new event source
- Start collecting events and receive several sample events.
Only those events that matched the regular expression specified in the previous step will be displayed.
For example, events with the following data were received:
McAfeeWG|time_stamp=[01/Jan/2015:02:12:31 +0800]|auth_user=jsmith|src_ip=10.10.69.1|server_ip=192.0.2.1|host=www.example.com|url_port=80|status_code=301|bytes_from_client=279|bytes_to_client=1149|categories=Business, Software/Hardware|rep_level=Minimal Risk|method=GET|url=http://www.example.com/|media_type=text/html|application_name=|user_agent=Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 10.0; Windows NT 6.2; WOW64; Trident/6.0)|block_res=0|block_reason=|virus_name=|hash=|filename=|filesize=753|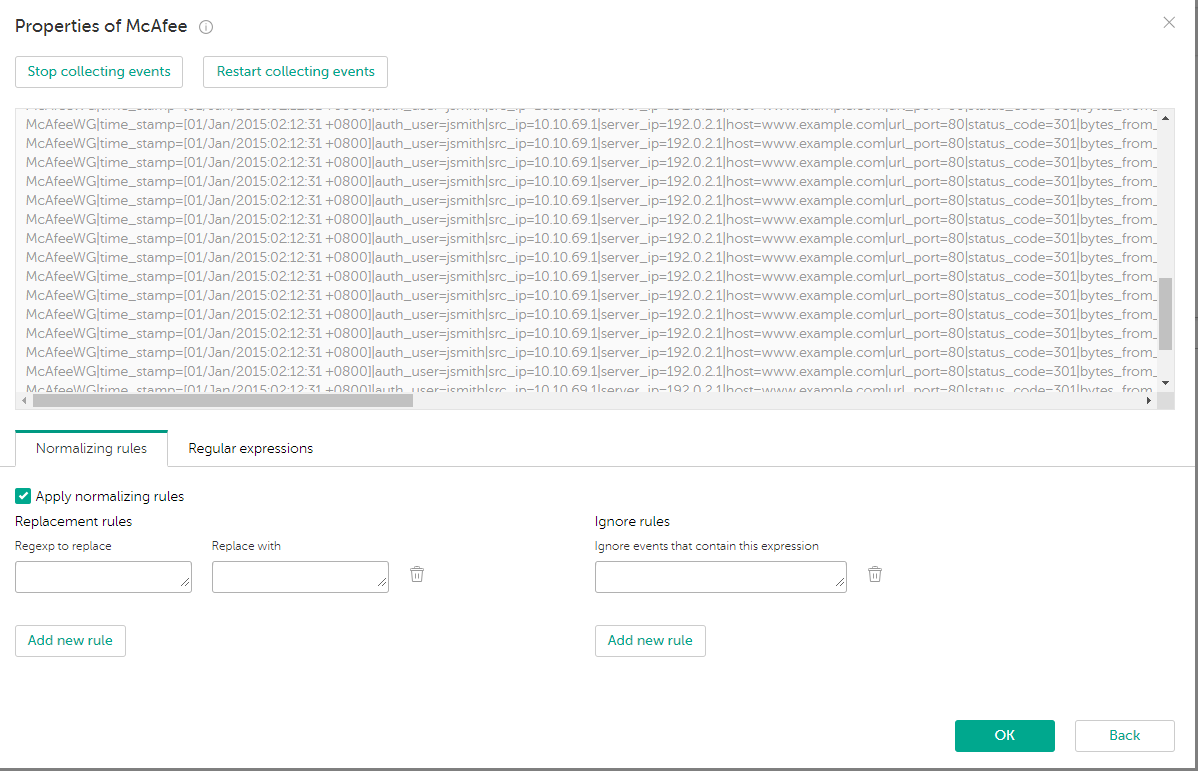
Collecting events
- Stop collecting events. Regular expressions for URL and IP will be specified automatically. Replace these expressions with custom ones. Then add regular expressions of
CONTEXTtype.To match the user name contained in the events, add an expression named
RE_USERNAME. Specify the following value for the expression:auth_user\=(.*?)(?:\|)To match the source IP address, add an expression named
RE_SRCIP. Specify the following value for the expression:src_ip\=(.*?)(?:\|)To match the URL, add an expression named
RE_URL. Specify the following value for the expression:url\=(.*?)(?:\|)To match the HTTP status code, add an expression named
RE_HTTPCODE. Specify the following value for the expression:status_code=(\d+)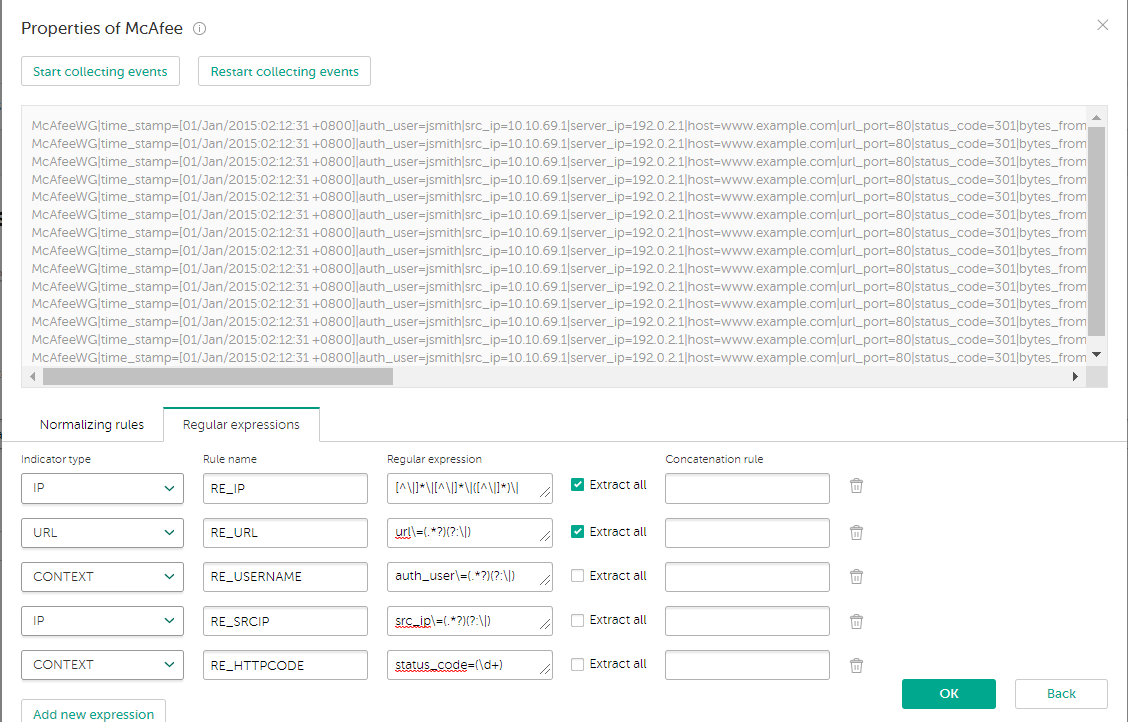
Specifying custom regular expressions
- Specify an event output format that contains these regular expressions:
eventName=%Category% matchedIndicator=%MatchedIndicator% url=%RE_URL% src=%RE_SRCIP% ip=%RE_IP% http_code=%RE_HTTPCODE% usrName=%RE_USERNAME% %RecordContext%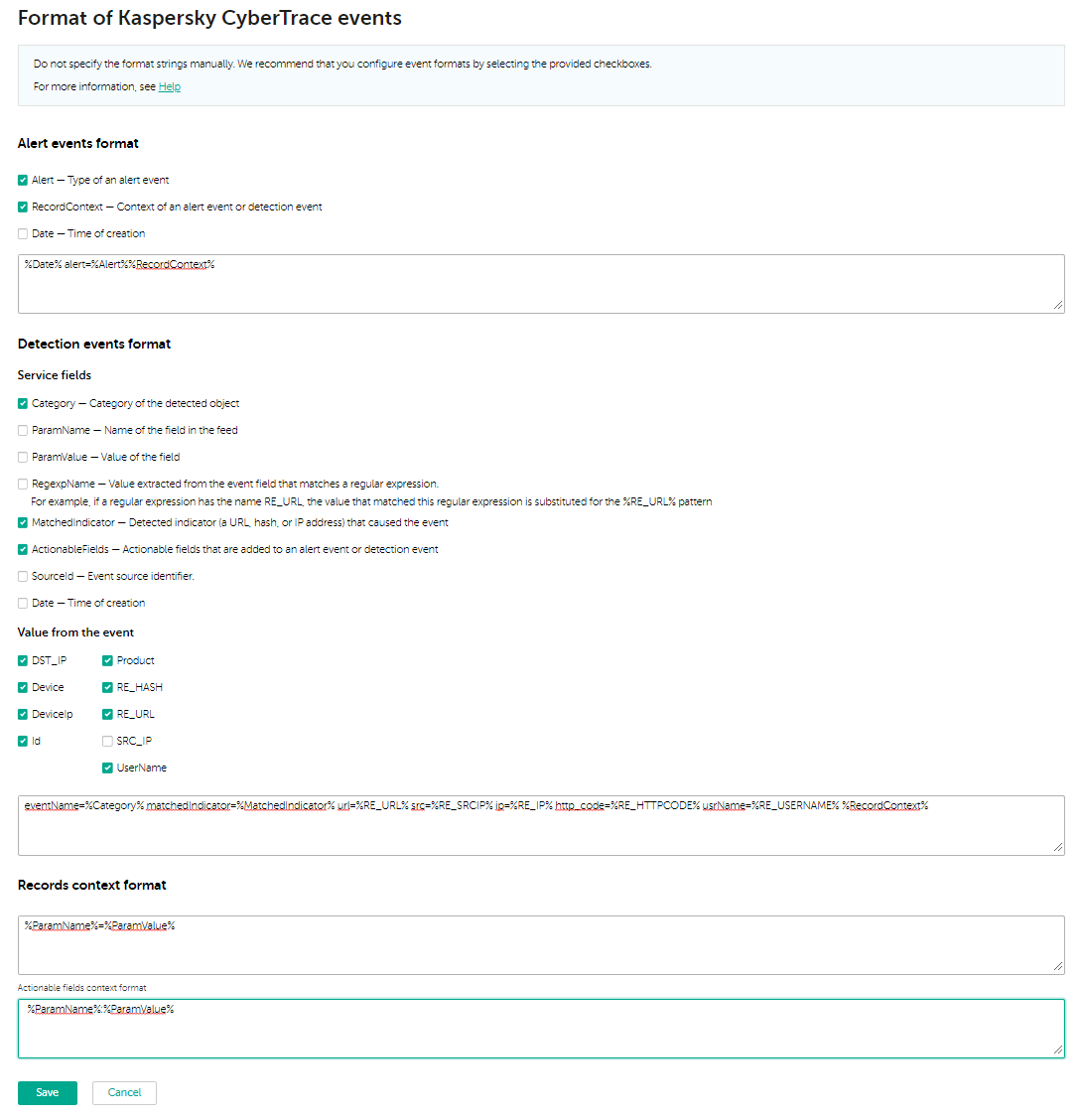
Specifying the output format of events
After the steps above are done, the detected events will contain the context fields. For example, an event from Kaspersky CyberTrace can have the following information:
device=McAfee eventName=KL_IP_Reputation matchedIndicator=192.0.2.1 url=- src=10.10.69.1 ip=192.0.2.1 http_code=301 category=test usrName=jsmith first_seen=01.01.2017 00:00 ip=192.0.2.1 ip_geo=ru last_seen=20.11.2019 10:02 popularity=1 threat_score=75
Page topRegular expressions for popular devices
This section provides regular expressions that are to be used for parsing events issued by popular devices.
Devices of different versions can issue events of different format, so it may be that you must use other regular expressions than those provided in this section.
FireEye devices
The events from FireEye devices require the following regular expressions:
- Events in CEF format
Field
Regular expression
URL1
filePath=([^\s]*?)\sURL2
cs5=([^\s]*?)\sMD5
fileHash=([^\s]*?)\sSrcIp
src=([^\s]*?)\sDstIp
dst=([^\s]*?)\s - Events in CSV format
Field
Regular expression
URL1
cnchost=([^,]*?),URL2
objurl=([^,]*?),MD5
fileHash=([^,]*?),SrcIp
src=([^,]*?),DstIp
dst=([^,]*?),
Blue Coat SG devices
The events from Blue Coat SG devices require the following regular expressions:
- SYSLOG events
Field
Regular expression
URL
OBSERVED\s"(?:.*?)"\s(.*?)\sURL2
http\s(.*?)\s\d+\s(.*?)\s
Websense devices
The events from Websense devices require the following regular expressions:
- CEF events
Field
Regular expression
URL
request\=(.*?)(?:\s|$)IP address
dst\=(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})(?:\s|$) - LEEF events
Field
Regular expression
URL
url\=(.*?)(?:\s|$)IP address
dst\=(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})(?:\s|$) - key-value pairs
Field
Regular expression
URL
url\=(.*?)(?:\s|$)IP address
dst_ip\=(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})(?:\s|$)Squid devices
The events from Squid devices require the following regular expressions:
Field |
Regular expression |
URL |
|
McAfee Web Gateway devices
The events from McAfee Web Gateway devices require the following regular expressions:
- Standard events
Field
Regular expression
URL
url\=(.*?)(?:\|)IP address
server_ip\=(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})(?:\|) - CEF events
Field
Regular expression
URL
request\=(.*?)(?:\s|$)IP address
dst\=(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})(?:\s|$) - SYSLOG events
Field
Regular expression
URL
(?:GET|POST)\s(.*?)(?:\s)
Check Point URL Filtering devices
The events from Check Point URL Filtering devices require the following regular expressions:
- SYSLOG events
Field
Regular expression
IP address
(?:dst)\s(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})
Juniper Networks SRX devices
The events from Juniper Networks SRX devices require the following regular expressions:
- SYSLOG events
Field
Regular expression
IP address
(?:\sdestination-address)\="(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})"\s
Check Point Firewall devices
The events from Check Point Firewall devices require the following regular expressions:
- SYSLOG events
Field
Regular expression
IP address
dst\:(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})
Palo Alto Networks devices
The events from Palo Alto Networks devices require the following regular expressions:
- LEEF events
Field
Regular expression
IP address
dst\=(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})(?:\s|$) - SYSLOG events
Field
Regular expression
IP address
(?:dst.*?)(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}) - CEF events
Field
Regular expression
IP address
dst\=(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})(?:\s|$)
Fortinet FortiGate devices
The events from Fortinet FortiGate devices require the following regular expressions:
- SYSLOG events
Field
Regular expression
IP address
(?:dst.*?)(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})
Cisco IPS devices
The events from Cisco IPS devices require the following regular expressions:
Field |
Regular expression |
IP address |
|
Snort devices
The events from Snort devices require the following regular expressions:
- UNIFIED2 events
Field
Regular expression
IP address
(?:destination.*?)(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}) - CSV events
Field
Regular expression
IP address
(?:.*?,.*?,.*?,.*?,)(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})
Alternatively, you can use the following regular expressions for parsing events of all types:
Field |
Regular expression |
IP address |
|
Cisco IronPort devices
The events from Cisco IronPort devices require the following regular expressions:
- SYSLOG events
Field
Regular expression
URL
(?:GET|POST)\s(.*?)\sIP address
(?:NONE|DIRECT|DEFAULT_PARENT)\/(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})
Event format settings
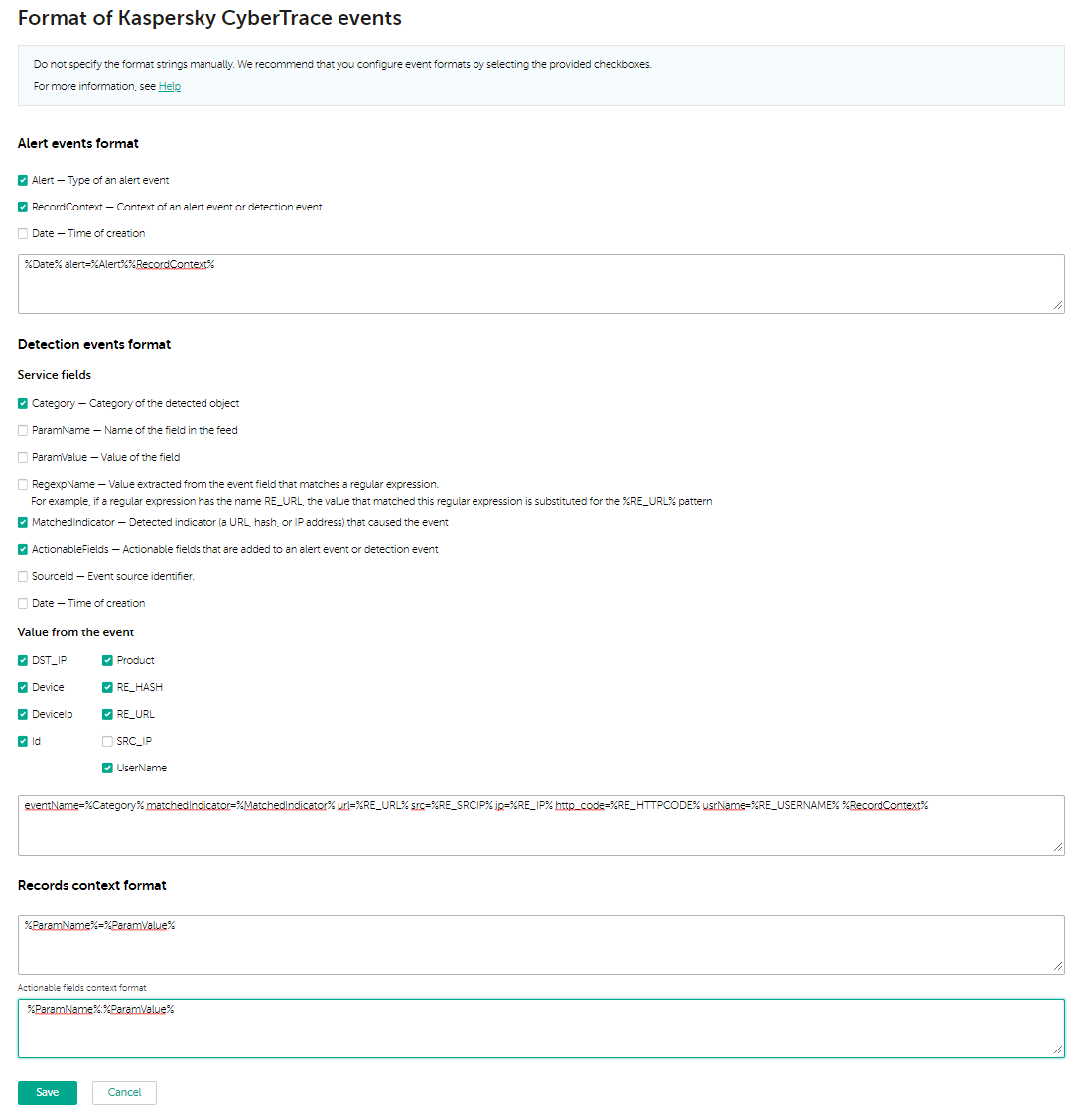
You can manage the settings for formats of events in the CyberTrace web user interface by selecting the Settings tab and then the Events format tab. Depending on the item selected in the drop-down list with all available tenants in the upper-left area of the window, you edit either the general event format settings (if General is selected) or the event format settings for a particular settings tenant (if a particular settings tenant is selected).
Kaspersky CyberTrace events formats
On the Events format tab, you can specify the formats of detection events, alert events, record context, and actionable fields context.
We do not recommend changing the format of events format manually. Select the check boxes with the patterns that you want to use in outgoing events and Kaspersky CyberTrace will update the format automatically.
Some event sources may require that you change the event format, depending on your integration. For more information, see the section "Setting event formats for specific event sources" below.
For more information about formats and patterns that you can specify, see About event formats and patterns.
This tab has the following text fields:
- Alert events format—Specify the format for outgoing events that inform the event target software of the state of Feed Service.
- Detection events format—Specify the format for outgoing detection events.
This section consists of two subsections:
- Service fields
Values of these fields are patterns generated by Kaspersky CyberTrace.
Select the check boxes with the patterns that you want to use in outgoing detection events. Kaspersky CyberTrace will update the format automatically.
- Value from the event
Values of these fields are extracted from the incoming events with regular expressions defined for the event source.
Select the check boxes with the patterns that you want to use in outgoing detection events. Kaspersky CyberTrace will update the format automatically.
- Service fields
- Records context format—Specify the format in which the names and values of the feed fields are inserted into outgoing events.
- Actionable fields context format—Specify the format in which the names and values of the actionable feed fields are inserted into outgoing events.
Setting event formats for specific SIEM solutions
The correct format of alert and detection events depends on your SIEM solution. If you change the format of events in CyberTrace, you may also need to update your integration with the SIEM solution.
For ArcSight:
- You may need to update the event formats and actionable fields.
For more information, see Step 3. Configuring CyberTrace for interaction with ArcSight.
For Qradar:
- You may need to add parsing for new fields.
For more information, see Step 5. Retrieving custom event properties.
For RSA NetWitness:
- You may need to specify how new fields are parsed.
For more information, see Step 2. Sending events from Feed Service to RSA NetWitness and RSA NetWitness troubleshooting.
For LogRhythm:
- You may need to specify how new fields are parsed.
For more information, see Adding Kaspersky CyberTrace events.
Specifying the format of detection and alert events
Kaspersky CyberTrace allows you to specify the format of detection and alert events by selecting the needed patterns.
To specify the format of detection events:
- Select the patterns that must appear in detection events.
- Click the Save button at the bottom of the page.
To specify the format of alert events:
- Select the patterns that must appear in alert events.
- Click the Save button at the bottom of the page.
You can specify the format of alert events if the General tenant is selected in the drop-down list with all available tenants, in the upper-left area of the window.
Page topAbout event format patterns
You can use formats and patterns to include specific information into the events generated by Kaspersky CyberTrace.
Formats are strings that determine the format of an event or pattern. Patterns are special wildcards that you can use when specifying formats. A pattern is replaced by actual data when an event is generated.
About alert and detection events
You can specify formats for two types of events generated by Kaspersky CyberTrace:
- Detection events
These are outgoing events that hold information about detected matches with indicators.
For more information about the format of detection events, see "Detection events format" below.
- Alert events
These are outgoing events that inform the event target software about the state of Feed Service.
For more information about the format of alert events, see "Alert events format" below.
Record context format
The %RecordContext% format specifies how context fields must be added to an event. You can specify a format for this pattern in the Records context format field.
You can use the following patterns in the %RecordContext% format:
- %ParamName%
The name of the field in the feed.
- %ParamValue%
The value of the field.
The %RecordContext% format is used in the formats of detection and alert events:
- Detection events
The %RecordContext% pattern determines the format of the context fields passed in a detection event.
For example, if %RecordContext% is
%ParamName%=%ParamValue%, then for a feed with the"Ip"and"Geo"fields, the following string can be produced (note the space symbol between the data of the two fields):"Ip=192.0.2.100 Geo=ru,br,ua,cz,us". - Alert events
The %RecordContext% pattern determines the format of the context fields passed in an alert event.
For more information about information contained in alert fields, see Alert events sent by Kaspersky CyberTrace.
The fields are specific for each type of alert event. For example, if %RecordContext% is
%ParamName%=%ParamValue%, and a feed is updated, the following string can be produced:"feed=Phishing_URL_Data_Feed.json records=200473".
Actionable field context format
The %ActionableFields% format specifies how actionable fields must be added to an event. You can set a separate format for this pattern in the Actionable fields context format field.
You can use the following patterns in the %ActionableFields% format:
- %ParamName%
The name of the actionable field.
- %ParamValue%
The value of the actionable field.
The %ActionableFields% format is used in the format of detection events:
The %ActionableFields% pattern determines the format of the actionable fields passed in a detection event.
For example, if %ActionableFields% is %ParamName%:%ParamValue%, and the cn1 and cn2 fields are specified for the feed, then the following string can be produced: "cn1:Example Device cn2:Example Environment".
Alert events format
You can specify this format in the Alert events format field.
You can use the following patterns in this format:
- %Alert%
The type of the event.
- %Date%
Current date and time in the
Mon DD HH:MM:SSformat. - %RecordContext%
Context of the event, as described in the "Record context format" section above.
The following is an example of the alert events format:
%Date% alert=%Alert%%RecordContext% |
If a feed update event is generated, the example above produces the following event:
Apr 16 09:05:41 alert=KL_ALERT_UpdatedFeed feed=Phishing_URL_Data_Feed.json records=200473 |
Detection events format
You can specify this format in the Detection events format field.
You can use the following patterns in this format:
- %Category%
Category of the detected object.
- Regular expression name
This pattern is a name of the regular expression. It is substituted by a value extracted from the event field that matches a regular expression. For example, if a regular expression has the name
RE_URL, the pattern for it is%RE_URL%, and the generated event holds the value that matched this regular expression. - %MatchedIndicator%
Detected indicator (a URL, hash, or IP address) that caused the event.
