Contents
- Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 Help
- What's new
- About Kaspersky Security Center
- Architecture
- Hardware and software requirements
- Compatible Kaspersky applications and solutions
- Licenses and features of Kaspersky Security Center 15.1
- About compatibility of Kaspersky Security Center components
- Comparison of Kaspersky Security Center: Windows-based vs. Linux-based
- About Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console
- Kaspersky Security Center 15.1
- Basic concepts
- Administration Server
- Hierarchy of Administration Servers
- Virtual Administration Server
- Mobile Device Server
- Web Server
- Network Agent
- Administration groups
- Managed device
- Unassigned device
- Administrator's workstation
- Management plug-in
- Management web plug-in
- Policies
- Policy profiles
- Tasks
- Task scope
- How local application settings relate to policies
- Distribution point
- Connection gateway
- Main installation scenario
- Ports used by Kaspersky Security Center
- Certificates for work with Kaspersky Security Center
- About Kaspersky Security Center certificates
- About Administration Server certificate
- Requirements for custom certificates used in Kaspersky Security Center
- Scenario: Specifying the custom Administration Server certificate
- Replacing the Administration Server certificate by using the klsetsrvcert utility
- Connecting Network Agents to Administration Server by using the klmover utility
- Reissuing the Web Server certificate
- Schemas for data traffic and port usage
- Administration Server and managed devices on LAN
- Primary Administration Server on LAN and two secondary Administration Servers
- Administration Server on LAN, managed devices on internet, reverse proxy in use
- Administration Server on LAN, managed devices on internet, connection gateway in use
- Administration Server in DMZ, managed devices on internet
- Interaction of Kaspersky Security Center components and security applications: more information
- Conventions used in interaction schemas
- Administration Server and DBMS
- Administration Server and Administration Console
- Administration Server and client device: Managing the security application
- Upgrading software on a client device through a distribution point
- Hierarchy of Administration Servers: primary Administration Server and secondary Administration Server
- Hierarchy of Administration Servers with a secondary Administration Server in DMZ
- Administration Server, a connection gateway in a network segment, and a client device
- Administration Server and two devices in DMZ: a connection gateway and a client device
- Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Activating and managing the security application on a mobile device
- Deployment best practices
- Hardening Guide
- Administration Server deployment
- Connection safety
- Accounts and authentication
- Managing protection of Administration Server
- Managing protection of client devices
- Configuring protection for managed applications
- Administration Server maintenance
- Event transfer to third-party systems
- Security recommendations for third-party information systems
- Recommendations for using Kaspersky security applications
- Preparation for deployment
- Planning Kaspersky Security Center deployment
- Typical schemes of protection system deployment
- About planning Kaspersky Security Center deployment in an organization's network
- Selecting a structure for protection of an enterprise
- Standard configurations of Kaspersky Security Center
- Selecting a DBMS for Administration Server
- Configuring the MariaDB x64 server for working with Kaspersky Security Center 15.1
- Configuring the MySQL x64 server for working with Kaspersky Security Center 15.1
- Configuring the PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro server for working with Kaspersky Security Center 15.1
- Managing mobile devices with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android
- Providing internet access to Administration Server
- About distribution points
- Increasing the limit of file descriptors for the klnagent service
- Calculating the number and configuration of distribution points
- Hierarchy of Administration Servers
- Virtual Administration Servers
- Information about limitations of Kaspersky Security Center
- Network load
- Preparing to mobile device management
- Information about Administration Server performance
- Network settings for interaction with external services
- Planning Kaspersky Security Center deployment
- Deploying Network Agent and the security application
- Initial deployment
- Configuring installers
- Installation packages
- MSI properties and transform files
- Deployment with third-party tools for remote installation of applications
- About remote installation tasks in Kaspersky Security Center
- Deployment by capturing and copying the image of a device
- Incorrect copying of a hard drive image
- Deployment using group policies of Microsoft Windows
- Forced deployment through the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center
- Running stand-alone packages created by Kaspersky Security Center
- Options for manual installation of applications
- Creating an MST file
- Remote installation of applications on devices with Network Agent installed
- Managing device restarts in the remote installation task
- Suitability of databases updating in an installation package of a security application
- Using tools for remote installation of applications in Kaspersky Security Center for running relevant executable files on managed devices
- Monitoring the deployment
- Configuring installers
- Virtual infrastructure
- Support of file system rollback for devices with Network Agent
- Local installation of applications
- Local installation of Network Agent
- Installing Network Agent in silent mode
- Installing Network Agent for Linux in silent mode (with an answer file)
- Preparing a device running Astra Linux in the closed software environment mode for installation of Network Agent
- Installing Network Agent for Linux in interactive mode
- Local installation of the application management plug-in
- Installing applications in silent mode
- Installing applications by using stand-alone packages
- Network Agent installation package settings
- Viewing the Privacy Policy
- Initial deployment
- Deploying mobile device management systems
- Deploying a system for management using iOS MDM protocol
- Installing iOS MDM Server
- Installing iOS MDM Server in silent mode
- iOS MDM Server deployment scenarios
- Simplified deployment scheme
- Deployment scheme involving Kerberos constrained delegation (KCD)
- Receiving an APNs certificate
- Renewing an APNs certificate
- Configuring a reserve iOS MDM Server certificate
- Installing an APNs certificate on an iOS MDM Server
- Configuring access to Apple Push Notification service
- Issuing and installing a shared certificate on a mobile device
- Adding a KES device to the list of managed devices
- Connecting KES devices to the Administration Server
- Integration with Public Key Infrastructure
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Server
- Deploying a system for management using iOS MDM protocol
- Hardening Guide
- Installation of Kaspersky Security Center
- Preparing for installation
- Accounts for work with the DBMS
- Scenario: Authenticating Microsoft SQL Server
- Scenario: Authenticating MySQL Server
- Scenario: Authenticating PostgreSQL Server
- Recommendations on Administration Server installation
- Creating accounts for the Administration Server services on a failover cluster
- Defining a shared folder
- Remote installation with Administration Server tools through Active Directory group policies
- Remote installation through delivery of the UNC path to a stand-alone package
- Updating from the Administration Server shared folder
- Installing images of operating systems
- Specifying the address of the Administration Server
- Standard installation
- Step 1. Reviewing the License Agreement and Privacy Policy
- Step 2. Selecting an installation method
- Step 3. Installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Step 4. Selecting network size
- Step 5. Selecting a database
- Step 6. Configuring the SQL Server
- Step 7. Selecting an authentication mode
- Step 8. Unpacking and installing files on the hard drive
- Custom installation
- Step 1. Reviewing the License Agreement and Privacy Policy
- Step 2. Selecting an installation method
- Step 3. Selecting the components to be installed
- Step 4. Installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Step 5. Selecting network size
- Step 6. Selecting a database
- Step 7. Configuring the SQL Server
- Step 8. Selecting an authentication mode
- Step 9. Selecting the account to start Administration Server
- Step 10. Selecting the account for running the Kaspersky Security Center services
- Step 11. Selecting a shared folder
- Step 12. Configuring the connection to Administration Server
- Step 13. Defining the Administration Server address
- Step 14. Administration Server address for connection of mobile devices
- Step 15. Selecting application management plug-ins
- Step 16. Unpacking and installing files on the hard drive
- Deployment of the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
- Scenario: Deployment of a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
- About the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
- Preparing a file server for a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
- Preparing nodes for a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
- Installing Kaspersky Security Center on the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster nodes
- Starting and stopping cluster nodes manually
- Installing Administration Server on a Windows Server failover cluster
- Step 1. Reviewing the License Agreement and Privacy Policy
- Step 2. Selecting the type of installation on a cluster
- Step 3. Specifying the name of the virtual Administration Server
- Step 4. Specifying the network details of the virtual Administration Server
- Step 5. Specifying a cluster group
- Step 6. Selecting a cluster data storage
- Step 7. Specifying an account for remote installation
- Step 8. Selecting the components to be installed
- Step 9. Selecting network size
- Step 10. Selecting a database
- Step 11. Configuring the SQL Server
- Step 12. Selecting an authentication mode
- Step 13. Selecting the account to start Administration Server
- Step 14. Selecting the account for running the Kaspersky Security Center services
- Step 15. Selecting a shared folder
- Step 16. Configuring the connection to Administration Server
- Step 17. Defining the Administration Server address
- Step 18. Administration Server address for connection of mobile devices
- Step 19. Unpacking and installing files on the hard drive
- Installing Administration Server in silent mode
- Installing Administration Console on the administrator's workstation
- Changes in the system after Kaspersky Security Center installation
- Removing the application
- About upgrading Kaspersky Security Center
- Initial setup of Kaspersky Security Center
- Hardening Guide
- Administration Server quick start wizard
- About quick start wizard
- Starting Administration Server quick start wizard
- Step 1. Configuring a proxy server
- Step 2. Selecting the application activation method
- Step 3. Selecting the protection areas and operating systems
- Step 4. Selecting plug-ins for managed applications
- Step 5. Downloading distribution packages and creating installation packages
- Step 6. Configuring Kaspersky Security Network usage
- Step 7. Configuring email notifications
- Step 8. Configuring update management
- Step 9. Creating an initial protection configuration
- Step 10. Connecting mobile devices
- Step 11. Downloading updates
- Step 12. Device discovery
- Step 13. Closing the quick start wizard
- Configuring the connection of Administration Console to Administration Server
- Configuring the internet access settings for Administration Server
- Connecting out-of-office devices
- Scenario: Connecting out-of-office devices through a connection gateway
- Scenario: Connecting out-of-office devices through a secondary Administration Server in DMZ
- About connecting out-of-office devices
- Connecting external desktop devices to Administration Server
- About connection profiles for out-of-office users
- Creating a connection profile for out-of-office users
- About switching Network Agent to other Administration Servers
- Creating a Network Agent switching rule by network location
- Notifications of events
- Encrypt communication with TLS
- Configuring the interface
- Discovering networked devices
- Scenario: Discovering networked devices
- Unassigned devices
- Device discovery
- Working with Windows domains. Viewing and changing the domain settings
- Configuring retention rules for unassigned devices
- Working with IP ranges
- Working with the Active Directory groups. Viewing and modifying group settings
- Creating rules for moving devices to administration groups automatically
- Using VDI dynamic mode on client devices
- Equipment inventory
- Licensing
- Kaspersky applications. Centralized deployment
- Replacing third-party security applications
- Installing applications using a remote installation task
- Installing applications using Remote installation wizard
- Working with the management plug-ins
- Viewing a protection deployment report
- Remote removal of applications
- Working with installation packages
- Creating an installation package
- Creating stand-alone installation packages
- Creating custom installation packages
- Viewing and editing properties of custom installation packages
- Obtaining the Network Agent installation package from the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit
- Distributing installation packages to secondary Administration Servers
- Distributing installation packages through distribution points
- Transferring application installation results to Kaspersky Security Center
- Defining the KSN proxy server address for installation packages
- Receiving up-to-date versions of applications
- Preparing a Windows device for remote installation
- Preparing a Linux device and installing Network Agent on a Linux device remotely
- Preparing a macOS device for remote installation of Network Agent
- Kaspersky applications: licensing and activation
- Licensing of managed applications
- Viewing information about license keys in use
- Adding a license key to the Administration Server repository
- Deleting an Administration Server license key
- Deploying a license key to client devices
- Automatic distribution of a license key
- Creating and viewing a license key usage report
- Viewing information about the application license keys
- Exporting a license key file
- Configuring network protection
- Scenario: Configuring network protection
- Policy setup and propagation: Device-centric approach
- About device-centric and user-centric security management approaches
- Manual setup of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy
- Manual setup of the group update task for Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Manual setup of the group task for scanning a device with Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Scheduling the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
- Manual setup of the group task for updates installation and vulnerabilities fix
- Setting the maximum number of events in the event repository
- Setting the maximum storage period for the information about fixed vulnerabilities
- Managing tasks
- Creating a task
- Creating the Administration Server task
- Creating a task for specific devices
- Creating a local task
- Displaying an inherited group task in the workspace of a nested group
- Automatically turning on devices before starting a task
- Automatically turning off a device after a task is completed
- Limiting task run time
- Exporting a task
- Importing a task
- Converting tasks
- Starting and stopping a task manually
- Pausing and resuming a task manually
- Monitoring task execution
- Viewing task run results stored on the Administration Server
- Configuring filtering of information about task run results
- Modifying a task. Rolling back changes
- Comparing tasks
- Accounts to start tasks
- Exporting task execution history
- Change tasks password wizard
- Creating a hierarchy of administration groups subordinate to a virtual Administration Server
- Policies and policy profiles
- Hierarchy of policies, using policy profiles
- Managing policies
- Creating a policy
- Displaying inherited policy in a subgroup
- Activating a policy
- Activating a policy automatically at the Virus outbreak event
- Applying an out-of-office policy
- Modifying a policy. Rolling back changes
- Comparing policies
- Viewing the policy distribution status chart
- Deleting a policy
- Copying a policy
- Exporting a policy
- Importing a policy
- Converting policies
- Managing policy profiles
- Device moving rules
- Cloning device moving rules
- Software categorization
- Prerequisites for installing applications on devices of a client organization
- Viewing and editing local application settings
- Updating Kaspersky Security Center and managed applications
- Scenario: Regular updating Kaspersky databases and applications
- About updating Kaspersky databases, software modules, and applications
- About using diff files for updating Kaspersky databases and software modules
- Enabling the Downloading diff files feature
- Creating the task for downloading updates to the repository of the Administration Server
- Creating the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task
- Configuring the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task
- Verifying downloaded updates
- Configuring test policies and auxiliary tasks
- Viewing downloaded updates
- Automatic installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security updates on devices
- Offline model of update download
- Enabling and disabling the offline model of update download
- Automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components
- Enabling and disabling automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components
- Automatic distribution of updates
- Distributing updates to client devices automatically
- Distributing updates to secondary Administration Servers automatically
- Assigning distribution points automatically
- Assigning a device a distribution point manually
- Removing a device from the list of distribution points
- Downloading updates by distribution points
- Deleting software updates from the repository
- Patch installation for a Kaspersky application in cluster mode
- Managing third-party applications on client devices
- Installing third-party software updates
- Scenario: Updating third-party software
- Viewing information about available updates for third-party applications
- Approving and declining software updates
- Synchronizing updates from Windows Update with Administration Server
- Installing updates on devices manually
- Configuring Windows updates in a Network Agent policy
- Fixing third-party software vulnerabilities
- Scenario: Finding and fixing third-party software vulnerabilities
- About finding and fixing software vulnerabilities
- Viewing information about software vulnerabilities
- Viewing statistics of vulnerabilities on managed devices
- Scanning applications for vulnerabilities
- Fixing vulnerabilities in applications
- Fixing vulnerabilities in an isolated network
- Scenario: Fixing third-party software vulnerabilities in an isolated network
- About fixing third-party software vulnerabilities in an isolated network
- Configuring the Administration Server with internet access to fix vulnerabilities in an isolated network
- Configuring isolated Administration Servers to fix vulnerabilities in an isolated network
- Transmitting patches and installing updates in an isolated network
- Disabling the option to transmit patches and install updates in an isolated network
- Ignoring software vulnerabilities
- Selecting user fixes for vulnerabilities in third-party software
- Rules for update installation
- Groups of applications
- Using Application Control to manage executable files
- Obtaining and viewing a list of executable files stored on client devices
- Creating application categories for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policies
- Creating an application category with content added manually
- Creating an application category that includes executable files from selected devices
- Creating an application category that includes executable files from a specific folder
- Adding event-related executable files to the application category
- Configuring application startup management on client devices
- Viewing the results of static analysis of startup rules applied to executable files
- Viewing the applications registry
- Changing the software inventory start time
- About license key management of third-party applications
- Creating licensed applications groups
- Managing license keys for licensed applications groups
- Inventory of executable files
- Viewing information about executable files
- Installing third-party software updates
- Monitoring and reporting
- Scenario: Monitoring and reporting
- Monitoring traffic lights and logged events in Administration Console
- Working with reports, statistics, and notifications
- Working with reports
- Managing statistics
- Configuring event notification
- Creating a certificate for an SMTP server
- Event selections
- Device selections
- Monitoring of applications installation and uninstallation
- Events of Kaspersky Security Center components
- Blocking frequent events
- Controlling changes in the status of virtual machines
- Monitoring the anti-virus protection status using information from the system registry
- Viewing and configuring the actions when devices show inactivity
- Disabling Kaspersky announcements
- Adjustment of distribution points and connection gateways
- Standard configuration of distribution points: Single office
- Standard configuration of distribution points: Multiple small remote offices
- Assigning a managed device to act as a distribution point
- Connecting a Linux device as a gateway in the demilitarized zone
- Connecting a Linux device to the Administration Server via a connection gateway
- Adding a connection gateway in the DMZ as a distribution point
- Assigning distribution points automatically
- About local installation of Network Agent on a device selected as distribution point
- About using a distribution point as connection gateway
- Adding IP ranges to the list of ranges polled by a distribution point
- Using a distribution point as a push server
- Other routine work
- Managing Administration Servers
- Creating a hierarchy of Administration Servers: adding a secondary Administration Server
- Connecting to an Administration Server and switching between Administration Servers
- Access rights to Administration Server and its objects
- Conditions of connection to an Administration Server over the internet
- Encrypted connection to an Administration Server
- Configuring an allowlist of IP addresses to connect to Administration Server
- Using the klscflag utility to close port 13291
- Disconnecting from an Administration Server
- Adding an Administration Server to the console tree
- Removing an Administration Server from the console tree
- Adding a virtual Administration Server to the console tree
- Changing an Administration Server service account. Utility tool klsrvswch
- Changing DBMS credentials
- Changing the Administration Server shared folder
- Resolving issues with Administration Server nodes
- Viewing and modifying the settings of an Administration Server
- Adjusting the general settings of Administration Server
- Administration Console interface settings
- Event processing and storage on the Administration Server
- Viewing log of connections to the Administration Server
- Control of virus outbreaks
- Limiting traffic
- Configuring Web Server
- Working with internal users
- Backup and restoration of Administration Server settings
- Backup copying and restoration of Administration Server data
- Backup of Administration Server data task
- Data backup and recovery utility (klbackup)
- Data backup and recovery in interactive mode
- Data backup and recovery in silent mode
- Using the klbackup utility to switch managed devices under management of another Administration Server
- Backup and restoring Administration Server data when using MySQL or MariaDB
- Optimizing backup and restoration of Administration Server data
- Migration to Kaspersky Security Center Linux by using Administration Server data backup
- Moving Administration Server to another device
- Avoiding conflicts between multiple Administration Servers
- Two-step verification
- Scenario: configuring two-step verification for all users
- About two-step verification
- Enabling two-step verification for your own account
- Enabling two-step verification for all users
- Disabling two-step verification for a user account
- Disabling required two-step verification for all users
- Excluding accounts from two-step verification
- Editing the name of a security code issuer
- Configuring two-step verification for your own account
- Managing administration groups
- Managing client devices
- Connecting client devices to the Administration Server
- Manually connecting a client device to the Administration Server. Klmover utility
- Tunneling the connection between a client device and the Administration Server
- Remotely connecting to the desktop of a client device
- Connecting to devices through Windows Desktop Sharing
- Configuring the restart of a client device
- Auditing actions on a remote client device
- Checking the connection between a client device and the Administration Server
- Identifying client devices on the Administration Server
- Moving devices to an administration group
- Changing the Administration Server for client devices
- Moving devices connected to Administration Server through connection gateways to another Administration Server
- Clusters and server arrays
- Turning on, turning off, and restarting client devices remotely
- About the usage of the continuous connection between a managed device and the Administration Server
- About forced synchronization
- About connection schedule
- Sending messages to device users
- Managing Kaspersky Security for Virtualization
- Configuring the switching of device statuses
- Tagging devices and viewing assigned tags
- Remote diagnostics of client devices. Kaspersky Security Center remote diagnostics utility
- Connecting the remote diagnostics utility to a client device
- Generating a dump file for an application
- Enabling and disabling tracing, downloading the trace file
- Downloading application settings
- Downloading event logs
- Downloading multiple diagnostic information items
- Starting diagnostics and downloading the results
- Starting, stopping, and restarting applications
- UEFI protection devices
- Settings of a managed device
- General policy settings
- Network Agent policy settings
- Managing user accounts
- Working with user accounts
- Adding an account of an internal user
- Editing an account of an internal user
- Changing the number of allowed password entry attempts
- Configuring the check of the name of an internal user for uniqueness
- Adding a security group
- Adding a user to a group
- Configuring access rights to application features. Role-based access control
- Assigning the user as a device owner
- Delivering messages to users
- Viewing the list of user mobile devices
- Installing a certificate for a user
- Viewing the list of certificates issued to a user
- About the administrator of a virtual Administration Server
- Remote installation of operating systems and applications
- Creating images of operating systems
- Installing images of operating systems
- Configuring the KSN proxy server address
- Adding drivers for Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE)
- Adding drivers to an installation package with an operating system image
- Configuring sysprep.exe utility
- Deploying operating systems on new networked devices
- Deploying operating systems on client devices
- Creating installation packages of applications
- Issuing a certificate for installation packages of applications
- Installing applications on client devices
- Managing object revisions
- Deletion of objects
- Mobile Device Management
- Scenario: Mobile Device Management deployment
- About group policy for managing iOS MDM devices
- Enabling Mobile Device Management
- Modifying the Mobile Device Management settings
- Disabling Mobile Device Management
- Working with commands for mobile devices
- Working with certificates of mobile devices
- Starting the Certificate installation wizard
- Step 1. Selecting certificate type
- Step 2. Selecting device type
- Step 3. Selecting a user
- Step 4. Selecting certificate source
- Step 5. Assigning a tag to the certificate
- Step 6. Specifying certificate publishing settings
- Step 7. Selecting user notification method
- Step 8. Generating the certificate
- Configuring certificate issuance rules
- Integration with public key infrastructure
- Enabling support of Kerberos Constrained Delegation
- Adding iOS mobile devices to the list of managed devices
- Adding Android mobile devices to the list of managed devices
- Managing iOS MDM devices
- Signing an iOS MDM profile by a certificate
- Adding a configuration profile
- Installing a configuration profile on a device
- Removing the configuration profile from a device
- Adding a new device by publishing a link to a profile
- Adding a new device through profile installation by the administrator
- Adding a provisioning profile
- Installing a provisioning profile to a device
- Removing a provisioning profile from a device
- Adding a managed application
- Installing an app on a mobile device
- Removing an app from a device
- Configuring roaming on an iOS MDM mobile device
- Viewing information about an iOS MDM device
- Disconnecting an iOS MDM device from management
- Sending commands to a device
- Checking the execution status of commands sent
- Managing KES devices
- Data encryption and protection
- Data repositories
- Kaspersky Security Network (KSN)
- About KSN
- Setting up access to Kaspersky Security Network
- Enabling and disabling KSN
- Viewing the accepted KSN Statement
- Viewing the KSN proxy server statistics
- Accepting an updated KSN Statement
- Enhanced protection with Kaspersky Security Network
- Checking whether the distribution point works as KSN proxy server
- Switching between Online Help and Offline Help
- Managing Administration Servers
- Export of events to SIEM systems
- Configuring event export to SIEM systems
- Before you begin
- About events in Kaspersky Security Center
- About event export
- About configuring event export in a SIEM system
- Marking of events for export to SIEM systems in Syslog format
- About exporting events using Syslog format
- About exporting events using CEF and LEEF formats
- Configuring Kaspersky Security Center for export of events to a SIEM system
- Exporting events directly from the database
- Viewing export results
- Using SNMP for sending statistics to third-party applications
- Working in a cloud environment
- About work in a cloud environment
- Scenario: Deployment for a cloud environment
- Prerequisites for deploying Kaspersky Security Center in a cloud environment
- Hardware requirements for the Administration Server in a cloud environment
- Licensing options in a cloud environment
- Database options for work in a cloud environment
- Working in Amazon Web Services cloud environment
- About work in Amazon Web Services cloud environment
- Creating IAM roles and IAM user accounts for Amazon EC2 instances
- Ensuring that the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server has the permissions to work with AWS
- Creating an IAM role for the Administration Server
- Creating an IAM user account for work with Kaspersky Security Center
- Creating an IAM role for installation of applications on Amazon EC2 instances
- Working with Amazon RDS
- Working in Microsoft Azure cloud environment
- Working in Google Cloud
- Prerequisites for client devices in a cloud environment necessary for work with Kaspersky Security Center
- Creating installation packages required to configure cloud environment
- Configuring cloud environment
- About the Configure cloud environment wizard
- Step 1. Selecting the application activation method
- Step 2. Selecting the cloud environment
- Step 3. Authorization in the cloud environment
- Step 4. Configuring synchronization with Cloud and choosing further actions
- Step 5. Configuring Kaspersky Security Network in the cloud environment
- Step 6. Configuring email notifications in the cloud environment
- Step 7. Creating an initial configuration of the protection of the cloud environment
- Step 8. Selecting the action when the operating system must be restarted during installation (for the cloud environment)
- Step 9. Receiving updates by the Administration Server
- Checking configuration
- Cloud device group
- Network segment polling
- Installing applications on devices in a cloud environment
- Viewing the properties of cloud devices
- Synchronization with cloud
- Using deployment scripts for deploying security applications
- Deployment of Kaspersky Security Center in Yandex.Cloud
- Appendices
- Advanced features
- Kaspersky Security Center operation automation. klakaut utility
- Custom tools
- Network Agent disk cloning mode
- Preparing a reference device with Network Agent installed for creating an image of operating system
- Configuring receipt of messages from File Integrity Monitor
- Administration Server maintenance
- Access to public DNS servers
- User notification method window
- Device selection window
- Define the name of the new object window
- Application categories section
- Features of using the management interface
- Reference information
- Searching and exporting data
- Settings of tasks
- Global list of subnets
- Usage of Network Agent for Windows, Linux, and macOS: Comparison
- Advanced features
- Basic concepts
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Deployment diagram of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Ports used by Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface
- Pinning and unpinning sections of the main menu
- Scenario: Installation and initial setup of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Installation
- Installing Kaspersky Security Center (Standard installation)
- Installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console connected to Administration Server installed on failover cluster nodes
- Upgrading Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Certificates for work with Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Migration from Kaspersky Security Center Windows
- About migration to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console
- About migration to Kaspersky Security Center Linux
- About migration to Kaspersky XDR Expert
- Exporting group objects from Kaspersky Security Center Windows
- Importing the export file to Kaspersky Security Center Linux
- Switching managed devices to be under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux
- Signing in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and signing out
- Identity and Access Manager in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- About Identity and Access Manager
- Enabling Identity and Access Manager: scenario
- Configuring Identity and Access Manager in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Registering Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks application in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Lifetime of tokens and authorization timeout for Identity and Access Manager
- Downloading and distributing the IAM certificates
- Disabling Identity and Access Manager
- Configuring domain authentication by using the NTLM and Kerberos protocols
- Configuring Administration Server
- Configuring the connection of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to Administration Server
- Configuring Administration Server connection events logging
- Configuring internet access settings for Administration Server
- Setting the maximum number of events in the event repository
- Connection settings of UEFI protection devices
- Creating a hierarchy of Administration Servers: adding a secondary Administration Server
- Viewing the list of secondary Administration Servers
- Deleting a hierarchy of Administration Servers
- Administration Server maintenance
- Configuring the interface
- Managing virtual Administration Servers
- Enabling account protection from unauthorized modification
- Two-step verification
- Scenario: Configuring two-step verification for all users
- About two-step verification
- Enabling two-step verification for your own account
- Enabling required two-step verification for all users
- Disabling two-step verification for a user account
- Disabling required two-step verification for all users
- Excluding accounts from two-step verification
- Generating a new secret key
- Editing the name of a security code issuer
- Configuring two-step verification for your own account
- Prohibit new users from setting up two-step verification for themselves
- Backup copying and restoration of Administration Server data
- Moving Administration Server to another device
- Initial setup of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Quick start wizard (Kaspersky Security Center Web Console)
- Step 1. Specifying the internet connection settings
- Step 2. Downloading required updates
- Step 3. Selecting the assets to secure
- Step 4. Selecting encryption in solutions
- Step 5. Configuring installation of plug-ins for managed applications
- Step 6. Installing the selected plug-ins
- Step 7. Downloading distribution packages and creating installation packages
- Step 8. Configuring Kaspersky Security Network
- Step 9. Selecting the application activation method
- Step 10. Specifying the third-party update management settings
- Step 11. Creating a basic network protection configuration
- Step 12. Configuring email notifications
- Step 13. Performing a network poll
- Step 14. Closing the quick start wizard
- Connecting out-of-office devices
- Scenario: Connecting out-of-office devices through a connection gateway
- Scenario: Connecting out-of-office devices through a secondary Administration Server in DMZ
- About connecting out-of-office devices
- Connecting external desktop devices to Administration Server
- About connection profiles for out-of-office users
- Creating a connection profile for out-of-office users
- About switching Network Agent to other Administration Servers
- Creating a Network Agent switching rule by network location
- Quick start wizard (Kaspersky Security Center Web Console)
- Protection deployment wizard
- Starting Protection deployment wizard
- Selecting the installation package
- Selecting a method for distribution of key file or activation code
- Selecting Network Agent version
- Selecting devices
- Step 5. Specifying the remote installation task settings
- Step 6. Restart management
- Step 7. Removing incompatible applications before installation
- Step 8. Moving devices to Managed devices
- Step 9. Selecting accounts to access devices
- Step 10. Starting installation
- Kaspersky applications deployment through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Scenario: Kaspersky applications deployment through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Getting plug-ins for Kaspersky applications
- Downloading and creating installation packages for Kaspersky applications
- Changing the limit on the size of custom installation package data
- Downloading distribution packages for Kaspersky applications
- Checking that Kaspersky Endpoint Security is deployed successfully
- Creating stand-alone installation packages
- Viewing the list of stand-alone installation packages
- Creating custom installation packages
- Distributing installation packages to secondary Administration Servers
- Installing applications using a remote installation task
- Specifying settings for remote installation on Unix devices
- Starting and stopping Kaspersky applications
- Mobile Device Management
- Replacing third-party security applications
- Discovering networked devices
- Kaspersky applications: licensing and activation
- Licensing of managed applications
- Adding a license key to the Administration Server repository
- Adding an Administration Server license key
- Deploying a license key to client devices
- Automatic distribution of a license key
- Viewing information about license keys in use
- Deleting a license key from the repository
- Revoking consent with an End User License Agreement
- Renewing licenses for Kaspersky applications
- Using Kaspersky Marketplace to choose Kaspersky business solutions
- Configuring network protection
- Scenario: Configuring network protection
- About device-centric and user-centric security management approaches
- Policy setup and propagation: Device-centric approach
- Policy setup and propagation: User-centric approach
- Network Agent policy settings
- Enabling and disabling the low resource consumption mode for Network Agent
- Manual setup of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy
- Configuring Kaspersky Security Network
- Checking the list of the networks protected by Firewall
- Disabling the scan of network drives
- Excluding software details from the Administration Server memory
- Configuring access to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows interface on workstations
- Saving important policy events in the Administration Server database
- Manual setup of the group update task for Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Granting offline access to the external device blocked by Device Control
- Removing applications or software updates remotely
- Tasks
- Managing client devices
- Settings of a managed device
- Creating administration groups
- Adding devices to an administration group manually
- Moving devices or clusters to an administration group manually
- Creating device moving rules
- Copying device moving rules
- Conditions for a device moving rule
- About clusters and server arrays
- Properties of a cluster or server array
- Viewing and configuring the actions when devices show inactivity
- About device statuses
- Configuring the switching of device statuses
- Remotely connecting to the desktop of a client device
- Connecting to devices through Windows Desktop Sharing
- Device selections
- Device tags
- Creating a device tag
- Renaming a device tag
- Deleting a device tag
- Viewing devices to which a tag is assigned
- Viewing tags assigned to a device
- Tagging a device manually
- Removing an assigned tag from a device
- Viewing rules for tagging devices automatically
- Editing a rule for tagging devices automatically
- Creating a rule for tagging devices automatically
- Running rules for auto-tagging devices
- Deleting a rule for tagging devices automatically
- Managing device tags by using the klscflag utility
- Policies and policy profiles
- About policies and policy profiles
- About lock and locked settings
- Inheritance of policies and policy profiles
- Managing policies
- Viewing the list of policies
- Creating a policy
- Modifying a policy
- General policy settings
- Enabling and disabling a policy inheritance option
- Copying a policy
- Moving a policy
- Exporting a policy
- Importing a policy
- Viewing the policy distribution status chart
- Activating a policy automatically at the Virus outbreak event
- Deleting a policy
- Managing policy profiles
- Data encryption and protection
- Users and user roles
- About user roles
- Viewing user accounts and sessions
- Configuring access rights to application features. Role-based access control
- Adding an account of an internal user
- Creating a security group
- Editing an account of an internal user
- Editing a security group
- Assigning a role to a user or a security group
- Adding user accounts to an internal security group
- Assigning a user as a device owner
- Assigning a user as a Linux device owner after installation of Network Agent
- Deleting a user or a security group
- Changing the password for a user account
- Creating a user role
- Editing a user role
- Editing the scope of a user role
- Deleting a user role
- Associating policy profiles with roles
- Changing account password
- Revoking local administrator rights
- Managing object revisions
- Deletion of objects
- Kaspersky Security Network (KSN)
- Scenario: Upgrading Kaspersky Security Center and managed security applications
- Updating Kaspersky databases and applications
- Scenario: Regular updating Kaspersky databases and applications
- About updating Kaspersky databases, software modules, and applications
- Creating the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task
- Verifying downloaded updates
- Creating the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task
- Enabling and disabling automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components
- Automatic installation of updates for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Approving and declining software updates
- Updating Administration Server
- Enabling and disabling the offline model of update download
- Updating Kaspersky databases and software modules on offline devices
- Backing up and restoring web plug-ins
- Adjustment of distribution points and connection gateways
- Standard configuration of distribution points: Single office
- Standard configuration of distribution points: Multiple small remote offices
- About assigning distribution points
- Assigning distribution points automatically
- Assigning distribution points manually
- Modifying the list of distribution points for an administration group
- Forced synchronization
- Enabling a push server
- Managing third-party applications on client devices
- Installing third-party software updates
- Scenario: Updating third-party software
- Installing third-party software updates
- Creating the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
- Find vulnerabilities and required updates task settings
- Creating the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task
- Adding rules for update installation
- Creating the Install Windows Update updates task
- Viewing information about available third-party software updates
- Exporting the list of available software updates to a file
- Approving and declining third-party software updates
- Creating the Perform Windows Update synchronization task
- Updating third-party applications automatically
- Fixing third-party software vulnerabilities
- Scenario: Finding and fixing third-party software vulnerabilities
- About finding and fixing software vulnerabilities
- Fixing third-party software vulnerabilities
- Creating the Fix vulnerabilities task
- Creating the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task
- Adding rules for update installation
- Selecting user fixes for vulnerabilities in third-party software
- Viewing information about software vulnerabilities detected on all managed devices
- Viewing information about software vulnerabilities detected on the selected managed device
- Viewing statistics of vulnerabilities on managed devices
- Exporting the list of software vulnerabilities to a file
- Ignoring software vulnerabilities
- Managing applications run on client devices
- Using Application Control to manage executable files
- Application Control modes and categories
- Obtaining and viewing a list of executable files stored on client devices
- Creating application category with content added manually
- Creating an application category that includes executable files from selected devices
- Creating an application category that includes executable files from selected folder
- Viewing the list of application categories
- Adding event-related executable files to the application category
- Configuring Application Control in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy
- Obtaining and viewing a list of applications installed on client devices
- Using Application Control to manage executable files
- Creating an installation package of a third-party application from the Kaspersky database
- Viewing and modifying the settings of an installation package of a third-party application from the Kaspersky database
- Settings of an installation package of a third-party application from the Kaspersky database
- Application tags
- Installing third-party software updates
- Monitoring and reporting
- Scenario: Monitoring and reporting
- About types of monitoring and reporting
- Dashboard and widgets
- Reports
- Events and event selections
- About Kaspersky Security Center events
- Using event selections
- Creating an event selection
- Editing an event selection
- Viewing a list of an event selection
- Exporting an event selection
- Importing an event selection
- Viewing details of an event
- Exporting events to a file
- Viewing an object history from an event
- Deleting events
- Deleting event selections
- Setting the storage term for an event
- Events of Kaspersky Security Center components
- Blocking frequent events
- Receiving events from Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers
- Notifications and device statuses
- Kaspersky announcements
- Viewing information about the detects of threats
- Cloud Discovery
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console activity logging
- Integration between Kaspersky Security Center and other solutions
- Establishing a background connection
- Exporting events to SIEM systems
- Configuring event export to SIEM systems
- Before you begin
- About events in Kaspersky Security Center
- About event export
- About configuring event export in a SIEM system
- Marking of events for export to SIEM systems in Syslog format
- About exporting events using CEF and LEEF formats
- Converting events to the CEF or LEEF format
- About exporting events using Syslog format
- Configuring Kaspersky Security Center for export of events to a SIEM system
- Exporting events directly from the database
- Viewing export results
- Working with Kaspersky Security Center Web Console in a cloud environment
- Cloud environment configuration in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Step 1. Checking the required plug-ins and installation packages
- Step 2. Licensing the application
- Step 3. Selecting the cloud environment and authorization
- Step 4. Segment polling, configuring synchronization with Cloud and choosing further actions
- Step 5. Selecting an application to create a policy and tasks for
- Step 6. Configuring Kaspersky Security Network for Kaspersky Security Center
- Step 7. Creating an initial configuration of protection
- Network segment polling via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Adding connections for cloud segment polling
- Deleting a connection for cloud segment polling
- Configuring the polling schedule via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Viewing the results of cloud segment polling via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Viewing the properties of cloud devices via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Synchronization with Cloud: Configuring the moving rule
- Remote installation of applications to the Azure virtual machines
- Creating Backup of the Administration Server data task by using a cloud DBMS
- Cloud environment configuration in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Remote diagnostics of client devices
- Opening the remote diagnostics window
- Enabling and disabling tracing for applications
- Downloading trace files of an application
- Deleting trace files
- Downloading application settings
- Downloading event logs
- Starting, stopping, restarting the application
- Running the remote diagnostics of Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent and downloading the results
- Running an application on a client device
- Generating a dump file for an application
- Running remote diagnostics on a Linux-based client device
- Downloading and deleting files from Quarantine and Backup
- Changing the language of the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface
- API Reference Guide
- Best Practices for Service Providers
- Planning Kaspersky Security Center deployment
- Deployment and initial setup
- Recommendations on Administration Server installation
- Configuring protection on a client organization's network
- Manual setup of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy
- Manual setup of the group update task for Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Manual setup of the group task for scanning a device with Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Scheduling the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
- Manual setup of the group task for updates installation and vulnerabilities fix
- Building a structure of administration groups and assigning distribution points
- Hierarchy of policies, using policy profiles
- Tasks
- Device moving rules
- Software categorization
- About multi-tenant applications
- Backup and restoration of Administration Server settings
- Deploying Network Agent and the security application
- Initial deployment
- Configuring installers
- Installation packages
- MSI properties and transform files
- Deployment with third-party tools for remote installation of applications
- General information about the remote installation tasks in Kaspersky Security Center
- Deployment using group policies of Microsoft Windows
- Forced deployment through the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center
- Running stand-alone packages created by Kaspersky Security Center
- Options for manual installation of applications
- Remote installation of applications on devices with Network Agent installed
- Managing device restarts in the remote installation task
- Suitability of databases updating in an installation package of an anti-virus application
- Removing incompatible third-party security applications
- Removing password-protected Network Agent by using the command prompt
- Using tools for remote installation of applications in Kaspersky Security Center for running relevant executable files on managed devices
- Monitoring the deployment
- Configuring installers
- Virtual infrastructure
- Support of file system rollback for devices with Network Agent
- Initial deployment
- About connection profiles for out-of-office users
- Deploying the Mobile Device Management feature
- Other routine work
- Sizing Guide
- About this Guide
- Information about limitations of Kaspersky Security Center
- Calculations for Administration Servers
- Calculations for distribution points and connection gateways
- Logging of information about events for tasks and policies
- Specific considerations and optimal settings of certain tasks
- Details of network load spread among Administration Server and protected devices
- Contact Technical Support
- Sources of information about the application
- Glossary
- Active key
- Additional (or reserve) license key
- Administration Console
- Administration group
- Administration Server
- Administration Server certificate
- Administration Server client (Client device)
- Administration Server data backup
- Administrator rights
- Administrator's workstation
- Amazon EC2 instance
- Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
- Anti-virus databases
- Anti-virus protection service provider
- Application Shop
- Authentication Agent
- Available update
- AWS Application Program Interface (AWS API)
- AWS IAM access key
- AWS Management Console
- Backup folder
- Broadcast domain
- Centralized application management
- Client administrator
- Cloud Discovery
- Cloud environment
- Configuration profile
- Connection gateway
- Demilitarized zone (DMZ)
- Device owner
- Direct application management
- Distribution point
- Event repository
- Event severity
- Forced installation
- Group task
- Hardening Guide
- Home Administration Server
- HTTPS
- IAM role
- IAM user
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Incompatible application
- Installation package
- Internal users
- iOS MDM device
- iOS MDM profile
- iOS MDM Server
- JavaScript
- Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN)
- Kaspersky Security Center Administrator
- Kaspersky Security Center Operator
- Kaspersky Security Center System Health Validator (SHV)
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Server
- Kaspersky Security Network (KSN)
- Kaspersky update servers
- KES device
- Key file
- License term
- Licensed applications group
- Local installation
- Local task
- Managed devices
- Management plug-in
- Manual installation
- MITM attack
- Mobile Device Server
- Network Agent
- Network anti-virus protection
- Network protection status
- Patch importance level
- Policy
- Program settings
- Protection status
- Provisioning profile
- Remote installation
- Restoration
- Restoration of Administration Server data
- Service provider's administrator
- Shared certificate
- SSL
- Task
- Task for specific devices
- Task settings
- UEFI protection device
- Update
- Upgrade of Kaspersky Security Center
- Virtual Administration Server
- Virus activity threshold
- Virus outbreak
- Vulnerability
- Windows Server Update Services (WSUS)
- Information about third-party code
- Trademark notices
- Known issues
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 Help
|
Find out what's new in the latest application release. |
|
Configuring network protection Manage the security of the organization. |
|
Hardware and software requirements Check which operating systems and application versions are supported. |
|
Kaspersky applications. Updating databases and software modules Maintain the reliability of the protection system. |
|
Plan the use of resources, install the Administration Server, install Network Agent and security applications on client devices, and consolidate devices into administration groups. |
|
View your infrastructure, protection statuses, and statistics. Manage access to cloud services using Cloud Discovery. |
|
Discover existing and new devices on your organization's network. |
|
Replacing third-party security applications Learn methods for uninstalling incompatible applications. |
|
Kaspersky applications. Centralized deployment Deploy Kaspersky applications. |
|
Adjustment of distribution points and connection gateways Configure distribution points. |
|
Upgrading Kaspersky Security Center from a previous version Upgrade Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 from a previous version. |
|
Best Practices for Service Providers (Online Help only) Learn recommendations on how to deploy, configure, and use the application, as well as ways to resolve typical issues in the application operation. |
|
Kaspersky applications. Licensing and activation Activate Kaspersky applications in a few steps. |
|
Sizing Guide (Online Help only) For optimal performance under varying conditions, take into account the number of networked devices, network topology, and set of Kaspersky Security Center features that you require. |
|
Exporting events to SIEM systems Configure exporting events to SIEM systems for analysis. |
|
Vulnerability and patch management Find and fix vulnerabilities in third-party software. |
|
Working in a cloud environment Deploy Kaspersky Security Center in cloud environments: Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform. |
|
Frequently Asked Questions (English only) Find instructions on how to resolve common issues. |
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business Quick Start Guide Get started with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business: install and configure this solution. You can also examine the feature comparison of Kaspersky Security Center, to choose the most appropriate way of managing the network security. |
|
|
What's new
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 has several new features and improvements:
- Cloud Discovery. This is a new feature that allows you to monitor attempts to use cloud services on managed devices running Windows, and to block access to cloud services that you consider unwanted. This feature is only available in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Domain controller polling now allows you to poll a Samba domain controller through a Linux-based distribution point. Additional improvements were made to support polling of large domains.
- Enhanced remote diagnostics of Linux-based managed devices.
- Extended hardware inventory of macOS devices. Network Agent on a macOS device sends the MAC address and device serial number to Administration Server.
- You can now check the connection to a SIEM system.
- The maximum password length for an internal user was increased to 256 characters.
- When you migrate from Kaspersky Security Center Windows to Kaspersky Security Center Linux, you can now switch the managed devices to be under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux through restoring the certificate and private key of Administration Server from a backup copy.
- When you run the Cleaner tool or the klmover utility to remove a password-protected Network Agent, you are prompted to enter the uninstallation password.
- Upgrade from Kaspersky Security for Windows Server to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows no longer requires the target device to restart.
- A user can be assigned as a device owner during or after installation of Network Agent on a client device on Linux.
- You can now receive a report on remote installation when you install software on the managed devices through custom scripts.
- When you execute several custom scripts on a managed device, you can set a priority for each script to define the execution order. The scripts will be executed from the one with the highest priority to the one with the lowest priority.
- Extended policy audit. You can now view the contents of a policy revision and save a policy revision to a file. Currently, these features are only available for the Administration Server policy and Network Agent policy.
- User experience improvements, including:
- Main menu personalization by pinning sections of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console for quick access from the Pinned section.
- Optimized work with tables. The default view of each table now contains the most frequently used columns. Also, you can now select all items on the current page or in the entire table, as well as sort items in the entire table.
- Improved report delivery configuration. You can now specify up to 20 email addresses to send the report to, and the report delivery schedule.
- You can revoke local administrator rights from accounts on Linux-based managed devices. This provides you with an extra layer of control of user accounts. For example, you can revoke local administrator rights after a one-time assignment is complete.
- You can change the local account password on Linux-based managed devices, for example, when a user forgets the local account password or to perform a scheduled password change.
- In the User certificates management subsection, you can specify which root certificates to install. These certificates can be used, for example, to verify the authenticity of websites or web servers.
- Report on network attacks now includes the MAC address and port of the attacking device.
- A new option to force an internal user to change a password at the next attempt to sign in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- A commercial license is not checked anymore when you export events to a SIEM system in the CEF or LEEF formats.
- When you migrate from one Kaspersky application to another and your current application is password-protected, you can now specify the uninstallation password in the remote installation task.
- Exchange ActiveSync is no longer supported.
Kaspersky Security Center 14.2
Kaspersky Security Center 14.2 has several new features and improvements:
- A new Hardening Guide was released. We highly recommend that you carefully read the guide and follow the security recommendations to configure Kaspersky Security Center and your network infrastructure.
Also, please install the latest update to Kaspersky Security Center. This update includes infrastructure protection features such as two-step verification of user accounts and other improvements.
- Access to Kaspersky servers is now verified automatically. If access to the servers by using the system DNS is not possible, the application uses the public DNS.
- User rights on a virtual Administration Server are available for configuration any time, independently from the primary Administration Server. Also, you can assign primary Server users the rights to manage a virtual Server.
- Kaspersky Security Center now supports work with the following DBMSs:
- PostgreSQL 13.x
- PostgreSQL 14.x
- Postgres Pro 13.x (all editions)
- Postgres Pro 14.x (all editions)
- MariaDB 10.1, 10.4, 10.5
- You can use Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to export policies and tasks to a file, and then import the policies and tasks to Kaspersky Security Center Windows or Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
- The Do not use proxy server option has been removed from the following tasks:
- Download updates to the Administration Server repository
- Download updates to the repositories of distribution points
- To protect client devices in a cloud environment, you can deploy Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows instead of Kaspersky Security for Windows Server. This feature is now available after the release of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.0 for Windows.
- Work with the encryption keys is now limited by the access rights for the General features: Encryption Key Management functional area. Users of Kaspersky Security Center can now export encryption keys if they have the Read right, and can import encryption keys if they have the Write right.
Kaspersky Security Center 14
Kaspersky Security Center 14 has several new features and improvements:
- You can install updates and fix vulnerabilities of third-party software (excluding Microsoft software) in an isolated network. Such networks include Administration Servers and managed devices that have no internet access. To fix vulnerabilities in this kind of network, you need to download required updates by using an Administration Server with internet access, and then transmit the patches to the isolated Administration Servers.
- Connection profiles for out-of-office users have been added for macOS devices. By using connection profiles, you can configure the rules for Network Agents on macOS devices to connect to the same or different Administration Servers, depending on the device location.
- Network Agent can now be installed on devices running Microsoft Windows 10 IoT Enterprise.
- In the Report on threats, you can now filter the threat list to view only those threats that were detected by Cloud Sandbox.
- Kaspersky Security Center now supports Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Linux Nodes 1.3 as a managed application.
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console has several new features and improvements:
- You can configure the Dashboard-only mode for employees who do not manage the network but who want to view the network protection statistics in Kaspersky Security Center (for example, a top manager). When a user has this mode enabled, only a dashboard with a predefined set of widgets is displayed. Thus, he or she can monitor the statistics specified in the widgets, for example, the protection status of all managed devices, the number of recently detected threats, or the list of the most frequent threats in the network.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console now supports Kaspersky Security for iOS as a security application.
- In the task properties, you can specify whether or not you want to apply the task to subgroups and secondary Administration Servers (including virtual ones).
- Kaspersky Security Center now supports Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Linux Nodes 1.3 as a managed application.
Kaspersky Security Center 13.2
Kaspersky Security Center 13.2 has several new features and improvements:
- You can now install Administration Server, Administration Console, Kaspersky Security Center 13.2 Web Console, and Network Agent on the following new operation systems (see the software requirements for details):
- Microsoft Windows 11
- Microsoft Windows 10 21H2 (October 2021 Update)
- Windows Server 2022
- You can use MySQL 8.0 as the database.
- You can deploy Kaspersky Security Center on a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster, to provide high availability of Kaspersky Security Center.
- Kaspersky Security Center now works with IPv6 addresses, as well as IPv4 addresses. Administration Server can poll networks that have devices with IPv6 addresses.
Kaspersky Security Center 13.2 Web Console has several new features and improvements:
- You can now manage mobile devices running Android via Kaspersky Security Center 13.2 Web Console.
- Kaspersky marketplace is available as a new menu section: you can search for a Kaspersky application via Kaspersky Security Center 13.2 Web Console.
- Kaspersky Security Center now supports the following Kaspersky applications:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum 2.0
- Kaspersky Sandbox 2.0
- Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks 3.1
Kaspersky Security Center 13.1
Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 has several new features and improvements:
- The integration with SIEM systems has been improved. You can now export events to SIEM systems via the encrypted channel (TLS). The feature is available for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and MMC-based Administration Console.
- You can now receive patches for the Administration Server as a distribution package, which you can use for future updates to later versions.
- A new section, Alerts, has been added for Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum to Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 Web Console. Several new widgets are also added for working with the threats detected by Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum.
- In Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 Web Console, you can now receive notifications about expiring licenses for Kaspersky applications.
- The response time for Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 Web Console has been decreased.
Kaspersky Security Center 13
The following features are added to Kaspersky Security Center 13 Web Console:
- Implemented two-step verification. You can enable two-step verification to reduce the risk of unauthorized access to Kaspersky Security Center 13 Web Console.
- Implemented domain authentication by using the NTLM and Kerberos protocols (single sign-on). The single sign-on feature allows a Windows user to enable secure authentication in Kaspersky Security Center 13 Web Console without having to re-enter the password on the corporate network.
- You can now configure a plug-in to work with Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response. You can use this integration to view incidents and manage workstations.
- You can now specify settings for Kaspersky Security Center 13 Web Console in the installation wizard of Administration Server.
- Notifications are displayed about new releases of updates and patches. You can install an update immediately or later at any time. You can now install patches for Administration Server via Kaspersky Security Center 13 Web Console.
- When working with tables, you can now specify the order and the width of columns, sort data, and specify the page size.
- You can now open any report by clicking its name.
- Kaspersky Security Center 13 Web Console is now available in the Korean language.
- A new section, Kaspersky announcements, is available in the Monitoring & reporting menu. This section keeps you informed by providing information related to your version of Kaspersky Security Center and the managed applications installed on the managed devices. Kaspersky Security Center periodically updates the information in this section by removing outdated announcements and adding new information. However, you can disable Kaspersky announcements if you want.
- Implemented additional authentication after changing the settings of a user account. You can enable protecting a user account from unauthorized modification. If this option is enabled, modifying user account settings requires authorization by a user with modification rights.
The following features are added to Kaspersky Security Center 13:
- Implemented two-step verification. You can enable two-step verification to reduce the risk of unauthorized access to the Administration Console. If this option is enabled, modifying user account settings requires authorization of the user with the rights for modification. You can now enable or disable two-step verification for KES devices.
- You can send messages to Administration Server over HTTP. A reference guide and a Python library for working with the OpenAPI of Administration Server are now available.
- You can issue a reserve certificate for use in iOS MDM profiles, to ensure seamless switching of managed iOS devices after the iOS MDM Server certificate expires.
- The multi-tenancy applications folder is no longer displayed in Administration Console.
About Kaspersky Security Center
The section contains information about the purpose of Kaspersky Security Center, its main features and components, and ways to purchase Kaspersky Security Center.
Information provided in Online Help may differ from information provided in documents shipped with the application; in this case, Online Help is considered up-to-date. You can proceed to Online Help by clicking links in the application interface, or by clicking the Online Help link in documents. Online Help can be updated without prior notice. You can switch between Online Help and Offline Help if necessary.
Kaspersky Security Center is designed for centralized execution of basic administration and maintenance tasks on an organization's network. The application provides the administrator access to detailed information about the organization's network security level; it allows configuring all the components of protection built using Kaspersky applications.
Kaspersky Security Center is an application aimed at corporate network administrators and employees responsible for protection of devices in a wide range of organizations.
Using Kaspersky Security Center, you can do the following:
- Create a hierarchy of Administration Servers to manage the organization's network, as well as networks at remote offices or client organizations.
The client organization is an organization whose anti-virus protection is ensured by the service provider.
- Create a hierarchy of administration groups to manage a selection of client devices as a whole.
- Manage an anti-virus protection system built based on Kaspersky applications.
- Create images of operating systems and deploy them on client devices over the network, as well as perform remote installation of applications by Kaspersky and other software vendors.
- Remotely manage applications by Kaspersky and other vendors installed on client devices. Install updates, find and fix vulnerabilities.
- Perform centralized deployment of license keys for Kaspersky applications to client devices, monitor their use, and renew licenses.
- Receive statistics and reports about the operation of applications and devices.
- Receive notifications about critical events during the operation of Kaspersky applications.
- Manage mobile devices.
- Manage encryption of information stored on the hard drives of devices and removable drives and users' access to encrypted data.
- Perform inventory of hardware connected to the organization's network.
- Centrally manage files moved to Quarantine or Backup by security applications, as well as manage files for which processing by security applications has been postponed.
You can purchase Kaspersky Security Center through Kaspersky (for example, at https://www.kaspersky.com) or through partner companies.
If you purchase Kaspersky Security Center through Kaspersky, you can copy the application from our website. Information that is required for application activation is sent to you by email after your payment is processed.
Updates functionality (including providing anti-virus signature updates and codebase updates), as well as KSN functionality may not be available in the software in the U.S.
Architecture
This section provides a description of the components of Kaspersky Security Center and their interaction.
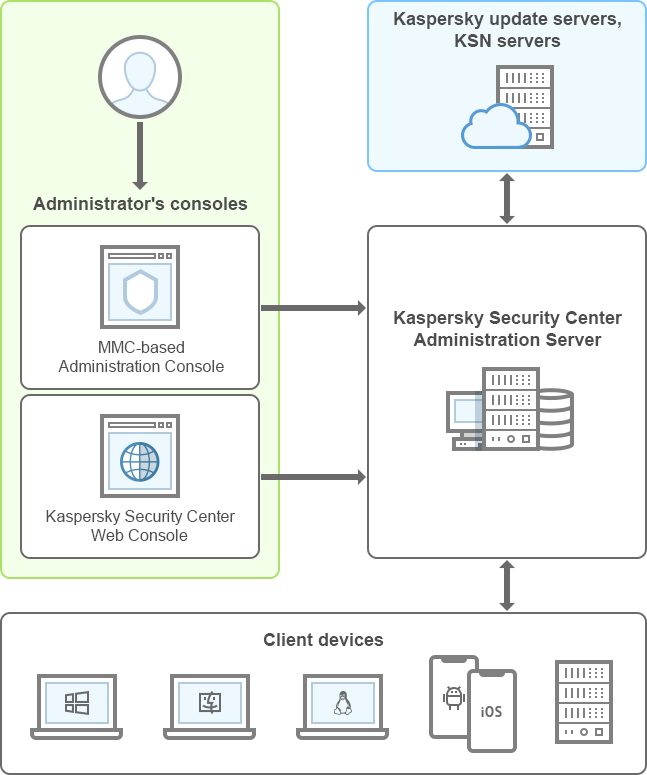
Kaspersky Security Center architecture
Kaspersky Security Center comprises the following main components:
- Administration Console (also referred to as Console). Provides a user interface to the administration services of Administration Server and Network Agent. Administration Console is implemented as a snap-in for Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Administration Console allows remote connection to Administration Server over the internet.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. Provides a web interface for creating and maintaining the protection system of a client organization's network that is managed by Kaspersky Security Center.
- Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server (also referred to as Server). Centralizes storage of information about applications installed on the organization's network and about how to manage them.
- Kaspersky update servers. HTTP(S) servers at Kaspersky from which Kaspersky applications download database and application module updates.
- KSN servers. Servers that contain a Kaspersky database with constantly updated information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software. Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky applications to threats, improves the performance of some protection components, and reduces the likelihood of false positives.
- Client devices. Client company's devices protected by Kaspersky Security Center. Each device that has to be protected must have one of the Kaspersky security applications installed.
Hardware and software requirements
- Administration Server requirements
- Web Console requirements
- Mobile servers requirements
- Administration Console requirements
- Network Agent requirements
Administration Server requirements
Minimum hardware requirements:
- CPU with an operating frequency of 1 GHz or higher. For a 64-bit operating system, the minimum CPU frequency is 1.4 GHz.
- RAM: 4 GB.
- Available disk space: 10 GB. When Vulnerability and patch management is used, at least 100 GB of free disk space must be available.
For deployment in cloud environments, the requirements for Administration Server and database server are the same as the requirements for physical Administration Server (depending on how many devices you want to manage).
Software requirements:
- Microsoft Data Access Components (MDAC) 2.8
- Microsoft Windows DAC 6.0
- Microsoft Windows Installer 4.5
The following operating systems are supported:
- Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard/Datacenter/Essentials/Foundation/Server Core 64-bit
- Windows Server 2016 Standard/Datacenter/Essentials/Server Core (Installation Option) (LTSB) 64-bit
- Windows Server 2019 Standard/Datacenter/Core 64-bit
- Windows Server 2022 Standard/Datacenter/Core 64-bit
- Windows Storage Server 2019 64-bit
The following virtualization platforms are supported:
- VMware vSphere 6.7
- VMware vSphere 7.0
- Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2019 64-bit
- Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2022 64-bit
- Citrix XenServer 7.1 LTSR
- Citrix XenServer 8.x
- Parallels Desktop 18
- Oracle VM VirtualBox 7.x
The following database servers are supported (can be installed on a different device):
- Microsoft SQL Server 2016 (all editions) 64-bit
- Microsoft SQL Server 2017 (all editions) on Windows/Linux 64-bit
- Microsoft SQL Server 2019 (all editions) on Windows/Linux 64-bit (requires additional actions)
- Microsoft SQL Server 2022 (all editions) on Windows/Linux 64-bit
- MySQL 5.7 Community 32-bit/64-bit
- MySQL Standard Edition 8.0 (release 8.0.20 and later) 32-bit/64-bit
- MySQL Enterprise Edition 8.0 (release 8.0.20 and later) 32-bit/64-bit
- MariaDB 10.5 (build 10.5.27 and later) 32-bit/64-bit
- MariaDB Galera Cluster 10.3 32-bit/64-bit with InnoDB storage engine
- PostgreSQL 13.x 64-bit
- PostgreSQL 14.x 64-bit
- PostgreSQL 15.x 64-bit
- Postgres Pro 13.x Windows/Linux 64-bit
- Postgres Pro 14.x Windows/Linux 64-bit
Refer to the following topic for details and limitations: Selecting a DBMS.
SIEM and other information management systems:
- HP (Micro Focus) ArcSight ESM 7.0
- IBM QRadar 7.3
- Splunk 7.1
Web Console requirements
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server
Minimum hardware requirements:
- CPU: 4 cores, operating frequency of 2.5 GHz
- RAM: 8 GB
- Available disk space: 40 GB
Minimum requirements for the Administration Server certificate:
- Certificate signature algorithm SHA-2
- Minimum key length 2048
If you need to reissue the certificate, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Knowledge Base.
Operating systems supported by Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server
Operating systems. Microsoft Windows (64-bit versions only)
|
Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard/Datacenter/Foundation/Essentials/Server Core Windows Server 2016 Standard/Datacenter/Essentials/Server Core (Installation Option) (LTSB) Windows Server 2019 Standard/Datacenter/Core Windows Server 2022 Standard/Datacenter/Core Windows Storage Server 2019 |
Virtualization platforms |
VMware vSphere 6.7 VMware vSphere 7.0 Citrix XenServer 7.1 LTSR Citrix XenServer 8.x Parallels Desktop 18 Oracle VM VirtualBox 7.x |
Client devices
For a client device, use of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console requires only a browser.
The minimum screen resolution is 1366x768 pixels.
The hardware and software requirements for the device are identical to the requirements of the browser that is used with Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Browsers:
- Google Chrome 128.0.6613.120 or later
- Microsoft Edge 128.0.2739.67 or later
- Safari 17.6 on macOS
- "Yandex" Browser 24.7.3.1081 or later
- Mozilla Firefox Extended Support Release 115.14.0 or later
Mobile servers requirements
iOS Mobile Device Management (iOS MDM) Server
Hardware requirements:
- CPU with an operating frequency of 1 GHz or higher. For a 64-bit operating system, the minimum CPU frequency is 1.4 GHz.
- RAM: 2 GB.
- Available disk space: 2 GB.
Software requirements: Microsoft Windows (the version of the supported operating system is defined by the Administration Server requirements).
Page top
Administration Console requirements
Hardware requirements:
- CPU with an operating frequency of 1 GHz or higher. For a 64-bit operating system, the minimum CPU frequency is 1.4 GHz.
- RAM: 512 MB.
- Available disk space: 1 GB.
Software requirements:
- Microsoft Windows operating system (supported version of the operating system is determined by the requirements of Administration Server):
- Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard/Datacenter/Foundation/Essentials 64-bit
- Windows Server 2016 Standard/Datacenter/Essentials (LTSB) 64-bit
- Windows Server 2019 Standard/Datacenter 64-bit
- Windows Server 2022 Standard/Datacenter 64-bit
- Windows Storage Server 2019 64-bit
- Microsoft Management Console 2.0
- Microsoft Windows Installer 4.5
- Microsoft Internet Explorer 11.0 running on:
- Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2
- Microsoft Windows Server 2016
- Microsoft Windows Server 2019
- Microsoft Windows Storage Server 2019
- Microsoft Edge running on Microsoft Windows Server 2022 Standard
Network Agent requirements
Minimum hardware requirements:
- CPU with an operating frequency of 1 GHz or higher. For a 64-bit operating system, the minimum CPU frequency is 1.4 GHz.
- RAM: 512 MB.
- Available disk space: 1 GB.
Software requirement for Linux-based devices: the Perl language interpreter version 5.10 or later must be installed.
Operating systems supported by Network Agent
Operating systems. Microsoft Windows |
Windows Embedded POSReady 2009 with latest Service Pack 32-bit Windows Embedded 7 Standard with Service Pack 1 32-bit/64-bit Windows Embedded 8.1 Industry Pro 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 Enterprise 2015 LTSB 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 Enterprise 2016 LTSB 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 IoT Enterprise 2015 LTSB 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 IoT Enterprise 2016 LTSB 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 Enterprise 2019 LTSC 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 IoT Enterprise version 1703 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 IoT Enterprise version 1709 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 IoT Enterprise version 1803 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 IoT Enterprise version 1809 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 20H2 IoT Enterprise 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 21H2 IoT Enterprise 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 IoT Enterprise 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 IoT Enterprise version 1909 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 IoT Enterprise LTSC 2021 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 IoT Enterprise version 1607 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 TH1 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 TH2 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 RS1 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 RS2 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 RS3 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 RS4 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 RS5 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 RS6 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 19H1 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 19H2 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 20H1 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 20H2 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 21H1 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 21H2 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 10 22H2 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 32-bit/64-bit Windows 11 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 64-bit Windows 11 22H2 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 64-bit Windows 11 23H2 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 64-bit Windows 11 24H2 Home/Pro/Pro for Workstations/Enterprise/Education 64-bit Windows 8 Pro/Enterprise 32-bit/64-bit Windows 8.1 Pro/Enterprise 32-bit/64-bit Windows 7 Home/Pro/Enterprise/Ultimate with Service Pack 1 32-bit/64-bit Microsoft Windows XP Professional with Service Pack 2 32-bit/64-bit (supported by Network Agent version 10.5.1781 only) Windows XP Professional with Service Pack 3 and later 32-bit (supported by Network Agent version 14.0.0.20023) Windows XP Professional for Embedded Systems with Service Pack 3 32-bit (supported by Network Agent version 14.0.0.20023) Windows MultiPoint Server 2011 Standard/Premium 64-bit Windows Server 2008 Standard/Enterprise/Datacenter/Foundation with Service Pack 2 32-bit/64-bit Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard/Datacenter/Enterprise/Foundation/ with Service Pack 1 and later 64-bit Windows Server 2012 Standard/Datacenter/Essentials/Foundation/Server Core 64-bit Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard/Datacenter/Essentials/Foundation/Server Core 64-bit Windows Server 2016 Standard/Datacenter/Essentials/Server Core (Installation Option) (LTSB) 64-bit Windows Server 2019 Standard/Datacenter/Core 64-bit Windows Server 2019 RS5 Standard/Essentials 64-bit Windows Server 2022 Standard/Datacenter/Core 64-bit Windows Server 2022 21H2 Standard/Datacenter 64-bit Windows Storage Server 2019 64-bit |
Operating systems. Linux |
Debian GNU/Linux 10.х (Buster) 32-bit/64-bit Debian GNU/Linux 11.х (Bullseye) 32-bit/64-bit Debian GNU/Linux 12 (Bookworm) 32-bit/64-bit Ubuntu Server 18.04 LTS (Bionic Beaver) 64-bit Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa) 64-bit Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS (Jammy Jellyfish) 64-bit Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS ARM 64-bit Ubuntu Server 24.04 LTS (Noble Numbat) 64-bit CentOS 6.7 and later 32-bit CentOS 6.х (up to 6.6) 32-bit/64-bit CentOS 7.x 64-bit CentOS Stream 8 64-bit CentOS Stream 9 64-bit CentOS Stream 9 ARM 64-bit Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 6.x 32-bit/64-bit Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 7.x 64-bit Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 8.x 64-bit Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 9.x 64-bit SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 (all Service Packs) 64-bit SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 (all Service Packs) 64-bit SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 (all Service Packs) ARM 64-bit openSUSE 15 64-bit EulerOS 2.0 SP10 64-bit EulerOS 2.0 SP10 ARM 64-bit Astra Linux Special Edition RUSB.10015-01 (operational update 1.5) 64-bit Astra Linux Special Edition RUSB.10015-01 (operational update 1.6) 64-bit Astra Linux Special Edition RUSB.10015-16 (release 1) (operational update 1.6) 64-bit Astra Linux Special Edition RUSB.10015-17 (operational update 1.7.3) 64-bit Astra Linux Special Edition RUSB.10015-01 (operational update 1.7) 64-bit Astra Linux Special Edition RUSB.10015-01 (operational update 1.8) 64-bit Astra Linux Special Edition RUSB.10015-37 (operational update 7.7) 64-bit Astra Linux Special Edition RUSB.10152-02 (operational update 4.7) ARM 64-bit Astra Linux Common Edition (operational update 2.12) 64-bit ALT Workstation 10.1 64-bit ALT Server 10.1 64-bit ALT Education 10.1 64-bit ALT SP Server 10 32-bit/64-bit ALT SP Server 10 ARM 64-bit ALT SP Workstation 10 32-bit/64-bit ALT SP Workstation 10 ARM 64-bit ALT Server 10 64-bit ALT Server 10 ARM 64-bit ALT Workstation 10 32-bit/64-bit ALT 8 SP Workstation (8.4) ARM 64-bit ALT 8 SP Server (8.4) ARM 64-bit ALT 8 SP Server (LKNV.11100-01) 32-bit/64-bit ALT 8 SP Server (LKNV.11100-02) 32-bit/64-bit ALT 8 SP Server (LKNV.11100-03) 32-bit/64-bit ALT 8 SP Workstation (LKNV.11100-01) 32-bit/64-bit ALT 8 SP Workstation (LKNV.11100-02) 32-bit/64-bit ALT 8 SP Workstation (LKNV.11100-03) 32-bit/64-bit Mageia 4 32-bit Oracle Linux 7 64-bit Oracle Linux 8 64-bit Oracle Linux 9 64-bit Linux Mint 20.x 64-bit Linux Mint 21.1 and later 64-bit AlterOS 7.5 and later 64-bit GosLinux IC6/7.17 64-bit GosLinux IC6/7.2 64-bit SberOS 3.3.1 64-bit Platform V SberLinux OS Server (SLO) 8.8 64-bit Platform V SberLinux OS Server (SLO) 8.9.2 64-bit RED OS 7.3 ARM 64-bit RED OS 7.3 Server 64-bit RED OS 7.3 Certified Edition 64-bit RED OS 8 Certified Edition 64-bit ROSA Enterprise Linux Server 7.9 64-bit ROSA Enterprise Linux Desktop 7.9 64-bit ROSA COBALT 7.9 64-bit ROSA CHROME 12 64-bit AlmaLinux 8 and later 64-bit AlmaLinux 9 and later 64-bit Rocky Linux 8 and later 64-bit Rocky Linux 9 and later 64-bit Atlant, Alcyone build, version 2022.02 64-bit MSVSPHERE 9.2 SERVER 64-bit MSVSPHERE 9.2 ARM 64-bit SynthesisM Server 8.6 64-bit SynthesisM Client 8.6 64-bit OSnova 2.10 64-bit Kylin 10 64-bit EMIAS 1.0 64-bit Amazon Linux 2 64-bit MosOS 15.4 Arbat 64-bit OS MES (Moscow Electronic School) 64-bit |
Operating systems. macOS |
macOS 12.x macOS 13.x macOS 14.x |
For Network Agent, the Apple Silicon (M1) architecture is also supported, as well as Intel.
The following virtualization platforms are supported:
- VMware vSphere 6.7
- VMware vSphere 7.0
- Parallels Desktop 18
- Oracle VM VirtualBox 7.x
- Citrix XenServer 7.1 LTSR
- Citrix XenServer 8.x
- Kernel-based Virtual Machine (all Linux operating systems supported by Network Agent)
On the devices running Windows 10 version RS4 or RS5, Kaspersky Security Center might be unable to detect some vulnerabilities in folders where case sensitivity is enabled.
Before installing Network Agent on the devices running Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2, make sure that you have installed the security update KB3063858 for OS Windows (Security Update for Windows 7 (KB3063858), Security Update for Windows 7 for x64-based Systems (KB3063858), Security Update for Windows Server 2008 (KB3063858), Security Update for Windows Server 2008 x64 Edition (KB3063858), Security Update for Windows Server 2008 R2 x64 Edition (KB3063858).
In Microsoft Windows XP, Network Agent might not perform some operations correctly.
You can install or update Network Agent for Windows XP in Microsoft Windows XP only. The supported editions of Microsoft Windows XP and their corresponding versions of the Network Agent are listed in the list of supported operating systems. You can download the required version of the Network Agent for Microsoft Windows XP from this page.
We recommend that you install the same version of the Network Agent as Kaspersky Security Center.
Kaspersky Security Center fully supports Network Agent of the same or newer versions.
Network Agent for macOS is provided together with Kaspersky security application for this operating system.
Page top
Compatible Kaspersky applications and solutions
Kaspersky Security Center supports centralized deployment and management of all Kaspersky applications and solutions that are currently supported. The table below shows what Kaspersky applications and solutions are supported by MMC-based Administration Console and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. To find out versions of the applications and solutions, refer to the Product Support Lifecycle webpage.
List of Kaspersky applications and solutions supported by Kaspersky Security Center
Name of Kaspersky application or solution |
Supported by MMC-based Administration Console |
Supported by Kaspersky Security Center Web Console |
|---|---|---|
For workstations |
||
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows |
|
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux |
|
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux Elbrus Edition |
|
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac |
|
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent |
|
|
Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows |
|
|
Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Linux |
|
|
For industrial solutions |
||
Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Nodes |
|
|
Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Linux Nodes |
|
|
Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks (centralized deployment is not supported) |
|
|
For mobile devices |
||
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android |
|
|
Kaspersky Security for iOS |
|
|
For file servers |
||
Kaspersky Security for Windows Server |
|
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows |
|
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux |
|
|
For virtual environments |
||
Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent |
|
|
Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Agentless |
|
|
For mail and collaboration servers |
||
Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers |
|
|
For detection of targeted attacks |
||
Kaspersky Sandbox Server |
|
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum |
|
|
Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response |
|
|
For KasperskyOS devices |
||
Kaspersky IoT Secure Gateway |
|
|
KasperskyOS Thin Client |
|
|
Reputation databases |
||
Kaspersky Private Security Network |
|
|
Licenses and features of Kaspersky Security Center 15.1
Kaspersky Security Center requires a license for some of its features.
The table below shows which license covers what features of Kaspersky Security Center.
To enable the features of Kaspersky Security Center, you must activate Administration Server by adding an Administration Server license key.
You have to manually add a license key for each Administration Server.
Licenses and Kaspersky Security Center features
Features of Kaspersky Security Center |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mobile device management (that is, management of users' iOS and Android devices) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configure cloud environment for work in cloud environments such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exporting events to SIEM systems: QRadar by IBM and ArcSight by Micro Focus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
About compatibility of Kaspersky Security Center components
In the table below, you can find information about the compatibility of Kaspersky Security Center components.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Security Center components
Component |
Compatible with |
|---|---|
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 Administration Server |
|
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 Web Console |
Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server of the following versions: 15.1 and 14.2. |
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 Primary Administration Server |
Secondary Administration Servers:
|
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 Secondary Administration Server |
Primary Administration Servers:
|
We recommend that you use the latest version of both Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. Otherwise, the functionality of Kaspersky Security Center may be limited. You can install and upgrade Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console independently. In this case, you have to ensure that the version of the installed Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is compatible with the version of Administration Server to which you connect.
If you have the latest version of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and the previous version of Kaspersky Security Center, and an error occurs during domain authentication, the error text will contain a default message.
Page top
Comparison of Kaspersky Security Center: Windows-based vs. Linux-based
Kaspersky provides Kaspersky Security Center as an on-premises solution for two platforms—Windows and Linux. In the Windows-based solution, you install Administration Server on a Windows device, and the Linux-based solution has the Administration Server version that is designed to be installed on a Linux device. This Online Help contains information about Kaspersky Security Center Windows. For detailed information about the Linux-based solution, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Linux Online Help.
The table below lets you compare the main features of Kaspersky Security Center as a Windows-based solution and as a Linux-based solution.
Feature comparison of Kaspersky Security Center working as a Windows-based solution and Linux-based solution
Feature or property |
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Windows-based solution |
Linux-based solution |
Administration Server location |
On-premises |
On-premises |
Database management system (DBMS) location |
On-premises |
On-premises |
Operating system to install Administration Server on |
Windows |
Linux |
Administration console type |
On-premises and web-based |
Web-based |
Operating system to install the web-based administration console on |
Windows or Linux |
Linux |
Hierarchy of Administration Servers |
|
|
Administration group hierarchy |
|
|
Network polling |
|
(by IP ranges, domain controllers, Samba 4 Active Directory, Microsoft Active Directory) |
Maximum number of managed devices |
100,000 |
50,000 (with PostgreSQL and Postgres Pro) |
Protection of Windows, macOS, and Linux-managed devices |
|
|
Protection of mobile devices |
|
|
Protection of virtual machines |
|
|
Protection of public cloud infrastructure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Application policies |
|
|
Tasks for Kaspersky applications |
|
|
Kaspersky Security Network |
|
|
KSN Proxy |
|
|
Kaspersky Private Security Network |
|
|
Centralized deployment of license keys for Kaspersky applications |
|
|
Updating anti-virus databases automatically |
|
|
Support for virtual Administration Servers |
|
|
Installing third-party software updates and fixing third-party software vulnerabilities |
|
|
Notifications about events that occurred on managed devices |
|
|
Creating and managing user accounts |
|
|
Sign-in to the console by using domain authentication |
|
(Single Sign-on is not supported) |
Integration with SIEM systems |
|
(by using Syslog only) |
Monitoring the policies and tasks status |
|
|
Deployment of the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster |
|
|
Installing Administration Server on a Windows Server failover cluster |
|
|
Using SNMP to send Administration Server statistics to third-party applications |
|
|
Remote diagnostics of client devices |
|
|
Remote connection to the desktop of a client device |
|
|
Managing object revisions |
|
|
Updating Kaspersky applications automatically |
|
|
Deployment of operating systems on client devices |
|
|
Web Server for publishing installation packages and other files |
|
|
Viewing and working with alerts detected by Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum |
|
|
Using Administration Server as WSUS server |
|
|
Integration with Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response |
|
|
Support for Adaptive Anomaly Control |
|
|
Support of clusters and server arrays in administration groups |
|
|
Managing third-party licenses |
|
|
About Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console
Using Kaspersky Security Center as an on-premises application means that you install Kaspersky Security Center, including Administration Server, on a local device and manage the network security system through the Microsoft Management Console-based Administration Console (available only in Kaspersky Security Center Windows) or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
However, you can use Kaspersky Security Center as a cloud service instead. In this case Kaspersky Security Center is installed and maintained for you by Kaspersky experts in the cloud environment, and Kaspersky gives you access to the Administration Server as a service. You manage the network security system through the cloud-based Administration Console named Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. This console has an interface similar to the interface of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
The interface and documentation of Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console are available in the following languages:
- English
- French
- German
- Italian
- Japanese
- Portuguese (Brazil)
- Russian
- Simplified Chinese
- Spanish
- Spanish (LATAM)
- Traditional Chinese
More information about Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console and its features is available in the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console documentation and in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business documentation.
Page top
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1
This section provides information about using Kaspersky Security Center 15.1.
Information provided in Online Help may differ from information provided in documents shipped with the application; in this case, Online Help is considered up-to-date. You can proceed to Online Help by clicking links in the application interface, or by clicking the Online Help link in documents. Online Help can be updated without prior notice. You can switch between Online Help and Offline Help if necessary.
Administration Server
Kaspersky Security Center components enable remote management of Kaspersky applications installed on client devices.
Devices with the Administration Server component installed will be referred to as Administration Servers (also referred to as Servers). Administration Servers must be protected, including physical protection, against any unauthorized access.
Administration Server is installed on a device as a service with the following set of attributes:
- With the name "Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server"
- Set to start automatically when the operating system starts
- With the LocalSystem account or the user account selected during the installation of Administration Server
Administration Server performs the following functions:
- Storage of the administration groups' structure
- Storage of information about the configuration of client devices
- Organization of repositories for application distribution packages
- Remote installation of applications to client devices and removal of applications
- Updating application databases and software modules of Kaspersky applications
- Management of policies and tasks on client devices
- Storage of information about events that have occurred on client devices
- Generation of reports on the operation of Kaspersky applications
- Deployment of license keys to client devices and storing information about the license keys
- Forwarding notifications about the progress of tasks (such as detection of viruses on a client device)
Naming Administration Servers in the application interface
In the interface of the MMC-based Administration Console and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, Administration Servers can have the following names:
- Name of the Administration Server device, for example: "device_name" or "Administration Server: device_name".
- IP address of the Administration Server device, for example: "IP_address" or "Administration Server: IP_address".
- Secondary Administration Servers and virtual Administration Servers have custom names that you specify when you connect a virtual or a secondary Administration Server to the primary Administration Server.
- If you use Kaspersky Security Center Web Console installed on a Linux device, the application displays the names of the Administration Servers that you specified as trusted in the response file.
You can connect to Administration Server by using Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Hierarchy of Administration Servers
Administration Servers can be arranged in a hierarchy. Each Administration Server can have several secondary Administration Servers (referred to as secondary Servers) on different nesting levels of the hierarchy. The nesting level for secondary Servers is unrestricted. The administration groups of the primary Administration Server will then include the client devices of all secondary Administration Servers. Thus, isolated and independent sections of networks can be managed by different Administration Servers which are in turn managed by the primary Server.
Virtual Administration Servers are a particular case of secondary Administration Servers.
The hierarchy of Administration Servers can be used to do the following:
- Decrease the load on Administration Server (compared to a single installed Administration Server for an entire network).
- Decrease intranet traffic and simplify work with remote offices. You do not have to establish connections between the primary Administration Server and all networked devices, which may be located, for example, in different regions. It is sufficient to install a secondary Administration Server in each network segment, distribute devices among administration groups of secondary Servers, and establish connections between the secondary Servers and the primary Server over fast communication channels.
- Distribute responsibilities among the anti-virus security administrators. All capabilities for centralized management and monitoring of the anti-virus security status in corporate networks remain available.
- How service providers use Kaspersky Security Center. The service provider only needs to install Kaspersky Security Center and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. To manage a large number of client devices of various organizations, a service provider can add virtual Administration Servers to the hierarchy of Administration Servers.
Each device included in the hierarchy of administration groups can be connected to one Administration Server only. You must independently monitor the connection of devices to Administration Servers. Use the feature for device search in administration groups of different Servers based on network attributes.
Virtual Administration Server
Virtual Administration Server (also referred to as virtual Server) is a component of Kaspersky Security Center intended for managing anti-virus protection of the network of a client organization.
Virtual Administration Server is a particular case of a secondary Administration Server and has the following restrictions as compared with a physical Administration Server:
- Virtual Administration Server can be created only on a primary Administration Server.
- Virtual Administration Server uses the primary Administration Server database in its operation. Data backup and restoration tasks, as well as update scan and download tasks, are not supported on a virtual Administration Server.
- Virtual Server does not support creation of secondary Administration Servers (including virtual Servers).
In addition, virtual Administration Server has the following restrictions:
- In the virtual Administration Server properties window, the number of sections is limited.
- To install Kaspersky applications remotely on client devices managed by the virtual Administration Server, you must make sure that Network Agent is installed on one of the client devices, in order to ensure communication with the virtual Administration Server. Upon first connection to the virtual Administration Server, the device is automatically assigned as a distribution point, thus functioning as a connection gateway between the client devices and the virtual Administration Server.
- A virtual Server can poll the network only through distribution points.
- To restart a malfunctioning virtual Server, Kaspersky Security Center restarts the primary Administration Server and all virtual Administration Servers.
- Users created on a virtual Server cannot be assigned a role on the Administration Server.
The administrator of a virtual Administration Server has all privileges on this particular virtual Server.
Page top
Mobile Device Server
Mobile Device Server is a component of Kaspersky Security Center that provides access to mobile devices and allows managing them through Administration Console. Mobile Device Server receives information about mobile devices and stores their profiles.
Kaspersky Security Center includes iOS MDM Server as a Mobile Device Server. This Mobile Device Server is used for managing mobile devices that support Apple Push Notification service (APNs).
Mobile Device Servers of Kaspersky Security Center allow you to manage the following objects:
- An individual mobile device.
- Several mobile devices.
- Several mobile devices connected to a cluster of servers simultaneously. After connecting to a cluster of servers, the mobile devices server installed in this cluster is displayed in Administration Console as a single server.
Web Server
Kaspersky Security Center Web Server (hereinafter also referred to as Web Server) is a component of Kaspersky Security Center that is installed together with Administration Server. Web Server is designed for transmission, over a network, of stand-alone installation packages, iOS MDM profiles, and files from a shared folder.
When you create a stand-alone installation package, it is automatically published on Web Server. The link for downloading the stand-alone package is displayed in the list of created stand-alone installation packages. If necessary, you can cancel publication of the stand-alone package or you can publish it on Web Server again.
When you create an iOS MDM profile for a user's mobile device, it is also automatically published on Web Server. The published profile is automatically deleted from Web Server as soon as it is successfully installed on the user's mobile device.
The shared folder is used for storage of information that is available to all users whose devices are managed through the Administration Server. If a user has no direct access to the shared folder, he or she can be given information from that folder by means of Web Server.
To provide users with information from a shared folder by means of Web Server, the administrator must create a subfolder named "public" in the shared folder and paste the relevant information into it.
