Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows 11.2.0
- Čeština (Česká republika)
- Deutsch
- Español (España)
- Español (México)
- Français
- Italiano
- Magyar (Magyarország)
- Polski (Polska)
- Português (Brasil)
- Português (Portugal)
- Română (România)
- Tiếng Việt (Việt Nam)
- Türkçe (Türkiye)
- Русский
- العربية (الإمارات العربية المتحدة)
- 한국어 (대한민국)
- 简体中文
- 繁體中文
- 日本語(日本)
- Čeština (Česká republika)
- Deutsch
- Español (España)
- Español (México)
- Français
- Italiano
- Magyar (Magyarország)
- Polski (Polska)
- Português (Brasil)
- Português (Portugal)
- Română (România)
- Tiếng Việt (Việt Nam)
- Türkçe (Türkiye)
- Русский
- العربية (الإمارات العربية المتحدة)
- 한국어 (대한민국)
- 简体中文
- 繁體中文
- 日本語(日本)
- Frequently asked questions
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- What's new
- Application licensing
- Managing the application via the local interface
- Installing and removing the application
- Activating the application
- Application interface
- Starting and stopping the application
- Kaspersky Security Network
- Behavior Detection
- Exploit Prevention
- Host Intrusion Prevention
- Limitations of audio and video device control
- Enabling and disabling Host Intrusion Prevention
- Managing application trust groups
- Managing application rights
- Changing application rights for trust groups and groups of applications
- Modifying application rights
- Disabling downloads and updates of application rights from the Kaspersky Security Network database
- Disabling the inheritance of restrictions from the parent process
- Excluding specific application actions from application rights
- Deleting obsolete application rights
- Protecting operating system resources and identity data
- Remediation Engine
- File Threat Protection
- Enabling and disabling File Threat Protection
- Automatic pausing of File Threat Protection
- File Threat Protection settings
- Changing the security level
- Changing the action taken on infected files by the File Threat Protection component
- Forming the protection scope of the File Threat Protection component
- Using heuristic analysis in the operation of the File Threat Protection component
- Using scan technologies in the operation of the File Threat Protection component
- Optimizing file scanning
- Scanning compound files
- Changing the scan mode
- Web Threat Protection
- Enabling and disabling Web Threat Protection
- Web Threat Protection settings
- Changing the web traffic security level
- Changing the action to take on malicious web traffic objects
- Web Threat Protection scanning of links to check them against databases of phishing and malicious web addresses
- Using heuristic analysis in the operation of the Web Threat Protection component
- Editing the list of trusted web addresses
- Mail Threat Protection
- Network Threat Protection
- Firewall
- BadUSB Attack Prevention
- AMSI Protection Provider
- Application Control
- Device Control
- Enabling and disabling Device Control
- About access rules
- Editing a device access rule
- Adding or excluding records to or from the event log
- Adding a Wi-Fi network to the trusted list
- Editing a connection bus access rule
- Actions with trusted devices
- Adding a device to the Trusted list from the application interface
- Adding devices to the Trusted list based on the device model or ID
- Adding devices to the Trusted list based on the mask of the device ID
- Configuring user access to a trusted device
- Removing a device from the list of trusted devices
- Importing the list of trusted devices
- Exporting the list of trusted devices
- Obtaining access to a blocked device
- Editing templates of Device Control messages
- Anti-Bridging
- Web Control
- Enabling and disabling Web Control
- Web resource content categories
- Actions with web resource access rules
- Migrating web resource access rules from previous versions of the application
- Exporting and importing the list of web resource addresses
- Monitoring user Internet activity
- Editing masks for web resource addresses
- Editing templates of Web Control messages
- Adaptive Anomaly Control
- Enabling and disabling Adaptive Anomaly Control
- Actions with Adaptive Anomaly Control rules
- Enabling and disabling an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule
- Modifying the action taken when an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule is triggered
- Creating and editing an exclusion for an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule
- Deleting an Adaptive Anomaly Control rule exclusion
- Importing exclusions for Adaptive Anomaly Control rules
- Exporting exclusions for Adaptive Anomaly Control rules
- Applying updates for Adaptive Anomaly Control rules
- Editing Adaptive Anomaly Control message templates
- Viewing Adaptive Anomaly Control reports
- Network Protection
- Updating databases and application software modules
- Scanning the computer
- Starting or stopping a scan task
- Configuring scan task settings
- Changing the security level
- Changing the action to take on infected files
- Generating a list of objects to scan
- Selecting the type of files to scan
- Optimizing file scanning
- Scanning compound files
- Using scan methods
- Using scan technologies
- Selecting the run mode for the scan task
- Starting a scan task under the account of a different user
- Scanning removable drives when they are connected to the computer
- Background scan
- Working with active threats
- Checking the integrity of application modules