- %SourceId%
Event source identifier. This is the name that you specified for the event source on the Matching tab.
The identifier of the preconfigured event source is
Default. - %Confidence%
The level of confidence. This value is taken from the indicator confidence value of a feed that contains matched indicators from the detection event.
- %IndicatorInfo%
The link to the Kaspersky CyberTrace Web page that contains information about the detected indicator.
- %ActionableFields%
Actionable fields, as described in the "Actionable field context format" section above.
- %RecordContext%
Context of the event, as described in the "Record context format section" above.
The following is an example of the OutputSettings > EventFormat element:
%Date% event_name=%Category% source=%SourceId% matchedIndicator=%MatchedIndicator% url=%RE_URL% ip=%RE_IP% md5=%RE_MD5% sha1=%RE_SHA1% sha256=%RE_SHA256% usrName=%RE_USERNAME% indicatorInfo=%IndicatorInfo% confidence=%Confidence%%RecordContext% |
The example above produces the following events:
Apr 16 09:05:41 eventName=KL_Malicious_Hash_MD5 source=ExampleSource matchedIndicator=C912705B4BBB14EC7E78FA8B370532C9 url=- src=192.0.2.4 ip=192.0.2.23 md5=C912705B4BBB14EC7E78FA8B370532C9 sha1=- sha256=- usrName=ExampleUser indicatorInfo=https://127.0.0.1/indicators?value=C912705B4BBB14EC7E78FA8B370532C9 confidence=100 MD5=C912705B4BBB14EC7E78FA8B370532C9 SHA1=8CBB395D31A711D683B1E36842AE851D5D000BAD SHA256=F6E62E9B3AF38A6BF331922B624844AAEB2D3658C4F0A54FA4651EAA6441C933 file_size=2989 first_seen=10.07.2016 23:53 last_seen=13.04.2020 08:08 popularity=1 threat=HEUR:Trojan.Win32.Generic |
Patterns for ArcSight
Feed Service sends service events in the CEF format. The event formats for ArcSight must comply with the requirements of the CEF format.
For detection events, specify the following format:
|
In addition to the general patterns, the detection events format for ArcSight uses the following regular expression patterns referenced by regular expression names:
%DST_IP%—Destination IP address.%DeviceIp%—IP address of the endpoint device where the event occurred.%RE_HASH%—Hash contained in the event.%RE_URL%—URL contained in the event.%Device%—Device vendor.%Product%—Device name.%UserName%—Name of the user that was active on the endpoint device.%Id%—Event identifier.
For alert events, specify the following format:
|
In the format above, 4 (or another value from 1 to 10) is the level (severity) of the alert events from Kaspersky CyberTrace.
Patterns for RSA NetWitness
The values of the detection and alert event formats must correspond to the event formats set in the v20_cybertracemsg.xml file. If you change the formats, edit the v20_cybertracemsg.xml file accordingly.
The following is an example of the detection events format:
|
In addition to the general patterns, the detection events format for RSA Net Witness uses the following regular expression patterns referenced by regular expression names:
%RE_URL%—URL contained in the event.%RE_HASH%—Hash contained in the event.%DST_IP%—Destination IP address.%SRC_IP%—Source IP address.%DeviceIp%—IP address of the endpoint device where the event occurred.%Device%—Device vendor.%DeviceAction%—Action taken by the device.%UserName%—Name of the user that was active on the endpoint device.
Alert events sent by Kaspersky CyberTrace
This section describes alert events that can be generated by Kaspersky CyberTrace.
KL_ALERT_ConfigurationUpdated
This event is generated if Feed Service has reloaded the configuration file.
This event has no context fields.
KL_ALERT_FeedBecameAvailable
This event is generated if a feed that can be used with the current certificate has become available.
This event has the following field:
- feed
Feed name.
KL_ALERT_FeedBecameUnavailable
This event is generated if a feed that is being used with the current certificate has become unavailable.
This event has the following context field:
- feed
Feed name.
KL_ALERT_OutdatedFeed
This event is generated if a feed has not been updated during the specified period.
This event has the following context field:
- feed
Feed name.
KL_ALERT_ServiceUnavailable
This event is generated when the watchdog module has detected that Feed Service has crashed or frozen.
This event has no context fields.
KL_ALERT_ServiceStopped
This event is generated when Feed Service is stopped successfully.
This event has no context fields.
KL_ALERT_ServiceStarted
This event is generated when Feed Service is started successfully.
This event has no context fields.
KL_ALERT_UpdatedFeed
This event is generated when a feed is updated and loaded by Feed Service. This means that new indicators from the feed can be used in the matching process. Please note that these indicators may be added to the database later, as they are loaded asynchronously.
This event has the following context fields:
- feed
Feed name.
- records
The number of records loaded from the feed.
KL_ALERT_FailedToUpdateFeed
This event is generated when Feed Service fails to load a new feed (for example, due to the limitation on the number of indicators that are imposed by the license key) and continues using an old feed.
This event has the following context fields:
- feed
Feed name.
- error
Error message from Feed Utility or the text "
Error while applying feed <FeedName>".
KL_ALERT_LicenseExpires
This event is generated to inform you that the license key that is being used will expire in less than 30 days.
This event has the following context fields:
- license_name
Name of the license key.
- expiration_date
Expiration date of the license key.
KL_ALERT_LicenseExpired
This event is generated when a current license key has expired.
This event has the following context fields:
- license_name
Name of the license key.
- expiration_date
Expiration date of the license key.
KL_ALERT_EPSLimitExceeded
This event is generated when the limit on the number of processed events per second (EPS) imposed by the licensed key or licensing level has been exceeded.
This event has the following context fields:
- current_eps
Actual number of EPS that arrive in Feed Service.
- license_limit_eps
Limit on the number of EPS that is imposed by the license key or licensing level.
KL_ALERT_EPSHardLimit
This event is generated when Feed Service limits the number of events processed per second to the maximum number of events for the current license key or licensing level. The limit applies regardless of the number of incoming events.
- license_limit_eps
Limit on the number of EPS that is imposed by the license key or licensing level.
KL_ALERT_LicenseChanged
This event is generated when Kaspersky CyberTrace starts to use another license key or licensing level.
This event has the following context fields:
- license_name
Name of the license key.
If no license key is used, this context field is not included.
- expiration_date
Expiration date of the license key.
If no license key is used, this context field is not included.
- licensing_level
Licensing level of the key, if a license key is used.
Licensing level, if a license key is not used.
KL_ALERT_RetroScanCompleted
This event is generated when the retrospective scan task succeeded.
This event has the following context fields:
- iocs_rescanned
Number of scanned indicators.
- iocs_detected
Number of detected indicators.
- retroscan_report
Link to the result of the retrospective scan.
This field is absent if the value of the iocs_detected field is 0.
KL_ALERT_RetroScanError
This event is generated when the retrospective scan task failed.
This event has the following context field:
- error
Short text error description.
KL_ALERT_RetroScanStorageExceeded
This event is generated when the limit on the size of the saved events has been exceeded.
This event has the following context field:
- storage_size_limit
Limit on the size of the saved events.
KL_ALERT_FreeSpaceEnds
This event is generated when the available disk space becomes low.
This event has the following context field:
- msg
Amount of disk space that is still available for the indicator database.
The message has the following format: "Free space left: %FreeSpace% Mb", where %FreeSpace% is the remaining number of MB available for the indicator database.
KL_ALERT_IndicatorsStoreLimitExceeded
This event is generated when the limit on the size of the saved indicators has been exceeded.
This event has the following context fields:
- current_indicators_count
Current number of indicators.
- license_limit_indicators
Limit on the number of indicators that is imposed by the license key.
KL_ALERT_IndicatorsStoreHardLimit
This event is generated when Kaspersky CyberTrace limits adding and updating of indicators.
This event has the following context fields:
- license_limit_indicators
Limit on the number of indicators that are imposed by the license key.
- msg
Message that new indicators cannot be added to the database due to the limitation on the number of indicators that is imposed by the license key.
User settings
You can manage the user accounts settings by selecting the Settings tab, and then the Users tab.
The Users tab contains the following tabs:
- Local accounts
On this tab, you can add a new user account, and change or delete existing user accounts.
- LDAP
On this tab, you can provide the option to use domain user accounts for authentication in Kaspersky CyberTrace Web.
Working with local accounts
Kaspersky CyberTrace supports multiple users mode. On the Local accounts tab, you can add a new user account, and change or delete existing user accounts.
The form for managing user accounts settings can be disabled due to restrictions imposed by the licensing level. In this case, only the admin account will be available.
To add a new account:
- Click the Add new user button.
The New user window opens.
- Enter the account login in the Login field.
If you are using domain authentication along with local accounts, do not create local accounts with the names defined for existing domain accounts.
- Enter the full name in the Full name field.
You can leave this field blank.
- Set your password in the Password field and repeat it in the Confirm password field.
Your password must be from six to 16 characters long and must contain at least one lowercase letter, one uppercase letter, and one special character.
- Choose your role in the drop-down list:
- Analyst. Analysts have access to all features of Kaspersky CyberTrace, except those reserved for Administrators.
- Administrator. Administrators can manage user accounts and configure Kaspersky CyberTrace.
The default role is Analyst.
Administrators can download logs that may contain data considered private, security-related, or sensitive. In addition, administrators can browse the search results for all users.
- Click OK to create an account.
To edit a user:
- Click the
 button next to the user that you want to edit.
button next to the user that you want to edit.The Change user window opens.
- Edit one of the fields.
- Click OK.
To delete a user:
- Click the
 button next to the user that you want to delete.
button next to the user that you want to delete.The Delete user window opens.
- Click Delete.
- Click Yes to confirm that you want to delete the selected user.
Configuring LDAP authentication
Kaspersky CyberTrace supports LDAP user authentication to allow logging on as a domain user. This section explains how to configure this type of authentication by using Kaspersky CyberTrace Web.
Kaspersky CyberTrace supports the use of Active Directory only if the domain controller is running Windows. The use of Active Directory with Linux-based domain controllers is possible, but not guaranteed.
The LDAP section allows you to perform the following actions:
- Enable LDAP authentication
- Test the connection to the LDAP server
- Specify connection settings
- Configure accounts filtering
Enabling LDAP authentication
To enable LDAP authentication,
Click the LDAP auth enabled toggle button.
The LDAP server will now be used for user authentication.
When LDAP authentication is enabled, you still can interact with Kaspersky CyberTrace under a local user account.
Testing the connection to the LDAP server
Go through the procedure below to make sure that a connection to the LDAP server is established.
To test the connection to the LDAP server:
- Click the Test connection with LDAP link.
The Test connection with LDAP window opens.
- Specify the following settings:
- User name for test connection
- User password for test connection
- Click Test.
A connection test can be performed only if you specified all the necessary settings for connecting to the server.
Connection settings
In the Connection settings section of the LDAP tab, you can specify the following settings:
- IP address or FQDN (fully qualified domain name) and port of the LDAP server
This setting is stored in the
AuthenticationServer > ConnectionStringelement of the kl_feed_service.conf file. - SSL-secured connection
You can enable the use of a secure connection to the LDAP server by using Kaspersky CyberTrace Web.
This setting is stored in the
useEncryptionattribute of theAuthenticationServer > ConnectionStringelement of the kl_feed_service.conf file - Path to the LDAP database
The path to the database containing user accounts that can access Kaspersky CyberTrace.
Accounts filtering
The Accounts filtering section contains filtering rules for administrator and analyst accounts.
You can configure the following properties:
- Account format
You can select one of two formats:
- User Principal Name
If this option is selected, users must provide a user name that is not an email address when performing authentication (for example user, but not user@domain.com).
- SAM Account Name
If this option is selected, users must provide a user name in the following format when performing authentication: Domain\User.
- User Principal Name
- Administrator accounts filter
The filter for LDAP user accounts that defines which users must be assigned the Administrator role depending on their common name in Active Directory.
If this value is not specified, all users who login using LDAP authentication and pass the analyst account filter will be assigned the Analyst role.
This setting is stored in the
AuthenticationServers > AdministratorAccountsFilterelement of the kl_feed_service.conf file. - Analyst account filter
The filter for LDAP user accounts that defines which users must be assigned the Analyst role depending on their common name in Active Directory.
If this value is not specified, all users who login using LDAP authentication and do not pass the administrator account filter will be assigned the Analyst role.
This setting is stored in the
AuthenticationServers > AnalystAccountsFilterelement of the kl_feed_service.conf file.As an example, in the figure below the filters are configured so that the users who are members of the
Adminsgroup will be assigned the Administrator role, and the users who are members of either theOperatorsor theAnalystsgroup will be assigned the Analyst role.
Example of accounts filters
If the AdministratorAccountsFilter and AnalystAccountsFilter elements of the kl_feed_service.conf file contain values, and the user that is trying to log in is not included in any of the specified groups, Kaspersky CyberTrace will return an error and deny access to the web user interface for this user.
Logging settings
You can manage the logging settings in the CyberTrace web user interface by selecting the Settings tab, and then the Logging tab.
Under Logging settings, you can set the following settings:
- Log directory—Directory in which log files are to be stored
- Log level
The following values are possible:
- None
Logging is turned off.
Corresponds to the
nonlog level in the kl_feed_service_log.conf configuration file. - Error
Only errors are logged.
Corresponds to the
errlog level in the kl_feed_service_log.conf configuration file. - Info
Errors and information messages are logged.
Corresponds to the
inflog level in the kl_feed_service_log.conf configuration file. - Debug
All messages are logged
Corresponds to the
anylog level in the kl_feed_service_log.conf configuration file.
- None
- Maximum log size (MB)—In megabytes
- Delete old logs when Feed Service starts—Option of removing log files created by previous sessions
- Write to syslog—Option of whether logging must be performed by the syslog daemon
If this option is selected, all the other settings are ignored.
This option is available only on Linux systems.
For information about the contents of log files, see section "Feed Service logging", subsection "Log file contents".
Page topLicensing settings
You can manage the Kaspersky CyberTrace licensing in the CyberTrace Web by selecting the Settings tab, and then the Licensing tab.
On the Licensing tab, you can view information about license keys and perform the following actions:
- Add a new license key
- Remove a license key
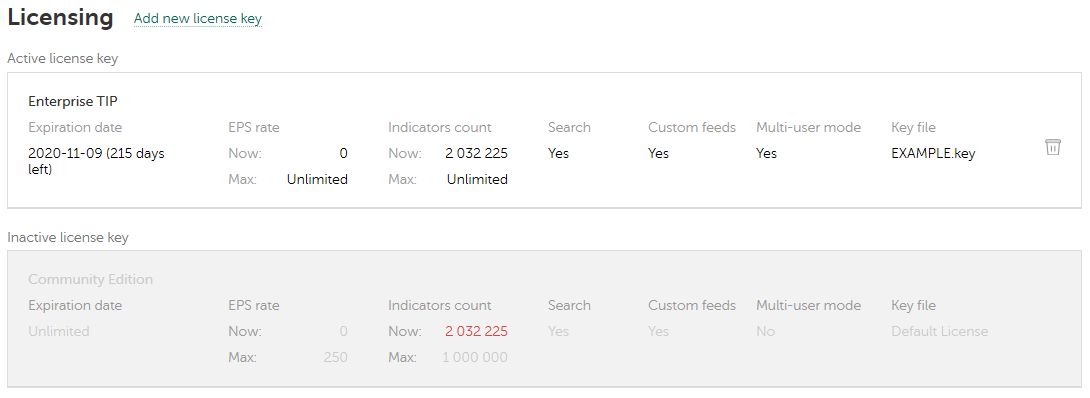
Licensing tab
The Licensing tab contains a list of license keys. The active license key is highlighted, and all inactive keys are unavailable (dimmed).
For each license key, the following information is available:
- Licensing level of the key
- Expiration date of the key
- Limit on the events per second (EPS) number
- The current number of indicators loaded into Kaspersky CyberTrace
This item displays the number of unique indicators for all enabled suppliers. Also note that if an indicator is present in multiple suppliers, duplications of this indicator are discarded from the total number.
- The maximum number of indicators allowed with this licensing level
- Information whether the search feature in CyberTrace Web is available
- Information whether custom feeds can be used
- Information whether multiuser mode is available
- License key file name
About the licensing
This section describes the licensing levels of Kaspersky CyberTrace.
Commercial licensing levels and Community Edition
The Kaspersky CyberTrace licensing policy provides two licensing level types:
- Community Edition
This is a limited licensing level that can be used without a license key. This licensing level does not have an expiration date.
If no license key is installed, the Community Edition licensing level is used.
The Community Edition licensing level has the following limitations:
- Multi-user mode is not available. Kaspersky CyberTrace has a single account with the Administrator role that can perform all operations.
- No more than 250 events per second are processed.
- No more than 1,000,000 records can be loaded from all feeds.
- Commercial licensing levels
These licensing levels are available with a license key and are suited for different enterprise scenarios.
License keys are created by Kaspersky specialists. To obtain a license key, contact your technical account manager (TAM).
Information contained in the license key
A license key is a sequence of bits that you can apply to use a certain licensing level of Kaspersky CyberTrace.
A license key contains the following information:
- Licensing level
- Expiration date
- Limit on events per second (EPS)
- Limit on the total number of indicators that can be loaded from Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds
In addition, a license key lists available features: the Search feature, use of third-party feeds, multi-user mode, multitenancy mode, and IOCs export.
License keys are stored in the %service_dir%/httpsrv/lic directory. You can manage license keys by using the Settings > Licensing tab.
Active and additional license keys
A license key may be active or additional.
An active license key is a license key that is currently used by Kaspersky CyberTrace. Kaspersky CyberTrace cannot have more than one active license key.
An additional license key is a license key that is not currently in use. The additional license key automatically becomes active when the current active license key expires. An additional license key can be added only if an active license key has already been added.
Kaspersky CyberTrace chooses an active license key to use, based on the expiration date of the license key. If there is a single license key that has not expired, this key is used as an active key. If there are several license keys that have not expired, the license key with the nearest expiration date is chosen. If all keys have expired, the Community Edition licensing level is used.
License key expiration notifications
Kaspersky CyberTrace sends alerts and generates events when license keys expire or are about to expire.
If less than 30 days are left until the key expires, Kaspersky CyberTrace displays an alert in CyberTrace Web and generates a KL_ALERT_LicenseExpires event.
After the license key expires, Kaspersky CyberTrace displays an alert in CyberTrace Web and generates a KL_ALERT_LicenseExpired event. Afterward, Kaspersky CyberTrace automatically searches for an additional license key and makes it active. If there are no additional license keys, Kaspersky CyberTrace changes its licensing level to Community Edition, displays an alert in CyberTrace Web, and generates a KL_ALERT_LicenseChanged event.
Licensing and DMZ
Kaspersky CyberTrace does not send any licensing information to Kaspersky. Licensing functionality works in scenarios involving a DMZ.
Page topLimitations imposed by license keys
This section describes limitations that are imposed on the Kaspersky CyberTrace functionality by license keys of different licensing levels.
Limit on events per second (EPS)
For the Community Edition licensing level, Kaspersky CyberTrace processes no more events per second than permitted by the licensing level.
Several commercial licensing levels have EPS limits specified in the licensing key. Kaspersky CyberTrace limits EPS for these licensing levels in two stages.
At the first stage, if the EPS limit is exceeded at any point in time, Kaspersky CyberTrace displays alerts in Kaspersky CyberTrace Web and generates the KL_ALERT_EPSLimitExceeded event. All events above the EPS limit continue to be processed.
At the second stage, if the EPS limit was continuously exceeded for a period of seven days, the limit takes effect. Kaspersky CyberTrace displays alerts in Kaspersky CyberTrace Web and generates the KL_ALERT_EPSHardLimit event. Kaspersky CyberTrace starts to process events within the limit imposed by the license key. After you change the license key or start to process no more events than are specified in the licensing key, this limitation ceases to apply.
Limit on the number of indicators
If the license key or licensing level sets a limit on the total number of indicators, Kaspersky CyberTrace reads, in total, no more records from all the feeds than are permitted by the license key or licensing level.
For the Community Edition licensing level, if the number of indicators exceeds a limit, Kaspersky CyberTrace sends the KL_ALERT_IndicatorsStoreHardLimit service event and then, through its Web UI, displays a notification that there is a limitation on the adding and updating of indicators. When the KL_ALERT_IndicatorsStoreHardLimit event is generated, Kaspersky CyberTrace stops reading new records.
For other licensing levels, if the number of indicators exceeds a limit, Kaspersky CyberTrace sends the KL_ALERT_IndicatorsStoreLimitExceeded service event, and then displays a notification through its Web UI. This notification informs that Kaspersky CyberTrace will set a restriction on the adding and updating of indicators after five days. Then, if the total number of indicators continuously exceed a limit for this period, Kaspersky CyberTrace sends the KL_ALERT_IndicatorsStoreHardLimit service event and displays another notification informing that the limitation has taken effect. When the KL_ALERT_IndicatorsStoreHardLimit event is generated, Kaspersky CyberTrace stops reading new records.
After you change the license key or start to process no more indicators than are specified in the licensing key, this limitation ceases to apply.
Limit on the use of custom feeds
If the license key does not allow the use of custom feeds, only Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds can be used. OSINT feeds cannot be used in this case.
Other limitations
The following features can be disabled by the license key or licensing level:
- Search feature in Kaspersky CyberTrace Web
- Multi-user mode
If multi-user mode is disabled, you can sign in under the
adminaccount only. This user account has the Administrator role.
Adding a license key
You can add an active key or an additional license key to Kaspersky CyberTrace by using Web UI.
To add a license key:
- In Kaspersky CyberTrace Web, select the Settings tab, and then the Licensing tab.
- Click Add new license key.
The Add a license key window opens.
- Click Browse.
Your browser opens a window where you can select a file.
- Select a license key.
License keys are created by Kaspersky specialists. To obtain a license key, contact your technical account manager (TAM).
- Confirm the selection.
- In the Add a license key window, click Add.
Kaspersky CyberTrace will import the selected key. If there is no active key, the imported key will be selected as an active key.
Deleting a license key
You can delete license keys by using Kaspersky CyberTrace Web UI.
To delete a license key:
- In Kaspersky CyberTrace Web, select the Settings tab, and then the Licensing tab.
- Click the Delete icon (
 ) for the license key that you want to delete.
) for the license key that you want to delete.The Delete the license key window opens.
- Click Delete to delete the license key.
Confirmation of the deletion will be displayed.
- Click Close.
Tenants settings
Kaspersky CyberTrace supports a multi-tenant architecture that allows you to manage tenants. A tenant is a client-specific set of configuration parameters. By default, Kaspersky CyberTrace uses a General tenant that provides the overall settings. You can create or edit the Kaspersky CyberTrace tenants in CyberTrace Web by selecting the Settings tab, and then the Tenants tab.
On the Tenants tab, you can view information about the tenants that are used in Kaspersky CyberTrace and perform the following actions:
- Add a new tenant
- Edit a tenant configuration
- Delete a tenant
Adding tenants
To add a tenant:
- Click the Add new tenant link.
The New tenant window opens.
- Specify a name for the new tenant in the Tenant field.
- Specify a description for this tenant in the Description field.
- Select a SIEM.
You can select a SIEM supported by Kaspersky CyberTrace or a custom one (a non-supported SIEM solution).
This SIEM will be used in the tenant for sending events to CyberTrace.
Depending on the selected SIEM, CyberTrace will specify regular expressions, detection events, and service events that are used in integration with this solution.
For the full list of supported SIEMs, see subsection "Supported SIEM solutions" below.
- Specify connection parameters specific for the tenant that Kaspersky CyberTrace will use for incoming events:
- Select what type of connection you want to use.
- In the IP address and Port fields, specify an IP address and port.
- In the UNIX socket field, specify a UNIX socket.
- Specify an IP address and port specific for the tenant that Kaspersky CyberTrace will use for outgoing events.
- Click Save.
Editing a tenant configuration
To edit a tenant configuration:
- Click the Edit button next to the tenant that you want to edit.
- Edit the tenant configuration:
- Tenant name
You cannot change the tenant name for the General tenant.
- Description
- Tenant name
- Click Save.
Deleting tenants
To delete a tenant:
- Click Delete next to the tenant that you want to delete.
- Confirm that you want to delete the tenant.
Supported SIEM solutions
Kaspersky CyberTrace supports integration with several SIEM solutions. Thus, CyberTrace uses a number of preset settings for each SIEM, such as settings for parsing events and event format settings (for detection and service events).
The following SIEM solutions are supported:
- Splunk
- ArcSight ESM
- RSA NetWitness
- IBM QRadar
- LogRhythm
- Kaspersky Unified Monitoring and Analysis Platform
Indicators export settings
You can export information related to the indicators to a CSV file. This report contains data about indicators exported from the indicator database and filtered by specified rules. This section explains how to create an export task that can be published as a report file in the CSV format and how to configure the data that must be included in this report.
