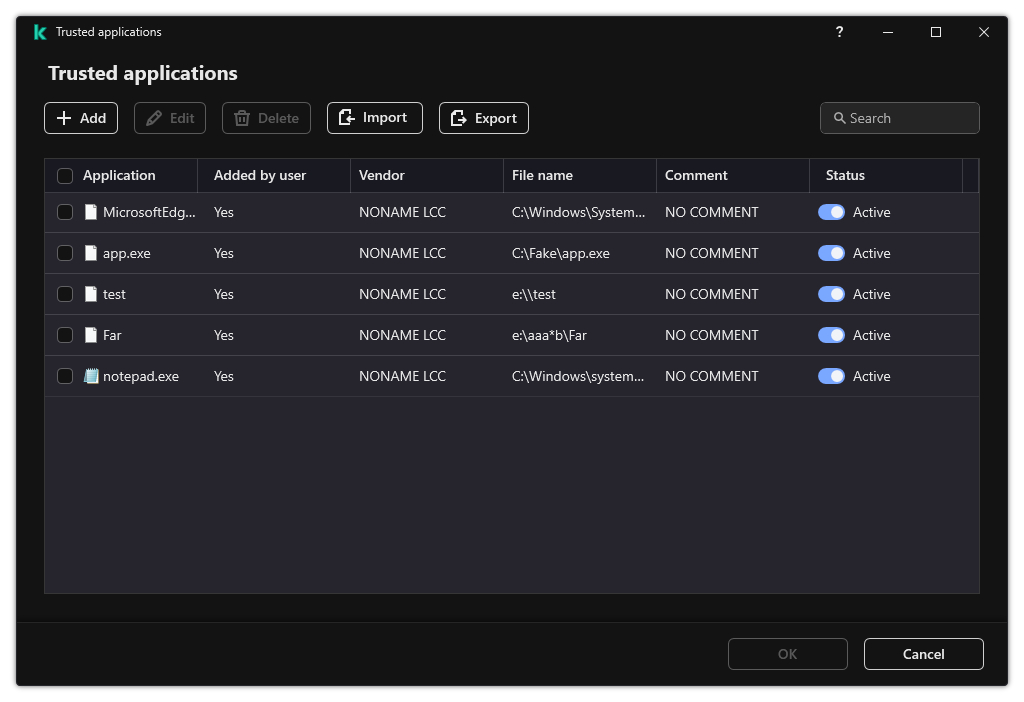
Contents
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Installing and removing the application
- Deployment through Kaspersky Security Center
- Installing the application locally using the Wizard
- Remotely installing the application using System Center Configuration Manager
- Description of setup.ini file installation settings
- Change application components
- Upgrading from a previous version of the application
- Remove the application
- Application licensing
- About the End User License Agreement
- About the license
- About the license certificate
- About subscription
- About license key
- About activation code
- About the key file
- Comparison of application functionality depending on license type for workstations
- Comparison of application functionality depending on license type for servers
- Activating the application
- Viewing license information
- Purchasing a license
- Renewing subscription
- Data provision
- Getting started
- About the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Management Plug-in
- Special considerations when working with different versions of management plug-ins
- Special considerations when using encrypted protocols for interacting with external services
- Application interface
- Getting started
- Managing policies
- Task management
- Configuring local application settings
- Starting and stopping Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Pausing and resuming computer protection and control
- Creating and using a configuration file
- Restoring the default application settings
- Malware Scan
- Updating databases and application software modules
- Database and application module update scenarios
- Starting and stopping an update task
- Starting an update task under the rights of a different user account
- Selecting the update task run mode
- Adding an update source
- Configuring updates from a shared folder
- Updating application modules
- Using a proxy server for updates
- Last update rollback
- Working with active threats
- Computer protection
- File Threat Protection
- Enabling and disabling File Threat Protection
- Automatic pausing of File Threat Protection
- Changing the action taken on infected files by the File Threat Protection component
- Forming the protection scope of the File Threat Protection component
- Using scan methods
- Using scan technologies in the operation of the File Threat Protection component
- Optimizing file scanning
- Scanning compound files
- Changing the scan mode
- Web Threat Protection
- Mail Threat Protection
- Enabling and disabling Mail Threat Protection
- Changing the action to take on infected email messages
- Forming the protection scope of the Mail Threat Protection component
- Scanning compound files attached to email messages
- Email messages attachment filtering
- Exporting and importing extensions for attachment filtering
- Scanning emails in Microsoft Office Outlook
- Network Threat Protection
- Firewall
- BadUSB Attack Prevention
- AMSI Protection
- Exploit Prevention
- Behavior Detection
- Enabling and disabling Behavior Detection
- Selecting the action to take on detecting malware activity
- Protection of shared folders against external encryption
- Enabling and disabling protection of shared folders against external encryption
- Selecting the action to take on detection of external encryption of shared folders
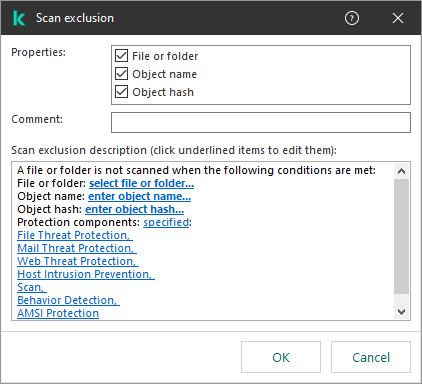
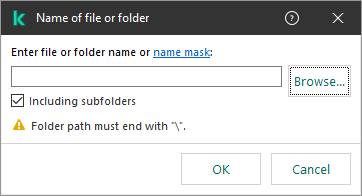
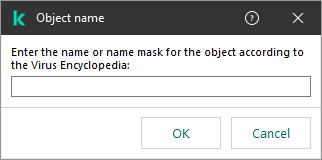
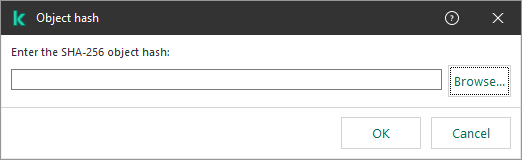
- Creating an exclusion for protection of shared folders against external encryption
- Configuring addresses of exclusions from protection of shared folders against external encryption
- Exporting and importing a list of exclusions from protection of shared folders against external encryption
- Host Intrusion Prevention
- Remediation Engine
- Kaspersky Security Network
- Encrypted connections scan
- Wipe Data
- File Threat Protection
- Computer control
- Web Control
- Device Control
- Enabling and disabling Device Control
- About access rules
- Editing a device access rule
- Editing a connection bus access rule
- Managing access to mobile devices
- Control of printing
- Control of Wi-Fi connections
- Monitoring usage of removable drives
- Changing the caching duration
- Actions with trusted devices
- Obtaining access to a blocked device
- Editing templates of Device Control messages
- Anti-Bridging
- Adaptive Anomaly Control
- Enabling and disabling Adaptive Anomaly Control
- Enabling and disabling an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule
- Modifying the action taken when an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule is triggered
- Creating an exclusion for an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule
- Exporting and importing exclusions for Adaptive Anomaly Control rules
- Applying updates for Adaptive Anomaly Control rules
- Editing Adaptive Anomaly Control message templates
- Viewing Adaptive Anomaly Control reports
- Application Control
- Application Control functionality limitations
- Receiving information about the applications that are installed on users' computers
- Enabling and disabling Application Control
- Selecting the Application Control mode
- Managing Application Control rules
- Adding a trigger condition for the Application Control rule
- Adding executable files from the Executable files folder to the application category
- Adding event-related executable files to the application category
- Adding an Application Control rule
- Changing the status of an Application Control rule via Kaspersky Security Center
- Exporting and importing Application Control rules
- Viewing events resulting from operation of the Application Control component
- Viewing a report on blocked applications
- Testing Application Control rules
- Application activity monitor
- Rules for creating name masks for files or folders
- Editing Application Control message templates
- Best practices for implementing a list of allowed applications
- Network ports monitoring
- Log Inspection
- File Integrity Monitor
- Password protection
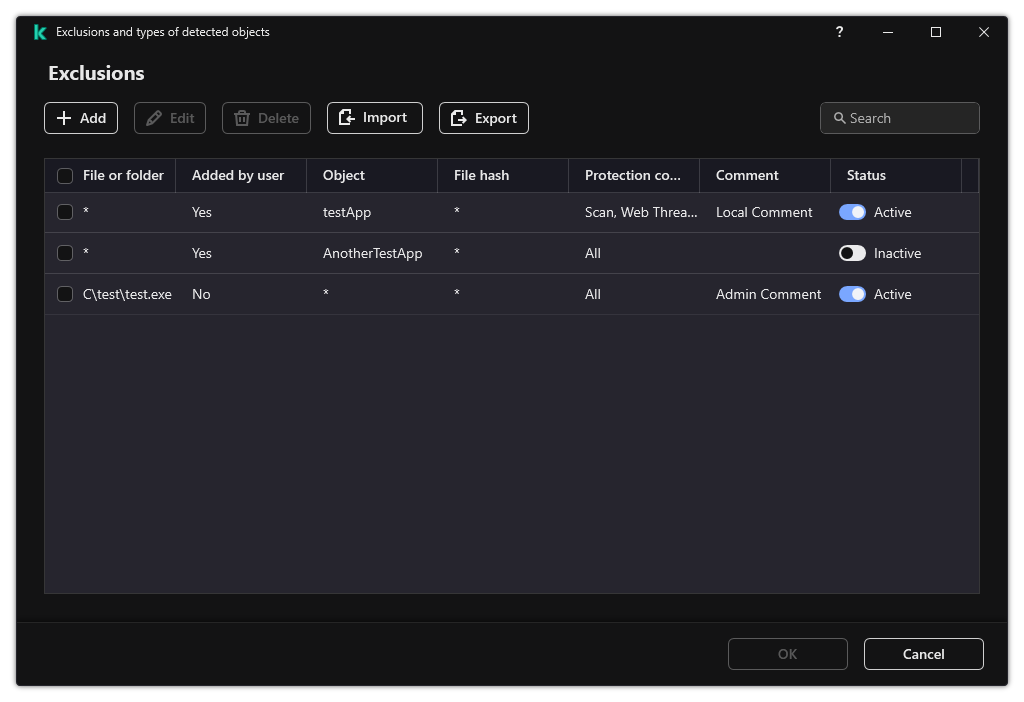
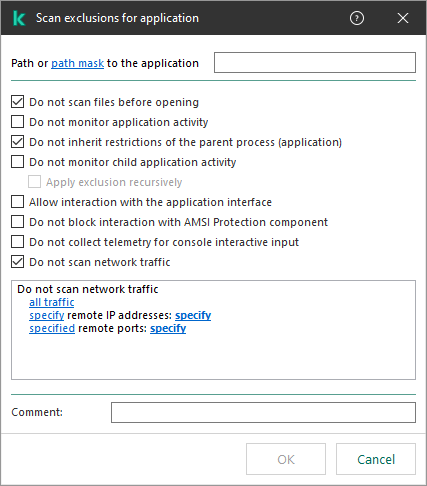
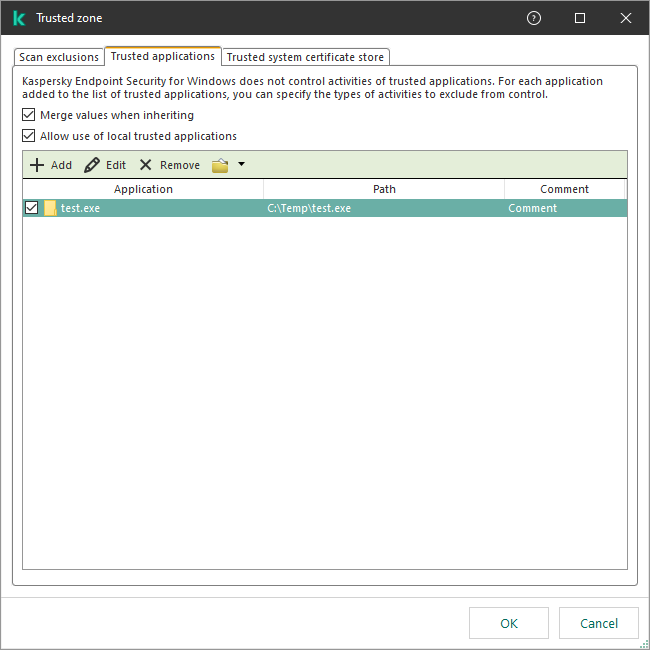
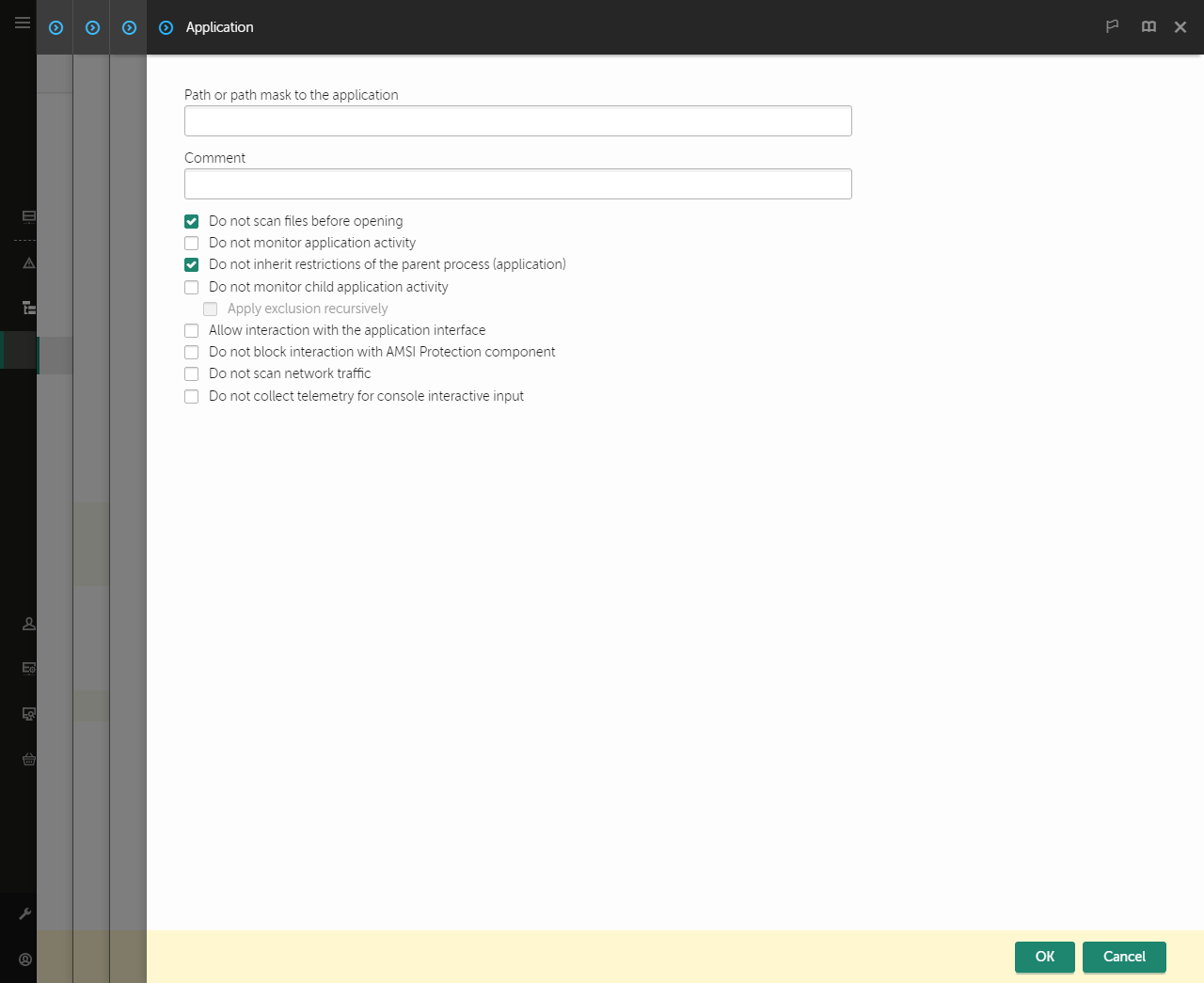
- Trusted zone
- Managing Backup
- Notification service
- Managing reports
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security Self-Defense
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security performance and compatibility with other applications
- Data Encryption
- Encryption functionality limitations
- Changing the length of the encryption key (AES56 / AES256)
- Kaspersky Disk Encryption
- Special features of SSD drive encryption
- Starting Kaspersky Disk Encryption
- Creating a list of hard drives excluded from encryption
- Exporting and importing a list of hard drives excluded from encryption
- Enabling Single Sign-On (SSO) technology
- Managing Authentication Agent accounts
- Using a token and smart card with Authentication Agent
- Hard drive decryption
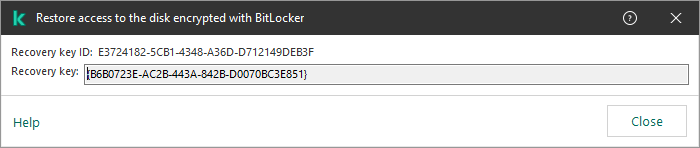
- Restoring access to a drive protected by Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology
- Signing in with the Authentication Agent service account
- Updating the operating system
- Eliminating errors of encryption functionality update
- Selecting the Authentication Agent tracing level
- Editing Authentication Agent help texts
- Removing leftover objects and data after testing the operation of Authentication Agent
- BitLocker Management
- File Level Encryption on local computer drives
- Encrypting files on local computer drives
- Forming encrypted file access rules for applications
- Encrypting files that are created or modified by specific applications
- Generating a decryption rule
- Decrypting files on local computer drives
- Creating encrypted packages
- Restoring access to encrypted files
- Restoring access to encrypted data after operating system failure
- Editing templates of encrypted file access messages
- Encryption of removable drives
- Viewing data encryption details
- Working with encrypted devices when there is no access to them
- Detection and Response solutions
- KSWS to KES Migration Guide
- Correspondence of KSWS and KES components
- Correspondence of KSWS and KES settings
- Migrating KSWS components
- Migrating KSWS tasks and policies
- Installing KES instead of KSWS
- Migrating the [KSWS+KEA] configuration to [KES+built-in agent] configuration
- Making sure Kaspersky Security for Windows Server was successfully removed
- Activating KES with a KSWS key
- Special considerations for migrating high-load servers
- Example of migration from [KSWS+KEA] to KES
- Managing the application on a Core Mode server
- Managing the application from the command line
- Installing the application
- Activating the application
- Remove the application
- AVP commands
- SCAN. Malware Scan
- UPDATE. Updating databases and application software modules
- ROLLBACK. Last update rollback
- TRACES. Tracing
- START. Start the profile
- STOP. Stopping a profile
- STATUS. Profile status
- STATISTICS. Profile operation statistics
- RESTORE. Restoring files from Backup
- EXPORT. Exporting application settings
- IMPORT. Importing application settings
- ADDKEY. Applying a key file
- LICENSE. Licensing
- RENEW. Purchasing a license
- PBATESTRESET. Reset the disk check results before encrypting the disk
- EXIT. Exit the application
- EXITPOLICY. Disabling policy
- STARTPOLICY. Enabling policy
- DISABLE. Disabling protection
- SPYWARE. Spyware detection
- KSN. Switching between KSN / KPSN
- KESCLI commands
- Scan. Malware Scan
- GetScanState. Scan completion status
- GetLastScanTime. Determining the scan completion time
- GetThreats. Obtaining data on detected threats
- UpdateDefinitions. Updating databases and application software modules
- GetDefinitionState. Determining the update completion time
- EnableRTP. Enabling protection
- GetRealTimeProtectionState. File Threat Protection status
- Version. Identifying the application version
- Detection and Response management commands
- Error codes
- Appendix. Application profiles
- Managing the application through the REST API
- Sources of information about the application
- Contacting Technical Support
- Limitations and warnings
- Glossary
- Active key
- Additional key
- Administration group
- Anti-virus databases
- Archive
- Authentication Agent
- Certificate issuer
- Database of malicious web addresses
- Database of phishing web addresses
- Disinfection
- False alarm
- Infectable file
- Infected file
- IOC
- IOC file
- License certificate
- Mask
- Network Agent
- Normalized form of the address of a web resource
- OLE object
- OpenIOC
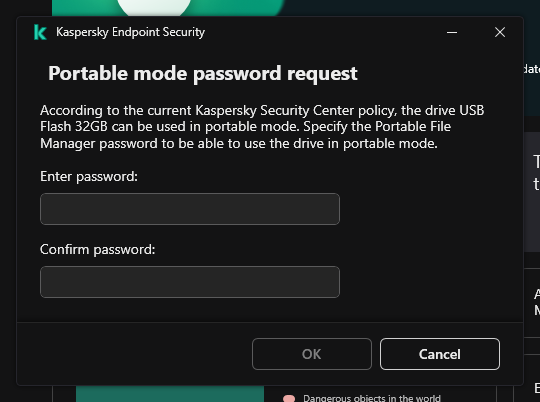
- Portable File Manager
- Protection scope
- Scan scope
- Task
- Trusted Platform Module
- Appendices
- Appendix 1. Application settings
- File Threat Protection
- Web Threat Protection
- Mail Threat Protection
- Network Threat Protection
- Firewall
- BadUSB Attack Prevention
- AMSI Protection
- Exploit Prevention
- Behavior Detection
- Host Intrusion Prevention
- Remediation Engine
- Kaspersky Security Network
- Log Inspection
- Web Control
- Device Control
- Application Control
- Adaptive Anomaly Control
- File Integrity Monitor
- Endpoint Sensor
- Kaspersky Sandbox
- Endpoint Detection and Response
- Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA)
- Full Disk Encryption
- File Level Encryption
- Encryption of removable drives
- Templates (data encryption)
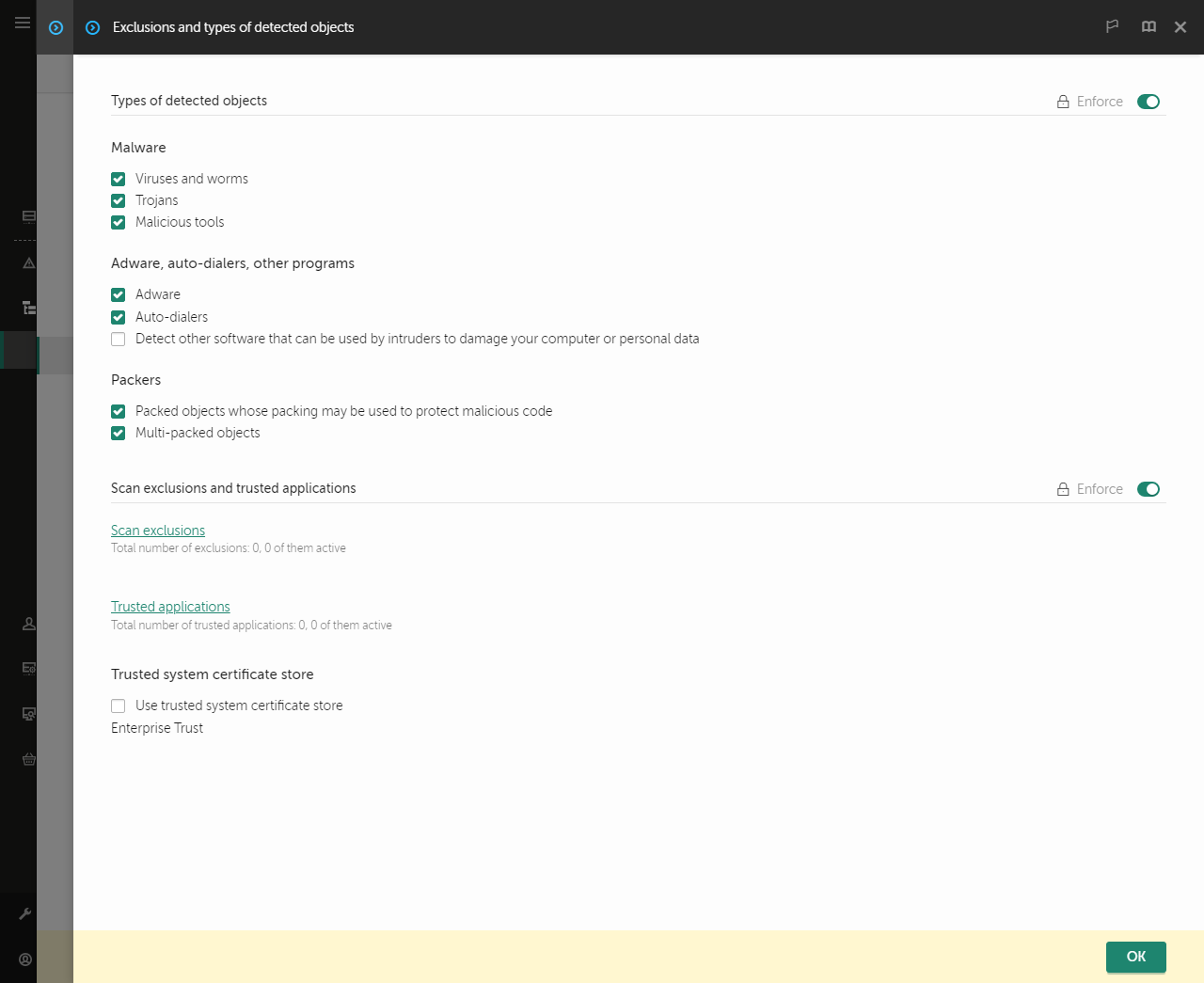
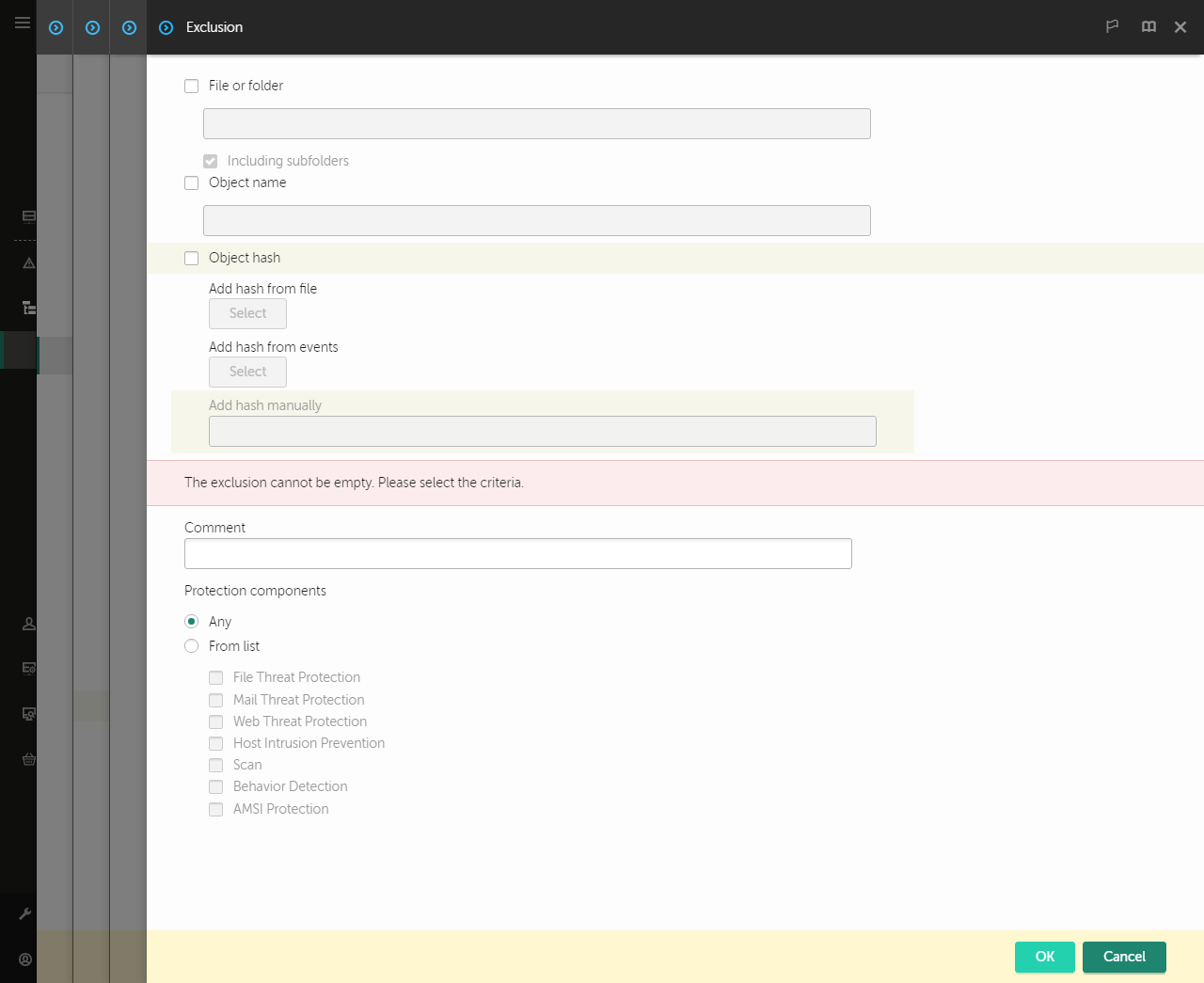
- Exclusions
- Application settings
- Reports and storage
- Network settings
- Interface
- Manage Settings
- Updating databases and application software modules
- Appendix 2. Application trust groups
- Appendix 3. File extensions for quick removable drives scan
- Appendix 4. File Types for the Mail Threat Protection attachment filter
- Appendix 5. Network settings for interaction with external services
- Appendix 6. Application events
- Appendix 7. Supported file extensions for Execution prevention
- Appendix 8. Supported script interpreters for Execution prevention
- Appendix 9. IOC scan scope in the registry (RegistryItem)
- Appendix 10. IOC file requirements
- Appendix 1. Application settings
- Information about third-party code
- Trademark notices
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help
 What's new in version 12.1
What's new in version 12.1
- Added a built-in agent for managing the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response component that is part of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform solution. You no longer need Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in order to use EDR (KATA). Kaspersky Endpoint Security can perform all Kaspersky Endpoint Agent functions.
- What's new in each version of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
 Getting started
Getting started
- Deployment of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Initial setup of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Licensing of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
 Eliminating threats
Eliminating threats
- On workstations
- On servers
- Reacting to detection of an Indicator of Compromise (Network isolation → Quarantine → Execution prevention)
 Using KES as part of other solutions
Using KES as part of other solutions
 Data provision
Data provision
What's new
Update 12.1
Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.1 for Windows offers the following features and improvements:
- A built-in agent for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform solution has been added. You no longer need Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in order to use EDR (KATA). All functions of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent will be performed by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. To migrate Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policies, use the Migration Wizard. After updating the application, Kaspersky Endpoint Security switches to using the built-in agent and removes Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. Kaspersky Endpoint Agent has been added to the list of incompatible software. Kaspersky Endpoint Security has built-in agents for all Detection and Response solutions, therefore installing Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to integrate with those solutions is no longer necessary.
- Azure WVD compatibility mode is now supported. This feature allows correctly displaying the state of the Azure virtual machine in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform console. Azure WVD compatibility mode allows assigning a permanent unique Sensor ID to these virtual machines.
- Now you can configure user access to mobile devices in iTunes or similar applications. That is, you can, for example, allow the mobile device to be used only in iTunes and block using the mobile device as a removable drive. The application also supports these rules for the Android Debug Bridge (ADB) application.
- Kaspersky Security Center version 11 is no longer supported. Upgrade Kaspersky Security Center to the latest version.
Update 12.0
Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.0 for Windows offers the following features and improvements:
- The operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security on servers has been improved. Now you can migrate from Kaspersky Security for Windows Server to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows and use a single solution to protect workstations and servers. To migrate the application settings, run the Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard. The KSWS license key can be used to activate KES. After migrating to KES, you do not even need to restart the server. For more information about migrating to KES, see Migration Guide.
- The licensing of the application as part of a paid virtual machine image in Amazon Machine Image (AMI) has been improved. There is no need to activate the application separately. In this case, Kaspersky Security Center uses the license key for the cloud environment that is already added to the application.
- Device Control is improved:
- For portable devices (MTP), you can configure access rules (read/write), select users or a user group that have access to devices, or configure a device access schedule. Now you can create access rules for portable devices in the same way as for removable drives.
- Now you can configure user access to mobile devices in Android Debug Bridge (ADB) or similar applications. That is, you can, for example, allow the mobile device to be used only in ADB and block using the mobile device as a removable drive.
- Now you can recharge a mobile device by connecting it to the computer's USB port even if access to the mobile device is blocked.
- For printers, you can now configure printing permissions for users. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports control over access to local and network printers. Now you can allow or block printing on local or network printers for individual users.
- WPA3 protocol support has been added to control connections to Wi-Fi networks. Now you can select to use WPA3 protocol in the trusted Wi-Fi network settings and deny connection to the network using a less secure protocol.
Update 11.11.0
Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.11.0 for Windows offers the following features and improvements:
- Log Inspection component for servers has been added. Log Inspection monitors the integrity of the protected environment based on the results of Windows event log analysis. When the application detects signs of atypical behavior in the system, it informs the administrator, as this behavior may indicate an attempted cyber attack.
- File Integrity Monitor component for servers has been added. File Integrity Monitor detects changes to objects (files and folders) in a given monitoring area. These changes may indicate a computer security breach. When object changes are detected, the application informs the administrator.
- The alert details interface for Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum (EDR Optimum) has been improved. The elements of the threat development chain have been aligned, the links between the processes in the chain no longer overlap. This makes it easier to analyze the evolution of the threat.
- Application performance has been improved. For this purpose, network traffic processing by the Network Threat Protection component has been optimized.
- The option to upgrade Kaspersky Endpoint Security without a restart has been added. This lets you ensure uninterrupted operation of servers when upgrading the application. You can upgrade the application without a restart starting with version 11.10.0. You can also install patches without a restart starting with version 11.11.0.
- The Virus Scan task has been renamed in the Kaspersky Security Center Console. This task is now called Malware Scan.
Frequently asked questions
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (hereinafter also referred to as Kaspersky Endpoint Security) provides comprehensive computer protection against various types of threats, network and phishing attacks.
The application is not intended to be used in technological processes that involve automated control systems. To protect devices in such systems, it is recommended to use Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Nodes application.
Updates functionality (including providing anti-virus signature updates and codebase updates), as well as KSN functionality will not be available in the software in the U.S. territory from 12:00 AM Eastern Daylight Time (EDT) on September 10, 2024 in accordance with the restrictive measures.
Threat detection technologies
Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses a model based on machine learning. The model is developed by Kaspersky experts. Subsequently, the model is continuously fed with threat data from KSN (model training).
Kaspersky Endpoint Security receives threat data from the Kaspersky Security Network. Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is an infrastructure of cloud services providing access to the online Kaspersky Knowledge Base that contains information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses threat data added by Kaspersky virus analysts. Virus analysts evaluate objects if the reputation of an object cannot be determined automatically. |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the activity of an object in real time.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security receives data from the automatic object analysis system. The system processes all objects that are sent to Kaspersky. The system then determines the reputation of the object and adds the data to anti-virus databases. If the system cannot determine the reputation of the object, the system queries Kaspersky virus analysts.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security processes the object in a virtual machine. Kaspersky Sandbox analyzes the behavior of the object and decides on its reputation. This technology is available only if you are using the Kaspersky Sandbox solution.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans objects in an isolated environment provided by Kaspersky. Cloud Sandbox technology is permanently enabled and is available to all Kaspersky Security Network users regardless of the type of license they are using. If you have already deployed Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum, you can enable a separate counter for threats detected by Cloud Sandbox. |
Selection tree
Each type of threat is handled by a dedicated component. Components can be enabled or disabled independently, and their settings can be configured.
Selection tree
Section |
Component |
|---|---|
Essential Threat Protection
|
File Threat Protection The File Threat Protection component lets you prevent infection of the file system of the computer. By default, the File Threat Protection component permanently resides in the computer's RAM. The component scans files on all drives of the computer, as well as on connected drives. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and heuristic analysis. Web Threat Protection The Web Threat Protection component prevents downloads of malicious files from the Internet, and also blocks malicious and phishing websites. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and heuristic analysis. Mail Threat Protection The Mail Threat Protection component scans the attachments of incoming and outgoing email messages for viruses and other threats. By default, the Mail Threat Protection component permanently resides in the computer's RAM and scans all messages received or sent using the POP3, SMTP, IMAP, or NNTP protocols, or the Microsoft Office Outlook mail client (MAPI). The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and heuristic analysis. Network Threat Protection The Network Threat Protection component (also called Intrusion Detection System) monitors inbound network traffic for activity characteristic of network attacks. When Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects an attempted network attack on the user's computer, it blocks the network connection with the attacking computer. Descriptions of currently known types of network attacks and ways to counteract them are provided in Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases. The list of network attacks that the Network Threat Protection component detects is updated during database and application module updates. Firewall The Firewall blocks unauthorized connections to the computer while working on the Internet or local network. The Firewall also controls the network activity of applications on the computer. This allows you to protect your corporate LAN from identity theft and other attacks. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and predefined network rules. BadUSB Attack Prevention The BadUSB Attack Prevention component prevents infected USB devices emulating a keyboard from connecting to the computer. AMSI Protection AMSI Protection component is intended to support Antimalware Scan Interface from Microsoft. The Antimalware Scan Interface (AMSI) allows third-party applications with AMSI support to send objects (for example, PowerShell scripts) to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for an additional scan and then receive the results from scanning these objects. |
Advanced Threat Protection
|
Kaspersky Security Network Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is an infrastructure of cloud services providing access to the online Kaspersky Knowledge Base that contains information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software. The use of data from Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky Endpoint Security to new threats, improves the performance of some protection components, and reduces the likelihood of false positives. If you are participating in Kaspersky Security Network, KSN services provide Kaspersky Endpoint Security with information about the category and reputation of scanned files, as well as information about the reputation of scanned web addresses. Behavior Detection The Behavior Detection component receives data on the actions of applications on your computer and provides this information to other protection components to improve their performance. The Behavior Detection component utilizes Behavior Stream Signatures (BSS) for applications. If application activity matches a behavior stream signature, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the selected responsive action. Kaspersky Endpoint Security functionality based on behavior stream signatures provides proactive defense for the computer. Exploit Prevention The Exploit Prevention component detects program code that takes advantage of vulnerabilities on the computer to exploit administrator privileges or to perform malicious activities. For example, exploits can utilize a buffer overflow attack. To do so, the exploit sends a large amount of data to a vulnerable application. When processing this data, the vulnerable application executes malicious code. As a result of this attack, the exploit can start an unauthorized installation of malware. When there is an attempt to run an executable file from a vulnerable application that was not performed by the user, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks this file from running or notifies the user. Host Intrusion Prevention The Host Intrusion Prevention component prevents applications from performing actions that may be dangerous for the operating system, and ensures control over access to operating system resources and personal data. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases and the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service. Remediation Engine The Remediation Engine lets Kaspersky Endpoint Security roll back actions that have been performed by malware in the operating system. |
Security Controls
|
Application Control Application Control manages the startup of applications on users' computers. This allows you to implement a corporate security policy when using applications. Application Control also reduces the risk of computer infection by restricting access to applications. Device Control Device Control manages user access to devices that are installed on or connected to the computer (for example, hard drives, cameras, or Wi-Fi modules). This lets you protect the computer from infection when such devices are connected, and prevent loss or leaks of data. Web Control Web Control manages users' access to web resources. This helps reduce traffic and inappropriate use of work time. When a user tries to open a website that is restricted by Web Control, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks access or shows a warning. Adaptive Anomaly Control The Adaptive Anomaly Control component monitors and blocks actions that are not typical of the computers in a company's network. Adaptive Anomaly Control uses a set of rules to track non-typical behavior (for example, the Start of Microsoft PowerShell from office application rule). Rules are created by Kaspersky specialists based on typical scenarios of malicious activity. You can configure how Adaptive Anomaly Control handles each rule and, for example, allow the execution of PowerShell scripts that automate certain workflow tasks. Kaspersky Endpoint Security updates the set of rules along with the application databases. Log Inspection Log Inspection monitors the integrity of the protected environment based on the results of Windows event log analysis. When the application detects signs of atypical behavior in the system, it informs the administrator, as this behavior may indicate an attempted cyber attack. File Integrity Monitor File Integrity Monitor detects changes to objects (files and folders) in a given monitoring area. These changes may indicate a computer security breach. When object changes are detected, the application informs the administrator. |
Tasks
|
Malware Scan Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the computer for viruses and other threats. Malware Scan helps to rule out the possibility of spreading malware that was not detected by protection components, for example, due to a low security level. Update Kaspersky Endpoint Security downloads updated databases and application modules. Updating keeps the computer protected against the latest viruses and other threats. The application is updated automatically by default, but if necessary, you can update the databases and application modules manually. Last update rollback Kaspersky Endpoint Security rolls back the last update of databases and modules. This lets you roll back the databases and application modules to their previous versions when necessary, for example, when the new database version contains an invalid signature that causes Kaspersky Endpoint Security to block a safe application. Integrity check Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks the application modules in the application installation folder for corruption or modifications. If an application module has an incorrect digital signature, the module is considered corrupt. |
Data Encryption
|
File Level Encryption The component allows creating file encryption rules. You can select predefined folders for encryption, select a folder manually, or select individual files by extension. Full Disk Encryption The component allows encrypting the hard disk using Kaspersky Disk Encryption or BitLocker Drive Encryption. Encryption of removable drives The component allows protecting data on removable drives. You can use Full Disk Encryption (FDE) or File Level Encryption (FLE). |
Detection and Response
|
Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Built-in agent for the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum solution (hereinafter also "EDR Optimum"). Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response is a solution for protecting the corporate IT infrastructure from advanced cyber threats. The functionality of the solution combines automatic detection of threats with the ability to react to these threats to counteract advanced attacks including new exploits, ransomware, fileless attacks, as well as methods using legitimate system tools. For more information about the solution, refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help. Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Built-in agent for the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert solution (hereinafter also "EDR Expert"). EDR Expert offers more threat monitoring and response functionality than EDR Optimum. For more information about the solution, refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help. Kaspersky Sandbox Built-in agent for the Kaspersky Sandbox solution. The Kaspersky Sandbox solution detects and automatically blocks advanced threats on computers. Kaspersky Sandbox analyzes object behavior to detect malicious activity and activity characteristic of targeted attacks on the IT infrastructure of the organization. Kaspersky Sandbox analyzes and scans objects on special servers with deployed virtual images of Microsoft Windows operating systems (Kaspersky Sandbox servers). For details about the solution, refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox Help. Managed Detection and Response Built-in agent to support the operation of the Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response solution. The Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response (MDR) solution automatically detects and analyzes security incidents in your infrastructure. To do so, MDR uses telemetry data received from endpoints and machine learning. MDR sends incident data to Kaspersky experts. The experts can then process the incident and, for example, add a new entry to Anti-Virus databases. Alternatively, the experts can issue recommendations on processing the incident and, for example, suggest isolating computer from the network. For detailed information about how the solution works, please refer to the Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response Help. |
Distribution kit
The distribution kit includes the following distribution packages:
- Strong encryption (AES256)
This distribution package contains cryptographic tools that implement the AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) encryption algorithm with an effective key length of 256 bits.
- Lite encryption (AES56)
This distribution package contains cryptographic tools that implement the AES encryption algorithm with an effective key length of 56 bits.
Each distribution package contains the following files:
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security installation package. |
|
Files that are required for installing the application using any of the available methods. |
|
File for creating installation packages for Kaspersky Endpoint Security. |
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security Management Plug-in installation package for Kaspersky Security Center. |
|
Update package files that are used during installation. |
|
Files for removing incompatible software. |
|
File that contains a list of incompatible software. |
|
File where you can read through the terms of participation in Kaspersky Security Network. |
|
File where you can read through the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy. |
|
File that contains the internal settings of the distribution kit. |
|
Archive containing the files required for installing the Kaspersky Endpoint Security web plug-in. |
It is not recommended to change the values of these settings. If you want to change installation options, use the setup.ini file.
Page top
Hardware and software requirements
To ensure proper operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, your computer must meet the following requirements:
Minimum general requirements:
- 2 GB of free disk space on the hard drive;
- CPU:
- Workstation: 1 GHz;
- Server: 1.4 GHz;
- Support for the SSE2 instruction set.
- RAM:
- Workstation (x86): 1 GB;
- Workstation (x64): 2 GB;
- Server: 2 GB.
Workstations
Supported operating systems for workstations:
- Windows 7 Home / Professional / Ultimate / Enterprise Service Pack 1 or later;
- Windows 8 Professional / Enterprise;
- Windows 8.1 Professional / Enterprise;
- Windows 10 Home / Pro / Pro for Workstations / Education / Enterprise / Enterprise multi-session;
- Windows 11 Home / Pro / Pro for Workstations / Education / Enterprise.
For details about support for the Microsoft Windows 10 operating system, please refer to the Technical Support Knowledge Base.
For details about support for the Microsoft Windows 11 operating system, please refer to the Technical Support Knowledge Base.
Servers
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports core components of the application on computers running the Windows operating system for servers. You can use Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows instead of Kaspersky Security for Windows Server on servers and clusters of your organization (Cluster Mode). The application also supports Core Mode (see known issues).
Supported operating systems for servers:
- Windows Small Business Server 2011 Essentials / Standard (64-bit);
Microsoft Small Business Server 2011 Standard (64-bit) is supported only if Service Pack 1 for Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 is installed.
- Windows MultiPoint Server 2011 (64-bit);
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation / Standard / Enterprise / Datacenter Service Pack 1 or later;
- Windows Web Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 or later;
- Windows Server 2012 Foundation / Essentials / Standard / Datacenter (including Core Mode);
- Windows Server 2012 R2 Foundation / Essentials / Standard / Datacenter (including Core Mode);
- Windows Server 2016 Essentials / Standard / Datacenter (including Core Mode);
- Windows Server 2019 Essentials / Standard / Datacenter (including Core Mode);
- Windows Server 2022 Standard / Datacenter / Datacenter: Azure Edition (including Core Mode).
For details about support for the Microsoft Windows Server 2016 and Microsoft Windows Server 2019 operating systems, please refer to the Technical Support Knowledge Base.
For details about support for the Microsoft Windows Server 2022 operating system, please refer to the Technical Support Knowledge Base.
Unsupported operating systems for servers:
- Windows Server 2003 Standard / Enterprise / Datacenter SP2 or later;
- Windows Server 2003 R2 Foundation / Standard / Enterprise / Datacenter SP2 or later;
- Windows Server 2008 Standard / Enterprise / Datacenter SP2 or later;
- Windows Server 2008 Core Standard / Enterprise / Datacenter SP2 or later;
- Microsoft Small Business Server 2008 Standard / Premium SP2 or later.
Virtual platforms
Supported virtual platforms:
- VMware Workstation 17.0 Pro;
- VMware ESXi 8.0a;
- Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2019;
- Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops 7 2212;
- Citrix Provisioning 2212;
- Citrix Hypervisor 8.2 (Cumulative Update 1).
Terminal servers
Supported terminal server types:
- Microsoft Remote Desktop Services based on Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1;
- Microsoft Remote Desktop Services based on Windows Server 2012;
- Microsoft Remote Desktop Services based on Windows Server 2012 R2;
- Microsoft Remote Desktop Services based on Windows Server 2016;
- Microsoft Remote Desktop Services based on Windows Server 2019;
- Microsoft Remote Desktop Services based on Windows Server 2022.
Kaspersky Security Center support
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports operation with the following versions of Kaspersky Security Center:
- Kaspersky Security Center 12
- Kaspersky Security Center 13
- Kaspersky Security Center 13.1
- Kaspersky Security Center 13.2
- Kaspersky Security Center 13.2.2
- Kaspersky Security Center 14
- Kaspersky Security Center 14.1
- Kaspersky Security Center 14.2
- Kaspersky Security Center Linux 14.2
- Kaspersky Security Center Linux 15
- Kaspersky Security Center Linux 15.1
Comparison of available application features depending on the type of operating system
The set of available Kaspersky Endpoint Security features depends on the type of operating system: workstation or server (see the table below).
Comparison of Kaspersky Endpoint Security features
Feature |
Workstation |
Server |
|---|---|---|
Advanced Threat Protection |
|
|
Kaspersky Security Network |
|
|
Behavior Detection |
|
|
Exploit Prevention |
|
|
Host Intrusion Prevention |
|
– |
Remediation Engine |
|
|
Essential Threat Protection |
|
|
File Threat Protection |
|
|
Web Threat Protection |
|
|
Mail Threat Protection |
|
|
Firewall |
|
|
Network Threat Protection |
|
|
BadUSB Attack Prevention |
|
|
AMSI Protection |
|
|
Security Controls |
|
|
Log Inspection |
– |
|
Application Control |
|
|
Device Control |
|
|
Web Control |
|
|
Adaptive Anomaly Control |
|
– |
File Integrity Monitor |
– |
|
Data Encryption |
|
|
Kaspersky Disk Encryption |
|
– |
BitLocker Drive Encryption |
|
|
File Level Encryption |
|
– |
Encryption of removable drives |
|
– |
Detection and Response |
|
|
Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum |
|
|
Endpoint Detection and Response Expert |
|
|
Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) |
|
|
Kaspersky Sandbox |
|
|
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) |
|
|
Comparison of application functions depending on the management tools
The set of functions available in Kaspersky Endpoint Security depends on the management tools (see the table below).
You can manage the application using the following consoles of Kaspersky Security Center:
- Administration Console. Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in installed on the administrator's workstation.
- Web Console. Component of Kaspersky Security Center that is installed on the Administration Server. You can work in the Web Console through a browser on any computer that has access to the Administration Server.
You can also manage the application by using the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. The Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console is the cloud version of Kaspersky Security Center. This means that the Administration Server and other components of Kaspersky Security Center are installed in the cloud infrastructure of Kaspersky. For details on managing the application using the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console Help.
Comparison of Kaspersky Endpoint Security features
Feature |
Kaspersky Security Center |
Kaspersky Security Center |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Administration Console |
Web Console |
Cloud Console |
Advanced Threat Protection |
|
|
|
Kaspersky Security Network |
|
|
|
Kaspersky Private Security Network |
|
|
– |
Behavior Detection |
|
|
|
Exploit Prevention |
|
|
|
Host Intrusion Prevention |
|
|
|
Remediation Engine |
|
|
|
Essential Threat Protection |
|
|
|
File Threat Protection |
|
|
|
Web Threat Protection |
|
|
|
Mail Threat Protection |
|
|
|
Firewall |
|
|
|
Network Threat Protection |
|
|
|
BadUSB Attack Prevention |
|
|
|
AMSI Protection |
|
|
|
Security Controls |
|
|
|
Log Inspection |
|
|
|
Application Control |
|
|
|
Device Control |
|
|
|
Web Control |
|
|
|
Adaptive Anomaly Control |
|
|
|
File Integrity Monitor |
|
|
|
Data Encryption |
|
|
|
Kaspersky Disk Encryption |
|
|
– |
BitLocker Drive Encryption |
|
|
|
File Level Encryption |
|
|
– |
Encryption of removable drives |
|
|
– |
Detection and Response |
|
|
|
Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum |
– |
|
|
Endpoint Detection and Response Expert |
– |
– |
|
Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) |
|
|
– |
Kaspersky Sandbox |
– |
|
– |
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) |
|
|
|
Tasks |
|
|
|
Add key |
|
|
|
Change application components |
|
|
|
Inventory |
|
|
|
Update |
|
|
|
Update rollback |
|
|
|
Malware Scan |
|
|
|
Integrity check |
|
|
– |
Wipe Data |
|
|
|
Manage Authentication Agent accounts (Kaspersky Disk Encryption) |
|
|
– |
IOC Scan (EDR) |
– |
|
|
Move file to Quarantine (EDR) |
– |
|
|
Get file (EDR) |
– |
|
|
Delete file (EDR) |
– |
|
|
Process start (EDR) |
– |
|
|
Terminate process (EDR) |
– |
|
|
Compatibility with other applications
Prior to the installation, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks the computer for the presence of Kaspersky applications. The application also checks the computer for incompatible software.
Compatibility with third-party applications
The list of incompatible software is available in the incompatible.txt file that is included in the distribution kit.
![]() DOWNLOAD THE INCOMPATIBLE.TXT FILE
DOWNLOAD THE INCOMPATIBLE.TXT FILE
Compatibility with Kaspersky applications
Kaspersky Endpoint Security is incompatible with the following Kaspersky applications:
- Kaspersky Small Office Security.
- Kaspersky Internet Security.
- Kaspersky Anti-Virus.
- Kaspersky Total Security.
- Kaspersky Safe Kids.
- Kaspersky Free.
- Kaspersky Anti-Ransomware Tool.
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (including the Endpoint Sensor component).
- Kaspersky Sandbox (including Kaspersky Endpoint Agent).
- Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (including the Endpoint Sensor component).
If the Endpoint Agent component was installed on a computer using the deployment tools of other Kaspersky applications, the component will be automatically removed during installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Kaspersky Endpoint Security may also include the Endpoint Sensor / Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component if you selected Endpoint Agent in the list of application components.
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent.
- Kaspersky Fraud Prevention for Endpoint.
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security.
If Kaspersky applications from this list are installed on the computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security removes these applications. Please wait for this process to finish before continuing installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Skipping the incompatible software check
If Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects incompatible software on the computer, installation of the application will not continue. To continue the installation, you need to remove the incompatible software. However, if the vendor of third-party software has indicated in their documentation that their software is compatible with Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP), you can install Kaspersky Endpoint Security to a computer containing an application from this vendor. For example, the Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solution provider may declare their compatibility with third-party EPP systems. If this is the case, you need to start the installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security without running an incompatible software check. To do so, pass the following parameters to the installer:
SKIPPRODUCTCHECK=1. Disable the check for incompatible software. The list of incompatible software is available in the incompatible.txt file that is included in the distribution kit. If no value is set for this parameter and incompatible software is detected, the installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security will be terminated.SKIPPRODUCTUNINSTALL=1. Disable automatic removal of detected incompatible software. If no value is set for this parameter, Kaspersky Endpoint Security attempts to remove incompatible software.CLEANERSIGNCHECK=0. Disabling digital signature verification of detected incompatible software. If this parameter is not set, verification of digital signatures is disabled when deploying the application via Kaspersky Security Center. When the application is installed locally, digital signature verification is enabled by default.
You can pass parameters in the command line when locally installing the application.
Example: C:\KES\setup_kes.exe /pEULA=1 /pPRIVACYPOLICY=1 /pKSN=0 /pSKIPPRODUCTCHECK=1 /pSKIPPRODUCTUNINSTALL=1 /pCLEANERSIGNCHECK=0 /s |
To remotely install Kaspersky Endpoint Security, you need to add the appropriate parameters to the installation package generation file named kes_win.kud in [Setup] (see below). The kes_win.kud file is included in the distribution kit.
kes_win.kud
Installing and removing the application
Kaspersky Endpoint Security can be installed on a computer in the following ways:
- locally, by using the Setup Wizard.
- locally from the command line.
- remotely using Kaspersky Security Center.
- remotely through the Microsoft Windows Group Policy Management Editor (for more details, visit the Microsoft Technical Support website).
- remotely, by using the System Center Configuration Manager.
You can configure the application installation settings in several ways. If you simultaneously use multiple methods for configuring the settings, Kaspersky Endpoint Security applies the settings with the highest priority. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the following order of priorities:
- Settings received from the setup.ini file.
- Settings received from the installer.ini file.
- Settings received from the command line.
We recommend closing all running applications before starting the installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security (including remote installation).
Deployment through Kaspersky Security Center
Kaspersky Endpoint Security can be deployed on computers within a corporate network in several ways. You can choose the most suitable deployment scenario for your organization or combine several deployment scenarios at the same time. Kaspersky Security Center supports the following main deployment methods:
- Installing the application using the Protection Deployment Wizard.
Standard installation method is convenient if you are satisfied with the default settings of Kaspersky Endpoint Security and your organization has a simple infrastructure that does not require special configurations.
- Installing the application using the remote installation task.
Universal installation method, which allows to configure Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings and flexibly manage remote installation tasks. Installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security consists of the following steps:
Kaspersky Security Center also supports other methods of installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security, such as deployment within an operating system image. For details about other deployment methods, refer to Kaspersky Security Center Help.
Standard installation of the application
Kaspersky Security Center provides a Protection Deployment Wizard for installing the application on corporate computers. The Protection Deployment Wizard includes the following main actions:
- Selecting a Kaspersky Endpoint Security installation package.
An installation package is a set of files created for remote installation of a Kaspersky application via Kaspersky Security Center. The installation package contains a range of settings needed to install the application and get it running immediately after installation. The installation package is created using files with the .kpd and .kud extensions included in the application distribution kit. Kaspersky Endpoint Security installation package is common for all supported Windows versions and processor architecture types.
- Creating the Install application remotely task of the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
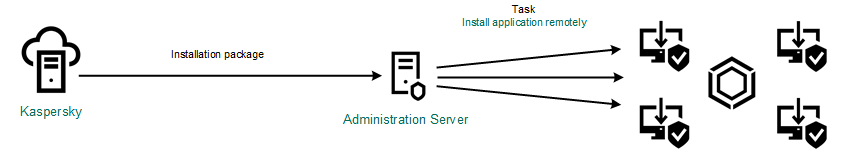
Kaspersky Endpoint Security deployment
How to run the Protection Deployment Wizard in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to start the Protection Deployment Wizard in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Creating an installation package
An installation package is a set of files created for remote installation of a Kaspersky application via Kaspersky Security Center. The installation package contains a range of settings needed to install the application and get it running immediately after installation. The installation package is created using files with the .kpd and .kud extensions included in the application distribution kit. Kaspersky Endpoint Security installation package is common for all supported Windows versions and processor architecture types.
How to create an installation package in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to create an installation package in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Installation package settings
Section |
Description |
|---|---|
Protection components |
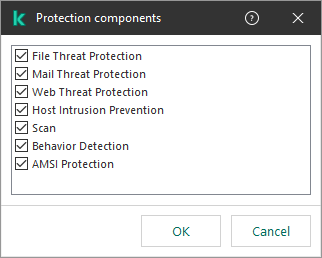
In this section, you can select the application components that will be available. You can change the set of application components at a later time by using the Change application components task. The BadUSB Attack Prevention component, Detection and Response component, and data encryption components are not installed by default. These components can be added in the installation package settings. If you need to install Detection and Response components, Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the following configurations:
Kaspersky Endpoint Security verifies the selection of components before installing the application. If the selected configuration of Detection and Response components is not supported, Kaspersky Endpoint Security cannot be installed. |
License key |
In this section, you can activate the application. To activate the application, you must select a license key. Before you do that, you must add the key to the Administration Server. For more details about adding keys to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server, please refer to Kaspersky Security Center Help. |
Incompatible Applications |
Carefully read the list of incompatible applications and allow removal of these applications. If incompatible applications are installed on the computer, installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security ends with an error. |
Installation settings |
Add the path to the file avp.com to the system variable %PATH%. You can add the installation path to the %PATH% variable for convenient use of the command line interface. Do not protect the installation process. Installation protection includes protection against replacement of the distribution package with malicious applications, blocking access to the installation folder of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, and blocking access to the system registry section containing application keys. However, if the application cannot be installed (for example, when performing remote installation with the help of Windows Remote Desktop), you are advised to disable protection of the installation process. Ensure compatibility with Citrix PVS (this is only necessary when working with Citrix PVS). You can enable support of Citrix Provisioning Services to install Kaspersky Endpoint Security to a virtual machine. Use Azure WVD compatibility mode. This feature allows correctly displaying the state of the Azure virtual machine in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform console. To monitor the performance of the computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends telemetry to KATA servers. Telemetry includes an ID of the computer (Sensor ID). Azure WVD compatibility mode allows assigning a permanent unique Sensor ID to these virtual machines. If the compatibility mode is turned off, the Sensor ID can change after the computer is restarted because of how Azure virtual machines work. This can cause duplicates of virtual machines to appear on the console. Path to application installation folder. You can change the installation path of Kaspersky Endpoint Security on a client computer. By default, the application is installed in the Configuration file. You can upload a file that defines the settings of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. You can create a configuration file in the local interface of the application. |
Updating databases in the installation package
The installation package contains anti-virus databases from the Administration Server repository that are up to date when the installation package is created. After creating the installation package, you can update the anti-virus databases in the installation package. This lets you reduce traffic consumption when updating anti-virus databases after installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
To update the anti-virus databases in the Administration Server repository, use the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task of the Administration Server. For more information about updating the anti-virus databases in the Administration Server repository, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
You can update the databases in the installation package only in the Administration Console and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. It is not possible to update the databases in the installation package in the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
How to update anti-virus databases in an installation package through the Web Console
Page top
Creating a remote installation task
The Install application remotely task is designed for remote installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. The Install application remotely task allows you to deploy the installation package of the application to all computers in the organization. Before deploying the installation package, you can update the anti-virus databases inside the package and select the available application components in the properties of the installation package.
How to create a remote installation task in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to create a remote installation task in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Installing the application locally using the Wizard
The interface of the application Setup Wizard consists of a sequence of windows corresponding to the application installation steps.
To install the application or upgrade the application from a previous version using the Setup Wizard:
- Copy the distribution kit folder to the user's computer.
- Run setup_kes.exe.
The Setup Wizard starts.
Preparing for installation
Before installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security on a computer or upgrading it from a previous version, the following conditions are checked:
- Presence of installed incompatible software (the list of incompatible software is available in the incompatible.txt file that is included in the distribution kit).
- Whether or not the hardware and software requirements are met.
- Whether or not the user has the rights to install the software product.
If any one of the previous requirements is not met, a relevant notification is displayed on the screen. For example, a notification about incompatible software (see the figure below).
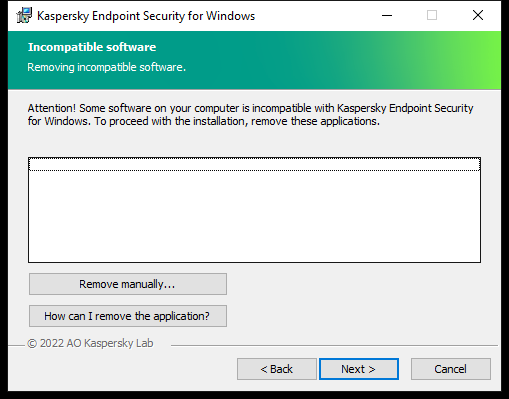
Removing incompatible software
If the computer meets the listed requirements, the Setup Wizard searches for Kaspersky applications that could lead to conflicts when running at the same time as the application being installed. If such applications are found, you are prompted to remove them manually.
If the detected applications include previous versions of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, all data that can be migrated (such as activation data and application settings) is retained and used during installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.1 for Windows, and the previous version of the application is automatically removed. This applies to the following application versions:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.6.0 for Windows (build 11.6.0.394).
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.7.0 for Windows (build 11.7.0.669).
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.8.0 for Windows (build 11.8.0.384).
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.9.0 for Windows (build 11.9.0.351).
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.10.0 for Windows (build 11.10.0.399).
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.11.0 for Windows (build 11.11.0.452).
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.0 for Windows (build 12.0.0.465).
Kaspersky Endpoint Security components
During the installation process, you can select the components of Kaspersky Endpoint Security that you want to install (see the figure below). The File Threat Protection component is a mandatory component that must be installed. You cannot cancel its installation.
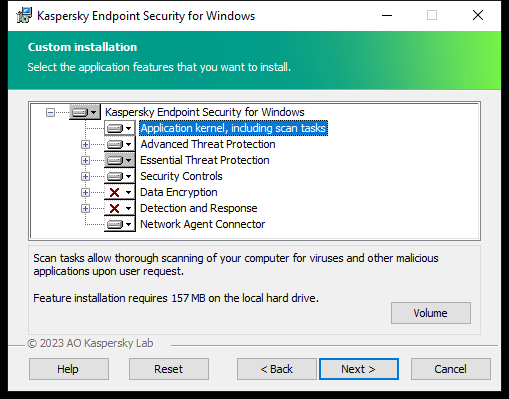
Selecting application components to install
By default, all application components are selected for installation except the following components:
You can change the available application components after the application is installed. To do so, you need to run the Setup Wizard again and choose to change the available components.
If you need to install Detection and Response components, Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the following configurations:
- Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum only
- Endpoint Detection and Response Expert only
- Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) only
- Kaspersky Sandbox only
- Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum and Kaspersky Sandbox
- Endpoint Detection and Response Expert and Kaspersky Sandbox
- Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) and Kaspersky Sandbox
Kaspersky Endpoint Security verifies the selection of components before installing the application. If the selected configuration of Detection and Response components is not supported, Kaspersky Endpoint Security cannot be installed.
Advanced settings
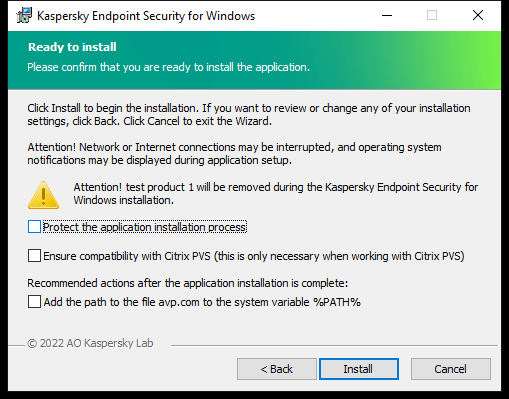
Advanced application installation settings
Protect the application installation process. Installation protection includes protection against replacement of the distribution package with malicious applications, blocking access to the installation folder of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, and blocking access to the system registry section containing application keys. However, if the application cannot be installed (for example, when performing remote installation with the help of Windows Remote Desktop), you are advised to disable protection of the installation process.
Ensure compatibility with Citrix PVS (this is only necessary when working with Citrix PVS). You can enable support of Citrix Provisioning Services to install Kaspersky Endpoint Security to a virtual machine.
Add the path to the file avp.com to the system variable %PATH%. You can add the installation path to the %PATH% variable for convenient use of the command line interface.
Page top
Remotely installing the application using System Center Configuration Manager
These instructions apply to System Center Configuration Manager 2012 R2.
To remotely install an application using System Center Configuration Manager:
- Open the Configuration Manager console.
- In the right part of the console, in the App management block, select Packages.
- In the upper part of the console in the control panel, click the Create package button.
This starts the New Package and Application Wizard.
- In the New Package and Application Wizard:
- In the Package section:
- In the Name field, enter the name of the installation package.
- In the Source folder field, specify the path to the folder containing the distribution package of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- In the Application type section, select the Standard program option.
- In the Standard program section:
- In the Name field, enter the unique name for the installation package (for example, the application name including the version).
- In the Command line field, specify the Kaspersky Endpoint Security installation options from the command line.
- Click the Browse button to specify the path to the executable file of the application.
- Make sure that the Run mode list has the Run with administrative rights item selected.
- In the Requirements section:
- Select the Run another program first check box if you want a different application to be started before installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Select the application from the Application drop-down list or specify the path to the executable file of this application by clicking the Browse button.
- Select the This program can run only on specified platforms option in the Platform requirements block if you want the application to be installed only in the specified operating systems.
In the list below, select the check boxes opposite the operating systems in which Kaspersky Endpoint Security will be installed.
This step is optional.
- Select the Run another program first check box if you want a different application to be started before installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- In the Summary section, check all entered values of the settings and click Next.
The created installation package will appear in the Packages section in the list of available installation packages.
- In the Package section:
- In the context menu of the installation package, select Deploy.
This starts the Deployment Wizard.
- In the Deployment Wizard:
- In the General section:
- In the Software field, enter the unique name of the installation package or select the installation package from the list by clicking the Browse button.
- In the Collection field, enter the name of the collection of computers on which the application will be installed, or select the collection by clicking the Browse button.
- In the Contains section, add distribution points (for more detailed information, please refer to the help documentation for System Center Configuration Manager).
- If required, specify the values of other settings in the Deployment Wizard. These settings are optional for remote installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- In the Summary section, check all entered values of the settings and click Next.
After the Deployment Wizard finishes, a task will be created for remote installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- In the General section:
Description of setup.ini file installation settings
The setup.ini file is used when installing the application from the command line or when using the Group Policy Editor of Microsoft Windows. To apply settings from the setup.ini file, place this file into the folder containing the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution package.
The setup.ini file consists of the following sections:
[Setup]– general settings of application installation.[Components]– selection of application components to be installed. If none of the components are specified, all components that are available for the operating system are installed. File Threat Protection is a mandatory component and is installed on the computer regardless of which settings are indicated in this section.[Tasks]– selection of tasks to be included in the list of Kaspersky Endpoint Security tasks. If no task is specified, all tasks are included in the task list of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
The alternatives to the value 1 are the values yes, on, enable, and enabled.
The alternatives to the value 0 are the values no, off, disable, and disabled.
Settings of the setup.ini file
Section |
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Path to the application installation folder. |
|
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security activation code. |
|
|
Acceptance of the terms of the End User License Agreement. The text of the License Agreement is included in the distribution kit of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Accepting the terms of the End User License Agreement is necessary for installing the application or upgrading the application version. |
|
|
Acceptance of the Privacy Policy. The text of the Privacy Policy is included in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution kit. To install the application or upgrade the application version, you must accept the Privacy Policy. |
|
|
Agreement or refusal to participate in Kaspersky Security Network (KSN). If no value is set for this parameter, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will prompt to confirm your consent or refusal to participate in KSN when Kaspersky Endpoint Security is first started. Available values:
The Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution package is optimized for use with Kaspersky Security Network. If you opted not to participate in Kaspersky Security Network, you should update Kaspersky Endpoint Security immediately after the installation is complete. |
|
|
Set the user name for accessing the features and settings of Kaspersky Endpoint Security (the Password protection component). The user name is set together with the |
|
|
Specify a password for accessing Kaspersky Endpoint Security features and settings (the password is specified together with the If you specified a password but did not specify a user name with the |
|
|
Specify the scope of the password for accessing Kaspersky Endpoint Security. When a user attempts to perform an action that is included in this scope, Kaspersky Endpoint Security prompts for the user's account credentials ( Available values:
For example, |
|
|
Enabling or disabling the application installation protection mechanism. Available values:
Installation protection includes protection against replacement of the distribution package with malicious applications, blocking access to the installation folder of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, and blocking access to the system registry section containing application keys. However, if the application cannot be installed (for example, when performing remote installation with the help of Windows Remote Desktop), you are advised to disable protection of the installation process. |
|
|
Enabling or disabling Azure WVD compatibility mode. Available values:
This feature allows correctly displaying the state of the Azure virtual machine in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform console. To monitor the performance of the computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends telemetry to KATA servers. Telemetry includes an ID of the computer (Sensor ID). Azure WVD compatibility mode allows assigning a permanent unique Sensor ID to these virtual machines. If the compatibility mode is turned off, the Sensor ID can change after the computer is restarted because of how Azure virtual machines work. This can cause duplicates of virtual machines to appear on the console. |
|
|
Automatic restart of the computer, if required after installation or upgrade of the application. If no value is set for this parameter, automatic computer restart is blocked. Restart is not required when installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Restart is required only if you have to remove incompatible applications prior to installation. Restart may also be required when updating the application version. |
|
|
In the %PATH% system variable, add the path to executable files located in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security setup folder. Available values:
|
|
|
Enables or disables protection of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security processes using AM-PPL technology (Antimalware Protected Process Light). For more details about AM-PPL technology, please visit the Microsoft website. AM-PPL technology is available for Windows 10 version 1703 (RS2) or later, and Windows Server 2019 operating systems. Available values:
|
|
|
Application upgrade mode:
You can upgrade the application without a restart starting with version 11.10.0. To upgrade an earlier version of the application, you must restart the computer. You can also install patches without a restart starting with version 11.11.0. Restart is not required when installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security. So, the upgrade mode of the application will be specified in the application settings. You can change this parameter in the application settings or in the policy. When upgrading already installed application, the priority of the parameter specified in the setup.ini file is higher than that of the parameter specified in the application settings or in the command line. For example, if |
|
|
Enable writing of registry keys from the setup.reg file to the registry. |
|
|
Enabling or disabling application tracing. After Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts, it saves trace files in the folder
|
|
|
Level of detail of traces. Available values:
|
|
|
Managing the application through the REST API. To manage the application through the REST API, you must specify the user name ( Available values:
To manage the application through the REST API, management using administrative systems must be allowed. To do so, set the |
|
|
User name of the Windows domain account used for managing the application through the REST API. Management of the application through the REST API is available only to this user. Enter the user name in the format Adding a user name is a prerequisite for managing the application through the REST API. |
|
|
Port used for managing the application through the REST API. Port 6782 is used by default. Make sure that the port is free. |
|
|
Certificate for identifying requests (for example, |
|
|
Installation of all components. If the parameter value Because of the way Detection and Response solutions are supported, Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum as well as Kaspersky Sandbox components are installed on the computer. The Endpoint Detection and Response Expert component is not compatible with this configuration. |
|
|
Mail Threat Protection. |
|
|
Web Threat Protection. |
|
|
AMSI Protection. |
|
|
Host Intrusion Prevention. |
|
|
Behavior Detection. |
|
|
Exploit Prevention. |
|
|
Remediation Engine. |
|
|
Firewall. |
|
|
Network Threat Protection. |
|
|
Web Control. |
|
|
Device Control. |
|
|
Application Control. |
|
|
Adaptive Anomaly Control. |
|
|
Log Inspection |
|
|
File Integrity Monitor |
|
|
File Level Encryption libraries. |
|
|
Full Disk Encryption libraries. |
|
|
BadUSB Attack Prevention. |
|
|
Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum (EDR Optimum). The component is not compatible with EDR Expert ( |
|
|
Endpoint Detection and Response Expert (EDR Expert). The component is not compatible with EDR Optimum ( |
|
|
Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA). The component is not compatible with EDR Expert ( |
|
|
Kaspersky Sandbox. |
|
|
Managed Detection and Response. |
|
|
Application management using administration systems. Administration systems include, for example, Kaspersky Security Center. In addition to Kaspersky administration systems, you can use third-party solutions. Kaspersky Endpoint Security provides an API for this purpose. Available values:
|
|
|
Full Scan task. Available values:
|
|
|
Critical Areas Scan task. Available values:
|
|
|
Update task. Available values:
|
Change application components
During installation of the application, you can select the components that will be available. You can change the available application components in the following ways:
- Locally, by using the Setup Wizard.
Application components are changed by using the normal method for a Windows operating system, which is through the Control Panel. Run the Application Setup Wizard and select the option to change the application components that are available. Follow the instructions on the screen.
- Remotely using Kaspersky Security Center.
The Change application components task allows you to change the components of Kaspersky Endpoint Security after the application is installed.
Please take into account the following special considerations when changing the application components:
- On computers running Windows Server, you cannot install all components of Kaspersky Endpoint Security (for example, the Adaptive Anomaly Control component is not available).
- If the hard drives on your computer are protected by Full Disk Encryption (FDE), you cannot remove the Full Disk Encryption component. To remove the Full Disk Encryption component, decrypt all the hard drives of the computer.
- If the computer has encrypted files (FLE) or the user uses encrypted removable drives (FDE or FLE), it will be impossible to access the files and removable drives after the Data Encryption components are removed. You can access the files and removable drives by reinstalling the Data Encryption components.
How to add or remove application components in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to add or remove application components in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Advanced Settings of the task
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Remove incompatible third-party applications |
The list of incompatible applications can be viewed in |
Use password for modifying the set of application components |
Administrators typically enable Password protection to restrict access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security. That is, to modify the selection of application components, you must enter credentials of a user that has the Remove / modify / restore the application permission. For example, you can use the KLAdmin account. |
Use Azure WVD compatibility mode |
This feature allows correctly displaying the state of the Azure virtual machine in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform console. To monitor the performance of the computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends telemetry to KATA servers. Telemetry includes an ID of the computer (Sensor ID). Azure WVD compatibility mode allows assigning a permanent unique Sensor ID to these virtual machines. If the compatibility mode is turned off, the Sensor ID can change after the computer is restarted because of how Azure virtual machines work. This can cause duplicates of virtual machines to appear on the console. |
Use the password to uninstall Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and Kaspersky Security for Windows Server |
Administrators typically enable Password protection in settings of these tasks to restrict access to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent (KEA) and Kaspersky Security for Windows Server (KSWS). That is, if you are migrating from the [KES+KEA] configuration to [KES+built-in agent], or if you are migrating from KSWS to KES, you must enter a password to remove these applications. |
Upgrading from a previous version of the application
When you update a previous version of the application to a newer version, consider the following:
- The localization of the new version of Kaspersky Endpoint Security must match the localization of the installed version of the application. If localizations of the applications do not match, the application upgrade will complete with an error.
- We recommend quitting all active applications before starting the update.
- Before updating, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the Full Disk Encryption functionality. If Full Disk Encryption could not be locked, the upgrade installation will not start. After updating the application, the Full Disk Encryption functionality will be restored.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports updates for the following versions of the application:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.6.0 for Windows (build 11.6.0.394).
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.7.0 for Windows (build 11.7.0.669).
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.8.0 for Windows (build 11.8.0.384).
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.9.0 for Windows (build 11.9.0.351).
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.10.0 for Windows (build 11.10.0.399).
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.11.0 for Windows (build 11.11.0.452).
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.0 for Windows (build 12.0.0.465).
Application upgrade methods
Kaspersky Endpoint Security can be updated on the computer in the following ways:
- locally, by using the Setup Wizard.
- locally from the command line.
- remotely using Kaspersky Security Center.
- remotely through the Microsoft Windows Group Policy Management Editor (for more details, visit the Microsoft Technical Support website).
- remotely, by using the System Center Configuration Manager.
If the application that is deployed in the corporate network features a set of components other than the default set, updating the application through the Administration Console (MMC) is different from updating the application through the Web Console and Cloud Console. When you update Kaspersky Endpoint Security, consider the following:
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console or Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
If you created an installation package for the new version of the application with the default set of components, then the set of components on a user's computer will not be changed. To use Kaspersky Endpoint Security with the default set of components, you need to open the installation package properties, change the set of components, then revert to the original set of components and save the changes.
- Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
The set of application components after the update will match the set of components in the installation package. That is, if the new version of the application has the default set of components, then, for example, BadUSB Attack Prevention will be removed from the computer, since this component is excluded from the default set. To continue using the application with the same set of components as before the update, select the required components in the installation package settings.
Upgrading the application without a restart
Upgrading the application without a restart provides uninterrupted server operation when the application version is updated.
Upgrading the application without a restart has the following limitations:
- You can upgrade the application without a restart starting with version 11.10.0. To upgrade an earlier version of the application, you must restart the computer.
- You can install patches without a restart starting with version 11.11.0. To install patches for earlier versions of the application, a computer restart may be required.
- Upgrading the application without a restart is not available on computers with enabled data encryption (Kaspersky encryption (FDE), BitLocker, File Level Encryption (FLE)). To upgrade the application on computers with enabled data encryption, the computer must be restarted.
- After changing application components or repairing the application, you must restart the computer.
How to select the application upgrade mode in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to select the application upgrade mode in the Web Console
How to select the application upgrade mode in the application interface
As a result, after upgrading the application without a restart, two versions of the application will be installed on the computer. The installer installs the new version of the application to separate subfolders in the Program Files and Program Data folders. The installer also creates a separate registry key for the new version of the application. You do not have to manually remove the previous version of the application. The previous version will be removed automatically when the computer is restarted.
You can check the Kaspersky Endpoint Security upgrade using the Kaspersky application version report in the Kaspersky Security Center console.
Page top
Remove the application
Removing Kaspersky Endpoint Security leaves the computer and user data unprotected against threats.
Removing the application remotely using Kaspersky Security Center
You can remotely uninstall the application by using the Uninstall application remotely task. When performing the task, Kaspersky Endpoint Security downloads the application uninstall utility to the user's computer. After completing uninstallation of the application, the utility will be automatically removed.
How to remove the application through the Administration Console (MMC)
How to remove the application through the Web Console and Cloud Console
Restart the computer to complete the uninstallation. To do so, Network Agent displays a pop-up window.
Removing the application remotely using Active Directory
You can remotely uninstall the application using a Microsoft Windows group policy. To uninstall the application, you need to open the Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc) and use the Group Policy Editor to create an application removal task (for more details, please visit the Microsoft Technical Support website).
If the application uninstallation operation is password protected, you need to do the following:
- Create a BAT file with the following contents:
msiexec.exe /x<GUID> KLLOGIN=<user name> KLPASSWD=<password> /qn<GUID>is the unique ID of the application. You can find out the GUID of the application by using the following command:wmic product where "Name like '%Kaspersky Endpoint Security%'" get Name, IdentifyingNumberExample:
msiexec.exe /x{6BB76C8F-365E-4345-83ED-6D7AD612AF76} KLLOGIN=KLAdmin KLPASSWD=!Password1 /qn - Create a new Microsoft Windows policy for the computers in the Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc).
- Use the new policy to run the created BAT file on the computers.
Removing the application locally
You can remove the application locally using the Setup Wizard. Kaspersky Endpoint Security is removed using the normal method for a Windows operating system, which is through the Control Panel. The Setup Wizard starts. Follow the instructions on the screen.
Selecting the application removal operation
You can specify which of the data that is used by the application you want to save for future use, during the next installation of the application (such as when upgrading to a newer version of the application). If you do not specify any data, the application will be completely removed (see the figure below).
Saving data after removal
You can save the following data:
- Activation data, which lets you avoid having to activate the application again. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically adds a license key if the license term has not expired prior to installation.
- Backup files – files that are scanned by the application and placed in Backup.
Backup files that are saved after removal of the application can be accessed only from the same version of the application that was used to save those files.
If you plan to use Backup objects after removal of the application, you must restore those objects before removing the application. However, Kaspersky experts do not recommend restoring objects from Backup because this may harm the computer.
- Operational settings of the application – values of application settings that are selected during application configuration.
- Local storage of encryption keys – data that provides access to files and drives that were encrypted before removal of the application. To ensure access to encrypted files and drives, make sure that you selected data encryption functionality when reinstalling Kaspersky Endpoint Security. No further action is required for access to previously encrypted files and drives.
You can also delete the application locally using the command line.
Page top
Application licensing
This section provides information about general concepts related to Kaspersky Endpoint Security licensing.
About the End User License Agreement
The End User License Agreement is a binding agreement between you and AO Kaspersky Lab stipulating the terms on which you may use the application.
We recommend carefully reading the terms of the License Agreement before using the application.
You can view the terms of the License Agreement in the following ways:
- When installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security in interactive mode.
- By reading the license.txt file. This document is included in the application distribution kit and is also located in the application installation folder
%ProgramFiles(x86)%\Kaspersky Lab\KES\Doc\<locale>\KES.
By confirming that you agree with the End User License Agreement when installing the application, you signify your acceptance of the terms of the End User License Agreement. If you do not accept the terms of the End User License Agreement, you must abort the installation.
Page top
About the license
A license is a time-limited right to use the application, granted under the End User License Agreement.
The license entitles you to use the application in accordance with the terms of the End User License Agreement, and to receive technical support. The list of available features and application usage term depend on the type of license under which the application was activated.
The following license types are provided:
- Trial – a free license intended for trying out the application.
A trial license usually has a short term. When the trial license expires, all Kaspersky Endpoint Security features become disabled. To continue using the application, you must purchase a commercial license.
You can activate the application under a trial license only once.
- Commercial – a paid license that is provided when you purchase Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Application functionality available under the commercial license depends on the choice of product. The selected product is indicated in the License Certificate. Information on available products may be found on the Kaspersky website.
When the commercial license expires, key features of the application become disabled. To continue using the application, you must renew your commercial license. If you are not planning to renew your license, you must remove the application from your computer.
About the license certificate
A license certificate is a document transferred to the user together with a key file or activation code.
The license certificate contains the following license information:
- License key or order number.
- Details of the user to whom the license is granted.
- Details of the application that can be activated using the license.
- Limitation on the number of licensed units (for example, the number of devices on which the application can be used under the license).
- License term start date.
- License expiration date or license term.
- License type.
About subscription
A subscription for Kaspersky Endpoint Security is a purchase order for the application with specific parameters (such as the subscription expiry date and number of devices protected). You can order a subscription for Kaspersky Endpoint Security from your service provider (such as your ISP). A subscription can be renewed manually or automatically, or you may cancel your subscription. You can manage your subscription on the website of the service provider.
Subscription can be limited (for one year, for example) or unlimited (without an expiry date). To keep Kaspersky Endpoint Security working after the limited subscription term expires, you need to renew your subscription. Unlimited subscription is renewed automatically if the vendor's services have been prepaid on time.
When a limited subscription expires, you may be provided a subscription renewal grace period during which the application continues to function. The availability and duration of such a grace period is decided by the service provider.
To use Kaspersky Endpoint Security under a subscription, you need to apply the activation code received from the service provider. After the activation code is applied, the active key is added. The active key determines the license for using the application under the subscription. You cannot activate the application under the subscription using a key file. The service provider can only provide an activation code. It is not possible to add a reserve key under a subscription.
Activation codes purchased under subscription may not be used to activate previous versions of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Page top
About license key
A license key is a sequence of bits that you can use to activate and then use the application in accordance with the terms of the End User License Agreement.
A license certificate is not provided for a key that is added under a subscription.
You can add a license key to the application by either applying a key file or entering an activation code.
The key can be blocked by Kaspersky if the terms of the End User License Agreement are violated. If the key has been blocked, you need to add a different key to continue using the application.
There are two types of keys: active and reserve.
An active key is a key that is currently used by the application. A trial or commercial license key can be added as the active key. The application cannot have more than one active key.
A reserve key is a key that entitles the user to use the application, but is not currently in use. At the expiry of the active key, a reserve key automatically becomes active. A reserve key can be added only if the active key is available.
A key for a trial license can be added only as an active key. It cannot be added as the reserve key. A trial license key cannot replace the active key to a commercial license.
If a key is added to the list of prohibited keys, the application functionality defined by the license used to activate the application remains available for eight days. The application notifies the user that the key has been added to the list of prohibited keys. After eight days, application functionality becomes limited to the functionality level that is available after license expiry. You can use protection and control components and run a scan using the application databases that were installed before the license expired. The application also continues to encrypt files that had been modified and encrypted before license expiration, but does not encrypt new files. Use of Kaspersky Security Network is not available.
Page top
About activation code
An activation code is a unique sequence of 20 alphanumeric characters. You enter an activation code to add a license key that activates Kaspersky Endpoint Security. You receive an activation code at the email address you specified after purchasing Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
To activate the application with an activation code, Internet access is required to connect to Kaspersky activation servers.
When the application is activated using an activation code, the active key is added. A reserve key can be added only by using an activation code and cannot be added using a key file.
If an activation code is lost after activating the application, you can restore the activation code. You may need an activation code, for example, to register a Kaspersky CompanyAccount. If the activation code was lost after the application activation, contact Kaspersky partner from whom you purchased the license.
Page top
About the key file
A key file is a file with the .key extension that you receive from Kaspersky. The purpose of a key file is to add a license key that activates the application.
You receive a key file at the email address that you provided when you purchased Kaspersky Endpoint Security or ordered the trial version of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
You do not need to connect to Kaspersky activation servers in order to activate the application with a key file.
You can recover a key file if it has been accidentally deleted. You may need a key file to register a Kaspersky CompanyAccount, for example.
To recover a key file, do one of the following:
- Contact the license seller.
- Obtain a key file on the Kaspersky website based on your existing activation code.
When the application is activated using a key file, an active key is added. A reserve key can be added only by using a key file and cannot be added using an activation code.
Page top
Comparison of application functionality depending on license type for workstations
The set of Kaspersky Endpoint Security functionality available on workstations depends on the license type (see table below).
See also the comparison of application functionality for servers
Comparison of Kaspersky Endpoint Security features
Feature |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business Select |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business Advanced |
Kaspersky Total Security |
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum |
Kaspersky Optimum Security |
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert |
Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security Standard |
Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security Enterprise |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Advanced Threat Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kaspersky Security Network |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Behavior Detection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exploit Prevention |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Host Intrusion Prevention |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remediation Engine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Essential Threat Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
File Threat Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Web Threat Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mail Threat Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Firewall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Network Threat Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BadUSB Attack Prevention |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AMSI Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Security Controls |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Log Inspection |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Application Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Device Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Web Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adaptive Anomaly Control |
– |
|
|
|
|
|
– |
|
File Integrity Monitor |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Data Encryption |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kaspersky Disk Encryption |
– |
|
|
|
|
|
– |
|
BitLocker Drive Encryption |
– |
|
|
|
|
|
– |
|
File Level Encryption |
– |
|
|
|
|
|
– |
|
Encryption of removable drives |
– |
|
|
|
|
|
– |
|
Detection and Response |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum |
– |
– |
– |
|
|
– |
– |
– |
Endpoint Detection and Response Expert |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
– |
– |
Kaspersky Sandbox (Kaspersky Sandbox license must be purchased separately) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comparison of application functionality depending on license type for servers
The set of Kaspersky Endpoint Security functionality available on servers depends on the license type (see table below).
See also the comparison of application functionality for workstations
Comparison of Kaspersky Endpoint Security features
Feature |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business Select |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business Advanced |
Kaspersky Total Security |
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum |
Kaspersky Optimum Security |
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert |
Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security Standard |
Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security Enterprise |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Advanced Threat Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kaspersky Security Network |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Behavior Detection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exploit Prevention |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Host Intrusion Prevention |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Remediation Engine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Essential Threat Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
File Threat Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Web Threat Protection |
– |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mail Threat Protection |
– |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Firewall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Network Threat Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BadUSB Attack Prevention |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AMSI Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Security Controls |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Log Inspection |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Application Control |
– |
|
|
|
|
|
– |
|
Device Control |
– |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Web Control |
– |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adaptive Anomaly Control |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
File Integrity Monitor |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Data Encryption |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kaspersky Disk Encryption |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
BitLocker Drive Encryption |
– |
|
|
|
|
|
– |
|
File Level Encryption |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Encryption of removable drives |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Detection and Response |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum |
– |
– |
– |
|
|
– |
– |
– |
Endpoint Detection and Response Expert |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
– |
– |
Kaspersky Sandbox (Kaspersky Sandbox license must be purchased separately) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Activating the application
Activation is the process of activating a license that allows you to use a fully functional version of the application until the license expires. The application activation involves adding a license key.
You can activate the application in one of the following ways:
- Locally from the application interface, by using the Activation Wizard You can add both the active key and the reserve key in this way.
- Remotely with the Kaspersky Security Center software suite by creating and then starting an add license key task. You can add both the active key and the reserve key in this way.
- Remotely by distributing key files and activation codes stored in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server key storage to client computers. For more details on distributing keys, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help. You can add both the active key and the reserve key in this way.
The activation code purchased under subscription is distributed in the first place.
- Using the command line.
It may take some time for the application to be activated with an activation code (during either remote or non-interactive installation) due to load distribution across activation servers of Kaspersky. If you need to activate the application right away, you may interrupt the ongoing activation process and start activation using the Activation Wizard.
Activating the application through Kaspersky Security Center
You can activate the application remotely through Kaspersky Security Center in the following ways:
- Using the Add key task.
This method lets you add a key to a specific computer or to computers that are part of an administration group.
- By distributing a key stored on the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server to the computers.
This method lets you automatically add a key to computers that are already connected to Kaspersky Security Center, and to new computers. To use this method, you need to first add the key to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server. For more details about adding keys to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server, please refer to Kaspersky Security Center Help.
- By adding the key to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security installation package.
This method lets you add the key in Installation package properties during Kaspersky Endpoint Security deployment. The application is automatically activated after the installation.
A trial version is provided for Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. The trial version is a special version of Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console designed to familiarize a user with the features of the application. In this version, you can perform actions in a workspace for a period of 30 days. All managed applications are automatically run under a trial license for Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, including Kaspersky Endpoint Security. However, you cannot activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security using its own trial license when the trial license for Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console expires. For detailed information about Kaspersky Security Center licensing, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console Help.
The trial version of Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console does not allow you to subsequently switch to a commercial version. Any trial workspace will be automatically deleted with all its contents after the 30-day period expires.
You can monitor the use of licenses in the following ways:
- View the Key usage report for the organization's infrastructure (Monitoring and reporting → Reports).
- View the statuses of computers on the Devices → Managed devices tab. If the application is not activated, the computer will have the
 Application is not activated status.
Application is not activated status. - View license information in the computer properties.
- View the key properties (Operations → Licensing).
How to activate the application in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to activate the application in the Web Console and Cloud Console
In the properties of the Add key task, you can add a reserve key to the computer. A reserve key becomes active when the active key expires or is deleted. The availability of a reserve key lets you avoid application functionality limitations when a license expires.
How to automatically add a license key to computers through the Administration Console (MMC)
How to automatically add a license key to computers through the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Using the Activation Wizard to activate the application
To activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security by using the Activation Wizard:
- In the main application window, go to the License section.
- Click Activate the application using a new license.
The Application Activation Wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the Activation Wizard.
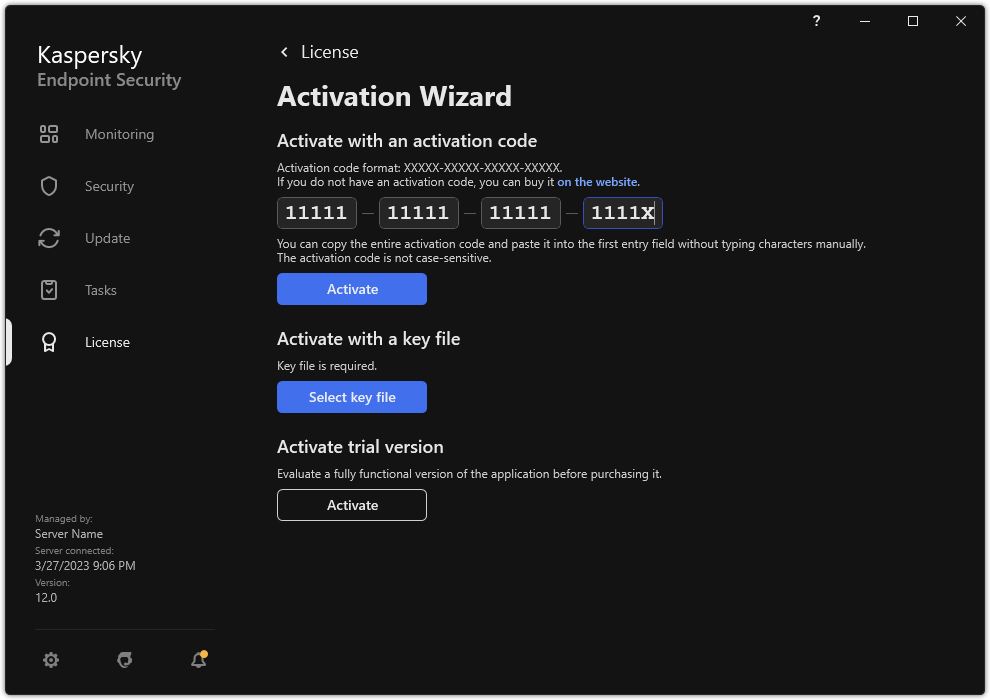
Activating the application
Viewing license information
To view information about a license:
In the main application window, go to the License section (see the figure below).
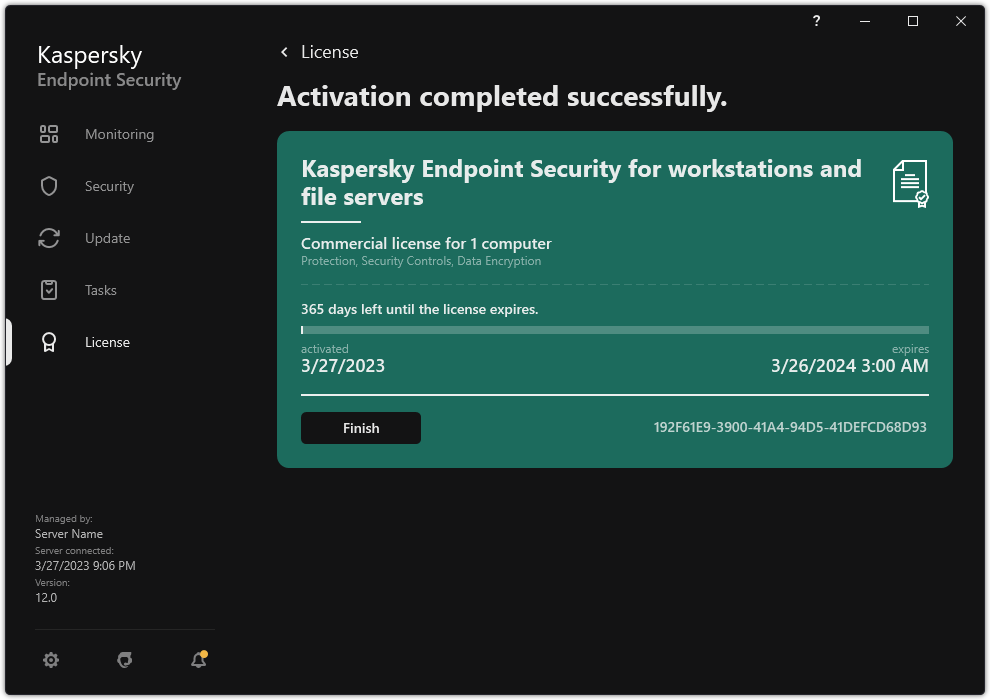
Licensing window
The section displays the following details:
- Key status. Several keys can be stored on a computer. There are two types of keys: active and reserve. The application cannot have more than one active key. A reserve key can become active only after the active key expires or after the active key is deleted by clicking Delete.
- Application name. Full name of the purchased Kaspersky application.
- License type. The following types of licenses are available: trial and commercial.
- Functionality. Application features that are available under your license. Features may include Protection, Security Controls, Data Encryption, and others. The list of available features is also provided in the License Certificate.
- Additional information about the license. Start date and end date of the license term (only for the active key), remaining duration of the license term.
License expiration time is displayed according to the time zone configured in the operating system.
- Key. A key is a unique alphanumeric sequence that is generated from an activation code or a key file.
In the Licensing window, you can also do one of the following:
- Buy license / Renew license. Opens the Kaspersky online store website, where you can purchase or renew a license. To do so, please enter your company information and pay for the order.
- Activate the application using a new license. Starts the Application Activation Wizard. In this Wizard you can add a key using an activation code or a key file. The Application Activation Wizard allows you to add an active key and only one reserve key.
Purchasing a license
You may purchase a license after installing the application. On purchasing a license, you receive an activation code or a key file for activating the application.
To purchase a license:
- In the main application window, go to the License section.
- Do one of the following:
- If no keys have been added or a key for trial license has been added, click the Buy license button.
- If the key for a commercial license is added, click the Renew license button.
A window will open with the website of the Kaspersky online store, where you can purchase a license.
Renewing subscription
When you use the application under subscription, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically contacts the activation server at specific intervals until your subscription expires.
If you use the application under unlimited subscription, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically checks the activation server for renewed keys in background mode. If a key is available on the activation server, the application adds it by replacing the previous key. In this way, unlimited subscription for Kaspersky Endpoint Security is renewed without user involvement.
If you are using the application under a limited subscription, on the expiration date of the subscription (or on the expiration date of the subscription renewal grace period), Kaspersky Endpoint Security notifies you about this and stops attempting to renew the subscription automatically. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security behaves in the same way as it does when a commercial license for the application expires: the application operates without updates and the Kaspersky Security Network is unavailable.
You can renew subscription on the website of the service provider.
To visit the website of the service provider from the application interface:
- In the main application window, go to the License section.
- Click Contact your subscription provider.
You can update subscription status manually. This may be required if the subscription has been renewed after the grace period and the application has not updated the subscription status automatically.
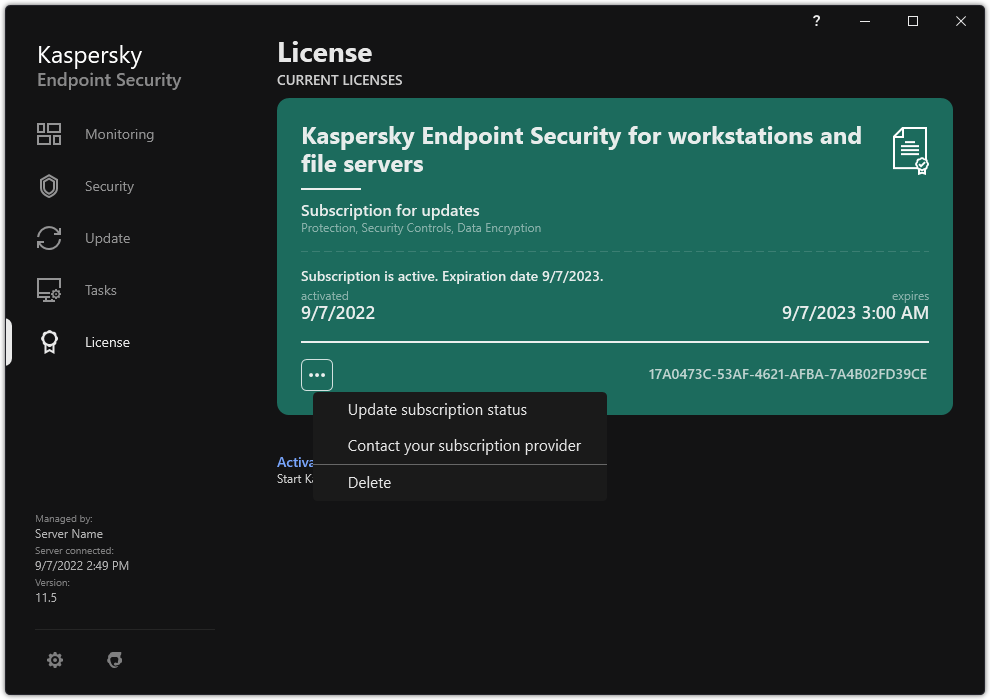
Renewing subscription
Page top
Data provision under the End User License Agreement
If an activation code is applied to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security, you agree to periodically send Kaspersky the following information automatically for the purposes of verifying correct use of the application:
- type, version, and localization of Kaspersky Endpoint Security;
- versions of installed updates for Kaspersky Endpoint Security;
- ID of the computer and ID of the specific Kaspersky Endpoint Security installation on the computer;
- serial number and active key identifier;
- type, version and bit rate of the operating system, and name of the virtual environment (if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed in a virtual environment);
- IDs of Kaspersky Endpoint Security components that are active when the information is transmitted.
Kaspersky may also use this information to generate statistics on the dissemination and use of Kaspersky software.
By using an activation code, you agree to automatically transmit the data listed above. If you do not agree to transmit this information to Kaspersky, you should use a key file to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
By accepting the terms of the End User License Agreement, you agree to automatically transmit the following information:
- When upgrading Kaspersky Endpoint Security:
- version of Kaspersky Endpoint Security;
- ID of Kaspersky Endpoint Security;
- active key;
- unique ID of the upgrade task start;
- unique ID of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security installation.
- When following links from the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface:
- version of Kaspersky Endpoint Security;
- version of the operating system;
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security activation date;
- license expiration date;
- key creation date;
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security installation date;
- ID of Kaspersky Endpoint Security;
- ID of the detected vulnerability in the operating system;
- ID of the last update installed for Kaspersky Endpoint Security;
- hash of the detected file with a threat, and the name of this threat according to the Kaspersky classification;
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security activation error category;
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security activation error code;
- number of days until key expiration;
- number of days that have elapsed since the key was added;
- number of days that have elapsed since the license expired;
- number of computers on which the current license is applied;
- active key;
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security license term;
- current status of the license;
- type of current license;
- application type;
- unique ID of the upgrade task start;
- unique ID of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security installation on the computer;
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface language.
Received information is protected by Kaspersky in accordance with the law and the requirements and applicable regulations of Kaspersky. Data is transmitted over encrypted communication channels.
Read the End User License Agreement and visit the Kaspersky website to learn more about how we receive, process, store, and destroy information about application usage after you accept the End User License Agreement and consent to the Kaspersky Security Network Statement. The license.txt and ksn_<language ID>.txt files contain the text of the End User License Agreement and Kaspersky Security Network Statement and are included in the application distribution kit.
Page top
Data provision when using Kaspersky Security Network
The set of data that Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends to Kaspersky depends on the type of license and the Kaspersky Security Network usage settings.
Use of KSN under license on no more than 4 computers
By accepting the Kaspersky Security Network Statement, you agree to automatically transmit the following information:
- information about KSN configuration updates: identifier of the active configuration, identifier of the configuration received, error code of the configuration update;
- information about files and URL addresses to be scanned: checksums of the scanned file (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) and file patterns (MD5), the size of the pattern, type of the detected threat and its name according to Rightholder's classification, identifier for the anti-virus databases, URL address for which the reputation is being requested, as well as the referrer URL address, the connection's protocol identifier and the number of the port being used;
- ID of the scan task that detected the threat;
- information about digital certificates being used needed to verify their authenticity: the checksums (SHA256) of the certificate used to sign the scanned object and the certificate's public key;
- identifier of the Software component performing the scan;
- IDs of the anti-virus databases and of the records in these anti-virus databases;
- Information about activation of the Software on the Computer: signed header of the ticket from the activation service (identifier of the regional activation center, checksum of the activation code, checksum of the ticket, ticket creation date, unique identifier of the ticket, ticket version, license status, start/end date and time of ticket validity, unique identifier of the license, license version), identifier of the certificate used to sign the ticket header, checksum (MD5) of the key file;
- Information about the Rightholder's Software: full version, type, version of the protocol used to connect to Kaspersky services.
Use of KSN under license on 5 or more computers
By accepting the Kaspersky Security Network Statement, you agree to automatically transmit the following information:
If the Kaspersky Security Network check box is selected and the Enable extended KSN mode check box is cleared, the application sends the following information:
- information about KSN configuration updates: identifier of the active configuration, identifier of the configuration received, error code of the configuration update;
- information about files and URL addresses to be scanned: checksums of the scanned file (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) and file patterns (MD5), the size of the pattern, type of the detected threat and its name according to Rightholder's classification, identifier for the anti-virus databases, URL address for which the reputation is being requested, as well as the referrer URL address, the connection's protocol identifier and the number of the port being used;
- ID of the scan task that detected the threat;
- information about digital certificates being used needed to verify their authenticity: the checksums (SHA256) of the certificate used to sign the scanned object and the certificate's public key;
- identifier of the Software component performing the scan;
- IDs of the anti-virus databases and of the records in these anti-virus databases;
- Information about activation of the Software on the Computer: signed header of the ticket from the activation service (identifier of the regional activation center, checksum of the activation code, checksum of the ticket, ticket creation date, unique identifier of the ticket, ticket version, license status, start/end date and time of ticket validity, unique identifier of the license, license version), identifier of the certificate used to sign the ticket header, checksum (MD5) of the key file;
- Information about the Rightholder's Software: full version, type, version of the protocol used to connect to Kaspersky services.
If the Enable extended KSN mode check box is selected in addition to the Kaspersky Security Network check box, the application sends the following information in addition to the information listed above:
- information about the results of categorization of the requested web-resources, which contains the processed URL and IP address of the host, the version of the Software's component that performed the categorization, the method of categorization and set of the categories defined for the web-resource;
- information about the software installed on the Computer: names of the software applications and software vendors, registry keys and their values, information about files of the installed software components (checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1), name, path to the file on the Computer, size, version and the digital signature);
- information about the state of anti-virus protection of the Computer: the versions and the release timestamps of the anti-virus databases being used, the ID of the task and the ID of Software that performs scanning;
- information about files being downloaded by the End User: the URL and IP addresses of the download and the download pages, download protocol identifier and connection port number, the status of the URLs as malicious or not, file's attributes, size and checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1), information about the process that downloaded the file (checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1), creation/build date and time, autoplay status, attributes, names of packers, information about signatures, executable file flag, format identifier, and entropy), file name and its path on the Computer, the file's digital signature and timestamp of its generation, the URL address where detection occurred, the script's number on the page that appears to be suspicious or harmful, information about HTTP requests generated and the response to them;
- information about the running applications and their modules: data about processes running on the system (process ID (PID), process name, information about the account the process was started from, the application and command that started the process, the sign of trusted program or process, the full path to the process's files and their checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1), and the starting command line, level of the process's integrity, a description of the product that the process belongs to (the name of the product and information about the publisher), as well as digital certificates being used and information needed to verify their authenticity or information about the absence of a file's digital signature), and information about the modules loaded into the processes (their names, sizes, types, creation dates, attributes, checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1), the paths to them on the Computer), PE-file header information, names of packers (if the file was packed);
- information about all potentially malicious objects and activities: name of the detected object and full path to the object on the computer, checksums of processed files (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1), detection date and time, names and sizes of infected files and paths to them, path template code, executable file flag, indicator of whether the object is a container, names of the packer (if the file was packed), file type code, file format ID, list of actions performed by malware and the decision made by the software and user in response to them, IDs of the anti-virus databases and of the records in these anti-virus databases that were used to make the decision, indicator of a potentially malicious object, the name of the detected threat according to the Rightholder’s classification, the level of danger, the detection status and detection method, reason for inclusion into the analyzed context and sequence number of the file in the context, checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1), the name and attributes of the executable file of the application through which the infected message or link was transmitted, depersonalized IP addresses (IPv4 and IPv6) of the host of the blocked object, file entropy, file autorun indicator, time when the file was first detected in the system, the number of times the file has been run since the last statistics were sent, information about the name, checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) and size of the mail client through which the malicious object was received, ID of the software task that performed the scan, indicator of whether the file reputation or signature was checked, file processing result, checksum (MD5) of the pattern collected for the object, the size of the pattern in bytes, and the technical specifications of the applied detection technologies;
- information about scanned objects: the assigned trust group to which and/or from which the file has been placed, the reason the file was placed in that category, category identifier, information about the source of the categories and the version of the category database, the file's trusted certificate flag, name of the file's vendor, file version, name and version of the software application which includes the file;
- information about vulnerabilities detected: the vulnerability ID in the database of vulnerabilities, the vulnerability danger class;
- information about emulation of the executable file: file size and its checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1), the version of the emulation component, emulation depth, an array of properties of logical blocks and functions within logical blocks obtained during the emulation, data from the executable file's PE headers;
- the IP addresses of the attacking computer (IPv4 and IPv6), the number of the port on the Computer that the network attack is directed at, identifier of the protocol of the IP packet containing the attack, the attack's target (organization name, website), flag for the reaction to the attack, the attack's weight, trust level;
- information about attacks associated with spoofed network resources, the DNS and IP addresses (IPv4 and IPv6) of visited websites;
- DNS and IP addresses (IPv4 or IPv6) of the requested web resource, information about the file and web client accessing the web resource, the name, size and checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) of the file, full path to the file and path template code, the result of checking its digital signature, and its status in KSN;
- information about rollback of malware actions: data on the file whose activity was rolled back (name of the file, full path to the file, its size and checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1)), data on successful and unsuccessful actions to delete, rename and copy files and restore the values in the registry (names of registry keys and their values), and information about system files modified by malware, before and after rollback;
- Information about the exclusions set for the Adaptive Anomaly Control component: the ID and status of the rule that was triggered, the action performed by the Software when the rule was triggered, the type of user account under which the process or the thread performs suspicious activity, information about the process that performed or was subject to the suspicious activity (script ID or process file name, full path to the process file, path template code, checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) of the process file); information about the object that performed the suspicious actions and about the object that was subject to the suspicious actions (registry key name or file name, full path to the file, path template code, and checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) of the file).
- information about loaded software modules: name, size and checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) of the module file, full path to it and the path template code, digital signature settings of the module file, data and time of signature creation, name of the subject and organization that signed the module file, ID of the process in which the module was loaded, name of the module supplier, and the sequence number of the module in the loading queue;
- information about the quality of Software interaction with the KSN services: start and end date and time of the period when the statistics were generated, information about the quality of requests and connection to each of the KSN services used (KSN service ID, number of successful requests, number of requests with responses from cache, number of unsuccessful requests (network problems, KSN being disabled in the Software settings, incorrect routing), time spread of the successful requests, time spread of the cancelled requests, time spread of the requests with exceeded time limit, number of connections to KSN taken from cache, number of successful connections to KSN, number of unsuccessful connections to KSN, number of successful transactions, number of unsuccessful transactions, time spread of the successful connections to KSN, time spread of the unsuccessful connections to KSN, time spread of the successful transactions, time spread of the unsuccessful transactions);
- if a potentially malicious object is detected, information is provided about data in the processes' memory: elements of the system object hierarchy (ObjectManager), data in UEFI BIOS memory, names of registry keys and their values;
- information about events in the systems logs: the event's timestamp, the name of the log in which the event was found, type and category of the event, name of the event's source and the event's description;
- information about network connections: version and checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) of the file from which process was started that opened the port, the path to the process's file and its digital signature, local and remote IP addresses, numbers of local and remote connection ports, connection state, timestamp of the port's opening;
- information about the date of Software installation and activation on the Computer: the ID of the partner that sold the license, the serial number of the license, the signed header of the ticket from the activation service (the ID of a regional activation center, the checksum of the activation code, the checksum of the ticket, the ticket creation date, the unique ID of the ticket, the ticket version, the license status, the ticket start/end date and time, the unique ID of the license, the license version), the ID of the certificate used to sign the ticket header, the checksum (MD5) of the key file, the unique ID of Software installation on the Computer, the type and ID of the application that gets updated, the ID of the update task;
- information about the set of all installed updates, and the set of most recently installed/removed updates, the type of event that caused the update information to be sent, duration since the installation of last update, information about any currently installed anti-virus databases;
- information about software operation on the computer: data on CPU usage, data on memory usage (Private Bytes, Non-Paged Pool, Paged Pool), number of active threads in the software process and pending threads, and the duration of software operation prior to the error;
- number of software dumps and system dumps (BSOD) since the Software was installed and since the time of the last update, the identifier and version of the Software module that crashed, the memory stack in the Software's process, and information about the anti-virus databases at the time of the crash;
- data on the system dump (BSOD): a flag indicating the occurrence of the BSOD on the Computer, the name of the driver that caused the BSOD, the address and memory stack in the driver, a flag indicating the duration of the OS session before the BSOD occurred, memory stack of driver that crashed, type of stored memory dump, flag for the OS session before BSOD lasted more than 10 minutes, unique identifier of the dump, timestamp of the BSOD;
- information about errors or performance problems that occurred during operation of the Software components: the status ID of the Software, error type, code and cause as well of the time when the error occurred, the IDs of the component, module and process of the product in which the error occurred, the ID of the task or update category during which the error occurred, logs of drivers used by the Software (error code, module name, name of the source file and the line where the error occurred);
- information about updates of anti-virus databases and Software components: the name, date and time of index files downloaded during the last update and being downloaded during the current update;
- information about abnormal termination of the Software operation: the creation timestamp of the dump, its type, the type of event that caused the abnormal termination of the Software operation (unexpected power-off, third-party application crash), date and time of the unexpected power-off;
- information about the compatibility of Software drivers with hardware and Software: information about OS properties that restrict the functionality of Software components (Secure Boot, KPTI, WHQL Enforce, BitLocker, Case Sensitivity), type of download Software installed (UEFI, BIOS), Trusted Platform Module (TPM) identifier, TPM specification version, information about the CPU installed on the Computer, operating mode and parameters of Code Integrity and Device Guard, operating mode of drivers and reason for use of the current mode, version of Software drivers, software and hardware virtualization support status of the Computer;
- information about third-party applications that caused the error: their name, version and localization, the error code and information about the error from the system log of applications, the address of the error and memory stack of the third-party application, a flag indicating the occurrence of the error in the Software component, the length of time the third-party application was in operation before the error occurred, checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) of the application process image, in which the error occurred, path to the application process image and template code of the path, information from the system log with a description of the error associated with the application, information about the application module, in which an error occurred (exception identifier, crash memory address as an offset in the application module, name and version of the module, identifier of the application crash in the Rightholder's plug-in and memory stack of the crash, duration of the application session before crash);
- version of the Software updater component, number of crashes of the updater component while running update tasks over the lifetime of the component, ID of the update task type, number of failed attempts of the updater component to complete update tasks;
- information about the operation of the Software system monitoring components: full versions of the components, date and time when the components were started, code of the event that overflowed the event queue and number of such events, the total number of queue overflow events, information about the file of the process of the initiator of the event (file name and its path on the Computer, template code of the file path, checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) of the process associated with the file, file version), identifier of the event interception that occurred, the full version of the interception filter, identifier of the type of the intercepted event, size of the event queue and the number of events between the first event in the queue and the current event, number of overdue events in the queue, information about the file of the process of the initiator of the current event (file name and its path on the Computer, template code of the file path, checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) of the process associated with the file), duration of the event processing, maximum duration of the event processing, probability of sending statistics, information about OS events for which the processing time limit was exceeded (date and time of the event, number of repeated initializations of anti-virus databases, date and time of the last repeated initialization of anti-virus databases after their update, event processing delay time for each system monitoring component, number of queued events, number of processed events, number of delayed events of the current type, total delay time for the events of the current type, total delay time for all events);
- information from the Windows event tracing tool (Event Tracing for Windows, ETW) in the event of Software performance problems, suppliers of SysConfig / SysConfigEx / WinSATAssessment events from Microsoft: information about the Computer (model, manufacturer, form factor of the housing, version), information about Windows performance metrics (WinSAT assessments, Windows performance index), domain name, information about physical and logical processors (number of physical and logical processors, manufacturer, model, stepping level, number of cores, clock frequency, CPUID, cache characteristics, logic processor characteristics, indicators of supported modes and instructions), information about RAM modules (type, form factor, manufacturer, model, capacity, granularity of memory allocation), information about network interfaces (IP and MAC addresses, name, description, configuration of network interfaces, breakdown of number and size of network packages by type, speed of network exchange, breakdown of number of network errors by type), configuration of IDE controller, IP addresses of DNS servers, information about the video card (model, description, manufacturer, compatibility, video memory capacity, screen permission, number of bits per pixel, BIOS version), information about plug-and-play devices (name, description, device identifier [PnP, ACPI], information about disks and storage devices (number of disks or flash drives, manufacturer, model, disk capacity, number of cylinders, number of tracks per cylinder, number of sectors per track, sector capacity, cache characteristics, sequential number, number of partitions, configuration of SCSI controller), information about logical disks (sequential number, partition capacity, volume capacity, volume letter, partition type, file system type, number of clusters, cluster size, number of sectors per cluster, number of empty and occupied clusters, letter of bootable volume, offset address of partition in relation to the start of the disk), information about BIOS motherboard (manufacturer, release date, version), information about motherboard (manufacturer, model, type), information about physical memory (shared and free capacity), information about operating system services (name, description, status, tag, information about processes [name and PID]), energy consumption parameters for the Computer, configuration of interrupt controller, path to Windows system folders (Windows and System32), information about the OS (version, build, release date, name, type, installation date), size of page file, information about monitors (number, manufacturer, screen permission, resolution capacity, type), information about video card driver (manufacturer, release date, version);
- information from ETW, suppliers of EventTrace / EventMetadata events from Microsoft: information on the sequence of system events (type, time, date, time zone), metadata about the file with tracing results (name, structure, tracing parameters, breakdown of number of trace operations by type), information about the OS (name, type, version, build, release date, start time);
- information from ETW, suppliers of Process / Microsoft Windows Kernel Process / Microsoft Windows Kernel Processor Power events from Microsoft: information about started and completed processes (name, PID, start parameters, command line, return code, power management parameters, start and completion time, access token type, SID, SessionID, number of descriptors installed), information about changes in thread priorities (TID, priority, time), information about disk operations of the process (type, time, capacity, number), history of changes to the structure and capacity of usable memory processes;
- information from ETW, suppliers of StackWalk / Perfinfo events from Microsoft: information about performance counters (performance of individual code sections, sequence of function calls, PID, TID, addresses and attributes of ISRs and DPCs);
- information from ETW, supplier of KernelTraceControl-ImageID events from Microsoft: information on executable files and dynamic libraries (name, image size, full path), information on PDB files (name, identifier), VERSIONINFO resource data for executable files (name, description, creator, localization, application version and identifier, file version and identifier);
- information from ETW, suppliers of FileIo / DiskIo / Image / Windows Kernel Disk events from Microsoft: information on file and disk operations (type, capacity, start time, completion time, duration, completion status, PID, TID, driver function call addresses, I/O Request Packet (IRP), Windows file object attributes), information about files involved in file and disk operations (name, version, size, full path, attributes, offset, image checksum, open and access options);
- information from ETW, supplier of PageFault events from Microsoft: information on memory page access errors (address, time, capacity, PID, TID, attributes of Windows file object, memory allocation parameters);
- information from ETW, supplier of Thread events from Microsoft: information on thread creation/completion, information on threads started (PID, TID, size of stack, priorities and allocation of CPU resources, I/O resources, memory pages between threads, stack address, address of init function, address of Thread Environment Block (TEB), Windows service tag);
- information from ETW, supplier of Microsoft Windows Kernel Memory events from Microsoft: information about memory management operations (completion status, time, quantity, PID), memory allocation structure (type, capacity, SessionID, PID);
- information about Software operation in the event of performance problems: Software installation identifier, type and value of drop in performance, information about the sequence of events within the Software (time, time zone, type, completion status, Software component identifier, Software operating scenario identifier, TID, PID, function call addresses), information about network connections to be checked (URL, direction of the connection, size of network package), information about PDB files (name, identifier, image size of executable file), information about files to be checked (name, full path, checksum), Software performance monitoring parameters;
- information about the last unsuccessful OS restart: the number of unsuccessful restarts since OS installation, data on the system dump (code and parameters of an error, name, version and checksum (CRC32) of the module that caused an error in the OS operation, error address as an offset in the module, checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) of the system dump);
- information to verify authenticity of digital certificates being used to sign files: the certificate's fingerprint, the checksum algorithm, the certificate's public key and serial number, the name of the issuer of the certificate, the result of certificate validation and the certificate's database identifier;
- information about the process executing the attack on the Software's self-defense: the name and size of the process file, its checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1), the full path to the process file and the template code of the file path, the creation/build timestamps, executable file flag, attributes of the process file, information about the certificate used to sign the process file, code of the account used to launch the process, ID of operations performed to access the process, type of resource with which the operation is performed (process, file, registry object, FindWindow search function), name of resource with which the operation is performed, flag indicating success of the operation, the status of the file of the process and its signature according to the KSN;
- information about the Rightholder's Software: full version, type, localization and operation state of Software used, versions of the installed Software components and their operation state, information about the installed Software updates, the value of the TARGET filter, the version of the protocol used to connect to the Rightholder's services;
- information about hardware installed on the Computer: type, name, model name, firmware version, parameters of built-in and connected devices, the unique identifier of the Computer with the installed Software;
- information about the versions of the operating system and installed updates, the word size, edition and parameters of the OS run mode, version and checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) of the OS kernel file, and OS startup date and time;
- executable and non-executable files, either entirely or partly;
- portions of the Computer's RAM;
- sectors involved in the process of booting the OS;
- network traffic data packets;
- web pages and emails containing suspicious and malicious objects;
- description of the classes and instances of classes of the WMI repository;
- application activity reports:
- the name, size and version of the file being sent, its description and checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1), file format identifier, the name of the file's vendor, the name of the product to which the file belongs, full path to the file on the Computer, template code of the path, the creation and modification timestamps of the file;
- start and end date/time of the validity period of the certificate (if the file has a digital signature), the date and the time of the signature, the name of the issuer of the certificate, information about the certificate holder, the fingerprint, the certificate's public key and appropriate algorithms, and the certificate's serial number;
- the name of the account from which the process is running;
- checksums (MD5, SHA2-256, SHA1) of the name of the Computer on which the process is running;
- titles of the process windows;
- Identifier for the anti-virus databases, name of the detected threat according to the Rightholder's classification;
- data about the installed license, its identifier, type and expiration date;
- local time of the Computer at the moment of the provision of information;
- names and paths of the files that were accessed by the process;
- names of registry keys and their values that were accessed by the process;
- URL and IP addresses that were accessed by the process;
- URL and IP addresses from which the running file was downloaded.
Data provision when using Detection and Response solutions
On computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed, data prepared for automatic sending to Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response, Kaspersky Sandbox and Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform servers is stored. Files are stored on computers in plain, non-encrypted form.
The specific set of data depends on the solution within which Kaspersky Endpoint Security is used.
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response
All data that the application stores locally on the computer, is deleted from the computer when Kaspersky Endpoint Security is uninstalled.
Data received as a result of IOC Scan task execution (standard task)
Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically submits data on the IOC Scan task execution results to Kaspersky Security Center.
The data in the IOC Scan task execution results may contain the following information:
- IP address from the ARP table
- Physical address from the ARP table
- DNS record type and name
- IP address of the protected computer
- Physical address (MAC-address) of the protected computer
- Identifier in the event log entry
- Data source name in the log
- Log name
- Event time
- MD5 and SHA256 hashes of the file
- Full name of the file (including path)
- File size
- Remote IP address and port to which connection was established during scan
- Local adapter IP address
- Port open on the local adapter
- Protocol as a number (in accordance with the IANA standard)
- Process name
- Process arguments
- Path to the process file
- Windows identifier (PID) of the process
- Windows identifier (PID) of the parent process
- User account that started the process
- Date and time when the process was started
- Service name
- Service description
- Path and name of the DLL service (for svchost)
- Path and name of the service executable file
- Windows identifier (PID) of the service
- Service type (for example, a kernel driver or adapter)
- Service status
- Service launch mode
- User account name
- Volume name
- Volume letter
- Volume type
- Windows registry value
- Registry hive value
- Registry key path (without hive and value name)
- Registry setting
- System (environment)
- Name and version of the operating system that is installed on the computer
- Network name of the protected computer
- Domain or group the protected computer belongs to
- Browser name
- Browser version
- Time when the web resource was last accessed
- URL from the HTTP request
- Name of the account used for the HTTP request
- File name of the process that made the HTTP request
- Full path to the file of the process that made the HTTP request
- Windows identifier (PID) of the process that made the HTTP request
- HTTP referer (HTTP request source URL)
- URI of the resource requested over HTTP
- Information about the HTTP user agent (the application that made the HTTP request)
- HTTP request execution time
- Unique identifier of the process that made the HTTP request
Data for creating a threat development chain
Data for creating a threat development chain is stored for seven days by default. The data is automatically sent to Kaspersky Security Center.
Data for creating a threat development chain may contain the following information:
- Incident date and time
- Detection name
- Scan mode
- Status of the last action related to the detection
- Reason why the detection processing failed
- Detected object type
- Detected object name
- Threat status after the object is processed
- Reason why execution of actions on the object failed
- Actions performed to roll back malicious actions
- Information about the processed object:
- Unique identifier of the process
- Unique identifier of the parent process
- Unique identifier of the process file
- Windows process identifier (PID)
- Process command line
- User account that started the process
- Code of the logon session in which the process is running
- Type of the session in which the process is running
- Integrity level of the process being processed
- Membership of the user account that started the process in the privileged local and domain groups
- Identifier of the processed object
- Full name of the processed object
- Identifier of the protected device
- Full name of the object (local file name or downloaded file web address)
- MD5 or SHA256 hash of the processed object
- Type of the processed object
- Creation date of the processed object
- Date when the processed object was last modified
- Size of the processed object
- Attributes of the processed object
- Organization that signed the processed object
- Result of the processed object digital certificate verification
- Security identifier (SID) of the processed object
- Time zone identifier of the processed object
- Web address of the processed object download (only for files on disk)
- Name of the application that downloaded the file
- MD5 and SHA256 hashes of the application that downloaded the file
- Name of the application that last modified the file
- MD5 and SHA256 hashes of the application that last modified the file
- Number of processed object starts
- Date and time when the processed object was first started
- Unique identifiers of the file
- Full name of the file (local file name or downloaded file web address)
- Path to the processed Windows registry variable
- Name of the processed Windows registry variable
- Value of the processed Windows registry variable
- Type of the processed Windows registry variable
- Indicator of the processed registry key membership in the autorun point
- Web address of the processed web request
- Link source of the processed web request
- User agent of the processed web request
- Type of the processed web request (GET or POST).
- Local IP port of the processed web request
- Remote IP port of the processed web request
- Connection direction (inbound or outbound) of the processed web request
- Identifier of the process into which the malicious code was embedded
Kaspersky Sandbox
All data that the application stores locally on the computer, is deleted from the computer when Kaspersky Endpoint Security is uninstalled.
Service data
Kaspersky Endpoint Security stores the following data processed during automatic response:
- Processed files and data entered by the user during configuration of the built-in agent of Kaspersky Endpoint Security:
- Quarantined files
- Public key of the certificate used for integration with Kaspersky Sandbox
- Cache of the built-in agent of Kaspersky Endpoint Security:
- Time when scan results were written to the cache
- MD5 hash of the scan task
- Scan task identifier
- Scan result for the object
- Queue of object scan requests:
- ID of the object in the queue
- Time when the object was placed in the queue
- Processing status of the object in the queue
- ID of the user session in the operating system where the object scan task was created
- System identifier (SID) of the operating system user whose account was used to create the task
- MD5 hash of the object scan task
- Information about the tasks for which the built-in agent of Kaspersky Endpoint Security is awaiting scan results from Kaspersky Sandbox:
- Time when the object scan task was received
- Object processing status
- ID of the user session in the operating system where the object scan task was created
- Identifier of the object scan task
- MD5 hash of the object scan task
- System identifier (SID) of the operating system user whose account was used to create the task
- XML schema of the automatically created IOC
- MD5 or SHA256 hash of the scanned object
- Processing errors
- Names of the objects for which the task was created
- Scan result for the object
Data in requests to Kaspersky Sandbox
The following data from requests from the built-in agent of Kaspersky Endpoint Security to Kaspersky Sandbox is stored locally on the computer:
- MD5 hash of the scan task
- Scan task identifier
- Scanned object and all related files
Data received as a result of IOC Scan task execution (stand-alone task)
Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically submits data on the IOC Scan task execution results to Kaspersky Security Center.
The data in the IOC Scan task execution results may contain the following information:
- IP address from the ARP table
- Physical address from the ARP table
- DNS record type and name
- IP address of the protected computer
- Physical address (MAC-address) of the protected computer
- Identifier in the event log entry
- Data source name in the log
- Log name
- Event time
- MD5 and SHA256 hashes of the file
- Full name of the file (including path)
- File size
- Remote IP address and port to which connection was established during scan
- Local adapter IP address
- Port open on the local adapter
- Protocol as a number (in accordance with the IANA standard)
- Process name
- Process arguments
- Path to the process file
- Windows identifier (PID) of the process
- Windows identifier (PID) of the parent process
- User account that started the process
- Date and time when the process was started
- Service name
- Service description
- Path and name of the DLL service (for svchost)
- Path and name of the service executable file
- Windows identifier (PID) of the service
- Service type (for example, a kernel driver or adapter)
- Service status
- Service launch mode
- User account name
- Volume name
- Volume letter
- Volume type
- Windows registry value
- Registry hive value
- Registry key path (without hive and value name)
- Registry setting
- System (environment)
- Name and version of the operating system that is installed on the computer
- Network name of the protected computer
- Domain or group the protected computer belongs to
- Browser name
- Browser version
- Time when the web resource was last accessed
- URL from the HTTP request
- Name of the account used for the HTTP request
- File name of the process that made the HTTP request
- Full path to the file of the process that made the HTTP request
- Windows identifier (PID) of the process that made the HTTP request
- HTTP referer (HTTP request source URL)
- URI of the resource requested over HTTP
- Information about the HTTP user agent (the application that made the HTTP request)
- HTTP request execution time
- Unique identifier of the process that made the HTTP request
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (EDR)
All data that the application stores locally on the computer, is deleted from the computer when Kaspersky Endpoint Security is uninstalled.
Service data
The built-in agent of Kaspersky Endpoint Security stores the following data locally:
- Processed files and data entered by the user during configuration of the built-in agent of Kaspersky Endpoint Security:
- Quarantined files
- Settings of the built-in agent of Kaspersky Endpoint Security:
- Public key of the certificate used for integration with Central Node
- License data
- Data required for integration with Central Node:
- Telemetry event packet queue
- Cache of IOC file identifiers received from Central Node
- Objects to be passed to the server within the Get file task
- The Get forensic task results reports
Data in requests to KATA (EDR)
When integrating with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, the following data is stored locally on the computer:
Data from the built-in agent of Kaspersky Endpoint Security requests to the Central Node component:
- In synchronization requests:
- Unique ID
- Basic part of the server web address
- Computer name
- Computer IP address
- Computer MAC address
- Local time on the computer
- Self-defense status of Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Name and version of the operating system that is installed on the computer
- Version of Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Versions of the application settings and task settings
- Task statuses: identifiers of tasks, execution statuses, error codes
- In requests for obtaining files from the server:
- Unique identifiers of files
- Unique Kaspersky Endpoint Security identifier
- Unique identifiers of certificates
- Basic part of the web address of the server with the Central Node component installed
- Host IP-address
- In the reports on task execution results:
- Host IP-address
- Information about the objects detected during an IOC scan or YARA scan
- Flags of the additional actions performed upon completion of tasks
- Task execution errors and return codes
- Task completion statuses
- Task completion time
- Versions of the settings used for execution of the tasks
- Information about the objects submitted to the server, quarantined objects, and objects restored from quarantine: paths to objects, MD5 and SHA256 hashes, identifiers of quarantined objects
- Information about the processes started or stopped on a computer at the server's request: PID and UniquePID, error code, MD5 and SHA256 hashes of the objects
- Information about the services started or stopped on a computer at the server's request: service name, startup type, error code, MD5 and SHA256 hashes of file images of the services
- Information about the objects for which a memory dump was made for a YARA scan (paths, dump file identifier)
- Files requested by the server
- Telemetry packets
- Data on running processes:
- Executable file name, including full path and extension
- Process autorun parameters
- Process ID
- Login session ID
- Login session name
- Date and time when the process was started
- MD5 and SHA256 hashes of the object
- Data on files:
- File path
- File name
- File size
- File attributes
- Date and time when the file was created
- Date and time when the file was last modified
- File description
- Company name
- MD5 and SHA256 hashes of the object
- Registry key (for autorun points)
- Data in errors that occur when information about objects was retrieved:
- Full name of the object that was processed when an error occurred
- Error code
- Telemetry data:
- Host IP-address
- Data type in the registry prior to the committed update operation
- Data in the registry key prior to the committed change operation
- The text of the processed script or a part of it
- Type of the processed object
- Way of passing a command to the command interpreter
Data from requests of the Central Node component to the built-in agent of Kaspersky Endpoint Security:
- Task settings:
- Task type
- Task schedule settings
- Names and passwords of the accounts under which the tasks can be run
- Versions of settings
- Identifiers of quarantined objects
- Paths to the objects
- MD5 and SHA256 hashes of the objects
- Command line to start the process with the arguments
- Flags of the additional actions performed upon completion of tasks
- IOC file identifiers to be retrieved from the server
- IOC files
- Service name
- Service startup type
- Folders for which the results of the Get forensic task must be received
- Masks of the object names and extensions for the Get forensic task
- Network isolation settings:
- Types of settings
- Versions of settings
- Lists of network isolation exclusions and exclusion settings: traffic direction, IP addresses, ports, protocols, and full paths to executable files
- Flags of the additional actions
- Time of automatic isolation disabling
- Execution prevention settings
- Types of settings
- Versions of settings
- Lists of execution prevention rules and rule settings: paths to objects, types of objects, MD5 and SHA256 hashes of objects
- Flags of the additional actions
- Event filtering settings:
- Module names
- Full paths to objects
- MD5 and SHA256 hashes of the objects
- Identifiers of the entries in Windows event log
- Digital certificate settings
- Traffic direction, IP addresses, ports, protocols, full paths to executable files
- User names
- User login types
- Types of telemetry events for which filters are applied
Data in YARA scan results
The built-in agent of Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically transfers YARA scan results to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform to build a threat development chain.
The data is temporarily stored locally in the queue for sending task execution results to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server. The data is deleted from the temporary storage once it has been sent.
YARA scan results contain the following data:
- MD5 and SHA256 hashes of the file
- Full name of the file
- File path
- File size
- Process name
- Process arguments
- Path to the process file
- Windows identifier (PID) of the process
- Windows identifier (PID) of the parent process
- User account that started the process
- Date and time when the process was started
Compliance with European Union legislation (GDPR)
Kaspersky Endpoint Security may transmit data to Kaspersky under the following scenarios:
- Using Kaspersky Security Network.
- Activating the application with an activation code.
- Updating application modules and anti-virus databases.
- Following links in the application interface.
- Dump writing.
Irrespective of the data classification and territory from which the data is received, Kaspersky adheres to high standards for data security and employs various legal, organizational and technical measures to protect the data of users, to guarantee data security and confidentiality, and also to ensure the fulfillment of users' rights as guaranteed by applicable legislation. The text of the Privacy Policy is included in the application distribution kit and is available on the Kaspersky website.
Prior to using Kaspersky Endpoint Security, please carefully read the description of transmitted data in the End User License Agreement and Kaspersky Security Network Statement. If specific data transmitted from Kaspersky Endpoint Security under any of the described scenarios may be classified as personal data according to your local legislation or standard, you must ensure that such data is processed legally and obtain the consent of end users for the collection and transmission of such data.
Read the End User License Agreement and visit the Kaspersky website to learn more about how we receive, process, store, and destroy information about application usage after you accept the End User License Agreement and consent to the Kaspersky Security Network Statement. The license.txt and ksn_<language ID>.txt files contain the text of the End User License Agreement and Kaspersky Security Network Statement and are included in the application distribution kit.
If you do not want to transmit data to Kaspersky, you can disable data provision.
Using Kaspersky Security Network
By using Kaspersky Security Network, you agree to automatically provide the data listed in the Kaspersky Security Network Statement. If you do not agree to provide this data to Kaspersky, use Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN) or disable the use of KSN. For more details about KPSN, please refer to the documentation on Kaspersky Private Security Network.
Activating the application with an activation code
By using an activation code, you agree to automatically provide the data listed in the End User License Agreement. If you do not agree to provide this data to Kaspersky, use a key file to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Updating application modules and anti-virus databases
By using Kaspersky servers, you agree to automatically provide the data listed in the End User License Agreement. Kaspersky requires this information to verify that Kaspersky Endpoint Security is being legitimately used. If you do not agree to provide this information to Kaspersky, use Kaspersky Security Center for database updates or Kaspersky Update Utility.
Following links in the application interface
By using links in the application interface, you agree to automatically provide the data listed in the End User License Agreement. The precise list of data transmitted in each specific link depends on where the link is located in the application interface and which problem it aims to resolve. If you do not agree to provide this data to Kaspersky, use the simplified application interface or hide the application interface.
Dump writing
If you have enabled dump writing, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will create a dump file that will contain all memory data from application processes at the moment when this dump file was created.
Page top
Getting started
After installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security, you can manage the application using the following interfaces:
- Local application interface.
- Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console
Kaspersky Security Center lets you remotely install and uninstall, start and stop Kaspersky Endpoint Security, configure application settings, change the set of available application components, add keys, and start and stop update and scan tasks.
The application can be managed via Kaspersky Security Center using the Kaspersky Endpoint Security Management Plug-in.
For more details on managing the application through Kaspersky Security Center, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console (hereinafter also referred to as Web Console) is a web application intended for centrally performing the main tasks to manage and maintain the security system of an organization's network. Web Console is a Kaspersky Security Center component that provides a user interface. For detailed information about Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console (hereinafter also referred to as the "Cloud Console") is a cloud-based solution for protecting and managing an organization's network. For detailed information about Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console Help.
Web Console and Cloud Console let you do the following:
- Monitor the status of your organization's security system.
- Install Kaspersky applications on devices within your network.
- Manage installed applications.
- View reports on the security system status.
Management of Kaspersky Endpoint Security through the Web Console, Cloud Console, and Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console all provide different management capabilities. The available components and tasks also vary for the different Consoles.
About the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Management Plug-in
The Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Management Plug-in enables interaction between Kaspersky Endpoint Security and Kaspersky Security Center. The Management Plug-in lets you manage Kaspersky Endpoint Security by using policies, tasks, and local application settings. Interaction with Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is provided by the web plug-in.
The version of the Management Plug-in may differ from the version of Kaspersky Endpoint Security application installed on the client computer. If the installed version of the Management Plug-in has less functionality than the installed version of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, the settings of the missing functions are not regulated by the Management Plug-in. These settings can be modified by the user in the local interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
The web plug-in is not installed by default in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. In contrast to the Management Plug-in for the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console, which is installed on the administrator workstation, the web plug-in must be installed on a computer that has Kaspersky Security Center Web Console installed. The functionality of the web plug-in is available to all administrators that have access to Web Console in a browser. You can view the list of installed web plug-ins in Web Console interface: Console settings → Web plug-ins. For more details about the compatibility of web plug-in versions and Web Console, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
Installing the web plug-in
You can install the web plug-in as follows:
- Install web plug-in using Quick Start Wizard of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Web Console automatically prompts you to run the Quick Start Wizard when connecting Web Console to the Administration Server for the first time. You can also run the Quick Start Wizard in the Web Console interface (Discovery & Deployment → Deployment & Assignment → Quick Start Wizard). The Quick Start Wizard can also check if the installed web plug-ins are up to date and download the necessary updates. For more details on the Quick Start Wizard for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
- Install web plug-in from the list of available distribution packages in Web Console.
To install the web plug-in, select the distribution package of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security web plug-in in the Web Console interface: Console settings → Web plug-ins. The list of available distribution packages is updated automatically after new versions of Kaspersky applications are released.
- Download the distribution package to the Web Console from an external source.
To install the web plug-in, add the ZIP-archive of the distribution package for the Kaspersky Endpoint Security web plug-in in the Web Console interface: Console settings → Web plug-ins. The distribution package of the web plug-in can be downloaded on the Kaspersky website, for example.
Updating the Management Plug-in
To update the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Management Plug-in, download the latest version of the plug-in (included in distribution kit) and run the plug-in installation wizard.
If a new version of the web plug-in becomes available, Web Console will display the notification Updates are available for utilized plug-ins. You can proceed to update the web plug-in version from this Web Console notification. You can also manually check for new web plug-in updates in the Web Console interface (Console settings → Web plug-ins). The previous version of the web plug-in will be automatically removed during the update.
When the web plug-in is updated, already existing items (for example, policies or tasks) are saved. The new settings of items implementing new functions of Kaspersky Endpoint Security will appear in existing items and will have the default values.
You can update the web plug-in as follows:
- Update the web plug-in in the list of web plug-ins in online mode.
To update the web plug-in, you must select the distribution package of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security web plug-in in the Web Console interface (Console settings → Web plug-ins). Web Console checks for available updates on Kaspersky servers and downloads the relevant updates.
- Update the web plug-in from a file.
To update the web plug-in, you must select the ZIP-archive of the distribution package for the Kaspersky Endpoint Security web plug-in in the Web Console interface: Console settings → Web plug-ins. The distribution package of the web plug-in can be downloaded on the Kaspersky website, for example. You can update the Kaspersky Endpoint Security web plug-in only to a more recent version. The web plug-in cannot be updated to an older version.
If any item is opened (such as a policy or task), the web plug-in checks its compatibility information. If the version of the web plug-in is equal to or later than the version specified in the compatibility information, you can change the settings of this item. Otherwise, you cannot use the web plug-in to change the settings of the selected item. It is recommended to update the web plug-in.
Page top
Special considerations when working with different versions of management plug-ins
You can manage Kaspersky Endpoint Security via Kaspersky Security Center only if you have a Management Plug-in whose version is equal to or later than the version specified in the information regarding the compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security with the Management Plug-in. You can view the minimum required version of the Management Plug-in in the installer.ini file included in the distribution kit.
If any item is opened (such as a policy or task), the Management Plug-in checks its compatibility information. If the version of the Management Plug-in is equal to or later than the version specified in the compatibility information, you can change the settings of this item. Otherwise, you cannot use the Management Plug-in to change the settings of the selected item. It is recommended to upgrade the Management Plug-in.
If the Kaspersky Endpoint Security Management Plug-in is installed in the Administration Console, please consider the following when installing a new version of the Management Plug-in:
- The previous version of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security Management Plug-in will be removed.
- The new version of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security Management Plug-in supports management of the previous version of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows on users' computers.
- You can use the new version of the Management Plug-in to change the settings in policies, tasks, and other items created by the previous version of the Management Plug-in.
- For new settings, the new version of the Management Plug-in assigns the default values when a policy, policy profile, or task are saved for the first time.
After the Management Plug-in is upgraded, it is recommended to check and save the values of the new settings in policies and policy profiles. If you do not do this, the new groups of Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings on the user's computer will take the default values and can be edited (the
 attribute). It is recommended to check the settings starting with policies and policy profiles at the top level of the hierarchy. It is also recommended to use the user account that has access rights to all functional areas of Kaspersky Security Center.
attribute). It is recommended to check the settings starting with policies and policy profiles at the top level of the hierarchy. It is also recommended to use the user account that has access rights to all functional areas of Kaspersky Security Center.To learn about the new capabilities of the application, please refer to the Release Notes or the application help.
- If a new parameter has been added to a group of settings in the new version of the Management Plug-in, the previously defined status of the
 /
/  attribute for this group of settings is not changed.
attribute for this group of settings is not changed.
Special considerations when using encrypted protocols for interacting with external services
Kaspersky Endpoint Security and Kaspersky Security Center uses an encrypted communication channel with TLS (Transport Layer Security) to work with external services of Kaspersky. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses external services for the following functions:
- updating databases and application software modules;
- activating the application with an activation code (activation 2.0);
- using Kaspersky Security Network.
Use of TLS secures the application by providing the following features:
- Encryption. The contents of messages are confidential and are not disclosed to third-party users.
- Integrity. The message recipient is certain that the message contents have not been modified since the message was forwarded by the sender.
- Authentication. The recipient is certain that communication is established only with a trusted Kaspersky server.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses public key certificates for server authentication. A public key infrastructure (PKI) is required for working with certificates. A Certificate Authority is part of a PKI. Kaspersky uses its own Certificate Authority because Kaspersky services are highly technical and not public. In this case, when root certificates of Thawte, VeriSign, GlobalTrust and others are revoked, the Kaspersky PKI remains operational without disruptions.
Environments that have MITM (software and hardware tools that support parsing of the HTTPS protocol) are considered to be unsafe by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Errors may be encountered when working with Kaspersky services. For example, there may be errors regarding the use of self-signed certificates. These errors may occur because an HTTPS Inspection tool from your environment does not recognize the Kaspersky PKI. To rectify these problems, you must configure exclusions for interacting with external services.
Page top
Application interface
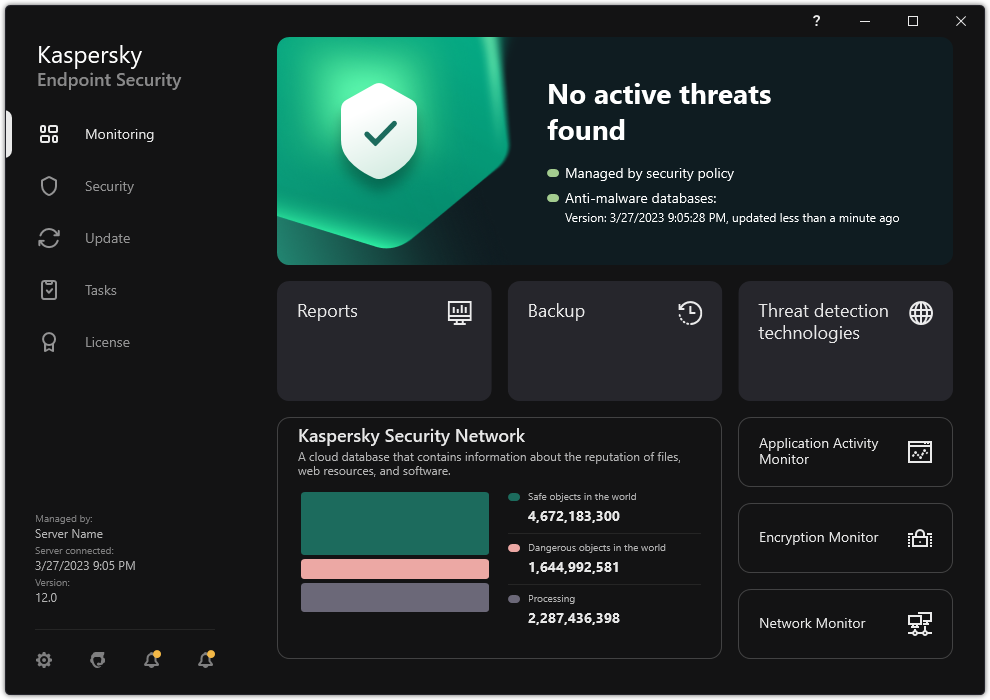
Main application window
Monitoring |
|
Security |
Operating status of installed components. You can also proceed to configuring components or viewing reports. |
Update |
Manage Kaspersky Endpoint Security update tasks. You can update anti-virus databases and application modules and roll back the last update. An administrator can hide the section from the user or restrict task management. |
Tasks |
Manage Kaspersky Endpoint Security scan tasks. You can run a malware scan and application integrity check. An administrator can hide tasks from a user or restrict management of tasks. |
License |
Application licensing. You can purchase a license, activate the application or renew a subscription. You can also view information about the current license. |
|
Configure application settings. An administrator can prohibit changes to settings in Kaspersky Security Center. |
|
Information about the application: current version of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, database release date, key, and other information. You can also proceed to Kaspersky information resources that provide useful information, recommendations, and answers to frequently asked questions on how to purchase, install, and use the application. |
|
Messages containing information about available updates and requests for access to encrypted files and devices. |
Application icon in the taskbar notification area
Immediately after installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, the application icon appears in the Microsoft Windows taskbar notification area.
The icon serves the following purposes:
- It indicates application activity.
- It acts as a shortcut to the context menu and main window of the application.
The following application icon statuses are provided for displaying application operating information:
- The
 icon signifies that critically important protection components of the application are enabled. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will display a warning
icon signifies that critically important protection components of the application are enabled. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will display a warning  if the user is required to perform an action, for example, restart the computer after updating the application.
if the user is required to perform an action, for example, restart the computer after updating the application. - The
 icon signifies that critically important protection components of the application are disabled or have malfunctioned. Protection components may malfunction, for example, if the license has expired or as a result of an application error. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will display a warning
icon signifies that critically important protection components of the application are disabled or have malfunctioned. Protection components may malfunction, for example, if the license has expired or as a result of an application error. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will display a warning  with a description of the problem in computer protection.
with a description of the problem in computer protection.
The context menu of the application icon contains the following items:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. Opens the main application window. In this window, you can adjust the operation of application components and tasks, and view the statistics of processed files and detected threats.
- Pause protection / Resume protection. Pause the operation of all protection and control components that are not marked by a lock (
 ) in the policy. Prior to performing this operation, it is recommended to disable the Kaspersky Security Center policy.
) in the policy. Prior to performing this operation, it is recommended to disable the Kaspersky Security Center policy.Prior to pausing the operation of protection and control components, the application requests the password for accessing Kaspersky Endpoint Security (account password or temporary password). You can then select the pause period: for a specific amount of time, until a restart, or upon user request.
This context menu item is available if Password Protection is enabled. To resume the operation of protection and control components, click Resume protection in the context menu of the application.
Pausing the operation of protection and control components does not affect the performance of update and malware scan tasks. The application also continues using Kaspersky Security Network.
- Disable policy / Enable policy. Disables a Kaspersky Security Center policy on the computer. All Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings are available for configuration, including settings that have a closed lock in the policy (
 ). If the policy is disabled, the application requests the password for accessing Kaspersky Endpoint Security (account password or temporary password). This context menu item is available if Password Protection is enabled. To enable the policy, select Enable policy in the context menu of the application.
). If the policy is disabled, the application requests the password for accessing Kaspersky Endpoint Security (account password or temporary password). This context menu item is available if Password Protection is enabled. To enable the policy, select Enable policy in the context menu of the application. - Settings. Opens the application settings window.
- Support. This opens a window containing the information necessary for contacting Kaspersky Technical Support.
- About. This item opens an information window with application details.
- Exit. This item quits Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Clicking this context menu item causes the application to be unloaded from the computer RAM.
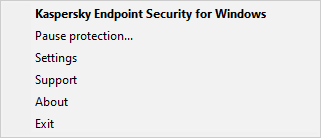
Application icon context menu
Simplified application interface
If a Kaspersky Security Center policy configured to display the simplified application interface is applied to a client computer on which Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed, the main application window is not available on this client computer. Right-click to open the context menu of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security icon (see the figure below) containing the following items:
- Disable policy / Enable policy. Disables a Kaspersky Security Center policy on the computer. All Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings are available for configuration, including settings that have a closed lock in the policy (
 ). If the policy is disabled, the application requests the password for accessing Kaspersky Endpoint Security (account password or temporary password). This context menu item is available if Password Protection is enabled. To enable the policy, select Enable policy in the context menu of the application.
). If the policy is disabled, the application requests the password for accessing Kaspersky Endpoint Security (account password or temporary password). This context menu item is available if Password Protection is enabled. To enable the policy, select Enable policy in the context menu of the application. - Tasks. Drop-down list containing the following items:
- Integrity check.
- Rollback of databases to their previous version.
- Full Scan.
- Custom Scan.
- Critical Areas Scan.
- Update.
- Support. This opens a window containing the information necessary for contacting Kaspersky Technical Support.
- Exit. This item quits Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Clicking this context menu item causes the application to be unloaded from the computer RAM.
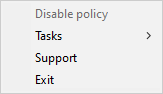
Context menu of the application icon when displaying the simplified interface
Configuring the display of the application interface
You can configure the application interface display mode for a user. The user can interact with the application in the following ways:
- Display simplified interface. On a client computer, the main application window is inaccessible, and only the icon in the Windows notification area is available. In the context menu of the icon, the user can perform a limited number of operations with Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Kaspersky Endpoint Security also displays notifications above the application icon.
- Display user interface. On a client computer, the main window of Kaspersky Endpoint Security and the icon in the Windows notification area are available. In the context menu of the icon, the user can perform operations with Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Kaspersky Endpoint Security also displays notifications above the application icon.
- Do not display. On a client computer, no signs of Kaspersky Endpoint Security operation are displayed. The icon in the Windows notification area and notifications are not available.
How to configure the application interface display mode in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to configure the application interface display mode in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Getting started
After deploying the application on client computers, to work with Kaspersky Endpoint Security from Kaspersky Security Center Web Console you need to perform the following actions:
- Create and configure a policy.
You can use policies to apply identical Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings to all client computers within an administration group. The Quick Start Wizard of Kaspersky Security Center automatically creates a policy for Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Create the Update and Malware Scan tasks.
The Update task is required for keeping computer security up to date. When the task is performed, Kaspersky Endpoint Security updates the anti-virus databases and application modules. The Update task is created automatically by the Administration Server quick start wizard. To create the Update task, install the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Management Plug-in while running the Wizard.
The Malware Scan task is required for the timely detection of viruses and other malware. You need to manually create the Malware Scan task.
How to create a Malware Scan task in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to create a Malware Scan task in the Web Console
Page top
Managing policies
A policy is a collection of application settings that are defined for an administration group. You can configure multiple policies with different values for one application. An application can run under different settings for different administration groups. Each administration group can have its own policy for an application.
Policy settings are sent to client computers by Network Agent during synchronization. By default, the Administration Server performs synchronization immediately after policy settings are changed. UDP port 15000 on the client computer is used for synchronization. The Administration Server performs synchronization every 15 minutes by default. If synchronization fails after policy settings were changed, the next synchronization attempt will be performed according to the configured schedule.
Active and inactive policy
A policy is intended for a group of managed computers and can be active or inactive. The settings of an active policy are saved on client computers during synchronization. You cannot simultaneously apply multiple policies to one computer, therefore only one policy may be active in each group.
You can create an unlimited number of inactive policies. An inactive policy does not affect application settings on computers in the network. Inactive policies are intended as preparations for emergency situations, such as a virus attack. If there is an attack via flash drives, you can activate a policy that blocks access to flash drives. In this case, the active policy automatically becomes inactive.
Out-of-office policy
An out-of-office policy is activated when a computer leaves the organization network perimeter.
Settings inheritance
Policies, like administration groups, are arranged in a hierarchy. By default, a child policy inherits settings from the parent policy. Child policy is a policy for nested hierarchy levels, that is a policy for nested administration groups and secondary Administration Servers. You can disable the inheritance of settings from the parent policy.
Each policy setting has the ![]() attribute, which indicates if the settings can be modified in the child policies or in the local application settings. The
attribute, which indicates if the settings can be modified in the child policies or in the local application settings. The ![]() attribute is applicable only if inheritance of parent policy settings is enabled for the child policy. Out-of-office policies do not affect other policies through the hierarchy of administration groups.
attribute is applicable only if inheritance of parent policy settings is enabled for the child policy. Out-of-office policies do not affect other policies through the hierarchy of administration groups.
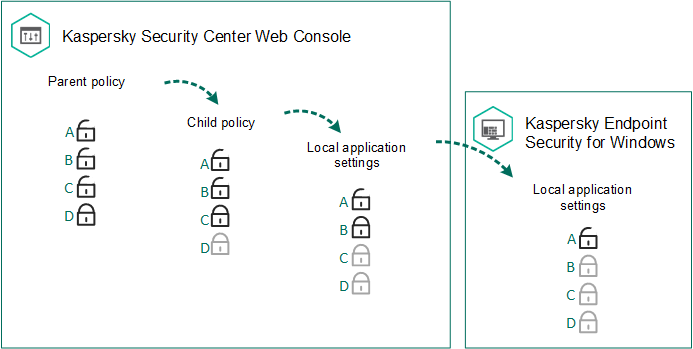
Settings inheritance
The rights to access policy settings (read, write, execute) are specified for each user who has access to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and separately for each functional scope of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. To configure the rights to access policy settings, go to the Security section of the properties window of the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
Creating a policy
How to create a policy in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to create a policy in the Web Console and Cloud Console
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings will be configured on client computers during the next synchronization. You can view information about the policy that is being applied to the computer in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface by clicking the ![]() button on the main screen (for example, the policy name). To do so, in the settings of the Network Agent policy, you need to enable the receipt of extended policy data. For more details about a Network Agent policy, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
button on the main screen (for example, the policy name). To do so, in the settings of the Network Agent policy, you need to enable the receipt of extended policy data. For more details about a Network Agent policy, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
Security level indicator
The security level indicator is displayed in the upper part of the Properties: <Policy name> window. The indicator can take one of the following values:
- High protection level. The indicator takes this value and turns green if all components from the following categories are enabled:
- Critical. This category includes the following components:
- File Threat Protection.
- Behavior Detection.
- Exploit Prevention.
- Remediation Engine.
- Important. This category includes the following components:
- Kaspersky Security Network.
- Web Threat Protection.
- Mail Threat Protection.
- Host Intrusion Prevention.
- Critical. This category includes the following components:
- Medium protection level. The indicator takes this value and turns yellow if one of the important components is disabled.
- Low protection level. The indicator takes this value and turns red in one of the following cases:
- One or multiple critical components are disabled.
- Two ore more important components are disabled.
If the indicator has the Medium protection level or Low protection level value, a link that opens the Advanced settings window appears to the right of the indicator. In this window, you can enable any of the recommended protection components.
Page top
Task management
You can create the following types of tasks to administer Kaspersky Endpoint Security through Kaspersky Security Center:
- Local tasks that are configured for an individual client computer.
- Group tasks that are configured for client computers within administration groups.
- Tasks for a selection of computers.
You can create any number of group tasks, tasks for a selection of computers, or local tasks. For more details about working with administration groups and selections of computers, please refer to Kaspersky Security Center Help.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the following tasks:
- Malware Scan. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the computer areas specified in the task settings for viruses and other threats. The Malware Scan task is required for the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security and is created during the Quick Start Wizard. It is recommended to schedule the task to run at least once a week.
- Add key. Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds a key for activating applications, including an additional key. Before running the task, make sure that the number of computers, on which the task is to be executed, does not exceed the number of computers allowed by the license.
- Change application components. Kaspersky Endpoint Security installs or removes components on client computers according to the list of components specified in the task settings. The File Threat Protection component cannot be removed. The optimal set of Kaspersky Endpoint Security components helps to conserve computer resources.
- Inventory. Kaspersky Endpoint Security receives information about all application executable files that are stored on computers. The Inventory task is performed by the Application Control component. If the Application Control component is not installed, the task will end with an error.
- Update. Kaspersky Endpoint Security updates databases and application modules. The Update task is required for the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security and is created during the Quick Start Wizard. It is recommended to configure a schedule that runs the task at least once per day.
- Wipe data. Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes files and folders from users' computers immediately or if there is no connection with Kaspersky Security Center for a long time.
- Update rollback. Kaspersky Endpoint Security rolls back the last update of databases and application modules. This may be necessary if, for example, new databases contain incorrect data that could cause Kaspersky Endpoint Security to block a safe application.
- Integrity check. Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes application files, checks files for corruption or modifications, and verifies the digital signatures of application files.
- Manage Authentication Agent accounts. Kaspersky Endpoint Security configures the Authentication Agent account settings. An Authentication Agent is needed for working with encrypted drives. Before the operating system is loaded, the user needs to complete authentication with the Agent.
Tasks are run on a computer only if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is running.
Add a new task
How to create a task in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to create a task in the Web Console and Cloud Console
A new task will be displayed in the list of tasks. The task will have the default settings. To configure the task settings, you need to go to the task properties. To run a task, you need to select the check box opposite the task and click the Start button. After the task has started, you can pause the task and resume it later.
In the list of tasks, you can monitor the task results, which include the task status and the statistics for task performance on computers. You can also create a selection of events to monitor the completion of tasks (Monitoring and reporting → Event selections). For more details on event selection, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help. Task execution results are also saved locally in Windows event log and in Kaspersky Endpoint Security reports.
Task access control
The rights to access Kaspersky Endpoint Security tasks (read, write, execute) are defined for each user who has access to Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server, through the settings of access to functional areas of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. To configure access to the functional areas of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, go to the Security section of the properties window of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server. For more details on task management through Kaspersky Security Center, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
You can configure users' rights to access tasks using a policy (task management mode). For example, you can hide group tasks in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface.
Task management settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Allow use of local tasks |
If the check box is selected, local tasks are displayed in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security local interface. When there are no additional policy restrictions, the user can configure and run tasks. However, configuring task run schedule remains unavailable for the user. The user can run tasks only manually. If the check box is cleared, use of local tasks is stopped. In this mode, local tasks do not run according to schedule. Tasks cannot be started or configured in the local interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, or when working with the command line. A user can still start a scan of a file or folder by selecting the Scan for viruses option in the context menu of the file or folder. The scan task is started with the default values of settings for the custom scan task. |
Allow group tasks to be displayed |
If the check box is selected, group tasks are displayed in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security local interface. The user can view the list of all tasks in the application interface. If the check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays an empty task list. |
Allow management of group tasks |
If the check box is selected, users can start and stop group tasks specified in Kaspersky Security Center. Users can start and stop tasks in the application interface or in the simplified application interface. If the check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts scheduled tasks automatically, or the administrator starts tasks manually in Kaspersky Security Center. |
Configuring local application settings
In Kaspersky Security Center, you can configure Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings on a particular computer. They are the local application settings. Some settings may be inaccessible for editing. These settings are locked by the ![]() attribute in the policy properties.
attribute in the policy properties.
How to configure the local application settings in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to configure the local application settings in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Starting and stopping Kaspersky Endpoint Security
After installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security to a user's computer, the application is started automatically. By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security is started after operating system startup. It is not possible to configure automatic startup of the application in the operating system settings.
Downloading Kaspersky Endpoint Security anti-virus databases after the operating system starts can take up to two minutes depending on the capabilities of the computer. During this time, the level of computer protection is reduced. The downloading of anti-virus databases when Kaspersky Endpoint Security is started on an already started operating system does not cause a reduction in the level of computer protection.
How to configure the startup of Kaspersky Endpoint Security in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to configure the startup of Kaspersky Endpoint Security in the Web Console
How to configure the startup of Kaspersky Endpoint Security in the application interface
Kaspersky experts recommend against manually stopping Kaspersky Endpoint Security because doing so exposes the computer and your personal data to threats. If necessary, you can pause computer protection for as long as you need to, without stopping the application.
You can monitor the application status by using the Protection Status widget.
How to start or stop Kaspersky Endpoint Security in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to start or stop Kaspersky Endpoint Security in the Web Console
How to start or stop Kaspersky Endpoint Security from the command line
Page top
Pausing and resuming computer protection and control
Pausing computer protection and control means disabling all protection and control components of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for some time.
The application status is displayed using the application icon in the taskbar notification area.
- The
 icon signifies that computer protection and control are paused.
icon signifies that computer protection and control are paused. - The
 icon signifies that computer protection and control are enabled.
icon signifies that computer protection and control are enabled.
Pausing or resuming computer protection and control does not affect scan or update tasks.
If any network connections are already established when you pause or resume computer protection and control, a notification about the termination of these network connections is displayed.
To pause computer protection and control:
- Right-click to bring up the context menu of the application icon that is in the taskbar notification area.
- In the context menu, select Pause protection (see the figure below).
This context menu item is available if Password Protection is enabled.
- Select one of the following options:
- Pause for <time period> – computer protection and control will resume after the amount of time that is specified in the drop-down list below.
- Pause until application restart – computer protection and control will resume after you restart the application or restart the operating system. Automatic startup of the application must be enabled to use this option.
- Pause – computer protection and control will resume when you decide to re-enable them.
- Click Pause protection.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security will pause the operation of all protection and control components that are not marked by a lock (![]() ) in the policy. Prior to performing this operation, it is recommended to disable the Kaspersky Security Center policy.
) in the policy. Prior to performing this operation, it is recommended to disable the Kaspersky Security Center policy.