- Password protection
- Managing reports
- Notification service
- Managing Backup
- Advanced application settings
- Managing the application via the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console
- Special considerations when working with different versions of management plug-ins
- Starting and stopping Kaspersky Endpoint Security on a client computer
- Configuring Kaspersky Endpoint Security settings
- Managing Tasks
- Managing policies
- Data Encryption
- Encryption functionality limitations
- Changing the length of the encryption key (AES56 / AES256)
- Enabling Single Sign-On (SSO) technology
- Special considerations for file encryption
- Full Disk Encryption
- File Level Encryption on local computer drives
- Encrypting files on local computer drives
- Forming encrypted file access rules for applications
- Encrypting files that are created or modified by specific applications
- Generating a decryption rule
- Decrypting files on local computer drives
- Creating encrypted packages
- Extracting encrypted packages
- Restoring access to encrypted data after operating system failure
- Encryption of removable drives
- Using the Authentication Agent
- Using a token and smart card with Authentication Agent
- Editing Authentication Agent help messages
- Limited support for characters in Authentication Agent help messages
- Selecting the Authentication Agent trace level
- Managing Authentication Agent accounts
- Adding a command for creating an Authentication Agent account
- Adding an Authentication Agent account editing command
- Adding a command for deleting an Authentication Agent account
- Restoring Authentication Agent account credentials
- Responding to a user request to restore Authentication Agent account credentials
- Removing objects and data that remained after test operation of Authentication Agent
- Viewing data encryption details
- Managing encrypted files with limited file encryption functionality
- Working with encrypted devices when there is no access to them
- Obtaining access to encrypted devices through the application interface
- Granting user access to encrypted devices
- Providing a user with a recovery key for hard drives encrypted with BitLocker
- Creating the executable file of Restore Utility
- Restoring data on encrypted devices using the Restore Utility
- Responding to a user request to restore data on encrypted devices
- Creating an operating system rescue disk
- Application Control
- Managing Application Control rules
- Receiving information about the applications that are installed on users’ computers
- Creating application categories
- Step 1. Selecting the category type
- Step 2. Entering a user category name
- Step 3. Configuring the conditions for including applications in a category
- Step 4. Configuring the conditions for excluding applications from a category
- Step 5. Settings
- Step 6. Repository folder
- Step 7. Creating a custom category
- Adding executable files from the Executable files folder to the application category
- Adding event-related executable files to the application category
- Adding and modifying an Application Control rule using Kaspersky Security Center
- Changing the status of an Application Control rule via Kaspersky Security Center
- Testing Application Control rules using Kaspersky Security Center
- Viewing events resulting from test operation of the Application Control component
- Report on blocked applications in test mode
- Viewing events resulting from operation of the Application Control component
- Report on blocked applications
- Best practices for implementing white list mode
- Managing Application Control rules
- Integration with other Kaspersky solutions
- Sending user messages to the Kaspersky Security Center server
- Viewing user messages in the Kaspersky Security Center event storage
- Remote administration of the application through Kaspersky Security Center 11 Web Console and Cloud Console
- About Kaspersky Endpoint Security management web plug-in
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security deployment
- Getting started
- Activation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Uninstalling Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Starting and stopping Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Updating databases and application software modules
- Managing Tasks
- Managing policies
- Configuring local application settings
- Policy settings
- Kaspersky Security Network
- Behavior Detection
- Exploit Prevention
- Host Intrusion Prevention
- Remediation Engine
- File Threat Protection
- Web Threat Protection
- Mail Threat Protection
- Network Threat Protection
- Firewall
- BadUSB Attack Prevention
- AMSI Protection Provider
- Application Control
- Device Control
- Web Control
- Adaptive Anomaly Control
- Endpoint Sensor
- Managing Tasks
- Scan from context menu
- Removable drives scan
- Background scan
- Application settings
- Network options
- Exclusions
- Reports and Storage
- Interface
- Managing the application from the command line
- Commands
- SCAN. Virus Scan
- UPDATE. Updating databases and application software modules
- ROLLBACK. Rolling back the last update
- TRACES. Traces
- START. Starting a profile
- STOP. Stopping a profile
- STATUS. Profile status
- STATISTICS. Profile operation statistics
- RESTORE. Restoring files
- EXPORT. Exporting application settings
- IMPORT. Importing application settings
- ADDKEY. Applying a key file.