The Indicators export tab displays the Indicators export tasks list with existing export tasks and allows you to do the following:
- Add a new export task.
- Manage existing export tasks.
You can perform the following actions with existing export tasks:
- Edit existing export tasks.
- Delete existing export tasks.
- Enable the scheduled task that regularly updates the indicators export task.
- Launch the export task.
Adding a new export task
To create a new export task:
- Click Add task.
The Add indicators export task window opens.
- In the Task properties section, specify the following settings for every field:
- Task name
The name of the export task.
- Maximum records
You can specify the maximum number of indicators that can be included in the report.
The maximum possible value is
50000. - Export every
Update frequency (in hours) for generating a report.
- Delimiter
The delimiter for splitting of fields in the report file. By default, this value is
';'.
- Task name
- In the Limit access to specified credentials section, specify the following information for every field:
- Use authorization to download indicators export
Specify this setting if you want to use authentication for downloading the indicators export.
If this setting is used, specify the credentials:
- User name
User name that must be used when requesting a report.
This user name is intended only for access to a specific report and it is not the same as the Kaspersky CyberTrace user account.
- Password
Password that must be used when requesting a report.
- User name
- Use authorization to download indicators export
- In the Fields to export section, specify filtering rules for the fields that you want to export:
- Field name
Name of the field to which filtering rules are applied and/or that must be exported.
- Condition
Filtering condition that is applied to the field.
- Value
Filtering criteria for the field. This value must meet the requirements described in the "Working with indicators" section.
- Include
Specify this setting if you want to include the field in the report file.
By default, this field must be included in the report file.
- Output name
Name of the output field which must contain the values from the exported field.
In the CSV report file, output fields have the same order that you specify through Kaspersky CyberTrace Web. If you change the position of the export rule to increase or decrease its priority, the new priority level will be retained in the CSV report file.
- Field name
- If necessary, specify the rules for sorting data in the Sort conditions section:
- Field name
Specify the field you want to sort.
- Direction
You can sort your values in ascending or descending order. This order is retained in the CSV report file.
- Field name
- Click Next.
The Export preview window opens. This window displays a table with an example of an indicators export.
- Click Add to apply the specified settings and add this task to the Indicators export tasks list.
If you want to change the setting specified in the previous step, click Back.
If you want to reset all the settings and close the window, click Cancel.
Managing an existing export task
To edit an existing export task:
- In the Indicators export tasks list, locate the task that you need, and then click Edit.
- Change the settings as described in the instructions above.
To delete an existing export task:
In the Indicators export tasks list, locate the task that you need, and then click Delete.
To enable scheduled indicators export:
Click the Enable scheduled export task toggle button.
If this setting is turned off, you cannot access reports that were created earlier.
To launch an export task:
In the Indicators export tasks list, locate the task that you need, and then click Launch export.
After that, the report with the exported indicators becomes available for download at the following address:
https://%CyberTrace_WebAddress%/reports/%iocexport_name%
where %iocexport_name% is the name of the specified export task.
Retrospective scan settings
Kaspersky CyberTrace allows you to save events containing indicators that are not detected, and then perform a retrospective scan of these events. This section explains how to configure Kaspersky CyberTrace for using the retrospective scan.
The Retrospective scanning tab allows you to do the following:
- Enable or disable the retrospective scan.
- View the current size of saved events.
- Remove saved events.
Saved events cannot be removed when the retrospective scan is in progress. If you want to disable the retrospective scan and removed the saved events, you must wait until the current retroscan task is finished.
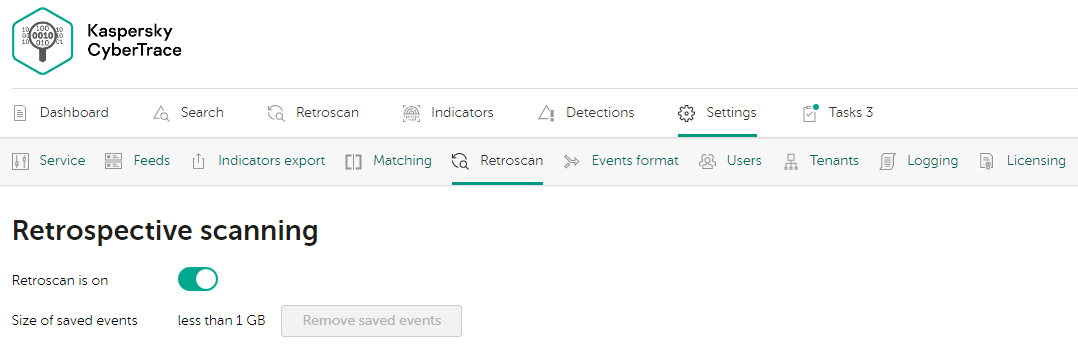
Retrospective scanning tab
- On the General settings tab, manage the following settings:
- Set the frequency of the scheduled retrospective scan task or disable the scan on schedule. If 1 month is selected, retrospective scan starts every 30 days.
- Enable or disable the size limit for events that must be saved for the retrospective scan.
- Set the maximum size of events (in gigabytes) that must be saved for the retrospective scan.
- Set how long (in days) the events used for the retrospective scan must be stored.
- Set how long (in days) the results of the retrospective scan must be stored.
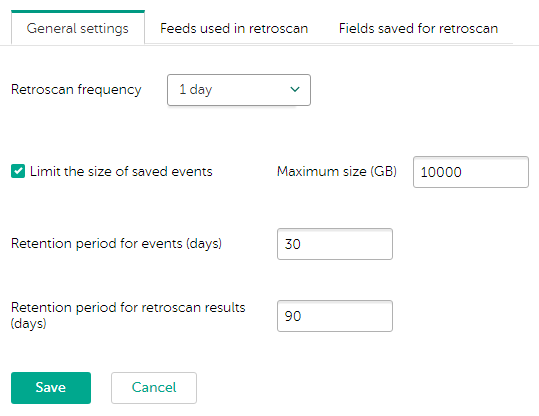
General settings tab
- On the Feeds used in retroscan tab, enable or disable feeds that must be used in the retrospective scan.

Feeds used in retroscan tab
- On the Fields saved for retroscan tab, configure the following settings:
- Enable or disable saving events related to a specific tenant for use in the retrospective scan.
If you exclude a tenant from the retrospective scan, the regular expressions contained in this tenant become unavailable for selection.
- Select regular expressions contained in a tenant for use in the retrospective scan.
You must select at least one regular expression.
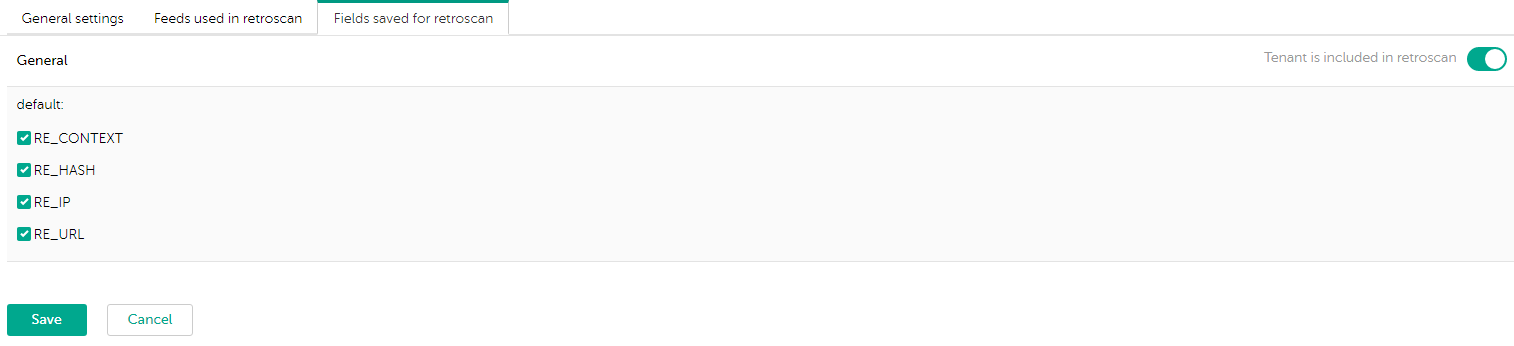
Fields saved for retroscan tab
- Enable or disable saving events related to a specific tenant for use in the retrospective scan.
Feed Service Guide
This section explains how Feed Service works, how to configure it, and how to manage it from the command line or by using a script.
About Feed Service
Feed Service is one of the components of Kaspersky CyberTrace. It runs as a service and works as follows:
- Feed Service listens on a specified port for incoming events.
- Feed Service matches indicators in received events against those in the feeds that are used.
- Feed Service generates events in the specified format that contains detected indicators on the basis of the incoming events and the feed records involved in the detection process.
- Feed Service sends the generated events to the specified address and port.
Managing Feed Service by using systemd (Linux)
You can manage Feed Service by using systemd.
You can use all standard systemd commands to manage Feed Service.
Checking the service status
To check the status of Feed Service, use the following command:
systemctl status cybertrace.service
Starting, stopping, restarting the service
To start Feed Service, use the following command:
systemctl start cybertrace.service
Feed Service begins to receive events only after it has loaded the feeds into memory and has sent the KL_ALERT_ServiceStarted event.
To stop Feed Service, use the following command:
systemctl stop cybertrace.service
To restart Feed Service, use the following command:
systemctl restart cybertrace.service
Adding and removing the service from the list of services loaded on boot
By default, Feed Service is loaded on boot. You can change this behavior with the following commands.
To add Feed Service to the list of services loaded on boot, use the following command:
systemctl enable cybertrace.service
To remove Feed Service from the list of services loaded on boot, use the following command:
systemctl disable cybertrace.service
Managing Feed Service using the script (Windows)
The %service_dir%\bin\kl_control.bat file is a script for managing Feed Service.
Command-line options
The script supports the following command-line options:
start—Starts Feed Service and the watchdog Windows service.The script prints the information about whether this operation succeeded or failed.
Feed Service begins to receive events only after it has loaded the feeds into memory and has sent the KL_ALERT_ServiceStarted event.
stop—Stops Feed Service and the watchdog Windows service.The script prints the information about whether this operation succeeded or failed.
restart—Restarts the services of Kaspersky CyberTrace: stops them and starts them again.The script prints the information about whether this operation succeeded or failed.
status—Prints the information about the status of the services of Kaspersky CyberTrace.reloaddb—Instructs Feed Service to reload the feeds it is using.help—Prints the Help information: how to use the kl_control.bat script.
You can use only one option at a time.
The script can also be launched without parameters. In this case, it prints the list of the available options and their descriptions.
Example
The following command starts Feed Service:
|
Managing Feed Service from the command line (Linux)
You can run the Feed Service binary file from the command line.
We recommend that you use systemd to manage Feed Service. Running Feed Service from the command line is intended for troubleshooting purposes.
The binary file uses the flags described in the following table.
Flags for kl_feed_service
Flag |
Value |
Description |
|
Path to the configuration file |
Path to the configuration file. You can use absolute or relative paths. If a relative path is specified, it is calculated relative to the Feed Service binary file. |
|
|
Runs Feed Service in watchdog mode. |
|
|
Prints the Feed Service version. If flags except |
|
Path to the PID file. |
Path to the PID file. You can use absolute or relative paths. If a relative path is specified, it is calculated relative to the Feed Service binary file. This flag is optional. By default, PID file is created in a directory with the Feed Service binary file. |
|
|
Prints the information about flags that can be used with kl_feed_service. If other flags are specified, they will be ignored. |
Example
The following command runs Feed Service in watchdog mode and specifies serv.conf as the configuration file.
./kl_feed_service -w -c "./serv.conf" |
Managing Feed Service from the command line (Windows)
You can run the Feed Service binary file from the command line.
We recommend managing Feed Service by using the script. Running Feed Service from the command line is intended for troubleshooting purposes.
The binary file uses the flags described in the following table.
Flags for kl_feed_service.exe
Flag |
Description |
|
Adds Feed Service to the list of Windows services. |
|
Removes Feed Service from the list of Windows services. |
|
Starts Feed Service as a Windows service. Note that only Service Control Manager can run kl_feed_service.exe with this flag. If the user tries to run kl_feed_service.exe with this flag, an error occurs. |
|
Prints the Feed Service version and exits. If flags except |
|
Prints the information about flags that can be used with kl_feed_service.exe and exits. |
If no flag is specified, the kl_feed_service.exe program prints the list of available flags to the screen.
Feed Service uses the configuration file that resides in the same folder as the kl_feed_service.exe binary file.
Page topFeed Service configuration reference
This section describes the configuration file of Feed Service.
We recommend that you configure Feed Service by using the Settings > Service tab. Use this section only for configuration that cannot be done from the web interface.
About the configuration file (Feed Service)
Feed Service reads settings from a configuration file.
Editing the configuration file
If the configuration file is absent or does not follow the rules specified in this section, Feed Service does not start and prints an error message.
To avoid potential issues, make a backup copy of the Feed Service configuration file before you make any changes in the file. If Kaspersky CyberTrace does not work properly after you have reconfigured Feed Service, replace the configuration file with its backup copy.
Applying changes made to the configuration file
You have to reload the configuration file or restart Feed Service after you edit the configuration file for the changes to take effect.
You can apply changes made to certain elements of the configuration file by reloading the configuration file but without restarting Feed Service.
These elements include:
InputSettings > RegExpsFeedsOutputSettings > RecordFieldContextFormatOutputSettings > AlertFormatOutputSettings > EventFormat
To reload the configuration file without restarting Feed Service,
Run the script for managing Feed Service with the reloadconfig option.
To apply changes made to other elements of the configuration file, you have to restart Feed Service.
To restart Feed Service,
Run the script for managing Feed Service with the restart option.
Configuration file location (Linux)
In Linux, the configuration file used by Feed Service can be specified in the following ways:
- When Feed Service is started from the command line, the path to a configuration file can be specified as an argument. By default, this path is
../etc/kl_feed_service.conf. - When Feed Service is managed using the script, the path to the configuration file is specified in the script parameters. By default, this path is
%service_dir%/etc/kl_feed_service.conf.
Configuration file location (Windows)
The configuration file used by Feed Service is named kl_feed_service.conf and resides in the same directory as the Feed Service binary file.
Case sensitivity
All the names used in the configuration file (for example, pattern names or feed fields) are case-sensitive.
Using special characters
To use special characters (for example, an ampersand or angle brackets) in regular expressions and other parameters, enclose the text of the elements in a CDATA section.
The following example uses braces around parameters:
<RecordFieldContextFormat><![CDATA[{%ParamName%=%ParamValue%}]]></RecordFieldContextFormat> |
EULA
Specifies whether the terms of the End User License Agreement (EULA) were accepted by a user.
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Possible values
This element has the following possible values.
EULA element possible values
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
The terms of the End User License Agreement (EULA) were accepted by a user. |
|
The terms of the End User License Agreement (EULA) were not accepted by a user. In this case, Kaspersky CyberTrace cannot be used. |
Example
The following is an example of a EULA element.
<EULA>accepted</EULA> |
IndicatorDatabaseSettings
Defines the indicator database settings.
Path
IndicatorDatabaseSettings
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- ConnectionString
Specifies the IP address and port that will be used for accessing the indicator database.
For more information about this element, see the "IndicatorDatabaseSettings > ConnectionString" section below.
IndicatorDatabaseSettings > ConnectionString
This element must contain a string with an IP address and a port. See the example below.
This element is mandatory.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<IndicatorDatabaseSettings> <ConnectionString>127.0.0.1:9200</ConnectionString> </IndicatorDatabaseSettings> |
Domains
Contains configuration for tenants.
Path
Domains
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested element:
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<Domains> <Domain name="Example Domain"> ... </Domain> <Domain name="Example Domain 2"> ... </Domain> </Domains>
|
Domain
Defines configuration for a single feed in a tenant.
Path
Domains > Domain
Attributes
This element has the following attributes.
Domain element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Tenant name |
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- Description
Tenant description
This element is optional.
- InputSettings
Input connection settings specific for this tenant. See InputSettings.
- OutputSettings
Output connection settings specific for this tenant. See OutputSettings.
This section is for a specific tenant. It cannot have AlertConnectionString and AlertFormat as nested elements.
- Feeds
Feed settings for the feeds used in this tenant.
For more information about this element, see the Domain > Feeds section below.
Domain > Feeds
Feed settings for the feeds used in the tenant.
This element is a container for the following nested element:
- Feed
Settings for a specific feed in a tenant.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<Domain name="CustomDomain"> <Description>Custom domain description</Description> <InputSettings> ... </InputSettings> <OutputSettings> ... </OutputSettings> <Feeds> ... </Feeds> </Domain> |
Domain > Feeds > Feed
Defines configuration for a single tenant.
Path
Domains > Domain > Feeds > Feed
Attributes
This element has the following attributes.
Feed element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Feed name. Must correspond to the name of a feed in the Feeds > Feed element. |
|
Specifies if the feed is used in the tenant. The feed must be enabled in the corresponding Feeds > Feed element to be used in a tenant. If the feed is enabled in the tenant, the value is If the feed is disabled in the tenant, the value is |
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested element:
- ActionableFields
Actionable fields for this feed in this tenant.
The specified actionable fields replace actionable fields that are defined for this feed in the Feeds > Feed > ActionableFields element (if such fields are defined).
This element is optional.
For more information, see Feeds > Feed > ActionableFields.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<Feed feedname=ExampleFeed used="true"> <ActionableFields> <ActionableField name="ExampleField" output_name="ExampleOutputField"/> ... </ActionableFields> </Feed> |
InputSettings
Contains input settings for the General tenant.
This element defines the IP address and port that Feed Service will listen on for incoming events, normalizing rules for processing the events, and regular expressions for parsing the events.
Path
InputSettings
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- RegExps
Contains Boost regular expressions that are used to parse incoming events originating from different sources.
- ConnectionString
Specifies the IP address and port (or the Windows-named pipe) that the service will listen on for incoming events.
- EventDelimiter
Specifies the rule for the splitting of incoming events,
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<InputSettings> <RegExps> ... </RegExps> <ConnectionString>0.0.0.0:9999</ConnectionString> </InputSettings> |
RegExps
Contains Boost regular expressions that are used to parse incoming events originating from different sources.
Path
InputSettings > RegExps
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested element:
- Source
Contains parameters for a specific event source.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<RegExps> <Source id="default"> ... </Source> <Source id="ExampleSource1"> ... </Source> <Source id="ExampleSource2"> ... </Source> </RegExps> |
Source
Contains parameters for a specific event source.
The regular expressions and event normalizing rules specified in the configuration file are grouped by event sources that are represented by Source elements. Usually these event sources are devices that issue events, which afterward are checked by Feed Service. Every Source element contains a set of rules. There can be one or more Source elements in the InputSettings > RegExps element.
Rules workflow
The way Feed Service chooses rules from different Source elements is described in the following flow chart.
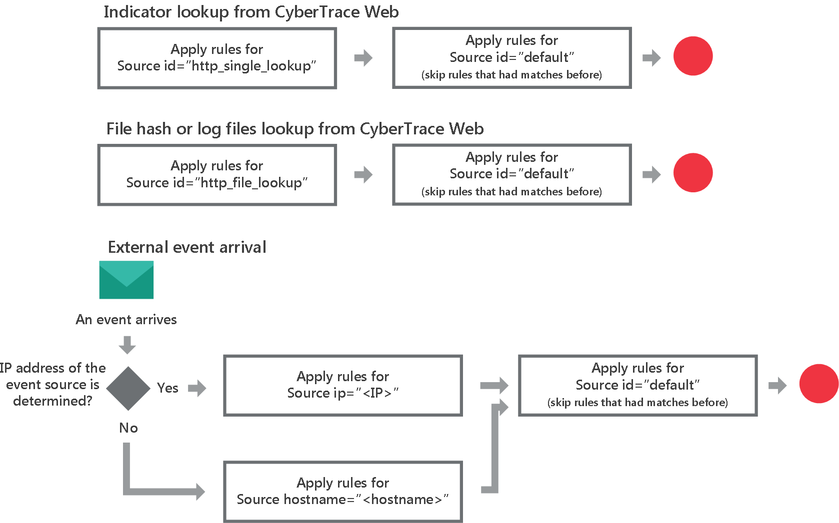
Choosing a rule
Note that event normalizing rules are applied first and regular expressions are applied afterwards.
The regular expressions of the default event source for finding URLs, IP addresses, and hashes are universal; that is, they can be used for parsing events issued by most devices. They can be used for parsing events that contain multiple URLs, but cannot be used, for example, for parsing events that contain URLs with no protocol specified. The use of universal regular expressions lowers the performance of Feed Service, compared to using device-specific regular expressions. Also, the universal regular expressions do not handle the dispersal, in an event, of different parts of a URL (for example, the host and the path). The universal regular expressions for finding hashes can extract symbol sequences that actually are not hashes.
Special event sources
There must be an event source with the default identifier (<Source id="default">). Rules of the default event source have lower priority than rules specific to the event source. Rules specific to the event source are applied first. Rules of the default event source are applied next. If a rule specific to the event source and a rule of the default event source have the same name, the rule of the default event source is applied only if the rule specific to the event source had no matches.
There are two special event sources that you can use: http_single_lookup (<Source id="http_single_lookup">) and http_file_lookup (<Source id="http_file_lookup">).
The rules of the http_single_lookup event source are used when single values are searched for by using CyberTrace Web.
The rules of the http_file_lookup event source are used when hashes of specified files or indicators in log files are searched for by using CyberTrace Web. Therefore, if you have to search for values contained in a log file that has a special format, we recommend specifying rules for the http_file_lookup event source.
If the configuration file contains the http_single_lookup event source or the http_file_lookup event source, we strongly recommend that you do not remove the regular expressions specified in these special event sources by default and, instead, edit them as needed.
Path
InputSettings > RegExps > Source
Attributes
This element has the following attributes.
Source element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
A unique identifier of the event source. In detection events, the identifier of the event source can be referred to by the %SourceId% pattern. |
|
The IP address of the event source. If an event has arrived from an event source that has the specified IP address, the event is processed by using the rules contained in this The |
|
The host name of the event source. The value of the host name is extracted from the event. In syslog events, the host name follows the timestamp (https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5424). For example, in the event If an event has arrived from an event source that has the specified host name and the IP address of the event source is not among those specified in the The hostname attribute cannot be set for the default, |
|
The regular expression that is used to determine if an event comes from the source. The specified regular expression is applied to an event. If the regular expression matches the event one or more times, the event is considered to be from the source. In this case, the event is processed by using the rules contained in this The hostname attribute cannot be set for the |
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- Regular expressions
Regular expressions that are used to parse incoming events originating from this source.
Each regular expression is a separate element with the name of the regular expression.
- NormalizingRules
Rules for modifying incoming events.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<Source id="CustomSource" ip="192.0.2.15"> <RE_MD5 type="MD5" extract="all">([\da-fA-F]{32})</RE_MD5> <RE_SHA1 type="SHA1" extract="all">([\da-fA-F]{40})</RE_SHA1> <RE_SHA256 type="SHA256" extract="all">([\da-fA-F]{64})</RE_SHA256> <NormalizingRules> ... </NormalizingRules> </Source> |
Source > Regular expression
Defines a regular expression for an event source.
Path
InputSettings > RegExps > Source > %RegexpName%
This element has the name of the regular expression.
Attributes
This element has the following attributes.
%RegexpName% element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Sets a rule for creating a compound value from data extracted from an event. For more information, see section "About regular expressions". |
|
The Possible values are The The |
|
Specifies the type of value that is extracted by this regular expression. Possible values:
|
|
Specifies if the extracted value that matched a specified regular expression must be used for a retrospective scan. If the extracted value must be used for the retrospective scan, the value of this attribute is If the extracted value must not be used for the retrospective scan, the value of this attribute is This attribute cannot be used within elements where the |
Value
This element contains a Boost regular expression.
For more information about specifying values for this parameter, see section "About regular expressions".
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<RE_MD5 type="MD5" use_for_retroscan="true" extract="all">([\da-fA-F]{32})</RE_MD5> |
Source > NormalizingRules
Defines rules for modifying incoming events.
For more information about normalizing rules, see Adding normalizing rules.
Path
InputSettings > RegExps > Source > NormalizingRules
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- Replace
These elements specify replacing rules.
- Ignore
These elements specify ignoring rules.
NormalizingRules > Replace
Defines a replacing rule.
This element has the following attributes.
Replace element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies a regular expression for the rule. |
|
Specifies the replacement sequence. |
NormalizingRules > Ignore
Defines an ignoring rule
This element has the following attributes.
Ignore element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies a regular expression for the rule. |
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<NormalizingRules> <Replace input="^\<(\d+)\>" output="NEW_EVENT\:\1\s" /> <Ignore input="Device0002" /> </NormalizingRules> |
ConnectionString
Specifies the IP address and port (or the Windows-named pipe) that the service will listen on for incoming events.