Application icon context menu
To resume computer protection and control:
- Right-click to bring up the context menu of the application icon that is in the taskbar notification area.
- In the context menu, select Resume protection.
You can resume computer protection and control at any time, regardless of the computer protection and control pause option that you selected previously.
Page top
Creating and using a configuration file
A configuration file with Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings lets you accomplish the following tasks:
- Perform local installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security via the command line with predefined settings.
To do so, you must save the configuration file in the same folder where the distribution package is located.
- Perform remote installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security via Kaspersky Security Center with predefined settings.
- Migrate Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings from one computer to another (see the instructions below).
To create a configuration file:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Manage settings.
- Click Export.
- In the window that opens, specify the path to where you want to save the configuration file, and enter its name.
To use the configuration file for local or remote installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, you must name it install.cfg.
- Save the file.
To import Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings from a configuration file:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Manage settings.
- Click Import.
- In the window that opens, enter the path to the configuration file.
- Open the file.
All values of Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings will be set according to the selected configuration file.
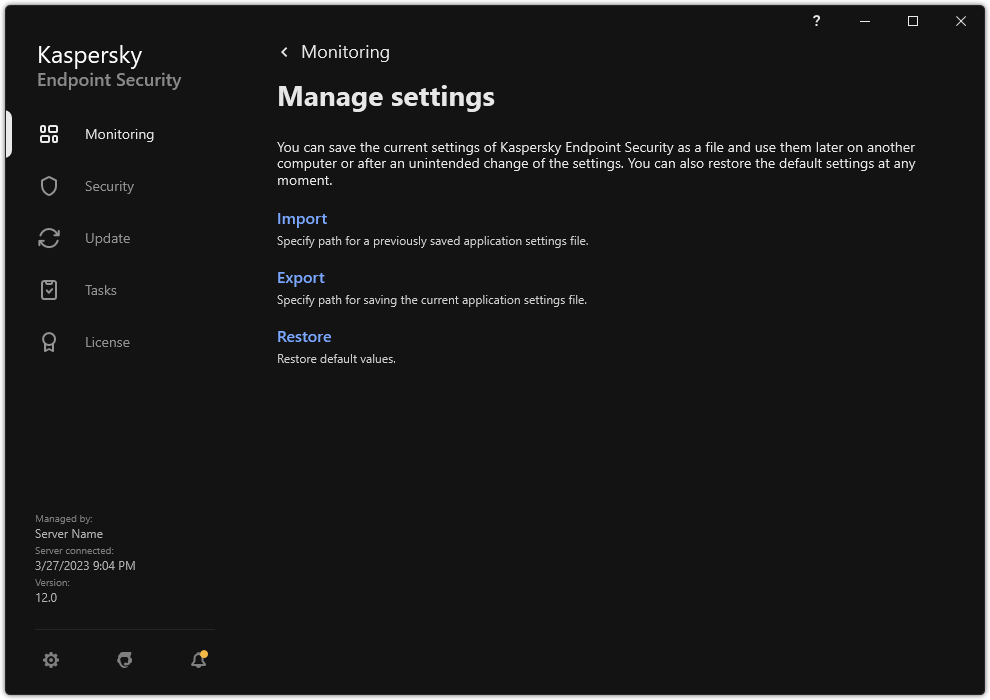
Managing the application settings
Page top
Restoring the default application settings
You can restore the application settings recommended by Kaspersky at any time. When the settings are restored, the Recommended security level is set for all protection components.
To restore the default application settings:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Manage settings.
- Click Restore.
- Save your changes.

Managing the application settings
Malware Scan
Malware scan is vital to computer security. Regularly run malware scans to rule out the possibility of spreading malware that is undetected by protection components due to a low security level setting or for other reasons.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan files whose contents are located in OneDrive cloud storage, and creates log entries stating that these files have not been scanned.
Full Scan
A thorough scan of the entire computer. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the following objects:
- Kernel memory;
- Objects that are loaded at startup of the operating system
- Boot sectors;
- Operating system backup
- All hard and removable drives
Kaspersky experts recommend that you do not change the scan scope of the Full Scan task.
To conserve computer resources, it is recommended to use a background scan task instead of a full scan task. This will not affect the security level of the computer.
Critical Areas Scan
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the kernel memory, running processes, and disk boot sectors.
Kaspersky experts recommend that you do not change the scan scope of the Critical Areas Scan task.
Custom Scan
Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the objects that are selected by the user. You can scan any object from the following list:
- System memory
- Objects that are loaded at startup of the operating system
- Operating system backup
- Microsoft Outlook mailbox
- Hard, removable, and network drives
- Any selected file
Background scan
Background scan is a scan mode of Kaspersky Endpoint Security that does not display notifications for the user. Background scan requires less computer resources than other types of scans (such as a full scan). In this mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans startup objects, the boot sector, system memory, and the system partition.
Integrity check
Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks the application modules for corruption or modifications.
Scanning the computer
A scan is vital to computer security. Regularly run malware scans to rule out the possibility of spreading malware that is undetected by protection components due to a low security level setting or for other reasons. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and heuristic analysis.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security has the following standard tasks predefined: Full Scan, Critical Areas Scan, Custom Scan. If your organization has the Kaspersky Security Center administration system deployed, you can create a Malware Scan task and configure the scan. The Background scan task is also available in Kaspersky Security Center. The background scan cannot be configured.
How to run a scan task in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to run a scan task in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to run a scan task in the application interface
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the computer and if a threat is detected, executes the action configured in application settings. Typically the application attempts to disinfect infected files. As a result, the infected files can receive the following statuses:
- Postponed. The infected file could not be disinfected. The application deletes the infected file after computer restart.
- Logged. The infected file could not be disinfected. The application adds information about detected infected files to the list of active threats.
- Write not supported or Write error. The infected file could not be disinfected. The application has no write access.
- Already processed. The application detected an infected file earlier. The application disinfects or deletes the infected file after computer restart.
Scan settings
Parameter
Description
Security level
Kaspersky Endpoint Security can use different groups of settings for running a scan. These groups of settings that are stored in the application are called security levels:
- High. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans all types of files. When scanning compound files, the application also scans mail-format files.
- Recommended. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans only the specified file formats on all hard drives, network drives, and removable storage media of the computer, and also embedded OLE objects. The application does not scan archives or installation packages.
- Low. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans only new or modified files with the specified extensions on all hard drives, removable drives, and network drives of the computer. The application does not scan compound files.
You can select one of the preset security levels or manually configure security level settings. If you change the security level settings, you can always revert back to the recommended security level settings.
Action on threat detection
Disinfect, delete if disinfection fails. If this option is selected, the application automatically attempts to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection fails, the application deletes the files.
Disinfect, block if disinfection fails. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically attempts to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection is not possible, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds the information about the infected files that are detected to the list of active threats.
Notify. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds the information about infected files to the list of active threats on detection of these files.
Before attempting to disinfect or delete an infected file, the application creates a backup copy of the file in case you need to restore the file or if it can be disinfected in the future.
On detection of infected files that are part of the Windows Store application, Kaspersky Endpoint Security attempts to delete the file.
Run Advanced Disinfection immediately
(available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console)
Advanced Disinfection during a virus scan task on a computer is performed only if the Advanced Disinfection feature is enabled in the properties of the policy applied to this computer.
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security disinfects the active infection immediately after it is detected during the execution of the virus scan task. After the active infection is disinfected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security reboots the computer without prompting the user.
If the check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not disinfect the active infection immediately after it is detected during the execution of the virus scan task. Kaspersky Endpoint Security generates active infection events in local application reports and on the Kaspersky Security Center side. The active infection can be disinfected when the virus scan task is run again with the Advanced Disinfection feature turned on. In this way, the system administrator can choose the appropriate time to do Advanced Disinfection and subsequently reboot the computers automatically.
Scan scope
List of objects that Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans while performing a scan task. Objects within the scan scope can include the kernel memory, running processes, boot sectors, system backup storage, mail databases, hard drive, removable drive or network drive, folder or file.
Scan schedule
Manually. Run mode in which you can start scan manually at a time when it is convenient for you.
By schedule. In this scan task run mode, the application starts the scan task in accordance with the schedule that you create. If this scan task run mode is selected, you can also start the scan task manually.
Postpone running after application startup for N minutes
Postponed start of the scan task after application startup. At operating system startup, many processes are running, therefore it is advantageous to postpone running the scan task instead of running it immediately after Kaspersky Endpoint Security startup.
Run skipped tasks
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the skipped scan task as soon as it becomes possible. The scan task may be skipped, for example, if the computer was off at the scheduled scan task start time. If the check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not run skipped scan tasks. Instead, it carries out the next scan task in accordance with the current schedule.
Run only when the computer is idle
Postponed start of the scan task when computer resources are busy. Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the scan task if the computer is locked or if the screen saver is on. If you have interrupted the execution of the task, for example by unlocking the computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically runs the task, continuing from the point where it was interrupted.
Run scan as
By default the scan task is run in the name of the user with whose rights you are registered in the operating system. The protection scope may include network drives or other objects that require special rights to access. You can specify a user that has the required rights in the application settings and run the scan task under this user's account.
File types
Kaspersky Endpoint Security considers files without an extension as executable ones. The application always scans executable files regardless of the file types that you select for scanning.
All files. If this setting is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks all files without exception (all formats and extensions).
Files scanned by format. If this setting is enabled, the application scans
only. Before scanning a file for malicious code, the internal header of the file is analyzed to determine the format of the file (for example, .txt, .doc, or .exe). The scan also looks for files with particular file extensions.Files scanned by extension. If this setting is enabled, the application scans infectable files only. The file format is then determined based on the file's extension.
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans files by their format. Scanning files by extension is less safe because a malicious file can have an extension that is not on the list of potentially infectable (for example,
.123).Scan only new and modified files
Scans only new files and those files that have been modified since the last time they were scanned. This helps reduce the duration of a scan. This mode applies both to simple and to compound files.
Skip objects scanned longer than N seconds
This sets a time limit for scanning a single object. After the specified amount of time, the application stops scanning a file. This helps reduce the duration of a scan.
Do not run multiple scan tasks at the same time
Postponed start of scan tasks if a scan is already running. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will enqueue new scan tasks if the current scan continues. This helps optimize the load on the computer. For example, let's assume that the application has started a Full Scan task according to the schedule. If a user attempts to start a quick scan from the application interface, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will enqueue this quick scan task and then automatically start this task after the Full Scan task is finished.
However, Kaspersky Endpoint Security immediately starts a scan task even if one of the following scan tasks is running:
- Scan of removable drives on connection.
- Scan from Context Menu.
- Critical Areas Scan that was started upon detection of an Indicator of Compromise (IoC).
If this check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you run multiple scan tasks at the same time. Running multiple scan tasks requires more computer resources.
Scan archives
Scanning ZIP, GZIP, BZIP, RAR, TAR, ARJ, CAB, LHA, JAR, ICE, and other archives. The application scans archives not only by extension, but also by format. When checking archives, the application performs a recursive unpacking. This allows to detect threats inside multi-level archives (archive within an archive).
Scan distribution packages
This check box enables/disables scanning of third-party distribution packages.
Scan files in Microsoft Office formats
Scans Microsoft Office files (DOC, DOCX, XLS, PPT and other Microsoft extensions). Office format files include OLE objects as well. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans office format files that are smaller than 1 MB, regardless of whether the check box is selected or not.
Scan email formats
Scanning email format files and the email database. The application scans PST and OST files used by MS Outlook and Windows Mail mail clients as well as EML files.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support the 64-bit version of MS Outlook email client. This means that Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan MS Outlook files (PST and OST files) if a 64-bit version of MS Outlook is installed on the computer, even if mail is included in the scan scope.
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security splits the mail-format file into its components (header, body, attachments) and scans them for threats.
If this check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the mail-format file as a single file.
Scan password-protected archives
If the check box is selected, the application scans password-protected archives. Before files in an archive can be scanned, you are prompted to enter the password.
If the check box is cleared, the application skips scanning of password-protected archives.
Do not unpack large compound files
If this check box is selected, the application does not scan compound files if their size exceeds the specified value.
If this check box is cleared, the application scans compound files of all sizes.
The application scans large files that are extracted from archives regardless of whether the check box is selected or not.
Machine learning and signature analysis
The machine learning and signature analysis method uses the Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases that contain descriptions of known threats and ways to neutralize them. Protection that uses this method provides the minimum acceptable security level.
Based on the recommendations of Kaspersky experts, machine learning and signature analysis is always enabled.
Heuristic Analysis
The technology was developed for detecting threats that cannot be detected by using the current version of Kaspersky application databases. It detects files that may be infected with an unknown virus or a new variety of a known virus.
When scanning files for malicious code, the heuristic analyzer executes instructions in the executable files. The number of instructions that are executed by the heuristic analyzer depends on the level that is specified for the heuristic analyzer. The heuristic analysis level ensures a balance between the thoroughness of searching for new threats, the load on the resources of the operating system, and the duration of heuristic analysis.
iSwift Technology
(available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface)
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scanning by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date that the file was last scanned on, and any modifications to the scanning settings. The iSwift technology is an advancement of the iChecker technology for the NTFS file system.
iChecker Technology
(available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface)
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scans by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date when the file was last scanned, and any modifications to the scan settings. There are limitations to iChecker Technology: it does not work with large files and applies only to files with a structure that the application recognizes (for example, EXE, DLL, LNK, TTF, INF, SYS, COM, CHM, ZIP, and RAR).
Scanning removable drives when they are connected to the computer
Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans all files that you run or copy, even if the file is located on a removable drive (File Threat Protection component). To prevent the spread of viruses and other malware, you can configure automatic scans of removable drives when they are connected to the computer. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically attempts to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection fails, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes the files. The component keeps a computer secure by running scans that implement machine learning, heuristic analysis (high level) and signature analysis. Kaspersky Endpoint Security also uses iSwift and iChecker scan optimization technologies. The technologies are always on and cannot be disabled.
How to configure running the Removable drives scan in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to configure running the Removable drives scan in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to configure running the Removable drives scan in the application interface
Removable drives scan task settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Action when a removable drive is connected |
Detailed Scan. If this item is selected, when a removable drive is connected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans all files on the removable drive, including files nested in compound objects, archives, distribution packages, and files in office formats. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan files in mail formats or password-protected archives. Quick Scan. If this option is selected, after a removable drive is connected Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans only files of specific formats that are most vulnerable to infection, and does not unpack compound objects. |
Maximum removable drive size |
If this check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the action that is selected in the Action when a removable drive is connected drop-down list on removable drives with a size not more than the specified maximum drive size. If the check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the action that is selected in the Action when a removable drive is connected drop-down list on removable drives of any size. |
Show scan progress |
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays the progress of removable drives scan in a separate window and in the Tasks section. If the check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs removable drives scan in the background. |
Block the stopping of the scan task |
If this check box is selected, then for the removable drives scan task in the local interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, the Stop button in the Tasks section and the Stop button in the removable drives scan window are not available. |
Background scan
Background scan is a scan mode of Kaspersky Endpoint Security that does not display notifications for the user. Background scan requires less computer resources than other types of scans (such as a full scan). In this mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans startup objects, the boot sector, system memory, and the system partition.
To conserve computer resources, it is recommended to use a background scan task instead of a full scan task. This will not affect the security level of the computer. These tasks have the same scan scope. To optimize the load on the computer, the application does not run a Full Scan task and a Background Scan task at the same time. If you have already ran a Full Scan task, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not start a Background Scan task for seven days after the Full Scan task is completed.
A background scan is started in the following cases:
- After an anti-virus database update.
- 30 minutes after Kaspersky Endpoint Security is started.
- Every six hours.
- When the computer is idling for five minutes or more (the computer is locked or the screensaver is on).
Background scan when the computer is idling is interrupted when any of the following conditions are true:
- The computer went into active mode.
If the background scan has not been run for more than ten days, the scan is not interrupted.
- The computer (laptop) has switched to battery mode.
When performing a background scan, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan files whose contents are located in OneDrive cloud storage.
How to enable background scanning in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to enable background scanning in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to enable background scanning in the application interface
Scan from context menu
Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you run a scan of individual files for viruses and other malware from the context menu (see the figure below).
When performing a scan from the context menu, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan files whose contents are located in OneDrive cloud storage.
Scan from context menu
How to configure Scan from Context Menu in Administration Console (MMC)
How to configure Scan from Context Menu in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to configure Scan from Context Menu in the application interface
Scan from Context Menu task settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Security level |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security can use different groups of settings for running a scan. These groups of settings that are stored in the application are called security levels:
|
Action on threat detection |
Disinfect, delete if disinfection fails. If this option is selected, the application automatically attempts to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection fails, the application deletes the files. Disinfect, block if disinfection fails. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically attempts to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection is not possible, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds the information about the infected files that are detected to the list of active threats. Notify. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds the information about infected files to the list of active threats on detection of these files. |
File types |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security considers files without an extension as executable ones. The application always scans executable files regardless of the file types that you select for scanning. All files. If this setting is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks all files without exception (all formats and extensions). Files scanned by format. If this setting is enabled, the application scans infectable files only. Before scanning a file for malicious code, the internal header of the file is analyzed to determine the format of the file (for example, .txt, .doc, or .exe). The scan also looks for files with particular file extensions. Files scanned by extension. If this setting is enabled, the application scans infectable files only. The file format is then determined based on the file's extension. By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans files by their format. Scanning files by extension is less safe because a malicious file can have an extension that is not on the list of potentially infectable (for example, |
Scan only new and modified files |
Scans only new files and those files that have been modified since the last time they were scanned. This helps reduce the duration of a scan. This mode applies both to simple and to compound files. |
Skip objects scanned longer than N seconds |
This sets a time limit for scanning a single object. After the specified amount of time, the application stops scanning a file. This helps reduce the duration of a scan. |
Scan archives |
Scanning ZIP, GZIP, BZIP, RAR, TAR, ARJ, CAB, LHA, JAR, ICE, and other archives. The application scans archives not only by extension, but also by format. When checking archives, the application performs a recursive unpacking. This allows to detect threats inside multi-level archives (archive within an archive). |
Scan distribution packages |
The check box enables or disables scanning of distribution packages. |
Scan files in Microsoft Office formats |
Scans Microsoft Office files (DOC, DOCX, XLS, PPT and other Microsoft extensions). Office format files include OLE objects as well. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans office format files that are smaller than 1 MB, regardless of whether the check box is selected or not. |
Scan email formats |
Scanning email format files and the email database. The application scans PST and OST files used by MS Outlook and Windows Mail mail clients as well as EML files. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support the 64-bit version of MS Outlook email client. This means that Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan MS Outlook files (PST and OST files) if a 64-bit version of MS Outlook is installed on the computer, even if mail is included in the scan scope. If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security splits the mail-format file into its components (header, body, attachments) and scans them for threats. If this check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the mail-format file as a single file. |
Scan password-protected archives |
If the check box is selected, the application scans password-protected archives. Before files in an archive can be scanned, you are prompted to enter the password. If the check box is cleared, the application skips scanning of password-protected archives. |
Do not unpack large compound files |
If this check box is selected, the application does not scan compound files if their size exceeds the specified value. If this check box is cleared, the application scans compound files of all sizes. The application scans large files that are extracted from archives regardless of whether the check box is selected or not. |
Machine learning and signature analysis |
The machine learning and signature analysis method uses the Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases that contain descriptions of known threats and ways to neutralize them. Protection that uses this method provides the minimum acceptable security level. Based on the recommendations of Kaspersky experts, machine learning and signature analysis is always enabled. |
Heuristic Analysis |
The technology was developed for detecting threats that cannot be detected by using the current version of Kaspersky application databases. It detects files that may be infected with an unknown virus or a new variety of a known virus. When scanning files for malicious code, the heuristic analyzer executes instructions in the executable files. The number of instructions that are executed by the heuristic analyzer depends on the level that is specified for the heuristic analyzer. The heuristic analysis level ensures a balance between the thoroughness of searching for new threats, the load on the resources of the operating system, and the duration of heuristic analysis. |
iSwift Technology |
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scanning by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date that the file was last scanned on, and any modifications to the scanning settings. The iSwift technology is an advancement of the iChecker technology for the NTFS file system. |
iChecker Technology |
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scans by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date when the file was last scanned, and any modifications to the scan settings. There are limitations to iChecker Technology: it does not work with large files and applies only to files with a structure that the application recognizes (for example, EXE, DLL, LNK, TTF, INF, SYS, COM, CHM, ZIP, and RAR). |
Application Integrity Control
Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks the application modules for corruption or modifications. For example, if an application library has an incorrect digital signature, the library is considered corrupt. The Integrity check task is intended for checking application files. Run the Integrity check task if Kaspersky Endpoint Security detected a malicious object but did not neutralize it.
You can create the Integrity check task both in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and in the Administration Console. It is not possible to create a task in the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
Application integrity breaches may occur in the following cases:
- A malicious object modified files of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. In this case, perform the procedure for restoring Kaspersky Endpoint Security using the tools of the operating system. After restoration, run a full scan of the computer and repeat the integrity check.
- The digital signature expired. In this case, update Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
How to run an application integrity check through the Administration Console (MMC)
How to run an application integrity check through the Web Console
How to run an integrity check in the application interface
Integrity check task settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Scan schedule |
Manually. Run mode in which you can start scan manually at a time when it is convenient for you. By schedule. In this scan task run mode, the application starts the scan task in accordance with the schedule that you create. If this scan task run mode is selected, you can also start the scan task manually. |
Run skipped tasks |
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the skipped scan task as soon as it becomes possible. The scan task may be skipped, for example, if the computer was off at the scheduled scan task start time. If the check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not run skipped scan tasks. Instead, it carries out the next scan task in accordance with the current schedule. |
Run only when the computer is idle |
Postponed start of the scan task when computer resources are busy. Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the scan task if the computer is locked or if the screen saver is on. If you have interrupted the execution of the task, for example by unlocking the computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically runs the task, continuing from the point where it was interrupted. |
Editing the scan scope
The Scan scope is a list of paths to folders and paths that Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans when executing the task. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports environment variables and the * and ? characters when entering a mask.
To edit the scan scope, we recommend using the Custom Scan task. Kaspersky experts recommend that you do not change the scan scope of the Full Scan and Critical Areas Scan tasks.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security has the following predefined objects as part of the scan scope:
- My email.
Files relevant to the Outlook mail client: data files (PST), offline data files (OST).
- System memory.
- Startup Objects.
Memory occupied by processes and application executable files that are run at system startup.
- Disk boot sectors.
Hard disk and removable disk boot sectors.
- System Backup.
Contents of the System Volume Information folder.
- All external devices.
- All hard drives.
- All network drives.
We recommend creating a separate scan task for scanning network drives or shared folders. In the settings of the Malware Scan task, specify a user that has write access to this drive; this is necessary to mitigate detected threats. If the server where the network drive is located has its own security tools, do not run the scan task for that drive. In this way, you can avoid checking object twice and improve the performance of the server.
To exclude folders or files from the scan scope, add the folder or file to the trusted zone.
How to edit a scan scope in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to edit a scan scope in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to edit a scan scope in the application interface
Page top
Running a scheduled scan
Fully scanning the computer takes some time and resources of the computer. You should choose the optimum time to run a computer scan to avoid adversely impacting the performance of other software. Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you configure a normal schedule for scanning the computer. This is convenient if your organization has a work schedule. You can configure a computer scan to run at night or on weekends. If it is impossible to run the scan task for any reason (for example, the computer is off at that time), you can configure the skipped task to be run automatically as soon as this becomes possible.
If configuring an optimum scan schedule proves impossible, Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you run a computer scan when the following special conditions are met:
- After a database update.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs the computer scan with the updated signature databases.
- After application startup.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs a computer scan when a specified amount of time elapses after application startup. At operating system startup, many processes are running, therefore it is advantageous to postpone running the scan task instead of running it immediately after Kaspersky Endpoint Security startup.
- Wake-on-LAN.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs a computer scan on schedule even if the computer is powered off. To do so, the application uses the Wake-on-LAN feature of the operating system. The Wake-on-LAN feature allows remotely powering on the computer by sending a special signal over the local network. To use this feature, you must enable Wake-on-LAN in BIOS settings.
You can configure running the scan using Wake-on-LAN only for the Malware Scan task in Kaspersky Security Center. You cannot enable Wake-on-LAN for scanning the computer in the application interface.
- When the computer is idling.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs a computer scan on schedule when the screensaver is active or the screen is locked. If the user unlocks the computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security pauses the scan. This means that it may take several days for the application to complete a full computer scan.
How to configure the scan schedule in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to configure the scan schedule in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to configure the scan schedule in the application interface
Scan schedule settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Scan schedule |
Manually. Run mode in which you can start scan manually at a time when it is convenient for you. By schedule. In this scan task run mode, the application starts the scan task in accordance with the schedule that you create. If this scan task run mode is selected, you can also start the scan task manually. |
Postpone running after application startup for N minutes |
Postponed start of the scan task after application startup. At operating system startup, many processes are running, therefore it is advantageous to postpone running the scan task instead of running it immediately after Kaspersky Endpoint Security startup. |
Run skipped tasks |
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the skipped scan task as soon as it becomes possible. The scan task may be skipped, for example, if the computer was off at the scheduled scan task start time. If the check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not run skipped scan tasks. Instead, it carries out the next scan task in accordance with the current schedule. |
Run only when the computer is idle |
Postponed start of the scan task when computer resources are busy. Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the scan task if the computer is locked or if the screen saver is on. If you have interrupted the execution of the task, for example by unlocking the computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically runs the task, continuing from the point where it was interrupted. |
Use automatically randomized delay for task starts (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
If the check box is selected, the task is not run strictly on schedule, but randomly within a certain interval, that is, the start times of the task are spread out. Randomized start times help avoid a great number of computers simultaneously accessing the Administration Server when the task is run on schedule. The range of randomized start times is automatically calculated when the task is created, depending on the number of computers that have the task assigned. Subsequently, the task is always run at its calculated start time. However, whenever task settings are modified or the task is run manually, the calculated start time changes. If the check box is cleared, the task is run exactly at scheduled time. |
Stop task if it has been running longer than N (min) (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
Limiting the task execution time After the specified amount of time, Kaspersky Endpoint Security stops the task. The task is not marked as completed. Next time Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs the task, it will be run from the beginning and on schedule. To reduce the task execution time, you can, for example, configure the scan scope or optimize the scan. |
Activate the device before the task is started through Wake-on-LAN (min) (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
If the check box is selected, the operating system of the computer is given a specified lead time to complete startup before the task is run. The default lead time is 5 minutes. Select the check box if you want to run the task on all computers including powered off computers. |
Running a scan as a different user
By default the scan task is run in the name of the user with whose rights you are registered in the operating system. The protection scope may include network drives or other objects that require special rights to access. You can specify a user that has the required rights in the application settings and run the scan task under this user's account.
You can run the following scans as a different user:
- Critical Areas Scan.
- Full Scan.
- Custom Scan.
- Scan from Context Menu.
You cannot configure user rights to run a Removable drives scan, a Background scan, or an Integrity check.
How to run a scan as a different user in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to run a scan as a different user in Web Console or Cloud Console
How to run a scan as a different user in the application interface
Page top
Scan optimization
You can optimize file scanning: reduce scan time and increase the operating speed of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. This can be achieved by scanning only new files and those files that have been modified since the previous scan. This mode applies both to simple and to compound files. You can also set a limit for scanning a single file. When the specified time interval expires, Kaspersky Endpoint Security excludes the file from the current scan (except archives and objects that include several files).
A common technique of concealing viruses and other malware is to implant them in compound files, such as archives or databases. To detect viruses and other malware that are hidden in this way, the compound file must be unpacked, which may slow down scanning. You can limit the types of compound files to be scanned and thereby speed up scanning.
You can also enable the iChecker and iSwift technologies. The iChecker and iSwift technologies optimize the speed of scanning files, by excluding files that have not been modified since the most recent scan.
How to optimize scanning in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to optimize scanning in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to optimize scanning in the application interface
Page top
Updating databases and application software modules
Updating the databases and application modules of Kaspersky Endpoint Security ensures up-to-date protection on your computer. New viruses and other types of malware appear worldwide on a daily basis. Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases contain information about threats and ways of neutralizing them. To detect threats quickly, you are urged to regularly update the databases and application modules.
Regular updates require a license in effect. If there is no current license, you will be able to perform an update only once.
The main update source for Kaspersky Endpoint Security is Kaspersky update servers.
Your computer must be connected to the Internet to successfully download the update package from Kaspersky update servers. By default, the Internet connection settings are determined automatically. If you are using a proxy server, you need to configure the proxy server settings.
Updates are downloaded over the HTTPS protocol. They may also be downloaded over the HTTP protocol when it is impossible to download updates over the HTTPS protocol.
While performing an update, the following objects are downloaded and installed on your computer:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases. Computer protection is provided using databases that contain signatures of viruses and other threats and information on ways to neutralize them. Protection components use this information when searching for and neutralizing infected files on your computer. The databases are constantly updated with records of new threats and methods for counteracting them. Therefore, we recommend that you update the databases regularly.
In addition to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the network drivers that enable the application's components to intercept network traffic are updated.
- Application modules. In addition to the databases of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, you can also update the application modules. Updating the application modules fixes vulnerabilities in Kaspersky Endpoint Security, adds new functions, or enhances existing functions.
While updating, the application modules and databases on your computer are compared against the up-to-date version at the update source. If your current databases and application modules differ from their respective up-to-date versions, the missing portion of the updates is installed on your computer.
Context help files can be updated together with application module updates.
If the databases are obsolete, the update package may be large, which may cause additional Internet traffic (up to several dozen MB).
Information about the current state of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases is displayed in the main application window or the tooltip that you see when you hover the cursor over the icon of the application in the notification area.
Information on update results and on all events that occur during the performance of the update task is logged in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security report.
Database and application module update scenarios
Updating the databases and application modules of Kaspersky Endpoint Security ensures up-to-date protection on your computer. New viruses and other types of malware appear worldwide on a daily basis. Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases contain information about threats and ways of neutralizing them. To detect threats quickly, you are urged to regularly update the databases and application modules.
The following objects are updated on users' computers:
- Anti-virus databases. Anti-virus databases include databases of malware signatures, description of network attacks, databases of malicious and phishing web addresses, databases of banners, spam databases, and other data.
- Application modules. Module updates are intended for eliminating vulnerabilities in the application and to improve computer protection methods. Module updates may change the behavior of application components and add new capabilities.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the following scenarios for updating databases and application modules:
- Update from Kaspersky servers.
Kaspersky update servers are located in various countries throughout the world. This ensures high reliability of updates. If an update cannot be performed from one server, Kaspersky Endpoint Security switches over to the next server.
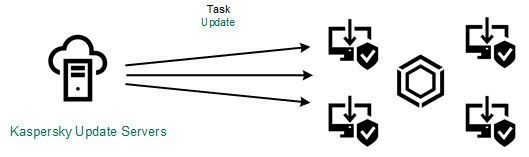
Update from Kaspersky servers
- Centralized update.
Centralized update reduces external Internet traffic, and provides for convenient monitoring of the update.
Centralized update consists of the following steps:
- Download the update package to a repository within the organization's network.
The update package is downloaded to the repository by the Administration Server task named Download updates to Administration Server repository.
- Download the update package to a shared folder (optional).
You can download the update package to a shared folder by using the following methods:
- Using Kaspersky Endpoint Security Update task. The task is intended for one of the computers in the local company network.
- Using the Kaspersky Update Utility. For detailed information about using Kaspersky Update Utility, refer to the Kaspersky Knowledge Base.
- Distribute the update package to client computers.
The update package is distributed to client computers by the Kaspersky Endpoint Security Update task. You can create an unlimited number of update tasks for each administration group.
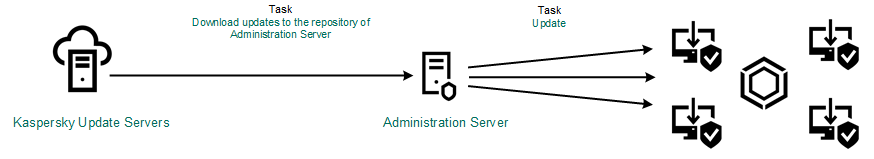
Updating from a server repository
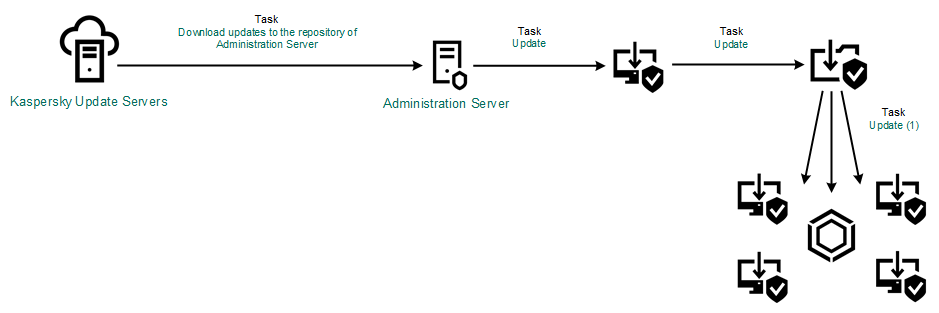
Updating from a shared folder
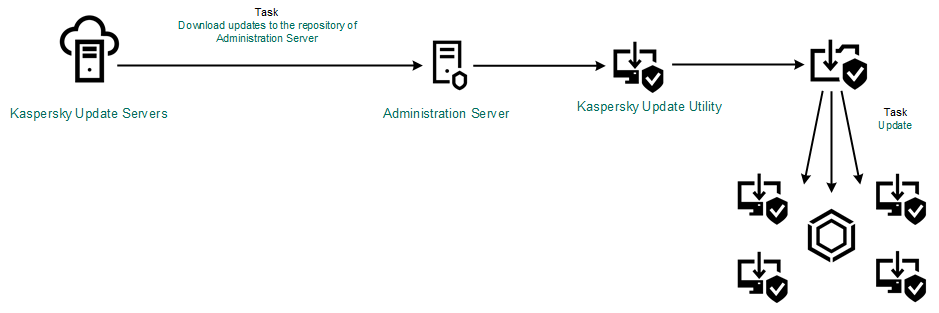
Updating using Kaspersky Update Utility
- Download the update package to a repository within the organization's network.
For the Web Console, the default list of update sources contains the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and Kaspersky update servers. For the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, the default list of update sources contains distribution points and Kaspersky update servers. For more details about distribution points, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console Help. You can add other update sources to the list. You can specify HTTP/FTP servers and shared folders as update sources. If an update cannot be performed from an update source, Kaspersky Endpoint Security switches over to the next one.
Updates are downloaded from Kaspersky update servers or from other FTP- or HTTP servers over standard network protocols. If connection to a proxy server is required for accessing the update source, specify the proxy server settings in Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings.
Updating from a server repository
To conserve Internet traffic, you can configure updates of databases and application modules on computers of the organization's LAN from a server repository. For this purpose, Kaspersky Security Center must download an update package to the repository (FTP- or HTTP server, network or local folder) from Kaspersky update servers. Other computers on the organization's LAN will be able to receive the update package from the server repository.
Configuring database and application module updates from a server repository consists of the following steps:
- Configure download of an update package to the Administration Server repository (Download updates to Administration Server repository task).
The Download updates to the Administration Server repository task is created automatically by the Administration Server quick start wizard, and this task may only have one single instance. By default, Kaspersky Security Center copies the update package to folder
\\<server name>\KLSHARE\Updates. For more information about downloading updates to the Administration Server repository, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help. - Configure database and application module updates from the specified server repository to the remaining computers on the organization's LAN (Update task).

Updating from a server repository
Updating from a shared folder
To conserve Internet traffic, you can configure updates of databases and application modules on computers of the organization's LAN from a shared folder. For this purpose, one of the computers on the organization's LAN must receive update packages from the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server or from Kaspersky update servers and then copy the received update package to the shared folder. Other computers on the organization's LAN will be able to receive the update package from this shared folder.
Configuring database and application module updates from a shared folder consists of the following steps:
- Configuring database and application module updates from a server repository.
- Enable copying of an update package to a shared folder on one of the computers on the enterprise LAN (see the instructions below).
- Configure database and application module updates from the specified shared folder to the remaining computers on the enterprise LAN (see the instructions below).
The version and localization of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security application that copies the update package to a shared folder must match the version and localization of the application that updates databases from the shared folder. If versions or localizations of the applications do not match, the database update may end with an error.

Updating from a shared folder
To enable copying of the update package to the shared folder:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Tasks.
The list of tasks opens.
The Update task must be assigned for one computer that will serve as the source of updates.
- Click the Update task of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
The task properties window opens.
The Update task is created automatically by the Administration Server quick start wizard. To create the Update task, install the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Management Plug-in while running the Wizard.
- Select the Application settings tab → Local mode.
- Configure the sources of updates.
The sources of updates can be Kaspersky update servers, Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server, other FTP- or HTTP servers, local folders, or network folders.
- Select the Copy updates to folder check box.
- In the Path field, enter the UNC path to the shared folder (for example,
\\Server\Share\Update distribution).If the field is left blank, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will copy the update package to the folder
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Kaspersky Lab\AVP11\Update distribution\. - Save your changes.
To configure updates from a shared folder:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Tasks.
The list of tasks opens.
- Click the Add button.
The Task Wizard starts.
- Configure the task settings:
- In the Application drop-down list, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (12.1).
- In the Task type drop-down list, select Update.
- In the Task name field, enter a brief description, for example, Updating from a shared folder.
- In the Select devices to which the task will be assigned block, select the task scope.
The Update task must be assigned to the computers of the organization's LAN, except the computer that serves as the update source.
- Select devices according to the selected task scope option and go to the next step.
- Exit the Wizard.
A new task will be displayed in the table of tasks.
- Click the newly created Update task.
The task properties window opens.
- Go to the Application settings section.
- Select the Local mode tab.
- In the Update source block, click Add.
- In the Source field, enter the path to the shared folder.
The source address must match the address that you previously specified in the Path field when you configured copying of the update package to the shared folder (see the instructions above).
- Click OK.
- Configure the priorities of update sources by using the Up and Down buttons.
- Save your changes.
Updating using Kaspersky Update Utility
To conserve Internet traffic, you can configure updates of databases and application modules on computers of the organization's LAN from a shared folder using the Kaspersky Update Utility. For this purpose, one of the computers on the organization's LAN must receive update packages from the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server or from Kaspersky update servers and then copy the received update packages to the shared folder using the utility. Other computers on the organization's LAN will be able to receive the update package from this shared folder.
Configuring database and application module updates from a shared folder consists of the following steps:
- Configuring database and application module updates from a server repository.
- Install the Kaspersky Update Utility on one of the computers of the organization's LAN.
- Configure copying of the update package to the shared folder in the Kaspersky Update Utility settings.
- Configure database and application module updates from the specified shared folder to the remaining computers on the organization's LAN.
The version and localization of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security application that copies the update package to a shared folder must match the version and localization of the application that updates databases from the shared folder. If versions or localizations of the applications do not match, the database update may end with an error.

Updating using Kaspersky Update Utility
You can download the Kaspersky Update Utility distribution package from the Kaspersky Technical Support website. After installing the utility, select the update source (for example, the Administration Server repository) and the shared folder to which the Kaspersky Update Utility will copy update packages. For detailed information about using Kaspersky Update Utility, refer to the Kaspersky Knowledge Base.
To configure updates from a shared folder:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Tasks.
The list of tasks opens.
- Click the Update task of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
The task properties window opens.
The Update task is created automatically by the Administration Server quick start wizard. To create the Update task, install the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Management Plug-in while running the Wizard.
- Select the Application settings tab → Local mode.
- In the list of update sources, click the Add button.
- In the Source field, enter the UNC path to the shared folder (for example,
\\Server\Share\Update distribution).The source address must match the address indicated in the Kaspersky Update Utility settings.
- Click OK.
- Configure the priorities of update sources by using the Up and Down buttons.
- Save your changes.
Updating in mobile mode
Mobile mode is the mode of Kaspersky Endpoint Security operation, when a computer leaves the organization network perimeter (offline computer). For more details about working with offline computers and out-of-office users, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
An offline computer outside of the organization's network cannot connect to the Administration Server to update databases and application modules. By default, only Kaspersky update servers are used as update source for updating databases and application modules in mobile mode. The use of a proxy server to connect to the Internet is determined by a special out-of-office policy. The out-of-office policy must be created separately. When Kaspersky Endpoint Security is switched to mobile mode, the update task is started every two hours.
To configure the update settings for mobile mode:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Tasks.
The list of tasks opens.
- Click the Update task of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
The task properties window opens.
The Update task is created automatically by the Administration Server quick start wizard. To create the Update task, install the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Management Plug-in while running the Wizard.
- Select the Application settings tab → Mobile mode.
- Configure the sources of updates. The sources of updates can be Kaspersky update servers, other FTP- and HTTP servers, local folders, or network folders.
- Save your changes.
As a result, the databases and application modules will be updated on user computers when they switch to mobile mode.
Page top
Starting and stopping an update task
Regardless of the selected update task run mode, you can start or stop a Kaspersky Endpoint Security update task at any time.
To start or stop an update task:
- In the main application window, go to the Update section.
- In the Update of databases and application modules tile, click the Update button if you want to start the update task.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security will start updating the application modules and databases. The application will display the task progress, the size of the downloaded files, and the update source. You can stop the task at any time by clicking the Stop update button.
To start or stop the update task when the simplified application interface is displayed:
- Right-click to bring up the context menu of the application icon that is in the taskbar notification area.
- In the Tasks drop-down list in the context menu, do one of the following:
- select a non-running update task to start it
- select a running update task to stop it
- select a paused update task to resume or restart it
Starting an update task under the rights of a different user account
By default, the Kaspersky Endpoint Security update task is started on behalf of the user whose account you have used to log in to the operating system. However, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may be updated from an update source that the user cannot access due to a lack of required rights (for example, from a shared folder that contains an update package) or an update source for which proxy server authentication is not configured. In the application settings, you can specify a user that has such rights and start the Kaspersky Endpoint Security update task under that user account.
To start an update task under a different user account:
- In the main application window, go to the Update section.
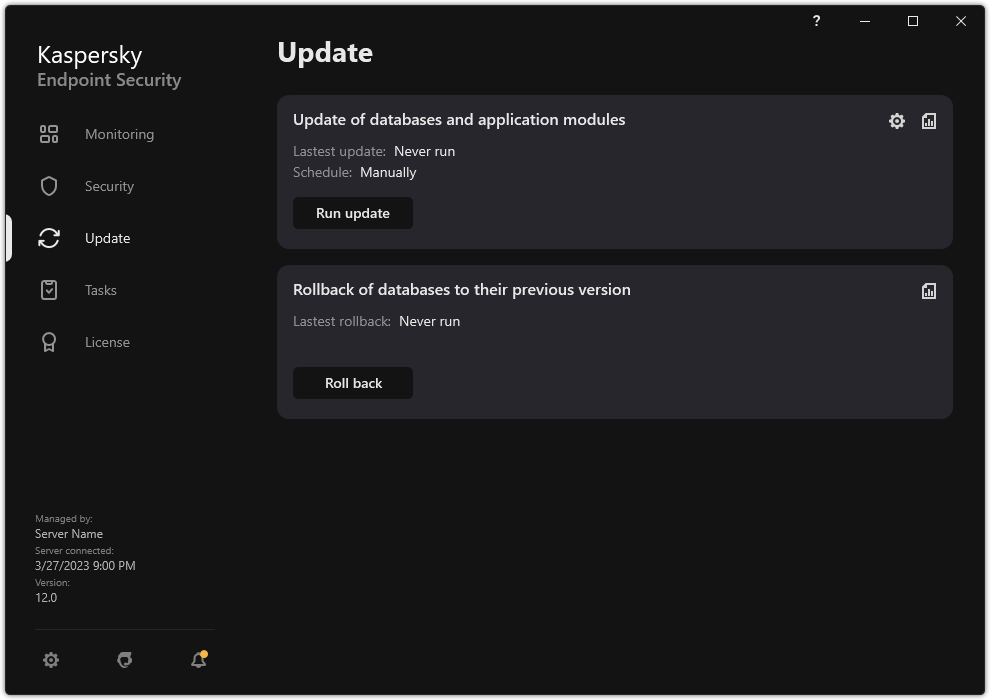
Local update tasks
- This opens the task list; select the Update of databases and application modules task and click
 .
.The task properties window opens.
- Click Run database updates with user rights.
- In the window that opens, select Other user.
- Enter the account credentials of a user with the necessary permissions to access the update source.
- Save your changes.
Selecting the update task run mode
If it is not possible to run the update task for any reason (for example, the computer is not on at that time), you can configure the skipped task to be start automatically as soon as this becomes possible.
You can postpone starting the update task after the application starts if you select the By schedule update task run mode, and if the start time of Kaspersky Endpoint Security matches the update task start schedule. The update task can only be run after the specified time interval elapses after the startup of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
To select the update task run mode:
- In the main application window, go to the Update section.

Local update tasks
- This opens the task list; select the Update of databases and application modules task and click
 .
.The task properties window opens.
- Click Run mode.
- In the window that opens, select the update task run mode:
- If you want Kaspersky Endpoint Security to run the update task depending on whether or not an update package is available from the update source, select Automatically. The frequency of checks by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for update packages increases during virus outbreaks and is less at other times.
- If you want to start an update task manually, select Manually.
- If you want to configure a schedule for running the update task, select other options. Configure the advanced settings for starting the update task:
- In the Postpone running after application startup for N minutes field, enter the time interval by which you want to postpone the start of the update task after the startup of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Select the Run scheduled scan on the next day if computer is turned off if you want Kaspersky Endpoint Security to run missed update tasks at the first opportunity.
- Save your changes.
Adding an update source
An update source is a resource that contains updates for databases and application modules of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Update sources include the Kaspersky Security Center server, Kaspersky update servers, and network or local folders.
The default list of update sources includes Kaspersky Security Center and Kaspersky update servers. You can add other update sources to the list. You can specify HTTP/FTP servers and shared folders as update sources.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support updates from HTTPS servers unless they are Kaspersky's update servers.
If several resources are selected as update sources, Kaspersky Endpoint Security tries to connect to them one after another, starting from the top of the list, and performs the update task by retrieving the update package from the first available source.
To add an update source:
- In the main application window, go to the Update section.

Local update tasks
- This opens the task list; select the Update of databases and application modules task and click
 .
.The task properties window opens.
- Click the Select update sources button.
- In the window that opens, click the Add button.
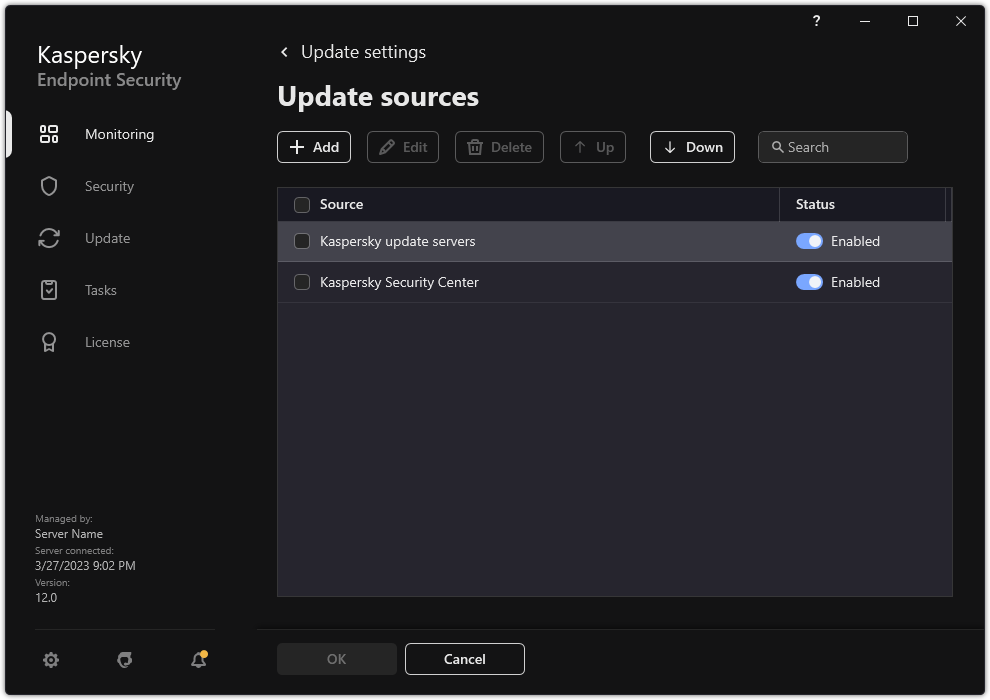
Sources of update
- In the window that opens, specify the address of the FTP or HTTP server, network folder or local folder that contains the update package.
The following path format is used for update source:
- For an FTP or HTTP server, enter its web address or IP address.
For example,
http://dnl-01.geo.kaspersky.com/or93.191.13.103.For an FTP server, you can specify the authentication settings within the address in the following format:
ftp://<user name>:<password>@<node>:<port>. - For a network folder, enter the UNC path.
For example,
\\ Server\Share\Update distribution. - For a local folder, enter the full path to that folder.
For example,
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Kaspersky Lab\AVP11\Update distribution\.
- For an FTP or HTTP server, enter its web address or IP address.
- Click the Select button.
- Configure the priorities of update sources by using the Up and Down buttons.
- Save your changes.
Configuring updates from a shared folder
To conserve Internet traffic, you can configure updates of databases and application modules on computers of the organization's LAN from a shared folder. For this purpose, one of the computers on the organization's LAN must receive update packages from the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server or from Kaspersky update servers and then copy the received update package to the shared folder. Other computers on the organization's LAN will be able to receive the update package from this shared folder.
Configuring database and application module updates from a shared folder consists of the following steps:
- Enabling the copying of an update package to a shared folder on one of the computers on the local area network.
- Configure database and application module updates from the specified shared folder to the remaining computers on the organization's LAN.
To enable copying of the update package to the shared folder:
- In the main application window, go to the Update section.

Local update tasks
- This opens the task list; select the Update of databases and application modules task and click
 .
.The task properties window opens.
- In the Distributing updates block, select the Copy updates to folder check box.
- Enter the UNC path to the shared folder (for example,
\\Server\Share\Update distribution). - Save your changes.
To configure updates from a shared folder:
- In the main application window, go to the Update section.

Local update tasks
- This opens the task list; select the Update of databases and application modules task and click
 .
. - The task properties window opens.
- Click Select update sources.
- In the window that opens, click the Add button.
- In the window that opens, enter the path to the shared folder.
The source address must match the address that you previously specified when you configured copying of the update package to the shared folder (see the instructions above).
- Click Select.
- Configure the priorities of update sources by using the Up and Down buttons.
- Save your changes.
Updating application modules
Application module updates fix errors, improve performance, and add new features. When a new application module update becomes available, you need to confirm installation of the update. You can confirm installation of an application module update either in the application interface or in Kaspersky Security Center. Whenever an update is available, the application displays a notification in the main window of Kaspersky Endpoint Security: ![]() . If application module updates require reviewing and accepting the terms of the End User License Agreement, the application installs updates after the terms of the End User License Agreement have been accepted. For details about keeping track of application module updates and confirming an update in Kaspersky Security Center, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
. If application module updates require reviewing and accepting the terms of the End User License Agreement, the application installs updates after the terms of the End User License Agreement have been accepted. For details about keeping track of application module updates and confirming an update in Kaspersky Security Center, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
After installing an application update, you may be required to restart your computer.
To configure application module updates:
- In the main application window, go to the Update section.

Local update tasks
- This opens the task list; select the Update of databases and application modules task and click
 .
.The task properties window opens.
- In the Downloading and installing updates of application modules block, select the Download updates of application modules check box.
- Select the application module updates that you want to install.
- Install critical and approved updates. If this option is selected, when application module updates are available Kaspersky Endpoint Security installs critical updates automatically and all other application module updates only after their installation is approved locally via the application interface or on the side of Kaspersky Security Center.
- Install only approved updates. If this option is selected, when application module updates are available Kaspersky Endpoint Security installs them only after their installation is approved locally via the application interface or on the side of Kaspersky Security Center. This option is selected by default.
- Save your changes.
Using a proxy server for updates
You may be required to specify proxy server settings to download database and application module updates from the update source. If there are multiple update sources, proxy server settings are applied for all sources. If a proxy server is not needed for some update sources, you can disable use of a proxy server in the policy properties. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will also use a proxy server to access Kaspersky Security Network and activation servers.
To configure a connection to update sources through a proxy server:
- In the main window of the Web Console, click
 .
.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- Go to the Configuring Internet access section.
- Select the Use proxy server check box.
- Configure the proxy server connection settings: proxy server address, port, and authentication settings (user name and password).
- Save your changes.
To disable use of a proxy server for a specific administration group:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Policies & Profiles.
- Click the name of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
The policy properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- Go to General settings → Network settings.
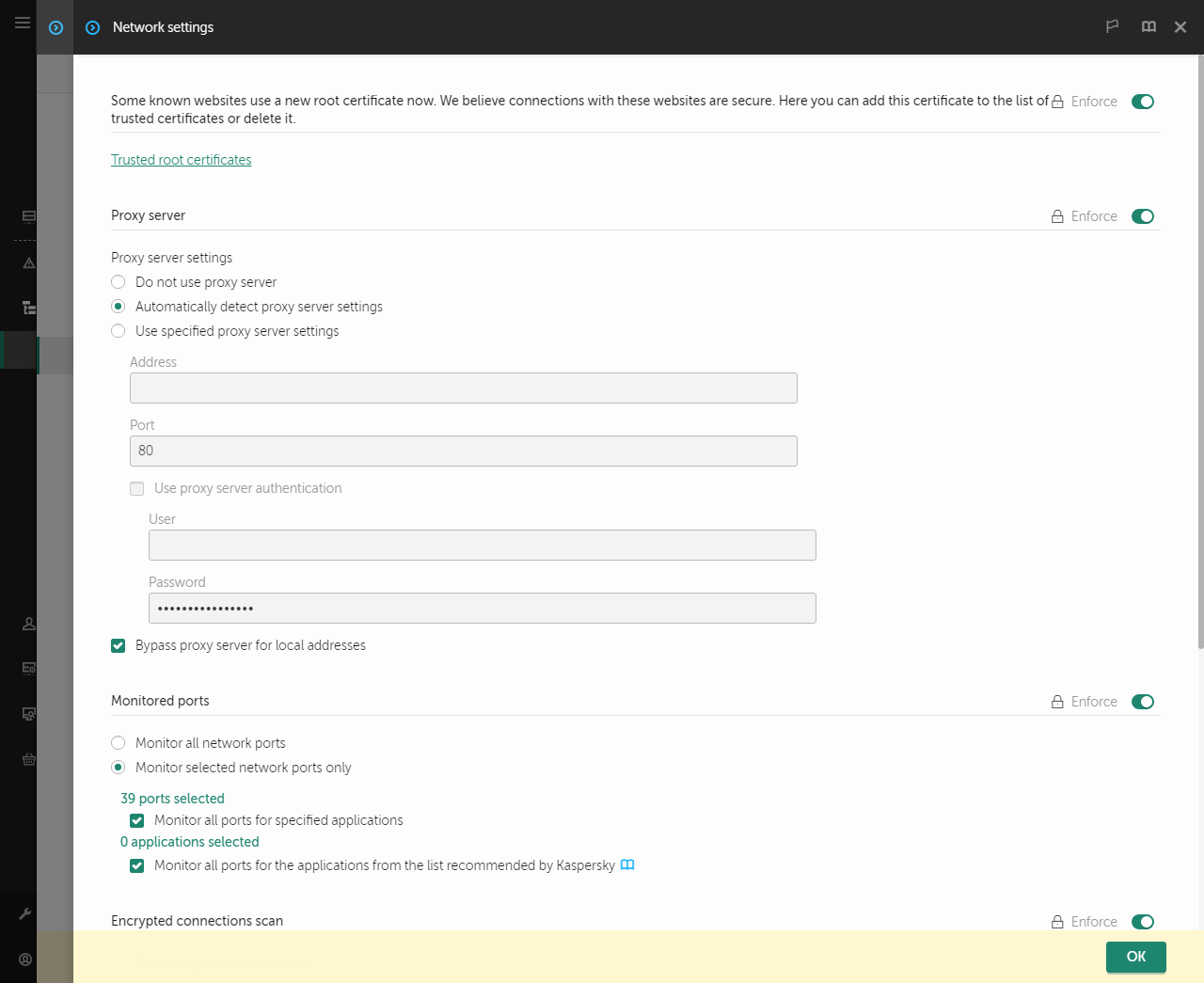
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows network settings.
- In the Proxy server settings block, select Bypass proxy server for local addresses.
- Save your changes.
To configure the proxy server settings in the application interface:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Network settings.
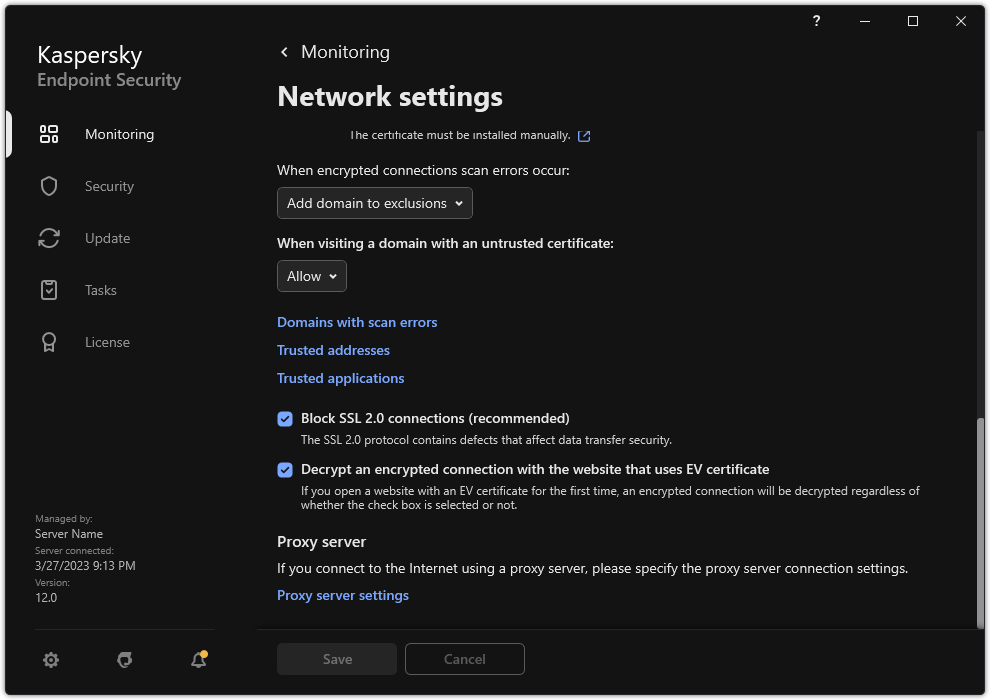
Application network settings
- In the Proxy server block, click the Proxy server settings link.
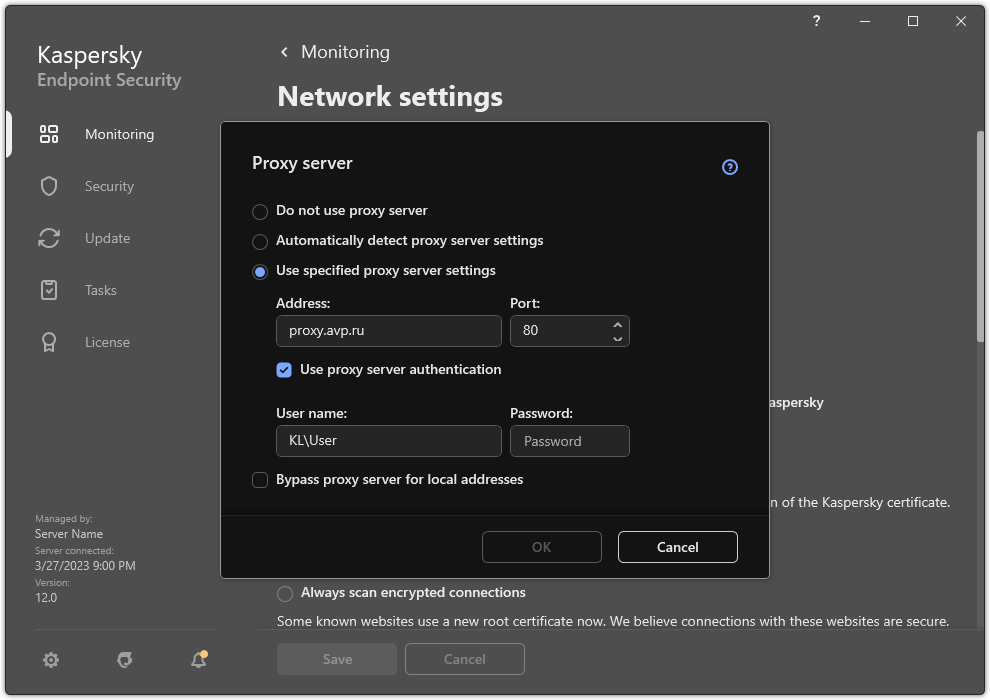
Proxy server connection settings
- In the window that opens, select one of the following options for determining the proxy server address:
- Automatically detect proxy server settings.
This option is selected by default. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the proxy server settings that are defined in the operating system settings.
- Use specified proxy server settings.
If you selected this option, configure the settings for connecting to the proxy server: proxy server address and port.
- Automatically detect proxy server settings.
- If you want to enable authentication on the proxy server, select the Use proxy server authentication check box and provide your user account credentials.
- If you want to disable proxy server use when updating databases and application modules from a shared folder, select the Bypass proxy server for local addresses check box.
- Save your changes.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will use the proxy server to download application module and database updates. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will also use the proxy server to access KSN servers and Kaspersky activation servers. If authentication is required on the proxy server but the user account credentials were not provided or are incorrect, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will prompt you for the user name and password.
Page top
Last update rollback
After the databases and application modules are updated for the first time, the function of rolling back the databases and application modules to their previous versions becomes available.
Each time that a user starts the update process, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates a backup copy of the current databases and application modules. This lets you roll back the databases and application modules to their previous versions when necessary. Rolling back the last update is useful, for example, when the new database version contains an invalid signature that causes Kaspersky Endpoint Security to block a safe application.
To roll back the last update:
- In the main application window, go to the Update section.

