Recovering data by using the FDERT Restore Utility
If the hard drive fails, the file system may be corrupt. If this is the case, data protected by Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology will be unavailable. You can decrypt the data and copy the data to a new drive.
Data recovery on a drive protected by Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology consists of the following steps:
- Create a stand-alone Restore Utility (see the figure below).
- Connect a drive to a computer that does not have Kaspersky Endpoint Security encryption components installed.
- Run the Restore Utility and diagnose the hard drive.
- Access data on the drive. To do so, enter the credentials of the Authentication Agent or start the recovery procedure (Request-Response).
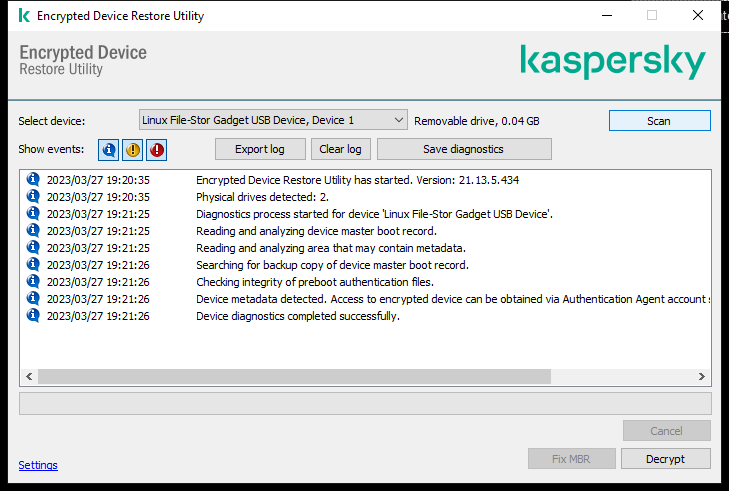
FDERT Restore Utility
Creating a standalone restore utility
To create the executable file of Restore Utility:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the window that opens, click the Restore encrypted device button.
Encrypted device Restore Utility starts.
- Click the Create Stand-alone Restore Utility button in the window of Restore Utility.
- Save the stand-alone Restore Utility to computer memory.
As a result, the executable file of the Restore Utility (fdert.exe) will be saved in the specified folder. Copy the Restore Utility to a computer that does not have Kaspersky Endpoint Security encryption components. This prevents the drive from being encrypted again.
The data needed to restore access to encrypted devices using the Restore Utility resides in the memory of the user's computer in unencrypted form for some time. To reduce the risk of unauthorized access to such data, you are advised to restore access to encrypted devices on trusted computers.
Recovering data on a hard drive
To restore access to an encrypted device using the Restore Utility:
- Run the file named fdert.exe, which is the executable file of the Restore Utility. This file is created by Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- In the Restore Utility window, select the encrypted device to which you want to restore access.
- Click the Scan button to allow the utility to define which of the actions should be taken on the device: whether it should be unlocked or decrypted.
If the computer has access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security encryption functionality, the Restore Utility prompts you to unlock the device. While unlocking the device does not decrypt it, the device becomes directly accessible as a result of being unlocked. If the computer does not have access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security encryption functionality, the Restore Utility prompts you to decrypt the device.
- If you want to import diagnostic information, click the Save diagnostics button.
The utility will save an archive with files containing diagnostic information.
- Click the Fix MBR button if diagnostics of the encrypted system hard drive has returned a message about problems involving the master boot record (MBR) of the device.
Fixing the master boot record of the device can speed up the process of obtaining information that is needed for unlocking or decrypting the device.
- Click the Unlock or Decrypt button depending on the results of diagnostics.
- If you want to restore data using an Authentication Agent account, select the Use Authentication Agent account settings option and enter the credentials of the Authentication Agent.
This method is possible only when restoring data on a system hard drive. If the system hard drive was corrupted and Authentication Agent account data has been lost, you must obtain an access key from the corporate LAN administrator to restore data on an encrypted device.
- If you want to start the recovery procedure, do the following:
- Select the Specify device access key manually option.
- Click the Receive access key button and save the request access file to computer memory (a file with the FDERTC extension).
- Send the request access file to the corporate LAN administrator.
Do not close the Receive device access key window until you have received the access key. When this window is opened again, you will not be able to apply the access key that was previously created by the administrator.
- Receive and save the access file (a file with the FDERTR extension) created and sent to you by the corporate LAN administrator (see the instructions below).
- Download the access file in the Receive device access key window.
- If you are decrypting a device, you must configure additional decryption settings:
- Specify area to decrypt:
- If you want to decrypt the entire device, select the Decrypt entire device option.
- If you want to decrypt a portion of the data on a device, select the Decrypt individual device areas option and specify the decryption area boundaries.
- Select the location for writing the decrypted data:
- If you want the data on the original device to be rewritten with the decrypted data, clear the Decrypt to a disk image file check box.
- If you want to save decrypted data separately from the original encrypted data, select the Decrypt to a disk image file check box and use the Browse button to specify the path where to save the VHD file.
- Specify area to decrypt:
- Click OK.
The device unlocking / decryption process starts.
How to create an encrypted data access file in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to create an encrypted data access file in the Web Console
Page top