This element is mandatory.
Path
InputSettings > ConnectionString
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Value
The value is formatted as <ip_address>:<port> (if an IP address and port are used) or as \\.\pipe\<pipe_name> (if a Windows-named pipe is used).
The IP address must consist of four decimal octets, each separated by a dot. The value in each octet must be less than 256.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<ConnectionString>0.0.0.0:9999</ConnectionString> |
EventDelimiter
Specifies the rule for the splitting of incoming events.
Path
InputSettings > EventDelimiter
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Value
The value rule must have the following format:
<EventDelimiter>%START_EVENT_SYMBOLS%</EventDelimiter>
The %START_EVENT_SYMBOLS% value contains the regular expression that corresponds to the beginning of the substring of the incoming event.
The rule processes all occurrences of the %START_EVENT_SYMBOLS% value. If the %START_EVENT_SYMBOLS% value is found in the string of the incoming event, this string will be split into multiple events by the addition of the newline character (\n) before every matched substring.
If the %START_EVENT_SYMBOLS% value does not match any substring of the incoming string, the incoming string is considered a single event.
If an event contains newline characters (\n), such an event will be split by using both the %START_EVENT_SYMBOLS% value and newline characters as event delimiters.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<EventDelimiter><![CDATA[;]]></EventDelimiter> |
Feeds
Defines how events must be checked against feeds.
Path
Feeds
Attributes
This element has the following attributes:
Feeds element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
This attribute specifies how many times a field from an event can be matched against feeds. For example, a certain URL can match many feed records, so there will be many detection events. The This attribute is optional. If it is omitted, the number of generated events is not limited. |
|
This attribute specifies the update period (in minutes) for the feeds. You can use one of the following values: The value This attribute is optional. If it is omitted, the value |
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested element:
- Feed
Every Feed element describes a feed.
A configuration file must contain at least one Feed element.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<Feeds per_scan_detect_limit="10000" update_frequency="30"> <Feed filename="Demo_Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed.json" enabled="true" confidence="100"> ... </Feed> <Feed filename="Demo_Malicious_Hash_Data_Feed.json" enabled="true" confidence="100"> ... </Feed> <Feed filename="Demo_IP_Reputation_Data_Feed.json" enabled="true" confidence="100"> ... </Feed> </Feeds> |
Feed
Describes a feed or supplier.
Path
Feeds > Feed
Attributes
This element has the following attributes:
Feed element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies if the feed or supplier is enabled globally (across all tenants). |
|
The name of the supplier or the file name of the feed in the directory specified in the ServiceSettings > Bases element. This attribute is mandatory. |
|
The level of confidence of the feed or supplier. You can use values in the range of This attribute is mandatory. |
|
The period (in hours) following the last feed update, after which a notification about the outdated feed ( To turn off notifications for this feed, set this parameter to We recommend that you set this parameter to For third-party suppliers, this parameter is set to This attribute is optional. |
|
The period (in hours), after which indicators of compromise from the feed or supplier are removed from the database. If the indicator is detected on the basis of the incoming event, it is not removed from the database, but the feed that contains this indicator or the supplier that provided it can no longer be used in the matching process. To enable an infinite time limit for the feed or supplier invalidation, set this attribute to This attribute is mandatory (except for Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds). |
|
Name of the feed or supplier vendor. This attribute is optional. |
|
Specifies if the indicators from the feed or supplier must be used for retrospective scan. If the indicators must be used for retrospective scan, the value of this attribute is If the indicators must not be used for retrospective scan, the value of this attribute is |
|
Indicates that the supplier was added with the REST API. If the supplier was added with the REST API, the value of this attribute is This attribute is optional. |
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- Field
This element is obsolete starting from Kaspersky CyberTrace version 4.0.
A Field element specifies the rules for checking an event against the records of the feed.
For more information about this element, see section "About feed matching rules".
- ActionableFields
Defines actionable fields.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<Feed filename="Demo_Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed.json" enabled="true" confidence="100"> <ActionableFields> ... </ActionableFields> </Feed> |
Feed > ActionableFields
Defines the fields that must be inserted into the outgoing events apart from the context. An outgoing event contains context and actionable fields.
Path
Feeds > Feed > ActionableFields
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested element:
- ActionableField
Defines a single actionable field.
ActionableFields > ActionableField
Defines a single actionable field.
This element has the following attributes:
ActionableField element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
The name of the field as it is used in the feed |
|
Contains the name of the field as it will be inserted into outgoing events. If the |
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<ActionableFields> <ActionableField name="information" output_name="cs4"/> <ActionableField name="threat" output_name="cs3"/> </ActionableFields> |
About feed matching rules
Starting from Kaspersky CyberTrace version 4.0, the Feeds > Feed > Field element is obsolete. Information in this section applies only to Kaspersky CyberTrace 3.1.0 and below.
Feed Service checks incoming events against the feeds specified in the Feeds > Feed elements. For each specified feed, matching rules are set with one or more Field elements. Each Field element describes how a particular field in the feed must match the data from incoming events.
The following is an example of a Field element:
<Field name="mask" matching_type="Url" input_regexp_to_match="RE_URL" category="KL_BotnetCnC_URL" /> |
The Field element must have the following attributes:
nameThe name of the field in the feed must be specified in the
nameattribute. Note that field names are case-sensitive. For example, fields"md5"and"MD5"are different fields.To specify nested fields, use the
'/'delimiter. For example,name="detail/info"specifies theinfofield in a feed that has the following content:[ { "hash":"234D123...", "detail": [ { "info" : "some value" } ] } ].matching_typeThe type of matching must be specified in the
matching_typeattribute.The following values are possible:
"Url"The event field will be checked for conformance to the URL masks stored in the feed. For more information about the masks stored in feeds, contact your technical account manager (TAM).
"Exact"Comparison of two strings will be performed: the event field and the field stored in the feed.
"Hash"The event field will be checked to determine whether it is equal to the one stored in the feed. This matching type is used only for hashes.
input_regexp_to_matchName of a regular expression that is used for matching. The value of this attribute must be one of the regular expression names from the
InputSettings > RegExpselement.categoryThe category that will be used in the outgoing event.
All the attributes of the Field element are required.
The following is an example of the feed matching rules for a specific feed:
<Feed filename="Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed.json"> <Field name="mask" matching_type="Url" input_regexp_to_match="RE_URL" category="KL_BotnetCnC_URL" /> <Field name="files/MD5" matching_type="Hash" input_regexp_to_match="RE_MD5" category="KL_BotnetCnC_Hash_MD5" /> <Field name="files/SHA1" matching_type="Hash" input_regexp_to_match="RE_SHA1" category="KL_BotnetCnC_Hash_SHA1" /> <Field name="files/SHA256" matching_type="Hash" input_regexp_to_match="RE_SHA256" category="KL_BotnetCnC_Hash_SHA256" /> </Feed> |
The following is an example of the feed matching rules for a specific feed for ArcSight:
<Feed filename="Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed.json"> <Field name="mask" matching_type="Url" input_regexp_to_match="RE_URL" category="KL_BotnetCnC_URL" /> <Field name="files/MD5" matching_type="Hash" input_regexp_to_match="RE_HASH" category="KL_BotnetCnC_Hash_MD5" /> <Field name="files/SHA1" matching_type="Hash" input_regexp_to_match="RE_HASH" category="KL_BotnetCnC_Hash_SHA1" /> <Field name="files/SHA256" matching_type="Hash" input_regexp_to_match="RE_HASH" category="KL_BotnetCnC_Hash_SHA256" /> </Feed> |
If you have events that contain the event source IP address, we recommend that you check them against IP Reputation Data Feed. This must be done because the event source may be a bot or a malicious device of some other kind that takes part in a DoS attack on the user resources. To check such events against IP Reputation Data Feed, add an SRC_IP regular expression to find the event source IP addresses. Also, add a rule for IP Reputation Data Feed to use the SRC_IP regular expression, so that the configuration file will contain the following records:
<Feed filename="IP_Reputation_Data_Feed.json"> <Field name="ip" matching_type="Exact" input_regexp_to_match="RE_IP" category="KL_IP_Reputation" /> <Field name="ip" matching_type="Exact" input_regexp_to_match="SRC_IP" category="KL_IP_Reputation" /> </Feed> |
Also, add the reference to the value found by the SRC_IP regular expression (%SRC_IP%) to the OutputSettings > EventFormat element.
IoCExports
Contains indicators export settings.
Path
IoCExports
Attributes
This element has the following attributes.
IoCExports element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Path to a directory that will contain the report. This path can be either absolute or relative. |
Nested elements
The IoCExports element is a container for the following nested element:
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<IoCExports export_dir="../reports"> ... </IoCExports> |
IoCExport
Defines settings for a single report with exported data.
Path
IoCExports > IoCExport
Attributes
This element has the following attributes.
IoCExport element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
The name of the export task. The name can be in a range from 2 to 64 characters in length, must contain only Latin letters, digits (0-9), hyphens ( This attribute is mandatory. |
|
Specifies if a report must be generated. If the report must be generated, the value is If the report must not be generated, the value is This attribute is mandatory. |
|
Specifies the rule for splitting fields in the report file. Use one of the following characters as a delimiter: This attribute is mandatory. |
|
Specifies the update period (in minutes) for the export task. The following values are possible: This attribute is mandatory. |
|
Indicates whether the report file must contain column names as the first string. If the report file must contain column names as the first string, the value is If the report file must not contain column names as the first string, the value is This attribute is mandatory. |
|
Specifies the maximum number of indicators that can be included to the report file. The value must be a positive integer. The maximum number of records is 50,000. This attribute is mandatory. |
|
Specifies the identifier of the Kaspersky CyberTrace user who created the report. This attribute is mandatory. |
|
Specifies the credentials (user name and password) that must be used in the Basic authorization scheme when requesting a report. These credentials are stored encrypted. You can configure encryption by using the Kaspersky CyberTrace web user interface. This attribute is optional. |
Nested elements
The IoCExports > IoCExport element is a container for the following nested element:
- Filter
A configuration file must contain at least one Filter element.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<IoCExport name="report_csv_123" enabled="true" delimiter=";" update_frequency="1440" create_header="true" records_limit="10000" created_by="admin" credentials="Mhy5QB7R487xbULBQJn8CzpOdV2fQftPyBJPxgjLBXZb+x08"> ... </IoCExport> |
IoCExport > Filter
Defines the filtering rules for data to be exported.
Path
IoCExports > IoCExport > Filter
Attributes
This element has the following attributes.
Filter element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies the name of the field to which filtering rules are applied and /or which must be exported. You can specify indicator attribute names from the indicator database. For the list of possible names, see section "Working with indicators" The name can be in a range from 2 to 255 characters in length, must contain only lowercase ASCII characters and cannot begin with a hyphen ( This attribute is mandatory. |
|
Specifies filtering criteria for the field. It is allowed to use a This attribute is mandatory. |
|
Specifies whether the field values must be included in the report file. If the field values must be included to the report file, the value is If the field values must not be included in the report file, the value is This attribute is mandatory. |
|
Specifies the name of the field that must contain the values from the exported field. This attribute is mandatory if the following requirements are met:
|
|
Specifies the sorting order for field values. The following values are possible:
|
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<Filter field="ioc_type" value="MD5;SHA1" sort="desc" included="false"/> <Filter field="supplier_name" value="IP Reputation Data Feed" included="true" output_name="feed"/> <Filter field="supplier_confidence" value="*" included="false"/> <Filter field="added_timestamp" value="[*;25.12.2019]" sort="asc" included="false"/> |
RetroScan
Contains retrospective scan settings.
Path
RetroScan
Attributes
This element has the following attributes.
RetroScan element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Indicates if a retrospective scan mechanism is enabled. If the retrospective scan is enabled, the value is If the retrospective scan is disabled, the value is The preset value is This attribute is mandatory. |
|
The maximum size of the events (in MB) that must be saved for the retrospective scan. The preset value is This attribute is mandatory. |
|
The maximum time interval (in days) during which the events that must be saved for the retrospective scan are stored. The preset value is This attribute is mandatory. |
|
The maximum time interval (in days) during which the results of the retrospective scan are stored. The preset value is This attribute is mandatory. |
|
Frequency (in hours) of the retrospective scan scheduled task. The preset value is This attribute is mandatory. |
SendEventFilters
Contains filtering rules for detection events from Kaspersky CyberTrace. You can specify several filtering rules at once.
Path
SendEventFilters
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested element:
- Filter
A filtering rule.
SendEventFilters > Filter
This element defines a filtering rule.
For more information about this element and possible values of its attributes, see section "Working with indicators".
This element has the following attributes:
ActionableField element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
The name of the indicator attribute from the indicator database to which filtering rules are applied. |
|
Filtering rule. Kaspersky CyberTrace sends a detection event if the value of the indicator attribute matches the specified value.
|
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<SendEventFilters> <Filter attribute="ioc_supplier_context.last_seen" value="[01.02.2013;01.02.2015]"/> <Filter attribute="ioc_supplier_context.popularity" value="5"/> <Filter attribute="ioc_updated_timestamp" value="[%NOW%-3;%NOW%]"/> </SendEventFilters> |
OutputSettings
Contains output settings for the General tenant.
Defines the address and port of the event target software to send the outgoing events to, and the format of the outgoing events.
Path
OutputSettings
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- EventFormat
Specifies the format of outgoing events.
For more information about the values of this element, see About event formats and patterns.
The EventFormat element is mandatory.
- RecordFieldContextFormat
Specifies how context fields must be added to an event.
For more information about the values of this element, see About event formats and patterns.
The RecordFieldContextFormat element is mandatory.
- ActionableFieldContextFormat
Specifies how actionable fields must be added to an event.
For more information about the values of this element, see About event formats and patterns.
The ActionableFieldContextFormat element is mandatory.
- AlertFormat
Specifies the format for outgoing events that inform the event target software of the Feed Service state.
For more information about the values of this element, see About event formats and patterns.
The AlertFormat element is optional. If it is absent from the configuration file, no notification is made.
- ConnectionString
Specifies the IP address and port (or the Windows-named pipe) to which the service will send outgoing events.
The ConnectionString element is mandatory.
For more information about this element, see the "OutputSettings > ConnectionString" section below.
- AlertConnectionString
Specifies the IP address (or host) and port to which the service will send service alerts.
The AlertConnectionString element is optional.
For more information about this element, see the "OutputSettings > AlertConnectionString" section below.
- FinishedEventFormat
Specifies the format of the informational event that is generated for each processed event.
The FinishedEventFormat element is mandatory.
For more information about this element, see the "OutputSettings > FinishedEventFormat" section below.
OutputSettings > ConnectionString
Specifies the IP address (or host) and port to which the service will send service alerts.
The string is formatted as <ip_address>:<port> (if an IP address and port are used) or as \\.\pipe\<pipe_name> (if a Windows-named pipe is used). The IP address must consist of four decimal octets, each separated by a dot. The value in each octet must be less than 256.
OutputSettings > AlertConnectionString
Specifies the IP address (or host) and port to which the service will send service alerts.
The value of this element is formatted as <ip_address>:<port> (if an IP address and port are used) or as \\.\pipe\<pipe_name> (if a Windows-named pipe is used). The IP address must consist of four decimal octets, each separated by a dot. The value in each octet must be less than 256.
The AlertConnectionString element is optional. If the element is omitted, the enabled attribute with the false value is used for this element.
This element has the following attributes:
AlertConnectionString element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Defines whether Feed Service sends alert events to the specified IP address and port. Possible values: If the value is If the value is |
OutputSettings > FinishedEventFormat
Specifies the format of the informational event that is generated after an event is processed.
If this parameter is enabled, Kaspersky CyberTrace will generate an informational event for each event that it processes. An informational event is generated even if there were no detections.
The FinishedEventFormat element is mandatory.
The value of this element specifies the event format. You can use the %RecordContext% pattern and regular expression names in the format. For more information about patterns, see About event formats and patterns.
The %RecordContext% pattern will provide the following fields, if used:
- category
It is
"LookupFinished"for events of this type. - sent_events
The number of events sent to a SIEM solution.
- total
Concatenation of the following substrings formed for every category assigned to detection events:
<category>:<number_of_detections>;If there were no detections, the sent_events parameter is set to
0, and the total string is empty.
This element has the following attributes:
FinishedEventFormat element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Defines whether special informational events are generated. Possible values: If the value is If the value is This attribute is optional. |
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<OutputSettings> <RecordFieldContextFormat><![CDATA[ %ParamName%=%ParamValue%]]></RecordFieldContextFormat> <AlertFormat>%Date% alert=%Alert%%RecordContext%</AlertFormat> <EventFormat>%RE_DATE% category=%Category% matchedIndicator=%MatchedIndicator% url=%RE_URL% src=%SRC_IP% ip=%RE_IP% md5=%RE_MD5% sha1=%RE_SHA1% sha256=%RE_SHA256% usrName=%RE_USERNAME%%RecordContext%</EventFormat> <FinishedEventFormat enabled="true">LookupFinished %RecordContext%</FinishedEventFormat> <ActionableFieldContextFormat><![CDATA[ %ParamName%:%ParamValue%]]></ActionableFieldContextFormat> <ConnectionString>127.0.0.1:9998</ConnectionString> <AlertConnectionString>192.0.2.145:9998</AlertConnectionString> </OutputSettings> |
ServiceSettings
Defines settings for the Feed Service process.
Path
ServiceSettings
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- Bases
Specifies the path to the directory that contains feeds from Kaspersky. If a relative path is set, it is calculated relative to the directory that contains the service binary file.
The Bases element is mandatory.
- BasesBackup
Specifies the path to the directory that contains backup version of feeds from Kaspersky. If a relative path is set, it is calculated relative to the directory that contains the service binary file.
The BasesBackup element is mandatory.
- BasesDownload
Specifies the path to the directory that contains downloaded feeds from Kaspersky. If a relative path is set, it is calculated relative to the directory that contains the service binary file.
The BasesDownload element is mandatory.
- TemporaryDir
The directory for temporary files.
The TemporaryDir element is optional. If it is omitted, the default value is used.
In Linux, the default value is
/tmp.In Windows, the default value is
%TEMP%(the current Windows user's temporary folder). - OutdatedBasesAlertPeriod
The time interval in hours following the last feed update, after which a notification about an outdated feed is sent to the event target. To turn off notifications, set this parameter to
0. This setting is taken into account for every feed that has no outdated_alert_period attribute.The OutdatedBasesAlertPeriod element is optional. If it is omitted, the default value
0is used. - ScannersCount
The number of scanners. Every scanner handles a single TCP connection.
If you want to run Feed Service in watchdog mode, specify one scanner in addition to the number of scanners needed for Feed Service itself. This must be done because the watchdog module uses an additional scanner.
The ScannersCount element is optional. If it is omitted, the default value
9is used. - ScanningThreadsPerScanner
The number of threads per scanner.
The ScanningThreadsPerScanner element is optional. If it is omitted, the default value
8is used. - EventSendingRetriesCount
Number of times Feed Service tries to resend a detection event to a SIEM solution if the first attempt at sending fails. If the value of
EventSendingRetriesCountis0, Feed Service sends each detection event one time and does not attempt to resend it.Maximum possible value is
10. The preset value is3.The EventSendingRetriesCount element is mandatory.
- EventSendingRetriesTimеout
Time interval between attempts made by Feed Service to resend a detection event to a SIEM solution, in seconds. Maximum possible value is
60.The EventSendingRetriesTimеout element is mandatory.
The preset value is
10. - FeedsRollbackEnabled
Specifies if feeds rollback is enabled or disabled.
If feeds rollback is enabled, feeds are rolled back when Kaspersky CyberTrace fails to upload new indicators into the Matching engine after feeds are updated. Kaspersky CyberTrace removes new indicators from the database and uses the previous feeds.
Possible values:
true— feeds rollback is enabled.false— feeds rollback is disabled.
Kaspersky CyberTrace reads FeedsRollbackEnabled only during initialization and does not reread it after.
By default, there is no FeedsRollbackEnabled element in the configuration file. If this element is missing, feeds rollback is enabled.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<ServiceSettings> <Bases>../feeds</Bases> <BasesBackup>../feeds/backup</BasesBackup> <BasesDownload>../feeds/download</BasesDownload> <TemporaryDir>/tmp</TemporaryDir> <OutdatedBasesAlertPeriod>120</OutdatedBasesAlertPeriod> <ScannersCount>9</ScannersCount> <ScanningThreadsPerScanner>8</ScanningThreadsPerScanner> <EventSendingRetriesCount>3</EventSendingRetriesCount> <EventSendingRetriesTimеout>10</EventSendingRetriesTimеout> <FeedsRollbackEnabled>true</FeedsRollbackEnabled> </ServiceSettings> |
GUISettings
Defines settings for the CyberTrace Web.
Path
GUISettings
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- HTTPServer
Contains the CyberTrace HTTP service parameters.
- FeedUtil
Contains the Feed Utility parameters.
- AuthenticationServers
Defines settings for connection to the LDAP servers.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<GUISettings> <HTTPServer> ... </HTTPServer> <FeedUtil> ... </FeedUtil> <AuthenticationServers> ... </AuthenticationServers> </GUISettings> |
HTTPServer
Contains the CyberTrace HTTP service parameters.
Path
GUISettings > HTTPServer
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Optional
The HTTPServer element is optional. If it is omitted, the default values are used.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- ConnectionString
Specifies the IP address and port where the CyberTrace HTTP service is available.
The
ConnectionStringelement is optional. If it is omitted, the127.0.0.1:443IP address and port are used. After the installation process is complete, the default value of the HTTPServer > ConnectionString element is0.0.0.0:443. - SSLCertificatePath
Path to the PEM-formatted certificate on a local computer for HTTPS connections. If a relative path is specified, it is calculated relative to the executable file.
For security reasons, do not store your certificate in a shared folder accessible over a network and do not specify the path to a network shared folder containing your certificate.
The SSLCertificatePath element is optional. If it is omitted, the
../httpsrv/kl_feed_service_cert.pemfile is used. - SSLPrivateKeyPath
Path to the PEM-formatted private key on a local computer for HTTPS connections. If a relative path is specified, it is calculated relative to the executable file.
For security reasons, do not store your private key in a shared folder accessible over a network and do not specify the path to a network shared folder containing your private key.
The SSLPrivateKeyPath element is optional. If it is omitted, the
../httpsrv/kl_feed_service_private.pemfile is used. - TemplatesPath
Path to the directory that contains layout pages for CyberTrace HTTP Service. If a relative path is specified, it is calculated relative to the executable file.
The TemplatesPath element is optional. If it is omitted, the
../httpsrv/templates/directory is used. - ResourcesIP
Contains the IP address or hostname that is used in the
%IndicatorInfo%field of detection events, in the service events to notify that a retrospective scan completes, and in the result of exporting an indicator.The ResourcesIP element is mandatory. The default value is
127.0.0.1.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<HTTPServer> <ResourcesIP>127.0.0.1</ResourcesIP> <ConnectionString>0.0.0.0:443</ConnectionString> <TemplatesPath>../httpsrv/templates</TemplatesPath> <SSLCertificatePath>../httpsrv/kl_feed_service_cert.pem</SSLCertificatePath> <SSLPrivateKeyPath>../httpsrv/kl_feed_service_private.pem</SSLPrivateKeyPath> </HTTPServer> |
FeedUtil
Contains the Feed Utility parameters.
Path
GUISettings > FeedUtil
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested element:
- ConfigurationPath
Path to the Feed Utility configuration file.
The ConfigurationPath element is mandatory.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<FeedUtil> <ConfigurationPath>../etc/kl_feed_util.conf</ConfigurationPath> </FeedUtil> |
AuthenticationServers
Defines settings for connection to the LDAP servers.
Path
GUISettings > AuthenticationServers
Attributes
This element has no attributes.
Mandatory
This element is mandatory.
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested element:
- AuthenticationServer
Contains the LDAP connection settings parameters.
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<AuthenticationServers> <AuthenticationServer type="LDAP" enabled="true"> ... </AuthenticationServer> </AuthenticationServers> |
AuthenticationServers > AuthenticationServer
Contains the LDAP connection settings parameters.
Path
GUISettings > AuthenticationServers > AuthenticationServer
Optional
The AuthenticationServer element is optional.
Attributes
This element has the following attributes.
AuthenticationServer element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies the type of server to connect. Possible values: This attribute is mandatory. |
|
Indicates whether the specified server must be used. Possible values: This attribute is mandatory. |
Nested elements
This element is a container for the following nested elements:
- ConnectionString
Contains the connection parameters for the LDAP server.
For more information about this element, see subsection "AuthenticationServer > ConnectionString" below.
- DomainName
The path to the database that contains the user accounts that can access Kaspersky CyberTrace.
For more information about this element, see subsection "AuthenticationServer > DomainName" below.
- AdministratorAccountsFilter
Contains filtering rules for user accounts that must be assigned the Administrator role.