Local update tasks
- In the Rollback of databases to their previous version tile, click the Roll back button.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security will start rolling back the last database update. The application will display the rollback progress, the size of the downloaded files, and the update source. You can stop the task at any time by clicking the Stop update button.
To start or stop a rollback task when the simplified application interface is displayed:
- Right-click to bring up the context menu of the application icon that is in the taskbar notification area.
- In the Tasks drop-down list in the context menu, do one of the following:
- Select a non-running rollback task to start it.
- Select a running rollback task to stop it.
- Select a paused rollback task to resume or restart it.
Working with active threats
Kaspersky Endpoint Security logs information about files that it has not processed for some reason. This information is recorded in the form of events in the list of active threats (see the figure below). To work with active threats, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the Advanced Disinfection technology. Advanced Disinfection works differently for workstations and servers. You can configure advanced disinfection in Malware Scan task settings and in application settings.
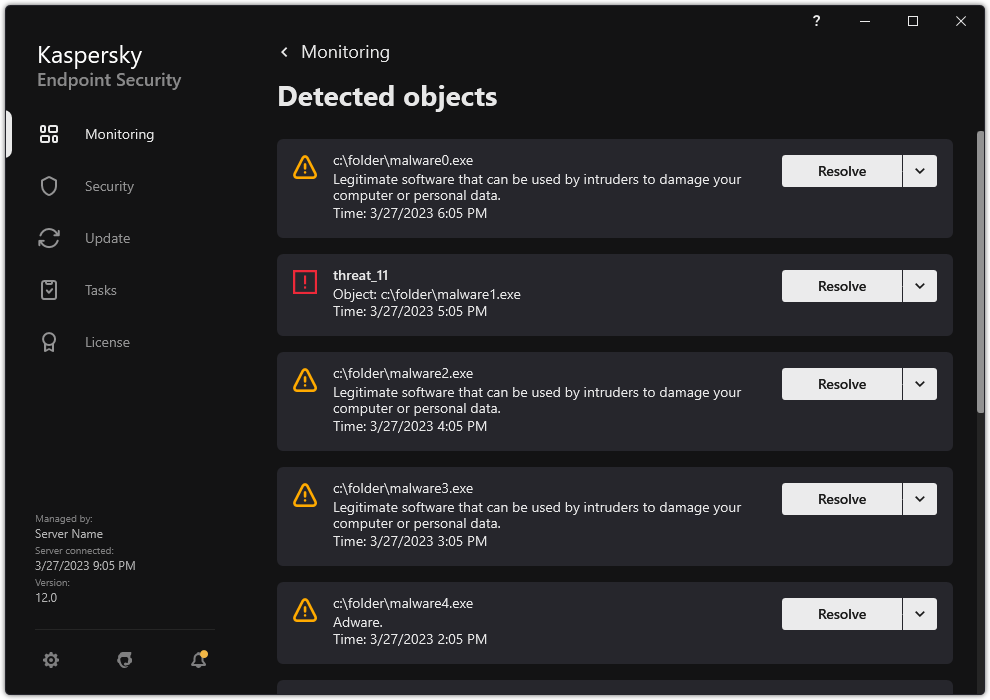
A list of active threats
Disinfection of active threats on workstations
To work with active threats on workstations, enable the Advanced Disinfection technology in the application settings. Next, configure the user experience in the Malware Scan task properties. There is a Run Advanced Disinfection immediately check box in the task properties. If the flag is set, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will perform disinfection without notifying the user. When the disinfection is complete, the computer will be rebooted. If the flag is unset, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will display a notification about active threats (see the figure below). You cannot close this notification without processing the file.
Advanced Disinfection during a virus scan task on a computer is performed only if the Advanced Disinfection feature is enabled in the properties of the policy applied to this computer.
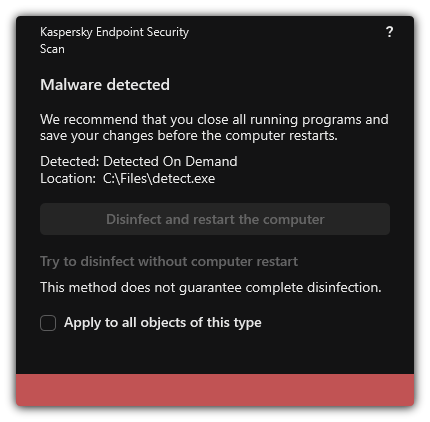
Notification about active threat
Page top
Disinfection of active threats on servers
To work with active threats on servers, you need to do the following:
- enable the Advanced Disinfection technology in the application settings;
- enable immediate Advanced Disinfection in the Malware Scan task properties.
If Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer running Windows for Servers, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not show the notification. Therefore, the user cannot select an action to disinfect an active threat. To disinfect a threat, you need to enable Advanced Disinfection technology in application settings and enable immediate Advanced Disinfection in Malware Scan task settings. Then you need to start a Malware Scan task.
Page top
Enabling or disabling Advanced Disinfection technology
If Kaspersky Endpoint Security cannot halt the execution of a piece of malware, you can use the Advanced Disinfection technology. By default, Advanced Disinfection is disabled because this technology uses a significant amount of computing resources. Therefore, you can enable Advanced Disinfection only when working with active threats.
Advanced Disinfection works differently for workstations and servers. To use the technology on servers, you must enable immediate advanced disinfection in the properties of the Malware Scan task. This prerequisite is not necessary to use the technology on workstations.
How to enable or disable the Advanced Disinfection technology in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to enable or disable the Advanced Disinfection technology in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to enable or disable the Advanced Disinfection technology in the application interface
As a result, the user cannot use most operating system features while Active Disinfection is in progress. When the disinfection is complete, the computer is rebooted.
Page top
Processing of active threats
An infected file is considered processed if Kaspersky Endpoint Security disinfected the file or removed the threat as part of scanning the computer for viruses and other malware.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security moves the file to the list of active threats if, for any reason, Kaspersky Endpoint Security failed to perform an action on this file according to the specified application settings while scanning the computer for viruses and other threats.
This situation is possible in the following cases:
- The scanned file is unavailable (for example, it is located on a network drive or on a removable drive without write privileges).
- In the Malware Scan task settings, the action on threat detection is set to Notify. Then, when the infected file notification was displayed on the screen, the user selected Skip.
If there are any unprocessed threats, Kaspersky Endpoint Security changes the icon to ![]() . In the main application window, the threat notification is displayed (see the figure below). In the Kaspersky Security Center console, the status of the computer is changed to Critical –
. In the main application window, the threat notification is displayed (see the figure below). In the Kaspersky Security Center console, the status of the computer is changed to Critical – ![]() .
.
How to process a threat in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to process a threat in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to process a threat in the application interface
Main application window when a threat is detected
Page top
File Threat Protection
The File Threat Protection component lets you prevent infection of the file system of the computer. By default, the File Threat Protection component permanently resides in the computer's RAM. The component scans files on all drives of the computer, as well as on connected drives. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and heuristic analysis.
The component scans the files accessed by the user or application. If a malicious file is detected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the file operation. The application then disinfects or deletes the malicious file, depending on the settings of the File Threat Protection component.
When attempting to access a file whose contents are stored in the OneDrive cloud, Kaspersky Endpoint Security downloads and scans the file contents.
Enabling and disabling File Threat Protection
By default, the File Threat Protection component is enabled and runs in the mode recommended by Kaspersky experts. For File Threat Protection, Kaspersky Endpoint Security can apply different groups of settings. These groups of settings that are stored in the application are called security levels: High, Recommended, Low. The Recommended security level settings are considered to be the optimal settings recommended by Kaspersky experts (see the table below). You can select one of the preset security levels or manually configure security level settings. If you change the security level settings, you can always revert back to the recommended security level settings.
To enable or disable the File Threat Protection component:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection.
- Use the File Threat Protection toggle to enable or disable the component.
- If you enabled the component, do one of the following in the Security level block:
- If you want to apply one of the preset security levels, select it with the slider:
- High. When this file security level is selected, the File Threat Protection component takes the strictest control of all files that are opened, saved, and started. The File Threat Protection component scans all file types on all hard drives, removable drives, and network drives of the computer. It also scans archives, installation packages, and embedded OLE objects.
- Recommended. This file security level is recommended by Kaspersky Lab experts. The File Threat Protection component scans only the specified file formats on all hard drives, removable drives, and network drives of the computer, and embedded OLE objects. The File Threat Protection component does not scan archives or installation packages. The values of settings for the recommended security level are provided in the table below.
- Low. The settings of this file security level ensure maximum scanning speed. The File Threat Protection component scans only files with specified extensions on all hard drives, removable drives, and network drives of the computer. The File Threat Protection component does not scan compound files.
- If you want to configure a custom security level, click the Advanced Settings button and define your own component settings.
You can restore the values of preset security levels by clicking the Restore recommended security level button.
- If you want to apply one of the preset security levels, select it with the slider:
- Save your changes.
File Threat Protection settings recommended by Kaspersky experts (recommended security level)
Parameter
Value
Description
File types
Files scanned by format
If this setting is enabled, the application scans infectable files only. Before scanning a file for malicious code, the internal header of the file is analyzed to determine the format of the file (for example, .txt, .doc, or .exe). The scan also looks for files with particular file extensions.
Heuristic Analysis
Light scan
The technology was developed for detecting threats that cannot be detected by using the current version of Kaspersky application databases. It detects files that may be infected with an unknown virus or a new variety of a known virus.
When scanning files for malicious code, the heuristic analyzer executes instructions in the executable files. The number of instructions that are executed by the heuristic analyzer depends on the level that is specified for the heuristic analyzer. The heuristic analysis level ensures a balance between the thoroughness of searching for new threats, the load on the resources of the operating system, and the duration of heuristic analysis.
Scan only new and modified files
On
Scans only new files and those files that have been modified since the last time they were scanned. This helps reduce the duration of a scan. This mode applies both to simple and to compound files.
Use iSwift technology
On
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scanning by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date that the file was last scanned on, and any modifications to the scanning settings. The iSwift technology is an advancement of the iChecker technology for the NTFS file system.
Use iChecker technology
On
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scans by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date when the file was last scanned, and any modifications to the scan settings. There are limitations to iChecker Technology: it does not work with large files and applies only to files with a structure that the application recognizes (for example, EXE, DLL, LNK, TTF, INF, SYS, COM, CHM, ZIP, and RAR).
Scan files in Microsoft Office formats
On
Scans Microsoft Office files (DOC, DOCX, XLS, PPT and other Microsoft extensions). Office format files include OLE objects as well. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans office format files that are smaller than 1 MB, regardless of whether the check box is selected or not.
Scan mode
Smart mode
In this mode, File Threat Protection scans an object based on an analysis of actions taken on the object. For example, when working with a Microsoft Office document, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the file when it is first opened and last closed. Intermediate operations that overwrite the file do not cause it to be scanned.
Action on threat detection
Disinfect, delete if disinfection fails
If this option is selected, the application automatically attempts to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection fails, the application deletes the files.
Automatic pausing of File Threat Protection
You can configure File Threat Protection to automatically pause at a specified time or when working with specific applications.
File Threat Protection should be paused only as a last resort when it conflicts with some applications. If any conflicts arise while a component is running, you are advised to contact Kaspersky Technical Support. The support experts will help you set up the File Threat Protection component to run simultaneously with other applications on your computer.
To configure automatic pausing of File Threat Protection:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection.
- Click Advanced Settings.
- In the Pause File Threat Protection block, click the Pause File Threat Protection link.
- In the window that opens, configure the settings for pausing File Threat Protection:
- Configure a schedule for automatically pausing File Threat Protection.
- Create a list of applications whose operation should cause File Threat Protection to pause its activities.
- Save your changes.
Changing the action taken on infected files by the File Threat Protection component
By default, the File Threat Protection component automatically tries to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection fails, the File Threat Protection component deletes these files.
To change the action taken on infected files by the File Threat Protection component:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection.
- In the Action on threat detection block, select the relevant option:
- Disinfect, delete if disinfection fails. If this option is selected, the application automatically attempts to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection fails, the application deletes the files.
- Disinfect, block if disinfection fails. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically attempts to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection is not possible, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds the information about the infected files that are detected to the list of active threats.
- Block. If this option is selected, the File Threat Protection component automatically blocks all infected files without attempting to disinfect them.
Before attempting to disinfect or delete an infected file, the application creates a backup copy of the file in case you need to restore the file or if it can be disinfected in the future.
- Save your changes.
Forming the protection scope of the File Threat Protection component
The protection scope refers to the objects that the component scans when enabled. The protection scopes of different components have different properties. The location and type of files to be scanned are properties of the protection scope of the File Threat Protection component. By default, the File Threat Protection component scans only potentially infectable files that are run from hard drives, removable drives and network drives.
When selecting the type of files to scan, consider the following:
- There is a low probability of introducing malicious code into files of certain formats and its subsequent activation (for example, TXT format). At the same time, there are file formats that contain executable code (such as .exe, .dll). The executable code may also be contained in files of formats that are not intended for this purpose (for example, the DOC format). The risk of intrusion and activation of malicious code in such files is high.
- An intruder may send a virus or another malicious application to your computer in an executable file that has been renamed with the .txt extension. If you select scanning of files by extension, the application skips this file during scanning. If scanning of files by format is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the file header regardless of its extension. If this analysis reveals that the file has the format of an executable file (for example, EXE), the application scans it.
To create the protection scope:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection.
- Click Advanced Settings.
- In the File types block, specify the type of files that you want the File Threat Protection component to scan:
- All files. If this setting is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks all files without exception (all formats and extensions).
- Files scanned by format. If this setting is enabled, the application scans infectable files only. Before scanning a file for malicious code, the internal header of the file is analyzed to determine the format of the file (for example, .txt, .doc, or .exe). The scan also looks for files with particular file extensions.
- Files scanned by extension. If this setting is enabled, the application scans infectable files only. The file format is then determined based on the file's extension.
- Click the Edit protection scope link.
- In the window that opens, select the objects that you want to add to the protection scope or exclude from it.
You cannot remove or edit objects that are included in the default protection scope.
- If you want to add a new object to the protection scope:
- Click Add.
The folder tree opens.
- Select an object to add to the protection scope.
You can exclude an object from scans without deleting it from the list of objects in the scan scope. To do so, clear the check box next to the object.
- Click Add.
- Save your changes.
Using scan methods
Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses a scanning technique called Machine learning and signature analysis. During signature analysis, Kaspersky Endpoint Security matches the detected object with records in its database. Based on the recommendations of Kaspersky experts, machine learning and signature analysis is always enabled.
To increase the effectiveness of protection, you can use heuristic analysis. When scanning files for malicious code, the heuristic analyzer executes instructions in the executable files. The number of instructions that are executed by the heuristic analyzer depends on the level that is specified for the heuristic analyzer. The heuristic analysis level ensures a balance between the thoroughness of searching for new threats, the load on the resources of the operating system, and the duration of heuristic analysis.
To configure the use of heuristic analysis in the operation of the File Threat Protection component:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection.
- Click Advanced Settings.
- If you want the application to use heuristic analysis for protection against file threats, select the Heuristic Analysis check box in the Scan methods block. Then use the slider to set the heuristic analysis level: Light scan, Medium scan or Deep scan.
- Save your changes.
Using scan technologies in the operation of the File Threat Protection component
To configure the use of scan technologies in the operation of the File Threat Protection component:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection.
- Click Advanced Settings.
- In the Scan technologies block, select the check boxes next to the names of technologies that you want to use for file threat protection:
- Use iSwift technology. This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scanning by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date that the file was last scanned on, and any modifications to the scanning settings. The iSwift technology is an advancement of the iChecker technology for the NTFS file system.
- Use iChecker technology. This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scans by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date when the file was last scanned, and any modifications to the scan settings. There are limitations to iChecker Technology: it does not work with large files and applies only to files with a structure that the application recognizes (for example, EXE, DLL, LNK, TTF, INF, SYS, COM, CHM, ZIP, and RAR).
- Save your changes.
Optimizing file scanning
You can optimize the file scanning that is performed by the File Threat Protection component by reducing the scan time and increasing the operating speed of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. This can be achieved by scanning only new files and those files that have been modified since the previous scan. This mode applies both to simple and to compound files.
You can also enable the use of the iChecker and iSwift technologies that optimize the speed of file scanning by excluding files that have not been modified since the most recent scan.
To optimize file scanning:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection.
- Click Advanced Settings.
- In the Optimization block, select the Scan only new and modified files check box.
- Save your changes.
Scanning compound files
A common technique of concealing viruses and other malware is to implant them in compound files, such as archives or databases. To detect viruses and other malware that are hidden in this way, the compound file must be unpacked, which may slow down scanning. You can limit the types of compound files to be scanned and thereby speed up scanning.
The method used to process an infected compound file (disinfection or deletion) depends on the type of file.
The File Threat Protection component disinfects compound files in the ZIP, GZIP, BZIP, RAR, TAR, ARJ, CAB, LHA, JAR and ICE formats and deletes files in all other formats (except mail databases).
To configure scanning of compound files:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection.
- Click Advanced Settings.
- In the Scan of compound files block, specify the types of compound files that you want to scan: archives, distribution package, or files in office formats.
- If scanning only new and modified files is disabled, configure the settings for scanning each type of compound file: scan all files of this type or only new files.
If scanning only new and modified files is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans only new and modified files of all types of compound files.
- Configure the advanced settings for scanning compound files.
- Do not unpack large compound files.
If this check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan compound files if their size exceeds the specified value.
If this check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans compound files of all sizes.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans large files that are extracted from archives, regardless of whether the Do not unpack large compound files check box is selected.
- Unpack compound files in the background.
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security provides access to compound files that are larger than the specified value before these files are scanned. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security unpacks and scans compound files in the background.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security provides access to compound files that are smaller than this value only after unpacking and scanning these files.
If the check box is not selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security provides access to compound files only after unpacking and scanning files of any size.
- Do not unpack large compound files.
- Save your changes.
Changing the scan mode
Scan mode refers to the condition that triggers file scanning by the File Threat Protection component. By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans files in smart mode. In this file scan mode, the File Threat Protection component decides whether or not to scan files after analyzing operations that are performed with the file by the user, by an application on behalf of the user (under the account that was used to log in or a different user account), or by the operating system. For example, when working with a Microsoft Office Word document, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the file when it is first opened and last closed. Intermediate operations that overwrite the file do not cause it to be scanned.
To change the file scan mode:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection.
- Click Advanced Settings.
- In the Scan mode block, select the required mode:
- Smart mode. In this mode, File Threat Protection scans an object based on an analysis of actions taken on the object. For example, when working with a Microsoft Office document, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the file when it is first opened and last closed. Intermediate operations that overwrite the file do not cause it to be scanned.
- On access and modification. In this mode, File Threat Protection scans objects whenever there is an attempt to open or modify them.
- On access. In this mode, File Threat Protection scans objects only upon an attempt to open them.
- On execution. In this mode, File Threat Protection only scans objects upon an attempt to run them.
- Save your changes.
Web Threat Protection
The Web Threat Protection component prevents downloads of malicious files from the Internet, and also blocks malicious and phishing websites. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and heuristic analysis.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans HTTP-, HTTPS- and FTP-traffic. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans URLs and IP addresses. You can specify the ports that Kaspersky Endpoint Security will monitor, or select all ports.
For HTTPS traffic monitoring, you need to enable encrypted connections scan.
When a user tries to open a malicious or phishing website, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block access and show a warning (see the figure below).
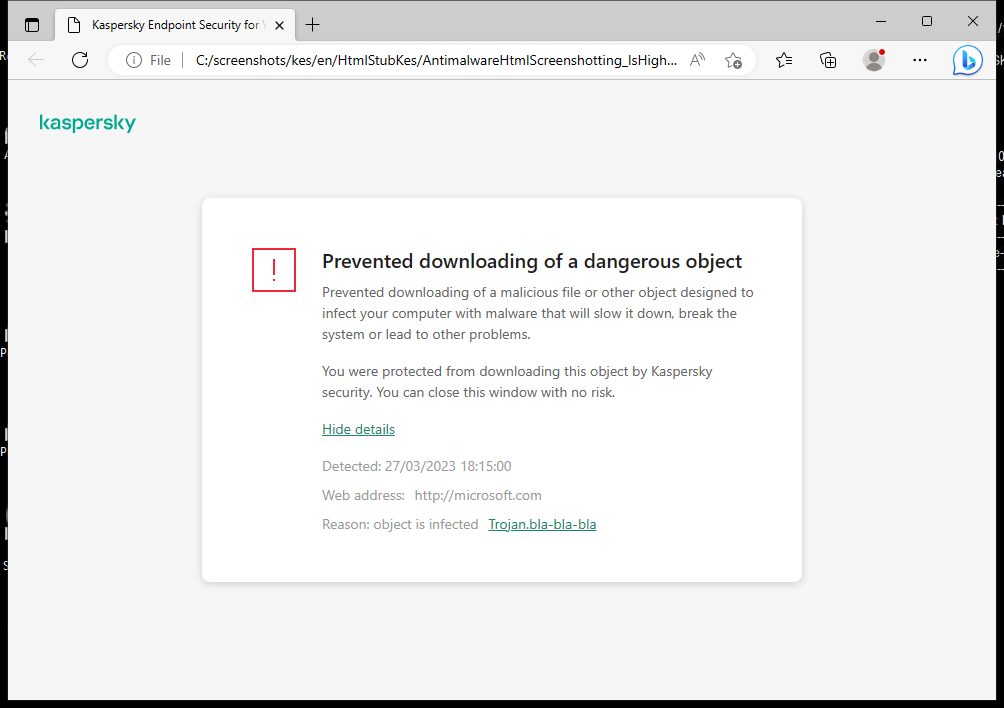
Website access denied message
Enabling and disabling Web Threat Protection
By default, the Web Threat Protection component is enabled and runs in the mode recommended by Kaspersky experts. For Web Threat Protection, the application can apply different groups of settings. These groups of settings that are stored in the application are called security levels: High, Recommended, Low. The Recommended web traffic security level settings are considered to be the optimal settings recommended by Kaspersky experts (see the table below). You can select one of the pre-installed security levels for web traffic that is received or transmitted via the HTTP and FTP protocols, or configure a custom web traffic security level. If you change the web traffic security level settings, you can always revert to the recommended web traffic security level settings.
You can select or configure the security level only in Administration Console (MMC) or the local interface of the application. You cannot select or configure the security level in Web Console or Cloud Console.
How to enable or disable the Web Threat Protection component in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to enable or disable the Web Threat Protection component in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to enable or disable the Web Threat Protection component
Web Threat Protection settings recommended by Kaspersky experts (recommended security level)
Parameter |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Check the web address against the database of malicious web addresses |
On |
Scanning the links to determine whether they are included in the database of malicious web addresses allows you to track websites that have been added to denylist. The database of malicious web addresses is maintained by Kaspersky, included in the application installation package, and updated during Kaspersky Endpoint Security database updates. |
Check the web address against the database of phishing web addresses |
On |
The database of phishing web addresses includes the web addresses of currently known websites that are used to launch phishing attacks. Kaspersky supplements this database of phishing links with addresses obtained from the international organization known as the Anti-Phishing Working Group. The database of phishing addresses is included in the application installation package and supplemented with Kaspersky Endpoint Security database updates. |
Use Heuristic Analysis (Web Threat Protection) |
Medium scan |
The technology was developed for detecting threats that cannot be detected by using the current version of Kaspersky application databases. It detects files that may be infected with an unknown virus or a new variety of a known virus. When web traffic is scanned for viruses and other applications that present a threat, the heuristic analyzer performs instructions in the executable files. The number of instructions that are executed by the heuristic analyzer depends on the level that is specified for the heuristic analyzer. The heuristic analysis level ensures a balance between the thoroughness of searching for new threats, the load on the resources of the operating system, and the duration of heuristic analysis. |
Use Heuristic Analysis (Anti-Phishing) |
On |
The technology was developed for detecting threats that cannot be detected by using the current version of Kaspersky application databases. It detects files that may be infected with an unknown virus or a new variety of a known virus. |
Action on threat detection |
Block |
If this option is selected and an infected object is detected in web traffic, the Web Threat Protection component blocks access to the object and displays a message in the browser. |
Page top
Configuring malicious web address detection methods
Web Threat Protection detects malicious web addresses using anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and heuristic analysis.
You can select malicious web address detection methods only in Administration Console (MMC) or the local interface of the application. You cannot select malicious web address detection methods in Web Console or Cloud Console. The default option is checking web addresses against the database of malicious addresses with heuristic analysis (medium scan).
Scanning using the database of malicious addresses
Scanning the links to determine whether they are included in the database of malicious web addresses allows you to track websites that have been added to denylist. The database of malicious web addresses is maintained by Kaspersky, included in the application installation package, and updated during Kaspersky Endpoint Security database updates.
Kaspersky Endpoint scans all links to determine if they are listed in databases of malicious web addresses. The application's secure connection scan settings do not affect the link scanning functionality. In other words, if encrypted connections scan is disabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks links against databases of malicious web addresses even if network traffic is transmitted over an encrypted connection.
Heuristic analysis
During heuristic analysis, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the activity of applications in the operating system. Heuristic analysis can detect threats for which there are currently no records in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases.
When web traffic is scanned for viruses and other applications that present a threat, the heuristic analyzer performs instructions in the executable files. The number of instructions that are executed by the heuristic analyzer depends on the level that is specified for the heuristic analyzer. The heuristic analysis level ensures a balance between the thoroughness of searching for new threats, the load on the resources of the operating system, and the duration of heuristic analysis.
How to enable or disable the use of heuristic analysis in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to enable or disable the use of heuristic analysis in the application interface
Page top
Anti-Phishing
Web Threat Protection checks links to see if they belong to phishing web addresses. This helps prevent phishing attacks. A phishing attack can be disguised, for example, as an email message supposedly from your bank with a link to the official website of the bank. By clicking the link, you go to an exact copy of the bank's website and can even see its real web address in the browser, even though you are on a counterfeit site. From this point forward, all of your actions on the site are tracked and can be used to steal your money.
Because links to phishing websites may be received not only in an email message but also from other sources such as messengers, the Web Threat Protection component monitors attempts to access a phishing website at the web traffic scan level and blocks access to such websites. Lists of phishing URLs are included with the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution kit.
You can configure Anti-Phishing only in Administration Console (MMC) or the local interface of the application. You cannot configure Anti-Phishing in Web Console or Cloud Console. By default, Anti-Phishing with heuristic analysis is enabled.
How to enable or disable Anti-Phishing in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to enable or disable Anti-Phishing in the application interface
Page top
Creating the list of trusted web addresses
In addition to malicious and phishing websites, Web Threat Protection can block other websites. For example, Web Threat Protection blocks HTTP traffic that does not satisfy RFC standards. You can create a list of URLs whose content you trust. The Web Threat Protection component does not analyze information from trusted web addresses to check them for viruses or other threats. This option may be useful, for example, if the Web Threat Protection component interferes with the downloading of a file from a known website.
A URL may be the address of a specific web page or the address of a website.
How to add a trusted web address using Administration Console (MMC)
How to add a trusted web address in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to add a trusted web address in the application interface
As a result, Web Threat Protection does not scan traffic of trusted web addresses. The user always can open a trusted website and download a file from that website. If you could not gain access to the website, check the settings of Encrypted connections scan, Web Control, and Network ports monitoring components. If Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects a file downloaded from a trusted website as malicious, you can add this file to exclusions.
You can also create a general list of exclusions for encrypted connections. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan HTTPS traffic of trusted web addresses when Web Threat Protection, Mail Threat Protection, Web Control components are doing their work.
Page top
Exporting and importing the list of trusted web addresses
You can export the list of trusted web addresses to an XML file. Then you can modify the file to, for example, add a large number of web addresses of the same type. You can also use the export/import function to back up the list of trusted web addresses or to migrate the list to a different server.
How to export and import a list of trusted web addresses in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to export and import a list of trusted web addresses in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Mail Threat Protection
The Mail Threat Protection component scans the attachments of incoming and outgoing email messages for viruses and other threats. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and heuristic analysis.
Mail Threat Protection can scan both incoming and outgoing messages. The application supports POP3, SMTP, IMAP, and NNTP in the following mail clients:
- Microsoft Office Outlook
- Mozilla Thunderbird
- Windows Mail
Mail Threat Protection does not support other protocols and mail clients.
Mail Threat Protection may not always be able to gain protocol-level access to messages (for example, when using the Microsoft Exchange solution). For this reason, Mail Threat Protection includes an extension for Microsoft Office Outlook. The extension allows scanning messages at the level of the mail client. The Mail Threat Protection extension supports operations with Outlook 2010, 2013, 2016, and 2019.
The Mail Threat Protection component does not scan messages if the mail client is open in a browser.
When a malicious file is detected in an attachment, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds information about the performed action to the message subject, for example, [Message has been processed] <message subject>.
Enabling and disabling Mail Threat Protection
By default, the Mail Threat Protection component is enabled and runs in the mode recommended by Kaspersky experts. For Mail Threat Protection, Kaspersky Endpoint Security applies different groups of settings. These groups of settings that are stored in the application are called security levels: High, Recommended, Low. The Recommended mail security level settings are considered to be the optimal settings recommended by Kaspersky experts (see the table below). You can select one of the pre-installed email security levels or configure a custom email security level. If you have changed the email security level settings, you can always revert to the recommended email security level settings.
To enable or disable the Mail Threat Protection component:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Mail Threat Protection.
- Use the Mail Threat Protection toggle to enable or disable the component.
- If you enabled the component, do one of the following in the Security level block:
- If you want to apply one of the preset security levels, select it with the slider:
- High. When this email security level is selected, the Mail Threat Protection component scans email messages most thoroughly. The Mail Threat Protection component scans incoming and outgoing email messages, and performs deep heuristic analysis. The High mail security level is recommended for high-risk environments. An example of such an environment is a connection to a free email service from a home network that is not guarded by centralized email protection.
- Recommended. The email security level that provides the optimal balance between the performance of Kaspersky Endpoint Security and email security. The Mail Threat Protection component scans incoming and outgoing email messages, and performs medium-level heuristic analysis. This mail traffic security level is recommended by Kaspersky specialists. The values of settings for the recommended security level are provided in the table below.
- Low. When this email security level is selected, the Mail Threat Protection component only scans incoming email messages, performs light heuristic analysis, and does not scan archives that are attached to email messages. At this mail security level, the Mail Threat Protection component scans email messages at maximum speed and uses a minimum of operating system resources. The Low mail security level is recommended for use in a well-protected environment. An example of such an environment might be an enterprise LAN with centralized email security.
- If you want to configure a custom security level, click the Advanced Settings button and define your own component settings.
You can restore the values of preset security levels by clicking the Restore recommended security level button.
- If you want to apply one of the preset security levels, select it with the slider:
- Save your changes.
Mail Threat Protection settings recommended by Kaspersky experts (recommended security level)
Parameter
Value
Description
Protection scope
Incoming and outgoing messages
The Protection scope includes objects that the component checks when it is run: incoming and outgoing messages or incoming messages only.
In order to protect your computers, you need only scan incoming messages. You can turn on scanning for outgoing messages to prevent infected files from being sent in archives. You can also turn on the scanning of outgoing messages if you want to prevent files in particular formats from being sent, such as audio and video files, for example.
Connect Microsoft Outlook extension
On
If the check box is selected, scanning of email messages transmitted via the POP3, SMTP, NNTP, IMAP protocols is enabled on the side of the extension integrated into Microsoft Outlook.
If mail is scanned using the extension for Microsoft Outlook, it is recommended to use Cached Exchange Mode. For more detailed information about Cached Exchange Mode and recommendations on its use, refer to the Microsoft Knowledge Base.
Scan attached archives
On
Scanning ZIP, GZIP, BZIP, RAR, TAR, ARJ, CAB, LHA, JAR, ICE, and other archives. The application scans archives not only by extension, but also by format. When checking archives, the application performs a recursive unpacking. This allows to detect threats inside multi-level archives (archive within an archive).
Scan attached files of Microsoft Office formats
On
Scans Microsoft Office files (DOC, DOCX, XLS, PPT and other Microsoft extensions). Office format files include OLE objects as well. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans office format files that are smaller than 1 MB, regardless of whether the check box is selected or not.
Attachment filter
Rename attachments of selected types
If this option is selected, the Mail Threat Protection component will replace the last extension character found in the attached files of the specified types with the underscore character (for example, attachment.doc_). Thus, in order to open the file, the user must rename the file.
Heuristic analysis
Medium scan
The technology was developed for detecting threats that cannot be detected by using the current version of Kaspersky application databases. It detects files that may be infected with an unknown virus or a new variety of a known virus.
When scanning files for malicious code, the heuristic analyzer executes instructions in the executable files. The number of instructions that are executed by the heuristic analyzer depends on the level that is specified for the heuristic analyzer. The heuristic analysis level ensures a balance between the thoroughness of searching for new threats, the load on the resources of the operating system, and the duration of heuristic analysis.
Action on threat detection
Disinfect, delete if disinfection fails
When an infected object is detected in an inbound or outbound message, Kaspersky Endpoint Security attempts to disinfect the detected object. The user will be able to access the message with a safe attachment. If the object cannot be disinfected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes the infected object. Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds information about the performed action to the message subject, for example, [Message has been processed] <message subject>.
Page top
Changing the action to take on infected email messages
By default, the Mail Threat Protection component automatically attempts to disinfect all infected email messages that are detected. If disinfection fails, the Mail Threat Protection component deletes the infected email messages.
To change the action to take on infected email messages:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Mail Threat Protection.
- In the Action on threat detection block, select the action for Kaspersky Endpoint Security to perform when an infected message is detected:
- Disinfect, delete if disinfection fails. When an infected object is detected in an inbound or outbound message, Kaspersky Endpoint Security attempts to disinfect the detected object. The user will be able to access the message with a safe attachment. If the object cannot be disinfected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes the infected object. Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds information about the performed action to the message subject, for example, [Message has been processed] <message subject>.
- Disinfect, block if disinfection fails. When an infected object is detected in an inbound message, Kaspersky Endpoint Security attempts to disinfect the detected object. The user will be able to access the message with a safe attachment. If the object cannot be disinfected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds a warning to the message subject. The user will be able to access the message with the original attachment. When an infected object is detected in an outbound message, Kaspersky Endpoint Security attempts to disinfect the detected object. If the object cannot be disinfected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks transmission of the message, and the mail client shows an error.
- Block. If an infected object is detected in an inbound message, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds a warning to the message subject. The user will be able to access the message with the original attachment. If an infected object is detected in an outbound message, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks transmission of the message, and the mail client shows an error.
- Save your changes.
Forming the protection scope of the Mail Threat Protection component
Protection scope refers to the objects that are scanned by the component when it is active. The protection scopes of different components have different properties. The properties of the protection scope of the Mail Threat Protection component include the settings for integrating the Mail Threat Protection component into mail clients, and the type of email messages and email protocols whose traffic is scanned by the Mail Threat Protection component. By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans both incoming and outgoing email messages and traffic of the POP3, SMTP, NNTP, and IMAP protocols, and is integrated into the Microsoft Office Outlook mail client.
To form the protection scope of the Mail Threat Protection component:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Mail Threat Protection.
- Click Advanced Settings.
- In the Protection scope block, select the messages to scan:
- Incoming and outgoing messages.
- Incoming messages only.
In order to protect your computers, you need only scan incoming messages. You can turn on scanning for outgoing messages to prevent infected files from being sent in archives. You can also turn on the scanning of outgoing messages if you want to prevent files in particular formats from being sent, such as audio and video files, for example.
If you choose to scan only incoming messages, it is recommended that you perform a one-time scan of all outgoing messages because there is a chance that your computer has email worms that are being spread over email. This helps to avoid problems resulting from unmonitored mass emailing of infected messages from your computer.
- In the Connectivity block, do the following:
- If you want the Mail Threat Protection component to scan messages that are transmitted via the POP3, SMTP, NNTP, and IMAP protocols before they are received on the user's computer, select the Scan POP3, SMTP, NNTP, and IMAP traffic check box.
If you do not want the Mail Threat Protection component to scan messages that are transmitted via the POP3, SMTP, NNTP, and IMAP protocols before they arrive on the user's computer, clear the Scan POP3, SMTP, NNTP, and IMAP traffic check box. In this case, messages are scanned by the Mail Threat Protection extension embedded in the Microsoft Office Outlook mail client after they are received on the user computer if the Connect Microsoft Outlook extension check box is selected.
If you use a mail client other than Microsoft Office Outlook, the Mail Threat Protection component does not scan messages that are transmitted via the POP3, SMTP, NNTP, and IMAP protocols, when the Scan POP3, SMTP, NNTP, and IMAP traffic check box is cleared.
- If you want to allow access to Mail Threat Protection component settings from Microsoft Office Outlook and enable scanning of messages that are transmitted via the POP3, SMTP, NNTP, IMAP, and MAPI protocols after they arrive on the computer using the extension that is embedded into Microsoft Office Outlook, select the Connect Microsoft Outlook extension check box.
If you want to block access to Mail Threat Protection component settings from Microsoft Office Outlook and disable scanning of messages that are transmitted via the POP3, SMTP, NNTP, IMAP, and MAPI protocols after they arrive on the computer using the extension that is embedded into Microsoft Office Outlook, clear the Connect Microsoft Outlook extension check box.
The Mail Threat Protection extension is embedded in the Microsoft Office Outlook mail client during installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- If you want the Mail Threat Protection component to scan messages that are transmitted via the POP3, SMTP, NNTP, and IMAP protocols before they are received on the user's computer, select the Scan POP3, SMTP, NNTP, and IMAP traffic check box.
- Save your changes.
Scanning compound files attached to email messages
You can enable or disable scanning of message attachments, limit the maximum size of message attachments to be scanned, and limit the maximum message attachment scan duration.
To configure scanning of compound files attached to email messages:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Mail Threat Protection.
- Click Advanced Settings.
- In the Scan of compound files block, configure the scan settings:
- Scan attached files of Microsoft Office formats. Scans Microsoft Office files (DOC, DOCX, XLS, PPT and other Microsoft extensions). Office format files include OLE objects as well. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans office format files that are smaller than 1 MB, regardless of whether the check box is selected or not.
- Scan attached archives. Scanning ZIP, GZIP, BZIP, RAR, TAR, ARJ, CAB, LHA, JAR, ICE, and other archives. The application scans archives not only by extension, but also by format. When checking archives, the application performs a recursive unpacking. This allows to detect threats inside multi-level archives (archive within an archive).
If during the scan, Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects a password for an archive in the text of the message, this password will be used to scan the content of the archive for malicious applications. In this case, the password is not saved. An archive is unpacked during scan. If an application error occurs during the unpacking process, you can manually delete the unpacked files that are saved to the following path: %systemroot%\temp. The files have the PR prefix.
- Do not scan archives larger than N MB. If this check box is selected, the Mail Threat Protection component excludes archives attached to email messages from scanning if their size exceeds the specified value. If the check box is cleared, the Mail Threat Protection component scans email attachment archives of any size.
- Limit the time for checking archives to N sec. If the check box is selected, the time that is allocated for scanning archives attached to email messages is limited to the specified period.
- Save your changes.
Email messages attachment filtering
The attachment filtering functionality is not applied to outgoing email messages.
Malicious applications can be distributed in the form of attachments in email messages. You can configure filtering based on the type of message attachments so that files of the specified types are automatically renamed or deleted. By renaming an attachment of a certain type, Kaspersky Endpoint Security can protect your computer against automatic execution of a malicious application.
To configure filtering of attachments:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Mail Threat Protection.
- Click Advanced Settings.
- In the Attachment filter block, do one of the following:
- Disable filtering. If this option is selected, the Mail Threat Protection component does not filter files that are attached to email messages.
- Rename attachments of selected types. If this option is selected, the Mail Threat Protection component will replace the last extension character found in the attached files of the specified types with the underscore character (for example, attachment.doc_). Thus, in order to open the file, the user must rename the file.
- Delete attachments of selected types. If this option is selected, the Mail Threat Protection component deletes attached files of the specified types from email messages.
- If you selected the Rename attachments of selected types option or the Delete attachments of selected types option during the previous step, select the check boxes opposite the relevant types of files.
- Save your changes.
Exporting and importing extensions for attachment filtering
You can export the list of attachment filter extensions to an XML file. You can use the export/import function to back up the list of extensions or to migrate the list to a different server.
How to export and import a list of attachment filter extensions in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to export and import a list of attachment filter extensions in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Scanning emails in Microsoft Office Outlook
During installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, the Mail Threat Protection extension is embedded into Microsoft Office Outlook (hereinafter also referred to as Outlook). It allows you to open the Mail Threat Protection component settings from within Outlook, and to specify when email messages are to be scanned for viruses and other threats. The Mail Threat Protection extension for Outlook can scan incoming and outgoing messages that are transmitted via the POP3, SMTP, NNTP, IMAP, and MAPI protocols. Kaspersky Endpoint Security also supports working with other email clients (including Microsoft Outlook Express, Windows Mail, and Mozilla Thunderbird).
The Mail Threat Protection extension supports operations with Outlook 2010, 2013, 2016, and 2019.
When working with the Mozilla Thunderbird mail client, the Mail Threat Protection component does not scan messages that are transmitted via the IMAP protocol for viruses and other threats if filters are used to move messages from the Inbox folder.
In Outlook, incoming messages are first scanned by the Mail Threat Protection component (if the Scan POP3, SMTP, NNTP, and IMAP traffic check box is selected in the interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security) and then by the Mail Threat Protection extension for Outlook. If the Mail Threat Protection component detects a malicious object in a message, it notifies you about this event.
The Mail Threat Protection component settings can be configured directly in Outlook if the Microsoft Outlook extension is connected in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface (see the figure below).
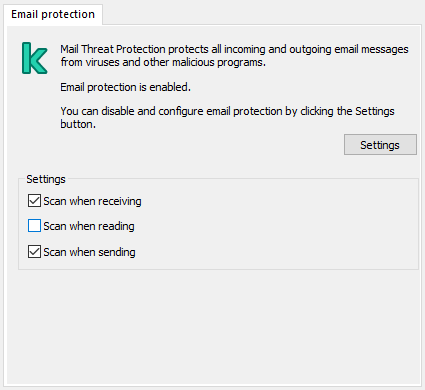
Mail Threat Protection component settings in Outlook
Outgoing messages are first scanned by the Mail Threat Protection extension for Outlook, and are then scanned by the Mail Threat Protection component.
If mail is scanned using the Mail Threat Protection extension for Outlook, it is recommended to use Cached Exchange Mode. For more detailed information about Cached Exchange Mode and recommendations on its use, refer to the Microsoft Knowledge Base.
To configure the operating mode of the Mail Threat Protection extension for Outlook:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Essential Threat Protection → Mail Threat Protection.
- In the Security level block, click the Settings button.
- In the Connectivity block, click the Settings button.
- In the Email protection window, do the following:
- Select the Scan when receiving check box if you want the Mail Threat Protection extension for Outlook to scan incoming messages as they arrive to the mailbox.
- Select the Scan when reading check box if you want the Mail Threat Protection extension for Outlook to scan incoming messages when the user opens them.
- Select the Scan when sending check box if you want the Mail Threat Protection extension for Outlook to scan outgoing messages as they are sent.
- Save your changes.
Network Threat Protection
The Network Threat Protection component scans inbound network traffic for activity that is typical of network attacks. When Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects an attempted network attack on the user's computer, it blocks the network connection with the attacking computer. Descriptions of currently known types of network attacks and ways to counteract them are provided in Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases. The list of network attacks that the Network Threat Protection component detects is updated during database and application module updates.
Enabling and disabling Network Threat Protection
By default, Network Threat Protection is enabled and running in the optimal mode. You can disable Network Threat Protection if necessary.
To enable or disable Network Threat Protection:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Network Threat Protection.
- Use the Network Threat Protection toggle to enable or disable the component.
- Save your changes.
As a result, if Network Threat Protection is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans inbound network traffic for activity that is typical of network attacks. When Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects an attempted network attack on the user's computer, it blocks the network connection with the attacking computer.
Page top
Blocking an attacking computer
To block an attacking computer:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Network Threat Protection.
- Select the Block attacking devices for N min check box.
If the check box is selected, the Network Threat Protection component adds the attacking computer to the blocked list. This means that the Network Threat Protection component blocks the network connection with the attacking computer after the first network attack attempt for the specified amount of time. This block automatically protects the user's computer against possible future network attacks from the same address. The minimum time an attacking computer must spend in the block list is one minute. The maximum time is 999 minutes.
You can view the block list in the Network Monitor tool window.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security clears the block list when the application is restarted and when the Network Threat Protection settings are changed.
- Set a different blocking duration for an attacking computer in the field to the right of the Block attacking devices for N min check box.
- Save your changes.
As a result, when Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects an attempted network attack launched against the user's computer, it will block all connections with the attacking computer.
Page top
Configuring addresses of exclusions from blocking
Kaspersky Endpoint Security can recognize a network attack and block an unsecured network connection that is transmitting a large number of packets (for example, from surveillance cameras). To work with trusted devices, you can add the IP addresses of these devices to the list of exclusions.
To configure addresses of exclusions from blocking:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Network Threat Protection.
- Click the Manage exclusions link.
- In the window that opens, click the Add button.
- Enter the IP address of the computer from which network attacks must not be blocked.
- Save your changes.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not track the activity from devices on the list of exclusions.
Page top
Exporting and importing the list of exclusions from blocking
You can export the list of exclusions to an XML file. Then you can modify the file to, for example, add a large number of addresses of the same type. You can also use the export/import function to back up the list of exclusions or to migrate the list to a different server.
How to export and import a list of exclusions in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to export and import a list of exclusions in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Configuring protection against network attacks by type
Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you manage protection against the following types of network attacks:
- Network Flooding is an attack on network resources of an organization (such as web servers). This attack consists of sending a large number of requests to overload the bandwidth of network resources. When this happens, users are unable to access the network resources of the organization.
- A Port Scanning attack consists of scanning UDP ports, TCP ports, and network services on the computer. This attack allows the attacker to identify the degree of vulnerability of the computer before conducting more dangerous types of network attacks. Port Scanning also enables the attacker to identify the operating system on the computer and select the appropriate network attacks for this operating system.
- A MAC spoofing attack consists of changing the MAC address of a network device (network card). As a result, an attacker can redirect data sent to a device to another device and gain access to this data. Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you block MAC Spoofing attacks and receive notifications about the attacks.
You can disable detection of these types of attacks in case some of your allowed applications perform operations that are typical for these types of attacks. This will help avoid false alarms.
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not monitor Network Flooding, Port Scanning, and MAC spoofing attacks.
To configure protection against network attacks by type:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Network Threat Protection.
- Use the toggle Treat port scanning and network flooding as attacks to enable or disable the detection of these attacks.
- Use the MAC Spoofing Protection toggle.
- In the On detecting a MAC spoofing attack block, select one of the following options:
- Inform.
- Block.
- Save your changes.
If this functionality is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security monitors network traffic for port scanning and network flooding. If such behavior is detected, the application notifies the user and sends the corresponding event to Kaspersky Security Center. The application provides information about the computer that is making the requests. This information is necessary for a timely response. However, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not block the computer that is making the requests because such traffic may be a normal occurrence on the corporate network.
Firewall
The Firewall blocks unauthorized connections to the computer while working on the Internet or local network. The Firewall also controls the network activity of applications on the computer. This allows you to protect your corporate LAN from identity theft and other attacks. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and predefined network rules.
Network Agent is used for interaction with Kaspersky Security Center. Firewall automatically creates network rules required for the application and the Network Agent to work. As a result, the Firewall opens several ports on the computer. Which ports are opened depends on computer's role (for example, distribution point). To learn more about the ports that will be opened on the computer, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
Network rules
You can configure network rules at the following levels:
- Network packet rules. Network packet rules impose restrictions on network packets, regardless of the application. Such rules restrict inbound and outbound network traffic through specific ports of the selected data protocol. Kaspersky Endpoint Security has predefined network packet rules with permissions recommended by Kaspersky experts.
- Application network rules. Application network rules impose restrictions on the network activity of a specific application. They factor in not only the characteristics of the network packet, but also the specific application to which this network packet is addressed or which issued this network packet.
Controlled access of applications to operating system resources, processes and personal data is provided by the Host Intrusion Prevention component by using application rights.
During the first startup of the application, the Firewall performs the following actions:
- Checks the security of the application using downloaded anti-virus databases.
- Checks the security of the application in Kaspersky Security Network.
You are advised to participate in Kaspersky Security Network to help the Firewall work more effectively.
- Places the application in one of the trust groups: Trusted, Low Restricted, High Restricted, Untrusted.
A trust group defines the rights that Kaspersky Endpoint Security refers to when controlling application activity. Kaspersky Endpoint Security places an application in a trust group depending on the level of danger that this application may pose to the computer.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security places an application in a trust group for the Firewall and Host Intrusion Prevention components. You cannot change the trust group only for the Firewall or Host Intrusion Prevention.
If you refused to participate in KSN or there is no network, Kaspersky Endpoint Security places the application in a trust group depending on the settings of the Host Intrusion Prevention component. After receiving the reputation of the application from KSN, the trust group can be changed automatically.
- It blocks network activity of the application depending on the trust group. For example, applications in the High Restricted trust group are not allowed to use any network connections.
The next time the application is started, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks the integrity of the application. If the application is unchanged, the component uses the current network rules for it. If the application has been modified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the application as if it were being started for the first time.
Network Rule Priorities
Each rule has a priority. The higher a rule is on the list, the higher its priority. If network activity is added to several rules, the Firewall regulates network activity according to the rule with the highest priority.
Network packet rules have a higher priority than network rules for applications. If both network packet rules and network rules for applications are specified for the same type of network activity, the network activity is handled according to the network packet rules.
Network rules for applications work in a particular way. Network rule for applications includes access rules based on the network status: Public network, Local network, Trusted network. For example, applications in the High Restricted trust group are not allowed any network activity in networks of all statuses by default. If a network rule is specified for an individual application (parent application), then the child processes of other applications will run according to the network rule of the parent application. If there is no network rule for the application, the child processes will run according to network access rule of the application's trust group.
For example, you have prohibited any network activity in networks of all statuses for all applications, except browser X. If you start browser Y installation (child process) from browser X (parent application), then browser Y installer will access the network and download the necessary files. After installation, browser Y will be denied any network connections according to the Firewall settings. To prohibit network activity of browser Y installer as a child process, you must add a network rule for the installer of browser Y.
Network connection statuses
The Firewall allows you to control network activity depending on the status of the network connection. Kaspersky Endpoint Security receives the network connection status from the computer's operating system. The status of the network connection in the operating system is set by the user when setting up the connection. You can change the status of the network connection in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings. The Firewall will monitor network activity depending on the network status in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings, and not in the operating system.
The network connection can have one of the following status types:
- Public network. The network is not protected by antivirus applications, firewalls, or filters (such as Wi-Fi in a cafe). When the user operates a computer that is connected to such a network, Firewall blocks access to files and printers of this computer. External users are also unable to access data through shared folders and remote access to the desktop of this computer. Firewall filters the network activity of each application according to the network rules that are set for it.
Firewall assigns Public network status to the Internet by default. You cannot change the status of the Internet.
- Local network. Network for users with restricted access to files and printers on this computer (such as for a corporate LAN or home network).
- Trusted network. Safe network in which the computer is not exposed to attacks or unauthorized data access attempts. Firewall permits any network activity within networks with this status.
Enabling or disabling Firewall
By default, Firewall is enabled and functions in the optimal mode.
To enable or disable Firewall:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Firewall.
- Use the Firewall toggle to enable or disable the component.
- Save your changes.
As a result, if the Firewall is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security controls network activity and blocks unauthorized network connections to your computer, as well as blocks unauthorized network activity of applications on your computer. Network activity is also controlled by the Network Threat Protection component. The Network Threat Protection component scans inbound network traffic for activity that is typical of network attacks.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security logs network attack events in its reports irrespective of the Firewall settings. Even if the Firewall blocks the network connection using rules and thus prevents a network attack, the Network Threat Protection component registers network attack events. It is required to generate statistical information about network attacks on the computers in your organization.
Page top
Changing the network connection status
Firewall assigns Public network status to the Internet by default. You cannot change the status of the Internet.
To change the network connection status:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Firewall.
- Click Available networks.
- Select the network connection whose status you want to change.
- In the Network type column, select the status of the network connection:
- Public network. The network is not protected by antivirus applications, firewalls, or filters (such as Wi-Fi in a cafe). When the user operates a computer that is connected to such a network, Firewall blocks access to files and printers of this computer. External users are also unable to access data through shared folders and remote access to the desktop of this computer. Firewall filters the network activity of each application according to the network rules that are set for it.
- Local network. Network for users with restricted access to files and printers on this computer (such as for a corporate LAN or home network).
- Trusted network. Safe network in which the computer is not exposed to attacks or unauthorized data access attempts. Firewall permits any network activity within networks with this status.
- Save your changes.
Managing network packet rules
You can perform the following actions while managing network packet rules:
- Create a new network packet rule.
You can create a new network packet rule by creating a set of conditions and actions that is applied to network packets and data streams.
- Enable or disable a network packet rule.
All network packet rules that are created by Firewall by default have Enabled status. When a network packet rule is enabled, Firewall applies this rule.
You can disable any network packet rule that is selected in the list of network packet rules. When a network packet rule is disabled, Firewall temporarily does not apply this rule.
A new custom network packet rule is added to the list of network packet rules by default with Enabled status.
- Edit the settings of an existing network packet rule.
After you create a new network packet rule, you can always return to editing its settings and modify them as needed.
- Change the Firewall action for a network packet rule.
In the list of network packet rules, you can edit the action that is taken by Firewall on detecting network activity that matches a specific network packet rule.
- Change the priority of a network packet rule.
You can raise or lower the priority of a network packet rule that is selected in the list.
- Remove a network packet rule.
You can remove a network packet rule to stop Firewall from applying this rule on detecting network activity and to stop this rule from showing in the list of network packet rules with Disabled status.
Creating a network packet rule
You can create a network packet rule in the following ways:
- Use the Network Monitor tool.
Network Monitor is a tool designed for viewing information about the network activity of a user's computer in real time. This is convenient because you do not need to configure all the rule settings. Some Firewall settings will be inserted automatically from Network Monitor data. Network Monitor is available only in the application interface.
- Configure the Firewall settings.
This lets you fine-tune the Firewall settings. You can create rules for any network activity, even if there is no network activity at the current time.
When creating network packet rules, remember that they have priority over network rules for applications.
How to use the Network Monitor tool to create a network packet rule in the application interface
How to use Firewall settings to create a network packet rule in the application interface
How to create a network packet rule in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to create a network packet rule in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Network packet rule settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Action |
Allow. Block. By application rules. If this option is selected, Firewall applies the application network rules to the network connection. |
Protocol |
Control network activity over the selected protocol: TCP, UDP, ICMP, ICMPv6, IGMP and GRE. If ICMP or ICMPv6 is selected as the protocol, you can define the ICMP packet type and code. If TCP or UDP is selected as the protocol type, you can specify the comma-delimited port numbers of the local and remote computers between which the connection is to be monitored. |
Direction |
Inbound (packet). Firewall applies the network rule to all inbound network packets. Inbound. Firewall applies the network rule to all network packets sent via a connection that was initiated by a remote computer. Inbound / Outbound. Firewall applies the network rule to both inbound and outbound network packets, regardless of whether the user's computer or a remote computer initiated the network connection. Outbound (packet). Firewall applies the network rule to all outbound network packets. Outbound. Firewall applies the network rule to all network packets sent via a connection that was initiated by the user's computer. |
Network adapters |
Network adapters that can send and/or receive network packets. Specifying the settings of network adapters makes it possible to differentiate between network packets sent or received by network adapters with identical IP addresses. |
Time to live (TTL) |
Restrict control of network packets based on their time to live (TTL). |
Remote address |
Network addresses of remote computers that can send and receive network packets. Firewall applies the network rule to the specified range of remote network addresses. You can include all IP addresses in a network rule, create a separate list of IP addresses, specify a range of IP addresses, or select a subnet (Trusted networks, Local networks, Public networks). You can also specify a DNS name of a computer instead of its IP address. You should use DNS names only for LAN computers or internal services. Interaction with cloud services (such as Microsoft Azure) and other Internet resources should be handled by the Web Control component. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports DNS names starting from version 11.7.0. If you specify a DNS name for version 11.6.0 or older, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may apply the relevant rule to all addresses. |
Local address |
Network addresses of computers that can send and receive network packets. Firewall applies a network rule to the specified range of local network addresses. You can include all IP addresses in a network rule, create a separate list of IP addresses, or specify a range of IP addresses. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports DNS names starting from version 11.7.0. If you specify a DNS name for version 11.6.0 or older, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may apply the relevant rule to all addresses. Sometimes the local address cannot be obtained for applications. If this is the case, this parameter is ignored. |
Enabling or disabling a network packet rule
To enable or disable a network packet rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Firewall.
- Click Packet rules.
This opens a list of default network packet rules that are set by Firewall.
- Select the necessary network packet rule in the list.
- Use the toggle in the Status column to enable or disable the rule.
- Save your changes.
Changing the Firewall action for a network packet rule
To change the Firewall action that is applied to a network packet rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Firewall.
- Click Packet rules.
This opens a list of default network packet rules that are set by Firewall.
- Select it in the list of network packet rules and click the Edit button.
- In the Action drop-down list, select the action to be performed by Firewall on detecting this kind of network activity:
- Allow.
- Block.
- By application rules. If this option is selected, Firewall applies the application network rules to the network connection.
- Save your changes.
Changing the priority of a network packet rule
The priority of a network packet rule is determined by its position in the list of network packet rules. The topmost network packet rule in the list of network packet rules has the highest priority.
Every manually created network packet rule is added to the end of the list of network packet rules and is of the lowest priority.
Firewall executes rules in the order in which they appear in the list of network packet rules, from top to bottom. According to each processed network packet rule that applies to a particular network connection, Firewall either allows or blocks network access to the address and port that are specified in the settings of this network connection.
To change the network packet rule priority:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Firewall.
- Click Packet rules.
This opens a list of default network packet rules that are set by Firewall.
- In the list, select the network packet rule whose priority you want to change.
- Use the Up / Down buttons to set the priority of the network rule.
- Save your changes.
Exporting and importing network packet rules
You can export the list of network packet rules to an XML file. Then you can modify the file to, for example, add a large number of rules of the same type. You can use the export/import function to back up the list of network packet rules or to migrate the list to a different server.
How to export and import a list of network packet rules in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to export and import a list of network packet rules in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Defining network packet rules in XML
Firewall allows exporting network packet rules in XML format. Then you can modify the file to, for example, add a large number of rules of the same type.
The XML file contains two main nodes: Rules and Resources. The Rules node lists network packet rules. This node contains rules configured by default (predefined rules) as well as rules added by the user (custom rules).
Network packet rule markup
Network packet rule settings in XML format
Parameter |
Description |
Value |
|---|---|---|
|
Priority of the rule. The lower the value, the higher the priority. |
Integer The priority value must consist of 4 digits. The nodes in the XML file must be arranged by priority value, starting with |
|
ID of the rule. |
|
|
Status of the rule. |
|
|
ID of the rule type. |
|
|
ID of the application to which the network packet rule belongs. |
If the rule does not belong to any application, the value is |
|
Main ID of the resource with rule settings. You can use this identifier to locate a block with rule settings in the |
Integer |
|
ID of the network type. |
|
|
Value of the Action parameter. |
|
|
|
|
The Resources node contains network packet rule settings. Custom network packet rule settings are listed in the <key name="0004"> block.
Custom network packet rule markup
Custom network packet rule settings
Parameter |
Description |
Value |
|---|---|---|
|
ID of the parameter block. |
Integer |
|
Value of the Remote ports parameter. |
List of remote port ranges. |
|
Value of the Local ports parameter. |
List of local port ranges. |
|
Value of the Network adapters parameter. |
|
|
Internal ID of the structure. |
Integer It is recommended to leave this parameter unchanged. |
|
Value of the Protocol parameter. |
|
|
Value of the Direction parameter. |
|
|
Value of the ICMP type parameter. |
|
|
Value of the ICMP code parameter. |
|
|
Structure attribute pointer. |
Integer It is recommended to leave this parameter unchanged. |
|
Value of the Time to live (TTL) parameter. |
Value in seconds. If disabled, the value is |
|
|
|
|
Main ID of the resource (see the |
Integer |
|
ID of the parent group. |
Integer It is recommended to leave this parameter unchanged. |
|
Status of the rule. |
|
|
Name of the network packet rule. |
String |
Managing application network rules
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security groups all applications that are installed on the computer by the name of the vendor of the software whose file or network activity it monitors. Application groups are in turn categorized into trust groups. All applications and application groups inherit properties from their parent group: application control rules, application network rules, and their execution priority.
Like the Host Intrusion Prevention component, by default the Firewall component applies the network rules for an application group when filtering the network activity of all applications within the group. The application group network rules define the rights of applications within the group to access different network connections.
By default, Firewall creates a set of network rules for each application group that is detected by Kaspersky Endpoint Security on the computer. You can change the Firewall action that is applied to the application group network rules that are created by default. You cannot edit, remove, disable, or change the priority of application group network rules that are created by default.
You can also create a network rule for an individual application. Such a rule will have a higher priority than the network rule of the group to which the application belongs.
Creating an application network rule
By default, application activity is controlled by network rules that are defined for the trust group to which Kaspersky Endpoint Security assigned the application when it started the first time. If necessary, you can create network rules for an entire trust group, for an individual application, or for a group of applications that are within a trust group.
Manually defined network rules have a higher priority than network rules that were determined for a trust group. In other words, if manually defined application rules differ from the application rules determined for a trust group, Firewall controls application activity according to the manually defined rules for applications.
By default, Firewall creates the following network rules for each application:
- Any network activity in Trusted networks.
- Any network activity in Local networks.
- Any network activity in Public networks.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security controls the network activity of applications according to predefined network rules as follows:
- Trusted and Low Restricted: all network activity is allowed.
- High Restricted and Untrusted: all network activity is blocked.
Predefined application rules cannot be edited or deleted.
You can create an application network rule in the following ways:
- Use the Network Monitor tool.
Network Monitor is a tool designed for viewing information about the network activity of a user's computer in real time. This is convenient because you do not need to configure all the rule settings. Some Firewall settings will be inserted automatically from Network Monitor data. Network Monitor is available only in the application interface.
- Configure the Firewall settings.
This lets you fine-tune the Firewall settings. You can create rules for any network activity, even if there is no network activity at the current time.
When creating network rules for applications, remember that network packet rules have priority over application network rules.
How to use Firewall settings to create an application network rule in the application interface
How to create an application network rule in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to create an application network rule in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Application network rule settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Action |
Allow. Block. |
Protocol |
Control network activity over the selected protocol: TCP, UDP, ICMP, ICMPv6, IGMP and GRE. If ICMP or ICMPv6 is selected as the protocol, you can define the ICMP packet type and code. If TCP or UDP is selected as the protocol type, you can specify the comma-delimited port numbers of the local and remote computers between which the connection is to be monitored. |
Direction |
Inbound. Inbound / Outbound. Outbound. |
Remote address |
Network addresses of remote computers that can send and receive network packets. Firewall applies the network rule to the specified range of remote network addresses. You can include all IP addresses in a network rule, create a separate list of IP addresses, specify a range of IP addresses, or select a subnet (Trusted networks, Local networks, Public networks). You can also specify a DNS name of a computer instead of its IP address. You should use DNS names only for LAN computers or internal services. Interaction with cloud services (such as Microsoft Azure) and other Internet resources should be handled by the Web Control component. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports DNS names starting from version 11.7.0. If you specify a DNS name for version 11.6.0 or older, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may apply the relevant rule to all addresses. |
Local address |
Network addresses of computers that can send and receive network packets. Firewall applies a network rule to the specified range of local network addresses. You can include all IP addresses in a network rule, create a separate list of IP addresses, or specify a range of IP addresses. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports DNS names starting from version 11.7.0. If you specify a DNS name for version 11.6.0 or older, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may apply the relevant rule to all addresses. Sometimes the local address cannot be obtained for applications. If this is the case, this parameter is ignored. |
Enabling and disabling an application network rule
To enable or disable an application network rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Firewall.
- Click Rules for applications.
This opens the list of application rules.
- In the list of applications, select the application or group of applications for which you want to create or edit a network rule.
- Right-click to open the context menu and select Details and rules.
The application rules and properties window opens.
- Select the Network rules tab.
- In the list of network rules for an application group, select the relevant network rule.
The network rule properties window opens.
- Set the Active or Inactive status of the network rule.
You cannot disable an application group network rule that is created by Firewall by default.
- Save your changes.
Changing the Firewall action for an application network rule
You can change the Firewall action that is applied to all network rules for an application or application group that were created by default, and change the Firewall action for a single custom network rule for an application or application group.
To change the Firewall action for all network rules for an application or group of applications:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Firewall.
- Click Rules for applications.
This opens the list of application rules.
- If you want to change the Firewall action that is applied to all network rules that are created by default, select an application or group of applications in the list. Manually created network rules are left unchanged.
- Right-click to open the context menu, select Network rules, then select the action that you want to assign:
- Inherit.
- Allow.
- Block.
- Save your changes.
To change the Firewall response for one network rule for an application or application group:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Firewall.
- Click Rules for applications.
This opens the list of application rules.
- In the list, select the application or group of applications for which you want to change the action for one network rule.
- Right-click to open the context menu and select Details and rules.
The application rules and properties window opens.
- Select the Network rules tab.
- Select the network rule for which you want to change the Firewall action.
- In the Permission column, right-click to bring up the context menu and select the action that you want to assign:
- Inherit.
- Allow.
- Deny.
- Log events.
- Save your changes.
Changing the priority of an application network rule
The priority of a network rule is determined by its position in the list of network rules. Firewall executes the rules in the order in which they appear in the list of network rules, from top to bottom. According to each processed network rule that applies to a particular network connection, Firewall either allows or blocks network access to the address and port that are indicated in the settings of this network connection.
Manually created network rules have a higher priority than default network rules.
You cannot change the priority of application group network rules that are created by default.
To change the priority of a network rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → Firewall.
- Click Rules for applications.
This opens the list of application rules.
- In the list of applications, select the application or group of applications for which you want to change the priority of a network rule.
- Right-click to open the context menu and select Details and rules.
The application rules and properties window opens.
- Select the Network rules tab.
- Select the network rule whose priority you want to change.
- Use the Up / Down buttons to set the priority of the network rule.
- Save your changes.
Network Monitor
Network Monitor is a tool designed for viewing information about the network activity of a user's computer in real time.
To start Network Monitor:
In the main application window, in the Monitoring section, click the Network Monitor tile.
The Network Monitor window opens. In this window, information about the network activity of the computer is shown on four tabs:
- The Network activity tab shows all currently active network connections with the computer. Both outbound and inbound network connections are displayed. On this tab, you can also create network packet rules for Firewall operation.
- The Open ports tab lists all open network ports of the computer. On this tab, you can also create network packet rules and application rules for Firewall operation.
- The Network traffic tab shows the volume of inbound and outbound network traffic between the user's computer and other computers in the network to which the user is currently connected.
- The Blocked computers tab lists the IP addresses of remote computers whose network activity has been blocked by the Network Threat Protection component after detecting network attack attempts from such IP addresses.
BadUSB Attack Prevention
Some viruses modify the firmware of USB devices to trick the operating system into detecting the USB device as a keyboard. As a result, the virus may execute commands under your user account to download malware, for example.
The BadUSB Attack Prevention component prevents infected USB devices emulating a keyboard from connecting to the computer.
When a USB device is connected to the computer and identified as a keyboard by the operating system, the application prompts the user to enter a numerical code generated by the application from this keyboard or using On-Screen Keyboard if available (see the figure below). This procedure is known as keyboard authorization.
If the code has been entered correctly, the application saves the identification parameters – VID/PID of the keyboard and the number of the port to which it has been connected – in the list of authorized keyboards. Keyboard authorization does not need to be repeated when the keyboard is reconnected or after the operating system is restarted.
When the authorized keyboard is connected to a different USB port of the computer, the application shows a prompt for authorization of this keyboard again.
If the numerical code has been entered incorrectly, the application generates a new code. You can configure the number of attempts for entering the numerical code. If the numerical code is entered incorrectly several times or the keyboard authorization window is closed (see figure below), the application blocks input from this keyboard. When the USB device blocking time elapses or the operating system is restarted, the application prompts the user to perform keyboard authorization again.
The application allows use of an authorized keyboard and blocks a keyboard that has not been authorized.
The BadUSB Attack Prevention component is not installed by default. If you need the BadUSB Attack Prevention component, you can add the component in the properties of the installation package before installing the application or change the available application components after installing the application.
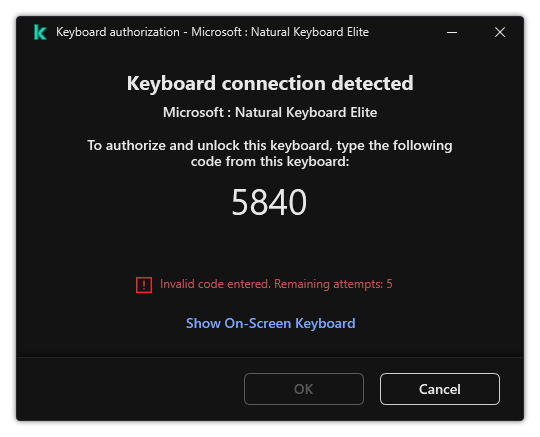
Keyboard authorization
Enabling and disabling BadUSB Attack Prevention
USB devices identified by the operating system as keyboards and connected to the computer before installation of the BadUSB Attack Prevention component are considered authorized after installation of the component.
To enable or disable BadUSB Attack Prevention:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → BadUSB Attack Prevention.
- Use the BadUSB Attack Prevention toggle to enable or disable the component.
- In the USB keyboard authorization upon connection block, adjust security settings for entering the authorization code:
- Maximum number of USB device authorization attempts. Automatically blocking the USB device if the authorization code is entered incorrectly the specified number of times. Valid values are 1 to 10. For example, if you allow 5 attempts to enter the authorization code, the USB device is blocked after the fifth failed attempt. Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays the blocking duration for the USB device. After this time elapses, you can have 5 attempts to enter the authorization code.
- Timeout when reaching the maximum number of attempts. Blocking duration of the USB device after the specified number of failed attempts to enter the authorization code. Valid values are 1 to 180 (minutes).
- Save your changes.
As a result, if BadUSB Attack Prevention is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security requires authorization of a connected USB device identified as a keyboard by the operating system. The user cannot use an unauthorized keyboard until it is authorized.
Page top
Using On-Screen Keyboard for authorization of USB devices
On-Screen Keyboard should be used only for authorization of USB devices that do not support the input of random characters (e.g. bar code scanners). It is not recommended to use On-Screen Keyboard for authorization of unknown USB devices.
To allow or prohibit the use of On-Screen Keyboard for authorization:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → BadUSB Attack Prevention.
- Use the Prohibit use of On-Screen Keyboard for authorization of USB devices check box to block or allow use of the On-Screen Keyboard for authorization.
- Save your changes.
AMSI Protection
AMSI Protection component is intended to support Antimalware Scan Interface from Microsoft. The Antimalware Scan Interface (AMSI) allows third-party applications with AMSI support to send objects (for example, PowerShell scripts) to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for an additional scan and then receive the results from scanning these objects. Third-party applications may include, for example, Microsoft Office applications (see the figure below). For details on AMSI, please refer to the Microsoft documentation.
The AMSI Protection can only detect a threat and notify a third-party application about the detected threat. Third-party application after receiving a notification of a threat does not allow to perform malicious actions (for example, terminates).
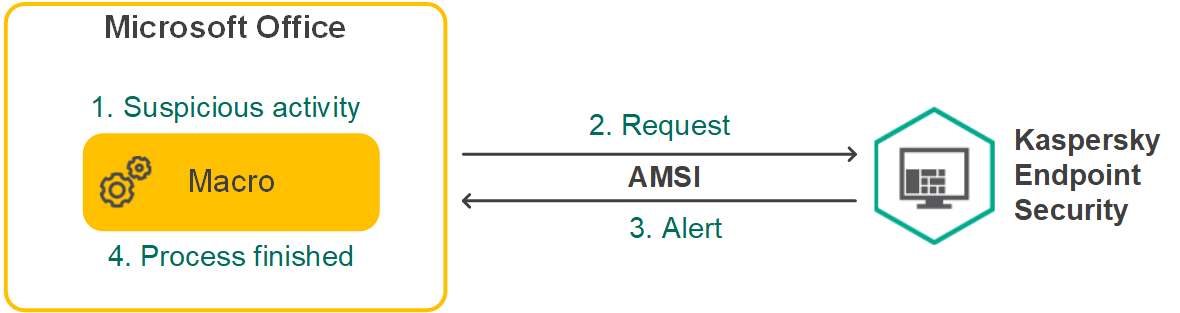
AMSI operation example
AMSI Protection component may decline a request from a third-party application, for example, if this application exceeds maximum number of requests within a specified interval. Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends information about a rejected request from a third-party application to the Administration Server. The AMSI Protection component does not deny requests from those third-party applications for which continuous integration with the AMSI Protection component is enabled.
AMSI Protection is available for the following operating systems for workstations and servers:
- Windows 10 Home / Pro / Pro for Workstations / Education / Enterprise;
- Windows 11 Home / Pro / Pro for Workstations / Education / Enterprise;
- Windows Server 2016 Essentials / Standard / Datacenter (including Core Mode);
- Windows Server 2019 Essentials / Standard / Datacenter (including Core Mode);
- Windows Server 2022 Standard / Datacenter / Datacenter: Azure Edition (including Core Mode).
Enabling and disabling the AMSI Protection
By default, the AMSI Protection is enabled.
To enable or disable the AMSI Protection:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → AMSI Protection.
AMSI Protection settings
- Use the AMSI Protection toggle to enable or disable the component.
- Save your changes.
Using AMSI Protection to scan compound files
A common technique for concealing viruses and other malware is to embed them in compound files such as archives. To detect viruses and other malware that are hidden in this way, the compound file must be unpacked, which may slow down scanning. You can limit the types of compound files to be scanned, thus speeding up scanning.
To configure AMSI Protection scans of compound files:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Essential Threat Protection → AMSI Protection.

AMSI Protection settings
- In the Scan of compound files block, specify the types of compound files that you want to scan: archives, distribution package, or files in office formats.
- In the Size limit block, do one of the following:
- To block the AMSI Protection component from unpacking large compound files, select the Do not unpack large compound files check box and specify the required value in the Maximum file size field. The AMSI Protection component will not unpack compound files that are larger than the specified size.
- To allow the AMSI Protection component to unpack large compound files, clear the Do not unpack large compound files check box.
The AMSI Protection component scans large files that are extracted from archives, regardless of whether the Do not unpack large compound files check box is selected.
- Save your changes.
Exploit Prevention
The Exploit Prevention component detects program code that takes advantage of vulnerabilities on the computer to exploit administrator privileges or to perform malicious activities. For example, exploits can utilize a buffer overflow attack. To do so, the exploit sends a large amount of data to a vulnerable application. When processing this data, the vulnerable application executes malicious code. As a result of this attack, the exploit can start an unauthorized installation of malware. When there is an attempt to run an executable file from a vulnerable application that was not performed by the user, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks this file from running or notifies the user.
Enabling and disabling Exploit Prevention
By default, Exploit Prevention is enabled and runs in the mode recommended by Kaspersky experts. You can disable Exploit Prevention if necessary.
To enable or disable Exploit Prevention:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Advanced Threat Protection → Exploit Prevention.
- Use the Exploit Prevention toggle to enable or disable the component.
- Save your changes.
As a result, if Exploit Prevention is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will monitor executable files that are run by vulnerable applications. If Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects that an executable file from a vulnerable application was run by something other than the user, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will perform the selected action (for example, will block the operation).
Page top
Selecting an action to take when an exploit is detected
By default, on detection of an exploit, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks operations attempted by the exploit.
To choose an action to be taken when an exploit is detected:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Advanced Threat Protection → Exploit Prevention.
- Select the relevant action in the On detecting exploit block:
- Block operation. If this item is selected, on detecting an exploit, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the operations of this exploit and makes a log entry with information about this exploit.
- Notify. If this item is selected, when Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects an exploit it logs an entry containing information about the exploit and adds information about this exploit to the list of active threats.
- Save your changes.
System processes memory protection
By default, protection of system process memory is enabled.
To enable or disable system process memory protection:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Advanced Threat Protection → Exploit Prevention.
- Use the Enable system process memory protection toggle to enable or disable this feature.
- Save your changes.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block external processes that attempt to access system processes.
Page top
Behavior Detection
The Behavior Detection component receives data on the actions of applications on your computer and provides this information to other protection components to improve their performance. The Behavior Detection component utilizes Behavior Stream Signatures (BSS) for applications. If application activity matches a behavior stream signature, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the selected responsive action. Kaspersky Endpoint Security functionality based on behavior stream signatures provides proactive defense for the computer.
Enabling and disabling Behavior Detection
By default, Behavior Detection is enabled and runs in the mode recommended by Kaspersky experts. You can disable Behavior Detection if necessary.
It is not recommended to disable Behavior Detection unless absolutely necessary because doing so would reduce the effectiveness of the protection components. The protection components may request data collected by the Behavior Detection component to detect threats.
To enable or disable Behavior Detection:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Advanced Threat Protection → Behavior Detection.
Behavior Detection settings
- Use the Behavior Detection toggle to enable or disable the component.
- Save your changes.
As a result, if Behavior Detection is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will use behavior stream signatures to analyze the activity of applications in the operating system.
Page top
Selecting the action to take on detecting malware activity
In order to choose what to do if an application engages in malicious activity, perform the following steps:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Advanced Threat Protection → Behavior Detection.

Behavior Detection settings
- Select the relevant action in the On detecting malware activity block:
- Delete file. If this item is selected, on detecting malicious activity Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes the executable file of the malicious application and creates a backup copy of the file in Backup.
- Terminate the application. If this item is selected, on detecting malicious activity Kaspersky Endpoint Security terminates this application.
- Notify. If this item is selected and malware activity of an application is detected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds information about the malware activity of the application to the list of active threats.
- Save your changes.
Protection of shared folders against external encryption
The component monitors operations performed only with those files that are stored on mass storage devices with the NTFS file system and that are not encrypted with EFS.
Protection of shared folders against external encryption provides for analysis of activity in shared folders. If this activity matches a behavior stream signature that is typical for external encryption, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the selected action.
By default, protection of shared folders against external encryption is disabled.
After Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed, the protection of shared folders against external encryption will be limited until the computer is restarted.
Enabling and disabling protection of shared folders against external encryption
After Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed, the protection of shared folders against external encryption will be limited until the computer is restarted.
To enable or disable protection of shared folders against external encryption:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Advanced Threat Protection → Behavior Detection.

Behavior Detection settings
- Use the Enable protection of shared folders against external encryption toggle to enable or disable detection of activity that is typical of external encryption.
- Save your changes.
Selecting the action to take on detection of external encryption of shared folders
To select the action to take on detection of external encryption of shared folders:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Advanced Threat Protection → Behavior Detection.

Behavior Detection settings
- Select the relevant action in the Protection of shared folders against external encryption block:
- Block connection for N min. (from 1 to 43800). If this option is selected and Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects an attempt to modify files in shared folders, it takes the following actions:
- Blocks access to file modification for the session that initiated the malicious activity (the file will be read-only).
- Creates backup copies of files that are being modified.
- Adds an entry to local application interface reports.
- Sends information about the detected malicious activity to Kaspersky Security Center.
Also, if the Remediation Engine component is enabled, the modified files are restored from backup copies.
- Notify. If this option is selected and Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects an attempt to modify files in shared folders, it takes the following actions:
- Adds an entry to local application interface reports.
- Adds an entry to the list of active threats.
- Sends information about the detected malicious activity to Kaspersky Security Center.
- Block connection for N min. (from 1 to 43800). If this option is selected and Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects an attempt to modify files in shared folders, it takes the following actions:
- Save your changes.
Creating an exclusion for protection of shared folders against external encryption
Excluding a folder can reduce the amount of false positives if your organization uses data encryption when exchanging files using shared folders. For example, Behavior Detection can raise false positives when the user works with files with the ENC extension in a shared folder. Such activity matches a behavioral pattern that is typical for external encryption. If you have encrypted files in a shared folder to protect data, add that folder to exclusions.
How to create an exclusion for protection of shared folders using the Administration Console (MMC)
How to create an exclusion for protection of shared folders using the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to create an exclusion for protection of shared folders in the application interface
Page top
Configuring addresses of exclusions from protection of shared folders against external encryption
The Audit Logon service must be enabled to enable exclusions of addresses from protection of shared folders against external encryption. By default, the Audit Logon service is disabled (for detailed information about enabling the Audit Logon service, please visit the Microsoft website).
The functionality for excluding addresses from shared folder protection does not work on a remote computer if the remote computer was turned on before Kaspersky Endpoint Security was started. You can restart this remote computer after Kaspersky Endpoint Security is started to ensure that the functionality for excluding addresses from shared folder protection works on this remote computer.
To exclude remote computers that perform external encryption of shared folders:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Advanced Threat Protection → Behavior Detection.

Behavior Detection settings
- In the Exclusions block, click the Configure addresses of exclusions link.
- If you want to add an IP address or computer name to the list of exclusions, click the Add button.
- Enter the IP address or name of the computer from which external encryption attempts must not be handled.
- Save your changes.
Exporting and importing a list of exclusions from protection of shared folders against external encryption
You can export the list of exclusions to an XML file. Then you can modify the file to, for example, add a large number of addresses of the same type. You can also use the export/import function to back up the list of exclusions or to migrate the list to a different server.
How to export and import a list of exclusions in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to export and import a list of exclusions in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Host Intrusion Prevention
This component is available if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for workstations. This component is unavailable if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for servers.
The Host Intrusion Prevention component prevents applications from performing actions that may be dangerous for the operating system, and ensures control over access to operating system resources and personal data. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases and the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service.
The component controls the operation of applications by using application rights. Application rights include the following access parameters:
- Access to operating system resources (for example, automatic startup options, registry keys)
- Access to personal data (such as files and applications)
Network activity of applications is controlled by the Firewall using network rules.
During the first startup of the application, the Host Intrusion Prevention component performs the following actions:
- Checks the security of the application using downloaded anti-virus databases.
- Checks the security of the application in Kaspersky Security Network.
You are advised to participate in Kaspersky Security Network to help the Host Intrusion Prevention component work more effectively.
- Places the application in one of the trust groups: Trusted, Low Restricted, High Restricted, Untrusted.
A trust group defines the rights that Kaspersky Endpoint Security refers to when controlling application activity. Kaspersky Endpoint Security places an application in a trust group depending on the level of danger that this application may pose to the computer.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security places an application in a trust group for the Firewall and Host Intrusion Prevention components. You cannot change the trust group only for the Firewall or Host Intrusion Prevention.
If you refused to participate in KSN or there is no network, Kaspersky Endpoint Security places the application in a trust group depending on the settings of the Host Intrusion Prevention component. After receiving the reputation of the application from KSN, the trust group can be changed automatically.
- Blocks application actions depending on the trust group. For example, applications from the High Restricted trust group are denied access to the operating system modules.
The next time the application is started, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks the integrity of the application. If the application is unchanged, the component uses the current application rights for it. If the application has been modified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the application as if it were being started for the first time.
Enabling and disabling Host Intrusion Prevention
By default, the Host Intrusion Prevention component is enabled and runs in the mode recommended by Kaspersky experts.
How to enable or disable the Host Intrusion Prevention component in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to enable or disable the Host Intrusion Prevention component in the application interface
If the Host Intrusion Prevention component is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will place an application in a trust group depending on the level of danger that this application may pose to the computer. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will then block the actions of the application depending on the trust group.
Page top
Managing application trust groups
When each application is started for the first time, the Host Intrusion Prevention component checks the security of the application and places the application into one of the trust groups.
At the first stage of the application scan, Kaspersky Endpoint Security searches the internal database of known applications for a matching entry and at the same time sends a request to the Kaspersky Security Network database (if an Internet connection is available). Based on the results of the search in the internal database and the Kaspersky Security Network database, the application is placed into a trust group. Each time the application is subsequently started, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends a new query to the KSN database and places the application into a different trust group if the reputation of the application in the KSN database has changed.
You can select a trust group to which Kaspersky Endpoint Security must automatically assign all unknown applications. Applications that were started before Kaspersky Endpoint Security are automatically moved to the trust group defined in Host Intrusion Prevention component settings.
For applications that were started before Kaspersky Endpoint Security, only network activity is controlled. Control is performed according to the network rules defined in the Firewall settings.
Changing the trust group of an application
When each application is started for the first time, the Host Intrusion Prevention component checks the security of the application and places the application into one of the trust groups.
Kaspersky specialists do not recommend moving applications from the automatically assigned trust group to a different trust group. Instead, you can modify rights for an individual application if necessary.
How to change the trust group of an application in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to change the trust group of an application in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to change the trust group of an application in the application interface
As a result, the application will be put into the other trust group. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will then block the actions of the application depending on the trust group. The ![]() (user-defined) status will be assigned to the application. If the reputation of the application is changed in Kaspersky Security Network, the Host Intrusion Prevention component will leave this application's trust group unchanged.
(user-defined) status will be assigned to the application. If the reputation of the application is changed in Kaspersky Security Network, the Host Intrusion Prevention component will leave this application's trust group unchanged.
Configuring trust group rights
The optimal application rights are created for different trust groups by default. The settings of rights for application groups that are in a trust group inherit values from the settings of the trust group rights.
How to change trust group rights in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to change trust group rights in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to change trust group rights in the application interface
The trust group rights will be changed. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will then block the actions of the application depending on the trust group. The ![]() status (Custom settings) will be assigned to the trust group.
status (Custom settings) will be assigned to the trust group.
Selecting a trust group for applications started before Kaspersky Endpoint Security
For applications that were started before Kaspersky Endpoint Security, only network activity is controlled. Control is performed according to the network rules defined in the Firewall settings. To specify which network rules must be applied to network activity monitoring for such applications, you must select a trust group.
As a result, an application that is started before Kaspersky Endpoint Security will be put into the other trust group. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will then block the actions of the application depending on the trust group.
Page top
Selecting a trust group for unknown applications
During the first startup of an application, the Host Intrusion Prevention component determines the trust group for the application. If you do not have Internet access or if Kaspersky Security Network has no information about this application, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will place the application into the Low Restricted group by default. When information about a previously unknown application is detected in KSN, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will update the rights of this application. You can then manually edit the application rights.
How to select a trust group for unknown applications in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to select a trust group for unknown applications in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to select a trust group for unknown applications in the application interface
Page top
Selecting a trust group for digitally signed applications
Kaspersky Endpoint Security always places applications signed by Microsoft certificates or Kaspersky certificates into the Trusted group.
How to select a trust group for digitally signed applications in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to select a trust group for digitally signed applications in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to select a trust group for digitally signed applications in the application interface
Page top
Managing application rights
By default, application activity is controlled based on the application rights that are defined for the specific trust group that Kaspersky Endpoint Security assigned to the application when it started for the first time. If necessary, you can edit the application rights for an entire trust group, for an individual application, or for a group of applications within a trust group.
Manually defined application rights have a higher priority than application rights that were defined for a trust group. In other words, if manually defined application rights differ from the application rights defined for a trust group, the Host Intrusion Prevention component controls application activity according to the manually defined application rights.
The rules that you create for applications are inherited by child applications. For example, if you deny all network activity for cmd.exe, all network activity will also be denied for notepad.exe if it is started using cmd.exe. When an application is not a child of the application it runs from, rules are not inherited.
How to change application rights in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to change application rights in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to change application rights in the application interface
Page top
Protecting operating system resources and personal data
The Host Intrusion Prevention component manages the rights of applications to take actions on various categories of operating system resources and personal data. Kaspersky specialists have established preset categories of protected resources. For example, the Operating system category has a Startup settings subcategory that lists all the registry keys associated with autorun of applications. You cannot edit or delete the preset categories of protected resources or the protected resources that are within these categories.
How to add a protected resource in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to add a protected resource in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to add a protected resource in the application interface
Kaspersky Endpoint Security will control access to the added operating system resources and to personal data. Kaspersky Endpoint Security controls an application's access to resources based on the trust group assigned to the application. You can also change the trust group of an application.
Page top
Deleting information about unused applications
Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses application rights to control the activities of applications. Application rights are determined by their trust group. Kaspersky Endpoint Security puts an application into a trust group when the application is started for the first time. You can manually change the trust group of an application. You can also manually configure the rights of an individual application. Kaspersky Endpoint Security stores the following information about an application: trust group of the application, and rights of the application.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes information about unused applications to save computer resources. Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes application information according to the following rules:
- If the trust group and rights of an application were determined automatically, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes information about this application after 30 days. It is not possible to change the storage term for application information or turn off automatic deletion.
- If you manually put an application into a trust group or configured its access rights, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes information about this application after 60 days (default storage term). You can change the storage term for application information, or turn off automatic deletion (see the instructions below).
When you start an application whose information has been deleted, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the application as if it were starting for the first time.
Page top
Monitoring Host Intrusion Prevention
You can receive reports on the operation of the Host Intrusion Prevention component. Reports contain information about operations with computer resources performed by the application (allowed or forbidden). Reports also contain information about the applications that utilize each resource.
To monitor Host Intrusion Prevention operations, you need to enable report writing. For example, you can enable forwarding of reports for individual applications in the Host Intrusion Prevention component settings.
When configuring Host Intrusion Prevention monitoring, take into account the potential network load when forwarding events to Kaspersky Security Center. You can also enable saving of reports only in the local log of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Page top
Protecting access to audio and video
Cybercriminals can use special programs to try to gain access to devices that record audio and video (such as microphones or webcams). Kaspersky Endpoint Security controls when applications receive an audio stream or video stream and protects data against unauthorized interception.
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows receiving audio and video streams only for applications from the Trusted group. The applications from Low Restricted, High Restricted and Untrusted groups are not allowed to receive the audio stream and video stream from devices. You can manually allow applications to receive the audio stream and video stream.
Special features of audio stream protection
Audio stream protection has the following special characteristics:
- The Host Intrusion Prevention component must be enabled for this functionality to work.
- If the application started receiving the audio stream before the Host Intrusion Prevention component was started, Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows the application to receive the audio stream and does not show any notifications.
- If you moved the application to the Untrusted group or High Restricted group after the application began receiving the audio stream, Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows the application to receive the audio stream and does not show any notifications.
- After the settings for the application's access to sound recording devices have been changed (for example, if the application has been blocked from receiving the audio stream), this application must be restarted to stop it from receiving the audio stream.
- Control of access to the audio stream from sound recording devices does not depend on an application's webcam access settings.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security protects access to only built-in microphones and external microphones. Other audio streaming devices are not supported.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security cannot guarantee the protection of an audio stream from such devices as DSLR cameras, portable video cameras, and action cameras.
- When you run audio and video recording or playback applications for the first time since installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, audio and video playback or recording may be interrupted. This is necessary in order to enable the functionality that controls access to sound recording devices by applications. The system service that controls audio hardware will be restarted when Kaspersky Endpoint Security is run for the first time.
Special features of application webcam access protection
Webcam access protection functionality has the following special considerations and limitations:
- The application controls video and still images derived from the processing of webcam data.
- The application controls the audio stream if it is part of the video stream received from the webcam.
- The application controls only webcams connected via USB or IEEE1394 that are displayed as Imaging Devices in the Windows Device Manager.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the following webcams:
- Logitech HD Webcam C270
- Logitech HD Webcam C310
- Logitech Webcam C210
- Logitech Webcam Pro 9000
- Logitech HD Webcam C525
- Microsoft LifeCam VX-1000
- Microsoft LifeCam VX-2000
- Microsoft LifeCam VX-3000
- Microsoft LifeCam VX-800
- Microsoft LifeCam Cinema
Kaspersky cannot guarantee support for webcams that are not specified in this list.
Remediation Engine
The Remediation Engine lets Kaspersky Endpoint Security roll back actions that have been performed by malware in the operating system.
When rolling back malware activity in the operating system, Kaspersky Endpoint Security handles the following types of malware activity:
- File activity
Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- Deletes executable files that were created by malware (on all media except network drives).
- Deletes executable files that were created by programs that have been infiltrated by malware.
- Restores files that have been modified or deleted by malware.
The file recovery feature has a number of limitations.
- Registry activity
Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- Deletes registry keys that were created by malware.
- Does not restore registry keys that have been modified or deleted by malware.
- System activity
Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- Terminates processes that have been initiated by malware.
- Terminates processes into which a malicious application has penetrated.
- Does not resume processes that have been halted by malware.
- Network activity
Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- Blocks the network activity of malware.
- Blocks the network activity of processes that have been infiltrated by malware.
A rollback of malware actions can be started by the File Threat Protection or Behavior Detection component, or during a malware scan.
Rolling back malware operations affects a strictly defined set of data. Rollback has no adverse effects on the operating system or on the integrity of your computer data.
How to enable or disable the Remediation Engine component in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to enable or disable the Remediation Engine component in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to enable or disable the Remediation Engine component in the application interface
As a result, if Remediation Engine is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will roll back the actions taken by malicious applications in the operating system.
Page top
Kaspersky Security Network
To protect your computer more effectively, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses data that is received from users around the globe. Kaspersky Security Network is designed for obtaining this data.
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is an infrastructure of cloud services providing access to the online Kaspersky Knowledge Base that contains information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software. The use of data from Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky Endpoint Security to new threats, improves the performance of some protection components, and reduces the likelihood of false positives. If you are participating in Kaspersky Security Network, KSN services provide Kaspersky Endpoint Security with information about the category and reputation of scanned files, as well as information about the reputation of scanned web addresses.
Use of Kaspersky Security Network is voluntary. The application prompts you to use KSN during initial configuration of the application. Users can begin or discontinue participation in KSN at any time.
For more detailed information about sending Kaspersky statistical information that is generated during participation in KSN, and about the storage and destruction of such information, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Network Statement and the Kaspersky website. The ksn_<language ID>.txt file with the text of the Kaspersky Security Network Statement is included in the application distribution kit.
The infrastructure of Kaspersky reputation databases
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the following infrastructure solutions for working with Kaspersky reputation databases:
- Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is the solution that is used by most Kaspersky applications. KSN participants receive information from Kaspersky and send Kaspersky information about objects detected on the user's computer to be analyzed additionally by Kaspersky analysts and to be included in the reputation and statistical databases.
- Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN) is a solution that enables users of computers hosting Kaspersky Endpoint Security or other Kaspersky applications to obtain access to Kaspersky reputation databases, and to other statistical data without sending data to Kaspersky from their own computers. KPSN is designed for corporate customers who are unable to participate in Kaspersky Security Network for any of the following reasons:
- Local workstations are not connected to the Internet.
- Transmission of any data outside the country or outside the corporate LAN is prohibited by law or restricted by corporate security policies.
By default, Kaspersky Security Center uses KSN. You can configure the use of KPSN in the Administration Console (MMC), in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, and in the command line. It is not possible to configure the use of KPSN in the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
For more details about KPSN, please refer to the documentation on Kaspersky Private Security Network.
Enabling and disabling the usage of Kaspersky Security Network
To enable or disable the usage of Kaspersky Security Network:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Advanced Threat Protection → Kaspersky Security Network.
- Use the Kaspersky Security Network toggle to enable or disable the component.
If you enabled the use of KSN, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will display the Kaspersky Security Network Statement. Please read and accept the Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) Statement terms of use if you agree to them.
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the Extended KSN mode. Extended KSN mode is a mode in which Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends additional data to Kaspersky.
- If required, flip the Enable extended KSN mode toggle off.
- Save your changes.
As a result, if use of KSN is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses information about the reputation of files, web resources, and applications received from Kaspersky Security Network.
Page top
Limitations of Kaspersky Private Security Network
Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN) is a solution that enables users of computers hosting Kaspersky Endpoint Security or other Kaspersky applications to obtain access to Kaspersky reputation databases, and to other statistical data without sending data to Kaspersky from their own computers. Kaspersky Private Security Network lets you use your own local reputation database to check the reputation of objects (files or web addresses). The reputation of an object added to the local reputation database has a higher priority than one added to KSN/KPSN. For example, imagine that Kaspersky Endpoint Security is scanning a computer and requests the reputation of a file in KSN/KPSN. If the file has an Untrusted reputation in the local reputation database but has a Trusted reputation in KSN/KPSN, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will detect the file as Untrusted and will take the action defined for detected threats.
However, in some cases Kaspersky Endpoint Security might not request the reputation of an object in KSN/KPSN. If this is the case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not receive data from the local reputation database of KPSN. Kaspersky Endpoint Security might not request the reputation of an object in KSN/KPSN for the following reasons:
- Kaspersky applications are using offline reputation databases. Offline reputation databases are designed to optimize resources during operation of Kaspersky applications and to protect critically important objects on the computer. Offline reputation databases are created by Kaspersky experts based on data from Kaspersky Security Network. Kaspersky applications update offline reputation databases with anti-virus databases of the specific application. If offline reputation databases contain information about an object being scanned, the application does not request the reputation of this object from KSN/KPSN.
- Scan exclusions (trusted zone) are configured in the application settings. If this is the case, the application does not take into account the reputation of the object in the local reputation database.
- The application uses scan optimization technologies, such as iSwift or iChecker, or is caching reputation requests to KSN / KPSN. If this is the case, the application might not request the reputation of previously scanned objects.
- To optimize its workload, the application scans files of a certain format and size. The list of relevant formats and size limits are determined by Kaspersky experts. This list is updated with the application's anti-virus databases. You can also configure scan optimization settings in the application interface, for example, for the File Threat Protection component.
Enabling and disabling cloud mode for protection components
Cloud mode refers to the application operating mode in which Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses a light version of anti-virus databases. Kaspersky Security Network supports the operation of the application when light anti-virus databases are being used. The light version of anti-virus databases lets you use approximately half of the computer RAM that would otherwise be used with the usual databases. If you do not participate in Kaspersky Security Network or if cloud mode is disabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security downloads the full version of anti-virus databases from Kaspersky servers.
When using Kaspersky Private Security Network, cloud mode functionality is available starting with Kaspersky Private Security Network version 3.0.
To enable or disable cloud mode for protection components:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Advanced Threat Protection → Kaspersky Security Network.
- Use the Enable cloud mode toggle to enable or disable the component.
- Save your changes.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security downloads a light version or full version of anti-virus databases during the next update.
If the light version of anti-virus databases is not available for use, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically switches to the premium version of anti-virus databases.
Page top
KSN Proxy settings
User computers managed by Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server can interact with KSN via the KSN Proxy service.
The KSN Proxy service provides the following capabilities:
- The user's computer can query KSN and submit information to KSN even without direct access to the Internet.
- The KSN Proxy service caches processed data, thereby reducing the load on the external network communication channel and speeding up receipt of the information that is requested by the user's computer.
By default, after KSN is enabled and the KSN Statement is accepted, the application uses a proxy server to connect to Kaspersky Security Network. The proxy server used by the application is the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server via TCP port 13111. Therefore, if KSN Proxy is not available, you need to verify the following:
- The ksnproxy service is running on the Administration Server.
- The Firewall on the computer is not blocking port 13111.
You can configure the use of KSN Proxy as follows: enable or disable KSN Proxy, and configure the port for the connection. To do so, you need to open the Administration Server properties. For details on KSN Proxy configuration, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help. You can also enable or disable KSN Proxy for individual computers in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
How to enable or disable KSN Proxy in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to enable or disable KSN Proxy in the Web Console
The KSN Proxy address matches the Administration Server address. When the Administration Server domain name is changed, you need to manually update the KSN Proxy address.
To configure the KSN Proxy address:
- In the Administration Console, go to the folder Administration Server → Additional → Remote installation → Installation packages.
- In the context menu of the Installation packages folder, select Properties.
- On the General tab in the opened window, specify the new address of the KSN proxy server.
- Save your changes.
Checking the reputation of a file in Kaspersky Security Network
If you are doubtful of the security of a file, you can check its reputation in Kaspersky Security Network.
You can check the reputation of a file if you have accepted the terms of the Kaspersky Security Network Statement.
To check the reputation of a file in Kaspersky Security Network:
Open the file context menu and select the Check reputation in KSN option (see the figure below).

File context menu
Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays the file reputation:
![]() Trusted (Kaspersky Security Network). The application considers a file trusted if one or more of the following conditions are met:
Trusted (Kaspersky Security Network). The application considers a file trusted if one or more of the following conditions are met:
- the file is digitally signed by a trusted vendor;
- the file has a trusted reputation in Kaspersky Security Network;
- the user has placed the file in the Trusted group.
![]() Legitimate software that can be used by intruders to damage your computer or personal data. Although they do not have any malicious functions, such applications can be exploited by intruders. For details on legitimate software that could be used by criminals to harm the computer or personal data of a user, please refer to the Kaspersky IT Encyclopedia website. You can add these applications to the trusted list.
Legitimate software that can be used by intruders to damage your computer or personal data. Although they do not have any malicious functions, such applications can be exploited by intruders. For details on legitimate software that could be used by criminals to harm the computer or personal data of a user, please refer to the Kaspersky IT Encyclopedia website. You can add these applications to the trusted list.
![]() Untrusted (Kaspersky Security Network). A virus or other application that poses a threat.
Untrusted (Kaspersky Security Network). A virus or other application that poses a threat.
![]() Unknown (Kaspersky Security Network). Kaspersky Security Network does not have any information about the file. You can scan a file using anti-virus databases (the Scan for viruses option in the context menu).
Unknown (Kaspersky Security Network). Kaspersky Security Network does not have any information about the file. You can scan a file using anti-virus databases (the Scan for viruses option in the context menu).
Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays the KSN solution that was used to determine the reputation of the file: Kaspersky Security Network or Kaspersky Private Security Network.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security also displays additional information about the file (see the figure below).
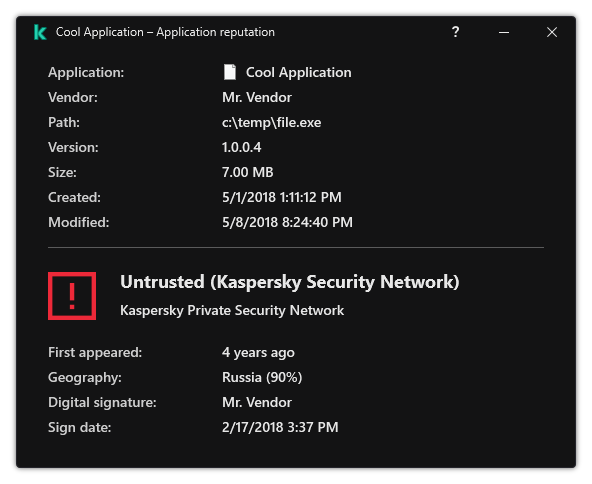
Reputation of a file in Kaspersky Security Network
Page top
Encrypted connections scan
After installation, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds a Kaspersky certificate to the system storage for trusted certificates (Windows certificate store). Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses this certificate to scan encrypted connections. Kaspersky Endpoint Security also includes the use of system storage of trusted certificates in Firefox and Thunderbird to scan the traffic of these applications.
The Web Control, Mail Threat Protection, Web Threat Protection components can decrypt and scan network traffic transmitted over encrypted connections using the following protocols:
- SSL 3.0.
- TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2, TLS 1.3.
Enabling encrypted connections scan
To enable the scanning of encrypted connections:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Network settings.
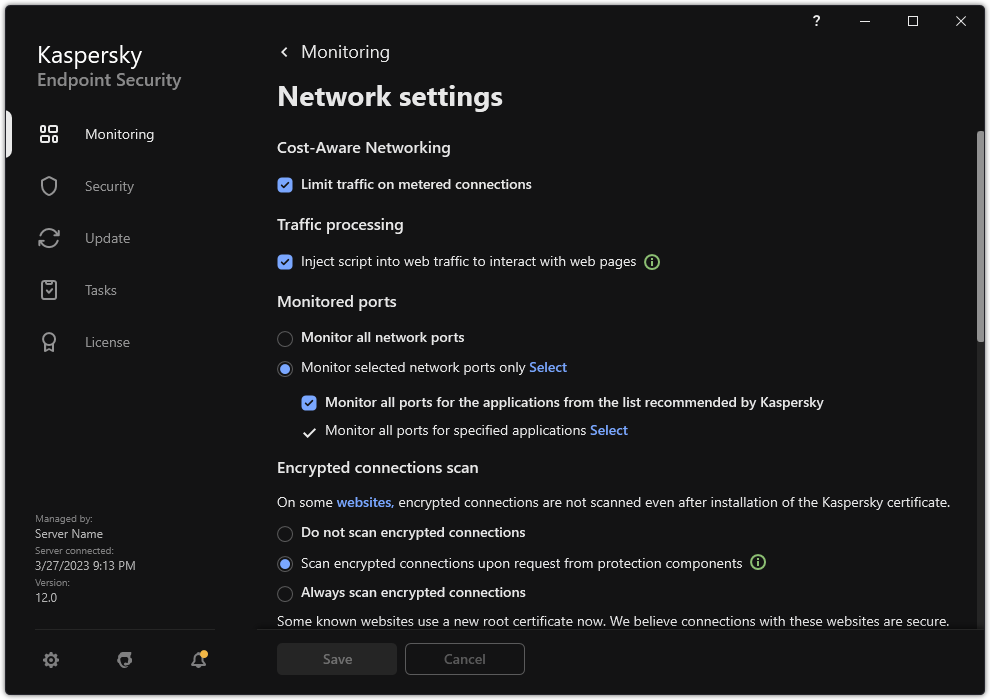
Encrypted connections scan settings
- In the Encrypted connections scan block, select the encrypted connection scanning mode:
- Do not scan encrypted connections. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not have access to the contents of websites whose addresses begin with
https://. - Scan encrypted connections upon request from protection components. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will scan encrypted traffic only when requested by the Web Threat Protection, Mail Threat Protection, and Web Control components.
- Always scan encrypted connections. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will scan encrypted network traffic even if protection components are disabled.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan encrypted connections that were established by trusted applications for which traffic scanning is disabled. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan encrypted connections from the predefined list of trusted websites. The predefined list of trusted websites is created by Kaspersky experts. This list is updated with the application's anti-virus databases. You can view the predefined list of trusted websites only in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface. You cannot view the list in the Kaspersky Security Center Console.
- Do not scan encrypted connections. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not have access to the contents of websites whose addresses begin with
- If necessary, add scan exclusions: trusted addresses and applications.
- Configure the settings for scanning encrypted connections (see the table below).

Additional settings for scanning encrypted connections
- Save your changes.
Encrypted connections scan settings
Parameter
Description
Trusted root certificates
List of trusted root certificates. Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you install trusted root certificates on user computers if, for example, you need to deploy a new certification center. The application lets you add a certificate to a special Kaspersky Endpoint Security certificate store. In this case, the certificate is considered trusted only for the Kaspersky Endpoint Security application. In other words, the user can gain access to a website with the new certificate in the browser. If another application tries to gain access to the website, you can get a connection error because of a certificate issue. To add to the system certificate store, you can use Active Directory group policies.
When visiting a domain with an untrusted certificate
- Allow. When visiting a domain with an untrusted certificate, Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows the network connection.
When opening a domain with an untrusted certificate in a browser, Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays an HTML page showing a warning and the reason why visiting that domain is not recommended. A user can click the link from the HTML warning page to obtain access to the requested web resource.
If a third-party application or service establishes a connection with a domain with an untrusted certificate, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates its own certificate to scan traffic. The new certificate has the Untrusted status. This is necessary to warn the third-party application about the untrusted connection because the HTML page cannot be shown in this case and the connection can be established in background mode.
- Block connection. When visiting a domain with an untrusted certificate, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the network connection. When opening a domain with an untrusted certificate in a browser, Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays an HTML page showing the reason why that domain is blocked.
When encrypted connections scan errors occur
- Block connection. If this item is selected, when an encrypted connection scan error occurs, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the network connection.
- Add domain to exclusions. If this item is selected, when an encrypted connection scan error occurs, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds the domain that resulted in the error to the list of domains with scan errors and does not monitor encrypted network traffic when this domain is visited. You can view a list of domains with encrypted connections scan errors only in the local interface of the application. To clear the list contents, you need to select Block connection. Kaspersky Endpoint Security also generates an event for the encrypted connection scan error.
Block SSL 2.0 connections (recommended)
If the check box is selected, the application blocks network connections established over the SSL 2.0 protocol.
If the check box is cleared, the application does not block network connections established over the SSL 2.0 protocol and does not monitor network traffic transmitted over these connections.
Decrypt an encrypted connection with the website that uses EV certificate
EV certificates (Extended Validation Certificates) confirm the authenticity of websites and enhance the security of the connection. Browsers use a lock icon in their address bar to indicate that a website has an EV certificate. Browsers may also fully or partially color the address bar in green.
If the check box is selected, the application decrypts and monitors encrypted connections with websites that use an EV certificate.
If the check box is cleared, the application does not have access to the contents of HTTPS traffic. For this reason, the application monitors HTTPS traffic only based on the website address, for example,
https://bing.com.If you are opening a website with an EV certificate for the first time, the encrypted connection will be decrypted regardless of whether or not the check box is selected.
- Allow. When visiting a domain with an untrusted certificate, Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows the network connection.
Installing trusted root certificates.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you install trusted root certificates on user computers if, for example, you need to deploy a new certification center. The application lets you add a certificate to a special Kaspersky Endpoint Security certificate store. In this case, the certificate is considered trusted only for the Kaspersky Endpoint Security application. In other words, the user can gain access to a website with the new certificate in the browser. If another application tries to gain access to the website, you can get a connection error because of a certificate issue. To add to the system certificate store, you can use Active Directory group policies.
How to install trusted root certificates in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to install trusted root certificates in Web Console and Cloud Console
How to install trusted root certificates in the application interface
As a result, when scanning traffic, in addition to the system certificate store, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses its own certificate store.
Page top
Scanning encrypted connections with an untrusted certificate
After installation, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds a Kaspersky certificate to the system storage for trusted certificates (Windows certificate store). Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses this certificate to scan encrypted connections. When visiting a domain with an untrusted certificate, you can allow or deny user access to that domain (see the instructions below).
If you have allowed the user to visit domains with untrusted certificates, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- When visiting a domain with an untrusted certificate in the browser, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the Kaspersky certificate to scan traffic. Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays a HTML page with a warning and information about the reason why it is not recommended to visit the relevant domain (see the figure below). A user can click the link from the HTML warning page to obtain access to the requested web resource. After following this link, during the next hour Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not display warnings about an untrusted certificate when visiting other resources on this same domain. Kaspersky Endpoint Security also generates an event about establishing an encrypted connection with an untrusted certificate.
- If a third-party application or service establishes a connection with a domain with an untrusted certificate, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates its own certificate to scan traffic. The new certificate has the Untrusted status. This is necessary to warn the third-party application about the untrusted connection because the HTML page cannot be shown in this case and the connection can be established in background mode. Therefore, if a third-party application has built-in certificate verification tools, the connection may be terminated. In that case, you must contact the owner of the domain and set up a trusted connection. If setting up a trusted connection is impossible, you can add that third-party application to the list of trusted applications. Kaspersky Endpoint Security also generates an event about establishing an encrypted connection with an untrusted certificate.
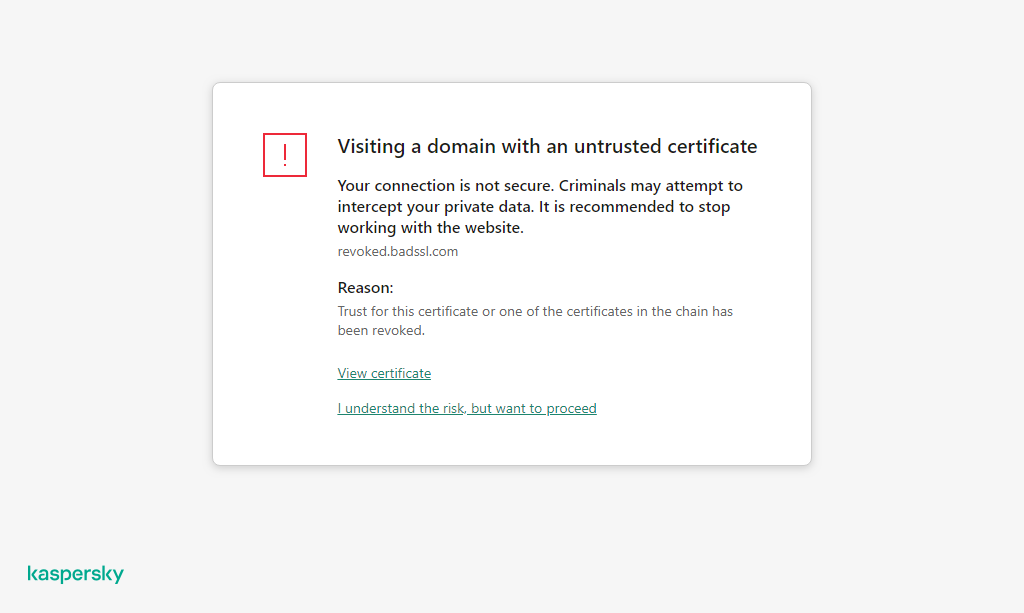
Warning about visiting a domain with an untrusted certificate
Page top
Scanning encrypted connections in Firefox and Thunderbird
After installation, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds a Kaspersky certificate to the system storage for trusted certificates (Windows certificate store). By default, Firefox and Thunderbird use their own proprietary Mozilla certificate store instead of the Windows certificate store. If Kaspersky Security Center is deployed in your organization and a policy is being applied to a computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically enables use of the Windows certificate store in Firefox and Thunderbird to scan the traffic of these applications. If a policy is not being applied to the computer, you can choose the certificate storage that will be used by Mozilla applications. If you selected the Mozilla certificate store, manually add a Kaspersky certificate to it. This will help avoid errors when working with HTTPS traffic.
To scan traffic in the Mozilla Firefox browser and the Thunderbird mail client, you must enable the Encrypted Connections Scan. If Encrypted Connections Scan is disabled, the application does not scan traffic in the Mozilla Firefox browser and Thunderbird mail client.
Prior to adding a certificate to the Mozilla store, export the Kaspersky certificate from the Windows Control Panel (browser properties). For details about exporting the Kaspersky certificate, please refer to the Technical Support Knowledge Base. For details about adding a certificate to storage, visit the Mozilla technical support website.
You can choose the certificate store only in the local interface of the application.
To choose a certificate store for scanning encrypted connections in Firefox and Thunderbird:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Network settings.
- In the Mozilla Firefox and Thunderbird block, select the Use the selected certificate store to scan encrypted connections in Mozilla applications check box.
- Select a certificate store:
- Use Windows certificate store (recommended). The Kaspersky root certificate is added to this store during installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Use Mozilla certificate store. Mozilla Firefox and Thunderbird use their own certificate stores. If the Mozilla certificate store is selected, you need to manually add the Kaspersky root certificate to this store through the browser properties.
- Save your changes.
Excluding encrypted connections from scanning
Most web resources use encrypted connections. Kaspersky experts recommend that you enable Encrypted connections scan. If encrypted connections scan interferes with work-related activity, you can add a website to exclusions referred to as trusted addresses. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan HTTPS traffic of trusted web addresses when Web Threat Protection, Mail Threat Protection, Web Control components are doing their work.
If a trusted application uses an encrypted connection, you can disable encrypted connections scan for this application. For example, you can disable encrypted connections scan for cloud storage applications that use two-factor authentication with their own certificate.
How to exclude a web address from encrypted connection scans in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to exclude a web address from encrypted connection scans in Web Console and Cloud Console
How to exclude a web address from encrypted connection scans in the application interface
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan encrypted connections when errors occur and adds the website to a special list of Domains with scan errors. Kaspersky Endpoint Security compiles a separate list for each user and does not send data to Kaspersky Security Center. You can enable blocking the connection when a scan error occurs. You can view a list of domains with encrypted connections scan errors only in the local interface of the application.
To view the list of domains with scan errors:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Network settings.
- In the Encrypted connections scan block, click the Domains with scan errors button.
A list of domains with scan errors opens. To reset the list, enable blocking connection when scan errors occur in the policy, apply the policy, then reset the parameter to its initial value and apply the policy again.
Kaspersky specialists make a list of global exceptions — trusted websites that Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not check regardless of the application settings.
To view the global exclusions from encrypted traffic scans:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Network settings.
- In the Encrypted connections scan block, click the list of trusted websites link.
This opens a list of websites compiled by Kaspersky experts. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan protected connections for websites on the list. The list may be updated when Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases and modules are updated.
Page top
Wipe Data
Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you use a task to remotely delete data from users' computers.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes data as follows:
- In silent mode;
- On hard drives and removable drives;
- For all user accounts on the computer.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the Wipe data task no matter which licensing type is being used, even after the license has expired.
Data Wipe modes
This task enables you to delete data in the following modes:
- Immediate data deletion.
In this mode, you can, for example, delete outdated data to free up disk space.
- Postponed data deletion.
This mode is intended, for example, to protect data on a laptop in case it is lost or stolen. You can configure automatic data deletion if the laptop goes outside the boundaries of the corporate network and has not been synchronized with Kaspersky Security Center in a long time.
It is not possible to set a schedule for deleting data in task properties. You can only delete data immediately after starting the task manually, or configure delayed data deletion if there is no connection with Kaspersky Security Center.
Limitations
Data Wipe has the following limitations:
- Only a Kaspersky Security Center administrator can manage the Wipe data task. You cannot configure or start a task in the local interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- For the NTFS file system, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes only the names of the main data streams. Alternate data stream names cannot be deleted.
- When you delete a symbolic link file, Kaspersky Endpoint Security also deletes the files whose paths are specified in the symbolic link.
Creating a Wipe data task
To delete data on users' computers:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Tasks.
The list of tasks opens.
- Click the Add button.
The Task Wizard starts.
- Configure the task settings:
- In the Application drop-down list, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (12.1).
- In the Task type drop-down list, select Wipe data.
- In the Task name field, enter a brief description, for example, Wipe data (Anti-Theft).
- In the Select devices to which the task will be assigned block, select the task scope.
- Select devices according to the selected task scope option. Go to the next step.
If new computers are added to an administration group within the task scope, the immediate data deletion task is run on the new computers only if the task is completed within 5 minutes of the addition of the new computers.
- Exit the Wizard.
A new task will be displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the Wipe data task of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
The task properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- Select the data deletion method:
- Delete by means of the operating system. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the operating system resources to delete files without sending them to the recycle bin.
- Delete completely, no recovery possible. Kaspersky Endpoint Security overwrites files with random data. It is practically impossible to restore data after it is deleted.
- If you want to postpone data deletion, select the Automatically wipe data when there is no connection to Kaspersky Security Center for more than N days check box. Define the number of days.
The postponed data deletion task will be performed each time that a connection with Kaspersky Security Center is absent for the defined period of time.
When configuring postponed data deletion, bear in mind that employees may turn off their computer before going on vacation. In this case, the absent connection term may be exceeded and data will be deleted. Also consider the work schedule of offline users. For more details about working with offline computers and out-of-office users, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
If the check box is cleared, the task will be performed immediately after synchronization with Kaspersky Security Center.
- Create a list of objects to delete:
- Folders. Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes all files in the folder, and its subfolders. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support masks and environment variables for entering a folder path.
- Files by extension. Kaspersky Endpoint Security searches for files with the specified extensions on all computer drives, including removable drives. Use the "
;" or "," characters to specify multiple extensions. - Predefined scope. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will delete files from the following areas:
- Documents. Files in the standard Documents folder of the operating system, and its subfolders.
- Cookies. Files in which the browser saves data from the websites visited by the user (such as user authorization data).
- Desktop. Files in the standard Desktop folder of the operating system, and its subfolders.
- Temporary Internet Explorer files. Temporary files related to the operation of Internet Explorer, such as copies of web pages, images, and media files.
- Temporary files. Temporary files related to the operation of applications installed on the computer. For example, Microsoft Office applications create temporary files containing backup copies of documents.
- Outlook files. Files related to the operation of the Outlook mail client: data files (PST), offline data files (OST), offline address book files (OAB), and personal address book files (PAB).
- User profile. Set of files and folders that store operating system settings for the local user account.
You can create a list of objects to delete on each tab. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will create a consolidated list and delete files from this list when a task is complete.
You cannot delete files that are required for operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Save your changes.
- Select the check box next to the task.
- Click the Run button.
As a result, data on users' computers will be deleted according to the selected mode: immediate or when a connection is absent. If Kaspersky Endpoint Security cannot delete a file, such as when a user is currently using a file, the application does not attempt to delete it again. To complete data deletion, run the task again.
Page top
Web Control
Web Control manages users' access to web resources. This helps reduce traffic and inappropriate use of work time. When a user tries to open a website that is restricted by Web Control, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block access or show a warning (see the figure below).
Kaspersky Endpoint Security monitors only HTTP- and HTTPS traffic.
For HTTPS traffic monitoring, you need to enable encrypted connections scan.
Methods for managing access to websites
Web Control lets you configure access to websites by using the following methods:
- Website category. Websites are categorized according to the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, heuristic analysis, and the database of known websites (included in application databases). For example, you can restrict user access to the Social networks category or to other categories.
- Data type. You can restrict users' access to data on a website, and hide graphic images, for example. Kaspersky Endpoint Security determines the data type based on the file format and not based on its extension.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan files within archives. For example, if image files were placed in an archive, Kaspersky Endpoint Security identifies the Archives data type and not Graphics.
- Individual address. You can enter a web address or use masks.
You can simultaneously use multiple methods for regulating access to websites. For example, you can restrict access to the "Office files" data type just for the Web-based mail website category.
Website access rules
Web Control manages users' access to websites by using access rules. You can configure the following advanced settings for a website access rule:
- Users to which the rule applies.
For example, you can restrict Internet access through a browser for all users of the company except the IT department.
- Rule schedule.
For example, you can restrict Internet access through a browser during working hours only.
Access rule priorities
Each rule has a priority. The higher a rule is on the list, the higher its priority. If a website has been added to multiple rules, Web Control regulates access to the website based on the rule with the highest priority. For example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may identify a corporate portal as a social network. To restrict access to social networks and provide access to the corporate web portal, create two rules: one block rule for the Social networks website category and one allow rule for the corporate web portal. The access rule for the corporate web portal must have a higher priority than the access rule for social networks.
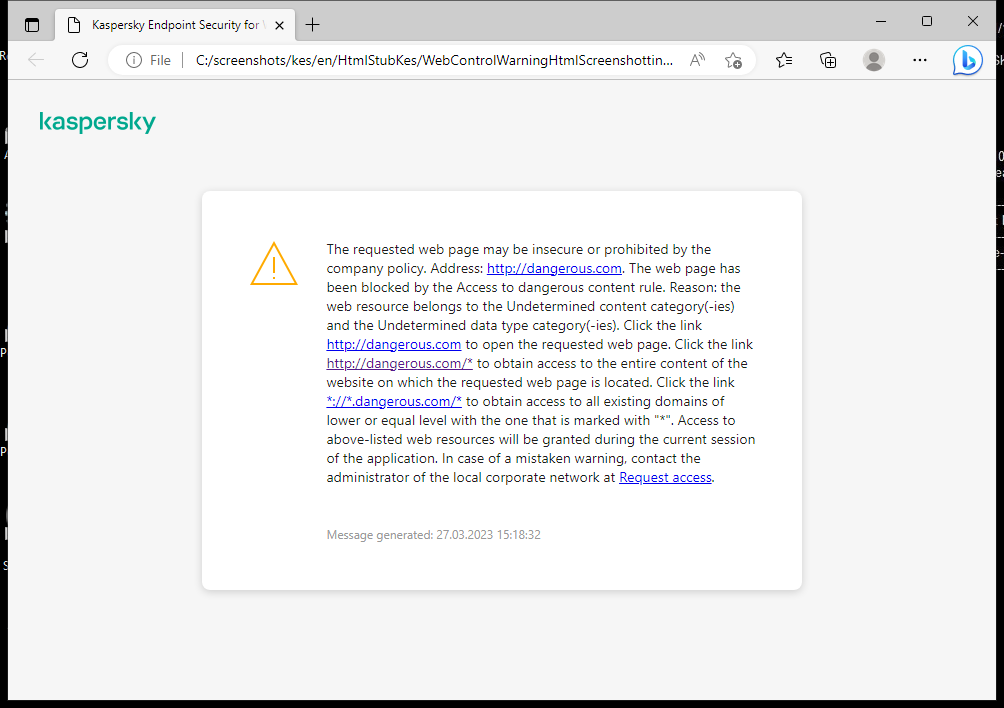
Web Control messages
Enabling and disabling Web Control
By default, Web Control is enabled.
To enable or disable Web Control:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Web Control.
- Use the Web Control toggle to enable or disable the component.
- Save your changes.
Actions with web resource access rules
It is not recommended to create more than 1000 rules of access to web resources, as this can cause the system to become unstable.
A web resource access rule is a set of filters and actions that Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs when the user visits web resources that are described in the rule during the time span that is indicated in the rule schedule. Filters allow you to precisely specify a pool of web resources to which access is controlled by the Web Control component.
The following filters are available:
- Filter by content. Web Control categorizes web resources by content and data type. You can control user access to web resources with content and data falling into the types defined by these categories. When the users visit web resources that belong to the selected content category and / or data type category, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the action that is specified in the rule.
- Filter by web resource addresses. You can control user access to all web resource addresses or to individual web resource addresses and / or groups of web resource addresses.
If filtering by content and filtering by web resource addresses are specified, and the specified web resource addresses and / or groups of web resource addresses belong to the selected content categories or data type categories, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not control access to all web resources in the selected content categories and / or data type categories. Instead, the application controls access only to the specified web resource addresses and / or groups of web resource addresses.
- Filter by names of users and user groups. You can specify the names of users and / or groups of users for which access to web resources is controlled according to the rule.
- Rule schedule. You can specify the rule schedule. The rule schedule determines the time span during which Kaspersky Endpoint Security monitors access to web resources covered by the rule.
After Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed, the list of rules of the Web Control component is not blank. The Default rule is preset. This rule is applied to any web resources that are not covered by other rules, and allows or blocks access to these web resources for all users.
Adding a web resource access rule
To add or edit a web resource access rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Web Control.
- In the Settings block, click the Rules of access to web resources button.
- In the window that opens, click the Add button.
The Rule of access to web resources window opens.
- In the Rule name field, enter the name of the rule.
- Select the On status for the web resource access rule.
You can use the toggle to disable the web resource access rule at any time.
- In the Action block, select the relevant option:
- Allow. If this value is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows access to web resources that match the parameters of the rule.
- Block. If this value is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks access to web resources that match the parameters of the rule.
- Warn. If this value is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays a warning that a web resource is unwanted when the user attempts to access web resources that match the rule. By using links from the warning message, the user can obtain access to the requested web resource.
- In the Content of the filter block, select the relevant content filter:
- By content categories. You can control user access to web resources by category (for example, the Social networks category).
- By types of data. You can control user access to web resources based on the specific data type of its published data (for example, Graphics).
To configure the content filter:
- Click the Settings link.
- Select the check boxes next to the names of the required categories of content and/or data types.
Selecting the check box next to the name of a content category and/or data type means that Kaspersky Endpoint Security applies the rule to control access to web resources that belong to the selected categories of content and/or data types.
- Return to the window for configuring the web resource access rule.
- In the Addresses block, select the relevant web resource address filter:
- To all addresses. Web Control will not filter web resources by address.
- To individual addresses. Web Control will filter only web resource addresses from the list. To create a list of web resource addresses:
- Click the Add address or Add a group of addresses button.
- In the window that opens, create a list of web resource addresses. You can enter a web address or use masks. You can also export a list of web resource addresses from a TXT file.
- Return to the window for configuring the web resource access rule.
If Encrypted Connections Scan is disabled, for the HTTPS protocol you can only filter by the server name.
- In the Users block, select the relevant filter for users:
- To all users. Web Control will not filter web resources for specific users.
- To individual users and / or groups. Web Control will filter web resources only for specific users. To create a list of users to whom you want to apply the rule:
- Click Add.
- In the window that opens, select the users or group of users to whom you want to apply the web resource access rule.
- Return to the window for configuring the web resource access rule.
- In the Rule schedule drop-down list, select the name of the necessary schedule or generate a new schedule based on the selected rule schedule. To do so:
- Click Edit or add new.
- In the window that opens, click the Add button.
- In the window that opens, enter the rule schedule name.
- Configure the web resource access schedule for users.
- Return to the window for configuring the web resource access rule.
- Save your changes.
Assigning priorities to web resource access rules
Each rule has a priority. The higher a rule is on the list, the higher its priority. If a website has been added to multiple rules, Web Control regulates access to the website based on the rule with the highest priority. For example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may identify a corporate portal as a social network. To restrict access to social networks and provide access to the corporate web portal, create two rules: one block rule for the Social networks website category and one allow rule for the corporate web portal. The access rule for the corporate web portal must have a higher priority than the access rule for social networks.
You can assign priorities to each rule from the list of rules, by arranging the rules in a certain order.
To assign a priority to a web resource access rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Web Control.
- In the Settings block, click the Rules of access to web resources button.
- In the window that opens, select the rule whose priority you want to change.
- Use the Up and Down buttons to move the rule to the relevant position in the list of web resource access rules.
- Save your changes.
Enabling and disabling a web resource access rule
To enable or disable a web resource access rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Web Control.
- In the Settings block, click the Rules of access to web resources button.
- In opened window, select the rule that you want to enable or disable.
- In the State column, do the following:
- If you want to enable the use of the rule, select the On value.
- If you want to disable the use of the rule, select the Off value.
- Save your changes.
Exporting and importing Web Control rules
You can export the list of Web Control rules to an XML file. Then you can modify the file to, for example, add a large number of addresses of the same type. You can use the export/import function to back up the list of Web Control rules or to migrate the list to a different server.
How to export and import a list of Web Control rules in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to export and import a list of Web Control rules in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Testing web resource access rules
To check the consistency of Web Control rules, you can test them. For this purpose, the Web Control component includes a Rules Diagnostics function.
To test the web resource access rules:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Web Control.
- In the Settings block, click the Rules diagnostics link.
The Rules diagnostics window opens.
- If you want to test the rules that Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses to control access to a specific web resource, select the Specify address check box. Enter the address of the web resource in the field below.
- If you want to test the rules that Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses to control access to web resources for specified users and / or groups of users, specify a list of users and / or groups of users.
- If you want to test the rules that Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses to control access to web resources of certain content categories and/or data type categories, select the Filter content check box and choose the relevant option from the drop-down list (By content categories, By types of data, or By content categories and types of data).
- If you want to test the rules with account of the time and day of the week when an attempt is made to access the web resources that are specified in the rule diagnostics conditions, select the Include time of access attempt check box. Then specify the day of the week and the time.
- Click Scan.
Test completion is followed by a message with information about the action that is taken by Kaspersky Endpoint Security, according to the first rule that is triggered on the attempt to access the specified web resource (allow, block, or warning). The first rule to be triggered is the one with a rank on the list of Web Control rules which is higher than that of other rules meeting the diagnostics conditions. The message is displayed on the right of the Scan button. The following table lists the remaining triggered rules, specifying the action taken by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. The rules are listed in the order of declining priority.
Page top
Exporting and importing the list of web resource addresses
If you have created a list of web resource addresses in a web resource access rule, you can export it to a .txt file. You can subsequently import the list from this file to avoid creating a new list of web resource addresses manually when configuring an access rule. The option of exporting and importing the list of web resource addresses may be useful if, for example, you create access rules with similar parameters.
To import or export a list of web resource addresses to a file:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Web Control.
- In the Settings block, click the Rules of access to web resources button.
- Select the rule whose list of web resource addresses you want to export or import.
- To export the list of trusted web addresses, do the following in the Addresses block:
- Select the addresses that you want to export.
If you did not select any address, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will export all addresses.
- Click Export.
- In the window that opens, enter the name of the TXT file to which you want to export the list of web resource addresses, and select the folder in which you want to save this file.
- Save the file.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security exports the list of web resource addresses to a TXT file.
- Select the addresses that you want to export.
- To import the list of web resources, do the following in the Addresses block:
- Click Import.
In the window that opens, select the TXT file from which you want to import the list of web resources.
- Open the file.
If the computer already has a list of addresses, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will prompt you to delete the existing list or add new entries to it from the TXT file.
- Click Import.
- Save your changes.
Monitoring user Internet activity
Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you log data on user visits to all websites, including allowed websites. This enables you to obtain the complete history of browser views. Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends user activity events to Kaspersky Security Center, to the local log of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, and to the Windows Event log. To receive events in Kaspersky Security Center, you need to configure the settings of events in a policy in the Administration Console or Web Console. You can also configure the transmission of Web Control events by email and the display of on-screen notifications on the user's computer.
Browsers that support the monitoring function: Microsoft Edge, Microsoft Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Yandex Browser, Mozilla Firefox. User activity monitoring does not work in other browsers.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates the following user Internet activity events:
- Block the website (Critical events status
 ).
). - Visit to a non-recommended website (Warnings status
 ).
). - Visit to an allowed website (Informational messages status
 ).
).
Prior to enabling user Internet activity monitoring, you must do the following:
- Inject a web page interaction script into web traffic (see the instructions below). The script enables registration of Web Control events.
- For HTTPS traffic monitoring, you need to enable encrypted connections scan.
To inject a web page interaction script into web traffic:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Network settings.

