Using traffic processing rules
You can manage user access to web resources by using traffic processing rules. These rules are divided into bypass rules, access rules, and protection rules. You can create groups of access rules and groups of protection rules or add rules outside of groups.
Kaspersky Web Traffic Security begins processing traffic by checking bypass rules. If access to the web resource is allowed, the application proceeds to scan the traffic by applying access rules. Based on the results of access rule processing, the application either blocks the web resource or proceeds to scan the traffic by applying protection rules. The algorithm for traffic processing rules is displayed in the figure below.
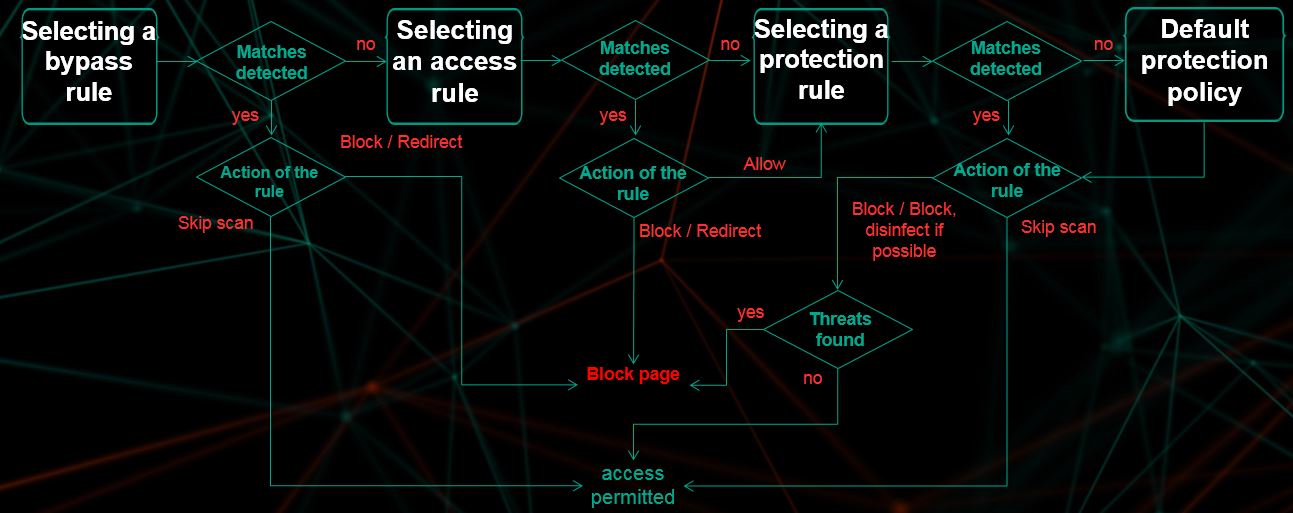
Algorithm for traffic processing rules
Kaspersky Web Traffic Security applies rules in the order of their position in the rules table, from top to bottom. If the conditions configured for the rule are not satisfied, the application proceeds to the next rule. As soon as conditions specified in a rule are satisfied, processing parameters specified in that rule are applied to the traffic, and further condition matching is stopped.
If a workspace is available, the priority of workspace rules is determined by the position of the Workspace rules row in the general rules table. In this case, rules are also applied in the order of their position in the table, from top to bottom. Workspace rules will be applied after traffic is scanned according to the rules that are positioned higher in the table. If none of the workspace rules are triggered, the application proceeds to scan traffic in accordance with the rules after Workspace rules in the table.
A default bypass rule is created when the application is installed. According to this rule, access to web resources whose value of the Content-Length HTTP header exceeds 10240 KB is allowed for all users without scans by the Anti-Virus and Anti-Phishing modules. This setting ensures a balance between application performance and network traffic security. You can edit, disable, or delete the default bypass rule.
If no rule contains conditions suitable for a specific web resource, traffic is processed according to the default protection policy. In this case, the application allows access to the web resource if it has not been blocked as a result of scans by the Anti-Virus and Anti-Phishing modules. A default protection policy is created during installation of Kaspersky Web Traffic Security and is displayed in the Settings section, Protection settings subsection. In the default protection policy settings, you can specify the actions that the application must apply to various types of objects.