The AdministratorAccountsFilter element must not contain the value that is specified in the AnalystAccountsFilter element.
The AdministratorAccountsFilter element can be empty.
- AnalystAccountsFilter
Contains filtering rules for user accounts that must be assigned the Analyst role.
The AnalystAccountsFilter element must not contain the value that is specified in the AdministratorAccountsFilter element.
The AnalystAccountsFilter element can be empty. If the value is not specified, all user accounts that access Kaspersky CyberTrace will have the Analyst role.
This element is mandatory.
AuthenticationServer > ConnectionString
IP address or FQDN (fully qualified domain name), and port of the LDAP server.
This element is mandatory and cannot be empty.
This element has the following attributes.
ConnectionString element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Indicates whether to use an SSL connection. If an SSL connection is used, the value is If an SSL connection is not used, the value is |
|
Specifies a response timeout from the LDAP server, in seconds. The range of values for this attribute is from |
AuthenticationServer > DomainName
The path to the database that contains the user accounts that can access Kaspersky CyberTrace.
This element is mandatory and cannot be empty.
This element has the following attributes.
DomainName element attributes
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Indicates whether to use the User Principal Name (UPN) format. Specify Otherwise, specify |
Example
The following is an example of this element.
<AuthenticationServer type="LDAP" enabled="true"> <ConnectionString use_encryption="false" connection_timeout="20">ldap.example.com:389</ConnectionString> <DomainName use_principal_name="true">dc=testing,dc=con</DomainName> <AdministratorAccountsFilter>cn=theadministrator</AdministratorAccountsFilter> <AnalystAccountsFilter>cn=users_an</AnalystAccountsFilter> </AuthenticationServer> |
Feed Service logging
This section describes how Feed Service logs its activity.
Enabling logging
By default, logging is disabled. To enable logging, use the kl_feed_service_log.conf file in the bin directory where the binary file of the service is located. Fill in the kl_feed_service_log.conf file as described in this section. This file is used by Feed Service and the watchdog module. A change in the contents of the kl_feed_service_log.conf file results in the new settings being applied; this process takes several seconds.
Enabling logging decreases the performance of Feed Service. Use logging only if you encounter problems and errors.
Logging and data security
If you enable logging, Feed Service can write to the log files any of the following information that can be considered private, security-related, or sensitive:
- Unmodified data (URLs, IP addresses, hashes, and other data) as it is received by Feed Service.
- The results of checking events against a feed.
Log files are regular text files. No information written to the log files is encrypted. The log files have standard inherited access rights. We recommend that you assign the directory for storing log files the appropriate rights so that only the administrator can read the log files.
Kaspersky CyberTrace does not send log files or any data contained in them to Kaspersky. For technical support purposes, your Technical Account Manager can ask you to provide log files.
Log files are stored until they are explicitly deleted by a user. If the Append parameter in the logging configuration file is 0, the previous log files are deleted when Feed Service is started. If the Append parameter in the logging configuration file is 1, the information is retained during the full cycle of Feed Service usage
If you uninstall Kaspersky CyberTrace, these log files will not be deleted if the directory with log files is located outside of the Feed Service installation directory (as specified by the LogsFolder parameter).
For more information about data written to the log files, see subsection "Log file contents" below.
Logging configuration file
The kl_feed_service_log.conf file is an XML file. Its fields are described in the table below.
Parameter |
Description |
Mandatory / optional |
|---|---|---|
WriteLog |
Log level. One of the following values can be used:
|
Optional By default, |
LogsFolder |
The directory where to store log files. Absolute and relative paths can be used. On Windows, you cannot use the following symbols in the
If you use environment variables in the |
Optional By default, the |
SizeLimit |
The maximum size of the log file, in MB. If |
Optional By default, |
Append |
Indicates whether old log files must be removed ( |
Optional By default, |
UseSyslog |
Indicates whether the system daemon syslog will be used for logging (1) or not (0). This parameter is not used in Windows. |
Optional By default, |
Configuration file example
The following kl_feed_service_log.conf file example enables logging at the dbg logging level. Logs will be stored in the logs subdirectory of the directory where the Feed Service binary file resides.
<Logging> <WriteLog>dbg</WriteLog> <LogsFolder>logs</LogsFolder> <SizeLimit>0</SizeLimit> <Append>0</Append> <UseSyslog>0</UseSyslog> </Logging> |
Log files name format
Feed Service writes messages to files named "kl_feed_service-<pid>-<date_time>.log" or "kl_feed_service-<pid>-<date_time>_<index>.log".
The watchdog module writes messages to files named "kl_feed_servicewd-<pid>-<date_time>.log" or "kl_feed_servicewd-<pid>-<date_time>_<index>.log".
Log file contents
If the err logging level is used, Feed Service writes the following information to the log:
- Feed Service version and PID of the service process.
- The Feed Service configuration file parameters.
- Path to the directory with feeds.
- Errors occurred when normalizing a URL.
- Errors occurred while establishing a TCP connection.
- Watchdog messages:
- Feed Service freezing or crashing.
- Restarting Feed Service.
- Errors that occurred while changing the state of CyberTrace Web interface elements. Identifiers of user sessions where these errors occurred.
- Information about errors that occurred while handling CyberTrace Web HTTP requests:
- Request method, GET or POST.
- Request path for GET and POST requests.
- GET request parameters. For POST requests, the request body is not logged.
- Total elapsed time for handling the request.
If the inf logging level is used, Feed Service writes the following information to the log:
- Information to be written at the
errlogging level. - Establishing or closing a TCP connection.
- Receiving and sending TCP requests and responses.
- Switching Feed Service to same-socket mode.
- Putting new databases into effect.
- Detecting an event that matches some record in a feed.
- Incoming event.
Note that incoming events can contain private data, and so we recommend that you protect the log files from unauthorized access.
- Messages about navigating CyberTrace Web pages. Identifiers of user sessions for these messages.
If the dbg logging level is used, Feed Service writes the following information to the log:
- Information to be written at the
inflogging level. - Substrings in events information that regular expressions match.
- The result of checking an event against a feed.
- Sending test messages to and from the watchdog module.
- Messages about actions performed on CyberTrace Web pages. Identifiers of user sessions for these messages.
- Information about successful CyberTrace Web HTTP requests:
- Request method, GET or POST.
- Request path for GET and POST requests.
- GET request parameters. For POST requests, the request body is not logged.
- Total elapsed time for handling the request.
About resending detection events
By default, if an error occurs when Feed Service is sending a detection event to a SIEM solution, this event is sent again after a period of time specified in the configuration file.
You can configure how many times Feed Service attempts to send each detection event and the interval between attempts by using the EventSendingRetriesCount and EventSendingRetriesTimеout elements of the configuration file.
Feed Service in ReplyBack mode
In some cases, it is necessary for Feed Service to send responsive events back to the event source to the same socket from which the original events are received (ReplyBack mode).
To shift Feed Service to ReplyBack mode:
Send X-KF-ReplyBack as the first message after a TCP connection with Feed Service is established.
During the current TCP session every responsive event will be sent back to the same socket from which the original event was received. The setting specified in the OutputSettings > ConnectionString element of the configuration file will be ignored.
You can configure Feed Service to send an informational event indicating that event checking has finished.
To enable sending finishing events, perform one of the following actions:
- Set the
enableattribute of theOutputSettings > FinishedEventFormatelement of the Feed Service configuration file totrue. - Send
X-KF-SendFinishedEventX-KF-ReplyBackas the first message after a TCP connection with Feed Service is established.In this case, the
enableattribute of theOutputSettings > FinishedEventFormatelement in the Feed Service configuration file will be ignored.
To instruct Feed Service that it must shift to ReplyBack mode and send finishing events:
Send X-KF-SendFinishedEventX-KF-ReplyBack as the first message after a TCP connection with Feed Service is established.
By default, in ReplyBack mode, Kaspersky CyberTrace does not save the statistics of the detection events received during the current connection.
To save the statistics of the detection events in ReplyBack mode:
- If you want Feed Service to send finishing events, send
X-KF-SendFinishedEventX-KF-ReplyBackX-KF-SaveStatisticas the first message after a TCP connection with Feed Service is established. - If you do not want Feed Service to send finishing events, send
X-KF-ReplyBackX-KF-SaveStatisticas the first message after a TCP connection with Feed Service is established.
Features of event processing by Feed Service
This section outlines the way in which Feed Service processes incoming events.
Feed Service receives and sends events using TCP. Events are encoded in UTF-8.
Feed Service processes special characters in incoming events as follows:
- Feed Service treats the line feed character (0x0A) as the delimiter between events.
Thus, text before a line feed character and text after it belong to different events.
- Feed Service ignores the carriage return character (0x0D).
Limitations on Feed Service incoming events
Feed Service processes events that are no larger than 64 kilobytes (KB). If an incoming event exceeds 64 KB, Feed Service splits it into several events and processes them separately. Thus, an indicator can be split in two and may not be extracted and checked.
We recommend that you configure the event source (the SIEM software), or the normalization rules, or both, so that the incoming events will not exceed 64 KB in size.
Page topWorking with feeds
Feed Utility is a tool that can download, filter, and compile Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds according to a specified set of rules defined in its configuration file. These rules can also be set by using Kaspersky CyberTrace Web.
Downloading
Feed Utility downloads archives containing feeds from the update servers. Each downloaded archive contains one feed. Before downloading Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds, Feed Utility checks whether they are newer than those being used. Before downloading OSINT and third-party feeds, Feed Utility does not perform such checking.
Feed Utility uses a certificate for authentication. The certificate also defines which Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds can be downloaded by Feed Utility. For example, if you have a demo certificate, Feed Utility can download only demo feeds.
Processing and filtering
After the archives containing feeds are downloaded, Feed Utility unpacks the archives and processes the original feed files. The feed files are modified according to a combination of feed rules, filtering rules, and other parameters specified in the Feed Utility configuration file. These parameters define the data that will be included in the resulting feeds, the output format of the resulting feeds, and the maximum number of records in the resulting feed.
Filtering is the process of modifying the original feed files according to specified filtering criteria. Filtering criteria are defined in the filtering rules for each feed. Depending on the intended Feed Utility usage scenario, you may want to create a feed that uses only a subset of information contained in the original feed. This can be achieved by using a combination of feed rules and filtering rules.
Default filtering rules
The default Feed Utility configuration file that is shipped in the Kaspersky CyberTrace distribution kit contains the following filtering rule for IP Reputation Data Feed and Demo IP Reputation Data Feed:
Only feed records whose threat_score parameter is not less than 75 are detected.
Kaspersky considers malicious those IP addresses whose threat_score is not less than 75. IP addresses whose threat_score is less than 75 are considered related to spam and posing no threat.
If you reduce the boundary value or remove the filter, you will have many detections by Demo IP Reputation Data Feed and IP Reputation Data Feed that will be mere notifications about detecting spam IP addresses.
To remove the filter:
- Open the Settings > Feeds page of Kaspersky CyberTrace Web.
- For Demo IP Reputation Data Feed (or IP Reputation Data Feed) remove the filtering rule for the
threat_scorefield.
Compiling
If you use Feed Utility with Feed Service, feeds that contain URL masks must be converted to binary format. Feed Utility compiles the URL masks extracted from these feeds and creates binary files which are then used by Feed Service to quickly match URLs from received events to URL masks. Compiling is performed automatically by Feed Utility, if the UrlMatcherField option is specified in the feed rules.
Reloading
When notified, Feed Service reloads the feeds for use, that is, it unloads the old feeds from memory and loads the new ones.
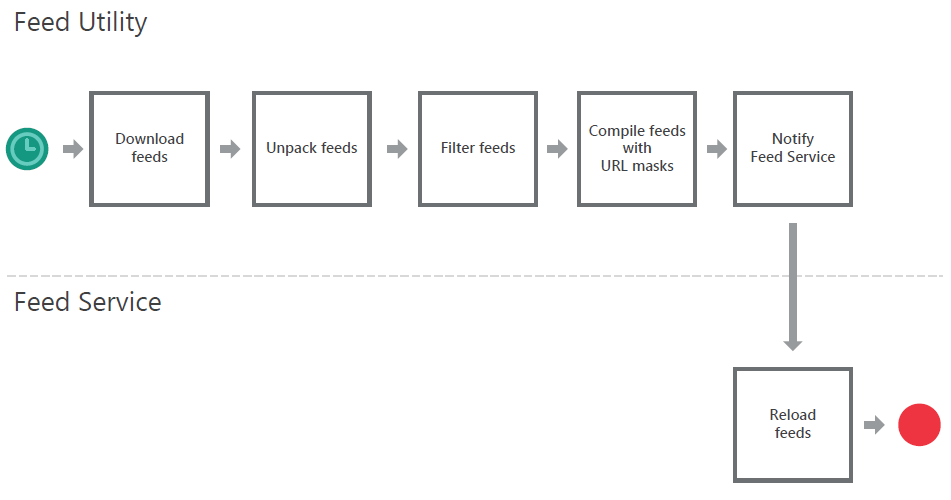
Updating feeds
Page topFeed Utility command-line options
Feed Utility is a console application. You can invoke it from the command line.
Syntax
Feed Utility uses the following syntax in Linux:
./kl_feed_util [options]
Feed Utility uses the following syntax in Windows:
kl_feed_util.exe [options]
Options
The following options are available:
-h [ --help ]Prints the help message.
-v [ --verbose ]Enables verbose mode.
If verbose mode is enabled, Feed Utility prints detailed information about its activity to the screen. If verbose mode is disabled, brief information is printed.
-s [ --silent ]Enables silent mode.
If silent mode is enabled, Feed Utility does not print information about its activity to the screen.
-c [ --config ] argSpecifies the path to the configuration file. The path must be specified in the
argargument.You can use absolute or relative paths. If a relative path is specified, it is calculated relative to the Feed Utilty binary file.
The default value for this parameter is
kl_feed_util.conf. Feed Utility searches for this file in the directory where its binary file is located.-d [ --download ]Enables downloading mode.
If this option is specified, Feed Utility downloads feeds, but does not process them.
Downloaded files will be located in the directory specified in the
WorkDirparameter of the Feed Utility configuration file.-u [ --unpack ]Unpack downloaded feeds.
If this option is specified, Feed Utility unpacks the feeds after downloading.
This option can be used only in combination with
-dor-poption.-p [ --processing ]Enables processing mode.
If this option is specified, Feed Utility processes feeds, but does not download or unpack them. Feed Utility does not delete the original feed files.
Feed Utility looks for feeds in the directory specified in the
WorkDirparameter of the Feed Utility configuration file.In processing mode, Feed Utility does not delete the original feed files, located in the
WorkDirdirectory. This may lead to a situation where this directory contains several versions of one feed file. In this case, Feed Utility will print an error message. To avoid this situation, you must manually delete the original feed files from theWorkDirdirectory after they are processed by Feed Utility.-f [--feed] argDownload or process the specified feed.
The name of the feed must be specified in the
argargument. This name must correspond to the value of theNameparameter specified in feed rules (Feeds>Feed>Name).You can specify more than one feed. In this case, separate feed names with a semicolon (
;).This parameter can be used with
-dand-pparameters.-i [--input]Parses an external feed and converts it to JSON format according to parsing rules defined for this feed.
The name of the feed must be specified with
-fformat.--set-proxy username:password@host:portWrites specified proxy connection settings to the Feed Utility configuration file. The
usernameandpasswordparameters are written in encrypted form.Specify the user name in the
usernameparameter, password in thepasswordparameter, and proxy server address and port in thehostandportparameters.If a proxy server does not require authentication, use the
--set-proxy host:portformat.--set-taxii username:password@feedname@taxii-address@collectionnameWrites specified TAXII server connection settings to the Feed Utility configuration file. The
usernameandpasswordparameters are written in encrypted form.If a TAXII server does not require authentication, use the
feedname@taxii-address@collectionnameformat.--set-basic-auth username:password@feednameWrites the specified basic authentication settings to the Feed Utility configuration file. The
usernameandpasswordparameters are written in encrypted form.If a password is not required, use the
username:@feednameformat.--speedtestMeasures the average speed with which Feed Utility downloads feeds from Kaspersky servers.
You can combine this parameter with the
-сparameter to specify the path to the configuration file that will be used.
Syntax examples
The following command runs Feed Utility with default parameters. Feed Utility will download, unpack, and process feeds.
- In Linux:
./kl_feed_util
- In Windows:
kl_feed_util.exe
The following command runs Feed Utility in verbose mode with a configuration file named custom_configuration.conf, which is located in the same directory as the utility binary file.
- In Linux:
./kl_feed_util -v -c custom_configuration.conf
- In Windows:
kl_feed_util.exe -v -c custom_configuration.conf
The following command makes Feed Utility download and unpack feeds.
- In Linux:
./kl_feed_util -d -u
- In Windows:
kl_feed_util.exe -d -u
With the following command, Feed Utility processes the unpacked feeds. In this case, Feed Utility does not download the feeds; it only looks for the unpacked feed files and processes them.
- In Linux:
./kl_feed_util -p
- In Windows:
kl_feed_util.exe -p
The following command makes Feed Utility unpack and process feeds.
- In Linux:
./kl_feed_util -u -p
- In Windows:
kl_feed_util.exe -u -p
The following command makes Feed Utility download, unpack, and process the specified feed.
- In Linux:
./kl_feed_util -f Demo_Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed
- In Windows:
kl_feed_util.exe -f Demo_Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed
The following command specifies proxy connection parameters. These parameters are written to the configuration file.
- In Linux:
./kl_feed_util --set-proxy 'user:pass@proxy.example.com:3128'
- In Windows:
kl_feed_util.exe --set-proxy 'user:pass@proxy.example.com:3128'
The following command specifies proxy connection parameters for a proxy that does not require authentication. These parameters are written to the configuration file.
- In Linux:
./kl_feed_util --set-proxy 'proxy.example.com:3128'
- In Windows:
kl_feed_util.exe --set-proxy 'proxy.example.com:3128'
The following command specifies TAXII server connection parameters. These parameters are written to the configuration file.
- In Linux:
./kl_feed_util --set-taxii '
user:pass@Example_Feed_Name@http://example.com@Example_Collection' - In Windows:
kl_feed_util.exe --set-taxii '
user:pass@Example_Feed_Name@http://example.com@Example_Collection'
The following command displays an average speed with which Feed Utility downloads the feeds from Kaspersky servers.
- In Linux:
./kl_feed_util --speedtest
- In Windows:
kl_feed_util.exe --speedtest
Output example
The following example demonstrates a typical Feed Utility output. Feed Utility downloads demo feeds, and then unpacks and processes them.
2018-08-03 16:20:31.815 7f9b01c58740 INF KL Feed Utility, version: 1.1.91.0/Release 2018-08-03 16:20:31.815 7f9b01c58740 INF Built at 2018-08-02T15:06:50Z for Linux/x86_64 2018-08-03 16:20:31.815 7f9b01c58740 INF Running at Linux/x86_64 version #1 SMP Debian 3.16.43-2 (2017-04-30) 2018-08-03 16:20:31.815 7f9b01c58740 INF Current locale is en_US.UTF-8 2018-08-03 16:20:31.992 7f9b01c58740 INF feed #85(Demo_Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed) version 2018-08-03T12:47:26.893 is available 2018-08-03 16:20:32.404 7f9b01c58740 INF update of feed #85(Demo_Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed) is extracted to /opt/feed_util/bin/tmp/Demo_Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed.json 2018-08-03 16:20:32.586 7f9b01c58740 INF feed #86(Demo_Malicious_Hash_Data_Feed) version 2018-08-03T12:44:53.82 is available 2018-08-03 16:20:32.992 7f9b01c58740 INF update of feed #86(Demo_Malicious_Hash_Data_Feed) is extracted to /opt/feed_util/bin/tmp/Demo_Malicious_Hash_Data_Feed.json 2018-08-03 16:20:33.172 7f9b01c58740 INF feed #87(Demo_IP_Reputation_Data_Feed) version 2018-08-03T12:57:57.017 is available 2018-08-03 16:20:33.406 7f9b01c58740 INF update of feed #87(Demo_IP_Reputation_Data_Feed) is extracted to /opt/feed_util/bin/tmp/Demo_IP_Reputation_Data_Feed.json 2018-08-03 16:20:34.414 7f9b01c58740 INF 3 of 3 feeds downloaded 2018-08-03 16:20:34.416 7f9afedb9700 INF start processing of feed #87(Demo_IP_Reputation_Data_Feed) 2018-08-03 16:20:34.416 7f9aff5ba700 INF start processing of feed #86(Demo_Malicious_Hash_Data_Feed) 2018-08-03 16:20:34.425 7f9b007ea700 INF start processing of feed #85(Demo_Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed) 2018-08-03 16:20:34.855 7f9b01c58740 INF 3 of 3 feeds processed 2018-08-03 16:20:35.255 7478 INF Starting the speed test... 2018-08-03 16:20:35.874 7478 INF 500.00 MiB downloaded in 14399 ms, average speed is 34.72 MiB/s 2018-08-03 16:20:36.133 7478 INF 500.00 MiB downloaded in 14304 ms, average speed is 34.96 MiB/s 2018-08-03 16:20:36.421 7478 INF 500.00 MiB downloaded in 13402 ms, average speed is 37.31 MiB/s 2018-08-03 16:20:36.679 7478 INF Overall average speed was 35.66 MiB/s |
About the configuration file (Feed Utility)
Feed Utility reads settings from a configuration file.
Editing the configuration file
If the configuration file is absent or does not follow the rules specified in this section, Feed Utility does not start and prints an error message.
We recommend that you create a backup copy of the Feed Utility configuration file before you make any changes in it. If Kaspersky CyberTrace does not work properly after you have reconfigured Feed Utility, replace the configuration file with its backup copy.
Configuration file location (Linux)
In Linux, the configuration file used by Feed Utility is named kl_feed_util.conf and is located in the %service_dir%/etc directory.
Configuration file location (Windows)
The configuration file used by Feed Utility is named kl_feed_util.conf and resides in the same directory as the Feed Utility binary file, %service_dir%/bin.
Encoding requirements
The Feed Utility configuration file, including all paths that it specifies, must be in UTF-8 encoding. If you use non-ASCII symbols in the configuration file, and the file is not in UTF-8 encoding, Feed Utility will not start.
Absolute and relative paths
When defining directories and files used by Feed Utility, you can use absolute and relative paths. If a relative path is specified, it is calculated from the directory that contains the Feed Utility binary file.
Page topConfiguration file parameters (Feed Utility)
Feed Utility reads the configuration parameters, feed rules, filtering rules, and parsing rules for feeds from the configuration file. This file is in XML format and has several groups of parameters.
The paths in the configuration file must contain only the characters used in the operating system locale, otherwise Feed Utility will not work.
Feed (feed rules, filtering rules, and parsing rules)
The Feed parameter contains rules for a particular feed. This element has several types of nested parameters:
- Feed rules specify how this particular feed must be processed by Feed Utility.
- Filtering rules are criteria that Feed Utility uses to filter the original feed files. Filtering rules are a part of feed rules for each feed.
- Parsing rules are rules for custom feeds (OSINT feeds, and other feeds that are not Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds). These parameters specify how each feed must be parsed by Feed Utility.
This parameter has the following attributes:
enabledSpecifies whether Feed Utility must download and process this feed.
If
enabledis true, Feed Utility downloads and processes the feed. Ifenabledis false, Feed Utility skips this feed.
The following example demonstrates how feed rules, filtering rules, and parsing rules are nested in the configuration file.
<Settings> ... <Feeds> ... <Feed enabled="true"> <Name>Malicious_Hash_Data_Feed</Name> <!-- Other feed rules for this feed --> <Filters> <Field name="popularity" value="4;5"/> <!-- Other filtering rules for this feed --> </Filters> </Feed> <Feed> <Name>Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed</Name> <!-- Other feed rules for this feed --> <!-- This feed has no filtering rules --> </Feed> ... </Feeds> ... </Settings> |
FeedsDir
The FeedsDir parameter specifies the directory where Feed Utility puts processed feed files.
WorkDir
The WorkDir parameter specifies the directory where Feed Utility puts the downloaded and unpacked feed files.
If this parameter is not specified, Feed Utility uses the default temporary directory of the operating system.
WorkDir cannot be equal to FeedsDir.
CertFile
The CertFile parameter specifies the path to the certificate file. This certificate is used by Feed Utility to download feeds.
The certificate file must be in PEM format.
SourceIPs
The SourceIPs parameter specifies the IP addresses that are used by Feed Utility to download feeds.
This parameter is optional. If it is omitted or has an empty value, Feed Utility resolves Kaspersky server addresses by their domain names.
You can specify one or more IPv4 addresses in this parameter. To specify several IP addresses, use the semicolon (";") as a delimiter.
The following example demonstrates specifying IP addresses in the SourceIPs parameter.
<SourceIPs>192.0.2.1;192.0.2.2</SourceIPs> |
SourceDomains
The SourceDomains parameter specifies the domain names that are used by Feed Utility to download feeds.