Application network settings
- In the Traffic processing block, select the Inject script into web traffic to interact with web pages check box.
- Save your changes.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will inject a web page interaction script into web traffic. This script enables registration of Web Control events for the application event log, OS event log, and reports.
To configure logging of Web Control events on the user's computer:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Interface.
- In the Notifications block, click the Notification settings button.
- In the window that opens, select the Web Control section.
This opens the table of Web Control events and notification methods.
- Configure the notification method for each event: Save in local report or Save in Windows Event Log.
To log allowed website visit events, you need to also configure Web Control (see the instructions below).
In the events table, you can also enable an on-screen notification and an email notification. To send notifications by email, you need to configure the SMTP server settings. For more details about sending notifications by email, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
- Save your changes.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security begins logging user Internet activity events.
Web Control sends user activity events to Kaspersky Security Center as follows:
- If you are using Kaspersky Security Center, Web Control sends events for all the objects that make up the web page. For this reason, multiple events may be created when one web page is blocked. For example, when blocking the web page http://www.example.com, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may relay events for the following objects: http://www.example.com, http://www.example.com/icon.ico, http://www.example.com/file.js, etc.
- If you are using the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, Web Control groups events and sends only the protocol and domain of the website. For instance, if a user visits non-recommended web pages http://www.example.com/main, http://www.example.com/contact, and http://www.example.com/gallery, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will send only one event with the http://www.example.com object.
To enable logging of events for visiting allowed websites:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Web Control.
- In the Additional block, click the Advanced Settings button.
- In the window that opens, select the Log the opening of allowed pages check box.
- Save your changes.
As a result, you will be able to view the full browser history.
Page top
Editing templates of Web Control messages
Depending on the type of action that is specified in the properties of Web Control rules, Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays a message of one of the following types when users attempt to access Internet resources (the application substitutes an HTML page with a message for the HTTP server response):
- Warning message. This message warns the user that visiting the web resource is not recommended and/or violates the corporate security policy. Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays a warning message if the Warn option is selected in the settings of the rule that describes this web resource.
If the user believes that the warning is mistaken, the user may click the link from the warning to send a pre-generated message to the local corporate network administrator.
- Message informing of blocking of a web resource. Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays a message informing that a web resource is blocked if the Block option is selected in the settings of the rule that describes this web resource.
If the user believes that the web resource is blocked by mistake, the user may click the link in the web resource block notification message to send a pre-generated message to the local corporate network administrator.
Special templates are provided for the warning message, the message informing that a web resource is blocked, and the message sent to the LAN administrator. You can modify their content.
To change the template for Web Control messages:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Web Control.
- In the Templates block, configure the templates for Web Control messages:
- Warning. The entry field consists of a template of the message that is displayed if a rule for warning about attempts to access an unwanted web resource is triggered.
- Message about blocking. The entry field contains the template of the message that appears if a rule which blocks access to a web resource is triggered.
- Message to administrator. Template of the message to be sent to the LAN administrator if the user considers the block to be a mistake. After the user requests to provide access, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends an event to Kaspersky Security Center: Web page access blockage message to administrator. The event description contains a message to administrator with substituted variables. You can view these events in the Kaspersky Security Center console using the predefined event selection User requests. If your organization does not have Kaspersky Security Center deployed or there is no connection to the Administration Server, the application will send a message to administrator to the specified email address.
- Save your changes.
Editing masks for web resource addresses
Using a web resource address mask (also referred to as "address mask") may be useful if you need to enter numerous similar web resource addresses when creating a web resource access rule. If crafted well, one address mask can replace a large number of web resource addresses.
When creating an address mask, follow these rules:
- The
*character replaces any sequence that contains zero or more characters.For example, if you enter the
*abc*address mask, the access rule is applied to all web resources that contain the sequenceabc. Example:http://www.example.com/page_0-9abcdef.html. - A sequence of
*.characters (known as a domain mask) lets you select all domains of an address. The*.domain mask represents any domain name, subdomain name, or a blank line.Example: the
*.example.commask represents the following addresses:http://pictures.example.com. The domain mask*.representspictures.http://user.pictures.example.com. The domain mask*.representspictures.anduser.http://example.com. The domain mask*.is interpreted as a blank line.
- The
www.character sequence at the start of the address mask is interpreted as a*.sequence.Example: the address mask
www.example.comis interpreted as*.example.com. This mask covers the addresseswww2.example.comandwww.pictures.example.com. - If an address mask does not start with the
*character, the content of the address mask is equivalent to the same content with the*.prefix. - If an address mask ends with a character other than
/or*, the content of the address mask is equivalent to the same content with the/*postfix.Example: the address mask
http://www.example.comcovers such addresses ashttp://www.example.com/abc, wherea,b, andcare any characters. - If an address mask ends with the
/character, the content of the address mask is equivalent to the same content with the/*.postfix. - The character sequence
/*at the end of an address mask is interpreted as/*or an empty string. - Web resource addresses are verified against an address mask, taking into account the protocol (http or https):
- If the address mask contains no network protocol, this address mask covers addresses with any network protocol.
Example: the address mask
example.comcovers the addresseshttp://example.comandhttps://example.com. - If the address mask contains a network protocol, this address mask only covers addresses with the same network protocol as that of the address mask.
Example: the address mask
http://*.example.comcovers the addresshttp://www.example.combut does not coverhttps://www.example.com.
- If the address mask contains no network protocol, this address mask covers addresses with any network protocol.
- An address mask that is in double quotes is treated without considering any additional replacements, except the
*character if it has been initially included in the address mask. Rules 5 and 7 do not apply to address masks enclosed in double quotation marks (see examples 14 – 18 in the table below). - The user name and password, connection port, and character case are not taken into account during comparison with the address mask of a web resource.
Examples of how to use rules for creating address masks
No.
Address mask
Address of web resource to verify
Is the address covered by the address mask
Comment
1
*.example.com
http://www.123example.com
No
See rule 1.
2
*.example.com
http://www.123.example.com
Yes
See rule 2.
3
*example.com
http://www.123example.com
Yes
See rule 1.
4
*example.com
http://www.123.example.com
Yes
See rule 1.
5
http://www.*.example.com
http://www.123example.com
No
See rule 1.
6
www.example.com
http://www.example.com
Yes
See rules 3, 2, 1.
7
www.example.com
https://www.example.com
Yes
See rules 3, 2, 1.
8
http://www.*.example.com
http://123.example.com
Yes
See rules 3, 4, 1.
9
www.example.com
http://www.example.com/abc
Yes
See rules 3, 5, 1.
10
example.com
http://www.example.com
Yes
See rules 3, 1.
11
http://example.com/
http://example.com/abc
Yes
See rule 6.
12
http://example.com/*
http://example.com
Yes
See rule 7.
13
http://example.com
https://example.com
No
See rule 8.
14
"example.com"
http://www.example.com
No
See rule 9.
15
"http://www.example.com"
http://www.example.com/abc
No
See rule 9.
16
"*.example.com"
http://www.example.com
Yes
See rules 1, 9.
17
"http://www.example.com/*"
http://www.example.com/abc
Yes
See rules 1, 9.
18
"www.example.com"
http://www.example.com; https://www.example.com
Yes
See rules 9, 8.
19
www.example.com/abc/123
http://www.example.com/abc
No
An address mask contains more information than the address of a web resource.
Device Control
Device Control manages user access to devices that are installed on or connected to the computer (for example, hard drives, cameras, or Wi-Fi modules). This lets you protect the computer from infection when such devices are connected, and prevent loss or leaks of data.
Device access levels
Device Control controls access at the following levels:
- Device type. For example, printers, removable drives, and CD/DVD drives.
You can configure device access as follows:
- Allow –
 .
. - Block –
 .
. - By rules (printers and portable devices only) –
 .
. - Depends on connection bus (except Wi-Fi) –
 .
. - Block with exceptions (Wi-Fi only) –
 .
.
- Allow –
- Connection bus. A connection bus is an interface used for connecting devices to the computer (for example, USB or FireWire). Therefore, you can restrict the connection of all devices, for example, over USB.
You can configure device access as follows:
- Allow –
 .
. - Block –
 .
.
- Allow –
- Trusted devices. Trusted devices are devices to which users that are specified in the trusted device settings have full access at all times.
You can add trusted devices based on the following data:
- Devices by ID. Each device has a unique identifier (Hardware ID, or HWID). You can view the ID in the device properties by using operating system tools. Example device ID:
SCSI\CDROM&VEN_NECVMWAR&PROD_VMWARE_SATA_CD00\5&354AE4D7&0&000000. Adding devices by ID is convenient if you want to add several specific devices. - Devices by model. Each device has a vendor ID (VID) and a product ID (PID). You can view the IDs in the device properties by using operating system tools. Template for entering the VID and PID:
VID_1234&PID_5678. Adding devices by model is convenient if you use devices of a certain model in your organization. This way, you can add all devices of this model. - Devices by ID mask. If you are using multiple devices with similar IDs, you can add devices to the trusted list by using masks. The
*character replaces any set of characters. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support the?character when entering a mask. For example,WDC_C*. - Devices by model mask. If you are using multiple devices with similar VIDs or PIDs (for example, devices from the same manufacturer), you can add devices to the trusted list by using masks. The
*character replaces any set of characters. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support the?character when entering a mask. For example,VID_05AC & PID_ *.
- Devices by ID. Each device has a unique identifier (Hardware ID, or HWID). You can view the ID in the device properties by using operating system tools. Example device ID:
Device Control regulates user access to devices by using access rules. Device Control also lets you save device connection/disconnection events. To save events, you need to configure the registration of events in a policy.
If access to a device depends on the connection bus (the ![]() status), Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not save device connection/disconnection events. To enable Kaspersky Endpoint Security to save device connection/disconnection events, allow access to the corresponding type of device (the
status), Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not save device connection/disconnection events. To enable Kaspersky Endpoint Security to save device connection/disconnection events, allow access to the corresponding type of device (the ![]() status) or add the device to the trusted list.
status) or add the device to the trusted list.
When a device that is blocked by Device Control is connected to the computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block access and show a notification (see the figure below).
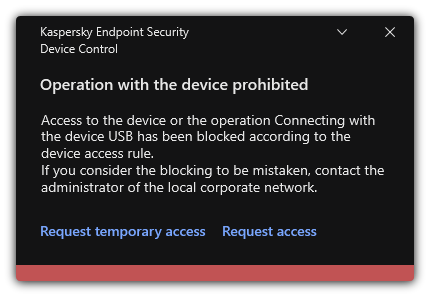
Device Control notification
Device Control operating algorithm
Kaspersky Endpoint Security makes a decision on whether to allow access to a device after the user connects the device to the computer (see the figure below).
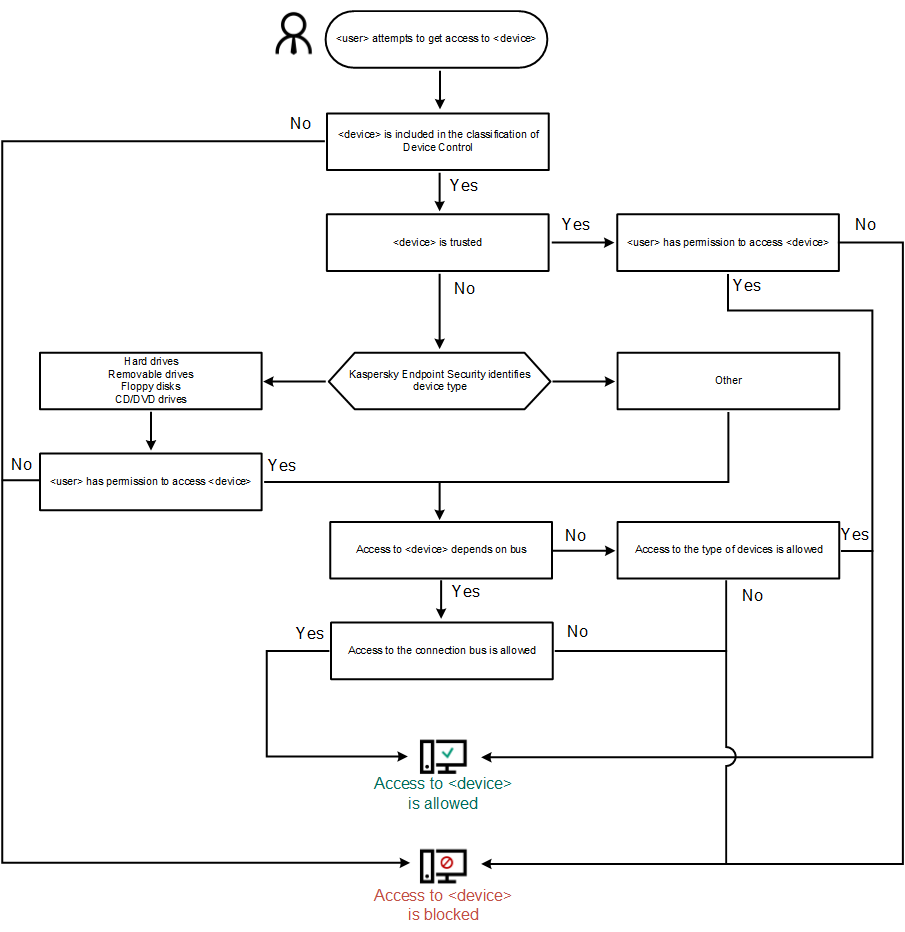
Device Control operating algorithm
If a device is connected and access is allowed, you can edit the access rule and block access. In this case, the next time someone attempts to access the device (such as to view the folder tree, or perform read or write operations), Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks access. A device without a file system is blocked only the next time that the device is connected.
If a user of the computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed must request access to a device that the user believes was blocked by mistake, send the user the request access instructions.
Enabling and disabling Device Control
By default, Device Control is enabled.
To enable or disable Device Control:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Device Control.
- Use the Device Control toggle to enable or disable the component.
- Save your changes.
As a result, if Device Control is enabled, the application relays information about connected devices to Kaspersky Security Center. You can view the list of connected devices in Kaspersky Security Center in the Advanced → Storage → Hardware folder.
Page top
About access rules
Access rules comprise a group of settings that determine which users can access devices that are installed or connected to the computer. You cannot add a device that is outside of Device Control classification. Access to such devices is allowed for all users.
Device Access Rules
The group of settings for an access rule differs depending on the type of device (see the table below).
Access rule settings
Devices |
Access control |
Schedule for access to a device |
Assignment of users and/or a group of users |
Priority |
Read/write permission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Hard drives |
|
|
|
|
|
Removable drives (including USB flash drives) |
|
|
|
|
|
Floppy disks |
|
|
|
|
|
CD/DVD drives |
|
|
|
|
|
Portable devices (MTP) |
|
|
|
|
|
Local printers |
|
– |
|
|
– |
Network printers |
|
– |
|
|
– |
Modems |
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
Tape devices |
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
Multifunctional devices |
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
Smart card readers |
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
Windows CE USB ActiveSync devices |
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
External network adapters |
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
Bluetooth |
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
Cameras and scanners |
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
Access rules for Wi-Fi networks
A Wi-Fi network access rule determines whether the use of Wi-Fi networks is allowed (the ![]() status) or forbidden (the
status) or forbidden (the ![]() status). You can add a trusted Wi-Fi network (the
status). You can add a trusted Wi-Fi network (the ![]() status) to a rule. Use of a trusted Wi-Fi network is allowed without limitations. By default, a Wi-Fi network access rule allows access to any Wi-Fi network.
status) to a rule. Use of a trusted Wi-Fi network is allowed without limitations. By default, a Wi-Fi network access rule allows access to any Wi-Fi network.
Connection bus access rules
Connection bus access rules determine whether the connection of devices is allowed (the ![]() status) or forbidden (the
status) or forbidden (the ![]() status). Rules that allow access to buses are created by default for all connection buses that are present in the classification of the Device Control component.
status). Rules that allow access to buses are created by default for all connection buses that are present in the classification of the Device Control component.
Keyboard and mouse cannot be locked using Device Control. If you prohibit access to the USB connection bus, the user will continue to work with a keyboard and mouse connected via USB. The BadUSB Attack Prevention component is designed to prevent infected USB devices imitating keyboards from connecting to the computer.
Page top
Editing a device access rule
A device access rule is a group of settings that determine how users can access devices that are installed or connected to the computer. These settings include access to a specific device, an access schedule, and read or write permissions.
To edit a device access rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Device Control.
- In the Access settings block, click the Devices and Wi-Fi networks button.
The opened window shows access rules for all devices that are included in the Device Control component classification.
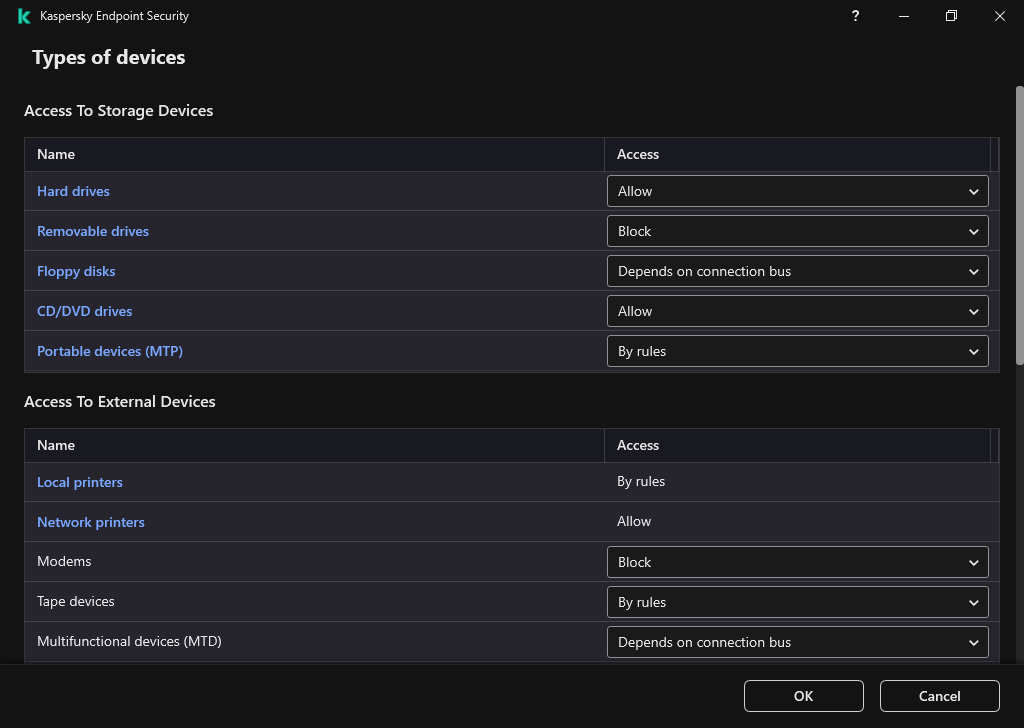
Types of devices in the Device Control component
- In the Access To Storage Devices block, select the access rule that you want to edit. The block contains devices that have a file system for which you can configure additional access settings. By default, a device access rule grants all users full access to the specified type of devices at any time.
- In the Access column, select the appropriate device access option:
- Allow.
- Block.
- Depends on connection bus.
To block or allow access to a device, configure access to the connection bus.
- By rules.
This option lets you configure user rights, permissions, and a schedule for device access.
- In the Users' rights block, click the Add button.
This opens a window for adding a new device access rule.
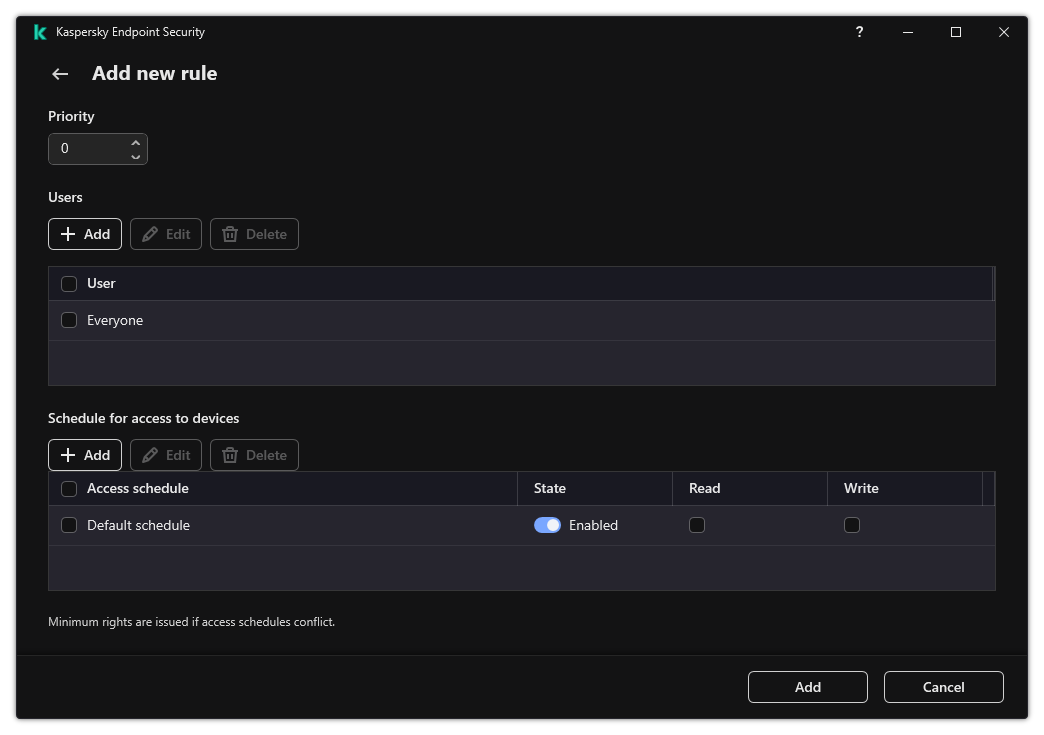
Device Control rule settings
- Assign a priority to the rule. A rule includes the following attributes: user account, schedule, permissions (read/write), and priority.
A rule has a specific priority. If a user has been added to multiple groups, Kaspersky Endpoint Security regulates device access based on the rule with the highest priority. Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows to assign priority from 0 to 10,000. The higher the value, the higher the priority. In other words, an entry with the value of 0 has the lowest priority.
For example, you can grant read-only permissions to the Everyone group and grant read/write permissions to the administrators group. To do so, assign a priority of 1 for the administrators group and assign a priority of 0 for the Everyone group.
The priority of a block rule is higher than the priority of an allow rule. In other words, if a user has been added to multiple groups and the priority of all rules are the same, Kaspersky Endpoint Security regulates device access based on any existing block rule.
- Set the Enabled status for the device access rule.
- Configure users' device access permissions: read and/or write.
- Select the users or group of users to whom you want to apply the device access rule.
- Configure a device access schedule for users.
- Click Add.
- In the Access column, select the appropriate device access option:
- In the Access To External Devices block, select the rule and configure access: Allow, Block, or Depends on connection bus. If necessary, configure access to the connection bus.
- In the Access to Wi-Fi networks block, click the Wi-Fi link and configure access: Allow, Block, or Block with exceptions. If necessary, add Wi-Fi networks to the trusted list.
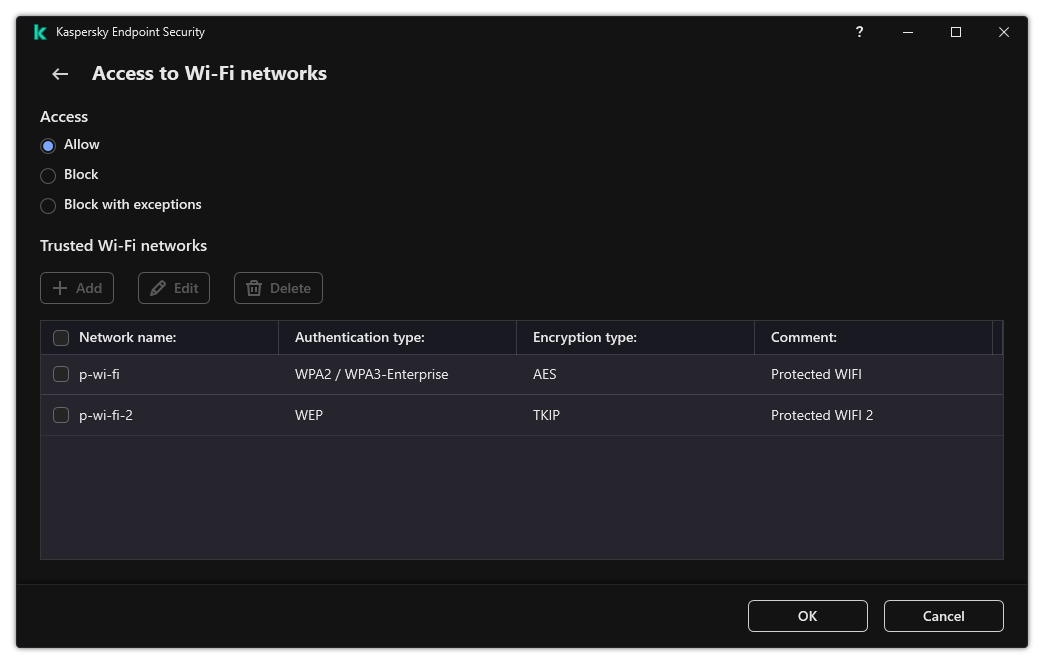
Wi-Fi access settings
- Save your changes.
Editing a connection bus access rule
To edit a connection bus access rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Device Control.
- In the Access settings block, click the Connection buses button.
The opened window shows access rules for all connection buses that are included in the Device Control component classification.
- Select the access rule that you want to edit.
- In the Access column, select whether or not to allow access to the connection bus: Allow or Block.
If you have changed access to the connection bus Serial Port (COM) or Parallel Port (LPT), you must restart the computer to activate the access rule.
- Save your changes.
Managing access to mobile devices
Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows you to control access to data on mobile devices running Android and iOS. Mobile devices belong to the category of portable devices (MTP). Therefore, to configure data access on mobile devices, you need to edit the access settings for portable devices (MTP).
When a mobile device is connected to the computer, the operating system determines the device type. If Android Debug Bridge (ADB), iTunes or their equivalent applications are installed on the computer, the operating system identifies mobile devices as ADB or iTunes devices. In all other cases, the operating system may identify the mobile device type as a portable device (MTP) for file transfer, a PTP device (camera) for image transfer, or another device. The device type depends on the model of the mobile device and the selected USB connection mode. Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you configure individual access permissions for data on mobile devices in ADB applications, iTunes, or the file manager. In all other cases, Device Control allows access to mobile devices in accordance with portable devices (MTP) access rules.
Access to mobile devices
Mobile devices belong to the category of portable devices (MTP), therefore the settings for them are the same. You can select one of the following modes of access to mobile devices:
- Allow
 . Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows full access to mobile devices. You can open, create, modify, copy, or delete files on mobile devices using the file manager or ADB and iTunes applications. You can also charge the battery of the device by connecting the mobile device to a USB port of the computer.
. Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows full access to mobile devices. You can open, create, modify, copy, or delete files on mobile devices using the file manager or ADB and iTunes applications. You can also charge the battery of the device by connecting the mobile device to a USB port of the computer. - Block
 . Kaspersky Endpoint Security restricts access to mobile devices in the file manager and ADB and iTunes applications. The application allows access only to trusted mobile devices. You can also charge the battery of the device by connecting the mobile device to a USB port of the computer.
. Kaspersky Endpoint Security restricts access to mobile devices in the file manager and ADB and iTunes applications. The application allows access only to trusted mobile devices. You can also charge the battery of the device by connecting the mobile device to a USB port of the computer. - Depends on connection bus
 . Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows connecting to mobile devices in accordance with the USB connection status (Allow
. Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows connecting to mobile devices in accordance with the USB connection status (Allow  or Block
or Block  ).
). - By rules
 . Kaspersky Endpoint Security restricts access to mobile devices in accordance with rules. In the rules, you can configure access rights (read / write), select users or a group of users that can have access to mobile devices, and configure an access schedule for mobile devices. You can also restrict access to data on mobile devices through the ADB and iTunes applications.
. Kaspersky Endpoint Security restricts access to mobile devices in accordance with rules. In the rules, you can configure access rights (read / write), select users or a group of users that can have access to mobile devices, and configure an access schedule for mobile devices. You can also restrict access to data on mobile devices through the ADB and iTunes applications.
Configuring mobile device access rules
Access rules for portable devices (MTP), ADB devices, and iTunes devices are configured differently. For portable devices (MTP) and ADB devices, you can configure rules for individual users or groups of users and create a schedule for when the rules will apply. For iTunes devices, you cannot do that. You can only allow or deny access to data through the iTunes application for all users.
How to configure mobile device access rules in Administration Console (MMC)
How to configure mobile device access rules in Web Console and Cloud Console
How to configure mobile device access rules in the interface of the application
As a result, user access to mobile devices is restricted in accordance with rules. If you have prohibited access to mobile devices in the ADB and iTunes applications, when you connect a mobile devices, the ADB and iTunes applications are prevented from detecting the mobile device.
Trusted mobile devices
Trusted devices are devices to which users that are specified in the trusted device settings have full access at all times.
The procedure for adding a trusted mobile device is exactly the same as for other types of trusted devices. You can add a mobile device by ID or by device model.
To add a trusted mobile device by ID, you will need a unique ID (Hardware ID – HWID). You can find the ID in device properties by using operating system tools (see figure below). The Device Manager tool lets you do this. IDs of portable devices (MTP) and ADB, iTunes devices are different even for the same mobile device. The ID of a portable device (MTP) may look like this: 15131JECB07440. The ID of an ADB device may look like this: 6&370DEC2A&0&0001. Adding devices by ID is convenient if you want to add several specific devices. You can also use masks.
If you installed the ADB or iTunes applications after connecting a device to the computer, the unique ID of the device may be reset. This means that Kaspersky Endpoint Security will identify this device as a new device. If a device is trusted, add the device to the trusted list again.
To add a trusted mobile device by device model, you will need its Vendor ID (VID) and Product ID (PID). You can find the IDs in device properties by using operating system tools (see figure below). Template for entering the VID and PID: VID_18D1&PID_4EE5. Adding devices by model is convenient if you use devices of a certain model in your organization. This way, you can add all devices of this model.
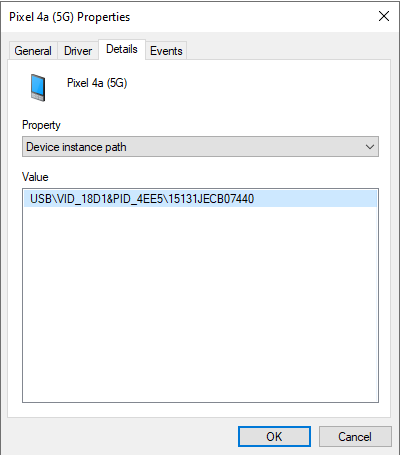
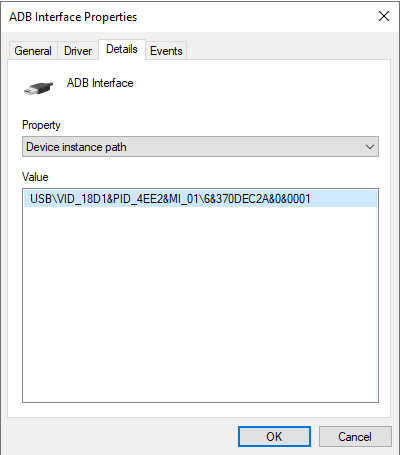
Device ID in Device Manager
Page top
Control of printing
You can use Control of printing to configure user access to local and network printers.
Local printer control
Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows configuring access to local printers on two levels: connecting and printing.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security controls local printer connection over the following buses: USB, Serial Port (COM), Parallel Port (LPT).
Kaspersky Endpoint Security controls the connection of local printers to COM and LPT ports only on the level of the bus. That is, to prevent the connection of printers to COM and LPT ports, you must prohibit the connection of all device types to COM and LPT buses. For printers connected to USB, the application exercises control on two levels: device type (local printers) and connection bus (USB). Therefore you can allow all device types except local printers to connect to USB.
You can select one of the following access modes to local printers via USB:
- Allow
 . Kaspersky Endpoint Security grants full access to local printers to all users. Users can connect printers and print documents using the means that the operating system provides.
. Kaspersky Endpoint Security grants full access to local printers to all users. Users can connect printers and print documents using the means that the operating system provides. - Block
 . Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the connection of local printers. The application allows connecting only trusted printers.
. Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the connection of local printers. The application allows connecting only trusted printers. - Depends on connection bus
 . Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows connecting to local printers in accordance with the USB bus connection status (Allow
. Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows connecting to local printers in accordance with the USB bus connection status (Allow  or Block
or Block  ).
). - By rules
 . To control printing, you must add printing rules. In the rules, you can select users or a group of users for which you want to allow or block access to printing documents on local printers.
. To control printing, you must add printing rules. In the rules, you can select users or a group of users for which you want to allow or block access to printing documents on local printers.
Network printer control
Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows configuring access to printing on network printers. You can select one of the following access modes to network printers:
- Allow and do not log. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not control printing on network printers. The application allows access to printing on network printers to all users and does not save printing information in the event log.
- Allow
 . Kaspersky Endpoint Security grants access to printing on network printers to all users.
. Kaspersky Endpoint Security grants access to printing on network printers to all users. - Block
 . Kaspersky Endpoint Security restricts access to network printers for all users. The application allows access only to trusted printers.
. Kaspersky Endpoint Security restricts access to network printers for all users. The application allows access only to trusted printers. - By rules
 . Kaspersky Endpoint Security grants access to printing in accordance with printing rules. In the rules, you can select users or a group of users that will be allowed or prevented from printing documents on network printer.
. Kaspersky Endpoint Security grants access to printing in accordance with printing rules. In the rules, you can select users or a group of users that will be allowed or prevented from printing documents on network printer.
Adding printing rules for printers
How to add printing rules in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to add printing rules in Web Console and Cloud Console
How to add printing rules in the application interface
Trusted printers
Trusted devices are devices to which users that are specified in the trusted device settings have full access at all times.
The procedure for adding trusted printers is exactly the same as for other types of trusted devices. You can add local printers by ID or device model. You can only add network printers by device ID.
To add a trusted local printer by ID, you will need a unique ID (Hardware ID – HWID). You can find the ID in device properties by using operating system tools (see figure below). The Device Manager tool lets you do this. The ID of a local printer may look like this: 6&2D09F5AF&1&C000. Adding devices by ID is convenient if you want to add several specific devices. You can also use masks.
To add a trusted local printer by device model, you will need its Vendor ID (VID) and Product ID (PID). You can find the IDs in device properties by using operating system tools (see figure below). Template for entering the VID and PID: VID_04A9&PID_27FD. Adding devices by model is convenient if you use devices of a certain model in your organization. This way, you can add all devices of this model.
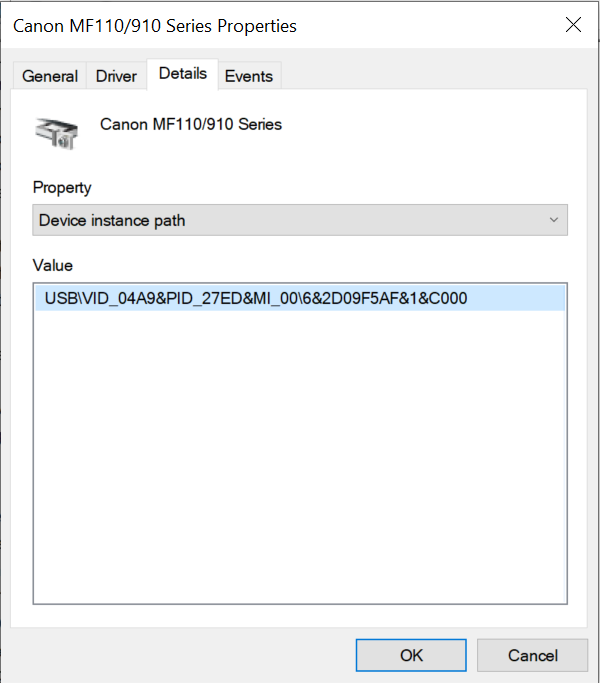
Device ID in Device Manager
To add a trusted network printer, you will need its device ID. For network printers, the device ID can be the network name of the printer (name of the shared printer), the IP address of the printer, or the URL of the printer.
Page top
Control of Wi-Fi connections
Device Control allows managing the Wi-Fi connection of the computer (laptop). Public Wi-Fi networks may be insecure, and using such networks can result in data loss. Device Control lets you block a user from connecting to Wi-Fi or allow connecting only to trusted networks. For example, you can allow connecting only to the corporate Wi-Fi network that is sufficiently secure. Device Control will block access to all Wi-Fi networks except those specified in the trusted list.
How to restrict Wi-Fi connections in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to restrict Wi-Fi connections in Web Console and Cloud Console
How to restrict Wi-Fi connections in the application interface
As a result, when a user tries connecting to a Wi-Fi network that is not listed as trusted, the application blocks the connection and displays a notification (see figure below).
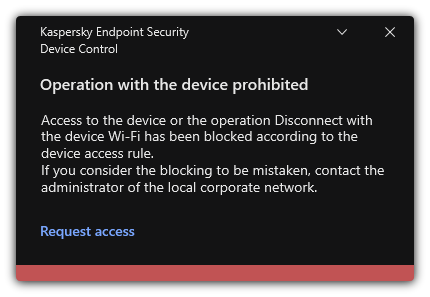
Device Control notification
Page top
Monitoring usage of removable drives
Monitoring usage of removable drives includes:
- Monitoring operations on files on removable drives.
- Monitoring connection and disconnection of trusted removable drives.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows monitoring connection and disconnection of all trusted devices and not only removable drives. You can turn on event logging in notification settings for the Device Control component. Events have the Informational severity level.
To enable monitoring of removable drive usage:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Device Control.
- In the Access settings block, click the Devices and Wi-Fi networks button.
The opened window shows access rules for all devices that are included in the Device Control component classification.

Types of devices in the Device Control component
- In the Access To Storage Devices block, select Removable drives.
- In the window that opens, select the Logging tab.
The settings of removable drive usage monitoring
- Turn on the Logging toggle.
- In the File operations block, select the operations that you want to monitor: Write, Delete.
- In the Filter by file formats block, select the formats of files whose associated operations should be logged by Device Control.
- Select the users or group of users whose use of removable drives you want to monitor.
- Save your changes.
As a result, when users write to files located on removable drives or delete files from removable drives, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will save information about such operations to the event log and send events to Kaspersky Security Center. You can view events associated with files on removable drives in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console in the workspace of the Administration Server node on the Events tab. For events to be displayed in the local Kaspersky Endpoint Security event log, you must select the File operation performed check box in the notifications settings for the Device Control component.
Page top
Changing the caching duration
The Device Control component registers events related to monitored devices, such as connection and disconnection of a device, reading a file from a device, writing a file to a device, and other events. Device Control then either allows or blocks the action according to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings.
Device Control saves information about events for a specific period of time called the caching period. If information about an event is cached and this event is repeated, there is no need to notify Kaspersky Endpoint Security about it or to show another prompt for granting access to the corresponding action, such as connecting a device. This makes it more convenient to work with a device.
An event is considered a duplicate event if all of the following event settings match the record in the cache:
- device ID
- SID of the user account attempting access
- Device category
- Action taken with the device
- Application permission for this action: allowed or denied
- Path to the process used to take the action
- File that is being accessed
Prior to changing the caching period, disable Kaspersky Endpoint Security Self-Defense. After changing the caching period, enable Self-Defense.
To change the caching period:
- Open the registry editor on the computer.
- In the registry editor, go to the following section:
- For 64-bit operating systems:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\KasperskyLab\protected\KES\environment] - For 32-bit operating systems:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\protected\KES\environment]
- For 64-bit operating systems:
- Open
DeviceControlEventsCachePeriodfor editing. - Define the number of minutes that Device Control must save information about an event before this information is deleted.
Actions with trusted devices
Trusted devices are devices to which users that are specified in the trusted device settings have full access at all times.
To work with trusted devices, you can grant access to an individual user, to a group of users, or to all users of the organization.
For example, if your organization does not allow the use of removable drives but administrators use removable drives in their work, you can allow removable drives only for a group of administrators. To do so, add removable drives to the trusted list and configure user access permissions.
It is not recommended to add more than 1000 trusted devices, as this can cause system instability.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows you to add a device to the trusted list in the following ways:
- If Kaspersky Security Center is not deployed in your organization, you can connect the device to the computer and add it to the trusted list in the application settings. To distribute the list of trusted devices to all computers in your organization, you can enable merging the lists of trusted devices in a policy or use the export / import procedure.
- If Kaspersky Security Center is deployed in your organization, you can detect all connected devices remotely and create a list of trusted devices in the policy. The list of trusted devices will be available on all computers to which the policy is applied.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows controlling the use of trusted devices (connection and disconnection). You can turn on event logging in notification settings for the Device Control component. Events have the Informational severity level.
Adding a device to the Trusted list from the application interface
By default, when a device is added to the list of trusted devices, access to the device is granted to all users (the Everyone group of users).
To add a device to the Trusted list from the application interface:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Device Control.
- In the Access settings block, click the Trusted devices button.
This opens the list of trusted devices.
- Click Select.
This opens the list of connected devices. The list of devices depends on the value that is selected in the Display connected devices drop-down list.
- In the list of devices, select the device that you want to add to the trusted list.
- In the Comment field, you can provide any relevant information about the trusted device.
- Select the users or group of users for whom you want to allow access to trusted devices.
- Save your changes.
Adding a device to the Trusted list from Kaspersky Security Center
Kaspersky Security Center receives information about devices if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on the computers and Device Control is enabled. It is not possible to add a device to the trusted list unless information about that device is available in Kaspersky Security Center.
You can add a device to the trusted list according to the following data:
- Devices by ID. Each device has a unique identifier (Hardware ID, or HWID). You can view the ID in the device properties by using operating system tools. Example device ID:
SCSI\CDROM&VEN_NECVMWAR&PROD_VMWARE_SATA_CD00\5&354AE4D7&0&000000. Adding devices by ID is convenient if you want to add several specific devices. - Devices by model. Each device has a vendor ID (VID) and a product ID (PID). You can view the IDs in the device properties by using operating system tools. Template for entering the VID and PID:
VID_1234&PID_5678. Adding devices by model is convenient if you use devices of a certain model in your organization. This way, you can add all devices of this model. - Devices by ID mask. If you are using multiple devices with similar IDs, you can add devices to the trusted list by using masks. The
*character replaces any set of characters. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support the?character when entering a mask. For example,WDC_C*. - Devices by model mask. If you are using multiple devices with similar VIDs or PIDs (for example, devices from the same manufacturer), you can add devices to the trusted list by using masks. The
*character replaces any set of characters. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support the?character when entering a mask. For example,VID_05AC & PID_ *.
To add devices to the list of trusted devices:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Security Controls → Device Control.
- In the right part of the window, select the Trusted devices tab.
- Select the Merge values when inheriting check box if you want to create a consolidated list of trusted devices for all computers in the company.
The lists of trusted devices in the parent and child policies will be merged. The lists will be merged provided that merging values when inheriting is enabled. Trusted devices from the parent policy are displayed in child policies in a read-only view. Changing or deleting trusted devices of the parent policy is not possible.
- Click the Add button and select a method for adding a device to the trusted list.
- To filter devices, select a device type from the Device type drop-down list (for example, Removable drives).
- In the Name / Model field, enter the device ID, model (VID and PID) or mask, depending on the selected addition method.
Adding devices by model mask (VID and PID) works as follows: if you enter a model mask that does not match any model, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks if the device ID (HWID) matches the mask. Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks only the part of the device ID that determines the manufacturer and the type of the device (
SCSI\CDROM&VEN_NECVMWAR&PROD_VMWARE_SATA_CD00\5&354AE4D7&0&000000). If the model mask matches this part of the device ID, the devices that match the mask will be added to the list of trusted devices on the computer. At the same time, the list of devices in Kaspersky Security Center remains empty when you click the Refresh button. To display the list of devices correctly, you can add devices by device ID mask. - To filter devices, in the Computer name field, enter the computer name or a mask for the name of the computer to which the device is connected.
The
*character replaces any set of characters. The?character replaces any single character. - Click the Refresh button.
The table displays a list of devices that satisfy the defined filtering criteria.
- Select the check boxes next to the names of devices that you want to add to the trusted list.
- In the Comment field, enter a description of the reason for adding devices to the trusted list.
- Click the Select button to the right of the Allow to users and / or groups of users field.
- Select a user or a group in Active Directory and confirm your selection.
By default, access to trusted devices is allowed for the Everyone group.
- Save your changes.
When a device is connected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks the list of trusted devices for an authorized user. If the device is trusted, Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows access to the device with all permissions, even if access to the device type or connection bus is denied. If the device is untrusted and access is denied, you can request access to the locked device.
Page top
Exporting and importing the list of trusted devices
To distribute the list of trusted devices to all computers in your organization, you can use the export/import procedure.
For example, if you need to distribute a list of trusted removable drives, you need to do the following:
- Sequentially connect removable drives to your computer.
- In the Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings, add the removable drives to the trusted list. If required, configure user access permissions. For example, allow only administrators to access removable drives.
- Export the list of trusted devices in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings (see the instructions below).
- Distribute the trusted device list file to other computers in your organization. For example, place the file in a shared folder.
- Import the list of trusted devices in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings on other computers in the organization (see the instructions below).
To import or export the list of trusted devices:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Device Control.
- In the Access settings block, click the Trusted devices button.
This opens the list of trusted devices.
- To export the list of trusted devices:
- Select the trusted devices that you want to export.
- Click Export.
- In the window that opens, specify the name of the XML file to which you want to export the list of trusted devices, and select the folder in which you want to save this file.
- Save the file.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security exports the entire list of trusted devices to the XML file.
- To import the list of trusted devices:
- In the Import drop-down list, select the relevant action: Import and add to existing or Import and replace existing.
- In the window that opens, select the XML file from which you want to import the list of trusted devices.
- Open the file.
If the computer already has a list of trusted devices, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will prompt you to delete the existing list or add new entries to it from the XML file.
- Save your changes.
When a device is connected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks the list of trusted devices for an authorized user. If the device is trusted, Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows access to the device with all permissions, even if access to the device type or connection bus is denied.
Page top
Obtaining access to a blocked device
When configuring Device Control, you can accidentally block access to a device that is necessary for work.
If Kaspersky Security Center is not deployed in your organization, you can provide access to a device in the settings of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. For example, you can add the device to the trusted list or temporarily disable Device Control.
If Kaspersky Security Center is deployed in your organization and a policy has been applied to computers, you can provide access to a device in the Administration Console.
Online mode for granting access
You can grant access to a blocked device in online mode only if Kaspersky Security Center is deployed in the organization and a policy has been applied to the computer. The computer must have the capability to establish a connection with the Administration Server.
Granting access in online mode consists of the following steps:
- The user sends the administrator a message containing an access request.
- The administrator receives a message with the request in the Kaspersky Security Center console.
The Kaspersky Security Center console has a preset event selection User requests for easy tracking of messages from users.
- The administrator adds the device to the trusted list.
You can add a trusted device in a policy for the administration group or in the local application settings for an individual computer.
- The administrator updates the settings of Kaspersky Endpoint Security on the user's computer.
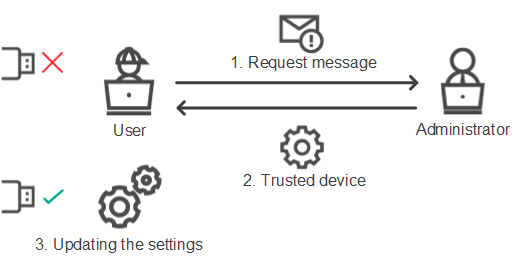
Schematic for granting access to a device in online mode
Offline mode for granting access
You can grant access to a blocked device in offline mode only if Kaspersky Security Center is deployed in the organization and a policy has been applied to the computer. In the policy settings, in the Device Control section, the Allow request for temporary access check box must be selected.
If you need to grant temporary access to a blocked device but you cannot add the device to the trusted list, you can grant access to the device in offline mode. This way, you can grant access to a blocked device even if the computer does not have network access or if the computer is outside of the corporate network.
Granting access in offline mode consists of the following steps:
- The user creates a request access file and sends it to the administrator.
- The administrator creates an access key from the request access file and sends it to the user.
- The user activates the access key.
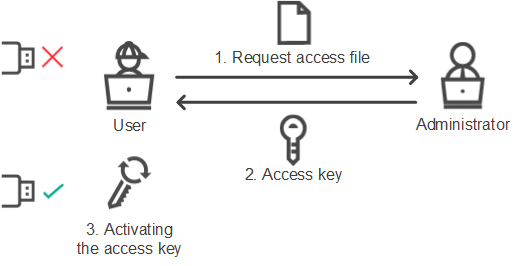
Schematic for granting access to a device in offline mode
Online mode for granting access
You can grant access to a blocked device in online mode only if Kaspersky Security Center is deployed in the organization and a policy has been applied to the computer. The computer must have the capability to establish a connection with the Administration Server.
A user requests access to a blocked device as follows:
- Connect the device to the computer.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security will show a notification stating that access to the device is blocked (see the figure below).
- Click the Request access link.
This opens a window with a message for the administrator. This message contains information about the blocked device.
- Click Send.

Device Control notification
After this, the administrator will receive an event Device access blockage message to administrator in the Kaspersky Security Center console. The event contains user name, computer name, information about the device the user is trying to access, and other data. You can configure the method of notifying the administrator about such events and, for example, choose an email notification. The Kaspersky Security Center console has a preset event selection User requests for easy tracking of messages from users.
In order to grant access you need to add a device to the trusted list. After updating Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings on the computer, the user will receive access to the device.
Page top
Offline mode for granting access
You can grant access to a blocked device in offline mode only if Kaspersky Security Center is deployed in the organization and a policy has been applied to the computer. In the policy settings, in the Device Control section, the Allow request for temporary access check box must be selected.
A user requests access to a blocked device as follows:
- Connect the device to the computer.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security will show a notification stating that access to the device is blocked (see the figure below).
- Click the Request temporary access link.
This opens a window containing a list of connected devices.
- In the list of connected devices, select the device to which you want to gain access.
- Click Generate request access file.
- In the Access duration field, specify the period of time for which you want to have access to the device.
- Save the file to computer memory.
As a result, a request access file with the *.akey extension will be downloaded to computer memory. Use any available method to send the device request access file to the corporate LAN administrator.

Device Control notification
As a result, the blocked device access key will be downloaded to computer memory. An access key file has the *.acode extension. Use any available method to send the blocked device access key to the user.
The user activates the access key as follows:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Device Control.
- In the Access request block, click the Request access to device button.
- In the window that opens, click the Activate access key button.
- In the window that opens, select the file with the device access key received from the corporate LAN administrator.
This opens a window containing information about access provision.
- Click OK.
As a result, the user receives access to the device for the time period set by the administrator. The user receives the full set of rights for accessing the device (read and write). When the key expires, access to the device will be blocked. If the user requires permanent access to the device, add the device to the trusted list.
Page top
Editing templates of Device Control messages
When the user attempts to access a blocked device, Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays a message stating that access to the device is blocked or that an operation with the device contents is forbidden. If the user believes that access to the device was mistakenly blocked or that an operation with device contents was forbidden by mistake, the user can send a message to the local corporate network administrator by clicking the link in the displayed message about the blocked action.
Templates are available for messages about blocked access to devices or forbidden operations with device contents, and for the message sent to the administrator. You can modify the message templates.
To edit the templates for Device Control messages:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Device Control.
- In the Message templates block, configure templates for Device Control messages:
- Message about blocking. Template of the message that appears when a user attempts to access a blocked device. This message also appears when a user attempts to perform an operation on the device contents that was blocked for this user.
- Message to administrator. A template of the message that is sent to the LAN administrator when the user believes that access to the device is blocked or an operation with device content is forbidden by mistake. After the user requests to provide access, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends an event to Kaspersky Security Center: Device access blockage message to administrator. The event description contains a message to administrator with substituted variables. You can view these events in the Kaspersky Security Center console using the predefined event selection User requests. If your organization does not have Kaspersky Security Center deployed or there is no connection to the Administration Server, the application will send a message to administrator to the specified email address.
- Save your changes.
Anti-Bridging
Anti-Bridging inhibits the creation of network bridges by preventing the simultaneous establishment of multiple network connections for a computer. This lets you protect a corporate network from attacks over unprotected, unauthorized networks.
Anti-Bridging regulates the establishment of network connections by using connection rules.
Connection rules are created for the following predefined types of devices:
- Network adapters;
- Wi-Fi adapters;
- Modems.
If a connection rule is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security:
- Blocks the active connection when establishing a new connection, if the device type specified in the rule is used for both connections;
- Blocks connections that are established using the types of devices for which lower-priority rules are used.
Enabling Anti-Bridging
Anti-Bridging is disabled by default.
To enable Anti-Bridging:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Device Control.
- In the Access settings block, click the Anti-Bridging button.
- Use the Enable Anti-Bridging toggle to enable or disable this feature.
- Save your changes.
After Anti-Bridging is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks already established connections according to the connection rules.
Page top
Changing the status of a connection rule
To change the status of a connection rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Device Control.
- In the Access settings block, click the Anti-Bridging button.
- In the Rules for devices block, select the rule whose status you want to change.
- Use the toggles in the Control column to enable or disable the rule.
- Save your changes.
Change the priority of a connection rule
To change the priority of a connection rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Device Control.
- In the Access settings block, click the Anti-Bridging button.
- In the Rules for devices block, select the rule whose priority you want to change.
- Use the Up / Down buttons to set the priority of the connection rule.
The higher a rule is positioned in the table of rules, the higher its priority. Anti-Bridging blocks all connections except one connection established using the type of device for which the highest-priority rule is used.
- Save your changes.
Adaptive Anomaly Control
This component is available if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for workstations. This component is unavailable if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for servers.
The Adaptive Anomaly Control component monitors and blocks actions that are not typical of the computers in a company's network. Adaptive Anomaly Control uses a set of rules to track non-typical behavior (for example, the Start of Microsoft PowerShell from office application rule). Rules are created by Kaspersky specialists based on typical scenarios of malicious activity. You can configure how Adaptive Anomaly Control handles each rule and, for example, allow the execution of PowerShell scripts that automate certain workflow tasks. Kaspersky Endpoint Security updates the set of rules along with the application databases. Updates to the sets of rules must be confirmed manually.
Adaptive Anomaly Control settings
Configuring Adaptive anomaly control consists of the following steps:
- Training Adaptive Anomaly Control.
After you enable Adaptive Anomaly Control, its rules work in training mode. During the training, Adaptive Anomaly Control monitors rule triggering and sends triggering events to Kaspersky Security Center. Each rule has its own duration of the training mode. The duration of the training mode is set by Kaspersky experts. Normally, the training mode is active for two weeks.
If a rule is not triggered at all during the training, Adaptive Anomaly Control will consider the actions associated with this rule as non-typical. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block all actions associated with that rule.
If a rule was triggered during training, Kaspersky Endpoint Security logs events in the rule triggering report and the Triggering of rules in Smart Training state repository.
- Analyzing the rule triggering report.
The administrator analyzes the rule triggering report or the contents of the Triggering of rules in Smart Training state repository. Then the administrator can select the behavior of Adaptive Anomaly Control when the rule is triggered: either block or allow. The administrator can also continue to monitor how the rule works and extend the duration of the training mode. If the administrator does not take any action, the application will also continue to work in training mode. The training mode term is restarted.
Adaptive Anomaly Control is configured in real time. Adaptive Anomaly Control is configured via the following channels:
- Adaptive Anomaly Control automatically starts to block the actions associated with the rules that were never triggered in training mode.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds new rules or removes obsolete ones.
- The administrator configures the operation of the Adaptive Anomaly Control after reviewing the rule triggering report and the contents of the Triggering of rules in Smart Training state repository. It is recommended to check the rule triggering report and the contents of the Triggering of rules in Smart Training state repository.
When a malicious application attempts to perform an action, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block the action and display a notification (see figure below).
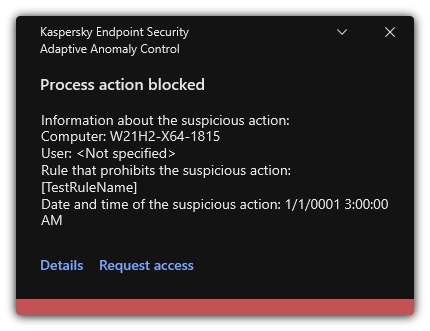
Adaptive Anomaly Control notification
Adaptive Anomaly Control operating algorithm
Kaspersky Endpoint Security decides whether to allow or block an action that is associated with a rule based on the following algorithm (see the figure below).
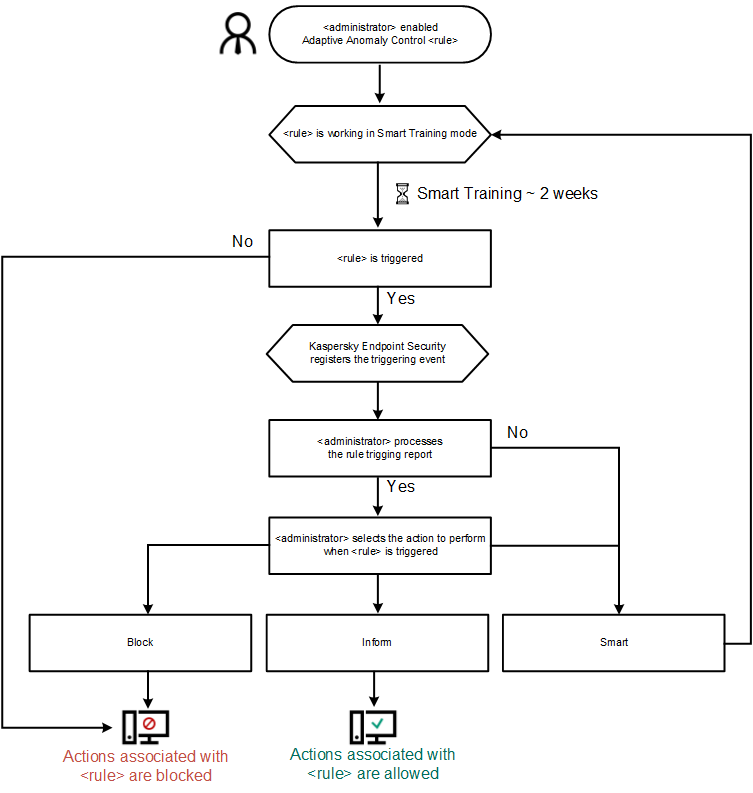
Adaptive Anomaly Control operating algorithm
Enabling and disabling Adaptive Anomaly Control
Adaptive Anomaly Control is enabled by default.
To enable or disable Adaptive Anomaly Control:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Adaptive Anomaly Control.
- Use the Adaptive Anomaly Control toggle to enable or disable the component.
- Save your changes.
As a result, the Adaptive Anomaly Control will switch to the training mode. During training, Adaptive Anomaly Control monitors rule triggering. When training is complete, Adaptive Anomaly Control starts to block actions that are not typical of the computers in a company's network.
If your organization has started to use some new tools, and Adaptive Anomaly Control blocks the actions of those tools, you can reset the results of the training mode and repeat the training. To do this, you need to change the action that is taken when the rule is triggered (for example, set it to Notify). Then you need to re-enable the training mode (set the Smart value).
Page top
Enabling and disabling an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule
To enable or disable an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Adaptive Anomaly Control.
- In the Rules block, click the Edit rules button.
The Adaptive Anomaly Control rule list opens.
- In the table, select a set of rules (for example, Activity of office applications) and expand the set.
- Select a rule (for example, Start of Microsoft PowerShell from office application).
- Use the toggle switch in the State column to enable or disable the Adaptive Anomaly Control rule.
- Save your changes.
Modifying the action taken when an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule is triggered
To edit the action that is taken when an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule is triggered:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Adaptive Anomaly Control.
- In the Rules block, click the Edit rules button.
The Adaptive Anomaly Control rule list opens.
- Select a rule in the table.
- Click Edit.
The Adaptive Anomaly Control rule properties window opens.
- In the Action block, select one of the following options:
- Smart. If this option is selected, the Adaptive Anomaly Control rule works in Smart training state for a period of time defined by Kaspersky experts. In this mode, when an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule is triggered, Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows the activity covered by the rule and logs an entry in the Triggering of rules in Smart Training state storage of the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server. When the time period set for working in Smart Training state ends, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the activity covered by an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule and logs an entry containing information about the activity.
- Block. If this action is selected, when an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule is triggered Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the activity covered by the rule and logs an entry containing information about the activity.
- Notify. If this action is selected, when an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule is triggered Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows the activity covered by the rule and logs an entry containing information about the activity.
- Save your changes.
Creating an exclusion for an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule
You cannot create more than 1,000 exclusions for Adaptive Anomaly Control rules. It is not recommended to create more than 200 exclusions. To reduce the number of exclusions used, it is recommended to use masks in the settings of exclusions.
An exclusion for an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule includes a description of the source and target objects. The source object is the object performing the actions. The target object is the object on which the actions are being performed. For example, you have opened a file named file.xlsx. As a result, a library file with the DLL extension is loaded into the computer memory. This library is used by a browser (executable file named browser.exe). In this example, file.xlsx is the source object, Excel is the source process, browser.exe is the target object, and Browser is the target process.
To create an exclusion for an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Adaptive Anomaly Control.
- In the Rules block, click the Edit rules button.
The Adaptive Anomaly Control rule list opens.
- Select a rule in the table.
- Click Edit.
The Adaptive Anomaly Control rule properties window opens.
- In the Exclusions block, click the Add button.
The exclusion properties window opens.
- Select the user for which you want to configure an exclusion.
Adaptive Anomaly Control does not support exclusions for user groups. If you select a user group, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not apply the exclusion.
- In the Description field, enter a description of the exclusion.
- Define the settings of the source object or source process started by the object:
- Source process. Path or mask of the path to the file or folder containing files (for example,
C:\Dir\File.exeorDir\*.exe). - Source process hash. File hash code.
- Source object. Path or mask of the path to the file or folder containing files (for example,
C:\Dir\File.exeorDir\*.exe). For example, file pathdocument.docm, which uses a script or macro to start the target processes.You can also specify other objects to exclude, such as a web address, macro, command in the command line, registry path, or others. Specify the object according to the following template:
object://<object>,where<object>refers to the name of the object, for example,object://web.site.example.com,object://VBA, object://ipconfig,object://HKEY_USERS. You can also use masks, for example,object://*C:\Windows\temp\*. - Source object hash. File hash code.
The Adaptive Anomaly Control rule is not applied to actions performed by the object, or to processes started by the object.
- Source process. Path or mask of the path to the file or folder containing files (for example,
- Specify the settings of the target object or target processes started on the object.
- Target process. Path or mask of the path to the file or folder containing files (for example,
C:\Dir\File.exeorDir\*.exe). - Target process hash. File hash code.
- Target object. The command to start the target process. Specify the command using the following pattern
object://<command>, for example,object://cmdline:powershell -Command "$result = 'C:\Windows\temp\result_local_users_pwdage txt'". You can also use masks, for example,object://*C:\Windows\temp\*. - Target object hash. File hash code.
The Adaptive Anomaly Control rule is not applied to actions taken on the object, or to processes started on the object.
- Target process. Path or mask of the path to the file or folder containing files (for example,
- Save your changes.
Exporting and importing exclusions for Adaptive Anomaly Control rules
To export or import the list of exclusions for selected rules:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Adaptive Anomaly Control.
- In the Rules block, click the Edit rules button.
The Adaptive Anomaly Control rule list opens.
- To export the list of rules:
- Select the rules whose exceptions you want to export.
- Click Export.
- In the window that opens, specify the name of the XML file to which you want to export the list of exclusions, and select the folder in which you want to save this file.
- Confirm that you want to export only the selected exclusions, or export the entire list of exclusions.
- Save the file.
- To import the list of rules:
- Click Import.
- In the window that opens, select the XML file from which you want to import the list of exclusions.
- Open the file.
If the computer already has a list of exclusions, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will prompt you to delete the existing list or add new entries to it from the XML file.
- Save your changes.
Applying updates for Adaptive Anomaly Control rules
New Adaptive Anomaly Control rules may be added to the table of rules and existing Adaptive Anomaly Control rules may be deleted from the table of rules when anti-virus databases are updated. Kaspersky Endpoint Security distinguishes Adaptive Anomaly Control rules that are to be deleted or added to the table, if an update for these rules has not been applied.
Until the update is applied, Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays the Adaptive Anomaly Control rules set to be deleted by the update in the table of rules and assigns the Disabled status to them. It is not possible to change the settings of these rules.
To apply updates for Adaptive Anomaly Control rules:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Adaptive Anomaly Control.
- In the Rules block, click the Edit rules button.
The Adaptive Anomaly Control rule list opens.
- In the window that opens, click the Approve updates button.
The Approve updates button is available if an update for Adaptive Anomaly Control rules is available.
- Save your changes.
Editing Adaptive Anomaly Control message templates
When a user tries to do an action, blocked by Adaptive Anomaly Control rules, Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays a message that potentially harmful actions are blocked. If the user believes that an action was mistakenly blocked, the user can use the link in the message text to send a message to the local corporate network administrator.
Special templates are available for the message about blocking potentially harmful actions and for the message to be sent to the administrator. You can modify the message templates.
To edit a message template:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Adaptive Anomaly Control.
- In the Templates block, configure the templates for Adaptive Anomaly Control messages:
- Message about blocking. Template of the message that is displayed to a user when an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule that blocks a non-typical action is triggered.
- Message to administrator. Template of the message that a user can be sent to the local corporate network administrator if the user considers the blocking to be a mistake. After the user requests to provide access, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends an event to Kaspersky Security Center: Application activity blockage message to administrator. The event description contains a message to administrator with substituted variables. You can view these events in the Kaspersky Security Center console using the predefined event selection User requests. If your organization does not have Kaspersky Security Center deployed or there is no connection to the Administration Server, the application will send a message to administrator to the specified email address.
- Save your changes.
Viewing Adaptive Anomaly Control reports
To view Adaptive Anomaly Control reports:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Security Controls → Adaptive Anomaly Control.
The settings of the Adaptive Anomaly Control component are displayed in the right part of the window.
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to view a report on the settings of Adaptive Anomaly Control rules, click Report on Adaptive Anomaly Control rules state.
- If you want to view a report on the triggering of Adaptive Anomaly Control rules, click Report on triggered Adaptive Anomaly Control rules.
- The report generation process starts.
The report is displayed in a new window.
Page top
Application Control
Application Control manages the startup of applications on users' computers. This allows you to implement a corporate security policy when using applications. Application Control also reduces the risk of computer infection by restricting access to applications.
Configuring Application Control consists of the following steps:
- Creating application categories.
The administrator creates categories of applications that the administrator wants to manage. Categories of applications are intended for all computers in the corporate network, regardless of administration groups. To create a category, you can use the following criteria: KL category (for example, Browsers), file hash, application vendor, and other criteria.
- Creating Application Control rules.
The administrator creates Application Control rules in the policy for the administration group. The rule includes the categories of applications and the startup status of applications from these categories: blocked or allowed.
- Selecting the Application Control mode.
The administrator chooses the mode for working with applications that are not included in any of the rules (application denylist and allowlist).
When a user attempts to start a prohibited application, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block the application from starting and will display a notification (see the figure below).
A test mode is provided to check the configuration of Application Control. In this mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does the following:
- Allows the startup of applications, including prohibited ones.
- Shows a notification about the startup of a prohibited application and adds information to the report on the user's computer.
- Sends data about the startup of prohibited applications to Kaspersky Security Center.
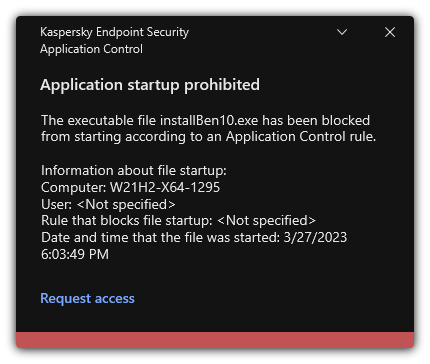
Application Control notification
Application Control operating modes
The Application Control component operates in two modes:
- Denylist. In this mode, Application Control allows users to start all applications except for applications that are prohibited in Application Control rules.
This mode of Application Control is enabled by default.
- Allowlist. In this mode, Application Control blocks users from starting any applications except for applications that are allowed and not prohibited in Application Control rules.
If the allow rules of Application Control are fully configured, the component blocks the startup of all new applications that have not been verified by the LAN administrator, while allowing the operation of the operating system and of trusted applications that users rely on in their work.
You can read the recommendations on configuring Application Control rules in allowlist mode.
Application Control can be configured to operate in these modes both by using the Kaspersky Endpoint Security local interface and by using Kaspersky Security Center.
However, Kaspersky Security Center offers tools that are not available in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security local interface, such as the tools that are needed for the following tasks:
- Creating application categories.
Application Control rules created in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console are based on your custom application categories and not on inclusion and exclusion conditions as is the case in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security local interface.
- Receiving information about applications that are installed on corporate LAN computers.
This is why it is recommended to use Kaspersky Security Center to configure the operation of the Application Control component.
Application Control operating algorithm
Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses an algorithm to make a decision about starting an application (see the figure below).
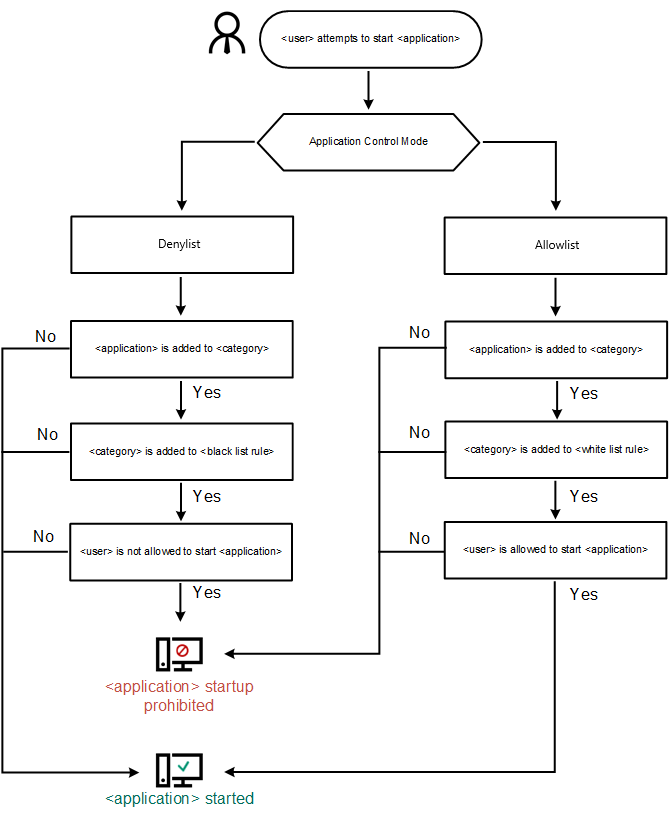
Application Control operating algorithm
Application Control functionality limitations
Operation of the Application Control component is limited in the following cases:
- When the application version is upgraded, importing Application Control component settings is not supported.
- If there is no connection with KSN servers, Kaspersky Endpoint Security receives information about the reputation of applications and their modules only from local databases.
The list of applications that Kaspersky Endpoint Security designates as KL category Other applications \ Applications, trusted according to reputation in KSN may differ depending on whether or not a connection to KSN servers is available.
- At the Kaspersky Security Center database, information on 150,000 processed files may be stored. Once this number of records has been achieved, new files will not be processed. To resume inventory operations, you must delete the files that were previously inventoried in the Kaspersky Security Center database from the computer on which Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed.
- The component does not control the startup of scripts unless the script is sent to the interpreter via the command line.
If the startup of an interpreter is allowed by Application Control rules, the component will not block a script started from this interpreter.
If at least one of the scripts specified in the interpreter command line is blocked from start by Application control rules, the component blocks all the scripts, specified in the interpreter command line.
- The component does not control the startup of scripts from interpreters that are not supported by Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the following interpreters:
- Java
- PowerShell
The following types of interpreters are supported:
- %ComSpec%;
- %SystemRoot%\\system32\\regedit.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\regedit.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\system32\\regedt32.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\system32\\cscript.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\system32\\wscript.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\system32\\msiexec.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\system32\\mshta.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\system32\\rundll32.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\system32\\wwahost.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\syswow64\\cmd.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\syswow64\\regedit.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\syswow64\\regedt32.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\syswow64\\cscript.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\syswow64\\wscript.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\syswow64\\msiexec.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\syswow64\\mshta.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\syswow64\\rundll32.exe;
- %SystemRoot%\\syswow64\\wwahost.exe.
Receiving information about the applications that are installed on users' computers
To create optimal Application Control rules, it is recommended to first get a picture of the applications that are used on computers on the corporate LAN. To do this, you can obtain the following information:
- Vendors, versions, and localizations of applications used on the corporate LAN.
- Frequency of application updates.
- Application usage policies adopted in the company (this may be security policies or administrative policies).
- Storage location of application distribution packages.
Information about applications that are used on corporate LAN computers is available in the Applications registry folder and in the Executable files folder. The Applications registry folder and the Executable files folder are located in the Application management folder in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console tree.
The Applications registry folder contains the list of applications that were detected by
which is installed on the client computer.The Executable files folder contains a list of all executable files that have ever been started on client computers or that were detected during the inventory task of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
To view general information about the application and its executable files, and the list of computers on which an application is installed, open the properties window of an application that is selected in the Applications registry folder or in the Executable files folder.
To open the application properties window in the Applications registry folder:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the Administration Console tree, select Additional → Application management → Applications registry.
- Select an application.
- In the context menu of the application, select Properties.
To open the properties window for an executable file in the Executable files folder:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the Administration Console tree, select the Additional → Application management → Executable files folder.
- Select an executable file.
- In the context menu of the executable file, select Properties.
Enabling and disabling Application Control
By default, Application Control is disabled.
To enable or disable Application Control:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Application Control.
- Use the Application Control toggle to enable or disable the component.
- Save your changes.
As a result, if Application Control is enabled, the application forwards information about running executable files to Kaspersky Security Center. You can view the list of running executable files in Kaspersky Security Center in the Executable files folder. To receive information about all executable files instead of only running executable files, run the Inventory task.
Page top
Selecting the Application Control mode
To select the Application Control mode:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Application Control.
- In the Application Startup Control mode block, select one of the following options:
- Blocked applications. If this option is selected, Application Control allows all users to start any applications, except in cases that satisfy the conditions of Application Control block rules.
- Allowed applications. If this option is selected, Application Control blocks all users from starting any applications, except in cases that satisfy the conditions of Application Control allow rules.
The Golden Image rule and Trusted Updaters rule are initially defined for Allowlist mode. These Application Control rules correspond to KL categories. The "Golden Image" KL category includes programs that ensure normal operation of the operating system. The "Trusted Updaters" KL category includes updaters for the most reputable software vendors. You cannot delete these rules. The settings of these rules cannot be edited. By default, the Golden Image rule is enabled and the Trusted Updaters rule is disabled. All users are allowed to start applications that match the trigger conditions of these rules.
All rules created during the selected mode are saved after the mode is changed so that the rules can be used again. To revert back to using these rules, all you have to do is select the necessary mode.
- In the Action at startup of blocked applications block, select the action to be performed by the component when a user attempts to start an application that is blocked by Application Control rules.
- Select the Control DLL modules load check box if you want Kaspersky Endpoint Security to monitor the loading of DLL modules when applications are started by users.
Information about the module and the application that loaded the module will be saved to a report.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security monitors only the DLL modules and drivers that have been loaded since the check box was selected. Restart the computer after selecting the check box if you want Kaspersky Endpoint Security to monitor all DLL modules and drivers, including ones that are loaded before Kaspersky Endpoint Security is started.
When enabling control over the loading of DLL modules and drivers, make sure that one of the following rules is enabled in the Application Control settings: the default Golden Image rule or another rule that contains the "Trusted certificates" KL category and ensures that trusted DLL modules and drivers are loaded before Kaspersky Endpoint Security is started. Enabling control of the loading of DLL modules and drivers when the Golden Image rule is disabled may cause instability in the operating system.
We recommend turning on password protection for configuring application settings, so that it is possible to turn off the rules blocking critical DLL modules and drivers form start, without modifying Kaspersky Security Center policy settings.
- Save your changes.
Managing Application Control rules
Kaspersky Endpoint Security controls the startup of applications by users by means of rules. An Application Control rule specifies the triggering conditions and actions performed by the Application Control component when the rule is triggered (allowing or blocking application startup by users).
Rule-triggering conditions
A rule-triggering condition has the following correlation: "condition type - condition criterion - condition value". Based on the rule-triggering conditions, Kaspersky Endpoint Security applies (or does not apply) a rule to an application.
The following types of conditions are used in rules:
- Inclusion conditions. Kaspersky Endpoint Security applies the rule to the application if the application matches at least one of the inclusion conditions.
- Exclusion conditions. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not apply the rule to the application if the application matches at least one of the exclusion conditions and does not match any of the inclusion conditions.
Rule-triggering conditions are created using criteria. The following criteria are used to create rules in Kaspersky Endpoint Security:
- Path to the folder containing the executable file of the application or path to the executable file of the application.
- Metadata: application executable file name, application executable file version, application name, application version, application vendor.
- Hash of the executable file of the application.
- Certificate: issuer, subject, thumbprint.
- Inclusion of the application in a KL category.
- Location of the application executable file on a removable drive.
The criterion value must be specified for each criterion used in the condition. If the parameters of the application being started match the values of criteria specified in the inclusion condition, the rule is triggered. In this case, Application Control performs the action prescribed in the rule. If application parameters match the values of criteria specified in the exclusion condition, Application Control does not control startup of the application.
If you have selected a certificate as a rule-triggering condition, you need to ensure that this certificate is added to the trusted system storage on the computer, and check the trusted system storage usage settings in the application.
Decisions made by the Application Control component when a rule is triggered
When a rule is triggered, Application Control allows users (or user groups) to start applications or blocks startup according to the rule. You can select individual users or groups of users that are allowed or not allowed to start applications that trigger a rule.
If a rule does not specify those users allowed to start applications satisfying the rule, this rule is called a block rule.
If a rule that does not specify any users who are not allowed to start applications that match the rule, this rule is called an allow rule.
The priority of a block rule is higher than the priority of an allow rule. For example, if an Application Control allow rule has been assigned for a user group while an Application Control block rule has been assigned for one user in this user group, this user will be blocked from starting the application.
Operating status of a rule
Application Control rules can have one of the following operating statuses:
- Enabled. This status means that the rule is used when the Application Control component is running.
- Disabled. This status means that the rule is ignored when the Application Control component is running.
- Testing. This status signifies that Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows the startup of applications to which the rules apply but logs information about the startup of such applications in the report.
Adding a trigger condition for the Application Control rule
For more convenience when creating Application Control rules, you can create application categories.
It is recommended to create a "Work applications" category that covers the standard set of applications that are used at the company. If different user groups use different sets of applications in their work, a separate application category can be created for each user group.
To create an application category in the Administration Console:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the Administration Console tree, select the Additional → Application management → Application categories folder.
- Click the New category button in the workspace.
The user category creation wizard starts.
- Follow the instructions of the user category creation wizard.
Step 1. Selecting the category type
At this step, select one of the following types of application categories:
- Category with content added manually. If you selected this type of category, at the "Configuring the conditions for including applications in a category" step and the "Configuring the conditions for excluding applications from a category" step, you will be able to define the criteria whereby executable files will be included into the category.
- Category that includes executable files from selected devices. If you selected this type of category, at the "Settings" step you will be able to specify a computer whose executable files will be automatically included in the category.
- Category that includes executable files from a specific folder. If you selected this type of category, at the "Repository folder" step you will be able to specify a folder from which executable files will be automatically included in the category.
When creating a category with content added automatically, Kaspersky Security Center performs inventory on files with the following formats: EXE, COM, DLL, SYS, BAT, PS1, CMD, JS, VBS, REG, MSI, MSC, CPL, HTML, HTM, DRV, OCX, and SCR.
Step 2. Entering a user category name
At this step, specify a name for the application category.
Step 3. Configuring the conditions for including applications in a category
This step is available if you selected the Category with content added manually category type.
At this step, in the Add drop-down list, select the conditions for including applications into the category:
- From the list of executable files. Add applications from the list of executable files on the client device to the custom category.
- From file properties. Specify detailed data of executable files as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
- Metadata from files in folder. Select a folder on the client device that contains executable files. Kaspersky Security Center will indicate the metadata of these executable files as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
- Checksums of the files in the folder. Select a folder on the client device that contains executable files. Kaspersky Security Center will indicate the hashes of these executable files as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
- Certificates for the files from the folder. Select a folder on the client device that contains executable files signed with certificates. Kaspersky Security Center will indicate the certificates of these executable files as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
It is not recommended to use conditions whose properties do not have the Certificate thumbprint parameter specified.
- MSI installer files metadata. Select the MSI package. Kaspersky Security Center will indicate the metadata of executable files packed in this MSI package as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
- Checksums of the files from the MSI installer of the application. Select the MSI package. Kaspersky Security Center will indicate the hashes of executable files packed in this MSI package as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
- From KL category. Specify a KL category as a condition for adding applications to the custom category. A KL category is a list of applications that have shared theme attributes. The list is maintained by Kaspersky experts. For example, the KL category known as "Office applications" includes applications from the Microsoft Office suite, Adobe Acrobat, and others.
You can select all KL categories to generate an extended list of trusted applications.
- Specify path to application. Select a folder on the client device. Kaspersky Security Center will add executable files from this folder to the custom category.
- Select certificate from repository. Select certificates that were used to sign executable files as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
It is not recommended to use conditions whose properties do not have the Certificate thumbprint parameter specified.
- Drive type. Specify the type of storage device (all hard drives and removable drives, or only removable drives) as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
Step 4. Configuring the conditions for excluding applications from a category
This step is available if you selected the Category with content added manually category type.
Applications specified at this step are excluded from the category even if these applications were specified at the "Configuring the conditions for including applications in a category" step.
At this step, in the Add drop-down list, select conditions for excluding applications from the category:
- From the list of executable files. Add applications from the list of executable files on the client device to the custom category.
- From file properties. Specify detailed data of executable files as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
- Metadata from files in folder. Select a folder on the client device that contains executable files. Kaspersky Security Center will indicate the metadata of these executable files as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
- Checksums of the files in the folder. Select a folder on the client device that contains executable files. Kaspersky Security Center will indicate the hashes of these executable files as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
- Certificates for the files from the folder. Select a folder on the client device that contains executable files signed with certificates. Kaspersky Security Center will indicate the certificates of these executable files as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
- MSI installer files metadata. Select the MSI package. Kaspersky Security Center will indicate the metadata of executable files packed in this MSI package as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
- Checksums of the files from the MSI installer of the application. Select the MSI package. Kaspersky Security Center will indicate the hashes of executable files packed in this MSI package as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
- From KL category. Specify a KL category as a condition for adding applications to the custom category. A KL category is a list of applications that have shared theme attributes. The list is maintained by Kaspersky experts. For example, the KL category known as "Office applications" includes applications from the Microsoft Office suite, Adobe Acrobat, and others.
You can select all KL categories to generate an extended list of trusted applications.
- Specify path to application. Select a folder on the client device. Kaspersky Security Center will add executable files from this folder to the custom category.
- Select certificate from repository. Select certificates that were used to sign executable files as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
- Drive type. Specify the type of storage device (all hard drives and removable drives, or only removable drives) as a condition for adding applications to the custom category.
Step 5. Settings
This step is available if you selected the Category that includes executable files from selected devices category type.
At this step, click the Add button and specify the computers whose executable files will be added to the application category by Kaspersky Security Center. All executable files from the specified computers presented in the Executable files folder will be added to the application category by Kaspersky Security Center.
At this step, you can also configure the following settings:
- Algorithm for hash function calculation. To select an algorithm, you must select at least one of the following check boxes:
- Calculate SHA-256 for files in this category (supported by Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 2 for Windows and later versions).
- Calculate MD5 for files in this category (supported by versions earlier than Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 2 for Windows).
- Synchronize data with Administration Server repository check box. Select this check box if you want Kaspersky Security Center to periodically clear the application category and add to it all executable files from the specified computers presented in the Executable files folder.
If the Synchronize data with Administration Server repository check box is cleared, Kaspersky Security Center will not make any modifications to an application category after it is created.
- Scan period (h) field. In this field, you can specify the period of time (in hours) after which Kaspersky Security Center clears the application category and adds to it all executable files from the specified computers presented in the Executable files folder.
The field is available if the Synchronize data with Administration Server repository check box is selected.
Step 6. Repository folder
This step is available if you selected the Category that includes executable files from a specific folder category type.
At this step, specify the folder in which Kaspersky Security Center will search for executable files to automatically add applications to the application category.
At this step, you can also configure the following settings:
- Include dynamic-link libraries (DLL) in this category check box. Select this check box if you want dynamic-link libraries (DLL files) to be included in the application category.
Including DLL files in the application category may reduce the performance of Kaspersky Security Center.
- Include script data in this category check box. Select this check box if you want scripts to be included in the application category.
Including scripts in the application category may reduce the performance of Kaspersky Security Center.
- Algorithm for hash function calculation. To select an algorithm, you must select at least one of the following check boxes:
- Calculate SHA-256 for files in this category (supported by Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 2 for Windows and later versions).
- Calculate MD5 for files in this category (supported by versions earlier than Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 2 for Windows).
- Force folder scan for changes check box. Select this check box if you want Kaspersky Security Center to periodically search for executable files in the folder used for automatically adding to the application category.
If the Force folder scan for changes check box is cleared, Kaspersky Security Center searches for executable files in the folder used for automatically adding to the application category only if changes have been made in the folder, files have been added to it or deleted from it.
- Scan period (h) field. In this field, you can specify the time interval (in hours) after which Kaspersky Security Center will search for executable files in the folder used for automatically adding to the application category.
This field is available if the Force folder scan for changes check box is selected.
Step 7. Creating a custom category
Exit the Wizard.
To add a new trigger condition for an Application Control rule in the application interface:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Application Control.
- Click the Blocked applications or Allowed applications button.
This opens the list of Application Control rules.
- Select the rule for which you want to configure a trigger condition.
The Application Control rule properties open.
- Select the Conditions: N tab or Exclusions: N tab and click the Add button.
- Select the trigger conditions for the Application Control rule:
- Conditions from properties of started applications. In the list of running applications, you can select the applications to which the Application Control rule will be applied. Kaspersky Endpoint Security also lists applications that were previously running on the computer. You need to select the criterion that you want to use to create one or multiple rule trigger conditions: File hash, Certificate, KL category, Metadata or Path to file or folder.
- Conditions "KL category". A KL category is a list of applications that have shared theme attributes. The list is maintained by Kaspersky experts. For example, the KL category known as "Office applications" includes applications from the Microsoft Office suite, Adobe Acrobat, and others.
- Custom condition. You can select the application file and select one of the rule trigger conditions: File hash, Certificate, Metadata or Path to file or folder.
- Condition by file drive (removable drive). The Application Control rule is applied only to files that are run on a removable drive.
- Conditions from properties of files in the specified folder. The Application Control rule is applied only to files in the specified folder. You can also include or exclude files from subfolders. You need to select the criterion that you want to use to create one or multiple rule trigger conditions: File hash, Certificate, KL category, Metadata or Path to file or folder.
- Save your changes.
When adding conditions, please take into account the following special considerations for Application Control:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support an MD5 file hash and does not control startup of applications based on an MD5 hash. An SHA256 hash is used as a rule trigger condition.
- It is not recommended to use only the Issuer and Subject criteria as rule trigger conditions. Use of these criteria is unreliable.
- If you are using a symbolic link in the Path to file or folder field, you are advised to resolve the symbolic link for correct operation of the Application Control rule. To do so, click the Resolve symbolic link button.
Adding executable files from the Executable files folder to the application category
In the Executable files folder the list of executable files detected on computers is displayed. Kaspersky Endpoint Security generates a list of executable files after executing the Inventory task.
To add executable files from the Executable files folder to the application category:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the Administration Console tree, select Additional → Application management → Executable files folder.
- In the workspace, select the executable files that you want to add to the application category.
- Right-click to open the context menu for the selected executable files and select Add to category.
- In the window that opens, do the following:
- In the upper part of the window, choose one of the following options:
- Add to a new application category. Choose this option if you want to create a new application category and add executable files to it.
- Add to an existing application category. Choose this option if you want to select an existing application category and add executable files to it.
- In the Rule type block, select one of the following options:
- Rules for adding to inclusions. Select this option if you want to create a condition that adds executable files to the application category.
- Rules for adding to exclusions. Select this option if you want to create a condition that excludes executable files from the application category.
- In the Parameter used as a condition block, select one of the following options:
- Certificate details (or SHA-256 hashes for files without a certificate).
- Certificate details (files without a certificate will be skipped).
- Only SHA-256 (files without a hash will be skipped).
- Only MD5 (discontinued mode, only for Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 1 version).
- In the upper part of the window, choose one of the following options:
- Save your changes.
Adding event-related executable files to the application category
To add executable files related to Application Control events to the application category:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the Administration Server node of the Administration Console tree, select the Events tab.
- Choose a selection of events related to operation of the Application Control component (Viewing events resulting from operation of the Application Control component, Viewing events resulting from test operation of the Application Control component) in the Event selections drop-down list.
- Click the Run selection button.
- Select the events whose associated executable files you want to add to the application category.
- Right-click to open the context menu for the selected events and select Add to category.
- In the window that opens, configure the settings of the application category:
- In the upper part of the window, choose one of the following options:
- Add to a new application category. Choose this option if you want to create a new application category and add executable files to it.
- Add to an existing application category. Choose this option if you want to select an existing application category and add executable files to it.
- In the Rule type block, select one of the following options:
- Rules for adding to inclusions. Select this option if you want to create a condition that adds executable files to the application category.
- Rules for adding to exclusions. Select this option if you want to create a condition that excludes executable files from the application category.
- In the Parameter used as a condition block, select one of the following options:
- Certificate details (or SHA-256 hashes for files without a certificate).
- Certificate details (files without a certificate will be skipped).
- Only SHA-256 (files without a hash will be skipped).
- Only MD5 (discontinued mode, only for Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 1 version).
- In the upper part of the window, choose one of the following options:
- Save your changes.
Adding an Application Control rule
To add an Application Control rule using Kaspersky Security Center:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Security Controls → Application Control.
In the right part of the window, the settings of the Application Control component are displayed.
- Click Add.
The Application Control rule window opens.
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to create a new category:
- Click Create a category.
The user category creation wizard starts.
- Follow the instructions of the user category creation wizard.
- In the Category drop-down list, select the created application category.
- Click Create a category.
- If you want to edit an existing category:
- In the Category drop-down list, select the created application category that you want to edit.
- Click Properties.
- Modify the settings of the selected application category.
- Save your changes.
- In the Category drop-down list, select the created application category based on which you want to create a rule.
- If you want to create a new category:
- In the Subjects and their rights table, click the Add button.
- In the window that opens, specify the list of users and/or user groups for which you want to configure permission to start applications from the selected category.
- In the Subjects and their rights table, do the following:
- If you want to allow users and/or groups of users to start applications that belong to the selected category, select the Allow check box in the relevant rows.
- If you want to block users and/or groups of users from starting applications that belong to the selected category, select the Deny check box in the relevant rows.
- Select the Deny for other users check box if you want all users that do not appear in the Subject column and that are not part of the group of users specified in the Subject column to be blocked from starting applications that belong to the selected category.
- If you want Kaspersky Endpoint Security to consider applications included in the selected application category as trusted updaters allowed to create other executable files that will be subsequently allowed to run, select the Trusted Updaters check box.
When Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings are migrated, the list of executable files created by trusted updaters is migrated as well.
- Save your changes.
To add an Application Control rule:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Application Control.
- Click the Blocked applications or Allowed applications button.
This opens the list of Application Control rules.
- Click Add.
This opens the Application Control rule settings window.
- On the General settings tab, define the main settings of the rule:
- In the Rule name field, enter the name of the rule.
- In the Description field, enter a description of the rule.
- Compile or edit a list of users and/or groups of users who are allowed or not allowed to start applications that meet the rule trigger conditions. To do this, click the Add button in the Subjects and their rights table.
The rule applies to all users by default.
If there is no user specified in the table, the rule cannot be saved.
- In the Subjects and their rights table, use the toggle to define the right of users to start applications.
- Select the Deny for other users check box if you want the application to prevent applications that satisfy rule triggering conditions from running for all users that are not listed in the Subjects and their rights table and are not members of user groups listed in the Subjects and their rights table.
If the Deny for other users check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not control the startup of applications by users that are not specified in the Subjects and their rights table and that do not belong to the groups of users specified in the Subjects and their rights table.
- Select the Trusted Updaters check box if you want Kaspersky Endpoint Security to consider applications matching the rule trigger conditions as trusted updaters. Trusted Updaters are applications that are allowed to create other executable files that will be allowed to run subsequently.
If an application triggers multiple rules, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sets the Trusted Updaters flag if the following conditions are satisfied:
- All rules allow the application to run.
- At least one rule has the Trusted Updaters check box selected.
- On the Conditions: N tab, create or edit the list of inclusion conditions for triggering the rule.
- On the Exclusions: N tab, create or edit the list of exclusion conditions for triggering the rule.
When Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings are migrated, the list of executable files created by trusted updaters is migrated as well.
- Save your changes.
Changing the status of an Application Control rule via Kaspersky Security Center
To change the status of an Application Control rule in Administration Console:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Security Controls → Application Control.
In the right part of the window, the settings of the Application Control component are displayed.
- In the Status column, left-click to display the context menu and select one of the following:
- On. This status means that the rule is used when the Application Control component is running.
- Off. This status means that the rule is ignored when the Application Control component is running.
- Test. This status means that Kaspersky Endpoint Security always allows the startup of applications to which the rule applies but logs information about the startup of such applications in the report.
- Save your changes.
To change the status of an Application Control rule in the Administration Console:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Application Control.
- Click the Blocked applications or Allowed applications button.
This opens the list of Application Control rules.
- In the Status column, open the context menu and select one of the following:
- Enabled. This status means that the rule is used when the Application Control component is running.
- Disabled. This status means that the rule is ignored when the Application Control component is running.
- Testing. This status means that Kaspersky Endpoint Security always allows the startup of applications to which this rule applies but logs information about the startup of such applications in the report.
- Save your changes.
Exporting and importing Application Control rules
You can export the list of Application Control rules to an XML file. You can use the export/import function to back up the list of Application Control rules or to migrate the list to a different server.
When exporting and importing Application Control rules, please keep in mind the following special considerations:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security exports the list of rules only for the active Application Control mode. In other words, if Application Control is operating in denylist mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security exports rules only for this mode. To export the list of rules for allowlist mode, you need to switch the mode and run the export operation again.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses application categories for Application Control rules to work. When migrating the list of Application Control rules to a different server, you also need to migrate the list of application categories. For more details on exporting or importing application categories, please refer to Kaspersky Security Center Help.
How to export and import a list of Application Control rules in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to export and import a list of Application Control rules in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Viewing events resulting from operation of the Application Control component
To view events resulting from the operation of the Application Control component received by Kaspersky Security Center:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the Administration Server node of the Administration Console tree, select the Events tab.
- Click the Create a selection button.
- In the window that opens, go to the Events section.
- Click the Clear all button.
- In the Events table, select the Application startup prohibited check box.
- Save your changes.
- In the Event selections drop-down list, select the created selection.
- Click the Run selection button.
Viewing a report on blocked applications
To view the report on blocked applications:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the Administration Server node of the Administration Console tree, select the Reports tab.
- Click the New report template button.
The New Report Template Wizard starts.
- Follow the instructions of the Report Template Wizard. At the Selecting the report template type step, select Other → Report on prohibited applications.
After you have finished with the New Report Template Wizard, the new report template appears in the table on the Reports tab.
- Open the report by double-clicking it.
The report generation process starts. The report is displayed in a new window.
Page top
Testing Application Control rules
To ensure that Application Control rules do not block applications required for work, it is recommended to enable testing of Application Control rules and analyze their operation after creating new rules. When testing of Application Control rules is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not block applications whose startup is forbidden by Application Control, but will instead send notifications about their startup to the Administration Server.
An analysis of the operation of Application Control rules requires a review of the resultant Application Control events that are reported to Kaspersky Security Center. If test mode results in no blocked startup events for all applications required for the work of the computer user, this means that the correct rules were created. Otherwise, you are advised to update the settings of the rules you have created, create additional rules, or delete the existing rules.
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows the startup of all applications except for applications prohibited by the rules.
Page top
Enabling and disabling Application Control rule testing
To enable or disable testing of Application Control rules in Kaspersky Security Center:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Security Controls → Application Control.
In the right part of the window, the settings of the Application Control component are displayed.
- In the Control mode drop-down list, select one of the following items:
- Denylist. If this option is selected, Application Control allows all users to start any applications, except in cases that satisfy the conditions of Application Control block rules.
- Allowlist. If this option is selected, Application Control blocks all users from starting any applications, except in cases that satisfy the conditions of Application Control allow rules.
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to enable testing of Application Control rules, select the Test rules option in the Action drop-down list.
- If you want to enable Application Control to manage the startup of applications on user computers, in the drop-down list, select Apply rules.
- Save your changes.
To enable testing of Application Control rules or to select a blocking action for Application Control:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Application Control.
- Click the Blocked applications or Allowed applications button.
This opens the list of Application Control rules.
- In the Status column, select Testing.
This status means that Kaspersky Endpoint Security always allows the startup of applications to which this rule applies but logs information about the startup of such applications in the report.
- Save your changes.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not block applications whose startup is forbidden by the Application Control component, but will send notifications about their startup to the Administration Server. You can also configure the display of notifications about rule testing on the user's computer (see figure below).
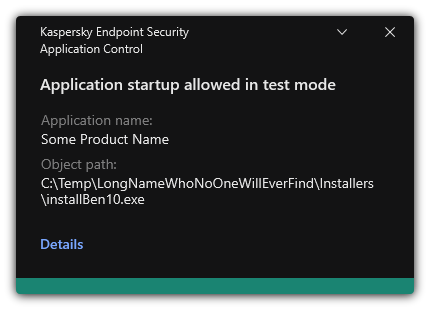
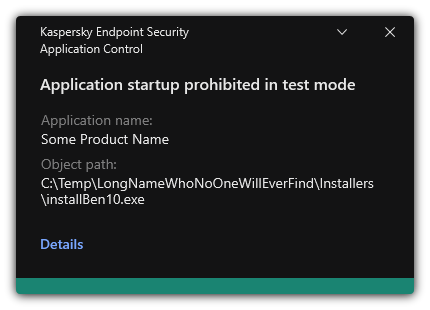
Application Control notifications in test mode
Page top
Viewing a report on blocked applications in test mode
To view the report on blocked applications in test mode:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the Administration Server node of the Administration Console tree, select the Reports tab.
- Click the New report template button.
The New Report Template Wizard starts.
- Follow the instructions of the Report Template Wizard. At the Selecting the report template type step, select Other → Report on prohibited applications in test mode.
After you have finished with the New Report Template Wizard, the new report template appears in the table on the Reports tab.
- Open the report by double-clicking it.
The report generation process starts. The report is displayed in a new window.
Page top
Viewing events resulting from test operation of the Application Control component
To view Application Control testing events received by Kaspersky Security Center:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the Administration Server node of the Administration Console tree, select the Events tab.
- Click the Create a selection button.
- In the window that opens, go to the Events section.
- Click the Clear all button.
- In the Events table, select the Application startup prohibited in test mode and Application startup allowed in test mode check boxes.
- Save your changes.
- In the Event selections drop-down list, select the created selection.
- Click the Run selection button.
Application activity monitor
This component is available if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for workstations. This component is unavailable if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for servers.
Application Activity Monitor is a tool designed for viewing information about the activity of applications on a user's computer in real time.
Using the Application Activity Monitor requires installing the Application Control and Host Intrusion Prevention components. If these components are not installed, the Application Activity Monitor section in the main application window is hidden.
To start Application Activity Monitor:
In the main application window, in the Monitoring section, click the Application Activity Monitor tile.
In this window, information about the activity of applications on the user's computer is presented on three tabs:
- The All applications tab displays information about all applications installed on the computer.
- The Running tab displays information about the computer resource consumption by each application in real time. From this tab, you can also proceed to configure permissions for an individual application.
- The Run at startup tab displays the list of applications that are started when the operating system starts.
If you want to hide application activity information on the user's computer, you can restrict user access to the Application Activity Monitor tool.
Page top
Rules for creating name masks for files or folders
A mask of a file or folder name is a representation of the name of a folder or name and extension of a file using common characters.
You can use the following common characters to create a file or folder name mask:
- The
*(asterisk) character, which takes the place of any set of characters (including an empty set). For example, theC:\*.txtmask will include all paths to files with thetxtextension located in folders and subfolders on the (C:) drive. - The
?(question mark) character, which takes the place of any single character, except the\and/characters (delimiters of the names of files and folders in paths to files and folders). For example, the maskC:\Folder\???.txtwill include paths to all files residing in the folder namedFolderthat have the TXT extension and a name consisting of three characters.
Editing Application Control message templates
When a user attempts to start an application that is blocked by an Application Control rule, Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays a message stating that the application is blocked from starting. If the user believes that an application was mistakenly blocked from starting, the user can use the link in the message text to send a message to the local corporate network administrator.
Special templates are available for the message that is displayed when an application is blocked from starting and for the message sent to the administrator. You can modify the message templates.
To edit a message template:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Application Control.
- In the Templates of messages about application blocking block, configure templates for Application Control messages:
- Message about blocking. Template of the message that is displayed when an Application Control rule that blocks an application from starting is triggered. The notification about a blocked application is shown in the figure below.
You cannot configure message templates for Application Control in test mode. Application Control in test mode displays preset notifications.
- Message to administrator. Template of the message that a user can send to the corporate LAN administrator if the user believes that an application was blocked by mistake. After the user requests to provide access, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends an event to Kaspersky Security Center: Application startup blockage message to administrator. The event description contains a message to administrator with substituted variables. You can view these events in the Kaspersky Security Center console using the predefined event selection User requests. If your organization does not have Kaspersky Security Center deployed or there is no connection to the Administration Server, the application will send a message to administrator to the specified email address.
- Message about blocking. Template of the message that is displayed when an Application Control rule that blocks an application from starting is triggered. The notification about a blocked application is shown in the figure below.
- Save your changes.

Application Control notification
Best practices for implementing a list of allowed applications
When planning implementation of a list of allowed applications, it is recommended to perform the following actions:
- Form the following types of groups:
- User groups. Groups of users for whom you need to allow use of various sets of applications.
- Administration groups. One or multiple groups of computers to which Kaspersky Security Center will apply the list of allowed applications. It is necessary to create multiple groups of computers if different allowlist settings are used for those groups.
- Create a list of applications that must be allowed to start.
Prior to creating a list, you are advised to do the following:
- Run the inventory task.
Information about the creation, reconfiguration, and startup of an inventory task is available in the Task management section.
- View the list of executable files.
- Run the inventory task.
Configuring allowlist mode for applications
When configuring the allowlist mode, it is recommended to perform the following actions:
- Create application categories containing the applications that must be allowed to start.
You can select one of the following methods for creating application categories:
- Category with content added manually. You can manually add to this category by using the following conditions:
- File metadata. Kaspersky Security Center adds all executable files accompanied by the specified metadata to the application category.
- File hash code. Kaspersky Security Center adds all executable files with the specified hash to the application category.
Use of this condition excludes the capability to automatically install updates because different versions of files will have a different hash.
- File certificate. Kaspersky Security Center adds all executable files signed with the specified certificate to the application category.
- KL category. Kaspersky Security Center adds all applications that are in the specified KL category to the application category.
- Application folder. Kaspersky Security Center adds all executable files from this folder to the application category.
Use of the Application folder condition may be unsafe because any application from the specified folder will be allowed to start. It is recommended to apply rules that use the application categories with the Application folder condition only to those users for whom the automatic installation of updates must be allowed.
- Category that includes executable files from a specific folder. You can specify a folder from which executable files will be automatically assigned to the created application category.
- Category that includes executable files from selected devices. You can specify a computer for which all executable files will be automatically assigned to the created application category.
When using this method of creating application categories, Kaspersky Security Center receives information about applications on the computer from the Executable files folder.
- Category with content added manually. You can manually add to this category by using the following conditions:
- Select the allowlist mode for the Application Control component.
- Create Application Control rules using the created application categories.
The Golden Image rule and Trusted Updaters rule are initially defined for Allowlist mode. These Application Control rules correspond to KL categories. The "Golden Image" KL category includes programs that ensure normal operation of the operating system. The "Trusted Updaters" KL category includes updaters for the most reputable software vendors. You cannot delete these rules. The settings of these rules cannot be edited. By default, the Golden Image rule is enabled and the Trusted Updaters rule is disabled. All users are allowed to start applications that match the trigger conditions of these rules.
- Determine the applications for which automatic installation of updates must be allowed.
You can allow automatic installation of updates in one of the following ways:
- Specify an extended list of allowed applications by allowing the startup of all applications that belong to any KL category.
- Specify an extended list of allowed applications by allowing the startup of all applications that are signed with certificates.
To allow the startup of all applications signed with certificates, you can create a category with a certificate-based condition that uses only the Subject parameter with the value *.
- For the Application control rule, select the Trusted Updaters parameter. If this check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security considers the applications included in the rule as Trusted Updaters. Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows the startup of applications that have been installed or updated by applications included in the rule, provided that no blocking rules are applied to those applications.
When Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings are migrated, the list of executable files created by trusted updaters is migrated as well.
- Create a folder and place within it the executable files of applications for which you want to allow automatic installation of updates. Then create an application category with the "Application folder" condition and specify the path to that folder. Then create an allow rule and select this category.
Use of the Application folder condition may be unsafe because any application from the specified folder will be allowed to start. It is recommended to apply rules that use the application categories with the Application folder condition only to those users for whom the automatic installation of updates must be allowed.
Testing the allowlist mode
To ensure that Application Control rules do not block applications required for work, it is recommended to enable testing of Application Control rules and analyze their operation after creating new rules. When testing is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not block applications whose startup is forbidden by Application Control rules, but will instead send notifications about their startup to the Administration Server.
When testing the allowlist mode, it is recommended to perform the following actions:
- Determine the testing period (ranging from several days to two months).
- Enable testing of Application Control rules.
- Examine the events resulting from testing the operation of Application Control and reports on blocked applications in test mode to analyze the testing results.
- Based on the analysis results, make changes to the allowlist mode settings.
In particular, based on the test results, you can add executable files related to events to an application category.
Support for allowlist mode
After selecting a blocking action for Application Control, it is recommended to continue supporting allowlist mode by performing the following actions:
- Examine the events resulting from the operation of Application Control and reports on blocked runs to analyze the effectiveness of Application Control.
- Analyze users' requests to access applications.
- Analyze unfamiliar executable files by checking their reputation in Kaspersky Security Network.
- Prior to installing updates for the operating system or for software, install those updates on a test group of computers to check how they will be processed by Application Control rules.
- Add the necessary applications to categories used in Application Control rules.
Network ports monitoring
During the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, the Web Control, Mail Threat Protection and Web Threat Protection components monitor data streams that are transmitted via specific protocols and that pass through specific open TCP and UDP ports on user computer. For example, the Mail Threat Protection component analyzes information transmitted via SMTP, while the Web Threat Protection component analyzes information transmitted via HTTP and FTP.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security divides TCP and UDP ports of the user's computer into several groups, depending on the likelihood of their being compromised. Some network ports are reserved for vulnerable services. You are advised to monitor these ports more thoroughly because they have a greater likelihood of being targeted by a network attack. If you use non-standard services that rely on non-standard network ports, these network ports may also be targeted by an attacking computer. You can specify a list of network ports and a list of applications that request network access. These ports and applications then receive special attention from the Mail Threat Protection and Web Threat Protection components during network traffic monitoring.
Enabling monitoring of all network ports
To enable monitoring of all network ports:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Network settings.