The syntax of the information transfer link is as follows:
https://<Web Server name>:<HTTPS port>/public/<object>
where:
<Web Server name>is the name of Kaspersky Security Center Web Server.<HTTPS port>is an HTTPS port of Web Server that has been defined by the Administrator. The HTTPS port can be set in the Web Server section of the properties window of Administration Server. The default port number is 8061.<object>is the subfolder or file to which the user has access.
The administrator can send the new link to the user in any convenient way, such as by email.
By using this link, the user can download the required information to a local device.
Page top
Network Agent
Interaction between Administration Server and devices is performed by the Network Agent component of Kaspersky Security Center. Network Agent must be installed on all devices on which Kaspersky Security Center is used to manage Kaspersky applications.
Network Agent is installed on a device as a service, with the following set of attributes:
- With the name "Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent"
- Set to start automatically when the operating system starts
- Using the LocalSystem account
A device that has Network Agent installed is called a managed device or device.
You can install Network Agent on a Windows, Linux, or Mac device. You can get the component from one of the following sources:
- Installation package in Administration Server storage (you must have Administration Server installed)
- Installation package located at Kaspersky web servers
You do not have to install Network Agent on the device where you install Administration Server, because the server version of Network Agent is automatically installed together with Administration Server.
The name of the process that Network Agent starts is klnagent.exe.
Network Agent synchronizes the managed device with the Administration Server. We recommend that you set the synchronization interval (also referred to as the heartbeat) to 15 minutes per 10,000 managed devices.
Administration groups
An administration group (hereinafter also referred to as group) is a logical set of managed devices combined on the basis of a specific trait for the purpose of managing the grouped devices as a single unit within Kaspersky Security Center.
All managed devices within an administration group are configured to do the following:
- Use the same application settings (which you can specify in group policies).
- Use a common operating mode for all applications through the creation of group tasks with specified settings. Examples of group tasks include creating and installing a common installation package, updating the application databases and modules, scanning the device on demand, and enabling real-time protection.
A managed device can belong to only one administration group.
You can create hierarchies that have any degree of nesting for Administration Servers and groups. A single hierarchy level can include secondary and virtual Administration Servers, groups, and managed devices. You can move devices from one group to another without physically moving them. For example, if a worker's position in the enterprise changes from that of accountant to developer, you can move this worker's device from the Accountants administration group to the Developers administration group. Thereafter, the device will automatically receive the application settings required for developers.
Managed device
A managed device is a device running Windows, Linux, or macOS on which Network Agent is installed, or a mobile device on which a Kaspersky security application is installed. You can manage such devices by creating tasks and policies for applications installed on these devices. You can also receive reports from managed devices.
You can make a non-mobile managed device function as a distribution point and as a connection gateway.
A device can be managed by only one Administration Server. One Administration Server can manage up to 100,000 devices, including mobile devices.
Page top
Unassigned device
An unassigned device is a device on the network that has not been included in any administration group. You can perform some actions on unassigned devices, for example, move them to administration groups or install applications on them.
When a new device is discovered on your network, this device goes to the Unassigned devices administration group. You can configure rules for devices to be moved automatically to other administration groups after the devices are discovered.
Page top
Administrator's workstation
Administrator's workstation is a device on which Administration Console is installed or that you use to open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. Administrators can use these devices for centralized remote management of Kaspersky applications installed on client devices.
After Administration Console is installed on your device, its icon appears, allowing you to start Administration Console. Find it in the Start → Programs → Kaspersky Security Center menu.
There are no restrictions on the number of administrator's workstations. From any administrator's workstation you can manage administration groups of several Administration Servers on the network at once. You can connect an administrator's workstation to an Administration Server (physical or virtual) of any level of the hierarchy.
You can include an administrator's workstation in an administration group as a client device.
Within the administration groups of any Administration Server, the same device can function as an Administration Server client, an Administration Server, or an administrator's workstation.
Page top
Management plug-in
Kaspersky applications are managed through Administration Console by using a dedicated component named management plug-in. Each Kaspersky application that can be managed through Kaspersky Security Center includes a management plug-in.
Using the application management plug-in, you can perform the following actions in Administration Console:
- Creating and editing application policies and settings, as well as the settings of application tasks.
- Obtaining information about application tasks, application events, as well as application operation statistics received from client devices.
You can download management plug-ins from the Kaspersky Technical Support webpage.
Management web plug-in
A special component—the management web plug-in—is used for remote administration of Kaspersky software by means of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. Hereinafter, a management web plug-in is also referred to as a management plug-in. A management plug-in is an interface between Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and a specific Kaspersky application. With a management plug-in, you can configure tasks and policies for the application.
You can download management web plug-ins from the Kaspersky Technical Support webpage.
The management plug-in provides the following:
- Interface for creating and editing application tasks and settings
- Interface for creating and editing policies and policy profiles for remote and centralized configuration of Kaspersky applications and devices
- Transmission of events generated by the application
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console functions for displaying operational data and events of the application, and statistics relayed from client devices
Policies
A policy is a set of Kaspersky application settings that are applied to an administration group and its subgroups. You can install several Kaspersky applications on the devices of an administration group. Kaspersky Security Center provides a single policy for each Kaspersky application in an administration group. A policy has one of the following statuses (see the table below):
The status of the policy
Status |
Description |
|---|---|
Active |
The current policy that is applied to the device. Only one policy may be active for a Kaspersky application in each administration group. Devices apply the settings values of an active policy for a Kaspersky application. |
Inactive |
A policy that is not currently applied to a device. |
Out-of-office |
If this option is selected, the policy becomes active when the device leaves the corporate network. |
Policies function according to the following rules:
- Multiple policies with different values can be configured for a single application.
- Only one policy can be active for the current application.
- You can activate an inactive policy when a specific event occurs. For example, you can enforce stricter anti-virus protection settings during virus outbreaks.
- A policy can have child policies.
Generally, you can use policies as preparations for emergency situations, such as a virus attack. For example, if there is an attack via flash drives, you can activate a policy that blocks access to flash drives. In this case, the current active policy automatically becomes inactive.
In order to prevent maintaining multiple policies, for example, when different occasions assume changing of several settings only, you may use policy profiles.
A policy profile is a named subset of policy settings values that replaces the settings values of a policy. A policy profile affects the effective settings formation on a managed device. Effective settings are a set of policy settings, policy profile settings, and local application settings that are currently applied for the device.
Policy profiles function according to the following rules:
- A policy profile takes an effect when a specific activation condition occurs.
- Policy profiles contain values of settings that differ from the policy settings.
- Activation of a policy profile changes the effective settings of the managed device.
- A policy can include a maximum of 100 policy profiles.
Policy profiles
Sometimes it may be necessary to create several instances of a single policy for different administration groups; you might also want to modify the settings of those policies centrally. These instances might differ by only one or two settings. For example, all the accountants in an enterprise work under the same policy—but senior accountants are allowed to use flash drives, while junior accountants are not. In this case, applying policies to devices only through the hierarchy of administration groups can be inconvenient.
To help you avoid creating several instances of a single policy, Kaspersky Security Center enables you to create policy profiles. Policy profiles are necessary if you want devices within a single administration group to run under different policy settings.
A policy profile is a named subset of policy settings. This subset is distributed on target devices together with the policy, supplementing it under a specific condition called the profile activation condition. Profiles only contain settings that differ from the "basic" policy, which is active on the managed device. Activation of a profile modifies the settings of the "basic" policy that were initially active on the device. The modified settings take values that have been specified in the profile.
Tasks
Kaspersky Security Center manages Kaspersky security applications installed on devices by creating and running tasks. Tasks are required for installing, launching, and stopping applications, scanning files, updating databases and software modules, and performing other actions on applications.
Tasks for a specific application can be created only if the management plug-in for that application is installed.
Tasks can be performed on the Administration Server and on devices.
The following tasks are performed on the Administration Server:
- Automatic distribution of reports
- Downloading of updates to the repository of the Administration Server
- Backup of Administration Server data
- Maintenance of the database
- Windows Update synchronization
- Creation of an installation package based on the operating system (OS) image of a reference device
The following types of tasks are performed on devices:
- Local tasks—Tasks that are performed on a specific device
Local tasks can be modified either by the administrator, by using Administration Console tools, or by the user of a remote device (for example, through the security application interface). If a local task has been modified simultaneously by the administrator and the user of a managed device, the changes made by the administrator will take effect because they have a higher priority.
- Group tasks—Tasks that are performed on all devices of a specific group
Unless otherwise specified in the task properties, a group task also affects all subgroups of the selected group. A group task also affects (optionally) devices that have been connected to secondary and virtual Administration Servers deployed in the group or any of its subgroups.
- Global tasks—Tasks that are performed on a set of devices, regardless of whether they are included in any group
For each application, you can create any number of group tasks, global tasks, or local tasks.
You can make changes to the settings of tasks, view the progress of tasks, and copy, export, import, and delete tasks.
A task is started on a device only if the application for which the task was created is running.
Results of tasks are saved in the Microsoft Windows event log and the Kaspersky Security Center event log, both centrally on the Administration Server and locally on each device.
Do not include private data in task settings. For example, avoid specifying the domain administrator password.
Task scope
The scope of a task is the set of devices on which the task is performed. The types of scope are as follows:
- For a local task, the scope is the device itself.
- For an Administration Server task, the scope is the Administration Server.
- For a group task, the scope is the list of devices included in the group.
When creating a global task, you can use the following methods to specify its scope:
- Specifying certain devices manually.
You can use an IP address (or IP range), NetBIOS name, or DNS name as the device address.
- Importing a list of devices from a TXT file with the device addresses to be added (each address must be placed on an individual line).
If you import a list of devices from a file or create a list manually, and if devices are identified by their names, the list can only contain devices for which information has already been entered into the Administration Server database. Moreover, the information must have been entered when those devices were connected or during device discovery.
- Specifying a device selection.
Over time, the scope of a task changes as the set of devices included in the selection change. A selection of devices can be made on the basis of device attributes, including software installed on a device, and on the basis of tags assigned to devices. Device selection is the most flexible way to specify the scope of a task.
Tasks for device selections are always run on a schedule by the Administration Server. These tasks cannot be run on devices that lack connection to the Administration Server. Tasks whose scope is specified by using other methods are run directly on devices and therefore do not depend on the device connection to the Administration Server.
Tasks for device selections are not run on the local time of a device; instead, they are run on the local time of the Administration Server. Tasks whose scope is specified by using other methods are run on the local time of a device.
How local application settings relate to policies
You can use policies to set identical values of the application settings for all devices in a group.
The values of the settings that a policy specifies can be redefined for individual devices in a group by using local application settings. You can set only the values of settings that the policy allows to be modified, that is, the unlocked settings.
The value of a setting that the application uses on a client device is defined by the lock position ( ) for that setting in the policy:
) for that setting in the policy:
- If a setting modification is locked, the same value (defined in the policy) is used on all client devices.
- If a setting modification is unlocked, the application uses a local setting value on each client device instead of the value specified in the policy. The setting can then be changed in the local application settings.
This means that, when a task is run on a client device, the application applies settings that have been defined in two different ways:
- By task settings and local application settings, if the setting is not locked against changes in the policy.
- By the group policy, if the setting is locked against changes.
Local application settings are changed after the policy is first applied in accordance with the policy settings.
Distribution point
Distribution point (previously known as update agent) is a device with Network Agent installed that is used for distribution of updates, remote installation of applications, and retrieval of information about networked devices. Distribution points accelerate update distribution and free up Administration Server resources.
The features and use cases of Network Agent installed on a device used as a distribution point vary depending on the operating system.
A distribution point can perform the following functions:
- Distribute files received from the Administration Server to client devices within the group (including distribution through multicasting using UDP).
The list of files that can be transferred by distribution points includes:
- Updates of Kaspersky databases and software modules
- Third-party software updates
- Installation packages
- Windows updates when you use Administration Server as a WSUS server
Updates can be received either from the Administration Server or from Kaspersky update servers. In the latter case, an update task must be created for the distribution point. Distribution point devices running macOS cannot download updates from Kaspersky update servers.
If one or more devices running macOS are within the scope of the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task, the task completes with the Failed status, even if it has successfully completed on all Windows devices.
- Distribute policies and group tasks through multicasting using UDP.
- Act as a gateway for connection to the Administration Server for devices in an administration group.
If a direct connection between managed devices within the group and the Administration Server cannot be established, you can use the distribution point as connection gateway to the Administration Server for this group. In this case, managed devices connect to the connection gateway, which in turn connects to the Administration Server.
The presence of a distribution point that functions as connection gateway does not block the option of a direct connection between managed devices and the Administration Server. If the connection gateway is not available, but direct connection with the Administration Server is technically possible, managed devices are connected to the Administration Server directly.
- Poll the network to detect new devices and update information about existing ones. A distribution point can apply the same device discovery methods as the Administration Server.
- Perform remote installation of third-party software and Kaspersky applications by using tools of the distribution point operating system. Note that the distribution point can perform installation on client devices without Network Agent.
This feature allows you to remotely transfer Network Agent installation packages to client devices located on networks to which the Administration Server has no direct access.
- Act as a proxy server participating in Kaspersky Security Network (KSN).
You can enable KSN proxy server on distribution point side to make the device act as a KSN proxy server. In this case, the KSN proxy service (ksnproxy) is run on the device.
Files are transmitted from the Administration Server to a distribution point over HTTP or, if SSL connection is enabled, over HTTPS. Using HTTP or HTTPS results in a higher level of performance, compared to SOAP, through cutting traffic.
Devices with Network Agent installed can be assigned distribution points either manually (by the administrator), or automatically (by the Administration Server). The full list of distribution points for specified administration groups is displayed in the report about the list of distribution points.
The scope of a distribution point is the administration group to which it has been assigned by the administrator, as well as its subgroups of all levels of embedding. If multiple distribution points have been assigned in the hierarchy of administration groups, Network Agent on the managed device connects to the nearest distribution point in the hierarchy.
A network location can also be the scope of distribution points. The network location is used for manual creation of a set of devices to which the distribution point will distribute updates. Network location can be determined only for devices running a Windows operating system.
If distribution points are assigned automatically by the Administration Server, it assigns them by broadcast domains, not by administration groups. This occurs when all broadcast domains are known. Network Agent exchanges messages with other Network Agents in the same subnet and then sends Administration Server information about itself and other Network Agents. Administration Server can use that information to group Network Agents by broadcast domains. Broadcast domains are known to Administration Server after more than 70% Network Agents in administration groups are polled. Administration Server polls broadcast domains every two hours. After distribution points are assigned by broadcast domains, they cannot be re-assigned by administration groups.
If the administrator manually assigns distribution points, they can be assigned to administration groups or network locations.
Network Agents with the active connection profile do not participate in broadcast domain detection.
Kaspersky Security Center assigns each Network Agent a unique IP multicast address that differs from every other address. This allows you to avoid network overload that might occur due to IP overlaps.
If two or more distribution points are assigned to a single network area or to a single administration group, one of them becomes the active distribution point, and the rest become standby distribution points. The active distribution point downloads updates and installation packages directly from the Administration Server, while standby distribution points receive updates from the active distribution point only. In this case, files are downloaded once from the Administration Server and then are distributed among distribution points. If the active distribution point becomes unavailable for any reason, one of the standby distribution points becomes active. The Administration Server automatically assigns a distribution point to act as standby.
The distribution point status (Active/Standby) is displayed with a check box in the klnagchk report.
A distribution point requires at least 4 GB of free disk space. If the free disk space of the distribution point is less than 2 GB, Kaspersky Security Center creates a security issue with the Warning importance level. The security issue will be published in the device properties, in the Security issues section.
Running remote installation tasks on a device assigned as a distribution point requires additional free disk space. The volume of free disk space must exceed the total size of all installation packages to be installed.
Running any updating (patching) tasks and vulnerability fix tasks on a device assigned as a distribution point requires additional free disk space. The volume of free disk space must be at least twice the total size of all patches to be installed.
Devices functioning as distribution points must be protected, including physical protection, against any unauthorized access.
Connection gateway
A connection gateway is a Network Agent acting in a special mode. A connection gateway accepts connections from other Network Agents and tunnels them to the Administration Server through its own connection with the Server. Unlike an ordinary Network Agent, a connection gateway waits for connections from the Administration Server rather than establishes connections to the Administration Server.
A connection gateway can receive connections from up to 10,000 devices.
You have two options for using connection gateways:
- We recommend that you install a connection gateway in a demilitarized zone (DMZ). For other Network Agents installed on out-of-office devices, you need to specially configure a connection to Administration Server through the connection gateway.
A connection gateway does not in any way modify or process data that is transmitted from Network Agents to Administration Server. Moreover, it does not write this data into any buffer and therefore cannot accept data from a Network Agent and later forward it to Administration Server. If Network Agent attempts to connect to Administration Server through the connection gateway, but the connection gateway cannot connect to Administration Server, Network Agent perceives this as if Administration Server is inaccessible. All data remains on Network Agent (not on the connection gateway).
A connection gateway cannot connect to Administration Server through another connection gateway. It means that Network Agent cannot simultaneously be a connection gateway and use a connection gateway to connect to Administration Server.
All connection gateways are included in the list of distribution points in the Administration Server properties.
- You can also use connection gateways within the network. For example, automatically assigned distribution points also become connection gateways in their own scope. However, within an internal network, connection gateways do not provide considerable benefit. They reduce the number of network connections received by Administration Server, but do not reduce the volume of incoming data. Even without connection gateways, all devices could still connect to Administration Server.
Main installation scenario
Following this scenario, you can deploy Administration Server, as well as install Network Agent and security applications on networked devices. You can use this scenario both for a closer look at the application and for the application installation for further work.
Installation of Kaspersky Security Center consists of the following steps:
- Preparation work
- Installation of Kaspersky Security Center and a Kaspersky security application on the Administration Server device
- Centralized deployment of Kaspersky security applications on client devices
Deployment of Kaspersky Security Center in cloud environments and deployment of Kaspersky Security Center for service providers are described in other Help sections.
We recommend that you assign a minimum of one hour for Administration Server installation and a minimum of one working day for completion of the scenario. We also recommend that you install a security application, such as Kaspersky Security for Windows Server or Kaspersky Endpoint Security, on the device that will act as Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
Upon completion of the scenario, protection will be deployed on the organization's network in the following way:
- The DBMS will be installed for the Administration Server.
- Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server will be installed.
- All required policies and tasks will be created; the default settings of policies and tasks will be specified.
- Security applications (for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows) and Network Agent will be installed on managed devices.
- Administration groups will be created (possibly combined into a hierarchy).
- Mobile device protection will be deployed, if necessary.
- Distribution points will be assigned, if necessary.
Kaspersky Security Center installation proceeds in stages:
Preparation work
- Getting the necessary files
Make sure that you have a license key (activation code) for Kaspersky Security Center or license keys (activation codes) for Kaspersky security applications.
Unpack the archive that you received from your vendor. This archive contains the license keys (KEY files), activation codes, and the list of Kaspersky applications that can be activated by each license key.
If you first want to try out Kaspersky Security Center, you can get a free 30-day trial at the Kaspersky website.
For detailed information about the licensing of the Kaspersky security applications that are not included in Kaspersky Security Center, you can refer to the documentation of those applications.
- Selecting a structure for protection of an organization
Find out more about the Kaspersky Security Center components. Select the protection structure and the network configuration which suit your organization best. Based on the network configuration and throughput of communication channels, define the number of Administration Servers to use and how they must be distributed among your offices (if you run a distributed network).
To obtain and maintain optimum performance under varying operational conditions, please take into account the number of networked devices, network topology, and set of Kaspersky Security Center features that you require (for more details, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Sizing Guide).
Define whether a hierarchy of Administration Servers will be used in your organization. To do this, you must evaluate whether it is possible and expedient to cover all client devices with a single Administration Server or it is necessary to build a hierarchy of Administration Servers. You may also have to build a hierarchy of Administration Servers that is identical to the organizational structure of the organization whose network you want to protect.
If you have to ensure protection of mobile devices, perform all prerequisite actions required for configuration of an iOS MDM Server.
Make sure that the devices that you selected as Administration Servers, as well as those for Administration Console installation, meet all the hardware and software requirements.
- Preparation for the use of custom certificates
If your organization's Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) requires that you use custom certificates issued by a specific certification authority (CA), prepare those certificates and make sure that they meet all the requirements.
- Preparation for Kaspersky Security Center licensing
If you plan to use a Kaspersky Security Center version with Mobile Device Management, Integration with SIEM systems, and/or with Vulnerability and patch management support, make sure that you have a key file or activation code for the application licensing.
- Preparation for licensing of managed security applications
During protection deployment, you have to provide Kaspersky with the active license keys for the applications that you intend to manage through Kaspersky Security Center (see the list of manageable security applications). For detailed information about the licensing of any security application, you can refer to the documentation of this application.
- Selecting the hardware configuration of the Administration Server and DBMS
Plan the hardware configuration for the DBMS and the Administration Server, taking into account the number of devices on your network.
- Selecting a DBMS
When selecting a DBMS, take into account the number of managed devices to be covered by this Administration Server. If your network includes fewer than 10 000 devices and you do not plan to increase this number, you can choose a free-of-charge DBMS, such as SQL Express, or MySQL, and install it on the same device as Administration Server. Alternatively, you can choose the MariaDB DBMS that allows you to manage up to 20 000 devices. If your network includes more than 10 000 devices (or if you plan to expand your network up to that number of devices), we recommend that you choose a paid-for SQL DBMS and install it on a dedicated device. A paid DBMS can work with multiple Administration Servers, but a DBMS that is free of charge can work with only one.
If you select SQL Server DBMS, note that you can migrate the data stored in the database to MySQL, MariaDB, or Azure SQL DBMS. To perform the migration, back up your data and restore it into the new DBMS.
- Installing the DBMS and creating the database
Find out more about the accounts for work with the DBMS and install your DBMS.
Before installation choose a supported DBMS. You can select, for example, PostgreSQL, Postgres Pro, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, or MariaDB.
For information about how to install the selected DBMS, refer to its documentation.
If you install MariaDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Postgres Pro, use the recommended settings to ensure the DBMS functions properly.
Write down and save the DBMS settings because you will need them during Administration Server installation. These settings include the SQL Server name, number of the port used for connecting to SQL Server, and account name and password for accessing the SQL Server.
If you decide to install PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro DBMS, ensure that you specified a password for the superuser. If the password is not specified, Administration Server might not be able to connect to the database.
By default, the Kaspersky Security Center Installer creates the database for storage of Administration Server information, but you can opt out of creating this database and use a different database instead. In this case, make sure that the database has been created, you know its name, and the account under which the Administration Server will gain access to this database has the db_owner role for it.
If necessary, contact your DBMS administrator for more information.
- Configuring ports
Make sure that all the necessary ports are open for interaction between components in accordance with your selected security structure.
If you have to provide Internet access to the Administration Server, configure the ports and specify the connection settings, depending on the network configuration.
- Checking accounts
Make sure that you have all local administrator rights required for successful installation of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and further protection deployment on the devices. Local administrator rights on client devices are required for Network Agent installation on these devices. After Network Agent is installed, you can use it to install applications on devices remotely, without using the account with the device administrator rights.
By default, on the device selected for Administration Server installation, the Kaspersky Security Center Installer creates three local accounts under which Administration Server and the Kaspersky Security Center services will be run:
- KL-AK-*: Administration Server service account
- NT Service/KSC*: Account for other services from the Administration Server pool
- KlPxeUser: Account for deployment of operating systems
You can opt out of creating accounts for the Administration Server services and other services. You use your existing accounts instead, such as domain accounts, if you plan to install Administration Server on a failover cluster, or plan to use domain accounts instead of local accounts for any other reason. In this case, make sure that the accounts intended for running Administration Server and the Kaspersky Security Center services have been created, are non-privileged and have all permissions required for access to the DBMS. (If you plan further deployment of operating systems on devices through Kaspersky Security Center, do not opt out of creating accounts.)
Installation of Kaspersky Security Center and a Kaspersky security application on the Administration Server device
- Installing the Administration Server, Administration Console, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, and management plug-ins for security applications
Download Kaspersky Security Center from the Kaspersky website. You can download the full package, Web Console only, or Administration Console only.
Install Administration Server on the device that you selected (or multiple devices, if you plan to use multiple Administration Servers). You can select standard or custom installation of Administration Server. Administration Console will be installed together with Administration Server. It is recommended to install the Administration Server on a dedicated server instead of a domain controller.
Standard installation is recommended if you want to try out Kaspersky Security Center by, for example, testing its operation on a small area within your network. During standard installation, you only configure the database. You can also install only the default set of management plug-ins for Kaspersky applications. You can also use standard installation if you already have some experience working with Kaspersky Security Center and are able to specify all relevant settings after standard installation.
Custom installation is recommended if you plan to modify the Kaspersky Security Center settings, such as a path to the shared folder, accounts and ports for connection to the Administration Server, and database settings. Custom installation enables you to specify which Kaspersky management plug-ins to install. If necessary, you can start custom installation in silent mode.
Administration Console and the server version of Network Agent are installed together with Administration Server. You can also choose to install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console during the installation.
If you want, install Administration Console and/or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console on the administrator's workstation separately to manage Administration Server over the network.
- Initial setup and licensing
When Administration Server installation is complete, at the first connection to the Administration Server the quick start wizard starts automatically. Perform initial configuration of Administration Server according to the existing requirements. During the initial configuration stage, the wizard uses the default settings to create the policies and tasks that are required for protection deployment. However, the default settings may be less than optimal for the needs of your organization. If necessary, you can edit the settings of policies and tasks (Configuring protection on a client organization's network, Scenario: Configuring network protection).
If you plan to use the features that are outside the basic functionality, license the application. You can do this at one of the steps of the quick start wizard.
- Checking Administration Server installation for success
When all the previous steps are complete, Administration Server is installed and ready for further use.
Make sure that Administration Console is running and you can connect to the Administration Server through Administration Console. Also, make sure that the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task is available in Administration Server (in the Tasks folder of the console tree), as well as the policy for Kaspersky Endpoint Security (in the Policies folder of the console tree).
When the check is complete, proceed to the steps below.
Centralized deployment of Kaspersky security applications on client devices
- Discovering networked devices
This step is part of the quick start wizard. You can also start the device discovery manually. Kaspersky Security Center receives the addresses and names of all devices detected on the network. You can then use Kaspersky Security Center to install Kaspersky applications and software from other vendors on the detected devices. Kaspersky Security Center regularly starts device discovery, which means that if any new instances appear in the network, they will be detected automatically.
- Installing Network Agent and security applications on networked devices
Deployment of protection (Configuring protection on a client organization's network, Scenario: Configuring network protection) of an organization's network entails installation of Network Agent and security applications (for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security) on devices that have been detected by Administration Server during the device discovery.
Security applications protect devices against viruses and/or other programs posing a threat. Network Agent ensures communication between the device and Administration Server. Network Agent settings are configured automatically by default.
If you want, you can install Network Agent in silent mode with a response file or without a response file.
Before you start install Network Agent and the security applications on networked devices, make sure that these devices are accessible (that is, turned on). You can install Network Agent on virtual machines as well as on physical devices.
Security applications and Network Agent can be installed remotely or locally.
Remote installation—Using the Protection deployment wizard, you can remotely install the security application (for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows) and Network Agent on devices that have been detected by Administration Server in the organization's network. Normally, the Remote installation task successfully deploys protection to most networked devices. However, it may return an error on some devices if, for example, a device is turned off or cannot be accessed for any other reason. In this case, we recommend that you connect to the device manually and use local installation.
Local installation—Used on network devices on which protection could not be deployed using the remote installation task. To install protection on such devices, create a stand-alone installation package that you can run locally on those devices.
Network Agent installation on devices running Linux and macOS operating systems is described in the documentation for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, respectively. Although devices running Linux and macOS operating systems are considered less vulnerable than devices running Windows, we recommend that you nonetheless install security applications on such devices.
After installation, make sure that the security application is installed on managed devices. Run a Kaspersky software version report and view its results.
- Deploying license keys to client devices
Deploy license keys to client devices to activate managed security applications on those devices.
- Configuring mobile device protection
This step is part of the quick start wizard.
If you want to manage enterprise mobile devices, take the necessary steps for preparation and deploy Mobile Device Management.
- Creating an administration group structure
In some cases, deploying protection on networked devices in the most convenient way may require you to divide the entire pool of devices into administration groups taking into account the structure of the organization. You can create moving rules to distribute devices among groups, or you can distribute devices manually. You can assign group tasks for administration groups, define the scope of policies, and assign distribution points.
Make sure that all managed devices have been correctly assigned to the appropriate administration groups, and that there are no longer any unassigned devices on the network.
- Assigning distribution points
Kaspersky Security Center assigns distribution points to administration groups automatically, but you can assign them manually, if necessary. We recommend that you use distribution points on large-scale networks to reduce the load on the Administration Server, and on networks that have a distributed structure to provide the Administration Server with access to devices (or device groups) communicated through channels with low throughput rates. You can use devices running Linux as distribution points, as well as devices running Windows.
Ports used by Kaspersky Security Center
The tables below show the default ports that must be open on Administration Servers and on client devices. If you want, you can change default port numbers.
The table below shows the default ports that must be open on Administration Server. However, if you install the Administration Server and the database on different devices, you must make available the necessary ports on the device where the database is located (for example, port 3306 for MySQL Server, port 1433 for Microsoft SQL Server, or port 5432 for PostgreSQL and Postgres Pro). Please refer to the DBMS documentation for the relevant information.
Ports that must be open on Administration Server
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
Port purpose |
Scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
8060 |
klcsweb |
TCP |
Transmitting published installation packages to client devices |
Publishing installation packages. You can change the default port number in the Web Server section of the Administration Server properties window in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
8061 |
klcsweb |
TCP (TLS) |
Transmitting published installation packages to client devices |
Publishing installation packages. You can change the default port number in the Web Server section of the Administration Server properties window in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
13000 |
klserver |
TCP (TLS) |
Receiving connections from Network Agents and secondary Administration Servers; also used on secondary Administration Servers for receiving connections from the primary Administration Server (for example, if the secondary Administration Server is in DMZ) |
Managing client devices and secondary Administration Servers. You can change the number of the default port for receiving connections from Network Agents when configuring connection ports; you can change the number of default port for receiving connections from secondary Administration Servers when creating a hierarchy of Administration Servers in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
13000 |
klserver |
UDP |
Receiving information about devices that were turned off from Network Agents |
Managing client devices. You can change the default port number in the Network Agent policy settings in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
13291 |
klserver |
TCP (TLS) |
Receiving connections from Administration Console to Administration Server |
Managing Administration Server. You can change the default port number in the Administration Server properties window in the Administration Console. |
13299 |
klserver |
TCP (TLS) |
Receiving connections from Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to the Administration Server; receiving connections to the Administration Server over OpenAPI |
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, OpenAPI. You can change the default port number in the Administration Server properties window (in the Connection ports subsection of the General section) in the Administration Console, or when creating a hierarchy of Administration Servers in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
14000 |
klserver |
TCP |
Receiving connections from Network Agents |
Managing client devices. You can change the default port number when configuring connection ports during the installation of Kaspersky Security Center, or when manually connecting a client device to the Administration Server. |
13111 (only if KSN proxy service is run on the device) |
ksnproxy |
TCP |
Receiving requests from managed devices to KSN proxy server |
KSN proxy server. You can change the default port number in the Administration Server properties window. |
15111 (only if KSN proxy service is run on the device) |
ksnproxy |
UDP |
Receiving requests from managed devices to KSN proxy server |
KSN proxy server. You can change the default port number in the Administration Server properties window. |
17000 |
klactprx |
TCP (TLS) |
Receiving connections for application activation from managed devices (except for mobile devices) |
Activation proxy server used by non-mobile devices to activate Kaspersky applications with activation codes. You can change the default port number in the Administration Server properties window. |
17100 (only if you manage mobile devices) |
klactprx |
TCP (TLS) |
Receiving connections for application activation from mobile devices |
Activation proxy server for mobile devices. You can change the default port number in the Administration Server properties window. |
19170 |
klserver |
HTTPS (TLS) |
Tunneling connections to managed devices by using the klsctunnel utility |
Remotely connecting to managed devices by using Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. You can change the default port number in the Administration Server properties window (in the Additional ports subsection of the General section) in the Administration Console only. |
13292 (only if you manage mobile devices) |
klserver |
TCP (TLS) |
Receiving connections from mobile devices |
Mobile Device Management. You can change the default port number in the Administration Server properties window in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
13294 (only if you manage mobile devices) |
klserver |
TCP (TLS) |
Receiving connections from UEFI protection devices |
Managing UEFI protection client devices. You can change the default port number when connecting mobile devices, or later in the Administration Server properties window (in the Additional ports subsection of the General section) in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
13296 |
klserver |
TCP (TLS) |
Publishing Kaspersky Security Center metrics for Prometheus |
Publishing Kaspersky Security Center metrics that will be further obtained by Prometheus. You can view the metrics via the following link: https://< You can change the default port number in the Administration Server properties window in the Administration Console. |
30522, 30523 (ports on the localhost interface) |
klnagent |
TCP |
Receiving Kaspersky application updates from Administration Server by using the FileTransferBridge component |
The Administration Server device that receives Kaspersky application updates. |
The table below shows the port that must be open on the iOS MDM Server (only if you manage mobile devices).
Port used by Kaspersky Security Center iOS MDM Server
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
Port purpose |
Scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
443 |
kliosmdmservicesrv
|
TCP (TLS) |
Receiving connections from iOS mobile devices |
Mobile Device Management. You can change the default port number when installing iOS MDM Server. |
The table below shows the port that must be open on Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server. It can be the same device where Administration Server is installed or a different device.
Port used by Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
Port purpose |
Scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
8080
|
Node.js: Server-side JavaScript
|
TCP (TLS) |
Receiving connections from browser to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console |
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. You can change the default port number when installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console on a device running Windows or on a Linux platform. If you install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console on the Linux ALT operating system, you must specify a port number other than 8080, because port 8080 is used by the operating system. |
The table below shows the port that must be open on managed devices where Network Agent is installed.
Ports used by Network Agent
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
Port purpose |
Scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
15000 |
klnagent
|
UDP |
Management signals from Administration Server or Distribution point to Network Agents |
Managing client devices. You can change the default port number in the Network Agent policy settings in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
15000 |
klnagent |
UDP broadcast |
Getting data about other Network Agents within the same broadcasting domain (the data is then sent to the Administration Server) |
Delivering updates and installation packages. |
15001 |
klnagent |
UDP |
Receiving multicast requests from a distribution point (if in use) |
Receiving updates and installation packages from a distribution point. You can change the default port number in the distribution point properties window in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
30522, 30523 (ports on the localhost interface) |
klnagent |
TCP |
Receiving Kaspersky application updates from Administration Server by using the FileTransferBridge component |
Managed devices that receive Kaspersky application updates from Administration Server specified as a database update source. |
161 |
klnagent |
SNMP |
Monitoring and discovering networked devices. |
Device discoverability. |
Please note that the klnagent process can also request free ports from the dynamic port range of an endpoint operating system. These ports are allocated to the klnagent process automatically by the operating system, so klnagent process can use some ports that are used by another software. If the klnagent process affects that software operations, change the port settings in this software, or change the default dynamic port range in your operating system to exclude the port used by the software affected.
Also take into account that recommendations on the compatibility of Kaspersky Security Center with third-party software are described for reference only and may not be applicable to new versions of third-party software. The described recommendations for configuring ports are based on the experiences of Technical Support and our best practices.
The table below shows the ports that must be open on a managed device with Network Agent installed acting as a distribution point. The listed ports must be open on the distribution point devices in addition to the ports used by Network Agents (see table above).
Ports used by Network Agent functioning as distribution point
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
Port purpose |
Scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
13000 |
klnagent |
TCP (TLS) |
Receiving connections from Network Agents and from Kaspersky Security Center when the distribution point acts as a connection gateway in DMZ. If a device with installed Administration Server specified as a distribution point, port 13001 is used for SSL connection by default instead of 13000. |
Managing client devices, delivering updates and installation packages. See the following topic for details: Administration Server, a connection gateway in a network segment, and a client device. You can change the default port number in the distribution point properties window in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
13111 (only if KSN proxy service is run on the device)
|
ksnproxy
|
TCP
|
Receiving requests from managed devices to KSN proxy server
|
KSN proxy server. You can change the default port number in the distribution point properties window in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
15111 (only if KSN proxy service is run on the device)
|
ksnproxy |
UDP |
Receiving requests from managed devices to KSN proxy server |
KSN proxy server. You can change the default port number in the distribution point properties window in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
17111 (only if KSN proxy service is run on the device) |
ksnproxy |
HTTPS |
Receiving requests from managed devices to KSN proxy server |
KSN proxy server. You can change the default port number in the distribution point properties window in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
13295 (only if you use the distribution point as a push server) |
klnagent |
TCP (TLS) |
Receiving connections from client devices |
Push server. You can change the default port number in the distribution point properties window in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
Certificates for work with Kaspersky Security Center
This section contains information about Kaspersky Security Center certificates and describes how to issue a custom certificate for Administration Server.
About Kaspersky Security Center certificates
Kaspersky Security Center uses the following types of certificates to enable a secure interaction between the application components:
- Administration Server certificate
- Mobile certificate
- iOS MDM Server certificate
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Server certificate
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console certificate
By default, Kaspersky Security Center uses self-signed certificates (that is, issued by Kaspersky Security Center itself), but you can replace them with custom certificates to better meet the requirements of your organization's network and comply with the security standards. After Administration Server verifies whether a custom certificate meets all applicable requirements, this certificate assumes the same functional scope as a self-signed certificate. The only difference is that a custom certificate is not reissued automatically upon expiration. You replace certificates with custom ones by means of the klsetsrvcert utility or through the Administration Server properties section in Administration Console, depending on the certificate type. When you use the klsetsrvcert utility, you need to specify a certificate type by using one of the following values:
- C—Common certificate for ports 13000 and 13291.
- CR—Common reserve certificate for ports 13000 and 13291.
- M—Mobile certificate for port 13292.
- MR—Mobile reserve certificate for port 13292.
- MCA—Mobile certification authority for auto-generated user certificates.
You do not need to download the klsetsrvcert utility. It is included in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit. The utility is not compatible with previous Kaspersky Security Center versions.
The maximum validity period for any of the Administration Server certificates must be 397 days or less.
Administration Server certificates
An Administration Server certificate is required for authentication of Administration Server, as well as for secure interaction between Administration Server and Network Agent on managed devices or between primary Administration Server and secondary Administration Servers. When you connect Administration Console to Administration Server for the first time, you are prompted to confirm the use of the current Administration Server certificate. Such confirmation is also required every time the Administration Server certificate is replaced, after every reinstallation of Administration Server, and when connecting a secondary Administration Server to the primary Administration Server. This certificate is called common ("C").
The common ("C") certificate is automatically created when the Administration Server component is installed. The certificate consists of two parts:
- klserver.cer file; by default, it is located on the device where the Administration Server component is installed in C:\ProgramData\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\cert folder.
- Secret key located in Windows Protected Storage.
Also, a common reserve ("CR") certificate exists. Kaspersky Security Center automatically generates this certificate 90 days before the expiration of the common certificate. The common reserve certificate is subsequently used for seamless replacement of the Administration Server certificate. When the common certificate is about to expire, the common reserve certificate is used to maintain the connection with Network Agent instances installed on managed devices. With this purpose, the common reserve certificate automatically becomes the new common certificate 24 hours before the old common certificate expires.
You can also back up the Administration Server certificate separately from other Administration Server settings in order to move Administration Server from one device to another without data loss.
Mobile certificates
A mobile certificate ("M") is required for authentication of the Administration Server on mobile devices. You configure the use of the mobile certificate on the dedicated step of the quick start wizard.
Also, a mobile reserve ("MR") certificate exists: it is used for seamless replacement of the mobile certificate. Kaspersky Security Center automatically generates this certificate 60 days before the expiration of the common certificate. When the mobile certificate is about to expire, the mobile reserve certificate is used to maintain the connection with Network Agent instances installed on managed mobile devices. With this purpose, the mobile reserve certificate automatically becomes the new mobile certificate 24 hours before the old mobile certificate expires.
If the connection scenario requires the use of a client certificate on mobile devices (connection involving two-way SSL authentication), you can generate those certificates by means of the certificate authority for auto-generated user certificates ("MCA"). Also, the quick start wizard enables you to start using custom client certificates issued by a different certification authority, while integration with the domain Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) of your organization enables you to issue client certificates by means of your domain certification authority.
iOS MDM Server certificate
An iOS MDM Server certificate is required for authentication of Administration Server on mobile devices running the iOS operating system. The interaction with these devices is performed via the Apple mobile device management (MDM) protocol that involves no Network Agent. Instead, you install a special iOS MDM profile, containing a client certificate, on each device, to ensure two-way SSL authentication.
Also, the quick start wizard enables you to start using custom client certificates issued by a different certification authority, while integration with the domain Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) of your organization enables you to issue client certificates by means of your domain certification authority.
Client certificates are transmitted to iOS devices when you download those iOS MDM profiles. An iOS MDM Server client certificate is unique for each managed iOS device. You generate all iOS MDM Server client certificates by means of the certification authority for auto-generated user certificates ("MCA").
Kaspersky Security Center Web Server certificate
Kaspersky Security Center Web Server (hereinafter referred to as Web Server), a component of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server, uses a special type of certificate. This certificate is required for publishing Network Agent installation packages that you subsequently download to managed devices, as well as for publishing iOS MDM profiles, iOS apps, and Kaspersky Security for Mobile installation packages. For this purpose, Web Server can use various certificates.
If the mobile device support is disabled, Web Server uses one of the following certificates, in order of priority:
- Custom Web Server certificate that you specified manually by means of Administration Console
- Common Administration Server certificate ("C")
If the mobile device support is enabled, Web Server uses one of the following certificates, in order of priority:
- Custom Web Server certificate that you specified manually by means of Administration Console
- Custom mobile certificate
- Self-signed mobile certificate ("M")
- Common Administration Server certificate ("C")
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console certificate
The Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server (hereinafter referred to as Web Console) has its own certificate. When you open a website, a browser verifies whether your connection is trusted. The Web Console certificate allows you to authenticate the Web Console and is used to encrypt traffic between a browser and the Web Console.
When you open the Web Console, the browser may inform you that the connection to the Web Console is not private and the Web Console certificate is invalid. This warning appears because the Web Console certificate is self-signed and automatically generated by Kaspersky Security Center. To remove this warning, you can do one of the following:
- Replace the Web Console certificate with a custom one (recommended option). Create a certificate that is trusted in your infrastructure and that meets the requirements for custom certificates.
- Add the Web Console certificate to the list of trusted browser certificates. We recommend that you use this option only if you cannot create a custom certificate.
About Administration Server certificate
Two operations are performed based on the Administration Server certificate: Administration Server authentication during connection by Administration Console and data exchange with devices. The certificate is also used for authentication when the primary Administration Servers are connected to secondary Administration Servers.
Certificate issued by Kaspersky
The Administration Server certificate is created automatically during installation of the Administration Server component and it is stored in the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\cert folder.
The Administration Server certificate is valid for five years, if the certificate was generated by Administration Server version 12.2 or earlier. Otherwise, the certificate validity term is limited to 397 days. A new certificate is generated by the Administration Server as the reserve certificate 90 days before the expiration date of the current certificate. Subsequently, the new certificate automatically replaces the current certificate one day before the expiration date. All Network Agents on the client devices are automatically reconfigured to authenticate the Administration Server with the new certificate.
Custom certificates
If necessary, you can assign a custom certificate for the Administration Server. For example, this may be necessary for better integration with the existing PKI of your enterprise or for custom configuration of the certificate fields.
The maximum validity period for any of the Administration Server certificates must be 397 days or less.
When replacing the certificate, all Network Agents that were previously connected to Administration Server through SSL, will lose their connection and will return "Administration Server authentication error." To eliminate this error, you will have to restore the connection after the certificate replacement.
If the Administration Server certificate is lost, you must reinstall the Administration Server component, and then restore the data in order to recover it.
If you open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console in different browsers and download the Administration Server certificate file in the Administration Server properties window, the downloaded files have different names.
Page top
Requirements for custom certificates used in Kaspersky Security Center
The table below shows the requirements for custom certificates specified for different components of Kaspersky Security Center.
Requirements for Kaspersky Security Center certificates
Certificate type |
Requirements |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
Common certificate, Common reserve certificate ("C", "CR") |
Minimum key length: 2048. Basic constraints:
Key Usage:
Extended Key Usage (optional): server authentication, client authentication. |
Extended Key Usage parameter is optional. Path Length Constraint value may be an integer different from "None", but not less than 1. |
Mobile certificate, Mobile reserve certificate ("M", "MR") |
Minimum key length: 2048. Basic constraints:
Key Usage:
Extended Key Usage (optional): server authentication. |
Extended Key Usage parameter is optional. Path Length Constraint value may be an integer different from "None", if Common certificate has a Path Length Constraint value not less than 1. |
Certificate CA for auto-generated user certificates ("MCA") |
Minimum key length: 2048. Basic constraints:
Key Usage:
Extended Key Usage (optional): server authentication, client authentication. |
Extended Key Usage parameter is optional. Path Length Constraint value may be an integer different from "None," if Common certificate has a Path Length Constraint value not less than 1. |
Web Server certificate |
Extended Key Usage: server authentication. The PKCS #12 / PEM container from which the certificate is specified includes the entire chain of public keys. The Subject Alternative Name (SAN) of the certificate is present; that is, the value of the The certificate meets the effective requirements of browsers imposed on server certificates, as well as the current baseline requirements of the CA/Browser Forum. |
|
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console certificate |
The PEM container from which the certificate is specified includes the entire chain of public keys. The Subject Alternative Name (SAN) of the certificate is present; that is, the value of the The certificate meets the effective requirements of browsers to server certificates, as well as the current baseline requirements of the CA/Browser Forum. |
Encrypted certificates are not supported by Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
Scenario: Specifying the custom Administration Server certificate
You can assign the custom Administration Server certificate, for example, for better integration with the existing public key infrastructure (PKI) of your enterprise or for custom configuration of the certificate fields. It is useful to replace the certificate immediately after installation of Administration Server and before the quick start wizard finishes.
The maximum validity period for any of the Administration Server certificates must be 397 days or less.
Prerequisites
The following conditions must be met:
- The new certificate must be created in the PKCS#12 format (for example, by means of the organization's PKI).
- For the new certificate, the requirements listed in the table below must be met.
- In the table below, pay attention to the requirement "CA: true," which means that the new certificate must be issued by a trusted certification authority (CA). The new certificate with the requirement "CA: true" must include the entire chain of trust and a private key, which must be stored in a file with the pfx or p12 extension.
Requirements for the Administration Server certificates
Certificate type
Requirements
Common certificate, common reserve certificate ("C", "CR")
Minimum key length: 2048.
Basic constraints:
- Path Length Constraint: None
Path Length Constraint value may be an integer different from "None," but not less than 1.
Key Usage:
- Digital signature
- Certificate signing
- Key encryption
- CRL Signing
Extended Key Usage (EKU): server authentication and client authentication. The EKU is optional, but if your certificate contains it, the server and client authentication data must be specified in the EKU.
Mobile certificate, mobile reserve certificate ("M", "MR")
Minimum key length: 2048.
Basic constraints:
- CA: true
- Path Length Constraint: None
Path Length Constraint value may be an integer different from "None" if the common certificate has a Path Length Constraint value not less than 1.
Key Usage:
- Digital signature
- Certificate signing
- Key encryption
- CRL Signing
Extended Key Usage (EKU): server authentication. The EKU is optional, but if your certificate contains it, the server authentication data must be specified in the EKU.
Certificate CA for auto-generated user certificates ("MCA")
Minimum key length: 2048.
Basic constraints:
- CA: true
- Path Length Constraint: None
Path Length Constraint value may be an integer different from "None" if the Common certificate has a Path Length Constraint value not less than 1.
Key Usage:
- Digital signature
- Certificate signing
- Key encryption
- CRL Signing
Extended Key Usage (EKU): client authentication. The EKU is optional, but if your certificate contains it, the client authentication data must be specified in the EKU.
- Path Length Constraint: None
Certificates issued by a public CA do not have the certificate signing permission. To use such certificates, make sure that you installed Network Agent version 13 or later on distribution points or connection gateways in your network. Otherwise, you will not be able to use certificates without the signing permission.
Stages
Specifying the Administration Server certificate proceeds in stages:
- Replacing the Administration Server certificate
Use the command-line klsetsrvcert utility for this purpose.
- Specifying a new certificate and restoring connection of Network Agents to the Administration Server
When the certificate is replaced, all Network Agents that were previously connected to Administration Server through SSL lose their connection and return "Administration Server authentication error." To specify the new certificate and restore the connection, use the command-line klmover utility.
- Specifying a new certificate in the settings of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
After you replace the certificate, specify it in the settings of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. Otherwise, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console will not be able to connect to the Administration Server.
Results
When you finish the scenario, the Administration Server certificate is replaced and the server is authenticated by Network Agents on the managed devices.
Replacing the Administration Server certificate by using the klsetsrvcert utility
To replace the Administration Server certificate:
From the command line, run the following utility:
klsetsrvcert [-t <type> {-i <inputfile> [-p <password>] [-o <chkopt>] | -g <dnsname>}][-f <time>][-r <calistfile>][-l <logfile>]
You do not need to download the klsetsrvcert utility. It is included in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit. It is not compatible with previous Kaspersky Security Center versions.
The description of the klsetsrvcert utility parameters is presented in the table below.
Values of the klsetsrvcert utility parameters
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Type of certificate to be replaced. Possible values of the
|
|
Schedule for changing the certificate, using the format "DD-MM-YYYY hh:mm" (for ports 13000 and 13291). Use this parameter if you want to replace the common or common reserve certificate before it expires. Specify the time when managed devices must synchronize with Administration Server on a new certificate. |
|
Container with the certificate and a private key in the PKCS#12 format (file with the .p12 or .pfx extension). |
|
Password used for protection of the p12 container. The certificate and a private key are stored in the container, therefore, the password is required to decrypt the file with the container. |
|
Certificate validation parameters (semicolon separated). To use a custom certificate without signing permission, specify To change encryption key length for certificate types C or CR, specify |
|
A new certificate will be created for the specified DNS name. |
|
Trusted root Certificate Authority list, format PEM. |
|
Results output file. By default, the output is redirected into the standard output stream. |
For example, to specify the custom Administration Server certificate, use the following command:
klsetsrvcert -t C -i <inputfile> -p <password> -o NoCA
After the certificate is replaced, all Network Agents connected to Administration Server through SSL lose their connection. To restore it, use the command-line klmover utility.
To avoid losing the Network Agents connections, use the following commands:
- To install the new certificate,klsetsrvcert.exe -t CR -i <inputfile> -p <password> -o NoCA
- To specify the date when the new certificate will be applied,klsetsrvcert.exe -f "DD-MM-YYYY hh:mm"
where "DD-MM-YYYY hh:mm" is the date 3–4 weeks later than the current date. The time shift for changing the certificate to the new one will allow the new certificate to be distributed to all Network Agents.
Connecting Network Agents to Administration Server by using the klmover utility
After you replace the Administration Server certificate by using the command-line klsetsrvcert utility, you need to establish the SSL connection between Network Agents and Administration Server because the connection is broken.
To specify the new Administration Server certificate and restore the connection:
From the command line, run the following utility:
klmover [-address <server address>] [-pn <port number>] [-ps <SSL port number>] [-nossl] [-cert <path to certificate file>]
The administrator rights are required to run the utility.
This utility is automatically copied to the Network Agent installation folder, when Network Agent is installed on a client device.
To prevent intruders from moving devices out of your Administration Server's control, we strongly recommend enabling password protection for running the klmover utility. To enable password protection, select the Use uninstallation password option in the Network Agent policy settings.
The klmover utility requires local administrator rights. Password protection for running the klmover utility can be omitted for devices operated without local administrator rights.
Enabling the Use uninstallation password also enables password protection for the Cleaner tool (cleaner.exe).
You cannot use the klmover utility for client devices connected to Administration Server through connection gateways. For such devices you have to either reconfigure Network Agent or reinstall Network Agent and specify connection gateway.
The description of the klmover utility parameters is presented in the table below.
Values of the klmover utility parameters
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Address of the Administration Server for connection. You can specify an IP address, the NetBIOS name, or the DNS name. |
|
Number of the port through which non-encrypted connection to the Administration Server is established. The default port number is 14000. |
|
Number of the SSL port through which encrypted connection to the Administration Server is established by using SSL. The default port number is 13000. |
|
Use non-encrypted connection to the Administration Server. If the key is not in use, Network Agent is connected to the Administration Server by using encrypted SSL protocol. |
|
Use the specified certificate file for authentication of access to Administration Server. |
|
Name of the virtual Administration Server. |
|
Network Agent disk cloning mode. Use one of the following parameters to configure the disk cloning mode:
|
For example, to connect Network Agent to Administration Server, run the following command:
klmover -address kscserver.mycompany.com -logfile klmover.log
Reissuing the Web Server certificate
The Web Server certificate used in Kaspersky Security Center is required for publishing Network Agent installation packages that you subsequently download to managed devices, as well as for publishing iOS MDM profiles, iOS apps, and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mobile installation packages. Depending on the current application configuration, various certificates can function as the Web Server certificate (for more detail, see About Kaspersky Security Center certificates).
You may need to reissue the Web Server certificate to meet the specific security requirements of your organization or to maintain continuous connection of your managed devices before starting to upgrade the application. Kaspersky Security Center provides two ways of reissuing the Web Server certificate; the choice between the two methods depends on whether you have mobile devices connected and managed through the mobile protocol (i.e., by using the mobile certificate).
If you have never specified your own custom certificate as the Web Server certificate in the Web Server section of the Administration Server properties window, the mobile certificate acts as the Web Server certificate. In this case, the Web Server certificate reissuance is performed through the reissuance of the mobile protocol itself.
To reissue the Web Server certificate when you have no mobile devices managed through the mobile protocol:
- In the console tree, right-click the name of the relevant Administration Server and in the context menu select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window that opens, in the left pane, select the Administration Server connection settings section.
- In the list of subsections, select the Certificates subsection.
- If you plan to continue using the certificate issued by Kaspersky Security Center, do the following:
- On the right pane, in the Administration Server authentication by mobile devices group of settings, select the Certificate issued through Administration Server option and click the Reissue button.
- In the Reissue certificate window that opens, in the Connection address and Activation term group of settings, select the relevant options and click OK.
- In the confirmation window, click Yes.
Alternatively, if you plan to use your own custom certificate, do the following:
- Check whether your custom certificate meets the requirements of Kaspersky Security Center and the requirements for trusted certificates by Apple. If necessary, modify the certificate.
- Select the Other certificate option and click the Browse button.
- In the Certificate window that opens, in the Certificate type field select the type of your certificate and then specify the certificate location and settings:
- If you have selected PKCS #12 container, click the Browse button next to the Certificate file field and specify the certificate file on your hard drive. If the certificate file is password-protected, enter the password in the Password (if any) field.
- If you have selected X.509 certificate, click the Browse button next to the Private key (.prk, .pem) field and specify the private key on your hard drive. If the private key is password-protected, enter the password in the Password (if any) field. Then click the Browse button next to the Public key (.cer) field and specify the private key on your hard drive.
- In the Certificate window, click OK.
- In the confirmation window, click Yes.
The mobile certificate is reissued to be used as the Web Server certificate.
To reissue the Web Server certificate when you have any mobile devices managed through the mobile protocol:
- Generate your custom certificate and prepare it for the usage in Kaspersky Security Center. Check whether your custom certificate meets the requirements of Kaspersky Security Center and the requirements for trusted certificates by Apple. If necessary, modify the certificate.
You can use the kliossrvcertgen.exe utility for certificate generation.
- In the console tree, right-click the name of the relevant Administration Server and in the context menu select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window that opens, in the left pane, select the Web Server section.
- In the Over HTTPS menu, select the Specify another certificate option.
- In the Over HTTPS menu, click the Change button.
- In the Certificate window that opens, in the Certificate type field select the type of your certificate:
- If you have selected PKCS #12 container, click the Browse button next to the Certificate file field and specify the certificate file on your hard drive. If the certificate file is password-protected, enter the password in the Password (if any) field.
- If you have selected X.509 certificate, click the Browse button next to the Private key (.prk, .pem) field and specify the private key on your hard drive. If the private key is password-protected, enter the password in the Password (if any) field. Then click the Browse button next to the Public key (.cer) field and specify the private key on your hard drive.
- In the Certificate window, click OK.
- If necessary, in the Administration Server properties window, in the Web Server HTTPS port field change the number of the HTTPS port for Web Server. Click OK.
The Web Server certificate is reissued.
Schemas for data traffic and port usage
This section provides schemas for data traffic between Kaspersky Security Center components, managed security applications, and external servers under various configurations. The schemas are provided with numbers for the ports that must be available on the local devices.
Administration Server and managed devices on LAN
The figure below shows the traffic of the data if Kaspersky Security Center is deployed on a local area network (LAN) only.
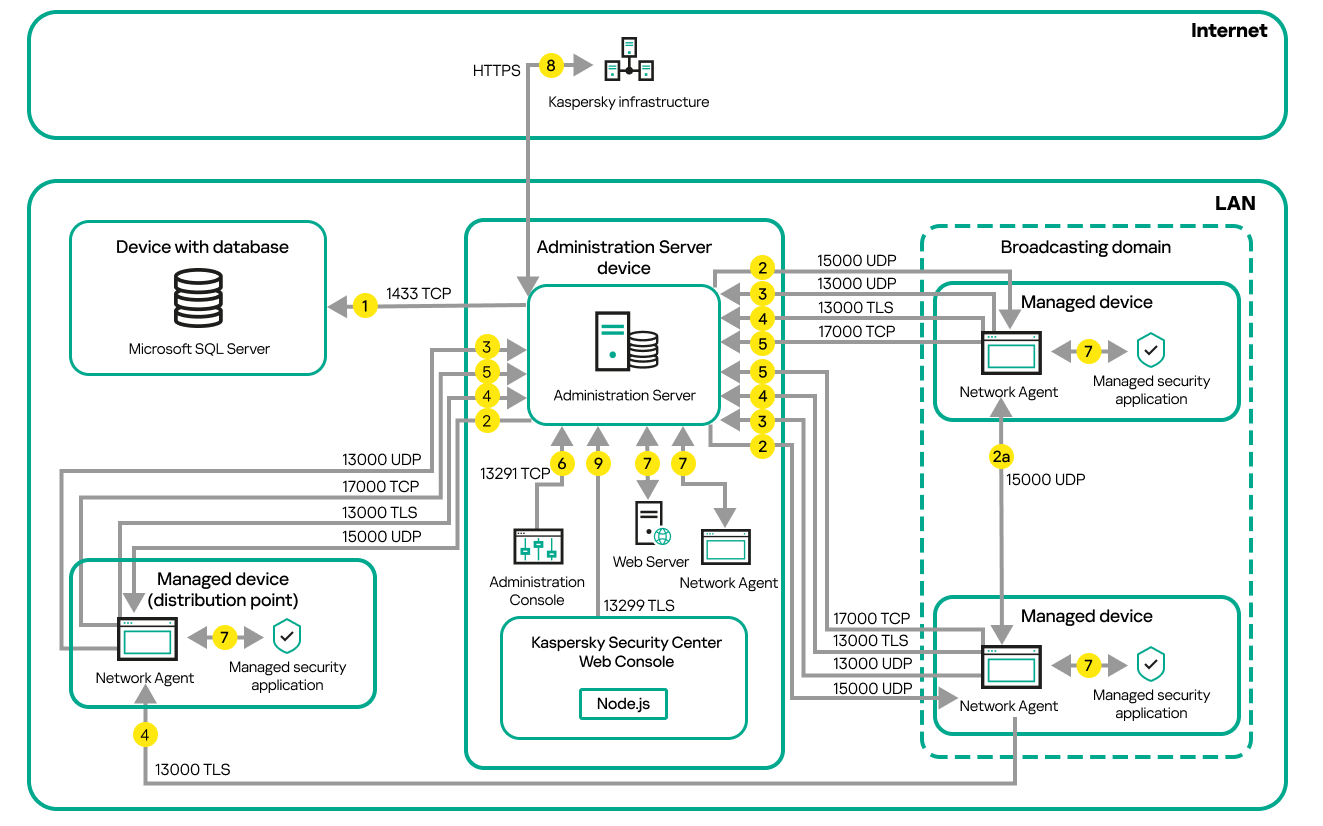
Administration Server and managed devices on a local area network (LAN)
The figure shows how different managed devices connect to the Administration Server in different ways: directly or via a distribution point. Distribution points reduce the load on the Administration Server during update distribution and optimize network traffic. However, distribution points are only needed if the number of managed devices is large enough. If the number of managed devices is small, all the managed devices can receive updates from the Administration Server directly.
The arrows indicate the initiation of traffic: each arrow points from a device that initiates the connection to the device that "answers" the call. The number of the port and the name of the protocol used for data transfer are provided. Each arrow has a number label, and details about the corresponding data traffic are as follows:
- Administration Server sends data to the database. If you install the Administration Server and the database on different devices, you must make available the necessary ports on the device where the database is located (for example, port 3306 for MySQL Server, or port 1433 for Microsoft SQL Server). Please refer to the DBMS documentation for the relevant information.
- Requests for communication from the Administration Server are transferred to all non-mobile managed devices through UDP port 15000.
Network Agents send requests to each other within one broadcasting domain. The data is then sent to the Administration Server and is used for defining the limits of the broadcasting domain and for automatic assignment of distribution points (if this option is enabled).
If Administration Server does not have direct access to the managed devices, communication requests from Administration Server to these devices are not sent directly.
- Information about shutdown of the managed devices is transferred from Network Agent to the Administration Server through UDP port 13000.
- The Administration Server receives connection from Network Agents and from secondary Administration Servers through TLS port 13000.
If you used an earlier version of Kaspersky Security Center, the Administration Server on your network can receive connection from Network Agents through non-TLS port 14000. Kaspersky Security Center also supports connection of Network Agents through port 14000, although using TLS port 13000 is recommended.
The distribution point was called "Update agent" in earlier versions of Kaspersky Security Center.
- The managed devices (except for mobile devices) request activation through TCP port 17000. This is not necessary if the device has its own access to the internet; in this case, the device sends the data to Kaspersky servers over the internet directly.
- Data from MMC-based Administration Console is transferred to the Administration Server through port 13291. (The Administration Console can be installed on the same or on a different device.)
- Applications on a single device exchange local traffic (either on the Administration Server or on a managed device). No external ports have to be opened.
- Data from the Administration Server to the Kaspersky servers (such as KSN data or information about licenses) and data from the Kaspersky servers to the Administration Server (such as application updates and anti-virus database updates) are transferred using the HTTPS protocol.
If you do not want your Administration Server to have access to the internet, you must manage this data manually.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server sends data to the Administration Server, which may be installed on the same or on a different device, through TLS port 13299.
Primary Administration Server on LAN and two secondary Administration Servers
The figure below shows the hierarchy of Administration Servers: the primary Administration Server is on a local area network (LAN). A secondary Administration Server is in the demilitarized zone (DMZ); another secondary Administration Server is on the internet.
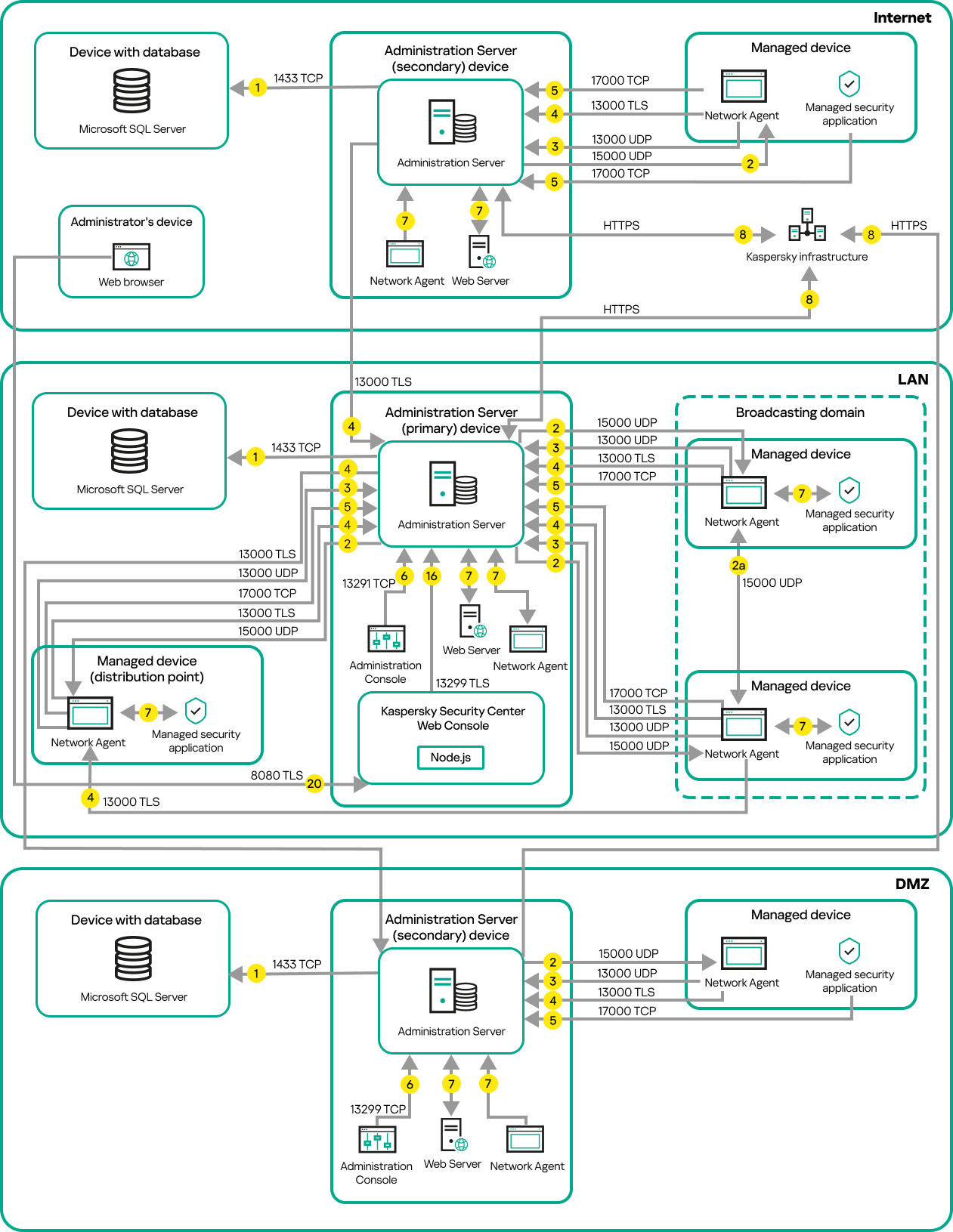
Hierarchy of Administration Servers: primary Administration Server and two secondary Administration Servers
The arrows indicate the initiation of traffic: each arrow points from a device that initiates the connection to the device that "answers" the call. The number of the port and the name of the protocol used for data transfer are provided. Each arrow has a number label, and details about the corresponding data traffic are as follows:
- Administration Server sends data to the database. If you install the Administration Server and the database on different devices, you must make available the necessary ports on the device where the database is located (for example, port 3306 for MySQL Server, or port 1433 for Microsoft SQL Server). Please refer to the DBMS documentation for the relevant information.
- Requests for communication from the Administration Server are transferred to all non-mobile managed devices through UDP port 15000.
Network Agents send requests to each other within one broadcasting domain. The data is then sent to the Administration Server and is used for defining the limits of the broadcasting domain and for automatic assignment of distribution points (if this option is enabled).
If Administration Server does not have direct access to the managed devices, communication requests from Administration Server to these devices are not sent directly.
- Information about shutdown of the managed devices is transferred from Network Agent to the Administration Server through UDP port 13000.
- The Administration Server receives connection from Network Agents and from secondary Administration Servers through TLS port 13000.
If you used an earlier version of Kaspersky Security Center, the Administration Server on your network can receive connection from Network Agents through non-TLS port 14000. Kaspersky Security Center also supports connection of Network Agents through port 14000, although using TLS port 13000 is recommended.
The distribution point was called "Update agent" in earlier versions of Kaspersky Security Center.
- The managed devices (except for mobile devices) request activation through TCP port 17000. This is not necessary if the device has its own access to the internet; in this case, the device sends the data to Kaspersky servers over the internet directly.
- Data from MMC-based Administration Console is transferred to the Administration Server through port 13291. (The Administration Console can be installed on the same or on a different device.)
- Applications on a single device exchange local traffic (either on the Administration Server or on a managed device). No external ports have to be opened.
- Data from the Administration Server to the Kaspersky servers (such as KSN data or information about licenses) and data from the Kaspersky servers to the Administration Server (such as application updates and anti-virus database updates) are transferred using the HTTPS protocol.
If you do not want your Administration Server to have access to the internet, you must manage this data manually.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server sends data to the Administration Server, which may be installed on the same or on a different device, through TLS port 13299.
9a. Data from the browser, which is installed on a separate device of the administrator, is transferred to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server through TLS port 8080. The Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server can be installed either on the Administration Server or on another device.
Administration Server on LAN, managed devices on internet, reverse proxy in use
The figure below shows data traffic if the Administration Server is on a local area network (LAN) and the managed devices, including mobile devices, are on the internet. In this figure, a reverse proxy of your choice is in use. Refer to the documentation of the application for details.
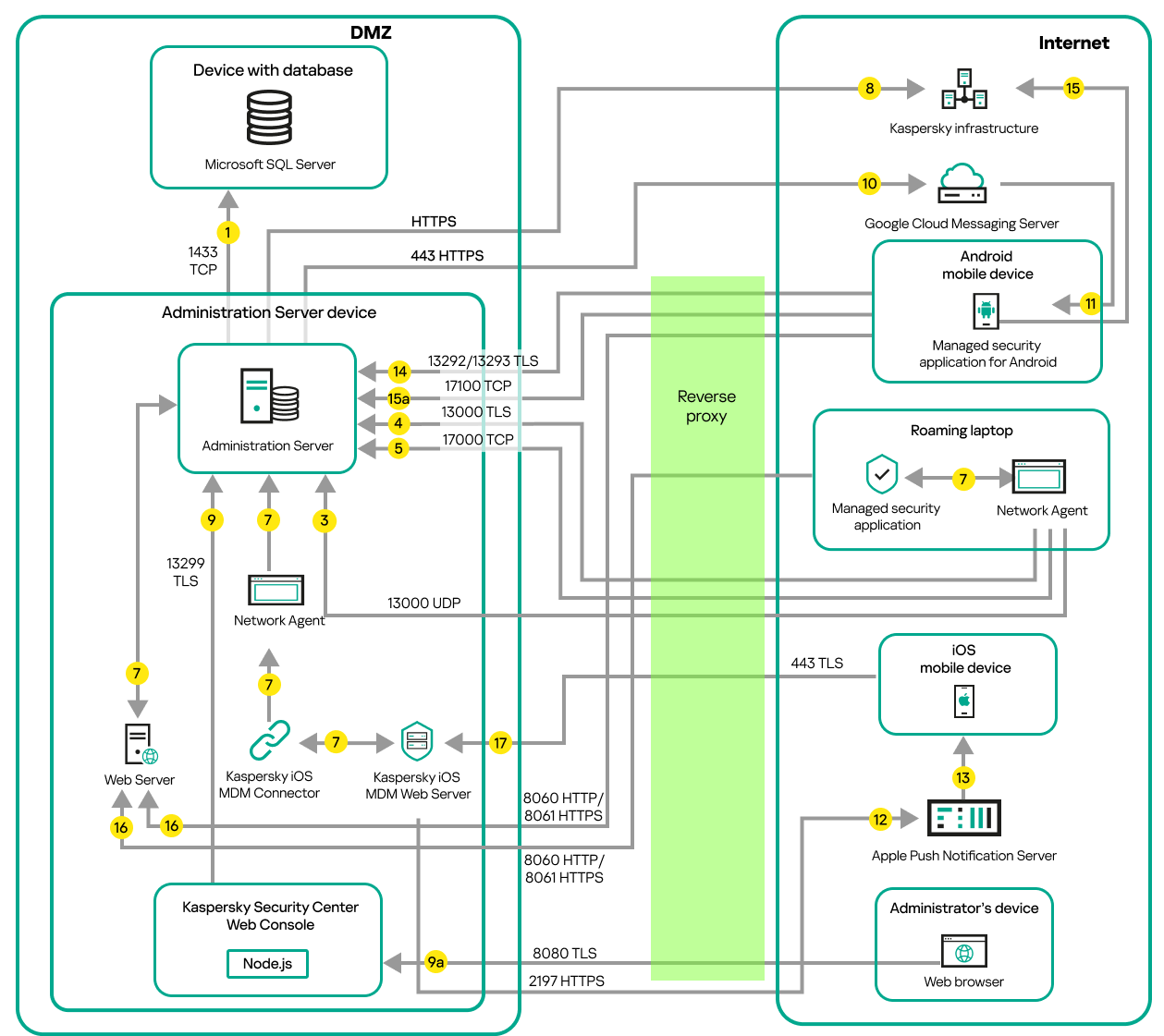
Administration Server on a local area network; managed devices connect to the Administration Server through a reverse proxy
This deployment scheme is recommended if you do not want the mobile devices to connect to the Administration Server directly and do not want to assign a connection gateway in the DMZ.
The arrows indicate the initiation of traffic: each arrow points from a device that initiates the connection to the device that "answers" the call. The number of the port and the name of the protocol used for data transfer are provided. Each arrow has a number label, and details about the corresponding data traffic are as follows:
- Administration Server sends data to the database. If you install the Administration Server and the database on different devices, you must make available the necessary ports on the device where the database is located (for example, port 3306 for MySQL Server, or port 1433 for Microsoft SQL Server). Please refer to the DBMS documentation for the relevant information.
- Requests for communication from the Administration Server are transferred to all non-mobile managed devices through UDP port 15000.
Network Agents send requests to each other within one broadcasting domain. The data is then sent to the Administration Server and is used for defining the limits of the broadcasting domain and for automatic assignment of distribution points (if this option is enabled).
If Administration Server does not have direct access to the managed devices, communication requests from Administration Server to these devices are not sent directly.
- Information about shutdown of the managed devices is transferred from Network Agent to the Administration Server through UDP port 13000.
- The Administration Server receives connection from Network Agents and from secondary Administration Servers through TLS port 13000.
If you used an earlier version of Kaspersky Security Center, the Administration Server on your network can receive connection from Network Agents through non-TLS port 14000. Kaspersky Security Center also supports connection of Network Agents through port 14000, although using TLS port 13000 is recommended.
The distribution point was called "Update agent" in earlier versions of Kaspersky Security Center.
- The managed devices (except for mobile devices) request activation through TCP port 17000. This is not necessary if the device has its own access to the internet; in this case, the device sends the data to Kaspersky servers over the internet directly.
- Data from MMC-based Administration Console is transferred to the Administration Server through port 13291. (The Administration Console can be installed on the same or on a different device.)
- Applications on a single device exchange local traffic (either on the Administration Server or on a managed device). No external ports have to be opened.
- Data from the Administration Server to the Kaspersky servers (such as KSN data or information about licenses) and data from the Kaspersky servers to the Administration Server (such as application updates and anti-virus database updates) are transferred using the HTTPS protocol.
If you do not want your Administration Server to have access to the internet, you must manage this data manually.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server sends data to the Administration Server, which may be installed on the same or on a different device, through TLS port 13299.
9a. Data from the browser, which is installed on a separate device of the administrator, is transferred to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server through TLS port 8080. The Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server can be installed either on the Administration Server or on another device.
- For Android mobile devices only: data from the Administration Server is transferred to Google servers. This connection is used to notify Android mobile devices that they are required to connect to the Administration Server. Then push notifications are sent to the mobile devices.
- For Android mobile devices only: push notifications from Google servers are sent to the mobile device. This connection is used to notify mobile devices that they are required to connect to the Administration Server.
- For iOS mobile devices only: data from the iOS MDM Server is transferred to Apple Push Notification servers. Then push notifications are sent to the mobile devices.
- For iOS mobile devices only: push notifications are sent from Apple servers to the mobile device. This connection is used to notify iOS mobile devices that they are required to connect to the Administration Server.
- For mobile devices only: data from the managed application is transferred to the Administration Server (or to the connection gateway) through TLS port 13292 / 13293—directly or through a reverse proxy.
- For mobile devices only: data from the mobile device is transferred to the Kaspersky infrastructure.
If a mobile device does not have internet access, the data is transferred to Administration Server through port 17100, and the Administration Server sends it to the Kaspersky infrastructure; however, this scenario applies very rarely.
- Requests for packages from managed devices, including mobile devices, are transferred to the Web Server, which is on the same device as the Administration Server.
- For iOS mobile devices only: data from the mobile device is transferred through TLS port 443 to the iOS MDM Server, which is on the same device as the Administration Server or on the connection gateway.
Administration Server on LAN, managed devices on internet, connection gateway in use
The figure below shows data traffic if the Administration Server is on a local area network (LAN) and the managed devices, including mobile devices, are on the internet. A connection gateway is in use.
This deployment scheme is recommended if you do not want the mobile devices to connect to the Administration Server directly and do not want to use a reverse proxy or corporate firewall.
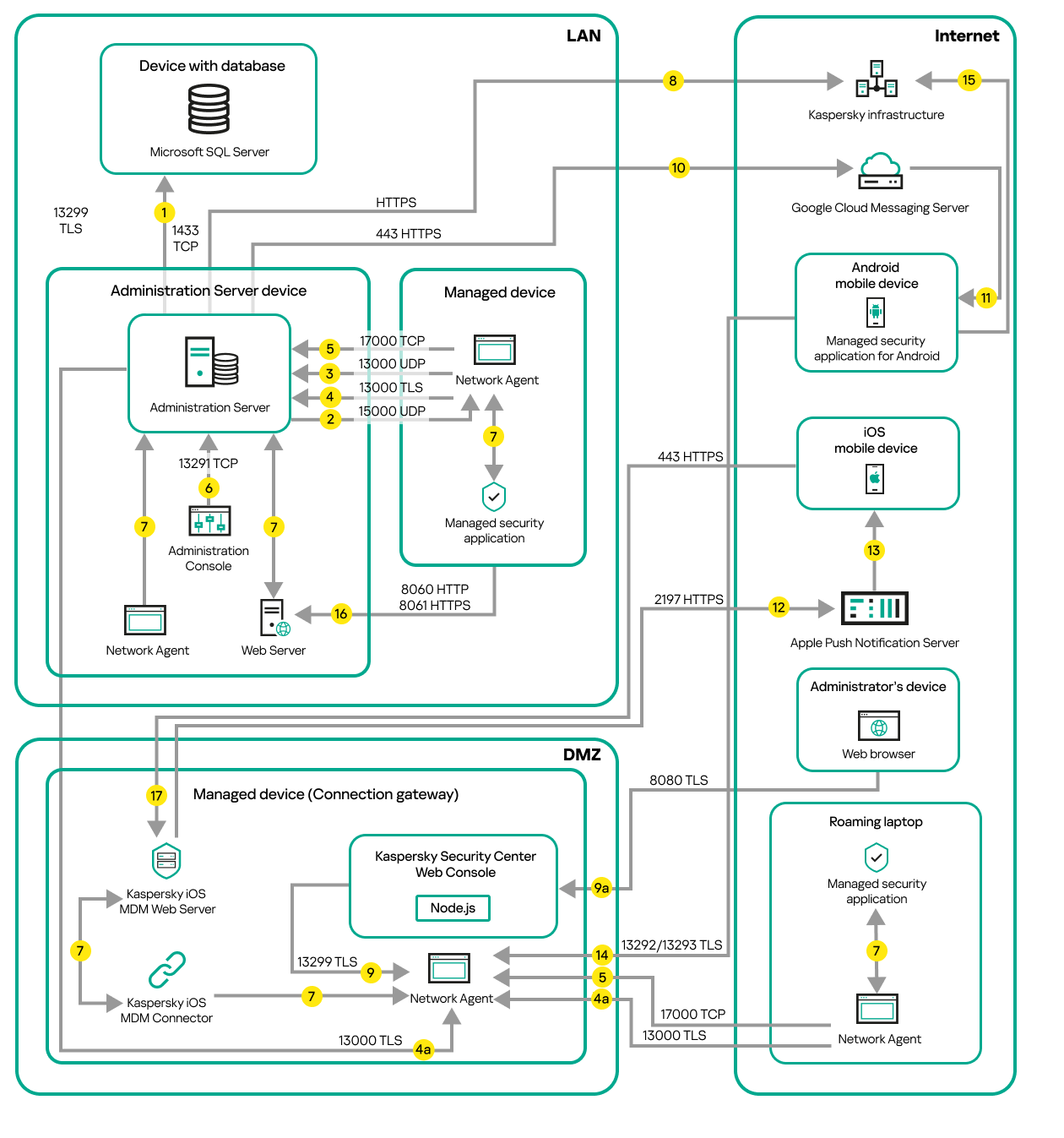
Managed mobile devices connected to the Administration Server through a connection gateway
In this figure, the managed devices are connected to the Administration Server through a connection gateway that is located in the DMZ. No reverse proxy or corporate firewall is in use.
The arrows indicate the initiation of traffic: each arrow points from a device that initiates the connection to the device that "answers" the call. The number of the port and the name of the protocol used for data transfer are provided. Each arrow has a number label, and details about the corresponding data traffic are as follows:
- Administration Server sends data to the database. If you install the Administration Server and the database on different devices, you must make available the necessary ports on the device where the database is located (for example, port 3306 for MySQL Server, or port 1433 for Microsoft SQL Server). Please refer to the DBMS documentation for the relevant information.
- Requests for communication from the Administration Server are transferred to all non-mobile managed devices through UDP port 15000.
Network Agents send requests to each other within one broadcasting domain. The data is then sent to the Administration Server and is used for defining the limits of the broadcasting domain and for automatic assignment of distribution points (if this option is enabled).
If Administration Server does not have direct access to the managed devices, communication requests from Administration Server to these devices are not sent directly.
- Information about shutdown of the managed devices is transferred from Network Agent to the Administration Server through UDP port 13000.
- The Administration Server receives connection from Network Agents and from secondary Administration Servers through TLS port 13000.
If you used an earlier version of Kaspersky Security Center, the Administration Server on your network can receive connection from Network Agents through non-TLS port 14000. Kaspersky Security Center also supports connection of Network Agents through port 14000, although using TLS port 13000 is recommended.
The distribution point was called "Update agent" in earlier versions of Kaspersky Security Center.
4a. A connection gateway in DMZ also receives connection from the Administration Server through TLS port 13000. Because a connection gateway in DMZ cannot reach the Administration Server's ports, the Administration Server creates and maintains a permanent signal connection with a connection gateway. The signal connection is not used for data transfer; it is only used for sending an invitation to the network interaction. When the connection gateway needs to connect to the Server, it notifies the Server through this signal connection, and then the Server creates the required connection for data transfer.
Out-of-office devices connect to the connection gateway through TLS port 13000 as well.
- The managed devices (except for mobile devices) request activation through TCP port 17000. This is not necessary if the device has its own access to the internet; in this case, the device sends the data to Kaspersky servers over the internet directly.
- Data from MMC-based Administration Console is transferred to the Administration Server through port 13291. (The Administration Console can be installed on the same or on a different device.)
- Applications on a single device exchange local traffic (either on the Administration Server or on a managed device). No external ports have to be opened.
- Data from the Administration Server to the Kaspersky servers (such as KSN data or information about licenses) and data from the Kaspersky servers to the Administration Server (such as application updates and anti-virus database updates) are transferred using the HTTPS protocol.
If you do not want your Administration Server to have access to the internet, you must manage this data manually.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server sends data to the Administration Server, which may be installed on the same or on a different device, through TLS port 13299.
9a. Data from the browser, which is installed on a separate device of the administrator, is transferred to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server through TLS port 8080. The Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server can be installed either on the Administration Server or on another device.
- For Android mobile devices only: data from the Administration Server is transferred to Google servers. This connection is used to notify Android mobile devices that they are required to connect to the Administration Server. Then push notifications are sent to the mobile devices.
- For Android mobile devices only: push notifications from Google servers are sent to the mobile device. This connection is used to notify mobile devices that they are required to connect to the Administration Server.
- For iOS mobile devices only: data from the iOS MDM Server is transferred to Apple Push Notification servers. Then push notifications are sent to the mobile devices.
- For iOS mobile devices only: push notifications are sent from Apple servers to the mobile device. This connection is used to notify iOS mobile devices that they are required to connect to the Administration Server.
- For mobile devices only: data from the managed application is transferred to the Administration Server (or to the connection gateway) through TLS port 13292 / 13293—directly or through a reverse proxy.
- For mobile devices only: data from the mobile device is transferred to the Kaspersky infrastructure.
If a mobile device does not have internet access, the data is transferred to Administration Server through port 17100, and the Administration Server sends it to the Kaspersky infrastructure; however, this scenario applies very rarely.
