Incidents detected by a neural network element of an ML model
An ML model neural network element based on the Forecaster detector is trained on a specific subset of tags and can predict the current behavior of tags. In this case, an incident is any substantial discrepancy between the observed (actual) values of tags and the predicted values of tags resulting from operations of the ML model element. In the model element settings, you can view which tags are analyzed by the neural network (Input tags parameter) and which tags' behavior is predicted (Output tags parameter).
An ML model built based on the Forecaster detector consists of one or several ML model elements that operate in parallel. In the History and Monitoring sections, you can select a specific branch of the ML model to display the incidents registered as a result of a specific model element operation on the MSE graphs. Registered incidents are displayed as color-coded dot indicators in the lower part of the MSE graph.
The MSE graph also displays the predicted tag values and MSEs for the selected element of the ML model. MSE (mean square error) is an indicator of the difference between predicted values from actual values, calculated cumulatively for all tags included in the selected element of the ML model. The higher the MSE value, the more the behavior of tags will differ from the expected (normal) behavior. The MSE threshold is the critical MSE value that, when exceeded, causes the Forecaster detector to register an incident. The MSE threshold on an MSE graph is shown as an orange line.
The MSE graph is displayed in the lower part of the History section (see the figure below).
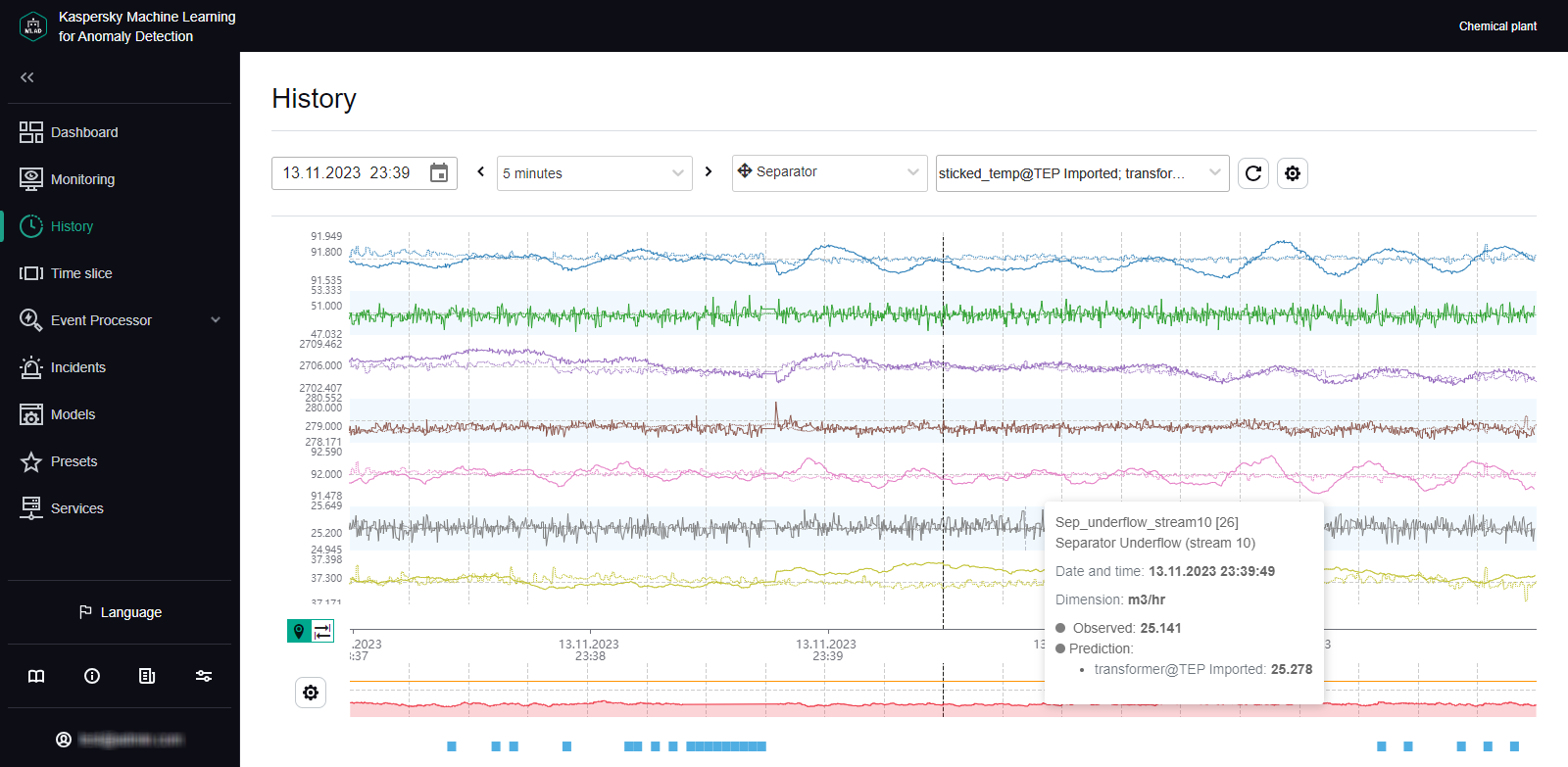
MSE graph in the History section
For each incident, the application automatically identifies the tags whose behavior had a stronger influence on incident registration. These tags are used to form the Tags for event #N preset, which is available for selection in the History section. Tags that are included in the Tags for event #N preset are sorted in descending order of their deviation from expected behavior. The first, most anomalous tag is also displayed in the incidents table in the Incidents section. The incidents table also indicates the MSE threshold and the actual MSE value at the moment when the incident was registered.
Information obtained when viewing the Tags for event #N preset is not actually diagnostic information for the purposes of identifying the causes of an incident, but you can still use this information when analyzing the values of tags with the largest deviations in behavior. The tag whose behavior was the first to deviate from the norm and caused subsequent deviations in other tags is referred to as the causal tag. In some cases, the causal tag may not be at the top of the list in the Tags for event #N preset and may even be entirely absent from this preset. This could happen due to the following reasons:
- Minor amplitude changes in the behavior of the causal tag had a multiplier effect and caused significant deviations in other tags that were included in the Tags for event #N preset.
- The causal tag is not analyzed by the ML model, and Kaspersky MLAD registers derivative changes in the behavior of tags caused by the deviation of the causal tag.
- Changes in the behavior of the causal tag had a delayed effect, and by the time an anomaly occurred in the operation of the monitored asset, the behavior of the causal tag returned to normal.