Network ports monitoring settings
- In the Monitored ports block, select Monitor all network ports.
- Save your changes.
Creating a list of monitored network ports
To create a list of monitored network ports:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Network settings.
- In the Monitored ports block, select Monitor selected network ports only.
- Click Select.
This opens a list of network ports that are normally used for transmission of email and network traffic. This list of network ports is included in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security package.
- Use the toggle in the Status column to enable or disable network port monitoring.
- If a network port is not shown in the list of network ports, add it by doing the following:
- Click Add.
- In the window that opens, enter the network port number and brief description.
- Set the Active or Inactive status for the network port monitoring.
- Save your changes.
When the FTP protocol runs in passive mode, the connection can be established via a random network port that is not added to the list of monitored network ports. To protect such connections, enable monitoring of all network ports or configure control of network ports for applications that establish FTP connections.
Page top
Creating a list of applications for which all network ports are monitored
You can create a list of applications for which Kaspersky Endpoint Security monitors all network ports.
We recommend including applications that receive or transmit data via the FTP protocol in the list of applications for which Kaspersky Endpoint Security monitors all network ports.
To create a list of applications for which all network ports are monitored:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Network settings.
- In the Monitored ports block, select Monitor selected network ports only.
- Select the Monitor all ports for the applications from the list recommended by Kaspersky check box.
If this check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security monitors all ports for the following applications:
- Adobe Acrobat Reader.
- Apple Application Support.
- Google Chrome.
- Microsoft Edge.
- Mozilla Firefox.
- Internet Explorer.
- Java.
- mIRC.
- Opera.
- Pidgin.
- Safari.
- Mail.ru Agent.
- Yandex Browser.
- Select the Monitor all ports for specified applications check box.
- Click Select.
This opens a list of applications for which Kaspersky Endpoint Security monitors network ports.
- Use the toggle in the Status column to enable or disable network port monitoring.
- If an application is not included in the list of applications, add it as follows:
- Click Add.
- In the window that opens, enter the path to the executable file of the application and a brief description.
- Set the Active or Inactive status for network ports monitoring.
- Save your changes.
Exporting and importing lists of monitored ports
Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the following lists to monitor network ports: list of network ports and list of applications whose ports are monitored by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. You can export lists of monitored ports to an XML file. Then you can modify the file to, for example, add a large number of ports with the same description. You can also use the export/import function to back up the lists of monitored ports or to migrate the lists to a different server.
How to export and import lists of monitored ports in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to export / import lists of monitored ports in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Log Inspection
This component is available if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for servers. This component is unavailable if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for workstations.
Starting with version 11.11.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes the Log Inspection component. Log Inspection monitors the integrity of the protected environment based on the Windows event log analysis. When the application detects signs of atypical behavior in the system, it informs the administrator, as this behavior may indicate an attempted cyber attack.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes Windows event logs and detects violation in accordance with rules. The component includes predefined rules. Predefined rules are powered by heuristic analysis. You can also add your own rules (custom rules). When a rule triggers, the application creates an event with the Critical status (see figure below).
If you want to use Log Inspection, make sure security the audit policy is configured and the system is logging the relevant events (for details, see the Microsoft technical support website.).

Log Inspection notification
Configuring predefined rules
Predefined rules include templates of abnormal activity on the protected computer. Abnormal activity can signify an attempted attack. Predefined rules are powered by heuristic analysis. Seven predefined rules are available for Log Inspection. You can enable or disable any of the rules. Predefined rules cannot be deleted.
You can configure the triggering criteria for rules that monitor events for the following operations:
- Password brute-force detection
- Network login detection
How to configure predefined rules in Administration Console (MMC)
How to configure predefined rules in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to configure predefined rules in the application interface.
As a result, when the rule triggers, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates Critical event.
Page top
Adding custom rules
You can set your own Log Inspection rule triggering criteria. To do so, you must enter an event ID and select an event source. You can look up the event ID on the Microsoft technical support website. You can select an event source from among the standard logs: Application, Security or System. You can also specify the log of a third-party application. You can find out the name of the third-party application log using the Event Viewer tool. Third-party application logs are kept in the Application and Services Logs folder (for example, the Windows PowerShell log).
The application does not check if the specified log is actually present in the Windows event log. If there is a mistake in the name of the log, the application does not monitor events from that log.
The list of custom rules already includes three rules created by Kaspersky experts.
How to add a custom rule in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to add a custom rule in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to add a custom rule in the application interface
As a result, when the rule triggers, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates Critical event.
Page top
File Integrity Monitor
This component is available if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for servers. This component is unavailable if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for workstations.
File Integrity Monitor works only on servers with NTFS or ReFS file system.
Starting with version 11.11.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes the File Integrity Monitor component. File Integrity Monitor detects changes to objects (files and folders) in a given monitoring area. These changes may indicate a computer security breach. When object changes are detected, the application informs the administrator.
To use File Integrity Monitor you need to configure component's scope, i.e. select objects, the state of which should be monitored by the component.
You can view information about the results of File Integrity Monitor operation in Kaspersky Security Center and in the interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
Editing the monitoring scope
File Integrity Monitor cannot work without a specified monitoring scope. This means you must specify the paths to the files and folders whose changes File Integrity Monitor will control. We recommend adding rarely modified objects or objects that only the administrator has access to. This will reduce the number of File Integrity Monitor events.
To reduce the number of events, you can also add exclusions to the monitoring rules. Exclusion entries have a higher priority than monitoring scope entries. For example, the organization uses an application whose files you want to monitor for integrity. To do so, you need to add the path to the folder with the application (for example, C:\Users\Testadmin\Desktop\Utilities). You can exclude log files from the monitoring rule because such files do not affect system security. Moreover, the application constantly modifies log files, which results in a great number of similar events. To avoid this, add log files to exceptions (for example, C:\Users\Testadmin\Desktop\Utilities\*.log).
How to edit a monitoring scope in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to edit a monitoring scope in the Web Console
How to edit a monitoring scope in the application interface
Page top
Viewing system integrity information
Information about the results of File Integrity Monitor operation is displayed in the following ways:
Events in the Kaspersky Security Center Console and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface
Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends an event to Kaspersky Security Center if a change in files is detected. You can configure the event selection to view events from File Integrity Monitor component. For more details on event selection settings, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface provides a separate report for the File Integrity Monitor component.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security has event aggregation tools to reduce the number of File Integrity Monitor events. Kaspersky Endpoint Security enables event aggregation in the following cases:
- too frequent changes to a single object (more than five times per minute)
- too frequent triggering of a single monitoring rule (more than 10 times per minute)
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates separate events on object modifications until the aggregation tools are triggered. At this point, Kaspersky Endpoint Security enables event aggregation and creates a corresponding event. Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs event aggregation for 24 hours (the aggregation period) or until Kaspersky Endpoint Security is stopped. After restarting Kaspersky Endpoint Security or after the aggregation period is over, the application generates special events: Report on an atypical event for the aggregation period and Report on object change for the aggregation period. These reports contain information about the start and the end of the aggregation period and the number of aggregated events.
Status of the computer in the Kaspersky Security Center Console
When events with severity level Critical ![]() or Warning
or Warning ![]() are received from File Integrity Monitor component, Kaspersky Security Center changes the status of the computer to Critical
are received from File Integrity Monitor component, Kaspersky Security Center changes the status of the computer to Critical  or Warning
or Warning  .
.
Receiving computer status from a managed application (Device status defined by application condition) should be enabled in Kaspersky Security Center in the lists of conditions that must be met to assign the Critical ![]() or Warning
or Warning ![]() status to a device. Conditions for assigning a status to a device are configured in the properties window of the administration group.
status to a device. Conditions for assigning a status to a device are configured in the properties window of the administration group.
Computer status and all reasons for status changes are displayed in the list of devices of the administration group. For more details on computer statuses, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
Reports in the Kaspersky Security Center Console
Kaspersky Security Center provides two types of reports:
- Top 10 devices with File Integrity Monitor / System Integrity Monitoring rules most frequently triggered.
- Top 10 rules of File Integrity Monitor / System Integrity Monitoring that were triggered on devices most frequently.
Password protection
Multiple users with different levels of computer literacy can share a computer. If users have unrestricted access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security and its settings, the overall level of computer protection may be reduced. Password protection lets you restrict users' access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security according to the permissions granted to them (for example, permission to exit the application).
If the user that started the Windows session (session user) has the permission to perform the action, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not request the user name and password or a temporary password. The user receives access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security in accordance with the granted permissions.
If a session user does not have the permission to perform an action, the user can obtain access to the application in the following ways:
- Enter a user name and password.
This method is suitable for day-to-day operations. To perform a password-protected action, you must enter the domain account credentials of the user with the required permission. In this case, the computer must be in that domain. If the computer is not in the domain, you can use the KLAdmin account.
- Enter a temporary password.
This method is suitable for granting temporary permissions to perform blocked actions (for example, exiting the application) to users outside the corporate network. When a temporary password expires or a session ends, Kaspersky Endpoint Security reverts its settings to their previous state.
When a user attempts to perform a password-protected action, Kaspersky Endpoint Security prompts the user for the user name and password or temporary password (see the figure below).
In the password entry window, you can switch languages only by pressing ALT+SHIFT. Using other shortcuts, even if they are configured in the operating system, do not work for switching languages.
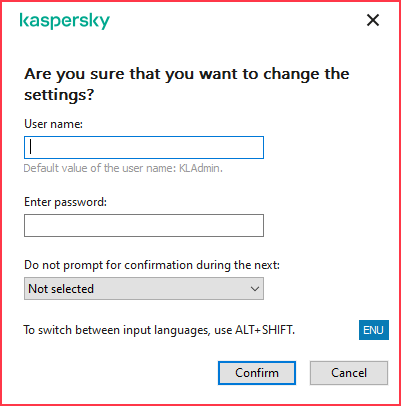
Kaspersky Endpoint Security access password prompt
User name and password
To access Kaspersky Endpoint Security, you must enter your domain account credentials. Password protection supports the following accounts:
- KLAdmin. An Administrator account with unrestricted access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security. The KLAdmin account has the right to perform any action that is password-protected. The permissions for the KLAdmin account cannot be revoked. When you enable password protection, Kaspersky Endpoint Security prompts you to set a password for the KLAdmin account.
- The Everyone group. A built-in Windows group that includes all users within the corporate network. Users in the Everyone group can access the application according to the permissions that are granted to them.
- Individual users or groups. User accounts for which you can configure individual permissions. For example, if an action is blocked for the Everyone group, you can allow this action for an individual user or a group.
- Session user. Account of the user who started the Windows session. You can switch to another session user when prompted for a password (the Save password for current session check box). In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security regards the user whose account credentials were entered as the session user instead of the user who started the Windows session.
Temporary password
A temporary password can be used to grant temporary access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for an individual computer outside of the corporate network. The Administrator generates a temporary password for an individual computer in the computer properties in Kaspersky Security Center. The Administrator selects the actions that will be protected with the temporary password, and specifies the temporary password's validity period.
Password protection operating algorithm
Kaspersky Endpoint Security decides whether to allow or block a password-protected action based on the following algorithm (see the figure below).
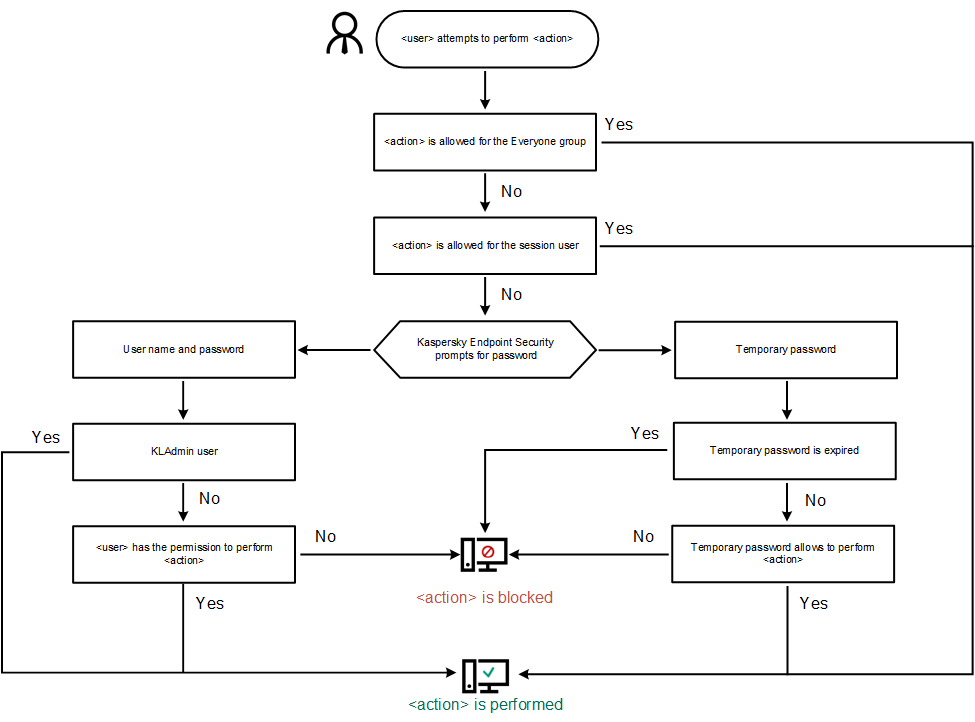
Password protection operating algorithm
Enabling Password protection
Password protection lets you restrict users' access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security according to the permissions granted to them (for example, permission to exit the application).
To enable password protection:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Interface.
- Use the Password protection toggle to enable or disable the component.
- Specify the password for the KLAdmin account and confirm it.
The KLAdmin account has the right to perform any action that is password-protected.
If a computer is running under a policy, the Administrator can reset the password for the KLAdmin account in the policy properties. If the computer is not connected to Kaspersky Security Center and you have forgotten the password for the KLAdmin account, it is not possible to recover the password.
- Set permissions for all users within the corporate network:
- In the account table, click Edit to open the list of permissions for the Everyone group.
The Everyone group is a built-in Windows group that includes all users within the corporate network.
- Select the check boxes next to the actions that users will be allowed to perform without entering the password.
If a check box is cleared, the users are blocked from performing the action. For example, if the check box next to the Exit the application permission is cleared, you can exit the application only if you are logged in as KLAdmin, or as an individual user who has the required permission, or if you enter a temporary password.
Password protection permissions have some important aspects to consider. Make sure that all conditions for accessing Kaspersky Endpoint Security are fulfilled.
- In the account table, click Edit to open the list of permissions for the Everyone group.
- Save your changes.
When password protection is enabled, the application will restrict users' access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security according to the permissions granted to the Everyone group. You can perform the actions that are blocked for the Everyone group only if you use the KLAdmin account, another account that is granted the required permissions, or if you enter a temporary password.
You can disable Password protection only if you are logged in as KLAdmin. It is not possible to disable password protection if you are using any other user account or a temporary password.
During the password check, you can select the Save password for current session check box. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not prompt for a password when a user attempts to perform another password-protected action for the duration of the session.
Page top
Granting permissions to individual users or groups
You can grant access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security to individual users or groups. For example, if exiting the application is blocked for the Everyone group, you can grant the Exit the application permission to an individual user. As a result, you can exit the application only if you are logged in as that user or as KLAdmin.
You can use account credentials to access the application only if the computer is in the domain. If the computer is not in the domain, you can use the KLAdmin account or a temporary password.
To grant permissions to individual users or groups:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Interface.
- In the account table, click Add.
- In the window that opens, click the Select user or group button.
The standard Select Users or Groups dialog opens.
- Select a user or a group in Active Directory and confirm your selection.
- In the Permissions list, select the check boxes next to the actions that the selected user or group will be allowed to perform without being prompted for a password.
If a check box is cleared, the users are blocked from performing the action. For example, if the check box next to the Exit the application permission is cleared, you can exit the application only if you are logged in as KLAdmin, or as an individual user who has the required permission, or if you enter a temporary password.
Password protection permissions have some important aspects to consider. Make sure that all conditions for accessing Kaspersky Endpoint Security are fulfilled.
- Save your changes.
As a result, if access to the application is restricted for the Everyone group, users will be granted permissions to access Kaspersky Endpoint Security according to the users' individual permissions.
Page top
Using a temporary password to grant permissions
A temporary password can be used to grant temporary access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for an individual computer outside of the corporate network. This is necessary to allow the user to perform a blocked action without obtaining the KLAdmin account credentials. To use a temporary password, the computer must be added to Kaspersky Security Center.
Temporary password
Page top
Special aspects of Password protection permissions
Password protection permissions have some important aspects and limitations to consider.
Configure application settings
If a user's computer is running under a policy, make sure that all the required settings in the policy are available for editing (the ![]() attributes are open).
attributes are open).
Exit the application
There are no special considerations or limitations.
Disable protection components
- It is not possible to grant the permission to disable protection components for the Everyone group. To allow users other than KLAdmin to disable control components, add a user or group that has the Disable protection components permission in the Password Protection settings.
- If a user's computer is running under a policy, make sure that all the required settings in the policy are available for editing (the
 attributes are open).
attributes are open). - To disable protection components in the application settings, a user must have the Configure application settings permission.
- To disable protection components from the context menu (by using the Pause protection menu item), a user must have the Disable protection components permission in addition to the Disable control components permission.
Disable control components
- It is not possible to grant the permission to disable control components for the Everyone group. To allow users other than KLAdmin to disable control components, add a user or group that has the Disable control components permission in the Password Protection settings.
- If a user's computer is running under a policy, make sure that all the required settings in the policy are available for editing (the
 attributes are open).
attributes are open). - To disable control components in the application settings, a user must have the Configure application settings permission.
- To disable control components from the context menu (by using the Pause protection menu item), a user must have the Disable control components permission in addition to the Disable protection components permission.
Disable Kaspersky Security Center policy
You cannot grant the "Everyone" group the permission to disable the Kaspersky Security Center policy. To allow users other than KLAdmin to disable the policy, add a user or group that has the Disable Kaspersky Security Center policy permission in the Password Protection settings.
Remove key
There are no special considerations or limitations.
Remove / modify / restore the application
If you have allowed removing, modifying, and restoring the application for the "All" group, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not request a password when the user attempts to carry out these operations. Therefore, any user including users from outside the domain, can install, modify, or restore the application.
Restore access to data on encrypted drive
You can restore access to data on encrypted drives only if you are logged in as KLAdmin. Permission to perform this action cannot be granted to any other user.
View reports
There are no special considerations or limitations.
Restore from Backup
There are no special considerations or limitations.
Page top
Resetting the KLAdmin password
If you forgot your KLAdmin account password, you can reset the password in policy properties. You cannot reset the password in the application interface.
You can perform password-protected actions using a temporary password. In this case, you do not need to enter KLAdmin credentials.
If the computer is not connected to Kaspersky Security Center and you have forgotten the password for the KLAdmin account, it is not possible to recover the password.
How to reset the KLAdmin account password using the Administration Console (MMC)
How to reset the KLAdmin account password in Web Console and Cloud Console
As a result, the password of your KLAdmin account is updated after the policy is applied.
Page top
Trusted zone
A trusted zone is a system administrator-configured list of objects and applications that Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not monitor when active.
The administrator forms the trusted zone independently, taking into account the features of the objects that are handled and the applications that are installed on the computer. It may be necessary to include objects and applications in the trusted zone when Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks access to a certain object or application, if you are sure that the object or application is harmless. An administrator can also allow a user to create their own local trusted zone for a specific computer. This way, users can create their own local lists of exclusions and trusted applications in addition to the general trusted zone in a policy.
Creating a scan exclusion
A scan exclusion is a set of conditions that must be fulfilled so that Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not scan a particular object for viruses and other threats.
Scan exclusions make it possible to safely use legitimate software that can be exploited by criminals to damage the computer or user data. Although they do not have any malicious functions, such applications can be exploited by intruders. For details on legitimate software that could be used by criminals to harm the computer or personal data of a user, please refer to the Kaspersky IT Encyclopedia website.
Such applications may be blocked by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. To prevent them from being blocked, you can configure scan exclusions for the applications in use. To do so, add the name or name mask that is listed in the Kaspersky IT Encyclopedia to the trusted zone. For example, you often use the Radmin application for remote administration of computers. Kaspersky Endpoint Security regards this activity as suspicious and may block it. To prevent the application from being blocked, create a scan exclusion with the name or name mask that is listed in the Kaspersky IT Encyclopedia.
If an application that collects information and sends it to be processed is installed on your computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may classify this application as malware. To avoid this, you can exclude the application from scanning by configuring Kaspersky Endpoint Security as described in this document.
Scan exclusions can be used by the following application components and tasks that are configured by the system administrator:
- Behavior Detection.
- Exploit Prevention.
- Host Intrusion Prevention.
- File Threat Protection.
- Web Threat Protection.
- Mail Threat Protection.
- Malware Scan tasks.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan an object if the drive or folder containing this object is included in the scan scope at the start of one of the scan tasks. However, the scan exclusion is not applied when a custom scan task is started for this particular object.
How to create a scan exclusion in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to create a scan exclusion in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to create a scan exclusion in the application interface
Path mask examples: Paths to files located in any folder:
Paths to files located in a specified folder:
Paths to files located in all folders with a specified name:
|
Selecting types of detectable objects
To select types of detectable objects:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Exclusions and types of detected objects.
- In the Types of detected objects block, select check boxes opposite the types of objects that you want Kaspersky Endpoint Security to detect:
- Save your changes.
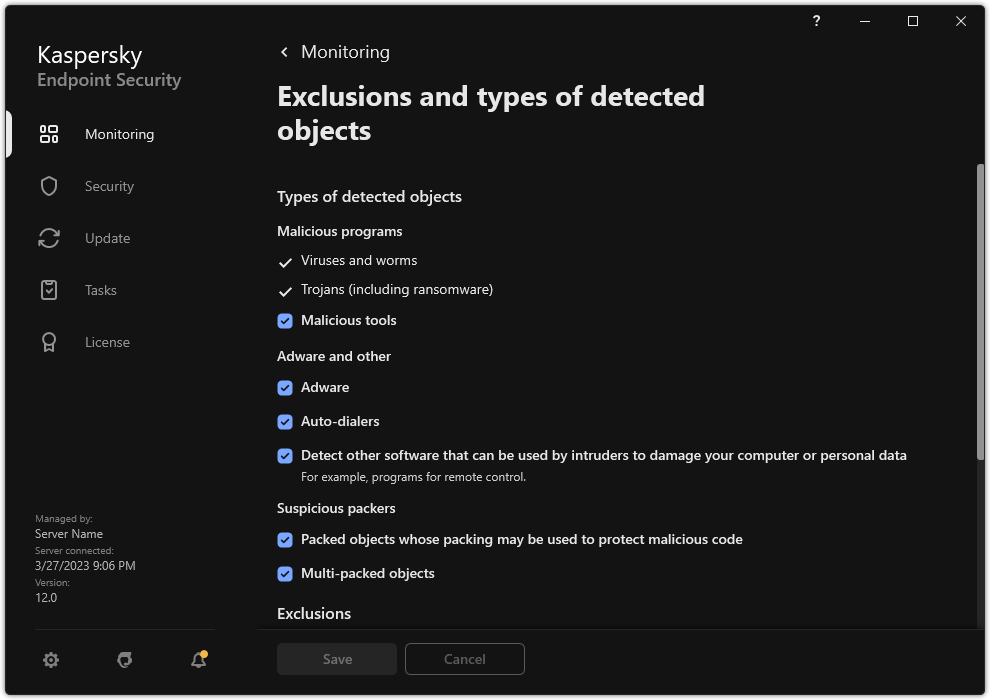
Types of detectable objects
Editing the list of trusted applications
The list of trusted applications is a list of applications whose file and network activity (including malicious activity) and access to the system registry are not monitored by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security monitors objects that are opened, executed, or saved by any application process and controls the activity of all applications and network traffic that is generated by them. After an application is added to the list of trusted applications, Kaspersky Endpoint Security stops monitoring the application's activity.
The difference between scan exclusions and trusted applications is that for exclusions Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan files, while for trusted applications it does not control the initiated processes. If a trusted application creates a malicious file in a folder which is not included in scan exclusions, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will detect the file and eliminate the threat. If the folder is added to exclusions, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will skip this file.
For example, if you consider objects that are used by the standard Microsoft Windows Notepad application to be safe, meaning that you trust this application, you can add Microsoft Windows Notepad to the list of trusted applications so that the objects used by this application are not monitored. This will increase computer performance, which is especially important when using server applications.
In addition, certain actions that are classified by Kaspersky Endpoint Security as suspicious may be safe within the context of the functionality of a number of applications. For example, the interception of text that is typed from the keyboard is a routine process for automatic keyboard layout switchers (such as Punto Switcher). To take account of the specifics of such applications and exclude their activity from monitoring, we recommend that you add such applications to the trusted applications list.
Trusted applications help to avoid compatibility issues between Kaspersky Endpoint Security and other applications (for example, the problem of double-scanning of the network traffic of a third-party computer by Kaspersky Endpoint Security and by another anti-virus application).
At the same time, the executable file and process of the trusted application are still scanned for viruses and other malware. An application can be fully excluded from Kaspersky Endpoint Security scanning by means of scan exclusions.
How to add an application to the trusted list in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to add an application to the trusted list in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to add an application to the trusted list in the application interface
Trusted application settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Do not scan files before opening |
All files that are opened by the application are excluded from scans by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. For example, if you are using applications to back up files, this feature helps reduce the consumption of resources by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. |
Do not monitor application activity |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not monitor the application's file- and network activity in the operating system. Application activity is monitored by the following components: Behavior Detection, Exploit Prevention, Host Intrusion Prevention, Remediation Engine and Firewall. |
Do not inherit restrictions from the parent process (application) |
The restrictions configured for the parent process will not be applied by Kaspersky Endpoint Security to a child process. The parent process is started by an application for which application rights (Host Intrusion Prevention) and application network rules (Firewall) are configured. |
Do not monitor child application activity |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not monitor the file activity or network activity of applications that are started by this application. |
Allow interaction with the application interface |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security Self-Defense blocks all attempts to manage application services from a remote computer. If the check box is selected, the remote access application is allowed to manage Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings through the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface. |
Do not block interaction with AMSI Protection component |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not monitor the trusted application's requests for objects to be scanned by the AMSI Protection component. |
Do not collect telemetry for console interactive input |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not send telemetry data about managing the application on the console. Telemetry data is used by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (EDR). |
Do not scan network traffic |
Network traffic initiated by the application will be excluded from scans by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. You can exclude either all traffic or only encrypted traffic from scans. You can also exclude individual IP addresses and port numbers from scans. |
Comment |
If necessary, you can provide a brief comment for the trusted application. Comments help simplify searches and sorting of trusted applications. |
Status |
Status of the trusted application:
|
Exporting and importing the trusted zone
A trusted zone is a system administrator-configured list of objects and applications that Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not monitor when active. The trusted zone consists of the following lists: scan exclusions and trusted applications. You can export these lists to XML files and other formats. Then you can modify the file to, for example, add a large number of exclusions of the same type. You can also use the export/import function to back up the list of exclusions and the list of trusted applications, or to migrate the lists to a different server.
The application uses the following formats for exporting and importing the list of exclusions:
- XML is available in Administration Console (MMC), Web Console, and Cloud Console.
- DAT is available only for import in the Administration Console (MMC). The purpose of this format is to maintain compatibility with older versions of the application. You can convert a DAT file to XML in the Administration Console (MMC) to migrate exclusion lists to Web Console.
- CSV is only available in the local interface of the application.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the XML format for exporting and importing the list of trusted applications.
How to export and import the trusted zone in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to export or import the trusted zone in Web Console and Cloud Console
How to export or import the trusted zone in the application interface
Using trusted system certificate storage
Use of system certificate storage lets you exclude applications signed by a trusted digital signature from virus scans. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically assigns such applications to the Trusted group.
To begin using trusted system certificate storage:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Exclusions and types of detected objects.
- In the Trusted system certificate store drop-down list, select which system store must be considered as trusted by Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Save your changes.
Managing Backup
Backup stores backup copies of files that were deleted or modified during disinfection. A backup copy is a file copy created before the file was disinfected or deleted. Backup copies of files are stored in a special format and do not pose a threat.
Backup copies of files are stored in the folder C:\ProgramData\Kaspersky Lab\KES.21.13\QB.
Users in the Administrators group are granted full permission to access this folder. Limited access rights to this folder are granted to the user whose account was used to install Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not provide the capability to configure user access permissions to backup copies of files.
Sometimes it is not possible to maintain the integrity of files during disinfection. If you partially or completely lose access to important information in a disinfected file after disinfection, you can attempt to restore the file from its backup copy to its original folder.
If Kaspersky Endpoint Security is running under the management of Kaspersky Security Center, backup copies of files may be transmitted to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server. For more details about managing backup copies of files in Kaspersky Security Center, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help system.
Configuring the maximum storage period for files in Backup
The default maximum storage period for copies of files in Backup is 30 days. After expiration of the maximum storage term, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes the oldest files from Backup.
To configure the maximum storage period for files in Backup:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Reports and Storage.
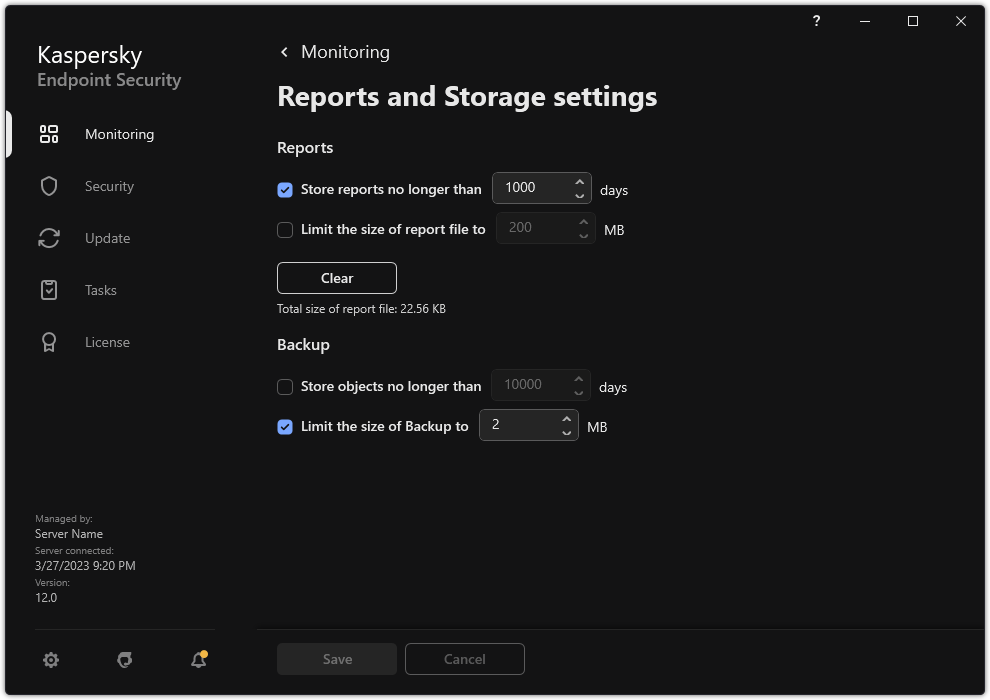
Backup settings
- If you want to limit the storage period for copies of files in Backup, select the Store objects no longer than N days check box in the Backup block. Enter the maximum storage duration for copies of files in Backup.
- Save your changes.
Configuring the maximum size of Backup
You can specify the maximum size of Backup. The size of Backup is unlimited by default. After the maximum size is reached, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes the oldest files from Backup.
To configure the maximum size of Backup:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Reports and Storage.

Backup settings
- In the Backup block, select the Limit the size of Backup to N MB check box. If the check box is selected, the maximum storage size is limited to the defined value. By default, the maximum size is 1024 MB. To avoid exceeding the maximum storage size, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes the oldest files from storage when the maximum storage size is reached.
- Save your changes.
Restoring files from Backup
If malicious code is detected in a file, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the file, assigns the Infected status to it, places a copy of it in Backup, and attempts to disinfect it. If file disinfection succeeds, the status of the backup copy of the file changes to Disinfected. The file becomes available in its original folder. If a file cannot be disinfected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes it from its original folder. You can restore the file from its backup copy to its original folder.
Files with the Will be deleted on computer restart status cannot be restored. Restart the computer, and the file status will change to Disinfected or Deleted. You can also restore the file from its backup copy to its original folder.
Upon detecting malicious code in a file that is part of the Windows Store application, Kaspersky Endpoint Security immediately deletes the file without moving a copy of the file to Backup. You can restore the integrity of the Windows Store application by using the appropriate tools of the Microsoft Windows 8 operating system (see the Microsoft Windows 8 help files for details on restoring a Windows Store application).
The set of backup copies of files is presented as a table. For a backup copy of a file, the path to the original folder of the file is displayed. The path to the original folder of the file may contain personal data.
If several files with identical names and different content located in the same folder are moved to Backup, only the file that was last placed in Backup can be restored.
To restore files from Backup:
- In the main application window, in the Monitoring section, click the Backup tile.
- This opens the list of files in Backup; in that list, select the files that you want to restore and click Restore.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security restores files from the selected backup copies to their original folders.
Page top
Deleting backup copies of files from Backup
Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes backup copies of files with any status from Backup after the storage term configured in application settings has elapsed. You can also manually delete any copy of a file from Backup.
To delete backup copies of files from Backup:
- In the main application window, in the Monitoring section, click the Backup tile.
- This opens the list of files in Backup; in this list, select files that you want to delete from Backup and click Delete.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes the selected backup copies of files from Backup.
Page top
Notification service
All sorts of events occur during the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Notifications of these events can be either be purely informational or contain critical information. For example, notifications may inform of a successful database and application modules update or log component errors that need remedying.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the logging of information about events in the operation of the Microsoft Windows application log and / or the Kaspersky Endpoint Security event log.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security delivers notifications in the following ways:
- using pop-up notifications in the Microsoft Windows taskbar notification area;
- by email.
You can configure the delivery of event notifications. The method of notification delivery is configured for each type of event.
When using the table of events to configure the notification service, you can perform the following actions:
- Filter notification service events by column values or by custom filter conditions.
- Use the search function for notification service events.
- Sort notification service events.
- Change the order and set of columns that are displayed in the list of notification service events.
Configuring event log settings
To configure event log settings:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Interface.
- In the Notifications block, click the Notification settings button.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security components and tasks are shown in the left part of the window. The right part of the window lists the events generated for the selected component or task.
Events may contain the following user data:
- Paths to files scanned by Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Paths to registry keys modified during the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Microsoft Windows user name.
- Addresses of web pages opened by the user.
- In the left part of the window, select the component or task for which you want to configure the event log settings.
- Select check boxes opposite the relevant events in the Save in local report and Save in Windows Event Log columns.
Events whose check boxes are selected in the Save in local report column are displayed in the application logs. Events that have the check box in the Save in Windows Event Log column selected are displayed in Windows logs in the
Applicationchannel. - Save your changes.
Configuring the display and delivery of notifications
To configure the display and delivery of notifications:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Interface.
- In the Notifications block, click the Notification settings button.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security components and tasks are shown in the left part of the window. The right part of the window lists events generated for the selected component or the selected task.
Events may contain the following user data:
- Paths to files scanned by Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Paths to registry keys modified during the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Microsoft Windows user name.
- Addresses of web pages opened by the user.
- In the left part of the window, select the component or task for which you want to configure the delivery of notifications.
- In the Notify on screen column, select check boxes next to relevant events.
Information about the selected events is displayed on the screen as pop-up messages in the Microsoft Windows taskbar notification area.
- In the Notify by email column, select check boxes next to relevant events.
Information about the selected events is delivered by email if the mail notification delivery settings are configured.
- Click OK.
- If you enabled email notifications, configure the settings for email delivery:
- Click Email notification settings.
- Select the Notify about events check box to enable delivery of information about Kaspersky Endpoint Security events selected in the Notify by email column.
- Specify the email notification delivery settings.
- Click OK.
- Save your changes.
Configuring the display of warnings about the application status in the notification area
To configure the display of application status warnings in the notification area:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Interface.
- In the Show application's status in notifications area block, select the check boxes opposite those categories of events about which you want to see notifications in the notification area of Microsoft Windows.
- Save your changes.
When events associated with the selected categories occur, the application icon in the notification area will change to ![]() or
or ![]() depending on the severity of the warning.
depending on the severity of the warning.
Messaging between users and the administrator
The Application Control, Device Control, Web Control and Adaptive Anomaly Control components enable LAN users whose computers have Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed to send messages to the administrator.
A user may need to send a message to the local corporate network administrator in the following cases:
- Device Control blocked access to the device.
The message template for a request to access a blocked device is available in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface in the Device Control section.
- Application Control blocked the startup of an application.
The message template for a request to allow the startup of a blocked application is available in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface in the Application Control section.
- Web Control blocked access to a web resource.
The message template for a request to access a blocked web resource is available in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface in the Web Control section.
The method used to send messages and the utilized template depends on whether or not there is an active Kaspersky Security Center policy running on the computer that has Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed, and whether or not there is a connection with the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server. The following scenarios are possible:
- If a Kaspersky Security Center policy is not running on the computer that has Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed, a user's message is sent to the local area network administrator by email.
The message fields are populated with the values of fields from the template defined in the local interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- If a Kaspersky Security Center policy is running on the computer that has Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed, the standard message is sent to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
In this case, user messages are available for viewing in the Kaspersky Security Center event storage (see instruction below). The message fields are populated with the values of fields from the template defined in the Kaspersky Security Center policy.
- If a Kaspersky Security Center out-of-office policy is running on the computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed, the method used to send messages depends on whether or not there is a connection with Kaspersky Security Center.
- If a connection with Kaspersky Security Center is established, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends the standard message to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
- If a connection with Kaspersky Security Center is absent, a user's message is sent to the local area network administrator by email.
In both cases, the message fields are populated with the values of fields from the template defined in the Kaspersky Security Center policy.
To view a user message in the Kaspersky Security Center event storage:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the Administration Server node of the Administration Console tree, select the Events tab.
The Kaspersky Security Center workspace displays all events occurring during the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, including messages to the administrator that are received from LAN users.
- To configure the event filter, in the Event selections drop-down list, select User requests.
- Select the message sent to the administrator.
- Click the Open event properties window button in the right part of the Administration Console workspace.
Managing reports
Information about the operation of each Kaspersky Endpoint Security component, data encryption events, the performance of each scan task, the update task and integrity check task, and the overall operation of the application is recorded in reports.
Reports are stored in the folder C:\ProgramData\Kaspersky Lab\KES.21.13\Report.
Reports may contain the following user data:
- Paths to files scanned by Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Paths to registry keys modified during the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Microsoft Windows user name.
- Addresses of web pages opened by the user.
The data in the report is presented in tabular form. Each table row contains information on a separate event. Event attributes are located in the table columns. Certain columns are compound ones which contain nested columns with additional attributes. To view additional attributes, click the ![]() button next to the name of the column. Events that are logged during the operation of various components or during the performance of various tasks have different sets of attributes.
button next to the name of the column. Events that are logged during the operation of various components or during the performance of various tasks have different sets of attributes.
The following reports are available:
- System audit report. Contains information about events occurring during the interaction between the user and the application and in the course of application operation in general, which are unrelated to any particular Kaspersky Endpoint Security components or tasks.
- Reports on the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security components.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security task reports.
- Data Encryption report. Contains information about events occurring during data encryption and decryption.
Reports use the following event importance levels:
![]() Informational messages. Reference events that normally do not contain important information.
Informational messages. Reference events that normally do not contain important information.
![]() Warnings. Events that need attention because they reflect important situations in the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Warnings. Events that need attention because they reflect important situations in the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
![]() Critical events. Events of critical importance that indicate problems in the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security or vulnerabilities in the protection of the user's computer.
Critical events. Events of critical importance that indicate problems in the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security or vulnerabilities in the protection of the user's computer.
For convenient processing of reports, you can modify the presentation of data on the screen in the following ways:
- Filter the event list by various criteria.
- Use the search function to find a specific event.
- View the selected event in a separate section.
- Sort the list of events by each report column.
- Display and hide events grouped by the event filter using the
 button.
button. - Change the order and arrangement of columns that are shown in the report.
You can save a generated report to a text file, if necessary. You can also delete report information on Kaspersky Endpoint Security components and tasks that are combined into groups.
If Kaspersky Endpoint Security is running under the management of Kaspersky Security Center, information about events may be relayed to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server (for more details, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help).
Viewing reports
If a user can view reports, the user can also view all events reflected in the reports.
To view reports:
- In the main application window, in the Monitoring section, click the Reports tile.
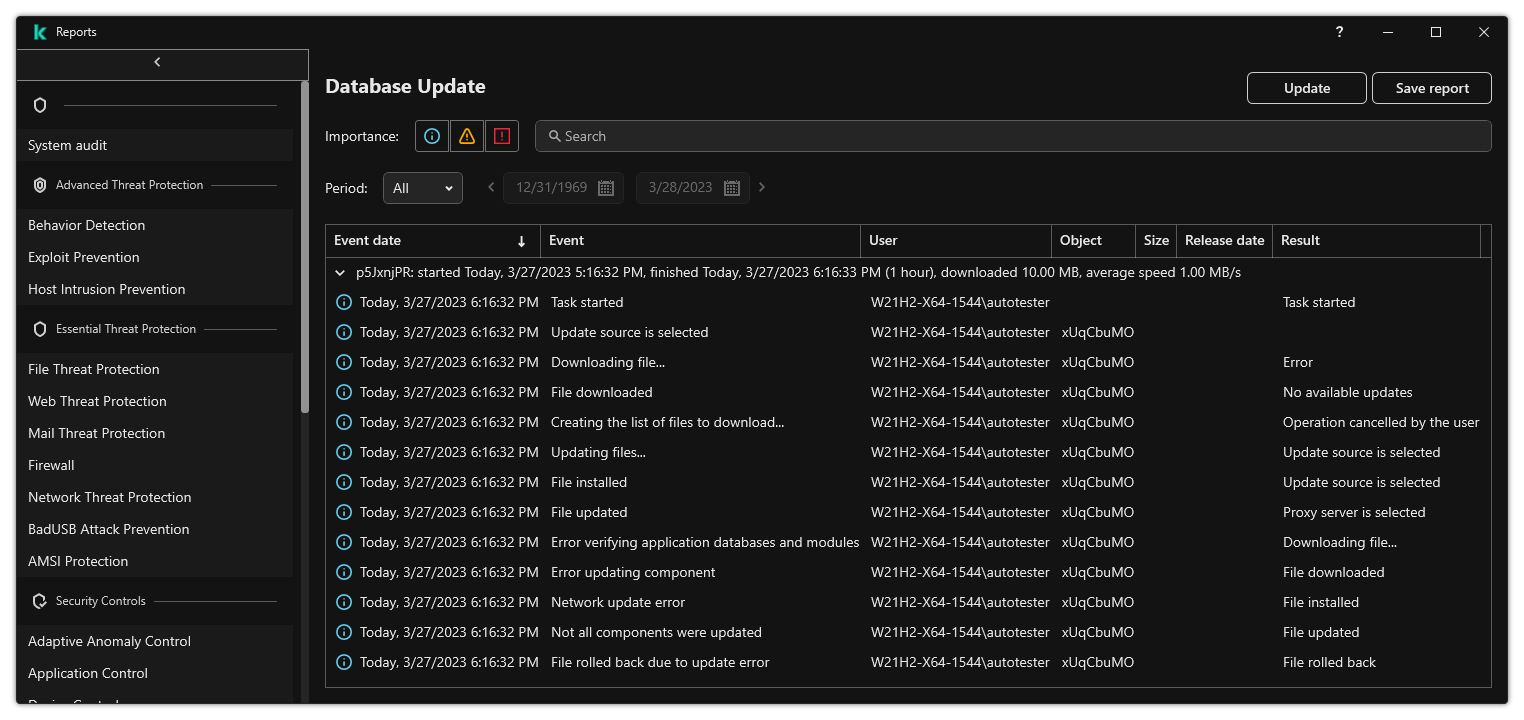
Reports
- In the list of components and tasks, select a component or task.
The right part of the window displays a report containing a list of events resulting from the operation of the selected component or selected task of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. You can sort events in the report based on the values in cells of one of the columns.
- To view detailed information about an event, select the event in the report.
A block with the event summary is displayed in the lower part of the window.
Page top
Configuring the maximum report storage term
The default maximum storage term for reports on events that are logged by Kaspersky Endpoint Security is 30 days. After that period of time, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes the oldest entries from the report file.
To modify the report maximum storage term:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Reports and Storage.

Report settings
- If you want to limit the report storage term, select the Store reports no longer than N days check box in the Reports block. Define the maximum report storage term.
- Save your changes.
Configuring the maximum size of the report file
You can specify the maximum size of the file that contains the report. By default, the maximum report file size is 1024 MB. To avoid exceeding the maximum report file size, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes the oldest entries from the report file when the maximum report file size is reached.
To configure the maximum report file size:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Reports and Storage.

Report settings
- In the Reports block, select the Limit the size of report file to N MB check box if you want to limit the size of a report file. Define the maximum size of the report file.
- Save your changes.
Saving a report to file
The user is personally responsible for ensuring the security of information from a report saved to file, and particularly for controlling and restricting access to this information.
You can save the report that you generate to a file in text format (TXT) or a CSV file.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security logs events in the report in the same way as they are displayed on the screen: in other words, with the same set and sequence of event attributes.
To save a report to file:
- In the main application window, in the Monitoring section, click the Reports tile.

Reports
- This opens a window; in this window, select the component or task.
A report is displayed in the right part of the window, which contains a list of events in the operation of the selected Kaspersky Endpoint Security component or task.
- If necessary, you can modify data presentation in the report by:
- Filtering events
- Running an event search
- Rearranging columns
- Sorting events
- Click the Save report button in the upper right part of the window.
- In the window that opens, specify the destination folder for the report file.
- Enter the name of the report file.
- Select the necessary report file format: TXT or CSV.
- Save your changes.
Clearing reports
To remove information from reports:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Reports and Storage.

Report settings
- In the Reports block, click the Clear button.
- If Password Protection is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may prompt you for user account credentials. The application prompts for account credentials if the user does not have the required permission.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security will delete all reports for all application components and tasks.
Page top
Kaspersky Endpoint Security Self-Defense
Self-Defense prevents other applications from performing actions that can interfere with the operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security and, for example, remove Kaspersky Endpoint Security from the computer. The set of available Self-Defense technologies for Kaspersky Endpoint Security depends on whether the operating system is 32-bit or 64-bit (refer to the table below).
Kaspersky Endpoint Security Self-Defense technologies
Technology |
Description |
x86 computer |
x64 computer |
|---|---|---|---|
Self-Defense mechanism |
The technology blocks access to the following application components:
|
|
|
AM-PPL (Antimalware Protected Process Light) |
The technology protects Kaspersky Endpoint Security processes against malicious actions. For more details about AM-PPL technology, please visit the Microsoft website. AM-PPL technology is available for Windows 10 version 1703 (RS2) or later, and Windows Server 2019 operating systems. |
|
|
External management defense mechanism |
This technology prevents remote administration applications (for example, TeamViewer or RemotelyAnywhere) from gaining access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security. |
|
– (except for Windows 7) |
Enabling and disabling Self-Defense
The Self-Defense mechanism of Kaspersky Endpoint Security is enabled by default.
To enable or disable Self-Defense:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Application settings.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows settings
- Use the Enable Self-Defense check box to enable or disable the Self-Defense mechanism.
- Save your changes.
Enabling and disabling AM-PPL support
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports Antimalware Protected Process Light technology (hereinafter referred to as "AM-PPL") from Microsoft. AM-PPL protects Kaspersky Endpoint Security processes against malicious actions (for example, terminating the application). AM-PPL allows only trusted processes to run. Kaspersky Endpoint Security processes are signed in accordance with Windows security requirements, and therefore they are trusted. For more details about AM-PPL technology, please visit the Microsoft website. AM-PPL technology is enabled by default.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security also has built-in mechanisms for protecting application processes. AM-PPL support lets you delegate process security functions to the operating system. You can thereby increase the speed of the application and reduce the consumption of computer resources.
AM-PPL technology is available for Windows 10 version 1703 (RS2) or later, and Windows Server 2019 operating systems.
To enable or disable AM-PPL technology:
- Turn off the application's Self-Defense mechanism.
The Self-Defense mechanism prevents modification and deletion of application processes in the computer memory, including changing the AM-PPL status.
- Run the command line interpreter (cmd.exe) as an administrator.
- Go to the folder where the Kaspersky Endpoint Security executable file is located.
- Type the following in the command line:
klpsm.exe enable– enable support for AM-PPL technology (see the figure below).klpsm.exe disable– disable support for AM-PPL technology.
- Restart Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Resume the application's Self-Defense mechanism.
Enabling support for AM-PPL technology
Protection of application services against external management
Protection of application services against external management blocks attempts by users and other applications to stop Kaspersky Endpoint Security services. Protection ensures the operation of the following services:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security service (avp)
- Kaspersky Seamless Update Service (avpsus)
To quit the application from the command line, disable the protection of Kaspersky Endpoint Security services against external management.
To enable or disable protection of application services against external management:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Application settings.

Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows settings
- Use the Enable external management of system services check box to enable or disable the protection of Kaspersky Endpoint Security services against external management.
- Save your changes.
As a result, when a user attempts to stop application services, a system window with an error message appears. The user can only manage application services from the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface.
Page top
Supporting remote administration applications
You may occasionally need to use a remote administration application while external management defense is enabled.
To enable the operation of remote administration applications:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Exclusions and types of detected objects.
- In the Exclusions block, click the Specify trusted applications link.
- In the window that opens, click the Add button.
- Select the executable file of the remote administration application.
You can also enter the path manually. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports environment variables and the
*and?characters when entering a mask. - Select the Allow interaction with the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface check box.
- Save your changes.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security performance and compatibility with other applications
The performance of Kaspersky Endpoint Security refers to the number of types of objects that can harm the computer that are detectable, as well as energy consumption and use of computer resources.
Selecting types of detectable objects
Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you fine-tune the protection of your computer and select the types of objects that the application detects during operation. Kaspersky Endpoint Security always scans the operating system for viruses, worms, and Trojans. You cannot disable scanning of these types of objects. Such malware can cause significant harm to the computer. For greater security on your computer, you can expand the range of detectable object types by enabling monitoring of legal software that can be used by criminals to damage your computer or personal data.
Using energy-saving mode
Energy consumption by applications is a key consideration for portable computers. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scheduled tasks usually use up considerable resources. When the computer is running on battery power, you can use energy-saving mode to consume power more sparingly.
In energy-saving mode, the following scheduled tasks are postponed automatically:
- Update task;
- Full Scan task;
- Critical Areas Scan task;
- Custom Scan task;
- Integrity Check task.
Whether or not energy saving mode is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security pauses encryption tasks when a portable computer switches to battery power. The application resumes encryption tasks when the portable computer switches from battery power to mains power.
Conceding computer resources to other applications
Consumption of computer resources by Kaspersky Endpoint Security when scanning the computer may increase the load on the CPU and hard drive subsystems as well as influence the performance of other applications. To resolve the problem of simultaneous operation during increased load on the CPU and hard drive subsystems, Kaspersky Endpoint Security can concede resources to other applications.
Using advanced disinfection technology
Today's malicious applications can penetrate the lowest levels of an operating system, which makes them virtually impossible to eliminate. After detecting malicious activity in the operating system, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs an extensive disinfection procedure that uses special advanced disinfection technology. Advanced disinfection technology is aimed at purging the operating system of malicious applications that have already started their processes in RAM and that prevent Kaspersky Endpoint Security from removing them by using other methods. The threat is neutralized as a result. While Advanced Disinfection is in progress, you are advised to refrain from starting new processes or editing the operating system registry. The advanced disinfection technology uses considerable operating system resources, which may slow down other applications.
After the Advanced Disinfection process has been completed on a computer running Microsoft Windows for workstations, Kaspersky Endpoint Security requests the user's permission to reboot the computer. After system reboot, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes malware files and starts a "lite" full scan of the computer.
A reboot prompt is impossible on a computer running Microsoft Windows for servers due to the specifics of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. An unplanned reboot of a file server can lead to problems involving temporary unavailability of file server data or loss of unsaved data. It is recommended to reboot a file server strictly according to schedule. This is why Advanced Disinfection technology is disabled by default for file servers.
If active infection is detected on a file server, an event is relayed to Kaspersky Security Center with information that Active Disinfection is required. To disinfect an active infection of a server, enable Active Disinfection technology for servers and start a Malware Scan group task at a time convenient for server users.
Enabling or disabling energy-saving mode
To enable or disable energy conservation mode:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Application settings.

Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows settings
- In the Performance block, use the Postpone scheduled tasks while running on battery power check box to enable or disable power saving mode.
When energy conservation mode is enabled and the computer is running on battery power, the following tasks are not run even if scheduled:
- Update
- Full Scan
- Critical Areas Scan
- Custom Scan
- Integrity check
- IOC Scan.
- Save your changes.
Enabling or disabling conceding of resources to other applications
Consumption of computer resources by Kaspersky Endpoint Security when scanning the computer may increase the load on the CPU and hard drive subsystems. This may slow down other applications. To optimize the performance, Kaspersky Endpoint Security provides a mode for transferring resources to other applications. In this mode, the operating system can decrease the priority of Kaspersky Endpoint Security scan task threads when the CPU load is high. This allows redistributing operating system resources to other applications. Thus, scan tasks will receive less CPU time. As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will take longer to scan the computer. By default, the application is configured to concede resources to other applications.
To enable or disable conceding of resources to other applications:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Application settings.

Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows settings
- In the Performance block, use the Concede resources to other applications check box to enable or disable conceding of resources to other applications.
- Save your changes.
Best practices for optimizing Kaspersky Endpoint Security performance
When deploying Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, you can use the following recommendations to configure computer protection and optimize performance.
General
Configure general settings of the application in accordance with the following recommendations:
- Upgrade Kaspersky Endpoint Security to the latest version.
Newer versions of the application have errors fixed, stability improved, and performance optimized.
- Enable protection components with default settings.
Default settings are considered optimal. This settings are recommended by Kaspersky experts. Default settings provide recommended protection level and optimal resource use. If necessary, you can restore the default application settings.
- Enable application performance optimization features.
The application has performance optimization features: energy conservation mode and conceding of resources to other applications. Make sure these options are enabled.
Malware Scan on workstations
Enabling Background scan is recommended for Malware Scan of workstations. Background scan is a scan mode of Kaspersky Endpoint Security that does not display notifications for the user. Background scan requires less computer resources than other types of scans (such as a full scan). In this mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans startup objects, the boot sector, system memory, and the system partition. Background scan settings are considered optimal. This settings are recommended by Kaspersky experts. Thus for performing a Malware Scan of the computer, you can use just the background scan mode without using other scan tasks.
If background scanning does not suit your needs, configure the Malware Scan task in accordance with the following recommendations:
- Configure the optimal computer scan schedule.
You can configure the task to run when the computer is operating under minimum load. For example, you can configure the task to run at night or on weekends.
If users turn off their computers at the end of the day, you can configure the scan task as follows:
- Enable Wake-on-LAN. The Wake-on-LAN feature allows remotely powering on the computer by sending a special signal over the local network. To use this feature, you must enable Wake-on-LAN in BIOS settings. You can also have the computer automatically turned off after the scan finishes.
- Disable the "Run missed tasks" feature. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will skip missed tasks when the user turns on the computer. Running tasks after the computer is turned on can inconvenience the user because the scan requires a big commitment of resources.
If you could not configure an optimal scan schedule, set tasks to run only when the computer is idle. Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the scan task if the computer is locked or if the screen saver is on. If you have interrupted the execution of the task, for example by unlocking the computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically runs the task, continuing from the point where it was interrupted.
- Define a scan scope.
Select the following objects to scan:
- Kernel memory;
- Running processes and Startup Objects;
- Boot sectors;
- System drive (%systemdrive%).
- Turn on iSwift and iChecker technologies.
- iSwift technology.
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scanning by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date that the file was last scanned on, and any modifications to the scanning settings. The iSwift technology is an advancement of the iChecker technology for the NTFS file system.
- iChecker technology.
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scans by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date when the file was last scanned, and any modifications to the scan settings. There are limitations to iChecker Technology: it does not work with large files and applies only to files with a structure that the application recognizes (for example, EXE, DLL, LNK, TTF, INF, SYS, COM, CHM, ZIP, and RAR).
You can only turn on iSwift and iChecker technologies in the Administration Console (MMC) and Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface. You cannot turn on these technologies in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- iSwift technology.
- Disable the scanning of password-protected archives.
If the scanning of password-protected archives is enabled, a password prompt is displayed before the archive is scanned. Because the task is recommended to be scheduled during out-of-office hours, the user cannot enter the password. You can scan password-protected archives manually.
Malware Scan on the servers
Configure the Malware Scan task in accordance with the following recommendations:
- Configure the optimal computer scan schedule.
You can configure the task to run when the computer is operating under minimum load. For example, you can configure the task to run at night or on weekends.
- Turn on iSwift and iChecker technologies.
- iSwift technology.
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scanning by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date that the file was last scanned on, and any modifications to the scanning settings. The iSwift technology is an advancement of the iChecker technology for the NTFS file system.
- iChecker technology.
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scans by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date when the file was last scanned, and any modifications to the scan settings. There are limitations to iChecker Technology: it does not work with large files and applies only to files with a structure that the application recognizes (for example, EXE, DLL, LNK, TTF, INF, SYS, COM, CHM, ZIP, and RAR).
You can only turn on iSwift and iChecker technologies in the Administration Console (MMC) and Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface. You cannot turn on these technologies in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- iSwift technology.
- Disable the scanning of password-protected archives.
If the scanning of password-protected archives is enabled, a password prompt is displayed before the archive is scanned. Because the task is recommended to be scheduled during out-of-office hours, the user cannot enter the password. You can scan password-protected archives manually.
Kaspersky Security Network
To protect your computer more effectively, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses data that is received from users around the globe. Kaspersky Security Network is designed for obtaining this data.
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is an infrastructure of cloud services providing access to the online Kaspersky Knowledge Base that contains information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software. The use of data from Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky Endpoint Security to new threats, improves the performance of some protection components, and reduces the likelihood of false positives. If you are participating in Kaspersky Security Network, KSN services provide Kaspersky Endpoint Security with information about the category and reputation of scanned files, as well as information about the reputation of scanned web addresses.
Edit Kaspersky Security Network settings in accordance with the following recommendations:
- Disable extended KSN mode.
Extended KSN mode is a mode in which Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends additional data to Kaspersky.
- Configure Kaspersky Private Security Network.
Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN) is a solution that enables users of computers hosting Kaspersky Endpoint Security or other Kaspersky applications to obtain access to Kaspersky reputation databases, and to other statistical data without sending data to Kaspersky from their own computers.
- Enable Cloud mode.
Cloud mode refers to the application operating mode in which Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses a light version of anti-virus databases. Kaspersky Security Network supports the operation of the application when light anti-virus databases are being used. The light version of anti-virus databases lets you use approximately half of the computer RAM that would otherwise be used with the usual databases. If you do not participate in Kaspersky Security Network or if cloud mode is disabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security downloads the full version of anti-virus databases from Kaspersky servers.
Data Encryption
Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you encrypt files and folders that are stored on local and removable drives, or entire removable drives and hard drives. Data encryption minimizes the risk of information leaks that may occur when a portable computer, removable drive or hard drive is lost or stolen, or when data is accessed by unauthorized users or applications. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption algorithm.
If the license has expired, the application does not encrypt new data, and old encrypted data remains encrypted and available for use. In this event, encrypting new data requires the application be activated with a new license that permits the use of encryption.
If your license has expired, or the End User License Agreement has been violated, the license key, Kaspersky Endpoint Security, or encryption components has been removed, the encrypted status of previously encrypted files is not guaranteed. This is because some applications, such as Microsoft Office Word, create a temporary copy of files during editing. When the original file is saved, the temporary copy replaces the original file. As a result, on a computer that has no or inaccessible encryption functionality, the file remains unencrypted.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security offers the following aspects of data protection:
- File Level Encryption on local computer drives. You can compile lists of files by extension or group of extensions and lists of folders stored on local computer drives, and create rules for encrypting files that are created by specific applications. After a policy is applied, Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts and decrypts the following files:
- files individually added to lists for encryption and decryption;
- files stored in folders added to lists for encryption and decryption;
- files created by separate applications.
- Encryption of removable drives. You can specify a default encryption rule, according to which the application applies the same action to all removable drives, or specify encryption rules for individual removable drives.
The default encryption rule has a lower priority than encryption rules created for individual removable drives. Encryption rules created for removable drives of the specified device model have a lower priority than encryption rules created for removable drives with the specified device ID.
To select an encryption rule for files on a removable drive, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks whether or not the device model and ID are known. The application then performs one of the following operations:
- If only the device model is known, the application uses the encryption rule (if any) created for removable drives of the specific device model.
- If only the device ID is known, the application uses the encryption rule (if any) created for removable drives with the specific device ID.
- If the device model and ID are known, the application applies the encryption rule (if any) created for removable drives with the specific device ID. If no such rule exists, but there is an encryption rule created for removable drives with the specific device model, the application applies this rule. If no encryption rule is specified for the specific device ID nor for the specific device model, the application applies the default encryption rule.
- If neither the device model nor device ID is known, the application uses the default encryption rule.
The application lets you prepare a removable drive for using encrypted data stored on it in portable mode. After enabling portable mode, you can access encrypted files on removable drives connected to a computer without encryption functionality.
- Managing rules of application access to encrypted files. For any application, you can create an encrypted file access rule that blocks access to encrypted files or allows access to encrypted files only as ciphertext, which is a sequence of characters obtained when encryption is applied.
- Creating encrypted packages. You can create encrypted archives and protect access to such archives with a password. The contents of encrypted archives can be accessed only by entering the passwords with which you protected access to those archives. Such archives can be securely transmitted over networks or on removable drives.
- Full Disk Encryption. You can select an encryption technology: Kaspersky Disk Encryption or BitLocker Drive Encryption (hereinafter also referred to as simply "BitLocker").
BitLocker is a technology that is part of the Windows operating system. If a computer is equipped with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM), BitLocker uses it to store recovery keys that provide access to an encrypted hard drive. When the computer starts, BitLocker requests the hard drive recovery keys from the Trusted Platform Module and unlocks the drive. You can configure the use of a password and/or PIN code for accessing recovery keys.
You can specify the default full disk encryption rule and create a list of hard drives to be excluded from encryption. Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs full disk encryption by sector after the Kaspersky Security Center policy is applied. The application encrypts all logical partitions of hard drives simultaneously.
After the system hard drives have been encrypted, at the next computer startup the user must complete authentication using the
before the hard drives can be accessed and the operating system is loaded. This requires entering the password of the token or smart card connected to the computer, or the user name and password of the Authentication Agent account created by the local area network administrator using the Manage Authentication Agent accounts task. These accounts are based on Microsoft Windows accounts under which users log into the operating system. You can also use Single Sign-On (SSO) technology, which lets you automatically log in to the operating system using the user name and password of the Authentication Agent account.If you back up a computer and then encrypt the computer data, after which you restore the backup copy of the computer and encrypt the computer data again, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates duplicates of Authentication Agent accounts. To remove the duplicate accounts, you must use the klmover utility with the
dupfixkey. The klmover utility is included in the Kaspersky Security Center build. You can read more about its operation in the Kaspersky Security Center Help.Access to encrypted hard drives is possible only from computers on which Kaspersky Endpoint Security with full disk encryption functionality is installed. This precaution minimizes the risk of data leaks from an encrypted hard drive when an attempt to access it is made outside of the local area network of the company.
To encrypt hard drives and removable drives, you can use the Encrypt used disk space only function. It is recommended you only use this function for new devices that have not been previously used. If you are applying encryption to a device that is already in use, it is recommended you encrypt the entire device. This ensures that all data is protected – even deleted data that might still contain retrievable information.
Before beginning encryption, Kaspersky Endpoint Security obtains the map of file system sectors. The first wave of encryption includes sectors that are occupied by files at the moment when encryption is started. The second wave of encryption includes sectors that were written to after encryption began. After encryption is complete, all sectors containing data are encrypted.
After encryption is complete and a user deletes a file, the sectors that stored the deleted file become available for storing new information at the file system level but remain encrypted. Thus, as files are written to a new device and the device is regularly encrypted with the Encrypt used disk space only function enabled, all sectors will be encrypted after some time.
The data needed to decrypt files is provided by the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server that controlled the computer at the time of encryption. If the computer with encrypted objects was managed by a different Administration Server for some reason, you can obtain access to the encrypted data in one of the following ways:
- Administration Servers in the same hierarchy:
- You do not need to take any additional actions. The user will retain access to the encrypted objects. Encryption keys are distributed to all Administration Servers.
- Separated Administration Servers:
- Request access to encrypted objects from the LAN administrator.
- Restore data on encrypted devices using the Restore Utility.
- Restore the configuration of the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server that controlled the computer at the time of encryption from a backup copy and use this configuration on the Administration Server that now controls the computer with encrypted objects.
If there is no access to encrypted data, follow the special instructions for working with encrypted data (Restoring access to encrypted files, Working with encrypted devices when there is no access to them).
Encryption functionality limitations
Data Encryption has the following limitations:
- The application creates service files during encryption. Around 0.5% of non-fragmented free space on the hard drive is required to store them. If there is not enough non-fragmented free space on the hard drive, encryption will not start until enough space is freed up.
- You can manage all data encryption components in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console and in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. In the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, you can only manage Bitlocker.
- Data encryption is available only when using Kaspersky Endpoint Security with the Kaspersky Security Center administration system or the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console (BitLocker only). Data Encryption when using Kaspersky Endpoint Security in offline mode is not possible because Kaspersky Endpoint Security stores encryption keys in Kaspersky Security Center.
- If Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer running Microsoft Windows for Servers, only full disk encryption using BitLocker Drive Encryption technology is available. If Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer running Windows for Workstations, data encryption functionality is fully available.
Full disk encryption using Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology is unavailable for hard drives that do not meet the hardware and software requirements.
Compatibility between the full disk encryption functionality of Kaspersky Endpoint Security and Kaspersky Anti-Virus for UEFI is not supported. Kaspersky Anti-Virus for UEFI starts before the operating system loads. When using full disk encryption, the application will detect the absence of an installed operating system on the computer. As a result, the operation of Kaspersky Anti-Virus for UEFI will end with an error. File Level Encryption (FLE) does not affect the operation of Kaspersky Anti-Virus for UEFI.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the following configurations:
- HDD, SSD, and USB drives.
Kaspersky Disk Encryption (FDE) technology supports working with SSD while preserving the performance and service life of SSD drives.
- Drives connected via bus: SCSI, ATA, IEEE1934, USB, RAID, SAS, SATA, NVME.
- Non-removable drives connected via SD or MMC bus.
- Drives with 512-byte sectors.
- Drives with 4096-byte sectors that emulate 512 bytes.
- Drives with the following type of partitions: GPT, MBR, and VBR (removable drives).
- Embedded software of the UEFI 64 and Legacy BIOS standard.
- Embedded software of the UEFI standard with Secure Boot support.
Secure Boot is a technology designed to verify digital signatures for UEFI loader applications and drivers. Secure Boot blocks the startup of UEFI applications and drivers that are unsigned or signed by unknown publishers. Kaspersky Disk Encryption (FDE) fully supports Secure Boot. Authentication Agent is signed by a Microsoft Windows UEFI Driver Publisher certificate.
On some devices (for example, Microsoft Surface Pro and Microsoft Surface Pro 2), an out-of-date list of digital signature verification certificates may be installed by default. Prior to encrypting the drive, you need to update the list of certificates.
- Embedded software of the UEFI standard with Fast Boot support.
Fast Boot is a technology that helps the computer start up faster. When Fast Boot technology is enabled, normally the computer loads only the minimum set of UEFI drivers required for starting the operating system. When Fast Boot technology is enabled, USB keyboards, mice, USB tokens, touchpads and touchscreens may not work while Authentication Agent is running.
To use Kaspersky Disk Encryption (FDE), it is recommended to disable Fast Boot technology. You can use the FDE Test Utility to test the operation of Kaspersky Disk Encryption (FDE).
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support the following configurations:
- The boot loader is located on one drive while the operating system is on a different drive.
- The system contains embedded software of the UEFI 32 standard.
- The system has Intel Rapid Start Technology and drives that have a hibernation partition even when Intel Rapid Start Technology is disabled.
- Drives in MBR format with more than 10 extended partitions.
- The system has a swap file located on a non-system drive.
- Multiboot system with multiple simultaneously installed operating systems.
- Dynamic partitions (only primary partitions are supported).
- Drives with less than 0.5% free unfragmented disk space.
- Drives with a sector size different from 512 bytes or 4096 bytes that emulate 512 bytes.
- Hybrid drives.
- The system has third-party loaders.
- Drives with compressed NTFS directories.
- Kaspersky Disk Encryption (FDE) technology is incompatible with other full disk encryption technologies (such as BitLocker, McAfee Drive Encryption, and WinMagic SecureDoc).
- Kaspersky Disk Encryption (FDE) technology is incompatible with ExpressCache technology.
- Creating, deleting, and modifying partitions on an encrypted drive is not supported. You could lose data.
- File system formatting is not supported. You could lose data.
If you need to format a drive that was encrypted with Kaspersky Disk Encryption (FDE) technology, format the drive on a computer that does not have Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows and use only full disk encryption.
An encrypted drive that is formatted with the quick format option may be mistakenly identified as encrypted the next time it is connected to a computer that has Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows installed. User data will be unavailable.
- Authentication Agent supports no more than 100 accounts.
- Single Sign-On technology is incompatible with other technologies of third-party developers.
- Kaspersky Disk Encryption (FDE) technology is not supported on the following models of devices:
- Dell Latitude E6410 (UEFI mode)
- HP Compaq nc8430 (Legacy BIOS mode)
- Lenovo ThinkCentre 8811 (Legacy BIOS mode).
- Authentication Agent does not support working with USB tokens when Legacy USB Support is enabled. Only password-based authentication will be possible on the computer.
- When encrypting a drive in Legacy BIOS mode, you are advised to enable Legacy USB Support on the following models of devices:
- Acer Aspire 5560G
- Acer Aspire 6930
- Acer TravelMate 8572T
- Dell Inspiron 1420
- Dell Inspiron 1545
- Dell Inspiron 1750
- Dell Inspiron N4110
- Dell Latitude E4300
- Dell Studio 1537
- Dell Studio 1569
- Dell Vostro 1310
- Dell Vostro 1320
- Dell Vostro 1510
- Dell Vostro 1720
- Dell Vostro V13
- Dell XPS L502x
- Fujitsu Celsius W370
- Fujitsu LifeBook A555
- HP Compaq dx2450 Microtower PC
- Lenovo G550
- Lenovo ThinkPad L530
- Lenovo ThinkPad T510
- Lenovo ThinkPad W540
- Lenovo ThinkPad X121e
- Lenovo ThinkPad X200s (74665YG)
- Samsung R530
- Toshiba Satellite A350
- Toshiba Satellite U400 10O
- MSI 760GM-E51 (motherboard)
Changing the length of the encryption key (AES56 / AES256)
Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption algorithm. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the AES encryption algorithm with an effective key length of 256 or 56 bits. The data encryption algorithm depends on the AES encryption library that is included in the distribution package: Strong encryption (AES256) or Lite encryption (AES56). The AES encryption library is installed together with the application.
Changing the length of the encryption key is available only for Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.2.0 or later.
Changing the encryption key length consists of the following steps:
- Decrypt objects that Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypted before you begin changing the encryption key length:
After the encryption key length is changed, objects that were previously encrypted become unavailable.
- Remove Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Install Kaspersky Endpoint Security from the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution package containing a different encryption library.
You can also change the encryption key length by upgrading the application. The key length can be changed through an application upgrade only if the following conditions are met:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security version 10 Service Pack 2 or later is installed on the computer.
- Data encryption components (File Level Encryption, Full Disk Encryption) are not installed on the computer.
By default, data encryption components are not included in Kaspersky Endpoint Security. The BitLocker Management component does not affect the change in the length of the encryption key.
To change the encryption key length, run the kes_win.msi or setup_kes.exe file from the distribution package containing the necessary encryption library. You can also remotely upgrade the application by using the installation package.
It is impossible to change the length of the encryption key using the distribution package of the same version of the application that is installed on your computer without first uninstalling the application.
Page top
Kaspersky Disk Encryption
Kaspersky Disk Encryption is available only for computers running a Windows operating system for workstations. For computers running a Windows operating system for servers, use BitLocker Drive Encryption technology.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports full disk encryption in FAT32, NTFS and exFat file systems.
Before starting full disk encryption, the application runs a series of checks to determine if the device can be encrypted, which includes checking the system hard drive for compatibility with Authentication Agent or with BitLocker encryption components. To check for compatibility, the computer must be restarted. After the computer has been rebooted, the application performs all the necessary checks automatically. If the compatibility check is successful, full disk encryption starts after the operating system has loaded and the application has started. If the system hard drive is found to be incompatible with Authentication Agent or with BitLocker encryption components, the computer must be restarted by pressing the Reset hardware button. Kaspersky Endpoint Security logs information about the incompatibility. Based on this information, the application does not start full disk encryption at operating system startup. Information about this event is logged in Kaspersky Security Center reports.
If the hardware configuration of the computer has changed, the incompatibility information logged by the application during the previous check should be deleted in order to check the system hard drive for compatibility with Authentication Agent and BitLocker encryption components. To do so, prior to full disk encryption, type avp pbatestreset in the command line. If the operating system fails to load after the system hard drive has been checked for compatibility with Authentication Agent, you must remove the objects and data remaining after test operation of Authentication Agent by using the Restore Utility and then start Kaspersky Endpoint Security and execute the avp pbatestreset command again.
After full disk encryption has started, Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts all data that is written to hard drives.
If the user shuts down or restarts the computer during full disk encryption, Authentication Agent is loaded before the next startup of the operating system. Kaspersky Endpoint Security resumes full disk encryption after successful authentication in Authentication Agent and operating system startup.
If the operating system switches to hibernation mode during full disk encryption, Authentication Agent is loaded when the operating system switches back from hibernation mode. Kaspersky Endpoint Security resumes full disk encryption after successful authentication in Authentication Agent and operating system startup.
If the operating system goes into sleep mode during full disk encryption, Kaspersky Endpoint Security resumes full disk encryption when the operating system comes out of sleep mode without loading Authentication Agent.
User authentication in the Authentication Agent can be performed in two ways:
- Enter the name and password of the Authentication Agent account created by the LAN administrator using Kaspersky Security Center tools.
- Enter the password of a token or smart card connected to the computer.
Use of a token or smart card is available only if the computer hard drives were encrypted using the AES256 encryption algorithm. If the computer hard drives were encrypted using the AES56 encryption algorithm, addition of the electronic certificate file to the command will be denied.
The authentication agent supports keyboard layouts for the following languages:
- English (UK)
- English (USA)
- Arabic (Algeria, Morocco, Tunis; AZERTY layout)
- Spanish (Latin America)
- Italian
- German (Germany and Austria)
- German (Switzerland)
- Portuguese (Brazil, ABNT2 layout)
- Russian (for 105-key IBM / Windows keyboards with the QWERTY layout)
- Turkish (QWERTY layout)
- French (France)
- French (Switzerland)
- French (Belgium, AZERTY layout)
- Japanese (for 106-key keyboards with the QWERTY layout)
A keyboard layout becomes available in the Authentication Agent if this layout has been added in the language and regional standards settings of the operating system and has become available on the welcome screen of Microsoft Windows.
If the Authentication Agent account name contains symbols that cannot be entered using keyboard layouts available in the Authentication Agent, encrypted hard drives can be accessed only after they are restored using the Restore Utility or after the Authentication Agent account name and password are restored.
Special features of SSD drive encryption
The application supports encryption of SSD drives, hybrid SSHD drives, and drives with the Intel Smart Response feature. The application does not support encryption of drives with the Intel Rapid Start feature. Disable the Intel Rapid Start feature prior to encrypting such a drive.
Encryption of SSD drives has the following special features:
- If an SSD drive is new and contains no confidential data, enable encryption of only occupied space. This lets you overwrite the relevant drive sectors.
- If an SSD drive is in use and it has confidential data, select one of the following options:
- Fully wipe the SSD drive (Secure Erase), install the operating system and run encryption of the SSD drive with the option to encrypt only occupied space enabled.
- Run encryption of the SSD drive with the option to encrypt only occupied space disabled.
Encryption of an SSD drive requires 5-10 GB of free space. The free space requirements for storing encryption administration data are provided in the table below.
Free space requirements for storing encryption administration data
SSD drive size (GB) |
Free space on primary partition of SSD drive (MB) |
Free space on secondary partition of SSD drive (MB) |
|---|---|---|
128 |
250 |
64 |
256 |
250 |
640 |
512 |
300 |
128 |
Starting Kaspersky Disk Encryption
Prior to starting full disk encryption, you are advised to make sure that the computer is not infected. To do so, start the Full Scan or Critical Areas Scan task. Performing full disk encryption on a computer that is infected by a rootkit may cause the computer to become inoperable.
Before you start disk encryption, you must check the settings of Authentication Agent accounts. Authentication Agent is needed for working with drives that are protected using Kaspersky Disk Encryption (FDE) technology. Before the operating system is loaded, the user needs to complete authentication with the Agent. Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows you to automatically create Authentication Agent accounts before encrypting a drive. You can enable automatic creation of Authentication Agent accounts in the Full Disk Encryption policy settings (see the instructions below). You can also use Single Sign-On (SSO) technology.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows you to automatically create Authentication Agent for the following user groups:
- All accounts on the computer. All accounts on the computer that have been active at any time.
- All domain accounts on the computer. All accounts on the computer that belong to some domain and that have been active at any time.
- All local accounts on the computer. All local accounts on the computer that have been active at any time.
- Service account with a one-time password. The service account is necessary to gain access to the computer, for example, when the user forgets the password. You can also use the service account as a reserve account. You must enter the name of the account (by default,
ServiceAccount). Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates a password automatically. You can find the password in the Kaspersky Security Center console. - Local administrator. Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates an Authentication Agent user account for the local administrator of the computer.
- Computer manager. Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates an Authentication Agent user account for the account of the computer manager. You can see which account has the computer manager role in computer properties in Active Directory. By default, the computer manager role is not defined, that is, it does not correspond to any account.
- Active account. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically creates an Authentication Agent account for the account that is active at the time of disk encryption.
The Manage Authentication Agent accounts task is designed for configuring user authentication settings. You can use this task to add new accounts, modify the settings of current accounts, or remove accounts if necessary. You can use local tasks for individual computers as well as group tasks for computers from separate administration groups or a selection of computers.
How to run Kaspersky Disk Encryption through the Administration Console (MMC)
How to run Kaspersky Disk Encryption through the Web Console and Cloud Console
You can use the Encryption Monitor tool to control the disk encryption or decryption process on a user's computer. You can run the Encryption Monitor tool from the main application window.
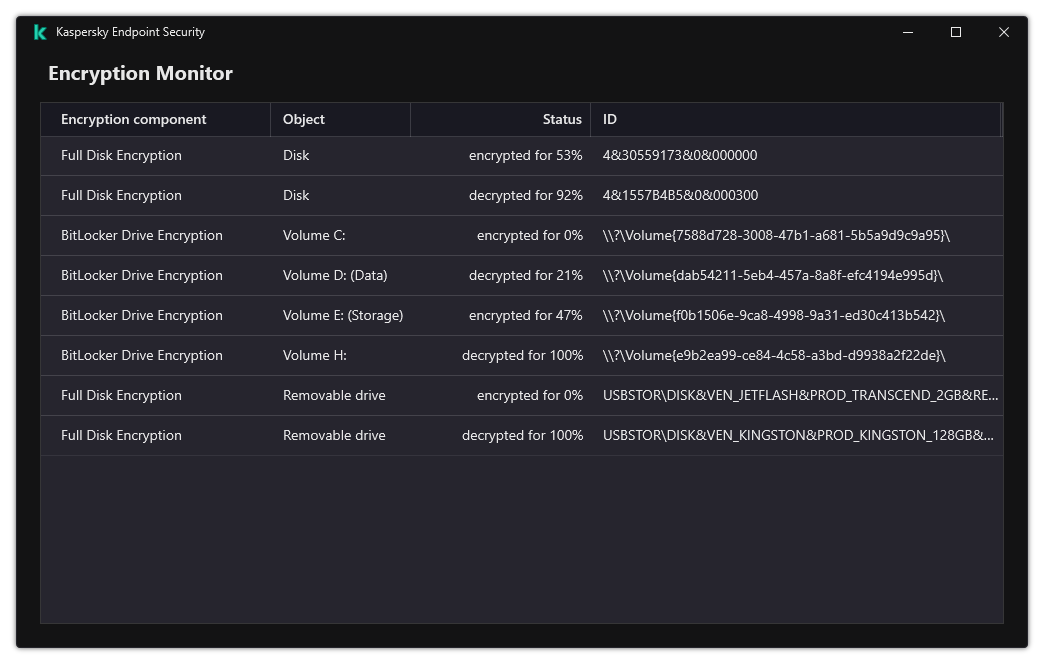
Encryption Monitor
If system hard drives are encrypted, the Authentication Agent loads before startup of the operating system. Use the Authentication Agent to complete authentication for obtaining access to encrypted system hard drives and load the operating system. After successful completion of the authentication procedure, the operating system loads. The authentication process is repeated every time the operating system restarts.
Kaspersky Disk Encryption component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Automatically create Authentication Agent accounts for users during encryption |
If this check box is selected, the application creates Authentication Agent accounts based on the list of Windows user accounts on the computer. By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses all local and domain accounts with which the user logged in to the operating system over the past 30 days. |
Automatically create Authentication Agent accounts for all users of this computer upon sign-in |
If this check box is selected, the application checks information about Windows user accounts on the computer before starting Authentication Agent. If Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects a Windows user account that has no Authentication Agent account, the application will create a new account for accessing encrypted drives. The new Authentication Agent account will have the following default settings: password-protected sign-on only, and password change on first authentication. Therefore, you do not need to manually add Authentication Agent accounts using the Manage Authentication Agent accounts task for computers with already encrypted drives. |
Save user name entered in Authentication Agent |
If the check box is selected, the application saves the name of the Authentication Agent account. You will not be required to enter the account name the next time you attempt to complete authorization in the Authentication Agent under the same account. |
Encrypt used disk space only (reduces encryption time) |
This check box enables / disables the option that limits the encryption area to only occupied hard drive sectors. This limit lets you reduce encryption time. Enabling or disabling the Encrypt used disk space only (reduces encryption time) feature after starting encryption does not modify this setting until the hard drives are decrypted. You must select or clear the check box before starting encryption. If the check box is selected, only portions of the hard drive that are occupied by files are encrypted. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically encrypts new data as it is added. If the check box is cleared, the entire hard drive is encrypted, including residual fragments of previously deleted and modified files. This option is recommended for new hard drives whose data has not been modified or deleted. If you are applying encryption on a hard drive that is already in use, it is recommended to encrypt the entire hard drive. This ensures protection of all data, even deleted data that is potentially recoverable. This check box is cleared by default. |
Use Legacy USB Support (not recommended) |
This check box enables/disables the Legacy USB Support function. Legacy USB Support is a BIOS/UEFI function that allows you to use USB devices (such as a security token) during the computer's boot phase before starting the operating system (BIOS mode). Legacy USB Support does not affect support for USB devices after the operating system is started. If the check box is selected, support for USB devices during initial startup of the computer will be enabled. When the Legacy USB Support function is enabled, the Authentication Agent in BIOS mode does not support working with tokens via USB. It is recommended to use this option only when there is a hardware compatibility issue and only for those computers on which the problem occurred. |
Creating a list of hard drives excluded from encryption
You can create a list of exclusions from encryption only for Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology.
To form a list of hard drives excluded from encryption:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Data Encryption → Full Disk Encryption.
- In the Encryption technology drop-down list, select Kaspersky Disk Encryption.
Entries corresponding to hard drives excluded from encryption appear in the Do not encrypt the following hard drives table. This table is empty if you have not previously formed a list of hard drives excluded from encryption.
- To add hard drives to the list of hard drives excluded from encryption:
- Click Add.
- In the window that opens, specify the values for Device name, Computer name, Disk type, Kaspersky Disk Encryption.
- Click Refresh.
- In the Name column, select the check boxes in the table rows corresponding to those hard drives that you want to add to the list of hard drives excluded from encryption.
- Click OK.
The selected hard drives appear in the Do not encrypt the following hard drives table.
- Save your changes.
Exporting and importing a list of hard drives excluded from encryption
You can export the list of hard drive encryption exclusions to an XML file. Then you can modify the file to, for example, add a large number of exclusions of the same type. You can also use the export/import function to back up the list of exclusions or to migrate the exclusions to a different server.
How to export and import a list of hard drive encryption exclusions in the Web Console
Page top
Enabling Single Sign-On (SSO) technology
Single Sign-On (SSO) technology allows you to automatically log into the operating system using the credentials of the Authentication Agent. This means that a user needs to enter a password only once when signing in to Windows (Authentication Agent account password). Single Sign-On technology also lets you automatically update the Authentication Agent account password when the Windows account password is changed.
When using Single Sign-on technology, the Authentication Agent ignores the password strength requirements specified in Kaspersky Security Center. You can set the password strength requirements in the operating system settings.
Enabling Single Sign-On technology
How to enable the use of Single Sign-On technology in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to enable use of Single Sign-On in the Web Console
For Single Sign-On to work, the Windows account password and the password for the Authentication Agent account must match. If the passwords do not match, the user needs to perform the authentication procedure twice: in the interface of the Authentication Agent and before loading the operating system. These actions need to be performed only once to synchronize the passwords. After that, Kaspersky Endpoint Security replaces the password of the Authentication Agent account with the password of the Windows account. When the Windows account password is changed, the application will automatically update the password for the Authentication Agent account.
Third-party credential providers
Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.10.0 adds support for third-party credential providers.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the third-party credential provider ADSelfService Plus.
When working with third-party credential providers, Authentication Agent intercepts the password before the operating system is loaded. This means that a user needs to enter a password only once when signing in to Windows. After signing in to Windows, the user can utilize the capabilities of a third-party credential provider for authentication in corporate services, for example. Third-party credential providers also allow users to independently reset their own password. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will automatically update the password for Authentication Agent.
If you are using a third-party credential provider that is not supported by the application, you may encounter some limitations in Single Sign-On technology operation. When signing in to Windows, two profiles will be available to the user: in-system credential provider and third-party credential provider. The icons of these profiles will be identical (see the figure below). The user will have the following options for continuing:
- If the user selects the third-party credential provider, Authentication Agent will not be able to synchronize the password with the Windows account. Therefore, if the user has changed the Windows account password, Kaspersky Endpoint Security cannot update the password for the Authentication Agent account. As a result, the user needs to perform the authentication procedure twice: in the interface of the Authentication Agent and before loading the operating system. In this case, the user can utilize the capabilities of a third-party credential provider for authentication in corporate services, for example.
- If the user selects the in-system credential provider, Authentication Agent will synchronize the passwords with the Windows account. In this case, the user cannot utilize the capabilities of a third-party provider for authentication in corporate services, for example.
System authentication profile and third-party authentication profile for Windows sign-in
Managing Authentication Agent accounts
Authentication Agent is needed for working with drives that are protected using Kaspersky Disk Encryption (FDE) technology. Before the operating system is loaded, the user needs to complete authentication with the Agent. The Manage Authentication Agent accounts task is designed for configuring user authentication settings. You can use local tasks for individual computers as well as group tasks for computers from separate administration groups or a selection of computers.
You cannot configure a schedule for starting the Manage Authentication Agent accounts task. It is also impossible to forcibly stop a task.
How to create the Manage Authentication Agent accounts task in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to create the Manage Authentication Agent accounts task in the Web Console
To add an Authentication Agent account, you need to add a special command to the Manage Authentication Agent accounts task. It is convenient to use a group task, for example, to add an administrator account to all computers.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows you to automatically create Authentication Agent accounts before encrypting a drive. You can enable automatic creation of Authentication Agent accounts in the Full Disk Encryption policy settings. You can also use Single Sign-On (SSO) technology.
How to add an Authentication Agent account through the Administration Console (MMC)
How to add an Authentication Agent account through the Web Console
To change the password and other settings of the Authentication Agent account, you need to add a special command to the Manage Authentication Agent accounts task. It is convenient to use a group task, for example, to replace the administrator token certificate on all computers.
How to change the Authentication Agent account through the Administration Console (MMC)
How to change the Authentication Agent account through the Web Console
To delete an Authentication Agent account, you need to add a special command to the Manage Authentication Agent accounts task. It is convenient to use a group task, for example, to delete the account of a dismissed employee.
How to delete an Authentication Agent account through the Administration Console (MMC)
How to delete an Authentication Agent account through the Web Console
To view the list of users who can complete authentication with the Agent and load the operating system, you need to go to the properties of the managed computer.
How to view the list of Authentication Agent accounts through the Administration Console (MMC)
How to view a list of Authentication Agent accounts through the Web Console
Page top
Using a token and smart card with Authentication Agent
A token or smart card can be used for authentication when accessing encrypted hard drives. To do so, you must add the electronic certificate file of a token or smart card to the Manage Authentication Agent accounts task.
Use of a token or smart card is available only if the computer hard drives were encrypted using the AES256 encryption algorithm. If the computer hard drives were encrypted using the AES56 encryption algorithm, addition of the electronic certificate file to the command will be denied.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the following tokens, smart card readers, and smart cards:
- SafeNet eToken PRO 64K (4.2b);
- SafeNet eToken PRO 72K Java;
- SafeNet eToken 4100-72K Java;
- SafeNet eToken 5100;
- SafeNet eToken 5105;
- SafeNet eToken 7300;
- EMC RSA SID 800;
- Gemalto IDPrime.NET 510;
- Gemalto IDPrime.NET 511;
- Rutoken ECP;
- Rutoken ECP Flash;
- Athena IDProtect Laser;
- SafeNet eToken PRO 72K Java;
- Aladdin-RD JaCarta PKI.
To add the file of a token or smart card electronic certificate to the command for creating an Authentication Agent account, you must first save the file using third-party software for managing certificates.
The token or smart-card certificate must have the following properties:
- The certificate must be compliant with the X.509 standard, and the certificate file must have DER encoding.
- The certificate contains an RSA key with a length of at least 1024 bits.
If the electronic certificate of the token or smart card does not meet these requirements, you cannot load the certificate file into the command for creating an Authentication Agent account.
The KeyUsage parameter of the certificate must have the value keyEncipherment or dataEncipherment. The KeyUsage parameter determines the purpose of the certificate. If the parameter has a different value, Kaspersky Security Center will download the certificate file but will display a warning.
If a user has lost a token or smart card, the administrator must add the file of a token or smart card electronic certificate to the command for creating an Authentication Agent account. Then the user must complete the procedure for receiving access to encrypted devices or restoring data on encrypted devices.
Page top
Hard drive decryption
You can decrypt hard drives even if there is no current license permitting data encryption.
To decrypt hard drives:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Data Encryption → Full Disk Encryption.
- In the Encryption technology drop-down list, select the technology with which the hard drives were encrypted.
- Do one of the following:
- In the Encryption mode drop-down list, select the Decrypt all hard drives option if you want to decrypt all encrypted hard drives.
- Add the encrypted hard drives that you want to decrypt to the Do not encrypt the following hard drives table.
This option is available only for Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology.
- Save your changes.
You can use the Encryption Monitor tool to control the disk encryption or decryption process on a user's computer. You can run the Encryption Monitor tool from the main application window.

Encryption Monitor
If the user shuts down or restarts the computer during decryption of hard drives that were encrypted using Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology, the Authentication Agent loads before the next startup of the operating system. Kaspersky Endpoint Security resumes hard drive decryption after successful authentication in the authentication agent and operating system startup.
If the operating system switches to hibernation mode during decryption of hard drives that were encrypted using Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology, Authentication Agent loads when the operating system comes out of hibernation mode. Kaspersky Endpoint Security resumes hard drive decryption after successful authentication in the authentication agent and operating system startup. After hard drive decryption, hibernation mode is unavailable until the first reboot of the operating system.
If the operating system goes into sleep mode during hard drive decryption, Kaspersky Endpoint Security resumes hard drive decryption when the operating system comes out of sleep mode without loading the Authentication Agent.
Page top
Restoring access to a drive protected by Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology
If a user has forgotten the password for accessing a hard drive protected by Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology, you need to start the recovery procedure (Request-Response). You can also use the service account to gain access to the hard disk if this feature is enabled in disk encryption settings.
Restoring access to the system hard drive
Restoring access to a system hard drive protected by Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology consists of the following steps:
- The user reports the request blocks to the administrator (see the figure below).
- The administrator enters the request blocks into Kaspersky Security Center, receives the response blocks and reports the response blocks to the user.
- The user enters the response blocks in the Authentication Agent interface and obtains access to the hard drive.
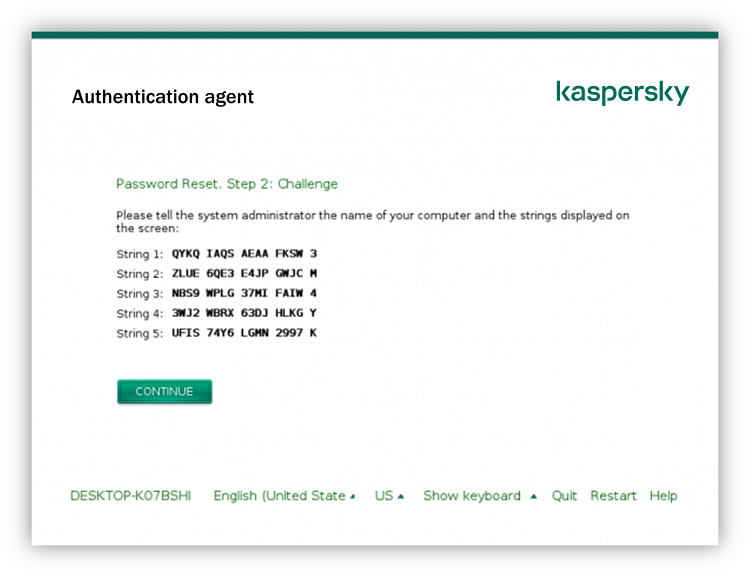
Restoring access to a system hard drive protected by Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology
To start the recovery procedure, the user needs to click the Forgot your password button in the Authentication Agent interface.
After completing the recovery procedure, the Authentication Agent will prompt the user to change the password.
Restoring access to a non-system hard drive
Restoring access to a non-system hard drive protected by Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology consists of the following steps:
- The user sends a request access file to the administrator.
- The administrator adds the request access file to Kaspersky Security Center, creates an access key file and sends the file to the user.
- The user adds the access key file to Kaspersky Endpoint Security and obtains access to the hard drive.
To start the recovery procedure, the user needs to attempt to access a hard drive. As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will create a request access file (a file with the KESDC extension), which the user needs to send to the administrator, for example, by email.
How to obtain an encrypted non-system hard drive access key file in the Web Console
Page top
Signing in with the Authentication Agent service account
Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows you to add an Authentication Agent service account when encrypting a drive. The service account is necessary to gain access to the computer, for example, when the user forgets the password. You can also use the service account as a reserve account. To add an account, select a service account in disk encryption settings and enter the name of the user account (by default, ServiceAccount). To authenticate using the agent, you will need a one-time password.
How to find out the one-time password in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to find out the one-time password in the Web Console
Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically updates the password every time a user authenticates with the service account. After authenticating using the agent, you must enter the Windows account password. When signing in with the service account, you cannot use the SSO technology.
Page top
Updating the operating system
There are a number of special considerations for updating the operating system of a computer that is protected by Full Disk Encryption (FDE). Update the operating system as follows: first update the OS on one computer, then update the OS on a small portion of the computers, then update the OS on all computers of the network.
If you are using Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology, Authentication Agent is loaded before the operating system is started. Using Authentication Agent, the user can sign in to the system and receive access to encrypted drives. Then the operating system begins loading.
If you start an update of the operating system on a computer that is protected using Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology, the OS Update Wizard will remove Authentication Agent. As a result, the computer can be locked because the OS loader will not be able to access the encrypted drive.
For details about safely updating the operating system, please refer to the Technical Support Knowledge Base.
Automatic updating of the operating system is available under the following conditions:
- The operating system is updated through WSUS (Windows Server Update Services).
- Windows 10 version 1607 (RS1) or later is installed on the computer.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security version 11.2.0 or later is installed on the computer.
If all the conditions are met, you can update the operating system in the usual way.
If you are using Kaspersky Disk Encryption (FDE) technology and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows version 11.1.0 or 11.1.1 is installed on the computer, you do not need to decrypt the hard drives to update Windows 10.
To update the operating system, you need to do the following:
- Prior to updating the system, copy the drivers named cm_km.inf, cm_km.sys, klfde.cat, klfde.inf, klfde.sys, klfdefsf.cat, klfdefsf.inf, and klfdefsf.sys to a local folder. For example, C:\fde_drivers.
- Run the system update installation with the
/ReflectDriversswitch and specify the folder containing the saved drivers:setup.exe /ReflectDrivers C:\fde_drivers
If you are using BitLocker Drive Encryption technology, you do not need to decrypt the hard drives to update Windows 10. For more details on BitLocker, please visit the Microsoft website.
Page top
Eliminating errors of encryption functionality update
Full Disk Encryption is updated when a previous version of the application is upgraded to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows 12.1.
When starting update of the Full Disk Encryption functionality the following errors may occur:
- Unable to initialize update.
- Device is incompatible with Authentication Agent.
To eliminate errors that occurred when you start update process of the Full Disk Encryption functionality in the new application version:
- Decrypt hard drives.
- Encrypt hard drives once again.
During update of the Full Disk Encryption functionality the following errors may occur:
- Unable to complete the update.
- Full Disk Encryption upgrade rollback completed with an error.
To eliminate errors that occurred during update process of the Full Disk Encryption functionality,
restore access to encrypted devices using Restore Utility.
Page top
Selecting the Authentication Agent tracing level
The application logs service information about the operation of the Authentication Agent and information about the user's operations with the Authentication Agent in the trace file.
To select the Authentication Agent tracing level:
- As soon as a computer with encrypted hard drives starts, press the F3 button to call up a window for configuring Authentication Agent settings.
- Select the tracing level in the Authentication Agent settings window:
- Disable debug logging (default). If this option is selected, the application does not log information about Authentication Agent events in the trace file.
- Enable debug logging. If this option is selected, the application logs information about the operation of the Authentication Agent and the user operations performed with the Authentication Agent in the trace file.
- Enable verbose logging. If this option is selected, the application logs detailed information about the operation of the Authentication Agent and the user operations performed with the Authentication Agent in the trace file.
The level of detail of entries under this option is higher compared to the level of the Enable debug logging option. A high level of detail of entries can slow down the startup of the Authentication Agent and the operating system.
- Enable debug logging and select serial port. If this option is selected, the application logs information about the operation of the Authentication Agent and the user operations performed with the Authentication Agent in the trace file, and relays it via the COM port.
If a computer with encrypted hard drives is connected to another computer via the COM port, Authentication Agent events can be examined from this other computer.
- Enable verbose debug logging and select serial port. If this option is selected, the application logs detailed information about the operation of the Authentication Agent and the user operations performed with the Authentication Agent in the trace file, and relays it via the COM port.
The level of detail of entries under this option is higher compared to the level of the Enable debug logging and select serial port option. A high level of detail of entries can slow down the startup of the Authentication Agent and the operating system.
Data is recorded in the Authentication Agent trace file if there are encrypted hard drives on the computer or during full disk encryption.
The Authentication Agent trace file is not sent to Kaspersky, unlike other trace files of the application. If necessary, you can manually send the Authentication Agent trace file to Kaspersky for analysis.
Page top
Editing Authentication Agent help texts
Before editing help messages of the Authentication Agent, please review the list of supported characters in a preboot environment (see below).
To edit Authentication Agent help messages:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Data Encryption → Common encryption settings.
- In the Templates block, click the Help button.
- In the window that opens, do the following:
- Select the Authentication tab to edit the help text shown in the Authentication Agent window when account credentials are being entered.
- Select the Change password tab to edit the help text shown in the Authentication Agent window when the password for the Authentication Agent account is being changed.
- Select the Recover password tab to edit the help text shown in the Authentication Agent window when the password for the Authentication Agent account is being recovered.
- Edit help messages.
If you want to restore the original text, click the By default button.
You can enter help text containing 16 lines or less. The maximum length of a line is 64 characters.
- Save your changes.
Limited support for characters in Authentication Agent help messages
In a preboot environment, the following Unicode characters are supported:
- Basic Latin alphabet (0000 - 007F)
- Additional Latin-1 characters (0080 - 00FF)
- Extended Latin-A (0100 - 017F)
- Extended Latin-B (0180 - 024F)
- Uncombined extended ID characters (02B0 - 02FF)
- Combined diacritical marks (0300 - 036F)
- Greek and Coptic alphabets (0370 - 03FF)
- Cyrillic (0400 - 04FF)
- Hebrew (0590 - 05FF)
- Arabic script (0600 - 06FF)
- Additional extended Latin (1E00 - 1EFF)
- Punctuation marks (2000 - 206F)
- Currency symbols (20A0 - 20CF)
- Letter-like symbols (2100 - 214F)
- Geometric figures (25A0 - 25FF)
- Presentation forms of Arabic script-B (FE70 - FEFF)
Characters that are not specified in this list are not supported in a preboot environment. It is not recommended to use such characters in Authentication Agent help messages.
Page top
Removing leftover objects and data after testing the operation of Authentication Agent
During application uninstallation, if Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects objects and data that remained on the system hard drive after test operation of Authentication Agent, application uninstallation is interrupted and becomes impossible until such objects and data are removed.
Objects and data may remain on the system hard drive after test operation of Authentication Agent only in exceptional cases. For example, this can happen if the computer has not been restarted after a Kaspersky Security Center policy with encryption settings was applied, or if the application fails to start after test operation of Authentication Agent.
You can remove objects and data that remained on the system hard drive after test operation of Authentication Agent in the following ways:
- Using the Kaspersky Security Center policy.
- using Restore Utility.
To use a Kaspersky Security Center policy to remove objects and data that remained after test operation of Authentication Agent:
- Apply to the computer a Kaspersky Security Center policy with settings configured to decrypt all computer hard drives.
- Start Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
To remove information about application incompatibility with Authentication Agent,
type the avp pbatestreset command in the command line.
BitLocker Management
BitLocker is an encryption technology built into Windows operating systems. Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows you to control and manage Bitlocker using Kaspersky Security Center. BitLocker encrypts logical volumes. BitLocker cannot be used for encryption of removable drives. For more details on BitLocker, refer to the Microsoft documentation.
BitLocker provides secure storage of access keys using a trusted platform module. A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a microchip developed to provide basic functions related to security (for example, to store encryption keys). A Trusted Platform Module is usually installed on the computer motherboard and interacts with all other system components via the hardware bus. Using TPM is the safest way to store BitLocker access keys, since TPM provides pre-startup system integrity verification. You can still encrypt drives on a computer without a TPM. In this case, the access key will be encrypted with a password. BitLocker uses the following authentication methods:
- TPM.
- TPM and PIN.
- Password.
After encrypting a drive, BitLocker creates a master key. Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends the master key to Kaspersky Security Center so that you can restore access to the disk, for example, if a user has forgotten the password.
If a user encrypts a disk using BitLocker, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will send information about disk encryption to Kaspersky Security Center. However, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not send the master key to Kaspersky Security Center, so it will be impossible to restore access to the disk using Kaspersky Security Center. For BitLocker to work correctly with Kaspersky Security Center, decrypt the drive and re-encrypt the drive using a policy. You can decrypt a drive locally or using a policy.
After encrypting the system hard drive, the user needs to go through BitLocker authentication to boot the operating system. After the authentication procedure, BitLocker will allow for users to log in. BitLocker does not support single sign-on technology (SSO).
If you are using Windows group policies, turn off BitLocker management in the policy settings. Windows policy settings may conflict with Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings. When encrypting a drive, errors may occur.
Starting BitLocker Drive Encryption
Prior to starting full disk encryption, you are advised to make sure that the computer is not infected. To do so, start the Full Scan or Critical Areas Scan task. Performing full disk encryption on a computer that is infected by a rootkit may cause the computer to become inoperable.
To use BitLocker Drive Encryption on computers running Windows operating systems for servers, installing the BitLocker Drive Encryption component may be required. Install the component using the operating system tools (Add Roles and Components Wizard). For more information about installing BitLocker Drive Encryption, refer to the Microsoft documentation.
How to run BitLocker Drive Encryption through the Administration Console (MMC)
How to run BitLocker Drive Encryption through the Web Console and Cloud Console
You can use the Encryption Monitor tool to control the disk encryption or decryption process on a user's computer. You can run the Encryption Monitor tool from the main application window.

Encryption Monitor
After the policy is applied, the application will display the following queries, depending on the authentication settings:
- TPM only. No user input required. The disk will be encrypted when the computer restarts.
- TPM + PIN / Password. If a TPM module is available, a PIN code prompt window appears. If a TPM module is not available, you will see a password prompt window for preboot authentication.
- Password only. You will see a password prompt window for preboot authentication.
If the Federal Information Processing standard compatibility mode is enabled for computer operating system, then in Windows 8 and earlier versions of operating system, a request for connecting a storage device is displayed to save the recovery key file. You can save multiple recovery key files on a single storage device.
After setting a password or a PIN, BitLocker will ask you to restart your computer to complete the encryption. Next, the user needs to go through the BitLocker authentication procedure. After the authentication procedure, the user must log on to the system. After the operating system has loaded, BitLocker will complete the encryption.
If there is no access to encryption keys, the user may request the local network administrator to provide a recovery key (if the recovery key was not saved earlier on the storage device or was lost).
BitLocker Drive Encryption component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Enable use of BitLocker authentication requiring pre-boot keyboard input on tablets |
This check box enables / disables the use of authentication requiring data input in a preboot environment, even if the platform does not have the capability for preboot input (for example, with touchscreen keyboards on tablets). The touchscreen of tablet computers is not available in the preboot environment. To complete BitLocker authentication on tablet computers, the user must connect a USB keyboard, for example. If the check box is selected, use of authentication requiring preboot input is allowed. It is recommended to use this setting only for devices that have alternative data input tools in a preboot environment, such as a USB keyboard in addition to touchscreen keyboards. If the check box is cleared, BitLocker Drive Encryption is not possible on tablets. |
Use hardware encryption (Windows 8 and later versions) |
If the check box is selected, the application applies hardware encryption. This lets you increase the speed of encryption and use less computer resources. |
Encrypt used disk space only (reduces encryption time) |
This check box enables / disables the option that limits the encryption area to only occupied hard drive sectors. This limit lets you reduce encryption time. Enabling or disabling the Encrypt used disk space only (reduces encryption time) feature after starting encryption does not modify this setting until the hard drives are decrypted. You must select or clear the check box before starting encryption. If the check box is selected, only portions of the hard drive that are occupied by files are encrypted. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically encrypts new data as it is added. If the check box is cleared, the entire hard drive is encrypted, including residual fragments of previously deleted and modified files. This option is recommended for new hard drives whose data has not been modified or deleted. If you are applying encryption on a hard drive that is already in use, it is recommended to encrypt the entire hard drive. This ensures protection of all data, even deleted data that is potentially recoverable. This check box is cleared by default. |
Authentication method |
Only password (Windows 8 and later versions) If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security prompts the user for a password when the user attempts to access an encrypted drive. This option can be selected when a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is not being used. Trusted platform module (TPM) If this option is selected, BitLocker uses a Trusted Platform Module (TPM). A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a microchip developed to provide basic functions related to security (for example, to store encryption keys). A Trusted Platform Module is usually installed on the computer motherboard and interacts with all other system components via the hardware bus. For computers running Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2, only encryption using a TPM module is available. If a TPM module is not installed, BitLocker encryption is not possible. Use of a password on these computers is not supported. A device equipped with a Trusted Platform Module can create encryption keys that can be decrypted only with the device. A Trusted Platform Module encrypts encryption keys with its own root storage key. The root storage key is stored within the Trusted Platform Module. This provides an additional level of protection against attempts to hack encryption keys. This action is selected by default. You can set an additional layer of protection for access to the encryption key, and encrypt the key with a password or a PIN:
|
Decrypting a hard drive protected by BitLocker
Users can decrypt a disk using the operating system (the Turn Off BitLocker function). After that, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will prompt the user to encrypt the disk again. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will be prompting to encrypt the disk unless you enable disk decryption in the policy.
How to decrypt a hard drive protected by BitLocker through the Administration Console (MMC)
How to decrypt a BitLocker-encrypted hard drive through the Web Console and Cloud Console
You can use the Encryption Monitor tool to control the disk encryption or decryption process on a user's computer. You can run the Encryption Monitor tool from the main application window.

Encryption Monitor
Page top
Restoring access to a drive protected by BitLocker
If a user has forgotten the password for accessing a hard drive encrypted by BitLocker, you need to start the recovery procedure (Request-Response).
If the computer's operating system has Federal Information Processing standard (FIPS) compatibility mode enabled, then in Windows 8 and older the recovery key file is saved to the removable drive before encryption. To restore access to the drive, insert the removable drive and follow the on-screen instructions.
Restoring access to a hard drive encrypted by BitLocker consists of the following steps:
- The user tells the administrator the recovery key ID (see the figure below).
- The administrator verifies the ID of the recovery key in the computer properties in Kaspersky Security Center. The ID that the user provided must match the ID that is displayed in the computer properties.
- If the recovery key IDs match, the administrator provides the user with the recovery key or sends a recovery key file.
A recovery key file is used for computers running the following operating systems:
- Windows 7;
- Windows 8;
- Windows Server 2008;
- Windows Server 2011;
- Windows Server 2012.
For all other operating systems, a recovery key is used.
- The user enters the recovery key and gains access to the hard drive.

Restoring access to a hard drive encrypted by BitLocker
Restoring access to a system drive
To start the recovery procedure, the user needs to press the Esc key at the pre-boot authentication stage.
After the operating system is loaded, Kaspersky Endpoint Security prompts the user to change the password or PIN code. After you set a new password or PIN code, BitLocker will create a new master key and send the key to Kaspersky Security Center. As a result, the recovery key and recovery key file will be updated. If the user has not changed the password, you can use the old recovery key the next time the operating system loads.
Windows 7 computers don't allow changing the password or PIN code. After the recovery key is entered and the operating system is loaded, Kaspersky Endpoint Security won't prompt the user to change the password or PIN code. Thus, it is impossible to set a new password or a PIN code. This issue stems from the peculiarities of the operating system. To continue, you need to re-encrypt the hard drive.
Restoring access to a non-system drive
To start the recovery procedure, the user needs to click the Forgot your password link in the window providing access to the drive. After gaining access to the encrypted drive, the user can enable automatic unlocking of the drive during Windows authentication in the BitLocker settings.
Page top
Pausing BitLocker protection to update software
There are a number of special considerations for updating the operating system, installing update packages for the operating system, or updating other software with BitLocker protection turned on. Installing updates may require restarting the computer multiple times. After each restart, the user must complete BitLocker authentication. To make sure updates install correctly, you can temporarily turn off BitLocker authentication. In this case the disk stays encrypted and the user has access to data after signing in to the system. To manage BitLocker authentication, you can use the BitLocker Protection Management task. You can use this task to specify the number of computer restarts that do not require BitLocker authentication. In this way, after updates are installed and the BitLocker Protection Management task is complete, BitLocker authentication is automatically enabled. You can enable BitLocker authentication at any time.
How to pause BitLocker protection using the Administration Console (MMC)
How to pause BitLocker protection using Web Console
As a result, when the task is running, after the next restart of the computer, BitLocker does not prompt the user for authentication. After each restart of the computer without BitLocker authentication, Kaspersky Endpoint Security generates a corresponding event and records the number of remaining restarts. Kaspersky Endpoint Security then sends the event to Kaspersky Security Center to be monitored by the administrator. You can also find out the number of remaining restarts in computer properties in the Kaspersky Security Center console.
When the specified number of restarts or the expiration time of the task is reached, BitLocker authentication is automatically turned on. To gain access to data, the user must complete BitLocker authentication.
On computers running Windows 7, BitLocker cannot count computer restarts. Counting restarts on Windows 7 computers is handled by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Thus to automatically turn on BitLocker authentication after each restart, Kaspersky Endpoint Security must be started.
To turn on BitLocker authentication ahead of time, open the BitLocker Protection Management task properties and select Request authentication each time in preboot.
Page top
File Level Encryption on local computer drives
This component is available if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for workstations. This component is unavailable if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for servers.
File encryption has the following special features:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts / decrypts files in predefined folders only for local user profiles of the operating system. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not encrypt or decrypt files in predefined folders of roaming user profiles, mandatory user profiles, temporary user profiles, or redirected folders.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not encrypt files whose modification could harm the operating system and installed applications. For example, the following files and folders with all nested folders are on the list of encryption exclusions:
- %WINDIR%;
- %PROGRAMFILES% and %PROGRAMFILES(X86)%;
- Windows registry files.
The list of encryption exclusions cannot be viewed or edited. While files and folders on the list of encryption exclusions can be added to the encryption list, they will not be encrypted during file encryption.
Encrypting files on local computer drives
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not encrypt files that are located in OneDrive cloud storage or in other folders that have OneDrive as their name. Kaspersky Endpoint Security also blocks the copying of encrypted files to OneDrive folders if those files are not added to the decryption rule.
To encrypt files on local drives:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Data Encryption → File Level Encryption.
- In the Encryption mode drop-down list, select According to rules.
- On the Encryption tab, click the Add button, and in the drop-down list select one of the following items:
- Select the Predefined folders item to add files from folders of local user profiles suggested by Kaspersky experts to an encryption rule.
- Documents. Files in the standard Documents folder of the operating system, and its subfolders.
- Favorites. Files in the standard Favorites folder of the operating system, and its subfolders.
- Desktop. Files in the standard Desktop folder of the operating system, and its subfolders.
- Temporary files. Temporary files related to the operation of applications installed on the computer. For example, Microsoft Office applications create temporary files containing backup copies of documents.
It is not recommended to encrypt temporary files, as this can cause data loss. For example, Microsoft Word creates temporary files when processing a document. If temporary files are encrypted, but the original file is not, the user may receive an Access Denied error when trying to save the document. Additionally, Microsoft Word might save the file, but it will not be possible to open the document the next time, i.e. the data will be lost.
- Outlook files. Files related to the operation of the Outlook mail client: data files (PST), offline data files (OST), offline address book files (OAB), and personal address book files (PAB).
- Select the Custom folder item to add a manually entered folder path to an encryption rule.
When adding a folder path, adhere to the following rules:
- Use an environment variable (for example,
%FOLDER%\UserFolder\). You can use an environment variable only once and only at the beginning of the path. - Do not use relative paths.
- Do not use the
*and?characters. - Do not use UNC paths.
- Use
;or,as a separator character.
- Use an environment variable (for example,
- Select the Files by extension item to add individual file extensions to an encryption rule. Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts files with the specified extensions on all local drives of the computer.
- Select the Files by groups of extensions item to add groups of file extensions to an encryption rule (for example, Microsoft Office documents). Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts files that have the extensions listed in the groups of extensions on all local drives of the computer.
- Select the Predefined folders item to add files from folders of local user profiles suggested by Kaspersky experts to an encryption rule.
- Save your changes.
As soon as the policy is applied, Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts the files that are included in the encryption rule and not included in the decryption rule.
File encryption has the following special features:
- If the same file is added to both an encryption rule and a decryption rule, then Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- If the file is not encrypted, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not encrypt this file.
- If the file is encrypted, Kaspersky Endpoint Security decrypts this file.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security continues to encrypt new files if these files meet the criteria of the encryption rule. For example, when you change the properties of an unencrypted file (path or extension), the file then meets the criteria of the encryption rule. Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts this file.
- When the user creates a new file whose properties meet the encryption rule criteria, Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts the file as soon as it is opened.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security postpones the encryption of open files until they are closed.
- If you move an encrypted file to another folder on the local drive, the file remains encrypted regardless of whether or not this folder is included in the encryption rule.
- If you decrypt a file and copy it to another local folder that is not included in the decryption rule, a copy of the file may be encrypted. To prevent the copied file from being encrypted, create a decryption rule for the target folder.
Forming encrypted file access rules for applications
To form encrypted file access rules for applications:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Data Encryption → File Level Encryption.
- In the Encryption mode drop-down list, select According to rules.
Access rules are applied only when in the According to rules mode. After applying access rules in According to rules mode, if you switch to Leave unchanged mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will ignore all access rules. All applications will have access to all encrypted files.
- In the right part of the window, select the Rules for applications tab.
- If you want to select applications exclusively from the Kaspersky Security Center list, click the Add button and in the drop-down list select the Applications from Kaspersky Security Center list item.
- Specify the filters to narrow down the list of applications in the table. To do so, specify the values of the Application, Vendor, and Period added parameters, and all check boxes from the Group block.
- Click Refresh.
- The table lists applications that match the applied filters.
- In the Application column, select check boxes opposite the applications for which you want to form encrypted file access rules.
- In the Rule for applications drop-down list, select the rule that will determine the access of applications to encrypted files.
- In the Actions for applications that were selected earlier drop-down list, select the action to be taken by Kaspersky Endpoint Security on encrypted file access rules that were previously formed for such applications.
The details of an encrypted file access rule for applications appear in the table on the Rules for applications tab.
- If you want to manually select applications, click the Add button and in the drop-down list select the Custom applications item.
- In the entry field, type the name or list of names of executable application files, including their extensions.
You can also add the names of executable files of applications from the Kaspersky Security Center list by clicking the Add from Kaspersky Security Center list button.
- If required, in the Description field, enter a description of the list of applications.
- In the Rule for applications drop-down list, select the rule that will determine the access of applications to encrypted files.
The details of an encrypted file access rule for applications appear in the table on the Rules for applications tab.
- In the entry field, type the name or list of names of executable application files, including their extensions.
- Save your changes.
Encrypting files that are created or modified by specific applications
You can create a rule by which Kaspersky Endpoint Security will encrypt all files created or modified by the applications specified in the rule.
Files that were created or modified by the specified applications before the encryption rule was applied will not be encrypted.
To configure encryption of files that are created or modified by specific applications:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Data Encryption → File Level Encryption.
- In the Encryption mode drop-down list, select According to rules.
Encryption rules are applied only in According to rules mode. After applying encryption rules in According to rules mode, if you switch to Leave unchanged mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will ignore all encryption rules. Files that were previously encrypted will remain encrypted.
- In the right part of the window, select the Rules for applications tab.
- If you want to select applications exclusively from the Kaspersky Security Center list, click the Add button and in the drop-down list select the Applications from Kaspersky Security Center list item.
- Specify the filters to narrow down the list of applications in the table. To do so, specify the values of the Application, Vendor, and Period added parameters, and all check boxes from the Group block.
- Click Refresh.
The table lists applications that match the applied filters.
- In the Application column, select the check boxes next to the applications whose created files you want to encrypt.
- In the Rule for applications drop-down list, select Encrypt all created files.
- In the Actions for applications that were selected earlier drop-down list, select the action to be taken by Kaspersky Endpoint Security on file encryption rules that were previously formed for such applications.
Information about the encryption rule for files created or modified by selected applications is displayed in the table on the Rules for applications tab.
- If you want to manually select applications, click the Add button and in the drop-down list select the Custom applications item.
- In the entry field, type the name or list of names of executable application files, including their extensions.
You can also add the names of executable files of applications from the Kaspersky Security Center list by clicking the Add from Kaspersky Security Center list button.
- If required, in the Description field, enter a description of the list of applications.
- In the Rule for applications drop-down list, select Encrypt all created files.
Information about the encryption rule for files created or modified by selected applications is displayed in the table on the Rules for applications tab.
- In the entry field, type the name or list of names of executable application files, including their extensions.
- Save your changes.
Generating a decryption rule
To generate a decryption rule:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Data Encryption → File Level Encryption.
- In the Encryption mode drop-down list, select According to rules.
- On the Decryption tab, click the Add button, and in the drop-down list select one of the following items:
- Select the Predefined folders item to add files from folders of local user profiles suggested by Kaspersky experts to a decryption rule.
- Select the Custom folder item to add a manually entered folder path to a decryption rule.
- Select the Files by extension item to add individual file extensions to a decryption rule. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not encrypt files with the specified extensions on all local drives of the computer.
- Select the Files by groups of extensions item to add groups of file extensions to a decryption rule (for example, Microsoft Office documents). Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not encrypt files that have the extensions listed in the groups of extensions on all local drives of the computer.
- Save your changes.
If the same file has been added to the encryption rule and the decryption rule, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not encrypt this file if it is not encrypted, and decrypts the file if it is encrypted.
Page top
Decrypting files on local computer drives
To decrypt files on local drives:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Data Encryption → File Level Encryption.
- In the right part of the window, select the Encryption tab.
- Remove files and folders that you want to decrypt from the encryption list. To do so, select files and select the Delete rule and decrypt files item in the context menu of the Remove button.
Files and folders removed from the encryption list are automatically added to the decryption list.
- Form a file decryption list.
- Save your changes.
As soon as the policy is applied, Kaspersky Endpoint Security decrypts encrypted files that are added to the decryption list.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security decrypts encrypted files if their parameters (file path / file name / file extension) change to match the parameters of objects added to the decryption list.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security postpones the decryption of open files until they are closed.
Page top
Creating encrypted packages
To protect your data when sending files to users outside the corporate network, you can use encrypted packages. Encrypted packages can be convenient for transferring large files on removable drives, as email clients have file size restrictions.
Before creating encrypted packages, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will prompt the user for a password. To reliably protect the data, you can enable password strength check and specify password strength requirements. This will prevent users from using short and simple passwords, for example, 1234.
How to enable password strength check when creating encrypted archives in the Web Console
You can create encrypted packages on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed with File Level Encryption available.
When adding a file to the encrypted package whose contents reside in OneDrive cloud storage, Kaspersky Endpoint Security downloads the contents of the file and performs encryption.
To create an encrypted package:
- In any file manager, select the files or folders that you want to add to the encrypted package. Right-click to open their context menu.
- In the context menu, select New encrypted package (see figure below).