- LICENSE. Licensing
- RENEW. Purchasing a license
- PBATESTRESET. Reset the pre-encryption check results
- EXIT. Exit the application
- EXITPOLICY. Disabling policy
- STARTPOLICY. Enabling policy
- DISABLE. Disabling protection
- SPYWARE. Spyware detection
- KESCLI commands
- Scan. Virus Scan
- GetScanState. Scan completion status
- GetLastScanTime. Determining the scan completion time
- GetThreats. Obtaining data on detected threats
- UpdateDefinitions. Updating databases and application software modules
- GetDefinitionState. Determining the update completion time
- EnableRTP. Enabling protection
- GetRealTimeProtectionState. File Threat Protection status
- Version. Identifying the application version
- Error codes
- Appendix. Application profiles
- Commands
- Managing the application through the REST API
- Sources of information about the application
- Contacting Technical Support
- Glossary
- Active key
- Additional key
- Administration group
- Anti-virus databases
- Archive
- Authentication Agent
- Certificate issuer
- Database of malicious web addresses
- Database of phishing web addresses
- Disinfection
- False alarm
- Infected file
- License certificate
- Mask
- Network Agent
- Network Agent Connector
- Normalized form of the address of a web resource
- OLE object
- Protection scope
- Scan scope
- Task
- Trusted Platform Module
- Information about third-party code
- Trademark notices
Updating databases and application software modules
Updating the databases and application modules of Kaspersky Endpoint Security ensures up-to-date protection on your computer. New viruses and other types of malware appear worldwide on a daily basis. Kaspersky Endpoint Security databases contain information about threats and ways of neutralizing them. To detect threats quickly, you are urged to regularly update the databases and application modules.
The following objects are updated on users' computers:
- Anti-virus databases. Anti-virus databases include databases of malware signatures, description of network attacks, databases of malicious and phishing web addresses, databases of banners, spam databases, and other data.
- Application modules. Module updates are intended for eliminating vulnerabilities in the application and to improve computer protection methods. Module updates may change the behavior of application components and add new capabilities.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security supports the following scenarios for updating databases and application modules:
- Update from Kaspersky servers.
Kaspersky update servers are located in various countries throughout the world. This ensures high reliability of updates. If an update cannot be performed from one server, Kaspersky Endpoint Security switches over to the next server.
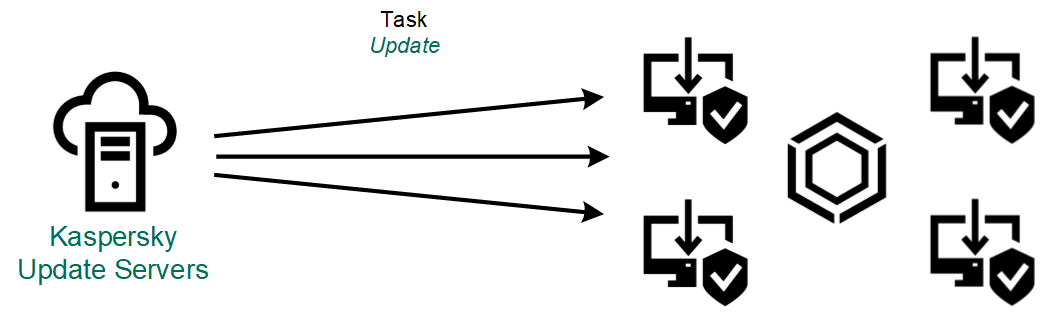
Update from Kaspersky servers.