- Requests for packages from managed devices, including mobile devices, are transferred to the Web Server, which is on the same device as the Administration Server.
- For iOS mobile devices only: data from the mobile device is transferred through TLS port 443 to the iOS MDM Server, which is on the same device as the Administration Server or on the connection gateway.
Administration Server in DMZ, managed devices on internet
The figure below shows data traffic if the Administration Server is in the demilitarized zone (DMZ) and the managed devices, including mobile devices, are on the internet.
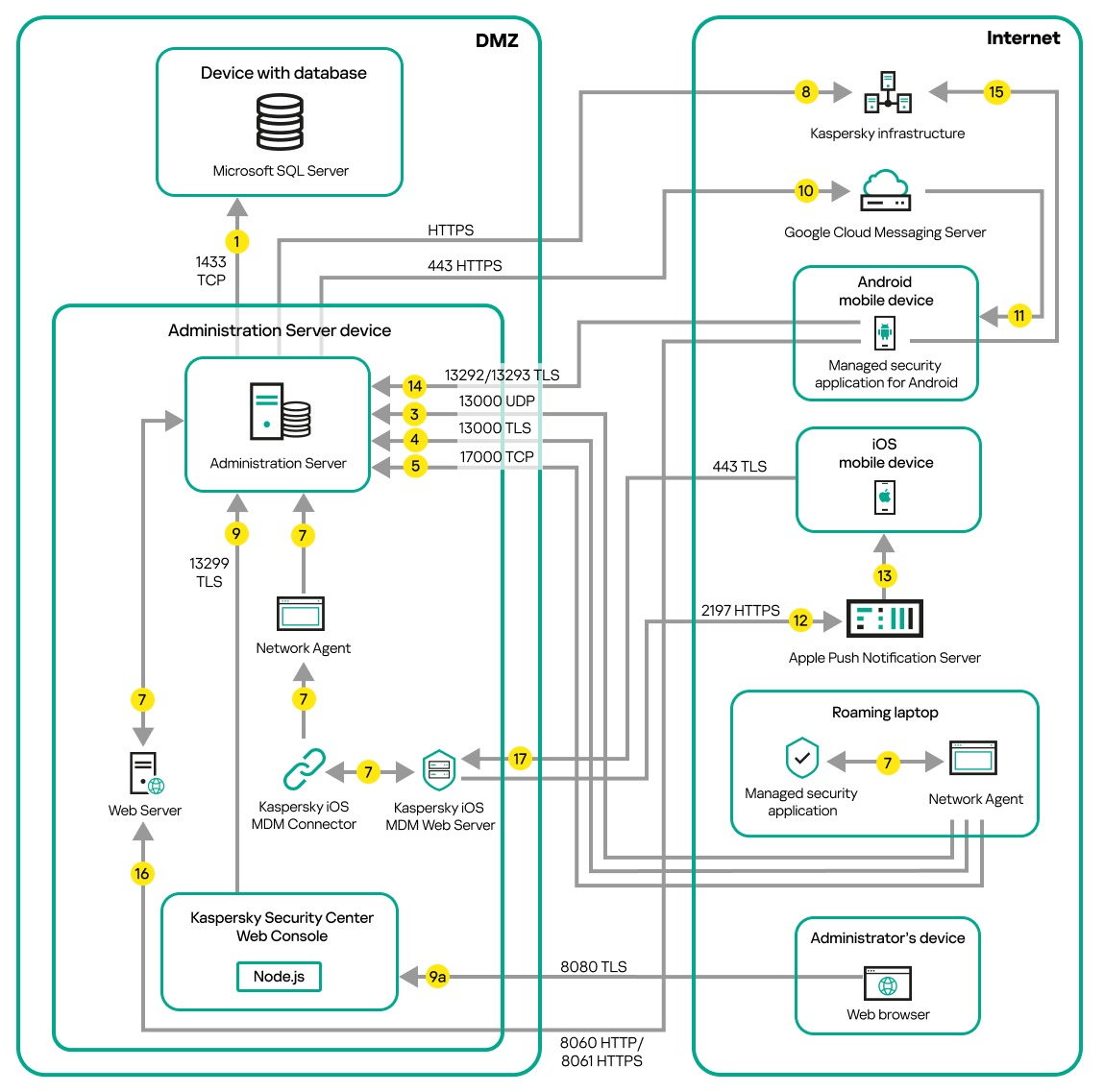
Administration Server in DMZ, managed mobile devices on the internet
In this figure, a connection gateway is not in use: the mobile devices connect to the Administration Server directly.
The arrows indicate the initiation of traffic: each arrow points from a device that initiates the connection to the device that "answers" the call. The number of the port and the name of the protocol used for data transfer are provided. Each arrow has a number label, and details about the corresponding data traffic are as follows:
- Administration Server sends data to the database. If you install the Administration Server and the database on different devices, you must make available the necessary ports on the device where the database is located (for example, port 3306 for MySQL Server, or port 1433 for Microsoft SQL Server). Please refer to the DBMS documentation for the relevant information.
- Requests for communication from the Administration Server are transferred to all non-mobile managed devices through UDP port 15000.
Network Agents send requests to each other within one broadcasting domain. The data is then sent to the Administration Server and is used for defining the limits of the broadcasting domain and for automatic assignment of distribution points (if this option is enabled).
If Administration Server does not have direct access to the managed devices, communication requests from Administration Server to these devices are not sent directly.
- Information about shutdown of the managed devices is transferred from Network Agent to the Administration Server through UDP port 13000.
- The Administration Server receives connection from Network Agents and from secondary Administration Servers through TLS port 13000.
If you used an earlier version of Kaspersky Security Center, the Administration Server on your network can receive connection from Network Agents through non-TLS port 14000. Kaspersky Security Center also supports connection of Network Agents through port 14000, although using TLS port 13000 is recommended.
The distribution point was called "Update agent" in earlier versions of Kaspersky Security Center.
- The managed devices (except for mobile devices) request activation through TCP port 17000. This is not necessary if the device has its own access to the internet; in this case, the device sends the data to Kaspersky servers over the internet directly.
- Data from MMC-based Administration Console is transferred to the Administration Server through port 13291. (The Administration Console can be installed on the same or on a different device.)
- Applications on a single device exchange local traffic (either on the Administration Server or on a managed device). No external ports have to be opened.
- Data from the Administration Server to the Kaspersky servers (such as KSN data or information about licenses) and data from the Kaspersky servers to the Administration Server (such as application updates and anti-virus database updates) are transferred using the HTTPS protocol.
If you do not want your Administration Server to have access to the internet, you must manage this data manually.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server sends data to the Administration Server, which may be installed on the same or on a different device, through TLS port 13299.
9a. Data from the browser, which is installed on a separate device of the administrator, is transferred to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server through TLS port 8080. The Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server can be installed either on the Administration Server or on another device.
- For Android mobile devices only: data from the Administration Server is transferred to Google servers. This connection is used to notify Android mobile devices that they are required to connect to the Administration Server. Then push notifications are sent to the mobile devices.
- For Android mobile devices only: push notifications from Google servers are sent to the mobile device. This connection is used to notify mobile devices that they are required to connect to the Administration Server.
- For iOS mobile devices only: data from the iOS MDM Server is transferred to Apple Push Notification servers. Then push notifications are sent to the mobile devices.
- For iOS mobile devices only: push notifications are sent from Apple servers to the mobile device. This connection is used to notify iOS mobile devices that they are required to connect to the Administration Server.
- For mobile devices only: data from the managed application is transferred to the Administration Server (or to the connection gateway) through TLS port 13292 / 13293—directly or through a reverse proxy.
- For mobile devices only: data from the mobile device is transferred to the Kaspersky infrastructure.
If a mobile device does not have internet access, the data is transferred to Administration Server through port 17100, and the Administration Server sends it to the Kaspersky infrastructure; however, this scenario applies very rarely.
- Requests for packages from managed devices, including mobile devices, are transferred to the Web Server, which is on the same device as the Administration Server.
- For iOS mobile devices only: data from the mobile device is transferred through TLS port 443 to the iOS MDM Server, which is on the same device as the Administration Server or on the connection gateway.
Interaction of Kaspersky Security Center components and security applications: more information
This section provides the schemas for interaction of Kaspersky Security Center components and managed security applications. The schemas provide the numbers of the ports that must be available and the names of the processes that open those ports.
Conventions used in interaction schemas
The following table provides the conventions used across the schemas.
Document conventions
Icon |
Meaning |
|
Administration Server |
|
Secondary Administration Server |
|
DBMS |
|
Client device (that has Network Agent and an application from Kaspersky Endpoint Security family installed, or has a different security application installed that Kaspersky Security Center can manage) |
|
Connection gateway |
|
Distribution point |
|
Mobile client device with Kaspersky Security for Mobile |
|
Browser on the user's device |
|
Process running on the device and opening a port |
|
Port and its number |
|
TCP traffic (the arrow direction shows the traffic flow direction) |
|
UDP traffic (the arrow direction shows the traffic flow direction) |
|
COM invoke |
|
DBMS transport |
|
DMZ boundary |
Administration Server and DBMS
Data from the Administration Server enter the SQL Server, MySQL, or MariaDB database.
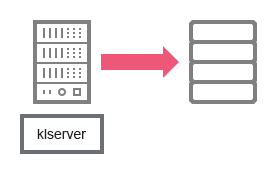
Administration Server and DBMS
If you install the Administration Server and the database on different devices, you must make available the necessary ports on the device where the database is located (for example, port 3306 for MySQL Server, or port 1433 for Microsoft SQL Server). Please refer to the DBMS documentation for the relevant information.
Administration Server and Administration Console
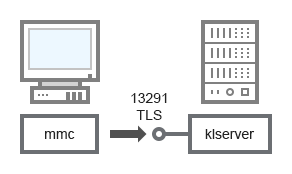
Administration Server and Administration Console
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Administration Server and Administration Console (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Administration Server |
13291 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Administration Console |
Administration Server and client device: Managing the security application
The Administration Server receives connection from Network Agents via SSL port 13000 (see figure below).
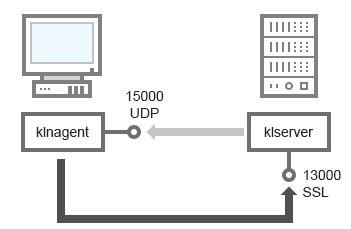
Administration Server and client device: managing the security application, connection via port 13000 (recommended)
If you used an earlier version of Kaspersky Security Center, the Administration Server on your network can receive connections from Network Agents via non-SSL port 14000 (see figure below). Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 also supports connection of Network Agents via port 14000, although using SSL port 13000 is recommended.
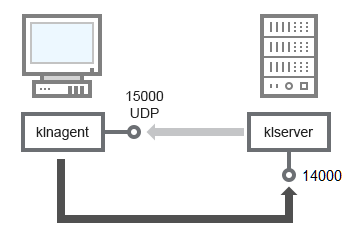
Administration Server and client device: managing the security application, connection via port 14000 (lower security)
For clarifications of schemas, see the table below.
Administration Server and client device: Managing the security application (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS (for TCP only) |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Network Agent |
15000 |
klnagent |
UDP |
Null |
Multicasting for Network Agents |
Administration Server |
13000 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Network Agents |
Administration Server |
14000 |
klserver |
TCP |
No |
Receiving connections from Network Agents |
Upgrading software on a client device through a distribution point
The client device connects to the distribution point via port 13000 and, if you are using the distribution point as a push server, also via port 13295; the distribution point multicasts to Network Agents via port 15000 (see figure below). Updates and installation packages are received from a distribution point via port 15001.
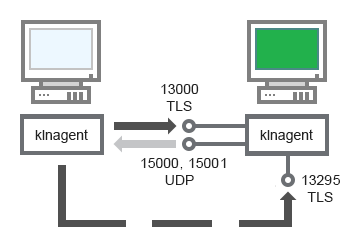
Upgrading software on a client device through a distribution point
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Upgrading software through a distribution point (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS (for TCP only) |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Network Agent |
15000 |
klnagent |
UDP |
Null |
Multicasting for Network Agents |
Network Agent |
15001 |
klnagent |
UDP |
Null |
Receiving updates and installation packages from a distribution point |
Distribution point |
13000 |
klnagent |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Network Agents |
Distribution point |
13295 |
klnagent |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from client devices (server push) |
Hierarchy of Administration Servers: primary Administration Server and secondary Administration Server
The schema (see figure below) shows how to use port 13000 to ensure interaction between Administration Servers combined into a hierarchy.
When combining two Administration Servers into a hierarchy, make sure that port 13291 is accessible on both Administration Servers. Administration Console connects to the Administration Server through port 13291.
Subsequently, when the Administration Servers are combined into a hierarchy, you will be able to administer both of them by using Administration Console connected to the primary Administration Server. Therefore, the accessibility of port 13291 of the primary Administration Server is the only prerequisite.
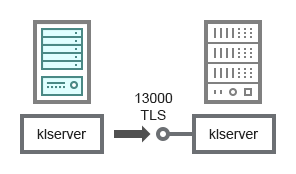
Hierarchy of Administration Servers: primary Administration Server and secondary Administration Server
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Hierarchy of Administration Servers (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Primary Administration Server |
13000 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from secondary Administration Servers |
Hierarchy of Administration Servers with a secondary Administration Server in DMZ
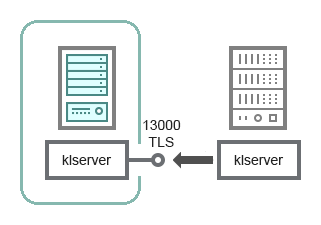
Hierarchy of Administration Servers with a secondary Administration Server in DMZ
The schema shows a hierarchy of Administration Servers in which the secondary Administration Server located in DMZ receives a connection from the primary Administration Server (see the table below for schema clarifications). When combining two Administration Servers into a hierarchy, make sure that port 13291 is accessible on both Administration Servers. Administration Console connects to the Administration Server through port 13291.
Subsequently, when the Administration Servers are combined into a hierarchy, you will be able to administer both of them by using Administration Console connected to the primary Administration Server. Therefore, the accessibility of port 13291 of the primary Administration Server is the only prerequisite.
Hierarchy of Administration Servers with a secondary Administration Server in DMZ (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Secondary Administration Server |
13000 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from the primary Administration Server |
Administration Server, a connection gateway in a network segment, and a client device
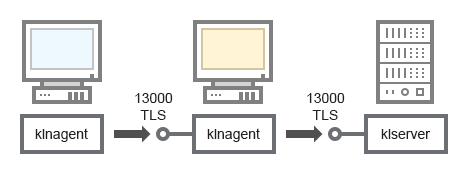
Administration Server, a connection gateway in a network segment, and a client device
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Administration Server, a connection gateway in a network segment, and a client device (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Administration Server |
13000 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Network Agents |
Network Agent |
13000 |
klnagent |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Network Agents |
Administration Server and two devices in DMZ: a connection gateway and a client device
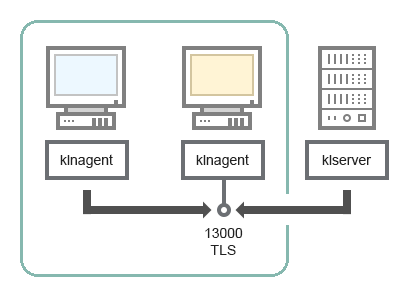
Administration Server with a connection gateway and a client device in DMZ
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Administration Server with a connection gateway in a network segment and a client device (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Network Agent |
13000 |
klnagent |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Network Agents |
Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
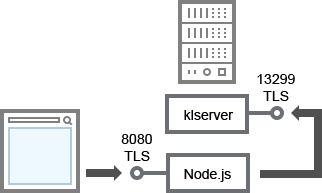
Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Administration Server |
13299 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to the Administration Server over OpenAPI |
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server or Administration Server |
8080 |
Node.js: Server-side JavaScript |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Kaspersky Security Center Web Console |
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console can be installed on the Administration Server or on another device.
Activating and managing the security application on a mobile device
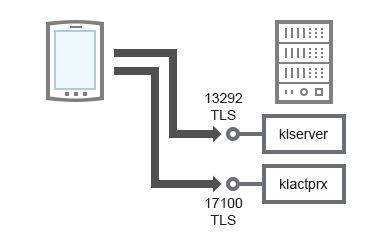
Activating and managing the security application on a mobile device
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Activating and managing the security application on a mobile device (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Administration Server |
13292 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Administration Console to Administration Server |
Administration Server |
17100 |
klactprx |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections for application activation from mobile devices |
Deployment best practices
Kaspersky Security Center is a distributed application. Kaspersky Security Center includes the following applications:
- Administration Server—The core component, designed for managing devices of an organization and storing data in a DBMS.
- Administration Console—The basic tool for the administrator. Administration Console is shipped together with Administration Server, but it can also be installed individually on one or several devices run by the administrator.
- Network Agent—Designed for managing the security application installed on a device, as well as getting information about that device and transferring this information to the Administration Server. Network Agents are installed on devices of an organization.
Deployment of Kaspersky Security Center on an organization's network is performed as follows:
- Installation of Administration Server
- Installation of Administration Console on the administrator's device
- Installation of Network Agent and the security application on devices of the enterprise
Hardening Guide
Kaspersky Security Center is designed for centralized execution of basic administration and maintenance tasks on an organization's network. The application provides the administrator access to detailed information about the organization's network security level. Kaspersky Security Center allows you to configure all components of protection built by using Kaspersky applications.
Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server has full access to protection management of client devices and is the most important component of the organization's security system. Therefore, increased protection methods are required for Administration Server.
Before configuring, create a Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server backup copy by using the Backup of Administration Server data task or the klbackup utility and save it in a safe location.
The Hardening Guide describes recommendations and features of configuring Kaspersky Security Center and its components, aimed to reduce the risks of its compromise.
The Hardening Guide contains the following information:
- Selecting the Administration Server architecture
- Configuring a secure connection to Administration Server
- Configuring accounts to access Administration Server
- Managing protection of Administration Server
- Managing protection of client devices
- Configuring protection for managed applications
- Administration Server maintenance
- Transferring information to third-party applications
- Security recommendations for third-party information systems
Administration Server deployment
Administration Server architecture
In general, the choice of a centralized management architecture depends on the location of protected devices, access from adjacent networks, delivery schemes of database updates, and so on.
At the initial stage of architecture development, we recommend getting acquainted with the Kaspersky Security Center components and their interaction with each other, as well as with schemas for data traffic and port usage.
Based on this information, you can form an architecture that specifies:
- The Administration Server location and network connections
- Organization of the administrator's workspaces, and methods of connecting to Administration Server
- Deployment methods for Network Agent and protection software
- Using distribution points
- Using virtual Administration Servers
- Using a hierarchy of Administration Servers
- Anti-virus database update scheme
- Other information flows
Selecting a device for the Administration Server installation
We recommend that you install Administration Server on a dedicated server in the organization infrastructure. If there is no other third-party software installed on the server, you can configure the security settings based on the requirements of Kaspersky Security Center, without depending on the requirements of third-party software.
You can deploy Administration Server on a physical server or on a virtual server. Please make sure that the selected device meets the hardware and software requirements.
Administration Server location
Devices managed by Administration Server can be located as follows:
On a local area network (LAN)
On the internet
In the demilitarized zone (DMZ)
At the same time, Administration Server can also be located in different segments: industrial, corporate, and DMZ segments.
If you use Kaspersky Security Center to manage protection of an isolated network segment, we recommend deploying Administration Server in a segment of the demilitarized zone (DMZ). This allows you to organize a proper network segmentation and minimize traffic flow to the protected segment, while maintaining full management capabilities and update delivery.
Restriction of deploying Administration Server on a domain controller, a terminal server, or a user device
We strongly do not recommend installing Administration Server on a domain controller, a terminal server, or a user device.
We recommend that you provide functional separation of the network key nodes. This approach allows you to maintain the operability of different systems when a node fails or is compromised. At the same time, you can create different security policies for each node.
For example, security restrictions usually applied to a domain controller can significantly reduce the performance of Administration Server and make it impossible to use some features of Administration Server. If an intruder gains privileged access to the domain controller, Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) database can be modified, damaged, or destroyed. Also, all systems and accounts managed by Active Directory can be compromised.
Accounts for installing and running Administration Server
We recommend running the Administration Server installation under a local administrator account to avoid using domain accounts to access the Administration Server database. A set of the required accounts and their rights depends on the selected DBMS type, DBMS location and method of the Administration Server database creation.
The KLAdmins and KLOperators groups are created automatically during Kaspersky Security Center installation. These groups are granted permissions to connect to the Administration Server and to process Administration Server objects.
Depending on the type of account that is used for installation of Kaspersky Security Center, the KLAdmins and KLOperators groups are created as follows:
- If the application is installed under a user account included in a domain, the groups are created on the Administration Server device and in the domain that includes Administration Server.
- If the application is installed under a system account, the groups are created on the Administration Server device only.
In order to avoid creating the KLAdmins and KLOperators groups in the domain and, as a result, providing privileges to manage Administration Server to an account outside the Administration Server device, we recommend installing Kaspersky Security Center under a local account.
During Administration Server installation, select the account that will be used to start Administration Server as a service. By default, the application creates a local account named KL-AK-*, under which the Administration Server service (the klserver service) will run.
If necessary, the Administration Server service can be run under the selected account. This account must be granted the required rights to access the DBMS. For security reasons, use a non-privilege account to run the Administration Server service.
To avoid the use of incorrect account settings, we recommend generating the account automatically.
Excluding Administration Server from a domain
If you use Administration Server to protect device groups of high-importance systems, we do not recommend including the Administration Server device in the domain. This allows you to differentiate Kaspersky Security Center management rights and prevent access to Administration Server in case the domain account is compromised.
Take into account that if you install Administration Server on a device included in the workgroup, the following scenarios of working with Administration Server will not be available:
- Using a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
- Using a Windows Server failover cluster
- Using SQL Server on a separate device
You can use SQL Server on a separate device only if Administration Server and SQL Server are included in the domain.
- Remote installation with Administration Server tools through Active Directory group policies
If you need to disconnect the Administration Server from the Active Directory domain, follow the steps described in the topic: How to change the name of the Kaspersky Security Center.
If it is necessary to install Administration Server on a device included in the workgroup, you can also use Kaspersky Security Center Linux instead of Kaspersky Security Center Windows.
Page top
Connection safety
Usage of TLS
We recommend prohibiting insecure connections to Administration Server. For example, you can prohibit connections that use HTTP in the Administration Server settings.
Please note that by default, several HTTP ports of Administration Server are closed. The remaining port is used for the Administration Server Web Server (8060). This port can be limited by the firewall settings of the Administration Server device.
Strict TLS settings
We recommend using TLS protocol version 1.2 and later, and restricting or prohibiting insecure encryption algorithms.
You can configure encryption protocols (TLS) used by Administration Server. Please note that at the time of the release of a version of Administration Server, the encryption protocol settings are configured by default to ensure secure data transfer.
Restricting access to the Administration Server database
We recommend restricting access to the Administration Server database. For example, grant access only from the Administration Server device. This reduces the likelihood of the Administration Server database being compromised due to known vulnerabilities.
You can configure the parameters according to the operating instructions of the used database, as well as provide closed ports on firewalls.
Prohibition of remote authentication by using Windows accounts
You can use the LP_RestrictRemoteOsAuth flag to prohibit SSPI connections from remote addresses. This flag allows you to prohibit remote authentication on Administration Server by using local or domain Windows accounts.
To switch the LP_RestrictRemoteOsAuth flag to the mode of prohibiting connections from the remote addresses:
- Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
- Execute the following command in the command line to specify the value of the LP_RestrictRemoteOsAuth flag:
klscflag.exe -fset -pv .core/.independent -s KLLIM -n LP_RestrictRemoteOsAuth -t d -v 1 - Restart the Administration Server service.
The LP_RestrictRemoteOsAuth flag does not work if remote authentication is performed through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console or Administration Console that is installed on the Administration Server device.
Authenticating Microsoft SQL Server
If Kaspersky Security Center uses Microsoft SQL Server as a DBMS, it is necessary to protect Kaspersky Security Center data transferred to or from the database and data stored in the database from unauthorized access. To do this, you must secure communication between Kaspersky Security Center and SQL Server. The most reliable way to provide secure communication is to install Kaspersky Security Center and SQL Server on the same device and use the shared memory mechanism for both applications. In all other cases, we recommend that you use an SSL/TLS certificate to authenticate the SQL Server instance.
Configuring an allowlist of IP addresses to connect to Administration Server
By default, users can log in to Kaspersky Security Center from any device where they can open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console or where MMC-based Administration Console is installed. However, you can configure Administration Server so that users can connect to it only from devices with allowed IP addresses. In this case, even if an intruder steals a Kaspersky Security Center account, he or she will be able to log in to Kaspersky Security Center only from IP addresses that are in the allowlist.
Page top
Accounts and authentication
Before performing the below steps, create a Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server backup copy using KL tools (Backup of Administration Server data or klbackup utility) and save it in a safe location.
Using two-step verification with Administration Server
Kaspersky Security Center provides two-step verification for users of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and Administration Console, based on the RFC 6238 standard (TOTP: Time-Based One-Time Password algorithm).
When two-step verification is enabled for your own account, every time you log in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console or Administration Console, you enter your user name, password, and an additional single-use security code. If you use domain authentication for your account, you only have to enter an additional single-use security code. To receive a single-use security code, you must install an authenticator app on your computer or your mobile device.
There are both software and hardware authenticators (tokens) that support the RFC 6238 standard. For example, software authenticators include Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, FreeOTP.
We strongly do not recommend installing the authenticator app on the same device from which the connection to Administration Server is established. You can install an authenticator app on your mobile device.
Using two-factor authentication for an operating system
We recommend using multi-factor authentication (MFA) for authentication on the Administration Server device by using a token, a smart card, or other method (if possible).
Prohibition on saving the administrator password
If you use Administration Console, we do not recommend saving the administrator password in the Administration Server connection dialog box.
If you use Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, we do not recommend saving the administrator password in the browser installed on the user device.
Authentication of an internal user account
By default, the password of an internal user account of Administration Server must comply with the following rules:
The password must be 8 to 256 characters long.
The password must contain characters from at least three of the groups listed below:
Uppercase letters (A-Z)
Lowercase letters (a-z)
Numbers (0-9)
Special characters (@ # $ % ^ & * - _ ! + = [ ] { } | : ' , . ? / \ ` ~ " ( ) ;)
The password must not contain any whitespaces, Unicode characters, or the combination of "." and "@", when "." is placed before "@".
By default, the maximum number of allowed attempts to enter a password is 10. You can change the number of allowed password entry attempts.
The Kaspersky Security Center user can enter an invalid password a limited number of times. After the limit is reached, the user account is blocked for one hour.
Dedicated administration group for Administration Server
We recommend creating a dedicated administration group for Administration Server. Grant this group special access rights and create a special security policy for it.
To avoid intentionally lowering the security level of Administration Server, we recommend restricting the list of accounts that can manage the dedicated administration group.
The KLAdmins and KLOperators groups
The KLAdmins and KLOperators groups are created automatically during Kaspersky Security Center installation. The KLAdmins group is granted all access rights. The KLOperators group is granted only Read and Execute rights. The rights granted to the KLAdmins group are locked.
You can view the KLAdmins and KLOperators groups, and make changes to these groups, by using the standard administrative tools of the operating system.
When developing regulations for working with Administration Server, it is necessary to determine whether the information security specialist needs full access (and inclusion in the KLAdmins group) to perform standard tasks.
Most of the basic administration tasks can be distributed between company departments (or different employees of the same department) and consequently between different accounts. You can also set up administration groups access differentiation in Kaspersky Security Center. As a result, it is possible to implement a scenario in which authorization under accounts from the KLAdmins group will be anomalous and could be considered an incident.
If Kaspersky Security Center was installed under a system account, groups are created only on the Administration Server device. In this case, we recommend making sure that only entries created during the installation of Kaspersky Security Center are included in the group. We do not recommend adding any groups to the KLAdmins group (local and/or domain) that is created automatically during the Kaspersky Security Center installation. You should also limit the rights to change this group. The KLAdmins group must include only single unprivileged accounts.
If the installation was performed under a domain user account, groups KLAdmins and KLOperators are created both on Administration Server and in the domain that includes Administration Server. A similar approach such as local account installation is recommended.
Restricting the Main Administrator role membership
We recommend restricting the Main Administrator role membership.
By default, after the Administration Server installation, the Main Administrator role is assigned to the local administrators group and the created KLAdmins group. It is useful for management, but it is critical from a security point of view, because the Main Administrator role has an extensive range of privileges, the assignment of this role to users should be strictly regulated.
Local administrators can be excluded from the list of users with administrator privileges of Kaspersky Security Center. The Main Administrator role cannot be removed from the KLAdmins group. You can include in the KLAdmins group the accounts that will be used to manage Administration Server.
If you use domain authentication, we recommend restricting the privileges of domain administrator accounts in Kaspersky Security Center. By default, these accounts have the Main Administrator role. Also, a domain administrator can include its account in the KLAdmins group to obtain the Main Administrator role. To avoid this, in the Kaspersky Security Center security settings you can add the Domain Admins group, and then define prohibiting rules for it. These rules must take precedence over the allowing ones.
You can also use the predefined user roles with an already configured set of rights.
Configuring access rights to application features
We recommend using flexible configuration of access rights to the features of Kaspersky Security Center for each user or group of users.
Role-based access control allows the creation of standard user roles with a predefined set of rights and the assignment of those roles to users depending on their scope of duties.
The main advantages of the role-based access control model:
- Ease of administration
- Role hierarchy
- Least privilege approach
- Segregation of duties
You can assign built-in roles to certain employees based on their positions, or create completely new roles.
While configuring roles, pay attention to the privileges associated with changing the protection state of Administration Server device and remote installation of third-party software:
- Managing administration groups.
- Operations with Administration Server.
- Remote installation.
- Changing the parameters for storing events and sending notifications.
This privilege allows you to set notifications that run a script or an executable module on the Administration Server device when an event occurs.
Separate account for remote installation of applications
In addition to the basic differentiation of access rights, we recommend restricting the remote installation of applications for all accounts (except for the Main Administrator or another specialized account).
We recommend using a separate account for remote installation of applications. You can assign a role or permissions to the separate account.
Securing Windows Privileged Access
We recommend taking into account Microsoft's recommendations for providing privileged access security. To view these recommendations, go to the Securing privileged access article.
One of the key points of recommendations is the implementation of Privileged Access Workstations (PAW).Using a managed service account (MSA) or a group managed service accounts (gMSA) to run the Administration Server service
Active Directory has a special type of accounts for securely running services, called group Managed Service Account (MSA/gMSA). Kaspersky Security Center supports managed service accounts (MSA) and group managed service accounts (gMSA). If these types of accounts are used in your domain, you can select one of them as the account for the Administration Server service.
Regular audit of all users
We recommend conducting a regular audit of all users on the Administration Server device. This allows you to respond to certain types of security threats associated with possible compromise of the device.
Page top
Managing protection of Administration Server
Selecting an Administration Server protection software
Depending on the type of the Administration Server deployment and the general protection strategy, select the application to protect the Administration Server device.
If you deploy Administration Server on a dedicated device, we recommend selecting the Kaspersky Endpoint Security application to protect the Administration Server device. This allows applying all available technologies to protect the Administration Server device, including behavioral analysis modules.
If Administration Server is installed on a device that exists in the infrastructure and has previously been used for other tasks, we recommend considering the following protection software:
- Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Nodes. We recommend installing this application on devices that are included in an industrial network. Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Nodes is an application that has certificates of compatibility with various manufacturers of industrial software.
- Recommended security solutions. If Administration Server is installed on a device with other software, we recommend taking into account the recommendations from that software vendor on the compatibility of security solutions (there may already be recommendations for selecting a security solution, and you may need to configure the trusted zone).
Creating a separate security policy for the protection application
We recommend that you create a separate security policy for the application that protects the Administration Server device. This policy must be different from the security policy for client devices. This allows specifying the most appropriate security settings for Administration Server, without affecting the protection level of other devices.
We recommend dividing devices into groups, and then placing the Administration Server device into a separate group for which you can create a special security policy.
Protection modules
If there are no special recommendations from the vendor of the third-party software installed on the same device as Administration Server, we recommend activating and configuring all available protection modules (after checking the operation of these protection modules for a certain time).
Configuring the firewall of the Administration Server device
On the Administration Server device, we recommend configuring the firewall to restrict the number of devices from which administrators can connect to Administration Server through Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
By default, Administration Server uses port 13291 to receive connections from Administration Console and port 13299 to receive connections from Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. We recommend restricting the number of devices from which Administration Server can be managed by using these ports.
Prohibition of launching the control panel
If you install Administration Server on a device running Microsoft Windows and use the protection application with the Application Launch Control module, you can prohibit the launch of the control panel (control.exe) for unprivileged users, for example, the Administrators group.
After creating the specified prohibiting control rules of the application launch, users with the privileges of the pre-defined Administrator role lose the ability to control other network accounts, including changing their logins and passwords.
Page top
Managing protection of client devices
Restricting of adding license keys to installation packages
Installation packages are stored in the Administration Server shared folder, in the Packages subfolder. If you add a license key to an installation package, the license key may be compromised because the shared Read access rights are enabled to the repository of installation packages.
To avoid compromising the license key, we do not recommend adding license keys to installation packages.
We recommend using automatic distribution of license keys to managed devices, deployment through the Add license key task for a managed application, and adding an activation code or a key file manually to the devices.
Automatic rules for moving devices between administration groups
We recommend restricting the use of automatic rules for moving devices between administration groups.
If you use automatic rules for moving devices, this may lead to propagation of policies that provide more privileges to the moved device than the device has before relocation.
Also, moving a client device to another administration group may lead to propagation of policy settings. These policy settings may be undesirable for distribution to guest and untrusted devices.
This recommendation does not apply for one-time initial allocation of devices to administration groups.
Security requirements for distribution points and connection gateways
Devices with Network Agent installed can act as a distribution point and perform the following functions:
- Distribute updates and installation packages received from Administration Server to client devices within the group.
- Perform remote installation of third-party software and Kaspersky applications on client devices.
- Poll the network to detect new devices and update information about existing ones. The distribution point can use the same methods of device detection as Administration Server.
Placing distribution points on the organization's network used for:
- Reducing the load on Administration Server
- Traffic optimization
- Providing Administration Server with access to devices in hard-to-reach parts of the network
Taking into account the available capabilities, we recommend protecting devices that act as distribution points from any type of unauthorized access (including physically).
Restricting automatic assignment of distribution points
To simplify administration and keep the network operability, we recommend using automatic assignment of distribution points. However, for industrial networks and small networks, we recommend that you avoid assigning distribution points automatically, since, for example, the private information of the accounts used for pushing remote installation tasks, can be transferred to distribution points by means of the operating system.
For industrial networks and small networks, you can manually assign devices to act as distribution points.
You can also view the Report on activity of distribution points.
Page top
Configuring protection for managed applications
Managed application policies
We recommend creating a policy for each type of the used applications and components of Kaspersky Security Center (Network Agent, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, and others). This policy must be applied to all managed devices (the root administration group) or to a separate group to which new managed devices are automatically moved according to the configured movement rules.
Specifying the password for disabling protection and uninstalling the application
To prevent intruders from disabling Kaspersky security applications, we strongly recommend enabling password protection for disabling protection and deinstallation of Kaspersky security applications. You can set the password, for example, for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, Kaspersky Security for Windows Servers, Network Agent, and other Kaspersky applications. After you enable password protection, we recommend locking these settings by closing the "lock."
Specifying the password for manual connection of a client device to the Administration Server (klmover utility)
The klmover utility allows you to manually connect a client device to the Administration Server. When Network Agent is installed on a client device, the utility is automatically copied to the Network Agent installation folder.
To prevent intruders from moving devices out of your Administration Server's control, we strongly recommend enabling password protection for running the klmover utility. To enable password protection, select the Use uninstallation password option in the Network Agent policy settings.
The klmover utility requires local administrator rights. Password protection for running the klmover utility can be omitted for devices operated without local administrator rights.
Enabling the Use uninstallation password also enables password protection for the Cleaner tool (cleaner.exe).
Using Kaspersky Security Network
In all policies of managed applications and in the Administration Server properties, we recommend enabling the use of Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) and accepting the KSN Statement. When you update or upgrade Administration Server, you can accept the updated KSN Statement. In some cases, when the use of cloud services is prohibited by law or other regulations, you can disable KSN.
Regular scan of managed devices
For all device groups, we recommend creating a task that periodically runs a full scan of devices.
Discovering new devices
We recommend properly configuring device discovery settings: set up integration with Active Directory and specify IP address ranges for discovering new devices.
For security purposes, you can use the default administration group that includes all new devices and the default policies affecting this group.
Selecting a shared folder
If you deploy Administration Server on the device running Windows with the selection of an existing shared folder (that is used, for example, for placing installation packages and storage of updated databases), we recommend ensuring that read rights are granted to the Everyone group, and write rights are granted to the KLAdmins group.
Page top
Administration Server maintenance
Backup copying of Administration Server data
Data backup allows you to restore Administration Server data without data loss.
By default, a data backup task is created automatically after the installation of Administration Server and is executed periodically, saving backups in the appropriate directory.Settings of the data backup task can be changed as follows:
- The backup frequency increases
- A special directory for saving copies is specified
- Passwords for backup copies is changed
If you store backup copies in a special directory, that is different from the default directory, we recommend limiting the access control list (ACL) for this directory. The Administration Server accounts and accounts of the Administration Server database must have the write access for this directory.
Administration Server maintenance
The Administration Server maintenance allows you to reduce the database volume, and improve the performance and operation reliability of the application. We recommend that you maintain Administration Server at least every week.
The Administration Server maintenance is performed using the dedicated task. The application performs the following actions when maintaining the Administration Server:
- Checks the database for errors
- Re-organizes database indexes
- Updates the database statistics
- Shrinks the database (if necessary)
Installing operating system updates and third-party software updates
We strongly recommend that you regularly install software updates for the operating system and third-party software on the Administration Server device.
Client devices do not require a continuous connection to Administration Server, so it is safe to reboot the Administration Server device after installing updates. All events registered on client devices during Administration Server downtime are sent to it after the connection is restored.
Page top
Event transfer to third-party systems
Monitoring and reporting
For timely response to security issues, we recommend configuring the monitoring and reporting features.
Export of events to SIEM systems
For fast detection of security issues before significant damage occurs, we recommend using event export in a SIEM system.
Email notifications of audit events
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to receive information about events that occur during the operation of Administration Server and Kaspersky applications installed on managed devices. For timely response to emergencies, we recommend configuring Administration Server to send notifications about the audit events, critical events, failure events, and warnings that it publishes.
Since these events are intra-system events, a small number of them can be expected, which is quite applicable for mailing.
Statistics of the Administration Server function
For timely response to security issues, we recommend configuring the sending of statistics of the Administration Server function to third-party applications, by using Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
Page top
Security recommendations for third-party information systems
Security recommendations from CIS Benchmarks
When using versions of operating systems, virtualization platforms, or database servers supported by Administration Server and Network Agent, we recommend applying the best information security practices from the Center for Internet Security (CIS), if any, to fine-tune these information systems.
Center for Internet Security (CIS) is a non-profit organization dedicated to improving security in the field of information technology. In particular, CIS develops and distributes safety standards such as CIS Controls and CIS Benchmarks. These standards are a set of recommendations and practices for ensuring the security of information systems.
The CIS portal contains recommendations for the versions of the following information systems supported by Administration Server and Network Agent:
- Operating systems of the following families:
- Windows for desktops
- Windows for servers
- Debian
- Ubuntu
- CentOS
- Oracle Linux
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server
- macOS
- VMware virtualization platforms
- Database servers:
- Microsoft SQL Server
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- PostgreSQL
Security recommendations for the Astra Linux operating system
When using the Astra Linux operating system, you should follow the security recommendations described in the Red Book for the corresponding version of Astra Linux.
Security recommendations for the RED OS operating system
When using the RED OS operating system, you should use the security recommendations described in the official RED OS documentation.
Page top
Recommendations for using Kaspersky security applications
Using the KLAdmin password in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
Multiple users with different levels of computer literacy can share a device with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows installed. If users have unrestricted access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows and its settings, the overall level of device protection may be reduced. Password protection allows you to restrict users' access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, according to the permissions granted to them (for example, permission to exit the application).
One of the ways to restrict access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows and its parameters is to use a KLAdmin account. The KLAdmin account is an administrator account with unrestricted access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. The KLAdmin account has the right to perform any password-protected action in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. The permissions for the KLAdmin account cannot be revoked. You can set the password for the KLAdmin account in the properties of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy. The Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows administrator is fully responsible for the safe use of the password for the KLAdmin account. If your organization has its own password policy, follow the instructions of that policy.
Our recommendations for protecting the organization from theft of the KLAdmin password are as follows:
- General requirements
Do not use the account name or part of the name as the password.
- Minimum password length requirements
Create a password that is at least 10 characters in length.
- Requirements for using multiple character types
Set a complex password that contains characters from different categories: lowercase and uppercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Password expiration requirements
Set a minimum password expiration date of 90 days. A new password must not match any of the last 24 passwords.
Preparation for deployment
This section describes steps you must take before deploying Kaspersky Security Center.
Planning Kaspersky Security Center deployment
This section provides information about the most convenient options for deployment of Kaspersky Security Center components on an organization's network, depending on the following criteria:
- Total number of devices
- Units (local offices, branches) that are detached organizationally or geographically
- Separate networks connected by narrow channels
- Need for internet access to the Administration Server
Typical schemes of protection system deployment
This section describes the standard deployment schemes of a protection system in an enterprise network using Kaspersky Security Center.
The system must be protected against any type of unauthorized access. We recommend that you install all available security updates for your operating system before installing the application on your device and physically protect Administration Server(s) and distribution point(s).
You can use Kaspersky Security Center to deploy a protection system on a corporate network by means of the following deployment schemes:
- Deploying a protection system through Kaspersky Security Center, in one of the following ways:
- Through Administration Console
- Through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
Kaspersky applications are automatically installed on client devices, which in turn are automatically connected to the Administration Server by using Kaspersky Security Center.
The basic deployment scheme is protection system deployment through Administration Console. Using Kaspersky Security Center Web Console allows you to launch installation of Kaspersky applications from a browser.
- Deploying a protection system manually using stand-alone installation packages generated by Kaspersky Security Center.
Installation of Kaspersky applications on client devices and the administrator's workstation is performed manually; the settings for connecting client devices to the Administration Server are specified when Network Agent is installed.
This deployment method is recommended in cases when remote installation is not possible.
Kaspersky Security Center also allows you to deploy your protection system using Microsoft Active Directory group policies.
Page top
About planning Kaspersky Security Center deployment in an organization's network
One Administration Server can support a maximum of 100,000 devices. If the total number of devices on an organization's network exceeds 100,000, multiple Administration Servers must be deployed on that network and combined into a hierarchy for convenient centralized management.
If an organization includes large-scale remote local offices (branches) with their own administrators, it is useful to deploy Administration Servers in those offices. Otherwise, those offices must be viewed as detached networks connected by low-throughput channels; see section "Standard configuration: A few large-scale offices run by their own administrators".
When detached networks connected with narrow channels are used, traffic can be saved by assigning one or several Network Agents to act as distribution points (see table for calculation of the number of distribution points). In this case, all devices on a detached network retrieve updates from such local update centers. Actual distribution points can download updates both from the Administration Server (default scenario), and from Kaspersky servers on the internet (see section "Standard configuration: Multiple small remote offices").
Section "Standard configurations of Kaspersky Security Center" provides detailed descriptions of the standard configurations of Kaspersky Security Center. When planning the deployment, choose the most suitable standard configuration, depending on the organization's structure.
At the stage of deployment planning, the assignment of the special certificate X.509 to the Administration Server must be considered. Assignment of the X.509 certificate to the Administration Server may be useful in the following cases (partial list):
- Inspecting secure socket layer (SSL) traffic by means of an SSL termination proxy or for using a reverse proxy
- Integration with the public keys infrastructure (PKI) of an organization
- Specifying required values in certificate fields
- Providing the required encryption strength of a certificate
Selecting a structure for protection of an enterprise
Selection of a structure for protection of an organization is defined by the following factors:
- Organization's network topology.
- Organizational structure.
- Number of employees in charge of the network protection, and allocation of their responsibilities.
- Hardware resources that can be allocated to protection management components.
- Throughput of communication channels that can be allocated to maintenance of protection components on the organizational network.
- Time limits for execution of critical administrative operations on the organization's network. Critical administrative operations include, for example, the distribution of anti-virus databases and modification of policies for client devices.
When you select a protection structure, it is recommended first to estimate the available network and hardware resources that can be used for the operation of a centralized protection system.
To analyze the network and hardware infrastructure, it is recommended that you follow the process below:
- Define the following settings of the network on which the protection will be deployed:
- Number of network segments.
- Speed of communication channels between individual network segments.
- Number of managed devices in each of the network segments.
- Throughput of each communication channel that can be allocated to maintain the operation of the protection.
- Determine the maximum allowed time for the execution of key administrative operations for all managed devices.
- Analyze information from steps 1 and 2, as well as data from load testing of the administration system. Based on the analysis, answer the following questions:
- Is it possible to serve all the clients with a single Administration Server, or is a hierarchy of Administration Servers required?
- Which hardware configuration of Administration Servers is required in order to deal with all the clients within the time limits specified in step 2?
- Is it required to use distribution points to reduce load on communication channels?
Upon obtaining answers to the questions in step 3 above, you can compile a set of allowed structures of the organization's protection.
On the organization's network you can use one of the following standard protection structures:
- One Administration Server. All client devices are connected to a single Administration Server. Administration Server functions as distribution point.
- One Administration Server with distribution points. All client devices are connected to a single Administration Server. Some of the networked client devices function as distribution points.
- Hierarchy of Administration Servers. For each network segment, an individual Administration Server is allocated and becomes part of a general hierarchy of Administration Servers. The primary Administration Server functions as distribution point.
- Hierarchy of Administration Servers with distribution points. For each network segment, an individual Administration Server is allocated and becomes part of a general hierarchy of Administration Servers. Some of the networked client devices function as distribution points.
Standard configurations of Kaspersky Security Center
This section describes the following standard configurations used for deployment of Kaspersky Security Center components on an organization's network:
- Single office
- A few large-scale offices, which are geographically detached and run by their own administrators
- Multiple small offices, which are geographically detached
Standard configuration: Single office
One or several Administration Servers can be deployed on the organization's network. The number of Administration Servers can be selected either based on available hardware, or on the total number of managed devices.
One Administration Server can support up to 100,000 devices. You must consider the possibility of increasing the number of managed devices in the near future: it may be useful to connect a slightly smaller number of devices to a single Administration Server.
Administration Servers can be deployed either on the internal network, or in the DMZ, depending on whether internet access to the Administration Servers is required.
If multiple Servers are used, it is recommended that you combine them into a hierarchy. Using an Administration Server hierarchy allows you to avoid dubbed policies and tasks, and handle the whole set of managed devices as if they are managed by a single Administration Server (that is, search for devices, build selections of devices, and create reports).
Standard configuration: A few large-scale offices run by their own administrators
If an organization has a few large-scale, geographically separate offices, you must consider the option of deploying Administration Servers at each of the offices. One or several Administration Servers can be deployed per office, depending on the number of client devices and hardware available. In this case, each of the offices can be viewed as a "Standard configuration: Single office". For ease of administration, it is recommended to combine all of the Administration Servers into a hierarchy (possibly multi-level).
If some employees move between offices with their devices (laptops), create Network Agent connection profiles in the Network Agent policy. Network Agent connection profiles are only supported for Windows and macOS devices.
Standard configuration: Multiple small remote offices
This standard configuration provides for a headquarters office and many remote small offices that may communicate with the HQ office over the internet. Each of the remote offices may be located behind a Network Address Translation (NAT), that is, no connection can be established between two remote offices because they are isolated.
An Administration Server must be deployed at the headquarters office, and one or multiple distribution points must be assigned to all other offices. If the offices are linked through the internet, it may be useful to create a Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task for the distribution points, so that they will download updates directly from Kaspersky servers, local or network folder, not from the Administration Server.
If some devices at a remote office have no direct access to the Administration Server (for example, access to the Administration Server is provided over the internet but some devices have no internet access), distribution points must be switched into connection gateway mode. In this case, Network Agents on devices at the remote office will be connected, for further synchronization, to the Administration Server—but through the gateway, not directly.
As the Administration Server, most probably, will not be able to poll the remote office network, it may be useful to turn this function over to a distribution point.
The Administration Server will not be able to send notifications to port 15000 UDP to managed devices located behind the NAT at the remote office. To resolve this issue, you can enable the mode of continuous connection to the Administration Server in the properties of devices acting as distribution points (Do not disconnect from the Administration Server check box). This mode is available if the total number of distribution points does not exceed 300. Use push servers to make sure that there is continuous connectivity between a managed device and the Administration Server. Refer to the following topic for details: Using a distribution point as a push server.
Selecting a DBMS for Administration Server
When selecting the database management system (DBMS) to be used by an Administration Server, you must take into account the number of devices covered by the Administration Server.
The following table lists the valid DBMS options, as well as the recommendations and restrictions on their use.
Recommendations and restrictions on DBMS
DBMS |
Recommendations and restrictions |
|---|---|
SQL Server Express Edition 2016 or later |
Use this DBMS if you intend to run a single Administration Server for less than 10,000 devices. It is recommended to disable the Software inventory task and disable (in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings) notifications of Administration Server on started applications. You can limit the maximum number of events in the event repository to prevent database overflow. Refer to the following topic for details: Calculation of database space. Concurrent use of the SQL Server Express Edition DBMS by Administration Server and another application is strictly forbidden. The Microsoft SQL Express database is not supported for the Perform Windows Update synchronization task. |
Local SQL Server edition, other than Express, 2016 or later |
No limitations. |
Remote SQL Server edition, other than Express, 2016 or later |
Only valid if both devices are in the same Windows domain; if the domains differ, a two-way trust relationship must be established between them. |
Local or remote MySQL 5.5, 5.6, or 5.7 (MySQL versions 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, and 5.5.5 are no longer supported) |
Use this DBMS if you intend to run a single Administration Server for less than 10,000 devices. It is recommended to disable the Software inventory task and disable (in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings) notifications of Administration Server on started applications. Refer to the following topic for details: Calculation of database space. |
Local or remote MySQL 8.0.20 or later |
Use this DBMS if you intend to run a single Administration Server for less than 50,000 devices. It is recommended to disable the Software inventory task and disable (in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings) notifications of Administration Server on started applications. Refer to the following topic for details: Calculation of database space. |
Local or remote MariaDB (see supported versions) |
Use this DBMS if you intend to run a single Administration Server for less than 20,000 devices. It is recommended to disable the Software inventory task and disable (in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings) notifications of Administration Server on started applications. Refer to the following topic for details: Calculation of database space. |
PostgreSQL, Postgres Pro (see supported versions) |
Use one of these DBMS if you intend to run a single Administration Server for less than 50,000 devices. It is recommended to disable the Software inventory task and disable (in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings) notifications of Administration Server on started applications. Refer to the following topic for details: Calculation of database space. |
If you are using SQL Server 2019 as a DBMS and you do not have cumulative patch CU12 or later, you have to perform the following after installing Kaspersky Security Center:
- Connect to SQL Server using SQL Management Studio.
- Run the following commands (if you chose a different name for the database, use that name instead of KAV):
USE KAVGOALTER DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION SET TSQL_SCALAR_UDF_INLINING = OFFGO - Restart the SQL Server 2019 service.
Otherwise, using SQL Server 2019 may result in errors, such as "There is insufficient system memory in resource pool 'internal' to run this query."
Configuring the MariaDB x64 server for working with Kaspersky Security Center 15.1
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 supports MariaDB DBMS. For more information about supported versions of MariaDB, see section Hardware and software requirements.
If you use the MariaDB DBMS for Kaspersky Security Center, enable support of InnoDB and MEMORY storage and of UTF-8 and UCS-2 encodings.
Recommended settings for the my.ini file
To configure the my.ini file:
- Open the my.ini file in a text editor.
- Add the following lines into the
[mysqld]section of the my.ini file:sort_buffer_size=10M
join_buffer_size=100M
join_buffer_space_limit=300M
join_cache_level=8
tmp_table_size=512M
max_heap_table_size=512M
key_buffer_size=200M
innodb_buffer_pool_size=
<value>innodb_thread_concurrency=20
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=0
innodb_lock_wait_timeout=300
max_allowed_packet=32M
max_connections=151
max_prepared_stmt_count=12800
table_open_cache=60000
table_open_cache_instances=4
table_definition_cache=60000
The value of the
innodb_buffer_pool_sizemust be no less than 80 percent of the expected KAV database size. Note that the specified memory is allocated at server startup. If the database size is smaller than the specified buffer size, only the required memory is allocated. If you use MariaDB 10.4.3 or older, the actual size of allocated memory is approximately 10 percent greater than the specified buffer size.It is recommended to use the parameter value
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=0, because the values "1" or "2" negatively affect the operating speed of MariaDB. Ensure that theinnodb_file_per_tableparameter is set to1.For MariaDB 10.6, additionally enter the following lines into the [mysqld] section:
optimizer_prune_level=0
optimizer_search_depth=8
By default, the optimizer add-ons join_cache_incremental, join_cache_hashed, and join_cache_bka are enabled. If these add-ons are not enabled, you must enable them.
To check whether optimizer add-ons are enabled:
- In the MariaDB client console, execute the command:
SELECT @@optimizer_switch; - Check that its output contains the following lines:
join_cache_incremental=onjoin_cache_hashed=onjoin_cache_bka=onIf these lines are present and have the value
on, then the optimizer add-ons are enabled.If these lines are missing or have the value
off, do the following:- Open the my.ini file in a text editor.
- Add the following lines into the
[mysqld]section of the my.ini file:optimizer_switch='join_cache_incremental=on'optimizer_switch='join_cache_hashed=on'optimizer_switch='join_cache_bka=on'
The add-ons join_cache_incremental, join_cache_hash, and join_cache_bka are enabled.
Configuring the MySQL x64 server for working with Kaspersky Security Center 15.1
If you use the MySQL DBMS for Kaspersky Security Center, enable support of InnoDB and MEMORY storage and of UTF-8 and UCS-2 encodings.
Recommended settings for the my.ini file
To configure the my.ini file:
- Open the my.ini file in a text editor.
- Add the following lines into the
[mysqld]section of the my.ini file:sort_buffer_size=10Mjoin_buffer_size=20Mtmp_table_size=600Mmax_heap_table_size=600Mkey_buffer_size=200Minnodb_buffer_pool_size=the real value must be no less than 80% of the expected KAV database sizeinnodb_thread_concurrency=20innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=0(in most cases, the server uses small transactions)innodb_lock_wait_timeout=300max_allowed_packet=32Mmax_connections=151max_prepared_stmt_count=12800table_open_cache=60000table_open_cache_instances=4table_definition_cache=60000Note that the memory specified in the
innodb_buffer_pool_sizevalue is allocated at server startup. If the database size is smaller than the specified buffer size, only the required memory is allocated. The actual size of allocated memory is approximately 10 percent greater than the specified buffer size. Refer to the MySQL documentation for details.It is recommended to use the parameter value
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 0, because the values "1" or "2" negatively affect the operating speed of MySQL. Ensure that theinnodb_file_per_tableparameter is set to1.
Configuring the PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro server for working with Kaspersky Security Center 15.1
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 supports PostgreSQL and Postgres Pro DBMSs. If you use one of these DBMSs, consider configuring the DBMS server parameters to optimize the DBMS work with Kaspersky Security Center.
The default path to the configuration file is: C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\<VERSION>\data\postgresql.conf
Recommended parameters for PostgreSQL and Postgres Pro:
shared_buffers =25 percent of the RAM value of the device where the DBMS is installedIf RAM is less than 1 GB, then leave the default value.
max_stack_depth =2MBtemp_buffers =24MBwork_mem =16MBmax_connections =151max_parallel_workers_per_gather =0maintenance_work_mem =128MB
Make sure the standard_conforming_strings parameter is set to its default value of on. Reload configuration or restart the server after updating the postgresql.conf file. Refer to the PostgreSQL documentation for details.
If you use Postgres Pro 15.7 or Postgres Pro 15.7.1, disable the enable_compound_index_stats parameter:
enable_compound_index_stats = off
For detailed information about PostgreSQL and Postgres Pro server parameters, and on how to specify them, refer to the corresponding DBMS documentation.
Refer to the following topic for details on how to create and configure accounts for PostgreSQL and Postgres Pro: Configuring accounts for work with PostgreSQL and Postgres Pro.
Page top
Managing mobile devices with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android
Mobile devices with installed Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android (hereinafter referred to as KES devices) are managed by means of the Administration Server. Kaspersky Security Center supports the following features for managing KES devices:
- Handling mobile devices as client devices:
- Membership in administration groups
- Monitoring, such as viewing statuses, events, and reports
- Modifying local settings and assigning policies for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android
- Sending commands in centralized mode
- Installing mobile apps packages remotely
Administration Server manages KES devices through TLS, TCP port 13292.
Providing internet access to Administration Server
The following cases require internet access to the Administration Server:
- Regular updating of Kaspersky databases, software modules, and applications
- Updating third-party software
By default, internet connection is not required for Administration Server to install Microsoft software updates on the managed devices. For example, the managed devices can download the Microsoft software updates directly from Microsoft Update servers or from Windows Server with Microsoft Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) deployed in your organization's network. Administration Server must be connected to the internet in the following cases:
- When you use Administration Server as WSUS server
- To install updates of third-party software other than Microsoft software
- Fixing third-party software vulnerabilities
Internet connection is required for Administration Server to perform the following tasks:
- To make a list of recommended fixes for vulnerabilities in Microsoft software. The list is created and regularly updated by Kaspersky specialists.
- To fix vulnerabilities in third-party software other than Microsoft software.
- Managing devices (laptops) of out-of-office users
- Managing devices in remote offices
- Interacting with primary or secondary Administration Servers located in remote offices
- Managing mobile devices
This section describes typical ways of providing access to the Administration Server over the internet. Each of the cases focusing on providing internet access to the Administration Server may require a dedicated certificate for the Administration Server.
Internet access: Administration Server on a local network
If the Administration Server is located on the internal network of an organization, you might want to make TCP port 13000 of the Administration Server accessible from outside by means of port forwarding. If mobile device management is required, you might want to make accessible port 13292 TCP.
Internet access: Administration Server in DMZ
If the Administration Server is located in the DMZ of the organization's network, it has no access to the organization's internal network. Therefore, the following limitations apply:
- The Administration Server cannot detect new devices.
- The Administration Server cannot perform initial deployment of Network Agent through forced installation on devices on the internal network of the organization.
This only applies to the initial installation of Network Agent. Any further upgrades of Network Agent or the security application installation can, however, be performed by the Administration Server. At the same time, the initial deployment of Network Agents can be performed by other means, for example, through group policies of Microsoft Active Directory.
- The Administration Server cannot send notifications to managed devices through port 15000 UDP, which is not critical for the Kaspersky Security Center functioning.
- The Administration Server cannot poll Active Directory. However, results of Active Directory polling are not required in most scenarios.
If the above limitations are viewed as critical, they can be removed by using distribution points located on the organization's network:
- To perform initial deployment on devices without Network Agent, you first install Network Agent on one of the devices and then assign it the distribution point status. As a result, initial installation of Network Agent on other devices will be performed by the Administration Server through this distribution point.
- To detect new devices on the internal network of the organization and poll Active Directory, you must enable the relevant device discovery methods on one of the distribution points.
To ensure a successful sending of notifications to port 15000 UDP on managed devices located on the internal network of the organization, you must cover the entire network with distribution points. In the properties of the distribution points that were assigned, select the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server check box. As a result, the Administration Server will establish a continuous connection to the distribution points while they will be able to send notifications to port 15000 UDP on devices that are on the organization's internal network (it can be an IPv4 or IPv6 network).
Internet access: Network Agent as connection gateway in DMZ
Administration Server can be located on the internal network of the organization, and in that network's DMZ there can be a device with Network Agent running as a connection gateway with reverse connectivity (Administration Server establishes a connection to Network Agent). In this case, the following conditions must be met to ensure internet access:
- Network Agent must be installed on the device that is in the DMZ. When you install Network Agent, in the Connection gateway window of the setup wizard, select Use Network Agent as a connection gateway in DMZ.
- The device with the installed connection gateway must be added as a distribution point. When you add the connection gateway, in the Add distribution point window, select the Select → Add connection gateway in DMZ by address option.
- To use an internet connection to connect external desktop devices to the Administration Server, the installation package for Network Agent must be corrected. In the properties of the created installation package, select the Advanced → Connect to Administration Server by using a connection gateway option, and then specify the newly created connection gateway.
For the connection gateway in the DMZ, Administration Server creates a certificate signed with the Administration Server certificate. If the administrator decides to assign a custom certificate to Administration Server, it must be done before a connection gateway is created in the DMZ.
If some employees use laptops that can connect to Administration Server either from the local network or over the internet, it may be useful to create a switching rule for Network Agent in the Network Agent's policy.
About distribution points
A device with Network Agent installed can be used as a distribution point. In this mode, Network Agent can perform the following functions:
- Distribute updates (these can be retrieved either from the Administration Server or from Kaspersky servers). In the latter case, the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task must be created for the device that serves as the distribution point:
- Install software (including initial deployment of Network Agents) on other devices.
- Poll the network to detect new devices and update information about existing ones. A distribution point can apply the same device discovery methods as the Administration Server.
Deployment of distribution points on an organization's network has the following objectives:
- Reducing the load on the Administration Server.
- Optimizing traffic.
- Providing the Administration Server with access to devices in hard-to-reach spots of the organization's network. The availability of a distribution point on the network behind a NAT (in relation to the Administration Server) allows the Administration Server to perform the following actions:
- Send notifications to devices over UDP on the IPv4 or IPv6 network
- Poll the IPv4 or IPv6 network
- Perform initial deployment
- Act as a push server
A distribution point is assigned for an administration group. In this case, the scope of the distribution point includes all devices within the administration group and all of its subgroups. However, the device that acts as the distribution point may not be included in the administration group to which it has been assigned.
You can make a distribution point function as a connection gateway. In this case, devices in the scope of the distribution point will be connected to the Administration Server through the gateway, not directly. This mode can be useful in scenarios that do not allow the establishment of a direct connection between the Administration Server and managed devices.
If you use a Linux-based device as a distribution point, we strongly recommend increasing the limit of file descriptors for the klnagent service, because if the scope of the distribution point includes many devices, the default maximum number of files that can be opened may not be enough.
Increasing the limit of file descriptors for the klnagent service
If the scope of a Linux-based distribution point includes many devices, the default limit of files that can be opened (file descriptors) may not be enough. To avoid this, you can increase the limit of file descriptors for the klnagent service.
To increase the limit of file descriptors for the klnagent service:
- On the Linux-based device that acts as a distribution point, open the
/lib/systemd/system/klnagent64.servicefile, and then specify the hard and soft limits of the file descriptors in theLimitNOFILEparameter of the[Service]section:LimitNOFILE=<soft_resource_limit>:<hard_resource_limit>For example,
LimitNOFILE=32768:131072. Note that the soft limit of the file descriptors must be less or equal to the hard limit. - Run the following command to ensure that the parameters are specified correctly:
systemd-analyze verify klnagent64.serviceIf the parameters are specified incorrectly, this command can output one of the following errors:
/lib/systemd/system/klnagent64.service:11: Failed to parse resource value, ignoring: 32768:13107If this error occurs, the symbols in the
LimitNOFILEline were specified incorrectly. You must check and correct the entered line./lib/systemd/system/klnagent64.service:11: Soft resource limit chosen higher than hard limit, ignoring: 32768:13107If this error occurs, the soft limit of the file descriptors you entered is more than the hard limit. You must check the entered line and ensure that the soft limit of the file descriptors is less or equal to the hard limit.
- Run the following command to reload the systemd process:
systemctl daemon-reload - Run the following command to restart the Network Agent service:
systemctl restart klnagent - Run the following command to ensure that the specified parameters are applied correctly:
less /proc/<nagent_proc_id>/limitswhere the
<nagent_proc_id>parameter is the identifier of the Network Agent process. You can run the following command to obtain the identifier:ps -ax | grep klnagent
For the Linux-based distribution point, the limit of files that can be opened is increased.
Page top
Calculating the number and configuration of distribution points
The more client devices a network contains, the more distribution points it requires. We recommend that you not disable automatic assignment of distribution points. When automatic assignment of distribution points is enabled, Administration Server assigns distribution points if the number of client devices is quite large and defines their configuration.
Using exclusively assigned distribution points
If you plan to use certain specific devices as distribution points (that is, exclusively assigned servers), you can opt out of using automatic assignment of distribution points. In this case, make sure that the devices that you intend to make distribution points have sufficient volume of free disk space, are not shut down regularly, and have Sleep mode disabled.
Number of exclusively assigned distribution points on a network that contains a single network segment, based on the number of networked devices
Number of client devices in the network segment |
Number of distribution points |
|---|---|
Less than 300 |
0 (Do not assign distribution points) |
More than 300 |
Acceptable: (N/10,000 + 1), recommended: (N/5000 + 2), where N is the number of networked devices |
Number of exclusively assigned distribution points on a network that contains multiple network segments, based on the number of networked devices
Number of client devices per network segment |
Number of distribution points |
|---|---|
Less than 10 |
0 (Do not assign distribution points) |
10–100 |
1 |
More than 100 |
Acceptable: (N/10,000 + 1), recommended: (N/5000 + 2), where N is the number of networked devices |
Using standard client devices (workstations) as distribution points
If you plan to use standard client devices (that is, workstations) as distribution points, we recommend that you assign distribution points as shown in the tables below in order to avoid excessive load on the communication channels and on Administration Server:
Number of workstations functioning as distribution points on a network that contains a single network segment, based on the number of networked devices
Number of client devices in the network segment |
Number of distribution points |
|---|---|
Less than 300 |
0 (Do not assign distribution points) |
More than 300 |
(N/300 + 1), where N is the number of networked devices; there must be at least 3 distribution points |
Number of workstations functioning as distribution points on a network that contains multiple network segments, based on the number of networked devices
Number of client devices per network segment |
Number of distribution points |
|---|---|
Less than 10 |
0 (Do not assign distribution points) |
10–30 |
1 |
31–300 |
2 |
More than 300 |
(N/300 + 1), where N is the number of networked devices; there must be at least 3 distribution points |
If a distribution point is shut down (or not available for some other reason), the managed devices in its scope can access the Administration Server for updates.
Hierarchy of Administration Servers
An MSP may run multiple Administration Servers. It can be inconvenient to administer several separate Administration Servers, so a hierarchy can be applied. A "primary/secondary" configuration for two Administration Servers provides the following options:
- A secondary Administration Server inherits policies and tasks from the primary Administration Server, thus preventing duplication of settings.
- Selections of devices on the primary Administration Server can include devices from secondary Administration Servers.
- Reports on the primary Administration Server can contain data (including detailed information) from secondary Administration Servers.
The primary Administration Server only receives data from non-virtual secondary Administration Servers within the scope of the options listed above. This limitation does not apply to virtual Administration Servers, which share the database with their primary Administration Server.
Page top
Virtual Administration Servers
On the basis of a physical Administration Server, multiple virtual Administration Servers can be created, which will be similar to secondary Administration Servers. Compared to the discretionary access model, which is based on access control lists (ACLs), the virtual Administration Server model is more functional and provides a larger degree of isolation. In addition to a dedicated structure of administration groups for assigned devices with policies and tasks, each virtual Administration Server features its own group of unassigned devices, own sets of reports, selected devices and events, installation packages, moving rules, etc. The functional scope of virtual Administration Servers can be used both by service providers (xSP) to maximize the isolation of customers, and by large-scale organizations with sophisticated workflows and numerous administrators.
Virtual Administration Servers are very similar to secondary Administration Servers, but with the following distinctions:
- A virtual Administration Server lacks most global settings and its own TCP ports.
- A virtual Administration Server has no secondary Administration Servers.
- A virtual Administration Server has no other virtual Administration Servers.
- A physical Administration Server views devices, groups, events, and objects on managed devices (items in Quarantine, applications registry, etc.) of all its virtual Administration Servers.
- A virtual Administration Server can only scan the network with distribution points connected.
Information about limitations of Kaspersky Security Center
The following table displays the limitations of the current version of Kaspersky Security Center.
Limitations of Kaspersky Security Center
Type of limitation |
Value |
|---|---|
Maximum number of managed devices per Administration Server |
100,000 |
Maximum number of devices with the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option selected |
300 |
Maximum number of administration groups |
10,000 |
Maximum number of events to store |
45,000,000 |
Maximum number of policies |
2000 |
Maximum number of tasks |
2000 |
Maximum total number of Active Directory objects (organizational units, OUs) and accounts of users, devices, and security groups) |
1,000,000 |
Maximum number of profiles in a policy |
100 |
Maximum number of secondary Administration Servers on a single primary Administration Server |
500 |
Maximum number of virtual Administration Servers |
500 |
Maximum number of devices that a single distribution point can cover (distribution points can cover non-mobile devices only) |
10,000 |
Maximum number of devices that may use a single connection gateway |
10,000, including mobile devices |
Maximum number of mobile devices per Administration Server |
100,000 minus the number of stationary managed devices |
Network load
This section contains information about the volume of network traffic that the client devices and Administration Server exchange during key administrative scenarios.
The main load on the network is caused by the following administrative scenarios in progress:
- Initial deployment of anti-virus protection
- Initial update of anti-virus databases
- Synchronization of a client device with Administration Server
- Regular updates of anti-virus databases
- Processing of events on client devices by Administration Server
Initial deployment of anti-virus protection
This section provides information about traffic volume values after Network Agent and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows are installed on the client device (see the table below).
The Network Agent is installed using forced installation, when the files required for setup are copied by Administration Server to a shared folder on the client device. After installation, the Network Agent retrieves the distribution package of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, using the connection to the Administration Server.
Traffic
Scenario |
Network Agent installation for a single client device |
Installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows on one client device (with databases updated) |
Concurrent installation of Network Agent and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows |
|---|---|---|---|
Traffic from a client device to Administration Server, KB |
1638.4 |
7843.84 |
9707.52 |
Traffic from Administration Server to a client device, KB |
69,990.4 |
259,317.76 |
329,318.4 |
Total traffic (for a single client device), KB |
71,628.8 |
267,161.6 |
339,025.92 |
After Network Agents are installed on the client devices, one of the devices in the administration group can be assigned to act as distribution point. It is used for distribution of installation packages. In this case, traffic volume transferred during initial deployment of anti-virus protection varies significantly depending on whether you are using IP multicasting.
If IP multicasting is used, installation packages are sent once to all running devices in the administration group. Thus, total traffic becomes N times smaller, where N stands for the total number of running devices in the administration group. If you are not using IP multicasting, the total traffic is identical to the traffic calculated as if the distribution packages are downloaded from the Administration Server. However, the package source is the distribution point, not the Administration Server.
Page top
Initial update of anti-virus databases
The traffic rates during initial update of anti-virus databases (when starting the database update task for the first time on a client device), are as follows:
- Traffic from a client device to Administration Server: 1,8 MB.
- Traffic from Administration Server to a client device: 113 MB.
- Total traffic (for a single client device): 114 MB.
The data may vary slightly depending upon the current version of the anti-virus database.
Page top
Synchronizing a client with the Administration Server
This scenario describes the state of the administration system when intensive data synchronization occurs between a client device and the Administration Server. Client devices connect to the Administration Server with the interval defined by the administrator. The Administration Server compares the status of data on a client device with that on the Server, records information in the database about the last client device connection, and synchronizes data.
This section contains information about traffic values for basic administration scenarios when connecting a client to the Administration Server (see table below). The data in the table may vary slightly depending upon the current version of the anti-virus database.
Traffic
Scenario |
Traffic from client devices to Administration Server, KB |
Traffic from Administration Server to client devices, KB |
Total traffic (for a single client device), KB |
Initial synchronization prior to updating databases on a client device |
699.44 |
568.42 |
1267.86 |
Initial synchronization after updating databases on a client device |
735.8 |
4474.88 |
5210.68 |
Synchronization with no changes on a client device and the Administration Server |
11.99 |
6.73 |
18.72 |
Synchronization after changing the value of a setting in a group policy |
9.79 |
11.39 |
21.18 |
Synchronization after changing the value of a setting in a group task |
11.27 |
11.72 |
22.99 |
Forced synchronization with no changes on a client device |
77.59 |
99.45 |
177.04 |
Overall traffic volume varies considerably depending on whether IP multicasting is used within administration groups. If IP multicasting is used, the total traffic volume decreases approximately by N times for the group, where N stands for the total number of devices included in the administration group.
The volume of traffic at initial synchronization before and after an update of the databases is specified for the following cases:
- Installing Network Agent and a security application on a client device
- Moving a client device to an administration group
- Applying a policy and tasks that have been created for the group by default, to a client device
The table specifies traffic rates in case of changes to one of the protection settings that are included in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings. Data for other policy settings may differ from data displayed in the table.
Page top
Additional update of anti-virus databases
The traffic rates in case of an incremental update of anti-virus databases 20 hours after the previous update are as follows:
- Traffic from a client device to Administration Server: 169 KB.
- Traffic from Administration Server to a client device: 16 MB.
- Total traffic (for a single client device): 16.3 MB.
The data in the table may vary slightly depending upon the current version of the anti-virus database.
Traffic volume varies significantly depending on whether IP multicasting is used within administration groups. If IP multicasting is used, the total traffic volume decreases approximately by N times for the group, where N stands for the total number of devices included in the administration group.
Page top
Processing of events from clients by Administration Server
This section provides information about traffic volume values when a client device encounters a "Virus detected" event, which is then sent to the Administration Server and registered in the database (see table below).
Traffic
Scenario |
Data transfer to Administration Server when a "Virus detected" event occurs |
Data transfer to Administration Server when nine "Virus detected" events occur |
|---|---|---|
Traffic from a client device to Administration Server, KB |
49.66 |
64.05 |
Traffic from Administration Server to a client device, KB |
28.64 |
31.97 |
Total traffic (for a single client device), KB |
78.3 |
96.02 |
Data in the table may vary slightly depending upon the current version of the anti-virus application and the events that are defined in its policy for registration in the Administration Server database.
Page top
Traffic per 24 hours
This section contains information about traffic rates for 24 hours of the administration system's activity in a "quiet" condition, when no data changes are made either by client devices or by the Administration Server (see table below).
Data presented in the table describe the network's condition after standard installation of Kaspersky Security Center and completion of the quick start wizard. The frequency of synchronization of the client device with Administration Server was 20 minutes; updates were downloaded to the Administration Server repository once per hour.
Traffic rates per 24 hours in idle state
Traffic flow |
Value |
|---|---|
Traffic from a client device to Administration Server, KB |
3235.84 |
Traffic from Administration Server to a client device, KB |
64,378.88 |
Total traffic (for a single client device), KB |
67,614.72 |
Preparing to mobile device management
This section provides the following information:
- About iOS MDM Server intended for management of iOS devices by installing dedicated iOS MDM profiles on them
- About management of mobile devices that have Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android installed
iOS MDM Server
iOS MDM Server allows you to manage iOS devices by installing dedicated iOS MDM profiles on them. The following features are supported:
- Device lock
- Password reset
- Data wipe
- Installation or removal of apps
- Use of an iOS MDM profile with advanced settings (such as VPN settings, email settings, Wi-Fi settings, camera settings, certificates, etc.)
iOS MDM Server is a web service that receives inbound connections from mobile devices through its TLS port (by default, port 443), which is managed by Kaspersky Security Center using Network Agent. Network Agent is installed locally on a device with an iOS MDM Server deployed.
When deploying an iOS MDM Server, the administrator must perform the following actions:
- Provide Network Agent with access to the Administration Server
- Provide mobile devices with access to the TCP port of the iOS MDM Server
This section addresses two standard configurations of an iOS MDM Server.
Standard configuration: Kaspersky Device Management for iOS in DMZ
An iOS MDM Server is located in the DMZ of an organization's local network with internet access. A special feature of this approach is the absence of any problems when the iOS MDM web service is accessed from devices over the internet.
Because management of an iOS MDM Server requires Network Agent to be installed locally, you must ensure the interaction of Network Agent with the Administration Server. You can ensure this by using one of the following methods:
- By moving the Administration Server to the DMZ.
- By using a connection gateway:
- On the device with iOS MDM Server deployed, connect Network Agent to the Administration Server through a connection gateway.
- On the device with iOS MDM Server deployed, assign Network Agent to act as connection gateway.
Standard configuration: iOS MDM Server on the local network of an organization
An iOS MDM Server is located on the internal network of an organization. Port 443 (default port) must be enabled for external access, for example, by publishing the iOS MDM web service on reverse proxy that supports Kerberos constrained delegation.
Any standard configuration requires access to Apple web services for the iOS MDM Server (range 17.0.0.0/8) through TCP port 2197. This port is used for notifying devices of new commands by means of a dedicated service named APNs.
Page top
Managing mobile devices with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android
Mobile devices with installed Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android (hereinafter referred to as KES devices) are managed by means of the Administration Server. Kaspersky Security Center supports the following features for managing KES devices:
- Handling mobile devices as client devices:
- Membership in administration groups
- Monitoring, such as viewing statuses, events, and reports
- Modifying local settings and assigning policies for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android
- Sending commands in centralized mode
- Installing mobile apps packages remotely
Administration Server manages KES devices through TLS, TCP port 13292.
Information about Administration Server performance
This section presents the results of performance testing of the Administration Server for different hardware configurations, as well as the limitations on connecting managed devices to the Administration Server.
Limitations on connection to an Administration Server
An Administration Server supports management of up to 100,000 devices without a loss in performance.
Limitations on connections to an Administration Server without a loss in performance:
- One Administration Server can support up to 500 virtual Administration Servers.
- The primary Administration Server supports no more than 1000 sessions simultaneously.
- Virtual Administration Servers support no more than 1000 sessions simultaneously.
Results of Administration Server performance testing
Results of Administration Server performance testing have allowed us to determine the maximum numbers of client devices with which Administration Server can be synchronized for specified time intervals. You can use this information to select the optimal scheme for deploying anti-virus protection on computer networks.
Devices with the following hardware configurations (see the tables below) were used for testing:
Administration Server hardware configuration
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
CPU |
Intel Xeon CPU E5630, clock speed of 2.53 GHz, 2 socket, 8 cores, 16 logical processors |
RAM |
26 GB |
Hard drive |
IBM ServeRAID M5014 SCSI Disk Device, 487 GB |
Operating system |
Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Standard, version 10.0.17763, build 17763 |
Network |
QLogic BCM5709C Gigabit Ethernet (NDIS VBD Client) |
Hardware configuration of the SQL Server device
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
CPU |
Intel Xeon CPU X5570, clock speed of 2.93 GHz, 2 socket, 8 cores, 16 logical processors |
RAM |
32 GB |
Hard drive |
Adaptec Array SCSI Disk Device, 2047 GB |
Operating system |
Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Standard, version 10.0.17763, build 17763 |
Network |
Intel 82576 Gigabit |
Administration Server supported creation of 500 virtual Administration Servers.
The synchronization interval was 15 minutes for every 10,000 managed devices (see the table below).
Summarized results of Administration Server load testing
Synchronization interval (min) |
Number of managed devices |
|---|---|
15 |
10,000 |
30 |
20,000 |
45 |
30,000 |
60 |
40,000 |
75 |
50,000 |
90 |
60,000 |
105 |
70,000 |
120 |
80,000 |
135 |
90,000 |
150 |
100,000 |
If you connect Administration Server to a MySQL or SQL Express database server, it is not recommended to use the application to manage more than 10,000 devices. For the MariaDB database management system, the maximum recommended number of managed devices is 20,000.
Page top
Results of KSN proxy server performance testing
If your enterprise network includes a large amount of client devices and they use the Administration Server as KSN proxy server, the Administration Server hardware must meet specific requirements to be able to process the requests from the client devices. You can use the testing results below to evaluate the Administration Server load on your network and plan the hardware resources to provide for normal functioning of the KSN proxy service.
The tables below show the hardware configuration of the Administration Server and SQL Server. This configuration was used for testing.
Administration Server hardware configuration
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
CPU |
Intel Xeon CPU E5450, clock speed of 3.00 GHz, 2 socket, 8 cores, 16 logical processors |
RAM |
32 GB |
Operating system |
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Standard |
SQL Server hardware configuration
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
CPU |
Intel Xeon CPU E5450, clock speed of 3.00 GHz, 2 socket, 8 cores, 16 logical processors |
RAM |
32 GB |
Operating system |
Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Standard |
The table below shows the results of the test.
Summarized results of KSN proxy server performance testing
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
Maximum number of requests processed per second |
4914 |
Maximum CPU utilization |
36% |
Network settings for interaction with external services
Kaspersky Security Center uses the following network settings for interacting with external services.
Network settings
Network settings |
Address |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Port: 443 Protocol: HTTPS |
activation-v2.kaspersky.com/activationservice/activationservice.svc |
Application activation. |
Port: 443 Protocol: HTTPS |
https://s00.upd.kaspersky.com https://s01.upd.kaspersky.com https://s02.upd.kaspersky.com https://s03.upd.kaspersky.com https://s04.upd.kaspersky.com https://s05.upd.kaspersky.com https://s06.upd.kaspersky.com https://s07.upd.kaspersky.com https://s08.upd.kaspersky.com https://s09.upd.kaspersky.com https://s10.upd.kaspersky.com https://s11.upd.kaspersky.com https://s12.upd.kaspersky.com https://s13.upd.kaspersky.com https://s14.upd.kaspersky.com https://s15.upd.kaspersky.com https://s16.upd.kaspersky.com https://s17.upd.kaspersky.com https://s18.upd.kaspersky.com https://s19.upd.kaspersky.com https://cm.k.kaspersky-labs.com |
Updating Kaspersky databases, software modules, and applications. |
Port: 443 Protocol: HTTPS |
https://downloads.upd.kaspersky.com |
|
Port: 80 Protocol: HTTP |
http://p00.upd.kaspersky.com http://p01.upd.kaspersky.com http://p02.upd.kaspersky.com http://p03.upd.kaspersky.com http://p04.upd.kaspersky.com http://p05.upd.kaspersky.com http://p06.upd.kaspersky.com http://p07.upd.kaspersky.com http://p08.upd.kaspersky.com http://p09.upd.kaspersky.com http://p10.upd.kaspersky.com http://p11.upd.kaspersky.com http://p12.upd.kaspersky.com http://p13.upd.kaspersky.com http://p14.upd.kaspersky.com http://p15.upd.kaspersky.com http://p16.upd.kaspersky.com http://p17.upd.kaspersky.com http://p18.upd.kaspersky.com http://p19.upd.kaspersky.com http://downloads0.kaspersky-labs.com http://downloads1.kaspersky-labs.com http://downloads2.kaspersky-labs.com http://downloads3.kaspersky-labs.com http://downloads4.kaspersky-labs.com http://downloads5.kaspersky-labs.com http://downloads6.kaspersky-labs.com http://downloads7.kaspersky-labs.com http://downloads8.kaspersky-labs.com http://downloads9.kaspersky-labs.com http://downloads.kaspersky-labs.com http://cm.k.kaspersky-labs.com |
Updating Kaspersky databases, software modules, and applications. |
Port: 443 Protocol: HTTPS |
ds.kaspersky.com |
Using Kaspersky Security Network. |
Port: 443, 1443 Protocol: HTTPS |
ksn-a-stat-geo.kaspersky-labs.com ksn-file-geo.kaspersky-labs.com ksn-verdict-geo.kaspersky-labs.com ksn-url-geo.kaspersky-labs.com ksn-a-p2p-geo.kaspersky-labs.com ksn-info-geo.kaspersky-labs.com ksn-cinfo-geo.kaspersky-labs.com |
Using Kaspersky Security Network. |
Protocol: HTTPS |
click.kaspersky.com redirect.kaspersky.com |
Following links from the interface. |
Port: 80 Protocol: HTTP |
http://crl.kaspersky.com http://ocsp.kaspersky.com |
These servers are part of the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and are necessary to verify the validity status of the Kaspersky digital signature certificates. The CRL is a list of revoked certificates. The OCSP allows you to request the status of a specific certificate in real time. These servers help to ensure the security of interaction with digital certificates and protect against possible attacks. |
Port: 443 Protocol: HTTPS |
https://ipm-klca.kaspersky.com |
For proper interaction of Kaspersky Security Center with external services, consider the following recommendations:
- Unencrypted network traffic must be allowed on ports 443 and 1443 on the network equipment and proxy server of your organization.