You can specify one or more domain names in this parameter. To specify several domain names, use the semicolon (";") as a delimiter. Feed Utility will attempt to download feeds from the specified domain names in the order they appear in the configuration file.
When SourceDomains and SourceIP parameters are used together, domains specified in the SourceDomains parameter are used before IP addresses specified in the SourceIP parameter. If all attempts to download feeds fail, Feed Utility will generate an error message.
You can use Unicode symbols in this parameter.
The following example demonstrates specifying IP addresses in the SourceDomains parameter.
<SourceDomains>updates1.example.com;updates2.example.com</SourceDomains> |
CreateExternalFeedInfoList path="PATH"
This parameter is obsolete. It is ignored in the current version of Kaspersky CyberTrace.
The CreateExternalFeedInfoList parameter specifies whether a list of supported OSINT feeds must be generated. This parameter is mandatory.
If this parameter is 1, Feed Utility creates a list of supported OSINT feeds, osint_feed_list.conf, in a directory specified in the path attribute. If you added any custom or third-party feeds to Kaspersky CyberTrace, Feed Utility also creates a list of these feeds, custom_feed_list.conf, in the same directory as osint_feed_list.conf.
If this parameter is 0, Feed Utility does not create a list of supported OSINT feeds.
The following example demonstrates specifying a path where the list must be created. In this example, the list will be created in a directory where Feed Utility binary is located.
<CreateExternalFeedInfoList path=".">1</CreateExternalFeedInfoList> |
NotifyKTFS path="PATH"
The NotifyKTFS parameter specifies whether Feed Service must be notified about the feed updates.
This parameter can be used only with json output format.
If this parameter is 1, Feed Utility notifies Feed Service that the feeds must be reloaded. A path to the Feed Service binary file must be specified in the path attribute of this parameter.
If this parameter is 0, Feed Utility does not notify Feed Service.
EULA
The EULA parameter specifies whether the terms of the End User License Agreement (EULA) were accepted by a user.
If this value is accepted, the terms of the EULA were accepted.
If this value is rejected, the terms of the EULA were not accepted. In this case, Feed Utility cannot be used.
RetryCount
The RetryCount parameter specifies the number of attempts to download a Kaspersky Threat Data Feed. Feed Utility tries to re-download a feed when a connection timeout, partial downloading, and other errors occur.
If the specified number of attempts were unsuccessful, Feed Utility displays an error message and continues its operation.
This parameter is used only for Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds. OSINT feeds and other custom feeds will not be re-downloaded by Feed Utility.
This parameter is optional. If this parameter is not specified, Feed Utility uses the default value of 10.
If this parameter is 0, the number of attempts is not limited.
SequentialDownload
The SequentialDownload parameter specifies whether Feed Utility must download feeds in sequential or parallel mode.
If this value is 1 or true, Feed Utility downloads feeds in sequential mode, one by one.
If this value is 0 or false, Feed Utility downloads feeds in parallel mode, all feeds at the same time.
By default, this parameter has the value of 0.
OutputFormat
The OutputFormat parameter defines the output format for all feeds. This parameter can have the following values:
jsonThe feeds are in JSON format. The feed files have a .json extension.
This is the default value. If the
OutputFormatparameter is omitted, this value is used to define the output format.txtThe feeds are in plain text format (UTF-8 with BOM). The feed files have a .txt extension.
delimiterattributeIn this format, record fields are separated with a delimiter. The default delimiter is
";". To specify a custom delimiter, use thedelimiterattribute as follows:<OutputFormat delimiter="%delimiter%">txt</OutputFormat>Here, substitute
%delimiter%with a symbol that must be used as a delimiter.indicatorPerLineattributeTo output one record field per line, set the
indicatorPerLineattribute to 1 as follows:<OutputFormat indicatorPerLine="1">txt</OutputFormat>If you use this attribute, subfields specified in the
RequiredFieldsfeed rule must have the same parent field. For example,"files/MD5;files/SHA1"is valid, while"files/MD5;whois/domain"is invalid and will result in an error.
If this output format is specified, all feed rules in the configuration file must include a
RequiredFieldsparameter. TheRequiredFieldsparameter specifies the order in which the fields are written to the output feed.csvSame as
txt. The feed files have a .csv extension.You can use
delimiterandindicatorPerLineattributes.openiocThe feeds are in OpenIOC format. The feed files have an .ioc extension.
You can specify the version of the OpenIOC format in the
versionattribute: it can be either1.0, or1.1. If the attribute is omitted, version1.1is used.Converting feeds to OpenIOC 1.0 format has some restrictions. Phishing URL Data Feed and Malicious URL Data Feed cannot be converted to OpenIOC 1.0 format; an error message is printed instead. For other feeds, only hash and IP address fields are converted. Converting feeds to OpenIOC 1.1 format has no such restrictions.
Feeds in OpenIOC format take significantly more hard disk space than the original feed files.
stixThe feeds will be in STIX format. The files will have an .xml extension.
For STIX format, feeds with URL masks must have the
typefield.Feeds in STIX format take significantly more hard disk space than the original feed files.
The following example demonstrates how the OutputFormat parameter is nested in the configuration file.
<Settings> ... <Feeds> <OutputFormat>json</OutputFormat> ... </Feeds> ... </Settings> |
CreateDiff
The CreateDiff parameter specifies whether Feed Utility must create feed diffs. Feed diffs are files that contain differences between the old and new version of a processed feed file. This parameter affects all feeds created by Feed Utility as follows:
- If this parameter is
0, Feed Utility does not create feed diffs. This is the default value. - If this parameter is
1, Feed Utility creates feed diffs.
If CreateDiff is 1, and new versions of feeds are downloaded, two additional files are created for each feed (%feed_name% is the name of the feed file):
The %feed_name%_new.jsonfile contains records that were added to the new version of the feed file.The %feed_name%_del.jsonfile contains records that were deleted in the new version of the feed file.
Feed diffs can be created only for feeds in JSON format that are contained in a single file:
- The
OutputFormatparameter must have thejsonvalue. - For each feed, the
UrlMatcherFieldparameter must be omitted or have an empty value. - For each feed, the
RecordsCountparameter must not have theperFileattribute, or this attribute must have a value of0.
To create feed diffs, Feed Utility uses a key field in the old and new version of the feed:
- If this feed contains non-nested
id,MD5,ip,url, ordomainfield, this field is used as a key field. - If none of the fields above are present, Feed Utility attempts to search for a field with unique values across the feed. If this attempt is not successful, a warning is generated.
The following example demonstrates how the OutputFormat parameter is nested in the configuration file.
<Settings> ... <Feeds> ... <CreateDiff>0</CreateDiff> ... </Feeds> ... </Settings> |
ProxySettings
The ProxySettings parameter specifies proxy settings for Feed Utility. If you specify a proxy server, Feed Utility will download feeds using the specified parameters.
The user name and password for the proxy are stored in the Feed Utility configuration file. This information is not provided to Kaspersky.
Proxy settings are specified in the following parameters:
HostHost of the proxy server.
You can specify a domain name or an IP address in this parameter.
PortPort of the proxy server.
UserEncrypted user name for proxy server authentication.
If a proxy server does not require authentication, leave this parameter empty.
This parameter is stored encrypted. Use the
--set-proxycommand-line option to set this parameter. If you do not use this option and enter your user name as plain text, connection to the proxy server will not be established.PasswordEncrypted password for proxy server authentication.
If a proxy server does not require authentication, leave this parameter empty.
This parameter is stored encrypted. Use the
--set-proxycommand-line option to set this parameter. If you do not use this option and enter your password as plain text, connection to the proxy server will not be established.
The following example demonstrates how proxy settings are nested in the configuration file.
<Settings> ... <ProxySettings> <Host></Host> <Port></Port> <User></User> <Password></Password> </ProxySettings> ... </Settings> |
LogSettings
The LogSettings parameter defines how Feed Utility logs its activity.
If you enable logging, Feed Utility can write to the log files any of the following information that can be considered private, security-related, or sensitive: Feed Utility configuration parameters, proxy host and port, and operations performed while downloading and processing feeds.
If logging is enabled, Feed Utility writes to log files the information about free hard disk space that available for the work and feed directories. Also, starting from this version, an average speed that the feeds have while loading will be written to logs.
Log files are regular text files. All information written to the log files is not encrypted. The log files have standard inherited access rights. We recommend that you assign the directory for storing log files the appropriate rights so that only the administrator can read the log files.
Log files are stored until they are explicitly deleted by a user.
Feed Utility does not send log files or any data contained in them to Kaspersky. For technical support purposes, your technical account manager (TAM) can ask you to provide log files.
Logging settings are specified in the following parameters:
EnableLogEnables logging.
If this value is
1ortrue, Feed Utility logs its activity.If this value is
0orfalse, Feed Utility does not log its activity.LogsDirDirectory where Feed Utility stores its log files.
CleanOldLogEnables removal of old log files.
If this value is
0, upon initialization, Feed Utility keeps old log files.If this value is
1, upon initialization, Feed Utility deletes old log files.
The following example demonstrates how logging settings are nested in the configuration file.
<Settings> ... <LogSettings> <EnableLog>0</EnableLog> <LogsDir>logs</LogsDir> <CleanOldLog>1</CleanOldLog> </LogSettings> </Settings> |
Feed rules
Individual feed rules in the Feed elements specify how each feed must be processed by Feed Utility.
By default, the configuration file has entries containing feed rules for all feeds. Entries for commercial feeds are commented. If you use a commercial certificate to download feeds, uncomment the entries for feeds that are available with your certificate.
Example of feed rules
The following is an example of feed rules. Feed rules are specified individually for each feed.
<Settings> ... <Feeds> <Feed enabled="true"> <Name>Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed</Name> <FeedID>65</FeedID> <Filters> <Field name="geo" value="RU"/> </Filters> <UrlMatcherField toRegex="false">mask</UrlMatcherField> <RequiredFields>mask;geo;first_seen;last_seen</RequiredFields> <RecordsCount perFile="100" total="1000" /> <FeedFields/> </Feed> <Feed enabled="false"> <Name>CustomFeed</Name> <Path>./custom_example/example_feed.json</Path> <Parsing type="json"> <MD5 type="MD5">files/MD5</MD5> </Parsing> <FeedFields/> </Feed> ... </Feeds> ... </Settings> |
Feed
This parent element contains feed rules for a feed. For more information about this parameter, see section "Configuration file parameters".
Name
This element specifies the name of the downloaded feed file.
After Feed Utility unpacks downloaded feeds, it searches for a file with a name that begins with a specified string. If several file names begin with the specified string, Feed Utility prints an error message and stops processing feeds. In this case, you must manually resolve this conflict, for example, by deleting the extra files from the directory where Feed Utility unpacks them. This directory is specified by the WorkDir parameter.
This parameter is case-insensitive.
This parameter must have a unique value. No two Feed elements can have the same value in this parameter.
FeedID
This element specifies the identifier of a feed. Feed Utility uses this parameter to download feeds from the update servers.
The enabled attribute specifies whether the feed must be processed by Feed Utility:
- If this attribute is
true, Feed Utility processes this feed. - If this attribute is
false, Feed Utility skips this feed.
Path
The Path parameter specifies the path and the file name for a custom or third-party feed.
Following value types are supported:
- Path and filename on the computer where Feed Utility binary is located.
- FTP or FTPS path and file name.
- HTTP or HTTPS URL.
- Network path (supported only in the Windows operating system).
This parameter has the following attributes:
certSpecifies the path to a certificate that will be used to download this feed via HTTPS or FTPS. This attribute is optional. If it is not specified, Feed Utility will not use a certificate.
Authentication type is provided in the Settings > Feeds > Feed parameter of the Feed Utility configuration file.
Authorization
Basic authentication settings for custom or third-party feeds.
This parameter has two nested elements:
UserEncrypted user name for basic authentication on a server from which the feeds are downloaded.
Use the
--set-basic-authcommand-line option to set this parameter. For STIX feeds that are downloaded from the TAXII server, use the--set-taxiioption.This element cannot be empty.
PasswordEncrypted password for basic authentication on a server from which the feeds are downloaded.
Use the
--set-basic-authcommand-line option to set this parameter. For STIX feeds that are downloaded from the TAXII server, use the--set-taxiioption.
If this type of authentication is not required, do not specify this parameter.
TAXII
The TAXII parameter specifies the location of a STIX feed. This element must contain the address of a Poll service of a TAXII server.
This parameter has the following attributes:
collection_nameThe name of the data collection for this STIX feed.
certPath to a certificate that must be used to download STIX feeds. This attribute must be used when downloading STIX feeds using the HTTPS or FTPS protocol.
The following example demonstrates specifying the location of a STIX feed:
<TAXII collection_name="example-collection">http://192.0.2.10:9000</TAXII> |
The following example demonstrates usage of this parameter:
<Feed> <Name>TAXII</Name> <TAXII collection_name="example-collection">http://192.0.2.10:9000</TAXII> <Authorization> <User>zQYq33rAY7dgImLtk8W0jQ==</User> <Password>OUYWpkPDoH+vv/IFfCrshw==</Password> </Authorization> </Feed> |
Filters
This element specifies filtering rules for the feed. Each filtering rule is defined in a Field element. For more information, see section "Filtering rules".
The Filters element is optional. If a Filters element contains no nested Field elements, Feed Utility treats this situation as if the Filters element is omitted. If there is no Filters element, no filtering is performed.
UrlMatcherField
This element defines how feeds with URL masks are processed by Feed Utility.
If you use Feed Utility as a part of CyberTrace together with Feed Service, feeds that contain URL masks must be converted to binary format.
If you use Feed Utility without Feed Service, you do not need to compile masks, so the UrlMatcherField element is not required in the FeedUtility configuration file.
This element has a value and an optional toRegex attribute:
- The value of this element specifies the name of the field in the feed that contains the URL mask.
- The optional
toRegexattribute of this element defines how the utility must process the feed.- If the
toRegexattribute is0,false, or is omitted, Feed Utility compiles the feed and creates binary files that can be used by Feed Service. - If the
toRegexattribute is1, ortrue, Feed Utility processes URL masks in the feeds so that they are converted to regular expressions.For each URL mask, Feed Utility creates a regular expression that matches all URLs covered by the URL mask. For example, if a URL mask is
botnet.example.com, the regular expression for it is((\/{2}|^)botnet\.example\.com(\/.*|$)). Like the URL mask, this regular expression matches all URLs in thebotnet.example.comdomain.The
toRegexattribute can be set to1only for those feeds that have thetypefield. Also, if theRequiredFieldselement is present among the feed rules, it must contain thetypefield.
- If the
For json output format, you can do the following:
- Compile feeds with URL masks to a binary file that can be used by Feed Service.
If you use Feed Service, the
UrlMatcherFieldelement is mandatory for feeds that contain URL masks: Malicious URL Feed, Phishing URL Feed, Botnet CnC URL Feed, and IoT URL Feed.<UrlMatcherField>%field_name%</UrlMatcherField> - Convert URL masks to regular expressions.
<UrlMatcherField toRegex=1>%field_name%</UrlMatcherField> - Do not convert URL masks.
Omit the
UrlMatcherFieldelement.
For csv and txt output formats, you can do the following:
- Convert URL masks to regular expressions.
<UrlMatcherField toRegex=1>%field_name%</UrlMatcherField> - Do not convert URL masks.
Omit the
UrlMatcherFieldelement.
For openioc and stix output formats, omit this element. You cannot use this element with these output formats.
RequiredFields
This element specifies fields that are included in the processed feed. This element is mandatory for txt and csv output formats. If the RequiredFields element is omitted, all fields of a record are written to the processed feed.
Field names are separated by a semi-colon (";"). The slash ("/") in a field name indicates a nested field (in terms of JSON format).
This element defines fields in the resulting feed; it does not work like a filtering rule. For example, if a <RequiredFields>id;mask</RequiredFields> feed rule is defined for a feed, the records in the processed feed will have only id and mask fields. Records that have at least one of the specified fields (id or mask) will also be included. Records that do not have at least one of the specified fields will be excluded because the absence of specified fields results in an empty record written to the processed feed. If you want to filter a feed so that only records with all the specified fields are included in resulting feed, you must use filtering rules. For information about using the RequiredFields element together with filtering criteria, see subsection "Excluding records with missing fields" in the "Filtering rules" section.
Record fields are written to csv and txt formats in the order they are listed in the RequiredFields element. Record fields are written in json format in the order in which they appear in the source feed. For openioc and stix formats, the order of records is not defined; records are written in the order of processing.
FeedFields
This element lists all fields present in a feed.
Do not change this parameter. Feed Utility automatically writes field values to it.
RecordsCount
This element specifies the maximum number of records that will be included in the processed feed.
This element has two attributes:
- The
totalattribute of this element defines the total number of first-level records that must be included in the processed files. Feed Utility includes only those records that match the filtering rules. If this value is0, this number is not limited, and all records are included.Note that the
totalattribute refers to first-level records, so the processed feed can contain more nested records than the value oftotal. For example, the original feed contains the following data:[
{
"time": "23.02.1992 15:43",
"urls":[
{
"url" : "http://url.biz/sample1"
},
{
"url" : "http://url.biz/sample2"
}
]
},
{
"time": "24.02.1992 15:43",
"urls":[
{
"url" : "http://url.biz/sample3"
},
{
"url" : "http://url.biz/sample4"
}
]
}
]
You can specify the following settings for this feed in the Feed Utility configuration file:
<OutputFormat>csv</OutputFormat>
<RequiredFields>urls/url</RequiredFields>
<RecordsCount total="1" />
The processed feed will contain two records because they are nested in one first-level record.
http://url.biz/sample1
http://url.biz/sample2
- The
perFileattribute of this element defines the maximum number of records that must be included in a single file. If the total number of records in one processed feed file is greater than this value, Feed Utility creates an additional feed file.For example, if
totalis1000,perFileis300, and Feed Utility finds 650 records that match filtering rules, then three files are created (two files with 300 records and one with 50 records).This attribute cannot be used in the following cases:
- The
perFileattribute cannot be used for feeds with URL masks that are compiled into binary format. - The
perFileattribute cannot be used with custom feeds that have parsing rules with thetypeattribute set tourlordomaintypes. Such feeds are also compiled into binary format by Feed Utility. To use theperFileattribute for these types of fields, you must change the field type tocontext.
- The
Parsing
This element contains parsing rules for custom feeds. For more information, see section "Parsing rules".
Page topFiltering rules
Filtering rules are criteria that Feed Utility uses to filter the original feed files.
Filtering rules are specified for each feed in a Filters element. Each filtering rule is set in a Field element: the field name is specified in the name attribute and the filtering criteria are specified in the value attribute. A field can have only one filtering rule associated with it; you cannot have two Field parameters for one field.
The following is an example of filtering rules for a feed. These rules specify that the output feed must include only records that have the popularity field equal to 4 or 5 and the mask field containing .ru or .com.
<Feed> ... <Filters> <Field name="popularity" value="4;5"/> <Field name="mask" value=".ru;.com"/> </Filters> ... <Feed> |
Feed Utility ignores leading and terminating space symbols, or tab symbols in the value of the "value" attribute.
Only those records that match all the specified criteria are included in the output file. If a filtering criterion is specified for a field, and the field is missing from a record, Feed Utility will not include this record in the output file.
Defining filtering criteria for numeric values
Numeric values are integers. Decimal values are not supported.
You can define filtering criteria for numeric fields in the following ways:
value="*"A field can have any value.
For example,
<Field name="type" value="*"/>means that thetypefield can have any value.value="%value%"Exact numeric value. A field must be equal to
%value%.For example,
<Field name="popularity" value="1"/>means that thepopularityfield must be equal to1.value="%value1%;%value2%"One of several numeric values. A field can have one of the specified numeric values (
%value1%or%value2%).You can specify additional values using
";"as a delimiter.For example,
<Field name="popularity" value="1;3"/>means that thepopularityfield must be equal to1or3, but not2.value="[%value1%;%value2%]"Range of numeric values.
A field can have one of the values in the specified range between
%value1%and%value2%.For example,
<Field name="popularity" value="[1;3]"/>means that thepopularityfield must have a value from1to3, including2.value="[%value1%;*]"orvalue="[*;%value1%]"Open range of numeric values. Same as range, but an asterisk (
*) specifies infinity.For example,
<Field name="popularity" value="[2;*]"/>means that the value of thepopularityfield must be greater than or equal to2.
Defining filtering criteria for strings
You can define filtering criteria for string fields in the following ways:
value="*"A field can have any value.
For example,
<Field name="mask" value="*"/>means that themaskfield can have any value.- value="
%string%"A field must contain the specified string.
For example,
<Field name="geo" value="ru"/>means that the value of thegeofield must contain"ru". value="%string1%;%string2%"Contains one or more of the specified strings.
For example,
<Field name="geo" value="ru;us"/>means that the value of thegeofield must contain"ru"or"us", or both"ru"and"us".
Defining filtering criteria for dates
Date values in feeds are formatted either in the pattern "DD.MM.YYYY" (for example, "26.04.2014"), in the pattern "YYYY-MM-DD" (for example "2014-04-26"), or in the pattern "MM/DD/YYYY" (for example, "04/26/2014").
You can define filtering criteria for fields with dates in the following ways:
value="*"A field can have any value.
For example,
<Field name="last_seen" value="*"/>means that thelast_seenfield can have any value.value="%date%"A field must contain the specified date.
For example,
<Field name="first_seen" value="14.10.2015"/>means that thefirst_seenfield value must be 14 October 2015.value="[%date1%;%date2%]"A field must contain the date in the specified range.
For example,
<Field name="first_seen" value="[01.02.2013;01.02.2015]"/>means thefirst_seenfield value must be from 1 February 2013 to 1 February 2015.value="[%date1%;*]"orvalue="[*;%date1%]"Open range of dates. Same as range of dates, that is,
value="[%date1%;%date2%]". But an asterisk (*) specifies infinity.For example,
<Field name="first_seen" value="[*;10.12.2015]"/>means that thefirst_seenfield value must be on or before 10 December 2015.
Excluding records with missing fields
In the original feed files, some records can have extra fields or can lack some fields. For records with extra fields, Feed Utility includes only those fields that are specified in the RequiredFields element of feed rules for a specified feed. For records that lack some fields, Feed Utility includes such records in the output if they contain at least one of the fields specified in the RequiredFields element. If some fields specified in the RequiredFields element are missing from a record in the original feed, the record in the processed feed will not contain them.
If you want to exclude records with missing fields from the output, you must create filtering rules for all required fields.
In the following example, Feed Utility will include records that have popularity, or mask, or both popularity and mask, fields.
<RequiredFields>popularity;mask</RequiredFields> |
If you want Feed Utility to include only those records that have both popularity and mask, create a filtering rule for both fields. You can specify criteria for field values, or use an asterisk (*) to specify any value.
In the following example, only records that have both fields (mask and popularity) are included in the resulting feed.
<Filters> <Field name="popularity" value="*"/> <Field name="mask" value="*"/> </Filters> <RequiredFields>popularity;mask</RequiredFields> |
You can specify exact criteria, in the same manner. The following example instructs Feed Utility to include only records that have the popularity field with a value of 5 and the mask field with any value.
<Filters> <Field name="popularity" value="5"/> <Field name="mask" value="*"/> </Filters> <RequiredFields>popularity;mask</RequiredFields> |
Parsing rules
Parsing rules are rules for custom feeds (feeds that are specified using the Path element). These parameters specify how each feed must be parsed by Feed Utility.
Parsing rules are defined in the Parsing element of feed rules for a custom feed.
The following is an example of parsing rules for a custom feed. These rules specify that the input feed is in JSON format. An MD5 parsing rule is defined for the files/md5 field in the input feed. Values in this field will be parsed as MD5 hashes.
<Feed> ... <Parsing type="json"> <MD5 type="MD5">files/md5</MD5> </Parsing> ... <Feed> |
Parsing element
The parent element, Parsing contains all nested parsing rules. Its attributes define the input format.
This element has the following attributes:
typeSpecifies the input feed type.
This attribute can have the following values:
json,stix,csv,xml,misp.delimiterSpecifies the delimiter for CSV input feeds. By default, this value is '
;'.rootElementSpecifies the root element path for XML input feeds.
You can use the '
*' and '?' wildcard characters as substitutes for any other character or group of characters. The '*' wildcard character can be used for a group of characters. The '?' wildcard character can be used for a single character.You cannot specify parts of the
rootElementpath with wildcard symbols only. For example,"Feeds/*/Contents"is invalid.
The following example demonstrates how to use the Parsing element for an XML input feed. In this case, parsing rules will be applied to elements nested inside the Feeds > Example > Contents element.
<Feed> ... <Parsing type="xml" rootElement="Feeds/Example/Contents"> ... </Parsing> ... <Feed> |
Individual parsing rules
Parsing rules for individual fields of an input feed must be nested inside the Parsing element. When Feed Utility processes the input feed, it creates the fields of the output feed according to these rules.