Creating an encrypted package
- In the window that opens, specify the password and confirm it.
The password must meet the complexity criteria specified in the policy.
- Click Create.
The encrypted package creation process starts. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not perform file compression when it creates an encrypted package. When the process finishes, a self-extracting password-protected encrypted package (an executable file with .exe extension – ![]() ) is created in the selected destination folder.
) is created in the selected destination folder.
To access files in an encrypted package, double-click it to start the Unpacking Wizard, then enter the password. If you forgot or lost your password, it is not possible to recover it and access the files in the encrypted package. You can recreate the encrypted package.
Page top
Restoring access to encrypted files
When files are encrypted, Kaspersky Endpoint Security receives an encryption key required for directly accessing the encrypted files. Using this encryption key, a user working under any Windows user account that was active during file encryption can directly access the encrypted files. Users working under Windows accounts that were inactive during file encryption must connect to Kaspersky Security Center in order to access the encrypted files.
Encrypted files may be inaccessible under the following circumstances:
- The user's computer stores encryption keys, but there is no connection with Kaspersky Security Center for managing them. In this case, the user must request access to encrypted files from the LAN administrator.
If access to Kaspersky Security Center does not exist, you must:
- request an access key for access to encrypted files on computer hard drives;
- to access encrypted files that are stored on removable drives, request separate access keys for encrypted files on each removable drive.
- Encryption components are deleted from the user's computer. In this event, the user may open encrypted files on local and removable disks but the contents of those files will appear encrypted.
The user may work with encrypted files under the following circumstances:
- Files are placed inside encrypted packages created on a computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed.
- Files are stored on removable drives on which portable mode has been allowed.
To gain access to encrypted files, the user needs to start the recovery procedure (Request-Response).
Recovering access to encrypted files consists of the following steps:
- The user sends a request access file to the administrator (see the figure below).
- The administrator adds the request access file to Kaspersky Security Center, creates an access key file and sends the file to the user.
- The user adds the access key file to Kaspersky Endpoint Security and gains access to the files.
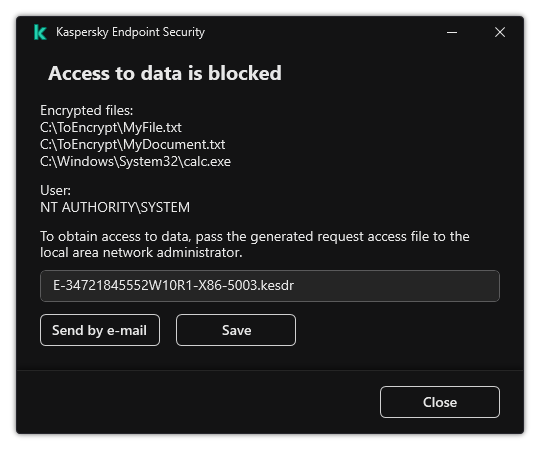
Restoring access to encrypted files
To start the recovery procedure, the user needs to attempt to access a file. As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will create a request access file (a file with the KESDC extension), which the user needs to send to the administrator, for example, by email.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security generates a request access file for access to all encrypted files stored on the computer's drive (local drive or removable drive).
How to obtain an encrypted data access key file in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to obtain an encrypted data access key file in the Web Console
After receiving the encrypted data access key file, the user needs to run the file by double-clicking it. As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will grant access to all encrypted files stored on the drive. To access encrypted files that are stored on other drives, you must obtain a separate access key file for each drive.
Page top
Restoring access to encrypted data after operating system failure
You can restore access to data after operating system failure only for file level encryption (FLE). You cannot restore access to data if full disk encryption (FDE) is used.
To restore access to encrypted data after operating system failure:
- Reinstall the operating system without formatting the hard drive.
- Install Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Establish a connection between the computer and the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server that controlled the computer when the data was encrypted.
Access to encrypted data will be granted under the same conditions that applied before operating system failure.
Page top
Editing templates of encrypted file access messages
To edit templates of encrypted file access messages:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Data Encryption → Common encryption settings.
- In the Templates block, click the Templates button.
- In the window that opens, do the following:
- If you want to edit the user message template, select the User's message tab. The following window opens when the user attempts to access an encrypted file while there is no key available on the computer for access to encrypted files (see figure below). Clicking the Send by e-mail button automatically creates a user message. This message is sent to the corporate LAN administrator along with the file requesting access to encrypted files.
- If you want to edit the administrator message template, select the Administrator's message tab. The user receives this message after access to encrypted files is granted.
- Edit the message templates.
- Save your changes.

Restoring access to encrypted files
Encryption of removable drives
This component is available if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for workstations. This component is unavailable if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for servers.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports encryption of files in FAT32 and NTFS file systems. If a removable drive with an unsupported file system is connected to the computer, the encryption task for this removable drive ends with an error and Kaspersky Endpoint Security assigns the read-only status to the removable drive.
To protect data on removable drives, you can use the following types of encryption:
- Full Disk Encryption (FDE).
Encryption of the entire removable drive, including the file system.
It is not possible to access encrypted data outside the corporate network. It is also impossible to access encrypted data inside the corporate network if the computer is not connected to Kaspersky Security Center (e.g. on a guest computer).
- File Level Encryption (FLE).
Encryption of only files on a removable drive. The file system remains unchanged.
Encryption of files on removable drives provides the capability to access data outside the corporate network using a special mode called portable mode.
During encryption, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates a master key. Kaspersky Endpoint Security saves the master key in the following repositories:
- Kaspersky Security Center.
- User's computer.
The master key is encrypted with the user's secret key.
- Removable drive.
The master key is encrypted with the public key of Kaspersky Security Center.
After encryption is complete, the data on the removable drive can be accessed within the corporate network as if was on an ordinary unencrypted removable drive.
Accessing encrypted data
When a removable drive with encrypted data is connected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- Checks for a master key in the local storage on the user's computer.
If the master key is found, the user gains access to the data on the removable drive.
If the master key is not found, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- Sends a request to Kaspersky Security Center.
After receiving the request, Kaspersky Security Center sends a response that contains the master key.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security saves the master key in the local storage on the user's computer for subsequent operations with the encrypted removable drive.
- Sends a request to Kaspersky Security Center.
- Decrypts the data.
Special features of removable drive encryption
Encryption of removable drives has the following special features:
- The policy with preset settings for removable drive encryption is formed for a specific group of managed computers. Therefore, the result of applying the Kaspersky Security Center policy configured for encryption / decryption of removable drives depends on the computer to which the removable drive is connected.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not encrypt / decrypt read-only files that are stored on removable drives.
- The following device types are supported as removable drives:
- Data media connected via the USB bus
- hard drives connected via USB and FireWire buses
- SSD drives connected via USB and FireWire buses
Starting encryption of removable drives
You can use a policy to decrypt a removable drive. A policy with defined settings for removable drive encryption is generated for a specific administration group. Therefore, the result of data decryption on removable drives depends on the computer to which the removable drive is connected.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports encryption in FAT32 and NTFS file systems. If a removable drive with an unsupported file system is connected to the computer, removable drive encryption ends with an error and Kaspersky Endpoint Security assigns read-only access for the removable drive.
Before encrypting files on a removable drive, make sure it is formatted and there are no hidden partitions (such as an EFI system partition). If the drive contains unformatted or hidden partitions, file encryption may fail with an error.
To encrypt removable drives:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Data Encryption → Encryption of removable drives.
- In the Encryption mode drop-down list, select the default action that you want Kaspersky Endpoint Security to perform on removable drives:
- Encrypt entire removable drive (FDE). Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts the contents of a removable drive sector by sector. As a result, the application encrypts not only the files stored on the removable drive but also its file systems, including the file names and folder structures on the removable drive.
- Encrypt all files (FLE). Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts all files that are stored on removable drives. The application does not encrypt the file systems of removable drives, including the names of files and folder structures.
- Encrypt new files only (FLE). Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts only those files that have been added to removable drives or that were stored on removable drives and have been modified after the Kaspersky Security Center policy was last applied.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not encrypt a removable drive that is already encrypted.
- If you want to use portable mode for encryption of removable drives, select the Portable mode check box.
Portable mode is a mode of file encryption (FLE) on removable drives that provides the ability to access data outside of a corporate network. Portable mode also lets you work with encrypted data on computers that do not have Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed.
- If you want to encrypt a new removable drive, it is recommended to select the Encrypt used disk space only check box. If the check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will encrypt all files, including the residual fragments of deleted or modified files.
- If you want to configure encryption for individual removable drives, define encryption rules.
- If you want to use full disk encryption of removable drives in offline mode, select the Allow encryption of removable drives in offline mode check box.
Offline encryption mode refers to encryption of removable drives (FDE) when there is no connection to Kaspersky Security Center. During encryption, Kaspersky Endpoint Security saves the master key only on the user's computer. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will send the master key to Kaspersky Security Center during the next synchronization.
If the computer on which the master key is saved is corrupted and data is not sent to Kaspersky Security Center, it is not possible to obtain access to the removable drive.
If the Allow encryption of removable drives in offline mode check box is cleared and there is no connection to Kaspersky Security Center, removable drive encryption is not possible.
- Save your changes.
After the policy is applied, when the user connects a removable drive or if a removable drive is already connected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security prompts the user for confirmation to perform the encryption operation (see the figure below).
The application lets you perform the following actions:
- If the user confirms the encryption request, Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts the data.
- If the user declines the encryption request, Kaspersky Endpoint Security leaves the data unchanged and assigns read-only access for this removable drive.
- If the user does not respond to the encryption request, Kaspersky Endpoint Security leaves the data unchanged and assigns read-only access for this removable drive. The application prompts for confirmation again when subsequently applying a policy or the next time this removable drive is connected.
If the user initiates safe removal of a removable drive during data encryption, Kaspersky Endpoint Security interrupts the data encryption process and allows removal of the removable drive before the encryption process has finished. Data encryption will be continued the next time the removable drive is connected to this computer.
If encryption of a removable drive failed, view the Data Encryption report in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface. Access to files may be blocked by another application. In this case, try unplugging the removable drive from the computer and connecting it again.
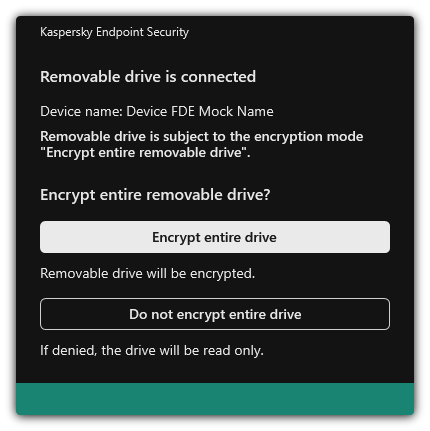
Removable drive encryption request
Page top
Adding an encryption rule for removable drives
To add an encryption rule for removable drives:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Data Encryption → Encryption of removable drives.
- Click the Add button, and in the drop-down list select one of the following items:
- If you want to add encryption rules for removable drives that are in the list of trusted devices of the Device Control component, select From list of trusted devices of this policy.
- If you want to add encryption rules for removable drives that are in the Kaspersky Security Center list, select From Kaspersky Security Center list of devices.
- In the Encryption mode for selected devices drop-down list, select the action to be performed by Kaspersky Endpoint Security on files stored on the selected removable drives.
- Select the Portable mode check box if you want Kaspersky Endpoint Security to prepare removable drives before encryption, making it possible to use encrypted files stored on them in portable mode.
Portable mode lets you use encrypted files stored on removable drives that are connected to computers without encryption functionality.
- Select the Encrypt used disk space only check box if you want Kaspersky Endpoint Security to encrypt only those disk sectors that are occupied by files.
If you are applying encryption on a drive that is already in use, it is recommended to encrypt the entire drive. This ensures that all data is protected - even deleted data that might still contain retrievable information. The Encrypt used disk space only function is recommended for new drives that have not been previously used.
If a device was previously encrypted using the Encrypt used disk space only function, after applying a policy in Encrypt entire removable drive mode, sectors that are not occupied by files will still not be encrypted.
- In the Actions for devices that were selected earlier drop-down list, select the action to be performed by Kaspersky Endpoint Security according to encryption rules that had been previously defined for removable drives:
- If you want the previously created encryption rule for the removable drive to remain unchanged, select Skip.
- If you want the previously created encryption rule for the removable drive to be replaced by the new rule, select Refresh.
- Save your changes.
The added encryption rules for removable drives will be applied to removable drives connected to any computers in the organization.
Page top
Exporting and importing a list of encryption rules for removable drives
You can export the list of removable drive encryption rules to an XML file. Then you can modify the file to, for example, add a large number of rules for the same type of removable drives. You can also use the export/import function to back up the list of rules or to migrate the rules to a different server.
How to export and import a list of removable drive encryption rules in the Web Console
Page top
Portable mode for accessing encrypted files on removable drives
Portable mode is a mode of file encryption (FLE) on removable drives that provides the ability to access data outside of a corporate network. Portable mode also lets you work with encrypted data on computers that do not have Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed.
Portable mode is convenient to use in the following cases:
- There is no connection between the computer and the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
- The infrastructure has changed with the change of the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security is not installed on the computer.
Portable File Manager
To work in portable mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security installs a special encryption module named Portable File Manager on a removable drive. The Portable File Manager provides an interface for working with encrypted data if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is not installed on the computer (see the figure below). If Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on your computer, you can work with encrypted removable drives using your usual file manager (for example, Explorer).
The Portable File Manager stores a key to encrypt files on a removable drive. The key is encrypted with the user password. The user sets a password before encrypting files on a removable drive.
The Portable File Manager starts automatically when a removable drive is connected to a computer on which Kaspersky Endpoint Security is not installed. If automatic startup of applications is disabled on the computer, manually start the Portable File Manager. To do so, run the file named pmv.exe that is stored on the removable drive.
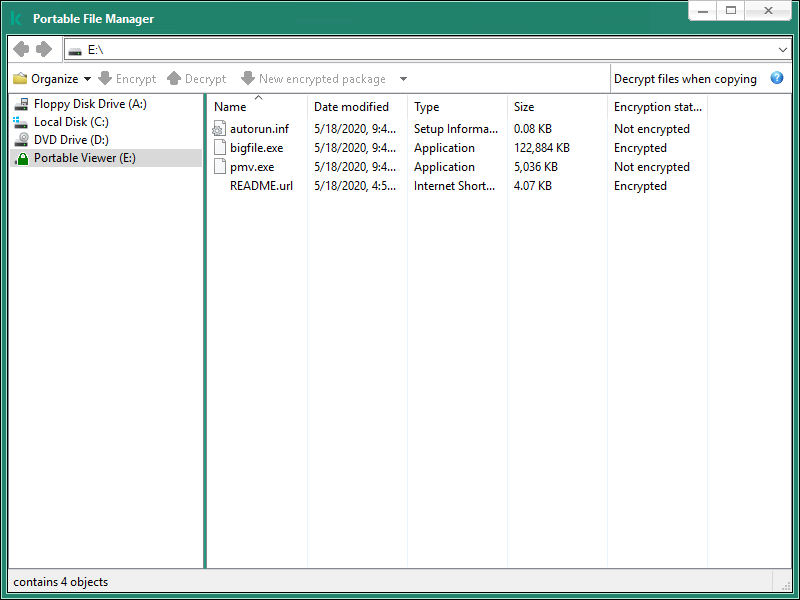
Portable File Manager
Support for portable mode for working with encrypted files
Kaspersky Endpoint Security will encrypt files on the removable drive. The Portable File Manager used for working with encrypted files will also be added to the removable drive. If there are already encrypted files on the removable drive, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will encrypt them again using its own key. This allows the user to access all files on the removable drive in portable mode.
Accessing encrypted files on a removable drive
After encrypting files on a removable drive with portable mode support, the following file access methods are available:
- If Kaspersky Endpoint Security is not installed on the computer, the Portable File Manager will prompt you to enter a password. You will need to enter the password each time you restart the computer or reconnect the removable drive.
- If the computer is located outside the corporate network and Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on the computer, the application will prompt you to enter the password or send the administrator a request to access the files. After gaining access to files on a removable drive, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will save the secret key in the computer's key storage. This will allow access to files in the future without entering a password or asking the administrator (see figure below).
- If the computer is located inside the corporate network and Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on the computer, you will get access to the device without entering a password. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will receive the secret key from the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server to which the computer is connected.
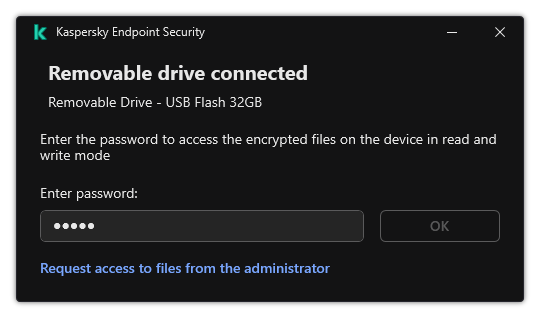
Accessing encrypted files on a removable drive
Recovering the password for working in portable mode
If you have forgotten the password for working in portable mode, you need to connect the removable drive to a computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed inside the corporate network. You will get access to the files because the secret key is stored in the computer's key storage or on the Administration Server. Decrypt and re-encrypt files with a new password.
Features of portable mode when connecting a removable drive to a computer from another network
If the computer is located outside the corporate network and Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on the computer, you can access the files in the following ways:
- Password-based access
After entering the password, you will be able to view, modify, and save files on the removable drive (transparent access). Kaspersky Endpoint Security can set a read-only access right for a removable drive if the following parameters are configured in the policy settings for encryption of removable drives:
- Portable mode support is disabled.
- The Encrypt all files or Encrypt new files only mode is selected.
In all other cases, you will get full access to the removable drive (read/write permission). You will be able to add and delete files.
You can change the removable drive access permissions even while the removable drive is connected to the computer. If the removable drive access permissions are changed, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block access to the files and prompt you for the password again.
After entering the password, you cannot apply encryption policy settings for the removable drive. In this case, it is impossible to decrypt or re-encrypt files on the removable drive.
- Ask the administrator for access to files
If you have forgotten the password for working in portable mode, ask the administrator for access to files. To access the files, the user needs to send the administrator a request access file (a file with the KESDC extension). The user can send the request access file by email, for example. The administrator will send an encrypted data access file (a file with the KESDR extension).
After you complete the Request-Response password recovery procedure, you will receive transparent access to files on the removable drive, and full access to the removable drive (read/write permission).
You can apply a removable drive encryption policy, and decrypt files, for example. After recovering the password or when the policy is updated, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will prompt you to confirm the changes.
How to obtain an encrypted data access file in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to obtain an encrypted data access file in the Web Console
Decryption of removable drives
You can use a policy to decrypt a removable drive. A policy with defined settings for removable drive encryption is generated for a specific administration group. Therefore, the result of data decryption on removable drives depends on the computer to which the removable drive is connected.
To decrypt removable drives:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Policies.
- Select the necessary policy and double-click to open the policy properties.
- In the policy window, select Data Encryption → Encryption of removable drives.
- If you want to decrypt all encrypted files that are stored on removable drives, in the Encryption mode drop-down list select Decrypt entire removable drive.
- To decrypt data that is stored on individual removable drives, edit the encryption rules for removable drives whose data you want to decrypt. To do so:
- In the list of removable drives for which encryption rules have been configured, select an entry corresponding to the removable drive you need.
- Click the Set a rule button to edit the encryption rule for the selected removable drive.
- In the context menu of the Set a rule button, click Decrypt entire removable drive.
- Save your changes.
As a result, if a user connects a removable drive or if it is already connected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security decrypts the removable drive. The application warns the user that the decryption process may take some time. If the user initiates safe removal of a removable drive during data decryption, Kaspersky Endpoint Security interrupts the data decryption process and allows removal of the removable drive before the decryption operation has finished. Data decryption will be continued the next time the removable drive is connected to the computer.
If decryption of a removable drive failed, view the Data Encryption report in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface. Access to files may be blocked by another application. In this case, try unplugging the removable drive from the computer and connecting it again.
Page top
Viewing data encryption details
While encryption or decryption in progress, Kaspersky Endpoint Security relays information about the status of encryption parameters applied to client computers to Kaspersky Security Center.
Viewing the encryption status
You can look at the status to monitor data encryption. Kaspersky Endpoint Security assigns the following encryption statuses:
- Does not meet the policy; canceled by user. The user has canceled data encryption.
- Does not meet the policy due to an error. Data encryption error, for example, a license is missing.
- Applying the policy. Reboot is required. Data encryption is in progress on the computer. Restart the computer to complete data encryption.
- No encryption policy specified. Data encryption is turned off in policy settings.
- Not supported. Data encryption components are not installed on the computer.
- Applying the policy. Data encryption and / or decryption is in progress on the computer.
To view the encryption status of computer data:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Managed Devices.
- On the Devices tab in the workspace, slide the scroll bar all the way to the right. If the Encryption status column is not displayed, add this column in Kaspersky Security Center console settings.
The Encryption status column shows the encryption status of data on computers in the selected administration group. This status is formed based on information about file encryption on local drives of the computer, and about full disk encryption.
- If the status of data encryption for the computer is Applying policy, you can monitor the encryption progress panel:
- Open the properties of the computer with the Applying policy status by double-clicking it.
- In the computer properties window, select the Applications section.
- In the list of Kaspersky applications installed on the computer, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- Click Statistics.
- Under Encryption of devices you can see the current progress of data encryption as a percentage.
Viewing encryption statistics on Kaspersky Security Center dashboards
To view the encryption status on Kaspersky Security Center dashboards:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- In the workspace to the right of the Administration Console tree, select the Statistics tab.
- Create a new page with details panes containing data encryption statistics. To do so:
- On the Statistics tab, click the Customize view button.
- In the window that opens, click the Add button.
- This opens a window; in that window, in the General section, enter the name of the page.
- In the Information panels section, click the Add button.
- In the window that opens in the Protection status group, select the Encryption of devices item.
- Click OK.
- If necessary, edit the settings of the details pane. To do so, use the View and Devices sections.
- Click OK.
- Repeat steps d – h of the instructions, selecting the Encryption of removable drives item in the Protection status section.
The details panes added appear in the Information panels list.
- Click OK.
The name of the page with details panes created at the previous steps appears in the Pages list.
- Click the Close button.
- On the Statistics tab, open the page that was created during the previous steps of the instructions.
The details panes appear, showing the encryption status of computers and removable drives.
Page top
Viewing file encryption errors on local computer drives
To view the file encryption errors on local computer drives:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Managed Devices.
- On the Devices tab, select the name of the computer in the list and right-click it to open the context menu.
- In the context menu of the computer, select the Properties item. In the window that opens, select the Protection section.
- Click the View data encryption errors link to open the Data encryption errors window.
This window shows the details of file encryption errors on local computer drives. When an error is corrected, Kaspersky Security Center removes the error details from the Data encryption errors window.
Page top
Viewing the data encryption report
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to create data encryption reports:
- Report on encryption status of managed devices. The report includes information on whether the encryption status of the computer complies with the encryption policy.
- Report on encryption status of mass storage devices. The report includes information about the encryption status of external devices and storage devices.
- Report on rights to access encrypted drives. The report includes information about the status of accounts that have access to encrypted drives.
- Report on file encryption errors. The report includes information about errors that occurred during the execution of data encryption or decryption tasks on computers.
- Report on blockage of access to encrypted files. The report includes information about applications being blocked from gaining access to encrypted files.
To view the data encryption report:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
- In the Administration Server node of the Administration Console tree, select the Reports tab.
- Click the New report template button.
The New Report Template Wizard starts.
- Follow the instructions of the Report Template Wizard. In the Selecting the report template type window in the Other section, select one of the data encryption reports.
After you have finished with the New Report Template Wizard, the new report template appears in the table on the Reports tab.
- Select the report template that was created at the previous steps of the instructions.
- In the context menu of the template, select Show report.
The report generation process starts. The report is displayed in a new window.
Page top
Working with encrypted devices when there is no access to them
Obtaining access to encrypted devices
A user may be required to request access to encrypted devices in the following cases:
- The hard drive was encrypted on a different computer.
- The encryption key for a device is not on the computer (for example, upon the first attempt to access the encrypted removable drive on the computer), and the computer is not connected to Kaspersky Security Center.
After the user has applied the access key to the encrypted device, Kaspersky Endpoint Security saves the encryption key on the user's computer and allows access to this device upon subsequent access attempts even if there is no connection to Kaspersky Security Center.
Access to encrypted devices can be obtained as follows:
- The user uses the Kaspersky Endpoint Security application interface to create a request access file with the kesdc extension and sends it to the corporate LAN administrator.
- The administrator uses the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console to create an access key file with the kesdr extension and sends it to the user.
- The user applies the access key.
Restoring data on encrypted devices
A user can use the Encrypted Device Restore Utility (hereinafter referred to as the Restore Utility) to work with encrypted devices. This may be required in the following cases:
- The procedure for using an access key to obtain access was unsuccessful.
- Encryption components have not been installed on the computer with the encrypted device.
The data needed to restore access to encrypted devices using the Restore Utility resides in the memory of the user's computer in unencrypted form for some time. To reduce the risk of unauthorized access to such data, you are advised to restore access to encrypted devices on trusted computers.
Data on encrypted devices can be restored as follows:
- The user uses the Restore Utility to create a request access file with the fdertc extension and sends it to the corporate LAN administrator.
- The administrator uses the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console to create an access key file with the fdertr extension and sends it to the user.
- The user applies the access key.
To restore data on encrypted system hard drives, the user can also specify the Authentication Agent account credentials in the Restore Utility. If the metadata of the Authentication Agent account has been corrupted, the user must complete the restoration procedure using a request access file.
Before restoring data on encrypted devices, it is recommended to cancel the Kaspersky Security Center policy or disable encryption in the Kaspersky Security Center policy settings on the computer where the procedure will be performed. This prevents the device from being encrypted again.
Recovering data by using the FDERT Restore Utility
If the hard drive fails, the file system may be corrupt. If this is the case, data protected by Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology will be unavailable. You can decrypt the data and copy the data to a new drive.
Data recovery on a drive protected by Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology consists of the following steps:
- Create a stand-alone Restore Utility (see the figure below).
- Connect a drive to a computer that does not have Kaspersky Endpoint Security encryption components installed.
- Run the Restore Utility and diagnose the hard drive.
- Access data on the drive. To do so, enter the credentials of the Authentication Agent or start the recovery procedure (Request-Response).
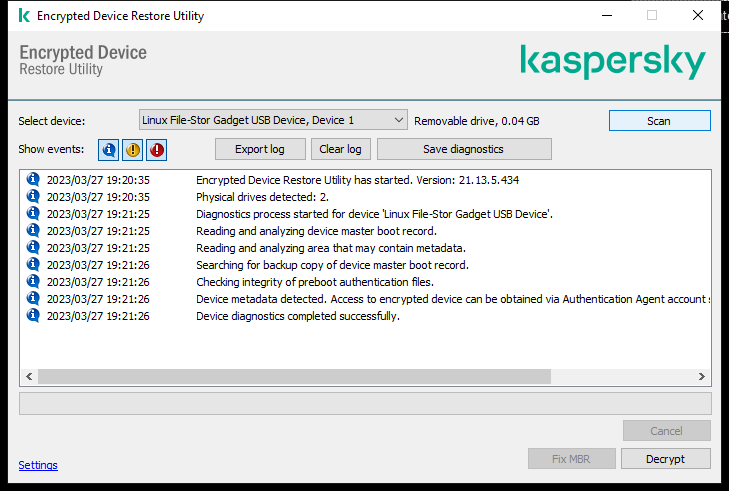
FDERT Restore Utility
Creating a standalone restore utility
To create the executable file of Restore Utility:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the window that opens, click the Restore encrypted device button.
Encrypted device Restore Utility starts.
- Click the Create Stand-alone Restore Utility button in the window of Restore Utility.
- Save the stand-alone Restore Utility to computer memory.
As a result, the executable file of the Restore Utility (fdert.exe) will be saved in the specified folder. Copy the Restore Utility to a computer that does not have Kaspersky Endpoint Security encryption components. This prevents the drive from being encrypted again.
The data needed to restore access to encrypted devices using the Restore Utility resides in the memory of the user's computer in unencrypted form for some time. To reduce the risk of unauthorized access to such data, you are advised to restore access to encrypted devices on trusted computers.
Recovering data on a hard drive
To restore access to an encrypted device using the Restore Utility:
- Run the file named fdert.exe, which is the executable file of the Restore Utility. This file is created by Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- In the Restore Utility window, select the encrypted device to which you want to restore access.
- Click the Scan button to allow the utility to define which of the actions should be taken on the device: whether it should be unlocked or decrypted.
If the computer has access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security encryption functionality, the Restore Utility prompts you to unlock the device. While unlocking the device does not decrypt it, the device becomes directly accessible as a result of being unlocked. If the computer does not have access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security encryption functionality, the Restore Utility prompts you to decrypt the device.
- If you want to import diagnostic information, click the Save diagnostics button.
The utility will save an archive with files containing diagnostic information.
- Click the Fix MBR button if diagnostics of the encrypted system hard drive has returned a message about problems involving the master boot record (MBR) of the device.
Fixing the master boot record of the device can speed up the process of obtaining information that is needed for unlocking or decrypting the device.
- Click the Unlock or Decrypt button depending on the results of diagnostics.
- If you want to restore data using an Authentication Agent account, select the Use Authentication Agent account settings option and enter the credentials of the Authentication Agent.
This method is possible only when restoring data on a system hard drive. If the system hard drive was corrupted and Authentication Agent account data has been lost, you must obtain an access key from the corporate LAN administrator to restore data on an encrypted device.
- If you want to start the recovery procedure, do the following:
- Select the Specify device access key manually option.
- Click the Receive access key button and save the request access file to computer memory (a file with the FDERTC extension).
- Send the request access file to the corporate LAN administrator.
Do not close the Receive device access key window until you have received the access key. When this window is opened again, you will not be able to apply the access key that was previously created by the administrator.
- Receive and save the access file (a file with the FDERTR extension) created and sent to you by the corporate LAN administrator (see the instructions below).
- Download the access file in the Receive device access key window.
- If you are decrypting a device, you must configure additional decryption settings:
- Specify area to decrypt:
- If you want to decrypt the entire device, select the Decrypt entire device option.
- If you want to decrypt a portion of the data on a device, select the Decrypt individual device areas option and specify the decryption area boundaries.
- Select the location for writing the decrypted data:
- If you want the data on the original device to be rewritten with the decrypted data, clear the Decrypt to a disk image file check box.
- If you want to save decrypted data separately from the original encrypted data, select the Decrypt to a disk image file check box and use the Browse button to specify the path where to save the VHD file.
- Specify area to decrypt:
- Click OK.
The device unlocking / decryption process starts.
How to create an encrypted data access file in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to create an encrypted data access file in the Web Console
Page top
Creating an operating system rescue disk
The operating system rescue disk can be useful when an encrypted hard drive cannot be accessed for some reason and the operating system cannot load.
You can load an image of the Windows operating system using the rescue disk and restore access to the encrypted hard drive using Restore Utility included in the operating system image.
To create an operating system rescue disk:
- Create an executable file for the Encrypted Device Restore Utility.
- Create a custom image of the Windows pre-boot environment. While creating the custom image of the Windows pre-boot environment, add the executable file of Restore Utility to the image.
- Save the custom image of the Windows pre-installation environment to bootable media such as a CD or removable drive.
Refer to Microsoft help files for instructions on creating a custom image of the Windows pre-boot environment (for example, in the Microsoft TechNet resource).
Detection and Response solutions
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports Detection and Response solutions using a built-in agent. To use Detection and Response, you must enable integration with these solutions when installing the application. The built-in agent supports:
- Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response (MDR);
- Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum 2.0 (EDR Optimum);
- Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert (EDR Expert);
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (Endpoint Detection and Response component);
- Kaspersky Sandbox 2.0.
You can use Kaspersky Endpoint Security with Detection and Response solution in different configurations, for example, [MDR+EDR Optimum 2.0+Kaspersky Sandbox 2.0].
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent supports interaction between the application and other Kaspersky solutions for detecting advanced threats (e.g. Kaspersky Sandbox). Kaspersky solutions are compatible with specific versions of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
To use Kaspersky Endpoint Agent as part of Kaspersky solutions, you must activate those solutions with a corresponding license key.
For complete information about the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent included in the software solution you are using, and for complete information about the standalone solution, please refer to the Help Guide of the relevant product:
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help
- Kaspersky Sandbox Help
- Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help
- Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help
- Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response Help
Distribution kit for Kaspersky Endpoint Security versions 11.2.0 – 11.8.0 includes Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. You can select Kaspersky Endpoint Agent when installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. As a result, two applications will be installed on your computer: KEA and KES. In Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.9.0 the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent distribution package is no longer part of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution kit.
Correspondence of KEA versions (as part of KES) to KES versions
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
|---|---|
11.8.0 |
3.11.0.216.mr1 |
11.7.0 |
3.11 |
11.6.0 |
3.10 |
11.5.0 |
3.9 |
11.4.0 |
3.9 |
11.3.0 |
3.9 |
11.2.0 |
3.9 |
Kaspersky is switching all Detection and Response to working with the Kaspersky Endpoint Security built-in agent instead of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. Kaspersky is gradually adding support for these solutions and phasing out Kaspersky Endpoint Agent (see table below). Starting with version 12.1, the application supports all Detection and Response solutions. In addition, starting with version 12.1, the application is no longer compatible with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, and installing both applications side by side on the same computer is no longer possible.
Deploying the built-in agent to manage Detection and Response solutions
Version of Kaspersky Endpoint Security |
Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response |
Kaspersky Sandbox |
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum |
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert |
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (Endpoint Detection and Response component) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
11.5.0 |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
11.6.0 |
Built-in agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
11.7.0 |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
11.8.0 |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
11.9.0 |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
11.10.0 |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
11.11.0 |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
12 |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
12.1 |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Built-in agent |
Policy and Task Migration for Kaspersky Endpoint Agent
Starting with version 11.7.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes a wizard for migrating from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to Kaspersky Endpoint Security. You can migrate policy and task settings for the following solutions:
- Kaspersky Sandbox
- Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum (EDR Optimum)
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (EDR)
A wizard for migrating from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to Kaspersky Endpoint Security works only in Web Console and Cloud Console. In the Administration Console (MMC), you can only migrate settings for Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (EDR) solution using the standard Kaspersky Security Center Policy and Task Migration Wizard.
It is recommended to begin with migrating Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to Kaspersky Endpoint Security on a single computer, then do it on a group of computers, and then complete the migration on all computers of the organization.
To migrate policy and task settings from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to Kaspersky Endpoint Security,
in the main window of the Web Console, select Operations → Migration from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
This runs the Policy and Task Migration Wizard. Follow the instructions of the Wizard.
Step 1. Policy migration
The Migration Wizard creates a new policy which merges the settings of Kaspersky Endpoint Security and Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policies. In the policy list, select Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policies whose settings you want to merge with the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy. Click a Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policy to select the Kaspersky Endpoint Security with which you want to merge settings. Make sure you selected the correct policies and go to the next step.
Step 2. Task migration
The Migration Wizard creates new tasks for Kaspersky Endpoint Security. In the task list, select Kaspersky Endpoint Agent tasks which you want to create for Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy. The Wizard supports tasks for Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response and Kaspersky Sandbox. Go to the next step.
Step 3. Wizard completion
Exit the Wizard. As a result, the wizard does the following:
- Creates a new Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
The policy merges settings from Kaspersky Endpoint Security and Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. The policy is called <Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy name> & <Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policy name>. The new policy has the Inactive status. To continue, change the statuses of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and Kaspersky Endpoint Security policies to Inactive and activate the new merged policy.
After migrating from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, please make sure that the new policy has the functionality for data transfer to the Administration Server (quarantine file data and threat development chain data) set up. Data transfer parameter values are not migrated from a Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policy.
When migrating from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (EDR) solution, you may encounter errors when connecting the computer to Central Node servers. The reason is that the migration wizard in Web Console skips the following policy settings and does not migrate them:
- Settings modification prohibition Settings for connecting to KATA servers ("lock").
By default, settings can be modified (the "lock" is open). Therefore the settings are not applied on the computer. You must prohibit the modification of settings and close the "lock".
- Crypto-container.
If you are using two-way authentication for connecting to Central Node servers, you must re-add the crypto-container. The migration wizard correctly migrates the TLS certificate of the server.
The Policy and Task Migration Wizard in Administration Console (MMC) migrates all settings for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (EDR) solution.
- Settings modification prohibition Settings for connecting to KATA servers ("lock").
- Creates new Kaspersky Endpoint Security tasks.
New tasks are copies of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent tasks for Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response and Kaspersky Sandbox. At the same time, the Wizard leaves Kaspersky Endpoint Agent tasks unchanged.
Migrating the [KES+KEA] configuration to [KES+built-in agent] configuration
Kaspersky Endpoint Security includes built-in agents for working with Detection and Response solutions. You no longer need a separate Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application to work with these solutions. When you deploy Kaspersky Endpoint Security on computers that have Kaspersky Endpoint Agent installed, Detection and Response solutions will continue working with Kaspersky Endpoint Security. In addition, the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is removed from the computer.
Distribution kit for Kaspersky Endpoint Security versions 11.2.0 – 11.8.0 includes Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. You can select Kaspersky Endpoint Agent when installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. As a result, two applications will be installed on your computer: KEA and KES. In Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.9.0 the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent distribution package is no longer part of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution kit.
Migrating the [KES+KEA] configuration to [KES+built-in agent] involves the following steps:
- Upgrading Kaspersky Security Center
Upgrade all Kaspersky Security Center components to version 13.2 or higher, including the Administration Agent on user computers and Web Console.
- Upgrading the Kaspersky Endpoint Security web plug-in
In Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, upgrade the Kaspersky Endpoint Security web plug-in to version 11.7.0 or higher. To manage EDR Optimum and Kaspersky Sandbox components, you must use Web Console.
To use Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (EDR), you will need a web plug-in for Kaspersky Endpoint Security version 12.1 or later.
- Migrating the policy and tasks
Use the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent Policy and Task Migration Wizard to migrate Kaspersky Endpoint Agent settings to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
This creates a new Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy. The new policy has the Inactive status. To apply the policy, open policy properties, accept the Kaspersky Security Network Statement and set the status to Active.
- Licensing functionality
If you use a common Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum or Kaspersky Optimum Security license to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows and Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, EDR Optimum functionality will be activated automatically after upgrading the application to version 11.7.0. You do not need to do anything else.
If you use a stand-alone Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Add-on license to activate EDR Optimum functionality, you must make sure that the EDR Optimum key is added to the Kaspersky Security Center repository and the automatic license key distribution functionality is enabled. After you upgrade the application to version 11.7.0, EDR Optimum functionality is activated automatically.
If you use a Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum or Kaspersky Optimum Security license to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, and a different license to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, you must replace the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows key with the common Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum or Kaspersky Optimum Security key. You can replace the key using the Add key task.
You do not need to activate Kaspersky Sandbox functionality. Kaspersky Sandbox functionality will be available immediately after upgrading and activating Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
Only the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform license can be used to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security as part of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform solution. After you upgrade the application to version 12.1, EDR (KATA) functionality is activated automatically. You do not need to do anything else.
- Upgrading the Kaspersky Endpoint Security application
To upgrade the application and migrate EDR Optimum and Kaspersky Sandbox functionality, a remote installation task is recommended.
To upgrade the application using a remote installation task, you must edit the following settings:
- Select components for Detection and Response solutions in the settings of the installation package.
- Exclude the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component in the settings of the installation package (for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows versions 11.2.0 – 11.8.0).
You can also upgrade the application using the following methods:
- Using Kaspersky update service (Seamless Update – SMU).
- Locally, by using the Setup Wizard.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports automatically selecting components when upgrading the application on a computer with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application installed. The automatic selection of components depends on the permissions of the user account that is upgrading the application.
If you are upgrading Kaspersky Endpoint Security using the EXE or MSI file under the system account (SYSTEM), Kaspersky Endpoint Security gains access to current licenses of Kaspersky solutions. Therefore, if the computer has, for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent installed and the EDR Optimum solution activated, the Kaspersky Endpoint Security installer automatically configures the set of components and selects the EDR Optimum component. This makes Kaspersky Endpoint Security switch to using the built-in agent and removes Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. Running the MSI installer under the system account (SYSTEM) is usually performed when upgrading via the Kaspersky update service (SMU) or when deploying an installation package via Kaspersky Security Center.
If you are upgrading Kaspersky Endpoint Security using an MSI file under a non-privileged user account, Kaspersky Endpoint Security lacks access to current licenses of Kaspersky solutions. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically selects components based on Kaspersky Endpoint Agent configuration. After that Kaspersky Endpoint Security switches to using the built-in agent and removes Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Computer restart
Restart your computer to finish upgrading the application with the built-in agent. When upgrading the application, the installer removes Kaspersky Endpoint Agent before the computer is restarted. After the computer is restarted, the installer adds the built-in agent. This means that Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not perform the functions of EDR and Kaspersky Sandbox until the computer is restarted.
- Checking the health of Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum and Kaspersky Sandbox
If after the upgrade, the computer has the Critical status in the Kaspersky Security Center console:
- Make sure that the computer has Administration Agent version 13.2 or higher installed.
- Check the operating status of the built-in agent by viewing the Application components status report. If a component has the Not installed status, install the component using the Change application components task.
- Make sure you accept the Kaspersky Security Network Statement in the new policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- Make sure EDR Optimum functionality is activated using the Application components status report. If a component has the Not covered by license status, make sure that the automatic license key distribution functionality of EDR Optimum is turned on.
Managed Detection and Response
|
Starting with version 11.6.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes a built-in agent for the Managed Detection and Response solution. The Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response (MDR) solution automatically detects and analyzes security incidents in your infrastructure. To do so, MDR uses telemetry data received from endpoints and machine learning. MDR sends incident data to Kaspersky experts. The experts can then process the incident and, for example, add a new entry to Anti-Virus databases. Alternatively, the experts can issue recommendations on processing the incident and, for example, suggest isolating computer from the network. For detailed information about how the solution works, please refer to the Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response Help. |
Integration with MDR
To set up integration with Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response, you must enable the Managed Detection and Response component and configure Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
You must enable the following components for Managed Detection and Response to work:
Enabling these components is non-optional. Otherwise Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response cannot function because it does not receive required telemetry data.
In addition, Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response uses data received from other application components. Enabling those components is optional. Components that provide additional data include:
For Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response to work with Administration Server via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you must also establish a new secure connection, a background connection. Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response prompts you to establish a background connection when you deploy the solution. Make sure the background connection is established. For details about the integration of Kaspersky Security Center with other Kaspersky solutions, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
Integration with Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response consists of the following steps:
- Configuring Kaspersky Private Security Network
Skip this step if you are using Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console automatically configures Kaspersky Private Security Network when installing the MDR plug-in.
Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN) is a solution that enables users of computers hosting Kaspersky Endpoint Security or other Kaspersky applications to obtain access to Kaspersky reputation databases, and to other statistical data without sending data to Kaspersky from their own computers.
Upload the Kaspersky Security Network configuration file in the Administration Server properties. The Kaspersky Security Network configuration file is located within the ZIP archive of the MDR configuration file. You can obtain the ZIP archive in the Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response Console. For details on configuring Kaspersky Private Security Network, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help. You can also upload a Kaspersky Security Network configuration file to the computer from the command line (see the instructions below).
How to configure Kaspersky Private Security Network from the command line
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will use Kaspersky Private Security Network to determine the reputation of files, applications, and websites. Kaspersky Security Network section of the policy settings will display the following operating status: KSN provider: Kaspersky Private Security Network.
You must enable extended KSN mode for Managed Detection and Response to work.
- Enabling Managed Detection and Response component
Load the BLOB configuration file in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy (see the instructions below). The BLOB file contains the client ID and information about the license for Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response. The BLOB file is located inside the ZIP archive of the MDR configuration file. You can obtain the ZIP archive in the Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response Console. For detailed information about a BLOB file, please refer to the Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response Help.
How to enable Managed Detection and Response component in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to enable Managed Detection and Response component in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to enable Managed Detection and Response component from the command line
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will verify the BLOB file. BLOB file verification includes checking the digital signature and the license term. If the BLOB file is successfully verified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will upload the file and send the file to the computer during the next synchronization with Kaspersky Security Center. Check the operating status of the component by viewing the Application components status report. You can also view the operating status of a component in reports in the local interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. The Managed Detection and Response component will be added to the list of Kaspersky Endpoint Security components.
Migration from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent
Kaspersky Endpoint Security version 11 and later supports the MDR solution. Kaspersky Endpoint Security versions 11 – 11.5.0 only sends telemetry data to Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response to enable threat detection. Kaspersky Endpoint Security version 11.6.0 has all the functionality of the built-in agent (Kaspersky Endpoint Agent).
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11 – 11.5.0, you must update databases to the latest version to work with the MDR solution. You must also install Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.6.0 or later, you do not need to install Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to use the MDR solution.
To migrate from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows:
- Configure integration with Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
- Disable the Managed Detection and Response component in the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policy.
If the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy also applies to computers that do not have Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11 – 11.5.0 installed, you must first create a separate Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policy for those computers. In the new policy, configure integration with Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response.
Page top
Endpoint Detection and Response
|
Starting with version 11.7.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes a built-in agent for the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum solution (hereinafter also "EDR Optimum"). Starting with version 11.8.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes a built-in agent for the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert solution (hereinafter also "EDR Expert"). Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response is a range of solutions for protecting the corporate IT infrastructure from advanced cyber threats. The functionality of the solutions combines automatic detection of threats with the ability to react to these threats to counteract advanced attacks including new exploits, ransomware, fileless attacks, as well as methods using legitimate system tools. EDR Expert offers more threat monitoring and response functionality than EDR Optimum. For details about the solutions, see the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help and the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help. Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response reviews and analyses threat development and provides security personnel or the Administrator with information about the potential attack that is necessary for a timely response. Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response displays alert details in a separate window. Alert Details is a tool for viewing the entirety of collected information about a detected threat. Alert details include, for example, the history of files appearing on the computer. For details about managing alert details, refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help and the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help. |
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response uses the following Threat Intelligence tools:
- The Kaspersky Security Network (hereinafter also referred to as "KSN") cloud service infrastructure, which provides access to real-time file, website, and software reputation information from the Kaspersky knowledge base. Using data from Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky applications to threats, improves the performance of some protection components, and reduces the likelihood of false positives. EDR Expert uses the Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN) solution, which sends data to regional servers without sending data from devices to the KSN.
- Integration with the Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal portal, which contains and displays information about the reputation of files and web addresses.
- Kaspersky Threats database.
- Cloud Sandbox technology that lets you run detected files in an isolated environment and check their reputation.
Integration with Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response
To integrate with Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response, you must add the Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum (EDR Optimum) component or the Endpoint Detection and Response Expert (EDR Expert) component, and configure Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
EDR Optimum, EDR Expert and EDR (KATA) components are not compatible with each other.
The following conditions must be fulfilled for Endpoint Detection and Response to work:
- Kaspersky Security Center version 13.2 or higher. In earlier versions of Kaspersky Security Center, it is impossible to activate the Endpoint Detection and Response feature.
- EDR Optimum can be managed in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
EDR Expert can be managed only using the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. You cannot manage this functionality using the Administration Console (MMC).
- The application is activated and the functionality is covered by the license.
- The Endpoint Detection and Response component is turned on.
- Application components that Endpoint Detection and Response depends on are enabled and operational. Endpoint Detection and Response depends on the following components:
Integration with Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response involves the following steps:
- Installing Endpoint Detection and Response components
You can select the EDR Optimum or EDR Expert component during installation or upgrade, as well as using the Change application components task.
You must restart your computer to finish upgrading the application with the new components.
- Activating Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response
You can acquire a license to use Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response in the following ways:
- Endpoint Detection and Response functionality is included in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows license.
The feature will be available immediately after activation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- Purchasing a separate license for EDR Optimum or EDR Expert (Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Add-on).
The feature will be available after you add a separate key for Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response. As a result, two keys are installed on the computer: a key for Kaspersky Endpoint Security and a key for Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response.
Licensing for the stand-alone Endpoint Detection and Response functionality is the same as the licensing of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Make sure that the EDR Optimum or EDR Expert functionality is included in the license and is running in the local interface of the application.
- Endpoint Detection and Response functionality is included in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows license.
- Enabling Endpoint Detection and Response components
You can enable or disable the component in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy settings.
The Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response component is enabled. Check the operating status of the component by viewing the Application components status report. You can also view the operating status of a component in reports in the local interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. The Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum or Endpoint Detection and Response Expert component is added to the list of Kaspersky Endpoint Security components.
- Enabling data transfer to Administration Server
To enable all the Endpoint Detection and Response features, data transfer must be enabled for the following types of data:
- Quarantine file data.
The data are required to obtain information about files quarantined on a computer through Web Console and Cloud Console. For example, you can download a file from quarantine for analysis in Web Console and Cloud Console.
- Threat development chain data.
The data are required to obtain information about threats detected on a computer in Web Console and Cloud Console. You can view alert details and take response actions in Web Console and Cloud Console.
How to enable data transfer to the Administration Server in Web Console and Cloud Console
- Quarantine file data.
Migration from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.7.0 or newer with the EDR Optimum component (built-in agent) installed, the support of integration with Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum solution is instantly available after the installation. The EDR Optimum component is not compatible with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. If Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is installed on the computer, when Kaspersky Endpoint Security is updated to version 11.7.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum continues working with Kaspersky Endpoint Security (migrating the [KES+KEA] configuration to [KES+built-in agent]). In addition, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent will be removed from the computer. To complete migration from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, you need to transfer policy and task settings using the Migration Wizard.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.4.0–11.6.0 for interoperability with Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum, the application includes Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. You can install Kaspersky Endpoint Agent side-by-side with Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Distribution kit for Kaspersky Endpoint Security versions 11.2.0 – 11.8.0 includes Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. You can select Kaspersky Endpoint Agent when installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. As a result, two applications will be installed on your computer: KEA and KES. In Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.9.0 the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent distribution package is no longer part of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution kit.
The Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert solution does not support interoperability with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. The Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert solution uses Kaspersky Endpoint Security with built-in agent (version 11.8.0 and later).
The EDR Optimum component as part of Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports interaction with the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum 2.0 solution. Interaction with Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum version 1.0 is not supported.
Page top
Scan for indicators of compromise (standard task)
An Indicator of Compromise (IOC) is a set of data about an object or activity that indicates unauthorized access to the computer (compromise of data). For example, many unsuccessful attempts to sign in to the system can constitute an Indicator of Compromise. The IOC Scan task allows finding Indicators of Compromise on the computer and taking threat response measures.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security searches for indicators of compromise using IOC files. IOC files are files containing the sets of indicators that the application tries to match to count a detection. IOC files must conform to the OpenIOC standard.
IOC Scan task run mode
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response lets you create standard IOC Scan tasks to detect compromised data. Standard IOC scan task is a group or local task that is created and configured manually in the Web Console. Tasks are run using IOC files prepared by the user. If you want to add an indicator of compromise manually, please read the requirements for IOC files.
The file that you can download by clicking the link below, contains a table with the full list of IOC terms of the OpenIOC standard.
![]() DOWNLOAD THE IOC_TERMS.XLSX FILE
DOWNLOAD THE IOC_TERMS.XLSX FILE
Kaspersky Endpoint Security also supports stand-alone IOC scan tasks when the application is used as part of the Kaspersky Sandbox solution.
Creating an IOC Scan task
You can create IOC Scan tasks manually:
- In alert details (only for EDR Optimum).
Alert Details is a tool for viewing the entirety of collected information about a detected threat. Alert details include, for example, the history of files appearing on the computer. For details about managing alert details, refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help and the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help.
- Using the Task Wizard.
You can configure the task for EDR Optimum in Web Console and Cloud Console. Task settings for EDR Expert are available only in Cloud Console.
To create a IOC Scan task:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Tasks.
The list of tasks opens.
- Click the Add button.
The Task Wizard starts.
- Configure the task settings:
- In the Application drop-down list, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (12.1).
- In the Task type drop-down list, select IOC Scan.
- In the Task name field, enter a brief description.
- In the Select devices to which the task will be assigned block, select the task scope.
- Select devices according to the selected task scope option. Go to the next step.
- Enter the account credentials of the user whose rights you want to use to run the task. Go to the next step.
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the task as the system user account (SYSTEM).
The system account (SYSTEM) does not have permission to perform the IOC Scan task on network drives. If you want to run the task for a network drive, select the account of a user that has access to that drive.
For standalone IOC Scan tasks on network drives, in the task properties you need to manually select the user account that has access to this drive.
- Exit the Wizard.
A new task will be displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the new task.
The task properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- Go to the IOC scan settings section.
- Load the IOC files to search for indicators of compromise.
After loading the IOC files, you can view the list of indicators from IOC files.
Adding or removing IOC files after running the task is not recommended. This can cause the IOC scan results to display incorrectly for prior runs of the task. To search indicators of compromise by new IOC files, it is recommended to add new tasks.
- Configure actions on IOC detection:
- Isolate computer from the network. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security isolates the computer from the network to prevent the threat from spreading. You can configure the duration of the isolation in Endpoint Detection and Response component settings.
- Move copy to Quarantine, delete object. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes the malicious object found on the computer. Before deleting the object, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates a backup copy in case the object needs to be restored later. Kaspersky Endpoint Security moves the backup copy to Quarantine.
- Run scan of critical areas. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs the Critical Areas Scan task. By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the kernel memory, running processes, and disk boot sectors.
- Go to the Advanced section.
- Select data types (IOC documents) that must be analyzed as part of the task.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically selects data types (IOC documents) for the IOC Scan task in accordance with the content of loaded IOC files. It is not recommended to deselect data types.
You can additionally configure scan scopes for the following data types:
- Files - FileItem. Set an IOC scan scope on the computer using preset scopes.
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans for IOCs only in important areas of the computer, such as the Downloads folder, the desktop, the folder with temporary operating system files, etc. You can also manually add the scan scope.
- Windows event logs - EventLogItem. Enter the time period when the events were logged. You can also select which Windows event logs must be used for IOC scanning. By default, the following event logs are selected: application event log, system event log, and security event log.
For the Windows registry - RegistryItem data type, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans a set of registry keys.
- Files - FileItem. Set an IOC scan scope on the computer using preset scopes.
- In the task properties window, select the Schedule tab.
- Configure the task schedule.
Wake-on-LAN is not available for this task. Make sure the computer is turned on to run the task.
- Save your changes.
- Select the check box next to the task.
- Click the Run button.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs the search for indicators of compromise on the computer. You can view the results of the task in task properties in the Results section. You can view the information about detected indicators of compromise in the task properties: Application settings → IOC Scan Results.
IOC scan results are kept for 30 days. After this period, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes the oldest entries.
Page top
Move file to Quarantine
When reacting to threats, Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response can create Move file to Quarantine tasks. This is necessary to minimize the consequences of the threat. Quarantine is a special local storage on the computer. The user can quarantine files that the user considers dangerous for the computer. Quarantined files are stored in an encrypted state and do not threaten the security of the device. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses Quarantine only when working with Detection and Response solutions: EDR Optimum, EDR Expert, KATA (EDR), Kaspersky Sandbox. In other cases Kaspersky Endpoint Security places the relevant file in Backup. For details on managing Quarantine as part of solutions, please refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox Help, Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help, and Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help.
You can create Move file to Quarantine tasks in the following ways:
- In alert details (only for EDR Optimum).
Alert Details is a tool for viewing the entirety of collected information about a detected threat. Alert details include, for example, the history of files appearing on the computer. For details about managing alert details, refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help and the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help.
- Using the Task Wizard.
You must enter the file path or hash (SHA256 or MD5), or both the file path and the file hash.
The Move file to Quarantine task has the following limitations:
- The file size must not exceed 100 MB.
- System Critical Objects (SCO) cannot be quarantined. SCOs are files that the operating system and the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows application require to be able to run.
- You can configure the task for EDR Optimum in Web Console and Cloud Console. Task settings for EDR Expert are available only in Cloud Console.
To create a Move file to Quarantine task:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Tasks.
The list of tasks opens.
- Click the Add button.
The Task Wizard starts.
- Configure the task settings:
- In the Application drop-down list, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (12.1).
- In the Task type drop-down list, select Move file to Quarantine.
- In the Task name field, enter a brief description.
- In the Select devices to which the task will be assigned block, select the task scope.
- Select devices according to the selected task scope option. Click the Next button.
- Enter the account credentials of the user whose rights you want to use to run the task. Click the Next button.
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the task as the system user account (SYSTEM).
- Finish the wizard by clicking the Finish button.
A new task will be displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the new task.
The task properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- In the list of files, click Add.
The file adding wizard starts.
- To add the file, you must enter the full path to the file, or both file hash and the path.
If the file is located on a network drive, enter the file path starting with
\\, and not the drive letter. For example,\\server\shared_folder\file.exe. If the file path contains a network drive letter, you can get a File not found error. - In the task properties window, select the Schedule tab.
- Configure the task schedule.
Wake-on-LAN is not available for this task. Make sure the computer is turned on to run the task.
- Click the Save button.
- Select the check box next to the task.
- Click the Run button.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security moves the file to Quarantine. If the file is locked by a different process, the task is displayed as Completed, but the file itself is quarantined only after the computer is restarted. After restarting the computer, confirm that the file is deleted.
The Move file to Quarantine task can finish with the Access denied error if you are trying to quarantine an executable file that is currently running. Create a terminate process task for the file and try again.
The Move file to Quarantine task can finish with the Not enough space in Quarantine storage error if you are trying to quarantine a file that is too large. Empty the Quarantine or make Quarantine larger. Then try again.
You can restore a file from Quarantine or empty the Quarantine using Web Console. You can restore objects locally on the computer using the command line.
Page top
Get file
You can get files from user computers. For example, you can configure getting an event log file created by a third-party application. To get the file, you must create a dedicated task. As a result of the execution of the task, the file is saved in Quarantine. You can download this file from Quarantine to your computer using Web Console. On the user's computer, the file remains in its original folder.
The file size must not exceed 100 MB.
You can configure the task for EDR Optimum in Web Console and Cloud Console. Task settings for EDR Expert are available only in Cloud Console.
To create a Get file task:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Tasks.
The list of tasks opens.
- Click the Add button.
The Task Wizard starts.
- Configure the task settings:
- In the Application drop-down list, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (12.1).
- In the Task type drop-down list, select Get file.
- In the Task name field, enter a brief description.
- In the Select devices to which the task will be assigned block, select the task scope.
- Select devices according to the selected task scope option. Click the Next button.
- Enter the account credentials of the user whose rights you want to use to run the task. Click the Next button.
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the task as the system user account (SYSTEM).
- Finish the wizard by clicking the Finish button.
A new task will be displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the new task.
The task properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- In the list of files, click Add.
The file adding wizard starts.
- To add the file, you must enter the full path to the file, or both file hash and the path.
If the file is located on a network drive, enter the file path starting with
\\, and not the drive letter. For example,\\server\shared_folder\file.exe. If the file path contains a network drive letter, you can get a File not found error. - In the task properties window, select the Schedule tab.
- Configure the task schedule.
Wake-on-LAN is not available for this task. Make sure the computer is turned on to run the task.
- Click the Save button.
- Select the check box next to the task.
- Click the Run button.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates a copy of the file and moves that copy to Quarantine. You can download the file from Quarantine in Web Console.
Page top
Delete file
You can remotely delete files using the Delete file task. For example, you can remotely delete a file when responding to threats.
The Delete file task has the following limitations:
- System Critical Objects (SCO) cannot be deleted. SCOs are files that the operating system and the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows application require to be able to run.
- You can configure the task for EDR Optimum in Web Console and Cloud Console. Task settings for EDR Expert are available only in Cloud Console.
To create a Delete file task:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Tasks.
The list of tasks opens.
- Click the Add button.
The Task Wizard starts.
- Configure the task settings:
- In the Application drop-down list, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (12.1).
- In the Task type drop-down list, select Delete file.
- In the Task name field, enter a brief description.
- In the Select devices to which the task will be assigned block, select the task scope.
- Select devices according to the selected task scope option. Click the Next button.
- Enter the account credentials of the user whose rights you want to use to run the task. Click the Next button.
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the task as the system user account (SYSTEM).
- Finish the wizard by clicking the Finish button.
A new task will be displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the new task.
The task properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- In the list of files, click Add.
The file adding wizard starts.
- To add the file, you must enter the full path to the file, or both file hash and the path.
If the file is located on a network drive, enter the file path starting with
\\, and not the drive letter. For example,\\server\shared_folder\file.exe. If the file path contains a network drive letter, you can get a File not found error. - In the task properties window, select the Schedule tab.
- Configure the task schedule.
Wake-on-LAN is not available for this task. Make sure the computer is turned on to run the task.
- Click the Save button.
- Select the check box next to the task.
- Click the Run button.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes the file from the computer. If the file is locked by a different process, the task is displayed as Completed, but the file itself is deleted only after the computer is restarted. After restarting the computer, confirm that the file is deleted.
The Delete file task can finish with the Access denied error if you are trying to delete an executable file that is currently running. Create a terminate process task for the file and try again.
Page top
Process start
You can remotely run files using the Start process task. For example, you can remotely run an utility that creates the computer configuration file. Next you can use the Get file task to receive the created file in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
You can configure the task for EDR Optimum in Web Console and Cloud Console. Task settings for EDR Expert are available only in Cloud Console.
To create a Start process task:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Tasks.
The list of tasks opens.
- Click Add.
The Task Wizard starts.
- Configure the task settings:
- In the Application drop-down list, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (12.6).
- In the Task type drop-down list, select Start process.
- In the Task name field, enter a brief description.
- In the Select devices to which the task will be assigned block, select the task scope.
- Select devices according to the selected task scope option. Click Next.
- Enter the account credentials of the user whose rights you want to use to run the task. Click Next.
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the task as the system user account (SYSTEM).
- Finish the wizard by clicking the Finish button.
A new task will be displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the new task.
- The task properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- Enter the process start command.
Suppose you want to run an utility (
utility.exe) that saves the information about the computer's configuration to a file namedconf.txtin the current folder (by default). The utility is in theC:\Users\admin\Diagnostic\folder. You must save the configuration file in theC:\Users\admin\Documents\Configurationfolder. Enter the following values:- Executable command –
C:\Users\admin\Diagnostic\utility.exe - Command line arguments (optional) –
/R conf.txt - Path to the working folder (optional) –
C:\Users\admin\Documents\Configuration
- Executable command –
- In the task properties window, select the Schedule tab.
- Configure the task schedule.
Wake-on-LAN is not available for this task. Make sure the computer is turned on to run the task.
- Click the Save button.
- Select the check box next to the task.
- Click Start.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs the command in silent mode and starts the process. You can view the results of the task in task properties in the Execution results section.
Page top
Terminate process
You can remotely terminate processes using the Terminate process task. For example, you can remotely terminate an Internet speed testing utility that was started using the Run process task.
If you want to prohibit running a file, you can configure the Execution prevention component. You can prohibit the execution of executable files, scripts, office format files.
The Terminate process task has the following limitations:
- Processes of System Critical Objects (SCO) cannot be terminated. SCOs are files that the operating system and the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows application require to be able to run.
- You can configure the task for EDR Optimum in Web Console and Cloud Console. Task settings for EDR Expert are available only in Cloud Console.
To create a Terminate process task:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Tasks.
The list of tasks opens.
- Click the Add button.
The Task Wizard starts.
- Configure the task settings:
- In the Application drop-down list, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (12.1).
- In the Task type drop-down list, select Terminate process.
- In the Task name field, enter a brief description.
- In the Select devices to which the task will be assigned block, select the task scope.
- Select devices according to the selected task scope option. Click the Next button.
- Enter the account credentials of the user whose rights you want to use to run the task. Click the Next button.
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the task as the system user account (SYSTEM).
- Finish the wizard by clicking the Finish button.
A new task will be displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the new task.
The task properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- To complete the process, you must select the file that you want to terminate. You can select a file in one of the following ways:
- Enter the full name to the file.
- Enter the hash of the file and the path to the file.
- Enter the PID of the process (only for local tasks).
If the file is located on a network drive, enter the file path starting with
\\, and not the drive letter. For example,\\server\shared_folder\file.exe. If the file path contains a network drive letter, you can get a File not found error. - In the task properties window, select the Schedule tab.
- Configure the task schedule.
Wake-on-LAN is not available for this task. Make sure the computer is turned on to run the task.
- Click the Save button.
- Select the check box next to the task.
- Click the Run button.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security terminates the process on the computer. For example, if a 'GAME' application is running and you terminate the game.exe process, the application is closed without saving data. You can view the results of the task in task properties in the Results section.
Page top
Execution prevention
Execution prevention allows managing the running of executable files and scripts, as well as opening office format files. In this way, you can, for example, prevent the execution of applications that you consider insecure. As a result, the spreading of the threat can be stopped. Execution prevention supports a set of office file extensions and a set of script interpreters.
Execution prevention rule
Execution prevention manages user access to files with execution prevention rules. Execution prevention rule is a set of criteria that the application takes into account when reacting to an object execution, for example when blocking object execution. The application identifies files by their paths or checksums calculated using MD5 and SHA256 hashing algorithms.
You can create Execution prevention rules:
- In alert details (only for EDR Optimum).
Alert Details is a tool for viewing the entirety of collected information about a detected threat. Alert details include, for example, the history of files appearing on the computer. For details about managing alert details, refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help and the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help.
- Using a group policy or local application settings.
You must enter the file path or hash (SHA256 or MD5), or both the file path and the file hash.
You can also manage Execution prevention locally using the command line.
Execution prevention has the following limitations:
- Prevention rules do not cover files on CDs or in ISO images. The application does not block execution or opening of these files.
- It is impossible to block the startup of system-critical objects (SCO). SCOs are files that the operating system and the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows application require to be able to run.
- It is not recommended to create more than 5000 run prevention rules, as this can cause system instability.
Execution prevention rule modes
The Execution prevention component can work in two modes:
- Statistics only
In this mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security publishes an event about attempts to run executable objects or open documents that match prevention rule criteria to the Windows event log and Kaspersky Security Center, but does not block the attempt to run or open the object or document. This mode is selected by default.
- Active
In this mode, the application blocks the execution of objects or opening of documents that match prevention rule criteria. The application also publishes an event about attempts to execute objects or open documents to the Windows event log and Kaspersky Security Center event log.
Managing Execution prevention
You can configure the component settings only in the Web Console.
To prevent execution:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Policies & Profiles.
- Click the name of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
The policy properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- Go to Detection and Response → Endpoint Detection and Response.
- Turn on the Execution Prevention ENABLED toggle.
- In the Action on execution or opening of forbidden object block, select the component operating mode:
- Block and write to report. In this mode, the application blocks the execution of objects or opening of documents that match prevention rule criteria. The application also publishes an event about attempts to execute objects or open documents to the Windows event log and Kaspersky Security Center event log.
- Log events only. In this mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security publishes an event about attempts to run executable objects or open documents that match prevention rule criteria to the Windows event log and Kaspersky Security Center, but does not block the attempt to run or open the object or document. This mode is selected by default.
- Create a list of execution prevention rules:
- Click Add.
- This opens a window; in this window, enter the name of the execution prevention rule (for example, Application A).
- In the Type drop-down list, select the object that you want to block: Executable file, Script, Microsoft Office document.
If you select a wrong object type, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not block the file or script.
- To add the file, you must enter the hash of the file (SHA256 or MD5), the full path to the file, or both the hash and the path.
If the file is located on a network drive, enter the file path starting with
\\, and not the drive letter. For example,\\server\shared_folder\file.exe. If the file path contains a network drive letter, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not block the file or script.Execution prevention supports a set of office file extensions and a set of script interpreters.
- Click OK.
- Save your changes.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the execution of objects: running executable files and scripts, opening office format files. You can, however, for example, open a script file in a text editor even if running the script is prevented. When blocking the execution of an object, Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays a standard notification (see figure below) if notifications are enabled in application settings.
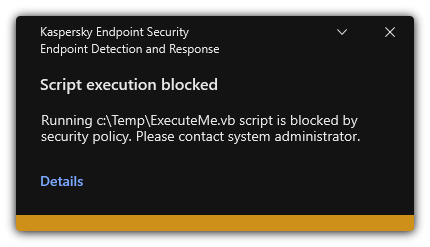
Execution prevention notification
Page top
Computer network isolation
Computer network isolation allows automatically isolating a computer from the network in response to the detection of an indicator of compromise (IOC) – this is the automatic mode. You can turn on Network isolation manually while you are investigating the detected threat – this is the manual mode.
When Network isolation is turned on, the application severs all active connections and blocks all new TCP/IP network connections on the computer except the following connections:
- Connections listed in Network isolation exclusions.
- Connections initiated by Kaspersky Endpoint Security services.
- Connections initiated by the Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent.
You can configure the component settings only in the Web Console.
Automatic Network isolation mode
You can configure Network isolation to be turned on automatically in response to an IOC detection. You can configure the automatic Network isolation mode with a group policy.
How to configure Network isolation to be turned on automatically in response to an IOC detection
You can configure Network isolation to be turned off automatically after a specified time elapses. By default, the application turns off Network isolation after 8 hours have passed from the time when it was turned on. You can also turn off Network isolation manually (see the instructions below). After turning off network isolation, the computer can use the Network without restrictions.
How to configure the delay for turning off Network isolation of a computer in automatic mode
Manual Network isolation mode
You can manually turn Network isolation on and off. You can configure the manual Network isolation mode using the computer properties in the Kaspersky Security Center console.
You can turn on Network isolation:
- In alert details (only for EDR Optimum).
Alert Details is a tool for viewing the entirety of collected information about a detected threat. Alert details include, for example, the history of files appearing on the computer. For details about managing alert details, refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help and the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help.
- Using local application settings.
How to turn on Network isolation of a computer manually
You can configure Network isolation to be turned off automatically after a specified time elapses. By default, the application turns off Network isolation after 8 hours have passed from the time when it was turned on. After turning off network isolation, the computer can use the Network without restrictions.
How to configure the delay for turning off Network isolation of a computer in manual mode
How to turn off Network isolation of a computer manually
You can also disable Network isolation locally using the command line.
Network isolation exclusions
You can configure Network isolation exclusions. Network connections that match the rules are not blocked on the computer when Network isolation is turned on.
To configure Network isolation exclusions, you can use a list of standard network profiles. By default, exclusions include network profiles containing rules that ensure uninterrupted operation of devices with the DNS/DHCP server and DNS/DHCP client roles. You can also modify the settings of standard network profiles or define exclusions manually (see instructions below).
Exclusions specified in policy properties are applied only if Network isolation is turned on automatically in response to a detected threat. Exclusions specified in computer properties are applied only if Network isolation is turned on manually in computer properties in the Kaspersky Security Center console or in alert details.
An active policy does not prevent applying exclusions from Network isolation configured in computer properties because these parameters have different usage scenarios.
How to add a Network isolation exclusion in automatic mode
How to add a Network isolation exclusion in manual mode
You can also view the Network isolation exclusion list locally using the command line. In this case, the computer must be isolated.
Page top
Cloud Sandbox
Cloud Sandbox is a technology that lets you detect advanced threats on a computer. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically forwards detected files to Cloud Sandbox for analysis. Cloud Sandbox runs these files in an isolated environment to identify malicious activity and decides on their reputation. Data on these files is then sent to Kaspersky Security Network. Therefore, if Cloud Sandbox has detected a malicious file, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will perform the appropriate action to eliminate this threat on all computers where this file is detected.
For Cloud Sandbox to operate, you must enable the use of Kaspersky Security Network.
If you are using Kaspersky Private Security Network, Cloud Sandbox technology is not available.
Cloud Sandbox technology is permanently enabled and is available to all Kaspersky Security Network users regardless of the type of license they are using. If you have already deployed Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum, you can enable a separate counter for threats detected by Cloud Sandbox. You can use this counter to generate statistics during analysis of detected threats.
To enable the Cloud Sandbox counter:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Policies & Profiles.
- Click the name of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
The policy properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- Go to Detection and Response → Endpoint Detection and Response.
- Turn on the Cloud Sandbox toggle.
- Save your changes.
Whenever there is a threat, Kaspersky Endpoint Security activates the counter for threats detected using Cloud Sandbox in the main application window under Threat detection technologies. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will also indicate the Cloud Sandbox threat detection technology in the Report on threats in the Kaspersky Security Center console.
Page top
Kaspersky Sandbox
|
Starting with version 11.7.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes a built-in agent for integration with Kaspersky Sandbox solution. The Kaspersky Sandbox solution detects and automatically blocks advanced threats on computers. Kaspersky Sandbox analyzes object behavior to detect malicious activity and activity characteristic of targeted attacks on the IT infrastructure of the organization. Kaspersky Sandbox analyzes and scans objects on special servers with deployed virtual images of Microsoft Windows operating systems (Kaspersky Sandbox servers). For details about the solution, refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox Help. |
The following configurations are possible for the Kaspersky Sandbox solution:
Kaspersky Sandbox 2.0
Kaspersky Sandbox 2.0 supports the [KES+built-in agent] configuration.
Minimum requirements:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.7.0 for Windows or later.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is not required.
- Kaspersky Security Center 13.2.
Kaspersky Sandbox 1.0
Kaspersky Sandbox 1.0 supports the [KES+KEA] configuration.
Minimum requirements:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.2.0 – 11.6.0 for Windows.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.8.
You can install Kaspersky Endpoint Agent from the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows distribution kit.
- Kaspersky Security Center 11.
Integration with Kaspersky Sandbox
Adding the Kaspersky Sandbox component is required for integration with Kaspersky Sandbox component. You can select the Kaspersky Sandbox component during installation or upgrade, as well as using the Change application components task.
To use the component, the following conditions must be met:
- Kaspersky Security Center 13.2. Earlier versions of Kaspersky Security Center do not allow the creation of standalone IOC Scan tasks for threat response.
- The component can be managed only using the Web Console. You cannot manage this component using the Administration Console (MMC).
- The application is activated and the functionality is covered by the license.
- Data transfer to Administration Server is enabled.
To use all the features of Kaspersky Sandbox, make sure quarantine file data transfer is enabled. The data are required to obtain information about files quarantined on a computer through Web Console. For example, you can download a file from quarantine for analysis in Web Console.
How to enable data transfer to the Administration Server in Web Console
- A background connection between Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and Administration Server is established
For Kaspersky Sandbox to work with Administration Server via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you must establish a new secure connection, a background connection. For details about the integration of Kaspersky Security Center with other Kaspersky solutions, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
Establishing a background connection in Web Console
If a background connection between Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and Administration Server is not established, stand-alone IOC scan tasks cannot be created as part of Threat Response.
- The Kaspersky Sandbox component is enabled.
You can enable or disable the integration with Kaspersky Sandbox in Web Console or locally using the command line.
To enable or disable the integration with Kaspersky Sandbox:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Policies & Profiles.
- Click the name of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
The policy properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- Go to Detection and Response → Kaspersky Sandbox.
- Use the Integration with Kaspersky Sandbox ENABLED toggle to enable or disable the component.
- Save your changes.
As a result, the Kaspersky Sandbox component is enabled. Check the operating status of the component by viewing the Application components status report. You can also view the operating status of a component in reports in the local interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. The Kaspersky Sandbox component will be added to the list of Kaspersky Endpoint Security components.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security saves information about the functioning of the Kaspersky Sandbox component to a report. The report also contains information about errors. If you get an error with a description fitting the Error code: XXX format (for example, 0xa67b01f4), contact Technical Support.
Migration from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.7.0 or newer with the Kaspersky Sandbox component (built-in agent) installed, interoperability with the Kaspersky Sandbox solution is available immediately after installation. The Kaspersky Sandbox component is not compatible with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. If Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is installed on the computer, when Kaspersky Endpoint Security is updated to version 11.7.0, Kaspersky Sandbox continues working with Kaspersky Endpoint Security (migrating the [KES+KEA] configuration to [KES+built-in agent]). In addition, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent will be removed from the computer. To complete migration from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, you need to transfer policy and task settings using the Migration Wizard.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.4.0–11.6.0 for interoperability with Kaspersky Sandbox, the application includes Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. You can install Kaspersky Endpoint Agent side-by-side with Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Distribution kit for Kaspersky Endpoint Security versions 11.2.0 – 11.8.0 includes Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. You can select Kaspersky Endpoint Agent when installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. As a result, two applications will be installed on your computer: KEA and KES. In Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.9.0 the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent distribution package is no longer part of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution kit.
The Kaspersky Sandbox component that is part of Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports interoperability with Kaspersky Sandbox solution 2.0. Kaspersky Sandbox solution 1.0 is not supported.
Page top
Adding a TLS certificate
To configure a trusted connection with Kaspersky Sandbox servers, you must prepare a TLS certificate. Next you must add the certificate to Kaspersky Sandbox servers and the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy. For details on preparing the certificate and adding the certificate to servers, refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox Help.
You can add a TLS certificate in Web Console or locally using the command line.
To add a TLS certificate in Web Console:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Policies & Profiles.
- Click the name of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
The policy properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- Go to Detection and Response → Kaspersky Sandbox.
- Click the Server connection settings link.
This opens the Kaspersky Sandbox server connection settings window.
- In the Server TLS certificate block, click Add and select the TLS certificate file.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security can only have one TLS certificate for a Kaspersky Sandbox server. If you have added a TLS certificate before, that certificate is revoked. Only the last added certificate is used.
- Configure advanced connections settings for Kaspersky Sandbox servers:
- Timeout. Connection timeout for Kaspersky Sandbox server. After the configured timeout elapses, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends a request to the next server. You can increase the connection timeout for Kaspersky Sandbox if your connection speed is low or if the connection is unstable. The recommended request timeout is 0.5 seconds or less.
- Kaspersky Sandbox request queue. Size of the request queue folder. When an object is accessed on the computer (executable launched or document opened, for example in DOCX or PDF format), Kaspersky Endpoint Security can also send the object to be scanned by Kaspersky Sandbox. If there are multiple requests, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates a request queue. By default, the size of the request queue folder is limited to 100 MB. After the maximum size is reached, Kaspersky Sandbox stops adding new requests to the queue and sends the corresponding event to Kaspersky Security Center. You can configure the size of the request queue folder depending on your server configuration.
- Save your changes.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security verifies the TLS certificate. If the certificate is successfully verified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uploads the certificate file to the computer during the next synchronization with Kaspersky Security Center. If you have added two TLS certificates, Kaspersky Sandbox will use the latest certificate to establish a trusted connection.
Page top
Add Kaspersky Sandbox servers
To connect computers to Kaspersky Sandbox servers with virtual images of operating systems, you must enter a server address and a port. For details about deploying virtual images and configuring Kaspersky Sandbox servers, refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox Help.
To add Kaspersky Sandbox servers to the Web Console:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Policies & Profiles.
- Click the name of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
The policy properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- Go to Detection and Response → Kaspersky Sandbox.
- In the Kaspersky Sandbox servers block, click Add.
- This opens a window; in the window, enter Kaspersky Sandbox server address (IPv4, IPv6, DNS) and port.
- Save your changes.
Scan for indicators of compromise (stand-alone task)
An Indicator of Compromise (IOC) is a set of data about an object or activity that indicates unauthorized access to the computer (compromise of data). For example, many unsuccessful attempts to sign in to the system can constitute an Indicator of Compromise. The IOC Scan task allows finding Indicators of Compromise on the computer and taking threat response measures.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security searches for indicators of compromise using IOC files. IOC files are files containing the sets of indicators that the application tries to match to count a detection. IOC files must conform to the OpenIOC standard. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically generates IOC files for Kaspersky Sandbox.
IOC Scan task run mode
The application creates stand-alone IOC scan tasks for Kaspersky Sandbox. Stand-alone IOC scan task is a group task that is automatically created when reacting to a threat detected by Kaspersky Sandbox. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically generates the IOC file. Custom IOC files are not supported. Tasks are automatically deleted 30 days after the creation time. For more details about stand-alone IOC scan tasks, refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox Help.
IOC Scan task settings
Kaspersky Sandbox may create and run IOC Scan tasks automatically when reacting to threats.
You can configure the settings only in the Web Console.
You need Kaspersky Security Center 13.2 for stand-alone IOC scan tasks of Kaspersky Sandbox to work.
To change the settings of the IOC Scan task:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Devices → Tasks.
The list of tasks opens.
- Click the IOC Scan task of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
The task properties window opens.
- Select the Application settings tab.
- Go to the IOC scan settings section.
- Configure actions on IOC detection:
- Move copy to Quarantine, delete object. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes the malicious object found on the computer. Before deleting the object, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates a backup copy in case the object needs to be restored later. Kaspersky Endpoint Security moves the backup copy to Quarantine.
- Run scan of critical areas. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs the Critical Areas Scan task. By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the kernel memory, running processes, and disk boot sectors.
- Configure the IOC Scan task run mode using the Run only when the computer is idle check box. This check box enables / disables the function that suspends the IOC Scan task when computer resources are limited. Kaspersky Endpoint Security pauses the IOC Scan task if the screensaver is off and the computer is unlocked.
This schedule option lets you conserve computer resources when the computer is being used.
- Save your changes.
You can view the results of the task in task properties in the Results section. You can view the information about detected indicators of compromise in the task properties: Application settings → IOC Scan Results.
IOC scan results are kept for 30 days. After this period, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes the oldest entries.
Page top
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (EDR)
|
Starting with version 12.1, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes a built-in agent for managing the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response component as part of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform solution. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is a solution designed for timely detection of sophisticated threats such as targeted attacks, advanced persistent threats (APT), zero-day attacks, and others. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform includes two functional blocks: Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack (hereinafter also referred to as "KATA") and Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (hereinafter also referred to as "EDR (KATA)"). You can purchase EDR (KATA) separately. For details about the solution, please refer to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help. |
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response uses the following Threat Intelligence tools:
- The Kaspersky Security Network (hereinafter also referred to as "KSN") cloud service infrastructure, which provides access to real-time file, website, and software reputation information from the Kaspersky knowledge base. Using data from Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky applications to threats, improves the performance of some protection components, and reduces the likelihood of false positives.
- Integration with the Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal portal, which contains and displays information about the reputation of files and web addresses.
- Kaspersky Threats database.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on individual computers on the corporate IT infrastructure and continuously monitors processes, open network connections, and files being modified. Information about events on the computer (telemetry data) is sent to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security also sends information to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server about threats discovered by the application as well as information about processing results for these threats.
The EDR (KATA) integration is configured on the Kaspersky Security Center console. The built-in agent is then managed using the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform console, including running tasks, managing quarantined objects, viewing reports, and other actions.
Integration with EDR (KATA)
To integrate with EDR (KATA), you must add the Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) component. You can select the EDR (KATA) component during installation or upgrade, as well as using the Change application components task.
EDR Optimum, EDR Expert and EDR (KATA) components are not compatible with each other.
The following conditions must be fulfilled for Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) to work:
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform version 4.1 or higher.
- Kaspersky Security Center version 13.2 or higher. In earlier versions of Kaspersky Security Center, it is impossible to activate the Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) feature.
- The application is activated and the functionality is covered by the license.
- The Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) component is turned on.
- Application components that Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) depends on are enabled and operational. The following components ensure the operation of EDR (KATA):
Integration with Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response involves the following steps:
- Installing Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) component
You can select the EDR (KATA) component during installation or upgrade, as well as using the Change application components task.
You must restart your computer to finish upgrading the application with the new components.
- Activating Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA)
You can acquire a license to use Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) in the following ways:
- Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) functionality is included in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows license.
The feature will be available immediately after activation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- Purchasing a separate license for EDR (KATA) (Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) Add-on).
The feature will be available after you add a separate key for Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA). As a result, two keys are installed on the computer: a key for Kaspersky Endpoint Security and a key for Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA).
Licensing for the stand-alone Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) functionality is the same as the licensing of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Make sure that the EDR (KATA) functionality is included in the license and is running in the local interface of the application.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) functionality is included in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows license.
- Connecting to Central Node
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform requires establishing a trusted connection between Kaspersky Endpoint Security and the Central Node component. To configure a trusted connection, you must use a TLS certificate. You can get a TLS certificate in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform console (see instructions in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help). Then you must add the TLS certificate to Kaspersky Endpoint Security (see instructions below).
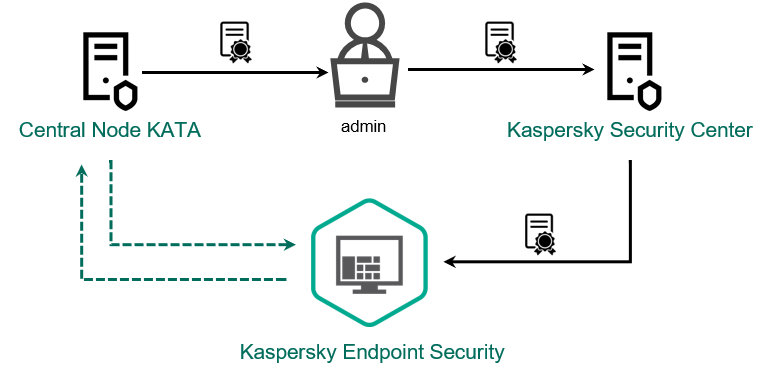
Adding a TLS certificate to Kaspersky Endpoint Security
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security only checks the TLS certificate of Central Node. To make the connection more secure, you can additionally enable the verification of the computer on Central Node (two-way authentication). To enable this verification, you must turn on two-way authentication in Central Node and Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings. To use two-way authentication, you will also need a crypto-container. A crypto-container is a PFX archive with a certificate and a private key. You can get a crypto-container in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform console (see instructions in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help).
How to connect a Kaspersky Endpoint Security computer to Central Node using the Web Console
As a result, the computer is added on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform console. Check the operating status of the component by viewing the Application components status report. You can also view the operating status of a component in reports in the local interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. The Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) component will be added to the list of Kaspersky Endpoint Security components.
Configuring telemetry
Telemetry is a list of events that have occurred on the protected computer. Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes telemetry data and sends it to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform during synchronization. Telemetry events arrive on the server almost continuously. Kaspersky Endpoint Security initiates synchronization with the server when any of the following conditions are satisfied:
- Synchronization interval has run out.
- The number of events in the buffer exceeds the upper limit.
Therefore, by default, the application synchronizes every 30 seconds or whenever the buffer holds 1024 events. You can configure the synchronization behavior in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy and select optimum values to match your network load (see instructions below).
If there is no connection between Kaspersky Endpoint Security and the server, the application queues new events. When the connection is restored, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends queued events to the server in proper order. To avoid overloading the server, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may skip some events. To enable this, you can optimize event transmission settings, for example, to set a maximum events-per-hour value (see instructions below).
If you are using Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform together with another solution which also uses telemetry, you can turn off telemetry for KATA (EDR) (see instructions above). This lets you optimize server load for these solutions. For example, if you have the Managed Detection and Response solution and KATA (EDR) deployed, you can use MDR telemetry and create Threat Response tasks in KATA (EDR).
How to configure EDR telemetry on the Administration Console (MMC)
How to configure EDR telemetry on the Web Console
Telemetry exclusions
To optimize transmitted data, you can add an executable file to the list of trusted applications. In that case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not send telemetry events for that application. This lets you reduce network traffic and minimize the amount of events from trusted objects.
Page top
KEA to KES Migration Guide for EDR (KATA)
Starting with version 12.1, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes a built-in agent for managing the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response component as part of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform solution. You no longer need a separate Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application to work with EDR (KATA). All functions of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent will be performed by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. The load on Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform servers will remain the same.
When you deploy Kaspersky Endpoint Security on computers that have Kaspersky Endpoint Agent installed, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (EDR) solution will continue working with Kaspersky Endpoint Security. In addition, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent will be removed from the computer. The same behavior in the system will occur when you update Kaspersky Endpoint Security to version 12.1 or higher.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security is not compatible with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. You cannot install both of these applications on the same computer.
The following conditions must be met for Kaspersky Endpoint Security to work as part of Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA):
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform version 4.1 or higher.
- Kaspersky Security Center version 13.2 or higher (including Network Agent) In earlier versions of Kaspersky Security Center, it is impossible to activate the Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) feature.
Steps for migrating [KES+KEA] configuration to [KES+built-in agent] for EDR (KATA)
- Upgrading the Kaspersky Endpoint Security Management Plug-in
EDR (KATA) component can be managed using the Kaspersky Endpoint Security Management Plug-in version 12.1 or higher. Depending on the type of Kaspersky Security Center console you are using, update the management plug-in in the Administration Console (MMC) or the web plug-in in the Web Console.
- Migrating policies and tasks
Transfer Kaspersky Endpoint Agent settings to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. The following options are available:
- A wizard for migrating from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to Kaspersky Endpoint Security. A wizard for migrating from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to Kaspersky Endpoint Security works only in Web Console
- A standard Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard. The Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard is only available in the Administration Console (MMC). For more details about Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
To make sure Kaspersky Endpoint Security works correctly on servers, it is recommended to add files important for the server's functioning to the trusted zone. For SQL servers, you must add MDF and LDF database files. For Microsoft Exchange servers, you must add CHK, EDB, JRS, LOG, and JSL files. You may use masks, for example,
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SQL Server\*.mdf.EDR telemetry exclusions do not migrate from the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policy to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy. Kaspersky Endpoint Security has its own exclusion tools - trusted applications. The operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security is optimized so that the absence of individual EDR telemetry exclusions will not cause any additional load on your computer in comparison with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses telemetry not only for EDR (KATA), but also for the operation of application protection components. Therefore, there is no need to transfer individual EDR telemetry exclusions. If you experience a decrease in computer performance, check the application's operation (see step 7 Checking performance).
- Licensing the EDR (KATA) functionality
To activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security as part of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform solution, you need a separate license for Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) Add-on. You can add the key using the Add key task. As a result, two keys will be added to the application: Kaspersky Endpoint Security and Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA).
Activating a Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) Add-on license on computers with previously activated EDR Optimum or EDR Expert features involves the following special considerations:
- If you are using a key file for licensing Kaspersky Endpoint Security with EDR Optimum or EDR Expert features, you cannot activate a standalone Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) Add-on license. You can either switch to using an activation code for licensing, or contact your service provider to obtain a new key file for activating Kaspersky Endpoint Security and EDR features. The service provider will provide one or more key files for licensing.
- If you are using a key file for licensing Kaspersky Endpoint Security without EDR Optimum or EDR Expert features, you can activate a standalone Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) Add-on license without having key files reissued.
- If you are using an activation code for licensing, Kaspersky activation server will automatically reissue the keys, and EDR (KATA) features will become available automatically. In this case, EDR Optimum and EDR Expert will be disabled.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows you to add up to two active keys: Kaspersky Endpoint Security key and Add-on type key. You can also add up to two reserve keys. One Kaspersky Endpoint Security reserve key and one Add-on type reserve key.
- Installing / Upgrading the Kaspersky Endpoint Security application
To migrate EDR (KATA) functionality during an application installation or upgrade, it is recommended to use the remote installation task. When creating a remote installation task, you need to select EDR (KATA) component in the installation package settings.
You can also upgrade the application using the following methods:
- Using the Kaspersky update service.
- Locally, by using the Setup Wizard.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports automatically selecting components when upgrading the application on a computer with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application installed. The automatic selection of components depends on the permissions of the user account that is upgrading the application.
If you are upgrading Kaspersky Endpoint Security using the EXE or MSI file under the system account (SYSTEM), Kaspersky Endpoint Security gains access to current licenses of Kaspersky solutions. Therefore, if the computer has Kaspersky Endpoint Agent installed and EDR (KATA) solution activated, the Kaspersky Endpoint Security installer automatically configures the set of components and selects the EDR (KATA) component. This makes Kaspersky Endpoint Security switch to using the built-in agent and removes Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. Running the MSI installer under the system account (SYSTEM) is usually performed when upgrading via the Kaspersky update service or when deploying an installation package via Kaspersky Security Center.
If you are upgrading Kaspersky Endpoint Security using an MSI file under a non-privileged user account, Kaspersky Endpoint Security lacks access to current licenses of Kaspersky solutions. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically selects components based on a set of components of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. After that Kaspersky Endpoint Security switches to using the built-in agent and removes Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports upgrading without computer restart. You can select the application upgrade mode in policy properties.
- Checking the application operation
If after application installation or upgrade, the computer has the Critical status in the Kaspersky Security Center console:
- Make sure that the computer has Network Agent version 13.2 or higher installed.
- Check the operating status of the built-in agent by viewing the Application components status report. If a component has the Not installed status, install the component using the Change application components task. If a component has the Not covered by license status, make sure that you have activated the built-in agent functionality.
- Make sure you accept the Kaspersky Security Network Statement in the new policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- Checking the connection to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server
Check the connection to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server. To do so:
- Check that you have a valid certificate.
- Check the server connection settings.
- Check the event log.
If a connection to the server is established, the application sends the event Successful connection to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server. If there is no successful connection event and there are no events with connection errors, check the event log settings and enable event sending for Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA).
The server connection status does not affect the computer status in the Kaspersky Security Center console. Therefore, if there is no connection to the server, the computer can still have the OK status. Check the event log to verify the connection to the server.
- Checking performance
If your computer's performance has slowed down after installing or updating an application, you can optimize data transfer. To do so:
- Disable the EDR (KATA) component and check that the performance degradation is due to EDR (KATA).
- For trusted applications, turn off telemetry collection on console input operations (enabled by default).
- Add applications that reduce computer performance to the list of trusted applications.
- Contact Kaspersky Technical Support. Support experts will help you to configure telemetry filtering in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. This will reduce the amount of traffic. If your computer performance is affected by a certain application, attach the distribution package of that application to the request.
Managing Quarantine
Quarantine is a special local storage on the computer. The user can quarantine files that the user considers dangerous for the computer. Quarantined files are stored in an encrypted state and do not threaten the security of the device. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses Quarantine only when working with Detection and Response solutions: EDR Optimum, EDR Expert, KATA (EDR), Kaspersky Sandbox. In other cases Kaspersky Endpoint Security places the relevant file in Backup. For details on managing Quarantine as part of solutions, please refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox Help, Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help, and Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the system account (SYSTEM) to quarantine files.
You can configure quarantine settings only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console. You can also use Kaspersky Security Center Console to manage quarantined objects (restore, delete, add, etc). Locally, on the computer, you can only restore the object using the command line.
Configuring the maximum Quarantine size
By default, the size of the Quarantine is limited to 200 MB. After the maximum size is reached, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes the oldest files from the Quarantine.
If the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (EDR) solution is deployed in your organization, we recommend increasing the size of Quarantine. When doing a YARA scan, the application may encounter a large memory dump. If the size of the memory dump exceeds the size of Quarantine, the YARA scan finishes with an error and the memory dump is not quarantined. We recommend setting the size of Quarantine equal to the total size of the RAM on the computer (for example, 8 GB).
How to configure the maximum quarantine size in the Web Console and Cloud Console
Page top
Sending data about quarantined files to Kaspersky Security Center
To perform actions with quarantined objects in Web Console, you must enable the sending of quarantined files data to the Administration Server. For example, you can download a file from quarantine for analysis in Web Console. The sending of quarantined files data must be enabled for all functionality of Kaspersky Sandbox and Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response to work.
How to enable the transfer of quarantined files data to the Web Console
As a result, you can view a list of files, quarantined on your computer, in the Kaspersky Security Center Console. You can use Kaspersky Security Center Console to manage quarantined objects (restore, delete, add, etc). For more details about working with Quarantine, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
Page top
Restoring files from Quarantine
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security restores files to their original folder. If the destination folder has been deleted or the user does not have access rights to that folder, the application places the file in the %DataRoot%\QB\Restored folder. Then you must manually move the file to the destination folder.
To restore files from Quarantine:
- In the main window of the Web Console, select Operations → Repositories → Quarantine.
- This opens the list of files in Quarantine; in that list, select the files that you want to restore and click Restore.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security restores the file. If the destination folder already has a file with the same name, the application cancels the restoration of the file. For EDR Optimum and EDR Expert solutions, the application deletes the file after restoration. For other solutions, the applications keeps a copy of the file in Quarantine.
Page top
KSWS to KES Migration Guide
|
Starting with version 11.8.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows supports the basic functionality of the Kaspersky Security for Windows Server (KSWS) solution. Kaspersky Security for Windows Server protects servers running Microsoft Windows operating systems and network attached storages against viruses and other computer security threats which servers and network attached storages are exposed to while exchanging files. For detailed information about how the solution works, please refer to the Kaspersky Security for Windows Server Help. Starting with Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.8.0, you can migrate from Kaspersky Security for Windows Server to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows and use the same solution for protecting workstations and servers. |
Software requirements
Before you begin the migration from KSWS to KES, make sure your server satisfies the hardware and software requirements of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. The lists of supported operating system versions are different for KES and KSWS. For example, KES does not support servers running Windows Server 2003.
Minimum software requirements for migrating from KSWS to KES:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows 12.0.
- Kaspersky Security 11.0.1 for Windows Server.
If you have an earlier version of Kaspersky Security for Windows Server installed, we recommend upgrading the application to the latest version. The Policies and tasks conversion wizard does not support earlier versions of Kaspersky Security for Windows Server.
- Kaspersky Security Center 14.2
If you have an earlier version of Kaspersky Security Center installed, update it to 14.2 or later. In this version of Kaspersky Security Center, the Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard lets you migrate policies into a profile rather than into a policy. In this version of Kaspersky Security Center, the Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard also lets you migrate a broader range of policy settings.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.10.
If you have an earlier version of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent installed, we recommend upgrading the application to the latest version. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports migrating a [KSWS+KEA] configuration to [KES+built-in agent] starting with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.10.
Migration recommendations
When migrating from KSWS to KES, observe the following recommendations:
- Plan the KSWS to KES migration time in advance. Choose a time when servers are operating under the lightest load, for example, during the weekend.
- After the migration, turn on application components gradually. That is, for example, start by enabling the File Threat Protection component alone, then enable other protection components, then enable control components, and so on. At each step, you must make sure the application is working correctly, and monitor the performance of the server. The architecture of KES differs from KSWS, therefore the operating system may also behave differently.
- Carry out the migration gradually. First migrate a single server, then multiple servers, then carry out the migration on all servers of the organization.
- Migrate different types of servers separately. That is, for example, first migrate database servers, then mail servers, and so on.
- Migration on high-load servers involves some special considerations.
Migration steps
Migration from KSWS to KES is performed semi-automatically. This is necessary because of differing architectures of the applications. To migrate policy settings, you must run the Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard (the migration wizard). After migrating policy settings, you must manually configure settings that the migration wizard cannot migrate automatically (for example, Password protection settings). After the migration, it is also recommended to check if the migration wizard correctly migrated all settings.
Migrate from KSWS to KES in the following order:
- Migrate KSWS tasks and policies
After migrating the policies and tasks, you must perform additional configuration steps. We also recommend to make sure that Kaspersky Endpoint Security provides the necessary level of security after migration from KSWS.
The Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard for Kaspersky Security for Windows Server is only available in the Administration Console (MMC). Policy and task settings cannot be migrated in the Web Console and Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
- Install Kaspersky Endpoint Security
You can install Kaspersky Endpoint Security in the following ways:
- Installing KES after removing KSWS (recommended).
- Installing KES on top of KSWS.
- Activate KES with a KSWS key
- Confirm that the application is in working order after migration
After migrating from KSWS to KES, make sure that the application is operating correctly. Check the status of the server in the console (should be OK). Make sure no errors are reported for the application, also check the time of the last connection to the Administration Server, the time of the last database update and the server protection status.
Pay special attention to the migration of exclusion lists, trusted applications, trusted web addresses, Application Control rules.
Correspondence of KSWS and KES components
When migrating from KSWS to KES, the set of components is migrated only when the application is being installed locally.
Correspondence of Kaspersky Security for Windows Server and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows components
Kaspersky Security for Windows Server component |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows component |
|---|---|
Basic functionality |
Application kernel, including scan tasks |
Log Inspection |
Log Inspection |
Device Control |
Device Control |
Firewall Management |
(not supported) KSWS Firewall functions are performed by the system-level Firewall. In KES, a separate component is responsible for the Firewall functionality. After migration, you can configure the Kaspersky Endpoint Security Firewall. |
File Integrity Monitor |
File Integrity Monitor |
Exploit Prevention |
Exploit Prevention |
System Tray Icon |
(not supported) You can configure user interaction in the application interface settings. |
Integration with Kaspersky Security Center |
Network Agent Connector |
Endpoint Agent |
(not supported) In Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.9.0 the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent distribution package is no longer part of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution kit. You must download the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent distribution package separately. |
Network Threat Protection |
Network Threat Protection |
Anti-Cryptor |
Behavior Detection |
Anti-Cryptor for NetApp |
(not supported) |
Traffic Security |
Web Threat Protection Mail Threat Protection Web Control |
On-Demand Scan |
Application kernel, including scan tasks |
ICAP Network Storage Protection |
(not supported) Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support Network-Attached Storages Protection components. If you need these components, you can continue using Kaspersky Security for Windows Server. |
RPC Network Storage Protection |
(not supported) Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support Network-Attached Storages Protection components. If you need these components, you can continue using Kaspersky Security for Windows Server. |
Real-Time File Protection |
File Threat Protection |
Script Monitoring |
(not supported) Script Monitoring is handled by other components, for example, AMSI Protection. |
KSN Usage |
Kaspersky Security Network |
Applications Launch Control |
Application Control |
Performance counters |
(not supported) |
Correspondence of KSWS and KES settings
When migrating policies and tasks, KES is configured in accordance with KSWS settings. Settings of application components that KSWS does not have are set to default values.
Application settings
Scalability, interface and scanning settings
Supplementary
User permissions for application management
User access permissions for Kaspersky Security Service management
Real-time server protection
Local activity control
Network-Attached Storages Protection
RPC Network Storage Protection
ICAP Network Storage Protection
Network activity control
System Inspection
Logs and notifications
Interaction with Administration Server
Tasks
Baseline File Integrity Monitor
Rollback of Application Database Update
Rule Generator for Applications Launch Control
Rule Generator for Device Control
Page top
Migrating KSWS components
Prior to the local installation, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks the computer for the presence of Kaspersky applications. If Kaspersky Security for Windows Server is installed on the computer, KES detects the set of KSWS components that are installed and selects the same components for installation.
KES components that KSWS does not have are installed as follows:
- AMSI Protection, Host Intrusion Prevention, Remediation Engine are installed with default settings.
- BadUSB Attack Prevention, Adaptive Anomaly Control, Data Encryption, Detection and Response components are ignored.
When installed remotely, the KES application ignores the set of installed KSWS components. The installer installs components that you select in properties of the installation package. After installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security and migrating policies and tasks, KES settings are configured in accordance with KSWS settings.
Page top
Migrating KSWS tasks and policies
You can migrate KSWS policy and task settings in the following ways:
- Using the Policies and Tasks Batch Conversion Wizard (hereinafter also referred to as the Migration Wizard).
The Migration Wizard for KSWS is available only in the Administration Console (MMC). Policy and task settings cannot be migrated in the Web Console and Cloud Console.
The batch conversion wizard works differently for different versions of Kaspersky Security Center. We recommend upgrading the solution to version 14.2 or higher. In this version of Kaspersky Security Center, the Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard lets you migrate policies into a profile rather than into a policy. In this version of Kaspersky Security Center, the Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard also lets you migrate a broader range of policy settings.
- Using the New Policy Wizard for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The New Policy Wizard lets you create a KES policy based on a KSWS policy.
KSWS policy migration procedures are different when using Migration Wizard and the New Policy Wizard.
Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard
The migration wizard transfers KSWS policy settings into the policy profile instead of KES policy settings. The policy profile is a set of policy settings that is activated on a computer if the computer satisfies the configured activation rules. The UpgradedFromKSWS device tag is selected as the triggering criterion of the policy profile. Kaspersky Security Center automatically adds the UpgradedFromKSWS tag to all computers on which you install KES on top of KSWS using the remote installation task. If you chose a different installation method, you can assign the tag to devices manually.
To add a tag to a device:
- Create a new tag for servers —
UpgradedFromKSWS.For more details about creating tags for devices, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
- Create a new administration group in the Kaspersky Security Center console and add servers to which you want to assign the tag to this group.
You can group servers using the selection tool. For more details about working with selections, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
- Select all servers of the administration group in the Kaspersky Security Center console, open the properties of the selected servers and assign the tag.
If you are migrating multiple KSWS policies, each policy is converted to a profile within one overarching policy. If the KSWS policy already contains profiles, these profiles are also migrated as profiles. As a result you will get a single policy that includes profiles corresponding to all KSWS policies.
How to use the Policies and Tasks Batch Conversion Wizard to migrate KSWS policy settings
The new policy profile with KSWS settings will be named UpgradedFromKSWS <Name of the Kaspersky Security for Windows Server policy>. In profile properties, the migration wizard automatically selects the UpgradedFromKSWS device tag as the triggering criterion. Thus the settings from the policy profile are applied to servers automatically.
Wizard for creating a policy based on a KSWS policy
When a KES policy is created based on a KSWS policy, the wizard transfers settings to the new policy accordingly. That is, one KES policy will correspond to one KSWS policy. The wizard does not convert the policy to a profile.
How to use the New Policy Wizard to migrate KSWS policy settings
Additional configuration of policies and tasks after migration
KSWS and KES have different sets of components and policy settings, so after migration you must verify that policy settings satisfy your corporate security requirements.
Check the following basic policy settings:
- Password protection. KSWS Password protection settings are not migrated. Kaspersky Endpoint Security has a built-in Password protection feature. If necessary, turn on Password protection and set a password.
- Trusted zone. The methods used by KSWS and KES for selecting objects differ. When migrating, KES supports exclusions defined as individual files or paths to file / folder. If KSWS has exclusions configured as a predefined area or a script URL, such exclusions are not migrated. After migration, you must add such exclusions manually.
To make sure Kaspersky Endpoint Security works correctly on servers, it is recommended to add files important for the server's functioning to the trusted zone. For SQL servers, you must add MDF and LDF database files. For Microsoft Exchange servers, you must add CHK, EDB, JRS, LOG, and JSL files. You may use masks, for example,
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SQL Server\*.mdf. - Firewall. KSWS Firewall functions are performed by the system-level Firewall. In KES, a separate component is responsible for the Firewall functionality. After migration, you can configure the Kaspersky Endpoint Security Firewall.
- Kaspersky Security Network. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support configuring KSN for individual components. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses KSN for all application components. To use KSN, you must accept the new terms and conditions of the Kaspersky Security Network Statement.
- Web Control. Blocking rules for web traffic category control are migrated to a single blocking rule in Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Kaspersky Endpoint Security ignores allowing rules for category control. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support all categories of Kaspersky Security for Windows Server. Categories that do not exist in Kaspersky Endpoint Security are not migrated. Therefore, web resource classification rules with unsupported categories are not migrated. If necessary, add Web Control rules.
- Proxy server. The proxy server connection password is not migrated. Enter the password to be used for connecting to the proxy server manually.
- Schedules of individual components. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support configuring schedules for individual components. The components are always on while Kaspersky Endpoint Security is operational.
- Set of components. The set of available Kaspersky Endpoint Security features depends on the type of operating system: workstation or server. For example, out of encryption tools, only BitLocker Drive Encryption is available on servers.
 attribute. The state of the
attribute. The state of the  attribute is not migrated. The
attribute is not migrated. The  attribute will have the default value. By default, almost all settings in the new policy have a prohibition applied on modifying settings in child policies and in the local application interface. The attribute has the
attribute will have the default value. By default, almost all settings in the new policy have a prohibition applied on modifying settings in child policies and in the local application interface. The attribute has the  value for policy settings in the Managed Detection and Response section and in the User support group of settings (Interface section). If necessary, configure the inheritance of settings from the parent policy.
value for policy settings in the Managed Detection and Response section and in the User support group of settings (Interface section). If necessary, configure the inheritance of settings from the parent policy.- Working with active threats. Advanced Disinfection works differently for workstations and servers. You can configure advanced disinfection in Malware Scan task settings and in application settings.
- Upgrading the application. To install major updates and patches without restarting, you must change the application upgrade mode. By default, the Install application updates without restart feature is disabled.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. Kaspersky Endpoint Security has a built-in agent for working with Detection and Response solutions. If necessary, transfer Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policy settings to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
- Update tasks. Make sure that the settings of the Update task were migrated correctly. Instead of KSWS's three tasks, KES uses a single KES task. You may optimize the Update tasks and remove superfluous tasks.
- Other tasks. Application Control, Device Control, and File Integrity Monitor components work differently in KSWS and KES. KES does not use Baseline File Integrity Monitor, Applications Launch Control Generator, Rule Generator for Device Control tasks. Therefore these tasks are not migrated. After migration, you can configure the File Integrity Monitor, Application Control, Device Control components.
Installing KES instead of KSWS
You can install Kaspersky Endpoint Security in the following ways:
- Installing KES after removing KSWS (recommended).
- Installing KES on top of KSWS.
Removing Kaspersky Security for Windows Server
You can remove the application remotely using the Uninstall application remotely task or locally on the server. You may need to restart the server after removing KSWS. If you want to install Kaspersky Endpoint Security without a restart, please make sure that Kaspersky Security for Windows Server is completely removed. If the application is not completely removed, installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security may cause faulty operation of the server. Making sure that the application is completely removed is also recommended if you have used the kavremover utility. The kavremover utility does not support managing KSWS.
After removing KSWS, install Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows using any available method.
Installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security
Administrators typically enable Password protection to restrict access to KSWS. This means that you will need to enter the password to remove KSWS. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support password transfer to remove Kaspersky Security for Windows Server when installing KES on top of KSWS. You can transfer the password only if you are installing KES on the command line. Therefore, before removing KSWS, you must turn off Password protection in application settings and turn Password protection back on in application settings after you complete the migration from KSWS to KES.
When you install KES remotely, components that you have selected in installation package properties are installed on the server. We recommend selecting default components in installation package properties. A restart is not necessary when installing KES on top of KSWS.
Prior to the local installation, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks the computer for the presence of Kaspersky applications. If Kaspersky Security for Windows Server is installed on the computer, KES detects the set of KSWS components that are installed and selects the same components for installation. A restart is not necessary when installing KES on top of KSWS.
If installing KES on top of KSWS failed, you can roll back the installation. After rolling back the installation, it is recommended to restart the server and try again.
KSWS settings and tasks are not migrated when Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows is installed. To migrate settings and tasks, run the Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard.
You can check the list of installed components in the Security section of the application interface, using the status command, or in the Kaspersky Security Center console in computer properties. You can change the set of components after installation by using the Change application components.
Migrating the [KSWS+KEA] configuration to [KES+built-in agent] configuration
To support using Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows as part of EDR (KATA), EDR Optimum, EDR Expert, Kaspersky Sandbox, and MDR, a built-in agent has been added to the application. You no longer need a separate Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application to work with these solutions.
When migrating from KSWS to KES, the EDR (KATA), EDR Optimum, EDR Expert, Kaspersky Sandbox, and MDR solutions continue to work with Kaspersky Endpoint Security. In addition, the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is removed from the computer.
Migrating the [KSWS+KEA] configuration to [KES+built-in agent] involves the following steps:
- Migrating from KSWS to KES
Migrating from KSWS to KES involves installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security instead of Kaspersky Security for Windows Server.
To carry out the migration, you must select the components needed to support Detection and Response solutions as part of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. After installing the application, Kaspersky Endpoint Security switches to using the built-in agent and removes Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Migrating the policy and tasks
Migrating [KSWS+KEA] policies and tasks to [KES+built-in agent] involves the following steps:
- Migrating policies and tasks from KSWS to KES using the Policies and Tasks Batch Conversion Wizard (only available on the Administration Console (MMC)).
As a result, a policy profile with the UpgradedFromKSWS <Name of the Kaspersky Security for Windows Server policy> name is added to the KES policy. New KES tasks are also created with <KSWS task name> (converted) names.
- Migrating policies and tasks from KEA to KES using the wizard for migration from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent (only available on the Web Console and Cloud Console).
As a result, a new policy is created with the name <Name of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy> & <Name of the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policy>. New tasks and KES tasks are also created.
- Migrating policies and tasks from KSWS to KES using the Policies and Tasks Batch Conversion Wizard (only available on the Administration Console (MMC)).
- Licensing functionality
If you use a common Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum or Kaspersky Optimum Security license to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows and Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, EDR Optimum functionality will be activated automatically after upgrading the application to version 11.7.0. You do not need to do anything else.
If you use a stand-alone Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Add-on license to activate EDR Optimum functionality, you must make sure that the EDR Optimum key is added to the Kaspersky Security Center repository and the automatic license key distribution functionality is enabled. After you upgrade the application to version 11.7.0, EDR Optimum functionality is activated automatically.
If you use a Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum or Kaspersky Optimum Security license to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, and a different license to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, you must replace the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows key with the common Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum or Kaspersky Optimum Security key. You can replace the key using the Add key task.
You do not need to activate Kaspersky Sandbox functionality. Kaspersky Sandbox functionality will be available immediately after upgrading and activating Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
Only the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform license can be used to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security as part of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform solution. After you upgrade the application to version 12.1, EDR (KATA) functionality is activated automatically. You do not need to do anything else.
- Checking the health of Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum and Kaspersky Sandbox
If after the upgrade, the computer has the Critical status in the Kaspersky Security Center console:
- Make sure that the computer has Administration Agent version 13.2 or higher installed.
- Check the operating status of the built-in agent by viewing the Application components status report. If a component has the Not installed status, install the component using the Change application components task.
- Make sure you accept the Kaspersky Security Network Statement in the new policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
Make sure EDR Optimum functionality is activated using the Application components status report. If a component has the Not covered by license status, make sure that the automatic license key distribution functionality of EDR Optimum is turned on.
Making sure Kaspersky Security for Windows Server was successfully removed
Make sure Kaspersky Security for Windows Server is completely removed:
- The
%ProgramFiles%\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security for Windows Server\folder does not exist. - The following services are not present:
- Kaspersky Security Service (KAVFS)
- Kaspersky Security Management (KAVFSGT)
- Kaspersky Security Exploit Prevention (KAVFSSLP)
- Kaspersky Security Script Checker (KAVFSSCS)
You can check running services in Task Manager or by issuing the
sc querycommand (see figure below). - The following drivers are not present:
- klam.sys
- klflt.sys
- klramdisk.sys
- klelaml.sys
- klfltdev.sys
- klips.sys
- klids.sys
- klwtpee
You can check installed drivers in the
C:\Windows\System32\driversfolder or by issuing thesc querycommand. If a service or driver are missing, you will get the following response:
Making sure Kaspersky Security for Windows Server services and drivers were successfully removed
If application or driver files remain on the server, delete the relevant files manually. If Kaspersky Security for Windows Server services are still running on the server, stop (sc stop) and delete (sc delete) the services manually. To stop the klam.sys driver, use the fltmc unload klam command.
Activating KES with a KSWS key
After installing the application, you can activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (KES) using a Kaspersky Security for Windows Server (KSWS) license key. The activation process after migration depends on the KSWS activation method (see the table below).
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support the Kaspersky Security for Storage license. To work with this license, you need to use Kaspersky Security for Windows Server.
To activate KES with the KSWS key you can use only the activation code. If you are using a key file to activate the application, you need to contact Technical Support for a Kaspersky Endpoint Security key file.
Activating Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows with a Kaspersky Security for Windows Server key
Kaspersky Security for Windows Server activation method |
Migrating the key to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. |
|---|---|
Automatic distribution of the KSWS license key to computers. |
If automatic key distribution is enabled in KSWS license key properties, KES is automatically activated with the KSWS key. |
The KSWS key is added by a task. |
If your KSWS is activated using the task, the KSWS license key is deleted during migration from KSWS. You must activate the application again. For example, you can add a license key to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows installation package. |
The KSWS key is added locally in the application interface. |
If your KSWS is activated locally using the Application Activation Wizard, the KSWS license key is deleted during migration from KSWS. You must activate the application again. For example, you can add a license key to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows installation package. |
The KSWS key is added to the installation package. |
If your KSWS is activated using the key from the installation package, the KSWS license key is deleted during migration from KSWS. You must activate the application again. For example, you can add a license key to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows installation package. |
Paid virtual machine image (Amazon Machine Image – AMI) in Amazon Web Services (AWS). |
If you purchased Kaspersky Security Center as a paid virtual machine image (Amazon Machine Image – AMI) in Amazon Web Services (AWS), activating KES is not required. In this case, Kaspersky Security Center uses the AWS subscription that is already added to the application. |
Ready-made free-of-charge Kaspersky Security Center image with your own license (Bring Your Own License – BYOL model). |
If you are using an out-of-the-box free Kaspersky Security Center image with your own license in a cloud environment (the Bring Your Own License – BYOL model), you must activate the application using any available method. You will need a Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security license. |
Special considerations for migrating high-load servers
On high-load servers, it is important to monitor performance and avoid faults. After migration to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, we recommend temporarily disabling application components that use substantial server resources relative to other components. After you make sure that the server is performing as normal, you can turn the application components back on.
We recommend migrating high-load servers as follows:
- Create a Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy with default settings.
Default settings are considered optimal. This settings are recommended by Kaspersky experts. Default settings provide recommended protection level and optimal resource use.
- In policy settings, turn off the following components: Network Threat Protection, Behavior Detection, Exploit Prevention, Remediation Engine, Application Control.
If your organization has the Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response (MDR) solution deployed, upload the BLOB configuration file to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
- Remove Kaspersky Security for Windows Server from the server.
- Install Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows with the default set of components.
If your organization has Detection and Response solutions deployed, select the relevant components in the properties of the installation package.
- Check the settings of the application:
- The application is activated with the KSWS license key.
- The new policy is applied. Previously selected components are disabled.
- Make sure the server is working. Make sure that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows is not using more than 1% of the server's resources.
- If necessary, create scan exclusions, add trusted applications, create a list of trusted web addresses.
- Turn on Behavior Detection, Exploit Prevention, Remediation Engine components. Make sure that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows is not using more than 1% of the server's resources.
- Turn on the Network Threat Protection component. Make sure that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows is not using more than 2% of the server's resources.
- Turn on the Application Control component in rule testing mode.
- Make sure Application Control is working. If necessary, add new Application Control rules and turn off rule testing mode after confirming that Application Control is working.
After migrating from KSWS to KES, make sure that the application is operating correctly. Check the status of the server in the console (should be OK). Make sure no errors are reported for the application, also check the time of the last connection to the Administration Server, the time of the last database update and the server protection status.
Page top
Example of migration from [KSWS+KEA] to KES
When migrating from Kaspersky Security for Windows Server (KSWS) to Kaspersky Endpoint Security (KES), you can use the follow recommendations to configure server protection and optimize performance. Here we will look at an example of migration for a single organization.
Infrastructure of the organization
The company has the following equipment installed:
- Kaspersky Security Center 14.2
The administrator manages Kaspersky solutions using the Administration Console (MMC). Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum (EDR Optimum) is also deployed
In Kaspersky Security Center, three administration groups are created, containing servers of the organization: two administration groups for SQL servers and an administration group for Microsoft Exchange servers. Each administration group is managed by its own policy. Database Update and On-demand scan tasks are created for all servers in the organization.
The KSWS activation key is added to Kaspersky Security Center. Automatic key distribution is enabled.
- SQL servers with Kaspersky Security for Windows Server 11.0.1 and Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.11 installed. The SQL servers are combined into two clusters.
KSWS is managed by SQL_Policy(1) and SQL_Policy(2) policies. Database Update, On-demand scan tasks are also created.
- A Microsoft Exchange server with Kaspersky Security for Windows Server 11.0.1 and Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.11 installed.
KSWS is managed by the Exchange_Policy policy. Database Update, On-demand scan tasks are also created.
Planning the migration
The migration involves the following steps:
- Migrating KSWS tasks and policies using the Policies and Tasks Batch Conversion Wizard.
- Migrating the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policy using the Policies and Tasks Batch Conversion Wizard.
- Using tags to activate policy profiles in the properties of the new policy.
- Installing KES instead of KSWS.
- Activating EDR Optimum.
- Confirming that KES is working.
The migration scenario is initially performed on one of the cluster of SQL servers. Then the migration scenario is performed on the other cluster of SQL servers. Then the migration scenario is performed on the Microsoft Exchange.
Migrating KSWS tasks and policies using the Policies and Tasks Batch Conversion Wizard.
To migrate KSWS tasks, you can use the Policies and Tasks Batch Conversion Wizard (the migration wizard). As a result, instead of the SQL_Policy(1), SQL_Policy(2), and Exchange_Policy policies, you will get a single policy with three profiles for SQL and Microsoft Exchange servers respectively. The new policy profile with KSWS settings will be named UpgradedFromKSWS <Name of the Kaspersky Security for Windows Server policy>. In profile properties, the migration wizard automatically selects the UpgradedFromKSWS device tag as the triggering criterion. Thus the settings from the policy profile are applied to servers automatically.
Migrating the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policy using the Policies and Tasks Batch Conversion Wizard
To migrate Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policies, you can use the Policies and Tasks Batch Conversion Wizard. The Policy and Task Migration Wizard for Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is only available in the Web Console.
Using tags to activate policy profiles in the properties of the new policy
Select the device tag that you assigned earlier as the profile activation condition. Open policy properties and select General rules for policy profile activation as the profile activation condition.
Installing KES instead of KSWS
Before installing KES, you must disable Password protection in KSWS policy properties.
Installing KES involves the following steps:
- Prepare the installation package. In installation package properties, select the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows 12.0 distribution kit and select the default set of components.
- Create a Install application remotely task for one of the SQL server administration groups.
- In task properties, select the installation package and the license key file.
- Wait until the task successfully completes.
- Repeat KES installation for remaining administration groups.
Kaspersky Security Center automatically adds the UpgradedFromKSWS tag to names of computers on the console after the KES installation is complete.
To check the KES installation, you can use the Report on protection deployment. You can also check the device status. To confirm application activation, you can use the Report on usage of license keys.
Activating EDR Optimum
You can activate EDR Optimum functionality using a stand-alone Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Add-on license. You must confirm that the EDR Optimum key is added to the Kaspersky Security Center repository and the automatic license key distribution functionality is enabled.
To check EDR Optimum activation, you can use the Report on status of application components.
Confirming that KES is working
To confirm that KES is working, you can check and see that no errors are reported. The device status must be OK. Update and malware scan tasks and successfully completed.
Page top
Managing the application on a Core Mode server
A server in Core Mode does not have a GUI. Therefore you can only manage the application remotely using the Kaspersky Security Center console or locally on the command line.
Managing the application using the Kaspersky Security Center console
Installing the application using the Kaspersky Security Center console is not different from installing it the normal way. When creating an installation package, you can add a license key to activate the application. You can use a Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows key or a Kaspersky Security for Windows Server key.
On a Core Mode server, the following application components are not available: Web Threat Protection, Mail Threat Protection, Web Control, BadUSB Attack Prevention, File Level Encryption (FLE), Kaspersky Disk Encryption (FDE).
Restart is not required when installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Restart is required only if you have to remove incompatible applications prior to installation. Restart may also be required when updating the application version. The application cannot display a window to prompt the user to restart the server. You can learn about the need to restart the server from reports in the Kaspersky Security Center console.
Managing the application on Core Mode server is not different from managing a computer. You can use policies and tasks to configure the application.
Managing the application on Core Mode servers involves the following special considerations:
- The Core Mode server does not have a GUI, therefore Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not display a warning telling the user that Advanced Disinfection is needed. To disinfect a threat, you need to enable Advanced Disinfection technology in application settings and enable immediate Advanced Disinfection in Malware Scan task settings. Then you need to start a Malware Scan task.
- BitLocker Drive Encryption is only available with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM). A PIN / password cannot be used for encryption because the application is unable to display the password prompt window for preboot authentication. If the operating system has Federal Information Processing standard (FIPS) compatibility mode enabled, connect a removable drive for saving the encryption key before you begin encrypting the drive.
Managing the application from the command line
When you cannot use a GUI, you can manage Kaspersky Endpoint Security from the command line.
To install the application to a Core Mode server, run the following command:
setup_kes.exe /pEULA=1 /pPRIVACYPOLICY=1 /s
To activate the application, run the following command:
avp.com license /add <activation code or key file>
To check application profile statuses, run the following command:
avp.com status
To view the list of application management commands, run the following command:
avp.com help
Managing the application from the command line
You can manage Kaspersky Endpoint Security from the command line. You can view the list of commands for managing the application by executing the HELP command. To read about the syntax of a specific command, enter HELP <command>.
Special characters in the command must be escaped. To escape the characters &, |, (, ), <, >, ^, use the ^ character (for example, to use the & character, enter ^&). To escape the % character, enter %%.
Installing the application
Kaspersky Endpoint Security can be installed from the command line in one of the following modes:
- In interactive mode by using the Application Setup Wizard.
- In silent mode. After installation is started in silent mode, your involvement in the installation process is not required. To install the application in silent mode, use the
/sand/qnkeys.Prior to installing the application in silent mode, please open and read the End User License Agreement and the text of the Privacy Policy. The End User License Agreement and the text of the Privacy Policy are included in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution kit. You may proceed to install the application only if you have fully read, understand, and accept the provisions and terms of the End User License Agreement, you understand and agree that your data will be processed and transmitted (including to third-party countries) in accordance with the Privacy Policy, and you have fully read and understand the Privacy Policy. If you do not accept the provisions and terms of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy, please do not install or use Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
You can view the list of commands for installing the application by executing the /h command. To get help on the installation command syntax, type setup_kes.exe /h. As a result, the installer displays a window with a description of command options (see the figure below).
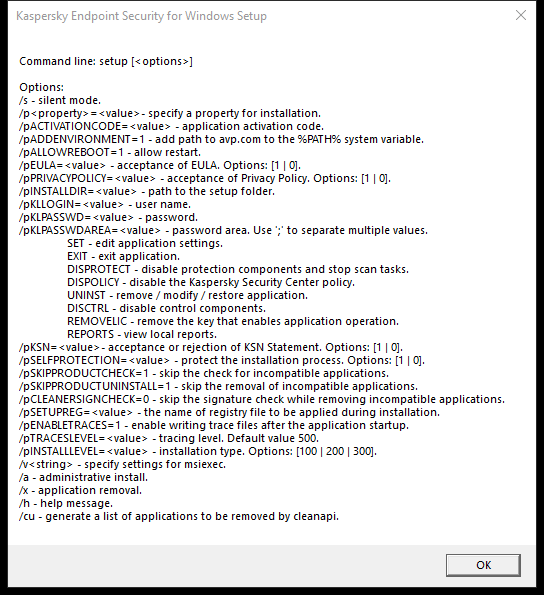
Description of installation command options
To install the application or upgrade a previous version of the application:
- Run the command line interpreter (cmd.exe) as an administrator.
- Go to the folder where the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution package is located.
- Run the following command:
setup_kes.exe /pEULA=1 /pPRIVACYPOLICY=1 [/pKSN=1|0] [/pALLOWREBOOT=1] [/pSKIPPRODUCTCHECK=1] [/pSKIPPRODUCTUNINSTALL=1] [/pKLLOGIN=<user name> /pKLPASSWD=<password> /pKLPASSWDAREA=<password scope>] [/pENABLETRACES=1|0 /pTRACESLEVEL=<tracing level>] [/s]or
msiexec /i <distribution kit name> EULA=1 PRIVACYPOLICY=1 [KSN=1|0] [ALLOWREBOOT=1] [SKIPPRODUCTCHECK=1] [KLLOGIN=<user name> KLPASSWD=<password> KLPASSWDAREA=<password scope>] [ENABLETRACES=1|0 TRACESLEVEL=<tracing level>] [/qn]
As a result, the application is installed on the computer. You can confirm that application is installed and check application settings by issuing the status command.
Application installation settings
|
Acceptance of the terms of the End User License Agreement. The text of the License Agreement is included in the distribution kit of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Accepting the terms of the End User License Agreement is necessary for installing the application or upgrading the application version. |
|
|
Acceptance of the Privacy Policy. The text of the Privacy Policy is included in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution kit. To install the application or upgrade the application version, you must accept the Privacy Policy. |
|
|
Agreement or refusal to participate in Kaspersky Security Network (KSN). If no value is set for this parameter, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will prompt to confirm your consent or refusal to participate in KSN when Kaspersky Endpoint Security is first started. Available values:
The Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution package is optimized for use with Kaspersky Security Network. If you opted not to participate in Kaspersky Security Network, you should update Kaspersky Endpoint Security immediately after the installation is complete. |
|
|
Automatic restart of the computer, if required after installation or upgrade of the application. If no value is set for this parameter, automatic computer restart is blocked. Restart is not required when installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Restart is required only if you have to remove incompatible applications prior to installation. Restart may also be required when updating the application version. |
|
|
Disable the check for incompatible software. The list of incompatible software is available in the incompatible.txt file that is included in the distribution kit. If no value is set for this parameter and incompatible software is detected, the installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security will be terminated. |
|
|
Disable automatic removal of detected incompatible software. If no value is set for this parameter, Kaspersky Endpoint Security attempts to remove incompatible software. Automatic removal of incompatible software cannot be enabled when installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security using the msiexec installer. Use setup_kes.exe to enable the automatic removal of incompatible software. |
|
|
Verification of digital signatures of detected incompatible software files. To remove incompatible software, Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs the installer file of the software. If the installer file does not have a digital signature, Kaspersky Endpoint Security considers the file untrusted and halts the removal of incompatible software to avoid running potentially malicious code. If the application cannot verify the digital signature of the incompatible software file that was detected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security installation is stopped with an error. The default value is different depending on the software installation method:
|
|
|
Set the user name for accessing the features and settings of Kaspersky Endpoint Security (the Password protection component). The user name is set together with the |
|
|
Specify a password for accessing Kaspersky Endpoint Security features and settings (the password is specified together with the If you specified a password but did not specify a user name with the |
|
|
Specify the scope of the password for accessing Kaspersky Endpoint Security. When a user attempts to perform an action that is included in this scope, Kaspersky Endpoint Security prompts for the user's account credentials (
|
|
|
Enabling or disabling application tracing. After Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts, it saves trace files in the folder
|
|
|
Level of detail of traces. Available values:
|
|
|
Enabling or disabling Azure WVD compatibility mode. Available values:
This feature allows correctly displaying the state of the Azure virtual machine in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform console. To monitor the performance of the computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends telemetry to KATA servers. Telemetry includes an ID of the computer (Sensor ID). Azure WVD compatibility mode allows assigning a permanent unique Sensor ID to these virtual machines. If the compatibility mode is turned off, the Sensor ID can change after the computer is restarted because of how Azure virtual machines work. This can cause duplicates of virtual machines to appear on the console. |
|
|
Enables or disables protection of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security processes using AM-PPL technology (Antimalware Protected Process Light). For more details about AM-PPL technology, please visit the Microsoft website. AM-PPL technology is available for Windows 10 version 1703 (RS2) or later, and Windows Server 2019 operating systems. Available values:
|
|
|
Application upgrade mode:
You can upgrade the application without a restart starting with version 11.10.0. To upgrade an earlier version of the application, you must restart the computer. You can also install patches without a restart starting with version 11.11.0. Restart is not required when installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security. So, the upgrade mode of the application will be specified in the application settings. You can change this parameter in the application settings or in the policy. When upgrading already installed application, the priority of the command line parameter is lower than that of the parameter specified in the application settings or in the setup.ini file. For example, if |
|
|
Managing the application through the REST API. To manage the application through the REST API, you must specify the user name ( Available values:
To manage the application through the REST API, management using administrative systems must be allowed. To do so, set the |
|
|
User name of the Windows domain account used for managing the application through the REST API. Management of the application through the REST API is available only to this user. Enter the user name in the format Adding a user name is a prerequisite for managing the application through the REST API. |
|
|
Port used for managing the application through the REST API. Port 6782 is used by default. Make sure that the port is free. |
|
|
Certificate for identifying requests (for example, |
|
|
Application management using administration systems. Administration systems include, for example, Kaspersky Security Center. In addition to Kaspersky administration systems, you can use third-party solutions. Kaspersky Endpoint Security provides an API for this purpose. Available values:
|
|
Example:
|
||
After Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed, the trial license is activated unless you provided an activation code in the setup.ini file. A trial license usually has a short term. When the trial license expires, all Kaspersky Endpoint Security features become disabled. To continue using the application, you need to activate the application with a commercial license by using the Application Activation Wizard or a special command.
When installing the application or upgrading the application version in silent mode, use of the following files is supported:
- setup.ini – general settings for application installation
- install.cfg – settings of Kaspersky Endpoint Security operation
- setup.reg – registry keys
Registry keys from the setup.reg file are written to the registry only if the
setup.regvalue is set for theSetupRegparameter in the setup.ini file. The setup.reg file is generated by Kaspersky experts. It is not recommended to modify the contents of this file.
To apply settings from the setup.ini, install.cfg, and setup.reg files, place these files into the folder containing the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution package. You can also put the setup.reg file in a different folder. If you do so, you need to specify the path to the file in the following application installation command: SETUPREG=<path to the setup.reg file>.
Activating the application
To activate the application from the command line,
type the following string in the command line:
avp.com license /add <activation code or key file> [/login=<user name> /password=<password>]
You need to enter the user account credentials (/login=<user name> /password=<password>) if Password Protection is enabled.
Remove the application
Kaspersky Endpoint Security can be uninstalled from the command line in one of the following ways:
- In interactive mode by using the Application Setup Wizard.
- In silent mode. After uninstallation is started in silent mode, your involvement in the removal process is not required. To uninstall the application in silent mode, use the
/sand/qnswitches.
To uninstall the application in silent mode:
- Run the command line interpreter (cmd.exe) as an administrator.
- Go to the folder where the Kaspersky Endpoint Security distribution package is located.
- Run the following command:
- If the removal process is not password protected:
setup_kes.exe /s /xor
msiexec.exe /x <GUID> /qn<GUID>is the unique ID of the application. You can find out the GUID of the application by using the following command:wmic product where "Name like '%Kaspersky Endpoint Security%'" get Name, IdentifyingNumber - If the removal process is password protected:
setup_kes.exe /pKLLOGIN=<user name> /pKLPASSWD=<password> /s /xor
msiexec.exe /x <GUID> KLLOGIN=<user name> KLPASSWD=<password> /qn
Example:
msiexec.exe /x {9A017278-F7F4-4DF9-A482-0B97B70DD7ED} KLLOGIN=KLAdmin KLPASSWD=!Password1 /qn - If the removal process is not password protected:
AVP commands
To manage Kaspersky Endpoint Security from the command line:
- Run the command line interpreter (cmd.exe) as an administrator.
- Go to the folder where the Kaspersky Endpoint Security executable file is located.
- To execute a command, enter:avp.com <command> [options]
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will execute the command (see figure below).
Managing the application from the command line
SCAN. Malware Scan
Run the Malware Scan task.
Command syntax
Scan scope |
|
|
A space-separated list of files and folders. Long paths must be enclosed in quotation marks. Short paths (MS-DOS format) do not need to be enclosed in quotation marks. For example:
|
|
Run the Malware Scan task. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the following objects:
|
|
Scan the Kernel memory |
|
Scan the Objects that are loaded at startup of the operating system |
|
Scan Outlook mailbox |
|
Scan removable drives. |
|
Scan hard drives. |
|
Scan network drives. |
|
Scan the files in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security Backup. |
|
Scan the files and folders from a list. Each file in the list must be on a new row. Long paths must be enclosed in quotation marks. Short paths (MS-DOS format) do not need to be enclosed in quotation marks. For example:
|
Action on threat detection |
|
|
Notify. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds the information about infected files to the list of active threats on detection of these files. |
|
Disinfect, block if disinfection fails. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically attempts to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection is not possible, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds the information about the infected files that are detected to the list of active threats. |
|
Disinfect, delete if disinfection fails. If this option is selected, the application automatically attempts to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection fails, the application deletes the files. This action is selected by default. |
|
Disinfect the infected files that are detected. If disinfection fails, delete the infected files. Also delete compound files (for example, archives) if the infected file cannot be disinfected or deleted. |
|
Delete infected files. Also delete compound files (for example, archives) if the infected file cannot be deleted. |
File types |
|
|
Files scanned by extension. If this setting is enabled, the application scans infectable files only. The file format is then determined based on the file's extension. |
|
Files scanned by format. If this setting is enabled, the application scans infectable files only. Before scanning a file for malicious code, the internal header of the file is analyzed to determine the format of the file (for example, .txt, .doc, or .exe). The scan also looks for files with particular file extensions. |
|
All files. If this setting is enabled, the application checks all files without exception (all formats and extensions). This is the default setting. |
Scan exclusions |
|
|
RAR, ARJ, ZIP, CAB, LHA, JAR, and ICE archives are excluded from the scan scope. |
|
Mail databases, incoming and outgoing e-mails are excluded from the scan scope. |
|
Files that match the file mask are excluded from the scan scope. For example:
|
|
Files that take longer to scan than the specified time limit (in seconds) are excluded from the scan scope. |
|
Files that are larger than the specified size limit (in megabytes) are excluded from the scan scope. |
Saving events to a report file mode (for Scan, Updater and Rollback profiles only) |
|
|
Save only critical events to the report file. |
|
Save all events to a report file. |
Scan technologies |
|
|
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scans by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date when the file was last scanned, and any modifications to the scan settings. There are limitations to iChecker Technology: it does not work with large files and applies only to files with a structure that the application recognizes (for example, EXE, DLL, LNK, TTF, INF, SYS, COM, CHM, ZIP, and RAR). |
|
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scanning by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date that the file was last scanned on, and any modifications to the scanning settings. The iSwift technology is an advancement of the iChecker technology for the NTFS file system. |
Advanced settings |
|
|
File with the Malware Scan task settings. The file must be created manually and saved in TXT format. The file can have the following contents: |
Example:
|
UPDATE. Updating databases and application software modules
Run the Update task.
Command syntax
Update task settings |
|
|
Start of the Update task that was created automatically after the application was installed. You can change the settings of the Update task in the local application interface or in the console of Kaspersky Security Center. If this setting is not configured, Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the Update task with the default settings or with the settings specified in the command. You can configure the Update task settings as follows:
|
Update source |
|
|
Address of a HTTP or FTP server, or of a shared folder with the update package. You can specify only one update source. If the update source is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the default source: Kaspersky update servers. |
Saving events to a report file mode (for Scan, Updater and Rollback profiles only) |
|
|
Save only critical events to the report file. |
|
Save all events to a report file. |
Advanced settings |
|
|
File with the Update task settings. The file must be created manually and saved in TXT format. The file can have the following contents: |
Example:
|
ROLLBACK. Last update rollback
Roll back the last anti-virus database update. This lets you roll back the databases and application modules to their previous version when necessary, for example, when the new database version contains an invalid signature that causes Kaspersky Endpoint Security to block a safe application.
Command syntax
Saving events to a report file mode (for Scan, Updater and Rollback profiles only) |
|
|
Save only critical events to the report file. |
|
Save all events to a report file. |
Example:
|
TRACES. Tracing
Enable / disable tracing. Trace files are stored on the computer as long as the application is in use, and are deleted permanently when the application is removed. Trace files, except trace files of Authentication Agent, are stored in the folder %ProgramData%\Kaspersky Lab\KES.21.13\Traces. By default, tracing is disabled.
Command syntax
Tracing level |
|
|
Level of detail of traces. Available values:
|
Advanced settings |
|
|
Run a command with the |
|
Use the OutputDebugString function and save the trace file. The OutputDebugString function sends a character string to the application debugger to display on screen. For details, visit the MSDN website. |
|
Save one trace file (no size limit). |
|
Save traces to a limited number of files of limited size and overwrite the older files when the maximum size is reached. |
|
Save traces to dump files. |
Examples:
|
START. Start the profile
Start the profile (for example, to update databases or to enable a protection component).
Command syntax
Profile |
|
|
Profile name. A Profile is a Kaspersky Endpoint Security component, task or feature. You can view the list of available profiles by executing the |
Saving events to a report file mode (for Scan, Updater and Rollback profiles only) |
|
|
Save only critical events to the report file. |
|
Save all events to a report file. |
Example:
|
STOP. Stopping a profile
Stop the running profile (for example, stop scanning, stop removable drives scan, or disable a protection component).
To execute this command, Password protection must be enabled. The user must have the Disable protection components and Disable control components permissions.
Command syntax
Profile |
|
|
Profile name. A Profile is a Kaspersky Endpoint Security component, task or feature. You can view the list of available profiles by executing the |
Authentication |
|
|
User account credentials with the required Password protection permissions. |
STATUS. Profile status
Show status information for application profiles (for example, running or completed). You can view the list of available profiles by executing the HELP STATUS command.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security also displays information about the status of service profiles. Information about the status of service profiles may be required when you are contacting Kaspersky Technical Support.
Command syntax
If you enter the command without a profile, Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays the status for all profiles of the application.
Page top
STATISTICS. Profile operation statistics
View statistical information about an application profile (for example, scan duration or the number of threats detected.) You can view the list of available profiles by running the HELP STATISTICS command.
Command syntax
RESTORE. Restoring files from Backup
You can restore a file from Backup to its original folder. If a file with the same name already exists at the specified path, the application will ask for confirmation to replace the file. The file that is being restored is copied keeping its original name.
To execute this command, Password protection must be enabled. The user must have the Restore from Backup permission.
Backup stores backup copies of files that were deleted or modified during disinfection. A backup copy is a file copy created before the file was disinfected or deleted. Backup copies of files are stored in a special format and do not pose a threat.
Backup copies of files are stored in the folder C:\ProgramData\Kaspersky Lab\KES.21.13\QB.
Users in the Administrators group are granted full permission to access this folder. Limited access rights to this folder are granted to the user whose account was used to install Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not provide the capability to configure user access permissions to backup copies of files.
Command syntax
Advanced settings |
|
|
Overwrite an existing file. |
|
The name of the file to be restored. |
Authentication |
|
|
User account credentials with the required Password protection permissions. |
Example:
|
EXPORT. Exporting application settings
Export Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings to a file. The file will be located in the C:\Windows\SysWOW64 folder.
Command syntax
Profile |
|
|
Profile name. A Profile is a Kaspersky Endpoint Security component, task or feature. You can view the list of available profiles by executing the |
File to export |
|
|
The name of the file to which the application settings will be exported. You can export Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings to a DAT or CFG configuration file, to a TXT text file, or to an XML document. |
Examples:
|
IMPORT. Importing application settings
Imports settings for Kaspersky Endpoint Security from a file that was created with the EXPORT command.
To execute this command, Password protection must be enabled. The user must have the Configure application settings permission.
Command syntax
File to import |
|
|
The name of the file from which the application settings will be imported. You can import Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings from a DAT or CFG configuration file, a TXT text file, or an XML document. |
Authentication |
|
|
User account credentials with the required Password protection permissions. |
Example:
|
ADDKEY. Applying a key file
Apply the key file to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security. If the application is already activated, the key will be added as a reserve one.
Command syntax
Key file |
|
|
Key file name. |
Authentication |
|
|
User account credentials. These credentials need to be entered only if Password protection is enabled. |
Example:
|
LICENSE. Licensing
Perform operations with the license keys of Kaspersky Endpoint Security or with the keys of EDR Optimum or EDR Expert (Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Add-on).
To execute this command and remove a license key, Password protection must be enabled. The user must have the Remove key permission.
Command syntax
Operation |
|
|
Apply the key file to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security. If the application is already activated, the key will be added as a reserve one. |
|
Activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security using an activation code. If the application is already activated, the key will be added as a reserve one. |
|
Update the status of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security license. As a result, the application receives up-to-date license status information from Kaspersky activation servers. |
|
Update the status of the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Add-on license. As a result, the application receives up-to-date license status information from Kaspersky activation servers. |
|
Remove the license key of the application. Reserve key will also be removed. |
|
Remove the license key of Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Add-on. Reserve key will also be removed. |
Authentication |
|
|
User account credentials with the required Password protection permissions. |
Example:
|
PBATESTRESET. Reset the disk check results before encrypting the disk
Reset the compatibility check results for Full Disk Encryption(FDE), including both the Kaspersky Disk Encryption and BitLocker Drive Encryption technologies.
Before running Full Disk Encryption, the application performs a number of checks to verify that the computer can be encrypted. If the computer does not support Full Disk Encryption, Kaspersky Endpoint Security logs information about the incompatibility. The next time you try to encrypt, the application does not perform this check and warns you that encryption is not possible. If the hardware configuration of the computer has changed, the compatibility check results previously logged by the application must be reset to re-check the system hard drive for compatibility with Kaspersky Disk Encryption or BitLocker drive encryption technologies.
EXIT. Exit the application
Exits Kaspersky Endpoint Security. The application will be unloaded from the computer's RAM.
To execute this command, Password protection must be enabled. The user must have the Exit the application permission.
Command syntax
EXITPOLICY. Disabling policy
Disables a Kaspersky Security Center policy on the computer. All Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings are available for configuration, including settings that have a closed lock in the policy (![]() ).
).
To execute this command, Password protection must be enabled. The user must have the Disable Kaspersky Security Center policy permission.
Command syntax
STARTPOLICY. Enabling policy
Enables a Kaspersky Security Center policy on the computer. The application settings will be configured according to the policy.
Page top
DISABLE. Disabling protection
Disables File Threat Protection on a computer with an expired Kaspersky Endpoint Security license. It is not possible to run this command on a computer that has the application that is not activated or has a valid license.
Page top
SPYWARE. Spyware detection
Enable / disable spyware detection. By default, spyware detection is enabled.
Command syntax
KSN. Switching between KSN / KPSN
Selecting a Kaspersky solution for determining the reputation of files or websites. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the following infrastructure solutions for working with Kaspersky reputation databases:
- Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is the solution that is used by most Kaspersky applications. KSN participants receive information from Kaspersky and send Kaspersky information about objects detected on the user's computer to be analyzed additionally by Kaspersky analysts and to be included in the reputation and statistical databases.
- Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN) is a solution that enables users of computers hosting Kaspersky Endpoint Security or other Kaspersky applications to obtain access to Kaspersky reputation databases, and to other statistical data without sending data to Kaspersky from their own computers. KPSN is designed for corporate customers who are unable to participate in Kaspersky Security Network for any of the following reasons:
- Local workstations are not connected to the Internet.
- Transmission of any data outside the country or outside the corporate LAN is prohibited by law or restricted by corporate security policies.
Command syntax
Kaspersky Security Network configuration file |
|
|
|
Name of the configuration file containing Kaspersky Private Security Network settings. This file has the PKCS7 or PEM extension. |
|
Example:
|
||
KESCLI commands
KESCLI commands let you receive information about the state of computer protection using the OPSWAT component, and let you perform standard tasks such as Malware Scan and Update tasks.
You can view the list of KESCLI commands by using the --help command or by using the abbreviated command -h.
To manage Kaspersky Endpoint Security from the command line:
- Run the command line interpreter (cmd.exe) as an administrator.
- Go to the folder where the Kaspersky Endpoint Security executable file is located.
- To execute a command, enter:kescli <command> [options]
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will execute the command (see figure below).
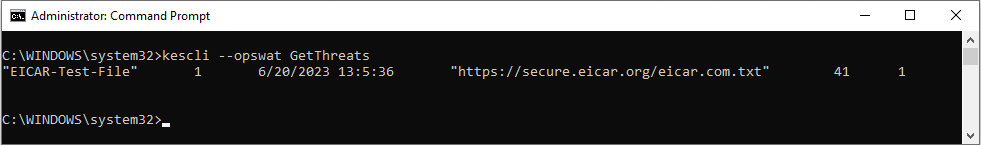
Managing the application from the command line
Scan. Malware Scan
Run the Malware Scan (Full Scan) task.
To run the task, the administrator must Allow use of local tasks in the policy.
Command syntax
You can check the completion status of a Malware Scan task by using the GetScanState command and view the date and time when the scan was last completed by using the GetLastScanTime command.
Scan scope |
|
|
|
Action on threat detection |
|
|
Notify. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds the information about infected files to the list of active threats on detection of these files. |
|
Disinfect, delete if disinfection fails. If this option is selected, the application automatically attempts to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection fails, the application deletes the files. This action is selected by default. |
Example:
|
GetScanState. Scan completion status
Receive information about the status of the Malware Scan (Full Scan) task completion:
1– the scan is in progress.0– the scan is not running.
Command syntax
GetLastScanTime. Determining the scan completion time
Receive information about the date and time of the last Malware Scan (Full Scan) task completion.
Command syntax
GetThreats. Obtaining data on detected threats
Receive a list of detected threats (Threats report). This report contains information about threats and virus activity during the last 30 days prior to creating the report.
Command syntax
When this command is executed, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will send a response in the following format:
<name of detected object> <type of object> <detection date and time> <path to file> <action on threat detection> <threat danger level>