- When Administration Server interacts with Kaspersky update servers and Kaspersky Security Network servers, it is necessary to avoid hijacking network traffic with certificate substitution (
To download updates through the HTTP or HTTPS protocol by using the klscflag utility:
- Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
- If you want to download updates through the HTTP protocol, run one of the following commands:
- On the device with Administration Server installed:
klscflag.exe -fset -pv klserver -s Updater -n DisableKLHttps -t d -v 1 - On a distribution point:
klscflag.exe -fset -pv klnagent -s Updater -n DisableKLHttps -t d -v 1
If you want to download updates through the HTTPS protocol, run one of the following commands:
- On the device with Administration Server installed:
klscflag.exe -fset -pv klserver -s Updater -n DisableKLHttps -t d -v 0 - On a distribution point:
klscflag.exe -fset -pv klnagent -s Updater -n DisableKLHttps -t d -v 0
- On the device with Administration Server installed:
Deploying Network Agent and the security application
To manage devices in an organization, you have to install Network Agent on each of them. Deployment of distributed Kaspersky Security Center on corporate devices normally begins with installation of Network Agent on them.
In Microsoft Windows XP, Network Agent might not perform the following operations correctly: downloading updates directly from Kaspersky servers (as a distribution point); functioning as a KSN proxy server (as a distribution point); and detecting third-party vulnerabilities (if Vulnerability and patch management is used).
Initial deployment
If a Network Agent has already been installed on a device, remote installation of applications on that device is performed through this Network Agent. The distribution package of an application to be installed is transferred over communication channels between Network Agents and Administration Server, along with the installation settings defined by the administrator. To transfer the distribution package, you can use relay distribution nodes, that is, distribution points, multicast delivery, etc. For more details on how to install applications on managed devices with Network Agent already installed, see below in this section.
You can perform initial installation of Network Agent on devices running Windows, using one of the following methods:
- With third-party tools for remote installation of applications.
- By cloning an image of the administrator's hard drive with the operating system and Network Agent: using tools provided by Kaspersky Security Center for handling disk images, or using third-party tools.
- With Windows group policies: using standard Windows management tools for group policies, or in automatic mode, through the corresponding, dedicated option in the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center.
- In forced mode, using special options in the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center.
- By sending device users links to stand-alone packages generated by Kaspersky Security Center. Stand-alone packages are executable modules that contain the distribution packages of selected applications with their settings defined.
- Manually, by running application installers on devices.
The following methods can be used for the initial installation of Network Agent on a device running Linux:
- By connecting to the managed device through SSH and running the remote installation task.
- By running the package installation on the managed device.
The following methods can be used for the initial installation of Network Agent on a device running macOS:
- By running the remote installation task on the macOS distribution point.
- By sending device users links to stand-alone packages generated by Kaspersky Security Center. Stand-alone packages are executable modules that contain the distribution packages of selected applications, with pre-defined settings.
When selecting a method and a strategy for deployment of applications on a managed network, you must consider a number of factors (partial list):
- Organization's network configuration.
- Total number of devices.
- Presence of devices on the organization's network, which are not members of any Active Directory domain, and the presence of uniform accounts with administrator rights on those devices.
- Capacity of the channel between the Administration Server and devices.
- Type of communication between Administration Server, and remote subnets and the capacity of the network channels in those subnets.
- Security settings applied on remote devices at the start of deployment (such as use of UAC and Simple File Sharing mode).
Configuring installers
Before starting deployment of Kaspersky applications on a network, you must specify the installation settings, that is, those defined during the application installation. When installing Network Agent, you should specify, at a minimum, an address for connection to Administration Server; some advanced settings may also be required. Depending on the installation method that you have selected, you can define settings in different ways. In the simplest case (manual interactive installation on a selected device), all relevant settings can be defined through the user interface of the installer.
This method of defining the settings is inappropriate for silent installation of applications on groups of devices. In general, the administrator must specify values for settings in centralized mode; those values can subsequently be used for silent installation on selected networked devices.
Page top
Installation packages
The first and main method of defining the installation settings of applications is all-purpose and thus suitable for all installation methods, both with Kaspersky Security Center tools, and with most third-party tools. This method consists of creating installation packages of applications in Kaspersky Security Center.
Installation packages are generated using the following methods:
- Automatically, from specified distribution packages, on the basis of included descriptors (files with the kud extension that contain rules for installation and results analysis, and other information)
- From the executable files of installers or from installers in native format (.msi, .deb, .rpm), for standard or supported applications
Generated installation packages are organized hierarchically as folders with subfolders and files. In addition to the original distribution package, an installation package contains editable settings (including the installer's settings and rules for processing such cases as necessity of restarting the operating system in order to complete installation), as well as minor auxiliary modules.
Values of installation settings that would be specific for an individual supported application can be defined in the user interface of Administration Console when the installation package is created. When performing remote installation of applications through Kaspersky Security Center tools, installation packages are delivered to devices so that running the installer of an application makes all administrator-defined settings available for that application. When using third-party tools for installation of Kaspersky applications, you only have to ensure the availability of the entire installation package on the device, that is, the availability of the distribution package and its settings. Installation packages are created and stored by Kaspersky Security Center in a dedicated subfolder of the shared folder.
Do not specify any details of privileged accounts in the parameters of installation packages.
For the instruction about using this configuration method for Kaspersky applications before deployment through third-party tools, see section "Deployment using group policies of Microsoft Windows".
Immediately after Kaspersky Security Center installation, a few installation packages are automatically generated; they are ready for installation and include Network Agent packages and security application packages for Microsoft Windows.
Although the license key for an application can be set in the properties of an installation package, it is advisable to avoid this method of license distribution because there it is easy to obtain read access to installation packages. You should use automatically distributed license keys or installation tasks for license keys.
Page top
MSI properties and transform files
Another way of configuring installation on Windows platform is to define MSI properties and transform files. This method can be applied in the following cases:
- When installing through Windows group policies, by using regular Microsoft tools or other third-party tools for handling Windows group policies.
- When installing applications by using third-party tools intended for handling installers in Microsoft Installer format.
Deployment with third-party tools for remote installation of applications
When any tools for remote installation of applications (such as Microsoft System Center) are available in an organization, it is convenient to perform initial deployment by using those tools.
The following actions must be performed:
- Select the method for configuring installation that best suits the deployment tool to be used.
- Define the mechanism for synchronization between the modification of the settings of installation packages (through the Administration Console interface) and the operation of selected third-party tools used for deployment of applications from installation package data.
- When performing installation from a shared folder, you must make sure that this file resource has sufficient capacity.
About remote installation tasks in Kaspersky Security Center
Kaspersky Security Center provides various mechanisms for remote installation of applications, which are implemented as remote installation tasks (forced installation, installation by copying a hard drive image, installation through group policies of Microsoft Windows). You can create a remote installation task both for a specified administration group and for specific devices or a selection of devices (such tasks are displayed in Administration Console, in the Tasks folder). When creating a task, you can select installation packages (those of Network Agent and / or another application) to be installed within this task, as well as specify certain settings that define the method of remote installation. In addition, you can use the Remote installation wizard, which is based on creation of a remote installation task and results monitoring.
Tasks for administration groups affect both devices included in a specified group and all devices in all subgroups within that administration group. A task covers devices of secondary Administration Servers included in a group or any of its subgroups if the corresponding setting is enabled in the task.
Tasks for specific devices refresh the list of client devices at each run in accordance with the selection contents at the moment the task starts. If a selection includes devices that have been connected to secondary Administration Servers, the task will run on those devices, too. For details on those settings and installation methods see below in this section.
To ensure a successful operation of a remote installation task on devices connected to secondary Administration Servers, you must use the relaying task to relay installation packages used by your task to corresponding secondary Administration Servers in advance.
Page top
Deployment by capturing and copying the image of a device
If you need to install Network Agent on devices on which an operating system and other software also must be installed (or reinstalled), you can use the mechanism of capturing and copying the image of that device.
To perform deployment by capturing and copying a hard drive:
- Create a reference device with an operating system and the relevant software installed, including Network Agent and a security application.
- Capture the reference image on the device and distribute that image on new devices through the dedicated task of Kaspersky Security Center.
To capture and install disk images, you can use either third-party tools available in the organization, or the feature provided (under the Vulnerability and patch management license) by Kaspersky Security Center.
If you use any third-party tools to process disk images, you must delete the information that Kaspersky Security Center uses to identify the managed device, when performing deployment on a device from a reference image. Otherwise, Administration Server will not be able to properly distinguish devices that have been created by copying the same image.
When capturing a disk image with Kaspersky Security Center tools, this issue is solved automatically.
Copying a disk image with third-party tools
When applying third-party tools for capturing the image of a device with Network Agent installed, use one of the following methods:
- Recommended method. When installing Network Agent on a reference device, capture the device image before the first run of Network Agent service (because unique information identifying the device is created at the first connection of Network Agent to the Administration Server). After that, it is recommended that you avoid running Network Agent service until the completion of the image capturing operation.
- On the reference device, stop the Network Agent service and run the klmover utility with the -dupfix key. The utility klmover is included in the installation package of Network Agent. Avoid any subsequent runs of Network Agent service until the image capturing operation completes.
- Make sure that klmover will be run with the -dupfix key before (mandatory requirement) the first run of the Network Agent service on target devices, at the first launch of the operating system after the image deployment. The utility klmover is included in the installation package of Network Agent.
- Use the Network Agent disk cloning mode.
If the hard drive image has been copied incorrectly, you can resolve this problem.
You can also capture the image of a device without Network Agent installed. To do this, perform image deployment on target devices and then deploy Network Agent. If using this method, provide access to the network folder with stand-alone installation packages from a device.
Incorrect copying of a hard drive image
If a hard drive image with Network Agent installed has been copied without following the rules of deployment, some devices may be displayed together in Administration Console under a single icon with a name that changes constantly.
You can resolve this issue using one of the following methods:
- Removing Network Agent
This method is the most reliable. You must remove Network Agent on devices that have been incorrectly copied from the image, using third-party tools, and then install it again. Network Agent cannot be removed through Kaspersky Security Center tools, because Administration Server cannot distinguish between faulty devices (they all share the same icon in Administration Console).
- Running the klmover utility with the "-dupfix" key
Use third-party tools to run the klmover utility, located in the Network Agent installation folder, with the "-dupfix" key (klmover -dupfix) once on faulty devices (those incorrectly copied from the image). You cannot run the utility with Kaspersky Security Center tools, because Administration Server cannot distinguish between faulty devices (they all share the same icon in Administration Console).
Then delete the icon on which the faulty devices had been displayed before you run the utility.
- Toughening up the rule for detection of incorrectly copied devices.
This method is only applicable if Administration Server and Network Agents version 10 Service Pack 1 or later are installed.
The rule for detection of incorrectly copied Network Agents must be toughened so that changing the NetBIOS name of a device results in an automatic "fix" of those Network Agents (with the assumption that all of the copied devices have unique NetBIOS names).
On the device with Administration Server, you must import the reg file shown below to the Registry and then restart the Administration Server service.
- If a 32-bit operating system is installed on the device with Administration Server:
REGEDIT4
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\Components\34\1093\1.0.0.0\ServerFlags]
"KLSRV_CheckClones"=dword:00000003
- If a 64-bit operating system is installed on the device with Administration Server:
REGEDIT4
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\34\1093\1.0.0.0\ServerFlags]
"KLSRV_CheckClones"=dword:00000003
Deployment using group policies of Microsoft Windows
It is recommended that you perform the initial deployment of Network Agents through Microsoft Windows group policies if the following conditions are met:
- This device is member of an Active Directory domain.
- The deployment scheme allows you to wait for the next routine restart of target devices before starting deployment of Network Agents on them (or you can force a Windows group policy to be applied to those devices).
This deployment scheme consists of the following:
- The application distribution package in Microsoft Installer format (MSI package) is located in a shared folder (a folder where the LocalSystem accounts of target devices have read permissions).
- In the Active Directory group policy, an installation object is created for the distribution package.
- The installation scope is set by specifying the organizational unit (OU) and / or the security group, which includes the target devices.
- The next time a target device logs in to the domain (before device users log in to the system), all installed applications are checked for the presence of the required application. If the application is not found, the distribution package is downloaded from the resource specified in the policy and is then installed.
An advantage of this deployment scheme is that assigned applications are installed on target devices while the operating system is loading, that is, even before the user logs in to the system. Even if a user with sufficient rights removes the application, it will be reinstalled at the next launch of the operating system. This deployment scheme's shortcoming is that changes made by the administrator to the group policy will not take effect until the devices are restarted (if no additional tools are involved).
You can use group policies to install both Network Agent and other applications if their respective installers are in Windows Installer format.
When this deployment scheme is selected, you must also assess the load on the file resource from which files will be copied to devices after applying the Windows group policy.
Handling Microsoft Windows policies through the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center
The simplest way to install applications through group policies of Microsoft Windows is to select the Assign package installation in Active Directory group policies option in the properties of the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center. In this case, Administration Server automatically performs the following actions when you run the task:
- Creates required objects in the group policy of Microsoft Windows.
- Creates dedicated security groups, includes the target devices in those groups, and assigns installation of selected applications for them. The set of security groups will be updated at every task run, in accordance with the pool of devices at the moment of the run.
To make this feature operable, in the task properties, specify an account that has write permissions in Active Directory group policies.
If you intend to install both Network Agent and another application through the same task, selecting the Assign package installation in Active Directory group policies option causes the application to create an installation object in the Active Directory policy for Network Agent only. The second application selected in the task will be installed through the tools of Network Agent as soon as the latter is installed on the device. If you want to install an application other than Network Agent through Windows group policies, you must create an installation task for this installation package only (without the Network Agent package). Not every application can be installed using Microsoft Windows group policies. To find out about this capability, you can refer to information about the possible methods for installing the application.
If required objects are created in the group policy by using Kaspersky Security Center tools, the shared folder of Kaspersky Security Center will be used as the source of the installation package. When planning the deployment, you must correlate the reading speed for this folder with the number of devices and the size of the distribution package to be installed. It may be useful to locate the shared folder of Kaspersky Security Center in a high-performance dedicated file repository.
In addition to its ease of use, automatic creation of Windows group policies through Kaspersky Security Center has this advantage: when planning Network Agent installation, you can easily specify the Kaspersky Security Center administration group into which devices will be automatically moved after installation completes. You can specify this group in the New task wizard or in the settings window of the remote installation task.
When handling Windows group policies through Kaspersky Security Center, you can specify devices for a group policy object by creating a security group. Kaspersky Security Center synchronizes the contents of the security group with the current set of devices in the task. When using other tools for handling group policies, you can associate objects of group policies with selected OUs of Active Directory directly.
Unassisted installation of applications through policies of Microsoft Windows
The administrator can create objects required for installation in a Windows group policy on his or her own behalf. In this case, he or she can provide links to packages stored in the shared folder of Kaspersky Security Center, or upload those packages to a dedicated file server and then provide links to them.
The following installation scenarios are possible:
- The administrator creates an installation package and sets up its properties in Administration Console. The group policy object provides a link to the MSI file of this package stored in the shared folder of Kaspersky Security Center.
- The administrator creates an installation package and sets up its properties in Administration Console. Then the administrator copies the entire EXEC subfolder of this package from the shared folder of Kaspersky Security Center to a folder on a dedicated file resource of the organization. The group policy object provides a link to the MSI file of this package stored in a subfolder on the dedicated file resource of the organization.
- The administrator downloads the application distribution package (including that of Network Agent) from the internet and uploads it to the dedicated file resource of the organization. The group policy object provides a link to the MSI file of this package stored in a subfolder on the dedicated file resource of the organization. The installation settings are defined by configuring the MSI properties or by configuring MST transform files.
Forced deployment through the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center
To perform the initial deployment of Network Agent or other applications, you can force installation of selected installation packages by using the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center—provided that each device has a user account(s) with local administrator rights.
Forced installation can also be applied if devices cannot be directly accessed by Administration Server: for example, devices are on isolated networks, or they are on a local network while the Administration Server item is in DMZ.
In case of initial deployment, Network Agent is not installed. Therefore, in the settings of the remote installation task, you cannot select distribution of files required for application installation by using Network Agent. You can only choose to distribute files by using operating system resources through Administration Server or distribution points.
The Administration Server service must run under an account that has administrative privileges on the target devices. Alternatively, you can specify an account that has access to the admin$ share in the settings of the remote installation task.
By default, the remote installation task connects to devices by using the credentials of the account under which the Administration Server is running. It is important to clarify that this is the account used for accessing the admin$ share, rather than the account under which the remote installation task runs. Installation is carried out under the LocalSystem account.
You can specify target devices either explicitly (with a list), by selecting the Kaspersky Security Center administration group to which they belong; or by creating a selection of devices based upon a specific criterion. The installation start time is defined by the task schedule. If the Run missed tasks setting is enabled in the task properties, the task can be run either immediately after target devices are turned on or when they are moved to the target administration group.
Forced installation consists of delivering installation packages to target devices, subsequent copying of files to the admin$ resource on each of the target devices, and remote registration of supporting services on those devices. Delivery of installation packages to target devices is performed through a Kaspersky Security Center feature that ensures network interaction. The following conditions must be met in this case:
- Target devices are accessible from the Administration Server side or from the distribution point side.
- Name resolution for target devices functions properly on the network.
- The administrative shares (admin$) remain enabled on target devices.
- The following system services are running on target devices:
- Server (LanmanServer)
By default, this service is running.
- DCOM Server Process Launcher (DcomLaunch)
- RPC Endpoint Mapper (RpcEptMapper)
- Remote Procedure Call (RpcSs)
- Server (LanmanServer)
- Port TCP 445 is open on target devices to enable remote access through Windows tools.
TCP 139, UDP 137, and UDP 138 are used by older protocols and are no longer necessary for current applications.
Dynamic outbound access ports must be allowed on the firewall for connections from the Administration Server and distribution points to target devices.
- The Active Directory domain policy security settings are allowed to provide the operation of the NTLM protocol during the deployment of Network Agent.
- On target devices running Microsoft Windows XP, Simple File Sharing mode is disabled.
- On target devices, the access sharing and security model are set as Classic – local users authenticate as themselves. It can in no way be Guest only – local users authenticate as Guest.
- Target devices are members of the domain, or uniform accounts with administrator rights are created on target devices in advance.
To successfully deploy Network Agent or other applications to a device that is not joined to a Windows Server 2003 or later Active Directory domain, you must disable remote UAC on that device. Remote UAC is one of the reasons that prevent local administrative accounts from accessing admin$, which is necessary for forced deployment of Network Agent or other applications. Disabling remote UAC does not affect local UAC.
During installation on new devices that have not yet been allocated to any of the Kaspersky Security Center administration groups, you can open the remote installation task properties and specify the administration group to which devices will be moved after Network Agent installation.
When creating a group task, keep in mind that each group task affects all devices in all nested groups within a selected group. Therefore, you must avoid duplicating installation tasks in subgroups.
A simplified way to create tasks for forced installation of applications is automatic installation. To do this, you must open the administration group properties, open the list of installation packages, and then select the ones that must be installed on devices in this group. As a result, the selected installation packages will be automatically installed on all devices in this group and all of its subgroups. The time interval over which the packages will be installed depends on the network throughput and the total number of networked devices.
To reduce the load on Administration Server during the delivery of installation packages to target devices, you can select installation via distribution points in the installation task. Note that this installation method places a significant load on devices acting as distribution points. Therefore, it is recommended that you select devices that meet the requirements for distribution points. If you use distribution points, you have to make sure that they are present in each of the isolated subnets hosting target devices.
Using distribution points as local installation centers may also be useful when performing installation on devices in subnets communicated with Administration Server via a low-capacity channel while a broader channel is available between devices in the same subnet.
The free disk space in the partition with the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit folder must exceed, by many times, the total size of the distribution packages of installed applications.
Page top
Running stand-alone packages created by Kaspersky Security Center
The above-described methods of initial deployment of Network Agent and other applications cannot always be implemented because it is not possible to meet all of the applicable conditions. In such cases, you can create a common executable file called a stand-alone installation package through Kaspersky Security Center, using installation packages with the relevant installation settings that have been prepared by the administrator. The stand-alone installation package is stored in the shared folder of Kaspersky Security Center.
You can use Kaspersky Security Center to send selected users an email message containing a link to this file in the shared folder, prompting them to run the file (either in interactive mode, or with the key "-s" for silent installation). You can attach the stand-alone installation package to an email message and then send it to the users of devices that have no access to the shared folder of Kaspersky Security Center. The administrator can also copy the stand-alone package to a removable drive, deliver it to a relevant device, and then run it later.
You can create a stand-alone package from a Network Agent package, a package of another application (for example, the security application), or both. If the stand-alone package has been created from Network Agent and another application, installation starts with Network Agent.
When creating a stand-alone package with Network Agent, you can specify the administration group to which new devices (those that have not been allocated to any of the administration groups) will be automatically moved when Network Agent installation completes on them.
Stand-alone packages can run in interactive mode (by default), displaying the result for installation of applications they contain, or they can run in silent mode (when run with the key "-s"). Silent mode can be used for installation from scripts, for example, from scripts configured to run after an operating system image is deployed. The result of installation in silent mode is determined by the return code of the process.
Options for manual installation of applications
Administrators or experienced users can install applications manually in interactive mode. They can use either original distribution packages or installation packages generated from them and stored in the shared folder of Kaspersky Security Center. By default, installers run in interactive mode and prompt users for all required values. However, when running the process setup.exe from the root of an installation package with the key "-s", the installer will be running in silent mode and with the settings that have been defined when configuring the installation package.
When running setup.exe from the root of an installation package stored in the shared folder of Kaspersky Security Center, the package will first be copied to a temporary local folder, and then the application installer will be run from the local folder.
Page top
Creating an MST file
To transform the content of an MSI package and apply custom settings to an existing MSI file, you have to create a transformation file in the MST format. To do this, use the Orca.exe editor that is included in the Windows SDK.
To create an MST file:
- Run the Orca.exe editor.
- Go to the File tab, and in the menu, click Open.
- Select the Kaspersky Network Agent.msi file.
- Go to the Transformation tab, and in the menu, select New transformation.
- In the Tables column, select Property and write the following values:
- EULA=1
- SERVERADDRESS=<Administration Server address>
Click the Save button.
- Go to the Transform tab, and in the menu, select Generate Transform.
- In the window that opens, specify a name for the transformation file you create, and then click the Save button.
The MST file is saved.
Page top
Remote installation of applications on devices with Network Agent installed
If an operable Network Agent connected to the primary Administration Server (or to any of its secondary Servers) is installed on a device, you can upgrade Network Agent on this device, as well as install, upgrade, or remove any supported applications through Network Agent.
You can enable the Using Network Agent option in the properties of the remote installation task.
If this option is selected, installation packages with installation settings defined by the administrator will be transferred to target devices over communication channels between Network Agent and the Administration Server.
To optimize the load on the Administration Server and minimize traffic between the Administration Server and the devices, it is useful to assign distribution points on every remote network or in every broadcasting domain (see sections "About distribution points" and "Building a structure of administration groups and assigning distribution points"). In this case, installation packages and the installer settings are distributed from the Administration Server to target devices through distribution points.
Moreover, you can use distribution points for broadcasting (multicast) delivery of installation packages, which allows reducing network traffic significantly when deploying applications.
When transferring installation packages to target devices over communication channels between Network Agents and the Administration Server, all installation packages that have been prepared for transfer will also be cached in the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\.working\FTServer folder. When using multiple large installation packages of various types and involving a large number of distribution points, the size of this folder may increase dramatically.
Files cannot be deleted from the FTServer folder manually. When original installation packages are deleted, the corresponding data will be automatically deleted from the FTServer folder.
The data received by distribution points is saved in the folder %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1103\$FTClTmp.
Files cannot be deleted from the $FTClTmp folder manually. As tasks using data from this folder complete, the contents of this folder will be deleted automatically.
Because installation packages are distributed over communication channels between Administration Server and Network Agents from an intermediate repository in a format optimized for network transfers, no changes are allowed in installation packages stored in the original folder of each installation package. Those changes will not be automatically registered by Administration Server. If you need to modify the files of installation packages manually (although you are recommended to avoid this scenario), you must edit any of the settings of an installation package in Administration Console. Editing the settings of an installation package in Administration Console causes Administration Server to update the package image in the cache that has been prepared for transfer to target devices.
Page top
Managing device restarts in the remote installation task
Devices often need a restart to complete the remote installation of applications (particularly on Windows).
If you use the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center, in the New task wizard or in the properties window of the task that has been created (Operating system restart section), you can select the action to perform when the Windows device requires a restart:
- Do not restart the device. In this case, no automatic restart will be performed. To complete the installation, you must restart the device (for example, manually or through the device management task). Information about the required restart will be saved in the task results and in the device status. This option is suitable for installation tasks on servers and other devices where continuous operation is critical.
- Restart the device. In this case, the device is always restarted automatically if a restart is required for completion of the installation. This option is useful for installation tasks on devices that provide for regular pauses in their operation (shutdown or restart).
- Prompt user for action. In this case, the restart reminder is displayed on the screen of the client device, prompting the user to restart it manually. Some advanced settings can be defined for this option: text of the message for the user, the message display frequency, and the time interval after which a restart will be forced (without the user's confirmation). The Prompt user for action is the most suitable for workstations where users need a possibility of selecting the most convenient time for a restart.
Suitability of databases updating in an installation package of a security application
Before starting the protection deployment, you must keep in mind the possibility of updating anti-virus databases (including modules of automatic patches) shipped together with the distribution package of the security application. It is useful to update the databases in the installation package of the application before starting the deployment (for example, by using the corresponding command in the context menu of a selected installation package). This will reduce the number of restarts required for completion of protection deployment on target devices.
Page top
Using tools for remote installation of applications in Kaspersky Security Center for running relevant executable files on managed devices
Using the New package wizard, you can select any executable file and define the settings of the command line for it. For this you can add to the installation package either the selected file itself or the entire folder in which this file is stored. Then you must create the remote installation task and select the installation package that has been created.
While the task is running, the specified executable file with the defined settings of the command prompt will be run on target devices.
If you use installers in Microsoft Windows Installer (MSI) format, Kaspersky Security Center analyzes the installation results by means of standard tools.
If the Vulnerability and patch management license is available, Kaspersky Security Center (when creating an installation package for any supported application in the corporate environment) also uses rules for installation and analysis of installation results that are in its updatable database.
Otherwise, the default task for executable files waits for the completion of the running process, and of all its child processes. After completion of all of the running processes, the task will be completed successfully regardless of the return code of the initial process. To change such behavior of this task, before creating the task, you have to manually modify the .kpd files that were generated by Kaspersky Security Center in the folder of the newly created installation package and its subfolders.
.kpd files use ASCII encoding. .kud files use Unicode encoding.
For the task not to wait for the completion of the running process, set the value of the Wait setting to 0 in the [SetupProcessResult] section:
Example: [SetupProcessResult] Wait=0 |
For the task to wait only for the completion of the running process on Windows, not for the completion of all child processes, set the value of the WaitJob setting to 0 in the [SetupProcessResult], section, for example:
Example: [SetupProcessResult] WaitJob=0 |
For the task to complete successfully or return an error depending on the return code of the running process, create an executable .bat file that saves the error code to a file, for example:
Example: echo [ResponseResult] > setup.log echo ResultCode=2 >> setup.log exit 0 |
And then modify the .kud files that were generated by Kaspersky Security Center in the folder of the newly created installation package:
Example: [SetupMainResult] File=setup.log Section=ResponseResult Value=ResultCode [SetupMainResult_SuccessCodes] 0=Installation completed successfully. [SetupMainResult_ErrorCodes] 1=Installation script error 2=Custom error |
In this case, any code other than those listed will result in an error returned.
To display a string with a comment on the successful completion of the task or an error in the task results, enter brief descriptions of errors corresponding to return codes of the process in the [SetupProcessResult_SuccessCodes] and [SetupProcessResult_ErrorCodes] sections, for example:
Example: [SetupProcessResult_SuccessCodes] 0= Installation completed successfully 3010=A restart is required to complete the installation [SetupProcessResult_ErrorCodes] 1602=Installation canceled by the user 1603=Fatal error during installation |
To use Kaspersky Security Center tools for managing the device restart (if a restart is required to complete an operation), list the return codes of the process that indicate that a restart must be performed, in the [SetupProcessResult_NeedReboot] section:
Example: [SetupProcessResult_NeedReboot] 3010= |
Monitoring the deployment
To monitor the Kaspersky Security Center deployment and make sure that a security application and Network Agent are installed on managed devices, you have to check the traffic light in the Deployment section. This traffic light is located in the workspace of the Administration Server node in the main window of Administration Console. The traffic light reflects the current deployment status. The number of devices with Network Agent and security applications installed is displayed next to the traffic light. When any installation tasks are running, you can monitor their progress here. If any installation errors occur, the number of errors is displayed here. You can view the details of any error by clicking the link.
You can also use the deployment schema in the workspace of the Managed devices folder on the Groups tab. The chart reflects the deployment process, showing the number of devices without Network Agent, with Network Agent, or with Network Agent and a security application.
For more details on the progress of the deployment (or the operation of a specific installation task) open the results window of the relevant remote installation task: Right-click the task and select Results in the context menu. The window displays two lists: the upper one contains the task statuses on devices, while the lower one contains task events on the device that is currently selected in the upper list.
Information about deployment errors are added to the Kaspersky Event Log on Administration Server. Information about errors is also available through the corresponding event selection in the Administration Server node on the Events tab.
Page top
Configuring installers
This section provides information about the files of Kaspersky Security Center installers and the installation settings, as well as recommendations on how to install Administration Server and Network Agent in silent mode.
General information
Installers of Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 components (Administration Server, Network Agent, and Administration Console) are built on Windows Installer technology. An MSI package is the core of an installer. This format of packaging allows using all of the advantages provided by Windows Installer: scalability, availability of a patching system, transformation system, centralized installation through third-party solutions, and transparent registration with the operating system.
Installation in silent mode (with a response file)
The installers of Administration Server and Network Agent have the feature of working with the response file (ss_install.xml), where the parameters for installation in silent mode without user participation are integrated. The ss_install.xml file is located in the same folder as the MSI package; it is used automatically during installation in silent mode. You can enable the silent installation mode with the command line key "/s".
An overview of an example run follows:
setup.exe /s |
Before you start the installer in silent mode, read the End User License Agreement (EULA). If the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit does not include a TXT file with the text of the EULA, you can download the file from the Kaspersky website.
The ss_install.xml file is an instance of the internal format of parameters of the Kaspersky Security Center installer. Distribution packages contain the ss_install.xml file with the default parameters.
Please do not modify the ss_install.xml file manually. This file can be modified through the tools of Kaspersky Security Center, when editing the parameters of the installation packages in Administration Console.
To modify the response file for Administration Server installation:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center distribution package. If you use a full package EXE file, unpack it.
- From the Server folder, open the command line, and then run the following command:
setup.exe /r ss_install.xml
The Kaspersky Security Center installer starts.
- Follow the wizard's steps to configure the Kaspersky Security Center installation.
When you complete the wizard, the response file is automatically modified according to the new settings that you specified.
Installation of Network Agent in silent mode (without a response file)
You can install Network Agent with a single .msi package, specifying the values of MSI properties in the standard way. This scenario allows Network Agent to be installed by using group policies.
Do not rename the installation package Kaspersky Network Agent.msi. Renaming this package may cause installation errors during future updates of Network Agent.
To avoid conflicts between parameters defined through MSI properties and parameters defined in the response file, you can disable the response file by setting the property DONT_USE_ANSWER_FILE=1. The MSI file is located in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution package, in the Packages\NetAgent\exec folder. An example of a run of the Network Agent installer with an .msi package is as follows.
Installation of Network Agent in silent mode requires acceptance of the terms of the End User License Agreement. Use the EULA=1 parameter only if you have fully read, understand and accept the terms of the End User License Agreement.
Example:
|
You can also define the installation parameters for an .msi package by preparing the response file in advance (one with an .mst extension). This command appears as follows:
Example:
|
You can specify several response files in a single command.
Partial installation configuration through setup.exe
When running installation of applications through setup.exe, you can add the values of any properties of MSI to the MSI package.
This command appears as follows:
Example: /v"PROPERTY_NAME1=PROPERTY_VALUE1 PROPERTYNAME2=PROPERTYVALUE2" |
Administration Server installation parameters
The table below describes the MSI properties that you can configure when installing Administration Server. All of the parameters are optional, except for EULA and PRIVACYPOLICY.
Parameters of Administration Server installation in silent mode
MSI property |
Description |
Available values |
|---|---|---|
EULA |
Acceptance of the terms of the License Agreement (required) |
|
PRIVACYPOLICY |
Acceptance of the terms of the Privacy Policy (required) |
|
INSTALLATIONMODETYPE |
Type of Administration Server installation |
|
INSTALLDIR |
Application installation folder |
String value. |
ADDLOCAL |
List of components to install (separated by commas) |
CSAdminKitServer, NAgent, CSAdminKitConsole, NSAC, MobileSupport, KSNProxy, SNMPAgent, GdiPlusRedist, Microsoft_VC90_CRT_x86, Microsoft_VC100_CRT_x86. Minimum list of components sufficient for proper Administration Server installation:
|
NETRANGETYPE |
Network size |
|
SRV_ACCOUNT_TYPE |
Way of specifying the user for the operation of the Administration Server service |
|
SERVERACCOUNTNAME |
User name for the service |
String value. |
SERVERACCOUNTPWD |
User password for the service |
String value. |
DBTYPE |
Database type |
|
MYSQLSERVERNAME |
Full name of MySQL or MariaDB server |
String value. |
MYSQLSERVERPORT |
Number of port for connection to MySQL or MariaDB server |
Numerical value. |
MYSQLDBNAME |
Name of MySQL or MariaDB server database |
String value. |
MYSQLACCOUNTNAME |
User name for connection to MySQL or MariaDB server database |
String value. |
MYSQLACCOUNTPWD |
User password for connection to MySQL or MariaDB server database |
String value. |
MSSQLCONNECTIONTYPE |
Type of use of MSSQL database |
|
MSSQLSERVERNAME |
Full name of SQL Server instance |
String value. |
MSSQLDBNAME |
Name of SQL Server database |
String value. |
MSSQLAUTHTYPE |
Method of authentication for connection to SQL Server |
|
MSSQLACCOUNTNAME |
User name for connection to SQL Server in SQLServer mode |
String value. |
MSSQLACCOUNTPWD |
User password for connection to SQL Server in SQLServer mode |
String value. |
CREATE_SHARE_TYPE |
Method of specifying the shared folder |
|
EXISTSHAREFOLDERNAME |
Full path to an existing shared folder |
String value. |
SERVERPORT |
Port number to connect to Administration Server |
Numerical value. |
SERVERSSLPORT |
Number of port for establishing SSL connection to Administration Server |
Numerical value. |
SERVERADDRESS |
Administration Server address |
String value. |
SERVERCERT2048BITS |
Size of the key for the Administration Server certificate (bits) |
|
MOBILESERVERADDRESS |
Address of the Administration Server for connection of mobile devices; ignored if the MobileSupport component has not been selected |
String value. |
Network Agent installation parameters
The table below describes the MSI properties that you can configure when installing Network Agent. All of the parameters are optional, except for EULA and SERVERADDRESS.
Parameters of Network Agent installation in silent mode
MSI property |
Description |
Available values |
|---|---|---|
EULA |
Acceptance of the terms of the License Agreement |
|
DONT_USE_ANSWER_FILE |
Read installation settings from response file |
|
INSTALLDIR |
Path to the Network Agent installation folder |
String value. |
SERVERADDRESS |
Administration Server address (required) |
String value. |
SERVERPORT |
Number of port for connection to Administration Server |
Numerical value. |
SERVERSSLPORT |
Number of the port for encrypted connection to Administration Server by using SSL protocol |
Numerical value. |
USESSL |
Whether to use SSL connection |
|
OPENUDPPORT |
Whether to open a UDP port |
|
UDPPORT |
UDP port number |
Numerical value. |
USEPROXY |
Whether to use a proxy server. For compatibility purposes, it is not recommended to specify proxy connection settings in the Network Agent installation package settings. |
|
PROXYLOCATION (PROXYADDRESS:PROXYPORT)
|
Proxy address and number of port for connection to proxy server |
String value. |
PROXYLOGIN |
Account for connection to proxy server |
String value. |
PROXYPASSWORD |
Password of account for connection to proxy server (Do not specify any details of privileged accounts in the parameters of installation packages.) |
String value. |
GATEWAYMODE |
Connection gateway use mode |
|
GATEWAYADDRESS |
Connection gateway address |
String value. |
CERTSELECTION |
Method of receiving a certificate |
|
CERTFILE |
Path to the certificate file |
String value. |
VMVDI |
Enable dynamic mode for Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) |
|
VMOPTIMIZE |
Whether the Network Agent settings are optimal for hypervisor |
|
LAUNCHPROGRAM |
Whether to start the Network Agent service after installation. The parameter is ignored if VMVDI=1 |
|
NAGENTTAGS |
Tag for Network Agent (has priority over the tag given in the response file) |
String value. |
Virtual infrastructure
Kaspersky Security Center supports the use of virtual machines. You can install Network Agent and the security application on each virtual machine, and you can protect virtual machines at the hypervisor level. In the first case, you can use either a standard security application or Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent to protect your virtual machines. In the second case, you can use Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Agentless.
Kaspersky Security Center supports rollbacks of virtual machines to their previous state.
Tips on reducing the load on virtual machines
When installing Network Agent on a virtual machine, you are advised to consider disabling some Kaspersky Security Center features that seem to be of little use for virtual machines.
When installing Network Agent on a virtual machine or on a template intended for generation of virtual machines, we recommend the following actions:
- If you are running a remote installation, in the properties window of the Network Agent installation package, in the Advanced section, select the Optimize settings for VDI option.
- If you are running an interactive installation through a wizard, in the wizard window, select the Optimize the Network Agent settings for the virtual infrastructure option.
Selecting those options alters the settings of Network Agent so that the following features remain disabled by default (before a policy is applied):
- Retrieving information about software installed
- Retrieving information about hardware
- Retrieving information about vulnerabilities detected
- Retrieving information about updates required
Usually, those features are not necessary on virtual machines because they use uniform software and virtual hardware.
Disabling the features is invertible. If any of the disabled features is required, you can enable it through the policy of Network Agent, or through the local settings of Network Agent. The local settings of Network Agent are available through the context menu of the relevant device in Administration Console.
Support of dynamic virtual machines
Kaspersky Security Center supports dynamic virtual machines. If a virtual infrastructure has been deployed on the organization's network, dynamic (temporary) virtual machines can be used in certain cases. The dynamic VMs are created under unique names based on a template that has been prepared by the administrator. The user works on a VM for a while and then, after being turned off, this virtual machine will be removed from the virtual infrastructure. If Kaspersky Security Center has been deployed on the organization's network, a virtual machine with installed Network Agent will be added to the Administration Server database. After you turn off a virtual machine, the corresponding entry must also be removed from the database of Administration Server.
To make functional the feature of automatic removal of entries on virtual machines, when installing Network Agent on a template for dynamic virtual machines, select the Enable dynamic mode for VDI option:
- For remote installation—In the properties window of the installation package of Network Agent (Advanced section)
- For interactive installation—In the Network Agent installation wizard
Avoid selecting the Enable dynamic mode for VDI option when installing Network Agent on physical devices.
If you want events from dynamic virtual machines to be stored on the Administration Server for a while after you remove those virtual machines, then, in the Administration Server properties window, in the Events repository section, select the Store events after devices are deleted option and specify the maximum storage term for events (in days).
Support of virtual machines copying
Copying a virtual machine with installed Network Agent or creating one from a template with installed Network Agent is identical to the deployment of Network Agents by capturing and copying a hard drive image. So, in general case, when copying virtual machines, you need to perform the same actions as when deploying Network Agent by copying a disk image.
However, the two cases described below showcase Network Agent, which detects the copying automatically. Owing to the above reasons, you do not have to perform the sophisticated operations described under "Deployment by capturing and copying the hard drive of a device":
- The Enable dynamic mode for VDI option was selected when Network Agent was installed—After each restart of the operating system, this virtual machine will be recognized as a new device, regardless of whether it has been copied or not.
- One of the following hypervisors is in use: VMware, HyperV, or Xen: Network Agent detects the copying of the virtual machine by the changed IDs of the virtual hardware.
Analysis of changes in virtual hardware is not absolutely reliable. Before applying this method widely, you must test it on a small pool of virtual machines for the version of the hypervisor currently used in your organization.
Support of file system rollback for devices with Network Agent
Kaspersky Security Center is a distributed application. Rolling back the file system to a previous state on a device with Network Agent installed will lead to data desynchronization and improper functioning of Kaspersky Security Center.
The file system (or a part of it) can be rolled back in the following cases:
- When copying an image of the hard drive.
- When restoring a state of the virtual machine by means of the virtual infrastructure.
- When restoring data from a backup copy or a recovery point.
Scenarios under which third-party software on devices with Network Agent installed affects the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\ folder are only critical scenarios for Kaspersky Security Center. Therefore, you must always exclude this folder from the recovery procedure, if possible.
Because the workplace rules of some organizations provide for rollbacks of the file system on devices, support for the file system rollback on devices with Network Agent installed has been added to Kaspersky Security Center, starting with version 10 Maintenance Release 1 (Administration Server and Network Agents must be of version 10 Maintenance Release 1 or later). When detected, those devices are automatically reconnected to the Administration Server with full data cleansing and full synchronization.
By default, support of file system rollback detection is enabled in Kaspersky Security Center 15.1.
As much as possible, avoid rolling back the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\ folder on devices with Network Agent installed, because full resynchronization of data requires a large amount of resources.
A rollback of the system state is absolutely not allowed on a device with Administration Server installed. Nor is a rollback of the database used by Administration Server.
You can restore a state of Administration Server from a backup copy only with the standard klbackup utility.
Page top
Local installation of applications
This section provides an installation procedure for applications that can be installed on local devices only.
To perform local installation of applications on a specific client device, you must have administrator rights on this device.
To install applications locally on a specific client device:
- Install Network Agent on the client device and configure the connection between the client device and Administration Server.
- Install the requisite applications on the device as described in the guides of these applications.
- Install a management plug-in for each of the installed applications on the administrator's workstation.
Kaspersky Security Center also supports the option of local installation of applications using a stand-alone installation package. Kaspersky Security Center does not support installation of all Kaspersky applications.
Local installation of Network Agent
To install Network Agent on a device locally:
- On the device, run the setup.exe file from the distribution package downloaded from the internet. Refer to the following topic for details: Obtaining the Network Agent installation package from the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit.
A window opens prompting you to select Kaspersky applications to install.
- In the application selection window, click the Install only Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent link to start the Network Agent setup wizard. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- Administration Server
- Proxy server configuration
- Connection gateway
- Administration Server certificate
- Agent tags
- Advanced settings
- Start application
When the setup wizard finishes, Network Agent will be installed on the device.
You can view the properties of the Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent service; you can also start, stop, and monitor Network Agent activity by means of standard Microsoft Windows tools: Computer Management\Services.
Installing Network Agent in silent mode
Network Agent can be installed in silent mode, that is, without the interactive input of installation parameters. Silent installation uses a Windows Installer package (MSI) for Network Agent. The MSI file is located in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution package, in the Packages\NetAgent\exec folder.
Do not rename the installation package Kaspersky Network Agent.msi. Renaming this package may cause installation errors during future updates of Network Agent.
Installation of Network Agent from the MSI package is possible only in silent mode, interactive installation from the MSI package is not supported.
To install Network Agent on a local device in silent mode:
- Read the End User License Agreement. Use the command below only if you understand and accept the terms of the End User License Agreement.
- Run the command
msiexec /i "Kaspersky Network Agent.msi" /qn <
setup_parameters>where
setup_parametersis a list of parameters and their respective values, separated by a space (PROP1=PROP1VAL PROP2=PROP2VAL).In the list of parameters, you must include
EULA=1. Otherwise Network Agent will not be installed.
If you are using the standard connection settings for Kaspersky Security Center, and Network Agent on remote devices, run the command:
|
/l*vx is the key for writing logs. The log is created during the installation of Network Agent and saved at C:\windows\temp\nag_inst.log.
In addition to nag_inst.log, the application creates the $klssinstlib.log file, which contains the installation log. This file is stored in the %windir%\temp or %temp% folder. For troubleshooting purposes, you or a Kaspersky Technical Support specialist may need both log files—nag_inst.log and $klssinstlib.log.
If you need to additionally specify the port for connection to the Administration Server run the command:
|
The parameter SERVERPORT corresponds to the number of port for connection to Administration Server.
The names and possible values for parameters that can be used when installing Network Agent in silent mode are listed in the Network Agent installation parameters section.
Installing Network Agent for Linux in silent mode (with an answer file)
You can install Network Agent on Linux devices by using an answer file—a text file that contains a custom set of installation parameters: variables and their respective values. Using this answer file allows you to run an installation in silent mode, that is, without user participation.
To perform installation of Network Agent for Linux in silent mode:
- Prepare the relevant Linux device for remote installation. Download and create the remote installation package, by using a .deb or .rpm package of Network Agent, by means of any suitable package management system.
- If you want to install Network Agent on devices with the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 operating system, install the insserv-compat package first to configure Network Agent.
If you want to install Network Agent on devices that use the operating system RED OS 7.3.4 or later or MSVSPHERE 9.2 or later, install the libxcrypt-compat package for the correct function of Network Agent.
- Read the End User License Agreement. Follow the steps below only if you understand and accept the terms of the End User License Agreement.
- Set the value of the KLAUTOANSWERS environment variable by entering the full name of the answer file (including the path), for example, as follows:
export KLAUTOANSWERS=/tmp/nagent_install/answers.txt - Create the answer file (in TXT format) in the directory that you have specified in the environment variable. Add to the answer file a list of variables in the VARIABLE_NAME=variable_value format, each variable on a separate line.
For correct usage of the answer file, you must include in it a minimum set of the three required variables:
- KLNAGENT_SERVER
- KLNAGENT_AUTOINSTALL
- EULA_ACCEPTED
You can also add any optional variables to use more specific parameters of your remote installation. The following table lists all of the variables that can be included in the answer file:
- Install Network Agent:
- To install Network Agent from an RPM package to a 32-bit operating system, execute the following command:
# rpm -i klnagent-<build number>.i386.rpm - To install Network Agent from an RPM package to a 64-bit operating system, execute the following command:
# rpm -i klnagent64-<build number>.x86_64.rpm - To install Network Agent from an RPM package on a 64-bit operating system for the Arm architecture, execute the following command:
# rpm -i klnagent64-<build number>.aarch64.rpm - To install Network Agent from a DEB package to a 32-bit operating system, execute the following command:
# apt-get install ./klnagent_<build number>_i386.deb - To install Network Agent from a DEB package to a 64-bit operating system, execute the following command:
# apt-get install ./klnagent64_<build number>_amd64.deb - To install Network Agent from a DEB package on a 64-bit operating system for the Arm architecture, execute the following command:
# apt-get install ./klnagent64_<build number>_arm64.deb
- To install Network Agent from an RPM package to a 32-bit operating system, execute the following command:
Installation of Network Agent for Linux starts in silent mode; the user is not prompted for any actions during the process.
Page top
Preparing a device running Astra Linux in the closed software environment mode for installation of Network Agent
Prior to the installation of Network Agent on a device running Astra Linux in the closed software environment mode, you must perform two preparation procedures—the one in the instructions below and general preparation steps for any Linux device.
Before you begin:
- Make sure that the device on which you want to install Network Agent for Linux is running one of the supported Linux distributions.
- Download the necessary Network Agent installation file from the Kaspersky website.
Run the commands provided in this instruction under an account with root privileges.
To prepare a device running Astra Linux in the closed software environment mode for installation of Network Agent:
- Open the
/etc/digsig/digsig_initramfs.conffile, and then specify the following setting:DIGSIG_ELF_MODE=1 - In the command line, run the following command to install the compatibility package:
apt install astra-digsig-oldkeys - Create a directory for the application key:
mkdir -p /etc/digsig/keys/legacy/kaspersky/ - Place the application key /opt/kaspersky/ksc64/share/kaspersky_astra_pub_key.gpg in the directory created in the previous step:
cp kaspersky_astra_pub_key.gpg /etc/digsig/keys/legacy/kaspersky/If the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit does not include the kaspersky_astra_pub_key.gpg application key, you can download it by clicking the link: https://media.kaspersky.com/utilities/CorporateUtilities/kaspersky_astra_pub_key.gpg.
- Update the RAM disks:
update-initramfs -u -k allReboot the system.
- Perform the preparation steps common for any Linux device.
The device is prepared. You can now proceed to the installation of Network Agent.
Page top
Installing Network Agent for Linux in interactive mode
This article describes how to install Network Agent on Linux devices in the interactive mode, by specifying installation parameters step by step. Alternatively, you can use an answer file—a text file that contains a custom set of installation parameters: variables and their respective values. Using this answer file allows you to run an installation in silent mode, that is, without user participation.
If you want to install Network Agent on devices that use the operating system RED OS 7.3.4 or later or MSVSPHERE 9.2 or later, install the libxcrypt-compat package for the correct function of Network Agent.
To install Network Agent in interactive mode:
- Run the Network Agent installation. Depending on your Linux distribution, run one of the following commands:
- To install Network Agent from an RPM package to a 32-bit operating system:
# yum -i klnagent-<build number>.i386.rpm - To install Network Agent from an RPM package to a 64-bit operating system:
# yum -i klnagent64-<build number>.x86_64.rpm - To install Network Agent from an RPM package on a 64-bit operating system for the Arm architecture:
# yum -i klnagent64-<build number>.aarch64.rpm - To install Network Agent from a DEB package to a 32-bit operating system:
# apt install ./klnagent_<build number>_i386.deb - To install Network Agent from a DEB package to a 64-bit operating system:
# apt install ./klnagent64_<build number>_amd64.deb - To install Network Agent from a DEB package on a 64-bit operating system for the Arm architecture:
# apt install ./klnagent64_<build number>_arm64.deb
- To install Network Agent from an RPM package to a 32-bit operating system:
- Run the Network Agent configuration:
# /opt/kaspersky/klnagent64/bin/setup/postinstall.pl - Read the End User License Agreement (EULA). The text is displayed in the command line window. Press the space bar to view the next text segment. Then, when prompted, enter one the following values:
- Enter
yif you understand and accept the terms of the EULA. - Enter
nif you do not accept the terms of the EULA. To use Network Agent, you must accept the terms of the EULA. - Enter
rto show the EULA again.
- Enter
- Enter the Administration Server DNS name or IP address.
- Enter the Administration Server port number. By default, port 14000 is used.
- Enter the Administration Server SSL port number. By default, port 13000 is used.
- Enter
yif you want to use SSL encryption for traffic between Network Agent and Administration Server. Otherwise, entern. - Select one of the following options to configure Network Agent:
[1]—Do not configure a connection gateway.Your device will not act as a connection gateway and will not connect to Administration Server through a connection gateway.
[2]—Do not use a connection gateway.Your device will not connect to Administration Server through a connection gateway.
[3]—Connect to Server by using a connection gateway.Your device will connect to Administration Server through a connection gateway.
[4]—Use as a connection gateway.Your device will act as a connection gateway.
Network Agent is installed on a Linux device.
Local installation of the application management plug-in
To install the application management plug-in:
On a device with Administration Console installed, run the klcfginst.exe executable file, which is included in the application distribution package.
The klcfginst.exe file is included in all applications that can be managed through Kaspersky Security Center. Installation is facilitated by the wizard and requires no manual configuration of settings.
Page top
Installing applications in silent mode
To install an application in silent mode:
- Open the main window of Kaspersky Security Center.
- In the Remote installation folder of the console tree, in the Installation packages subfolder select the installation package of the relevant application or create a new one for that application.
The installation package will be stored on the Administration Server in the Packages service folder that is in the shared folder. A separate subfolder corresponds to each installation package.
- Open the folder storing the required installation package in one of the following ways:
- By copying the folder corresponding to the relevant installation package from the Administration Server to the client device. Then open the copied folder on the client device.
- By opening from the client device the shared folder that corresponds to the requisite installation package on the Administration Server.
If the shared folder is located on a device that has Microsoft Windows Vista installed, you must set the Disabled value for the User account control: Run all administrators in Admin Approval Mode setting (Start → Control Panel → Administration → Local security policy → Security settings).
- Depending on the selected application, do the following:
- For Kaspersky Anti-Virus for Windows Workstations, Kaspersky Anti-Virus for Windows Servers, and Kaspersky Security Center, navigate to the exec subfolder and run the executable file (the file with the .exe extension) with the /s key.
- For other Kaspersky applications, run the executable file (a file with the .exe extension) with the /s key from the open folder.
Running the executable file with the
EULA=1andPRIVACYPOLICY=1keys means that you have fully read, understand and accept the terms of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy, respectively. You are also aware that your data will be handled and transmitted (including to third countries) as described in the Privacy Policy. The text of the License Agreement and the Privacy Policy is included in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit. Accepting the terms of the License Agreement and the Privacy Policy is necessary for installing the application or upgrading a previous version of the application.
Installing applications by using stand-alone packages
Kaspersky Security Center lets you create stand-alone installation packages for applications. A stand-alone installation package is an executable file that can be located on the Web Server, sent by email, or transferred to a client device by another method. The received file can be run locally on the client device to install an application without involving Kaspersky Security Center.
To install an application using a stand-alone installation package:
- Connect to the necessary Administration Server.
- In the Remote installation folder of the console tree, select the Installation packages subfolder.
- In the workspace, select the installation package of the required application.
- Start the process of creating a stand-alone installation package in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Create stand-alone installation package in the context menu of the installation package.
- By clicking the Create stand-alone installation package link in the workspace of the installation package.
The Stand-alone installation package creation wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
At the final step of the wizard, select a method for transferring the stand-alone installation package to the client device.
- Transfer the stand-alone installation package to the client device.
- Run the stand-alone installation package on the client device.
The application is now installed on the client device with the settings specified in the stand-alone package.
When you create a stand-alone installation package, it is automatically published on Web Server. The link for downloading the stand-alone package is displayed in the list of created stand-alone installation packages. If necessary, you can cancel publication of the selected stand-alone package and republish it on the Web Server. By default, port 8060 is used for downloading stand-alone installation packages.
Page top
Network Agent installation package settings
To configure a Network Agent installation package:
- In the Remote installation folder of the console tree, select the Installation packages subfolder.
The Remote installation folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder by default.
- In the context menu of the Network Agent installation package, select Properties.
The Network Agent installation package properties window opens.
General
The General section displays general information about the installation package:
- Installation package name
- Name and version of the application for which the installation package has been created
- Installation package size
- Installation package creation date
- Path to the installation package folder
Settings
This section presents the settings required to ensure proper functioning of Network Agent immediately after it is installed. The settings in this section are available only on devices running Windows.
In the Destination folder group of settings, you can select the client device folder in which Network Agent will be installed.
In the following group of settings, you can set a password for the Network Agent remote uninstallation task:
- Use uninstallation password
- Status
- Protect Network Agent service against unauthorized removal or termination, and prevent changes to the settings
- Automatically install applicable updates and patches for components that have the Undefined status
Connection
In this section, you can configure connection of Network Agent to the Administration Server. To establish a connection, you can use the SSL or UDP protocol. For configuring the connection, specify the following settings:
- Administration Server
- Port
- SSL port
- Use Server certificate
- Use SSL
- Use UDP port
- UDP port number
- Open Network Agent ports in Microsoft Windows Firewall
- Use proxy server
For compatibility purposes, it is not recommended to specify proxy connection settings in the Network Agent installation package settings.
Advanced
In the Advanced section, you can configure how to use the connection gateway. For this purpose, you can do the following:
- Use Network Agent as a connection gateway in the demilitarized zone (DMZ) to connect to Administration Server, communicate with it, and keep data on the Network Agent safe during data transmission.
- Connect to Administration Server by using a connection gateway to reduce the number of connections to the Administration Server. In this case, enter the address of the device that will act as the connection gateway in the Connection gateway address field.
- Configure the connection for Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) if your network includes virtual machines. For this purpose, do the following:
- Allow running the user registration utility after Network Agent installation
Additional components
In this section you can select additional components for concurrent installation with Network Agent.
Tags
The Tags section displays a list of keywords (tags) that can be added to client devices after Network Agent installation. You can add and remove tags from the list, as well as rename them.
If the check box is selected next to a tag, this tag is automatically added to managed devices during Network Agent installation.
If the check box is cleared next to a tag, the tag will not automatically be added to managed devices during Network Agent installation. You can manually add this tag to devices.
When removing a tag from the list, it is automatically removed from all devices to which it was added.
Revision history
In this section, you can view the history of the installation package revisions. You can compare revisions, view revisions, save revisions to a file, and add and edit revision descriptions.
Network Agent installation package settings available to a specific operating system are given in the table below.
Network Agent installation package settings
Property section |
Windows |
Mac |
Linux |
|---|---|---|---|
General |
|
|
|
Settings |
|
|
|
Connection |
|
(except for the Open Network Agent ports in Microsoft Windows Firewall and Use only automatic detection of proxy server options) |
(except for the Open Network Agent ports in Microsoft Windows Firewall and Use only automatic detection of proxy server options) |
Advanced |
|
|
|
Additional components |
|
|
|
Tags |
|
(except for the automatic tagging rules) |
(except for the automatic tagging rules) |
Revision history |
|
|
|
Viewing the Privacy Policy
The Privacy Policy is available online at https://www.kaspersky.com/products-and-services-privacy-policy; it is also available offline. You can read the Privacy Policy, for example, before installing Network Agent.
To read the Privacy Policy offline:
- Start the installer of Kaspersky Security Center.
- In the installer window, proceed to the Extract installation packages link.
- In the list that opens, select Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent, and then click Next.
The privacy_policy.txt file appears on your device, in the folder that you specified, in the NetAgent subfolder.
Page top
Deploying mobile device management systems
This section describes the deployment of mobile device management systems using iOS MDM and Kaspersky Endpoint Security protocols.
Deploying a system for management using iOS MDM protocol
Kaspersky Security Center lets you manage mobile devices running iOS. iOS MDM devices are iOS mobile devices that are connected to an iOS MDM Server and managed by an Administration Server.
Mobile devices are connected to an iOS MDM Server through the following steps:
- The administrator installs the iOS MDM Server.
- The administrator gets an Apple Push Notification Service (APNs) certificate.
The APNs certificate lets Administration Server connect to the APNs server to send push notifications to iOS MDM devices.
- The administrator installs the APNs certificate on the iOS MDM Server.
- The administrator creates an iOS MDM profile for the user of the iOS mobile device.
The iOS MDM profile contains a collection of settings for connecting iOS mobile devices to the Administration Server.
After the iOS MDM profile is installed and the iOS MDM device is synchronized with the Administration Server, the device is displayed in the Mobile devices folder, which is a subfolder of the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree.
Installing iOS MDM Server
To install iOS MDM Server on a local device:
- Run the setup.exe executable file.
A window opens prompting you to select Kaspersky applications to install.
In the applications selection window, click the Install iOS MDM Server link to run the iOS MDM Server setup wizard.
- Select a destination folder.
The default destination folder is <Disk>:\Program Files\Kaspersky Lab\Mobile Device Management for iOS. If such a folder does not exist, it is created automatically during the installation. You can change the destination folder by using the Browse button.
- In the Specify the settings for connection to iOS MDM Server window of the wizard, in the External port for connection to iOS MDM service field, specify an external port for connecting mobile devices to the iOS MDM service.
External port 5223 is used by mobile devices for communication with the APNs server. Make sure that port 5223 is open in the firewall for connection with the address range 17.0.0.0/8.
Port 443 is used for connection to iOS MDM Server by default. If port 443 is already in use by another service or application, it can be replaced with, for example, port 9443.
The iOS MDM Server uses external port 2197 to send notifications to the APNs server.
APNs servers run in load-balancing mode. Mobile devices do not always connect to the same IP addresses to receive notifications. The 17.0.0.0/8 address range is reserved for Apple, and it is therefore recommended to specify this entire range as an allowed range in Firewall settings.
- If you want to configure interaction ports for application components manually, select the Set up local ports manually option, and then specify values for the following settings:
- Port for connection to Network Agent. In this field, specify a port for connecting the iOS MDM service to Network Agent. The default port number is 9799.
- Local port to connect to iOS MDM service. In this field, specify a local port for connecting Network Agent to the iOS MDM service. The default port number is 9899.
It is recommended to use default values.
- In the External address of Mobile Device Server window of the wizard, in the Web address for remote connection to Mobile Device Server field, specify the address of the client device on which iOS MDM Server is to be installed.
This address will be used for connecting managed mobile devices to the iOS MDM service. The client device must be available for connection of iOS MDM devices.
You can specify the address of a client device in any of the following formats:
- Device FQDN (such as mdm.example.com)
- Device NetBIOS name
Please avoid adding the URL scheme and the port number in the address string: these values will be added automatically.
When the wizard finishes, iOS MDM Server is installed on the local device. The iOS MDM Server is displayed in the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree.
Page top
Installing iOS MDM Server in silent mode
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to install iOS MDM Server on a local device in silent mode, that is, without the interactive input of installation settings.
To install iOS MDM Server on a local device in silent mode:
- Read the End User License Agreement. Use the command below only if you understand and accept the terms of the End User License Agreement.
- Run the following command:
.\exec\setup.exe /s /v"DONT_USE_ANSWER_FILE=1 EULA=1 <setup_parameters>"where
setup_parametersis a list of settings and their respective values, separated with spaces (PROP1=PROP1VAL PROP2=PROP2VAL). The setup.exe file is located in the Server folder, which is part of the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit.
The names and possible values for parameters that can be used when installing iOS MDM Server in silent mode are listed in the table below. Parameters can be specified in any convenient order.
Parameters of iOS MDM Server installation in silent mode
Parameter name |
Parameter description |
Available values |
|---|---|---|
EULA |
Acceptance of the terms of the End User License Agreement. This parameter is mandatory. |
|
DONT_USE_ANSWER_FILE |
Whether or not to use an XML file with iOS MDM Server installation settings. The XML file is included in the installation package or stored on the Administration Server. You do not have to specify an additional path to the file. This parameter is mandatory. |
|
INSTALLDIR |
The iOS MDM Server installation folder. This parameter is optional. |
String value, for example, |
CONNECTORPORT |
Local port for connecting the iOS MDM service to Network Agent. The default port number is 9799. This parameter is optional. |
Numerical value. |
LOCALSERVERPORT |
Local port for connecting Network Agent to the iOS MDM service. The default port number is 9899. This parameter is optional. |
Numerical value. |
EXTERNALSERVERPORT |
Port for connecting a device to iOS MDM Server. The default port number is 443. This parameter is optional. |
Numerical value. |
EXTERNAL_SERVER_URL |
External address of the client device on which iOS MDM Server is to be installed. This address will be used for connecting managed mobile devices to the iOS MDM service. The client device must be available for connection through iOS MDM. The address must not include the URL scheme and number of the port because these values will be added automatically. This parameter is optional. |
|
WORKFOLDER |
Work folder of iOS MDM Server. If no work folder is specified, data will be written to the default folder. This parameter is optional. |
String value, for example, |
MTNCY |
Use of iOS MDM Server by multiple virtual Servers. This parameter is optional. |
|
Example:
|
The iOS MDM Server installation parameters are given in detail in section "Installing iOS MDM Server".
Page top
iOS MDM Server deployment scenarios
The number of copies of iOS MDM Server to be installed can be selected either based on available hardware or on the total number of mobile devices covered.
Please keep in mind that the recommended maximum number of mobile devices for a single installation of Kaspersky Device Management for iOS is 50,000 at most. In order to reduce the load, the entire pool of devices can be distributed among several servers that have iOS MDM Server installed.
Authentication of iOS MDM devices is performed through user certificates (any profile installed on a device contains the certificate of the device owner). Thus, two deployment schemes are possible for an iOS MDM Server:
- Simplified scheme
- Deployment scheme involving Kerberos constrained delegation (KCD)
Simplified deployment scheme
When deploying an iOS MDM Server under the simplified scheme, mobile devices connect to the iOS MDM web service directly. In this case, user certificates issued by Administration Server can only be applied for devices authentication. Integration with Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is impossible for user certificates.
Page top
Deployment scheme involving Kerberos constrained delegation (KCD)
To use the deployment scheme with Kerberos constrained delegation (KCD), the following requirements must be met:
- Administration Server and the iOS MDM Server are located on the internal network of the organization.
- A reverse proxy with KCD support is in use.
This deployment scheme provides for the following:
- Integration with the reverse proxy that supports KCD
- Use of KCD for authentication of mobile devices
- Integration with the PKI for applying user certificates
When using this deployment scheme, you must do the following:
- In Administration Console, in the settings of the iOS MDM web service, select the Ensure compatibility with Kerberos constrained delegation check box.
- As the certificate for the iOS MDM web service, specify the customized certificate that was defined when the iOS MDM web service was published on reverse proxy.
- User certificates for iOS devices must be issued by the Certificate Authority (CA) of the domain. If the domain contains multiple root CAs, user certificates must be issued by the CA that was specified when the iOS MDM web service was published on the reverse proxy.
You can ensure that the user certificate is in compliance with the this CA-issuance requirement by using one of the following methods:
- Specify the user certificate in the New iOS MDM profile wizard and in the Certificate installation wizard.
- Integrate the Administration Server with the domain's PKI and define the corresponding setting in the rules for issuance of certificates:
- In the console tree, expand the Mobile Device Management folder and select the Certificates subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Certificates folder, click the Configure certificate issuance rules button to open the Certificate issuance rules window.
- In the Integration with PKI section, configure integration with the Public Key Infrastructure.
- In the Issuance of mobile certificates section, specify the source of certificates.
Below is an example of setup of Kerberos Constrained Delegation (KCD) with the following assumptions:
- The iOS MDM web service is running on port 443.
- The name of the device with the reverse proxy is firewall.mydom.local.
- The name of device with the iOS MDM web service is iosmdm.mydom.local.
- The name of external publishing of the iOS MDM web service is iosmdm.mydom.global.
Service Principal Name for http/iosmdm.mydom.local
In the domain, you have to register the service principal name (SPN) for the device with the iOS MDM web service (iosmdm.mydom.local):
setspn -a http/iosmdm.mydom.local iosmdm
Configuring the domain properties of the device with the reverse proxy (firewall.mydom.local)
To delegate traffic, trust the device with the reverse proxy (firewall.mydom.local) to the service that is defined by the SPN (http/iosmdm.mydom.local).
To trust the device with the reverse proxy to the service defined by the SPN (http/iosmdm.mydom.local), the administrator must perform the following actions:
- In the Microsoft Management Console snap-in named "Active Directory Users and Computers", select the device with the reverse proxy installed (firewall.mydom.local).
- In the device properties, on the Delegation tab, set the Trust this computer for delegation to specified service only toggle to Use any authentication protocol.
- Add the SPN (http/iosmdm.mydom.local) to the Services to which this account can present delegated credentials list.
Special (customized) certificate for the published web service (iosmdm.mydom.global)
You have to issue a special (customized) certificate for the iOS MDM web service on the FQDN iosmdm.mydom.global and specify that it replaces the default certificate in the settings of iOS MDM web service in Administration Console.
Please note that the certificate container (file with the p12 or pfx extension) must also contain a chain of root certificates (public keys).
Publishing the iOS MDM web service on the reverse proxy
On the reverse proxy, for traffic that goes from a mobile device to port 443 of iosmdm.mydom.global, you have to configure KCD on the SPN (http/iosmdm.mydom.local), using the certificate issued for the FQDN (iosmdm.mydom.global). Please note that publishing, and the published web service must share the same server certificate.
Receiving an APNs certificate
If you already have an APNs certificate, please consider renewing it instead of creating a new one. When you replace the existing APNs certificate with a newly created one, the Administration Server loses the ability to manage the currently connected iOS mobile devices.
When the Certificate Signing Request (CSR) is created at the first step of the APNs Certificate Wizard, its private key is stored in the RAM of your device. Therefore, all the steps of the wizard must be completed within a single session of the application.
To receive an APNs certificate:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder of the console tree, select the Mobile Device Servers subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Mobile Device Servers folder, select an iOS MDM Server.
- In the context menu of the iOS MDM Server, select Properties.
This opens the properties window of the iOS MDM Server.
- In the properties window of the iOS MDM Server, select the Certificates section.
- In the Certificates section, in the Apple Push Notification certificate group of settings, click the Request new button.
The Receive APNs Certificate Wizard starts and the Request new window opens.
- Create a Certificate Signing Request (hereinafter referred to as CSR). To do this, perform the following actions:
- Click the Create CSR button.
- In the Create CSR window that opens, specify a name for your request, the names of your company and department, your city, region, and country.
- Click the Save button and specify a name for the file to which your CSR will be saved.
The private key of the certificate is saved in the device memory.
- Use your CompanyAccount to send the file with the CSR you have created to Kaspersky to be signed.
Signing of your CSR will only be available after you upload to CompanyAccount portal a key that allows using Mobile Device Management.
After your online request is processed, you will receive a CSR file signed by Kaspersky.
- Send the signed CSR file to Apple Inc. website, using a random Apple ID.
We recommend that you avoid using a personal Apple ID. Create a dedicated Apple ID to make it your corporate ID. After you have created an Apple ID, link it with the organization's mailbox, not a mailbox of an employee.
After your CSR is processed in Apple Inc., you will receive the public key of the APNs certificate. Save the file on disk.
- Export the APNs certificate together with the private key created when generating the CSR, in PFX file format. To do this:
- In the Request new APNs certificate window, click the Complete CSR button.
- In the Open window, choose a file with the public key of the certificate received from Apple Inc. as the result of CSR processing, and then click the Open button.
The certificate export process starts.
- In the next window, enter the private key password and click OK.
This password will be used for the APNs certificate installation on the iOS MDM Server.
- In the Save APNs certificate window, specify a file name for APNs certificate, choose a folder, and click Save.
The private and public keys of the certificate are combined, and the APNs certificate is saved in PFX format. After this, you can install the APNs certificate on the iOS MDM Server.
Renewing an APNs certificate
To renew an APNs certificate:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder of the console tree, select the Mobile Device Servers subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Mobile Device Servers folder, select an iOS MDM Server.
- In the context menu of the iOS MDM Server, select Properties.
This opens the properties window of the iOS MDM Server.
- In the properties window of the iOS MDM Server, select the Certificates section.
- In the Certificates section, in the Apple Push Notification certificate group of settings click the Renew button.
The APNs Certificate Renewal Wizard starts, the Renew APNs certificate window opens.
- Create a Certificate Signing Request (hereinafter referred to as CSR). To do this, perform the following actions:
- Click the Create CSR button.
- In the Create CSR window that opens, specify a name for your request, the names of your company and department, your city, region, and country.
- Click the Save button and specify a name for the file to which your CSR will be saved.
The private key of the certificate is saved in the device memory.
- Use your CompanyAccount to send the file with the CSR you have created to Kaspersky to be signed.
Signing of your CSR will only be available after you upload to CompanyAccount portal a key that allows using Mobile Device Management.
After your online request is processed, you will receive a CSR file signed by Kaspersky.
- Send the signed CSR file to Apple Inc. website, using a random Apple ID.
We recommend that you avoid using a personal Apple ID. Create a dedicated Apple ID to make it your corporate ID. After you have created an Apple ID, link it with the organization's mailbox, not a mailbox of an employee.
After your CSR is processed in Apple Inc., you will receive the public key of the APNs certificate. Save the file on disk.
- Request the public key of the certificate. To do this, perform the following actions:
- Proceed to Apple Push Certificates portal. To log in to the portal, use the Apple Id received at the initial request of the certificate.
- In the list of certificates, select the certificate whose APSP name (in "APSP: <number>" format) matches the APSP name of the certificate used by iOS MDM Server and click the Renew button.
The APNs certificate is renewed.
- Save the certificate created on the portal.
- Export the APNs certificate together with the private key created when generating the CSR, in PFX file format. To do this, perform the following actions:
- In the Renew APNs certificate window, click the Complete CSR button.
- In the Open window, choose a file with the public key of the certificate, received from Apple Inc. as the result of CSR processing, and click the Open button.
The certificate export process will start.
- In the next window, enter the private key password and click OK.
This password will be used for the APNs certificate installation on the iOS MDM Server.
- In the Renew APNs certificate window that opens, specify a file name for APNs certificate, choose a folder, and click Save.
The private and public keys of the certificate are combined, and the APNs certificate is saved in PFX format.
Configuring a reserve iOS MDM Server certificate
The iOS MDM Server functionality enables you to issue a reserve certificate. This certificate is intended for use in iOS MDM profiles, to ensure seamless switching of managed iOS devices after the iOS MDM Server certificate expires.
If your iOS MDM Server uses a default certificate issued by Kaspersky, you can issue a reserve certificate (or specify your own custom certificate as reserve) before the iOS MDM Server certificate expires. By default, the reserve certificate is automatically issued 60 days before the iOS MDM Server certificate expiration. The reserve iOS MDM Server certificate becomes the main certificate immediately after the iOS MDM Server certificate expiration. The public key is distributed to all managed devices through configuration profiles, so you do not have to transmit it manually.
To issue an iOS MDM Server reserve certificate or specify a custom reserve certificate:
- In the console tree, in the Mobile Device Management folder, select the Mobile Device Servers subfolder.
- In the list of Mobile Device Servers, select the relevant iOS MDM Server, and on the right pane, click the Configure iOS MDM Server button.
- In the iOS MDM Server settings window that opens, select the Certificates section.
- In the Reserve certificate block of settings, do one of the following:
- If you plan to continue using a self-signed certificate (that is, the one issued by Kaspersky):
- Click the Issue button.
- In the Activation date window that opens, select one of the two options for the date when the reserve certificate must be applied:
- If you want to apply the reserve certificate at the time of expiration of the current certificate, select the When current certificate expires option.
- If you want to apply the reserve certificate before the current certificate expires, select the After specified period (days) option. In the entry field next to this option, specify the duration of the period after which the reserve certificate must replace the current certificate.
The validity period of the reserve certificate that you specify cannot exceed the validity term of the current iOS MDM Server certificate.
- Click the OK button.
The reserve iOS MDM Server certificate is issued.
- If you plan to use a custom certificate issued by your certification authority:
- Click the Add button.
- In the File Explorer window that opens, specify a certificate file in the PEM, PFX, or P12 format, which is stored on your device, and then click the Open button.
Your custom certificate is specified as the reserve iOS MDM Server certificate.
- If you plan to continue using a self-signed certificate (that is, the one issued by Kaspersky):
You have a reserve iOS MDM Server certificate specified. The details of the reserve certificate are displayed in the Reserve certificate block of settings (certificate name, issuer name, expiration date, and the date the reserve certificate must be applied, if any).
Installing an APNs certificate on an iOS MDM Server
After you receive the APNs certificate, you must install it on the iOS MDM Server.
To install the APNs certificate on the iOS MDM Server:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder of the console tree, select the Mobile Device Servers subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Mobile Device Servers folder, select an iOS MDM Server.
- In the context menu of the iOS MDM Server, select Properties.
This opens the properties window of the iOS MDM Server.
- In the properties window of the iOS MDM Server, select the Certificates section.
- In the Certificates section, in the Apple Push Notification certificate group of settings click the Install button.
- Select the PFX file that contains the APNs certificate.
- Enter the password of the private key specified when exporting the APNs certificate.
The APNs certificate will be installed on the iOS MDM Server. The certificate details will be displayed in the properties window of the iOS MDM Server, in the Certificates section.
Page top
Configuring access to Apple Push Notification service
To ensure a proper functioning of the iOS MDM web service and timely responses of mobile devices to the administrator's commands, you need to specify an Apple Push Notification Service certificate (hereinafter referred to as APNs certificate) in the iOS MDM Server settings.
Interacting with Apple Push Notification (hereinafter referred to as APNs), the iOS MDM web service connects to the external address api.push.apple.com through port 2197 (outbound). Therefore, the iOS MDM web service requires access to port TCP 2197 for the range of addresses 17.0.0.0/8. From the iOS device side is access to port TCP 5223 for the range of addresses 17.0.0.0/8.
If you intend to access APNs from the iOS MDM web service side through a proxy server, you must perform the following actions on the device with the iOS MDM web service installed:
- Add the following strings to the registry:
- For 32-bit operating systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\Components\34\Connectors\KLIOSMDM\1.0.0.0\Conset
"ApnProxyHost"="<Proxy Host Name>"
"ApnProxyPort"="<Proxy Port>"
"ApnProxyLogin"="<Proxy Login>"
"ApnProxyPwd"="<Proxy Password>"
- For 64-bit operating systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\34\Connectors\KLIOSMDM\1.0.0.0\Conset
"ApnProxyHost"="<Proxy Host Name>"
"ApnProxyPort"="<Proxy Port>"
"ApnProxyLogin"="<Proxy Login>"
"ApnProxyPwd"="<Proxy Password>"
- Restart the iOS MDM web service.
Issuing and installing a shared certificate on a mobile device
To issue a shared certificate to a user:
- In the console tree, in the User accounts folder, select a user account.
- In the context menu of the user account, select Install certificate.
The Certificate installation wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
When the wizard finishes, a certificate will be created and added to the list of the user's certificates.
The issued certificate will be downloaded by the user, along with the installation package that contains the iOS MDM profile.
After the mobile device is connected to the iOS MDM Server, the iOS MDM profile settings will be applied on the user's device. The administrator will be able to manage the device after connection.
The user's mobile device connected to the iOS MDM Server is displayed in the Mobile Devices subfolder within the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree.
Page top
Adding a KES device to the list of managed devices
To add the KES device of a user to the list of managed devices using a link to Google Play:
- In the console tree, select the User accounts folder.
By default, the User accounts folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder.
- Select the account of the user whose mobile device you want add to the list of managed devices.
- In the context menu of the user account, select Add mobile device.
The Mobile device connection wizard starts. In the Certificate source window of the wizard, you have to specify the method for creating the shared certificate that Administration Server will use to identify the mobile device. You can specify a shared certificate in one of the following ways:
- Create a shared certificate automatically, by means of Administration Server tools, and then deliver the certificate to the device.
- Specify a shared certificate file.
- In the Device type window of the wizard, select Link to Google Play.
- In the User notification method window of the wizard, define the settings for notification of the mobile device user of certificate creation (with an SMS message, by email, or by displaying the information when the wizard has finished).
- In the certificate info window of the wizard, click the Finish button to close the wizard.
After the wizard finishes its activities, a link and a QR code will be sent to the mobile device of the user, allowing the user to download Kaspersky Endpoint Security from Google Play. The user proceeds to Google Play by using the link or by scanning the QR code. After this, the operating system of the device prompts the user to accept Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android installation. After Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android is downloaded and installed, the mobile device connects to the Administration Server and downloads a shared certificate. After the certificate is installed on the mobile device, the device is displayed in the Mobile devices folder, which is a subfolder of the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree.
If Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android has already been installed on the device, the user has to receive the Administration Server connection settings from the administrator and then enter them independently. After the connection settings are defined, the mobile device connects to the Administration Server. The administrator issues a shared certificate for the device and sends the user an email message or an SMS message with a login and password for the certificate download. The user downloads and installs the shared certificate. After the certificate is installed on the mobile device, the device is displayed in the Mobile devices folder, which is a subfolder of the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree. In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android will not be downloaded and installed again.
Page top
Connecting KES devices to the Administration Server
Depending on the method used for connection of devices to the Administration Server, two deployment schemes are possible for Kaspersky Device Management for iOS for KES devices:
- Scheme of deployment with direct connection of devices to the Administration Server
- Scheme of deployment involving a reverse proxy that supports Kerberos constrained delegation
Direct connection of devices to the Administration Server
KES devices can connect directly to port 13292 of the Administration Server.
Depending on the method used for authentication, two options are possible for connection of KES devices to the Administration Server:
- Connecting devices with a user certificate
- Connecting devices without a user certificate
Connecting a device with a user certificate
When connecting a device with a user certificate, that device is associated with the user account to which the corresponding certificate has been assigned through Administration Server tools.
In this case, two-way SSL authentication (mutual authentication) will be used. Both the Administration Server and the device will be authenticated with certificates.
Connecting a device without a user certificate
When connecting a device without a user certificate, that device is associated with none of the user's accounts on the Administration Server. However, when the device receives any certificate, the device will be associated with the user to which the corresponding certificate has been assigned through Administration Server tools.
When connecting that device to the Administration Server, one-way SSL authentication will be applied, which means that only the Administration Server is authenticated with the certificate. After the device retrieves the user certificate, the type of authentication will change to two-way SSL authentication (2-way SSL authentication, mutual authentication).
Page top
Scheme for connecting KES devices to the Server involving Kerberos constrained delegation (KCD)
The scheme for connecting KES devices to the Administration Server involving Kerberos constrained delegation (KCD) provides for the following:
- Integration with a reverse proxy that supports KCD.
- Use of Kerberos Constrained Delegation (hereinafter referred to as KCD) for authentication of mobile devices.
- Integration with Public Key Infrastructure (hereinafter referred to as PKI) for applying user certificates.
When using this connection scheme, please note the following:
- The type of connection of KES devices to the reverse proxy must be "two-way SSL authentication", that is, a device must connect to the reverse proxy through its proprietary user certificate. To do this, you need to integrate the user certificate into the installation package of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android, which has been installed on the device. This KES package must be created by the Administration Server specifically for this device (user).
- You must specify the special (customized) certificate instead of the default server certificate for the mobile protocol:
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Settings section, select the Open port for mobile devices check box and select Add certificate in the drop-down list.
- In the window that opens, specify the same certificate that was set on the reverse proxy when the point of access to the mobile protocol was published on the Administration Server.
- User certificates for KES devices must be issued by the Certificate Authority (CA) of the domain. Keep in mind that if the domain includes multiple root CAs, user certificates must be issued by the CA, which has been set in the publication on the reverse proxy.
You can make sure the user certificate is in compliance with the above-described requirement, using one of the following methods:
- Specify the special user certificate in the New package wizard and in the Certificate installation wizard.
- Integrate the Administration Server with the domain's PKI and define the corresponding setting in the rules for issuance of certificates:
- In the console tree, expand the Mobile Device Management folder and select the Certificates subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Certificates folder, click the Configure certificate issuance rules button to open the Certificate issuance rules window.
- In the Integration with PKI section, configure integration with the Public Key Infrastructure.
- In the Issuance of mobile certificates section, specify the source of certificates.
Below is an example of setup of Kerberos Constrained Delegation (KCD) with the following assumptions:
- Point of access to the mobile protocol on the Administration Server is set up on port 13292.
- The name of the device with the reverse proxy is firewall.mydom.local.
- The name of the device with Administration Server is ksc.mydom.local.
- Name of the external publishing of the point of access to the mobile protocol is kes4mob.mydom.global.
Domain account for Administration Server
You must create a domain account (for example, KSCMobileSrvcUsr) under which the Administration Server service will run. You can specify an account for the Administration Server service when installing the Administration Server or through the klsrvswch utility. The klsrvswch utility is located in the installation folder of Administration Server. The default installation path: <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
A domain account must be specified by the following reasons:
- The feature for management of KES devices is an integral part of Administration Server.
- To ensure a proper functioning of Kerberos Constrained Delegation (KCD), the receive side (i.e., the Administration Server) must run under a domain account.
Service Principal Name for http/kes4mob.mydom.local
In the domain, under the KSCMobileSrvcUsr account, add an SPN for publishing the mobile protocol service on port 13292 of the device with Administration Server. For the kes4mob.mydom.local device with Administration Server, this will appear as follows:
setspn -a http/kes4mob.mydom.local:13292 mydom\KSCMobileSrvcUsr
Configuring the domain properties of the device with the reverse proxy (firewall.mydom.local)
To delegate traffic, you must trust the device with the reverse proxy (firewall.mydom.local) to the service defined by the SPN (http/kes4mob.mydom.local:13292).
To trust the device with the reverse proxy to the service defined by the SPN (http/kes4mob.mydom.local:13292), the administrator must perform the following actions:
- In the Microsoft Management Console snap-in named "Active Directory Users and Computers", select the device with the reverse proxy installed (firewall.mydom.local).
- In the device properties, on the Delegation tab, set the Trust this computer for delegation to specified service only toggle to Use any authentication protocol.
- In the Services to which this account can present delegated credentials list, add the SPN http/kes4mob.mydom.local:13292.
Special (customized) certificate for the publishing (kes4mob.mydom.global)
To publish the mobile protocol of Administration Server, you must issue a special (customized) certificate for the FQDN kes4mob.mydom.global and specify it instead of the default server certificate in the settings of the mobile protocol of Administration Server in Administration Console. To do this, in the properties window of the Administration Server, in the Settings section select the Open port for mobile devices check box and then select Add certificate in the drop-down list.
Please note that the server certificate container (file with the p12 or pfx extension) must also contain a chain of root certificates (public keys).
Configuring publication on the reverse proxy
On the reverse proxy, for traffic that goes from the mobile device side to port 13292 of kes4mob.mydom.global, you have to configure KCD on the SPN (http/kes4mob.mydom.local:13292), using the server certificate issued for the FQND kes4mob.mydom.global. Please note that publishing and the published access point (port 13292 of the Administration Server) must share the same server certificate.