Each rule has the following format:
<OUTPUT_NAME type="VALUE_TYPE">INPUT_NAME</OUTPUT_NAME>
Above, the following rule name elements are used:
- OUTPUT_NAME defines the name of the field in the output feed. For example, if OUTPUT_NAME is MD5, the field with this value will also be named MD5 in the output feed.
OUTPUT_NAME preserves nested fields. If a field specified in the INPUT_NAME is nested, the field in the output feed will also be nested. For example, if OUTPUT_NAME is MD5_HASH and INPUT_NAME is files/md5, the field in the output feed will be files/MD5_HASH.
For JSON input feed, OUTPUT_NAME must always use the
Fieldvalue. Feed Utility uses the field names from the original feed. - VALUE_TYPE is the type of the values stored in this field.
These values will be handled by Feed Utility according to the specified type. For example, if the output feed contains domain names and URLs, then it will be compiled to the binary format.
Following value types are possible:
url—This value type is used for URLs.ip—This value type is used for IP addresses.md5—This value type is used for MD5 hashes.sha1—This value type is used for SHA1 hashes.sha256—This value type is used for SHA256 hashes.domain—This value type is used for domain names.context—This value type is used for context information.
- INPUT_NAME is the name of the field in the input feed. It must be defined according to the input feed format:
- For JSON input feeds, INPUT_NAME must contain the name of the field from the input feed. Nested fields must be delimited by '
/'. - For CSV input feeds, INPUT_NAME must contain the column number.
- For XML input feeds, INPUT_NAME must contain a path to one of the nested elements of the root element. Root element is defined in the
rootElementattribute ofParsingelement. The path is case sensitive. - For STIX and MISP input feeds,
Parsingelement must contain no parsing rules.
- For JSON input feeds, INPUT_NAME must contain the name of the field from the input feed. Nested fields must be delimited by '
The following example demonstrates parsing rule syntax for JSON input format:
<Feed> ... <Parsing type="json"> <Field type="url">URL</Field> <Field type="ip">IP</Field> <Field type="context">GEO</Field> <Field type="md5">files/md5</Field> </Parsing> ... <Feed> |
The following example demonstrates parsing rule syntax for CSV input format:
<Feed> ... <Parsing type="csv" delimiter=";"> <URL type="url">1</URL> <IP type="ip">2</IP> <GEO type="context">3</GEO> <MD5 type="md5">4</MD5> </Parsing> ... <Feed> |
The following example demonstrates parsing rule syntax for XML input format:
<Feed> ... <Parsing type="xml" rootElement="Feeds/Example/Contents"> <URL type="url">url</URL> <IP type="ip">ip</IP> <GEO type="context">context</GEO> <MD5 type="md5">md5_hash</MD5> </Parsing> ... <Feed> |
Feed Utility return codes
After Feed Utility finishes its execution, it indicates success, partial success, or failure with a return code. A return code can have one of the values described below.
Return code values
Feed Utility returns the following values:
0Success.
All the actions were successfully performed by Feed Utility.
For example, Feed Utility is configured to download and process two feeds, and both feeds were successfully downloaded and processed.
1Failure.
All the actions performed by Feed Utility failed or could not be performed.
For example, Feed Utility is configured to download and process two feeds, and Feed Utility could not download any feeds because of a network error.
This value is returned when no records are written to any of the processed feed files because of the filtering rules.
2Partial success.
Some of the actions were successfully performed by Feed Utility.
For example, Feed Utility is configured to download and process two feeds, and Feed Utility successfully downloaded and processed only one of the feeds.
This value is also returned when no records are written to one of the resulting feed files because of the filtering rules.
3Nothing to download.
This value is returned in the following cases:
- Feeds were not downloaded and processed by Feed Utility (when the value of the
enabledattribute in the Feed Utility configuration file isfalse) - Feeds were not updated because the latest version of feeds is already present
- Feeds were not downloaded and processed by Feed Utility (when the value of the
Output example (Linux)
The following example demonstrates receipt of a return code after Feed Utility has finished downloading and processing feeds. In this example, Feed Utility returns a value for partial success, because filtering rules for Botnet CnC URL Data Feed do not match any records in the original feed.
/opt/feed_util/bin $ ./kl_feed_util
2017-04-10 16:30:48.568 KL Feed Utility, version: 1.0.37.0/Release 2017-04-10 16:30:50.811 feed #66(Malicious_Hash_Data_Feed) version 2017-04-10T13:22:16.92 is available 2017-04-10 16:30:50.821 feed #65(Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed) version 2017-04-10T13:23:33.403 is available 2017-04-10 16:30:57.912 update of feed #65(Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed) is extracted to /opt/feed_util/bin/tmp/Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed.json 2017-04-10 16:31:09.448 update of feed #66(Malicious_Hash_Data_Feed) is extracted to /opt/feed_util/bin/tmp/Malicious_Hash_Data_Feed.json 2017-04-10 16:31:09.449 2 of 2 feeds downloaded 2017-04-10 16:31:14.984 failed to process feed #65(Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed): there is nothing to write with the current filtration settings 2017-04-10 16:31:35.610 1 of 2 feeds processed
/opt/feed_util/bin $ echo $?
2 |
Output example (Windows)
The following example demonstrates receipt of a return code after Feed Utility has finished downloading and processing feeds. In this example, Feed Utility returns a value for partial success, because filtering rules for Botnet CnC URL Data Feed do not match any records in the original feed.
C:\feed_util\bin>call kl_feed_util.exe && (echo Success.) || (echo Error or partial success.)
2017-05-03 15:56:08.393 KL Feed Utility, version: 1.0.56.0/Release 2017-05-03 15:56:08.656 feed #87(Demo_IP_Reputation_Data_Feed) version 2017-03-28T10:59:41.05 is available 2017-05-03 15:56:08.692 feed #85(Demo_Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed) version 2017-03-28T10:57:25.897 is available 2017-05-03 15:56:09.679 update of feed #87(Demo_IP_Reputation_Data_Feed) is extracted to C:\feed_util\bin\tmp\Demo_IP_Reputation_Data_Feed.json 2017-05-03 15:56:09.900 update of feed #85(Demo_Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed) is extracted to C:\feed_util\bin\tmp\Demo_Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed.json 2017-05-03 15:56:09.915 2 of 2 feeds downloaded 2017-05-03 15:56:09.929 start processing of feed #85(Demo_Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed) 2017-05-03 15:56:09.939 start processing of feed #87(Demo_IP_Reputation_Data_Feed) 2017-05-03 15:56:09.980 failed to process feed #85(Demo_Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed): there is nothing to write with the current filtration settings 2017-05-03 15:56:10.028 1 of 2 feeds processed Error or partial success. |
Using Password Utility
The Password Utility is a tool that allows you to reset the password for the admin account.
For default user name and password, see section "Logging in to CyberTrace".
Location
Use the following path to find the Password Utility:
- On Windows systems:
%service_dir%\tools\kl_access_util.exe - On Linux systems:
%service_dir%/tools/kl_access_util
Here %service_dir% is the directory where Kaspersky CyberTrace is installed.
Syntax
When you use this utility to reset the admin account, all other user accounts are deleted.
The Password Utility uses the following syntax:
- On Windows systems:
kl_access_util.exe [[--help|-h] | [--reset_default_user|-r] | [--version|-v]] - On Linux systems:
./kl_access_util [[--help|-h] | [--reset_default_user|-r] | [--version|-v]]
Options
The following table explains the command-line options.
Command-line options of kl_access_util
Option |
Description |
|
Prints the usage message to the screen. If this option is specified, all other options are ignored. |
|
Resets the password for the |
|
Prints the version information. |
Choosing the best feeds for your environment
You can reduce the load on your system by choosing the right feeds for your environment. Kaspersky CyberTrace Web allows you to compare the feeds that you use, and find and disable feeds that are not effective for your environment.
Effective feeds
Following are characteristics that can help you recognize effective feeds for your solution:
- High number of detections
- Frequent updates
The feeds that are updated frequently contain more accurate information.
Ineffective feeds
Following are characteristics that can help you recognize ineffective feeds for your solution:
- Many of the objects that are detected correctly are not harmful in your environment
- Many of the detections are false positives
- The feed contains a lot of records, but produces a low number of detections
Comparing feeds
To choose the best feeds for your solution, you can evaluate them by using the following criteria:
- Number of detections
- Number of false positives
- Number of records
- Update frequency
You can compare different characteristics of feeds by looking at the Dashboard of Kaspersky CyberTrace Web.
- To compare the number of detections, number of false positives, and number of records of different feeds, see tables and charts in the Supplier statistics section on the Dashboard tab of Kaspersky CyberTrace Web.
- To learn which types of indicators are frequently detected in your environment, see tables and charts in the Indicator statistics section.
Viewing feed fields
To decide whether to use a feed, you may want to see the list of its available fields. You can view the list of fields of a particular feed in the Kaspersky CyberTrace Web user interface.
To view the list of fields of a particular feed:
- Open the Settings tab of Kaspersky CyberTrace Web.
- Select the Feeds tab.
- Click the name of the feed to view its properties.
Upgrading and managing the installation
This section describes how to manage the Kaspersky CyberTrace installation after Kaspersky CyberTrace is installed.
Managing the installation on Linux systems
You can use the installation script to manage the RPM or DEB installation of Kaspersky CyberTrace.
The installation script can do the following:
- Install Kaspersky CyberTrace
- Upgrade Kaspersky CyberTrace
- Uninstall Kaspersky CyberTrace
- Change the Kaspersky CyberTrace configuration
Installation script command-line parameters
The installation script has the following command-line syntax:
run.sh [command]
Following commands are available:
helpDisplays the help message and exits.
installInstalls Kaspersky CyberTrace.
The installation script installs the software package and runs the configurator binary file. The configurator binary file performs an interactive setup of Feed Service, Feed Utility, and Log Scanner.
upgradeUpgrades Kaspersky CyberTrace from a previous version.
The installation script upgrades the software package, copies settings from the previous version of Feed Service, Feed Utility, and Log Scanner, and runs the configurator binary file.
removeRemoves (uninstalls) Kaspersky CyberTrace.
The installation script uninstalls the software package, removes the
/opt/kaspersky/ktfsdirectory, removes Feed Service from a list of system services, and removes crontab entries for Feed Service.changeChanges the Kaspersky CyberTrace configuration.
The installation script runs the configurator binary. The configurator binary performs an interactive setup of Feed Service, Feed Utility, and Log Scanner. For more information about the interactive setup, see subsection "Interactive setup with configurator" in section "Installation on Linux systems".
You can remove the specified proxy settings and stop using a proxy through Kaspersky CyberTrace Web.
Examples
The following command installs Kaspersky CyberTrace.
./run.sh install |
The following command upgrades Kaspersky CyberTrace.
./run.sh upgrade |
The following command uninstalls Kaspersky CyberTrace.
./run.sh remove |
The following command changes the Kaspersky CyberTrace configuration.
./run.sh change |
Managing the installation on Windows systems
You can use the executable installer to manage the installation of Kaspersky CyberTrace.
Executable installer options
The executable installer can do the following:
- Install Kaspersky CyberTrace
To install Kaspersky CyberTrace, run the executable installer and follow the instructions of the Kaspersky CyberTrace Setup Wizard.
- Uninstall Kaspersky CyberTrace
If you have an existing Kaspersky CyberTrace installation, running the executable installer enables the Remove button in the Kaspersky CyberTrace Setup Wizard. Clicking this button will uninstall Kaspersky CyberTrace from your computer.
When the existing installation is removed, all subdirectories and files in the installation directory are removed as well.
- Change the Kaspersky CyberTrace configuration
If you have an existing Kaspersky CyberTrace installation, running the executable installer enables the Change button in the Kaspersky CyberTrace Setup Wizard. Clicking this button allows you to reconfigure your installation of Kaspersky CyberTrace. Use this option if you want to change the installation settings or if the list of feeds available to you has been changed.
To be able to reconfigure the Kaspersky CyberTrace installation, run the executable installer as Administrator.
Upgrading Kaspersky CyberTrace from a previous version
This section describes how to upgrade Kaspersky CyberTrace from a previous version.
About the upgrade process
The upgrade process described in this section applies to Kaspersky CyberTrace versions 3.1.0 and above. If you have an older version of Kaspersky CyberTrace or Kaspersky Threat Feed Service, contact your Technical Account Manager (TAM).
You upgrade Kaspersky CyberTrace in two steps:
- Upgrade binary and other files.
- Upgrade the integration of Kaspersky CyberTrace with the SIEM solution.
This step is not relevant for Log Scanner.
How to learn the version of Kaspersky CyberTrace
You can find out the version of Kaspersky CyberTrace as follows:
- In Windows, view the version property of the kl_feed_service.exe binary file.
- In Linux, run the following command:
%service_dir%/bin/kl_feed_service -v
Upgrading automatically from 3.1 to 4.0 (Linux)
This section describes how to upgrade Kaspersky CyberTrace on Linux.
The instructions below apply to the RPM/DEB package installations.
Updating from 3.1 to 4.0
To upgrade Kaspersky CyberTrace automatically to a newer version:
- Run the following command with root privileges:
run.sh upgrade - At the beginning of the upgrade process, accept the request to stop Feed Service. If you decline to stop it, the upgrade fails.
At the end of the upgrade process, all the settings, user accounts data, available feeds, and certificates will be automatically transferred to the new version. If you have a commercial license key, you can add it to Kaspersky CyberTrace by using the Licensing tab.
After the upgrade process is finished, the actionable fields are not specified for new feeds that were not supported in the previous version. If needed, specify these fields manually on the Settings > Feeds tab.
Make sure that
/opt/kaspersky/ktfs/etc/kl_feed_service.confcontains only a single copy of the FalsePositive and InternalTI suppliers with corresponding standard names (Black_List.json and White_List.json). If not, the script displays an error and exits.After you finish the upgrade process, Feed Service will be launched automatically.
Note that the automatic upgrade functionality is available only if you have accepted the EULA in the installation that is being upgraded.
Page topUpgrading automatically from 3.1 to 4.0 (Windows)
This section describes how to upgrade Kaspersky CyberTrace on Windows.
The instructions below apply to installations done by using the executable installer.
Upgrading from 3.1 to 4.0
To upgrade Kaspersky CyberTrace automatically to a newer version:
- Run the executable installer that starts the upgrading process automatically.
- At the beginning of the upgrade process, accept the request to stop Feed Service. If you decline to stop it, the upgrade fails.
If Feed Service is stopped and the upgrade continues, all the settings, user accounts data, available feeds, and certificates will be automatically transferred to the new version. If you have a commercial license key, you can add it to Kaspersky CyberTrace on the Licensing tab.
After the upgrade process is finished, the actionable fields are not specified for new feeds that were not supported in the previous version. If needed, specify these fields manually on the Settings > Feeds tab.
Make sure that
/opt/kaspersky/ktfs/etc/kl_feed_service.confcontains only a single copy of the FalsePositive and InternalTI suppliers, with corresponding standard names (Black_List.json and White_List.json). If not, the installer displays an error and exits. - Change the settings during the upgrade process, if necessary.
After you finish the upgrade process, Feed Service will be launched automatically.
Note that automatic upgrade with the executable installer is available only if you have accepted the EULA in the installation that is being upgraded.
Page topUpgrading Kaspersky CyberTrace integration (QRadar)
This section describes how to finish the integration of Kaspersky CyberTrace with QRadar after the upgrade of the Kaspersky CyberTrace files.
The upgrade process described in this section applies to Kaspersky CyberTrace versions 3.1.0 and above. If you have an older version of Kaspersky CyberTrace or Kaspersky Threat Feed Service, contact your Technical Account Manager (TAM).
Finishing the integration of Kaspersky CyberTrace with QRadar consists of the following actions:
- Adding support of ICS Hash Data Feed
- Adding support of new alert events
- Adding events that correspond to new categories for APT feeds
- Adding events that correspond to new categories for the Internal TI list
In Kaspersky CyberTrace version 4.0, these categories are used instead of the following:
- KL_BlackList_URL
- KL_BlackList_IP
- KL_BlackList_Hash_MD5
- KL_BlackList_Hash_SHA1
- KL_BlackList_Hash_SHA256
If QRadar automatically receives configuration updates (including configuration file changes, vulnerabilities, QID maps, supportability scripts, and security threat information updates), the following features are included:
- Support of ICS Hash Data Feed
- Support of new alert events
- New categories of APT feeds
- New categories of the Internal TI list
Perform the procedure above manually only if it does not receive configuration updates automatically. To add these categories to QRadar, perform the actions described in sections "Importing QIDs to QRadar", "Sending a set of events to QRadar", and "Mapping events to QIDs". The categories mentioned above are included in the sample_initiallog.txt and sample_qid.txt files of the latest distribution kit of CyberTrace.
To finish the integration of Kaspersky CyberTrace with QRadar:
- Add the following categories to support ICS Hash Data Feed:
- KL_ICS_Hash_MD5
- KL_ICS_Hash_SHA1
- KL_ICS_Hash_SHA256
- Add new alert events:
- KL_ALERT_RetroScanError
- KL_ALERT_RetroScanCompleted
- KL_ALERT_RetroScanStorageExceeded
- KL_ALERT_IndicatorsStoreLimitExceeded
- KL_ALERT_IndicatorsStoreHardLimit
- KL_ALERT_FreeSpaceEnds
- Add new categories to support APT feeds:
- KL_APT_Hash_SHA1
- KL_APT_Hash_SHA256
- Add new categories to support the Internal TI list:
- KL_InternalTI_URL
- KL_InternalTI_IP
- KL_InternalTI_Hash_MD5
- KL_InternalTI_Hash_SHA1
- KL_InternalTI_Hash_SHA256
Upgrading Kaspersky CyberTrace integration (Splunk)
This section describes how to finish the integration of Kaspersky CyberTrace with Splunk after the upgrade of the Kaspersky CyberTrace files.
When upgrading the integration of Kaspersky CyberTrace with Splunk to version 3.1.0, import the new version of Kaspersky CyberTrace App for Splunk to Splunk. During the import, select the option shown in the picture below.

The application settings will be reset. The old settings will be saved in %SPLUNK_DIRECTORY%/etc/apps/Kaspersky-CyberTrace-App-for-Splunk/default.old.%CURRENT_DATE%, where %CURRENT_DATE% can be in the format yyyymmdd-hhmmss (for example, 20190725-161423). Kaspersky CyberTrace App for Splunk must be configured in its entirety, similarly to the way in which the old version was configured.
Upgrading Kaspersky CyberTrace integration (ArcSight)
This section describes how to finish the integration of Kaspersky CyberTrace with ArcSight after the upgrade of the Kaspersky CyberTrace files.
When upgrading the integration of Kaspersky CyberTrace with ArcSight to version 3.1.0, you must import a new version of the ARB package. During the import, you have to accept an upgrade of the current ARB package.
Page topUpgrading Kaspersky CyberTrace integration (RSA)
This section describes how to finish the integration of Kaspersky CyberTrace with RSA NetWitness after the upgrade of the Kaspersky CyberTrace files.
When upgrading the integration of Kaspersky CyberTrace with RSA NetWitness to version 3.1.0, import the cybertrace.ini and v20_cybertracemsg.xml files from the %service_dir%/integration/rsa/cybertrace directory to Log Decoder. After the import, restart Log Decoder.
If you update the v20_cybertracemsg.xml file, make sure that the actionable fields are specified for all feeds in use. For the full list of such fields, see section "Step 2. Sending events from Feed Service to RSA NetWitness".
Upgrading Kaspersky CyberTrace integration (LogRhythm)
This section describes how to finish the integration of Kaspersky CyberTrace with LogRhythm after the upgrade of the Kaspersky CyberTrace files.
Finishing the integration of Kaspersky CyberTrace with LogRhythm consists of the following steps:
- Adding new events to LogRhythm
- Removing obsolete events from LogRhythm
Step 1. Adding new events
To add new events to LogRhythm:
Add the following categories and alert events automatically or manually (as described in sections "Step 3 (optional). Adding Kaspersky CyberTrace events" and "Step 4 (optional). Adding Kaspersky CyberTrace rules"):
- KL_ICS_Hash_MD5
- KL_ICS_Hash_SHA1
- KL_ICS_Hash_SHA256
- KL_APT_Hash_SHA1
- KL_APT_Hash_SHA256
- KL_ALERT_RetroScanError
- KL_ALERT_RetroScanCompleted
- KL_ALERT_RetroScanStorageExceeded
- KL_ALERT_IndicatorsStoreLimitExceeded
- KL_ALERT_IndicatorsStoreHardLimit
- KL_ALERT_FreeSpaceEnds
- KL_InternalTI_URL
- KL_InternalTI_IP
- KL_InternalTI_Hash_MD5
- KL_InternalTI_Hash_SHA1
- KL_InternalTI_Hash_SHA256
Step 2. Removing obsolete events
To remove obsolete events from LogRhythm:
- Run LogRhythm Console.
- Select Deployment Manager > Tools > Knowledge > MPE Rule Builder.
The Rule Builder form opens.
- Click the Open rule library (
 ) button.
) button. - Double-click the rule you want to retire.
A preview window for the rule opens.
Rules for the following events must be retired:
- KL_BlackList_URL
- KL_BlackList_IP
- KL_BlackList_Hash_MD5
- KL_BlackList_Hash_SHA1
- KL_BlackList_Hash_SHA256
- KL_ALERT_FeedLoadedPartially
- Click the Retire rule (
 ) button.
) button. - In the Verify Retire window, click Yes.
Verify Retire window
Uninstalling Kaspersky CyberTrace
This section describes how to uninstall Kaspersky CyberTrace.
Uninstalling Kaspersky CyberTrace (Windows)
This section contains the uninstallation procedures for Kaspersky CyberTrace on Windows. After you uninstall Kaspersky CyberTrace, remove objects related to it from your SIEM solution.
Uninstalling Kaspersky CyberTrace (executable installer)
The following procedure describes how to uninstall the copy of Kaspersky CyberTrace that was installed by using the executable installer.
To unistall Kaspersky CyberTrace:
- Run the executable installer of Kaspersky CyberTrace.
The Kaspersky CyberTrace Setup Wizard starts.
- Click Remove.
- Follow the Wizard instructions.
Uninstalling Kaspersky CyberTrace (Linux)
This section contains the uninstallation procedures for Kaspersky CyberTrace on Linux. After you have performed uninstallation, remove objects related to Kaspersky CyberTrace from your SIEM solution.
Uninstalling (RPM and DEB installation)
Following is the procedure for uninstalling Kaspersky CyberTrace installed by using the DEB or RPM installation package.
To uninstall Kaspersky CyberTrace:
- Run the following command:
%service_dir%/run.sh remove - Follow the Wizard instructions.
Uninstalling (.tgz installation)
Following is the procedure for uninstalling Kaspersky CyberTrace installed from the .tgz archive.
To uninstall Kaspersky CyberTrace:
- Remove entries for Feed Service from crontab.
- Stop Feed Service by running the following commands:
systemctl stop cybertrace.servicesystemctl stop cybertrace_db.service - Remove Feed Service from the list of services started on boot by running the following commands:
systemctl disable cybertrace.servicesystemctl disable cybertrace_db.service - Remove the
%service_dir%directory together with its contents.
Removing Kaspersky CyberTrace objects (QRadar)
This section describes how to remove objects related to Kaspersky CyberTrace from QRadar after Kaspersky CyberTrace is uninstalled. Note that after you have removed these objects, events from Kaspersky CyberTrace persist in QRadar.
After you have uninstalled Kaspersky CyberTrace, uninstall Kaspersky Threat Feed App (if it is installed). If you will not install Kaspersky CyberTrace in future, you can also remove log sources related to Kaspersky CyberTrace (it can be the KL_Threat_Feed_Service_v2 and KL_Verification_Tool log sources).
To remove a log source from QRadar:
- In QRadar, select Admin, and under Data Sources select Log Sources.
The Log Sources window opens.
- Select the log source that you want to remove and click Delete.
Removing Kaspersky CyberTrace objects (Splunk)
This section describes how to remove objects related to Kaspersky CyberTrace from Splunk after Kaspersky CyberTrace is uninstalled. Note that after you have removed these objects, events from Kaspersky CyberTrace persist in Splunk.
After you have uninstalled Kaspersky CyberTrace, delete the %SPLUNKDIR%/etc/apps/Kaspersky-CyberTrace-App-for-Splunk directory, which contains Kaspersky CyberTrace App for Splunk, and restart Splunk. (Here %SPLUNKDIR% is the directory to which Splunk is installed.) You can restart Splunk either by using the GUI or by running the following command:
%SPLUNKDIR%/bin/splunk restart
Then, if you want, you can clear Splunk of events received from Kaspersky CyberTrace.
To clear Splunk of events received from Kaspersky CyberTrace:
- Run the Search & Reporting app by clicking its button in the Splunk GUI.