Managing the application from the command line
Object type |
|
|
Not known ( |
|
Viruses ( |
|
Trojan programs ( |
|
Malicious programs ( |
|
Advertisement programs ( |
|
Auto-dialer programs ( |
|
Applications that could be used by a cybercriminal to harm the user's computer or data ( |
|
Packed objects whose packing method may be used to protect malicious code ( |
|
Unknown objects ( |
|
Known applications ( |
|
Concealed files ( |
|
Applications requiring attention ( |
|
Anomalous behavior ( |
|
Not determined ( |
|
Ad banners ( |
|
Network attack ( |
|
Registry access ( |
|
Suspicious activity ( |
|
Vulnerabilities ( |
|
|
|
Unwanted email attachment ( |
|
Malware detected by Kaspersky Security Network ( |
|
Unknown link ( |
|
Other malware ( |
Action on threat detection |
|
|
Not known ( |
|
Threat was remediated ( |
|
Object was infected and has not been disinfected ( |
|
Object is in an archive and has not been disinfected ( |
|
Object has been disinfected ( |
|
Object has not been disinfected ( |
|
Object was deleted ( |
|
A backup copy of the object was created ( |
|
Object was moved to Backup ( |
|
Object was deleted on computer restart ( |
|
Object was disinfected on computer restart ( |
|
Object was moved to Backup by a user ( |
|
Object was added to exclusions ( |
|
Object was moved to Backup on computer restart ( |
|
False positive ( |
|
Process was terminated ( |
|
Object was not detected ( |
|
Cannot resolve the threat ( |
|
Object was restored ( |
|
Object was created as a result of threat activity ( |
|
Object was restored on computer restart ( |
|
Object was not processed ( |
Threat danger level |
|
|
Unknown |
|
High |
|
Medium scan |
|
Low |
|
Info (less than Low) |
UpdateDefinitions. Updating databases and application software modules
Run the Update task. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the default source: Kaspersky update servers.
To run the task, the administrator must Allow use of local tasks in the policy.
Command syntax
You can view the release date and time of the current antivirus databases by using the GetDefinitionsetState command.
GetDefinitionState. Determining the update completion time
Receive information about the release date and time of the antivirus databases in use.
Command syntax
EnableRTP. Enabling protection
Enable Kaspersky Endpoint Security protection components on the computer: File Threat Protection, Web Threat Protection, Mail Threat Protection, Network Threat Protection, Host Intrusion Prevention.
To enable protection components, the administrator must make sure that the relevant policy settings can be modified (![]() attributes are open).
attributes are open).
Command syntax
As a result, protection components are enabled even if you have prohibited the modification of application settings with Password protection.
You can check the operating status of File Threat Protection by using the GetRealTimeProtectionState command.
GetRealTimeProtectionState. File Threat Protection status
Receive information about the operating status of the File Threat Protection component:
1– the component is enabled.0– the component is disabled.
Command syntax
Version. Identifying the application version
Identify the version of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
Command syntax
You can also use the abbreviated command -v.
Detection and Response management commands
You can use the command line to manage built-in functionality of Detection and Response solutions (for example, Kaspersky Sandbox or Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum). You can manage Detection and Response solutions if management using the Kaspersky Security Center console is not possible. You can view the list of commands for managing the application by executing the HELP command. To read about the syntax of a specific command, enter HELP <command>.
To manage built-in features of Detection and Response solutions using the command line:
- Run the command line interpreter (cmd.exe) as an administrator.
- Go to the folder where the Kaspersky Endpoint Security executable file is located.
- To execute a command, enter:
avp.com <command> [options]
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will execute the command.
SANDBOX. Managing Kaspersky Sandbox
Commands for managing the Kaspersky Sandbox component:
- Enable or disable the Kaspersky Sandbox component.
The Kaspersky Sandbox component enables interoperability with the Kaspersky Sandbox solution.
- Configure the Kaspersky Sandbox component:
- Connect the computer to Kaspersky Sandbox servers.
The servers use deployed virtual images of Microsoft Windows operating systems to run objects that need to be scanned. You can enter an IP address (IPv4 or IPv6) or a fully qualified domain name. For details about deploying virtual images and configuring Kaspersky Sandbox servers, refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox Help.
- Configure connection timeout for Kaspersky Sandbox server.
Timeout for receiving a response to an object scanning request from the Kaspersky Sandbox server. After the timeout elapses, Kaspersky Sandbox redirects the request to the next server. The timeout value depends on the speed and stability of the connection. The default value is 5 seconds.
- Configure a trusted connection between the computer and Kaspersky Sandbox servers.
To configure a trusted connection with Kaspersky Sandbox servers, you must prepare a TLS certificate. Next you must add the certificate to Kaspersky Sandbox servers and the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy. For details on preparing the certificate and adding the certificate to servers, refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox Help.
- Connect the computer to Kaspersky Sandbox servers.
- Display the current settings of the component.
Command syntax
Operation |
|
|
Disable the Kaspersky Sandbox component. |
|
Enable the Kaspersky Sandbox component. |
|
Configure the Kaspersky Sandbox component. You can modify the following settings:
|
|
Display the current settings of the component. You get the following response:
|
Authentication |
|
|
User account credentials with the required Password protection permissions. |
Example:
|
PREVENTION. Managing Execution prevention
Disable Execution Prevention or show the current component settings, including the list of execution prevention rules.
Command syntax
Upon executing the prevention /show command, you will get the following response:
prevention.enable=true|false
prevention.mode=audit|prevent
prevention.rules
id: <rule ID>
target: script|process|document
md5: <MD5 hash of the file>
sha256: <SHA256 hash of the file>
pattern: <path to the object>
case-sensitive: true|false
Command return values:
-1means the command is not supported by the version of the application that is installed on the computer.0means the command was executed successfully.1means a mandatory argument was not passed to the command.2means a general error occurred.4means there was a syntax error.9– wrong operation (for example, an attempt to disable the component when it is already disabled).
ISOLATION. Managing Network isolation
Turn off Network isolation of the computer or display current settings of the component. Component settings also include a list of network connections added to exclusions.
Command syntax:
As a result of running the stat command, you receive the following response: Network isolation on|off.
RESTORE. Restoring files from Quarantine
You can restore a file from Quarantine to its original folder. Quarantine is a special local storage on the computer. The user can quarantine files that the user considers dangerous for the computer. Quarantined files are stored in an encrypted state and do not threaten the security of the device. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses Quarantine only when working with Detection and Response solutions: EDR Optimum, EDR Expert, KATA (EDR), Kaspersky Sandbox. In other cases Kaspersky Endpoint Security places the relevant file in Backup. For details on managing Quarantine as part of solutions, please refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox Help, Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help, and Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help.
To execute this command, Password protection must be enabled. The user must have the Restore from Backup permission.
The object is quarantined under the system account (SYSTEM).
Restoring files from Quarantine involves the following special considerations:
- If the destination folder has been deleted or the user does not have access rights to that folder, the application places the file in the
%DataRoot%\QB\Restoredfolder. Then you must manually move the file to the destination folder. - The application treats the name of the file being restored as case sensitive. If you do not observe the case when entering the file name, the application does not restore the file.
- If the destination folder already has a file with the same name, the application cancels the restoration of the file.
- If you are using the KATA (EDR) solution, the application saves a copy of the file in Quarantine after restoring the file. You can clear the Quarantine manually. For EDR Optimum and EDR Expert solutions, the application deletes the file after restoration.
Command syntax
Advanced settings |
|
|
Overwrite an existing file. |
|
The name of the file to be restored. |
Authentication |
|
|
User account credentials with the required Password protection permissions. |
Example:
|
Command return values:
-1means the command is not supported by the version of the application that is installed on the computer.0means the command was executed successfully.1means a mandatory argument was not passed to the command.2means a general error occurred.4means there was a syntax error.
IOCSCAN. Scan for indicators of compromise (IOC)
Run the Scan for indicators of compromise (IOC) task. An Indicator of Compromise (IOC) is a set of data about an object or activity that indicates unauthorized access to the computer (compromise of data). For example, many unsuccessful attempts to sign in to the system can constitute an Indicator of Compromise. The IOC Scan task allows finding Indicators of Compromise on the computer and taking threat response measures.
Command syntax
IOC files |
|
|
Full path to the IOC file that you want to use for scanning. You can specify multiple IOC files separated by spaces. The full path to the IOC file must be entered without the / For example, |
|
Path to the folder with IOC files that you want to use for scanning. IOC files are files containing the sets of indicators that the application tries to match to count a detection. IOC files must conform to the OpenIOC standard. For example, |
Data type for IOC scanning |
|
|
Analyze process data when performing the IOC scan (ProcessItem term). If the value of the argument is If the argument is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes process data only if the ProcessItem IOC document is described in the IOC file that is provided for the scan. |
|
Analyze file data when performing the IOC scan (ProcessItem and FileItem terms). You can select a file in one of the following ways:
|
|
Analyze Windows registry data when performing an IOC scan (RegistryItem term). If the value of the argument is If the argument is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the Windows registry only if the RegistryItem IOC document is described in the IOC file that is provided for the scan. For the RegistryItem data type, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans a set of registry keys. |
|
Analyze the data about records in the local DNS cache when performing the IOC scan (DnsEntryItem term). If the value of the argument is If the argument is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the local DNS cache only if the DnsEntryItem IOC document is described in the IOC file that is provided for the scan. |
|
Analyze the data about records in the ARP table when performing the IOC scan (ArpEntryItem term). If the value of the argument is If the argument is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the ARP table only if the ArpEntryItem IOC document is described in the IOC file that is provided for the scan. |
|
Analyze data about ports open for listening when performing the IOC scan (PortItem term). If the value of the argument is If the argument is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the table of active connections only if the PortItem IOC document is described in the IOC file that is provided for the scan. |
|
Analyze data about services installed on the device when performing the IOC scan (ServiceItem term). If the value of the argument is If the argument is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes service data only if the ServiceItem IOC document is described in the IOC file that is provided for the scan. |
|
Analyze environment data when performing the IOC scan (SystemInfoItem term). If the value of the argument is If the argument is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes environment data only if the SystemInfoItem IOC document is described in the IOC file that is provided for the scan. |
|
Analyze data about users when performing the IOC scan (UserItem term). If the value of the argument is If the argument is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes data about users created in the system only if the UserItem IOC document is described in the IOC file that is provided for the scan. |
|
Analyze data about volumes when performing the IOC scan (VolumeItem term). If the value of the argument is If the argument is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes volume data only if the VolumeItem IOC document is described in the IOC file that is provided for the scan. |
|
Analyze the data about records in the Windows event log when performing the IOC scan (EventLogItem term). If the value of the argument is If the argument is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the Windows event log if the EventLogItem IOC document is described in the IOC file that is provided for the scan. |
|
Take into consideration the date when the event was published in the Windows event log when determining the IOC scan scope for the corresponding IOC document. When performing an IOC scan, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans Windows event log entries published during the period from the specified time and date to the moment when the task is run. Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows specifying the event publication date as the value of the argument. The scan is performed only for events published in the Windows event log after the specified date and before the scan is run. If the argument is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans events with any publication date. The TaskSettings::BaseSettings::EventLogItem::datetime setting cannot be edited. The setting is used only if the EventLogItem IOC document is described in the IOC file provided for the scan. |
|
List of channel (log) names for which you want to perform an IOC scan. If the argument is specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans records published in the specified logs. The IOC document must have the EventLogItem term described. The name of the log is specified as a string in accordance with the name of the log (channel) specified in the properties of the log (the Full Name parameter) or in the event properties (the <Channel></Channel> parameter in the xml schema of the event). You can specify multiple channels separated by spaces. If the argument is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans records for channels |
|
Analyze file data when performing the IOC scan (FileItem term). If the value of the argument is If the argument is not specified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes file data only if the FileItem IOC document is described in the IOC file that is provided for the scan. |
|
Set IOC scan scope when analyzing data for the FileItem IOC document. You can set the following values for the scan scope:
If the argument is not specified, the scan is performed for critical areas. |
|
Set exclusion scope when analyzing data for the FileItem IOC document. You can specify multiple paths separated by spaces. |
|
User-defined IOC scan scope when analyzing data for the FileItem IOC document ( |
Command return values:
-1means the command is not supported by the version of the application that is installed on the computer.0means the command was executed successfully.1means a mandatory argument was not passed to the command.2means a general error occurred.4means there was a syntax error.
If the command was executed successfully (return value 0) and indicators of compromise were detected along the way, Kaspersky Endpoint Security outputs the following task result information to the command line:
|
ID of the IOC file from the header of the IOC file structure (the |
|
Description of the IOC file from the header of the IOC file structure (the |
|
List of IDs of all matched indicators. |
|
Data for each IOC document for which there was a match. |
MDRLICENSE. MDR activation
Perform operations with the BLOB configuration file to activate Managed Detection and Response. The BLOB file contains the client ID and information about the license for Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response. The BLOB file is located inside the ZIP archive of the MDR configuration file. You can obtain the ZIP archive in the Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response Console. For detailed information about a BLOB file, please refer to the Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response Help.
Administrator privileges are required for performing operations with a BLOB file. Managed Detection and Response settings in the policy must also be available for editing (![]() ).
).
Command syntax
Operation |
|
|
Apply the BLOB configuration file for integration with Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response (P7 file format). You can apply only one BLOB file. If a BLOB file was already added to the computer, the file will be replaced. |
|
Delete the BLOB configuration file. |
Authentication |
|
|
User account credentials with the required Password protection permissions. |
Example:
|
EDRKATA. Integration with EDR (KATA)
Commands for managing the Endpoint Detection and Response component (KATA):
- Enable or disable the EDR component (KATA).
The EDR component (KATA) provides interoperability with the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform solution.
- Configure the connection to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform servers.
- Display the current settings of the component.
Command syntax
Operation |
|
|
Disable the EDR component (KATA). |
|
Enable the EDR component (KATA). |
|
Configure the EDR component (KATA). You can modify the following settings:
|
|
Display the current settings of the component. |
Error codes
Errors may occur when working with the application through the command line. When errors occur, Kaspersky Endpoint Security shows an error message, for example, Error: Cannot start task 'EntAppControl'. Kaspersky Endpoint Security can also show additional information in the form of a code, for example, error=8947906D (see the table below).
Error codes
Error code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
This key is already in use |
|
License expired. Database updates are unavailable |
|
Key not found |
|
Digital signature is either missing or corrupted |
|
Data is corrupted |
|
Key file is corrupted |
|
License expired |
|
Key file is not specified |
|
Invalid key file |
|
Failed to save data |
|
Failed to read data |
|
I/O error |
|
Databases not found |
|
Licensing library not loaded |
|
Databases corrupted or updated manually |
|
Databases are corrupted |
|
Cannot use invalid key file to add a reserve key |
|
System error |
|
Denylist of keys corrupted |
|
File signature does not match the digital signature of Kaspersky |
|
Cannot use a key for trial license as a key for commercial license |
|
The license for beta testing is required to use the beta version of the application |
|
The key file is not compatible with this application. It is impossible to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows with a key file for another application. Please check the installed application |
|
License key is blocked by Kaspersky |
|
The application has already been used under a trial license. Cannot add a key for trial license again |
|
Key file is corrupted |
|
Digital signature is missing, corrupted, or does not match the Kaspersky digital signature |
|
Cannot add a key if the corresponding non-commercial license has expired |
|
The date the key file was created or used is invalid. Please check the system date |
|
Cannot add a key for trial license: another key for trial license is already active |
|
Denylist of keys corrupted or missing |
|
Update description missing or corrupted |
|
Internal data incompatible with this application |
|
Cannot use invalid key file to add a reserve key |
|
Error sending activation server request. Possible reasons: Internet connection error or temporary problems on the activation server. Try to activate the application later (in 1 to 2 hours) with the activation code. If this error reoccurs, contact your Internet provider |
|
Request contains incorrect activation code |
|
Cannot obtain response status |
|
Error occurred when saving temporary file |
|
Incorrect activation code is entered or invalid system date is set on the computer. Please check the system date on your computer |
|
Key not compatible with this application, or license expired |
|
Failed to receive a key file. Incorrect activation code was entered |
|
Activation server has returned error 400 |
|
Activation server has returned error 401 |
|
Activation server has returned error 403 |
|
Necessary resource is unavailable on the activation server. Activation server has returned error 404. Please check your Internet connection settings |
|
Activation server has returned error 405 |
|
Activation server has returned error 406 |
|
Proxy authentication is required. Please check your network settings |
|
Request timed out |
|
Activation server has returned error 409 |
|
Necessary resource is unavailable on the activation server. Activation server has returned error 410. Please check your Internet connection settings |
|
Activation server has returned error 411 |
|
Activation server has returned error 412 |
|
Activation server has returned error 413 |
|
Activation server has returned error 414 |
|
Activation server has returned error 415 |
|
Internal server error |
|
Functionality not supported |
|
Invalid gateway response. Please check your network settings |
|
Resource temporarily unavailable |
|
Gateway response timed out. Please check your network settings |
|
The protocol is not supported by the server |
|
Unknown http error |
|
Invalid resource ID |
|
Invalid URL |
|
Invalid destination folder |
|
Memory allocation error |
|
Error occurred when converting parameters to ANSI string (URL, folder, agent) |
|
Error occurred when creating worker thread |
|
Worker thread already running |
|
Worker thread not running |
|
Key file is not found on activation server |
|
Key is blocked |
|
Activation server internal error |
|
Not enough data in activation request |
|
The license that corresponds to the added key has already expired |
|
Invalid system date is set on the computer. Please check the system date value |
|
Trial license has expired |
|
Application activation period expired |
|
The limit of application activations has been exceeded for the specified code |
|
Activation procedure completed with system error |
|
Cannot use a key for trial license as a key for commercial license |
|
Activation code is required |
|
Cannot connect to activation server |
|
Activation server is unavailable. Please check your Internet connection settings and retry activation |
|
License has expired |
|
Cannot replace the active key with an expired key |
|
Cannot add a reserve key if the corresponding license expires before the current license |
|
Updated subscription key missing |
|
Invalid activation code |
|
Key already active |
|
License types that correspond to active and reserve keys do not match |
|
Component not supported by license |
|
Unable to add subscription key as a reserve key |
|
Transport layer generic error |
|
Failed to connect to activation server |
|
Invalid web address format |
|
Failed to convert proxy server address |
|
Failed to convert server address. Please check Internet connection settings |
|
Server connection attempt failed |
|
Access denied remotely |
|
Operation timed out |
|
Error sending HTTP request |
|
SSL connection error |
|
Operation interrupted by callback |
|
Too many redirects |
|
Recipient check failed |
|
Empty response from server |
|
Error sending data |
|
Error receiving data |
|
SSL certificate related problem |
|
SSL encryption related problem |
|
SSL certification center related problem |
|
Invalid contents of network packet |
|
Account access denied |
|
Invalid SSL certificate file |
|
Cannot shut down SSL connection |
|
Recurring error |
|
Invalid file with revoked certificates |
|
SSL certificate request error |
|
Unknown server error |
|
Internal server error |
|
No key available for the activation code entered |
|
Active key is blocked |
|
Required parameters of activation request are missing |
|
Invalid client number or password |
|
Invalid activation code |
|
The activation code is not compatible with this application. It is impossible to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows with an activation code for another application. Please check the installed application |
|
Activation code is required |
|
Activation period expired |
|
Number of activations with this code has been exceeded |
|
Invalid format of request ID |
|
Activation code already in use |
|
Failed to renew activation code |
|
Activation code is invalid for this region |
|
This activation code cannot be used for this localization of the application |
|
The activation code is intended for the new version of this application. Get a different activation code to activate the installed version of the application |
|
Activation server returned error 643 |
|
Activation server returned error 644 |
|
Activation server returned error 645 |
|
Activation server returned error 646 |
|
Activation server version 1.0 is required |
|
Incorrect activation code format |
|
Computer time is out of sync with activation server time |
|
Wrong application version |
|
Subscription has expired |
|
Number of activations exceeded |
|
Invalid ticket signature |
|
Additional data is needed |
|
Data verification failed |
|
Subscription inactive |
|
Activation server is under maintenance |
|
Unexpected error |
|
Invalid parameter transferred. For example, an empty list of activation server addresses |
|
Invalid activation code (invalid hash) |
|
Invalid user ID |
|
Invalid user password |
|
Invalid response from activation server |
|
Activation request has been interrupted |
|
Activation server has returned an empty forwarding list |
Appendix. Application profiles
A Profile is a Kaspersky Endpoint Security component, task or feature. Profiles are used to manage the application from the command line. You can use profiles to execute START, STOP, STATUS, STATISTICS, and EXPORT commands. Using profiles, you can configure application settings (for example, STOP DeviceControl) or run tasks (for example, START Scan_My_Computer).
The following profiles are available:
AdaptiveAnomaliesControl– Adaptive Anomaly Control.AMSI– AMSI Protection.BehaviorDetection– Behavior Detection.DeviceControl– Device control.EntAppControl– Application Control.File_MonitoringorFM– File Threat Protection.FirewallorFW– Firewall.HIPS– Host Intrusion prevention.IDS– Network Threat Protection.IntegrityCheck– Integrity check.LogInspector– Log Inspection.Mail_MonitoringorEM– Mail Threat Protection.Rollback– update rollback.Scan_ContextScan– Scan from context menu.Scan_IdleScan– Background scan.Scan_Memory– Kernel memory scan.Scan_My_Computer– Full scan.Scan_Objects– Custom scan.Scan_Qscan– Scan objects that are loaded at operation system startup.Scan_Removable_Drive– Removable drives scan.Scan_StartuporSTARTUP– Critical Areas Scan.Updater– Update.Web_MonitoringorWM– Web Threat Protection.WebControl– Web Control.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security also supports service profiles. Service profiles may be required when you are contacting Kaspersky Technical Support.
Page top
Managing the application through the REST API
Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you configure application settings, run a scan, update the anti-virus databases, and perform other tasks using third-party solutions. Kaspersky Endpoint Security provides an API for this purpose. The Kaspersky Endpoint Security REST API operates over HTTP and consists of a set of request/response methods. In other words, you can manage Kaspersky Endpoint Security through a third-party solution, and not the local application interface or the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
To start using REST API, you need to install Kaspersky Endpoint Security with support for the REST API. The REST client and Kaspersky Endpoint Security must be installed on the same computer.
To ensure safe interaction between Kaspersky Endpoint Security and the REST client:
- Configure REST client's protection from unauthorized access according the recommendations of the REST client developer. Configure REST client folder protection from writing with the help of Discretionary Access Control List – DACL.
- To run REST client, use a separate account with administrator rights. Deny interactive sign-in into the system for this account.
The application is managed through the REST API at http://127.0.0.1 or http://localhost. It is not possible to remotely manage Kaspersky Endpoint Security through the REST API.
![]() OPEN THE REST API DOCUMENTATION
OPEN THE REST API DOCUMENTATION
Installing the application with the REST API
To manage the application through the REST API, you need to install Kaspersky Endpoint Security with support for the REST API. If you manage Kaspersky Endpoint Security through the REST API, you cannot manage the application using Kaspersky Security Center.
Preparing for installing the application with REST API support
Secure interaction of Kaspersky Endpoint Security with the REST client requires configuring request identification. To do so, you must install a certificate and subsequently sign the payload of each request.
To create a certificate, you can use e.g. OpenSSL.
Example:
|
Use the RSA encryption algorithm with a key length of 2048 bits or more.
As a result, you will get a cert.pem certificate and a key.pem private key.
Installing the application with REST API support
To install Kaspersky Endpoint Security with REST API support:
- Run the command line interpreter (cmd.exe) as an administrator.
- Go to the folder that contains the distribution package for Kaspersky Endpoint Security version 11.2.0 or later.
- Install Kaspersky Endpoint Security with the following settings:
RESTAPI=1RESTAPI_User=<User name>User name for managing the application through the REST API. Enter the user name in the format
<DOMAIN>\<UserName>(for example,RESTAPI_User=COMPANY\Administrator). You can manage the application through the REST API only under this account. You can select only one user to work with the REST API.RESTAPI_Port=<Port>Port used for managing the application through the REST API. Port 6782 is used by default. Make sure that the port is free. Optional parameter.
RESTAPI_Certificate=<Path to certificate>Certificate for identifying requests (for example,
RESTAPI_Certificate=C:\cert.pem).You can install the certificate after installing the application or update the certificate after the certificate expires.
How to install a certificate for REST API request identification
AdminKitConnector=1Application management using administration systems. Management is allowed by default.
You can also use the setup.ini file to define the settings for working with the REST API.
Example:
setup_kes.exe /pEULA=1 /pPRIVACYPOLICY=1 /pKSN=1 /pALLOWREBOOT=1 /pAdminKitConnector=1 /pRESTAPI=1 /pRESTAPI_User=COMPANY\Administrator /pRESTAPI_Certificate=C:\cert.pem /s
As a result, you will be able to manage the application through the REST API. To verify its operation, open the REST API documentation using a GET request.
Example:
|
If you installed the application with REST API support, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically creates an allow rule in the Web Control settings for accessing web resources (Service Rule for REST API). This rule is needed to allow the REST client to access Kaspersky Endpoint Security at all times. For example, if you have restricted user access to web resources, this will not affect managing the application through the REST API. We recommend that you do not delete the rule or change the Service Rule for REST API settings. If you deleted the rule, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will restore it after restarting the application.
Page top
Working with the API
It is not possible to restrict access to the application through the REST API using Password Protection. For example, it is not possible to block a user from disabling protection through the REST API. You can configure Password Protection through the REST API and restrict user access to the application through the local interface.
To manage the application through the REST API, you need to run the REST client under the account that you specified when installing the application with REST API support. You can select only one user to work with the REST API.
![]() OPEN THE REST API DOCUMENTATION
OPEN THE REST API DOCUMENTATION
Managing the application through the REST API consists of the following steps:
- Get the current values of the application settings. To do so, send a GET request.
Example:
GET http://localhost:6782/kes/v1/settings/ExploitPrevention - The application will send a response with the structure and values of settings. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports XML- and JSON formats.
Example:
{"action": 0,"enableSystemProcessesMemoryProtection":true,"enabled": true} - Edit the application settings. Use the settings structure received in response to the GET request.
Example:
{"action": 0,"enableSystemProcessesMemoryProtection":false,"enabled": true} - Save application settings (the payload) in a JSON (payload.json).
- Sign the JSON in the PKCS7 format.
Example:
$ openssl smime -sign -inpayload.json -signer cert.pem -inkey key.pem -nodetach -binary -outform pem -out signed_payload.pemAs a result, you get a signed file with the payload of the request (
signed_payload.pem). - Edit the application settings. To do so, send a POST request and attach the signed file with the request payload (
signed_payload.pem).
The application applies the new settings and sends a response containing the application configuration results (the response can be empty). You can verify that the settings are updated using a GET request.
Page top
Sources of information about the application
This section contains a description of the sources of information about the application.
You can select the most convenient source of information depending on the importance and urgency of the issue.
Page top
Contacting Technical Support
If you cannot find a solution to your problem in the documentation or in other sources of information about Kaspersky Endpoint Security, we recommend that you contact Technical Support. Technical Support will answer your questions about installing and using Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Kaspersky provides support for Kaspersky Endpoint Security during the application's life cycle (refer to the application life cycle page). Before contacting Technical Support, please read the support rules.
You can contact Technical Support in one of the following ways:
- By visiting the Technical Support website
- By sending a request to Kaspersky Technical Support through the Kaspersky CompanyAccount portal
After you inform Kaspersky Technical Support specialists about your issue, they may ask you to create a trace file. The trace file allows tracing the process of performing application commands step by step and determining the stage of application operation at which an error occurs.
Technical Support specialists may also require additional information about the operating system, processes that are running on the computer, detailed reports on the operation of application components.
While running diagnostics, Technical Support experts may ask you to change application settings by:
- Activating the functionality for receiving extended diagnostic information.
- Configure individual components of the application by changing special settings that are not accessible through the standard user interface.
- Changing the settings for storage of diagnostic information.
- Configuring the interception and logging of network traffic.
Technical Support experts will provide all the information needed to perform these operations (description of the sequence of steps, settings to be modified, configuration files, scripts, additional command line functionality, debugging modules, special-purpose utilities, etc.) and inform you about the scope of data used for purposes of debugging. The extended diagnostic information is saved on the user's computer. The data is not automatically transmitted to Kaspersky.
The operations listed above should be performed only under the supervision of Technical Support specialists by following their instructions. Changing application settings on your own in ways not described in the Online Help or in Technical Support recommendations can cause slowdowns and crashes of the operating system, reduce the protection level of your computer, and damage the availability and integrity of information being processed.
Contents and storage of trace files
You are personally responsible for the security of the data that is stored on your computer, particularly for monitoring and restricting access to the data until it is submitted to Kaspersky.
Trace files are stored on the computer as long as the application is in use, and are deleted permanently when the application is removed.
Trace files, except trace files of Authentication Agent, are stored in the folder %ProgramData%\Kaspersky Lab\KES.21.13\Traces.
Trace files are named as follows: KES<21.13_dateXX.XX_timeXX.XX_pidXXX.><trace file type>.log.
You can view data saved in trace files.
All trace files contain the following common data:
- Event time.
- Number of the thread of execution.
The Authentication Agent trace file does not contain this information.
- Application component that caused the event.
- Degree of event severity (informational event, warning, critical event, error).
- A description of the event involving command execution by a component of the application and the result of execution of this command.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security saves user passwords to a trace file only in encrypted form.
Contents of SRV.log, GUI.log, and ALL.log trace files
SRV.log, GUI.log, and ALL.log trace files may store the following information in addition to general data:
- Personal data, including the last name, first name, and middle name, if such data is included in the path to files on the local computer.
- Data on the hardware installed on the computer (such as BIOS/UEFI firmware data). This data is written to trace files when performing Kaspersky Disk Encryption.
- The user name and password if they were transmitted openly. This data can be recorded in trace files during Internet traffic scanning.
- The user name and password if they are contained in HTTP headers.
- The name of the Microsoft Windows account if the account name is included in a file name.
- Your email address or a web address containing the name of your account and password if they are contained in the name of the object detected.
- Websites that you visit and redirects from these websites. This data is written to trace files when the application scans websites.
- Proxy server address, computer name, port, IP address, and user name used to sign in to the proxy server. This data is written to trace files if the application uses a proxy server.
- Remote IP addresses to which your computer established connections.
- Message subject, ID, sender's name and address of the message sender's web page on a social network. This data is written to trace files if the Web Control component is enabled.
- Network traffic data. This data is written to trace files if traffic monitoring components are enabled (such as Web Control).
- Data received from Kaspersky servers (such as the version of anti-virus databases).
- Statuses of Kaspersky Endpoint Security components and their operating data.
- Data on user activity in the application.
- Operating system events.
Contents of HST.log, BL.log, Dumpwriter.log, WD.log, AVPCon.dll.log trace files
In addition to general data, the HST.log trace file contains information about the execution of a database and application module update task.
In addition to general data, the BL.log trace file contains information about events occurring during operation of the application, as well as data required to troubleshoot application errors. This file is created if the application is started with the avp.exe –bl parameter.
In addition to general data, the Dumpwriter.log trace file contains service information required for troubleshooting errors that occur when the application dump file is written.
In addition to general data, the WD.log trace file contains information about events occurring during operation of the avpsus service, including application module update events.
In addition to general data, the AVPCon.dll.log trace file contains information about events occurring during the operation of the Kaspersky Security Center connectivity module.
Contents of performance trace files
Performance trace files are named as follows: KES<21.13_dateXX.XX_timeXX.XX_pidXXX.>PERF.HAND.etl.
In addition to general data, performance trace files contain information about the load on the processor, information about the loading time of the operating system and applications, and information about running processes.
Contents of the AMSI Protection component trace file
In addition to general data, the AMSI.log trace file contains information about the results of scans performed on requests from third-party applications.
Contents of trace files of the Mail Threat Protection component
The trace file mcou.OUTLOOK.EXE.log may contain parts of email messages, including email addresses, in addition to general data.
Contents of trace files of the Scan from Context Menu component
The shellex.dll.log trace file contains information about completion of the scan task and data required to debug the application, in addition to general information.
Contents of trace files of the application web plug-in
Trace files of the application web plug-in are stored on the computer on which Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is deployed, in the folder Program Files\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center Web Console\logs.
Trace files of the application web plug-in are named as follows: logs-kes_windows-<type of trace file>.DESKTOP-<date of file update>.log. Web Console begins writing data after installation and deletes the trace files after Web Console is removed.
Trace files of the application web plug-in contain the following information in addition to general data:
- KLAdmin user password for unlocking the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface (Password protection).
- Temporary password for unlocking the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface (Password protection).
- User name and password for the SMTP mail server (Email notifications).
- User name and password for the Internet proxy server (Proxy server).
- User name and password for the Change application components task.
- Account credentials and paths specified in Kaspersky Endpoint Security tasks and policy properties.
Contents of the Authentication Agent trace file
The Authentication Agent trace file is stored in the System Volume Information folder and is named as follows: KLFDE.{EB2A5993-DFC8-41a1-B050-F0824113A33A}.PBELOG.bin.
In addition to general data, the Authentication Agent trace file contains information about the operation of Authentication Agent and the actions performed by the user with Authentication Agent.
Page top
Application operation tracing
Application tracing is a detailed record of actions that performed by the application, and of messages about events that occurred during operation of the application.
Application tracing should be performed under the supervision of Kaspersky Technical Support.
To create an application trace file:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the window that opens, click the Support Tools button.
- Use the Enable application tracing toggle to enable or disable tracing of application operation.
- In the Tracing drop-down list, select an application tracing mode:
- With rotation. Save traces to a limited number of files of limited size and overwrite the older files when the maximum size is reached. If this mode is selected, you can define the maximum number of files for rotation and the maximum size for each file.
- Write to a single file. Save one trace file (no size limit).
- In the Level drop-down list, select the tracing level.
You are advised to clarify the required tracing level with a Technical Support specialist. In the absence of guidance from Technical Support, set the tracing level to Normal (500).
- Restart Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- To stop the tracing process, return to the Support Tools window and disable tracing.
You can also create trace files when installing the application from the command line, including by using the setup.ini file.
As a result, application operation trace file is created in the %ProgramData%\Kaspersky Lab\KES.21.13\Traces folder. After the trace file is created, send the file to Kaspersky Technical Support.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes trace files when the application is removed. You can also delete the files manually. To do so, you must disable tracing and stop the application.
Page top
Application performance tracing
Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you receive information about computer operating issues during use of the application. For example, you can receive information about delays in operating system loading after the application is installed. To do so, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates performance trace files. Performance tracing refer to the logging of actions performed by the application for the purpose of diagnosing performance issues of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. To receive information, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the Event Tracing for Windows service (ETW). Kaspersky Technical Support is responsible for diagnosing issues of Kaspersky Endpoint Security and establishing the reasons for those issues.
Application tracing should be performed under the supervision of Kaspersky Technical Support.
To create a performance trace file:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the window that opens, click the Support Tools button.
- Use the Enable performance tracing toggle to enable or disable tracing of application performance.
- In the Tracing drop-down list, select an application tracing mode:
- With rotation. Save traces to a limited number of files of limited size and overwrite the older files when the maximum size is reached. If this mode is selected, you can define the maximum size for each file.
- Write to a single file. Save one trace file (no size limit).
- In the Level drop-down list, select the tracing level:
- Light. Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the most important operating system processes related to performance.
- Detailed. Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes all operating system processes related to performance.
- In the Tracing type drop-down list, select the tracing type:
- Basic information. Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes processes while the operating system is running. Use this tracing type if a problem persists after the operating system is loaded, such as a problem accessing the Internet in the browser.
- On restart. Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes processes only while the operating system is loading. After the operating system is loaded, Kaspersky Endpoint Security stops tracing. Use this tracing type if the problem is related to delayed loading of the operating system.
- Restart the computer and try to reproduce the problem.
- To stop the tracing process, return to the Support Tools window and disable tracing.
As a result, a performance trace file is created in the %ProgramData%\Kaspersky Lab\KES.21.13\Traces folder. After the trace file is created, send the file to Kaspersky Technical Support.
Dump writing
A dump file contains all information about the working memory of Kaspersky Endpoint Security processes at the moment when the dump file was created.
Saved dump files may contain confidential data. To control access to data, you must independently ensure the security of dump files.
Dump files are stored on the computer as long as the application is in use, and are deleted permanently when the application is removed. Dump files are stored in the folder %ProgramData%\Kaspersky Lab\KES.21.13\Traces.
To enable or disable dump writing:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Application settings.
- In the Debug information block, use the Enable dump writing check box to enable or disable application dump writing.
- Save your changes.
Protecting dump files and trace files
Dump files and trace files contain information about the operating system, and may also contain user data. To prevent unauthorized access to such data, you can enable protection of dump files and trace files.
If protection of dump files and trace files is enabled, the files can be accessed by the following users:
- Dump files can be accessed by the system administrator and local administrator, and by the user that enabled the writing of dump files and trace files.
- Trace files can be accessed only by the system administrator and local administrator.
To enable or disable protection of dump files and trace files:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Application settings.
- In the Debug information block, use the Enable dump and trace files protection check box to enable or disable file protection.
- Save your changes.
Dump files and trace files that were written while protection was active remain protected even after this function is disabled.
Page top
Limitations and warnings
Kaspersky Endpoint Security has a number of limitations that are not critical to operation of the application.
Compatibility with Kaspersky Security Center
Detection and Response (EDR, MDR, Kaspersky Sandbox)
Page topGlossary
Active key
A key that is currently used by the application.
Additional key
A key that certifies the right to use the application but is not currently being used.
Administration group
A set of devices that share common functions and a set of Kaspersky applications installed on them. Devices are grouped so that they can be managed conveniently as a single unit. A group may include other groups. It is possible to create group policies and group tasks for each installed application in the group.
Anti-virus databases
Databases that contain information about computer security threats known to Kaspersky as of the anti-virus database release date. Anti-virus database signatures help to detect malicious code in scanned objects. Anti-virus databases are created by Kaspersky specialists and updated hourly.
Archive
One or several files packed into a single compressed file. A specialized application called an archiver is required for packing and unpacking data.
Authentication Agent
Interface that lets you complete authentication to access encrypted hard drives and load the operating system after the bootable hard drive has been encrypted.
Certificate issuer
Certification center that issued the certificate.
Database of malicious web addresses
A list of web addresses whose content may be considered to be dangerous. The list is created by Kaspersky specialists. It is regularly updated and is included in the Kaspersky application distribution kit.
Database of phishing web addresses
A list of web addresses which Kaspersky specialists have determined to be phishing-related. The database is regularly updated and is part of the Kaspersky application distribution kit.
Disinfection
A method of processing infected objects that results in complete or partial recovery of data. Not all infected objects can be disinfected.
False alarm
A false alarm occurs when the Kaspersky application reports an uninfected file as infected because the signature of the file is similar to that of a virus.
Infectable file
A file which, due to its structure or format, can be used by intruders as a "container" to store and spread malicious code. As a rule, these are executable files, with such file extensions as .com, .exe, and .dll. There is a fairly high risk of intrusion of malicious code in such files.
Infected file
A file which contains malicious code (code of known malware has been detected when scanning the file). Kaspersky does not recommend using such files, because they may infect your computer.
IOC
Indicator of Compromise. A set of data about a malicious object or activity.
IOC file
A file containing a set of indicators of compromise (IOCs) that the application tries to match to count a detection. The likelihood of detection can be higher if exact matches with multiple IOC files are found for the object as a result of the scan.
License certificate
A document that Kaspersky transfers to the user together with the key file or activation code. It contains information about the license granted to the user.
Mask
Representation of a file name and extension by using wildcards.
File masks can contain any characters that are allowed in file names, including wildcards:
- The
*(asterisk) character, which takes the place of any set of characters, except the\and/characters (delimiters of the names of files and folders in paths to files and folders). For example, the maskC:\*\*.txtwill include all paths to files with the TXT extension located in folders on the C: drive, but not in subfolders. - Two consecutive
*characters take the place of any set of characters (including an empty set) in the file or folder name, including the\and/characters (delimiters of the names of files and folders in paths to files and folders). For example, the maskC:\Folder\**\*.txtwill include all paths to files with the TXT extension located in folders nested within theFolder, except theFolderitself. The mask must include at least one nesting level. The maskC:\**\*.txtis not a valid mask. The ** mask is available only for creating scan exclusions. - The
?(question mark) character, which takes the place of any single character, except the\and/characters (delimiters of the names of files and folders in paths to files and folders). For example, the maskC:\Folder\???.txtwill include paths to all files residing in the folder namedFolderthat have the TXT extension and a name consisting of three characters.
Network Agent
A Kaspersky Security Center component that enables interaction between the Administration Server and Kaspersky applications that are installed on a specific network node (workstation or server). This component is common for all Kaspersky applications running under Windows. Dedicated versions of Network Agent are intended for applications running under other operating systems.
Normalized form of the address of a web resource
The normalized form of the address of a web resource is a textual representation of a web resource address that is obtained through normalization. Normalization is a process whereby the textual representation of a web resource address changes according to specific rules (for example, exclusion of the user login, password, and connection port from the text representation of the web resource address; additionally, the web resource address is changed from uppercase to lowercase characters).
Regarding the operation of protection components, the purpose of normalization of web resource addresses is to avoid scanning website addresses, which may differ in syntax while being physically equivalent, more than once.
Example: Non-normalized form of an address: www.Example.com\. Normalized form of an address: www.example.com. |
OLE object
An attached file or a file that is embedded in another file. Kaspersky applications allow scanning OLE objects for viruses. For example, if you insert a Microsoft Office Excel table into a Microsoft Office Word document, the table is scanned as an OLE object.
OpenIOC
Open standard of Indicator of Compromise (IOC) descriptions based on XML and including over 500 different Indicators of Compromise.
Portable File Manager
This is an application that provides an interface for working with encrypted files on removable drives when encryption functionality is not available on the computer.
Protection scope
Objects that are constantly being scanned by the Essential Threat Protection component when it is running. The protection scopes of different components have different properties.
Scan scope
Objects that Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans while performing a scan task.
Task
Functions performed by the Kaspersky application as tasks, for example: Real-time File Protection, Full Device Scan, Database Update.
Trusted Platform Module
A microchip developed to provide basic functions related to security (for example, for storing encryption keys). A Trusted Platform Module is usually installed on the computer motherboard and interacts with all other system components via the hardware bus.
Page top
Appendix 1. Application settings
You can use a policy, tasks, or the application interface to configure Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Detailed information about application components is provided in the corresponding sections.
File Threat Protection
The File Threat Protection component lets you prevent infection of the file system of the computer. By default, the File Threat Protection component permanently resides in the computer's RAM. The component scans files on all drives of the computer, as well as on connected drives. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and heuristic analysis.
The component scans the files accessed by the user or application. If a malicious file is detected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the file operation. The application then disinfects or deletes the malicious file, depending on the settings of the File Threat Protection component.
When attempting to access a file whose contents are stored in the OneDrive cloud, Kaspersky Endpoint Security downloads and scans the file contents.
File Threat Protection component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Security level (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
For File Threat Protection, Kaspersky Endpoint Security can apply different groups of settings. These groups of settings that are stored in the application are called security levels:
|
File types (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
All files. If this setting is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks all files without exception (all formats and extensions). Files scanned by format. If this setting is enabled, the application scans infectable files only. Before scanning a file for malicious code, the internal header of the file is analyzed to determine the format of the file (for example, .txt, .doc, or .exe). The scan also looks for files with particular file extensions. Files scanned by extension. If this setting is enabled, the application scans infectable files only. The file format is then determined based on the file's extension. |
Scan scope |
Contains objects that are scanned by the File Threat Protection component. A scan object may be a hard drive, removable drive, network drive, folder, file, or multiple files defined by a mask. By default, the File Threat Protection component scans files that are started on any hard drives, removable drives, or network drives. The protection scope for these objects cannot be changed or deleted. You can also exclude an object (such as removable drives) from scans. |
Machine learning and signature analysis (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
The machine learning and signature analysis method uses the Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases that contain descriptions of known threats and ways to neutralize them. Protection that uses this method provides the minimum acceptable security level. Based on the recommendations of Kaspersky experts, machine learning and signature analysis is always enabled. |
Heuristic Analysis (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
The technology was developed for detecting threats that cannot be detected by using the current version of Kaspersky application databases. It detects files that may be infected with an unknown virus or a new variety of a known virus. When scanning files for malicious code, the heuristic analyzer executes instructions in the executable files. The number of instructions that are executed by the heuristic analyzer depends on the level that is specified for the heuristic analyzer. The heuristic analysis level ensures a balance between the thoroughness of searching for new threats, the load on the resources of the operating system, and the duration of heuristic analysis. |
Action on threat detection |
Disinfect, delete if disinfection fails. If this option is selected, the application automatically attempts to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection fails, the application deletes the files. Disinfect, block if disinfection fails. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically attempts to disinfect all infected files that are detected. If disinfection is not possible, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds the information about the infected files that are detected to the list of active threats. Block. If this option is selected, the File Threat Protection component automatically blocks all infected files without attempting to disinfect them. Before attempting to disinfect or delete an infected file, the application creates a backup copy of the file in case you need to restore the file or if it can be disinfected in the future. |
Scan only new and modified files |
Scans only new files and those files that have been modified since the last time they were scanned. This helps reduce the duration of a scan. This mode applies both to simple and to compound files. |
Scan archives |
Scanning ZIP, GZIP, BZIP, RAR, TAR, ARJ, CAB, LHA, JAR, ICE, and other archives. The application scans archives not only by extension, but also by format. When checking archives, the application performs a recursive unpacking. This allows to detect threats inside multi-level archives (archive within an archive). |
Scan distribution packages |
This check box enables/disables scanning of third-party distribution packages. |
Scan files in Microsoft Office formats |
Scans Microsoft Office files (DOC, DOCX, XLS, PPT and other Microsoft extensions). Office format files include OLE objects as well. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans office format files that are smaller than 1 MB, regardless of whether the check box is selected or not. |
Do not unpack large compound files |
If this check box is selected, the application does not scan compound files if their size exceeds the specified value. If this check box is cleared, the application scans compound files of all sizes. The application scans large files that are extracted from archives regardless of whether the check box is selected or not. |
Unpack compound files in the background |
If the check box is selected, the application provides access to compound files that are larger than the specified value before these files are scanned. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security unpacks and scans compound files in the background. The application provides access to compound files that are smaller than this value only after unpacking and scanning these files. If the check box is not selected, the application provides access to compound files only after unpacking and scanning files of any size. |
Scan mode (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans files accessed by the user, operating system, or an application running under the user's account. Smart mode. In this mode, File Threat Protection scans an object based on an analysis of actions taken on the object. For example, when working with a Microsoft Office document, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the file when it is first opened and last closed. Intermediate operations that overwrite the file do not cause it to be scanned. On access and modification. In this mode, File Threat Protection scans objects whenever there is an attempt to open or modify them. On access. In this mode, File Threat Protection scans objects only upon an attempt to open them. On execution. In this mode, File Threat Protection only scans objects upon an attempt to run them. |
Use iSwift technology (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scanning by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date that the file was last scanned on, and any modifications to the scanning settings. The iSwift technology is an advancement of the iChecker technology for the NTFS file system. |
Use iChecker technology (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
This technology allows increasing scan speed by excluding certain files from scanning. Files are excluded from scans by using a special algorithm that takes into account the release date of Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the date when the file was last scanned, and any modifications to the scan settings. There are limitations to iChecker Technology: it does not work with large files and applies only to files with a structure that the application recognizes (for example, EXE, DLL, LNK, TTF, INF, SYS, COM, CHM, ZIP, and RAR). |
Pause File Threat Protection (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
This temporarily and automatically pauses operation of File Threat Protection at the specified time or when working with the specified applications. |
Web Threat Protection
The Web Threat Protection component prevents downloads of malicious files from the Internet, and also blocks malicious and phishing websites. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and heuristic analysis.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans HTTP-, HTTPS- and FTP-traffic. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans URLs and IP addresses. You can specify the ports that Kaspersky Endpoint Security will monitor, or select all ports.
For HTTPS traffic monitoring, you need to enable encrypted connections scan.
When a user tries to open a malicious or phishing website, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block access and show a warning (see the figure below).

Website access denied message
Web Threat Protection component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Security level (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
For Web Threat Protection, the application can apply different groups of settings. These groups of settings that are stored in the application are called security levels:
|
Action on threat detection |
Block. If this option is selected and an infected object is detected in web traffic, the Web Threat Protection component blocks access to the object and displays a message in the browser. Inform. If this option is selected and an infected object is detected in web traffic, Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows this object to be downloaded to the computer but adds information about the infected object to the list of active threats. |
Check the web address against the database of malicious web addresses (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
Scanning the links to determine whether they are included in the database of malicious web addresses allows you to track websites that have been added to denylist. The database of malicious web addresses is maintained by Kaspersky, included in the application installation package, and updated during Kaspersky Endpoint Security database updates. |
Use Heuristic Analysis (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
The technology was developed for detecting threats that cannot be detected by using the current version of Kaspersky application databases. It detects files that may be infected with an unknown virus or a new variety of a known virus. When web traffic is scanned for viruses and other applications that present a threat, the heuristic analyzer performs instructions in the executable files. The number of instructions that are executed by the heuristic analyzer depends on the level that is specified for the heuristic analyzer. The heuristic analysis level ensures a balance between the thoroughness of searching for new threats, the load on the resources of the operating system, and the duration of heuristic analysis. |
Check the web address against the database of phishing web addresses (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
The database of phishing web addresses includes the web addresses of currently known websites that are used to launch phishing attacks. Kaspersky supplements this database of phishing links with addresses obtained from the international organization known as the Anti-Phishing Working Group. The database of phishing addresses is included in the application installation package and supplemented with Kaspersky Endpoint Security database updates. |
Do not scan web traffic from trusted web addresses |
If the check box is selected, the Web Threat Protection component does not scan the content of web pages or websites whose addresses are included in the list of trusted web addresses. You can add both the specific address and the address mask of a web page/website to the list of trusted web addresses. You can also create a general list of exclusions for encrypted connections. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan HTTPS traffic of trusted web addresses when Web Threat Protection, Mail Threat Protection, Web Control components are doing their work. |
Mail Threat Protection
The Mail Threat Protection component scans the attachments of incoming and outgoing email messages for viruses and other threats. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and heuristic analysis.
Mail Threat Protection can scan both incoming and outgoing messages. The application supports POP3, SMTP, IMAP, and NNTP in the following mail clients:
- Microsoft Office Outlook
- Mozilla Thunderbird
- Windows Mail
Mail Threat Protection does not support other protocols and mail clients.
Mail Threat Protection may not always be able to gain protocol-level access to messages (for example, when using the Microsoft Exchange solution). For this reason, Mail Threat Protection includes an extension for Microsoft Office Outlook. The extension allows scanning messages at the level of the mail client. The Mail Threat Protection extension supports operations with Outlook 2010, 2013, 2016, and 2019.
The Mail Threat Protection component does not scan messages if the mail client is open in a browser.
When a malicious file is detected in an attachment, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds information about the performed action to the message subject, for example, [Message has been processed] <message subject>.
Mail Threat Protection component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Security level (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
For Mail Threat Protection, Kaspersky Endpoint Security applies different groups of settings. These groups of settings that are stored in the application are called security levels:
|
Action on threat detection |
Disinfect, delete if disinfection fails. When an infected object is detected in an inbound or outbound message, Kaspersky Endpoint Security attempts to disinfect the detected object. The user will be able to access the message with a safe attachment. If the object cannot be disinfected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes the infected object. Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds information about the performed action to the message subject, for example, [Message has been processed] <message subject>. Disinfect, block if disinfection fails. When an infected object is detected in an inbound message, Kaspersky Endpoint Security attempts to disinfect the detected object. The user will be able to access the message with a safe attachment. If the object cannot be disinfected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds a warning to the message subject. The user will be able to access the message with the original attachment. When an infected object is detected in an outbound message, Kaspersky Endpoint Security attempts to disinfect the detected object. If the object cannot be disinfected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks transmission of the message, and the mail client shows an error. Block. If an infected object is detected in an inbound message, Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds a warning to the message subject. The user will be able to access the message with the original attachment. If an infected object is detected in an outbound message, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks transmission of the message, and the mail client shows an error. |
Protection scope (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
The Protection scope includes objects that the component checks when it is run: incoming and outgoing messages or incoming messages only. In order to protect your computers, you need only scan incoming messages. You can turn on scanning for outgoing messages to prevent infected files from being sent in archives. You can also turn on the scanning of outgoing messages if you want to prevent files in particular formats from being sent, such as audio and video files, for example. |
Scan POP3, SMTP, NNTP, and IMAP traffic |
The check box enables / disables scanning by the Mail Threat Protection component of traffic that is transferred via the POP3, SMTP, NNTP, and IMAP protocols. |
Connect Microsoft Outlook extension |
If the check box is selected, scanning of email messages transmitted via the POP3, SMTP, NNTP, IMAP protocols is enabled on the side of the extension integrated into Microsoft Outlook. If mail is scanned using the extension for Microsoft Outlook, it is recommended to use Cached Exchange Mode. For more detailed information about Cached Exchange Mode and recommendations on its use, refer to the Microsoft Knowledge Base. |
Heuristic analysis (available only in the Administration Console (MMC) and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
The technology was developed for detecting threats that cannot be detected by using the current version of Kaspersky application databases. It detects files that may be infected with an unknown virus or a new variety of a known virus. When scanning files for malicious code, the heuristic analyzer executes instructions in the executable files. The number of instructions that are executed by the heuristic analyzer depends on the level that is specified for the heuristic analyzer. The heuristic analysis level ensures a balance between the thoroughness of searching for new threats, the load on the resources of the operating system, and the duration of heuristic analysis. |
Scan attached archives |
Scanning ZIP, GZIP, BZIP, RAR, TAR, ARJ, CAB, LHA, JAR, ICE, and other archives. The application scans archives not only by extension, but also by format. When checking archives, the application performs a recursive unpacking. This allows to detect threats inside multi-level archives (archive within an archive). If during the scan, Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects a password for an archive in the text of the message, this password will be used to scan the content of the archive for malicious applications. In this case, the password is not saved. An archive is unpacked during scan. If an application error occurs during the unpacking process, you can manually delete the unpacked files that are saved to the following path: %systemroot%\temp. The files have the PR prefix. |
Scan attached files of Microsoft Office formats |
Scans Microsoft Office files (DOC, DOCX, XLS, PPT and other Microsoft extensions). Office format files include OLE objects as well. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans office format files that are smaller than 1 MB, regardless of whether the check box is selected or not. |
Do not scan archives larger than N MB |
If this check box is selected, the Mail Threat Protection component excludes archives attached to email messages from scanning if their size exceeds the specified value. If the check box is cleared, the Mail Threat Protection component scans email attachment archives of any size. |
Limit the time for checking archives to N sec |
If the check box is selected, the time that is allocated for scanning archives attached to email messages is limited to the specified period. |
Attachment filter |
The attachment filter is not applied to outgoing email messages. Disable filtering. If this option is selected, the Mail Threat Protection component does not filter files that are attached to email messages. Rename attachments of selected types. If this option is selected, the Mail Threat Protection component will replace the last extension character found in the attached files of the specified types with the underscore character (for example, attachment.doc_). Thus, in order to open the file, the user must rename the file. Delete attachments of selected types. If this option is selected, the Mail Threat Protection component deletes attached files of the specified types from email messages. In the list of file masks, you can specify the types of attached files to rename or delete from email messages. |
Network Threat Protection
The Network Threat Protection component (also called Intrusion Detection System) monitors inbound network traffic for activity characteristic of network attacks. When Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects an attempted network attack on the user's computer, it blocks the network connection with the attacking computer. Descriptions of currently known types of network attacks and ways to counteract them are provided in Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases. The list of network attacks that the Network Threat Protection component detects is updated during database and application module updates.
Network Threat Protection component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Treat port scanning and network flooding as attacks |
Network Flooding is an attack on network resources of an organization (such as web servers). This attack consists of sending a large number of requests to overload the bandwidth of network resources. When this happens, users are unable to access the network resources of the organization. A Port Scanning attack consists of scanning UDP ports, TCP ports, and network services on the computer. This attack allows the attacker to identify the degree of vulnerability of the computer before conducting more dangerous types of network attacks. Port Scanning also enables the attacker to identify the operating system on the computer and select the appropriate network attacks for this operating system. If this check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security monitors network traffic to detect these attacks. If an attack is detected, the application notifies the user and sends the corresponding event to Kaspersky Security Center. The application provides information about the attacking computer, which is required for timely threat response actions. You can disable detection of these types of attacks in case some of your allowed applications perform operations that are typical for these types of attacks. This will help avoid false alarms. |
Block attacking devices for N min |
If the check box is selected, the Network Threat Protection component adds the attacking computer to the blocked list. This means that the Network Threat Protection component blocks the network connection with the attacking computer after the first network attack attempt for the specified amount of time. This block automatically protects the user's computer against possible future network attacks from the same address. The minimum time an attacking computer must spend in the block list is one minute. The maximum time is 999 minutes. You can view the block list in the Network Monitor tool window. Kaspersky Endpoint Security clears the block list when the application is restarted and when the Network Threat Protection settings are changed. |
Exclusions |
The list contains IP addresses from which Network Threat Protection does not block network attacks. The application does not log information on network attacks from the IP addresses that are in the list of exclusions. |
MAC Spoofing Protection |
A MAC spoofing attack consists of changing the MAC address of a network device (network card). As a result, an attacker can redirect data sent to a device to another device and gain access to this data. Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you block MAC Spoofing attacks and receive notifications about the attacks. |
Firewall
The Firewall blocks unauthorized connections to the computer while working on the Internet or local network. The Firewall also controls the network activity of applications on the computer. This allows you to protect your corporate LAN from identity theft and other attacks. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases, the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, and predefined network rules.
Network Agent is used for interaction with Kaspersky Security Center. Firewall automatically creates network rules required for the application and the Network Agent to work. As a result, the Firewall opens several ports on the computer. Which ports are opened depends on computer's role (for example, distribution point). To learn more about the ports that will be opened on the computer, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
Network rules
You can configure network rules at the following levels:
- Network packet rules. Network packet rules impose restrictions on network packets, regardless of the application. Such rules restrict inbound and outbound network traffic through specific ports of the selected data protocol. Kaspersky Endpoint Security has predefined network packet rules with permissions recommended by Kaspersky experts.
- Application network rules. Application network rules impose restrictions on the network activity of a specific application. They factor in not only the characteristics of the network packet, but also the specific application to which this network packet is addressed or which issued this network packet.
Controlled access of applications to operating system resources, processes and personal data is provided by the Host Intrusion Prevention component by using application rights.
During the first startup of the application, the Firewall performs the following actions:
- Checks the security of the application using downloaded anti-virus databases.
- Checks the security of the application in Kaspersky Security Network.
You are advised to participate in Kaspersky Security Network to help the Firewall work more effectively.
- Places the application in one of the trust groups: Trusted, Low Restricted, High Restricted, Untrusted.
A trust group defines the rights that Kaspersky Endpoint Security refers to when controlling application activity. Kaspersky Endpoint Security places an application in a trust group depending on the level of danger that this application may pose to the computer.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security places an application in a trust group for the Firewall and Host Intrusion Prevention components. You cannot change the trust group only for the Firewall or Host Intrusion Prevention.
If you refused to participate in KSN or there is no network, Kaspersky Endpoint Security places the application in a trust group depending on the settings of the Host Intrusion Prevention component. After receiving the reputation of the application from KSN, the trust group can be changed automatically.
- It blocks network activity of the application depending on the trust group. For example, applications in the High Restricted trust group are not allowed to use any network connections.
The next time the application is started, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks the integrity of the application. If the application is unchanged, the component uses the current network rules for it. If the application has been modified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the application as if it were being started for the first time.
Network Rule Priorities
Each rule has a priority. The higher a rule is on the list, the higher its priority. If network activity is added to several rules, the Firewall regulates network activity according to the rule with the highest priority.
Network packet rules have a higher priority than network rules for applications. If both network packet rules and network rules for applications are specified for the same type of network activity, the network activity is handled according to the network packet rules.
Network rules for applications work in a particular way. Network rule for applications includes access rules based on the network status: Public network, Local network, Trusted network. For example, applications in the High Restricted trust group are not allowed any network activity in networks of all statuses by default. If a network rule is specified for an individual application (parent application), then the child processes of other applications will run according to the network rule of the parent application. If there is no network rule for the application, the child processes will run according to network access rule of the application's trust group.
For example, you have prohibited any network activity in networks of all statuses for all applications, except browser X. If you start browser Y installation (child process) from browser X (parent application), then browser Y installer will access the network and download the necessary files. After installation, browser Y will be denied any network connections according to the Firewall settings. To prohibit network activity of browser Y installer as a child process, you must add a network rule for the installer of browser Y.
Network connection statuses
The Firewall allows you to control network activity depending on the status of the network connection. Kaspersky Endpoint Security receives the network connection status from the computer's operating system. The status of the network connection in the operating system is set by the user when setting up the connection. You can change the status of the network connection in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings. The Firewall will monitor network activity depending on the network status in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings, and not in the operating system.
The network connection can have one of the following status types:
- Public network. The network is not protected by antivirus applications, firewalls, or filters (such as Wi-Fi in a cafe). When the user operates a computer that is connected to such a network, Firewall blocks access to files and printers of this computer. External users are also unable to access data through shared folders and remote access to the desktop of this computer. Firewall filters the network activity of each application according to the network rules that are set for it.
Firewall assigns Public network status to the Internet by default. You cannot change the status of the Internet.
- Local network. Network for users with restricted access to files and printers on this computer (such as for a corporate LAN or home network).
- Trusted network. Safe network in which the computer is not exposed to attacks or unauthorized data access attempts. Firewall permits any network activity within networks with this status.
Firewall component settings
Parameter
Description
Packet rules
Table with a list of network packet rules. Network packet rules serve to impose restrictions on network packets, regardless of the application. Such rules restrict inbound and outbound network traffic through specific ports of the selected data protocol.
The table lists pre-configured network packet rules that are recommended by Kaspersky for optimum protection of the network traffic of computers that run on Microsoft Windows operating systems.
Firewall sets the execution priority of each network packet rule. Firewall processes network packet rules in the order in which they appear in the list of network packet rules, from top to bottom. Firewall locates the topmost network packet rule that is suitable for the network connection and applies it by either allowing or blocking network activity. Firewall then ignores all subsequent network packet rules for the specific network connection.
Network packet rules have higher priority than network rules for applications.
Available networks
This table contains information about network connections that Firewall detects on the computer.
The Public network status is assigned to the Internet by default. You cannot change the status of the Internet.
Rules for applications
Application
Table of applications that are controlled by the Firewall component. Applications are assigned to trust groups. A trust group defines the rights used by Kaspersky Endpoint Security when controlling network activity of applications.
You can select an application from a single list of all applications installed on computers under the influence of a policy and add the application to a trust group.
Network rules
Table of network rules for applications that are part of a trust group. In accordance with these rules, Firewall regulates the network activity of applications.
The table displays the predefined network rules that are recommended by Kaspersky experts. These network rules have been added to optimally protect the network traffic of computers running Windows operating systems. It is not possible to delete the predefined network rules.
BadUSB Attack Prevention
Some viruses modify the firmware of USB devices to trick the operating system into detecting the USB device as a keyboard. As a result, the virus may execute commands under your user account to download malware, for example.
The BadUSB Attack Prevention component prevents infected USB devices emulating a keyboard from connecting to the computer.
When a USB device is connected to the computer and identified as a keyboard by the operating system, the application prompts the user to enter a numerical code generated by the application from this keyboard or using On-Screen Keyboard if available (see the figure below). This procedure is known as keyboard authorization.
If the code has been entered correctly, the application saves the identification parameters – VID/PID of the keyboard and the number of the port to which it has been connected – in the list of authorized keyboards. Keyboard authorization does not need to be repeated when the keyboard is reconnected or after the operating system is restarted.
When the authorized keyboard is connected to a different USB port of the computer, the application shows a prompt for authorization of this keyboard again.
If the numerical code has been entered incorrectly, the application generates a new code. You can configure the number of attempts for entering the numerical code. If the numerical code is entered incorrectly several times or the keyboard authorization window is closed (see figure below), the application blocks input from this keyboard. When the USB device blocking time elapses or the operating system is restarted, the application prompts the user to perform keyboard authorization again.
The application allows use of an authorized keyboard and blocks a keyboard that has not been authorized.
The BadUSB Attack Prevention component is not installed by default. If you need the BadUSB Attack Prevention component, you can add the component in the properties of the installation package before installing the application or change the available application components after installing the application.

Keyboard authorization
BadUSB Attack Prevention component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Prohibit use of On-Screen Keyboard for authorization of USB devices |
If the check box is selected, the application blocks use of On-Screen Keyboard for authorization of a USB device from which an authorization code cannot be entered. |
Maximum number of USB device authorization attempts |
Automatically blocking the USB device if the authorization code is entered incorrectly the specified number of times. Valid values are 1 to 10. For example, if you allow 5 attempts to enter the authorization code, the USB device is blocked after the fifth failed attempt. Kaspersky Endpoint Security displays the blocking duration for the USB device. After this time elapses, you can have 5 attempts to enter the authorization code. |
Timeout when reaching the maximum number of attempts |
Blocking duration of the USB device after the specified number of failed attempts to enter the authorization code. Valid values are 1 to 180 (minutes). |
AMSI Protection
AMSI Protection component is intended to support Antimalware Scan Interface from Microsoft. The Antimalware Scan Interface (AMSI) allows third-party applications with AMSI support to send objects (for example, PowerShell scripts) to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for an additional scan and then receive the results from scanning these objects. Third-party applications may include, for example, Microsoft Office applications (see the figure below). For details on AMSI, please refer to the Microsoft documentation.
The AMSI Protection can only detect a threat and notify a third-party application about the detected threat. Third-party application after receiving a notification of a threat does not allow to perform malicious actions (for example, terminates).

AMSI operation example
AMSI Protection component may decline a request from a third-party application, for example, if this application exceeds maximum number of requests within a specified interval. Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends information about a rejected request from a third-party application to the Administration Server. The AMSI Protection component does not deny requests from those third-party applications for which continuous integration with the AMSI Protection component is enabled.
AMSI Protection is available for the following operating systems for workstations and servers:
- Windows 10 Home / Pro / Pro for Workstations / Education / Enterprise;
- Windows 11 Home / Pro / Pro for Workstations / Education / Enterprise;
- Windows Server 2016 Essentials / Standard / Datacenter (including Core Mode);
- Windows Server 2019 Essentials / Standard / Datacenter (including Core Mode);
- Windows Server 2022 Standard / Datacenter / Datacenter: Azure Edition (including Core Mode).
AMSI Protection settings
Parameter
Description
Scan archives
Scanning ZIP, GZIP, BZIP, RAR, TAR, ARJ, CAB, LHA, JAR, ICE, and other archives. The application scans archives not only by extension, but also by format. When checking archives, the application performs a recursive unpacking. This allows to detect threats inside multi-level archives (archive within an archive).
Scan distribution packages
This check box enables/disables scanning of third-party distribution packages.
Scan files in Microsoft Office formats
Scans Microsoft Office files (DOC, DOCX, XLS, PPT and other Microsoft extensions). Office format files include OLE objects as well. Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans office format files that are smaller than 1 MB, regardless of whether the check box is selected or not.
Do not unpack large compound files
If this check box is selected, the application does not scan compound files if their size exceeds the specified value.
If this check box is cleared, the application scans compound files of all sizes.
The application scans large files that are extracted from archives regardless of whether the check box is selected or not.
Exploit Prevention
The Exploit Prevention component detects program code that takes advantage of vulnerabilities on the computer to exploit administrator privileges or to perform malicious activities. For example, exploits can utilize a buffer overflow attack. To do so, the exploit sends a large amount of data to a vulnerable application. When processing this data, the vulnerable application executes malicious code. As a result of this attack, the exploit can start an unauthorized installation of malware. When there is an attempt to run an executable file from a vulnerable application that was not performed by the user, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks this file from running or notifies the user.
Exploit Prevention component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
On detecting exploit |
Block operation. If this item is selected, on detecting an exploit, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the operations of this exploit and makes a log entry with information about this exploit. Notify. If this item is selected, when Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects an exploit it logs an entry containing information about the exploit and adds information about this exploit to the list of active threats. |
Enable system process memory protection |
If this toggle button is switched on, Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks external processes that attempt to access system process memory. |
Behavior Detection
The Behavior Detection component receives data on the actions of applications on your computer and provides this information to other protection components to improve their performance. The Behavior Detection component utilizes Behavior Stream Signatures (BSS) for applications. If application activity matches a behavior stream signature, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the selected responsive action. Kaspersky Endpoint Security functionality based on behavior stream signatures provides proactive defense for the computer.
Behavior Detection component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
On detecting malware activity |
Delete file. If this option is selected, on detecting malicious activity Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes the executable file of the malicious application and creates a backup copy of the file in Backup. Terminate the application. If this option is selected, on detecting malicious activity Kaspersky Endpoint Security terminates this application. Notify. If this option is selected and malicious activity of an application is detected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not terminate this application but adds information about the malicious activity of this application to the list of active threats. |
Enable protection of shared folders against external encryption |
If the toggle button is switched on, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes activity in shared folders. If this activity matches a behavior stream signature that is typical for external encryption, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the selected action. Kaspersky Endpoint Security prevents external encryption of only those files that are located on media that have the NTFS file system and are not encrypted by the EFS system.
If the Remediation Engine component is enabled and the Block connection for N min option is selected, modified files are restored from backup copies. |
Exclusions |
List of computers from which attempts to encrypt shared folders will not be monitored. To apply the list of exclusions of computers from protection of shared folders against external encryption, you must enable Audit Logon in the Windows security audit policy. Audit Logon is disabled by default. For more details about a Windows security audit policy, please visit the Microsoft website. |
Host Intrusion Prevention
The Host Intrusion Prevention component prevents applications from performing actions that may be dangerous for the operating system, and ensures control over access to operating system resources and personal data. The component provides computer protection with the help of anti-virus databases and the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service.
The component controls the operation of applications by using application rights. Application rights include the following access parameters:
- Access to operating system resources (for example, automatic startup options, registry keys)
- Access to personal data (such as files and applications)
Network activity of applications is controlled by the Firewall using network rules.
During the first startup of the application, the Host Intrusion Prevention component performs the following actions:
- Checks the security of the application using downloaded anti-virus databases.
- Checks the security of the application in Kaspersky Security Network.
You are advised to participate in Kaspersky Security Network to help the Host Intrusion Prevention component work more effectively.
- Places the application in one of the trust groups: Trusted, Low Restricted, High Restricted, Untrusted.
A trust group defines the rights that Kaspersky Endpoint Security refers to when controlling application activity. Kaspersky Endpoint Security places an application in a trust group depending on the level of danger that this application may pose to the computer.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security places an application in a trust group for the Firewall and Host Intrusion Prevention components. You cannot change the trust group only for the Firewall or Host Intrusion Prevention.
If you refused to participate in KSN or there is no network, Kaspersky Endpoint Security places the application in a trust group depending on the settings of the Host Intrusion Prevention component. After receiving the reputation of the application from KSN, the trust group can be changed automatically.
- Blocks application actions depending on the trust group. For example, applications from the High Restricted trust group are denied access to the operating system modules.
The next time the application is started, Kaspersky Endpoint Security checks the integrity of the application. If the application is unchanged, the component uses the current application rights for it. If the application has been modified, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the application as if it were being started for the first time.
Host Intrusion Prevention component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Application rights |
Table of applications that are monitored by the Host Intrusion Prevention component. Applications are assigned to trust groups. A trust group defines the rights that Kaspersky Endpoint Security refers to when controlling application activity. You can select an application from a single list of all applications installed on computers under the influence of a policy and add the application to a trust group. Application access rights are presented in the following tables:
|
Protected resources |
The table contains categorized computer resources. The Host Intrusion Prevention component monitors attempts by other applications to access resources in the table. A resource can be a registry category, file or folder, or registry key. |
Trust group for applications launched before Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows starts working |
A trust group in which Kaspersky Endpoint Security will place applications that are started before Kaspersky Endpoint Security. |
Update rules for previously unknown applications from KSN |
If the check box is selected, the Host Intrusion Prevention component updates rights for previously unknown applications by using the Kaspersky Security Network database. |
Trust digitally signed applications |
If this check box is selected, the Host Intrusion Prevention component places the applications with the digital signature of trusted vendors in the Trusted group. Trusted vendors are those software vendors that are trusted by Kaspersky. You can also add vendor certificate to the trusted certificate store manually. If this check box is cleared, the Host Intrusion Prevention component does not consider such applications to be trusted, and uses other parameters to determine their trust group. |
Delete rules for applications that have not been started for longer than N days (from 1 to 90) |
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes information about the application (trust group and access rights) if the following conditions are met:
If the trust group and rights of an application were determined automatically, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes information about this application after 30 days. It is not possible to change the storage term for application information or turn off automatic deletion. The next time you start this application, Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes the application as if it were starting for the first time. |
Trust group for applications that could not be added to existing groups |
Items in this drop-down list determine to which trust group Kaspersky Endpoint Security will assign an unknown application. You can choose one of the following items:
|
Remediation Engine
The Remediation Engine lets Kaspersky Endpoint Security roll back actions that have been performed by malware in the operating system.
When rolling back malware activity in the operating system, Kaspersky Endpoint Security handles the following types of malware activity:
- File activity
Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- Deletes executable files that were created by malware (on all media except network drives).
- Deletes executable files that were created by programs that have been infiltrated by malware.
- Restores files that have been modified or deleted by malware.
The file recovery feature has a number of limitations.
- Registry activity
Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- Deletes registry keys that were created by malware.
- Does not restore registry keys that have been modified or deleted by malware.
- System activity
Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- Terminates processes that have been initiated by malware.
- Terminates processes into which a malicious application has penetrated.
- Does not resume processes that have been halted by malware.
- Network activity
Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- Blocks the network activity of malware.
- Blocks the network activity of processes that have been infiltrated by malware.
A rollback of malware actions can be started by the File Threat Protection or Behavior Detection component, or during a malware scan.
Rolling back malware operations affects a strictly defined set of data. Rollback has no adverse effects on the operating system or on the integrity of your computer data.
Page top
Kaspersky Security Network
To protect your computer more effectively, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses data that is received from users around the globe. Kaspersky Security Network is designed for obtaining this data.
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is an infrastructure of cloud services providing access to the online Kaspersky Knowledge Base that contains information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software. The use of data from Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky Endpoint Security to new threats, improves the performance of some protection components, and reduces the likelihood of false positives. If you are participating in Kaspersky Security Network, KSN services provide Kaspersky Endpoint Security with information about the category and reputation of scanned files, as well as information about the reputation of scanned web addresses.
Use of Kaspersky Security Network is voluntary. The application prompts you to use KSN during initial configuration of the application. Users can begin or discontinue participation in KSN at any time.
For more detailed information about sending Kaspersky statistical information that is generated during participation in KSN, and about the storage and destruction of such information, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Network Statement and the Kaspersky website. The ksn_<language ID>.txt file with the text of the Kaspersky Security Network Statement is included in the application distribution kit.
The infrastructure of Kaspersky reputation databases
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the following infrastructure solutions for working with Kaspersky reputation databases:
- Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is the solution that is used by most Kaspersky applications. KSN participants receive information from Kaspersky and send Kaspersky information about objects detected on the user's computer to be analyzed additionally by Kaspersky analysts and to be included in the reputation and statistical databases.
- Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN) is a solution that enables users of computers hosting Kaspersky Endpoint Security or other Kaspersky applications to obtain access to Kaspersky reputation databases, and to other statistical data without sending data to Kaspersky from their own computers. KPSN is designed for corporate customers who are unable to participate in Kaspersky Security Network for any of the following reasons:
- Local workstations are not connected to the Internet.
- Transmission of any data outside the country or outside the corporate LAN is prohibited by law or restricted by corporate security policies.
By default, Kaspersky Security Center uses KSN. You can configure the use of KPSN in the Administration Console (MMC), in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, and in the command line. It is not possible to configure the use of KPSN in the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
For more details about KPSN, please refer to the documentation on Kaspersky Private Security Network.
Kaspersky Security Network settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Enable extended KSN mode |
Extended KSN mode is a mode in which Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends additional data to Kaspersky. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses KSN to detect threats regardless of the toggle position. |
Enable cloud mode |
Cloud mode refers to the application operating mode in which Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses a light version of anti-virus databases. Kaspersky Security Network supports the operation of the application when light anti-virus databases are being used. The light version of anti-virus databases lets you use approximately half of the computer RAM that would otherwise be used with the usual databases. If you do not participate in Kaspersky Security Network or if cloud mode is disabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security downloads the full version of anti-virus databases from Kaspersky servers. If the toggle button is switched on, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the light version of anti-virus databases, which reduces the load on operating system resources. Kaspersky Endpoint Security downloads the light version of anti-virus databases during the next update after the check box was selected. If the toggle button is switched off, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the full version of anti-virus databases. Kaspersky Endpoint Security downloads the full version of anti-virus databases during the next update after the check box was cleared. |
Computer status when KSN servers are unavailable (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
The items in this drop-down list determine the status of a computer in Kaspersky Security Center when KSN servers are unavailable. |
Use KSN Proxy (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the KSN Proxy service. You can configure the KSN Proxy service settings in the Administration Server properties. |
Use KSN servers when KSN Proxy is not available (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses KSN servers when the KSN Proxy service is unavailable. KSN servers may be located both on the side of Kaspersky and on the side of third parties (when Kaspersky Private Security Network is used). |
Log Inspection
This component is available if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for servers. This component is unavailable if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for workstations.
Starting with version 11.11.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes the Log Inspection component. Log Inspection monitors the integrity of the protected environment based on the Windows event log analysis. When the application detects signs of atypical behavior in the system, it informs the administrator, as this behavior may indicate an attempted cyber attack.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security analyzes Windows event logs and detects violation in accordance with rules. The component includes predefined rules. Predefined rules are powered by heuristic analysis. You can also add your own rules (custom rules). When a rule triggers, the application creates an event with the Critical status (see figure below).
If you want to use Log Inspection, make sure security the audit policy is configured and the system is logging the relevant events (for details, see the Microsoft technical support website.).

Log Inspection notification
Log Inspection settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Predefined rules |
List of Log Inspection rules. Predefined rules include templates of abnormal activity on the protected computer. Abnormal activity can signify an attempted attack. |
Custom rules |
List of Log Inspection rules added by the user. You can set your own Log Inspection rule triggering criteria. To do so, you must enter an event ID and select an event source. You can select an event source from among the standard logs: Application, Security or System. You can also specify the log of a third-party application. |
Web Control
Web Control manages users' access to web resources. This helps reduce traffic and inappropriate use of work time. When a user tries to open a website that is restricted by Web Control, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block access or show a warning (see the figure below).
Kaspersky Endpoint Security monitors only HTTP- and HTTPS traffic.
For HTTPS traffic monitoring, you need to enable encrypted connections scan.
Methods for managing access to websites
Web Control lets you configure access to websites by using the following methods:
- Website category. Websites are categorized according to the Kaspersky Security Network cloud service, heuristic analysis, and the database of known websites (included in application databases). For example, you can restrict user access to the Social networks category or to other categories.
- Data type. You can restrict users' access to data on a website, and hide graphic images, for example. Kaspersky Endpoint Security determines the data type based on the file format and not based on its extension.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan files within archives. For example, if image files were placed in an archive, Kaspersky Endpoint Security identifies the Archives data type and not Graphics.
- Individual address. You can enter a web address or use masks.
You can simultaneously use multiple methods for regulating access to websites. For example, you can restrict access to the "Office files" data type just for the Web-based mail website category.
Website access rules
Web Control manages users' access to websites by using access rules. You can configure the following advanced settings for a website access rule:
- Users to which the rule applies.
For example, you can restrict Internet access through a browser for all users of the company except the IT department.
- Rule schedule.
For example, you can restrict Internet access through a browser during working hours only.
Access rule priorities
Each rule has a priority. The higher a rule is on the list, the higher its priority. If a website has been added to multiple rules, Web Control regulates access to the website based on the rule with the highest priority. For example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may identify a corporate portal as a social network. To restrict access to social networks and provide access to the corporate web portal, create two rules: one block rule for the Social networks website category and one allow rule for the corporate web portal. The access rule for the corporate web portal must have a higher priority than the access rule for social networks.


