How to protect your PC against file-encrypting ransomware
Protect your digital life
Ransomware is a kind of file-encrypting malware that encrypts your files and then demands ransom for decrypting them. Some of the programs encrypt the files without demanding ransom.
Recommendations on reducing risks of ransomware infection
Install a protection solution
Kaspersky applications with latest databases will block an attack and prevent a malware from being installed on your computer. Latest versions of Kaspersky applications feature a System Watcher component, which automatically creates backup copies of files if a suspicious program tries to access them.
Install updates
Keep your software, operating systems and Kaspersky applications updated, especially check patches that fix vulnerabilities on regular basis. The updated software operates on the most recent patch which narrows opportunities for attackers.
Updates are the main means for improving security, stability and performance of the systems, they remove vulnerabilities and prevent attackers from using those.
The software which is crucial to update:
- Operating system patches
- Browser plug-ins such as Flash, Silverlight, etc.
- VPN applications that provide access for remote employees and serve as a gateway to your network
Turn on all protection components of Kaspersky applications
All the components of Kaspersky applications are intended for maximum possible protection of devices and reducing the risks of ransomware infection. Ensure the following components are enabled:
- File Threat Protection
- Web Threat Protection
- Mail Threat Protection
- Behavior Detection
- Exploit Prevention
- AMSI Protection
- Remediation Engine
- Host Intrusion Prevention
- Kaspersky Security Network
Regularly back up your files to the cloud or an external drive
Backup and Restore is recommended to perform regularly. Even in case of a successful ransomware or file-encrypting attack, the backup data can be recovered what will reduce the harmful effects of the attack. To protect your files, create backup copies and store them in a cloud storage or a removable drive.
Do not open attachments in emails from unknown senders
Ransomware often spreads via email attachments. Cybercriminals aim to persuade you to open the attachment, which is why they title the emails as though they contained important information such as a court order, notice of intended prosecution, late fee notice or something similar. Always check the sender’s address before opening emails or attachments.
Use strong passwords for Windows accounts for remote connection
Weak passwords can be easily guessed or cracked, what may result in acquiring the access to sensitive data by attackers. To protect your personal data and your accounts from being hacked during remote connection, use strong passwords. For instructions, see this article.
If you are using a public network, attackers can use the Remote Desktop features for gaining access yo your devices. Connect to Remote Desktop over your home or corporate network only. For more information about the Remote Desktop features, see the Microsoft support website.
Protect shared folders
Attackers can use shared folders for file-encrypting, malware spreading and moving accross the network of your organization. Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows protects shared folders from encrypting and can help to set strong passwords.
Use Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KEDR) or Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response (MDR)
KEDR and MDR will detect and prevent an attack beforehand. Using these solutions, you can identify and monitor suspicious signals.
Protect administrator accounts
Make sure administrator accounts are protected by strong passwords that are changed regularly (for example, every 3 months). Use two-step verification if possible, to minimize the risks of attackers obtain control over the network in case they have managed to get access to user credentials.
Monitor suspicious activity
Regularly check event logs and operational data for suspicious activity. Monitor lateral movement around a network and pay attention to outbound traffic as an attacker usually needs connection to external networks or external tools for data theft.
Use caution when using PowerShell
The PowerShell solution is frequently used for attacks on Windows-devices. Ransomware and fileless threats also use PowerShell for attacks.
Limit execution of PowerShell scripts. Disable execution of the unassigned PowerShell scripts using politics. Enable execution of the PowerShell scripts only to the accounts which need it. Do not change the policy of restrictions of PowerShell (Set-ExecutionPolicy). On the devices protected by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, enable the Adaptive Anomaly Control component and switch the Activity of Script Engine and Frameworks rule into lock mode.
Configure policies
Configure the policies to minimize the amount of network information available to users whose accounts can be compromised. The network information should be limited as it can be retrieved by attackers from a breached device. Even if an attacker managed to compromise an account or a machine, the step outlined above will narrow further attacker opportunities and prevent the privilege-escalation of an administrator or other devices what will result in decreasing the scale of the attack.
