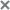Configuring Applications Launch Control task settings
To configure general Applications Launch Control task settings:
- Open the Applications Launch Control window.
- On the General tab, select the following settings in the Task mode section:
- In the Task mode drop-down list, specify the task mode.
- Clear or select the Repeat action taken for the first file launch on all the subsequent launches for this file check box.
- Clear or select the Deny the command interpreters launch with no command to execute.
- In the Rules managing block, configure settings for applying rules:
- Click the Rules list button to add allowing rules for the Applications Launch Control task.
Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows does not recognize paths that contain slashes ("/"). Use backslash ("\") to enter the path correctly.
- Select the mode for applying rules:
- Replace local rules with policy rules
The application applies the rule list specified in the policy for centralized application launch control on a group of protected devices. Local rule lists cannot be created, edited, or applied.
- Add policy rules to the local rules
The application applies the rule list specified in a policy together with local rule lists. You can edit the local rule lists using the Rule Generator for Applications Launch Control task.
- Replace local rules with policy rules
- Click the Rules list button to add allowing rules for the Applications Launch Control task.
- In the Rule usage scope section, specify the following settings:
- Apply rules to executable files.
- Monitor loading of DLL modules.
Controlling loading of DLL modules may affect the performance of the operating system.
- Apply rules to scripts and MSI packages.
- In the KSN Usage group box, configure the following application launch settings:
- Deny applications untrusted by KSN.
- Allow applications trusted by KSN.
- Users and / or user groups allowed to launch applications trusted in KSN:
- In the context menu of the Edit button, select the method for adding users.
The Select user or user group window opens.
- Select a user or user group.
- Click the OK button.
- In the context menu of the Edit button, select the method for adding users.
- On the Software Distribution Control tab, configure the settings for software distribution control.
- On the Task management tab, configure the task start schedule settings.
- Click the OK button in the Applications Launch Control window.
Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows immediately applies the new settings to the running task. Information about the date and time when the settings were modified, and the values of task settings before and after modification, are saved in the system audit log.
Page top