Using Firebase Cloud Messaging
To ensure timely delivery of commands to KES devices managed by the Android operating system, Kaspersky Security Center uses the mechanism of push notifications. Push notifications are exchanged between KES devices and Administration Server through Firebase Cloud Messaging (hereinafter referred to as FCM). In Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console, you can specify the Firebase Cloud Messaging settings to connect KES devices to the service.
To retrieve the settings of Firebase Cloud Messaging, you must have a Google account.
To enable the use of FCM:
- In Administration Console, select the Mobile Device Management node, and the Mobile devices folder.
- In the context menu of the Mobile devices folder, select Properties.
- In the folder properties, select the Firebase Cloud Messaging settings section.
- In the Firebase project number field, specify the FCM Sender ID.
- In the Private key file (in JSON format) field, select the private key file.
At the next synchronization with Administration Server, KES devices managed by Android operating systems will be connected to Firebase Cloud Messaging.
You can edit the Firebase Cloud Messaging settings by clicking the Reset settings button.
When you switch to a different Firebase project, you need to wait 10 minutes for FCM to resume.
FCM service runs in the following address ranges:
- From the KES device's side, access is required to ports 443 (HTTPS), 5228 (HTTPS), 5229 (HTTPS), and 5230 (HTTPS) of the following addresses:
- google.com
- fcm.googleapis.com
- android.apis.google.com
- All of the IP addresses listed in Google's ASN of 15169
- From the Administration Server side, access is required to port 443 (HTTPS) of the following addresses:
- fcm.googleapis.com
- All of the IP addresses listed in Google's ASN of 15169
If the proxy server settings (Advanced / Configuring Internet access) have been specified in the Administration Server properties in Administration Console, they will be used for interaction with FCM.
Configuring FCM: getting the Sender ID and private key file
To configure FCM:
- Register on the Google portal.
- Go to the Firebase console.
- Do one of the following:
- To create a new project, click Create a project and follow the instructions on the screen.
- Open an existing project.
- Click the gear icon and choose Project settings.
The Project settings window opens.
- Select the Cloud Messaging tab.
- Retrieve the relevant Sender ID from the Sender ID field in the Firebase Cloud Messaging API (V1) section.
- Select the Service accounts tab and click Generate new private key.
- In the window that opens, click Generate key to generate and download a private key file.
Firebase Cloud Messaging is now configured.
Page top
Integration with Public Key Infrastructure
Integration with Public Key Infrastructure (hereinafter referred to as PKI) is primarily intended for simplifying the issuance of domain user certificates by Administration Server.
The administrator can assign a domain certificate for a user in Administration Console. This can be done using one of the following methods:
- Assign the user a special (customized) certificate from a file in the Certificate installation wizard.
- Perform integration with PKI and assign PKI to act as the source of certificates for a specific type of certificates or for all types of certificates.
The settings of integration with PKI are available in the workspace of the Mobile Device Management / Certificates folder by clicking the Integrate with public key infrastructure link.
General principle of integration with PKI for issuance of domain user certificates
In Administration Console, click the Integrate with public key infrastructure link in the workspace of the Mobile Device Management / Certificates folder to specify a domain account that will be used by Administration Server to issue domain user certificates through the domain's CA (hereinafter referred to as the account under which integration with PKI is performed).
Please note the following:
- The settings of integration with PKI provide you the possibility to specify the default template for all types of certificates. Note that the rules for issuance of certificates (available in the workspace of the Mobile Device Management / Certificates folder by clicking the Configure certificate issuance rules button) allow you to specify an individual template for every type of certificates.
- A special Enrollment Agent (EA) certificate must be installed on the device with Administration Server, in the certificates repository of the account under which integration with PKI is performed. The Enrollment Agent (EA) certificate is issued by the administrator of the domain's CA (Certificate Authority).
The account under which integration with PKI is performed must meet the following criteria:
- It is a domain user.
- It is a local administrator of the device with Administration Server from which integration with PKI is initiated.
- It has the right to Log On As Service.
- The device with Administration Server installed must be run at least once under this account to create a permanent user profile.
Kaspersky Security Center Web Server
Kaspersky Security Center Web Server (hereinafter referred to as Web Server) is a component of Kaspersky Security Center. Web Server is designed for publishing stand-alone installation packages, stand-alone installation packages for mobile devices, iOS MDM profiles, and files from the shared folder.
The iOS MDM profiles and installation packages that have been created are published on Web Server automatically and then removed after the first download. The administrator can send the new link to the user in any convenient way, such as by email.
By clicking the link, the user can download the required information to a mobile device.
Web Server settings
If a fine-tuning of Web Server is required, the properties of Administration Console Web Server provide the possibility to change ports for HTTP (8060) and HTTPS (8061). In addition to changing ports, you can replace the server certificate for HTTPS and change the FQDN of Web Server for HTTP.
Page top
Installation of Kaspersky Security Center
This section describes installation of Kaspersky Security Center components. If you want to install the application locally on only one device, two installation options are available:
- Standard. This option is recommended if you want to try out Kaspersky Security Center by, for example, testing its operation on a small area within your network. During standard installation, you only configure the database. You can also install only the default set of management plug-ins for Kaspersky applications. You can also use standard installation if you already have some experience working with Kaspersky Security Center and are able to specify all relevant settings after standard installation.
- Custom. This option is recommended if you plan to modify the Kaspersky Security Center settings, such as a path to the shared folder, accounts and ports for connection to the Administration Server, and database settings. Custom installation enables you to specify which Kaspersky management plug-ins to install. If necessary, you can start custom installation in silent mode.
If at least one Administration Server is installed on the network, Servers can be installed on other devices remotely through the remote installation task using forced installation. When creating the remote installation task, you should use the Administration Server installation package: ksc_<version_number>.<build number>_full_<localization language>.exe.
Use this package if you want to install all the components required for full functionality of Kaspersky Security Center, or to upgrade the current versions of these components.
If you want to deploy the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster, you need to install Kaspersky Security Center on all nodes of the cluster.
Preparing for installation
Perform the following actions before launching the installation.
- Check the hardware and software requirements
Make sure that the hardware and software on the device meet the requirements for Administration Server and Administration Console.
- Select and install the database management system (DBMS)
Kaspersky Security Center stores its information in a database that is managed by a DBMS. Install the DBMS on the network before Kaspersky Security Center (learn more about how to select a DBMS). If you decide to install PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro DBMS, specify a password for the superuser. If the password is not specified, Administration Server might not be able to connect to the database.
It is recommended that you install the Administration Server on a dedicated server instead of a domain controller. However, if you install Kaspersky Security Center on a server that acts as a read-only domain controller (RODC), Microsoft SQL Server (SQL Express) must not be installed locally (on the same device). In this case, we recommend that you install Microsoft SQL Server (SQL Express) remotely (on a different device), or that you use MySQL, MariaDB, or PostgreSQL if you need to install the DBMS locally.
- Prepare folders for Administration Server, Network Agent, and Administration Console
Administration Server, Network Agent, and Administration Console should be installed in folders where case sensitivity is disabled. Additionally, case sensitivity must be disabled for the Administration Server shared folder and the Kaspersky Security Center hidden folder (%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\KasperskyLab\adminkit).
- Remove the old Network Agent
The server version of Network Agent is installed on the device together with Administration Server. Administration Server cannot be installed together with the regular version of Network Agent. If the server version of Network Agent is already installed on your device, remove it and start installation of Administration Server again. For details about the server version of Network Agent, refer to Changes in the system after Kaspersky Security Center installation.
- Check accounts
Installation of Kaspersky Security Center requires administrator rights on the device on which the installation is performed.
Kaspersky Security Center supports managed service accounts and group managed service accounts. If these types of accounts are used in your domain, and you want to specify one of them as the account for the Administration Server service, then first install the account on the same device on which you want to install Administration Server. For details about installation of managed service accounts on a local device, refer to the official Microsoft documentation.
Accounts for work with the DBMS
To install Administration Server and work with it, you need a Windows account under which you will run the Administration Server installer (hereinafter also referred to as the installer), a Windows account under which you will start the Administration Server service, and an internal DBMS account to access the DBMS. You can create new accounts or use existing ones. All these accounts require specific rights. A set of the required accounts and their rights depends on the following criteria:
- DBMS type:
- Microsoft SQL Server (with Windows authentication or SQL Server authentication)
- MySQL or MariaDB
- PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro
- DBMS location:
- Local DBMS. A local DBMS is a DBMS installed on the same device as Administration Server.
- Remote DBMS. A remote DBMS is a DBMS installed on a different device.
- Method of the Administration Server database creation:
- Automatic. During the Administration Server installation, you can automatically create an Administration Server database (hereinafter also referred to as a Server database) by using the installer.
- Manual. You can use a third-party application (for example, SQL Server Management Studio) or a script to create an empty database. After that, you can specify this database as the Server database during the Administration Server installation.
Follow the principle of least privilege when you grant rights and permissions to the accounts. This means that the granted rights should be only enough to perform the required actions.
The tables below contain information about the system rights and DBMS rights that you should grant to the accounts before you install and start Administration Server.
Microsoft SQL Server with Windows authentication
If you choose SQL Server as a DBMS, you can use Windows authentication to access SQL Server. Configure system rights for a Windows account used to run the installer and a Windows account used to start the Administration Server service. On SQL Server, create logins for both of these Windows accounts. Depending on the creation method of the Server database, grant the required SQL Server rights to these accounts as described in the table below. For more information on how to configure rights of the accounts, see Configuring accounts for work with SQL Server (Windows authentication).
DBMS: Microsoft SQL Server (including Express Edition) with Windows authentication
|
Automatic database creation (by the installer) |
Manual database creation (by the Administrator) |
|---|---|---|
Account under which the installer is running |
|
|
Rights of the account under which the installer is running |
|
|
Administration Server service account |
|
|
Rights of the Administration Server service account |
|
|
Microsoft SQL Server with SQL Server authentication
If you choose SQL Server as a DBMS, you can use SQL Server authentication to access SQL Server. Configure system rights for a Windows account used to run the installer and for a Windows account used to start the Administration Server service. On SQL Server, create a login with a password to use it for authentication. Then, grant this SQL Server account the required rights listed in the table below. For more information on how to configure rights of the accounts, see Configuring accounts for work with SQL Server (SQL Server authentication).
DBMS: Microsoft SQL Server (including Express Edition) with SQL Server authentication
|
Automatic database creation (by the installer) |
Manual database creation (by the Administrator) |
|---|---|---|
Account under which the installer is running |
|
|
Rights of the account under which the installer is running |
System rights: local administrator rights. |
System rights: local administrator rights. |
Administration Server service account |
|
|
Rights of the Administration Server service account |
System rights: the required rights assigned by the installer. |
System rights: the required rights assigned by the installer. |
Rights of the login used for SQL Server authentication |
SQL Server rights required to create a database and install Administration Server:
SQL Server rights required to work with Administration Server:
|
SQL Server rights:
|
Configuring SQL Server rights for Administration Server data recovery
To restore Administration Server data from the backup, run the klbackup utility under the Windows account used to install Administration Server. Before you start the klbackup utility, on SQL Server, grant the rights to the SQL Server login associated with this Windows account. The SQL Server rights are different depending on the Administration Server version. For the Administration Server version 14.2 or later, you can grant the sysadmin server-level role or the dbcreator server-level role.
SQL Server rights for the Administration Server database recovery
Administration Server version 14.2 or later |
Other Administration Server versions |
|---|---|
|
|
Before you start the klbackup utility, specify the KLSRV_SKIP_ADJUSTING_DBMS_ACCESS server flag. Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center. After that, execute the following command in the command line:
|
|
MySQL and MariaDB
If you choose MySQL or MariaDB as a DBMS, create a DBMS internal account and grant this account the required rights listed in the table below. The installer and the Administration Server service use this internal DBMS account to access the DBMS. Note that the database creation method does not affect the set of required rights. For more information on how to configure the account rights, see Configuring accounts for work with MySQL and MariaDB.
DBMS: MySQL and MariaDB
|
Automatic or manual database creation |
Account under which the installer is running |
|
Rights of the account under which the installer is running |
System rights: local administrator rights. |
Administration Server service account |
|
Rights of the Administration Server service account |
System rights: The required rights assigned by the installer. |
Rights of the DBMS internal account |
Schema privileges:
Global privileges for all schemes: PROCESS, SUPER. |
Configuring privileges for Administration Server data recovery
Rights that you granted to the internal DBMS account are enough to restore Administration Server data from the backup. To start the restore, run the klbackup utility under the Windows account used to install Administration Server.
PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro
If you choose PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro as a DBMS, you can use the Postgres user (the default Postgres role) or create a new Postgres role (hereinafter also referred to as a role) to access the DBMS. Depending on the creation method of the Server database, grant the required rights to the role as described in the table below. For more information on how to configure rights of the role, see Configuring accounts for work with PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro.
DBMS: PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro
|
Automatic database creation |
Manual database creation |
|
Account under which the installer is running |
|
|
|
Rights of the account under which the installer is running |
System rights: local administrator rights. |
System rights: local administrator rights. |
|
Administration Server service account |
|
|
|
Rights of the Administration Server service account |
System rights: The required rights assigned by the installer. |
System rights: The required rights assigned by the installer. |
|
Rights of the Postgres role |
The Postgres user does not require additional rights. |
Privileges for a new role: |
For a new role:
|
Configuring privileges for Administration Server data recovery
To restore Administration Server data from the backup, run the klbackup utility under the Windows account used to install Administration Server. Note that the Postgres role used to access to the DBMS must have the owner rights on the Administration Server database.
Configuring accounts for work with SQL Server (Windows authentication)
Prerequisites
Before you assign rights to the accounts, perform the following actions:
- Make sure that you log in to the system under the local administrator account.
- Install an environment for working with SQL Server.
- Make sure that you have a Windows account under which you will install Administration Server.
- Make sure that you have a Windows account under which you will start the Administration Server service.
- On SQL Server, create a login for the Windows account used to run the Administration Server installer (hereinafter also referred to as the installer). Also, create a login for the Windows account used to start the Administration Server service.
If you use SQL Server Management Studio, on the General page of the login properties window, select the Windows Authentication option.
If you want to install Administration Server and SQL Server on devices that are located in separate Windows domains, note that these domains must have two-way trust relationships to ensure the correct operation of Administration Server, including running tasks and applying policies. For information about the required accounts for work with various DBMSs and accounts' rights, see Accounts for work with the DBMS.
Configuring the accounts to install Administration Server (automatic creation of the Administration Server database)
To configure the accounts for the Administration Server installation:
- On SQL Server, assign the sysadmin server-level role to the login of the Windows account used to run the installer.
- Log in to the system under the Windows account used to run the installer.
- Run the Administration Server installer.
The Administration Server Setup wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- Select the custom installation of Administration Server option.
- Select the Microsoft SQL Server as a DBMS that stores the Administration Server database.
- Select the Microsoft Windows Authentication mode to establish a connection between Administration Server and SQL Server through a Windows account.
- Specify the Windows account used to start the Administration Server service.
You can select the Windows user account for which you created an SQL Server login earlier. Alternatively, you can automatically create a new Windows account in the KL-AK-* format by using the installer. In this case, the installer automatically creates an SQL Server login for this account. Regardless of the account choice, the installer assigns the required system rights and SQL Server rights to the Administration Server service account.
After the installation finishes, the Server database is created, and all the required system rights and SQL Server rights are assigned to the Administration Server service account. Administration Server is ready to use.
Configuring the accounts to install Administration Server (manual creation of the Administration Server database)
To configure the accounts for the Administration Server installation:
- On SQL Server, create an empty database. This database will be used as an Administration Server database (hereinafter also referred to as a Server database).
- For both SQL Server logins created for the Windows accounts, specify the public server-level role, and then configure the mapping to the created database:
- Server-level role: public
- Database role membership: db_owner, public
- Default schema: dbo
- Log in to the system under the Windows account used to run the installer.
- Run the Administration Server installer.
The Administration Server Setup wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- Select the custom installation of Administration Server option.
- Select the Microsoft SQL Server as a DBMS that stores the Administration Server database.
- Specify the name of the created database as the Administration Server database name.
- Select the Microsoft Windows Authentication mode to establish a connection between Administration Server and SQL Server through a Windows account.
- Specify the Windows account used to start the Administration Server service.
You can select the Windows user account for which you created an SQL Server login and configured the login rights earlier.
We do not recommend that you automatically create a new Windows account in the KL-AK-* format. In this case, the installer creates a new Windows account for which you have not created and configured an SQL Server account. Administration Server cannot use this account to start the Administration Server service. If it is necessary to create a KL-AK-* Windows account, do not start Administration Console after the installation. Do the following, instead:
- Stop the kladminserver service.
- On SQL Server, create an SQL Server login for the created KL-AK-* Windows account.
- Grant the rights to this SQL Server login and configure the mapping to the created database:
- Server-level role: public
- Database role membership: db_owner, public
- Default schema: dbo
- Restart the kladminserver service, and then run the Administration console.
After the installation finishes, the Administration Server will use the created database to store the Server data. Administration Server is ready to use.
Page top
Configuring accounts for work with SQL Server (SQL Server authentication)
Prerequisites
Before you assign rights to the accounts, perform the following actions:
- Make sure that you log in to the system under the local administrator account.
- Install an environment for working with SQL Server.
- Make sure that you have a Windows account under which you will install Administration Server.
- Make sure that you have a Windows account under which you will start the Administration Server service.
- On SQL Server, enable the SQL Server authentication mode.
If you use SQL Server Management Studio, in the SQL Server Properties window, on the Security page, select the SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode option.
- On SQL Server, create a login with a password. The Administration Server installer (hereinafter also referred to as the installer) and the Administration Server service will use this SQL Server account to access SQL Server.
If you use SQL Server Management Studio, on the General page of the login properties window, select the SQL Server authentication option.
If you want to install Administration Server and SQL Server on devices that are located in separate Windows domains, note that these domains must have two-way trust relationships to ensure the correct operation of Administration Server, including running tasks and applying policies. For information about the required accounts for work with various DBMSs and accounts' rights, see Accounts for work with the DBMS.
Configuring the accounts to install Administration Server (automatic creation of the Administration Server database)
To configure the accounts for the Administration Server installation:
- On SQL Server, map the SQL Server account to the default master database. The master database is a template for the Administration Server database (hereinafter also referred to as a Server database). The master database is used for mapping until the installer creates a Server database. Grant the following rights and permissions to the SQL Server account:
- Server-level role: public
- Database role membership for the master database: db_owner
- Default schema for the master database: dbo
- Permissions:
- CONNECT ANY DATABASE
- CONNECT SQL
- CREATE ANY DATABASE
- VIEW ANY DATABASE
- Log in to the system under the Windows account used to run the installer.
- Run the installer.
The Administration Server Setup wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- Select the custom installation of Administration Server option.
- Select the Microsoft SQL Server as a DBMS that stores the Administration Server database.
- Specify the Administration Server database name.
- Select the SQL Server Authentication mode to establish a connection between Administration Server and SQL Server through the created SQL Server account. Then, specify the SQL Server account credentials.
- Specify the Windows account used to start the Administration Server service.
You can select an existing Windows user account or create a new Windows account in the KL-AK-* format by using the installer. Regardless of the account choice, the installer assigns the required system rights to the Administration Server service account.
After the installation finishes, the Server database is created and all the required system rights are assigned to the Administration Server service account. Administration Server is ready to use.
You can cancel the mapping to the master database, because the installer created a Server database and configured the mapping to this database during the Administration Server installation.
Since the automatic database creation requires more permissions than normal work with Administration Server, you can revoke some permissions. On SQL Server, select the SQL Server account, and then grant the following rights for work with Administration Server:
- Server-level role: public
- Database role membership for the Server database: db_owner
- Default schema for the Server database: dbo
- Permissions:
- CONNECT SQL
- VIEW ANY DATABASE
Configuring the accounts to install Administration Server (manual creation of the Administration Server database)
To configure the accounts for the Administration Server installation:
- On SQL Server, create an empty database. This database will be used as an Administration Server database.
- On SQL Server, grant the following rights and permissions to the SQL Server account:
- Server-level role: public.
- Database role membership for the created database: db_owner.
- Default schema for the created database: dbo.
- Permissions:
- CONNECT SQL
- VIEW ANY DATABASE
- Log in to the system under the Windows account used to run the installer.
- Run the installer.
The Administration Server Setup wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- Select the custom installation of Administration Server option.
- Select the Microsoft SQL Server as a DBMS that stores the Administration Server database.
- Specify the name of the created database as the Administration Server database name.
- Select the SQL Server Authentication mode to establish a connection between Administration Server and SQL Server through the created SQL Server account. Then, specify the SQL Server account credentials.
- Specify the Windows account used to start the Administration Server service.
You can select an existing Windows user account or create a new Windows account in the KL-AK-* format by using the installer. Regardless of the account choice, the installer assigns the required system rights to the Administration Server service account.
After the installation finishes, the Administration Server will use the created database to store the Administration Server data. All the required system rights are assigned to the Administration Server service account. Administration Server is ready to use.
Page top
Configuring accounts for work with MySQL and MariaDB
Prerequisites
Before you assign rights to the accounts, perform the following actions:
- Make sure that you log in to the system under the local administrator account.
- Install an environment for working with MySQL or MariaDB.
- Make sure that you have a Windows account under which you will install Administration Server.
- Make sure that you have a Windows account under which you will start the Administration Server service.
Configuring the accounts to install Administration Server
To configure the accounts for the Administration Server installation:
- Run an environment for working with MySQL or MariaDB under the root account that you created when you installed the DBMS.
- Create an internal DBMS account with a password. The Administration Server installer (hereinafter also referred to as the installer) and the Administration Server service will use this internal DBMS account to access DBMS. Grant the following privileges to this account:
- Schema privileges:
- Administration Server database: ALL (excluding
GRANT OPTION) - System schemes (mysql and sys):
SELECT,SHOW VIEW - The sys.table_exists stored procedure:
EXECUTE
- Administration Server database: ALL (excluding
- Global privileges for all schemes:
PROCESS,SUPER
To create an internal DBMS account and grant the required privileges to this account, run the script below (in this script, the DBMS login is KSCAdmin, and the Administration Server database name is kav):
/* Create a user named KSCAdmin */CREATE USER 'KSCAdmin'/* Specify a password for KSCAdmin */IDENTIFIED BY '<password>';If you use MySQL 8.0 or earlier as a DBMS, note that for these versions the "Caching SHA2 password" authentication is not supported. Change the default authentication from "Caching SHA2 password" to "MySQL native password":
- To create a DBMS account that uses the "MySQL native password" authentication, execute the following command:
CREATE USER 'KSCAdmin'@'%' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY '<password>'; - To change the authentication for an existing DBMS account, execute the following command:
ALTER USER 'KSCAdmin'@'%' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY '<password>';
/* Grant privileges to KSCAdmin */GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'KSCAdmin';GRANT ALL ON kav.* TO 'KSCAdmin';GRANT SELECT, SHOW VIEW ON mysql.* TO 'KSCAdmin';GRANT SELECT, SHOW VIEW ON sys.* TO 'KSCAdmin';GRANT EXECUTE ON PROCEDURE sys.table_exists TO 'KSCAdmin';GRANT PROCESS ON *.* TO 'KSCAdmin';GRANT SUPER ON *.* TO 'KSCAdmin';If you use MariaDB 10.5 or earlier as a DBMS, you do not need to grant the EXECUTE privilege. In this case, exclude the following command from the script:
GRANT EXECUTE ON PROCEDURE sys.table_exists TO 'KSCAdmin'. - Schema privileges:
- To view the list of privileges granted to the DBMS account, run the following script:
SHOW grants for 'KSCAdmin'; - To create an Administration Server database manually, run the following script (in this script, the Administration Server database name is kav):
CREATE DATABASE kavDEFAULT CHARACTER SET asciiDEFAULT COLLATE ascii_general_ci;Use the same database name that you specify in the script that creates the DBMS account.
- Log in to the system under the Windows account used to run the installer.
- Run the installer.
The Administration Server Setup wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- Select the custom installation of Administration Server option.
- Select the MySQL or MariaDB as a DBMS that stores the Administration Server database.
- Specify the Administration Server database name. Use the same database name that you specify in the script.
- Specify the credentials of the DBMS account that you created by the script.
- Specify the Windows account used to start the Administration Server service.
You can select an existing Windows user account or automatically create a new Windows account in the KL-AK-* format by using the installer. Regardless of the account choice, the installer assigns the required system rights to the Administration Server service account.
After the installation finishes, the Administration Server database is created and Administration Server is ready to use.
Configuring accounts for work with PostgreSQL and Postgres Pro
Prerequisites
Before you assign rights to the accounts, perform the following actions:
- Make sure that you log in to the system under the local administrator account.
- Install an environment for working with PostgreSQL and Postgres Pro.
- Make sure that you have a Windows account under which you will install Administration Server.
- Make sure that you have a Windows account under which you will start the Administration Server service.
Configuring the accounts to install Administration Server (automatic creation of the Administration Server database)
To configure the accounts for the Administration Server installation:
- Run an environment for working with PostgreSQL and Postgres Pro.
- Choose a Postgres role to access the DBMS. You can use one of the following roles:
- The Postgres user (the default Postgres role).
If you use the Postgres user, you do not need to grant additional rights to it.
- A new Postgres role.
If you want to use a new Postgres role, create this role, and then grant it the CREATEDB privilege. To do this, run the following script (in this script, the role is KSCAdmin):
CREATE USER "KSCAdmin" WITH PASSWORD '<password>' CREATEDB;The created role will be used as an owner of the Administration Server database (hereinafter also referred to as the Server database).
- The Postgres user (the default Postgres role).
- Log in to the system under the Windows account used to run the Administration Server installer (hereinafter also referred to as the installer).
- Run the installer.
The Administration Server Setup wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- Select the custom installation of Administration Server option.
- Select the PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro as a DBMS that stores the Administration Server database.
- Specify the Server database name. The installer will automatically create the Server database.
- Specify the credentials of the Postgres role.
- Specify the Windows account used to start the Administration Server service.
You can select an existing Windows user account or automatically create a new Windows account in the KL-AK-* format by using the installer. Regardless of the account choice, the installer assigns the required system rights to the Administration Server service account.
After the installation finishes, the Server database is automatically created and Administration Server is ready to use.
Configuring the accounts to install Administration Server (manual creation of the Administration Server database)
To configure the accounts for the Administration Server installation:
- Run an environment for working with Postgres.
- Create a new Postgres role and an Administration Server database. Then, grant all privileges to the role on the Administration Server database. To do this, log in under the Postgres user in the Postgres database, and then run the following script (in this script, the role is KSCAdmin, the Administration Server database name is KAV):
CREATE USER "KSCAdmin" WITH PASSWORD '<password>';CREATE DATABASE "KAV" ENCODING 'UTF8';GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE "KAV" TO "KSCAdmin"; - Grant the following privileges to the created Postgres role:
- Privileges on all tables in the public schema: ALL
- Privileges on all sequences in the public schema: ALL
To do this, log in under the Postgres user in the Server database, and then run the following script (in this script, the role is KSCAdmin):
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA "public" TO "KSCAdmin";GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ALL SEQUENCES IN SCHEMA "public" TO "KSCAdmin"; - Log in to the system under the Windows account used to run the installer.
- Run the Administration Server installer.
The Administration Server Setup wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- Select the custom installation of Administration Server option.
- Select the PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro as a DBMS that stores the Administration Server database.
- Specify the Server database name. Use the same database name that you specify in the script. Note that the database name is case-sensitive.
- Specify the credentials of the Postgres role.
- Specify the Windows account used to start the Administration Server service.
You can select an existing Windows user account or automatically create a new Windows account in the KL-AK-* format by using the installer. Regardless of the account choice, the installer assigns the required system rights to the Administration Server service account.
After the installation finishes, the Administration Server will use the created database to store the Administration Server data. Administration Server is ready to use.
Page top
Scenario: Authenticating Microsoft SQL Server
Information in this section is only applicable to configurations in which Kaspersky Security Center uses Microsoft SQL Server as a database management system.
To protect Kaspersky Security Center data transferred to or from the database and data stored in the database from unauthorized access, you must secure communication between Kaspersky Security Center and SQL Server. The most reliable way to provide secure communication is to install Kaspersky Security Center and SQL Server on the same device and use the shared memory mechanism for both applications. In all other cases, we recommend that you use a SSL or TLS certificate to authenticate the SQL Server instance. You can use a certificate from a trusted certification authority (CA) or a self-signed certificate. We recommend that you use a certificate from a trusted CA because a self-signed certificate provides only limited protection.
SQL Server authentication proceeds in stages:
- Generating a self-signed SSL or TLS certificate for SQL Server according to the certificate requirements
If you already have a certificate for SQL Server, skip this step.
An SSL certificate is only applicable to SQL Server versions earlier than 2016 (13.x). In SQL Server 2016 (13.x) and later versions, use a TLS certificate.
For example, to generate a TLS certificate, enter the following command in PowerShell:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName SQL_HOST_NAME -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine -KeySpec KeyExchangeIn the command, instead of SQL_HOST_NAME you must type the SQL Server host name if the host is included in the domain or type the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the host if the host is not included in the domain. The same name—host name or FQDN—must be specified as an SQL Server instance name in the Administration Server setup wizard.
- Adding the certificate on the SQL Server instance
The instructions for this stage depend on the platform on which SQL Server is running. Refer to the official documentation for details:
To use the certificate on a failover cluster, you must install the certificate on each node of the failover cluster. For details, refer to the Microsoft documentation.
- Assigning the service account permissions
Ensure that the service account under which the SQL Server service is run has the Full control permission to access private keys. For details, refer to the Microsoft documentation.
- Adding the certificate to the list of trusted certificates for Kaspersky Security Center
On the Administration Server device, add the certificate to the list of trusted certificates. For details, refer to the Microsoft documentation.
- Enabling encrypted connections between the SQL Server instance and Kaspersky Security Center
On the Administration Server device, set value
1to the environment variableKLDBADO_UseEncryption. For example, in Windows Server 2012 R2, you can change environment variables by clicking Environment Variables on the Advanced tab of the System Properties window. Add a new variable, name itKLDBADO_UseEncryption, and then set value1. - Additional configuration to use TLS 1.2 protocol
If you use the TLS 1.2 protocol, then additionally do the following:
- Ensure that the installed version of SQL Server is a 64-bit application.
- Install Microsoft OLE DB Driver on the Administration Server device. For details, refer to the Microsoft documentation.
- On the Administration Server device, set value
1to the environment variableKLDBADO_UseMSOLEDBSQL. For example, in Windows Server 2012 R2, you can change environment variables by clicking Environment Variables on the Advanced tab of the System Properties window. Add a new variable, name itKLDBADO_UseMSOLEDBSQL, and then set value1.If the OLE DB Driver version is 19 or newer, also set value
MSOLEDBSQL19to the environment variableKLDBADO_ProviderName.
- Enabling usage of TCP/IP protocol on a named instance of SQL Server
If you use a named instance of SQL Server, then additionally enable usage of TCP/IP protocol and assign a TCP/IP port number to the SQL Server Database Engine. When you configure SQL Server connection in the Administration Server setup wizard, specify the SQL Server host name and the port number in the SQL Server instance name field.
Scenario: Authenticating MySQL Server
We recommend that you use a TLS certificate to authenticate the MySQL server. You can use a certificate from a trusted certification authority (CA) or a self-signed certificate.
Administration Server supports both one-way and two-way SSL authentication for MySQL.
Enable one-way SSL authentication
Follow these steps to configure one-way SSL authentication for MySQL:
- Generate a self-signed TLS certificate for the MySQL server
In PowerShell, change directory to the folder where you want to store certificates. Execute the following commands:
$CertCA = New-SelfSignedCertificate ` -Subject "CN=CertCA" ` -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\CurrentUser\My" ` -HashAlgorithm "SHA256" ` -NotAfter (Get-Date).AddDays(365) $CertCABase64 = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String($CertCA.RawData, [System.Base64FormattingOptions]::InsertLineBreaks) $CertLeaf = New-SelfSignedCertificate ` -Subject "CN=CertLeaf" ` –Signer $CertCA ` -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\CurrentUser\My" ` -HashAlgorithm "SHA256" ` -KeyExportPolicy Exportable ` -NotAfter (Get-Date).AddDays(365) $CertLeafBase64 = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String($CertLeaf.RawData, [System.Base64FormattingOptions]::InsertLineBreaks) $CertLeafRSACng = [System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.RSACertificateExtensions]::GetRSAPrivateKey($CertLeaf) $CertLeafKeyBytes = $CertLeafRSACng.Key.Export([System.Security.Cryptography.CngKeyBlobFormat]::Pkcs8PrivateBlob) $CertLeafKeyBase64 = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String($CertLeafKeyBytes, [System.Base64FormattingOptions]::InsertLineBreaks) $CertCAPemCert = @" -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- $CertCABase64 -----END CERTIFICATE----- "@ $CertLeafPemKey = @" -----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- $CertLeafKeyBase64 -----END PRIVATE KEY----- "@ $CertLeafPemCert = @" -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- $CertLeafBase64 -----END CERTIFICATE----- "@ # Output to file $CertCAPemCert | Out-File -FilePath ca-cert.pem -Encoding Ascii $CertLeafPemKey | Out-File -FilePath server-key.pem -Encoding Ascii $CertLeafPemCert | Out-File -FilePath server-cert.pem -Encoding AsciiThese commands create certificates for the current user and export the certificates to the PEM format. You only need the exported PEM files to authenticate the server. To remove the created certificates from Windows, execute the following command in PowerShell:
certmgr.mscLocate the created certificates in the Personal → Certificates folder and delete them.
- Create a server flag file
Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
Use the klscflag utility to create the KLSRV_MYSQL_OPT_SSL_CA server flag and specify the path to the certificate as its value.
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_MYSQL_OPT_SSL_CA -v <path toca-cert.pem>-t s - Configure the database
Specify the certificates in the my.cnf file. Open the my.cnf file in a text editor and add the following lines into the [mysqld] section:
[mysqld]ssl-ca="...\mysqlcerts\ca-cert.pem"ssl-cert="...\mysqlcerts\server-cert.pem"ssl-key="...\mysqlcerts\server-key.pem"
Enable two-way SSL authentication
Follow these steps to configure two-way SSL authentication for MySQL:
- Create server flag files
Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
Use the klscflag utility to create the server flags and specify the path to the certificate files as their values:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_MYSQL_OPT_SSL_CA -v <path toca-cert.pem> -t sklscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_MYSQL_OPT_SSL_CERT -v <path toserver-cert.pem> -t sklscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_MYSQL_OPT_SSL_KEY -v <path toserver-key.pem> -t s - Specify the passphrase (optional)
If the server-key.pem requires a passphrase, create a KLSRV_MARIADB_OPT_TLS_PASPHRASE flag and specify the passphrase as its value:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_MARIADB_OPT_TLS_PASPHRASE -v <passphrase> -t s - Configure the database
Specify the certificates in the my.cnf file. Open the my.cnf file in a text editor and add the following lines into the [mysqld] section:
[mysqld]ssl-ca="...\ca-cert.pem"ssl-cert="...\server-cert.pem"ssl-key="...\server-key.pem"
Scenario: Authenticating PostgreSQL Server
We recommend that you use a TLS certificate to authenticate the PostgreSQL server. You can use a certificate from a trusted certification authority (CA) or a self-signed certificate. Use a certificate from a trusted CA because a self-signed certificate provides only limited protection.
Administration Server supports both one-way and two-way SSL authentication for PostgreSQL.
Follow these steps to configure SSL authentication for PostgreSQL:
- Generate a certificate for the PostgreSQL server.
In an OpenSSL-based cross-platform utility, execute the following commands:
openssl req -new -x509 -days 365 -nodes -text -out psql.crt -keyout psql.key -subj "/CN=psql"chmod og-rwx psql.key - Generate a certificate for the Administration Server.
Run the following commands. The CN value should match the name of the user that connects to PostgreSQL on behalf of the Administration Server. The username is set to postgres by default.
openssl req -new -x509 -days 365 -nodes -text -out postgres.crt -keyout postgres.key -subj "/CN=postgres"chmod og-rwx postgres.key - Configure client certificate authentication.
Modify pg_hba.conf as follows:
hostssl all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5Ensure that pg_hba.conf doesn't include a record that starts with
host. - Specify the PostgreSQL certificate.
- Restart the PostgreSQL daemon.
Run the following command:
systemctl restart postgresql-14.service - Specify the server flag for the Administration Server.
- Restart the Administration Server service.
Recommendations on Administration Server installation
This section contains recommendations on how to install Administration Server. This section also provides scenarios for using a shared folder on the Administration Server device in order to deploy Network Agent on client devices.
Creating accounts for the Administration Server services on a failover cluster
By default, the installer automatically creates non-privileged accounts for services of Administration Server. This behavior is the most convenient for Administration Server installation on an ordinary device.
However, installation of Administration Server on a failover cluster requires a different scenario:
- Create non-privileged domain accounts for services of Administration Server and make them members of a global domain security group named KLAdmins.
- In the Administration Server Installer, specify the domain accounts that have been created for the services.
Defining a shared folder
When installing Administration Server, you can specify the location of the shared folder. You can also specify the location of the shared folder after installation, in the Administration Server properties. By default, the shared folder will be created on the device with Administration Server (with read rights for the Everyone subgroup). However, in some cases (such as high load or a need for access from an isolated network), it is useful to locate the shared folder on a dedicated file resource.
The shared folder is used occasionally in Network Agent deployment.
Case sensitivity for the shared folder must be disabled.
Remote installation with Administration Server tools through Active Directory group policies
If the target devices are located within a Windows domain (no workgroups), initial deployment (installation of Network Agent and the security application on devices that are not yet managed) has to be performed through group policies of Active Directory. Deployment is performed by using the standard task for remote installation of Kaspersky Security Center. If the network is large-scale, it is useful to locate the shared folder on a dedicated file resource to reduce the load on the disk subsystem of the Administration Server device.
Page top
Remote installation through delivery of the UNC path to a stand-alone package
If the users of networked devices in the organization have local administrator rights, another method of initial deployment is to create a stand-alone Network Agent package (or even a "coupled" Network Agent package together with the security application). After you create a stand-alone package, send users a link to that package, which is stored in the shared folder. Installation starts when users click the link.
Page top
Updating from the Administration Server shared folder
In the Anti-Virus update task, you can configure updating from the shared folder of Administration Server. If the task has been assigned to a large number of devices, it is useful to locate the shared folder on a dedicated file resource.
Page top
Installing images of operating systems
Operating system images are always installed through the shared folder: devices read operating system images from the shared folder. If deployment of images is planned on a large number of corporate devices, it is useful to locate the shared folder on a dedicated file resource.
Specifying the address of the Administration Server
When installing Administration Server, you can specify the address of the Administration Server. This address will be used as the default address when creating installation packages of Network Agent.
As the Administration Server address, you can specify the following:
- NetBIOS name of the Administration Server, which is specified by default
- Fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the Administration Server if the Domain Name System (DNS) on the organization's network has been configured and is functioning properly
- External address if the Administration Server is installed in the demilitarized zone (DMZ)
After that, you will be able to change the address of the Administration Server by using Administration Console tools; the address will not change automatically in Network Agent installation packages that have been already created.
Standard installation
Standard installation is an Administration Server installation that uses the default paths for application files, installs the default set of plug-ins, and does not enable Mobile Device Management.
To install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server on a local device:
Run the ksc_<version number>.<build number>_full_<localization language>.exe executable file.
A window opens prompting you to select Kaspersky applications to install. In the application selection window, click the Install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server link to start the Administration Server setup wizard. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Step 1. Reviewing the License Agreement and Privacy Policy
At this step of the setup wizard, you must read the License Agreement, which is to be concluded between you and Kaspersky, as well as the Privacy Policy.
You may also be prompted to view the License Agreements and Privacy Policies for application management plug-ins that are available in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit.
Please carefully read the License Agreement and Privacy Policy. If you agree with all the terms of the License Agreement and the Privacy Policy, confirm that by selecting the appropriate check boxes.
Installation of the application on your device will continue after you select both check boxes.
If you do not accept the License Agreement or the Privacy Policy, cancel installation by clicking the Cancel button.
Page top
Step 2. Selecting an installation method
In the installation type selection window, select Standard.
Standard installation is recommended if you want to try out Kaspersky Security Center by, for example, testing its operation on a small area within your enterprise network. During standard installation, you only configure the database. You do not specify any Administration Server settings: their respective default values are used instead. Standard installation does not allow you to select management plug-ins to install; only the default set of plug-ins is installed. During standard installation, no installation packages for mobile devices are created. However, you can create them later in Administration Console.
Page top
Step 3. Installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
This step is displayed only if you are using a 64-bit operating system. Otherwise, this step is not displayed, because Kaspersky Security Center Web Console does not work with 32-bit operating systems.
By default, both Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and MMC-based Administration Console will be installed.
If you want to install only Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
- Select Install only this one.
- Choose Web-based console in the drop-down list.
Installation of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console starts automatically after completion of Administration Server installation.
If you want to install only the MMC-based Administration console:
- Select Install only this one.
- Choose MMC-based console in the drop-down list.
Step 4. Selecting network size
Specify the size of the network on which Kaspersky Security Center is to be installed. Depending on the number of devices on the network, the wizard configures the installation and appearance of the application interface so that they match.
The following table lists the application installation settings and interface appearance settings, which are adjusted based on various network sizes.
Dependence of installation settings on the network scale selected
Settings |
1—100 devices |
101—1000 devices |
1001—5000 devices |
More than 5000 devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Display with the node for secondary and virtual Administration Servers, and all settings related to the secondary and virtual Administration Servers in the console tree |
Not available |
Not available |
Available |
Available |
Display with the Security sections in the properties windows of the Administration Server and administration groups |
Not available |
Not available |
Available |
Available |
Random distribution of startup time for the update task on client devices |
Not available |
Over an interval of 5 minutes |
Over an interval of 10 minutes |
Over an interval of 10 minutes |
If you connect Administration Server to a MySQL 5.7 or SQL Express database server, it is not recommended using the application to manage more than 10,000 devices. For the MariaDB database management system, the maximum recommended number of managed devices is 20,000.
Page top
Step 5. Selecting a database
At this step of the wizard, select one of the following database management systems (DBMS) that will be used to store the Administration Server database:
- Microsoft SQL Server or SQL Server Express
- MySQL or MariaDB
- PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro
It is recommended to install the Administration Server on a dedicated server instead of a domain controller. However, if you install Kaspersky Security Center on a server that acts as a read-only domain controller (RODC), Microsoft SQL Server (SQL Express) must not be installed locally (on the same device). In this case, we recommend that you install Microsoft SQL Server (SQL Express) remotely (on a different device), or that you use MySQL, MariaDB, or PostgreSQL if you need to install the DBMS locally.
The Administration Server database structure is provided in the klakdb.chm file, which is located in the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder. This file is also available in an archive on the Kaspersky portal: klakdb.zip.
Step 6. Configuring the SQL Server
At this step of the wizard, specify the following connection settings, depending on the database management system (DBMS) that you have selected:
- If you selected Microsoft SQL Server or SQL Server Express in the previous step:
- In the SQL Server instance name field, specify the name of the SQL Server on the network. To view a list of all SQL Servers that are on the network, click the Browse button. This field is blank by default.
If you connect to the SQL Server through a custom port, then together with the SQL Server host name specify the port number separated with a comma, for example:
SQL_Server_host_name,1433
If you secure communication between the Administration Server and SQL Server by means of a certificate, specify in the SQL Server instance name field the same host name that was used at the certificate generating. If you use a named instance of SQL Server, then together with the SQL Server host name specify the port number separated with a comma, for example:
SQL_Server_name,1433
If you use several instances of SQL Server on the same host, then additionally specify the instance name separated with a backslash, for example:
SQL_Server_name\SQL_Server_instance_name,1433
If a SQL Server on the enterprise network has the Always On feature enabled, specify the name of the availability group listener in the SQL Server instance name field. Note that Administration Server supports only the synchronous-commit availability mode when the Always On feature is enabled.
- In the Database name field, specify the name of the DBMS that has been created to store Administration Server data. The default value is KAV.
If at this stage you want to install SQL Server on the device from which you are installing Kaspersky Security Center, you must stop installation and restart it after SQL Server is installed. The supported SQL Server versions are listed in the system requirements.
If you want to install SQL Server on a remote device, you do not have to interrupt the Kaspersky Security Center setup wizard. Install SQL Server and resume installation of Kaspersky Security Center.
- In the SQL Server instance name field, specify the name of the SQL Server on the network. To view a list of all SQL Servers that are on the network, click the Browse button. This field is blank by default.
- If you selected MySQL or MariaDB in the previous step:
- In the SQL Server instance name field, specify the name of the DBMS instance. By default, the name is the IP address of the device on which Kaspersky Security Center is to be installed.
- In the Port field, specify the port for Administration Server connection to the DBMS. The default port number is 3306.
- In the Database name field, specify the name of the DBMS that has been created to store Administration Server data. The default value is KAV.
- If you selected PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro in the previous step:
- In the PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro Server field, specify the name of the DBMS instance. By default, the name is the IP address of the device on which Kaspersky Security Center is to be installed.
- In the Port field, specify the port for the Administration Server connection to the DBMS. The default port number is 5432.
- In the Database name field, specify the name of the DBMS that has been created to store Administration Server data. The default value is KAV.
Step 7. Selecting an authentication mode
Determine the authentication mode that will be used when Administration Server connects to the database management system (DBMS).
Depending on the DBMS that is selected, you can choose from the following authentication modes:
- For SQL Express or Microsoft SQL Server select one of the following options:
- Microsoft Windows Authentication mode. Verification of rights uses the account used for starting Administration Server.
- SQL Server Authentication mode. If you select this option, the account specified in the window is used to verify access rights. Fill in the Account and Password fields.
To see the entered password, click and hold the Show button.
For both authentication modes, the application checks if the database is available. If the database is not available, an error message is displayed, and you have to provide correct credentials.
If the Administration Server database is stored on another device and the Administration Server account does not have access to the database server, you must use SQL Server authentication mode when installing or upgrading Administration Server. This may occur when the device that stores the database is outside the domain or when Administration Server is installed under a LocalSystem account.
- For MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, or Postgres Pro, specify the account and password.
Step 8. Unpacking and installing files on the hard drive
After the installation of Kaspersky Security Center components is configured, you can start installing files on the hard drive.
If installation requires additional programs, the setup wizard will notify you, on the Installing Prerequisites page, before installation of Kaspersky Security Center begins. The required programs are installed automatically after you click the Next button.
On the last page, you can select which console to start for work with Kaspersky Security Center:
- Start MMC-based Administration Console
- Start Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
This option is available only if you opted to install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console in one of the previous steps.
You can also click Finish to close the wizard without starting work with Kaspersky Security Center. You can start the work later at any time.
At the first startup of Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you can perform the initial setup of the application.
When the setup wizard finishes, the following application components are installed on the hard drive on which the operating system was installed:
- Administration Server (together with the server version of Network Agent)
- Microsoft Management Console-based Administration Console
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console (if you chose to install it)
- Application management plug-ins available in the distribution kit
Additionally, Microsoft Windows Installer 4.5 will be installed if it was not installed previously.
Page top
Custom installation
Custom installation is an Administration Server installation during which you are prompted to select components to install and specify the folder in which the application must be installed.
Using this type of installation, you can configure the database and Administration Server, as well as install components that are not included in standard installation or management plug-ins for various Kaspersky security applications. You can also enable Mobile Device Management.
To install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server on a local device:
Run the ksc_<version number>.<build number>_full_<localization language>.exe executable file.
A window opens prompting you to select Kaspersky applications to install. In the application selection window, click the Install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server link to start the Administration Server setup wizard. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Step 1. Reviewing the License Agreement and Privacy Policy
At this step of the setup wizard, you must read the License Agreement, which is to be concluded between you and Kaspersky, as well as the Privacy Policy.
You may also be prompted to view the License Agreements and Privacy Policies for application management plug-ins that are available in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit.
Please carefully read the License Agreement and Privacy Policy. If you agree with all the terms of the License Agreement and the Privacy Policy, confirm that by selecting the appropriate check boxes.
Installation of the application on your device will continue after you select both check boxes.
If you do not accept the License Agreement or the Privacy Policy, cancel installation by clicking the Cancel button.
Page top
Step 2. Selecting an installation method
In the installation type selection window, specify Custom.
Custom installation allows you to modify the Kaspersky Security Center settings, such as the path to the shared folder, accounts and ports for connection to the Administration Server, and database settings. Custom installation allows you to specify which Kaspersky management plug-ins to install. During custom installation, you can create installation packages for mobile devices by enabling the corresponding option.
Page top
Step 3. Selecting the components to be installed
Select the components of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server that you want to install:
- Mobile Device Management. Select this check box if you must create installation packages for mobile devices when the Kaspersky Security Center setup wizard is running. You can also create installation packages for mobile devices manually, after Administration Server installation, by using Administration Console tools.
- SNMP agent. This component receives statistical information for the Administration Server over the SNMP protocol. The component is available if the application is installed on a device with SNMP installed.
After Kaspersky Security Center is installed, the .mib files required for receiving statistics are located in the SNMP subfolder of the application installation folder.
Network Agent and Administration Console are not displayed in the component list. These components are installed automatically and you cannot cancel their installation.
At this step you must specify a folder for installation of Administration Server components. By default, the components are installed to <Disk>:\Program Files\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center. If no such folder exists, this folder is created automatically during installation. You can change the destination folder by using the Browse button.
Page top
Step 4. Installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
This step is displayed only if you are using a 64-bit operating system. Otherwise, this step is not displayed, because Kaspersky Security Center Web Console does not work with 32-bit operating systems.
By default, both Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and MMC-based Administration Console will be installed.
If you want to install only Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
- Select Install only this one.
- Choose Web-based console in the drop-down list.
Installation of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console starts automatically after completion of Administration Server installation.
If you want to install only the MMC-based Administration console:
- Select Install only this one.
- Choose MMC-based console in the drop-down list.
Step 5. Selecting network size
Specify the size of the network on which Kaspersky Security Center is to be installed. Depending on the number of devices on the network, the wizard configures the installation and appearance of the application interface so that they match.
The following table lists the application installation settings and interface appearance settings, which are adjusted based on various network sizes.
Dependence of installation settings on the network scale selected
Settings |
1—100 devices |
101—1000 devices |
1001—5000 devices |
More than 5000 devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Display with the node for secondary and virtual Administration Servers, and all settings related to the secondary and virtual Administration Servers in the console tree |
Not available |
Not available |
Available |
Available |
Display with the Security sections in the properties windows of the Administration Server and administration groups |
Not available |
Not available |
Available |
Available |
Random distribution of startup time for the update task on client devices |
Not available |
Over an interval of 5 minutes |
Over an interval of 10 minutes |
Over an interval of 10 minutes |
If you connect Administration Server to a MySQL 5.7 or SQL Express database server, it is not recommended using the application to manage more than 10,000 devices. For the MariaDB database management system, the maximum recommended number of managed devices is 20,000.
Page top
Step 6. Selecting a database
At this step of the wizard, select one of the following database management systems (DBMS) that will be used to store the Administration Server database:
- Microsoft SQL Server or SQL Server Express
- MySQL or MariaDB
- PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro
It is recommended to install the Administration Server on a dedicated server instead of a domain controller. However, if you install Kaspersky Security Center on a server that acts as a read-only domain controller (RODC), Microsoft SQL Server (SQL Express) must not be installed locally (on the same device). In this case, we recommend that you install Microsoft SQL Server (SQL Express) remotely (on a different device), or that you use MySQL, MariaDB, or PostgreSQL if you need to install the DBMS locally.
The Administration Server database structure is provided in the klakdb.chm file, which is located in the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder. This file is also available in an archive on the Kaspersky portal: klakdb.zip.
Page top
Step 7. Configuring the SQL Server
At this step of the wizard, specify the following connection settings, depending on the database management system (DBMS) that you have selected:
- If you selected Microsoft SQL Server or SQL Server Express in the previous step:
- In the SQL Server instance name field, specify the name of the SQL Server on the network. To view a list of all SQL Servers that are on the network, click the Browse button. This field is blank by default.
If you connect to the SQL Server through a custom port, then together with the SQL Server host name specify the port number separated with a comma, for example:
SQL_Server_host_name,1433
If you secure communication between the Administration Server and SQL Server by means of a certificate, specify in the SQL Server instance name field the same host name that was used at the certificate generating. If you use a named instance of SQL Server, then together with the SQL Server host name specify the port number separated with a comma, for example:
SQL_Server_name,1433
If you use several instances of SQL Server on the same host, then additionally specify the instance name separated with a backslash, for example:
SQL_Server_name\SQL_Server_instance_name,1433
If a SQL Server on the enterprise network has the Always On feature enabled, specify the name of the availability group listener in the SQL Server instance name field. Note that Administration Server supports only the synchronous-commit availability mode when the Always On feature is enabled.
- In the Database name field, specify the name of the DBMS that has been created to store Administration Server data. The default value is KAV.
If at this stage you want to install SQL Server on the device from which you are installing Kaspersky Security Center, you must stop installation and restart it after SQL Server is installed. The supported SQL Server versions are listed in the system requirements.
If you want to install SQL Server on a remote device, you do not have to interrupt the Kaspersky Security Center setup wizard. Install SQL Server and resume installation of Kaspersky Security Center.
- In the SQL Server instance name field, specify the name of the SQL Server on the network. To view a list of all SQL Servers that are on the network, click the Browse button. This field is blank by default.
- If you selected MySQL or MariaDB in the previous step:
- In the SQL Server instance name field, specify the name of the DBMS instance. By default, the name is the IP address of the device on which Kaspersky Security Center is to be installed.
- In the Port field, specify the port for Administration Server connection to the DBMS. The default port number is 3306.
- In the Database name field, specify the name of the DBMS that has been created to store Administration Server data. The default value is KAV.
- If you selected PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro in the previous step:
- In the PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro Server field, specify the name of the DBMS instance. By default, the name is the IP address of the device on which Kaspersky Security Center is to be installed.
- In the Port field, specify the port for the Administration Server connection to the DBMS. The default port number is 5432.
- In the Database name field, specify the name of the DBMS that has been created to store Administration Server data. The default value is KAV.
Step 8. Selecting an authentication mode
Determine the authentication mode that will be used when Administration Server connects to the database management system (DBMS).
Depending on the DBMS that is selected, you can choose from the following authentication modes:
- For SQL Express or Microsoft SQL Server select one of the following options:
- Microsoft Windows Authentication mode. Verification of rights uses the account used for starting Administration Server.
- SQL Server Authentication mode. If you select this option, the account specified in the window is used to verify access rights. Fill in the Account and Password fields.
To see the entered password, click and hold the Show button.
For both authentication modes, the application checks if the database is available. If the database is not available, an error message is displayed, and you have to provide correct credentials.
If the Administration Server database is stored on another device and the Administration Server account does not have access to the database server, you must use SQL Server authentication mode when installing or upgrading Administration Server. This may occur when the device that stores the database is outside the domain or when Administration Server is installed under a LocalSystem account.
- For MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, or Postgres Pro, specify the account and password.
Step 9. Selecting the account to start Administration Server
Select the account that will be used to start Administration Server as a service.
- Generate the account automatically. The application creates an account named KL-AK-*, under which the kladminserver service will run.
You can select this option if you plan to locate the shared folder and the DBMS on the same device as Administration Server.
- Select an account. The Administration Server service (kladminserver) will run under the account that you selected.
You will have to select a domain account if, for example, you plan to use as the DBMS a SQL Server instance of any version, including SQL Express, that is located on another device, and/or you plan to locate the shared folder on another device.
Kaspersky Security Center supports managed service accounts (MSA) and group managed service accounts (gMSA). If these types of accounts are used in your domain, you can select one of them as the account for the Administration Server service.
Before specifying MSA or gMSA, you must install the account on the same device on which you want to install Administration Server. If the account is not installed yet, then cancel the Administration Server installation, install the account, and then restart the Administration Server installation. For details about installation of managed service accounts on a local device, refer to the official Microsoft documentation.
To specify MSA or gMSA:
- Click the Browse button.
- In the window that opens, click the Object type button.
- Select the Account for services type and click OK.
- Select the relevant account and click OK.
The account that you selected must have different permissions, depending on the DBMS that you plan for use.
For security reasons, please do not assign the privileged status to the account under which you run Administration Server.
The Administration Server account cannot be changed later. You need to reinstall the failover cluster to use another Administration Server account.
Step 10. Selecting the account for running the Kaspersky Security Center services
Select the account under which the services of Kaspersky Security Center will run on this device:
- Generate the account automatically. Kaspersky Security Center creates a local account named KlScSvc on this device in the kladmins group. The services of Kaspersky Security Center will be run under the account that has been created.
- Select an account. The Kaspersky Security Center services will be run under the account that you selected.
You will have to select a domain account if, for example, you intend to save reports to a folder located on a different device or if this is required by your organization's security policy. You may also have to select a domain account if you install Administration Server on a failover cluster.
For security reasons, do not grant privileged status to the account under which the services are run.
The KSN proxy service (ksnproxy), Kaspersky activation proxy service (klactprx), and Kaspersky authentication portal service (klwebsrv) will be run under the selected account.
Step 11. Selecting a shared folder
Define the location and name of the shared folder that will be used to do the following:
- Store the files necessary for remote installation of applications (these files are copied to Administration Server during creation of installation packages).
- Store updates that have been downloaded from an update source to Administration Server.
File sharing (read-only) will be enabled for all users.
You can select either of the following options:
- Create a shared folder. Create a new folder. In the text box, specify the path to the folder.
- Select an existing shared folder. Select a shared folder that already exists.
The shared folder can be a local folder on the device that is used for installation or a remote directory on any client device on the corporate network. You can click the Browse button to select the shared folder, or specify the shared folder manually by entering its UNC path (for example, \\server\Share) in the corresponding field.
By default, the installer creates a local Share subfolder in the application folder that contains the components of Kaspersky Security Center.
You can define a shared folder later if needed.
Page top
Step 12. Configuring the connection to Administration Server
Configure the connection to Administration Server:
You can also change the parameters for connecting to Administration Server later as follows:
- You can change port and SSL port numbers in the Connection ports section of the Administration Server properties. For more information about Administration Server connection ports, see Ports used by Kaspersky Security Center.
- You can change the encryption key length when replacing the Administration Server certificate with the klsetsrvcert utility by using the
-o RsaKeyLen:<key length>parameter.
Step 13. Defining the Administration Server address
Specify the Administration Server address in one of the following ways:
- DNS domain name. You can use this method if the network includes a DNS server and client devices can use it to receive the Administration Server address.
- NetBIOS name. You can use this method if client devices receive the Administration Server address using the NetBIOS protocol or if a WINS server is available on the network.
- IP address. You can use this method if Administration Server has a static IP address that will not be subsequently changed.
If you install Kaspersky Security Center on the active node of the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster, and you have created a secondary network adapter when preparing the cluster nodes, specify the IP address of this adapter. Otherwise, enter the IP address of the third-party load balancer that you use.
Page top
Step 14. Administration Server address for connection of mobile devices
This setup wizard step is available if you have selected Mobile Device Management for installation.
In the Address for connection of mobile devices window, specify the external address of the Administration Server for connection of mobile devices that are outside of the local network. You can specify the IP address or Domain Name System (DNS) of the Administration Server.
Page top
Step 15. Selecting application management plug-ins
Select the application management plug-ins that need to be installed with Kaspersky Security Center.
For ease of search, plug-ins are divided into groups depending on the type of secured objects.
Page top
Step 16. Unpacking and installing files on the hard drive
After the installation of Kaspersky Security Center components is configured, you can start installing files on the hard drive.
If installation requires additional programs, the setup wizard will notify you, on the Installing Prerequisites page, before installation of Kaspersky Security Center begins. The required programs are installed automatically after you click the Next button.
On the last page, you can select which console to start for work with Kaspersky Security Center:
- Start MMC-based Administration Console
- Start Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
This option is available only if you opted to install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console in one of the previous steps.
You can also click Finish to close the wizard without starting work with Kaspersky Security Center. You can start the work later at any time.
At the first startup of Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you can perform the initial setup of the application.
Page top
Deployment of the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
This section contains both general information about the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster, and instructions on the preparation and deployment of the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster in your network.
Scenario: Deployment of a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
A Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster provides high availability of Kaspersky Security Center and minimizes downtime of Administration Server in case of a failure. The failover cluster is based on two identical instances of Kaspersky Security Center installed on two computers. One of the instances works as an active node and the other one is a passive node. The active node manages protection of the client devices, while the passive one is prepared to take all of the functions of the active node in case the active node fails. When a failure occurs, the passive node becomes active and the active node becomes passive.
Prerequisites
You have hardware that meets the requirements for the failover cluster.
Stages
Kaspersky applications deployment proceeds in stages:
- Creating an account for Kaspersky Security Center services
Create a new domain group (in this scenario the name 'KLAdmins' is used for this group), and then grant the local administrator's permissions to the group on both nodes and on the file server. Then create two new domain user accounts, (in this scenario the names 'ksc' and 'rightless' are used for these accounts), and add the accounts to the KLAdmins domain group.
Add the user account, under which Kaspersky Security Center will be installed, to the previously created KLAdmins domain group.
- File server preparation
Prepare the file server to work as a component of the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster. Make sure that the file server meets the hardware and software requirements, create two shared folders for Kaspersky Security Center data, and configure permissions to access the shared folders.
How-to instructions: Preparing a file server for the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
- Preparation of active and passive nodes
Prepare two devices with identical hardware and software to work as the active and passive nodes.
How-to instructions: Preparing nodes for the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
- Database Management System (DBMS) installation
Select any of the supported DBMS, and then install the DBMS on a dedicated device. For information about how to install the DBMS refer to its documentation.
- Kaspersky Security Center installation
Install Kaspersky Security Center in the failover cluster mode on both nodes. You must first install Kaspersky Security Center on the active node, and then install it on the passive one.
Additionally, you can install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console on a separate device that is not a cluster node.
How-to instructions: Installing Kaspersky Security Center on the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster nodes
- Testing the failover cluster
Check that you configured the failover cluster correctly and that it works properly. For example, you can stop one of the Kaspersky Security Center services on the active node: kladminserver, klnagent, ksnproxy, klactprx, or klwebsrv. After the service is stopped, the protection management must be automatically switched to the passive node.
Results
The Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster is deployed. Please familiarize yourself with the events that lead to the switch between the active and passive nodes.
About the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
A Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster provides high availability of Kaspersky Security Center and minimizes downtime of Administration Server in case of a failure. The failover cluster is based on two identical instances of Kaspersky Security Center installed on two computers. One of the instances works as an active node and the other one is a passive node. The active node manages protection of the client devices, while the passive one is prepared to take all of the functions of the active node in case the active node fails. When a failure occurs, the passive node becomes active and the active node becomes passive.
Hardware and software requirements
To deploy a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster, you must have the following hardware:
- Two devices with identical hardware and software. These devices will act as the active and passive nodes.
- A file server that supports the CIFS/SMB protocol, version 2.0 or later. You must provide a dedicated device that will act as a file server.
Make sure you have provided high network bandwidth between the file server, and the active and passive nodes.
- A device with Database Management System (DBMS).
Deployment schemes
You can choose one of the following schemes to deploy Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster:
- A scheme that uses a secondary network adapter.
- A scheme that uses a third-party load balancer.
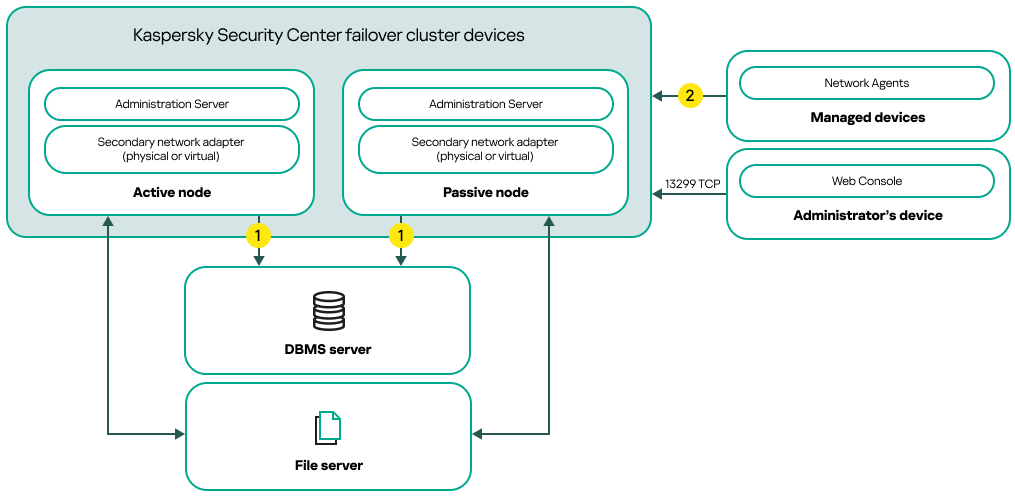
A scheme that uses a secondary network adapter
Scheme legend:
![]() Administration Server sends data to the database. Open the necessary ports on the device where the database is located, for example, port 3306 for MySQL Server, or port 1433 for Microsoft SQL Server. Please refer to the DBMS documentation for the relevant information.
Administration Server sends data to the database. Open the necessary ports on the device where the database is located, for example, port 3306 for MySQL Server, or port 1433 for Microsoft SQL Server. Please refer to the DBMS documentation for the relevant information.
![]() On the managed devices, open the following ports: TCP 13000, UDP 13000, and TCP 17000.
On the managed devices, open the following ports: TCP 13000, UDP 13000, and TCP 17000.
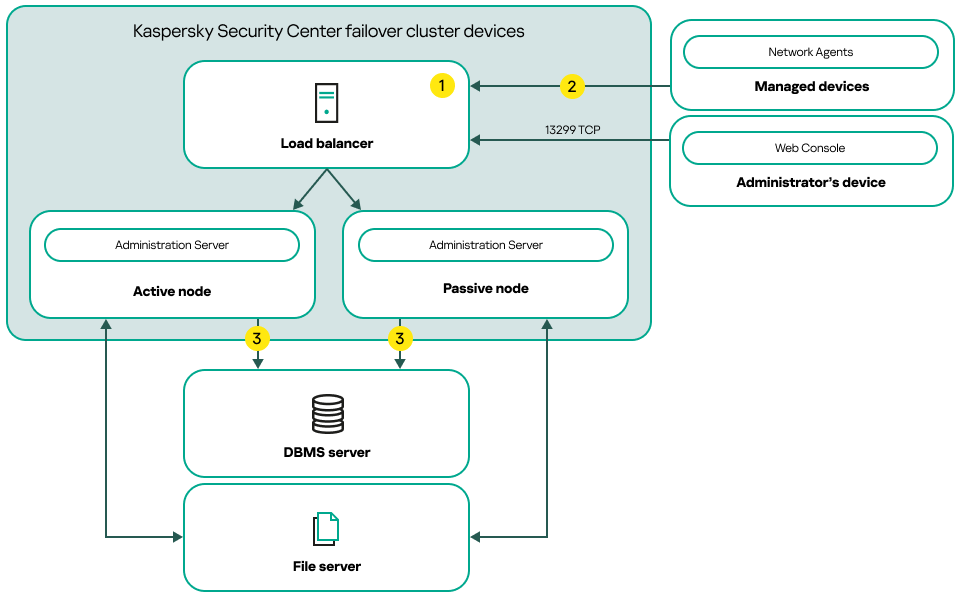
A scheme that uses a third-party load balancer
Scheme legend:
![]() On the load balancer device, open all of the Administration Server ports: TCP 13000, UDP 13000, TCP 13291, TCP 13299, and TCP 17000.
On the load balancer device, open all of the Administration Server ports: TCP 13000, UDP 13000, TCP 13291, TCP 13299, and TCP 17000.
![]() On the managed devices, open the following ports: TCP 13000, UDP 13000, and TCP 17000.
On the managed devices, open the following ports: TCP 13000, UDP 13000, and TCP 17000.
![]() Administration Server sends data to the database. Open the necessary ports on the device where the database is located, for example, port 3306 for MySQL Server, or port 1433 for Microsoft SQL Server. Please refer to the DBMS documentation for the relevant information.
Administration Server sends data to the database. Open the necessary ports on the device where the database is located, for example, port 3306 for MySQL Server, or port 1433 for Microsoft SQL Server. Please refer to the DBMS documentation for the relevant information.
Switch conditions
The failover cluster switches protection management of the client devices from the active node to the passive node if any of the following events occurs on the active node:
- The active node is broken due to a software or hardware failure.
- The active node was temporarily stopped for maintenance activities.
- At least one of the Kaspersky Security Center services (or processes) failed or was deliberately terminated by user. The Kaspersky Security Center services are the following ones: kladminserver, klnagent, klactprx, and klwebsrv.
- The network connection between the active node and the storage on the file server was interrupted or terminated.
Preparing a file server for a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
A file server works as a required component of a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster.
To prepare a file server:
- Make sure that the file server meets the hardware and software requirements.
- Make sure that the file server and both nodes (active and passive) are included in the same domain or the file server is the domain controller.
- On the file server, create two shared folders. One of them is used to keep information about the failover cluster state. The other one is used to store the data and settings of Kaspersky Security Center. You will specify paths to the shared folders while configuring the installation of Kaspersky Security Center.
- Grant full access permissions (both share permissions and NTFS permissions) to the created shared folders for the following user accounts and groups:
- Domain group KLAdmins.
- User accounts $<node1> and $<node2>. Here, <node1> and <node2> are the device names of the active and passive nodes.
The file server is prepared. To deploy the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster, follow the further instructions in this scenario.
Preparing nodes for a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
Prepare two devices to work as active and passive nodes for a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster.
To prepare nodes for a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster:
- Make sure that you have two devices that meet the hardware and software requirements. These devices will act as the active and passive nodes of the failover cluster.
- Make sure that the file server and both nodes are included in the same domain.
- Do one of the following:
- On each of the nodes, configure a secondary network adapter.
A secondary network adapter can be physical or virtual. If you want to use a physical network adapter, connect and configure it with standard operating system tools. If you want to use a virtual network adapter, create it by using third-party software.
Ensure that the following conditions are met:
- The secondary network adapters are disabled.
You can create the secondary network adapters in the disabled state or disable them after creation.
- The secondary network adapters on both nodes have the same IP address.
- The secondary network adapters are disabled.
- Use a third-party load balancer. For example, you can use an nginx server. In this case, do the following:
- Provide a dedicated Linux-based device with nginx installed.
- Configure load balancing. Set the active node as the main server and the passive node as the backup server.
- On the nginx server, open all of the Administration Server ports: TCP 13000, UDP 13000, TCP 13291, TCP 13299, and TCP 17000.
- On each of the nodes, configure a secondary network adapter.
- Restart both nodes and the file server.
- Map the two shared folders, that you created during the file server preparation step, to each of the nodes. You must map the shared folders as network drives. When mapping the folders, you can select any vacant drive letters. To access the shared folders, use the credentials of the user account that you created during step 1 of the scenario.
The nodes are prepared. To deploy the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster, follow the further instructions of the scenario.
Installing Kaspersky Security Center on the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster nodes
Kaspersky Security Center is installed on both nodes of the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster separately. First, you install the application on the active node, then on the passive one. When installing, you choose which node will be active and which will be passive.
Only a user from the KLAdmins domain group can install Kaspersky Security Center on every node.
To install Kaspersky Security Center on the active node of the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster:
- Run the ksc_15.1_<build number>_full_<language>.exe executable file.
A window opens and prompts you to select the Kaspersky applications to install. In the application selection window, click the Install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server link to start the Administration Server setup wizard. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- Please carefully read the License Agreement and Privacy Policy. If you agree with all the terms of the License Agreement and the Privacy Policy, select the following check boxes in the I confirm I have fully read, understood, and accept the following section:
- The terms and conditions of this EULA
- Privacy Policy describing the handling of data
Installation of the application on your device will continue after you select both check boxes.
If you do not accept the License Agreement or the Privacy Policy, cancel installation by clicking the Cancel button.
- Select Primary node of the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster to install the application on the active node.
- In the Shared folder window, do the following:
- In the State share and Data share fields, specify the paths to the shared folders that you created on the file server during its preparation.
- In the State share drive and Data share drive fields, select the network drives to which you mapped the shared folders during preparation of the nodes.
- Select the cluster connectivity mode: via a secondary network adapter or a third-party load balancer.
- Perform other steps of custom installation, starting with step 3.
In step 13, specify the IP address of a secondary network adapter if you have created an adapter when preparing the cluster nodes. Otherwise, enter the IP address of the third-party load balancer that you use.
Kaspersky Security Center is installed on the active node.
To install Kaspersky Security Center on the passive node of the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster:
- Run the ksc_15.1_<build number>_full_<language>.exe executable file.
A window opens and prompts you to select the Kaspersky applications to install. In the application selection window, click the Install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server link to start the Administration Server setup wizard. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- Please carefully read the License Agreement and Privacy Policy. If you agree with all the terms of the License Agreement and the Privacy Policy, select the following check boxes in the I confirm I have fully read, understood, and accept the following section:
- The terms and conditions of this EULA
- Privacy Policy describing the handling of data
Installation of the application on your device will continue after you select both check boxes.
If you do not accept the License Agreement or the Privacy Policy, cancel installation by clicking the Cancel button.
- Select Secondary node of the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster to install the application on the passive node.
- In the Shared folder window, in the State share field, specify a path to the shared folder with information about the cluster state that you created on the file server during its preparation.
- Click the Install button. When installation is over, click the Finish button.
Kaspersky Security Center is installed on the passive node. Now, you can test the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster to make sure that you configured it correctly and that the cluster works properly.
Starting and stopping cluster nodes manually
You may need to stop the entire Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster or temporarily detach one of the nodes of the cluster for maintenance. If this is the case, follow the instructions in this section. Do not try to start or stop the services or processes related to the failover cluster by using any other means. This may cause data loss.
Starting and stopping the entire failover cluster for maintenance
To start or stop the entire failover cluster:
- On the active node, go to <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
- Open the command line, and then run one of the following commands:
- To stop the cluster, run:
klfoc -stopcluster --stp klfoc - To start the cluster, run:
klfoc -startcluster --stp klfoc
- To stop the cluster, run:
The failover cluster is started or stopped, depending on the command that you run.
Maintaining one of the nodes
To maintain one of the nodes:
- On the active node, stop the failover cluster by using the
klfoc -stopcluster --stp klfoccommand. - On the node that you want to maintain, go to <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
- Open command line, and then detach the node from the cluster by running the
detach_node.cmdcommand. - On the active node, start the failover cluster by using the
klfoc -startcluster --stp klfoccommand. - Perform maintenance activities.
- On the active node, stop the failover cluster by using the
klfoc -stopcluster --stp klfoccommand. - On the node that was maintained, go to <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
- Open command line, and then attach the node to the cluster by running the
attach_node.cmdcommand. - On the active node, start the failover cluster by using the
klfoc -startcluster --stp klfoccommand.
The node is maintained and attached to the failover cluster.
Installing Administration Server on a Windows Server failover cluster
The procedure of installing Administration Server on a failover cluster differs from both standard and custom installation on a stand-alone device.
Perform the procedure described in this section on the node that contains a common data storage of the cluster.
To install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server on a cluster:
Run the ksc_<version number>.<build number>_full_<localization language>.exe executable file.
A window opens prompting you to select Kaspersky applications to install. In the application selection window, click the Install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server link to start the Administration Server setup wizard. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Step 1. Reviewing the License Agreement and Privacy Policy
At this step of the setup wizard, you must read the License Agreement, which is to be concluded between you and Kaspersky, as well as the Privacy Policy.
You may also be prompted to view the License Agreements and Privacy Policies for application management plug-ins that are available in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit.
Please carefully read the License Agreement and Privacy Policy. If you agree with all the terms of the License Agreement and the Privacy Policy, confirm that by selecting the appropriate check boxes.
Installation of the application on your device will continue after you select both check boxes.
If you do not accept the License Agreement or the Privacy Policy, cancel installation by clicking the Cancel button.
Page top
Step 2. Selecting the type of installation on a cluster
Select the type of installation on the cluster:
- Cluster (install on all cluster nodes)
This is the recommended option. If you select this option, Administration Server will be installed on all nodes of the cluster simultaneously.
At the step of selecting the Administration Console for installation, you will need to select the console that will be installed on the current cluster node. If you install a console only on the cluster node, in case of node failure, you will lose access to Administration Server. We recommend that during this step, you select the MMC-based Administration Console for installation on all cluster nodes. After you install Administration Server, install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console on a separate device that is not a cluster node. This allows you to manage Administration Server by using Kaspersky Security Center Web Console if the cluster node fails.
- Locally (install on this device only)
If you select this option, Administration Server will be installed only on the current node, as if on a stand-alone server, and Administration Server will not work as a cluster-aware application. For example, you may want to choose this option to save shared storage space if fault tolerance is not needed for Administration Server. In case of the current node failure, you will have to install Administration Server on another node and restore the Administration Server state from a backup.
Further steps are the same as when you use the standard or custom installation method, starting from the installation method selection step.
Page top
Step 3. Specifying the name of the virtual Administration Server
Specify the network name of the new virtual Administration Server. You will be able to use this name to connect Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to Administration Server.
The name that you specify must differ from the cluster name.
Page top
Step 4. Specifying the network details of the virtual Administration Server
To specify the network details of the new virtual Administration Server instance:
- In Network to use, select the domain network to which the current cluster node is connected.
- Do either of the following:
- If DHCP is used in the selected network to assign IP addresses, select the Use DHCP option.
- If DHCP is not used in the selected network, specify the required IP address.
The IP address that you specify must differ from the cluster IP address.
- Click Add to apply the specified settings.
You will be able to use the automatically assigned or the specified IP address to connect Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to Administration Server.
Page top
Step 5. Specifying a cluster group
A cluster group is a special failover cluster role that contains common resources for all nodes. You have two options:
- Creating a new cluster group.
This option is recommended in most cases. The new cluster group will contain all common resources that relate to the Administration Server instance.
- Selecting an existing cluster group.
Select this option if you want to use a common resource that is already associated with an existing cluster group. For example, you may want to use this option if you want to use a storage associated with an existing cluster group and if there are no other available storage for a new cluster group.
Step 6. Selecting a cluster data storage
To select a cluster data storage:
- In Available repositories, select the data storage to which the common resources of the virtual Administration Server instance will be installed.
- If the selected data storage contains several volumes, under Available sections on disk drive, select the required volume.
- In Installation path, enter the path on the common data storage to which the resources of the virtual Administration Server instance will be installed.
The data storage is selected.
Page top
Step 7. Specifying an account for remote installation
Specify the user name and password that will be used for remote installation of the virtual Administration Server instance on a passive node of the cluster.
The account that you specify must be granted administrative privileges on all nodes of the cluster.
Page top
Step 8. Selecting the components to be installed
Select the components of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server that you want to install:
- Mobile Device Management. Select this check box if you must create installation packages for mobile devices when the Kaspersky Security Center setup wizard is running. You can also create installation packages for mobile devices manually, after Administration Server installation, by using Administration Console tools.
- SNMP agent. This component receives statistical information for the Administration Server over the SNMP protocol. The component is available if the application is installed on a device with SNMP installed.
After Kaspersky Security Center is installed, the .mib files required for receiving statistics are located in the SNMP subfolder of the application installation folder.
Network Agent and Administration Console are not displayed in the component list. These components are installed automatically and you cannot cancel their installation.
At this step you must specify a folder for installation of Administration Server components. By default, the components are installed to <Disk>:\Program Files\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center. If no such folder exists, this folder is created automatically during installation. You can change the destination folder by using the Browse button.
Page top
Step 9. Selecting network size
Specify the size of the network on which Kaspersky Security Center is to be installed. Depending on the number of devices on the network, the wizard configures the installation and appearance of the application interface so that they match.
The following table lists the application installation settings and interface appearance settings, which are adjusted based on various network sizes.
Dependence of installation settings on the network scale selected
Settings |
1—100 devices |
101—1000 devices |
1001—5000 devices |
More than 5000 devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Display with the node for secondary and virtual Administration Servers, and all settings related to the secondary and virtual Administration Servers in the console tree |
Not available |
Not available |
Available |
Available |
Display with the Security sections in the properties windows of the Administration Server and administration groups |
Not available |
Not available |
Available |
Available |
Random distribution of startup time for the update task on client devices |
Not available |
Over an interval of 5 minutes |
Over an interval of 10 minutes |
Over an interval of 10 minutes |
If you connect Administration Server to a MySQL 5.7 or SQL Express database server, it is not recommended using the application to manage more than 10,000 devices. For the MariaDB database management system, the maximum recommended number of managed devices is 20,000.
Page top
Step 10. Selecting a database
At this step of the wizard, select one of the following database management systems (DBMS) that will be used to store the Administration Server database:
- Microsoft SQL Server or SQL Server Express
- MySQL or MariaDB
- PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro
It is recommended to install the Administration Server on a dedicated server instead of a domain controller. However, if you install Kaspersky Security Center on a server that acts as a read-only domain controller (RODC), Microsoft SQL Server (SQL Express) must not be installed locally (on the same device). In this case, we recommend that you install Microsoft SQL Server (SQL Express) remotely (on a different device), or that you use MySQL, MariaDB, or PostgreSQL if you need to install the DBMS locally.
The Administration Server database structure is provided in the klakdb.chm file, which is located in the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder. This file is also available in an archive on the Kaspersky portal: klakdb.zip.
Page top
Step 11. Configuring the SQL Server
At this step of the wizard, specify the following connection settings, depending on the database management system (DBMS) that you have selected:
- If you selected Microsoft SQL Server or SQL Server Express in the previous step:
- In the SQL Server instance name field, specify the name of the SQL Server on the network. To view a list of all SQL Servers that are on the network, click the Browse button. This field is blank by default.
If you connect to the SQL Server through a custom port, then together with the SQL Server host name specify the port number separated with a comma, for example:
SQL_Server_host_name,1433
If you secure communication between the Administration Server and SQL Server by means of a certificate, specify in the SQL Server instance name field the same host name that was used at the certificate generating. If you use a named instance of SQL Server, then together with the SQL Server host name specify the port number separated with a comma, for example:
SQL_Server_name,1433
If you use several instances of SQL Server on the same host, then additionally specify the instance name separated with a backslash, for example:
SQL_Server_name\SQL_Server_instance_name,1433
If a SQL Server on the enterprise network has the Always On feature enabled, specify the name of the availability group listener in the SQL Server instance name field. Note that Administration Server supports only the synchronous-commit availability mode when the Always On feature is enabled.
- In the Database name field, specify the name of the DBMS that has been created to store Administration Server data. The default value is KAV.
If at this stage you want to install SQL Server on the device from which you are installing Kaspersky Security Center, you must stop installation and restart it after SQL Server is installed. The supported SQL Server versions are listed in the system requirements.
If you want to install SQL Server on a remote device, you do not have to interrupt the Kaspersky Security Center setup wizard. Install SQL Server and resume installation of Kaspersky Security Center.
- In the SQL Server instance name field, specify the name of the SQL Server on the network. To view a list of all SQL Servers that are on the network, click the Browse button. This field is blank by default.
- If you selected MySQL or MariaDB in the previous step:
- In the SQL Server instance name field, specify the name of the DBMS instance. By default, the name is the IP address of the device on which Kaspersky Security Center is to be installed.
- In the Port field, specify the port for Administration Server connection to the DBMS. The default port number is 3306.
- In the Database name field, specify the name of the DBMS that has been created to store Administration Server data. The default value is KAV.
- If you selected PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro in the previous step:
- In the PostgreSQL or Postgres Pro Server field, specify the name of the DBMS instance. By default, the name is the IP address of the device on which Kaspersky Security Center is to be installed.
- In the Port field, specify the port for the Administration Server connection to the DBMS. The default port number is 5432.
In the Database name field, specify the name of the DBMS that has been created to store Administration Server data. The default value is KAV.
Page top
Step 12. Selecting an authentication mode
Determine the authentication mode that will be used when Administration Server connects to the database management system (DBMS).
Depending on the DBMS that is selected, you can choose from the following authentication modes:
- For SQL Express or Microsoft SQL Server select one of the following options:
- Microsoft Windows Authentication mode. Verification of rights uses the account used for starting Administration Server.
- SQL Server Authentication mode. If you select this option, the account specified in the window is used to verify access rights. Fill in the Account and Password fields.
To see the entered password, click and hold the Show button.
For both authentication modes, the application checks if the database is available. If the database is not available, an error message is displayed, and you have to provide correct credentials.
If the Administration Server database is stored on another device and the Administration Server account does not have access to the database server, you must use SQL Server authentication mode when installing or upgrading Administration Server. This may occur when the device that stores the database is outside the domain or when Administration Server is installed under a LocalSystem account.
For MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, or Postgres Pro, specify the account and password.
Page top
Step 13. Selecting the account to start Administration Server
Select the account that will be used to start Administration Server as a service.
- Generate the account automatically. The application creates an account named KL-AK-*, under which the kladminserver service will run.