Web Control messages
Web Control component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Rules of access to web resources |
List containing web resource access rules. Each rule has a priority. The higher a rule is on the list, the higher its priority. If a website has been added to multiple rules, Web Control regulates access to the website based on the rule with the highest priority. |
Default rule |
The Default rule is a rule for accessing web resources that are not covered by any other rule. The following options are available:
|
Templates |
Warning. The entry field consists of a template of the message that is displayed if a rule for warning about attempts to access an unwanted web resource is triggered. Message about blocking. The entry field contains the template of the message that appears if a rule which blocks access to a web resource is triggered. Message to administrator. Template of the message to be sent to the LAN administrator if the user considers the block to be a mistake. After the user requests to provide access, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends an event to Kaspersky Security Center: Web page access blockage message to administrator. The event description contains a message to administrator with substituted variables. You can view these events in the Kaspersky Security Center console using the predefined event selection User requests. If your organization does not have Kaspersky Security Center deployed or there is no connection to the Administration Server, the application will send a message to administrator to the specified email address. |
Log the opening of allowed pages |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security logs data on visits to all websites, including allowed websites. Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends events to Kaspersky Security Center, to the local log of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, and to the Windows Event log. To monitor user Internet activity, you need to configure the settings for saving events. Browsers that support the monitoring function: Microsoft Edge, Microsoft Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Yandex Browser, Mozilla Firefox. User activity monitoring does not work in other browsers. Monitoring user Internet activity may require more computer resources when decrypting HTTPS traffic. |
Device Control
Device Control manages user access to devices that are installed on or connected to the computer (for example, hard drives, cameras, or Wi-Fi modules). This lets you protect the computer from infection when such devices are connected, and prevent loss or leaks of data.
Device access levels
Device Control controls access at the following levels:
- Device type. For example, printers, removable drives, and CD/DVD drives.
You can configure device access as follows:
- Allow –
 .
. - Block –
 .
. - By rules (printers and portable devices only) –
 .
. - Depends on connection bus (except Wi-Fi) –
 .
. - Block with exceptions (Wi-Fi only) –
 .
.
- Allow –
- Connection bus. A connection bus is an interface used for connecting devices to the computer (for example, USB or FireWire). Therefore, you can restrict the connection of all devices, for example, over USB.
You can configure device access as follows:
- Allow –
 .
. - Block –
 .
.
- Allow –
- Trusted devices. Trusted devices are devices to which users that are specified in the trusted device settings have full access at all times.
You can add trusted devices based on the following data:
- Devices by ID. Each device has a unique identifier (Hardware ID, or HWID). You can view the ID in the device properties by using operating system tools. Example device ID:
SCSI\CDROM&VEN_NECVMWAR&PROD_VMWARE_SATA_CD00\5&354AE4D7&0&000000. Adding devices by ID is convenient if you want to add several specific devices. - Devices by model. Each device has a vendor ID (VID) and a product ID (PID). You can view the IDs in the device properties by using operating system tools. Template for entering the VID and PID:
VID_1234&PID_5678. Adding devices by model is convenient if you use devices of a certain model in your organization. This way, you can add all devices of this model. - Devices by ID mask. If you are using multiple devices with similar IDs, you can add devices to the trusted list by using masks. The
*character replaces any set of characters. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support the?character when entering a mask. For example,WDC_C*. - Devices by model mask. If you are using multiple devices with similar VIDs or PIDs (for example, devices from the same manufacturer), you can add devices to the trusted list by using masks. The
*character replaces any set of characters. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support the?character when entering a mask. For example,VID_05AC & PID_ *.
- Devices by ID. Each device has a unique identifier (Hardware ID, or HWID). You can view the ID in the device properties by using operating system tools. Example device ID:
Device Control regulates user access to devices by using access rules. Device Control also lets you save device connection/disconnection events. To save events, you need to configure the registration of events in a policy.
If access to a device depends on the connection bus (the ![]() status), Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not save device connection/disconnection events. To enable Kaspersky Endpoint Security to save device connection/disconnection events, allow access to the corresponding type of device (the
status), Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not save device connection/disconnection events. To enable Kaspersky Endpoint Security to save device connection/disconnection events, allow access to the corresponding type of device (the ![]() status) or add the device to the trusted list.
status) or add the device to the trusted list.
When a device that is blocked by Device Control is connected to the computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block access and show a notification (see the figure below).

Device Control notification
Device Control operating algorithm
Kaspersky Endpoint Security makes a decision on whether to allow access to a device after the user connects the device to the computer (see the figure below).

Device Control operating algorithm
If a device is connected and access is allowed, you can edit the access rule and block access. In this case, the next time someone attempts to access the device (such as to view the folder tree, or perform read or write operations), Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks access. A device without a file system is blocked only the next time that the device is connected.
If a user of the computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed must request access to a device that the user believes was blocked by mistake, send the user the request access instructions.
Device Control component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Allow request for temporary access (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
If the check box is selected, the Request access button is available through the local interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Using this button, the user can request temporary access to a blocked device. |
Devices and Wi-Fi networks
|
This table contains all possible types of devices according to the classification of the Device Control component, including their respective access statuses. |
Connection buses |
A list of all available connection buses according to the Device Control component's classification, including their respective access statuses. |
Trusted devices |
List of trusted devices and users who are granted access to these devices. |
Anti-Bridging |
Anti-Bridging inhibits the creation of network bridges by preventing the simultaneous establishment of multiple network connections for a computer. This lets you protect a corporate network from attacks over unprotected, unauthorized networks. Anti-Bridging blocks the establishment of multiple connections according to the priorities of devices. The higher a device is on the list, the higher its priority. If an active connection and a new connection are both of the same type (for example, Wi-Fi), Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the active connection and allows establishment of the new connection. If an active connection and a new connection are of different types (for example, a network adapter and Wi-Fi), Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks the connection with the lower priority and allows the connection with the higher priority. Anti-Bridging supports operation with the following types of devices: network adapter, Wi-Fi, and modem. |
Message templates |
Message about blocking. Template of the message that appears when a user attempts to access a blocked device. This message also appears when a user attempts to perform an operation on the device contents that was blocked for this user. Message to administrator. A template of the message that is sent to the LAN administrator when the user believes that access to the device is blocked or an operation with device content is forbidden by mistake. After the user requests to provide access, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends an event to Kaspersky Security Center: Device access blockage message to administrator. The event description contains a message to administrator with substituted variables. You can view these events in the Kaspersky Security Center console using the predefined event selection User requests. If your organization does not have Kaspersky Security Center deployed or there is no connection to the Administration Server, the application will send a message to administrator to the specified email address. |
Application Control
Application Control manages the startup of applications on users' computers. This allows you to implement a corporate security policy when using applications. Application Control also reduces the risk of computer infection by restricting access to applications.
Configuring Application Control consists of the following steps:
- Creating application categories.
The administrator creates categories of applications that the administrator wants to manage. Categories of applications are intended for all computers in the corporate network, regardless of administration groups. To create a category, you can use the following criteria: KL category (for example, Browsers), file hash, application vendor, and other criteria.
- Creating Application Control rules.
The administrator creates Application Control rules in the policy for the administration group. The rule includes the categories of applications and the startup status of applications from these categories: blocked or allowed.
- Selecting the Application Control mode.
The administrator chooses the mode for working with applications that are not included in any of the rules (application denylist and allowlist).
When a user attempts to start a prohibited application, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block the application from starting and will display a notification (see the figure below).
A test mode is provided to check the configuration of Application Control. In this mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does the following:
- Allows the startup of applications, including prohibited ones.
- Shows a notification about the startup of a prohibited application and adds information to the report on the user's computer.
- Sends data about the startup of prohibited applications to Kaspersky Security Center.

Application Control notification
Application Control operating modes
The Application Control component operates in two modes:
- Denylist. In this mode, Application Control allows users to start all applications except for applications that are prohibited in Application Control rules.
This mode of Application Control is enabled by default.
- Allowlist. In this mode, Application Control blocks users from starting any applications except for applications that are allowed and not prohibited in Application Control rules.
If the allow rules of Application Control are fully configured, the component blocks the startup of all new applications that have not been verified by the LAN administrator, while allowing the operation of the operating system and of trusted applications that users rely on in their work.
You can read the recommendations on configuring Application Control rules in allowlist mode.
Application Control can be configured to operate in these modes both by using the Kaspersky Endpoint Security local interface and by using Kaspersky Security Center.
However, Kaspersky Security Center offers tools that are not available in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security local interface, such as the tools that are needed for the following tasks:
- Creating application categories.
Application Control rules created in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console are based on your custom application categories and not on inclusion and exclusion conditions as is the case in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security local interface.
- Receiving information about applications that are installed on corporate LAN computers.
This is why it is recommended to use Kaspersky Security Center to configure the operation of the Application Control component.
Application Control operating algorithm
Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses an algorithm to make a decision about starting an application (see the figure below).

Application Control operating algorithm
Application Control component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Action at startup of blocked applications |
Apply rules. Kaspersky Endpoint Security manages the startup of applications according to the selected mode. Test rules. Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows the startup of an application that is blocked in the current Application Control mode, but logs information about the application startup in the report. |
Application Startup Control mode |
You can choose one of the following options:
When Allowlist mode is selected, two Application Control rules are automatically created:
You cannot edit the settings of or delete automatically created rules. You can enable or disable these rules. |
Control DLL modules load |
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security controls the loading of DLL modules when users attempt to start applications. Information about the DLL module and the application that loaded this DLL module is logged in the report. When enabling control over the loading of DLL modules and drivers, make sure that one of the following rules is enabled in the Application Control settings: the default Golden Image rule or another rule that contains the "Trusted certificates" KL category and ensures that trusted DLL modules and drivers are loaded before Kaspersky Endpoint Security is started. Enabling control of the loading of DLL modules and drivers when the Golden Image rule is disabled may cause instability in the operating system. Kaspersky Endpoint Security monitors only the DLL modules and drivers that have been loaded since the check box was selected. After selecting the check box, it is recommended to restart the computer to ensure that the application monitors all DLL modules and drivers, including those loaded before Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts. |
Templates of messages about application blocking |
Message about blocking. Template of the message that is displayed when an Application Control rule that blocks an application from starting is triggered. Message to administrator. Template of the message that a user can send to the corporate LAN administrator if the user believes that an application was blocked by mistake. After the user requests to provide access, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends an event to Kaspersky Security Center: Application startup blockage message to administrator. The event description contains a message to administrator with substituted variables. You can view these events in the Kaspersky Security Center console using the predefined event selection User requests. If your organization does not have Kaspersky Security Center deployed or there is no connection to the Administration Server, the application will send a message to administrator to the specified email address. |
Adaptive Anomaly Control
This component is available if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for workstations. This component is unavailable if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for servers.
The Adaptive Anomaly Control component monitors and blocks actions that are not typical of the computers in a company's network. Adaptive Anomaly Control uses a set of rules to track non-typical behavior (for example, the Start of Microsoft PowerShell from office application rule). Rules are created by Kaspersky specialists based on typical scenarios of malicious activity. You can configure how Adaptive Anomaly Control handles each rule and, for example, allow the execution of PowerShell scripts that automate certain workflow tasks. Kaspersky Endpoint Security updates the set of rules along with the application databases. Updates to the sets of rules must be confirmed manually.
Adaptive Anomaly Control settings
Configuring Adaptive anomaly control consists of the following steps:
- Training Adaptive Anomaly Control.
After you enable Adaptive Anomaly Control, its rules work in training mode. During the training, Adaptive Anomaly Control monitors rule triggering and sends triggering events to Kaspersky Security Center. Each rule has its own duration of the training mode. The duration of the training mode is set by Kaspersky experts. Normally, the training mode is active for two weeks.
If a rule is not triggered at all during the training, Adaptive Anomaly Control will consider the actions associated with this rule as non-typical. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block all actions associated with that rule.
If a rule was triggered during training, Kaspersky Endpoint Security logs events in the rule triggering report and the Triggering of rules in Smart Training state repository.
- Analyzing the rule triggering report.
The administrator analyzes the rule triggering report or the contents of the Triggering of rules in Smart Training state repository. Then the administrator can select the behavior of Adaptive Anomaly Control when the rule is triggered: either block or allow. The administrator can also continue to monitor how the rule works and extend the duration of the training mode. If the administrator does not take any action, the application will also continue to work in training mode. The training mode term is restarted.
Adaptive Anomaly Control is configured in real time. Adaptive Anomaly Control is configured via the following channels:
- Adaptive Anomaly Control automatically starts to block the actions associated with the rules that were never triggered in training mode.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security adds new rules or removes obsolete ones.
- The administrator configures the operation of the Adaptive Anomaly Control after reviewing the rule triggering report and the contents of the Triggering of rules in Smart Training state repository. It is recommended to check the rule triggering report and the contents of the Triggering of rules in Smart Training state repository.
When a malicious application attempts to perform an action, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will block the action and display a notification (see figure below).

Adaptive Anomaly Control notification
Adaptive Anomaly Control operating algorithm
Kaspersky Endpoint Security decides whether to allow or block an action that is associated with a rule based on the following algorithm (see the figure below).

Adaptive Anomaly Control operating algorithm
Adaptive Anomaly Control component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Report on Adaptive Anomaly Control rules state (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
This report contains information about the status of Adaptive Anomaly Control detection rules (for example, the Disabled or Block). The report is generated for all administration groups. |
Report on triggered Adaptive Anomaly Control rules (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
This report contains information about non-typical actions detected using Adaptive Anomaly Control. The report is generated for all administration groups. |
Rules |
Adaptive Anomaly Control table of rules. Rules are created by Kaspersky specialists based on typical scenarios of potentially malicious activity. |
Templates |
Message about blocking. Template of the message that is displayed to a user when an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule that blocks a non-typical action is triggered. Message to administrator. Template of the message that a user can be sent to the local corporate network administrator if the user considers the blocking to be a mistake. After the user requests to provide access, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends an event to Kaspersky Security Center: Application activity blockage message to administrator. The event description contains a message to administrator with substituted variables. You can view these events in the Kaspersky Security Center console using the predefined event selection User requests. If your organization does not have Kaspersky Security Center deployed or there is no connection to the Administration Server, the application will send a message to administrator to the specified email address. |
File Integrity Monitor
This component is available if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for servers. This component is unavailable if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for workstations.
File Integrity Monitor works only on servers with NTFS or ReFS file system.
Starting with version 11.11.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes the File Integrity Monitor component. File Integrity Monitor detects changes to objects (files and folders) in a given monitoring area. These changes may indicate a computer security breach. When object changes are detected, the application informs the administrator.
To use File Integrity Monitor you need to configure component's scope, i.e. select objects, the state of which should be monitored by the component.
You can view information about the results of File Integrity Monitor operation in Kaspersky Security Center and in the interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
File Integrity Monitor component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Event severity level |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security logs file modification events whenever a file in the monitoring scope is modified. The following event severity levels are available: Informational, Warning, Critical. |
Monitoring scope |
List of files and folders that File Integrity Monitor monitors. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports environment variables and the |
Exclusions |
List of exclusions from the monitoring scope. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports environment variables and the |
Endpoint Sensor
Endpoint Sensor is not included in Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.4.0.
You can manage the Endpoint Sensor in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console. It is not possible to manage Endpoint Sensor in the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
Endpoint Sensor is designed to interact with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is a solution designed for timely detection of sophisticated threats such as targeted attacks, advanced persistent threats (APT), zero-day attacks, and others. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform includes two functional blocks: Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack (hereinafter also referred to as "KATA") and Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (hereinafter also referred to as "EDR (KATA)"). You can purchase EDR (KATA) separately. For details about the solution, please refer to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help.
Managing Endpoint Sensor has the following limitations:
- You can configure Endpoint Sensor settings in a policy provided that Kaspersky Endpoint Security version 11.0.0 to 11.3.0 is installed on the computer. For more information about configuring Endpoint Sensor settings using the policy, refer to the help articles for the previous versions of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- If Kaspersky Endpoint Security version 11.4.0 and later is installed on the computer, you cannot configure Endpoint Sensor settings in the policy.
Endpoint Sensor is installed on client computers. On these computers, the component constantly monitors processes, active network connections, and files that are modified. Endpoint Sensor relays information to the KATA server.
The component functionality is available under the following operating systems:
- Windows 7 Service Pack 1 Home / Professional / Enterprise;
- Windows 8.1.1 Professional / Enterprise;
- Windows 10 RS3 Home / Professional / Education / Enterprise;
- Windows 10 RS4 Home / Professional / Education / Enterprise;
- Windows 10 RS5 Home / Professional / Education / Enterprise;
- Windows 10 RS6 Home / Professional / Education / Enterprise;
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation / Standard / Enterprise (64-bit);
- Windows Server 2012 Foundation / Standard / Enterprise (64-bit);
- Windows Server 2012 R2 Foundation / Standard / Enterprise (64-bit);
- Windows Server 2016 Essentials / Standard (64-bit).
For detailed information on KATA operation, refer to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help.
Page top
Kaspersky Sandbox
Starting with version 11.7.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes a built-in agent for integration with Kaspersky Sandbox solution. The Kaspersky Sandbox solution detects and automatically blocks advanced threats on computers. Kaspersky Sandbox analyzes object behavior to detect malicious activity and activity characteristic of targeted attacks on the IT infrastructure of the organization. Kaspersky Sandbox analyzes and scans objects on special servers with deployed virtual images of Microsoft Windows operating systems (Kaspersky Sandbox servers). For details about the solution, refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox Help.
The component can be managed only using the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. You cannot manage this component using the Administration Console (MMC).
Kaspersky Sandbox component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Server TLS certificate |
To configure a trusted connection with Kaspersky Sandbox servers, you must prepare a TLS certificate. Next you must add the certificate to Kaspersky Sandbox servers and the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy. For details on preparing the certificate and adding the certificate to servers, refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox Help. |
Timeout |
Connection timeout for Kaspersky Sandbox server. After the configured timeout elapses, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends a request to the next server. You can increase the connection timeout for Kaspersky Sandbox if your connection speed is low or if the connection is unstable. The recommended request timeout is 0.5 seconds or less. |
Kaspersky Sandbox request queue |
Size of the request queue folder. When an object is accessed on the computer (executable launched or document opened, for example in DOCX or PDF format), Kaspersky Endpoint Security can also send the object to be scanned by Kaspersky Sandbox. If there are multiple requests, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates a request queue. By default, the size of the request queue folder is limited to 100 MB. After the maximum size is reached, Kaspersky Sandbox stops adding new requests to the queue and sends the corresponding event to Kaspersky Security Center. You can configure the size of the request queue folder depending on your server configuration. |
Kaspersky Sandbox servers |
Kaspersky Sandbox server connection settings. The servers use deployed virtual images of Microsoft Windows operating systems to run objects that need to be scanned. You can enter an IP address (IPv4 or IPv6) or a fully qualified domain name. |
Action on threat detection |
Move copy to Quarantine, delete object. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes the malicious object found on the computer. Before deleting the object, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates a backup copy in case the object needs to be restored later. Kaspersky Endpoint Security moves the backup copy to Quarantine. Run scan of critical areas. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs the Critical Areas Scan task. By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the kernel memory, running processes, and disk boot sectors. Create IOC scan task. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically creates the IOC Scan task (autonomous IOC scan task). For this task, you can configure the run mode, scan scope, and action on IOC detection: delete object, run the Critical Areas Scan task. To modify other settings of the IOC Scan task, go to the task settings. |
IOC scan scope |
Critical file areas. If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does an IOC scan only in critical file areas of the computer: kernel memory and boot sectors. File areas on system drives of the computer. IF this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does an IOC scan on the system drive of the computer. |
Run IOC scan task |
Manually. Run mode in which you can start the IOC scan task manually at a time of your choosing. After threat is detected. Run mode in which Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs the IOC Scan task automatically whenever a threat is detected. Run only when the computer is idle. Run mode in which Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs the IOC Scan task if the screensaver is active or the screen is locked. If the user unlocks the computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security pauses the task. This means that the task can take several days to complete. |
Endpoint Detection and Response
Starting with version 11.7.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes a built-in agent for the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum solution (hereinafter also "EDR Optimum"). Starting with version 11.8.0, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes a built-in agent for the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert solution (hereinafter also "EDR Expert"). Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response is a range of solutions for protecting the corporate IT infrastructure from advanced cyber threats. The functionality of the solutions combines automatic detection of threats with the ability to react to these threats to counteract advanced attacks including new exploits, ransomware, fileless attacks, as well as methods using legitimate system tools. EDR Expert offers more threat monitoring and response functionality than EDR Optimum. For details about the solutions, see the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help and the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help.
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response reviews and analyses threat development and provides security personnel or the Administrator with information about the potential attack that is necessary for a timely response. Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response displays alert details in a separate window. Alert Details is a tool for viewing the entirety of collected information about a detected threat. Alert details include, for example, the history of files appearing on the computer. For details about managing alert details, refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help and the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help.
You can configure the EDR Optimum component in Web Console and Cloud Console. Component settings for EDR Expert are available only in Cloud Console.
Endpoint Detection and Response settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Network isolation |
Automatic isolation of the computer from the network in response to detected threats. When network isolation is turned on, the application severs all active connections and blocks all new TCP/IP connections on the computer. The application leaves only the following connections active:
|
Automatically unlock isolated computer in N hours |
Network isolation can be turned off automatically after a specified time or manually. By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security turns off Network isolation 5 hours after the start of the isolation. |
Network isolation exclusions |
List of rules for exclusions from network isolation. Network connections that match the rules are not blocked on computers when Network isolation is turned on. To configure Network isolation exclusions, you can use a list of standard network profiles. By default, exclusions include network profiles containing rules that ensure uninterrupted operation of devices with the DNS/DHCP server and DNS/DHCP client roles. You can also modify the settings of standard network profiles or define exclusions manually. Exclusions specified in policy properties are applied only if Network isolation is turned on automatically in response to a detected threat. Exclusions specified in computer properties are applied only if Network isolation is turned on manually in computer properties in the Kaspersky Security Center console or in alert details. |
Execution prevention |
Control the execution of executable files and scripts and opening of office format files. For example, you can prevent the execution of applications that are considered insecure on the selected computer. Execution prevention supports a set of office file extensions and a set of script interpreters. To use Execution prevention component, you need to add execution prevention rules. Execution prevention rule is a set of criteria that the application takes into account when reacting to an object execution, for example when blocking object execution. The application identifies files by their paths or checksums calculated using MD5 and SHA256 hashing algorithms. |
Action on execution or opening of forbidden object |
Block and write to report. In this mode, the application blocks the execution of objects or opening of documents that match prevention rule criteria. The application also publishes an event about attempts to execute objects or open documents to the Windows event log and Kaspersky Security Center event log. Log events only. In this mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security publishes an event about attempts to run executable objects or open documents that match prevention rule criteria to the Windows event log and Kaspersky Security Center, but does not block the attempt to run or open the object or document. This mode is selected by default. |
Cloud Sandbox |
Cloud Sandbox is a technology that lets you detect advanced threats on a computer. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically forwards detected files to Cloud Sandbox for analysis. Cloud Sandbox runs these files in an isolated environment to identify malicious activity and decides on their reputation. Data on these files is then sent to Kaspersky Security Network. Therefore, if Cloud Sandbox has detected a malicious file, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will perform the appropriate action to eliminate this threat on all computers where this file is detected. Cloud Sandbox technology is permanently enabled and is available to all Kaspersky Security Network users regardless of the type of license they are using. If this check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will enable the counter for threats detected using Cloud Sandbox in the main application window under Threat detection technologies. Kaspersky Endpoint Security will also indicate the Cloud Sandbox threat detection technology in application events and in the Report on threats in the Kaspersky Security Center console. |
Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA)
Kaspersky Endpoint Security version 12.1 now includes a built-in agent for managing the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response component as part of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform solution. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is a solution designed for timely detection of sophisticated threats such as targeted attacks, advanced persistent threats (APT), zero-day attacks, and others. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform includes two functional blocks: Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack (hereinafter also referred to as "KATA") and Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (hereinafter also referred to as "EDR (KATA)"). You can purchase EDR (KATA) separately. For details about the solution, please refer to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on individual computers on the corporate IT infrastructure and continuously monitors processes, open network connections, and files being modified. Information about events on the computer (telemetry data) is sent to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security also sends information to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server about threats discovered by the application as well as information about processing results for these threats.
The EDR (KATA) integration is configured on the Kaspersky Security Center console. The built-in agent is then managed using the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform console, including running tasks, managing quarantined objects, viewing reports, and other actions.
Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Settings for connecting to KATA servers |
Timeout. Maximum Central Node server response timeout. When the timeout runs out, Kaspersky Endpoint Security tries to connect to a different Central Node server. Server TLS certificate. TLS certificate for establishing a trusted connection with the Central Node server. You can get a TLS certificate in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform console (see instructions in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help). Use two-way authentication. Two-way authentication allows enabling an additional verification of the computer on the Central Node. To enable this verification, you must turn on two-way authentication in Central Node and Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings. To use two-way authentication, you will also need a crypto-container. A crypto-container is a PFX archive with a certificate and a private key. You can get a crypto-container in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform console (see instructions in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help). The crypto-container must be password-protected. It is not possible to add a crypto-container with a blank password. |
KATA servers |
Central node server connection settings. You can enter an IP address (IPv4 or IPv6). |
Send sync request to KATA server every (min) |
Frequency of synchronization requests sent to the Central Node server. During synchronization, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends information about modified application settings and tasks. |
Send telemetry to KATA |
This functionality lets you completely turn off the sending of telemetry to the server. If you are using Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform together with another solution which also uses telemetry, you can turn off telemetry for KATA (EDR). This lets you optimize server load for these solutions. For example, if you have the Managed Detection and Response solution and KATA (EDR) deployed, you can use MDR telemetry and create Threat Response tasks in KATA (EDR). |
Maximum events transmission delay (sec) |
The application synchronizes with the server to send events after the synchronization interval expires. The default setting is 30 seconds. |
Enable request throttling |
This feature helps optimize the load on the server. If the check box is selected, the application restricts the transmitted events. If the number of events exceeds the configured limits, Kaspersky Endpoint Security stops sending events. |
Maximum number of events per hour |
The application analyzes the telemetry data stream and restricts the sending of events if the event stream exceeds the configured events-per-hour limit. Kaspersky Endpoint Security resumes sending events after an hour. The default setting is 3000 events per hour. |
Percentage of event limit excess |
The application sorts events by type (for example, "changes in the registry" events) and restricts transmission of events if the ratio of events of the same type to the total number of events exceeds the configured limit in percent. Kaspersky Endpoint Security resumes sending events when the ratio of other events to the total number of events becomes big enough again. The default setting is 15 %. |
Full Disk Encryption
You can select an encryption technology: Kaspersky Disk Encryption or BitLocker Drive Encryption (hereinafter also referred to as simply "BitLocker").
Kaspersky Disk Encryption
After the system hard drives have been encrypted, at the next computer startup the user must complete authentication using the Authentication Agent before the hard drives can be accessed and the operating system is loaded. This requires entering the password of the token or smart card connected to the computer, or the user name and password of the Authentication Agent account created by the local area network administrator using the Manage Authentication Agent accounts task. These accounts are based on Microsoft Windows accounts under which users log into the operating system. You can also use Single Sign-On (SSO) technology, which lets you automatically log in to the operating system using the user name and password of the Authentication Agent account.
User authentication in the Authentication Agent can be performed in two ways:
- Enter the name and password of the Authentication Agent account created by the LAN administrator using Kaspersky Security Center tools.
- Enter the password of a token or smart card connected to the computer.
Use of a token or smart card is available only if the computer hard drives were encrypted using the AES256 encryption algorithm. If the computer hard drives were encrypted using the AES56 encryption algorithm, addition of the electronic certificate file to the command will be denied.
BitLocker Drive Encryption
BitLocker is an encryption technology built into Windows operating systems. Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows you to control and manage Bitlocker using Kaspersky Security Center. BitLocker encrypts logical volumes. BitLocker cannot be used for encryption of removable drives. For more details on BitLocker, refer to the Microsoft documentation.
BitLocker provides secure storage of access keys using a trusted platform module. A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a microchip developed to provide basic functions related to security (for example, to store encryption keys). A Trusted Platform Module is usually installed on the computer motherboard and interacts with all other system components via the hardware bus. Using TPM is the safest way to store BitLocker access keys, since TPM provides pre-startup system integrity verification. You can still encrypt drives on a computer without a TPM. In this case, the access key will be encrypted with a password. BitLocker uses the following authentication methods:
- TPM.
- TPM and PIN.
- Password.
After encrypting a drive, BitLocker creates a master key. Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends the master key to Kaspersky Security Center so that you can restore access to the disk, for example, if a user has forgotten the password.
If a user encrypts a disk using BitLocker, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will send information about disk encryption to Kaspersky Security Center. However, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not send the master key to Kaspersky Security Center, so it will be impossible to restore access to the disk using Kaspersky Security Center. For BitLocker to work correctly with Kaspersky Security Center, decrypt the drive and re-encrypt the drive using a policy. You can decrypt a drive locally or using a policy.
After encrypting the system hard drive, the user needs to go through BitLocker authentication to boot the operating system. After the authentication procedure, BitLocker will allow for users to log in. BitLocker does not support single sign-on technology (SSO).
If you are using Windows group policies, turn off BitLocker management in the policy settings. Windows policy settings may conflict with Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings. When encrypting a drive, errors may occur.
Kaspersky Disk Encryption component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Encryption mode |
Encrypt all hard drives. If this item is selected, the application encrypts all hard drives when the policy is applied. If the computer has several operating systems installed, after encryption you will be able to load only the operating system that has the application installed. Decrypt all hard drives. If this item is selected, the application decrypts all previously encrypted hard drives when the policy is applied. Leave unchanged. If this item is selected, the application leaves drives in their previous state when the policy is applied. If the drive was encrypted, it remains encrypted. If the drive was decrypted, it remains decrypted. This item is selected by default. |
During encryption, automatically create Authentication Agent accounts for Windows users |
If this check box is selected, the application creates Authentication Agent accounts based on the list of Windows user accounts on the computer. By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses all local and domain accounts with which the user logged in to the operating system over the past 30 days. |
Authentication Agent account creation settings |
All accounts on the computer. All accounts on the computer that have been active at any time. All domain accounts on the computer. All accounts on the computer that belong to some domain and that have been active at any time. All local accounts on the computer. All local accounts on the computer that have been active at any time. Service account with a one-time password. The service account is necessary to gain access to the computer, for example, when the user forgets the password. You can also use the service account as a reserve account. You must enter the name of the account (by default, Local administrator. Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates an Authentication Agent user account for the local administrator of the computer. Computer manager. Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates an Authentication Agent user account for the account of the computer manager. You can see which account has the computer manager role in computer properties in Active Directory. By default, the computer manager role is not defined, that is, it does not correspond to any account. Active account. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically creates an Authentication Agent account for the account that is active at the time of disk encryption. |
Automatically create Authentication Agent accounts for all users of this computer upon sign-in |
If this check box is selected, the application checks information about Windows user accounts on the computer before starting Authentication Agent. If Kaspersky Endpoint Security detects a Windows user account that has no Authentication Agent account, the application will create a new account for accessing encrypted drives. The new Authentication Agent account will have the following default settings: password-protected sign-on only, and password change on first authentication. Therefore, you do not need to manually add Authentication Agent accounts using the Manage Authentication Agent accounts task for computers with already encrypted drives. |
Save user name entered in Authentication Agent |
If the check box is selected, the application saves the name of the Authentication Agent account. You will not be required to enter the account name the next time you attempt to complete authorization in the Authentication Agent under the same account. |
Encrypt used disk space only (reduces encryption time) |
This check box enables / disables the option that limits the encryption area to only occupied hard drive sectors. This limit lets you reduce encryption time. Enabling or disabling the Encrypt used disk space only (reduces encryption time) feature after starting encryption does not modify this setting until the hard drives are decrypted. You must select or clear the check box before starting encryption. If the check box is selected, only portions of the hard drive that are occupied by files are encrypted. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically encrypts new data as it is added. If the check box is cleared, the entire hard drive is encrypted, including residual fragments of previously deleted and modified files. This option is recommended for new hard drives whose data has not been modified or deleted. If you are applying encryption on a hard drive that is already in use, it is recommended to encrypt the entire hard drive. This ensures protection of all data, even deleted data that is potentially recoverable. This check box is cleared by default. |
Use Legacy USB Support (not recommended) |
This check box enables/disables the Legacy USB Support function. Legacy USB Support is a BIOS/UEFI function that allows you to use USB devices (such as a security token) during the computer's boot phase before starting the operating system (BIOS mode). Legacy USB Support does not affect support for USB devices after the operating system is started. If the check box is selected, support for USB devices during initial startup of the computer will be enabled. When the Legacy USB Support function is enabled, the Authentication Agent in BIOS mode does not support working with tokens via USB. It is recommended to use this option only when there is a hardware compatibility issue and only for those computers on which the problem occurred. |
Password settings |
Authentication Agent account password strength settings. When using Single Sign-on technology, the Authentication Agent ignores the password strength requirements specified in Kaspersky Security Center. You can set the password strength requirements in the operating system settings. |
Use Single Sign-On (SSO) technology |
SSO technology makes it possible to use the same account credentials to access encrypted hard drives and to sign in to the operating system. If the check box is selected, you must enter the account credentials for accessing encrypted hard drives and then automatically logging in to the operating system. If the check box is cleared, to access encrypted hard drives and subsequently log into the operating system you must separately enter the credentials for accessing encrypted hard drives and the operating system user account credentials. |
Wrap third-party credential providers |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the third-party credential provider ADSelfService Plus. When working with third-party credential providers, Authentication Agent intercepts the password before the operating system is loaded. This means that a user needs to enter a password only once when signing in to Windows. After signing in to Windows, the user can utilize the capabilities of a third-party credential provider for authentication in corporate services, for example. Third-party credential providers also allow users to independently reset their own password. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will automatically update the password for Authentication Agent. If you are using a third-party credential provider that is not supported by the application, you may encounter some limitations in Single Sign-On technology operation. |
Help |
Authentication. Help text that appears in the Authentication Agent window when entering account credentials. Change password. Help text that appears in the Authentication Agent window when changing the password for the Authentication Agent account. Recover password. Help text that appears in the Authentication Agent window when recovering the password for the Authentication Agent account. |
BitLocker Drive Encryption component settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Encryption mode |
Encrypt all hard drives. If this item is selected, the application encrypts all hard drives when the policy is applied. If the computer has several operating systems installed, after encryption you will be able to load only the operating system that has the application installed. Decrypt all hard drives. If this item is selected, the application decrypts all previously encrypted hard drives when the policy is applied. Leave unchanged. If this item is selected, the application leaves drives in their previous state when the policy is applied. If the drive was encrypted, it remains encrypted. If the drive was decrypted, it remains decrypted. This item is selected by default. |
Enable use of BitLocker authentication requiring pre-boot keyboard input on tablets |
This check box enables / disables the use of authentication requiring data input in a preboot environment, even if the platform does not have the capability for preboot input (for example, with touchscreen keyboards on tablets). The touchscreen of tablet computers is not available in the preboot environment. To complete BitLocker authentication on tablet computers, the user must connect a USB keyboard, for example. If the check box is selected, use of authentication requiring preboot input is allowed. It is recommended to use this setting only for devices that have alternative data input tools in a preboot environment, such as a USB keyboard in addition to touchscreen keyboards. If the check box is cleared, BitLocker Drive Encryption is not possible on tablets. |
Use hardware encryption (Windows 8 and later versions) |
If the check box is selected, the application applies hardware encryption. This lets you increase the speed of encryption and use less computer resources. |
Encrypt used disk space only (Windows 8 and later versions) |
This check box enables / disables the option that limits the encryption area to only occupied hard drive sectors. This limit lets you reduce encryption time. Enabling or disabling the Encrypt used disk space only (reduces encryption time) feature after starting encryption does not modify this setting until the hard drives are decrypted. You must select or clear the check box before starting encryption. If the check box is selected, only portions of the hard drive that are occupied by files are encrypted. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically encrypts new data as it is added. If the check box is cleared, the entire hard drive is encrypted, including residual fragments of previously deleted and modified files. This option is recommended for new hard drives whose data has not been modified or deleted. If you are applying encryption on a hard drive that is already in use, it is recommended to encrypt the entire hard drive. This ensures protection of all data, even deleted data that is potentially recoverable. This check box is cleared by default. |
Authentication method |
Only password (Windows 8 and later versions) If this option is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security prompts the user for a password when the user attempts to access an encrypted drive. This option can be selected when a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is not being used. Trusted platform module (TPM) If this option is selected, BitLocker uses a Trusted Platform Module (TPM). A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a microchip developed to provide basic functions related to security (for example, to store encryption keys). A Trusted Platform Module is usually installed on the computer motherboard and interacts with all other system components via the hardware bus. For computers running Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2, only encryption using a TPM module is available. If a TPM module is not installed, BitLocker encryption is not possible. Use of a password on these computers is not supported. A device equipped with a Trusted Platform Module can create encryption keys that can be decrypted only with the device. A Trusted Platform Module encrypts encryption keys with its own root storage key. The root storage key is stored within the Trusted Platform Module. This provides an additional level of protection against attempts to hack encryption keys. This action is selected by default. You can set an additional layer of protection for access to the encryption key, and encrypt the key with a password or a PIN:
|
File Level Encryption
You can compile lists of files by extension or group of extensions and lists of folders stored on local computer drives, and create rules for encrypting files that are created by specific applications. After a policy is applied, Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts and decrypts the following files:
- files individually added to lists for encryption and decryption;
- files stored in folders added to lists for encryption and decryption;
- files created by separate applications.
This component is available if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for workstations. This component is unavailable if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for servers.
File encryption has the following special features:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts / decrypts files in predefined folders only for local user profiles of the operating system. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not encrypt or decrypt files in predefined folders of roaming user profiles, mandatory user profiles, temporary user profiles, or redirected folders.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not encrypt files whose modification could harm the operating system and installed applications. For example, the following files and folders with all nested folders are on the list of encryption exclusions:
- %WINDIR%;
- %PROGRAMFILES% and %PROGRAMFILES(X86)%;
- Windows registry files.
The list of encryption exclusions cannot be viewed or edited. While files and folders on the list of encryption exclusions can be added to the encryption list, they will not be encrypted during file encryption.
File Level Encryption component settings
Parameter
Description
Encryption mode
Leave unchanged. If this item is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security leaves the files and folders unchanged without encrypting or decrypting them.
According to rules. If this item is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts the files and folders according to encryption rules, decrypts the files and folders according to decryption rules, and regulates the access of applications to encrypted files according to application rules.
Decrypt all. If this item is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security decrypts all encrypted files and folders.
Encryption
This tab shows encryption rules for files stored on local drives. You can add files as follows:
- Predefined folders. Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows you to add the following areas:
Documents. Files in the standard Documents folder of the operating system, and its subfolders.
Favorites. Files in the standard Favorites folder of the operating system, and its subfolders.
Desktop. Files in the standard Desktop folder of the operating system, and its subfolders.
Temporary files. Temporary files related to the operation of applications installed on the computer. For example, Microsoft Office applications create temporary files containing backup copies of documents.
Outlook files. Files related to the operation of the Outlook mail client: data files (PST), offline data files (OST), offline address book files (OAB), and personal address book files (PAB).
- Custom folder. You can type the path to the folder. When adding a folder path, adhere to the following rules:
Use an environment variable (for example,
%FOLDER%\UserFolder\). You can use an environment variable only once and only at the beginning of the path.Do not use relative paths.
Do not use the
*and?characters.Do not use UNC paths.
Use
;or,as a separator character. - Files by extension. You can select extension groups from the list, such as the extension group Archives. You can also manually add the file extension.
Decryption
This tab shows decryption rules for files stored on local drives.
Rules for applications
The tab displays a table containing encrypted file access rules for applications and encryption rules for files that are created or modified by individual applications.
Encrypted packages
Password strength requirements to meet when creating encrypted packages.
Encryption of removable drives
This component is available if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for workstations. This component is unavailable if Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer that runs on Windows for servers.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports encryption of files in FAT32 and NTFS file systems. If a removable drive with an unsupported file system is connected to the computer, the encryption task for this removable drive ends with an error and Kaspersky Endpoint Security assigns the read-only status to the removable drive.
To protect data on removable drives, you can use the following types of encryption:
- Full Disk Encryption (FDE).
Encryption of the entire removable drive, including the file system.
It is not possible to access encrypted data outside the corporate network. It is also impossible to access encrypted data inside the corporate network if the computer is not connected to Kaspersky Security Center (e.g. on a guest computer).
- File Level Encryption (FLE).
Encryption of only files on a removable drive. The file system remains unchanged.
Encryption of files on removable drives provides the capability to access data outside the corporate network using a special mode called portable mode.
During encryption, Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates a master key. Kaspersky Endpoint Security saves the master key in the following repositories:
- Kaspersky Security Center.
- User's computer.
The master key is encrypted with the user's secret key.
- Removable drive.
The master key is encrypted with the public key of Kaspersky Security Center.
After encryption is complete, the data on the removable drive can be accessed within the corporate network as if was on an ordinary unencrypted removable drive.
Accessing encrypted data
When a removable drive with encrypted data is connected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- Checks for a master key in the local storage on the user's computer.
If the master key is found, the user gains access to the data on the removable drive.
If the master key is not found, Kaspersky Endpoint Security performs the following actions:
- Sends a request to Kaspersky Security Center.
After receiving the request, Kaspersky Security Center sends a response that contains the master key.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security saves the master key in the local storage on the user's computer for subsequent operations with the encrypted removable drive.
- Sends a request to Kaspersky Security Center.
- Decrypts the data.
Special features of removable drive encryption
Encryption of removable drives has the following special features:
- The policy with preset settings for removable drive encryption is formed for a specific group of managed computers. Therefore, the result of applying the Kaspersky Security Center policy configured for encryption / decryption of removable drives depends on the computer to which the removable drive is connected.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not encrypt / decrypt read-only files that are stored on removable drives.
- The following device types are supported as removable drives:
- Data media connected via the USB bus
- hard drives connected via USB and FireWire buses
- SSD drives connected via USB and FireWire buses
Encryption of removable drives component settings
Parameter
Description
Encryption mode
Encrypt entire removable drive. If this item is selected, when applying the policy with the specified encryption settings for removable drives, Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts removable drives sector by sector, including their file systems.
Encrypt all files. If this item is selected, when applying the policy with the specified encryption settings for removable drives, Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts all files that are stored on removable drives. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not re-encrypt files that are already encrypted. The contents of the file system of a removable drive, including the folder structure and names of encrypted files, are not encrypted and remain accessible.
Encrypt new files only. If this item is selected, when applying the policy with the specified encryption settings for removable drives, Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts only those files that were added or modified on removable drives after the Kaspersky Security Center policy was last applied. This encryption mode is convenient when a removable drive is used for both personal and work purposes. This encryption mode lets you leave all old files unchanged and encrypt only those files that the user creates on a work computer that has Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed and encryption functionality enabled. As a result, access to personal files is always available, regardless of whether or not Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on the computer with encryption functionality enabled.
Decrypt entire removable drive. If this item is selected, when applying the policy with the specified encryption settings for removable drives, Kaspersky Endpoint Security decrypts all encrypted files stored on removable drives as well as the file systems of the removable drives if they were previously encrypted.
Leave unchanged. If this item is selected, the application leaves drives in their previous state when the policy is applied. If the drive was encrypted, it remains encrypted. If the drive was decrypted, it remains decrypted. This item is selected by default.
Portable mode
This check box enables / disables the preparation of a removable drive that makes it possible to access files stored on this removable drive on computers outside of the corporate network.
If this check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security prompts the user to specify a password before encrypting files on a removable drive upon the application of the policy. The password is needed to access files encrypted on a removable drive on computers outside of the corporate network. You can configure the password strength.
Portable mode is available for the Encrypt all files or Encrypt new files only modes.
Encrypt used disk space only
This check box enables / disables the encryption mode in which only occupied disk sectors are encrypted. This mode is recommended for new drives whose data has not been modified or deleted.
If the check box is selected, only portions of the drive that are occupied by files are encrypted. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically encrypts new data as it is added.
If the check box is cleared, the entire drive is encrypted, including residual fragments of previously deleted and modified files.
The ability to encrypt only occupied space is available only for the Encrypt entire removable drive mode.
After encryption started, enabling / disabling the Encrypt used disk space only function will not change this setting. You must select or clear the check box before starting encryption.
Custom rules
This table contains devices for which custom encryption rules are defined. You can create encryption rules for individual removable drives in the following ways:
- Add a removable drive from the list of trusted devices for Device Control.
- Manually add a removable drive:
- By device ID (Hardware ID, or HWID)
- By device model: vendor ID (VID) and product ID (PID)
Allow encryption of removable drives in offline mode
If this check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security encrypts removable drives even when there is no connection to Kaspersky Security Center. In this case, the data required for decrypting removable drives is stored on the hard drive of the computer to which the removable drive is connected, and is not transmitted to Kaspersky Security Center.
If the check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not encrypt removable drives without a connection to Kaspersky Security Center.
Encryption password settings / Portable File Manager
Password strength settings for the Portable File Manager.
Templates (data encryption)
After data encryption, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may restrict access to data, for example, due to a change in the organization's infrastructure and a change in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server. If a user does not have access to encrypted data, the user can ask the administrator for access to the data. In other words, the user needs to send a request access file to the administrator. The user then needs to upload the response file received from the administrator to Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows you to request access to data from the administrator via email (see the figure below).

Requesting access to encrypted data
A template is provided for reporting a lack of access to encrypted data. For user convenience, you can fill out the following fields:
- To. Enter the email address of the administrator group with rights to the data encryption features.
- Subject. Enter the subject of the email with your request for access to encrypted files. You can, for example, add tags to filter messages.
- User's message. If necessary, change the contents of the message. You can use variables to get the necessary data (for example,
%USER_NAME%variable).
Exclusions
A trusted zone is a system administrator-configured list of objects and applications that Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not monitor when active.
The administrator forms the trusted zone independently, taking into account the features of the objects that are handled and the applications that are installed on the computer. It may be necessary to include objects and applications in the trusted zone when Kaspersky Endpoint Security blocks access to a certain object or application, if you are sure that the object or application is harmless. An administrator can also allow a user to create their own local trusted zone for a specific computer. This way, users can create their own local lists of exclusions and trusted applications in addition to the general trusted zone in a policy.
Scan exclusions
A scan exclusion is a set of conditions that must be fulfilled so that Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not scan a particular object for viruses and other threats.
Scan exclusions make it possible to safely use legitimate software that can be exploited by criminals to damage the computer or user data. Although they do not have any malicious functions, such applications can be exploited by intruders. For details on legitimate software that could be used by criminals to harm the computer or personal data of a user, please refer to the Kaspersky IT Encyclopedia website.
Such applications may be blocked by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. To prevent them from being blocked, you can configure scan exclusions for the applications in use. To do so, add the name or name mask that is listed in the Kaspersky IT Encyclopedia to the trusted zone. For example, you often use the Radmin application for remote administration of computers. Kaspersky Endpoint Security regards this activity as suspicious and may block it. To prevent the application from being blocked, create a scan exclusion with the name or name mask that is listed in the Kaspersky IT Encyclopedia.
If an application that collects information and sends it to be processed is installed on your computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may classify this application as malware. To avoid this, you can exclude the application from scanning by configuring Kaspersky Endpoint Security as described in this document.
Scan exclusions can be used by the following application components and tasks that are configured by the system administrator:
- Behavior Detection.
- Exploit Prevention.
- Host Intrusion Prevention.
- File Threat Protection.
- Web Threat Protection.
- Mail Threat Protection.
- Malware Scan tasks.
List of trusted applications
The list of trusted applications is a list of applications whose file and network activity (including malicious activity) and access to the system registry are not monitored by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security monitors objects that are opened, executed, or saved by any application process and controls the activity of all applications and network traffic that is generated by them. After an application is added to the list of trusted applications, Kaspersky Endpoint Security stops monitoring the application's activity.
The difference between scan exclusions and trusted applications is that for exclusions Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan files, while for trusted applications it does not control the initiated processes. If a trusted application creates a malicious file in a folder which is not included in scan exclusions, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will detect the file and eliminate the threat. If the folder is added to exclusions, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will skip this file.
For example, if you consider objects that are used by the standard Microsoft Windows Notepad application to be safe, meaning that you trust this application, you can add Microsoft Windows Notepad to the list of trusted applications so that the objects used by this application are not monitored. This will increase computer performance, which is especially important when using server applications.
In addition, certain actions that are classified by Kaspersky Endpoint Security as suspicious may be safe within the context of the functionality of a number of applications. For example, the interception of text that is typed from the keyboard is a routine process for automatic keyboard layout switchers (such as Punto Switcher). To take account of the specifics of such applications and exclude their activity from monitoring, we recommend that you add such applications to the trusted applications list.
Trusted applications help to avoid compatibility issues between Kaspersky Endpoint Security and other applications (for example, the problem of double-scanning of the network traffic of a third-party computer by Kaspersky Endpoint Security and by another anti-virus application).
At the same time, the executable file and process of the trusted application are still scanned for viruses and other malware. An application can be fully excluded from Kaspersky Endpoint Security scanning by means of scan exclusions.
Settings of exclusions
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Types of detected objects |
Regardless of the configured application settings, Kaspersky Endpoint Security always detects and blocks viruses, worms, and Trojans. They can cause significant harm to the computer. |
Exclusions |
This table contains information about scan exclusions. You can exclude objects from scans by using the following methods:
|
Trusted applications |
This table lists trusted applications whose activity is not monitored by Kaspersky Endpoint Security during its operation. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports environment variables and the Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support the The Application Control component regulates the startup of each of the applications regardless of whether or not the application is included in the table of trusted applications. |
Merge values when inheriting (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
This merges the list of scan exclusions and trusted applications in the parent and child policies of Kaspersky Security Center. To merge lists, the child policy must be configured to inherit the settings of the parent policy of Kaspersky Security Center. If the check box is selected, list items from the Kaspersky Security Center parent policy are displayed in child policies. This way you can, for example, create a consolidated list of trusted applications for the entire organization. Inherited list items in a child policy cannot be deleted or edited. Items on the list of scan exclusions and the list of trusted applications that are merged during inheritance can be deleted and edited only in the parent policy. You can add, edit or delete list items in lower-level policies. If items on lists of the child and parent policy match, these items are displayed as the same item of the parent policy. If the check box is not selected, list items are not merged when inheriting the settings of Kaspersky Security Center policies. |
Allow use of local exclusions / Allow use of local trusted applications (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
Local exclusions and local trusted applications (local trusted zone) – user-defined list of objects and applications in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for a specific computer. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not monitor objects and applications from the local trusted zone. This way, users can create their own local lists of exclusions and trusted applications in addition to the general trusted zone in a policy. If the check box is selected, a user can create a local list of scan exclusions and a local list of trusted applications. An administrator can use Kaspersky Security Center to view, add, edit, or delete list items in the computer properties. If the check box is cleared, a user can access only the general lists of scan exclusions and trusted applications generated in the policy. |
Trusted system certificate store |
If one of the trusted system certificate stores is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security excludes applications signed with a trusted digital signature from scans. Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically assigns such applications to the Trusted group. If Do not use is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans applications regardless of whether or not they have a digital signature. Kaspersky Endpoint Security places an application in a trust group depending on the level of danger that this application may pose to the computer. |
Application settings
You can configure the following general settings of the application:
- Operating mode
- Self-Defense
- Performance
- Debug information
- Computer status when settings are applied
Application settings
Parameter
Description
Start Kaspersky Endpoint Security on computer startup (recommended)
When the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security is started after the operating system loads, protecting the computer during the entire session.
When the check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security is not started after the operating system loads, until the user starts it manually. Computer protection is disabled and user data may be exposed to threats.
Use Advanced Disinfection technology (requires considerable computer resources)
If the check box is selected, a pop-up notification appears on the screen when malicious activity is detected in the operating system. In its notification, Kaspersky Endpoint Security offers the user to perform Advanced Disinfection of the computer. After the user approves this procedure, Kaspersky Endpoint Security neutralizes the threat. After completing the advanced disinfection procedure, Kaspersky Endpoint Security restarts the computer. The advanced disinfection technology uses considerable computing resources, which may slow down other applications.
When the application is in process of detecting an active infection, some operating system functionality can be unavailable. The availability of the operating system is restored when Advanced Disinfection is complete and the computer is restarted.
If Kaspersky Endpoint Security is installed on a computer running Windows for Servers, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not show the notification. Therefore, the user cannot select an action to disinfect an active threat. To disinfect a threat, you need to enable Advanced Disinfection technology in application settings and enable immediate Advanced Disinfection in Malware Scan task settings. Then you need to start a Malware Scan task.
Use Kaspersky Security Center as proxy server for activation
(available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console)
If this check box is selected, the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server is used as a proxy server when activating the application.
Enable Self-Defense
When this check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security prevents alteration or deletion of application files on the hard drive, memory processes, and entries in the system registry.
Enable external management of system services
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security allows management of application services from a remote computer. When an attempt is made to manage application services remotely, a notification is displayed in the Microsoft Windows taskbar, above the application icon (unless the notification service has been disabled by the user).
Postpone scheduled tasks while running on battery power
If the check box is selected, energy conservation mode is enabled. Kaspersky Endpoint Security postpones scheduled tasks. You can start scan and update tasks manually, if necessary.
When energy conservation mode is enabled and the computer is running on battery power, the following tasks are not run even if scheduled:
- Update
- Full Scan
- Critical Areas Scan
- Custom Scan
- Integrity check
- IOC Scan.
Concede resources to other applications
Consumption of computer resources by Kaspersky Endpoint Security when scanning the computer may increase the load on the CPU and hard drive subsystems. This may slow down other applications. To optimize the performance, Kaspersky Endpoint Security provides a mode for transferring resources to other applications. In this mode, the operating system can decrease the priority of Kaspersky Endpoint Security scan task threads when the CPU load is high. This allows redistributing operating system resources to other applications. Thus, scan tasks will receive less CPU time. As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will take longer to scan the computer. By default, the application is configured to concede resources to other applications.
Enable dump writing
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security writes dumps when it crashes.
If the check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not write dumps. The application also deletes existing dump files from the computer hard drive.
Enable dump and trace files protection
If the check box is selected, access to dump files is granted to the system administrator and local administrator as well as to the user who enabled dump writing. Only system and local administrators can access trace files.
If the check box is cleared, any user can access dump files and trace files.
Computer status when settings are applied
(available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console)
Settings for displaying the statuses of client computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed in the Web Console when errors occur while applying a policy or executing a task. The following statuses are available OK, Warning and Critical.
Install updates without computer restart
Upgrading the application without computer restart allows you to ensure uninterrupted operation of servers.
You can upgrade the application without a restart starting with version 11.10.0. To upgrade an earlier version of the application, you must restart the computer.
Starting with version 11.11.0 you can perform the following actions without restarting a computer:
- install patches
- change the set of application components
- install Kaspersky Endpoint Security over Kaspersky Security for Windows Server
The default value of the parameter varies depending on the type of the operating system. If the application is installed on a workstation, the upgrading the application without a restart option is disabled. If the application is installed on a server, the upgrading the application without a restart option is enabled.
Reports and storage
Reports
Information about the operation of each Kaspersky Endpoint Security component, data encryption events, the performance of each scan task, the update task and integrity check task, and the overall operation of the application is recorded in reports.
Reports are stored in the folder C:\ProgramData\Kaspersky Lab\KES.21.13\Report.
Backup
Backup stores backup copies of files that were deleted or modified during disinfection. A backup copy is a file copy created before the file was disinfected or deleted. Backup copies of files are stored in a special format and do not pose a threat.
Backup copies of files are stored in the folder C:\ProgramData\Kaspersky Lab\KES.21.13\QB.
Users in the Administrators group are granted full permission to access this folder. Limited access rights to this folder are granted to the user whose account was used to install Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not provide the capability to configure user access permissions to backup copies of files.
Quarantine
Quarantine is a special local storage on the computer. The user can quarantine files that the user considers dangerous for the computer. Quarantined files are stored in an encrypted state and do not threaten the security of the device. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses Quarantine only when working with Detection and Response solutions: EDR Optimum, EDR Expert, KATA (EDR), Kaspersky Sandbox. In other cases Kaspersky Endpoint Security places the relevant file in Backup. For details on managing Quarantine as part of solutions, please refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox Help, Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum Help, and Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert Help, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help.
Quarantine can only be configured using Web Console. You can also use Web Console to manage quarantined objects (restore, delete, add, etc). You can restore objects locally on the computer using the command line.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the system account (SYSTEM) to quarantine files.
Settings of reports and storage
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Store reports no longer than N days |
If the check box is selected, the maximum report storage term is limited to the defined time interval. The default maximum storage term for reports is 30 days. After that period of time, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes the oldest entries from the report file. |
Limit the size of report file to N MB |
If the check box is selected, the maximum report file size is limited to the defined value. By default, the maximum file size is 1024 MB. To avoid exceeding the maximum report file size, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes the oldest entries from the report file when the maximum report file size is reached. |
Store objects no longer than N days |
If the check box is selected, the maximum file storage term is limited to the defined time interval. The default maximum storage term for files is 30 days. After expiration of the maximum storage term, Kaspersky Endpoint Security deletes the oldest files from Backup. |
Limit the size of Backup to N MB |
If the check box is selected, the maximum storage size is limited to the defined value. By default, the maximum size is 1024 MB. To avoid exceeding the maximum storage size, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically deletes the oldest files from storage when the maximum storage size is reached. |
Limit the size of Quarantine to N MB |
Maximum Quarantine size in MB. For example, you can set the maximum Quarantine size to 200 MB. When Quarantine reaches maximum size, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends the corresponding event to Kaspersky Security Center and publishes the event in Windows Event Log. Meanwhile the application stops quarantining new objects. You must empty the Quarantine manually. |
Notify when the Quarantine storage reaches N percent |
Threshold value of the Quarantine. For example, you can set the Quarantine threshold to 50%. When Quarantine reaches the threshold, Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends the corresponding event to Kaspersky Security Center and publishes the event in Windows Event Log. Meanwhile the application continues quarantining new objects. |
Data transfer to Administration Server (available only in Kaspersky Security Center) |
Categories of events on client computers whose information must be relayed to the Administration Server. |
Network settings
You can configure the proxy server used for connecting to the Internet and updating anti-virus databases, select the network port monitoring mode, and configure encrypted connections scan.
Network options
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Limit traffic on metered connections |
If this check box is selected, the application limits its own network traffic when the Internet connection is limited. Kaspersky Endpoint Security identifies a high-speed mobile Internet connection as a limited connection and identifies a Wi-Fi connection as an unlimited connection. Cost-Aware Networking works on computers running Windows 8 or later. |
Inject script into web traffic to interact with web pages |
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security injects a web page interaction script into web traffic. This script ensures that the Web Control component can work correctly. The script enables registration of Web Control events. Without this script, you cannot enable user Internet activity monitoring. Kaspersky experts recommend injecting this web page interaction script into traffic to ensure correct operation of Web Control. |
Proxy server |
Settings of the proxy server used for Internet access of users of client computers. Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses these settings for certain protection components, including for updating databases and application modules. For automatic configuration of a proxy server, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the WPAD protocol (Web Proxy Auto-Discovery Protocol). If the IP address of the proxy server cannot be determined by using this protocol, the application uses the proxy server address that is specified in the Microsoft Internet Explorer browser settings. |
Bypass proxy server for local addresses |
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not use a proxy server when performing an update from a shared folder. |
Monitored ports |
Monitor all network ports. In this network port monitoring mode, the protection components (File Threat Protection, Web Threat Protection, Mail Threat Protection) monitor data streams that are transmitted via any open network ports of the computer. Monitor selected network ports only. In this network port monitoring mode, the protection components monitor the selected ports of the computer and the network activity of the selected applications. The list of network ports that are normally used for transmission of email and network traffic is configured according to the recommendations of Kaspersky experts. Monitor all ports for the applications from the list recommended by Kaspersky. This uses a predefined list of applications whose network ports are monitored by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. For example, this list includes Google Chrome, Adobe Reader, Java, and other applications. Monitor all ports for specified applications. This uses a list of applications whose network ports are monitored by Kaspersky Endpoint Security. |
Encrypted connections scan |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans encrypted network traffic transmitted over the following protocols:
Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan encrypted connections that were established by trusted applications for which traffic scanning is disabled. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan encrypted connections from the predefined list of trusted websites. The predefined list of trusted websites is created by Kaspersky experts. This list is updated with the application's anti-virus databases. You can view the predefined list of trusted websites only in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface. You cannot view the list in the Kaspersky Security Center Console. |
Trusted root certificates |
List of trusted root certificates. Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you install trusted root certificates on user computers if, for example, you need to deploy a new certification center. The application lets you add a certificate to a special Kaspersky Endpoint Security certificate store. In this case, the certificate is considered trusted only for the Kaspersky Endpoint Security application. In other words, the user can gain access to a website with the new certificate in the browser. If another application tries to gain access to the website, you can get a connection error because of a certificate issue. To add to the system certificate store, you can use Active Directory group policies. |
When visiting a domain with an untrusted certificate |
|
When encrypted connections scan errors occur |
|
Block SSL 2.0 connections (recommended) |
If the check box is selected, the application blocks network connections established over the SSL 2.0 protocol. If the check box is cleared, the application does not block network connections established over the SSL 2.0 protocol and does not monitor network traffic transmitted over these connections. |
Decrypt an encrypted connection with the website that uses EV certificate |
EV certificates (Extended Validation Certificates) confirm the authenticity of websites and enhance the security of the connection. Browsers use a lock icon in their address bar to indicate that a website has an EV certificate. Browsers may also fully or partially color the address bar in green. If the check box is selected, the application decrypts and monitors encrypted connections with websites that use an EV certificate. If the check box is cleared, the application does not have access to the contents of HTTPS traffic. For this reason, the application monitors HTTPS traffic only based on the website address, for example, If you are opening a website with an EV certificate for the first time, the encrypted connection will be decrypted regardless of whether or not the check box is selected. |
Trusted addresses |
This uses a list of web addresses for which Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan network connections. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not scan HTTPS traffic of trusted web addresses when Web Threat Protection, Mail Threat Protection, Web Control components are doing their work. You can enter a domain name or an IP address. Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support the Examples:
|
Trusted applications |
List of applications whose activity is not monitored by Kaspersky Endpoint Security during its operation. You can select the types of application activity that Kaspersky Endpoint Security will not monitor (for example, do not scan network traffic). Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports environment variables and the |
Use the selected certificate store to scan encrypted connections in Mozilla applications (available only in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
If this check box is selected, the application scans encrypted traffic in the Mozilla Firefox browser and Thunderbird mail client. Access to some websites via the HTTPS protocol may be blocked. To scan traffic in the Mozilla Firefox browser and the Thunderbird mail client, you must enable the Encrypted Connections Scan. If Encrypted Connections Scan is disabled, the application does not scan traffic in the Mozilla Firefox browser and Thunderbird mail client. The application uses the Kaspersky root certificate to decrypt and analyze encrypted traffic. You can select the certificate store that will contain the Kaspersky root certificate.
|
Interface
You can configure the settings of the application interface.
Interface settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Interaction with user (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
Display simplified interface. On a client computer, the main application window is inaccessible, and only the icon in the Windows notification area is available. In the context menu of the icon, the user can perform a limited number of operations with Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Kaspersky Endpoint Security also displays notifications above the application icon. Display user interface. On a client computer, the main window of Kaspersky Endpoint Security and the icon in the Windows notification area are available. In the context menu of the icon, the user can perform operations with Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Kaspersky Endpoint Security also displays notifications above the application icon. Hide Application Activity Monitor section. On the client computer, in the main window of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, the Application Activity Monitor button is not available. Application Activity Monitor is a tool designed for viewing information about the activity of applications on a user's computer in real time. Do not display. On a client computer, no signs of Kaspersky Endpoint Security operation are displayed. The icon in the Windows notification area and notifications are not available. |
Notification settings |
A table with the settings of notifications about events of different importance levels that may occur during the operation of a component, task, or the entire application. Kaspersky Endpoint Security shows notifications about these events on the screen, sends them by email, or logs them. |
Email notification settings |
SMTP server settings for delivery of notifications about events registered during operation of the application. |
Show application's status in notifications area |
Categories of application events that cause the Kaspersky Endpoint Security icon to change in the Microsoft Windows taskbar notification area ( |
Local anti-malware database status notifications |
Settings of notifications about outdated anti-virus databases used by the application. |
Password protection |
If the toggle button is switched on, Kaspersky Endpoint Security prompts the user for a password when the user attempts to perform an operation that is within the scope of Password Protection. The Password Protection scope includes forbidden operations (such as disabling protection components) and the user accounts to which the Password Protection scope is applied. After Password Protection is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security prompts you to set a password for performing operations. |
User support / Links to web resources (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
List of links to web resources containing information about technical support for Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Added links are displayed in the Support window of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security local interface instead of standard links. |
User support / Description (available only in the Kaspersky Security Center Console) |
Message that is displayed in the Support window of the local interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. |
Manage Settings
You can save the current Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings to a file and use them to quickly configure the application on a different computer. You can also use a configuration file when deploying the application through Kaspersky Security Center with an installation package. You can restore the default settings at any time.
Application configuration management settings are available only in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface.
Application configuration management settings
Settings |
Description |
|---|---|
Import |
Extract application settings from a file in CFG format and apply them. |
Export |
Save the current application settings to a file in CFG format. |
Restore |
You can restore the application settings recommended by Kaspersky at any time. When the settings are restored, the Recommended security level is set for all protection components. |
Updating databases and application software modules
Updating the databases and application modules of Kaspersky Endpoint Security ensures up-to-date protection on your computer. New viruses and other types of malware appear worldwide on a daily basis. Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases contain information about threats and ways of neutralizing them. To detect threats quickly, you are urged to regularly update the databases and application modules.
Regular updates require a license in effect. If there is no current license, you will be able to perform an update only once.
The main update source for Kaspersky Endpoint Security is Kaspersky update servers.
Your computer must be connected to the Internet to successfully download the update package from Kaspersky update servers. By default, the Internet connection settings are determined automatically. If you are using a proxy server, you need to configure the proxy server settings.
Updates are downloaded over the HTTPS protocol. They may also be downloaded over the HTTP protocol when it is impossible to download updates over the HTTPS protocol.
While performing an update, the following objects are downloaded and installed on your computer:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases. Computer protection is provided using databases that contain signatures of viruses and other threats and information on ways to neutralize them. Protection components use this information when searching for and neutralizing infected files on your computer. The databases are constantly updated with records of new threats and methods for counteracting them. Therefore, we recommend that you update the databases regularly.
In addition to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases, the network drivers that enable the application's components to intercept network traffic are updated.
- Application modules. In addition to the databases of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, you can also update the application modules. Updating the application modules fixes vulnerabilities in Kaspersky Endpoint Security, adds new functions, or enhances existing functions.
While updating, the application modules and databases on your computer are compared against the up-to-date version at the update source. If your current databases and application modules differ from their respective up-to-date versions, the missing portion of the updates is installed on your computer.
Context help files can be updated together with application module updates.
If the databases are obsolete, the update package may be large, which may cause additional Internet traffic (up to several dozen MB).
Information about the current state of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases is displayed in the main application window or the tooltip that you see when you hover the cursor over the icon of the application in the notification area.
Information on update results and on all events that occur during the performance of the update task is logged in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security report.
Application module and database update settings
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Databases update schedule |
Automatically. In this mode, the application checks the update source for availability of new update packages with a certain frequency. The frequency of checking for the update package increases during virus outbreaks and decreases when there are none. After detecting a fresh update package, Kaspersky Endpoint Security downloads it and installs updates on your computer. Manually. This update task run mode allows you to manually start the update task. By schedule. In this update task run mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security runs the update task in accordance with the schedule that you have specified. If this update task run mode is selected, you can also start the Kaspersky Endpoint Security update task manually. |
Run missed tasks |
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security starts the skipped update task as soon as this becomes possible. The update task can be skipped, for example, if the computer was turned off at the update task start time. If the check box is cleared, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not start missed update tasks. Instead, it runs the next update task in accordance with the current schedule. |
Update sources |
An update source is a resource that contains updates for databases and application modules of Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Update sources include the Kaspersky Security Center server, Kaspersky update servers, and network or local folders. The default list of update sources includes Kaspersky Security Center and Kaspersky update servers. You can add other update sources to the list. You can specify HTTP/FTP servers and shared folders as update sources. Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not support updates from HTTPS servers unless they are Kaspersky's update servers. If several resources are selected as update sources, Kaspersky Endpoint Security tries to connect to them one after another, starting from the top of the list, and performs the update task by retrieving the update package from the first available source. |
Run database updates as |
By default, the Kaspersky Endpoint Security update task is started on behalf of the user whose account you have used to log in to the operating system. However, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may be updated from an update source that the user cannot access due to a lack of required rights (for example, from a shared folder that contains an update package) or an update source for which proxy server authentication is not configured. In the application settings, you can specify a user that has such rights and start the Kaspersky Endpoint Security update task under that user account. |
Download updates of application modules |
Downloading application module updates with application database updates. If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security notifies the user about available application module updates and includes application module updates in the update package while running the update task. The way application module updates are applied is determined by the following settings:
If application module updates require reviewing and accepting the terms of the End User License Agreement, the application installs updates after the terms of the End User License Agreement have been accepted. This check box is selected by default. |
Copy updates to folder |
If this check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security copies the update package to the shared folder specified under the check box. After that, other computers on your LAN are able to receive the update package from this shared folder. This reduces Internet traffic because the update package is downloaded only once. The following folder is specified by default: |
Proxy server for updates (available only in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
Proxy server settings for Internet access of users of client computers to update application modules and databases. For automatic configuration of a proxy server, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the WPAD protocol (Web Proxy Auto-Discovery Protocol). If the IP address of the proxy server cannot be determined by using this protocol, Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the proxy server address that is specified in the Microsoft Internet Explorer browser settings. |
Bypass proxy server for local addresses (available only in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security interface) |
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security does not use a proxy server when performing an update from a shared folder. |
Appendix 2. Application trust groups
Kaspersky Endpoint Security categorizes all applications that are started on the computer into trust groups. Applications are categorized into trust groups depending on the level of threat that the applications pose to the operating system.
The trust groups are as follows:
- Trusted. This group includes applications for which one or more of the following conditions are met:
- Applications are digitally signed by trusted vendors.
- Applications are recorded in the trusted applications database of Kaspersky Security Network.
- The user has placed application in the Trusted group.
No operations are prohibited for these applications.
- Low Restricted. This group includes applications for which the following conditions are met:
- Applications are not digitally signed by trusted vendors.
- Applications are not recorded in the trusted applications database of Kaspersky Security Network.
- The user has placed application in the "Low Restricted" group.
Such applications are subject to minimal restrictions on access to operating system resources.
- High Restricted. This group includes applications for which the following conditions are met:
- Applications are not digitally signed by trusted vendors.
- Applications are not recorded in the trusted applications database of Kaspersky Security Network.
- The user has placed application in the High Restricted group.
Such applications are subject to high restrictions on access to operating system resources.
- Untrusted. This group includes applications for which the following conditions are met:
- Applications are not digitally signed by trusted vendors.
- Applications are not recorded in the trusted applications database of Kaspersky Security Network.
- The user has placed application in the Untrusted group.
For such applications, all operations are blocked.
Appendix 3. File extensions for quick removable drives scan
com – executable file of an application no larger than 64 KB
exe – executable file or self-extracting archive
sys – Microsoft Windows system file
prg – program text for dBase, Clipper or Microsoft Visual FoxPro, or a WAVmaker program
bin – binary file
bat – batch file
cmd – command file for Microsoft Windows NT (similar to a bat file for DOS), OS/2
dpl – compressed Borland Delphi library
dll – dynamic link library
scr – Microsoft Windows splash screen
cpl – Microsoft Windows control panel module
ocx – Microsoft OLE (Object Linking and Embedding) object
tsp – program running in split-time mode
drv – device driver
vxd – Microsoft Windows virtual device driver
pif – program information file
lnk – Microsoft Windows link file
reg – Microsoft Windows system registry key file
ini – configuration file which contains configuration data for Microsoft Windows, Windows NT, and some applications
cla – Java class
vbs – Visual Basic script
vbe – BIOS video extension
js, jse – JavaScript source text
htm – hypertext document
htt – Microsoft Windows hypertext header
hta – hypertext program for Microsoft Internet Explorer
asp – Active Server Pages script
chm – compiled HTML file
pht – HTML file with integrated PHP scripts
php – script that is integrated into HTML files
wsh – Microsoft Windows Script Host file
wsf – Microsoft Windows script
the – Microsoft Windows 95 desktop wallpaper file
hlp – Win Help file
msg – Microsoft Mail email message
plg – email message
mbx – saved Microsoft Office Outlook email message
doc* – Microsoft Office Word documents, such as: doc for Microsoft Office Word documents, docx for Microsoft Office Word 2007 documents with XML support, and docm for Microsoft Office Word 2007 documents with macro support
dot* – Microsoft Office Word document templates, such as: dot for Microsoft Office Word document templates, dotx for Microsoft Office Word 2007 document templates, dotm for Microsoft Office Word 2007 document templates with macro support
fpm – database program, Microsoft Visual FoxPro start file
rtf – Rich Text Format document
shs – Windows Shell Scrap Object Handler fragment
dwg – AutoCAD drawing database
msi – Microsoft Windows Installer package
otm – VBA project for Microsoft Office Outlook
pdf – Adobe Acrobat document
swf – Shockwave Flash package object
jpg, jpeg – compressed image graphics format
emf – Enhanced Metafile format file;
ico – object icon file
ov? – Microsoft Office Word executable files
xl* – Microsoft Office Excel documents and files, such as: xla, the extension for Microsoft Office Excel, xlc for diagrams, xlt for document templates, xlsx for Microsoft Office Excel 2007 workbooks, xltm for Microsoft Office Excel 2007 workbooks with macro support, xlsb for Microsoft Office Excel 2007 workbooks in binary (non-XML) format, xltx for Microsoft Office Excel 2007 templates, xlsm for Microsoft Office Excel 2007 templates with macro support, and xlam for Microsoft Office Excel 2007 plug-ins with macro support
pp* – Microsoft Office PowerPoint documents and files, such as: pps for Microsoft Office PowerPoint slides, ppt for presentations, pptx for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 presentations, pptm for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 presentations with macros support, potx for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 presentation templates, potm for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 presentation templates with macro support, ppsx for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 slide shows, ppsm for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 slide shows with macro support, and ppam for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 plug-ins with macro support
md* – Microsoft Office Access documents and files, such as: mda for Microsoft Office Access workgroups and mdb for databases
sldx – a Microsoft PowerPoint 2007 slide
sldm – a Microsoft PowerPoint 2007 slide with macro support
thmx – a Microsoft Office 2007 theme
Page top
Appendix 4. File Types for the Mail Threat Protection attachment filter
Note that the actual format of a file may not match its file name extension.
If you enabled filtering of email attachments, the Mail Threat Protection component may rename or delete files with the following extensions:
com – executable file of an application no larger than 64 KB
exe – executable file or self-extracting archive
sys – Microsoft Windows system file
prg – program text for dBase, Clipper or Microsoft Visual FoxPro, or a WAVmaker program
bin – binary file
bat – batch file
cmd – command file for Microsoft Windows NT (similar to a bat file for DOS), OS/2
dpl – compressed Borland Delphi library
dll – dynamic link library
scr – Microsoft Windows splash screen
cpl – Microsoft Windows control panel module
ocx – Microsoft OLE (Object Linking and Embedding) object
tsp – program running in split-time mode
drv – device driver
vxd – Microsoft Windows virtual device driver
pif – program information file
lnk – Microsoft Windows link file
reg – Microsoft Windows system registry key file
ini – configuration file which contains configuration data for Microsoft Windows, Windows NT, and some applications
cla – Java class
vbs – Visual Basic script
vbe – BIOS video extension
js, jse – JavaScript source text
htm – hypertext document
htt – Microsoft Windows hypertext header
hta – hypertext program for Microsoft Internet Explorer
asp – Active Server Pages script
chm – compiled HTML file
pht – HTML file with integrated PHP scripts
php – script that is integrated into HTML files
wsh – Microsoft Windows Script Host file
wsf – Microsoft Windows script
the – Microsoft Windows 95 desktop wallpaper file
hlp – Win Help file
msg – Microsoft Mail email message
plg – email message
mbx – saved Microsoft Office Outlook email message
doc* – Microsoft Office Word documents, such as: doc for Microsoft Office Word documents, docx for Microsoft Office Word 2007 documents with XML support, and docm for Microsoft Office Word 2007 documents with macro support
dot* – Microsoft Office Word document templates, such as: dot for Microsoft Office Word document templates, dotx for Microsoft Office Word 2007 document templates, dotm for Microsoft Office Word 2007 document templates with macro support
fpm – database program, Microsoft Visual FoxPro start file
rtf – Rich Text Format document
shs – Windows Shell Scrap Object Handler fragment
dwg – AutoCAD drawing database
msi – Microsoft Windows Installer package
otm – VBA project for Microsoft Office Outlook
pdf – Adobe Acrobat document
swf – Shockwave Flash package object
jpg, jpeg – compressed image graphics format
emf – Enhanced Metafile format file;
ico – object icon file
ov? – Microsoft Office Word executable files
xl* – Microsoft Office Excel documents and files, such as: xla, the extension for Microsoft Office Excel, xlc for diagrams, xlt for document templates, xlsx for Microsoft Office Excel 2007 workbooks, xltm for Microsoft Office Excel 2007 workbooks with macro support, xlsb for Microsoft Office Excel 2007 workbooks in binary (non-XML) format, xltx for Microsoft Office Excel 2007 templates, xlsm for Microsoft Office Excel 2007 templates with macro support, and xlam for Microsoft Office Excel 2007 plug-ins with macro support
pp* – Microsoft Office PowerPoint documents and files, such as: pps for Microsoft Office PowerPoint slides, ppt for presentations, pptx for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 presentations, pptm for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 presentations with macros support, potx for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 presentation templates, potm for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 presentation templates with macro support, ppsx for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 slide shows, ppsm for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 slide shows with macro support, and ppam for Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 plug-ins with macro support
md* – Microsoft Office Access documents and files, such as: mda for Microsoft Office Access workgroups and mdb for databases
sldx – a Microsoft PowerPoint 2007 slide
sldm – a Microsoft PowerPoint 2007 slide with macro support
thmx – a Microsoft Office 2007 theme
Page top
Appendix 5. Network settings for interaction with external services
Kaspersky Endpoint Security uses the following network settings for interacting with external services.
Network settings
Address |
Description |
|---|---|
Protocol: Port: |
Activating the application. |
Protocol: Port: |
Updating databases and application software modules. |
Protocol: Port: |
Requests emitted by the application may contain addresses of domains and the public IP address of the user because the application establishes a TCP/UDP connection with the DNS server. This information is needed, for example, to validate the certificate of a web resource when using HTTPS. If Kaspersky Endpoint Security is using a public DNS server, data processing is governed by the privacy policy of the relevant service. If you want to prevent Kaspersky Endpoint Security from using a public DNS server, contact Technical Support for a private patch. |
Protocol: |
|
Protocol: Port: |
Updating databases and application software modules. |
Protocol: Port: |
Using Kaspersky Security Network. |
Protocol: Port: |
Using Kaspersky Security Network. |
Protocol: |
Follow links from the interface. |
Settings, used for encryption
Address |
Description |
|---|---|
Protocol: Port: |
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). |
Appendix 6. Application events
Information about the operation of each Kaspersky Endpoint Security component, data encryption events, the completion of each malware scan task, update task and integrity check task, and the overall operation of the application is recorded in the Kaspersky Security Center event log and Windows event log.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security generates events of the following types: general events and specific events. Specific events are created only by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. Specific events have a simple ID, such as 000000cb. Specific events contain the following required parameters:
GNRL_EA_DESCRIPTIONis the content of the event.GNRL_EA_IDis the service ID of the event.GNRL_EA_SEVERITYis the status of the event.1– Informational message ,
, 2– Warning ,
, 3– Functional failure ,
, 4– Critical .
.EVENT_TYPE_DISPLAY_NAMEis the title of the event.TASK_DISPLAY_NAMEis the name of the application component that initiated the event.
General events can be created by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows as well as other Kaspersky applications (for example, Kaspersky Security for Windows Server). General events have a more complex ID, such as GNRL_EV_VIRUS_FOUND. In addition to required settings, general events contain advanced settings.
Critical
End User License Agreement violated
Databases are missing or corrupted
Databases are extremely out of date
Application autorun is disabled
Active threat detected. Advanced Disinfection should be started
Not enough space in Quarantine storage
Object not restored from Quarantine
Object not deleted from Quarantine
The application established a connection to a website with an untrusted certificate
Failed to verify an encrypted connection. The domain is added to the list of exclusions
Malicious object detected (local bases)
Malicious object detected (KSN)
Previously opened dangerous link detected
Application startup prohibited
Prohibited process was started before Kaspersky Endpoint Security startup
Operation with the device prohibited
Error distributing component updates
Cannot start two tasks at the same time
Error verifying application databases and modules
Error in interaction with Kaspersky Security Center
Not all components were updated
Update completed successfully, update distribution failed
Error applying file encryption / decryption rules
File encryption / decryption error
Error creating encrypted package
Error encrypting / decrypting device
Could not load encryption module
The task for managing Authentication Agent accounts ended with an error
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server unavailable
Object not quarantined (Kaspersky Sandbox)
Invalid Kaspersky Sandbox server certificate
The Kaspersky Sandbox node is unavailable
An error occurred while processing the object in Kaspersky Sandbox
Maximum load to Kaspersky Sandbox is exceeded
Kaspersky Sandbox license verification failed
Object not quarantined (Endpoint Detection and Response)
Process startup is not blocked
Script execution is not blocked
Error changing application components
There are patterns of a possible brute-force attack in the system
There are patterns of a possible Windows Event Log abuse
Atypical actions detected on behalf of a new service installed
Atypical logon that uses explicit credentials detected
There are patterns of a possible Kerberos forged PAC (MS14-068) attack in the system
Suspicious changes detected in the privileged built-in Administrators group
There is an atypical activity detected during a network logon session
Atypical event occurs too often. Event aggregation started
Report on an atypical event for the aggregation period
Error connecting to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server
Invalid Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server certificate
Invalid certificate of the agent on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server
Page top
Warning
Application crashed during previous session
Automatic updates are disabled
Protection components are disabled
Computer is running in safe mode
Quit and reopen the application to complete updating
The license allows the use of components that have not been installed
Advanced Disinfection completed
Cannot restore object from Backup
Suspicious network activity detected
Encrypted connection terminated
Processing of some OS functions is disabled
Quarantine storage is almost out of space
Object will be disinfected on restart
Object will be deleted on restart
Object deleted according to settings
The object scan result has been sent to a third-party application
Task settings applied successfully
Warning about undesirable content (local bases)
Warning about undesirable content (KSN)
Undesirable content was accessed after a warning
Temporary access to the device activated
Operation cancelled by the user
User has opted out of the encryption policy
Interrupted applying file encryption / decryption rules
File encryption / decryption interrupted
Device encryption / decryption interrupted
Failed to install or upgrade Kaspersky Disk Encryption drivers in the WinRE image
Application startup was blocked
Process was terminated by the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server administrator
The application was terminated by the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server administrator
File or stream was deleted by the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server administrator
File was quarantined on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server by administrator
Network activity of all third-party applications is blocked
Network activity of all third-party applications is unblocked
Object will be deleted after restart (Kaspersky Sandbox)
Total size of scan tasks exceeded the limit
Object startup allowed, event logged
Process startup allowed, event logged
Object will be deleted after restart (Endpoint Detection and Response)
Termination of network isolation
Restart required to complete the task
Application startup blockage message to administrator
Device access blockage message to administrator
Web page access blockage message to administrator
Application activity blockage message to administrator
Object changes too often. Event aggregation started
Report on object modification for the aggregation period
Monitoring scope includes incorrect objects
Page top
Informational message
Self-Defense restricted access to the protected resource
Subscription settings have changed
The application works and processes data under relevant laws and uses the appropriate infrastructure
Object restored from Quarantine
Object deleted from Quarantine
A backup copy of the object was created
Overwritten by a copy that was disinfected earlier
Password-protected archive detected
Information about detected object
The object is in the Kaspersky Private Security Network allowlist
The link is in the Kaspersky Private Security Network allowlist
Application placed in the trusted group
Application placed in restricted group
Host Intrusion Prevention was triggered
Application startup prohibited in test mode
Application startup allowed in test mode
A page that is allowed was opened
Operation with the device allowed
Update distribution completed successfully
File rolled back due to update error
Creating the list of files to download
Started applying file encryption / decryption rules
Finished applying file encryption / decryption rules
Resumed applying file encryption / decryption rules
File encryption / decryption started
File encryption / decryption completed
File has not been encrypted because it is an exclusion
Device encryption / decryption started
Device encryption / decryption completed
Device encryption / decryption resumed
Device encryption / decryption process has been switched to active mode
Device encryption / decryption process has been switched to passive mode
New Authentication Agent account created
Authentication Agent account deleted
Authentication Agent account password changed
Successful Authentication Agent login
Failed Authentication Agent login attempt
Hard drive accessed using the procedure of requesting access to encrypted devices
Account was not added. This account already exists
Account was not modified. This account does not exist
Account was not deleted. This account does not exist
FDE upgrade rollback successful
Failed to uninstall Kaspersky Disk Encryption drivers from the WinRE image
BitLocker recovery key was changed
BitLocker password / PIN was changed
BitLocker recovery key was saved to a removable drive
Processing of tasks from the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server is inactive
Endpoint Sensor connected to server
Connection to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server restored
Tasks from the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server are being processed
Object quarantined (Kaspersky Sandbox)
Object deleted (Kaspersky Sandbox)
Object quarantined (Endpoint Detection and Response)
Object deleted (Endpoint Detection and Response)
Application components successfully changed
Asynchronous Kaspersky Sandbox detection
Error removing the previous version of the application
Successful connection to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server
Page top
Appendix 7. Supported file extensions for Execution prevention
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports preventing the opening of office format files in certain applications. The information about supported file extensions and applications is listed in the following table.
Supported file extensions for Execution prevention
Application name |
Executable file |
File extension |
|---|---|---|
Microsoft Word |
winword.exe |
rtf doc dot docm docx dotx dotm docb |
WordPad |
wordpad.exe |
docx rtf |
Microsoft Excel |
excel.exe |
xls xlt xlm xlsx xlsm xltx xltm xlsb xla xlam xll xlw |
Microsoft PowerPoint |
powerpnt.exe |
ppt pot pps pptx pptm potx potm ppam ppsx ppsm sldx sldm |
Adobe Acrobat Foxit PDF Reader STDU Viewer Microsoft Edge Google Chrome Mozilla Firefox Yandex Browser Tor Browser |
acrord32.exe FoxitReader.exe STDUViewerApp.exe MicrosoftEdge.exe chrome.exe firefox.exe browser.exe tor.exe |
Appendix 8. Supported script interpreters for Execution prevention
Execution prevention supports the following script interpreters:
- AutoHotkey.exe
- AutoHotkeyA32.exe
- AutoHotkeyA64.exe
- AutoHotkeyU32.exe
- AutoHotkeyU64.exe
- InstallUtil.exe
- RegAsm.exe
- RegSvcs.exe
- autoit.exe
- cmd.exe
- control.exe
- cscript.exe
- hh.exe
- mmc.exe
- msbuild.exe
- mshta.exe
- msiexec.exe
- perl.exe
- powershell.exe
- python.exe
- reg.exe
- regedit.exe
- regedt32.exe
- regsvr32.exe
- ruby.exe
- rubyw.exe
- rundll32.exe
- runlegacycplelevated.exe
- wscript.exe
- wwahost.exe
Execution prevention supports working with Java applications in the Java runtime environment (java.exe and javaw.exe processes).
Page top
Appendix 9. IOC scan scope in the registry (RegistryItem)
When you add the RegistryItem data type to the IOC scan scope, Kaspersky Endpoint Security scans the following registry keys:
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\htafile
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\batfile
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\comfile
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Print\Monitors
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\NetworkProvider
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Class
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes\piffile
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes\htafile
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes\exefile
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes\comfile
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes\CLSID
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ShellServiceObjectDelayLoad
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Active Setup\Installed Components
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Image File Execution Options
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Aedebug
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon
Appendix 10. IOC file requirements
When creating IOC Scan tasks, consider the following
requirements and limitations:- The application supports IOC files with the IOC and XML extensions in the open standard OpenIOC versions 1.0 and 1.1 for describing indicators of compromise.
- If, when creating an IOC Scan task on the command line, you upload IOC files, some of which are not supported, when the task is run, the application uses only the supported IOC files. If, when creating an IOC Scan task on the command line, all of the IOC files that you upload turn out to be unsupported, the task can still be run, but it will not detect any indicators of compromise. It is not possible to upload unsupported IOC files using Web Console or Cloud Console.
- Semantic errors and unsupported IOC terms and tags in IOC files do not cause task execution to fail. In such sections of IOC files, the application detects no match.
- used in a single IOC Scan task must be unique. If there are IOC files with the same identifier, it might affect the task execution results.
- A single IOC file must not exceed 2 MB in size. Using larger files will cause IOC Scan tasks to terminate with an error. The total size of all files added to the IOC collection should not exceed 10 MB. If the total size of all files exceeds 10 MB, you need to split the IOC collection and create several IOC Scan tasks.
- It is recommended to create one IOC file per threat. This makes it easier to analyze the results of the IOC Scan task.
The file that you can download by clicking the link below, contains a table with the full list of IOC terms of the OpenIOC standard.
![]() DOWNLOAD THE IOC_TERMS.XLSX FILE
DOWNLOAD THE IOC_TERMS.XLSX FILE
Features and limitations of the application’s support for the OpenIOC standard are shown in the following table.
Features and limitations of support for OpenIOC version 1.0 and 1.1.
Supported conditions |
OpenIOC 1.0:
OpenIOC 1.1:
|
Supported condition attributes |
OpenIOC 1.1:
|
Supported operators |
|
Supported data types |
|
Features of data type interpretation |
The The application supports interpretation of the OpenIOC 1.0: Using the
OpenIOC 1.1: Using the Using the The application supports interpretation of the |
Information about third-party code
Information about third-party code is contained in the file legal_notices.txt, in the application installation folder.
Page top
Trademark notices
Registered trademarks and service marks are the property of their respective owners.
Adobe, Acrobat, Flash, Reader and Shockwave are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Adobe in the United States and/or other countries.
Amazon, Amazon Web Services, AWS are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates.
Apple, FireWire, iTunes and Safari are trademarks of Apple Inc.
AutoCAD is a trademark or registered trademark of Autodesk, Inc., and/or its subsidiaries and/or affiliates in the USA and/or other countries.
The Bluetooth word, mark and logos are owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc.
Borland is trademark or registered trademark of Borland Software Corporation.
Android, Google Public DNS, Google Chrome, Chrome are trademarks of Google LLC.
Citrix and Citrix Provisioning Services, and XenDesktop are trademarks of Citrix Systems, Inc. and/or one or more of its subsidiaries, and may be registered in the United States Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries.
Cloudflare, Cloudflare Workers, and the Cloudflare logo are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of Cloudflare, Inc. in the United States and other jurisdictions.
Dell and other trademarks are trademarks of Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries.
dBase is a trademark of dataBased Intelligence, Inc.
Docker and the Docker logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Docker, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries. Docker, Inc. and other parties may also have trademark rights in other terms used herein.
EMC is a trademark or registered trademark of EMC Corporation in the United States and/or elsewhere.
Foxit is a registered trademark of Foxit Corporation.
Radmin is a registered trademark of Famatech.
IBM is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation, registered in many jurisdictions worldwide.
Intel is a trademark of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
Cisco, Cisco AnyConnect are registered trademarks or trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries.
Lenovo, Lenovo ThinkPad are trademarks of Lenovo in the United States and/or elsewhere.
Linux is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries.
Logitech is either a registered trademark or trademark of Logitech in the United States and/or other countries.
LogMeIn Pro and Remotely Anywhere are trademarks of LogMeIn, Inc.
Mail.ru is a registered trademark of Mail.Ru, LLC.
McAfee is the trademark or registered trademark of McAfee LLC or its subsidiaries in the US and /or other countries.
Microsoft, Microsoft Edge, Access, Active Directory, ActiveSync, Bing, BitLocker, Excel, Internet Explorer, LifeCam Cinema, MSDN, MultiPoint, Outlook, PowerPoint, PowerShell, Visual Basic, Visual FoxPro, Windows, Windows PowerShell, Windows Server, Windows Store, MS-DOS, Skype, Surface, Hyper-V, SQL Server are trademarks of the Microsoft group of companies.
Mozilla, Firefox and Thunderbird are trademarks of the Mozilla Foundation in the U.S. and other countries.
NetApp is the trademark or the registered trademark of NetApp, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries.
Python is a trademark or registered trademark of the Python Software Foundation.
Java and JavaScript are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
VERISIGN is a registered trademark in the United States and elsewhere or an unregistered trademark of VeriSign, Inc. and its subsidiaries.
VMware, VMware ESXi and VMware Workstation are registered trademarks or trademarks of VMware, Inc. in the United States and/or other jurisdictions.
Tor is a registered trademark of The Tor Project, U.S. Registration No. 3,465,432.
Thawte is a trademark or registered trademark of Symantec Corporation or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries.
SAMSUNG is a trademark of SAMSUNG in the United States and other countries.
Page top
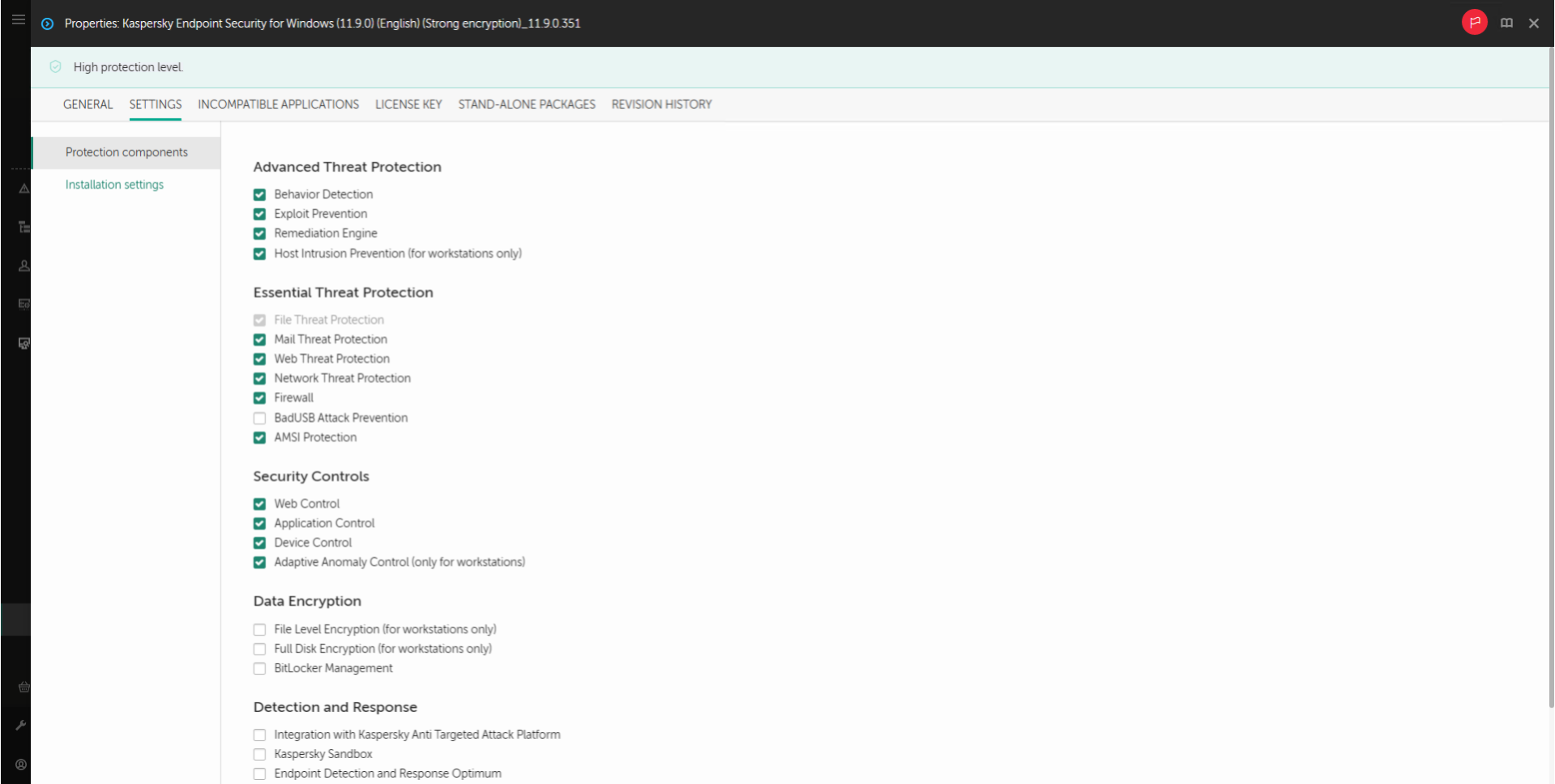
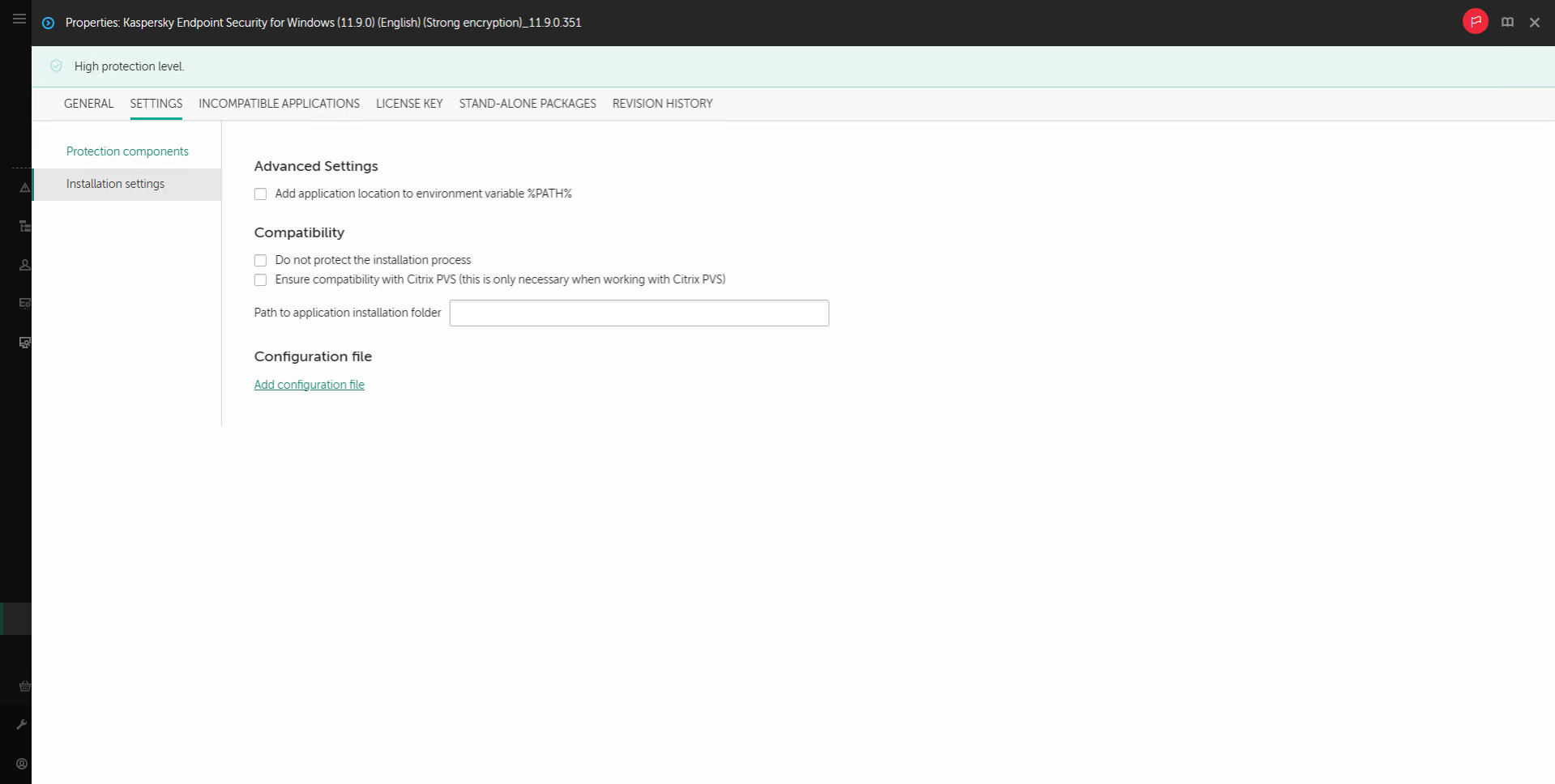

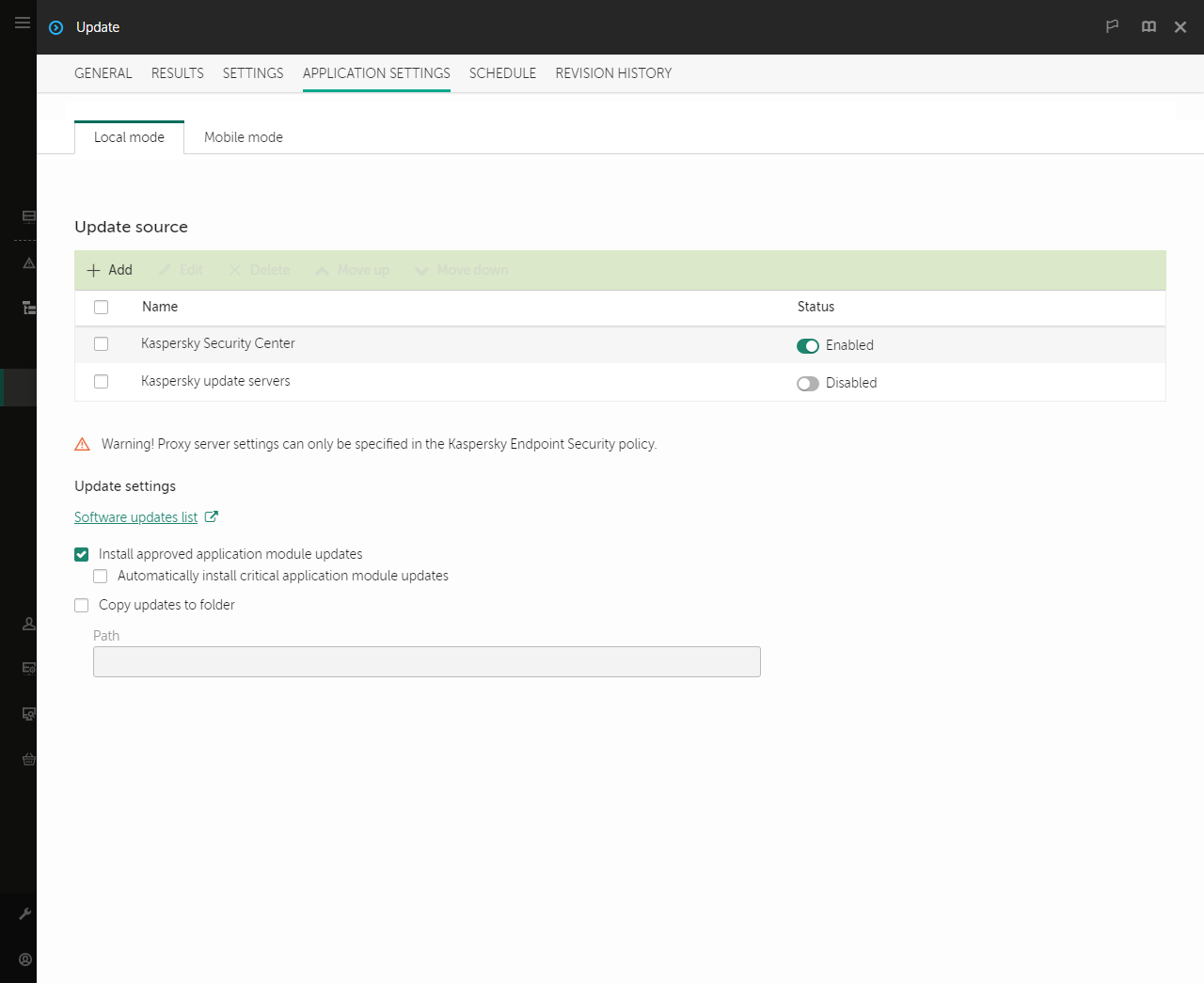
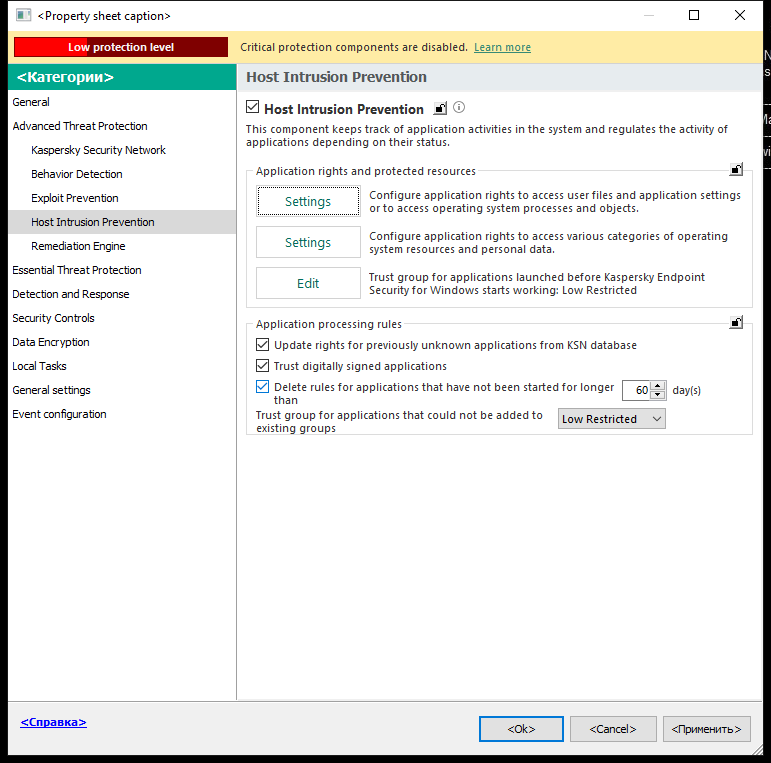
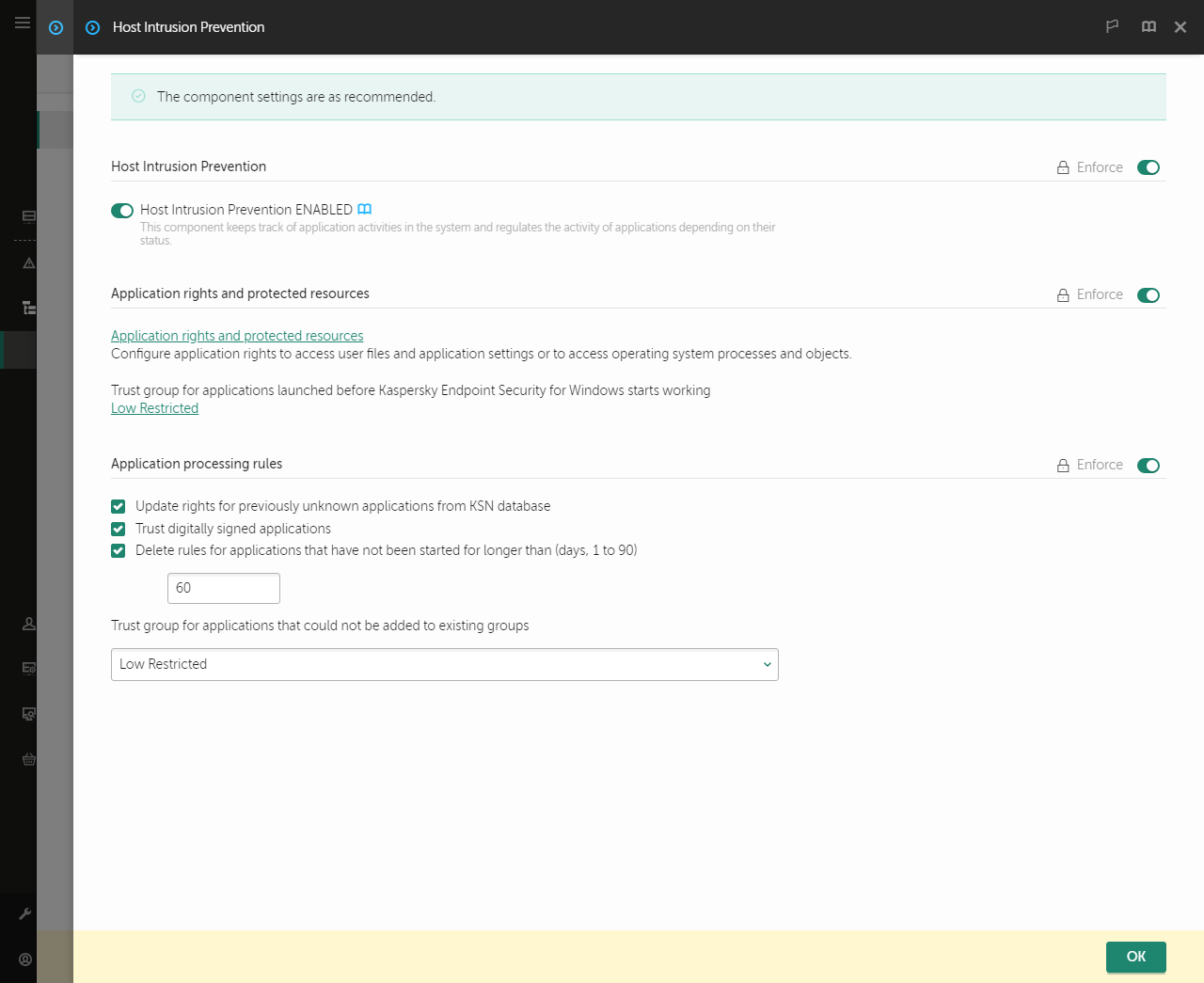
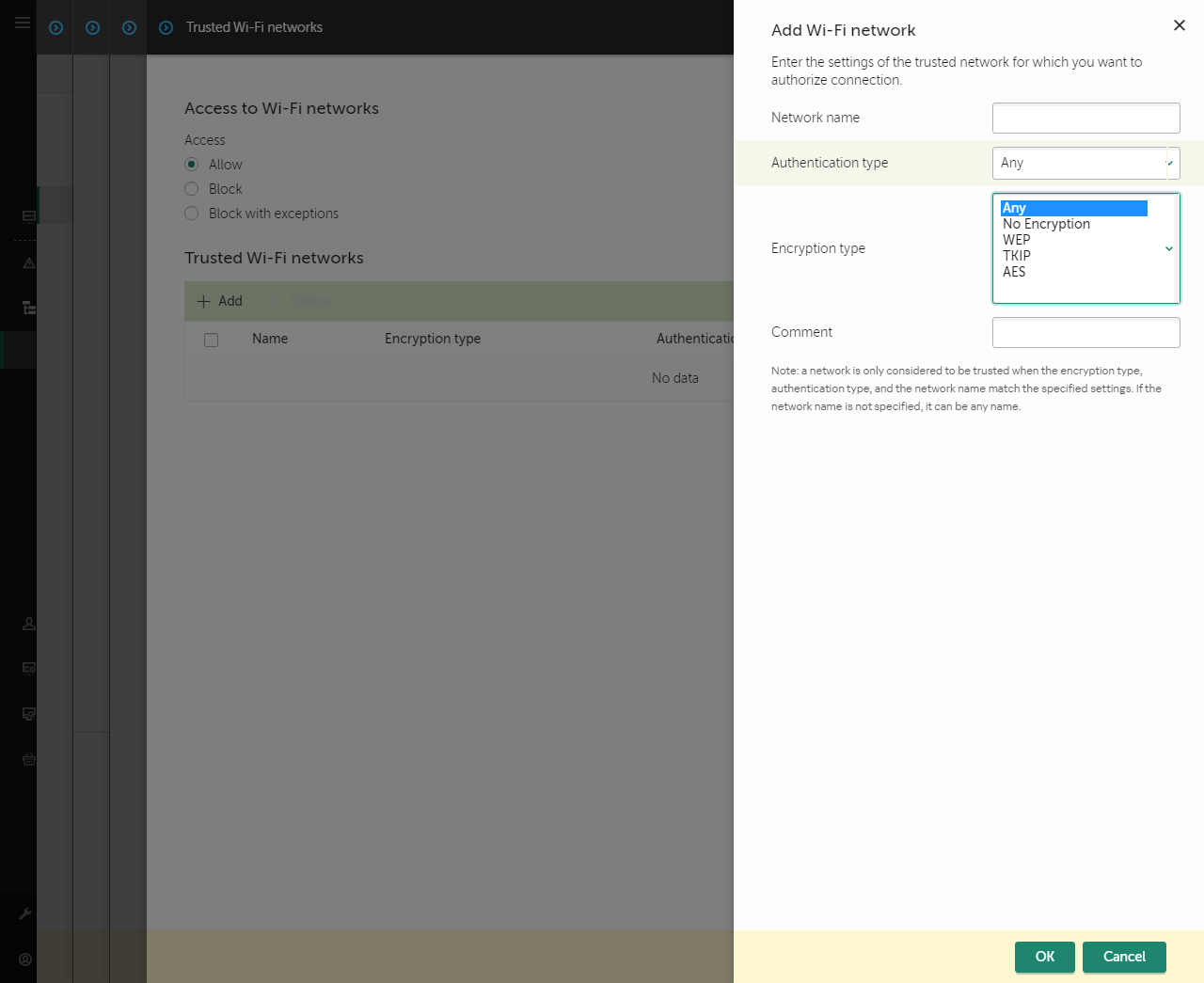
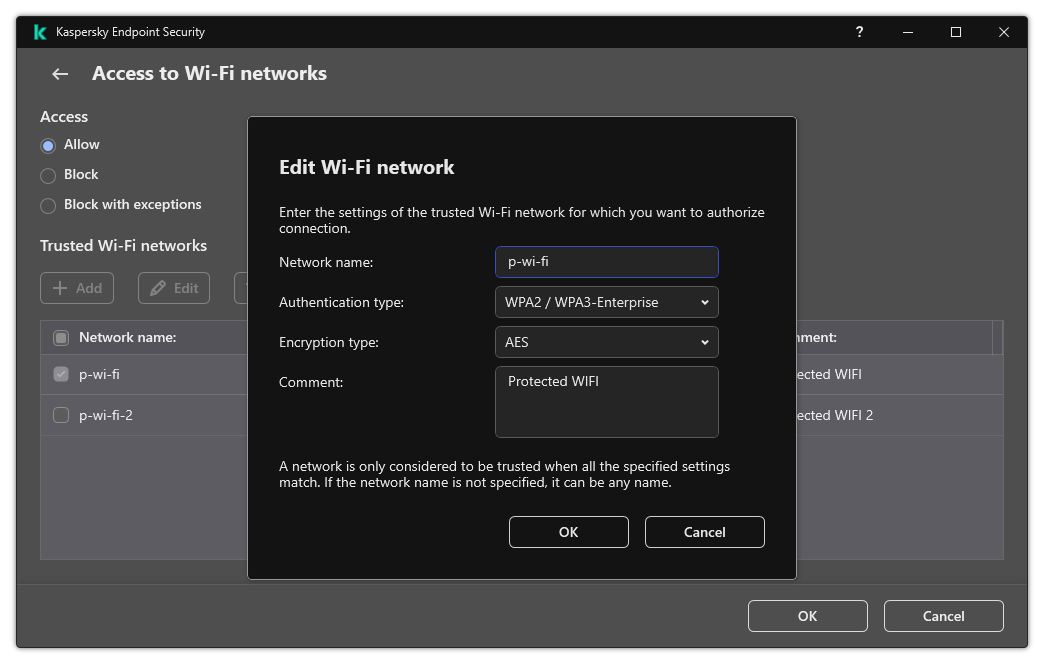
 ) above the list of computers and then click the
) above the list of computers and then click the