Monitoring user Internet activity
Kaspersky Endpoint Security lets you log data on user visits to all websites, including allowed websites. This enables you to obtain the complete history of browser views. Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends user activity events to Kaspersky Security Center, to the local log of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, and to the Windows Event log. To receive events in Kaspersky Security Center, you need to configure the settings of events in a policy in the Administration Console or Web Console. You can also configure the transmission of Web Control events by email and the display of on-screen notifications on the user's computer.
Browsers that support the monitoring function: Microsoft Edge, Microsoft Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Yandex Browser, Mozilla Firefox. User activity monitoring does not work in other browsers.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security creates the following user Internet activity events:
- Block the website (Critical status
 ).
). - Visit to a non-recommended website (Warning status
 ).
). - Visit to an allowed website (Info status
 ).
).
Prior to enabling user Internet activity monitoring, you must do the following:
- Inject a web page interaction script into web traffic (see the instructions below). The script enables registration of Web Control events.
- For HTTPS traffic monitoring, you need to enable encrypted connections scan.
Injecting a web page interaction script
How to inject a web page interaction script into web traffic in the Administration Console (MMC)
How to inject a web page interaction script into web traffic in the Web Console and Cloud Console
How to inject a web page interaction script into web traffic in the application interface
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will inject a web page interaction script into web traffic. This script enables registration of Web Control events for the application event log, OS event log, and reports.
Configuring logging of Web Control events
To configure logging of Web Control events on the user's computer:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select General settings → Interface.
- In the Notifications block, click the Configure notifications button.
- In the window that opens, select the Web Control section.
This opens the table of Web Control events and notification methods.
- Configure the notification method for each event: Save in local report or Save in Windows Event Log.
To log allowed website visit events, you need to also configure Web Control (see the instructions below).
In the events table, you can also enable an on-screen notification and an email notification. To send notifications by email, you need to configure the SMTP server settings. For more details about sending notifications by email, please refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Help.
- Save your changes.
As a result, Kaspersky Endpoint Security begins logging user Internet activity events.
Web Control sends user activity events to Kaspersky Security Center as follows:
- If you are using Kaspersky Security Center, Web Control sends events for all the objects that make up the web page. For this reason, multiple events may be created when one web page is blocked. For example, when blocking the web page http://www.example.com, Kaspersky Endpoint Security may relay events for the following objects: http://www.example.com, http://www.example.com/icon.ico, http://www.example.com/file.js, etc.
- If you are using the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, Web Control groups events and sends only the protocol and domain of the website. For instance, if a user visits non-recommended web pages http://www.example.com/main, http://www.example.com/contact, http://www.example.com/gallery, Kaspersky Endpoint Security will send only one event with the http://www.example.com object.
Logging events when visiting allowed websites
To enable logging of events when visiting allowed websites:
- In the main application window, click the
 button.
button. - In the application settings window, select Security Controls → Web Control.
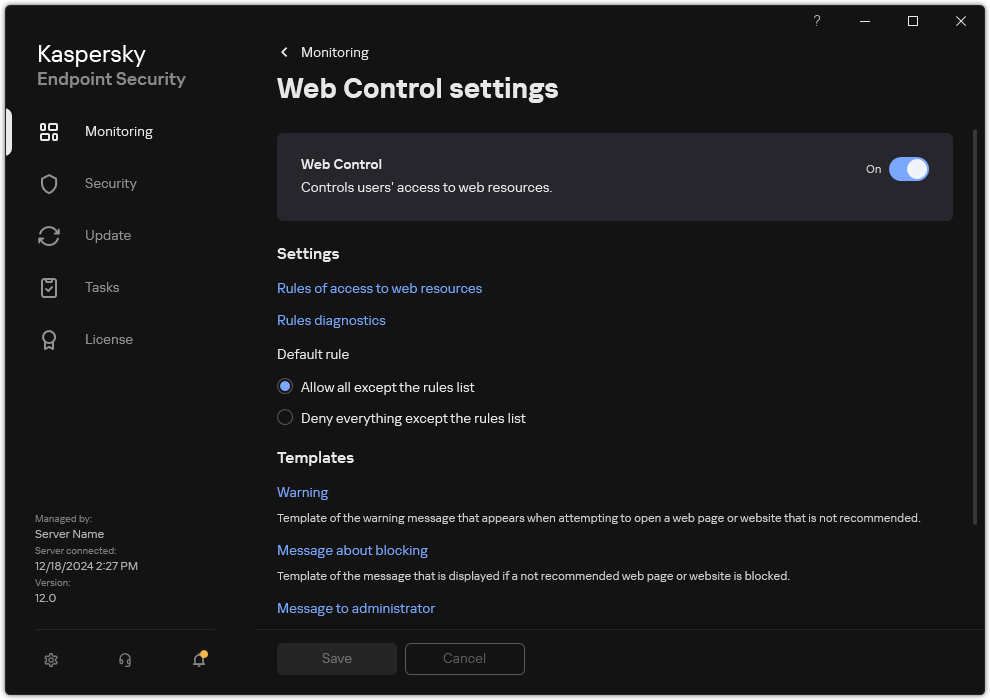
Web Control settings
- In the Additional block, click the Advanced Settings button.
- In the window that opens, select the Log the opening of allowed pages check box.
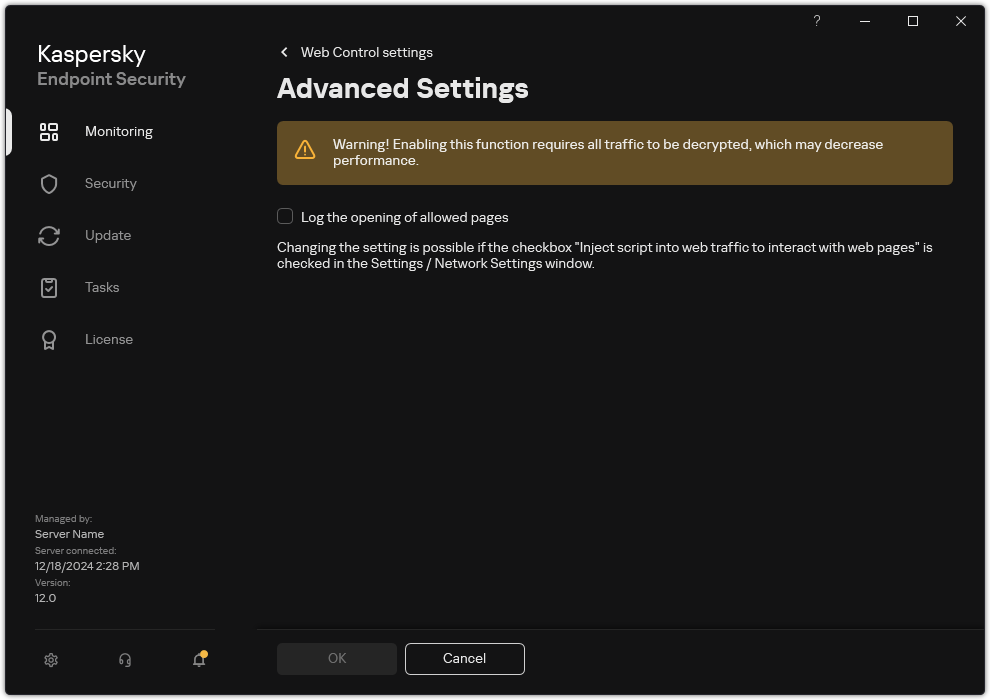
Web Control advanced settings
- Save your changes.
As a result, you will be able to view the full browser history.
Page top