Use IDS and IPS to detect and prevent network scans
The first step of an targeted attack is to collect information. Network scanning provides attackers with crucial information, such as open ports, active operating systems and software, and network device status. Preventing network scans will not let attackers gather the important information and will make attacks more difficult to implement.
Train your employees and promote their awareness
- Exercise caution with email attachments and check untrusted email addresses. Make sure the Mail Threat Protection component is enabled in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. The component scans and protects computers against malicious attachments.
- Be wary of strange links sent in emails or from other messaging platforms. Even if a link is sent by someone you know, they could have been hacked.
- Learn how to recognize malicious links and files, spot signs of suspicious activity on your devices and accounts, use strong passwords and two-step verification, regularly update the personal OS and software, log out your systems whenever they no longer require access.
Kaspersky offers a specialized cybersecurity course: Automated Security Awareness Platform. This platform provides knowledge and builds cyber-hygiene skills and practices.
Recommendations on configuring system settings
Create system restore points and back up your files
Regularly create system restore points and back up important files to a removable drive. This will allow you to restore the operating system to the uninfected state and quickly recover files in case of infection or system malfunction.
For more information about backup and restore features, see Microsoft support website.
Deny remote connection to your computer
To prevent cybercriminals from remotely connecting to your computer, disallow this type of connection in the computer settings:
- Open Search and enter "control panel". Select Control Panel.
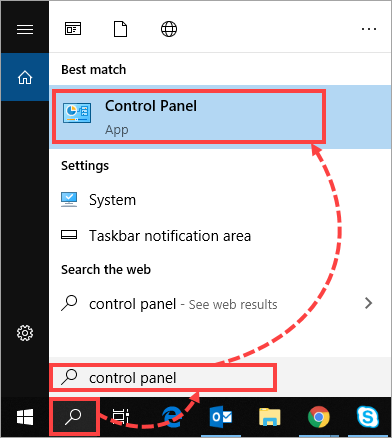
- Click System and Security and then select System.
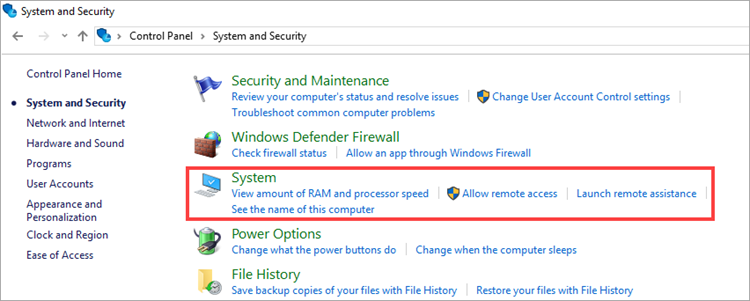
- Select System protection.
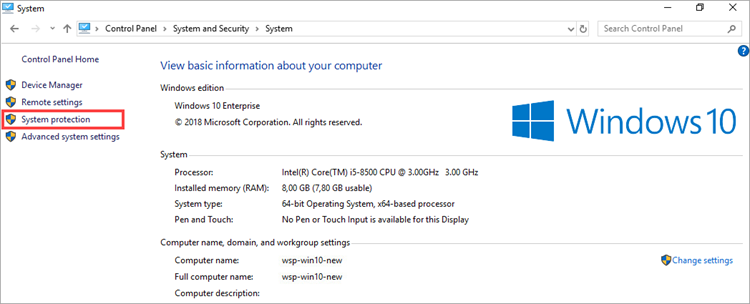
- Go to the Remote tab. Unselect the Allow Remote Assistance connections to this computer check box and select the Don't allow remote connections to this computer check box. Click OK.
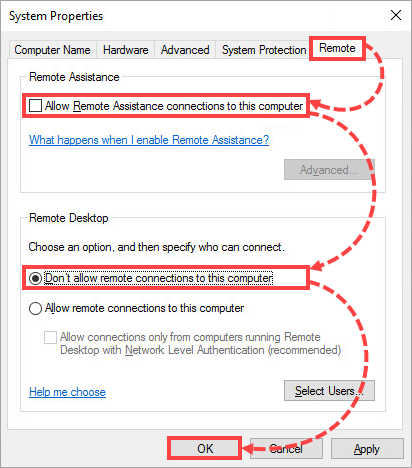
Remote access to your computer will be denied.