You can select this option if you plan to locate the shared folder and the DBMS on the same device as Administration Server.
- Select an account. The Administration Server service (kladminserver) will run under the account that you selected.
You will have to select a domain account if, for example, you plan to use as the DBMS a SQL Server instance of any version, including SQL Express, that is located on another device, and/or you plan to locate the shared folder on another device.
Kaspersky Security Center supports managed service accounts (MSA) and group managed service accounts (gMSA). If these types of accounts are used in your domain, you can select one of them as the account for the Administration Server service.
Before specifying MSA or gMSA, you must install the account on the same device on which you want to install Administration Server. If the account is not installed yet, then cancel the Administration Server installation, install the account, and then restart the Administration Server installation. For details about installation of managed service accounts on a local device, refer to the official Microsoft documentation.
To specify MSA or gMSA:
- Click the Browse button.
- In the window that opens, click the Object type button.
- Select the Account for services type and click OK.
- Select the relevant account and click OK.
The account that you selected must have different permissions, depending on the DBMS that you plan for use.
For security reasons, please do not assign the privileged status to the account under which you run Administration Server.
The Administration Server account cannot be changed later. You need to reinstall the failover cluster to use another Administration Server account.
Page top
Step 14. Selecting the account for running the Kaspersky Security Center services
Select the account under which the services of Kaspersky Security Center will run on this device:
- Generate the account automatically. Kaspersky Security Center creates a local account named KlScSvc on this device in the kladmins group. The services of Kaspersky Security Center will be run under the account that has been created.
- Select an account. The Kaspersky Security Center services will be run under the account that you selected.
You will have to select a domain account if, for example, you intend to save reports to a folder located on a different device or if this is required by your organization's security policy. You may also have to select a domain account if you install Administration Server on a failover cluster.
For security reasons, do not grant privileged status to the account under which the services are run.
The KSN proxy service (ksnproxy), Kaspersky activation proxy service (klactprx), and Kaspersky authentication portal service (klwebsrv) will be run under the selected account.
Page top
Step 15. Selecting a shared folder
Define the location and name of the shared folder that will be used to do the following:
- Store the files necessary for remote installation of applications (these files are copied to Administration Server during creation of installation packages).
- Store updates that have been downloaded from an update source to Administration Server.
File sharing (read-only) will be enabled for all users.
You can select either of the following options:
- Create a shared folder. Create a new folder. In the text box, specify the path to the folder.
- Select an existing shared folder. Select a shared folder that already exists.
The shared folder can be a local folder on the device that is used for installation or a remote directory on any client device on the corporate network. You can click the Browse button to select the shared folder, or specify the shared folder manually by entering its UNC path (for example, \\server\Share) in the corresponding field.
By default, the installer creates a local Share subfolder in the application folder that contains the components of Kaspersky Security Center.
You can define a shared folder later if needed.
Page top
Step 16. Configuring the connection to Administration Server
Configure the connection to Administration Server:
You can also change the parameters for connecting to Administration Server later as follows:
- You can change port and SSL port numbers in the Connection ports section of the Administration Server properties. For more information about Administration Server connection ports, see Ports used by Kaspersky Security Center.
- You can change the encryption key length when replacing the Administration Server certificate with the klsetsrvcert utility by using the
-o RsaKeyLen:<key length>parameter.
Step 17. Defining the Administration Server address
Specify the Administration Server address. You can select one of the following options:
- DNS domain name. You can use this method if the network includes a DNS server and client devices can use it to receive the Administration Server address.
- NetBIOS name. You can use this method if client devices receive the Administration Server address using the NetBIOS protocol or if a WINS server is available on the network.
- IP address. You can use this method if Administration Server has a static IP address that will not be subsequently changed.
Step 18. Administration Server address for connection of mobile devices
This setup wizard step is available if you have selected Mobile Device Management for installation.
In the Address for connection of mobile devices window, specify the external address of the Administration Server for connection of mobile devices that are outside of the local network. You can specify the IP address or Domain Name System (DNS) of the Administration Server.
Page top
Step 19. Unpacking and installing files on the hard drive
After the installation of Kaspersky Security Center components is configured, you can start installing files on the hard drive.
If installation requires additional programs, the setup wizard will notify you, on the Installing Prerequisites page, before installation of Kaspersky Security Center begins. The required programs are installed automatically after you click the Next button.
On the last page, you can select which console to start for work with Kaspersky Security Center:
- Start MMC-based Administration Console
- Start Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
This option is available only if you opted to install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console in one of the previous steps.
You can also click Finish to close the wizard without starting work with Kaspersky Security Center. You can start the work later at any time.
At the first startup of Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you can perform the initial setup of the application.
Page top
Installing Administration Server in silent mode
Administration Server can be installed in silent mode, that is, without the interactive input of installation settings.
To install Administration Server on a local device in silent mode:
- Read the End User License Agreement. Use the command below only if you understand and accept the terms of the End User License Agreement.
- Read the Privacy Policy. Use the command below only if you understand and agree that your data will be handled and transmitted (including to third countries) as described in the Privacy Policy.
- Run the command
setup.exe /s /v"DONT_USE_ANSWER_FILE=1 EULA=1 PRIVACYPOLICY=1 <
setup_parameters>"
where setup_parameters is a list of parameters and their respective values, separated with spaces (PARAM1=PARAM1VAL PARAM2=PARAM2VAL). The setup.exe file is located in the Server folder, which is part of the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit.
The names and possible values for parameters that can be used when installing Administration Server in silent mode are listed in the table below.
Parameters of Administration Server installation in silent mode
Parameter name |
Parameter description |
Available values |
|---|---|---|
EULA |
Acceptance of the terms of the License Agreement. |
|
PRIVACYPOLICY |
Acceptance of the terms of the Privacy Policy. |
|
INSTALLATIONMODETYPE |
Type of Administration Server installation. |
|
INSTALLDIR |
Path to the Administration Server installation folder. |
String value. |
ADDLOCAL |
List of Administration Server components (separated with commas) to be installed. |
CSAdminKitServer, NAgent, CSAdminKitConsole, NSAC, MobileSupport, KSNProxy, SNMPAgent, GdiPlusRedist, Microsoft_VC90_CRT_x86, Microsoft_VC100_CRT_x86. Minimum list of components sufficient for proper Administration Server installation:
|
NETRANGETYPE |
Network size (number of devices on the network). |
|
SRV_ACCOUNT_TYPE |
Mode for specifying the account under which Administration Server will be run as a service. |
|
SERVERACCOUNTNAME |
Name of the account under which Administration Server will be run as a service. You must specify a value for the parameter if SRV_ACCOUNT_TYPE=SrvAccountUser. |
String value. |
SERVERACCOUNTPWD |
Password of the account that will be used to start Administration Server as a service. You must specify a value for the parameter if SRV_ACCOUNT_TYPE=SrvAccountUser. |
String value. |
SERVERCER |
Size of the key for the Administration Server certificate (bits). |
|
DBTYPE |
Type of database that will be used to store the Administration Server database. This parameter is required. |
|
MYSQLSERVERNAME |
Full name of the SQL Server. You must specify a value for the parameter if DBTYPE=MySQL. |
String value. |
MYSQLSERVERPORT |
Number of the port for connecting to the SQL Server. You must specify a value for the parameter if DBTYPE=MySQL. |
Numerical value. |
MYSQLDBNAME |
Name of the database that will be created to store Administration Server data. You must specify a value for the parameter if DBTYPE=MySQL. |
String value. |
MYSQLACCOUNTNAME |
Name of the account for connection to the database. You must specify a value for the parameter if DBTYPE=MySQL. |
String value. |
MYSQLACCOUNTPWD |
Password of the account for connecting to the database. You must specify a value for the parameter if DBTYPE=MySQL. |
String value. |
MSSQLSERVERNAME |
Full name of the SQL Server. You must specify a value for the parameter if DBTYPE=MSSQL. |
String value. |
MSSQLDBNAME |
Name of the database. You must specify a value for the parameter if DBTYPE=MSSQL. |
String value. |
MSSQLAUTHTYPE |
Type of authorization when connecting to the SQL Server. You must specify a value for the parameter if DBTYPE=MSSQL. |
|
MSSQLACCOUNTNAME |
Name of the account for connection to the SQL Server. You must specify a value for the parameter if MSSQLAUTHTYPE=SQLServer. |
String value. |
MSSQLACCOUNTPWD |
Password of the account for connection to the SQL Server. You must specify a value for the parameter if MSSQLAUTHTYPE=SQLServer. |
String value. |
CREATE_SHARE_TYPE |
Method of specifying the shared folder. |
|
SHARELOCALPATH |
Full path to a local folder. You must specify a value for the parameter if CREATE_SHARE_TYPE=Create |
String value. |
SHAREFOLDERNAME |
Network name of a shared folder. You must specify a value for the parameter if CREATE_SHARE_TYPE=Create. |
String value. |
EXISTSHAREFOLDERNAME |
Full path to an existing shared folder. You must specify a value for the parameter if CREATE_SHARE_TYPE=ChooseExisting. |
String value. |
SERVERPORT |
Port number to connect to Administration Server. |
Numerical value. |
SERVERSSLPORT |
Number of the port for encrypted connection to Administration Server by using SSL protocol. |
Numerical value. |
SERVERADDRESS |
Administration Server address. |
String value. |
MOBILESERVERADDRESS |
Administration Server address for connection of mobile devices. |
String value. |
For a detailed description of the Administration Server setup parameters, please refer to the Custom installation section.
Installing Administration Console on the administrator's workstation
You can install Administration Console on the administrator's workstation separately and manage Administration Server over the network using that Console.
To install Administration Console on the administrator's workstation:
- Run the setup.exe executable file.
A window opens prompting you to select Kaspersky applications to install.
- In the application selection window, click the Install only Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console link to run the Administration Console setup wizard. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- Select a destination folder. By default, this will be <Disk>:\Program Files\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center Console. If such a folder does not exist, it is created automatically during the installation. You can change the destination folder by using the Browse button.
- On the last page of the setup wizard click the Start button to start installation of Administration Console.
When the wizard completes, Administration Console will be installed on the administrator's workstation.
To install Administration Console on the administrator's workstation in silent mode:
- Read the End User License Agreement. Use the command below only if you understand and accept the terms of the End User License Agreement.
- In the
Distrib\Consolefolder of the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit, run the setup.exe file by using the following command:setup.exe /s /v"EULA=1"If you want to install all management plug-ins from the
Distrib\Console\Pluginsfolder together with the Administration Console, run the following command:setup.exe /s /v"EULA=1" /pALLIf you want to specify which management plug-ins to install from the
Distrib\Console\Pluginsfolder together with the Administration Console, specify the plug-ins after the "/p" key and separate them with a semicolon:setup.exe /s /v"EULA=1" /pP1;P2;P3where
P1,P2,P3are plug-in names that correspond to the plug-in folder names in theDistrib\Console\Pluginsfolder. For example:setup.exe /s /v"EULA=1" /pKES4Mac;KESS;MDM4IOS
Administration Console and the management plug-ins (if any) will be installed on the administrator's workstation.
After installing Administration Console, you must connect to the Administration Server. To do this, run Administration Console and, in the window that opens, specify the name or the IP address of the device on which Administration Server is installed, as well as the settings of the account used to connect to it. After connection to Administration Server is established, you can manage the anti-virus protection system using this Administration Console.
You can remove Administration Console with standard Microsoft Windows add / remove tools.
Changes in the system after Kaspersky Security Center installation
Administration Console icon
After Administration Console is installed on your device, its icon appears, allowing you to start Administration Console. You can find Administration Console in the Start → Programs → Kaspersky Security Center menu.
Administration Server and Network Agent services
Administration Server and Network Agent are installed on the device as services with the properties listed below. The table also contains the attributes of other services that apply on the device after Administration Server installation.
Properties of Kaspersky Security Center services
Component |
Service name |
Displayed service name |
Account |
Administration Server |
kladminserver |
Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server |
User-defined or dedicated non-privileged account in KL-AK-* format created during installation |
Network Agent |
klnagent |
Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent |
Local system |
Web Server for accessing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and administering the organization's intranet |
klwebsrv |
Kaspersky web server |
Dedicated unprivileged KlScSvc account |
Activation proxy server |
klactprx |
Kaspersky activation proxy server |
Dedicated unprivileged KlScSvc account |
KSN proxy server |
ksnproxy |
Kaspersky Security Network proxy server |
Dedicated unprivileged KlScSvc account |
If you install Kaspersky Security Center on the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster nodes, the klfocsvc_klfoc service becomes available. The klnagent_klfoc and klfocsvc_klfoc services run under the Local system account. The kladminserver_klfoc service must be run under the 'ksc' account, and other services run under the 'rightless' account. The 'ksc' and 'rightless' accounts must be added in the KLAdmins group with the local administrator's permissions. For correct work of Kaspersky Security Center, you must use only the 'ksc' and 'rightless' accounts for running services. We do not recommend using other accounts with the same rights. The table below contains the properties of services that are applied on the device after Administration Server is installed on the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster.
Properties of services of Kaspersky Security Center installed in the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster
Component |
Service name |
Displayed service name |
Account |
Administration Server |
kladminserver_klfoc |
Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server |
ksc |
Network Agent |
klnagent_klfoc |
Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent |
Local system |
Web Server for accessing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and administering the organization's intranet |
klwebsrv_klfoc |
Kaspersky web server |
rightless |
Activation proxy server |
klactprx_klfoc |
Kaspersky activation proxy server |
rightless |
KSN proxy server |
ksnproxy_klfoc |
Kaspersky Security Network proxy server |
rightless |
Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster |
klfocsvc_klfoc |
Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster |
Local system |
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console services
If you install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console on the device, then the following services are deployed (see the table below):
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console services
Displayed service name |
Account |
Kaspersky Security Center Service Web Console |
NT Service/KSCSvcWebConsole |
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
|
Network service |
Kaspersky Security Center Product Plugins Server
|
NT Service/KSCWebConsolePlugin |
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Management Service
|
Local system |
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Message Queue
|
NT Service/KSCWebConsoleMessageQueue |
Network Agent server version
The server version of Network Agent will be installed on the device together with Administration Server. The server version of Network Agent is part of Administration Server, is installed and removed together with Administration Server, and can only interact with a locally installed Administration Server. You do not have to configure the connection of Network Agent to Administration Server: configuration is implemented programmatically because the components are installed on the same device. The server version of Network Agent is installed with the same properties as the standard Network Agent and performs the same application management functions. This version will be managed by the policy of the administration group to which the client device of Administration Server belongs. For the server version of Network Agent all tasks are created from the scope of those provided for Administration Server, except for the Server change task.
Network Agent cannot be installed separately on a device that already has Administration Server installed.
You can view the properties of each service of Administration Server and Network Agent, as well as monitor their operation using standard Microsoft Windows management tools: Computer management\Services. Information about the activity of the Kaspersky Administration Server service is stored in the Microsoft Windows system log in a separate Kaspersky Event Log branch on the device where the Administration Server is installed.
We recommend that you avoid starting and stopping services manually and leave service accounts in the service settings unchanged. If necessary, you can modify the Administration Server service account using the klsrvswch utility. Note that you must launch the klsrvswch utility on the Administration Server device under the account with administrator rights that was used to install Administration Server.
User accounts and security groups
The Administration Server Installer creates the following accounts by default:
- KL-AK-*: Administration Server service account
- KlScSvc: Account for other services from the Administration Server pool
- KlPxeUser: Account for deployment of operating systems
If you selected other accounts for the Administration Server service and other services while running the Installer, the specified accounts are used.
Local security groups named KLAdmins and KLOperators with their respective sets of rights are also created automatically on the device that has Administration Server installed.
It is not recommended to install the Administration Server on a domain controller; however, if you install Administration Server on the domain controller, you must start the installer with the domain administrator rights. In this case, the installer automatically creates domain security groups named KLAdmins and KLOperators. If you install Administration Server on a device that is not the domain controller, you must start the installer with the local administrator rights instead. In this case, the installer automatically creates local security groups named KLAdmins and KLOperators.
When configuring email notifications, you may have to create an account on the mail server for ESMTP authentication.
Removing the application
You can remove Kaspersky Security Center with standard Microsoft Windows add/remove tools. Removing the application requires starting a wizard that removes all application components from the device (including plug-ins). The wizard makes your default browser open a web page with a poll where you can tell us why you chose to stop using Kaspersky Security Center. If you have not selected removal of the shared folder (Share) during the wizard operation, you can delete it manually after completion of all related tasks.
After the application is removed, some of its files may remain in the system's temporary folder.
The Application removal task creation wizard will suggest that you store a backup copy of Administration Server.
When the application is removed from Microsoft Windows 7 and Microsoft Windows 2008, premature termination of the Application removal task creation wizard might occur. This can be avoided by disabling the User Account Control (UAC) in the operating system and restarting application removal.
Page top
About upgrading Kaspersky Security Center
This section contains information on how to upgrade Kaspersky Security Center from a previous version. You can upgrade Kaspersky Security Center in different ways, depending on whether Kaspersky Security Center was installed locally or on the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster nodes.
During the upgrade, concurrent use of the DBMS by Administration Server and another application is strictly forbidden.
Note that if you upgrade the Administration Server to the version 15.1, you will not be able to create new installation packages of Network Agent version 15 or earlier. However, previously created installation packages will be available.
When you upgrade Kaspersky Security Center from a previous version, all the installed plug-ins of supported Kaspersky applications are kept. The Administration Server plug-in and Network Agent plug-in are upgraded automatically (both for the Administration Console and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console).
Upgrading Kaspersky Security Center from a previous version
The following topic describes recommended preparation steps for the upgrade: Upgrading Kaspersky Security Center and managed security applications.
You can install version 15.1 of Administration Server on a device that has an earlier version of Administration Server installed (starting from version 11 (11.0.0.1131b)). When upgrading to version 15.1, all data and settings from the previous version of Administration Server are preserved.
If problems occur during Administration Server installation, you can restore the previous version of Administration Server using the backup copy of the Administration Server data created before the upgrade.
If at least one Administration Server of the new version has been installed on the network, you can upgrade other Administration Servers on the network using the remote installation task that uses the Administration Server installation package.
If you deployed the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster, you can also upgrade Kaspersky Security Center on its nodes.
To upgrade an earlier version of Administration Server to version 15.1:
- Run the ksc_15.1_<build number>_full_<language>.exe installation file for version 15.1 (you can download this file from the Kaspersky website).
- In the window that opens, click the Install Kaspersky Security Center link to start the Administration Server setup wizard. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- Read the License Agreement and Privacy Policy. If you agree with all the terms of the License Agreement and the Privacy Policy, select the following check boxes in the I confirm I have fully read, understood, and accept the following section:
- The terms and conditions of this EULA
- Privacy Policy describing the handling of data
Installation of the application on your device will continue after you select both check boxes. The setup wizard prompts you to create a backup of the Administration Server data for the earlier version.
Kaspersky Security Center supports data recovery from a backup created with an older version of Administration Server.
- If you want to create a backup of the Administration Server data, specify this in the Backup of Administration Server data window that opens.
A backup is created by the klbackup utility. This utility is included in the distribution kit, and is located at the root of the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder.
- Install Administration Server version 15.1 by following the setup wizard.
If a message appears that the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console service is busy, click the Ignore button in the wizard window.
We recommend that you avoid terminating the setup wizard. If you cancel the upgrade at the step of Administration Server installation may cause the upgraded version of Kaspersky Security Center to fail.
- For devices on which the earlier version of Network Agent is installed, create and run the task for remote installation of the new version of Network Agent.
We recommend that you upgrade the Network Agent for Linux to the same version as Kaspersky Security Center.
After completion of the remote installation task, the Network Agent version is upgraded.
Upgrading Kaspersky Security Center on the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster nodes
You can install Administration Server version 15.1 on every Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster node that has an earlier version of the Administration Server installed (starting from version 13.2). When upgrading to version 15.1, all data and settings from the previous version of Administration Server are preserved.
If you previously installed Kaspersky Security Center on devices locally, you can also upgrade Kaspersky Security Center on these devices.
To upgrade Kaspersky Security Center on the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster nodes:
- Perform the following actions on the active node of the cluster:
- Run the ksc_15.1_<build number>_full_<language>.exe executable file.
A window opens and prompts you to select the Kaspersky applications to upgrade. Click the Install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server link to start the Administration Server setup wizard. Follow the wizard instructions.
- Read the License Agreement and Privacy Policy. If you agree with all the terms of the License Agreement and the Privacy Policy, select the following check boxes in the I confirm I have fully read, understood, and accept the following section:
- The terms and conditions of this EULA
- Privacy Policy describing the handling of data
Select both check boxes to continue the installation.
If you do not accept the License Agreement or Privacy Policy, click the Cancel button to cancel the upgrade.
- Run the ksc_15.1_<build number>_full_<language>.exe executable file.
- Perform the same actions on the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster's passive node as on the active node.
- Start the cluster.
As a result, you installed the latest version of the Administration Server on the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster nodes.
Page top
Upgrading Kaspersky Security Center on the Microsoft failover cluster nodes
You can upgrade Administration Server version 15.1 on every Microsoft failover cluster node that has an earlier version of the Administration Server installed (starting from version 13.2). When upgrading to version 15.1, all data and settings from the previous version of Administration Server are preserved.
To upgrade Kaspersky Security Center on the Microsoft failover cluster nodes, perform the following actions on any node of the cluster:
- Run the ksc_15.1_<build number>_full_<language>.exe executable file.
A window opens and prompts you to select the Kaspersky applications to upgrade. Click the Install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server link to start the Administration Server setup wizard. Follow the wizard instructions.
- Read the License Agreement and Privacy Policy. If you agree with all the terms of the License Agreement and the Privacy Policy, select the following check boxes in the I confirm I have fully read, understood, and accept the following section:
- The terms and conditions of this EULA
- Privacy Policy describing the handling of data
Select both check boxes to continue the installation.
If you do not accept the License Agreement or Privacy Policy, click the Cancel button to cancel the upgrade.
- In the Type of installation on cluster window, select the Cluster (install on all cluster nodes).
Next, the installer configures and finishes upgrading the Administration Server on all nodes of the cluster. During the upgrade, the Administration Server settings cannot be changed.
As a result, you installed the latest version of the Administration Server on the Microsoft failover cluster nodes.
Page top
Initial setup of Kaspersky Security Center
This section describes steps you must take after the Kaspersky Security Center installation to perform its initial setup.
Hardening Guide
The Hardening Guide is intended for professionals who install and administer Kaspersky Security Center, as well as for those who provide technical support to organizations that use Kaspersky Security Center.
The Hardening Guide describes recommendations and features of configuring Kaspersky Security Center and its components, aimed to reduce the risks of its compromise.
Before configuring, create a Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server backup copy by using the Backup of Administration Server data task or the klbackup utility and save it in a safe location.
The Hardening Guide includes the following information:
- Selecting the Administration Server architecture
- Configuring a secure connection to Administration Server
- Configuring accounts to access Administration Server
- Managing protection of Administration Server and client devices
- Configuring protection for managed applications
- Administration Server maintenance
- Transferring information to third-party applications
Before you start to work with Administration Server, Kaspersky Security Center prompts you to read the brief version of the Hardening Guide.
Note that you cannot use Administration Server until you confirm that you have read the Hardening Guide.
To read the Hardening Guide:
- Open Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and log in to the console. The console checks whether you confirmed reading the current version of the Hardening Guide.
If you have not yet read the Hardening Guide, a window opens and displays a brief version of it.
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to view the brief version of the Hardening Guide as a text document, click the Open in new window link.
- If you want to view the full version of the Hardening Guide, click the Open the Hardening guide in Online Help link.
- After you read the Hardening Guide, select the I confirm that I have fully read and understand the Hardening guide check box, and then click the Accept button.
Now, you can work with Administration Server.
When a new version of the Hardening Guide appears, Kaspersky Security Center will prompt you to read it.
Page top
Administration Server quick start wizard
This section provides information about the Administration Server quick start wizard.
About quick start wizard
This section provides information about the Administration Server quick start wizard.
Administration Server quick start wizard allows you to create a minimum of necessary tasks and policies, adjust a minimum of settings, download and install plug-ins for managed Kaspersky applications, and create installation packages of managed Kaspersky applications. When the wizard is running, you can make the following changes to the application:
- Download and install plug-ins for managed applications. After the quick start wizard has finished, the list of installed management plug-ins is displayed in the Advanced → Details of application management plug-ins installed section of the Administration Server properties window.
- Create installation packages of managed Kaspersky applications. After the quick start wizard has finished, installation packages of Network Agent for Windows and managed Kaspersky applications are displayed in the Administration Server → Advanced → Remote installation → Installation packages list.
- Add key files or enter activation codes that can be automatically distributed to devices within administration groups. After the quick start wizard has finished, information about license keys is displayed in the Administration Server → Kaspersky Licenses list and in the License keys section of the Administration Server properties window.
- Configure interaction with Kaspersky Security Network .
- Set up email delivery of notifications of events that occur during operation of Administration Server and managed applications (successful notification delivery requires that the Messenger service run on the Administration Server and all recipient devices). After the quick start wizard has finished, the email notifications settings are displayed in the Notification section of the Administration Server properties window.
- Adjust the update settings and vulnerability fix settings for applications installed on devices.
- Create a protection policy for workstations and servers, as well as malware scan tasks, update download tasks, and data backup tasks, for the top level of the hierarchy of managed devices. After the quick start wizard has finished, the created tasks are displayed in the Administration Server → Tasks list, the policies corresponding to the plug-ins for managed applications are displayed in the Administration Server → Policies list.
The quick start wizard creates policies for managed applications, such as Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, unless such policies are already created for the Managed devices group. The quick start wizard creates tasks if tasks with the same names do not exist for the Managed devices group.
In Administration Console, Kaspersky Security Center automatically prompts you to run the quick start wizard after you have started it for the first time. You can also start the quick start wizard manually at any time.
Page top
Starting Administration Server quick start wizard
The application automatically prompts you to run the quick start wizard after Administration Server installation, at the first connection to it. You can also start the quick start wizard manually at any time.
To start the quick start wizard manually:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- In the context menu of the node, select All Tasks → Administration Server quick start wizard.
The wizard prompts you to perform initial configuration of the Administration Server. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
If you start the quick start wizard again, tasks and policies created at the previous run of the wizard cannot be created again.
Page top
Step 1. Configuring a proxy server
Specify the internet access settings for Administration Server. You must configure internet access to use Kaspersky Security Network and to download updates of anti-virus databases for Kaspersky Security Center and managed Kaspersky applications.
Select the Use proxy server option if you want to use a proxy server when connecting to the internet. If this option is selected, the fields are available for entering settings. Specify the following settings for a proxy server connection:
- Address
- Port number
- Bypass proxy server for local addresses
- Proxy server authentication
- User name
- Password
You can configure internet access later, separately from the quick start wizard.
Page top
Step 2. Selecting the application activation method
Select one of the following Kaspersky Security Center activation options:
- By inserting your activation code
If activation by inserting your activation code was not successful for any reason, you can activate the application by specifying a key file.
- By specifying a key file
- By postponing the application activation
If you choose to postpone application activation, you can add a license key later at any time.
Step 3. Selecting the protection areas and operating systems
Select the protection areas and operating systems that are in use on your network. When you select these options, you specify the filters for application management plug-ins and distribution packages on Kaspersky servers that you can download to install on client devices on your network. Select the options:
You can select the Kaspersky application packages from the list of available packages later, separately from the quick start wizard. To simplify the search for the required packages, you can filter the list of available packages by the following criteria:
- Protection area
- Type of downloaded software (distribution package, utility, plug-in, or web plug-in)
- Version of the Kaspersky application
- Localization language of the Kaspersky application
Step 4. Selecting plug-ins for managed applications
Select plug-ins for managed applications to install. A list of plug-ins located on Kaspersky servers is displayed. The list is filtered according to the options selected on the previous step of the wizard. By default, a full list includes plug-ins of all languages. To display only plug-in of specific language, select the language from Show the Administration Console localization language or drop-down list. The list of plug-ins includes the following columns:
After the plug-ins are selected, their installation starts automatically in a separate window. To install some plug-ins, you must accept the terms of the EULA. Read the text of EULA, select the I accept the terms of the License Agreement option and click the Install button. If you do not accept the terms of the EULA, the plug-in is not installed.
After the installation completes, close the installation window.
You can also select the management plug-ins later, separately from the quick start wizard.
Page top
Step 5. Downloading distribution packages and creating installation packages
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes encryption tool for the information stored on client devices. To download a distribution package of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows valid for the needs of your organization, consult the legislation of the country where the client devices of your organization are located.
In the Encryption type window, select one of the following encryption types:
- Strong encryption (AES256). This encryption type uses 256-bit key length.
- Lite encryption (AES56). This encryption type uses 56-bit key length.
The Encryption type window is displayed only if you have selected Workstations as a protection scope and Microsoft Windows as a platform.
After you have selected an encryption type, a list of distribution packages of both encryption types is displayed. A distribution package with the selected encryption type is selected in the list. The distribution package language corresponds to the Kaspersky Security Center language. If a distribution package of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows for the Kaspersky Security Center language does not exist, the English distribution package is selected.
In the list, you can select distribution package languages by means Show the Administration Console localization language or drop-down list.
Distributives of managed applications may require a specific minimum version of Kaspersky Security Center to be installed.
In the list, you can select distribution packages of any encryption type, different of that you have selected in the Encryption type window. After you have selected a distribution package for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, downloading of the distribution packages, corresponding to the components and platforms, starts. You can monitor the downloading progress in the Download status column. After the quick start wizard has finished, installation packages of Network Agent for Windows and managed Kaspersky applications are displayed in the Administration Server → Advanced → Remote installation → Installation packages list.
To finish downloading of some distribution packages you must accept EULA. When you click the Accept button, the text of EULA is displayed. To proceed to the next step of the wizard, you must accept the terms and conditions of the EULA and the terms and conditions of Kaspersky Privacy Policy. Select the options related to the EULA and Kaspersky Privacy Policy, and then click the Accept all button. If you do not accept the terms and conditions, the downloading of the package is canceled.
After you have accepted the terms and conditions of the EULA and the terms and conditions of Kaspersky Privacy Policy, the downloading of the distribution packages continues. When the downloading is finished, the Installation package is created status is displayed. Later, you can use installation packages to deploy Kaspersky applications on client devices.
You can create installation packages manually, separately from the quick start wizard. Go to Administration Server → Advanced → Remote installation → Installation packages in the Administration Console tree.
Page top
Step 6. Configuring Kaspersky Security Network usage
You can obtain access to the reputation databases of Kaspersky Security Network to ensure faster responses by Kaspersky applications to threats, improve the effectiveness of some protection components, and reduce the risk of false positives.
Read the KSN Statement, which is displayed in the window. Specify the settings for relaying information about Kaspersky Security Center operations to the Kaspersky Security Network knowledge base. Select one of the following options:
If you downloaded the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows plug-in, both KSN statements—the KSN Statement for Kaspersky Security Center and the KSN Statement for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows—are displayed. KSN statements for other managed Kaspersky applications whose plug-ins were downloaded are displayed in separate windows and you must accept (or not accept) each of the statements separately.
You can also set up Administration Server access to Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) later in the Administration Server properties window of Administration Console.
Page top
Step 7. Configuring email notifications
Configure the sending of notifications about events registered during the operation of Kaspersky applications on managed devices. These settings are used as the default settings for Administration Server.
To configure the delivery of notifications about events occurring in Kaspersky applications, use the following settings:
You can test the new email notification settings by clicking the Send test message button.
You can also configure event notifications later, separately from the quick start wizard.
Page top
Step 8. Configuring update management
Configure the settings for managing updates of applications installed on client devices.
You can configure these settings only if you have provided a license key with the Vulnerabilities and Patch management option.
In the Search for updates and install them group of settings, you can select a mode of Kaspersky Security Center update search and installation:
In the Windows Server Update Services group of settings, you can select the update synchronization source:
You can create the Find vulnerabilities and required updates and Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities tasks separately from the quick start wizard. To use Administration Server as the WSUS server, create the Perform Windows Update synchronization task, and then select the Use Administration Server as a WSUS server option in the Network Agent policy.
Page top
Step 9. Creating an initial protection configuration
The Configure initial protection window displays a list of policies and tasks that are created automatically. The following policies and tasks are created:
- Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent policy
- Policies for managed Kaspersky applications whose management plug-ins were installed earlier
- Administration Server maintenance task
- Backup of Administration Server data task
- Download updates to the Administration Server repository task
- Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
- Install update task
Wait for the creation of policies and tasks to complete before proceeding to the next step of the wizard.
If you have downloaded and installed the plug-in for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows 10 Service Pack 1 and later till the 11.0.1, during the creation of policies and tasks, a window opens for initial configuration of the trusted zone of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. The application will prompt you to add vendors verified by Kaspersky to the trusted zone for the purposes of excluding their applications from scans to prevent them from being accidentally blocked. You can create recommended exclusions now or create a list of exclusions later by selecting the following in the console tree: Policies → Kaspersky Endpoint Security properties menu → Advanced Threat Protection → Trusted zone → Settings → Add. The list of scan exclusions is available for editing at any time when using the application.
Operations on the trusted zone are performed by using tools integrated into Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. For detailed instructions on how to perform operations and a description of encryption features please refer to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help.
To finish initial configuration of the trusted zone and return to the wizard, click OK.
Click Next. This button becomes available after all necessary policies and tasks have been created.
You can also create the required tasks and policies later, separately from the quick start wizard.
Page top
Step 10. Connecting mobile devices
If you previously enabled the Mobile devices protection scope in the wizard settings, specify the settings for connecting the enterprise mobile devices of the managed organization. If you did not enable Mobile devices protection scope, this step is skipped.
At this step of the wizard, do the following:
- Configure ports for connection of mobile devices
- Configure Administration Server authentication
- Create or manage certificates
- Set up issuance, automatic updating, and encryption of general-type certificates
- Create a moving rule for mobile devices
To set up the ports for connection of mobile devices:
- Click the Configure button to the right of the Mobile device connection field.
- In the drop-down list, select Configure ports.
The Administration Server properties window opens, displaying the Additional ports section.
- In the Additional ports section, you can specify the mobile device connection settings:
- Click OK to save changes and return to the quick start wizard.
You will have to configure authentication of the Administration Server by mobile devices and authentication of mobile devices by the Administration Server. If you want, you can configure authentication later, separately from the quick start wizard.
To configure Administration Server authentication by mobile devices:
- Click the Configure button to the right of the Mobile device connection field.
- In the drop-down list, select Configure authentication.
The Administration Server properties window opens, displaying the Certificates section.
- Select the authentication option for mobile devices in the Administration Server authentication by mobile devices group of settings, and select the authentication option for UEFI protection devices in the Administration Server authentication by UEFI protection devices group of settings.
When Administration Server exchanges data with client devices, it is authenticated through the use of a certificate.
By default, Administration Server uses the certificate that was created during Administration Server installation. If you want, you can add a new certificate.
To add a new certificate (optional):
- Select Other certificate.
The Browse button appears.
- Click the Browse button.
- In the window that opens, specify the certificate settings:
- Certificate type
- Activation time:
- Click the Properties button to view the settings of the selected Administration Server certificate.
To reissue a certificate issued through Administration Server:
- Select Certificate issued through Administration Server.
- Click the Reissue button.
- In the window that opens, specify the following settings:
- Connection address:
- Activation time:
- Click OK to save changes and return to the Certificates window.
- Click OK to save changes and return to the quick start wizard.
To set up issuance, automatic updating, and encryption of general-type certificates for identification of mobile devices by Administration Server:
- Click the Configure button on the right of the Mobile device authentication field.
The Certificate issuance rules window opens, displaying the Issuance of mobile certificates section.
- If necessary, specify the following settings in the Issuance settings section:
- Certificate lifetime, days
- Certificate source
You can modify the certificate templates if integration with the public key infrastructure (PKI) has been configured in the Integration with PKI section. In this case, the following template selection fields are available:
- Default template
- Other template
- If necessary, specify the following settings for automatic issuance of certificates in the Automatic Updates settings section:
Certificates are automatically reissued by a Certification Authority.
- If necessary, in the Password protection settings section, specify the settings for decrypting certificates during installation.
Select the Prompt for password during certificate installation option to prompt the user for password when the certificate is installed on a mobile device. The password is used only once—during installation of the certificate on the mobile device.
The password will be automatically generated by Administration Server and sent to the email address that you specified. You can specify the user's email address, or your own email address if you want to use another method to forward the password to the user.
You can use the slider to specify the number of characters in the certificate decryption password.
The password prompting option is required, for example, to protect a shared certificate in a stand-alone Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android installation package. Password protection will prevent an intruder from obtaining access to the shared certificate through theft of the stand-alone installation package from Kaspersky Security Center Web Server.
If this option is disabled, the certificate is automatically decrypted during installation and the user will not be prompted for a password. By default, this option is disabled.
- Click OK to save changes and return to the quick start wizard window.
Click the Cancel button to return to the quick start wizard without saving any changes made.
To enable the function for moving mobile devices to an administration group that you choose,
In the Automatic moving of mobile devices field, select the Create a moving rule for mobile devices option.
If the Create a moving rule for mobile devices option is selected, the application automatically creates a moving rule that moves devices running Android and iOS to the Managed devices group:
- With Android operating systems on which a Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android and a mobile certificate are installed
- With iOS operating systems on which the iOS MDM profile with a shared certificate is installed
If such a rule already exists, the application does not create it again.
By default, this option is disabled.
Kaspersky no longer supports Kaspersky Safe Browser.
Page top
Step 11. Downloading updates
Updates for anti-virus databases for Kaspersky Security Center and managed Kaspersky applications are downloaded automatically. The updates are downloaded from Kaspersky servers.
To download updates separately from the quick start wizard, create and configure the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task.
Page top
Step 12. Device discovery
The Network poll window displays information about the status of network polling performed by the Administration Server.
You can view network devices detected by Administration Server and receive help on working with the Device discovery window by clicking the links in the lower part of the window.
You can poll your network later, separately from the quick start wizard. Use Administration Console to configure the polling of Windows domains, Active Directory, IP ranges, and IPv6 networks.
Step 13. Closing the quick start wizard
In the quick start wizard completion window, select the Run the Remote installation wizard option if you want to start automatic installation of anti-virus applications and/or Network Agent on devices on your network.
To complete the wizard, click the Finish button.
Page top
Configuring the connection of Administration Console to Administration Server
Administration Console is connected to Administration Server through SSL port TCP 13291. The same port can be used by klakaut automation objects.
Port TCP 14000 can be used for connecting Administration Console, distribution points, secondary Administration Servers, and klakaut automation objects, as well as for receiving data from client devices.
Normally, SSL port TCP 13000 can only be used by Network Agent, a secondary Administration Server, and the primary Administration Server in DMZ. In some cases, Administration Console may have to be connected through SSL port 13000:
- If a single SSL port is likely to be used both for Administration Console and for other activities (receiving data from client devices, connecting distribution points, connecting secondary Administration Servers).
- If a klakaut automation object is not connected to Administration Server directly but through a distribution point in the DMZ.
To allow the connection of Administration Console over port 13000:
- Open the system registry of the device on which Administration Server is installed (for example, locally, using the regedit command in the Start → Run menu).
- Go to the following hive:
- For 32-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\Components\34\.core\.independent\KLLIM
- For 64-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\34\.core\.independent\KLLIM
- For 32-bit systems:
- For the LP_ConsoleMustUsePort13291 (DWORD) key, set 00000000 as the value.
The default value specified for this key is 1.
- Restart the Administration Server service.
You will now be able to connect Administration Console to Administration Server over port 13000.
Page top
Configuring the internet access settings for Administration Server
You must configure internet access to use Kaspersky Security Network, and to download updates of anti-virus databases for Kaspersky Security Center and managed Kaspersky applications.
To specify the internet access settings for Administration Server:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server %s node.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, go to Advanced → Configuring internet access.
- Select the Use proxy server option if you want to use a proxy server when connecting to the internet. If this option is selected, the fields are available for entering settings. Specify the following settings for a proxy server connection:
You can also configure internet access by using the quick start wizard.
Page top
Connecting out-of-office devices
This section describes how to connect out-of-office devices (that is, managed devices that are located outside of the main network) to Administration Server.
Scenario: Connecting out-of-office devices through a connection gateway
This scenario describes how to connect managed devices that are located outside of the main network to Administration Server.
Prerequisites
The scenario has the following prerequisites:
- A demilitarized zone (DMZ) is organized in your organization's network.
- Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server is deployed on the corporate network.
Stages
This scenario proceeds in stages:
- Selecting a client device in the DMZ
This device will be used as a connection gateway. The device that you select must meet the requirements for connection gateways.
- Installing Network Agent in the connection gateway role
We recommend that you use a local installation to install Network Agent on the selected device.
By default, the installation file is located at: \\<server name>\KLSHARE\PkgInst\NetAgent_<version number>
In the Connection gateway window of the Network Agent setup wizard, select Use Network Agent as a connection gateway in DMZ. This mode simultaneously activates the connection gateway role and tells Network Agent to wait for connections from Administration Server, rather than establish connections to Administration Server.
Alternatively, you can install Network Agent on a Linux device and configure Network Agent to work as a connection gateway, but pay attention to the list of limitations of Network Agent running on Linux devices.
- Allowing connections in firewalls on the connection gateway
To make sure that Administration Server can actually connect to the connection gateway in the DMZ, allow connections to TCP port 13000 in all firewalls between Administration Server and the connection gateway.
If the connection gateway has no real IP address on the internet, but instead is located behind Network Address Translation (NAT), configure a rule to forward connections through NAT.
- Creating an administration group for external devices
Create a new group under the Managed devices group. This new group will contain external managed devices.
- Connecting the connection gateway to Administration Server
The connection gateway that you have configured is waiting for a connection from Administration Server. However, Administration Server does not list the device with the connection gateway among managed devices. This is because the connection gateway has not tried to establish a connection to Administration Server. Therefore, you need a special procedure to ensure that Administration Server initiates a connection to the connection gateway.
Do the following:
- Add the connection gateway as a distribution point.
- Move the connection gateway from the Unassigned devices group to the group that you have created for external devices.
The connection gateway is connected and configured.
- Connecting external desktop devices to Administration Server
Usually, external desktop devices are not moved inside the perimeter. Therefore, you need to configure them to connect to Administration Server through the gateway when installing Network Agent.
- Setting up updates for external desktop devices
If updates of security applications are configured to be downloaded from Administration Server, external devices download updates through the connection gateway. This has two disadvantages:
- This is unnecessary traffic, which takes up bandwidth of the company's internet communication channel.
- This is not necessarily the quickest way to get updates. It is very likely that it would be cheaper and faster for external devices to receive updates from Kaspersky update servers.
Do the following:
- Connecting traveling laptops to Administration Server
Traveling laptops are within the network sometimes and outside the network at other times. For effective management, you need them to connect to Administration Server differently depending on their location. For efficient use of traffic, they also need to receive updates from different sources, depending on their location.
You need to configure rules for out-of-office users: connection profiles and network location descriptions. Each rule defines the Administration Server instance to which traveling laptops must connect, depending on their location and the Administration Server instance from which they must receive updates.
Scenario: Connecting out-of-office devices through a secondary Administration Server in DMZ
If you want to connect managed devices that are located outside of the main network to Administration Server, you can do it by using a secondary Administration Server located in the demilitarized zone (DMZ).
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that you have done the following:
- A DMZ is organized in your organization's network.
- Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server is deployed on the internal network of the organization.
Stages
This scenario proceeds in stages:
- Selecting a client device in the DMZ
In the DMZ, select a client device that will be used as a secondary Administration Server.
- Installing Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server
Install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server on this client device.
- Creating a hierarchy of Administration Servers
If you place a secondary Administration Server in the DMZ, the secondary Administration Server must receive a connection from the primary Administration Server. To do this, add a new Administration Server as secondary so that the primary Administration Server connects to the secondary Administration Server through port 13000. When combining two Administration Servers into a hierarchy, make sure that port 13291 is accessible on both Administration Servers. Administration Console connects to an Administration Server through port 13291.
- Connecting out-of-office managed devices to the secondary Administration Server
You can connect out-of-office devices to the Administration Server in the DMZ in the same way that the connection is established between Administration Server and managed devices that are located in the main network. Out-of-office managed devices initiate the connection through port 13000.
About connecting out-of-office devices
Some managed devices are always located outside of the main network (for example, devices in a company's regional branches; kiosks, ATMs, and terminals installed at various points of sale; devices in the home offices of employees). Some devices travel outside the perimeter from time to time (for example, laptops of users who visit regional branches or a customer's office).
You still need to monitor and manage the protection of out-of-office devices—receive actual information about their protection status and keep the security applications on them in the up-to-date state. This is necessary because, for example, if such a device is compromised while being away from the main network, it could become a platform for propagating threats as soon as it connects to the main network. To connect out-of-office devices to Administration Server, you can use two methods:
- Connection gateway in the demilitarized zone (DMZ)
See the data traffic scheme: Administration Server on LAN, managed devices on the Internet, connection gateway in use
- Administration Server in DMZ
See the data traffic scheme: Administration Server in DMZ, managed devices on Internet
A connection gateway in the DMZ
A recommended method for connecting out-of-office devices to Administration Server is organizing a DMZ in the organization's network and installing a connection gateway in the DMZ. External devices will connect to the connection gateway, and Administration Server inside the network will initiate a connection to the devices via the connection gateway.
As compared to the other method, this one is more secure:
- You do not need to open access to Administration Server from outside the network.
- A compromised connection gateway does not pose a high risk to the safety of the network devices. A connection gateway does not actually manage anything itself and does not establish any connections.
Also, a connection gateway does not require many hardware resources.
However, this method has a more complicated configuration process:
- To act a device as a connection gateway in the DMZ, you need to install Network Agent and connect it to Administration Server in a specific way.
- You will not be able to use the same address for connecting to Administration Server for all situations. From outside the perimeter, you will need to use not just a different address (connection gateway address), but also a different connection mode: through a connection gateway.
- You also need to define different connection settings for laptops in different locations.
To add a connection gateway to a previously configured network:
- Install the Network Agent in the connection gateway mode.
- Reinstall the Network Agent on devices that you want to connect to the newly added connection gateway.
Administration Server in the DMZ
Another method is installing a single Administration Server in the DMZ.
This configuration is less secure than the other method. To manage external laptops in this case, Administration Server must accept connections from any address on the internet. It will still manage all devices in the internal network, but from the DMZ. Therefore, a compromised Server could cause an enormous amount of damage, despite the low likelihood of such an event.
The risk gets significantly lower if Administration Server in the DMZ does not manage devices in the internal network. Such a configuration can be used, for example, by a service provider to manage the devices of customers.
You might want to use this method in the following cases:
- If you are familiar with installing and configuring Administration Server, and do not want to perform another procedure to install and configure a connection gateway.
- If you need to manage more devices. The maximum capacity of Administration Server is 100,000 devices, while a connection gateway can support up to 10,000 devices.
This solution also has possible difficulties:
- Administration Server requires more hardware resources and one more database.
- Information about devices will be stored in two unrelated databases (for Administration Server inside the network and another one in the DMZ), which complicates monitoring.
- To manage all devices, Administration Server needs to be joined into a hierarchy, which complicates not only monitoring but also management. A secondary Administration Server instance imposes limitations on the possible structures of administration groups. You have to decide how and which tasks and policies to distribute to a secondary Administration Server instance.
- Configuring external devices to use Administration Server in the DMZ from the outside and to use the primary Administration Server from the inside is not simpler than to just configure them to use a conditional connection through a gateway.
- High security risks. A compromised Administration Server instance makes it easier to compromise its managed laptops. If this happens, the hackers just need to wait for one of the laptops to return to the corporate network so that they can continue their attack on the local area network.
Connecting external desktop devices to Administration Server
Desktop devices that are always outside of the main network (for example, devices in the company's regional branches; kiosks, ATMs, and terminals installed at various points of sale; devices in the home offices of employees) cannot be connected to Administration Server directly. They must be connected to Administration Server via a connection gateway that is installed in the demilitarized zone (DMZ). This configuration is made when installing Network Agent on those devices.
To connect external desktop devices to Administration Server:
- Create a new installation package for Network Agent.
- Open the properties of the created installation package and go to the Advanced section, and then select the Connect to Administration Server by using a connection gateway option.
The Connect to Administration Server by using a connection gateway setting is incompatible with the Use Network Agent as a connection gateway in DMZ setting. You cannot enable both of these settings at the same time.
- In Connection gateway address, specify the public address of the connection gateway.
If the connection gateway is located behind Network Address Translation (NAT) and does not have its own public address, configure a NAT gateway rule for forwarding connections from the public address to the internal address of the connection gateway.
- Create a stand-alone installation package based on the created installation package.
- Deliver the stand-alone installation package to the target devices, either electronically or on a removable drive.
- Install Network Agent from the stand-alone package.
External desktop devices are connected to Administration Server.
Page top
About connection profiles for out-of-office users
Out-of-office users of laptops (hereinafter also referred to as "devices") may need to change the method of connecting to an Administration Server or switch between Administration Servers depending on the current location of the device on the enterprise network.
Connection profiles are supported only for devices running Windows and macOS.
Using different addresses of a single Administration Server
Devices with Network Agent installed can connect to the Administration Server either from the organization's intranet or from the internet. This situation may require Network Agent to use different addresses for connection to Administration Server: the external Administration Server address for the Internet connection and the internal Administration Server address for the internal network connection.
To do this, you must add a profile (for connection to Administration Server from the Internet) to the Network Agent policy. Add the profile in the policy properties (Connectivity section, Connection profiles subsection). In the profile creation window, you must disable the Use to receive updates only option and select the Synchronize connection settings with the Administration Server settings specified in this profile option. If you use a connection gateway to access Administration Server (for example, in a Kaspersky Security Center configuration as that described in Internet access: Network Agent as connection gateway in DMZ), you must specify the address of the connection gateway in the corresponding field of the connection profile.
Switching between Administration Servers depending on the current network
If the organization has multiple offices with different Administration Servers and some of the devices with Network Agent installed move between them, you need Network Agent to connect to the Administration Server of the local network in the office where the device is currently located.
In this case, you must create a profile for connection to Administration Server in the properties of the policy of Network Agent for each of the offices, except for the home office where the original home Administration Server is located. You must specify the addresses of Administration Servers in connection profiles and enable or disable the Use to receive updates only option:
- Select the option if you need Network Agent to be synchronized with the home Administration Server, while using the local Server for downloading updates only.
- Disable this option if it is necessary for Network Agent to be managed completely by the local Administration Server.
After that, you must set up the conditions of switching to the newly created profiles: at least one condition for each of the offices, except for the home office. Every condition's purpose consists in detection of items that are specific for an office's network environment. If a condition is true, the corresponding profile gets activated. If none of the conditions is true, Network Agent switches to the home Administration Server.
Creating a connection profile for out-of-office users
An Administration Server connection profile is available only on devices running Windows and macOS.
To create a profile for connecting Network Agent to Administration Server for out-of-office users:
- In the console tree, select the administration group containing the client devices for which you need to create a profile for connecting Network Agent to the Administration Server.
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to create a connection profile for all devices in the group, select a Network Agent policy in the group workspace, on the Policies tab. Open the properties window of the selected policy.
- If you want to create a connection profile for a device in a group, select that device in the group workspace, on the Devices tab, and perform the following actions:
- Open the properties window of the selected device.
- In the Applications section of the device properties window, select Network Agent.
- Open the Network Agent properties window.
- In the properties window, in the Connectivity section, select the Connection profiles subsection.
- In the Administration Server connection profiles settings group, click the Add button.
By default, the list of connection profiles contains the <Offline mode> and <Home Administration Server> profiles. Profiles cannot be edited or removed.
The <Offline mode> profile does not specify any Server for connection. Therefore, Network Agent, when switched to that profile, does not attempt to connect to any Administration Server while applications installed on client devices run under out-of-office work policies. The <Offline mode> profile can be used if devices are disconnected from the network.
The <Home Administration Server> profile specifies the connection for Administration Server that was selected during Network Agent installation. The <Home Administration Server> profile is applied when a device is reconnected to the home Administration Server after it was running on an external network for some time.
- In the New profile window that opens, configure the connection profile:
- Profile name
- Administration Server
- Port
- SSL port
- Use SSL
- Click the Configure connection through proxy server link to configure connection through a proxy server. Select the Use proxy server option if you want to use a proxy server when connecting to the internet. If this option is selected, fields are available for entering settings. Specify the following settings for a proxy server connection:
- Proxy server address
- Port number
- Proxy server authentication
- User name (this field is available if the Proxy server authentication option is selected)
- Password (this field is available if the Proxy server authentication option is selected)
- Connection gateway settings
- Enable out-of-office mode
- Use to receive updates only
- Synchronize connection settings with the Administration Server settings specified in this profile
- Select the Enable out-of-office mode when Administration Server is not available option to allow the applications installed on a client device to use policy profiles for devices in out-of-office mode, as well as out-of-office policies, at any connection attempt if the Administration Server is not available. If no out-of-office policy has been defined for the application, the active policy will be used.
A profile for connecting Network Agent to Administration Server is created for out-of-office users. When Network Agent connects to Administration Server by using this profile, applications installed on the client device will use policies for devices in out-of-office mode or out-of-office policies.
About switching Network Agent to other Administration Servers
The initial settings of the Network Agent connection to Administration Server are defined when installing the Network Agent. To switch the Network Agent to other Administration Servers, you can use the switching rules. This feature is supported only for Network Agents installed on devices running Windows or macOS.
The switching rules can trigger on changing the following network parameters:
- Default gateway address.
- IP address of the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server.
- DNS suffix of the subnet.
- IP address of the network DNS server.
- Windows domain accessibility. This parameter is available only for devices running Windows.
- Subnet address and mask.
- IP address of the network WINS server. This parameter is available only for devices running Windows.
- DNS or NetBIOS name of the client device.
- SSL connection address accessibility.
If rules for switching the Network Agent to other Administration Servers have been created, the Network Agent responds to changes in the network parameters as follows:
- If the network settings comply with one of the rules created, Network Agent connects to the Administration Server specified in this rule. Applications installed on client devices switch to out-of-office policies, provided such behavior is enabled by a rule.
- If none of the rules apply, Network Agent reverts to the default settings of connection to the Administration Server specified during the installation. Applications installed on client devices switch back to active policies.
- If the Administration Server is not accessible, Network Agent uses out-of-office policies.
Network Agent switches to the out-of-office policy only if the Enable out-of-office mode when Administration Server is not available option is enabled in the Network Agent policy settings.
The settings of Network Agent connection to Administration Server are saved in a connection profile. In the connection profile, you can create rules for switching client devices to out-of-office policies, and you can configure the profile so that it could only be used for downloading updates.
Creating a Network Agent switching rule by network location
Network Agent-switching by network location is available only on devices running Windows and macOS.
To create a rule for Network Agent switching from one Administration Server to another if network settings change:
- In the console tree, select the administration group containing the devices for which you need to create a Network Agent switching rule by the network location description.
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to create a rule for all devices in the group, go to the group workspace and select a Network Agent policy on the Policies tab. Open the properties window of the selected policy.
- If you want to create a rule for a device selected from a group, go to the group workspace, select the device on the Devices tab, and perform the following actions:
- Open the properties window of the selected device.
- In the Applications section of the device properties window, select Network Agent.
- Open the Network Agent properties window.
- In the Properties window that opens, in the Connectivity section, select the Connection profiles subsection.
- In the Network location settings section, click the Add button.
- In the New description window that opens, configure the network location description and switching rule. Specify the following network location description settings:
- In the Switch conditions section, click the Add button to create a list of network location description conditions.
The conditions in a rule are combined by using the logical AND operator. To trigger a switching rule by the network location description, all of the rule switching conditions must be met.
- In the drop-down list, select the value that corresponds to the change in characteristics of the network to which the client device is connected:
- Default connection gateway address—The address of the main network gateway has changed.
- DHCP server address—The IP address of the network Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server has changed.
- DNS domain—The DNS suffix of the subnet has changed.
- DNS server address—The IP address of the network DNS server has changed.
- Windows domain accessibility (Windows only)—Changes the status of the Windows domain to which the client device is connected. Use this setting only for devices running Windows.
- Subnet—Changes the subnet address and mask.
- WINS server address (Windows only)—The IP address of the network WINS server has changed. Use this setting only for devices running Windows.
- Name resolvability—The DNS or NetBIOS name of the client device has changed.
- SSL connection address accessibility—The client device can or cannot (depending on the option that you select) establish an SSL connection with a specified Server (name:port). For each server, you can additionally specify an SSL certificate. In this case, the Network Agent verifies the Server certificate in addition to checking the capability of an SSL connection. If the certificate does not match, the connection fails.
- In the window that opens, specify the condition for Network Agent to be switched to another Administration Server. The name of the window depends on the value selected during the previous step. Specify the following settings of the switching condition:
- In the New description window, select the Description enabled option to enable the use of the new network location description.
A new switching rule by the network location description is created; any time its conditions are met, the Network Agent uses the connection profile specified in the rule to connect to the Administration Server.
The network location descriptions are checked for a match to the network layout in the order of their appearance in the list. If a network matches several descriptions, the first one will be used. You can change the order of rules on the list using the Up button (![]() ) and Down button (
) and Down button (![]() ).
).
Notifications of events
This section describes how to select a method for delivering administrator notifications about events on client devices, and how to configure event notification settings.
It also describes how to test the distribution of event notifications by using the Eicar test virus.
Configuring event notification
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to select a method of notifying the administrator of events on client devices and to configure notification:
- Email. When an event occurs, the application sends a notification to email addresses specified. You can edit the text of the notification.
- SMS. When an event occurs, the application sends a notification to the phone numbers specified. You can configure SMS notifications to be sent through the mail gateway.
- Executable file. When an event occurs on a device, the executable file is started on the administrator's workstation. Using the executable file, the administrator can receive the parameters of any event that has occurred.
To configure notification of events occurring on client devices:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Events tab.
- Click the Configure notifications and event export link and select the Configure notifications value in the drop-down list.
This opens the Properties: Events window.
- In the Notification section, select a notification method (by email, by SMS, or by running an executable file) and define the notification settings:
- In the Notification message field, enter the text that the application will send when an event occurs.
You can use the drop-down list to the right of the text field to add substitution settings with event details (for example, event description, or time of occurrence).
If the notification text contains a percent (%), you must specify it twice in succession to allow message sending. For example, "CPU load is 100%%".
- Click the Send test message button to check whether notification has been configured correctly.
The application sends a test notification to the specified user.
- Click OK to save the changes.
The re-adjusted notification settings are applied to all events that occur on client devices.
You can override notification settings for certain events in the Event configuration section of the Administration Server settings, of a policy settings, or of an application settings.
Testing notifications
To check whether event notifications are sent, the application uses the notification of the EICAR test "virus" detection on client devices.
To verify sending of event notifications:
- Stop the real-time file system protection task on a client device and copy the EICAR test "virus" to that client device. Now re-enable real-time protection of the file system.
- Run a scan task for client devices in an administration group or for specific devices, including one with the EICAR "virus".
If the scan task is configured correctly, the test "virus" will be detected. If notifications are configured correctly, you are notified that a virus has been detected.
In the workspace of the Administration Server node, on the Events tab, the Recent events selection displays a record of detection of a "virus".
The EICAR test "virus" contains no code that can do harm to your device. However, most manufacturers' security applications identify this file as virus. You can download the test "virus" from the official EICAR website.
Page top
Event notifications displayed by running an executable file
Kaspersky Security Center can notify the administrator about events on client devices by running an executable file. The executable file must contain another executable file with placeholders of the event to be relayed to the administrator (see the table below).
Placeholders for describing an event
Placeholder |
Placeholder description |
|---|---|
%SEVERITY% |
Event severity. Possible values:
|
%COMPUTER% |
Name of the device where the event occurred. Maximum length of the device name is 256 characters. |
%DOMAIN% |
Domain name of the device where the event occurred. |
%EVENT% |
Name of the event type. Maximum length of the event type name is 50 characters. |
%DESCR% |
Event description. Maximum length of the description is 1000 characters. |
%RISE_TIME% |
Event creation time. |
%KLCSAK_EVENT_TASK_DISPLAY_NAME% |
Task name. Maximum length of the task name is 100 characters. |
%KL_PRODUCT% |
Product name. |
%KL_VERSION% |
Product version number. |
%KLCSAK_EVENT_SEVERITY_NUM% |
Event severity number. Possible values:
|
%HOST_IP% |
IP address of the device where the event occurred. |
%HOST_CONN_IP% |
Connection IP address of the device where the event occurred. |
Example: Event notifications are sent by an executable file (such as script1.bat) inside which another executable file (such as script2.bat) with the %COMPUTER% placeholder is launched. When an event occurs, the script1.bat file is run on the administrator's device, which, in turn, runs the script2.bat file with the %COMPUTER% placeholder. The administrator then receives the name of the device where the event occurred. |
Encrypt communication with TLS
To fix vulnerabilities on your organization's corporate network, you can enable traffic encryption by using the TLS protocol. You can enable TLS encryption protocols and supported cipher suites on Administration Server and iOS MDM Server. Kaspersky Security Center supports the TLS protocol versions 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, and 1.3. You can select the required encryption protocol and cipher suites.
Kaspersky Security Center uses self-signed certificates. Additional configuration of the iOS devices is not required. You can also use your own certificates. Kaspersky specialists recommend to use certificates issued by trusted certificate authorities.
Administration Server
To configure allowed encryption protocols and cipher suites on Administration Server:
- Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
- Use the SrvUseStrictSslSettings flag to configure allowed encryption protocols and cipher suites on Administration Server. Enter the following command:
klscflag -fset -pv ".core/.independent" -s Transport -n SrvUseStrictSslSettings -v <value> -t dSpecify the <value> parameter of the SrvUseStrictSslSettings flag:
4—Only the TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 protocols are enabled. Also, cipher suites with TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 are enabled (these cipher suites are needed for backward compatibility with the previous versions of Kaspersky Security Center). This is the default value.Cipher suites supported for the TLS 1.2 protocol:
- ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
- ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384
- ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305
- AES256-GCM-SHA384 (cipher suite with TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384)
- ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
- ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
Cipher suites supported for the TLS 1.3 protocol:
- TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
- TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_AES_128_CCM_SHA256
5—Only the TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 protocols are enabled. For the TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 protocols, the specific cipher suites listed below are supported.Cipher suites supported for the TLS 1.2 protocol:
- ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
- ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384
- ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305
- ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
- ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
Cipher suites supported for the TLS 1.3 protocol:
- TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
- TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_AES_128_CCM_SHA256
We do not recommend using 0, 1, 2, or 3 as the parameter value of the SrvUseStrictSslSettings flag. These parameter values correspond to insecure TLS protocol versions (the TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1 protocols) and insecure cipher suites, and are used only for backward compatibility with earlier Kaspersky Security Center versions.
- Restart the following Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 services:
- Administration Server
- Web Server
- Activation Proxy
Traffic encryption by using the TLS protocol is enabled.
You can use the KLTR_TLS12_ENABLED and KLTR_TLS13_ENABLED flags to enable the support of the TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 protocols respectively. These flags are enabled by default.
To enable or disable the support of the TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 protocols:
- Run the klscflag utility.
Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
- Enter the one of the following commands at the Windows command prompt, using administrator rights:
- Use this command to enable or disable the support of the TLS 1.2 protocol:
klscflag -fset -pv ".core/.independent" -s Transport -n KLTR_TLS12_ENABLED -v <value> -t d - Use this command to enable or disable the support of the TLS 1.3 protocol:
klscflag -fset -pv ".core/.independent" -s Transport -n KLTR_TLS13_ENABLED -v <value> -t d
Specify the <value> parameter of the flag:
1—To enable the support of the TLS protocol.0—To disable the support of the TLS protocol.
- Use this command to enable or disable the support of the TLS 1.2 protocol:
iOS MDM Server
The connection between the iOS devices and the iOS MDM Server is encrypted by default.
To configure allowed encryption protocols and cipher suites on the iOS MDM Server:
- Open the system registry of the client device with iOS MDM Server installed (for example, locally, using the regedit command in the Start → Run menu).
- Go to the following hive:
- For 32-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\Components\34\Connectors\KLIOSMDM\1.0.0.0\Conset
- For 64-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\34\Connectors\KLIOSMDM\1.0.0.0\Conset
- For 32-bit systems:
- Create a key with the
StrictSslSettingsname. - Specify
DWORDas the key type. - Set the key value:
2—The TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, and TLS 1.2 protocols are enabled.3—Only the TLS 1.2 protocol is enabled (default value).
- Restart the Kaspersky Security Center iOS MDM Server service.
Configuring the interface
You can configure the Kaspersky Security Center interface:
- Show and hide objects in the console tree, workspace, and properties windows of objects (folders, sections), depending on the features being used.
- Show and hide elements of the main window (for example, console tree or standard menus such as Actions and View).
To configure the Kaspersky Security Center interface in accordance with the currently used set of features:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- On the menu bar of the main application window, select View → Configure interface.
- In the Configure interface window that opens, configure the display of interface elements using the following check boxes:
- Click OK.
To apply some of the changes, you have to close the main application window and then open it again.
To configure the display of elements in the main application window:
- On the menu bar of the main application window, select View → Configure.
- In the Configure view window that opens, configure the display of main window elements by using check boxes.
- Click OK.
Discovering networked devices
This section describes steps you must take after the Kaspersky Security Center installation.
Scenario: Discovering networked devices
You must perform device discovery before installation of the security applications. The Administration Server receives information about discovered devices and allows you to manage the devices through policies. Regular network polls are needed to update the list of devices available in the network.
Before you start network polling, make sure that the SMB protocol is enabled. Otherwise, Kaspersky Security Center cannot discover devices in the polled network. To enable the SMB protocol, follow the instructions for your operating system.
Discovery of networked devices proceeds in the following stages:
- Discover devices
The quick start wizard guides you through initial device discovery, and helps you find networked devices such as computers, tablets, and mobile phones. You can also perform device discovery manually.
- Configure scheduled polls
Decide which polling type(s) you want to use regularly. Enable the desired types and configure the poll schedule as you see fit. You can refer to the recommendations for network polling frequency.
- Set up rules for adding discovered devices to administration groups (Optional)
If new devices appear on your network, they are discovered during regular polls and are automatically included in the Unassigned devices group. You can set up device moving rules to automate the allocation of devices to the Managed devices group. You can also configure retention rules.
If you skip the step 3, the newly discovered devices are allocated to the Unassigned devices group. If you want, you can move these devices to the Managed devices group manually. If you move the devices to the Managed devices group manually, you can analyze information about each device and decide whether you want to move it to an administration group, and, if so, to which exact group.
Results
Completion of the scenario yields the following:
- Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server discovers the devices that are on the network and provides you with information about them.
- Future polls are set up and are conducted according to the specified schedule.
- The newly discovered devices are arranged according to the configured rules. (Or, if no rules are configured, the devices stay in the Unassigned devices group).
Unassigned devices
This section provides information about how to manage devices on an enterprise network if they are not included in an administration group.
Device discovery
This section describes the types of device discovery available in Kaspersky Security Center and provides information using each type.
The Administration Server receives information about the structure of the network and devices on this network through regular polling. The information is recorded to the Administration Server database. Administration Server can use the following types of polling:
- Windows network polling. The Administration Server can perform two kinds of Windows network poll: quick and full. During a quick poll, the Administration Server only retrieves information from the list of the NetBIOS names of devices in all network domains and workgroups. During a full poll, more information is requested from each client device, such as operating system name, IP address, DNS name, and NetBIOS name. By default, both quick poll and full poll are enabled. Windows network polling may fail to discover devices, for example, if the ports UDP 137, UDP 138, TCP 139 are closed on the router or by the firewall.
- Active Directory polling. The Administration Server retrieves information about the Active Directory unit structure and about DNS names of the devices from Active Directory groups. By default, this type of polling is enabled. We recommend that you use Active Directory polling if you use Active Directory; otherwise, the Administration Server does not discover any devices. If you use Active Directory but some of the networked devices are not listed as members, these devices cannot be discovered by Active Directory polling.
- IP range polling. The Administration Server polls the specified IP ranges using ICMP packets or the NBNS protocol and compiles a complete set of data on devices within those IP ranges. By default, this type of polling is disabled. It is not recommended to use this type of polling if you use Windows network polling and/or Active Directory polling.
- Zeroconf polling. A distribution point that polls the IPv6 network by using zero-configuration networking (also referred to as Zeroconf). By default, this type of polling is disabled. You can use Zeroconf polling if the distribution point runs Linux.
If you set up and enabled device moving rules, the newly discovered devices are automatically included in the Managed devices group. If no moving rules have been enabled, the newly discovered devices are automatically included in the Unassigned devices group.
You can modify device discovery settings for each type. For example, you may want to modify the polling schedule or to set whether to poll the entire domain forest or only a specific domain.
Before you start network polling, make sure that the SMB protocol is enabled. Otherwise, Kaspersky Security Center cannot discover devices in the polled network. To enable the SMB protocol, follow the instructions for your operating system.
Windows network polling
About Windows network polling
During a quick poll, the Administration Server only retrieves information from the list of the NetBIOS names of devices in all network domains and workgroups. During a full poll, the following information is requested from each client device:
- Operating system name
- IP address
- DNS name
- NetBIOS name
Both quick polls and full polls require the following:
- Ports UDP 137/138, TCP 139, UDP 445, TCP 445 must be available in the network.
- The SMB protocol is enabled.
- The Microsoft Computer Browser service must be used, and the primary browser computer must be enabled on the Administration Server.
- The Microsoft Computer Browser service must be used, and the primary browser computer must be enabled on the client devices:
- On at least one device, if the number of networked devices does not exceed 32.
- On at least one device for each 32 networked devices.
The full poll can run only if the quick poll has run at least once.
Viewing and modifying the settings for Windows network polling
To modify the settings for the Windows network polling:
- In the console tree, in the Device discovery folder, select the Domains subfolder.
You can proceed from the Unassigned devices folder to the Device discovery folder by clicking the Poll now button.
In the workspace of the Domains subfolder, the list of the devices is displayed.
- Click Poll now.
The domain properties window opens. If you want, modify the settings of Windows network polling:
If you want to perform the poll immediately, click Poll now. Both types of polls will start.
On the virtual Administration Server you can view and edit the polling settings of the Windows network in the properties window of the distribution point, in the Device discovery section.
Active Directory polling
Use Active Directory polling if you use Active Directory; otherwise, it is recommended to use other poll types. If you use Active Directory but some of the networked devices are not listed as members, these devices cannot be discovered by Active Directory polling.
Before you start network polling, make sure that the SMB protocol is enabled. Otherwise, Kaspersky Security Center cannot discover devices in the polled network. To enable the SMB protocol, follow the instructions for your operating system.
Viewing and modifying the settings for Active Directory polling
To view and modify the settings for polling Active Directory groups:
- In the console tree, in the Device discovery folder, select the Active Directory subfolder.
Alternatively, you can proceed from the Unassigned devices folder to the Device discovery folder by clicking the Poll now button.
- Click Configure polling.
The Active Directory properties window opens. If you want, modify the settings of Active Directory group polling:
If you want to perform the poll immediately, click the Poll now button.
On the virtual Administration Server, you can view and edit the polling settings of Active Directory groups in the properties window of the distribution point, in the Device discovery section.
IP range polling
The Administration Server polls the specified IP ranges using ICMP packets or the NBNS protocol and compiles a complete set of data on devices within those IP ranges. By default, this type of polling is disabled. It is not recommended to use this type of polling if you use Windows network polling and/or Active Directory polling.
Before you start network polling, make sure that the SMB protocol is enabled. Otherwise, Kaspersky Security Center cannot discover devices in the polled network. To enable the SMB protocol, follow the instructions for your operating system.
Viewing and modifying the settings for IP range polling
To view and modify the settings for polling IP range groups:
- In the console tree, in the Device discovery folder, select the IP ranges subfolder.
You can proceed from the Unassigned devices folder to the Device discovery folder by clicking Poll now.
- If you want, in the IP ranges subfolder click Add subnet to add an IP range for polling, and then click OK.
- Click Configure polling.
The IP ranges properties window opens. If you want, you can modify the settings of IP range polling:
If you want to perform the poll immediately, click Poll now. This button is only available if you selected Enable IP range polling.
On the virtual Administration Server, you can view and edit the settings for IP range polling in the distribution point properties window, in the Device discovery section. Client devices discovered during the poll of IP ranges are displayed in the Domains folder of the virtual Administration Server.
Zeroconf polling
This polling type is supported only for Linux-based distribution points.
A distribution point can poll networks that have devices with IPv6 addresses. In this case, IP ranges are not specified and the distribution point polls the whole network by using zero-configuration networking (referred to as Zeroconf). To start using Zeroconf, you must install the avahi-browse utility on the distribution point.
To enable Zeroconf polling:
- In the console tree, in the Device discovery folder, select the IP ranges subfolder.
You can proceed from the Unassigned devices folder to the Device discovery folder by clicking Poll now.
- Click Configure polling.
- In the IP ranges properties window that opens, select Enable polling with Zeroconf technology.
After that, the distribution point starts to poll your network. In this case, the specified IP ranges are ignored.
Page top
Working with Windows domains. Viewing and changing the domain settings
To modify the domain settings:
- In the console tree, in the Device discovery folder, select the Domains subfolder.
- Select a domain and open its properties window in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Properties in the context menu of the domain.
- By clicking the Show group properties link.
The Properties: <Domain name> window opens where you can configure the selected domain.
Configuring retention rules for unassigned devices
After Windows network polling is complete, the found devices are placed into subgroups of the Unassigned devices administration group. This administration group can be found at Advanced → Device discovery → Domains. The Domains folder is the parent group. It contains child groups named after the corresponding domains and workgroups that have been found during the network polling. The parent group may also contain the administration group of mobile devices. You can configure the retention rules of the unassigned devices for the parent group and for each of the child groups. The retention rules do not depend on the network polling settings and work even if the network polling is disabled.
To configure retention rules for unassigned devices:
- In the console tree, in the Device discovery folder, do one of the following:
- To configure settings of the parent group, right-click the Domains subfolder and select Properties.
The parent group properties window opens.
- To configure settings of a child group, right-click its name and select Properties.
The child group properties window opens.
- To configure settings of the parent group, right-click the Domains subfolder and select Properties.
- In the Devices section, specify the following settings:
Your changes are saved and applied.
Creating an IP range
To create an IP range:
- In the console tree, in the Device discovery folder, select the IP ranges subfolder.
- In the context menu of the folder, select New → IP range.
- In the New IP range window that opens, set up the new IP range.
The new IP range appears in the IP ranges folder.
Viewing and changing the IP range settings
To modify the IP range settings:
- In the console tree, in the Device discovery folder select the IP ranges subfolder.
- Select an IP range and open its properties window in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Properties in the context menu of the IP range.
- By clicking the Show group properties link.
The Properties: <IP range name> window opens where you can configure the properties of the selected IP range.
Working with the Active Directory groups. Viewing and modifying group settings
To modify the settings for the Active Director group:
- In the console tree, in the Device discovery folder, select the Active Directory subfolder.
- Select an Active Directory group and open its properties window in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Properties in the context menu of the IP range.
- By clicking the Show group properties link.
The Properties: <Active Directory group name> window opens where you can configure the selected Active Directory group.
Creating rules for moving devices to administration groups automatically
You can configure devices to be moved automatically to administration groups after they are discovered during a poll on an enterprise network.
To configure rules for moving devices to administration groups automatically:
- In the console tree, select the Unassigned devices folder.
- In the workspace of this folder, click Configure rules.
This opens the Properties: Unassigned devices window. In the Move devices section, configure the rules to move devices to administration groups automatically.
The first applicable rule in the list (from the top to the bottom of the list) will be applied to a device.
Using VDI dynamic mode on client devices
A virtual infrastructure can be deployed on a corporate network using temporary virtual machines. Kaspersky Security Center detects temporary virtual machines and adds information about them to the Administration Server database. After a user finishes using a temporary virtual machine, the machine is removed from the virtual infrastructure. However, a record about the removed virtual machine can be saved in the database of the Administration Server. Also, nonexistent virtual machines can be displayed in Administration Console.
To prevent information about nonexistent virtual machines from being saved, Kaspersky Security Center supports dynamic mode for Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI). The administrator can enable support of dynamic mode for VDI in the properties of the installation package of Network Agent to be installed on the temporary virtual machine.
When a temporary virtual machine is disabled, Network Agent notifies the Administration Server that the machine has been disabled. If the virtual machine has been disabled successfully, it is removed from the list of devices connected to the Administration Server. If the virtual machine is disabled with errors and Network Agent does not send a notification about the disabled virtual machine to the Administration Server, a backup scenario is used. In this scenario, the virtual machine is removed from the list of devices connected to the Administration Server after three unsuccessful attempts to synchronize with the Administration Server.
Enabling VDI dynamic mode in the properties of an installation package for Network Agent
To enable VDI dynamic mode:
- In the Remote installation folder of the console tree, select the Installation packages subfolder.
- In the context menu of the Network Agent installation package, select Properties.
The Properties: Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent window opens.
- In the Properties: Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent window, select the Advanced section.
- In the Advanced section, select the Enable dynamic mode for VDI option.
The device on which Network Agent is to be installed will be a part of VDI.
Searching for devices that are part of VDI
To find unassigned devices that make up part of VDI:
- Select Search from the context menu of the Unassigned devices folder.
To see a list of all devices that are part of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure, select Search from the context menu of the Administration Server folder.
- In the Search window, on the Virtual machines tab, select Yes in the Part of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure settings group.
- Click the Find now button.
The list of unassigned devices that are part of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure is displayed.
Moving devices from VDI to an administration group
To move devices that are part of VDI to an administration group:
- In the workspace of the Unassigned devices folder, click Configure rules.
This opens the properties window of the Unassigned devices folder.
- In the properties window of the Unassigned devices folder, in the Move devices section, click the Add button.
The New rule window opens.
- In the New rule window, select the Virtual machines section.
- In the This is a virtual machine drop-down list, select Yes.
A rule will be created for device relocation to an administration group.
Equipment inventory
The hardware list (Repositories → Hardware) that you use to inventory equipment is populated in two ways: automatically and manually. After each network polling, all detected devices are added to the list automatically; however, you can also add devices manually if you do not want to poll the network. You can add other devices to the list manually, for example, routers, printers, or device hardware.
In the properties of a device, you can view and edit detailed information about that device.
The hardware list may contain the following types of devices:
- Computers
- Mobile devices
- Network devices
- Virtual devices
- OEM components
- Computer peripherals
- Connected devices
- VoIP phones
- Network repositories
The administrator can assign the Enterprise equipment attribute to detected devices. This attribute can be assigned manually in the properties of a device, or the administrator can specify criteria for the attribute to be assigned automatically. In this case, the Enterprise equipment attribute is assigned by device type.
Kaspersky Security Center allows writing off equipment. To do this, select the Device is written off option in the properties of a device. The device is not displayed on the equipment list.
An administrator can manage the list of programmable logic controllers (PLC) in the Hardware folder. Detailed information on managing the PLC list is provided in the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Nodes User Guide.
Adding information about new devices
To add information about new devices on the network:
- In the Repositories folder of the console tree, select the Hardware subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Hardware folder, click the Add device button to open the New device window.
The New device window opens.
- In the New device window, in the Type drop-down list select a device type that you want to add.
- Click OK.
The device properties window opens on the General section.
- In the General section, fill in the entry fields with data on the device. The General section lists the following settings:
- Enterprise device. Select the check box if you want to assign the Enterprise attribute to the device. Using this attribute, you can search for devices in the Hardware folder.
- Device is written off. Select the check box if you do not want the device to be displayed in the list of devices in the Hardware folder.
- Click Apply.
The new device will be displayed in the workspace of the Hardware folder.
Configuring criteria used to define enterprise devices
To configure criteria of detection for enterprise devices:
- In the Repositories folder of the console tree, select the Hardware subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Hardware folder, click the Additional actions button and select Set up rule for Enterprise devices in the drop-down list.
The hardware properties window opens.
- In the hardware properties window, in the Enterprise devices section, select a method for assigning the Enterprise attribute to the device:
- Set the Enterprise device attribute manually for the device. The Enterprise hardware attribute is assigned to the device manually in the device properties window, in the General section.
- Set the Enterprise device attribute automatically for the device. In the By device type block of settings, specify device types to which the application will automatically assign the Enterprise attribute.
This option affects only the devices that were added through network polling. For the devices added manually, set the Enterprise attribute manually.
- Click OK.
The criteria of detection for enterprise devices are configured.
Configuring custom fields
To configure custom fields of devices:
- In the Repositories folder of the console tree, select the Hardware subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Hardware folder, click the Additional actions button and select Configure custom data fields in the drop-down list.
The hardware properties window opens.
- In the hardware properties window, select the Custom fields section and click the Add button.
The Add field window opens.
- In the Add field window, specify the name of the custom field that will be displayed in the hardware properties.
You can create multiple custom fields with unique names.
- Click OK.
The custom fields that have been added are displayed in the Custom fields section of the hardware properties. You can use custom fields to provide specific information about devices. For example, this could be the internal order number for a hardware purchase.
Licensing
This section provides information about general concepts related to Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 licensing.
Events of the licensing limit exceeded
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to get information about events when some licensing limits are exceeded by Kaspersky applications installed on client devices.
The importance level of such events when a licensing limit is exceeded is defined according to the following rules:
- If the currently used units covered by a single license constitute 90% to 100% of the total number of units covered by the license, the event is published with the Info importance level.
- If the currently used units covered by a single license constitute 100% to 110% of the total number of units covered by the license, the event is published with the Warning importance level.
- If the number of currently used units covered by a single license exceeds 110% of the total number of units covered by the license, the event is published with the Critical event importance level.
About licensing
This section contains information about the licensing of Kaspersky applications managed via Kaspersky Security Center.
About the license
A license is a time-limited right to use Kaspersky Security Center, granted under the terms of the signed License Contract (End User License Agreement).
The scope of services and validity period depend on the license under which the application is used.
The following license types are provided:
- Trial
A free license intended for trying out the application. A trial license usually has a short term.
When a trial license expires, all Kaspersky Security Center features become disabled. To continue using the application, you need to purchase a commercial license.
You can use the application under a trial license for only one trial period.
- Commercial
A paid license.
When a commercial license expires, key features of the application become disabled. To continue using Kaspersky Security Center, you must renew your commercial license. After a commercial license expires, you cannot continue using the application and must remove it from your device.
We recommend renewing your license before it expires, to ensure uninterrupted protection against all security threats.
About the End User License Agreement
The End User License Agreement (License Agreement or EULA) is a binding agreement between you and AO Kaspersky Lab stipulating the terms under which you may use the application.
Please carefully read the License Agreement before you start using the application.
Kaspersky Security Center and its components, for example, Network Agent, have their own EULA.
You can view the terms of the End User License Agreement for Kaspersky Security Center using the following methods:
- During installation of Kaspersky Security Center.
- By reading the license.txt document included in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit.
- By reading the license.txt document in the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder.
- By downloading the license.txt file from the Kaspersky website.
You can view the terms of the End User License Agreement for Network Agent for Windows, Network Agent for Mac, and Network Agent for Linux by using the following methods:
- During downloading of the Network Agent distribution package from the Kaspersky web servers.
- During installation of Network Agent for Windows, Network Agent for Mac, or Network Agent for Linux.
- By reading the license.txt document included in the Network Agent for Windows, Network Agent for Mac, or Network Agent for Linux distribution package.
- By reading the license.txt document in the Network Agent for Windows, Network Agent for Mac, or Network Agent for Linux installation folder.
- By downloading the license.txt file from the Kaspersky website.
You accept the terms of the End User License Agreement by confirming that you agree with the End User License Agreement when installing the application. If you do not accept the terms of the License Agreement, cancel the application installation and do not use the application.
Page top
About the license certificate
A license certificate is a document that you receive along with a key file or an activation code.
A license certificate contains the following information about the license provided:
- License key or order number
- Information about the user who has been granted the license
- Information about the application that can be activated under the license provided
- Limit of the number of licensing units (e.g., devices on which the application can be used under the license provided)
- License validity start date
- License expiration date or license term
- License type
About the license key
A license key is a sequence of bits that you can apply to activate and then use the application in accordance with the terms of the End User License Agreement. License keys are generated by Kaspersky specialists.
You can add a license key to the application using one of the following methods: by applying a key file or by entering an activation code. The license key is displayed in the application interface as a unique alphanumeric sequence after you add it to the application.
The license key may be blocked by Kaspersky in case the terms of the License Agreement have been violated. If the license key has been blocked, you need to add another one if you want to use the application.
A license key may be active or additional (or reserve).
An active license key is a license key that is currently used by the application. An active license key can be added for a trial or commercial license. The application cannot have more than one active license key.
An additional (or reserve) license key is a license key that entitles the user to use the application, but is not currently in use. The additional license key automatically becomes active when the license associated with the current active license key expires. An additional license key can be added only if an active license key has already been added.