- Delete the events from Kaspersky CyberTrace:
- In the Search field, type the following command:
index="main" sourcetype="kl_cybertrace_events" | deleteDeleting events from the
mainindex can be done only under the user account that has thecan_deleterole. You can add this role to a user account by selecting Settings > Roles in the Splunk main menu. - Next to the Search field, in the drop-down list for selecting the time interval of events to search, select All time.
- Click Search.

Search & reporting app
- In the Search field, type the following command:
Removing Kaspersky CyberTrace objects (ArcSight)
This section describes how to remove objects related to Kaspersky CyberTrace from ArcSight after Kaspersky CyberTrace is uninstalled. Note that after you have removed these objects, events from Kaspersky CyberTrace persist in ArcSight.
To remove objects related to Kaspersky CyberTrace from ArcSight:
- Remove the ARB package from ArcSight.
To do this, in ArcSight Console, remove the
/All Packages/Public/Kaspersky CyberTrace Connectorpackage. - Uninstall the ArcSight SmartConnector service that was used to receive events from Feed Service.
In Linux you do this as follows:
- Stop the ArcSight SmartConnector service by running the following command:
/etc/init.d/arc_%service_name% stopHere
%service_name%is the name of the ArcSight SmartConnector service specified during its installation. - Run the following command to uninstall the ArcSight SmartConnector:
%ConnectorInstallDir%/UninstallerData/Uninstall_ArcSightAgentsHere
%ConnectorInstallDir%is the directory to which the ArcSight SmartConnector was installed. - Remove the
%ConnectorInstallDir%directory.
In Windows you uninstall the ArcSight SmartConnector service by running the ArcSight SmartConnector uninstallation program.
- Stop the ArcSight SmartConnector service by running the following command:
- Uninstall the ArcSight Forwarding Connector that was used to send events to Feed Service.
Do this as follows:
- Stop the ArcSight Forwarding Connector service by running the following command:
/etc/init.d/arc_%FORWARDING% stopHere
%FORWARDING%is the name of the ArcSight Forwarding Connector service specified during its installation. - Run the following command to uninstall the ArcSight Forwarding Connector:
%ConnectorInstallDir%/UninstallerData/Uninstall_ArcSightAgentsHere
%ConnectorInstallDir%is the directory to which the ArcSight Forwarding Connector was installed. - Remove the
%ConnectorInstallDir%directory.
- Stop the ArcSight Forwarding Connector service by running the following command:
Removing Kaspersky CyberTrace objects (RSA NetWitness)
This section describes how to remove objects related to Kaspersky CyberTrace from RSA NetWitness after Kaspersky CyberTrace is uninstalled. Note that after you have removed these objects, events from Kaspersky CyberTrace persist in RSA NetWitness.
To remove objects related to Kaspersky CyberTrace from RSA Net Witness:
- Remove the
/etc/netwitness/ng/envision/etc/devices/cybertracedirectory from the computer on which Log Decoder runs. - From the Log Decoder settings, remove the
cybertraceforwarding rule similarly to the way that it was added. - If you will not forward events in future, disable the event forwarding by setting the
/decoder/config/logs.forwarding.enabledparameter tofalse. - Remove the
Kaspersky CyberTracedashboard similarly to the way that a dashboard can be created. - Remove the Kaspersky CyberTrace charts similarly to the way that you enabled them.
- Remove the
CyberTrace Reportreport similarly to the way that a report can be created. - Remove the Feed Service rules simillarly to the way that they were imported.
- If you added fields to the index-concentrator-custom.xml or table-map-custom.xml files, remove them from there.
- Restart Concentrator if you have changed index-concentrator-custom.xml.
- Restart Log Decoder.
Adding self-signed SSL certificates for CyberTrace Web
The SSL certificate and a private key that are generated during the installation of CyberTrace allow you to use CyberTrace Web via HTTPS. The certificate is self-signed, so the browser you use informs you about an untrusted connection. We recommend that you use a certificate that is trusted in your infrastructure. However if you cannot use a trusted certificate, you can add the self-signed certificate as trusted to your browser or operating system.
Generating SSL certificates for Kaspersky CyberTrace Web
CyberTrace Web uses an SSL certificate for HTTPS connections. By default, CyberTrace Web uses a self-signed certificate and a private key that are generated during the installation of CyberTrace. The generated certificate is valid for two years.
We recommend that you generate a certificate that will be trusted in your infrastructure, and then configure CyberTrace to use this certificate instead of the self-signed certificate.
Before making changes, create a backup copy of the existing private key, certificate, and Feed Service configuration file.
To generate a trusted certificate for CyberTrace Web:
- Create a private key and a trusted certificate:
- Create a new private and public key pair.
- Use the public key to generate an SSL Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
- Sign the CSR request by using the trusted CA.
This creates a trusted certificate for the private key.
- Convert the private key and the trusted certificate to the PEM format.
- Copy both the private key and the certificate to the
%service_dir%/httpsrvdirectory. - Edit the
GUISettings > HTTPServer > SSLCertificatePathandGUISettings > HTTPServer > SSLPrivateKeyPathelements of the Feed Service configuration file, if necessary, so that they will contain the paths to the certificate and private key, respectively.Save the Feed Service configuration file.
- Restart Feed Service.
Adding the self-signed certificate as trusted to a browser
The procedures in this section show you how to add the self-signed certificates generated during Kaspersky CyberTrace installation to the trusted storage. This will remove the security warnings generated by browsers.
The information in this section is applicable to the situation when a user gains access to CyberTrace Web from the same computer on which CyberTrace Web runs. If the GUISettings > HTTPServer > ConnectionString element of the Feed Service configuration file refers to an external interface, the CyberTrace Web website will not be considered trusted, because the self-signed certificate can be used only with the https://127.0.0.1 and https://localhost addresses.
To avoid potential security risks, we recommend using a trusted certificate signed by a certificate authority (CA). For more information, see section "Generating certificates for CyberTrace Web".
Causing a self-signed certificate to be trusted by a browser (CyberTrace Web is opened in Internet Explorer installed on a Windows system)
Gaining the browser's trust requires that you perform, in sequence, the following three procedures:
To save the certificate to a local file:
- Open the
https://127.0.0.1orhttps://localhostaddress in Internet Explorer.The browser informs you of a problem with the security certificate of the website.
Certificate error message
- Select the Continue to this website (not recommended) link.
The Certificate Error message appears in the address bar.
- Click Certificate Error.
The Untrusted Certificate window opens.
Untrusted Certificate window
- Select the View certificates link.
The Certificate window opens with information about the CyberTrace certificate.
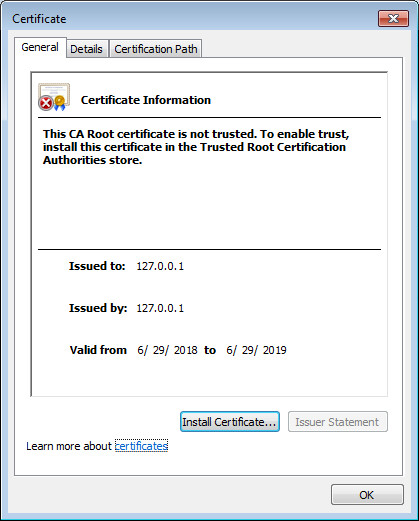
Certificate window
- Select the Details tab, and then click Copy to File to create a local copy of the certificate.
The Certificate Export Wizard starts.
Certificate Export Wizard
- Follow the Wizard instructions.
Use the default Wizard settings during the certificate export.
To start the certificate import process through Microsoft Management Console (MMC):
- From the Search box, navigate to the Run box, and then enter mmc.
You can now run MMC as Administrator.
Running the MMC
- In the MMC-based console that opens, select File > Add/Remove Snap-in.
Selecting Add/Remove Snap-in
The Add or Remove Snap-ins window opens.
- In the Available snap-ins list, select Certificates, and then click Add.
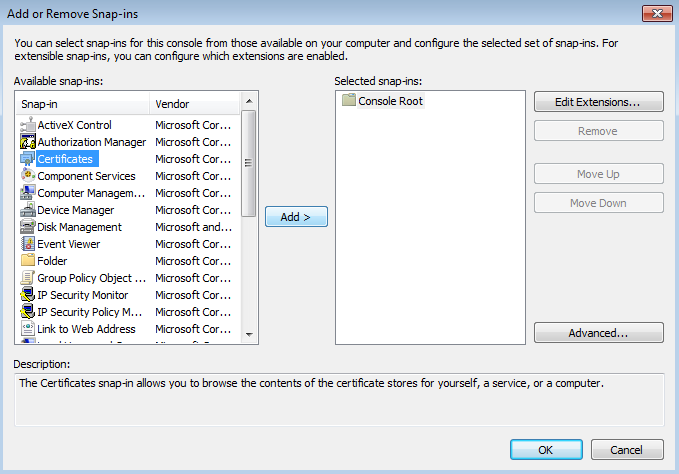
Adding a Certificates snap-in
The Certificates snap-in window opens.
- Select Computer account, and then click Next.
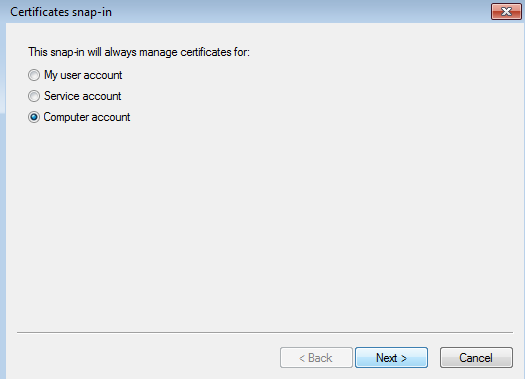
Selecting Computer account
In the Select Computer window that opens, click Finish.
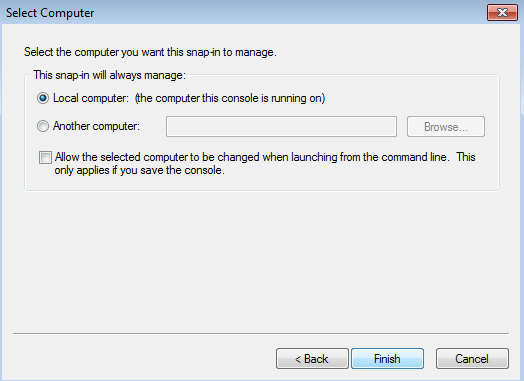
Selecting Local computer
- In the tree pane, select Certificates (Local Computer) > Trusted Root Certification Authorities, right-click Certificates, and then select All Tasks > Import.
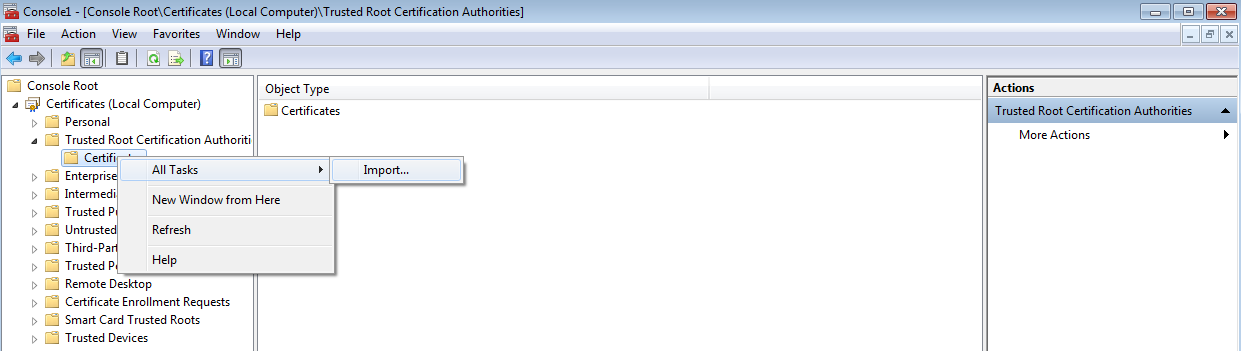
Selecting Import
The Certificate Import Wizard starts.
To add the saved certificate to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store:
- On the Welcome page of the Wizard, click Next.
Certificate Import Wizard
- Click Browse and select the certificate that was saved in the "To make the self-signed certificate for CyberTrace Web trusted when using Internet Explorer:" procedure above.
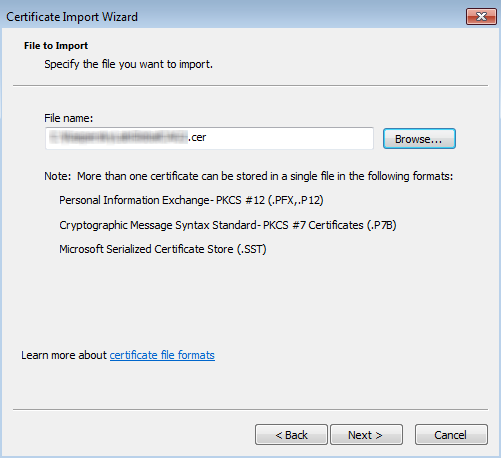
Importing the previously saved certificate
- On the next page of the Certificate Import Wizard, click Next.
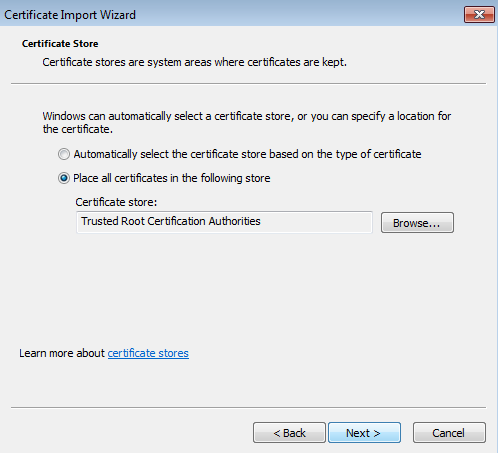
Selecting a certificate store
- On the last page of the Certificate Import Wizard, click Finish.
Completing the certificate import
- Close the MMC-based console and restart the browser.
The security problem (untrusted certificate) is resolved, as shown in the figure below.
Website identification
Causing a self-signed certificate to be trusted by a browser (CyberTrace Web opens in Google Chrome installed on a Windows system)
To make the self-signed certificate for CyberTrace Web trusted when using Google Chrome:
- Open the
https://127.0.0.1orhttps://localhostaddress in Google Chrome.A warning is displayed in the address bar that the connection to the site is not secure.
- Click the Not secure message.
A window opens with security details about the website.
Security details
- Click Certificate to view the certificate information. (When the mouse pauses over Certificate, a Show certificate tooltip appears.)
- In the Certificate window that opens, select the Details tab, and then click Copy to File to create a local copy of the certificate.
The Certificate Export Wizard starts.

Certificate Export Wizard
- Follow the Wizard instructions.
Use the default Wizard settings during the certificate export.
- After the certificate is saved to a local disk, open it and add it to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store, as described in the procedure for Internet Explorer.
- Restart the browser.
Causing a self-signed certificate to be trusted by a browser (CyberTrace Web opens in Mozilla Firefox)
You add CyberTrace Web to the list of Mozilla Firefox trusted sites so that the browser will not display warnings about the certificate.
Causing a self-signed certificate to be trusted by a browser (CyberTrace Web opens in a browser for Linux)
Procedures for using a browser to import a certificate as trusted (on Linux systems) vary depending on the browser and Linux distribution used. But the procedures share common steps: to open the browser settings form and use the form to import the certificate to a store.
To manually cause a self-signed certificate to be trusted by a browser on a Linux system:
- Create a
/usr/local/share/ca-certificates/directory if it does not exist on your computer:mkdir /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/ - Copy your root certificate (.crt file) to the created directory:
cp <full path to the certificate> /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/ - Update the certificates:
sudo update-ca-certificatesIf you do not have the ca-certificates package, install it with your package manager.
Removing a certificate from the list of trusted ones
After you have reconfigured or uninstalled CyberTrace, old certificates are no longer used by CyberTrace. You can remove them from the list of trusted certificates.
To remove a certificate from the list of trusted certificates (on Windows):
- Open the Certificates management console, and then run the following command:
certmgr.msc - In the tree pane, select Trusted Root Certification Authorities > Certificates.
Certificates management console
- In the results pane, right-click the added certificate, and then select Delete.
On a Linux system, the removal procedure is performed in a way that is similar to the addition of a certificate: open the list of the trusted certificates and remove those that you do not need.
Page topWatchdog module workflow
This section describes the watchdog module workflow.
How watchdog mode works (Linux)
Kaspersky CyberTrace can run in watchdog mode. In this case, a separate module monitors the service and re-launches it when it freezes or crashes. It works as follows:
- Every two minutes, the watchdog module sends a message to Feed Service.
- If this message is received, a response is sent back in the same TCP connection.
- If the watchdog module has not received the response, it performs the following steps:
- The watchdog module sends a notification (a
KL_ALERT_ServiceUnavailableevent) to the event target software that Feed Service is unavailable. - If logging is turned on, the watchdog module writes information about the Feed Service unavailability to the watchdog module log (a separate log).
- The watchdog module starts Feed Service.
- If logging is turned on, the watchdog module writes information about the restart of Feed Service to the watchdog module log.
- Feed Service sends a notification (a
KL_ALERT_ServiceStartedevent) to the event target software that Feed Service started.
- The watchdog module sends a notification (a
You can run Feed Service in watchdog mode from the command line or by using the script.
How watchdog mode works (Windows)
Kaspersky CyberTrace runs in watchdog mode: the watchdog service monitors Feed Service and re-launches it when it freezes or crashes. It works as follows:
- Every four minutes, the watchdog service sends a message to Feed Service.
- If this message is received, a response is sent back in the same TCP connection.
- If the watchdog service has not received the response, the following steps are performed:
- The watchdog service sends a notification (a
KL_ALERT_ServiceUnavailableevent) to the event target software that Feed Service is unavailable. - If logging is turned on, the watchdog service writes information about Feed Service unavailability to the watchdog service log (a separate log).
- The watchdog service starts Feed Service.
- If logging is turned on, the watchdog service writes information about the Feed Service restart to the watchdog service log.
- Feed Service sends a notification (a KL_ALERT_ServiceStarted event) to the event target software that Feed Service has started.
- The watchdog service sends a notification (a
When you run Feed Service in watchdog mode, make sure that one scanner (the ServiceSettings > ScannersCount element in the configuration file) is reserved for the watchdog module.
The watchdog service binary file kl_watchdog_service.exe is launched from the command line. The binary file uses the flags described in the following table.
Flags for kl_watchdog_service.exe
Flag |
Description |
--reg |
Adds the watchdog service to the list of Windows services. |
--del |
Removes the watchdog service from the list of Windows services. |
--svc |
Starts the watchdog service as a Windows service. Note that only Service Control Manager can run kl_watchdog_service.exe with this flag. If the user tries to run kl_watchdog_service.exe with this flag, an error occurs. |
--help (or -h) |
Prints information about flags that can be used with kl_watchdog_service.exe. |
If no flag is specified, the kl_watchdog_service.exe program prints the list of available flags to the screen.
Restarting Feed Service by the watchdog module
Feed Service can be launched in watchdog mode. In this case, the watchdog module monitors Feed Service to make sure that it keeps running. When the watchdog module detects that the service has crashed or frozen, it notifies the SIEM solution and restarts the service. Feed Service starts working and notifies the SIEM solution. Therefore, you can look in the SIEM solution log to learn the period during which Feed Service was not active.
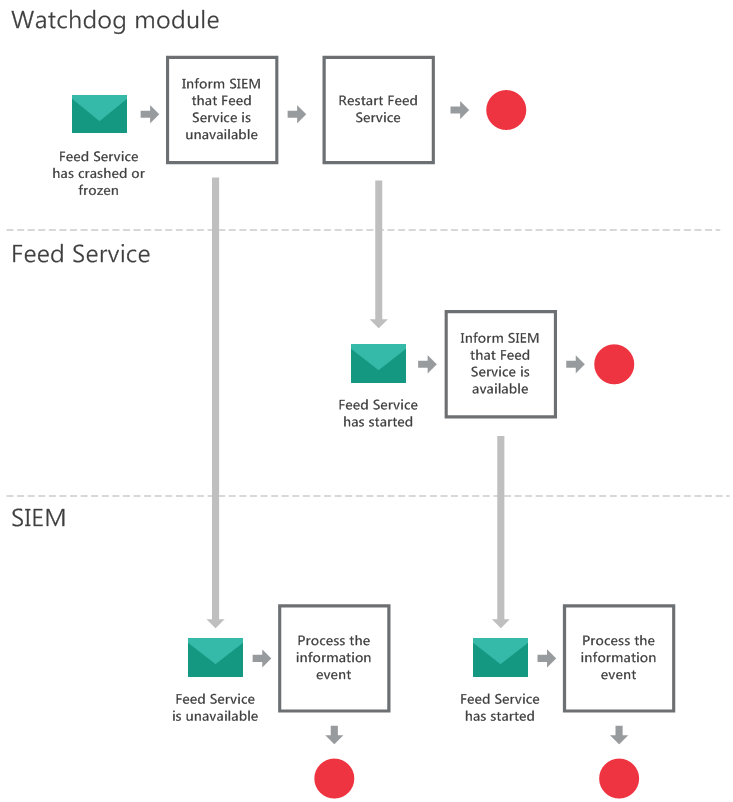
Restarting Feed Service using the watchdog module
Page topTesting the connection with Feed Service and the availability of feeds
This section explains how to test the connection with Feed Service and its ability to match events against specific feeds.
Before testing the connection with Feed Service, make sure that there is at least one unused scanner in the ServiceSettings > ScannersCount element of the configuration file.
Sending a ping request
You can send a ping request to test the connection with Feed Service. This method does not require any feeds to be enabled. You do not need a commercial certificate for Kaspersky Threat Data Feeds to use this method.
To test the connection with Feed Service by sending a ping request:
- Establish a TCP connection using the IP address and port that Feed Service listens on for incoming events (see section "Service settings").
- Send
X-KF-ReplyBackPINGas the first message. - Wait for the response.
If the response is PONG, it means that Feed Service is running and listening for incoming events on the specified IP address and port.
Sending a test event
Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Data Feeds contain records that are provided for test purposes only and do not represent malicious objects. You can use these records to make sure that Feed Service can match events against specific feeds. These records always appear in the feeds and will never be removed.
To test the connection with Feed Service by sending a test event:
- Establish a TCP connection using the IP address and port that Feed Service listens on for incoming events (see section "Service settings").
- Send
X-KF-SendFinishedEventX-KF-ReplyBackas the first message. - Send a test event containing a test record for the specific feed from the tables below.
The following table contains the test records for commercial feeds.
Test records (commercial feeds)
Feed used
Test records
Event category
Malicious URL Data Feed
http://fakess123.nu
KL_Malicious_URL
Phishing URL Data Feed
http://fakess123ap.nu
KL_Phishing_URL
Botnet CnC URL Data Feed
http://fakess123bn.nu
KL_BotnetCnC_URL
IP Reputation Data Feed
192.0.2.1
KL_IP_Reputation
Malicious Hash Data Feed
FEAF2058298C1E174C2B79AFFC7CF4DF
KL_Malicious_Hash_MD5
Mobile Malicious Hash Data Feed
60300A92E1D0A55C7FDD360EE40A9DC1
KL_Mobile_Malicious_Hash_MD5
Mobile Botnet CnC URL Data Feed
http://sdfed7233dsfg93acvbhl.su/steallallsms.php
KL_Mobile_BotnetCnC_URL
Ransomware URL Data Feed
http://fa7830b4811fbef1b187913665e6733c.com
KL_Ransomware_URL
Vulnerability Data Feed
D8C1F5B4AD32296649FF46027177C594
KL_Vulnerable_File_Hash_MD5
APT URL Data Feed
http://b046f5b25458638f6705d53539c79f62.com
KL_APT_URL
APT Hash Data Feed
7A2E65A0F70EE0615EC0CA34240CF082
KL_APT_Hash_MD5
APT IP Data Feed
192.0.2.4
KL_APT_IP
IoT URL Data Feed
http://e593461621ee0f9134c632d00bf108fd.com/.i
KL_IoT_URL
ICS Hash Data Feed
7A8F30B40C6564EFF95E678F7C43346C
KL_ICS_Hash_MD5
The following table contains the test records that can be used when only demo feeds are enabled.
Test records (demo feeds)
Feed used
Test records
Event category
DEMO Botnet_CnC_URL_Data_Feed
http://5a015004f9fc05290d87e86d69c4b237.com
KL_BotnetCnC_URL
DEMO IP_Reputation_Data_Feed
192.0.2.1
KL_IP_Reputation
DEMO Malicious_Hash_Data_Feed
776735A8CA96DB15B422879DA599F474
KL_Malicious_Hash_MD5
- Wait for the response:
- If the response is a detection event that contains the corresponding event category from the tables above, it means that Feed Service can receive events and match them against the specific feed.
- If the response is
LookupFinishedwithout event information, it means that Feed Service can receive events and perform matching, but the specific feed is disabled (see section "Enabling and disabling feeds").