Recommendations on configuring Kaspersky applications
- Set a password for accessing the Kaspersky application settings. For instructions, see Online Help:
- Enable the System Watcher feature in the Kaspersky application.
This feature blocks and rolls back malicious actions, detects and removes banners and creates backup copies of files upon suspicious access attempts. For setup instructions, see Online Help:
Recommendations on decrypting files
Try to restore the files
You can restore files using default Windows tools. See the instructions on the Microsoft support website.
Disable the automatic deletion of detected malicious files
If you have a Kaspersky application installed, open the application settings and clear the Perform recommended actions automatically check box in the General section.
We do not recommend removing infected files from quarantine as they may contain keys for decryption.
Send suspicious files for analysis
Contact Kaspersky Customer Service. Attach an encrypted file or email message to your request.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, submit a request to Kaspersky Technical Support via Kaspersky CompanyAccount.
Kaspersky engineers cannot guarantee that the corrupted files will be decrypted.
Run a scan and remove malware from your computer
Run a full scan of your computer to find the cause of infection and eliminate it. If you don't have any protection solutions installed, use a free Kaspersky tool: Kaspersky Security Cloud Free, Kaspersky Rescue Disk or Kaspersky Virus Removal Tool.
What to do if there is a suspicious file on the computer
If you have discovered a suspicious file that might have infected your computer or encrypted your files, you can:
- Scan files for known threats at OpenTIP. If necessary, inform Kaspersky experts about a false detection or a new malicious software. To do so:
- Click Submit to reanalyze on the scan results page.
- Enter your email address so that we can contact you if necessary.
- >Click Send.
- Contact Kaspersky Customer Service. Attach the suspicious file to your request and write in the description section "possible ransomware (cryptoransomware)".
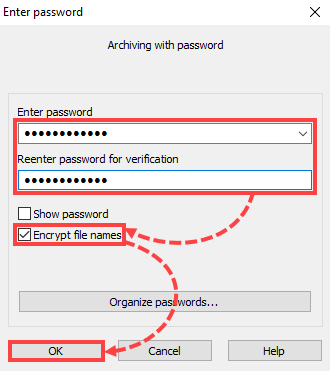
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, submit a request to Kaspersky Technical Support via Kaspersky CompanyAccount. - Send the files for analysis to newvirus@kaspersky.com. To do so, add the suspicious file to a ZIP or RAR archive. Set the word "infected" as a password for the archive and select the check box Encrypt file names. For instructions, see this article.
Possible ransomware file locations
- APPDATA
Windows NT/2000/XP — Drive:\Documents and Settings\%UserName%\Application Data\%USERPROFILE%\Local Settings\Application Data
Windows Vista/7/8/10 — Drive:\Users\%UserName%\AppData\Roaming\%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local
- TEMP (temporary catalog)
%TEMP%\xxxxxxx.tmp\, where x stands for a-z characters or 0-9 numerals
%TEMP%\xxxxxxx.tmp\xx\, where x stands for a-z characters or 0-9 numerals
%TEMP%\xxxxxxx\, where x stands for a-z characters or 0-9 numerals
%WINDIR%\Temp
- Internet Explorer temporary files folder
Windows NT/2000/XP — %USERPROFILE%\Local Settings\Temporary Internet Files\
Windows Vista/7/8/10 — %LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\Windows\Temporary Internet Files\content.ie5\xxxxxxxx, where x stands for a-z characters or 0-9 numerals
- Desktop
%UserProfile%\Desktop\
- Recycle bin
Disk:\Recycler\
Disk:\$Recycle.Bin\
Disk:\$Recycle.Bin\s-1-5-21-??????????-??????????-??????????-1000 (where ? stands for 0-9 numerals)
- System directory
%WinDir%
%SystemRoot%\system32\
- User's document folder
%USERPROFILE%\My Documents\
%USERPROFILE%\My Documents\Downloads
- Browser download folder
%USERPROFILE%\Downloads
- Startup folder
%USERPROFILE%\Start Menu\Programs\Startup