A license key for a trial license can be added as an active license key. A license key for a trial license cannot be added as an additional license key.
Page top
About the key file
A key file is a file with the .key extension provided to you by Kaspersky. Key files are designed to activate the application by adding a license key.
You receive a key file at the email address that you provided when you bought Kaspersky Security Center or ordered the trial version of Kaspersky Security Center.
You do not need to connect to Kaspersky activation servers in order to activate the application with a key file.
You can restore a key file if it has been accidentally deleted. You may need a key file to register a Kaspersky CompanyAccount, for example.
To restore your key file, perform any of the following actions:
- Contact the license seller.
- Receive a key file through Kaspersky website by using your available activation code.
- Export a license key file from other Administration Server.
About the subscription
Subscription to Kaspersky Security Center is an order for use of the application under the selected settings (subscription expiration date, number of protected devices). You can register your subscription to Kaspersky Security Center with your service provider (for example, your internet provider). A subscription can be renewed manually or in automatic mode; also, you can cancel it.
A subscription can be limited (for example, one-year) or unlimited (with no expiration date). To continue using Kaspersky Security Center after a limited subscription expires, you must renew it. An unlimited subscription is renewed automatically if it has been prepaid to the service provider in due dates.
When a limited subscription expires, you may be provided a grace period for renewal during which the application continues to function. The availability and duration of the grace period is defined by the service provider.
To use Kaspersky Security Center under subscription, you must apply the activation code received from the service provider.
You can apply a different activation code for Kaspersky Security Center only after your subscription expires or when you cancel it.
Depending on the service provider, the set of possible actions for subscription management may vary. The service provider might not provide a grace period for subscription renewal and so the application loses its functionality.
Activation codes purchased under subscription cannot be used for activating earlier versions of Kaspersky Security Center.
When the application is used under subscription, Kaspersky Security Center automatically attempts to access the activation server at specified time intervals until the subscription expires. This ensures that the information about the subscription is synchronized with the activation server. If access to the server using system DNS is not possible, the application uses public DNS servers. You can renew your subscription on the service provider's website.
You can update the information about the subscription manually, without waiting for Kaspersky Security Center to access the activation server. For example, this might be useful when you change the subscription settings.
To update the information about the subscription manually:
- In the console tree, select the Kaspersky Licenses folder.
- Click Additional actions, and from the drop-down list select Synchronize subscription settings with Licensing server.
The information about the subscription is updated on the activation server.
Page top
About the activation code
Activation code is a unique sequence of 20 alphanumeric characters. You enter an activation code to add a license key that activates Kaspersky Security Center. You receive the activation code through the email address that you specified after purchasing Kaspersky Security Center or after ordering the trial version of Kaspersky Security Center.
To activate the application by using the activation code, you need internet access to establish connection with Kaspersky activation servers. If access to the servers using system DNS is not possible, the application uses public DNS servers.
If the application was activated with an activation code, the application in some cases sends regular requests to Kaspersky activation servers in order to check the current status of the license key. You must provide the application internet access to make it possible to send requests.
If you have lost your activation code after installing the application, contact the Kaspersky partner from whom you purchased the license.
You cannot use key files for activating managed applications; only activation codes are accepted.
Revoking consent with an End User License Agreement
If you decide to stop protection of your client devices, you can uninstall managed Kaspersky applications and revoke your End User License Agreement (EULA) for these applications.
To revoke a EULA for managed Kaspersky applications:
- In the console tree, select Administration Server → Advanced → Accepted EULAs.
A list of EULAs—accepted upon creation of installation packages, at the seamless installation of updates, or upon deployment of Kaspersky Security for Mobile—is displayed.
- In the list, select the EULA that you want to revoke.
You can view the following properties of the EULA:
- Date when the EULA was accepted.
- The name of the user who accepted the EULA.
- Link to the terms of the EULA.
- List of the objects that are connected to the EULA: names of installation packages, names of seamless updates, names of mobile apps.
- Click the Revoke EULA button.
In the window that opens, you are informed that you must uninstall Kaspersky application corresponding to the EULA.
- Click the button to confirm revocation.
Kaspersky Security Center checks whether the installation packages (corresponding to the managed Kaspersky application whose EULA you want to revoke) are deleted.
You can revoke only the EULA for a managed Kaspersky application, whose installation packages are deleted.
The EULA is revoked. It is not displayed in the list of EULAs in the Administration Server → Advanced → Accepted EULAs section. You cannot protect client devices using a Kaspersky application whose EULA you have revoked.
About data provision
Data transferred to third parties
When using the Mobile Device Management functionality of the Software, for the purpose of timely delivery of commands to devices running the Android operating system through the push notification mechanism the Google Firebase Cloud Messaging service is used. If the User has configured the usage of the Google Firebase Cloud Messaging service, the User accepts to provide the following information to the Google Firebase Cloud Messaging service in automatic mode: installation IDs of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android applications to which push notifications must be sent.
To block exchange of information with the Google Firebase Cloud Messaging service, the User must roll back the usage settings of the Google Firebase Cloud Messaging service to their factory values.
When using the Mobile Device Management functionality of the Software, for the purpose of timely delivery of commands to devices running the iOS operating system through the push notification mechanism the Apple Push Notification Service (APNs) is used. If the User has installed an APNs certificate on an iOS MDM Server, created an iOS MDM profile with a collection of settings for connection of iOS mobile devices to the Software, and installed this profile on mobile devices, the User agrees to provide the following information to APNs in automatic mode:
- Token—Push token of the device. The server uses this token when sending push notifications to the device.
- PushMagic—String that must be included in the push notification. The string value is generated by the device.
Data processed locally
Kaspersky Security Center is designed for centralized execution of basic administration and maintenance tasks on an organization's network. Kaspersky Security Center provides the administrator with access to detailed information about the organization's network security level; Kaspersky Security Center lets the administrator configure all the components of protection based on Kaspersky applications. Kaspersky Security Center performs the following main functions:
- Detecting devices and their users on the organization's network
- Creating a hierarchy of administration groups for device management
- Installing Kaspersky applications on devices
- Managing the settings and tasks of installed applications
- Managing the updates for Kaspersky and third-party applications, and finding and fixing vulnerabilities
- Activating Kaspersky applications on devices
- Managing user accounts
- Viewing information about the operation of Kaspersky applications on devices
- Viewing reports
To perform its main functions Kaspersky Security Center can receive, store, and process the following information:
- Information about the devices on the organization's network received through scanning of Windows domain, Active Directory or Samba domain controllers, or through scanning of IP ranges. Administration Server gets data independently or receives data from Network Agent acting as a distribution point.
- Information from Active Directory and Samba about organizational units, domains, users, and groups. Administration Server gets data independently or receives data from Network Agent acting as a distribution point.
- Details of managed devices. Network Agent transfers the data listed below from the device to Administration Server. The User enters the display name and description of the device in the Administration Console interface or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface:
- Technical specifications of the managed device and its components required for device identification: device display name and description, Windows domain name and type, device name in Windows environment, DNS domain and DNS name, IPv4 address, IPv6 address, network location, MAC address, serial number, operating system type, whether the device is a virtual machine together with hypervisor type, and whether the device is a dynamic virtual machine as part of VDI.
- Other specifications of managed devices and their components required for audit of managed devices and for making decisions about whether specific patches and updates are applicable: Windows Update Agent (WUA) status, operating system architecture, operating system vendor, operating system build number, operating system release ID, operating system location folder, if the device is a virtual machine—the virtual machine type; the name of the virtual Administration Server that manages the device; cloud device data (cloud region, VPC, cloud availability zone, cloud subnet, cloud placement zone).
- Details of actions on managed devices: date and time of the last update, time the device was last visible on the network, restart waiting status, and time the device was turned on.
- Details of device user accounts and their work sessions.
- Data received by running remote diagnostics on a managed device: trace files, system information, details of Kaspersky applications installed on the device, dump files, event logs, the results of running the diagnostic scripts received from Kaspersky Technical Support.
- Distribution point operation statistics if the device is a distribution point. Network Agent transfers data from the device to Administration Server.
- Distribution point settings entered by the User in the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Data necessary for the connection of mobile devices to the Administration Server: certificate, mobile connection port, Administration Server connection address. The User enters the data in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Details of mobile devices transferred by using the iOS MDM protocol. The data listed below are transferred from the mobile device to Administration Server:
- Technical specifications of the mobile device and its components required for device identification: device name, model, operating system name and build number, device model number, IMEI number, UDID, MEID, serial number, amount of memory, modem firmware version, Bluetooth MAC address, Wi-Fi MAC address, and SIM card details (ICCID as part of the SIM card ID).
- Details of the mobile network used by the managed device: mobile network type, name of the currently used mobile network, name of the home mobile network, version of the mobile network operator settings, voice roaming and data roaming status, country code of the home network, residence country code, country code of the currently used network, and encryption level.
- Security settings of the mobile device: use of a password and its compliance with the policy settings, list of configuration profiles and provisioning profiles used for installation of third-party applications.
- Date of last synchronization with Administration Server and device management status.
- Details of Kaspersky applications installed on the device. The managed application transfers data from the device to Administration Server through Network Agent:
- Settings of Kaspersky applications installed on the managed device: Kaspersky application name and version, status, real-time protection status, last device scan date and time, number of threats detected, number of objects that failed to be disinfected, availability and status of the application components, time of last update and version of anti-virus databases, details of Kaspersky application settings and tasks, information about the active and reserve license keys, application installation date and ID.
- Application operation statistics: events related to the changes in the status of Kaspersky application components on the managed device and to the performance of tasks initiated by the application components.
- Device status defined by the Kaspersky application.
- Tags assigned by the Kaspersky application.
- Set of installed and applicable updates for the Kaspersky application.
- Data contained in events from Kaspersky Security Center components and Kaspersky managed applications. Network Agent transfers data from the device to Administration Server.
- Data necessary for the integration of Kaspersky Security Center with a SIEM system for event export. The User enters the data in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Settings of Kaspersky Security Center components and Kaspersky managed applications presented in policies and policy profiles. The User enters data in the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
- Task settings of Kaspersky Security Center components and Kaspersky managed applications. The User enters data in the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
- Data processed by the Vulnerability and patch management feature. Network Agent transfers the data listed below from the device to Administration Server:
- Details of applications and patches installed on managed devices (Applications registry).
- Information about the hardware detected on managed devices (Hardware registry).
If Network Agent is installed on a device running Windows, it sends to the Administration Server the following information about the device hardware:
- RAM
- Mass storage devices
- Motherboard
- CPU
- Network adapters
- Monitors
- Video adapter
- Sound card
If Network Agent is installed on a device running Linux or macOS, it sends to the Administration Server the following information about the device hardware, if this information is provided by the operating system:
- Total RAM volume
- Total volume of mass storage devices
- Motherboard
- CPU
- Network adapters
- Details of vulnerabilities in third-party software detected on managed devices.
- Details of updates available for third-party applications installed on managed devices.
- Details of Microsoft updates found by the WSUS feature.
- List of Microsoft updates found by the WSUS feature that must be installed on the device.
- Data required to download updates on isolated Administration Server to fix third-party software vulnerabilities on managed devices. The User enters and transmits data by using the Administration Server klscflag utility.
- Data necessary for work of Kaspersky Security Center with the cloud environments (Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Yandex Cloud). The User enters the data in the Administration Console or in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- User categories of applications. The User enters data in the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
- Details of executable files detected on managed devices by the Application Control feature. The User enters data in the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface. A complete list of data is provided in the Help files of the corresponding application.
- Details of files placed in Backup. The managed application transfers data from the device to Administration Server through Network Agent. A complete list of data is provided in the Help files of the corresponding application.
- Details of files placed in Quarantine. The managed application transfers data from the device to Administration Server through Network Agent. A complete list of data is provided in the Help files of the corresponding application.
- Details of files requested by Kaspersky specialists for detailed analysis. The managed application transfers data from the device to Administration Server through Network Agent. A complete list of data is provided in the Help files of the corresponding application.
- Details of the status and triggering of Adaptive Anomaly Control rules. The managed application transfers data from the device to Administration Server through Network Agent. A complete list of data is provided in the Help files of the corresponding application.
- Details of external devices (memory units, information transfer tools, information hardcopy tools, and connection buses) installed or connected to the managed device and detected by the Device Control feature. The managed application transfers data from the device to Administration Server through Network Agent. A complete list of data is provided in the Help files of the corresponding application.
- Information about encrypted devices and the encryption status. The managed application transfers data from the device to Administration Server through Network Agent.
- Details of data encryption errors on devices performed using the Data encryption feature of Kaspersky applications. The managed application transfers data from the device to Administration Server through Network Agent. A complete list of data is provided in the Help files of the corresponding application.
- List of managed programmable logic controllers (PLCs). The managed application transfers data from the device to Administration Server through Network Agent. A complete list of data is provided in the Help files of the corresponding application.
- Data required for creation of a threat development chain. The managed application transfers data from the device to Administration Server through Network Agent. A complete list of data is provided in the Help files of the corresponding application.
- Information about attempts by an organization's employees to access cloud services. The managed application transfers data from the device to Administration Server through Network Agent. A complete list of data is provided in the Help files of the corresponding application.
- Data required for Kaspersky Security Center integration with the Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response service (the dedicated plug-in must be installed for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console): integration initiation token, integration token, and user session token. The User enters the integration initiation token in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface. The Kaspersky MDR service transfers the integration token and the user session token through the dedicated plug-in.
- Details of the entered activation codes or specified key files. The User enters data in the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
- User accounts: name, description, full name, email address, main phone number, password, secret key generated by Administration Server, and one-time password for two-step verification. The User enters data in the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
- Data that Identity and Access Manager needs for centralized authentication and for providing Single Sign-on (SSO) between Kaspersky applications integrated with Kaspersky Security Center: installation and configuration settings of Identity and Access Manager, Identity and Access Manager user session, Identity and Access Manager tokens, client application statuses and resource server statuses. The User enters data in the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
- Revision history of management objects. The User enters data in the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
- IP address of the device on which a user created a revision. The IP address is defined by Administration Server automatically.
- Registry of deleted management objects. The User enters data in the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
- Installation packages created from the file, as well as installation settings. The User enters data in the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
- Data required for the display of announcements from Kaspersky in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. The User enters data in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
- Data required for the functioning of plug-ins of managed applications in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and saved by the plug-ins in the Administration Server database during their routine operation. The description and ways of providing the data are provided in the Help files of the corresponding application.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console user settings: localization language and theme of the interface, Monitoring panel display settings, information about the status of notifications (Already read / Not yet read), status of columns in spreadsheets (Show / Hide), Training mode progress. The User enters data in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
- Kaspersky Event Log for Kaspersky Security Center components and Kaspersky managed applications. Kaspersky Event Log is stored on each device and is never transferred to Administration Server.
- Certificate for secure connection of managed devices to the Kaspersky Security Center components. The User enters data by using the Administration Server klsetsrvcert utility.
- Certificates for establishing trust to the internal web resources of the organization. The User enters data in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
- Data required for the Kaspersky Security Center operation in cloud environments, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and Yandex.Cloud. Administration Server receives the data from the virtual machine on which it runs.
- Information about the User's acceptance of the terms and conditions of legal agreements with Kaspersky.
- The Administration Server data that the User enters in the following components:
- Administration Console
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Command-line terminal when using the klscflag utility
- Components interacting with the Administration Server via klakaut automation objects and Kaspersky Security Center OpenAPI
- Any data that the User enters in the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
The data listed above can be present in Kaspersky Security Center if one of the following methods is applied:
- The User enters data in the interface of the following components:
- Administration Console
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Command-line terminal when using the klscflag utility
- Components interacting with the Administration Server via klakaut automation objects and Kaspersky Security Center OpenAPI
- Network Agent automatically receives data from the device and transfers it to Administration Server.
- Network Agent receives data retrieved by the Kaspersky managed application and transfers it to Administration Server. The lists of data processed by Kaspersky managed applications are provided in the Help files for the corresponding applications.
- Administration server gets information about networked devices independently or receives information from a Network Agent acting as a distribution point.
- Data is transferred from the mobile device to Administration Server by using the iOS MDM protocol.
The listed data is stored in the Administration Server database. User names and passwords are stored in encrypted form.
All data listed above can be transferred to Kaspersky only through dump files, trace files, or log files of Kaspersky Security Center components, including log files created by installers and utilities.
Dump files, trace files, and log files of Kaspersky Security Center components contain random data of Administration Server, Network Agent, Administration Console, iOS MDM Server, and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. These files can contain personal and sensitive data. Dump files, trace files, and log files are stored on the device in non-encrypted form. Dump files, trace files, and log files are not transferred to Kaspersky automatically; however, the administrator can transfer data to Kaspersky manually upon request by Technical Support to resolve issues in the Kaspersky Security Center operation.
Following the links in the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, the User agrees to the automatic transfer of the following data:
- Kaspersky Security Center code
- Kaspersky Security Center version
- Kaspersky Security Center localization
- License ID
- License type
- Whether the license was purchased through a partner
The list of data provided via each link depends on the purpose and location of the link.
Kaspersky uses the received data in anonymized form and for general statistics only. Summary statistics are generated automatically from the originally received information and do not contain any personal or confidential data. As soon as new data is accumulated, the previous data is wiped (once a year). Summary statistics are stored indefinitely.
Kaspersky protects any information received in accordance with law and applicable Kaspersky rules. Data is transmitted over a secure channel.
Page top
Kaspersky Security Center licensing options
Kaspersky Security Center can work in the following modes:
- No license (basic functionality)
Kaspersky Security Center works in this mode before the application is activated or after the commercial license expires. Kaspersky Security Center with support of the basic functionality of Administration Console is delivered as a part of Kaspersky applications for protection of corporate networks. You can also download it from Kaspersky website.
- Commercial license
If you need additional functionality which is not included in the basic functionality of Administration Console, you must purchase a commercial license.
When adding a license key in the Administration Server properties window, ensure that you add a license key that lets you use Kaspersky Security Center. You can find this information at the Kaspersky website. Each solution webpage contains the list of applications included in this solution. Administration Server may accept unsupported license keys, for example a license key for Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud, but such license keys provide no new features in addition to the basic functionality of Administration Console.
Feature or property |
Kaspersky Security Center operation mode |
|
|---|---|---|
|
No license |
Commercial license |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mobile Device Management feature in MMC-based Administration Console |
|
(A license key must be added to the Administration Server properties.) |
Mobile device protection in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console |
|
(A license key must be added on each mobile device.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Licensing features of Kaspersky Security Center and managed applications
Licensing of Administration Server and managed applications involves the following:
- You can add license key or valid activation code to an Administration Server to activate Vulnerability and patch management, Mobile Device Management, or Integration with the SIEM systems. Some features of Kaspersky Security Center are only accessible depending on active key files or valid activation codes added to the Administration Server.
- You can add multiple activation codes and key files for managed applications to the Administration Server repository.
About Kaspersky Security Center licensing
If you activated one of the licensed features (for example, Mobile Device Management) using a key file, but you also want to use another licensed feature (for example, Vulnerability and patch management), you must purchase from your service provider a key file that activates both these features and you must activate Administration Server by using this key file.
Licensing features of managed applications
For licensing of managed applications, an activation code or key file can be deployed automatically or in any other convenient way. The following methods can be applied to deploy an activation code or key file:
- Automatic deployment
If you use different managed applications and you have to deploy a specific key file or activation code to devices, opt for other ways of deploying that activation code or key file.
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to automatically deploy available license keys to devices. For example, three license keys are stored in the Administration Server repository. You have selected the Automatically distribute license key to managed devices check box for all three license keys. A Kaspersky security application—for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows—is installed on the organization's devices. A new device is discovered to which a license key must be deployed. The application determines, for instance, that two of the license keys from the repository can be applied to the device: license key named Key_1 and license key named Key_2. One of these license keys is deployed to the device. In this case, it cannot be predicted which of the two license keys will be deployed to the device because automatic deployment of license keys does not provide for any administrator activity.
When a license key is deployed, the devices are recounted for that license key. You must make sure that the number of devices to which the license key was deployed does not exceed the license limit. If the number of devices exceeds the license limit, all devices that were not covered by the license will be assigned Critical status.
- Adding a key file or activation code to the installation package of a managed application
If you install a managed application using an installation package, you can specify an activation code or key file in this installation package or in the policy of the application. The license key will be deployed to managed devices at the next synchronization of the device with the Administration Server.
- Deployment through the add license key task for a managed application
If you opt for using the add license key task for a managed application, you can select the license key that must be deployed to devices and select the devices in any convenient way—for example, by selecting an administration group or a device selection.
- Adding an activation code or a key file manually to the devices
Kaspersky applications. Centralized deployment
This section describes the methods for remote installation of Kaspersky applications and their removal from networked devices.
Before deploying applications on client devices, make sure that the hardware and software of client devices meets the applicable requirements.
Network Agent is a component that provides for Administration Server connection with client devices. Therefore, it must be installed on each client device to be connected to the remote centralized control system. The device on which the Administration Server is installed can only use the server version of Network Agent. This version is included in Administration Server as a part that is installed and removed together with it. There is no need to install Network Agent on that device.
Network Agent can be installed remotely or locally like any application. During centralized deployment of security applications through Administration Console, you can install Network Agent jointly with security applications.
Network Agents can differ depending upon the Kaspersky applications with which they work. In some cases, Network Agent can be installed locally only (for details please refer to the documentation for the corresponding applications). You only have to install Network Agent on a client device once.
Kaspersky applications are managed through Administration Console by using management plug-ins. Therefore, to access the application management interface through Kaspersky Security Center, the corresponding management plug-in must be installed on the administrator's workstation.
You can perform remote installation of applications from the administrator's workstation in the Kaspersky Security Center main window.
To install software remotely, you must create a remote installation task.
The created task for remote installation will start according to its schedule. You can interrupt the installation procedure by stopping the task manually.
If remote installation of an application returns an error, you can find the cause of this error and fix it using the remote installation preparation utility.
You can track the progress of remote installation of Kaspersky applications on a network using the deployment report.
For details about management of the listed applications in Kaspersky Security Center, please refer to the documentation for the corresponding applications.
Replacing third-party security applications
Installation of Kaspersky security applications through Kaspersky Security Center may require removal of third-party software incompatible with the application being installed. Kaspersky Security Center provides several ways of removing the third-party applications.
Removing incompatible applications by using the installer
This option is available in Microsoft Management Console-based Administration Console only.
The installer method of removing incompatible applications is supported by various types of installation. Before the security application installation, all incompatible applications are removed automatically if the properties window of the installation package of this security application (Incompatible applications section) has the Uninstall incompatible applications automatically option selected.
Removing incompatible applications when configuring remote installation of an application
You can enable the Uninstall incompatible applications automatically option when you configure remote installation of a security application. In Microsoft Management Console (MMC) based Administration Console, this option is available in the Remote installation wizard. In Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you can find this option in the Protection deployment wizard. When this option is enabled, Kaspersky Security Center removes incompatible applications before installing a security application on a managed device.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Removing incompatible applications using Remote Installation Wizard
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Removing incompatible applications before installation
Removing incompatible applications through a dedicated task
To remove incompatible applications, use the Uninstall application remotely task. This task should be run on devices before the security application installation task. For example, in the installation task you can select On completing another task as the schedule type where the other task is Uninstall application remotely.
This method of uninstallation is useful when the security application installer cannot properly remove an incompatible application.
How-to instructions for Administration Console: Creating a task.
Page top
Installing applications using a remote installation task
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to install applications on devices remotely, using remote installation tasks. Those tasks are created and assigned to devices through a dedicated wizard. To assign a task more quickly and easily, you can specify devices (up to 1000 devices) in the wizard window in one of the following ways:
- Select networked devices detected by Administration Server. In this case, the task is assigned to specific devices. The specific devices can include devices in administration groups as well as unassigned devices.
- Specify device addresses manually or import addresses from a list. You can specify NetBIOS names, DNS names, IP addresses, and IP subnets of devices to which you want to assign the task.
- Assign task to a device selection. In this case, the task is assigned to devices included in a selection created earlier. You can specify the predefined selection or a custom one that you created.
- Assign task to an administration group. In this case, the task is assigned to devices included in an administration group created earlier.
For correct remote installation on a device with no Network Agent installed, the following ports must be opened: a) TCP 139 and 445; b) UDP 137 and 138. By default, these ports are opened on all devices included in the domain. They are opened automatically by the remote installation preparation utility.
Installing an application on selected devices
To install an application on selected devices:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- Run the task creation by clicking the Create a task button.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
In the Select the task type window of the New task wizard, in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server node select Install application remotely as the task type.
The New task wizard creates a task of remote installation of the selected application for specific devices. The newly created task is displayed in the workspace of the Tasks folder.
- Run the task manually or wait for it to launch according to the schedule specified by you in the task settings.
On completion of the remote installation task, the selected application will be installed on the selected devices.
Page top
Installing an application on client devices in an administration group
To install an application on client devices in an administration group:
- Establish a connection with the Administration Server that controls the relevant administration group.
- Select an administration group in the console tree.
- In the group workspace, select the Tasks tab.
- Run the task creation by clicking the Create a task button.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
In the Select the task type window of the New task wizard, in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server node select Install application remotely as the task type.
The New task wizard creates a group task of remote installation of the selected application. The new task appears in the workspace of the administration group on the Tasks tab.
- Run the task manually or wait for it to launch according to the schedule specified by you in the task settings.
On completion of the remote installation task, the selected application will be installed on client devices in the administration group.
Page top
Installing an application through Active Directory group policies
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to install Kaspersky applications on managed devices by using Active Directory group policies.
You can install applications by using Active Directory group policies only from installation packages that include Network Agent.
To install an application using Active Directory group policies:
- Start configuring the application installation by using Remote installation wizard.
- In the Defining remote installation task settings window of the Remote installation wizard, select the Assign package installation in Active Directory group policies option.
- In the Select accounts to access devices window of the Remote installation wizard, select the Account required (Network Agent is not used) option.
- Add the account with administrator privileges on the device where Kaspersky Security Center is installed or the account included in the Group Policy Creator Owners domain group.
- Grant the permissions to the selected account:
- Go to Control Panel → Administrative Tools and open Group Policy Management.
- Click the node with the required domain.
- Click the Delegation section.
- In the Permission drop-down list, select Link GPOs.
- Click Add.
- In the Select User, Computer, or Group window that opens, select the necessary account.
- Click OK to close the Select User, Computer, or Group window.
- In the Groups and users list, select the account that you have just added, and then click Advanced → Advanced.
- In the Permission entries list, double-click the account that you have just added.
- Grant the following permissions:
- Create Group objects
- Delete Group objects
- Create group Policy Container objects
- Delete group Policy Container objects
- Click OK to save the changes.
- Define other settings by following the instructions of the wizard.
- Run the created remote installation task manually or wait for its scheduled start.
The following remote installation sequence starts:
- When the task is running, the following objects are created in each domain that includes any client devices from the specified set:
- Group policy object (GPO) under the name Kaspersky_AK{GUID}.
- A security group that corresponds to the GPO. This security group includes client devices covered by the task. The content of the security group defines the scope of the GPO.
- Kaspersky Security Center installs the selected Kaspersky applications on client devices directly from Share, that is, the shared network folder of the application. In the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder, an auxiliary subfolder will be created that contains the .msi file for the application to be installed.
- When new devices are added to the task scope, they are added to the security group after the next start of the task. If the Run missed tasks option is selected in the task schedule, devices are added to the security group immediately.
- When devices are deleted from the task scope, they are deleted from the security group after the next start of the task.
- When a task is deleted from Active Directory, the GPO, the link to the GPO, and the corresponding security group are deleted, too.
If you want to apply another installation schema using Active Directory, you can configure the required settings manually. For example, this may be required in the following cases:
- When the anti-virus protection administrator does not have rights to make changes to the Active Directory of certain domains
- When the original installation package has to be stored on a separate network resource
- When it is necessary to link a GPO to specific Active Directory units
The following options for using an alternative installation scheme through Active Directory are available:
- If installation is to be performed directly from the Kaspersky Security Center shared folder, in the GPO properties you must specify the .msi file located in the exec subfolder of the installation package folder for the required application.
- If the installation package has to be located on another network resource, you must copy the whole exec folder content to it, because in addition to the file with .msi extension the folder contains configuration files generated when the package was created. To install the license key with the application, copy the key file to this folder as well.
Installing applications on secondary Administration Servers
To install an application on secondary Administration Servers:
- Establish a connection with the Administration Server that controls the relevant secondary Administration Servers.
- Make sure that the installation package corresponding to the application being installed is available on each of the selected secondary Administration Servers. If the installation package cannot be found on any of the secondary Servers, distribute it by using the installation package distribution task.
- Create the task of application installation on secondary Administration Servers in one of the following ways:
- If you want to create a task for secondary Administration Servers in the selected administration group, create a group task of remote installation for this group.
- If you want to create a task for specific secondary Administration Serves, create a task of remote installation for specific devices.
The Deployment task creation wizard starts to guide you through creation of the remote installation task. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
In the Select the task type window of the New task wizard, in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server section open the Advanced folder and select Install application on secondary Administration Servers remotely as the task type.
The New task wizard will create the task of remote installation of the selected application on specific secondary Administration Servers.
- Run the task manually or wait for it to launch according to the schedule specified by you in the task settings.
On completion of the remote installation task, the selected application will be installed on secondary Administration Servers.
Page top
Installing applications using Remote installation wizard
To install Kaspersky applications, you can use the Remote installation wizard. The Remote installation wizard allows remote installation of applications either through specially created installation packages or directly from a distribution package.
For proper operation of the Remote installation task on a client device that does not have Network Agent installed, the following ports must be open: TCP 139 and 445; UDP 137 and 138. By default, these ports are open for all devices included in the domain. They are opened automatically by the remote installation preparation utility.
To install the application on selected devices by using the Remote installation wizard:
- In the console tree, locate the Remote installation folder and select the Installation packages subfolder.
- In the workspace of the folder, select the installation package of the application that you have to install.
- In the context menu of the installation package, select Install application.
The Remote installation wizard starts.
- In the Select devices for installation window, you can create a list of devices on which the application will be installed:
- In the Defining remote installation task settings window, specify the settings for remote installation of the application.
In the Force installation package download settings group, specify how files that are required for the application installation are distributed to client devices:
- Using Network Agent
- Using operating system resources through Administration Server
- Using operating system resources through distribution points
- Number of attempts to install
Define what to do with client devices managed by another Administration Server:
Define the additional settings:
- In the Selecting a license key window, select a license key and a method for its distribution:
- Do not place license key in installation package (recommended)
- Place license key in installation package
The Selecting a license key window is displayed if the installation package does not include a license key.
If the installation package includes a license key, the License key properties window is displayed, containing the license key details.
- In the Selecting an operating system restart option window, specify whether the devices must be restarted if the operating system has to be restarted during installation of applications on them:
- In the Select accounts to access devices window, you can add the accounts that will be used to start the Remote installation task:
- In the Starting installation window, click the Next button to create and start a Remote installation task on the selected devices.
If the Starting installation window has the Do not run the task after the Remote installation wizard finishes option selected, the remote installation task will not start. You can start this task manually later. The task name corresponds to the name of the installation package for the application: Installation of <Installation package name>.
To install the application on devices in an administration group by using the Remote installation wizard:
- Establish a connection with the Administration Server that controls the relevant administration group.
- Select an administration group in the console tree.
- In the workspace of the group, click the Perform action button and select Install application in the drop-down list.
This will start the Remote installation wizard. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- At the final step of the wizard, click Next to create and run a remote installation task on the selected devices.
When the Remote installation wizard finishes, Kaspersky Security Center performs the following actions:
- Creates an installation package for application installation (if it was not created earlier). The installation package is located in the Remote installation folder, in the Installation packages subfolder, under a name that corresponds to the application name and version. You can use this installation package for the application installation in the future.
- Creates and runs a remote installation task for specific devices or for an administration group. The newly created remote installation task is stored in the Tasks folder or added to the tasks of the administration group for which it has been created. You can start this task manually later. The task name corresponds to the name of the installation package for the application: Installation of <Installation package name>.
Working with the management plug-ins
Kaspersky applications are managed through the Administration Console by using the management plug-ins. Each Kaspersky application that can be managed through Kaspersky Security Center includes a management plug-in. Using the application management plug-in, you can perform the following actions in the Administration Console:
- Create and edit application policies and settings, as well as the settings of application tasks.
- Obtain information about application tasks, application events, and application operation statistics received from client devices.
To check the list of installed plug-ins and its versions:
- In the Administration Console tree, right-click Administration Server <Server_name>, and select Properties.
- Click Advanced → Details of application management plug-ins installed.
The list of installed management plug-ins and their versions appears in the right pane.
You can install the plug-ins for managed applications when you run the Administration Server quick start wizard during the Kaspersky Security Center initial setup. Also, you can install the management plug-ins manually.
To install a management plug-in manually:
- Download the management plug-in for the Kaspersky application and the version required (for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows 12.6) from Kaspersky Technical Support webpage.
- If the Administration Console is running, close it.
- Unzip the downloaded plug-in file and run the klcfginst.msi or klcfginst.exe file. Follow the installation wizard's instructions.
- When the installation is complete, run the Administration Console and make sure the plug-in is presented in the list of installed plug-ins, as described in the previous procedure.
When you run the Administration Console after installation of a management plug-in that supports the Managed application quick start wizard, this wizard is started automatically. You can go through the steps of the Managed application quick start wizard to create default Kaspersky application policies and tasks. The wizard starts automatically only when you run the Administration Console after the initial plug-in installation or after you update the management plug-in to a version that is compatible with another version of the Kaspersky application for which tasks and policies have not yet been created. You can also start the Managed application quick start wizard manually.
To start the Managed application quick start wizard manually:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server node, select All Tasks → Managed application quick start wizard.
- The Managed application quick start wizard starts. Follow the wizard steps to create default Kaspersky application policies and tasks.
To remove a management plug-in:
- If the Administration Console is running, close it.
- Open Windows Registry editor.
- Find the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\Components\28\Pluginsfor 32-bit system.HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\28\Pluginsfor 64-bit system.
The key contains installed management plug-ins. For each plug-in, the
DisplayNamevalue contains the plug-in name, and theUninstallStringvalue contains the command to uninstall the plug-in. - Find the key for the plug-in you want to uninstall, and copy its
UninstallStringvalue to the clipboard. - Paste the value into the command string and run it with system administrator rights.
The management plug-in version must not be earlier than the Kaspersky managed application version. If you update the Kaspersky application on the devices, you must install the management plug-in of the same version.
When you open the policy that was created in an earlier version of plug-in, you will be asked to accept the Kaspersky Security Network Statement.
When you uninstall Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, all management plug-ins are also uninstalled.
If you open and save the policy in the plug-in version that is later than the version of the managed application, the policy will be updated, and you will not be able to open it in the plug-in of the earlier version.
Page top
Viewing a protection deployment report
You can use the protection deployment report to monitor the progress of network protection deployment.
To view a protection deployment report:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Reports tab.
- In the workspace of the Reports folder, select the report template named Report on protection deployment.
The workspace displays a report containing information about protection deployment on all networked devices.
You can generate a new protection deployment report and specify the type of data that it should include:
- For an administration group
- For specific devices
- For a device selection
- For all devices
Kaspersky Security Center assumes that protection is deployed on a device if a security application is installed and real-time protection enabled.
Page top
Remote removal of applications
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to uninstall applications from devices remotely through remote uninstallation tasks. Those tasks are created and assigned to devices through a dedicated wizard. To assign a task to devices more quickly and easily, you can specify devices in the wizard window in one of the following ways:
- Select networked devices detected by Administration Server. In this case, the task is assigned to specific devices. The specific devices can include devices in administration groups as well as unassigned devices.
- Specify device addresses manually or import addresses from a list. You can specify NetBIOS names, DNS names, IP addresses, and IP subnets of devices to which you want to assign the task.
- Assign task to a device selection. In this case, the task is assigned to devices included in a selection created earlier. You can specify the predefined selection or a custom one that you created.
- Assign task to an administration group. In this case, the task is assigned to devices included in an administration group created earlier.
Remote removal issues
When performing remote removal of third-party applications, administrators may encounter a warning stating, "Remote uninstallation has finished on this device with warnings: Application for removal is not installed." This issue typically arises when the application to be removed is installed only for the individual user who is currently logged in. If the user is not logged in, such an application becomes invisible and cannot be targeted for remote removal.
This behavior differs with applications intended for use by multiple users on the same device, where applications are globally visible and accessible by all users of the device.
Within Kaspersky Security Center, the application registry algorithm handles applications for individual users and applications for multiple users differently:
- Applications for multiple users are maintained in a real-time, up-to-date list of installed applications.
- Applications for individual users are monitored using a caching mechanism.
If a user was logged in at the time of application detection, Kaspersky Security Center caches information about that user's applications. Even if the user subsequently logs out, Kaspersky Security Center continues to display these applications as installed based on the cached data, although they are no longer visible or accessible on the device.
This discrepancy can result in situations where Kaspersky Security Center identifies an application as installed based on cached data, but the application removal task fails because the application is not accessible when the user is logged out.
By default, the lifetime of cached application data is set to 30 days. Administrators can modify this setting to reduce the cache duration, thereby minimizing discrepancies between the displayed data and actual application visibility on devices.
To adjust the cache lifetime to 1 hour (3600 seconds), run the following command on the Administration Server:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLNAG_INV_PERUSER_APPS_CACHE_NONACTIVE_SIDS_LIFETIME_SEC -t d -v 3600
After running this command, restart the Administration Server for the changes to take effect.
Source of information about installed applications
The Network Agent retrieves information about software installed on Windows devices from the following registry keys:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
Contains information about applications installed for all users.
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
Contains information about applications installed for all users.
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
Contains information about applications installed for the current user.
- HKEY_USER<...>\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
Contains information about applications installed for specific users.
Remote removal of an application from client devices of the administration group
To remove an application remotely from client devices of the administration group:
- Establish a connection with the Administration Server that controls the relevant administration group.
- Select an administration group in the console tree.
- In the group workspace, select the Tasks tab.
- Run the task creation by clicking the New task button.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
In the Select the task type window of the New task wizard, in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server node, in the Advanced folder select Uninstall application remotely as the task type.
The New task wizard creates a group task of remote removal of the selected application. The new task appears in the workspace of the administration group on the Tasks tab.
- Run the task manually or wait for it to launch according to the schedule specified by you in the task settings.
On completion of the remote removal task, the selected application will be removed from client devices in the administration group.
Page top
Remote removal of an application from selected devices
To remove an application remotely from selected devices:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- Run task creation by clicking New task.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
In the Select the task type window of the New task wizard, in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server node, in the Advanced folder select Uninstall application remotely as the task type.
The New task wizard creates a task of remote removal of the selected application from specific devices. The newly created task is displayed in the workspace of the Tasks folder.
- Run the task manually or wait for it to launch according to the schedule specified by you in the task settings.
Upon completion of the remote removal task, the selected application will be removed from the selected devices.
Page top
Working with installation packages
When creating remote installation tasks, the system uses installation packages containing sets of parameters necessary for software installation.
Installation packages can contain a key file. It is recommended that you avoid sharing access to installation packages that contain a key file.
You can use a single installation package several times.
Installation packages created for Administration Server are moved to the console tree and located in the Remote installation folder, in the Installation packages subfolder. Installation packages are stored on the Administration Server, in a service subfolder named Packages, within the specified shared folder.
Creating an installation package
This article describes the procedure of creating the following types of installation packages:
- Installation package for a Kaspersky application
- Installation package for a specified executable file
- Installation package for an application from the Kaspersky database
You do not have to create an installation package manually for the remote installation of Network Agent. It is created automatically during the installation of Kaspersky Security Center and stored in the Installation packages folder. If the package for the remote installation of Network Agent has been deleted, you can re-create it by selecting the nagent.kud file in the NetAgent folder of the Kaspersky Security Center distribution package.
To create an installation package:
- Connect to the necessary Administration Server.
- In the console tree, select Advanced → Remote installation → Installation packages.
- Start the creation of a new installation package in one of the following ways:
- Right-click the Installation packages folder, and then select New → Installation package from the context menu.
- Right-click in the empty area of the installation packages list, and then select Create → Installation package from the context menu.
- Click Create installation package in the installation packages list management section.
The New package wizard starts.
- Select one of the following installation package types by clicking the corresponding icon:
- Installation package for a Kaspersky application.
- Installation package for a specified executable file.
- Installation package for an application from the Kaspersky database.
- Specify the name of the installation package to be created.
You can specify any name.
- Select the application or executable file for which the installation package is to be created, in one of the following ways:
- Click the Browse button and, in the standard Windows Open window, select the distribution package of the required application located on available disks.
This option is applicable if you choose to create an installation package for a Kaspersky application or for a specified executable file.
- Click the Browse button and, in the Select application window, select the distribution package of the required application.
This option is applicable if you choose to create an installation package for an application from the Kaspersky database.
If you are creating an installation package for Administration Server, select the sc.kud file. The sc.kud file is located in the root folder of the Kaspersky Security Center distribution package.
Do not specify any details of privileged accounts in the parameters of installation packages.
- Click the Browse button and, in the standard Windows Open window, select the distribution package of the required application located on available disks.
- Review the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy.
When creating an installation package for an application, you may be prompted to view and accept an End User License Agreement and a Privacy Policy for that application.
Read both documents. If you agree with all the terms of the License Agreement and the Privacy Policy, accept them by selecting the corresponding check boxes.
The installation of the application on your device continues, and the creation of the installation package resumes.
If you are creating an installation package for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, you can choose the language for the License Agreement and Privacy Policy.
- If necessary, enable automatic installation of system components.
If you are creating an installation package for an application from the Kaspersky database, you can enable the automatic installation of necessary system components. The New package wizard displays a list of all available system components for the selected application. You can access this list at any time in the installation package properties.
If you are creating a patch installation package, the list includes all system components needed for the deployment of this patch.
- Click the Finish button to complete the package creation process.
Once the New package wizard completes, the new installation package appears in the workspace of the Installation packages folder in the console tree.
Creating stand-alone installation packages
You and device users in your organization can use stand-alone installation packages to install applications on devices manually.
A stand-alone installation package is an executable file (installer.exe) that you can store on Web Server, in a shared folder, or transfer to a client device by another method. You can also send a link to the stand-alone installation package by email. On the client device, the user can run the received file locally to install an application without involving Kaspersky Security Center.
Be sure that the stand-alone installation package is not available for unauthorized persons.
You can create stand-alone installation packages for Kaspersky applications and for third-party applications for Windows, macOS, and Linux platforms. To create a stand-alone installation package for a third-party application, you must create a custom installation package first.
The source to create stand-alone installation packages are installation packages in the list of created on the Administration Server.
To create a stand-alone installation package:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server → Advanced → Remote installation → Installation packages.
A list of installation packages available on Administration Server is displayed.
- In the list of installation packages, select an installation package for which you want to create a stand-alone package.
- In the context menu, select Create stand-alone installation package.
The Stand-alone installation package creation wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the first page of the wizard, if you have selected an installation package for the Kaspersky application and you want to install Network Agent together with the selected application, make sure that the Install Network Agent together with this application option is enabled.
By default, this option is enabled. We recommend enabling this option if you are not sure whether Network Agent is installed on the device. If Network Agent is already installed on the device, after the stand-alone installation package with Network Agent is installed, Network Agent will be updated to the newer version.
If you disable this option, Network Agent will not be installed on the device and the device will be unmanaged.
If a stand-alone installation package for the selected application already exists on Administration Server, the wizard informs you about this fact. In this case, you must select one of the following actions:
- Create stand-alone installation package. Select this option if, for example, you want to create a stand-alone installation package for a new application version and also want to retain a stand-alone installation package that you created for a previous application version. The new stand-alone installation package is placed in another folder.
- Use existing stand-alone installation package. Select this option if you want to use an existing stand-alone installation package. The process of package creation will not be started.
- Rebuild existing stand-alone installation package. Select this option if you want to create a stand-alone installation package for the same application again. The stand-alone installation package is placed in the same folder.
- On the next page of the wizard, select the Move unassigned devices to this group option and specify an administration group to which you want to move the client device after Network Agent installation.
By default, the device is moved to the Managed devices group.
If you do not want to move the client device to an administration group after Network Agent installation, select the Do not move devices option.
- On the next page of the wizard, when the process of the stand-alone installation package creation is finished, a result of the stand-alone package creation and a path to the stand-alone package are displayed.
You can click the links and do any of the following:
- Open the folder with the stand-alone installation package.
- Email the link to the created stand-alone installation package. To perform this action, you must have an email application launched.
- Sample HTML code for publishing the link on a website. A TXT file is created and opened in an application that is associated with a TXT format. In the file, the <a> HTML tag with attributes is displayed.
- On the next page of the wizard, if you want to open the list of stand-alone installation packages, enable the Open the list of stand-alone packages option.
- Click the FINISH button.
The Stand-alone installation package creation wizard closes.
The stand-alone installation package is created and placed in the PkgInst subfolder of the Administration Server shared folder. You can view the list of stand-alone packages by clicking the View the list of stand-alone packages button above the list of installation packages.
Page top
Creating custom installation packages
You can use custom installation packages to do the following:
- To install any application (for example, a text editor) on a client device, for example, by means of a task.
- To create a stand-alone installation package.
A custom installation package is a folder with a set of files. The source to create a custom installation package is an archive file. The archive file contains a file or files that must be included in the custom installation package. Creating a custom installation package, you can specify command-line parameters, for example, to install the application in a silent mode.
To create a custom installation package:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server → Advanced → Remote installation → Installation packages.
A list of installation packages available on Administration Server is displayed.
- Above the list of installation packages, click the Create installation package button.
The New package wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the first page of the wizard, select Create an installation package for the specified executable file.
- On the next page of the wizard, specify the custom installation package name.
- On the next page of the wizard, click the Browse button and, in a standard Windows Open window, choose an archive file located on the available disks to create a custom installation package.
You can upload a ZIP, CAB, TAR, or TAR.GZ archive. It is not possible to create an installation package from an SFX (self-extracting archive) file.
Files are downloaded to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
- On the next page of the wizard, specify the command-line parameters of an executable file.
You can specify command-line parameters to install the application from the installation package in a silent mode. Specifying command-line parameters is optional.
If you want, configure the following options:
- Copy entire folder to the installation package
- Convert settings to recommended values for applications recognized by Kaspersky Security Center
The process to create the custom installation package starts.
The wizard informs you when the process is finished.
If the custom installation package is not created, an appropriate message is displayed.
- Click the Finish button to close the wizard.
The installation package that you created is downloaded to the Packages subfolder of the Administration Server shared folder. After downloading, the custom installation package appears in the list of installation packages.
In the list of installation packages on Administration Server, you can view and edit custom installation package properties.
Page top
Viewing and editing properties of custom installation packages
After you created a custom installation package, you can view general information about the installation package and specify the installation settings in the properties window.
To view and edit properties of a custom installation package:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server → Advanced → Remote installation → Installation packages.
A list of installation packages available on Administration Server is displayed.
- In the context menu of an installation package, select Properties.
The properties window of the selected installation package opens.
- View the following information:
- Installation package name
- Application name packed into the custom installation package
- Application version
- Installation package creation date
- Path to the custom installation package on the Administration Server
- Executable file command line
- Specify the following settings:
- Installation package name
- Install required general system components
This option is only available when the application added to the installation package is recognized by Kaspersky Security Center.
- Executable file command line
This option is only available for packages that are not created on the basis of Kaspersky applications.
- Click the OK or Apply button to save the changes, if any.
The new settings are saved.
Obtaining the Network Agent installation package from the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit
You can obtain the Network Agent installation package from the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit, without needing to install Kaspersky Security Center. You can then use the installation package to install Network Agent on the client devices.
To obtain the Network Agent installation package from the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit:
- Run the ksc_<version number>.<build number>_full_<localization language>.exe executable file from the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit.
- In the window that opens, click the Extract installation packages link.
- In the list of installation packages, select the check box next to the Network Agent installation package, and then click the Next button.
- If necessary, click the Browse button to change the displayed folder to extract the installation package to.
- Click the Extract button.
The application extracts the Network Agent installation package.
- When the process is complete, click the Close button.
The Network Agent installation package is extracted to the selected folder.
You can use the installation package to install Network Agent by one of the following methods:
- Locally by running the setup.exe file from the extracted folder
- Via silent installation
- By using group policies of Microsoft Windows
Distributing installation packages to secondary Administration Servers
To distribute installation packages to secondary Administration Servers:
- Establish a connection with the Administration Server that controls the relevant secondary Administration Servers.
- Create a task of installation package distribution to secondary Administration Servers in one of the following ways:
- If you want to create a task for secondary Administration Servers in the selected administration group, launch the creation of a group task for this group.
- If you want to create a task for specific secondary Administration Servers, launch the creation of a task for specific devices.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
In the Select the task type window of the New task wizard, in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server node, in the Advanced folder select Distribute installation package as the task type.
The New task wizard will create the task of distributing the selected installation packages to specific secondary Administration Servers.
- Run the task manually or wait for it to launch according to the schedule you specified in the task settings.
The selected installation packages will be copied to the specific secondary Administration Servers.
Page top
Distributing installation packages through distribution points
You can use distribution points to distribute installation packages within an administration group.
After the installation packages are received from the Administration Server, distribution points automatically distribute them to client devices through IP multicasting. IP multicasting of new installation packages within an administration group occurs once. If a client device has been disconnected from the corporate network at the time of distribution, Network Agent (on the client device) automatically downloads the necessary installation package from a distribution point when the installation task is started.
Page top
Transferring application installation results to Kaspersky Security Center
After you have created the application installation package, you can configure it so that all diagnostic information about the results of the application installation is transferred to Kaspersky Security Center. For installation packages of Kaspersky applications, transfer of diagnostic information about the application installation results is configured by default, and no additional configuration is required.
To configure the transfer of diagnostic information about the results of application installation to Kaspersky Security Center:
- Navigate to the folder of the installation package created by using Kaspersky Security Center for the selected application. The folder can be found in the shared folder specified during Kaspersky Security Center installation.
- Open the file with the .kpd or .kud extension for editing (for example, in the Microsoft Windows Notepad editor).
The file has the format of a regular configuration .ini file.
- Add the following lines to the file:
[SetupProcessResult]Wait=1This command configures Kaspersky Security Center to wait for setup completion for the application, for which the installation package is created, and to analyze the installer return code. If you have to disable the transfer of diagnostic data, set the value of the Wait key to 0.
- Add the description of return codes for a successful installation. To do this, add the following lines to the file:
[SetupProcessResult_SuccessCodes]<return code>=[<description>]<return code 1>=[<description>]…Square brackets contain optional keys.
Syntax for the lines:
<return code>. Any number corresponding to the installer return code. The number of return codes can be arbitrary.<description>. Text description of the installation result. The description can be omitted.
- Add the description of return codes for a failed installation. To do this, add the following lines to the file:
[SetupProcessResult_ErrorCodes]<return code>=[<description>]<return code 1>=[<description>]…The syntax of these lines is identical to the syntax for the lines containing successful setup return codes.
- Close the .kpd or .kud file by saving all changes.
Finally, the results of installation of the user-defined application will be registered in the logs of Kaspersky Security Center and then shown in the list of events, in reports, and in task run logs.
Page top
Defining the KSN proxy server address for installation packages
In case the address or the domain of the Administration Server changes, you can define the KSN proxy server address for the installation package.
To define the KSN proxy server address for the installation package:
- In the console tree, in the Remote installation folder, double-click the Installation packages subfolder.
- In the menu that opens, select Properties.
- In the properties window that opens, select the General subsection.
- In the General subsection of the properties window, enter the address of the KSN proxy server.
The installation packages will use this address as default.
Page top
Receiving up-to-date versions of applications
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to receive up-to-date versions of corporate applications stored on Kaspersky servers.
To receive up-to-date versions of Kaspersky corporate applications:
- Do one of the following:
- In the console tree select the node the with the name of the required Administration Server, make sure the Monitoring tab is selected, and in the Deployment section click the There are new versions of Kaspersky applications available link.
The There are new versions of Kaspersky applications available link becomes visible when Administration Server finds a new version of a corporate application on a Kaspersky server.
- In the console tree, select Advanced → Remote installation → Installation packages, and in the workspace click Additional actions and from the drop-down list select View current versions of Kaspersky applications.
The list of the current version of Kaspersky applications is displayed.
- In the console tree select the node the with the name of the required Administration Server, make sure the Monitoring tab is selected, and in the Deployment section click the There are new versions of Kaspersky applications available link.
- You can filter the list of Kaspersky applications to simplify the search for the required application.
At the top of the Current application versions window, click the Filter link to filter the application list by the following criteria:
- Components. Use this criterion to filter the Kaspersky application list by the protection areas that are in use on your network.
- Type of downloaded software. Use this criterion to filter the Kaspersky application list by the application type.
- Software products and updates to display. Use this criterion to display available Kaspersky applications by specific versions.
- Displayed languages for software and updates. Use this criterion to display Kaspersky applications with a specific localization language.
Click the Apply button to apply the selected filters.
- Select the required application from the list.
- Download the application distribution package by clicking the link in the Distribution package web address string.
Updates of managed applications may require a specific minimum version of Kaspersky Security Center to be installed. If this version is later than your current version, these updates are displayed but cannot be approved. Also, no installation packages can be created from such updates until you upgrade Kaspersky Security Center. You are prompted to upgrade your Kaspersky Security Center instance to the required minimum version.
If the Download applications and create installation packages button is displayed for the application selected, you can click this button to download the application distribution package and create an installation package automatically. Kaspersky Security Center downloads the application distribution package to Administration Server, to the shared folder specified during installation of Kaspersky Security Center. The automatically created installation package is displayed in the Remote installation folder in the console tree, in the Installation packages subfolder.
After the Current application versions window is closed, the There are new versions of Kaspersky applications available link disappears from the Deployment section.
You can create installation packages for new versions of applications and manage newly created installation packages in the Remote installation folder in the console tree, in the Installation packages subfolder.
You can also open the Current application versions window by clicking the View current versions of Kaspersky applications link in the workspace of the Installation packages folder.
Preparing a Windows device for remote installation
Remote installation of the application on the client device may return an error for the following reasons:
- The task has already been successfully performed on this device.
In this case, the task does not have to be performed again.
- When a task was started, the device was shut down.
In this case, turn on the device, and then restart the task.
- There is no connection between the Administration Server and the Network Agent installed on the client device.
To determine the cause of the problem, use the utility designed for remote diagnostics of client devices (klactgui).
- If Network Agent is not installed on the device, the following issues may occur during remote installation:
- The client device has Disable simple file sharing enabled.
- The Server service is not running on the client device.
- The required ports are closed on the client device.
- The account that is used to perform the task has insufficient privileges.
To avoid issues that may occur during installation of the application on a client device without Network Agent installed, you must proceed as described in the procedure of forced deployment through the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center.
Previously, the riprep utility was used to prepare a device for remote installation. This is now considered an outdated method for configuring operating systems. The riprep utility is not recommended for use on operating systems newer than Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 R2.
Page top
Preparing a Linux device and installing Network Agent on a Linux device remotely
Network Agent installation comprises two steps:
- A Linux device preparation
- Network Agent remote installation
A Linux device preparation
To prepare a device running Linux for remote installation of Network Agent:
- Make sure that the following software is installed on the target Linux device:
- Sudo (for Ubuntu 10.04, Sudo version is 1.7.2p1 or later)
- Perl language interpreter version 5.10 or later
- Test the device configuration:
- Check whether you can connect to the device through an SSH client (such as PuTTY).
If you cannot connect to the device, open the
/etc/ssh/sshd_configfile and make sure that the following settings have the respective values listed below:PasswordAuthentication noChallengeResponseAuthentication yesDo not modify the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file if you can connect to the device with no issues; otherwise, you may encounter SSH authentication failure when running a remote installation task.
Save the file (if necessary) and restart the SSH service by using the
sudo service ssh restartcommand. - Disable the sudo password for the user account under which the device is to be connected.
- Use the
visudocommand in sudo to open the sudoers configuration file.In the file you have opened, add the following line to the end of the file: <
username> ALL = (ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL. In this case,<username>is the user account which is to be used for the device connection using SSH. If you are using the Astra Linux operating system, in the /etc/sudoers file, add the last line with the following text:%astra-admin ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL - Save the sudoers file and then close it.
- Connect to the device again through SSH and make sure that the Sudo service does not prompt you to enter a password; you can do this using the
sudo whoamicommand.
- Check whether you can connect to the device through an SSH client (such as PuTTY).
- Open the
/etc/systemd/logind.conffile, and then do one of the following:- Specify 'no' as a value for the KillUserProcesses setting:
KillUserProcesses=no. - For the KillExcludeUsers setting, type the user name of the account under which the remote installation is to be performed, for example,
KillExcludeUsers=root.
If the target device is running Astra Linux, add
export PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/binstring in the/home/<username>/.bashrcfile, where<username>is the user account which is to be used for the device connection using SSH.To apply the changed setting, restart the Linux device or execute the following command:
$ sudo systemctl restart systemd-logind.service - Specify 'no' as a value for the KillUserProcesses setting:
- If you want to install Network Agent on devices with the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 operating system, install the insserv-compat package first to configure Network Agent.
- If you want to install Network Agent on devices with the Astra Linux operating system running in the closed software environment mode, perform additional steps to prepare Astra Linux devices.
Network Agent remote installation
To install Network Agent on Linux devices remotely:
- Download and create an installation package:
- Before installing the package on the device, make sure that it already has all the dependencies (programs and libraries) installed for this package.
You can view the dependencies for each package on your own, using utilities that are specific for the Linux distribution on which the package is to be installed. For more details about utilities, refer to your operating system documentation.
- Download the Network Agent installation package by using the application interface or from the Kaspersky website.
- To create a remote installation package, use the following files:
- klnagent.kpd
- akinstall.sh
- .deb or .rpm package of Network Agent
- Before installing the package on the device, make sure that it already has all the dependencies (programs and libraries) installed for this package.
- Create a remote installation task with the following settings:
- On the Settings page of the New task wizard, select the Using operating system resources through Administration Server check box. Clear all other check boxes.
- On the Selecting an account to run the task page specify the settings of the user account that is used for device connection through SSH.
- Run the remote installation task. Use the option for the
sucommand to preserve the environment:-m, -p, --preserve-environment.
Preparing a device running SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 for installation of Network Agent
To install Network Agent on a device with the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 operating system,
Before the Network Agent installation, run the following command:
$ sudo zypper install insserv-compat
This enables you to install the insserv-compat package and configure Network Agent properly.
Run the rpm -q insserv-compat command to check whether the package is already installed.
If your network includes a lot of devices running SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15, you can use the special software for configuring and managing the company infrastructure. By using this software, you can automatically install the insserv-compat package on all necessary devices at once. For example, you can use Puppet, Ansible, Chef, or you can make your own script—use any method that is convenient for you.
If the device does not have the GPG signing keys for SUSE Linux Enterprise, you may encounter the following warning: Package header is not signed! Select the i option to ignore the warning.
Besides the insserv-compat package installation, make sure that you have completely prepared your Linux devices. After that, deploy and install Network Agent.
Page top
Preparing a macOS device for remote installation of Network Agent
To prepare a device running macOS for remote installation of Network Agent:
- Make sure that sudo is installed on the target macOS device.
- Test the device configuration:
- Make sure port 22 is open on the client device. To do this, in the System Preferences, open the Sharing pane, and then make sure the Remote Login check box is selected.
You can connect to the client device via Secure Shell (SSH) only through port 22. You cannot change the port number.
You can use the
ssh<device_name>command to log in to the macOS device remotely. In the Sharing pane, you can use the Allow access for option to set the scope of users who are allowed access to the macOS device. - Disable the sudo password for the user account under which the device is to be connected.
Use the
sudo visudocommand in the Terminal to open the sudoers configuration file. In the file that you have opened, in theUser privilege specificationentry specify the following:username ALL = (ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL. In this case,usernamestands for the user account, which is to be used for the device connection using SSH. - Save the sudoers file and then close it.
- Connect to the device again via SSH and make sure that the Sudo service does not prompt you to enter a password; you can do this using the
sudo whoamicommand.
- Make sure port 22 is open on the client device. To do this, in the System Preferences, open the Sharing pane, and then make sure the Remote Login check box is selected.
- Download and create an installation package:
- Download the Network Agent installation package using one of the following methods:
- In the console tree, by opening the context menu on Remote installation → Installation packages and selecting Show current application versions to choose from available packages
- By downloading the relevant version of Network Agent from Technical Support website at https://support.kaspersky.com/
- By requesting the installation package from Technical Support specialists
- To create a remote installation package, use the following files:
- klnagent.kud
- install.sh
- klnagentmac.dmg
- Download the Network Agent installation package using one of the following methods:
- Create a remote installation task with the following settings:
- On the Settings page of the New task wizard, select the Using operating system resources through Administration Server check box. Clear all other check boxes.
- On the Selecting an account to run the task page, to run the task specify the settings of the user account that is used for device connection via SSH.
The client device is ready for remote installation of Network Agent through the corresponding task that you have created.
Page top
Kaspersky applications: licensing and activation
This section describes the features of Kaspersky Security Center related to working with the license keys of managed Kaspersky applications.
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to perform centralized distribution of license keys for Kaspersky applications on client devices, monitor their use, and renew licenses.
When adding a license key using Kaspersky Security Center, the settings of the license key are saved on the Administration Server. Based on this information, the application generates a license key usage report and notifies the administrator of license expirations and violation of license restrictions that are set in the properties of license keys. You can configure notifications of the use of license keys within the Administration Server settings.
Licensing of managed applications
The Kaspersky applications installed on managed devices must be licensed by applying a key file or activation code to each of the applications. A key file or activation code can be deployed in the following ways:
- Automatic deployment
- The installation package of a managed application
- The Add license key task for a managed application
- Manual activation of a managed application
You can add a new active or reserve license key by any of the methods listed above. A Kaspersky application uses an active key at the current moment and stores a reserve key to apply after the active key expires. The application for which you add a license key defines whether the key is active or reserve. The key definition does not depend on the method that you use to add a new license key.
Automatic deployment
If you use different managed applications and you have to deploy a specific key file or activation code to devices, opt for other ways of deploying that activation code or key file.
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to automatically deploy available license keys to devices. For example, three license keys are stored in the Administration Server repository. You have selected the Automatically distribute license key to managed devices check box for all three license keys. A Kaspersky security application—for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows—is installed on the organization's devices. A new device is discovered to which a license key must be deployed. The application determines, for instance, that two of the license keys from the repository can be deployed to the device: license key named Key_1 and license key named Key_2. One of these license keys is deployed to the device. In this case, it cannot be predicted which of the two license keys will be deployed to the device because automatic deployment of license keys does not provide for any administrator activity.
When a license key is deployed, the devices are recounted for that license key. You must make sure that the number of devices to which the license key was deployed does not exceed the license limit. If the number of devices exceeds the license limit, all devices that were not covered by the license will be assigned Critical status.
Before deployment, the key file or activation code must be added to the Administration Server repository.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console:
or
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
Note that an automatically distributed license key may not be displayed in the virtual Administration Server repository in the following cases:
- The license key is not valid for the application.
- The virtual Administration Server does not have managed devices.
- The license key has already been used for devices managed by another virtual Administration Server and the limit on the number of devices has been reached.
Adding a key file or activation code to the installation package of a managed application
For security reasons, this option is not recommended. A key file or activation code added to an installation package may be compromised.
If you install a managed application using an installation package, you can specify an activation code or key file in this installation package or in the policy of the application. The license key will be deployed to managed devices at the next synchronization of the device with the Administration Server.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console:
or
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Adding a license key to an installation package
Deployment through the Add license key task for a managed application
If you opt for using the Add license key task for a managed application, you can select the license key that must be deployed to devices and select the devices in any convenient way—for example, by selecting an administration group or a device selection.
Before deployment, the key file or activation code must be added to the Administration Server repository.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console:
- Adding a license key to the Administration Server repository
- Deploying a license key to client devices
or
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
Adding an activation code or a key file manually to the devices
You can activate the installed Kaspersky application locally, by using the tools provided in the application interface. Please refer to the documentation of the installed application.
Viewing information about license keys in use
To view information about license keys in use,
In the console tree, select the Kaspersky Licenses folder.
The workspace of the folder displays a list of license keys used on client devices.
Next to each of the license keys an icon is displayed, corresponding to the type of use:
 —Information about the currently used license key is received from a client device connected to the Administration Server. The file of this license key is stored outside of the Administration Server.
—Information about the currently used license key is received from a client device connected to the Administration Server. The file of this license key is stored outside of the Administration Server. —The license key is stored in the Administration Server repository. Automatic distribution is disabled for this license key.
—The license key is stored in the Administration Server repository. Automatic distribution is disabled for this license key. —The license key is stored in the Administration Server repository. Automatic distribution is enabled for this license key.
—The license key is stored in the Administration Server repository. Automatic distribution is enabled for this license key.
You can view information about which license keys are used for activation of the application on a client device by opening the Applications section of the client device properties window.
To define the up-to-date settings of virtual Administration Server license keys, the Administration Server sends a request to Kaspersky activation servers at least once per day. If access to the servers using system DNS is not possible, the application uses public DNS servers.
If a license key is received from a client device, you cannot export it as a file.
Adding a license key to the Administration Server repository
To add a license key to the Administration Server repository:
- In the console tree, select the Kaspersky Licenses folder.
- Start the license key adding task in one of the following ways:
- Select Add activation code or key file in the context menu of the list of license keys.
- Click the Add activation code or key file link in the workspace of the list of license keys.
- Click the Add activation code or key file button.
The Add license key wizard starts.
- Select how you want to activate Administration Server: by using an activation code or by using a key file.
- Specify your activation code or a key file.
- Select the Automatically distribute license key to managed devices option if you want to distribute a relevant license key on your network immediately. If you do not select this option, you can manually distribute a license key later.
As a result, the key file is downloaded and the Add license key wizard is finished. You can now see the added license key in the list of Kaspersky licenses.
Deleting an Administration Server license key
To delete an Administration Server license key:
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window that opens, select the License keys section.
- Delete the license key by clicking the Remove button.
This deletes the license key.
If a reserve license key has been added, the reserve license key automatically becomes the active license key after the former active license key is deleted.
After the active license key of Administration Server is deleted, Vulnerability and patch management and Mobile Device Management become unavailable. You can add a deleted license key again or add a new license key.
Deploying a license key to client devices
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to distribute a license key to client devices through the License key distribution task.
Before deployment, add the license key to the Administration Server repository.
To distribute a license key to client devices:
- In the console tree, select the Kaspersky Licenses folder.
- In the workspace of the list of license keys, click the Automatically distribute license key to managed devices button.
The Application Activation task creation wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- In the list of applications, select the application for which you want to create a task.
- At the Add key step of the wizard, add the license key by using one of the following options:
- Select the Activation code option to add an activation code from the Kaspersky Security Center repository.
Click Select. In the window that opens, select the activation code, and then click OK.
- Select the Key file or key option, and then do the following:
- Click Select.
- In the context menu, select one of the options:
- Key file from folder.
In the window that opens, select the key file from your device, and then click Open.
- Key from Kaspersky Security Center repository.
In the window that opens, select the key from the Kaspersky Security Center repository, and then click OK.
- Key file from folder.
- Select the Activation code option to add an activation code from the Kaspersky Security Center repository.
- If you want to replace the active license key, clear the default Use as a reserve key check box.
For example, this is needed when the organization changes, and another organization's key is required on the device; or if the key was reissued, and a new license expires earlier than the current license. To avoid errors, you have to clear the Use as a reserve key check box.
If you want to find out more information about the issues that may occur when adding a license key to Kaspersky Security Center Windows and the ways to resolve them, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Knowledge Base.
- Check the license key information, and then click Next.
- At this step of the wizard, select the devices to which you want to assign the add key task. You can specify devices (up to 1000 devices) in one of the following ways:
- Select networked devices detected by Administration Server. In this case, the task is assigned to specific devices. The specific devices can include devices in administration groups as well as unassigned devices.
- Specify device addresses manually or import addresses from a list. You can specify NetBIOS names, DNS names, IP addresses, and IP subnets of devices to which you want to assign the task.
- Assign task to a device selection. In this case, the task is assigned to devices included in a selection created earlier. You can specify the predefined selection or a custom one that you created.
- Assign task to an administration group. In this case, the task is assigned to devices included in the administration group created earlier.
- At the Configure task schedule step of the wizard, create a schedule for task start:
- At the Define the task name step of the wizard, specify the name for the task. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- On the Finish task creation step of the wizard, click the Finish button to close the wizard.
If you want the task to start as soon as the wizard finishes, select the Run the task after the wizard finishes check box.
Tasks created through the Application Activation task creation wizard are tasks for specific devices stored in the Tasks folder of the console tree.
You can also create a group or local license key distribution task through the task creation wizard for an administration group and for a client device.
Automatic distribution of a license key
Kaspersky Security Center allows automatic distribution of license keys to managed devices if they are located in the license keys repository on the Administration Server. Automatic distribution of license keys does not apply to devices in the Unassigned devices folder.
To distribute a license key to managed devices automatically:
- In the console tree, select the Kaspersky Licenses folder.
- In the workspace of the folder, select the license key that you want to distribute to devices automatically.
- Open the properties window of the selected license key in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Properties in the context menu of the license key.
- By clicking the View license key properties link in the information box for the selected license key.
- In the license key properties window that opens, select the Automatically distributed license key check box. Close the license key properties window.
The license key will be automatically distributed to all compatible devices.
License key distribution is performed by means of Network Agent. No license key distribution tasks are created for the application.
During automatic distribution of a license key, the licensing limit on the number of devices is taken into account. (The licensing limit is set in the properties of the license key.) If the licensing limit is reached, distribution of this license key on devices ceases automatically.
The virtual Administration Server automatically distributes license keys from its repository and from the repository of the Administration Server. We recommend that you:
- Use the Add license key task to select the license key that must be deployed to devices.
- Avoid disabling the Allow automatic deployment of license keys from this virtual Administration Server to its devices option in the virtual Administration Server settings. Otherwise, the virtual Administration Server will not distribute license keys to devices, including the license keys from the Administration Server repository.
If you select the Automatically distributed license key check box in the license key properties window, a license key is distributed on your network immediately. If you do not select this option, you can manually distribute a license key later.
Creating and viewing a license key usage report
To create a report on usage of license keys on client devices:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Reports tab.
- Select the report template named License key usage report, or create a new report template of the same type.
The workspace of the license key usage report displays information about active and reserve license keys used on the client devices. The report also contains information about devices on which the license keys are used, and about restrictions specified in the properties of those license keys.
Viewing information about the application license keys
To learn what license keys are in use for a Kaspersky application:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, select the Managed devices node and go to the Devices tab.
- Right-click to open the context menu of the relevant device and select Properties.
- In the device properties window that opens, select the Applications section.
- In the list of applications that appears, select the application whose license keys you want to view, and then click the Properties button.
- In the application properties window that opens, select the License keys section.
The information is displayed in the workspace of this section.
Exporting a license key file
If your license key has been accidentally deleted and you want to restore it, you can export a license key file from other Administration Server.
To export a license key file, you must have the Export key file right in the General features: Key management functional area.
If a license key is received from a client device, you cannot export it.
To export a license key:
- In the console tree, select the Kaspersky Licenses folder.
- In the list, select the license key that you want to export as a file.
- In the information box that opens, click the Export key file link.
- In the window that opens, specify the path to the folder where you want to save a license key file, and then specify a file name. After that, click Save.
The license key file in .key format is exported to the selected folder.
If the license key whose file you exported was added to the Administration Server repository as an activation code, and you want to add the exported license key file to the repository of another Administration Server, you must add it as an activation code, not as a key file. Otherwise, an error occurs. You have to open the exported license key file in any convenient text editor, and then copy the activation code.
Page top
Configuring network protection
This section contains information about manual configuration of policies and tasks, about user roles, about building an administration group structure and hierarchy of tasks.
Scenario: Configuring network protection
The quick start wizard creates policies and tasks with the default settings. These settings may turn out to be sub-optimal or even disallowed by the organization. Therefore, we recommend that you fine-tune these policies and tasks and create other policies and tasks, if they are necessary for your network.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that you have done the following:
- Installed Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server
- Installed Kaspersky Security Center Web Console (optional)
- Completed the Kaspersky Security Center main installation scenario
- Completed the quick start wizard or manually created the following policies and tasks in the Managed devices administration group:
- Policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Group task for updating Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Policy of Network Agent
- Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
Configuring network protection proceeds in stages:
- Setup and propagation of Kaspersky application policies and policy profiles
To configure and propagate settings for Kaspersky applications installed on the managed devices, you can use two different security management approaches—device-centric or user-centric. These two approaches can also be combined. To implement device-centric security management, you can use tools provided in Microsoft Management Console-based Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. User-centric security management can be implemented through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console only.
- Configuring tasks for remote management of Kaspersky applications
Check the tasks created with the quick start wizard and fine-tune them, if necessary.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console:
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
If necessary, create additional tasks to manage the Kaspersky applications installed on the client devices.
- Evaluating and limiting the event load on the database
Information about events that occur during the operation of managed applications is transferred from a client device and registered in the Administration Server database. To reduce the load on the Administration Server, evaluate and limit the maximum number of events that can be stored in the database.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Setting the maximum number of events
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Setting the maximum number of events
Results
Upon completion of this scenario, your network will be protected by configuration of Kaspersky applications, tasks, and events received by the Administration Server:
- The Kaspersky applications are configured according to the policies and policy profiles.
- The applications are managed through a set of tasks.
- The maximum number of events that can be stored in the database is set.
When the network protection configuration is complete, you can proceed to configuring regular updates to Kaspersky databases and applications.
For details about how to configure automatic responses to threats detected by Kaspersky Sandbox, please refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox 2.0 Online Help.
Policy setup and propagation: Device-centric approach
When you complete this scenario, the applications will be configured on all of the managed devices in accordance with the application policies and policy profiles that you define.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that you have installed Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console (optional). If you installed Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you might also want to consider user-centric security management as an alternative or additional option to the device-centric approach.
Stages
The scenario of device-centric management of Kaspersky applications consists of the following steps:
- Configuring application policies
Configure settings for Kaspersky applications installed on the managed devices by creating a policy for each application. The set of policies will be propagated to the client devices.
When you configure the protection of your network in the quick start wizard, Kaspersky Security Center creates the default policy for the following applications:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows—for Windows-based client devices
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux—for Linux-based client devices
If you completed the configuration process by using this wizard, you do not have to create a new policy for this application. Proceed to the manual setup of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
If you have a hierarchical structure of several Administration Servers and/or administration groups, the secondary Administration Servers and child administration groups inherit the policies from the primary Administration Server by default. You can force the inheritance by the child groups and secondary Administration Servers to prohibit any modifications of the settings configured in the upstream policy. If you want only part of the settings to be forcibly inherited, you can lock them in the upstream policy. The rest unlocked settings will be available for modification in the downstream policies. The created hierarchy of policies will allow you to effectively manage devices in the administration groups.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Creating a policy
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating a policy
- Creating policy profiles (optional)
If you want devices within a single administration group to run under different policy settings, create policy profiles for those devices. A policy profile is a named subset of policy settings. This subset is distributed on target devices together with the policy, supplementing it under a specific condition called the profile activation condition. Profiles only contain settings that differ from the "basic" policy, which is active on the managed device.
By using profile activation conditions, you can apply different policy profiles, for example, to the devices located in a specific unit or security group of Active Directory, having a specific hardware configuration, or marked with specific tags. Use tags to filter devices that meet specific criteria. For example, you can create a tag called Windows, mark all devices running Windows operating system with this tag, and then specify this tag as an activation condition for a policy profile. As a result, Kaspersky applications installed on all devices running Windows will be managed by their own policy profile.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console:
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
- Propagating policies and policy profiles to the managed devices
By default, the Administration Server automatically synchronizes with managed devices every 15 minutes. You can circumvent auto-synchronization and run the synchronization manually by using the Force synchronization command. Also the synchronization is forced after you create or change a policy or a policy profile. During the synchronization, the new or changed policies and policy profiles are propagated to the managed devices.
If you use Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you can check whether the policies and policy profiles were delivered to a device. Kaspersky Security Center specifies the delivery date and time in the properties of the device.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Forced synchronization
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Forced synchronization
Results
When the device-centric scenario is complete, the Kaspersky applications are configured according to the settings specified and propagated through the hierarchy of policies.
The configured application policies and policy profiles will be applied automatically to the new devices added to the administration groups.
About device-centric and user-centric security management approaches
You can manage security settings from the standpoint of device features and from the standpoint of user roles. The first approach is called device-centric security management and the second is called user-centric security management. To apply different application settings to different devices you can use either or both types of management in combination. To implement device-centric security management, you can use tools provided in Microsoft Management Console-based Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. User-centric security management can be implemented through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console only.
Device-centric security management enables you to apply different security application settings to managed devices depending on device-specific features. For example, you can apply different settings to devices allocated in different administration groups. You can also differentiate the devices by usage of those devices in Active Directory, or their hardware specifications.
User-centric security management enables you to apply different security application settings to different user roles. You can create several user roles, assign an appropriate user role to each user, and define different application settings to the devices owned by users with different roles. For example, you may want to apply different application settings to devices of accountants and human resources (HR) specialists. As a result, when user-centric security management is implemented, each department—accounts department and HR department—has its own settings configuration for Kaspersky applications. A settings configuration defines which application settings can be changed by users and which are forcibly set and locked by the administrator.
By using user-centric security management you can apply specific application settings to individual users. This may be required when an employee has a unique role in the company or when you want to monitor security issues related to devices of a specific person. Depending on the role of this employee in the company, you can expand or limit the rights of this person to change application settings. For example, you might want to expand the rights of a system administrator who manages client devices in a local office.
You can also combine the device-centric and user-centric security management approaches. For example, you can configure a specific application policy for each administration group and then create policy profiles for one or several user roles of your enterprise. In this case, the policies and policy profiles are applied in the following order:
- The policies created for device-centric security management are applied.
- They are modified by the policy profiles according to the policy profile priorities.
- The policies are modified by the policy profiles associated with user roles.
Manual setup of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy
This section provides recommendations on how to configure the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy, which is created by the quick start wizard. You can perform the setup in the policy properties window.
When editing a setting, keep in mind that you must click the lock icon above the relevant setting in order to allow using its value on a workstation.
Configuring the policy in the Advanced Threat Protection section
For a full description of the settings in this section, please refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows documentation.
In the Advanced Threat Protection section, you can configure the use of Kaspersky Security Network for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. You can also configure Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows modules, such as Behavior Detection, Exploit Prevention, Host Intrusion Prevention, and Remediation Engine.
In the Kaspersky Security Network subsection, we recommend that you enable the Kaspersky Security Network option. Using this option helps to redistribute and optimize traffic on the network. If the Kaspersky Security Network option is disabled, you can enable direct use of KSN servers.
Configuring the policy in the Essential Threat Protection section
For a full description of the settings in this section, please refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows documentation.
In the Essential Threat Protection section of the policy properties window, we recommend that you specify additional settings in the Firewall and File Threat Protection subsections.
The Firewall subsection contains settings that allow you to control the network activity of applications on the client devices. A client device uses a network to which one of the following statuses is assigned: public, local, or trusted. Depending on the network status, Kaspersky Endpoint Security can allow or deny network activity on a device. When you add a new network to your organization, you must assign an appropriate network status to it. For example, if the client device is a laptop, we recommend that this device use the public or trusted network, because the laptop is not always connected to the local network. In the Firewall subsection, you can check whether you correctly assigned statuses to the networks used in your organization.
To check the list of networks:
- In the policy properties, go to Essential Threat Protection → Firewall.
- In the Available networks section, click the Settings button.
- In the Firewall window that opens, go to the Networks tab to view the list of networks.
In the File Threat Protection subsection, you can disable the scanning of network drives. Scanning network drives can place a significant load on network drives. It is more convenient to perform indirect scanning, on file servers.
To disable scanning of network drives:
- In the policy properties, go to Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection.
- In the Security level section, click the Settings button.
- In the File Threat Protection window that opens, on the General tab clear the All network drives check box.
Configuring the policy in the General Settings section
For a full description of the settings in this section, please refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows documentation.
In the General settings section of the policy properties window, we recommend that you specify additional settings in the Reports and Storage and Interface subsections.
In the Reports and Storage subsection, go to the Data transfer to Administration Server section. The About started applications check box specifies whether the Administration Server database saves information about all versions of all software modules on the networked devices. If this check box is selected, the saved information may require a significant amount of disk space in the Kaspersky Security Center database (dozens of gigabytes). Clear the About started applications check box if it is selected in the top-level policy.
If Administration Console manages the threat protection on the organization's network in centralized mode, disable the display of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows user interface on workstations. To do this, in the Interface subsection, go to the Interaction with user section, and then select Do not display user interface option.
To enable password protection on workstations, in the Interface subsection, go to the Password protection section, click the Settings button, and then select the Enable password protection check box.
Configuring the policy in the Event configuration section
In the Event configuration section, you should disable the saving of any events on Administration Server, except for the following ones:
- On the Critical tab:
- Application autorun is disabled
- Access denied
- Application startup prohibited
- Disinfection impossible
- End User License Agreement violated
- Could not load encryption module
- Cannot start two tasks at the same time
- Active threat detected. Advanced Disinfection should be started
- Network attack detected
- Not all components were updated
- Activation error
- Error enabling portable mode
- Error in interaction with Kaspersky Security Center
- Error disabling portable mode
- Error changing application components
- Error applying file encryption / decryption rules
- Policy cannot be applied
- Process terminated
- Network activity blocked
- On the Functional failure tab: Invalid task settings. Settings not applied
- On the Warning tab:
- Self-Defense is disabled
- Incorrect reserve key
- User has opted out of the encryption policy
- On the Info tab: Application startup prohibited in test mode
Manual setup of the group update task for Kaspersky Endpoint Security
The optimal and recommended schedule option for Kaspersky Endpoint Security versions 10 and later is When new updates are downloaded to the repository when the Use automatically randomized delay for task starts check box is selected.
Manual setup of the group task for scanning a device with Kaspersky Endpoint Security
The quick start wizard creates a group task for scanning a device. By default, the task is assigned a Run on Fridays at 7:00 PM schedule with automatic randomization, and the Run missed tasks check box is cleared.
This means that if devices in an organization are shut down on Fridays, for example, at 6:30 PM, the device scan task will never run. You must set up the most convenient schedule for this task based on the workplace rules adopted in the organization.
Scheduling the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
The quick start wizard creates the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task for Network Agent. By default, the task is assigned a Run on Tuesdays at 7:00 PM schedule with automatic randomization, and the Run missed tasks check box is selected.
If the organization's workplace rules provide for shutting down all devices at this time, the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task will run after the devices are turned on again, that is, on Wednesday morning. Such activity may be undesirable because a vulnerability scan may increase the load on CPUs and disk subsystems. You must set up the most convenient schedule for the task based on the workplace rules adopted in the organization.
Manual setup of the group task for updates installation and vulnerabilities fix
The quick start wizard creates a group task for updates installation and vulnerabilities fix for Network Agent. By default, the task is set up to run every day at 01:00 AM, with automatic randomization, and the Run missed tasks option is not enabled.
If the organization's workplace rules provide for shutting down devices overnight, the update installation will never run. You must set up the most convenient schedule for the vulnerability scan task based on the workplace rules adopted in the organization. It is also important to keep in mind that installation of updates may require restarting the device.
Setting the maximum number of events in the event repository
In the Events repository section of the Administration Server properties window, you can edit the settings of events storage in the Administration Server database by limiting the number of event records and record storage term. When you specify the maximum number of events, the application calculates an approximate amount of storage space required for the specified number. You can use this approximate calculation to evaluate whether you have enough free space on the disk to avoid database overflow. The default capacity of the Administration Server database is 400,000 events. The maximum recommended capacity of the database is 45 million events.
The application checks the database every 10 minutes. If the number of events reaches the specified maximum value plus 10,000, the application deletes the oldest events so that only the specified maximum number of events remains.
When the Administration Server deletes old events, it cannot save new events to the database. During this period of time, information about events that were rejected is written to the Kaspersky Event Log. The new events are queued and then saved to the database after the deletion operation is complete.
To limit the number of events that can be stored in the events repository on the Administration Server:
- Right-click the Administration Server, and then select Properties.
The Administration Server properties window opens.
- In the workspace of the Events repository section, specify the maximum number of events stored in the database.
- Click OK.
Additionally, you can change the settings of any task to save events related to the task progress, or save only task execution results. In doing so, you will reduce the number of events in the database, increase the speed of execution of scenarios associated with analysis of the event table in the database, and lower the risk that critical events will be overwritten by a large number of events.
Setting the maximum storage period for the information about fixed vulnerabilities
To set the maximum storage period in the database for the information about the vulnerabilities that have already been fixed on managed devices:
- Right-click the Administration Server, and then select Properties.
The Administration Server properties window opens.
- In the workspace of the Events repository section, specify the maximum storage period for the information about the fixed vulnerabilities in the database.
By default, the storage period is 90 days.
- Click OK.