- Centralized update.
Centralized update reduces external Internet traffic, and provides for convenient monitoring of the update.
Centralized update consists of the following steps:
- Download the update package to a repository within the organization's network.
The update package is downloaded to the repository by the Administration Server task named Download updates to Administration Server repository.
- Download the update package to a shared folder (optional).
You can download the update package to a shared folder by using the following methods:
- Using Kaspersky Endpoint Security Update task. The task is intended for one of the computers in the local company network.
- Using the Kaspersky Update Utility. For detailed information about using Kaspersky Update Utility, refer to Kaspersky Knowledge Base.
- Distribute the update package to client computers.
The update package is distributed to client computers by the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Update task. You can create an unlimited number of update tasks for each administration group.
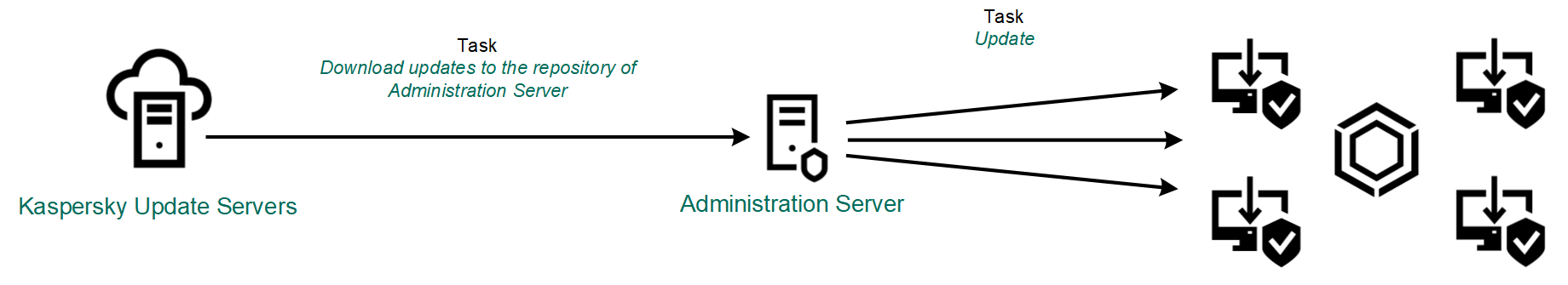
Updating from a server repository
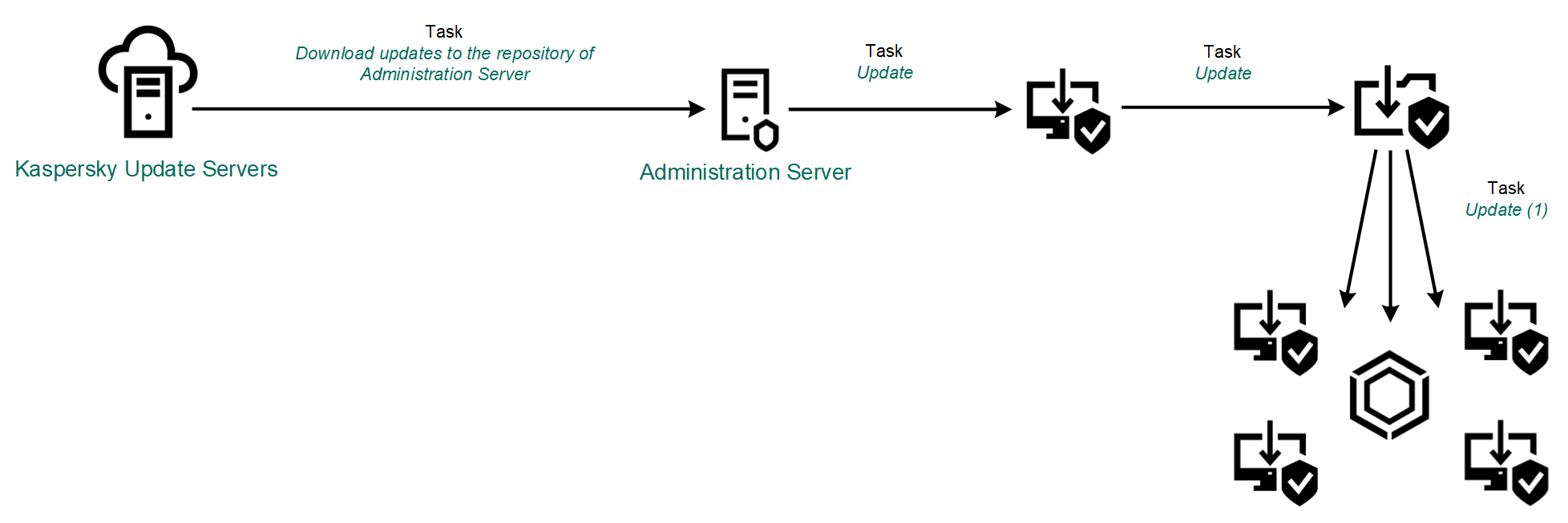
Updating from a shared folder
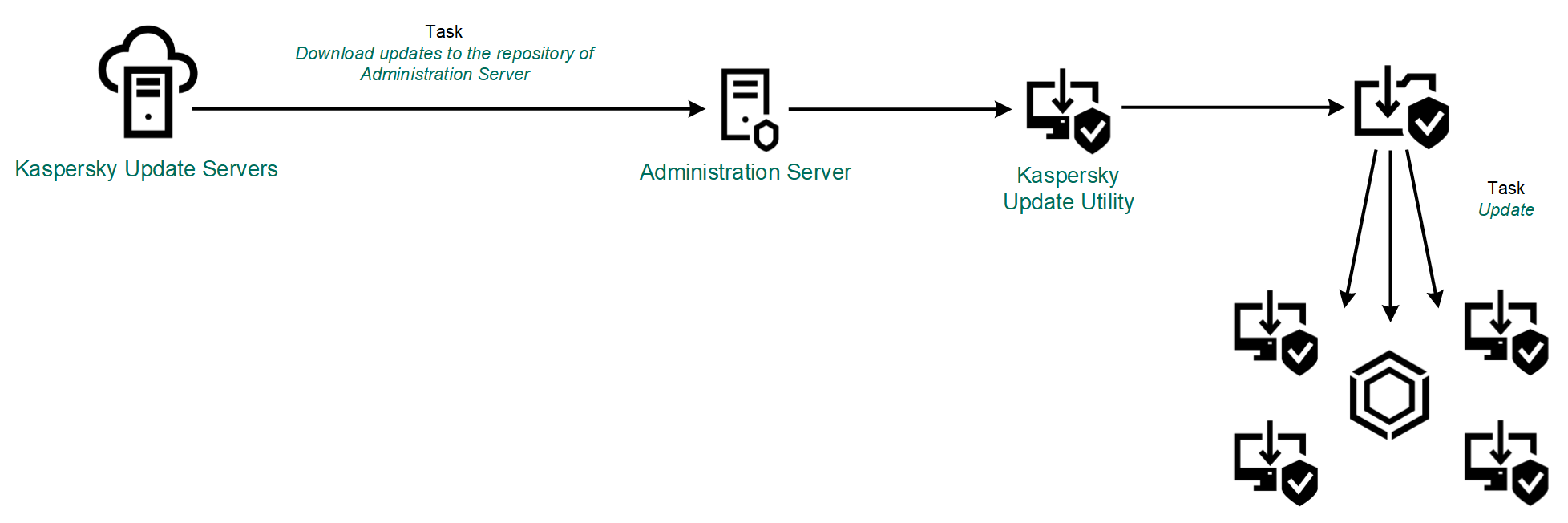
Updating using Kaspersky Update Utility
- Download the update package to a repository within the organization's network.
For the Web Console, the default list of update sources contains the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and Kaspersky update servers. For the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, the default list of update sources contains distribution points and Kaspersky update servers. For more details about distribution points, refer to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console Help. You can add other update sources to the list. You can specify HTTP/FTP servers and shared folders as update sources. If an update cannot be performed from an update source, Kaspersky Endpoint Security switches over to the next one.
Updates are downloaded from Kaspersky update servers or from other FTP- or HTTP servers over standard network protocols. If connection to a proxy server is required for accessing the update source, specify the proxy server settings in Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings.
|
In this section: Updating from a server repository |