The maximum storage period for the information about the fixed vulnerabilities is limited to the specified number of days. After that, the Administration Server maintenance task will delete the outdated information from the database.
Page top
Managing tasks
Kaspersky Security Center manages applications installed on devices, by creating and running various tasks. Tasks are required for installing, launching, and stopping applications, scanning files, updating databases and software modules, and performing other actions on applications.
Tasks are subdivided into the following types:
- Group tasks. Tasks that are performed on the devices of the selected administration group.
- Administration Server tasks. Tasks that are performed on the Administration Server.
- Tasks for specific devices. Tasks that are performed on selected devices, regardless of whether they are included in any administration groups.
- Local tasks. Tasks that are performed on a specific device.
An application task can only be created if the management plug-in for that application is installed on the administrator's workstation.
You can compile a list of devices (up to 1000 devices) for which a task will be created by in one of the following ways:
- By selecting networked devices discovered by Administration Server.
- By specifying a list of devices manually. You can use an IP address (or IP range), NetBIOS name, or DNS name as the device address.
- Import a list of devices from a .txt file containing the addresses of devices to be added (each address must be placed in an individual line).
If you import a list of devices from a file or create one manually, and devices are identified by their names, the list can only contain devices for which information has already been entered into the Administration Server database when those devices were connected or during device discovery.
For each application, you can create any number of group tasks, tasks for specific devices, or local tasks.
The exchange of task information between an application installed on a device and the Kaspersky Security Center database is carried out when Network Agent is connected to Administration Server.
You can make changes to the settings of tasks, view the progress of tasks, and copy, export, import, and delete tasks.
Tasks are started on a device only if the application for which the task was created is running. When the application is not running, all running tasks are canceled.
Results of completed tasks are saved in the event logs of Microsoft Windows and Kaspersky Security Center, both centrally on the Administration Server and locally on each device.
Do not include private data in task settings. For example, avoid specifying the domain administrator password.
Details of managing tasks for applications with multitenancy support
A group task for an application with multitenancy support is applied to the application depending on the hierarchy of Administration Servers and client devices. The virtual Administration Server from which the task is created must be in the same or a lower-level administration group than the client device on which the application is installed.
In events that correspond to task execution results, a service provider administrator is shown the information about the device on which the task executed. By contrast, a tenant administration is shown Multi-tenant node.
Creating a task
In Administration Console, you can create tasks directly in the folder of the administration group for which a group task is to be created, or in the workspace of the Tasks folder.
To create a group task in the folder of an administration group:
- In the console tree, select the administration group for which you want to create a task.
- In the group workspace, select the Tasks tab.
- Run the task creation by clicking the Create a task button.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
To create a task in the workspace of the Tasks folder:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- Run the task creation by clicking the Finish button.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Do not include private data in task settings. For example, avoid specifying the domain administrator password.
Creating the Administration Server task
The Administration Server performs the following tasks:
- Deliver reports
- Download updates to the Administration Server repository
- Backup of Administration Server data
- Administration Server maintenance
- Perform Windows Update synchronization
- Create installation package upon reference device OS image
- Install application remotely
- Uninstall application remotely
- Distribute installation package
- Install application on secondary Administration Servers remotely
On a virtual Administration Server, only the automatic report delivery task and the installation package creation task based on the reference device OS image are available. The repository of the virtual Administration Server displays updates downloaded to the primary Administration Server. Backup of virtual Administration Server data is performed together with backup of primary Administration Server data.
To create the Administration Server task:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- Start creation of the task in one of the following ways:
- By selecting New → Task in the context menu of the Tasks folder in the console tree.
- By clicking the Create a task button in the workspace of the Tasks folder.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
The Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server, Perform Windows Update synchronization, Administration Server maintenance, and Backup of Administration Server data tasks can be created only once. If the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server, Administration Server maintenance, Backup of Administration Server data, and Perform Windows Update synchronization tasks have already been created for the Administration Server, they will not be displayed in the task type selection window of the New task wizard.
Creating a task for specific devices
In Kaspersky Security Center, you can create tasks for specific devices. Devices that are in a set can be included in various administration groups or remain outside any administration groups. Kaspersky Security Center can perform the following main tasks for specific devices:
- Install an application remotely
- Send message to user
- Change the Administration Server
- Manage devices
- Verify updates
- Distribute installation packages
- Install application on secondary Administration Servers remotely
- Uninstall an application remotely
To create a task for specific devices:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- Start creation of the task in one of the following ways:
- By selecting New → Task in the context menu of the Tasks folder in the console tree.
- By clicking the Create a task button in the workspace of the Tasks folder.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Creating a local task
To create a local task for a device:
- Select the Devices tab in the workspace of the group that includes the device.
- From the list of devices on the Devices tab, select the device for which a local task must be created.
- Start creating the task for the selected device in one of the following ways:
- Click the Perform action button and select Create a task in the drop-down list.
- Click the Create a task link in the workspace of the device.
- Use the device properties as follows:
- In the context menu of the device, select Properties.
- In the device properties window that opens, select the Tasks section and click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Detailed instructions on how to create and configure local tasks are provided in the Guides for the respective Kaspersky applications.
Displaying an inherited group task in the workspace of a nested group
To enable the display of inherited tasks of a nested group in the workspace:
- Select the Tasks tab in the workspace of a nested group.
- In the workspace of the Tasks tab, click the Show inherited tasks button.
Inherited tasks are displayed in the list of tasks with one of the following icons:
 —If they were inherited from a group created on the primary Administration Server.
—If they were inherited from a group created on the primary Administration Server. —If they were inherited from a top-level group.
—If they were inherited from a top-level group.
If the inheritance mode is enabled, inherited tasks can only be edited in the group in which they have been created. Inherited tasks cannot be edited in the group which inherits the tasks.
Automatically turning on devices before starting a task
Kaspersky Security Center doesn't run tasks on devices that are turned off. You can configure Kaspersky Security Center to turn on these devices automatically before starting a task, by using the Wake-on-LAN function.
To configure the automatic turning on of devices before starting a task:
- In the task properties window, select the Schedule section.
- To configure actions on devices, click the Advanced link.
- In the Advanced window that opens, select the Turn on devices by using the Wake-on-LAN function before starting the task (min) check box, and then specify the time interval in minutes.
As a result, for the specified number of minutes before starting the task, Kaspersky Security Center turns on the devices and loads the operating system on them by using the Wake-on-LAN function. After the task is completed, the devices are automatically shut down if device users don't log in to the system. Note that Kaspersky Security Center automatically shuts down only the devices that are turned on by using the Wake-on-LAN function.
Kaspersky Security Center can start operating systems automatically only on the devices that support the Wake-on-LAN (WoL) standard.
Automatically turning off a device after a task is completed
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to configure a task in such a way that the devices to which it is distributed are automatically turned off after the task completes.
To automatically turn off a device after a task is complete:
- In the task properties window, select the Schedule section.
- Click the Advanced link to open the window for configuring actions on devices.
- In the Advanced window that opens, select the Shut down the devices after completing the task check box.
Limiting task run time
To limit the time during which a task is run on devices:
- In the task properties window, select the Schedule section.
- Open the window intended for configuration of actions on client devices, by clicking Advanced.
- In the Advanced window that opens, select the Stop the task if it runs longer than (min) check box and specify the time interval in minutes.
If the task is not yet complete on the device when the specified time interval expires, Kaspersky Security Center stops the task automatically.
Exporting a task
You can export group tasks and tasks for specific devices to a file. Administration Server tasks are not available for export.
To export a task:
- In the context menu of the task, select All tasks → Export.
- In the Save as window that opens, specify the file name path.
- Click the Save button.
The rights of local users are not exported.
Importing a task
You can import group tasks and tasks for specific devices. Administration Server tasks are not available for import.
To import a task:
- Select the list to which the task must be imported:
- If you want to import the task to the list of group tasks, in the workspace of the relevant administration group select the Tasks tab.
- If you want to import a task to the list of tasks for specific devices, select the Tasks folder in the console tree.
- Select one of the following options to import the task:
- In the context menu of the list of tasks, select All tasks → Import.
- Click the Import task from file link in the task list management block.
- In the window that opens, specify the path to the file from which you want to import a task.
- Click the Open button.
The task is displayed in the list of tasks.
If the newly imported task has an identical name to an existing task, the name of the imported task is expanded with the (<next sequence number>) index, for example: (1), (2).
Converting tasks
You can use Kaspersky Security Center to convert tasks from earlier versions of Kaspersky applications into those from up-to-date versions of the applications.
Conversion is available for tasks of the following applications:
- Kaspersky Anti-Virus 6.0 for Windows Workstations MP4
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 8 for Windows
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 for Windows
To convert tasks:
- In the console tree, select an Administration Server for which you want to convert tasks.
- In the Administration Server context menu, select All Tasks → Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard.
The Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
After the wizard completes its operation, new tasks are created that use the settings of tasks from earlier versions of the applications.
Starting and stopping a task manually
You can start and stop tasks manually using either of the following methods: through the context menu of the task, or through the properties window of the client device to which that task has been assigned.
Starting group tasks from the context menu of the device is only allowed to users included in the KLAdmins group.
To start or stop a task from the context menu or the properties window of the task:
- In the list of tasks, select a task.
- Start or stop the task in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Start or Stop in the context menu of the task.
- By clicking Start or Stop in the General section of the task properties window.
To start or stop a task from the context menu or the properties window of the client device:
- In the list of devices, select the device.
- Start or stop the task in one of the following ways:
- By selecting All tasks → Run task in the context menu of the device. Select the relevant task from the list of tasks.
The list of devices to which the task is assigned will be replaced with the device that you have selected. The task starts.
- By clicking the start button (
 ) or stop button (
) or stop button ( ) in the Tasks section of the device properties window.
) in the Tasks section of the device properties window.
- By selecting All tasks → Run task in the context menu of the device. Select the relevant task from the list of tasks.
Pausing and resuming a task manually
To pause or resume a running task manually:
- In the list of tasks, select a task.
- Pause or resume the task in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Pause or Resume in the context menu of the task.
- By selecting the General section in the task properties window and clicking Pause or Resume.
Monitoring task execution
To monitor task execution,
in the task properties window, select the General section.
In the middle part of the General section, the current task status is displayed.
Viewing task run results stored on the Administration Server
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to view the results for group tasks, tasks for specific devices, and Administration Server tasks.
To view the task results:
- In the task properties window, select the General section.
- Click the Results link to open the Task results window.
To view task results for a secondary Administration Server:
- In the task properties window, select the General section.
- Click the Results link to open the Task results window.
- Click Statistics from secondary Servers.
- Select the secondary Server for which you want to display the Task results window.
Configuring filtering of information about task run results
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to filter information about results for group tasks, tasks for specific devices, and Administration Server tasks. No filtering is available for local tasks.
To set up the filtering of information about task run results:
- In the task properties window, select the General section.
- Click the Results link to open the Task results window.
The upper table contains a list of all devices for which the task is assigned. The lower table displays the results of the task performed on the selected device.
- Right-click the relevant table to open the context menu and select Filter.
- In the Set filter window that opens, define the filter settings in the Events, Devices, and Time sections. Click OK.
The Task results window displays information that meets the settings specified in the filter.
Modifying a task. Rolling back changes
To modify a task:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- In the workspace of the Tasks folder, select a task and proceed to the task properties window using the context menu.
- Make the relevant changes.
In the Exclusions from task scope section, you can set up the list of subgroups to which the task is not applied.
- Click Apply.
The changes made to the task will be saved in the task properties window, in the Revision history section.
You can roll back changes made to a task, if necessary.
To roll back changes made to a task:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- Select the task in which changes must be rolled back, and proceed to the task properties window using the context menu.
- In the task properties window, select the Revision history section.
- In the list of task revisions, select the number of the revision to which you need to roll back changes.
- Click the Advanced button and select the Roll back value in the drop-down list.
Comparing tasks
You can compare tasks of the same type: for example, you can compare two malware scan tasks, but you cannot compare a malware scan task and an update installation task. After the comparison, you have a report that displays which settings of the tasks match and which settings differ. You can print the task comparison report or save it as a file. You may need task comparison when different units within a company are assigned various tasks of the same type. For example, employees at the accounting department have a task of malware scanning only local disks on their devices, while employees at the sales department communicate with customers so they have a task of scanning both local disks and email. You do not have to view all the task settings to quickly notice such difference; you can simply compare the tasks instead.
Only tasks of the same type can be compared.
Tasks can only be compared in pairs.
You can compare tasks in one of following ways: by selecting one task and comparing it to another, or by comparing any two tasks from the list of tasks.
To select one task and compare it to another:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- In the workspace of the Tasks folder, select the task that you want to compare to another.
- In the context menu of the task, select All tasks → Compare to another task.
- In the Select a task window, select the task for comparison.
- Click OK.
A report in HTML format that compares the two tasks is displayed.
To compare any two tasks from the list of tasks:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- In the Tasks folder, in the list of tasks, press the Shift or Ctrl key to select two tasks of the same type.
- In the context menu, select Compare.
A report in HTML format that compares the selected tasks is displayed.
When tasks are compared, if the passwords differ, asterisks (******) are displayed in the task comparison report.
If the password has been changed in the task properties, asterisks (******) are displayed in the revision comparison report (******).
Accounts to start tasks
You can specify an account under which the task should be run.
For example, to perform an on-demand scan task, you must have access rights to the object being scanned, and to perform an update task, you need authorized proxy server user rights. The capability to specify an account for the task run allows you to avoid problems with on-demand scan tasks and update tasks in case the user running a task does not have the required access rights.
During the execution of remote installation/uninstallation tasks, the specified account is used to download to client devices the files required to install/uninstall an application in case Network Agent is not installed or unavailable. If Network Agent is installed and available, the account is used if in accordance with task settings, file delivery is performed only by using Microsoft Windows utilities from the shared folder. In this case, the account must have the following rights on the device:
- Right to start applications remotely.
- Rights to use the Admin$ resource.
- Right to Log On As Service.
If the files are delivered to devices through Network Agent, the account will not be used. All file copying and installation operations are then performed by the Network Agent (LocalSystem account).
Exporting task execution history
If you encounter any issues with a task, you may need to investigate the underlying reasons. To do this, you can export and further analyze the task execution history.
To export task execution history:
- Create an empty TXT file in a directory on your device.
The task execution history will be exported into this file.
- Open the task results window.
- In the upper part of the task results window, select the device that is experiencing issues.
- In the lower part of the task results window, where the execution history for the selected device is displayed, select one or several events.
To select several events, use the Shift or Ctrl key.
- Right-click the selected event(s) to open the context menu and select Export.
The Events export wizard starts.
- At the Export file step of the wizard, click the Browse button, and then select the TXT file that you created for exporting the task execution history.
If you want to export only the selected event(s), enable the option Export selected events only.
If you want to export the entire history of task execution (all events), the option Export selected events only must be disabled.
- Click the Next button.
- At the Export format step of the wizard, enable one of the following options:
- Export as tab-delimited Unicode text
Enable this option if the exported data includes special characters and symbols from several languages and you need to ensure that all characters are preserved accurately when the TXT file with the exported data is opened in different applications.
- Export as tab-delimited text
Enable this option if you want to maintain compatibility with older systems or applications that may not support Unicode.
- Export as tab-delimited Unicode text
- Click the Next button to finish the wizard.
The task execution history is exported to the selected TXT file.
Page top
Change tasks password wizard
For a non-local task, you can specify an account under which the task must be run. You can specify the account during task creation or in the properties of an existing task. If the specified account is used in accordance with security instructions of the organization, these instructions might require changing the account password from time to time. When the account password expires and you set a new one, the tasks will not start until you specify the new valid password in the task properties.
The Change tasks password wizard enables you to automatically replace the old password with the new one in all tasks in which the account is specified. Alternatively, you can do it manually in the properties of each task.
To start the Change tasks password wizard:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks node.
- In the context menu of the node, select Change tasks password wizard.
Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Step 1. Specifying credentials
In the Account and Password fields, specify new credentials that are currently valid in your system (for example, in Active Directory). When you switch to the next step of the wizard, Kaspersky Security Center checks if the specified account name matches the account name in the properties of each non-local task. If the account names match, the password in the task properties will be automatically replaced with the new one.
If you fill in the Old password (optional) field, Kaspersky Security Center replaces the password only for those tasks in which both the account name and the old password are found. The replacement is performed automatically. In all other cases you have to choose an action to take in the next step of the wizard.
Step 2. Selecting an action to take
If you have not specified the old password on the first step of the wizard or the specified old password has not matched the passwords in the tasks, you need to choose an action to take for the found tasks.
For each task that has the Approval required status, decide whether you want to remove the password in the task properties or replace it with the new one. If you choose to remove the password, the task is switched to run under the default account.
Step 3. Viewing the results
On the last step of the wizard, view the results for each of the found task. To complete the wizard, click the Finish button.
Creating a hierarchy of administration groups subordinate to a virtual Administration Server
After the virtual Administration Server is created, it contains by default an administration group named Managed devices.
The procedure for creating a hierarchy of administration groups subordinate to a virtual Administration Server is the same as the procedure for creating a hierarchy of administration groups subordinate to the physical Administration Server.
You cannot add secondary and virtual Administration Servers to administration groups subordinate to a virtual Administration Server. This is due to limitations of virtual Administration Servers.
Policies and policy profiles
In Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you can create policies for Kaspersky applications. This section describes policies and policy profiles, and provides instructions for creating and modifying them.
Hierarchy of policies, using policy profiles
This section provides information about how to apply policies to devices in administration groups. This section also provides information about policy profiles.
Hierarchy of policies
In Kaspersky Security Center, you use policies for defining a single collection of settings to multiple devices. For example, the policy scope of application P defined for administration group G includes managed devices with application P installed that have been deployed in group G and all of its subgroups, except for subgroups where the Inherit from parent group check box is cleared in the properties.
A policy differs from any local setting by lock icons ( ) next to its settings. If a setting (or a group of settings) is locked in the policy properties, you must, first, use this setting (or group of settings) when creating effective settings and, second, you must write the settings or group of settings to the downstream policy.
) next to its settings. If a setting (or a group of settings) is locked in the policy properties, you must, first, use this setting (or group of settings) when creating effective settings and, second, you must write the settings or group of settings to the downstream policy.
Creation of the effective settings on a device can be described as follows: the values of all settings that have not been locked are taken from the policy, then they are overwritten with the values of local settings, and then the resulting collection is overwritten with the values of locked settings taken from the policy.
Policies of the same application affect each other through the hierarchy of administration groups: Locked settings from the upstream policy overwrite the same settings from the downstream policy.
There is a special policy for out-of-office users. This policy takes effect on a device when the device switches into out-of-office mode. Out-of-office policies do not affect other policies through the hierarchy of administration groups.
Page top
Policy profiles
Applying policies to devices only through the hierarchy of administration groups may be inconvenient in many circumstances. It may be necessary to create several instances of a single policy that differ in one or two settings for different administration groups, and synchronize the contents of those policies in the future.
To help you avoid such problems, Kaspersky Security Center supports policy profiles. A policy profile is a named subset of policy settings. This subset is distributed on target devices together with the policy, supplementing it under a specific condition called the profile activation condition. Profiles only contain settings that differ from the "basic" policy, which is active on the client device (computer or mobile device). Activation of a profile modifies the policy settings that were active on the device before the profile was activated. Those settings take values that have been specified in the profile.
The following restrictions are currently imposed on policy profiles:
- A policy can include a maximum 100 profiles.
- A policy profile cannot contain other profiles.
- A policy profile cannot contain notification settings.
Contents of a profile
A policy profile contains the following constituent parts:
- Name. Profiles with identical names affect each other through the hierarchy of administration groups with common rules.
- Subset of policy settings. Unlike the policy, which contains all the settings, a profile only contains settings that are actually required (locked settings).
- Activation condition is a logical expression with the device properties. A profile is active (supplements the policy) only when the profile activation condition becomes true. In all other cases, the profile is inactive and ignored. The following device properties can be included in that logical expression:
- Status of out-of-office mode.
- Properties of network environment—Name of the active rule for Network Agent connection.
- Presence or absence of specified tags on the device.
- Device location in Active Directory unit: explicit (the device is right in the specified OU), or implicit (the device is in an OU, which is within the specified OU at any nesting level).
- Device's membership in an Active Directory security group (explicit or implicit).
- Device owner's membership in an Active Directory security group (explicit or implicit).
- Profile disabling check box. Disabled profiles are always ignored and their respective activation conditions are not verified.
- Profile priority. The activation conditions of different profiles are independent, so several profiles can be activated simultaneously. If active profiles contain non-overlapping collections of settings, no problems will arise. However, if two active profiles contain different values of the same setting, an ambiguity will occur. This ambiguity is to be avoided through profile priorities: The value of the ambiguous variable will be taken from the profile that has the higher priority (the one that is rated higher in the list of profiles).
Behavior of profiles when policies affect each other through the hierarchy
Profiles with the same name are merged according to the policy merge rules. Profiles of an upstream policy have a higher priority than profiles of a downstream policy. If editing settings is prohibited in the upstream policy (it is locked), the downstream policy uses the profile activation conditions from the upstream one. If editing settings is allowed in the upstream policy, the profile activation conditions from the downstream policy are used.
Since a policy profile may contain the Device is offline property in its activation condition, profiles completely replace the feature of policies for out-of-office users, which will no longer be supported.
A policy for out-of-office users may contain profiles, but its profiles can only be activated after the device switches into out-of-office mode.
Page top
Inheritance of policy settings
A policy is specified for an administration group. Policy settings can be inherited, that is, received in the subgroups (child groups) of the administration group for which they were set. Hereinafter, a policy for a parent group is also referred to as a parent policy.
You can enable or disable two options of inheritance: Inherit settings from parent policy and Force inheritance of settings in child policies:
- If you enable Inherit settings from parent policy for a child policy and lock some settings in the parent policy, then you cannot change these settings for the child group. You can, however, change the settings that are not locked in the parent policy.
- If you disable Inherit settings from parent policy for a child policy, then you can change all the settings in the child group, even if some settings are locked in the parent policy.
- If you enable Force inheritance of settings in child policies in the parent group, this enables the Inherit settings from parent policy for each child policy. In this case, you cannot disable this option for any child policy. All the settings that are locked in the parent policy are forcibly inherited in the child groups, and you cannot change these settings in the child groups.
- In policies for the Managed devices group, the Inherit settings from parent policy does not affect any settings, because the Managed devices group does not have any upstream groups and therefore does not inherit any policies.
By default, the Inherit settings from parent policy option is enabled for a new policy.
If a policy has profiles, all the child policies inherit these profiles.
Page top
Managing policies
The applications installed on client devices are centrally configured by defining policies.
Policies created for applications in an administration group are displayed in the workspace, on the Policies tab. Before the name of each policy, an icon with its status is displayed.
After a policy is deleted or revoked, the application continues working with the settings specified in the policy. Those settings subsequently can be modified manually.
A policy is applied as follows: if a device is running resident tasks (real-time protection tasks), they keep running with the new setting values. Any periodic tasks (on-demand scan, update of application databases) that are started keep running with the values unchanged. Next time, they will be run with the new setting values.
Policies for applications with multitenancy support are inherited to lower-level administration groups as well as to upper-level administration groups: the policy is propagated to all client devices on which the application is installed.
If Administration Servers are structured hierarchically, secondary Administration Servers receive policies from the primary Administration Server and distribute them to client devices. When inheritance is enabled, policy settings can be modified on the primary Administration Server. After this, any changes made to the policy settings are propagated to inherited policies on secondary Administration Servers.
If the connection is terminated between the primary and secondary Administration Servers, the policy on the secondary Server continues, using the applied settings. Policy settings modified on the primary Administration Server are distributed to a secondary Administration Server after the connection is re-established.
If inheritance is disabled, policy settings can be modified on a secondary Administration Server independently from the primary Administration Server.
If the connection between Administration Server and a client device is interrupted, the client device starts running under the out-of-office policy (if it is defined), or the policy keeps running under the applied settings until the connection is re-established.
The results of policy distribution to the secondary Administration Server are displayed in the policy properties window of the console on the primary Administration Server.
The results of policy distribution to client devices are displayed in the policy properties window of the Administration Server to which they are connected.
Do not use private data in policy settings. For example, avoid specifying the domain administrator password.
Creating a policy
In Administration Console, you can create policies directly in the folder of the administration group for which a policy is to be created, or in the workspace of the Policies folder.
To create a policy in the folder of an administration group:
- In the console tree, select an administration group for which you want to create a policy.
- In the workspace of the group, select the Policies tab.
- Run the New policy wizard by clicking the New policy button.
The New policy wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
To create a policy in the workspace of the Policies folder:
- In the console tree, select the Policies folder.
- Run the New policy wizard by clicking the New policy button.
The New policy wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
You can create several policies for one application from the group, but only one policy can be active at a time. When you create a new active policy, the previous active policy becomes inactive.
When creating a policy, you can specify a minimum set of parameters required for the application to function properly. All other values are set to the default values applied during the local installation of the application. You can change the policy after it is created.
Do not use private data in policy settings. For example, avoid specifying the domain administrator password.
Settings of Kaspersky applications that are changed after policies are applied are described in detail in their respective Guides.
After the policy is created, the settings locked from editing (marked with the lock icon ( )) take effect on client devices regardless of which settings were previously specified for the application.
)) take effect on client devices regardless of which settings were previously specified for the application.
Displaying inherited policy in a subgroup
To enable the display of inherited policies for a nested administration group:
- In the console tree, select the administration group for which inherited policies have to be displayed.
- In the workspace of the selected group, select the Policies tab.
- In the context menu of the list of policies, select View → Inherited policies.
Inherited policies are displayed in the list of policies with the following icon:
 —If they were inherited from a group created on the primary Administration Server.
—If they were inherited from a group created on the primary Administration Server. —If they were inherited from a top-level group.
—If they were inherited from a top-level group.
When the settings inheritance mode is enabled, inherited policies are only available for modification in the group in which they were created. Modification of inherited policies is not available in the group that inherits them.
Page top
Activating a policy
To make a policy active for the selected group:
- In the workspace of the group, on the Policies tab select the policy that you have to make active.
- To activate the policy, perform one of the following actions:
- In the context menu of the policy, select Active policy.
- In the policy properties window open the General section and select Active policy from the Policy status settings group.
The policy becomes active for the selected administration group.
When a policy is applied to a large number of client devices, both the load on the Administration Server and the network traffic increase significantly for some time.
Page top
Activating a policy automatically at the Virus outbreak event
To make a policy perform automatic activation at a Virus outbreak event:
- In the Administration Server properties window, open the Virus outbreak section.
- Open the Policy activation window by clicking the Configure policies to activate when a virus outbreak event occurs link and add the policy to the selected list of policies that are activated when a virus outbreak is detected.
If a policy has been activated on the Virus outbreak event, you can return to the previous policy only by using the manual mode.
Applying an out-of-office policy
The out-of-office policy takes effect on a device if it is disconnected from the corporate network.
To apply an out-of-office policy:
In the policy properties window, open the General section and in the Policy status settings group, select Out-of-office policy.
The out-of-office policy will be applied to the devices if they are disconnected from the corporate network.
Page top
Modifying a policy. Rolling back changes
To modify a policy:
- In the console tree, select the Policies folder.
- In the workspace of the Policies folder, select a policy and proceed to the policy properties window using the context menu.
- Make the relevant changes.
- Click Apply.
The changes made to the policy will be saved in the policy properties, in the Revision history section.
You can roll back changes made to the policy, if necessary.
To roll back changes made to the policy:
- In the console tree, select the Policies folder.
- Select the policy in which changes must to be rolled back, and proceed to the policy properties window using the context menu.
- In the policy properties window, select the Revision history section.
- In the list of policy revisions, select the number of the revision to which you need to roll back changes.
- Click the Advanced button and select the Roll back value in the drop-down list.
Comparing policies
You can compare two policies for a single managed application. After the comparison, you have a report that displays which policy settings match and which settings differ. For example, you may have to compare policies if different administrators in their respective offices have created multiple policies for a single managed application, or if a single top-level policy has been inherited by all local offices and modified for each office. You can compare policies in one of the following ways: by selecting one policy and comparing it to another, or by comparing any two policies from the list of policies.
You can only compare policies that have current revisions in the revision history.
To compare one policy to another:
- In the console tree, select the Policies folder.
- In the workspace of the Policies folder, select the policy that you require to compare to another.
- In the context menu of the policy, select Compare policy to another policy.
- In the Select policy window, select the policy to which your policy must be compared.
- Click OK.
A report in HTML format is displayed for the comparison of the two policies for the same application.
To compare any two policies from the list of policies:
- In the Policies folder, in the list of policies, use the Shift or Ctrl key to select two policies for a single managed application.
- In the context menu, select Compare.
A report in HTML format is displayed for the comparison of the two policies for the same application.
The report on comparison of policy settings for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows also provides details of the comparison of policy profiles. You can minimize the results of policy profile comparison. To minimize the section, click the arrow icon ( ) next to the section name.
) next to the section name.
Viewing the policy distribution status chart
In Kaspersky Security Center, you can view the results of policy enforcement on each device.
To view the policy distribution status on each device:
- In the workspace of the group, on the Policies tab select the policy for which you want to view the distribution status.
The chart on the right pane displays the overview of policy enforcement.
- Click Details.
The Results of policy enforcement window opens.
You can export the results of policy enforcement to a CSV or TXT file.
Deleting a policy
To delete a policy:
- In the workspace of an administration group, on the Policies tab, select the policy that you want to delete.
- Delete the policy in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Delete in the context menu of the policy.
- By clicking the Delete policy link in the information box for the selected policy.
Copying a policy
To copy a policy:
- In the workspace of the required group, on the Policies tab select a policy.
- In the context menu of the policy, select Copy.
- In the console tree, select a group to which you want to add the policy.
You can add a policy to the group from which it was copied.
- From the context menu of the list of policies for the selected group, on the Policies tab select Paste.
The policy is copied with all its settings and is applied to the devices within the group to which it was copied. If you paste the policy into the same group from which it has been copied, the (<next sequence number>) index is automatically added to the policy name, for example: (1), (2).
An active policy becomes inactive while it is copied. If necessary, you can make it active.
Page top
Exporting a policy
To export a policy:
- Export a policy in one of the following ways:
- By selecting All tasks → Export in the context menu of the policy.
- By clicking the Export policy to file link in the information box for the selected policy.
- In the Save as window that opens, specify the policy file name and path. Click the Save button.
Importing a policy
To import a policy:
- In the workspace of the relevant group, on the Policies tab select one of the following ways of importing policies:
- By selecting All tasks → Import in the context menu of the list of policies.
- By clicking the Import policy from file button in the management block for policy list.
- In the window that opens, specify the path to the file from which you want to import a policy. Click the Open button.
The imported policy is displayed in the policy list. The settings and profiles of the policy are also imported. Regardless of the policy status that was selected during the export, the imported policy is inactive. You can change the policy status in the policy properties.
If the newly imported policy has a name identical to that of an existing policy, the name of the imported policy is expanded with the (<next sequence number>) index, for example: (1), (2).
Page top
Converting policies
Kaspersky Security Center can convert policies from earlier versions of managed Kaspersky applications to the up-to-date versions of the same applications. Converted policies keep the current administrator's settings specified before the update, as well as include new settings from the up-to-date versions of the applications. If a policy is converted to an up-to-date version of a managed Kaspersky application, you cannot open the policy on an Administration Server that has an earlier version of the application plug-in installed. Management plug-ins for Kaspersky applications determine whether conversion is available for the policies of these applications. For information about converting policies for each supported Kaspersky application, refer to the relevant Help from the following list:
- Kaspersky applications for workstations:
- Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity:
- Kaspersky applications for mobile devices:
- Kaspersky applications for file servers:
- Kaspersky applications for virtual machines:
- Kaspersky applications for mail systems and SharePoint / collaboration servers:
- Kaspersky applications for detection of targeted attacks:
- Kaspersky applications for KasperskyOS devices:
To convert policies:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server for which you want to convert policies.
- In the Administration Server context menu, select All Tasks → Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard.
The Policies and tasks batch conversion wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
After the wizard completes, new policies are created that use the current administrator's settings of policies and the new settings from the up-to-date versions of Kaspersky applications.
Page top
Managing policy profiles
Policy profile is a named collection of settings of a policy that is activated on a client device (computer or mobile device) when the device satisfies specified activation rules. Activation of a profile modifies the policy settings that were active on the device before the profile was activated. Those settings take values that have been specified in the profile.
Policy profiles are necessary for devices within a single administration group to run under different policy settings. For example, a situation may occur when policy settings have to be modified for some devices in an administration group. In this case, you can configure policy profiles for such a policy, which allows you to edit policy settings for selected devices in the administration group. For example, the policy prohibits running any GPS navigation software on all devices in the Users administration group. GPS navigation software is necessary only on a single device in the Users administration group—the device owned by the user employed as a courier. You can tag that device as simply "Courier" and reconfigure the policy profile so that it allows GPS navigation software to run only on the device tagged as "Courier", while preserving all the remaining policy settings. In this case, if a device tagged as "Courier" appears in the Users administration group, it will be allowed to run GPS navigation software. Running GPS navigation software will still be prohibited on other devices in the Users administration group unless they are tagged as "Courier", too.
Profiles are only supported by the following policies:
- Policies of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Policies of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac
- Policies of the Kaspersky Mobile Device Management plug-in ranging from version 10 Service Pack 1 to version 10 Service Pack 3 Maintenance Release 1
- Policies of the Kaspersky Device Management for iOS plug-in
- Policies of Kaspersky Security for Virtualization 5.1 Light Agent for Windows
- Policies of Kaspersky Security for Virtualization 5.1 Light Agent for Linux
Policy profiles simplify the management of the client devices that the policies apply to:
- The policy profile settings may differ from the policy settings.
- You do not have to maintain and manually apply several instances of a single policy that differ only by a few settings.
- You do not have to allocate a separate policy for out-of-office users.
- You can export and import policy profiles, as well as create new policy profiles based on existing ones.
- A single policy can have multiple active policy profiles. Only profiles that meet the activation rules effective on the device will be applied to that device.
- Profiles are subject to the policy hierarchy. An inherited policy includes all profiles of the higher-level policy.
Priorities of profiles
Profiles that have been created for a policy are sorted in descending order of priority. For example, if profile X is higher in the list of profiles than profile Y, then X has a higher priority than the latter. Multiple profiles can be simultaneously applied to a single device. If values of a setting vary in different profiles, the value from the highest-priority profile will be applied on the device.
Profile activation rules
A policy profile is activated on a client device when an activation rule is triggered. Activation rules are a set of conditions that, when met, start the policy profile on a device. An activation rule can contain the following conditions:
- Network Agent on a client device connects to the Administration Server that has a specified set of connection settings, such as Administration Server address, port number, and so forth.
- The client device is offline.
- The client device has been assigned specified tags.
- The client device is explicitly (the device is immediately located in the specified unit) or implicitly (the device is located in a unit that is in the specified unit at any nesting level) located in a specific unit of Active Directory, the device or its owner is located in a security group of Active Directory.
- The client device belongs to a specified owner, or the owner of the device is included in an internal security group of Kaspersky Security Center.
- The owner of the client device has been assigned a specified role.
Policies in the hierarchy of administration groups
If you are creating a policy in a low-level administration group, this new policy inherits all profiles of the active policy from the higher-level group. Profiles with identical names are merged. Policy profiles for the higher-level group have the higher priority. For example, in administration group A, policy P(A) has profiles X1, X2, and X3 (in descending order of priority). In administration group B, which is a subgroup of group A, policy P(B) has been created with profiles X2, X4, X5. Then policy P(B) will be modified with policy P(A) so that the list of profiles in policy P(B) will appear as follows: X1, X2, X3, X4, X5 (in descending order of priority). The priority of profile X2 will depend on the initial state of X2 of policy P(B) and X2 of policy P(A). After the policy P(B) is created, the policy P(A) is no longer displayed in subgroup B.
The active policy is recalculated every time you run Network Agent, enable and disable offline mode, or edit the list of tags assigned to the client device. For example, the RAM size has been increased on the device, which, in turn, has activated the policy profile that is applied on devices with large RAM size.
Properties and restrictions of policy profiles
Profiles have the following properties:
- Profiles of an inactive policy have no impact on client devices.
- If a policy is set to the Out-of-office policy status, profiles of the policy will also be applied when a device is disconnected from the corporate network.
- Profiles do not support static analysis of access to executable files.
- A policy profile cannot contain any settings of event notifications.
- If UDP port 15000 is used for connecting a device to Administration Server, the corresponding policy profile is activated within one minute after you assign a tag to the device.
- You can use rules for Network Agent connection to the Administration Server, when you create policy profile activation rules.
Creating a policy profile
Profile creation is available only for the policies of the following applications:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 1 for Windows and later versions
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 1 for Mac
- Kaspersky Mobile Device Management plug-in versions 10 Service Pack 1 to 10 Service Pack 3 Maintenance Release 1
- Kaspersky Device Management for iOS plug-in
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization 5.1 Light Agent for Windows and Linux
To create a policy profile:
- In the console tree, select the administration group for whose policy you have to create a policy profile.
- In the workspace of the administration group, select the Policies tab.
- Select a policy and switch to the policy properties window using the context menu.
- Open the Policy profiles section in the policy properties window and click the Add button.
The New policy profile wizard starts.
- In the Policy profile name window of the wizard, specify the following:
- Name of the policy profile
The profile name cannot include more than 100 characters.
- Policy profile status (Enabled or Disabled)
We recommend that you create and enable inactive policy profiles only after you are completely finished with the settings and conditions of policy profile activation.
- Name of the policy profile
- Select the After closing the New policy profile wizard, proceed to configuring the policy profile activation rule check box to start the New policy profile activation rule wizard. Follow the wizard steps.
- Edit the policy profile settings in the policy profile properties window, in the way you require.
- Save the changes by clicking OK.
The profile is saved. The profile will be activated on devices that meet the activation rules.
You can create multiple profiles for a single policy. Profiles that have been created for a policy are displayed in the policy properties, in the Policy profiles section. You can modify a policy profile and change the profile priority, as well as remove the profile.
Modifying a policy profile
Editing the settings of a policy profile
The capability to edit a policy profile is only available for policies of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
To modify a policy profile:
- In the console tree, select the administration group for which the policy profile has to be modified.
- In the workspace of the group, select the Policies tab.
- Select a policy and switch to the policy properties window using the context menu.
- Open the Policy profiles section in the policy properties.
This section contains a list of profiles that have been created for the policy. Profiles are displayed in the list in accordance with their priorities.
- Select a policy profile and click the Properties button.
- Configure the profile in the properties window:
- If necessary, in the General section, change the profile name and enable or disable the profile using the Enable profile check box.
- In the Activation rules section, edit the profile activation rules.
- Edit the policy settings in the corresponding sections.
- Click OK.
The modified settings will take effect either after the device is synchronized with the Administration Server (if the policy profile is active), or after an activation rule is triggered (if the policy profile is inactive).
Changing the priority of a policy profile
The priorities of policy profiles define the activation order of profiles on a client device. Priorities are used if identical activation rules are set for different policy profiles.
For example, two policy profiles have been created: Profile 1 and Profile 2 that differ by the respective values of a single setting (Value 1 and Value 2). The priority of Profile 1 is higher than that of Profile 2. Moreover, there are also profiles with priorities that are lower than that of Profile 2. The activation rules for those profiles are identical.
When an activation rule is triggered, Profile 1 will be activated. The setting on the device will take Value 1. If you remove Profile 1, then Profile 2 will have the highest priority, so the setting will take Value 2.
On the list of policy profiles, profiles are displayed in accordance with their respective priorities. The profile with the highest priority is ranked first. You can change the priority of a profile by using the up arrow  and the down arrow
and the down arrow  buttons.
buttons.
Deleting a policy profile
To delete a policy profile:
- In the console tree, select the administration group whose policy profile you want to delete.
- In the workspace of the administration group, select the Policies tab.
- Select a policy and switch to the policy properties window using the context menu.
- Open the Policy profiles section in the properties of the policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Select the policy profile that you want to delete and click the Delete button.
The policy profile will be deleted. The active status will pass either to another policy profile whose activation rules are triggered on the device, or to the policy.
Page top
Creating a policy profile activation rule
To create a policy profile activation rule:
- In the console tree, select the administration group for which you have to create a policy profile activation rule.
- In the workspace of the group, select the Policies tab.
- Select a policy and switch to the policy properties window using the context menu.
- Select the Policy profiles section in the policy properties window.
- Select the policy profile for which you need to create an activation rule, and click the Properties button.
The policy profile properties window opens.
If the list of policy profiles is empty, you can create a policy profile.
- Select the Activation rules section, and click the Add button.
The New policy profile activation rule wizard starts.
- In the Policy profile activation rules window, select the check boxes next to the conditions that must affect activation of the policy profile that you are creating:
- General rules for policy profile activation
- Rules for Active Directory usage
- Rules for a specific device owner
- Rules for hardware specifications
The number of additional pages of the wizard depends on the settings that you select at the first step. You can modify policy profile activation rules later.
- In the General conditions window, specify the following settings:
- In the Device is offline field, in the drop-down list specify the condition for device presence on the network:
- In the The device is in the specified network location box, use the drop-down lists to set up the policy profile activation if the Administration Server connection rule is executed / not executed on this device:
The General conditions window is displayed if the General rules for policy profile activation check box is selected.
- In the Conditions using tags window, specify the following settings:
The Conditions using tags window is displayed if the General rules for policy profile activation check box is selected.
- In the Conditions using Active Directory window, specify the following settings:
- Device owner's membership in Active Directory security group
- Device membership in Active Directory security group
- Device allocation in Active Directory organizational unit
The Conditions using Active Directory window is displayed if the Rules for Active Directory usage check box is selected.
- In the Conditions using the device owner window, specify the following settings:
- Device owner
- The device owner is included in an internal security group
- Activate policy profile by specific role of device owner
The Conditions using the device owner window is displayed if the Rules for a specific device owner check box is selected.
- In the Conditions using equipment specifications window, specify the following settings:
The Conditions using equipment specifications window is displayed if the Rules for hardware specifications check box is selected.
- In the Name of policy profile activation rule window, in the Rule name field, specify a name for the rule.
The profile will be saved. The profile will be activated on the device when activation rules are triggered.
Policy profile activation rules created for the profile are displayed in the policy profile properties in the Activation rules section. You can modify or remove any policy profile activation rule.
Multiple activation rules can be triggered simultaneously.
Device moving rules
We recommend that you automate the allocation of devices to administration groups by using device moving rules. A device moving rule consists of three main parts: a name, an execution condition (a logical expression with the device attributes), and a target administration group. A rule moves a device to the target administration group if the device attributes meet the rule execution condition.
All device moving rules have priorities. The Administration Server checks whether the device attributes meet the execution condition of each rule, in ascending order of priority. If the device attributes meet the execution condition of a rule, the device is moved to the target group, so the rule processing is complete for this device. If the device attributes meet the conditions of multiple rules, the device is moved to the target group of the rule with the highest priority (that is, has the highest rank in the list of rules).
Device moving rules can be created implicitly. For example, in the properties of an installation package or a remote installation task, you can specify the administration group to which the device must be moved after Network Agent is installed on it. Also, device moving rules can be created explicitly by the administrator of Kaspersky Security Center, in the list of moving rules. The list is located in Administration Console, in the properties of the Unassigned devices group.
By default, a device moving rule is intended for a one-time initial allocation of devices to administration groups. The rule moves devices from the Unassigned devices group only once. If a device once was moved by this rule, the rule will never move it again, even if you return the device to the Unassigned devices group manually. This is the recommended way of applying moving rules.
You can move devices that have already been allocated to some of the administration groups. To do this, in the properties of a rule, clear the Move only devices that do not belong to an administration group check box.
Applying moving rules to devices that have already been allocated to some of the administration groups significantly increases the load on the Administration Server.
The Move only devices that do not belong to an administration group check box is locked in the properties of automatically created moving rules. Such rules are created when you add the Install application remotely task or create a stand-alone installation package.
You can create a moving rule that would affect a single device repeatedly.
We strongly recommend that you avoid moving a single device from one group to another repeatedly (for example, in order to apply a special policy to that device, run a special group task, or update the device through a specific distribution point).
Such scenarios are not supported because they increase the load on Administration Server and network traffic to an extreme degree. These scenarios also conflict with the operating principles of Kaspersky Security Center (particularly in the area of access rights, events, and reports). Another solution must be found, for example, through the use of policy profiles, tasks for device selections, assignment of Network Agents according to the standard scenario.
Cloning device moving rules
When you have to create multiple device-moving rules with similar settings, you can clone an existing rule and then change the settings of the cloned rule. For example, this is useful when you must have several identical device-moving rules with different IP ranges and target groups.
To clone a device moving rule:
- Open the main application window.
- In the Unassigned devices folder, click Configure rules.
The Properties: Unassigned devices window opens.
- In the Move devices section, select the device moving rule that you want to clone.
- Click Clone rule.
A clone of the selected device moving rule will be added at the end of the list.
A new rule is created in the disabled state. You can edit and enable the rule at any time.
Page top
Software categorization
The main tool for monitoring the running of applications are Kaspersky categories (hereinafter also referred to as KL categories). KL categories help Kaspersky Security Center administrators to simplify the support of software categorization and minimize traffic going to managed devices.
User categories must only be created for applications that cannot be classified in any of the existing KL categories (for example, for custom-made software). User categories are created on the basis of an application installation package (MSI) or a folder with installation packages.
If a large collection of software is available, which has not been categorized through KL categories, it may be useful to create an automatically updated category. The checksums of executable files will be automatically added to this category on every modification of the folder containing distribution packages.
Do not create automatically updated categories of software for the folders My Documents, %windir%, %ProgramFiles%, and %ProgramFiles(x86)%. The pool of files in these folders is subject to frequent changes, which leads to an increased load on Administration Server and increased network traffic. You must create a dedicated folder with the collection of software and periodically add new items to it.
Page top
Prerequisites for installing applications on devices of a client organization
The process of remote installation of applications on devices of a client organization is identical to the remote installation process within an enterprise.
To install applications on devices of a client organization, the following actions must be performed:
- Before installing applications on devices of the client organization for the first time, install Network Agent on them.
When configuring the Network Agent installation package by the service provider, in Kaspersky Security Center, adjust the following settings in the properties window of the installation package:
- In the Connection section, in the Administration Server string, specify the address of the same virtual Administration Server that was specified during local installation of Network Agent on the distribution point.
- In the Advanced section, select the Connect to Administration Server by using a connection gateway check box. In the Connection gateway address string, specify the distribution point address. You can use either the device IP address or device name in the Windows network.
- Select Using operating system resources through distribution points as the download method for the Network Agent installation package. You can select the download method as follows:
- If you install application by using the remote installation task, you can specify the download method in one of the following ways:
- When creating a remote installation task in the Settings window
- In the remote installation task properties window, through the Settings section
- If you install applications using the Remote installation wizard, you can select the download method in the Settings window of this wizard.
- If you install application by using the remote installation task, you can specify the download method in one of the following ways:
- The account used by the distribution point for authorization must have access to the Admin$ resource on all client devices.
Viewing and editing local application settings
The Kaspersky Security Center administration system allows you to remotely manage local application settings on devices through Administration Console.
Local application settings are the settings of an application that are specific for a device. You can use Kaspersky Security Center to set local application settings for devices included in administration groups.
Detailed descriptions of settings of Kaspersky applications are provided in respective Guides.
To view or change the local settings of an application:
- In the workspace of the group to which the relevant device belongs, select the Devices tab.
- In the device properties window, in the Applications section, select the relevant application.
- Open the application properties window by double-clicking the application name or by clicking the Properties button.
The local settings window of the selected application opens so that you can view and edit those settings.
You can change the values of settings that have not been barred from modification by a group policy (that is, those not marked with the lock icon ( ) in a policy).
) in a policy).
Updating Kaspersky Security Center and managed applications
This section describes steps you must take to update Kaspersky Security Center and managed applications.
Scenario: Regular updating Kaspersky databases and applications
This section provides a scenario for regular updating of Kaspersky databases, software modules, and applications. After you complete the Configuring network protection scenario, you must maintain the reliability of the protection system to make sure that the Administration Servers and managed devices are kept protected against various threats, including viruses, network attacks, and phishing attacks.
Network protection is kept up-to-date by regular updates of the following:
- Kaspersky databases and software modules
- Installed Kaspersky applications, including Kaspersky Security Center components and security applications
When you complete this scenario, you can be sure of the following:
- Your network is protected by the most recent Kaspersky software, including Kaspersky Security Center components and security applications.
- The anti-virus databases and other Kaspersky databases critical for the network safety are always up-to-date.
Prerequisites
The managed devices must have a connection to the Administration Server. If they do not have a connection, consider updating Kaspersky databases, software modules, and applications manually or directly from the Kaspersky update servers.
Administration Server must have a connection to the internet.
Before you start, make sure that you have done the following:
- Deployed the Kaspersky security applications to the managed devices according to the scenario of deploying Kaspersky applications through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Created and configured all required policies, policy profiles, and tasks according to the scenario of configuring network protection.
- Assigned an appropriate amount of distribution points in accordance with the number of managed devices and the network topology.
Updating Kaspersky databases and applications proceeds in stages:
- Choosing an update scheme
There are several schemes that you can use to install updates to Kaspersky Security Center components and security applications. Choose the scheme or several schemes that meet the requirements of your network best.
- Creating the task for downloading updates to the repository of the Administration Server
This task is created automatically by the Kaspersky Security Center quick start wizard. If you did not run the wizard, create the task now.
This task is required to download updates from Kaspersky update servers to the repository of the Administration Server, as well as to update Kaspersky databases and software modules for Kaspersky Security Center. After the updates are downloaded, they can be propagated to the managed devices.
If your network has assigned distribution points, the updates are automatically downloaded from the Administration Server repository to the repositories of the distribution points. In this case the managed devices included in the scope of a distribution point download the updates from the repository of the distribution point instead of the Administration Server repository.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Creating the task for downloading updates to the repository of the Administration Server
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating the task for downloading updates to the repository of the Administration Server
- Creating the task for downloading updates to the repositories of distribution points (optional)
By default, the updates are downloaded to the distribution points from the Administration server. You can configure Kaspersky Security Center to download the updates to the distribution points directly from Kaspersky update servers. Download to the repositories of distribution points is preferable if the traffic between the Administration Server and the distribution points is more expensive than the traffic between the distribution points and Kaspersky update servers, or if your Administration Server does not have internet access.
When your network has assigned distribution points and the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task is created, the distribution points download updates from Kaspersky update servers, and not from the Administration Server repository.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Creating the task for downloading updates to the repositories of distribution points
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating the task for downloading updates to the repositories of distribution points
- Configuring distribution points
When your network has assigned distribution points, make sure that the Deploy updates option is enabled in the properties of all required distribution points. When this option is disabled for a distribution point, the devices included in the scope of the distribution point download updates from the repository of the Administration Server.
If you want the managed devices to receive updates only from the distribution points, enable the Distribute files through distribution points only option in the Network Agent policy.
- Optimizing the update process by using the offline model of update download or diff files (optional)
You can optimize the update process by using the offline model of update download (enabled by default) or by using diff files. For each network segment, you have to choose which of these two features to enable, because they cannot work simultaneously.
When the offline model of update download is enabled, Network Agent downloads the required updates to the managed device once the updates are downloaded to the Administration Server repository, before the security application requests the updates. This enhances the reliability of the update process. To use this feature, enable the Download updates and anti-virus databases from Administration Server in advance (recommended) option in the Network Agent policy.
If you do not use the offline model of update download, you can optimize traffic between the Administration Server and the managed devices by using diff files. When this feature is enabled, the Administration Server or a distribution point downloads diff files instead of entire files of Kaspersky databases or software modules. A diff file describes the differences between two versions of a file of a database or software module. Therefore, a diff file occupies less space than an entire file. This results in decrease in the traffic between the Administration Server or distribution points and the managed devices. To use this feature, enable the Download diff files option in the properties of the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task and/or the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task.
How-to instructions:
- Using diff files for updating Kaspersky databases and software modules
- Administration Console: Enabling and disabling the offline model of update download
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Enabling and disabling the offline model of update download
- Verifying downloaded updates (optional)
Before installing the downloaded updates, you can verify the updates through the Update verification task. This task sequentially runs the device update tasks and malware scan tasks configured through settings for the specified collection of test devices. Upon obtaining the task results, the Administration Server starts or blocks the update propagation to the remaining devices.
The Update verification task can be performed as part of the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task. In the properties of the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task, enable the Verify updates before distributing option in the Administration Console or the Run update verification option in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Verifying downloaded updates
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Verifying downloaded updates
- Approving and declining software updates
By default, the downloaded software updates have the Undefined status. You can change the status to Approved or Declined. The approved updates are always installed. If an update requires reviewing and accepting the terms of the End User License Agreement, then you first need to accept the terms. After that the update can be propagated to the managed devices. The undefined updates can only be installed on Network Agent and other Kaspersky Security Center components in accordance with the Network Agent policy settings. The updates for which you set Declined status will not be installed on devices. If a declined update for a security application was previously installed, Kaspersky Security Center will try to uninstall the update from all devices. Updates for Kaspersky Security Center components cannot be uninstalled.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Approving and declining software updates
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Approving and declining software updates
- Configuring automatic installation of updates and patches for Kaspersky Security Center components
The downloaded updates and patches for Network Agent and other Kaspersky Security Center components are installed automatically. If you have left the Automatically install applicable updates and patches for components that have the Undefined status option enabled in the Network Agent properties, then all updates will be installed automatically after they are downloaded to the repository (or several repositories). If this option is disabled, Kaspersky patches that have been downloaded and tagged with the Undefined status will be installed only after you change their status to Approved.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Enabling and disabling automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Enabling and disabling automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components
- Installation of updates for the Administration Server
Software updates for the Administration Server do not depend on the update statuses. They are not installed automatically and must be preliminarily approved by the administrator on the Monitoring tab in the Administration Console (Administration Server
<server name>→ Monitoring) or on the Notifications section in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console (Monitoring & reporting → Notifications). After that, the administrator must explicitly run installation of the updates. - Configuring automatic installation of updates for the security applications
Create the Update tasks for the managed applications to provide timely updates to the applications, software modules and Kaspersky databases, including anti-virus databases. To ensure timely updates, we recommend that you select the When new updates are downloaded to the repository option when configuring the task schedule.
If your network includes IPv6-only devices and you want to regularly update the security applications installed on these devices, make sure that the Administration Server (version no earlier than 13.2) and the Network Agent (version no earlier than 13.2) are installed on managed devices.
By default, updates for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux are installed only after you change the update status to Approved. You can change the update settings in the Update task.
If an update requires reviewing and accepting the terms of the End User License Agreement, then you first need to accept the terms. After that the update can be propagated to the managed devices.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Automatic installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security updates on devices
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Automatic installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security updates on devices
Results
Upon completion of the scenario, Kaspersky Security Center is configured to update Kaspersky databases and installed Kaspersky applications after the updates are downloaded to the repository of the Administration Server or to the repositories of distribution points. You can then proceed to monitoring the network status.
About updating Kaspersky databases, software modules, and applications
To be sure that the protection of your Administration Servers and managed devices is up-to-date, you must provide timely updates of the following:
- Kaspersky databases and software modules
Before downloading Kaspersky databases and software modules, Kaspersky Security Center checks if Kaspersky servers are accessible. If access to the servers using system DNS is not possible, the application uses public DNS servers. This is necessary to make sure anti-virus databases are updated and the level of security is maintained for the managed devices.
- Installed Kaspersky applications, including Kaspersky Security Center components and security applications
Depending on the configuration of your network, you can use the following schemes of downloading and distributing the required updates to the managed devices:
- By using a single task: Download updates to the Administration Server repository
- By using two tasks:
- The Download updates to the Administration Server repository task
- The Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task
- Manually through a local folder, a shared folder, or an FTP server
- Directly from Kaspersky update servers to Kaspersky Endpoint Security on the managed devices
- Through a local or network folder if Administration Server has no internet connection
Using the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task
In this scheme, Kaspersky Security Center downloads updates through the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task. In small networks that contain less than 300 managed devices in a single network segment or less than 10 managed devices in each network segment, the updates are distributed to the managed devices directly from the Administration Server repository (see figure below).
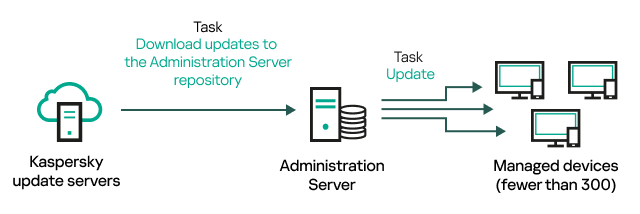
Updating by using the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task without distribution points
By default, the Administration Server communicates with Kaspersky update servers and downloads updates by using the HTTPS protocol. You can configure the Administration Server to use the HTTP protocol instead of HTTPS.
If your network contains more than 300 managed devices in a single network segment or if your network consists of several network segments with more than 9 managed devices in each network segment, we recommend that you use distribution points to propagate the updates to the managed devices (see figure below). Distribution points reduce the load on the Administration Server and optimize traffic between the Administration Server and the managed devices. You can calculate the number and configuration of distribution points required for your network.
In this scheme, the updates are automatically downloaded from the Administration Server repository to the repositories of the distribution points. The managed devices included in the scope of a distribution point download the updates from the repository of the distribution point instead of the Administration Server repository.
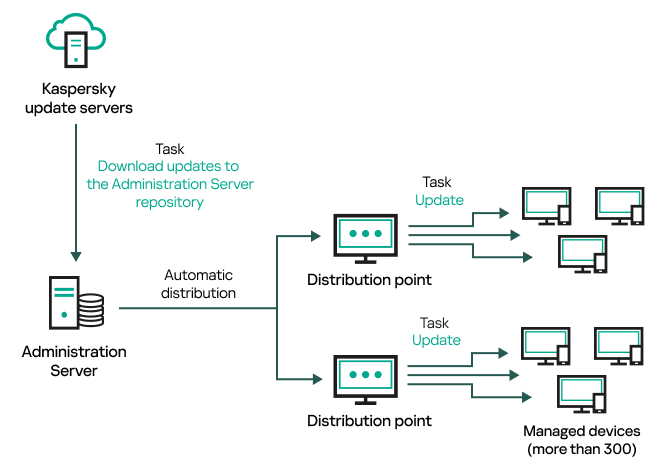
Updating by using the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task with distribution points
When the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task is complete, the following updates are downloaded to the Administration Server repository:
- Kaspersky databases and software modules for Kaspersky Security Center
These updates are installed automatically.
- Kaspersky databases and software modules for the security applications on the managed devices
These updates are installed through the Update task for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- Updates for the Administration Server
These updates are not installed automatically. The administrator must explicitly approve and run installation of the updates.
Local administrator rights are required for installing patches on the Administration Server.
- Updates for the components of Kaspersky Security Center
By default, these updates are installed automatically. You can change the settings in the Network Agent policy.
- Updates for the security applications
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows installs only those updates that you approve. (You can approve updates via the Administration Console or via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console). The updates are installed through the Update task and can be configured in the properties of this task.
The Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task is not available on virtual Administration Servers. The repository of the virtual Administration Server displays updates downloaded to the primary Administration Server.
You can configure the updates to be verified for operability and errors on a set of test devices. If the verification is successful, the updates are distributed to other managed devices.
Each Kaspersky application requests required updates from Administration Server. Administration Server aggregates these requests and downloads only those updates that are requested by any application. This ensures that the same updates are not downloaded multiple times and that unnecessary updates are not downloaded at all. When running the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task, Administration Server sends the following information to Kaspersky update servers automatically in order to ensure the downloading of relevant versions of Kaspersky databases and software modules:
- Application ID and version
- Application installation ID
- Active key ID
- Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task run ID
None of the transmitted information contains personal or other confidential data. AO Kaspersky Lab protects information in accordance with requirements established by law.
Using two tasks: the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task and the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task
You can download updates to the repositories of distribution points directly from the Kaspersky update servers instead of the Administration Server repository, and then distribute the updates to the managed devices (see figure below). Download to the repositories of distribution points is preferable if the traffic between the Administration Server and the distribution points is more expensive than the traffic between the distribution points and Kaspersky update servers, or if your Administration Server does not have internet access.
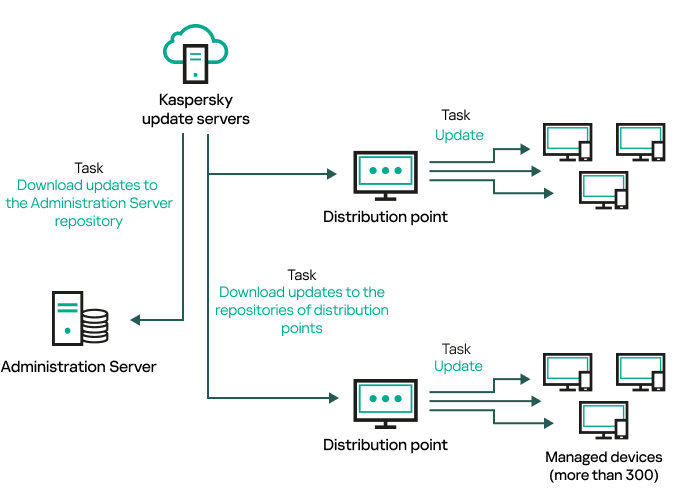
Updating by using the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task and the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task
By default, the Administration Server and distribution points communicate with Kaspersky update servers and download updates by using the HTTPS protocol. You can configure the Administration Server and/or distribution points to use the HTTP protocol instead of HTTPS.
To implement this scheme, create the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task in addition to the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task. After that the distribution points will download updates from Kaspersky update servers, and not from the Administration Server repository.
Distribution point devices running macOS cannot download updates from Kaspersky update servers.
If one or more devices running macOS are within the scope of the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task, the task completes with the Failed status, even if it has successfully completed on all Windows devices.
The Download updates to the Administration Server repository task is also required for this scheme, because this task is used to download Kaspersky databases and software modules for Kaspersky Security Center.
Manually through a local folder, a shared folder, or an FTP server
If the client devices do not have a connection to the Administration Server, you can use a local folder or a shared resource as a source for updating Kaspersky databases, software modules, and applications. In this scheme, you need to copy required updates from the Administration Server repository to a removable drive, then copy the updates to the local folder or the shared resource specified as an update source in the settings of Kaspersky Endpoint Security (see figure below).
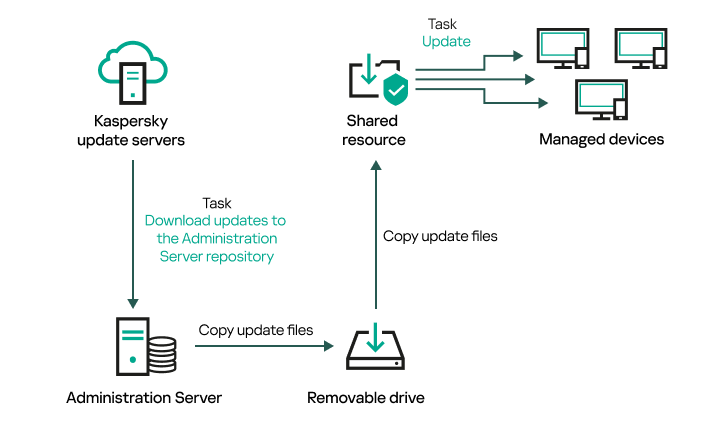
Updating through a local folder, a shared folder, or an FTP server
For more information about sources of updates in Kaspersky Endpoint Security, see the following Helps:
Directly from Kaspersky update servers to Kaspersky Endpoint Security on the managed devices
On the managed devices, you can configure Kaspersky Endpoint Security to receive updates directly from Kaspersky update servers (see figure below).
Updating security applications directly from Kaspersky update servers
In this scheme, the security application does not use the repositories provided by Kaspersky Security Center. To receive updates directly from Kaspersky update servers, specify Kaspersky update servers as an update source in the interface of the security application. For more information about these settings, see the following Helps:
Through a local or network folder if Administration Server has no internet connection
If Administration Server has no internet connection, you can configure the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task to download updates from a local or network folder. In this case, you must copy the required update files to the specified folder from time to time. For example, you can copy the required update files from one of the following sources:
- Administration Server that has an internet connection (see the figure below)
Because an Administration Server downloads only the updates that are requested by the security applications, the sets of security applications managed by the Administration Servers—the one that has an internet connection and the one that does not—must match.
If the Administration Server that you use to download updates has version 13.2 or earlier, open properties of the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task, and then enable the Download updates by using the old scheme option.
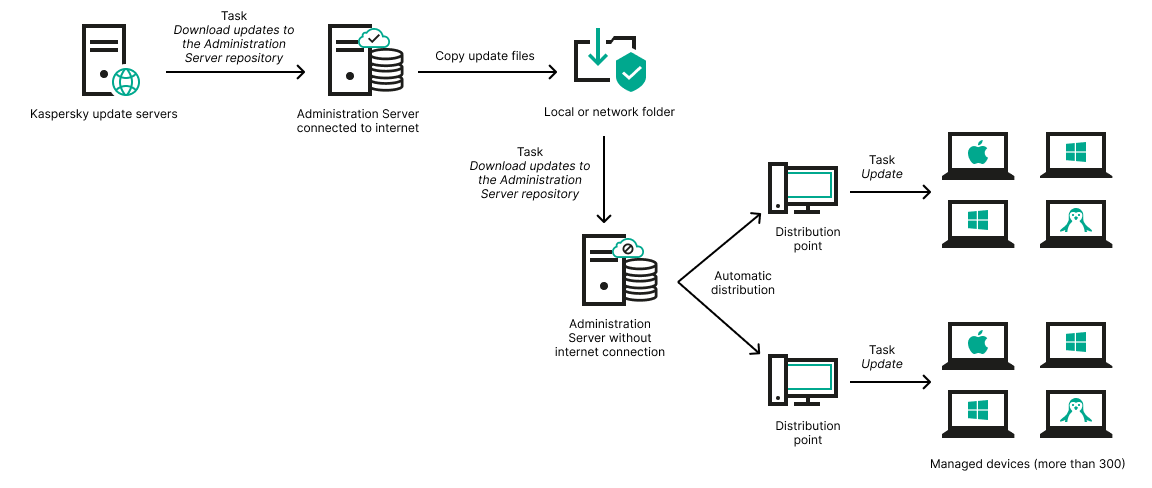
Updating through a local or network folder if Administration Server has no internet connection
- Kaspersky Update Utility
Because this utility uses the old scheme to download updates, open properties of the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task, and then enable the Download updates by using the old scheme option.
About using diff files for updating Kaspersky databases and software modules
When Kaspersky Security Center downloads updates from Kaspersky update servers, it optimizes traffic by using diff files. You can also enable the usage of diff files by devices (Administration Servers, distribution points, and client devices) that take updates from other devices on your network.
About the Downloading diff files feature
A diff file describes the differences between two versions of a file of a database or software module. The usage of diff files saves traffic inside your company's network because diff files occupy less space than entire files of databases and software modules. If the Downloading diff files feature is enabled on Administration Server or a distribution point, the diff files are saved on this Administration Server or distribution point. As a result, devices that take updates from this Administration Server or distribution point can use the saved diff files to update their databases and software modules.
To optimize the usage of diff files, we recommend that you synchronize the update schedule of devices with the update schedule of the Administration Server or distribution point from which the devices take updates. However, the traffic can be saved even if devices are updated several times less often than are the Administration Server or distribution point from which the devices take updates.
The Downloading diff files feature can be enabled only on Administration Servers and distribution points of versions starting from version 11. To save diff files on Administration Servers and distribution points of earlier versions, upgrade them to version 11 or later.
The Downloading diff files feature is incompatible with the offline model of update download. This means that Network Agents that use the offline model of update download do not download diff files even if the Downloading diff files feature is enabled on the Administration Server or distribution point that delivers updates to these Network Agents.
Distribution points do not use IP multicasting for automatic distribution of diff files.
Enabling the Downloading diff files feature
Prerequisites
Prerequisites for the scenario are as follows:
- Administration Servers and distribution points are upgraded to version 11 or later.
- Offline model of update download is disabled in the settings of the Network Agent policy.
Stages
- Enabling the feature on Administration Server
Enable the feature in the settings of a Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task.
- Enabling the feature for a distribution point
Enable the feature for a distribution point that receives updates by means of a Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task.
Then enable the feature for a distribution point that receives updates from Administration Server.
The feature is enabled in the Network Agent policy settings and—if the distribution points are assigned manually and if you want to override policy settings—in the Distribution points section of the Administration Server properties.
To check that the Downloading diff files feature is successfully enabled, you can measure the internal traffic before and after you perform the scenario.
Creating the task for downloading updates to the repository of the Administration Server
The Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task of the Administration Server is created automatically by the Kaspersky Security Center quick start wizard. You can create only one Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task. Therefore, you can create a Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task only if this task was removed from the Administration Server tasks list.
To create a Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- Start creation of the task in one of the following ways:
- In the context menu of the Tasks folder in the console tree, select New → Task.
- In the workspace of the Tasks folder, click the Create a task button.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the Select the task type page of the wizard, select Download updates to the Administration Server repository.
- On the Settings page of the wizard, specify the task settings as follows:
- On the Configure task schedule page of the wizard, you can create a schedule for task start. If necessary, specify the following settings:
- On the Define the task name page of the wizard, specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- On the Finish task creation page of the wizard, click the Finish button to close the wizard.
If you want the task to start as soon as the wizard finishes, select the Run the task after the wizard finishes check box.
After the wizard finishes, Download updates to the Administration Server repository appears in the list of Administration Server tasks in the workspace.
In addition to the settings that you specify during task creation, you can change other properties of a created task.
When Administration Server performs the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task, updates to databases and software modules are downloaded from the updates source and stored in the shared folder of Administration Server. If you create this task for an administration group, it will only be applied to Network Agents included in the specified administration group.
Updates are distributed to client devices and secondary Administration Servers from the shared folder of Administration Server.
Creating the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task
Distribution point devices running macOS cannot download updates from Kaspersky update servers.
If one or more devices running macOS are within the scope of the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task, the task completes with the Failed status, even if it has successfully completed on all Windows devices.
You can create the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task for an administration group. This task will run for distribution points included in the specified administration group.
You can use this task, for example, if the traffic between the Administration Server and the distribution point(s) is more expensive than the traffic between the distribution point(s) and Kaspersky update servers, or if your Administration Server does not have internet access.
To create the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task for a selected administration group:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- In the workspace of this folder, click the New task button.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the Select the task type page of the wizard, select the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server node, expand the Advanced folder, and then select the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task.
- On the Settings page of the wizard, specify the task settings as follows:
- On the Select Administration group page of the wizard, click Browse and select the administration group to which the task applies.
- On the Configure task schedule page of the wizard, you can create a schedule for task start. If necessary, specify the following settings:
- On the Define the task name page of the wizard, specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- On the Finish task creation page of the wizard, click the Finish button to close the wizard.
If you want the task to start as soon as the wizard finishes, select the Run the task after the wizard finishes check box.
When the wizard completes its operation, Download updates to the repositories of distribution points appears in the list of Network Agent tasks in the target administration group and in the Tasks workspace of the console.
In addition to the settings that you specify during task creation, you can change other properties of a created task.
When the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task is performed, updates for databases and software modules are downloaded from the update source and stored in the shared folder. Downloaded updates will only be used by distribution points that are included in the specified administration group and that have no update download task explicitly set for them.
In the Administration Server properties window, in the Sections pane select Distribution points. In the properties of each distribution point, in the Update source section you can specify the update source (Retrieve from Administration Server or Use task for forced download of updates). By default, Retrieve from Administration Server is selected for a distribution point that is assigned manually or automatically. These distribution points will use the results of the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task.
The properties of each distribution point specify the network folder that has been set up for that distribution point individually. The names of folders may vary for different distribution points. For this reason, we do not recommend that you change the network folder in the task properties if the task is created for a group of devices.
You can change the network folder with updates in the properties of the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task if you are creating a local task for a device.
Configuring the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task
To configure the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task:
- In the workspace of the Tasks console tree folder, select Download updates to the Administration Server repository in the task list.
- Open the task properties window in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Properties in the context menu of the task.
- By clicking the Configure task link in the information box for the selected task.
The Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task properties window opens. In this window, you can configure how the updates are downloaded to the Administration Server repository.
Verifying downloaded updates
Before installing updates to the managed devices, you can first check the updates for operability and errors through the Update verification task. The Update verification task is performed automatically as part of the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task. The Administration Server downloads updates from the source, saves them in the temporary repository, and runs the Update verification task. If the task completes successfully, the updates are copied from the temporary repository to the Administration Server shared folder (<Kaspersky Security Center installation folder>\Share\Updates). They are distributed to all client devices for which the Administration Server is the source of updates.
If, as a result of the Update verification task, updates located in the temporary repository are incorrect or if the Update verification task completes with an error, such updates are not copied to the shared folder. The Administration Server retains the previous set of updates. Also, the tasks that have the When new updates are downloaded to the repository schedule type are not started then. These operations are performed at the next start of the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task if scanning of the new updates completes successfully.
A set of updates is considered invalid if any of the following conditions is met on at least one test device:
- An update task error occurred.
- The real-time protection status of the security application changed after the updates were applied.
- An infected object was detected during running of the on-demand scan task.
- A runtime error of a Kaspersky application occurred.
If none of the listed conditions is true for any test device, the set of updates is considered valid, and the Update verification task is considered to have completed successfully.
Before you start to create the Update verification task, perform the prerequisites:
- Create an administration group with several test devices. You will need this group to verify updates on it.
We recommend using devices with the most reliable protection and the most popular application configuration across the network. This approach increases the quality and probability of virus detection during scans, and minimizes the risk of false positives. If viruses are detected on test devices, the Update verification task is considered unsuccessful.
- Create the Update and Malware scan tasks for an application supported by Kaspersky Security Center, for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows or Kaspersky Security for Windows Server. When creating the Update and Malware scan tasks, specify the administration group with the test devices.
The Update verification task sequentially runs the Update and Malware scan tasks on test devices to check that all updates are valid. In addition, when creating the Update verification task, you need to specify the Update and Malware scan tasks.
- Create the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task.
To make Kaspersky Security Center verify downloaded updates before distributing them to client devices:
- In the workspace of the Tasks folder, select the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task in the list of tasks.
- Open the task properties window in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Properties in the context menu of the task.
- By clicking the Configure task link in the information box for the selected task.
- If the Update verification task exists, click the Browse button. In the window that opens, select the Update verification task in the administration group with test devices.
- If you did not create the Update verification task earlier, click the Create button.
The Update verification task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- Click OK to close the properties window of the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task.
The automatic update verification is enabled. Now, you can run the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task and it will start from update verification.
Configuring test policies and auxiliary tasks
When creating an Update verification task, the Administration Server generates test policies, auxiliary group update tasks, and on-demand scan tasks.
Auxiliary group update and on-demand scan tasks take some time. These tasks are performed when the Update verification task is executed. The Update verification task is performed during execution of the Download updates to the repository task. The duration of the Download updates to the repository task includes auxiliary group update and on-demand scan tasks.
You can change the settings of test policies and auxiliary tasks.
To change settings of a test policy or an auxiliary task:
- In the console tree, select a group for which the Update verification task is created.
- In the group workspace, select one of the following tabs:
- Policies, if you want to edit the test policy settings.
- Tasks, if you want to change auxiliary task settings.
- In the tab workspace, select a policy or a task, whose settings you want to change.
- Open the policy (task) properties window in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Properties in the context menu of the policy (task).
- By clicking the Configure policy (Configure task) link in the information box for the selected policy (task).
To verify updates correctly, set the following restrictions on the modification of test policies and auxiliary tasks:
- In the auxiliary task settings:
- Save all tasks with the Critical event and Functional failure importance levels on Administration Server. Using the events of these types, the Administration Server analyzes the operation of applications.
- Use Administration Server as the source of updates.
- Specify the task schedule type: Manually.
- In the settings of test policies:
- Disable the iChecker and iSwift scanning acceleration technologies (Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection → Settings → Additional → Scan technologies).
- Select actions on infected objects: Disinfect; delete if disinfection fails / Disinfect; block if disinfection fails / Block. (Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection → Action on threat detection).
- In the settings of test policies and auxiliary tasks:
If the device requires a restart after installation of updates for software modules, it must be performed immediately. If the device is not restarted, it is not possible to test this type of updates. For some applications, installation of updates that require a restart may be prohibited or configured to prompt the user for confirmation first. These restrictions should be disabled in the settings of test policies and auxiliary tasks.
Viewing downloaded updates
To view the list of downloaded updates,
In the console tree, in the Repositories folder, select the Updates for Kaspersky databases and software modules subfolder.
The workspace of the Updates for Kaspersky databases and software modules folder shows the list of updates that have been saved on the Administration Server.
Automatic installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security updates on devices
You can configure automatic updates of databases and software modules of Kaspersky Endpoint Security on client devices.
To configure download and automatic installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security updates on devices:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- Create an Update task in one of the following ways:
- By selecting New → Task in the context menu of the Tasks folder in the console tree.
- By clicking the New task button in the workspace of the Tasks folder.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the Select the task type page of the wizard, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security as the task type, and then select Update as the task subtype.
- Follow the rest of the wizard instructions.
After the wizard finishes, an update task for Kaspersky Endpoint Security is created. The newly created task is displayed in the list of tasks in the workspace of the Tasks folder.
- In the workspace of the Tasks folder, select the update task that you have created.
- In the context menu of the task, select Properties.
- In the task properties window that opens, in the Sections pane select Options.
In the Options section, you can define the update task settings in local or mobile mode:
- Update settings for local mode: Connection is established between the device and the Administration Server.
- Update settings for mobile mode: No connection is established between Kaspersky Security Center and the device (for example, when the device is not connected to the internet).
- Click the Settings button to select the update source.
- Select the Download updates of application modules option to download and install software module updates together with the application databases.
If the check box is selected, Kaspersky Endpoint Security notifies the user about available software module updates and includes software module updates in the update package when running the update task. Configure the use of update modules:
- Install critical and approved updates. If any updates are available for software modules, Kaspersky Endpoint Security automatically installs those that have Critical status; the remaining updates will be installed after you approve them.
- Install approved updates only. If any software module updates are available, Kaspersky Endpoint Security installs them after their installation is approved; they will be installed locally through the application interface or through Kaspersky Security Center.
If updating the software module requires reviewing and accepting the terms of the License Agreement and Privacy Policy, the application installs updates after the terms of the License Agreement and Privacy Policy have been accepted by the user.
- Select the Copy updates to folder option in order for the application to save downloaded updates to a folder, and then click the Browse button to specify the folder.
- Click OK.
When the Update task is running, the application sends requests to Kaspersky update servers.
Some updates require installation of the latest versions of management plug-ins.
Offline model of update download
Network Agent on managed devices may sometimes not connect to the Administration Server to receive updates. For example, Network Agent may have been installed on a laptop that sometimes has no internet connection and no local network access. Moreover, the administrator may limit the time for connecting devices to the network. In such cases, devices with Network Agent installed cannot receive updates from the Administration Server according to the existing schedule. If you have configured the updating of managed applications (such as Kaspersky Endpoint Security) using Network Agent, each update requires a connection to the Administration Server. When no connection is established between Network Agent and the Administration Server, updating is not possible. You can configure the connection between Network Agent and the Administration Server so that Network Agent connects to the Administration Server at specified time intervals. At worst, if the specified connection intervals are overlaid with periods when no connection is available, the databases will never be updated. In addition, issues may occur when multiple managed applications simultaneously attempt to access the Administration Server to receive updates. In this case, the Administration Server may stop responding to requests (similarly to a DDoS attack).
To avoid such problems as those described above, an offline model for downloading updates and modules of managed applications is implemented in Kaspersky Security Center. This model provides a mechanism for distribution of updates, regardless of temporary problems caused by inaccessibility of Administration Server communication channels. The model also reduces load on the Administration Server.
How the offline model of update download works
When the Administration Server receives updates, it notifies Network Agent (on devices where it is installed) of the updates that will be required for managed applications. When Network Agent receives information about these updates, it downloads the relevant files from the Administration Server in advance. At the first connection with Network Agent, the Administration Server initiates an update download. After Network Agent downloads all the updates to a client device, the updates become available for applications on that device.
When a managed application on a client device attempts to access Network Agent for updates, Network Agent checks whether it has all required updates. If the updates are received from the Administration Server not more than 25 hours before they were requested by the managed application, Network Agent does not connect to the Administration Server but supplies the managed application with updates from the local cache instead. Connection with the Administration Server may not be established when Network Agent provides updates to applications on client devices, but connection is not required for updating.
To distribute the load on the Administration Server, Network Agent on a device connects to the Administration Server and download updates in random order during the time interval specified by the Administration Server. This time interval depends on the number of devices with Network Agent installed that download updates and on the size of those updates. To reduce the load on the Administration Server, you can use Network Agent as distribution points.
If the offline model of update download is disabled, updates are distributed according to the schedule of the update download task.
By default, the offline model of update download is enabled.
The offline model of update download is only used with managed devices on which the task for retrieving updates by managed applications has When new updates are downloaded to the repository selected as the schedule type. For other managed devices, the standard scheme is used for retrieving updates from the Administration Server in real-time mode.
We recommend that you disable the offline model of update download by using the settings of the Network Agent policies of relevant administration groups in these cases: if managed applications have the retrieval of updates set not from the Administration Server, but from Kaspersky servers or a network folder, and if the update download task has When new updates are downloaded to the repository selected as the schedule type.
Enabling and disabling the offline model of update download
We recommend that you avoid disabling the offline model of update download. Disabling it may cause failures in update delivery to devices. In certain cases, a Kaspersky Technical Support specialist may recommend that you clear the Download updates and anti-virus databases from Administration Server in advance check box. Then, you will have to make sure that the task for receiving updates for Kaspersky applications has been set up.
To enable or disable the offline model of update download for an administration group:
- In the console tree, select the administration group for which you need to enable the offline model of update download.
- In the group workspace, open the Policies tab.
- On the Policies tab, select the Network Agent policy.
- In the context menu of the policy, select Properties.
Open the properties window of the Network Agent policy.
- In the policy properties window, select the Manage patches and updates section.
- Select or clear the Download updates and anti-virus databases from Administration Server in advance (recommended) check box to enable or disable, respectively, the offline model of update download.
By default, the offline model of update download is enabled.
The offline model of update download will be enabled or disabled.
Automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components
By default, any updates and patches that have been downloaded are installed automatically for the following application components:
- Network Agent for Windows
- Administration Console
- iOS MDM Server
Automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components is available only for devices running Windows. You can disable automatic updating and patching for these components. In this case, any updates and patches that have been downloaded will be installed only after you change their status to Approved. Updates and patches with Undefined status will not be installed.
Enabling and disabling automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components
Automatic installation of updates and patches for Kaspersky Security Center components is enabled by default during Network Agent installation on the device. You can disable it during Network Agent installation, or disable it later by using a policy.
To disable automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components during local installation of Network Agent on a device:
- Start local installation of Network Agent on the device.
- At the Advanced settings step, clear the Automatically install applicable updates and patches for components that have Undefined status check box.
- Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Network Agent with disabled automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components will be installed on the device. You can enable automatic updating and patching later by using a policy.
To disable automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components during Network Agent installation on the device through an installation package:
- In the console tree, select the Remote installation → Installation packages folder.
- In the context menu of the Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent <version number> package, select Properties.
- In the installation package properties, in the Settings section clear the Automatically install applicable updates and patches for components that have the Undefined status check box.
Network Agent with disabled automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components will be installed from this package. You can enable automatic updating and patching later by using a policy.
If this check box was selected (or cleared) during Network Agent installation on the device, you can subsequently enable (or disable) automatic updating by using the Network Agent policy.
To enable or disable automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components by using the Network Agent policy:
- In the console tree, select the administration group for which you have to enable or disable automatic updating and patching.
- In the group workspace, open the Policies tab.
- On the Policies tab, select the Network Agent policy.
- In the context menu of the policy, select Properties.
Open the properties window of the Network Agent policy.
- In the policy properties window, select the Manage patches and updates section.
- Select or clear the Automatically install applicable updates and patches for components that have the Undefined status check box to enable or disable, respectively, automatic updating and patching.
- Set the lock for this check box.
The policy will be applied to the selected devices, and automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components will be enabled (or disabled) on these devices.
Automatic distribution of updates
Kaspersky Security Center allows automatic distribution and installation of updates on client devices and secondary Administration Servers.
Distributing updates to client devices automatically
To distribute updates of the selected application to client devices automatically immediately after they are downloaded to the Administration Server repository:
- Connect to the Administration Server, which manages the client devices.
- Create an update deployment task for the selected client devices in one of the following ways:
- If you need to distribute updates to client devices that belong to a selected administration group, create a task for the selected group.
- If you need to distribute updates to client devices that belong to different administration groups or belong to none of the administration groups, create a task for specific devices.
The New task wizard starts. Follow its instructions and perform the following actions:
- In the Task type wizard window, in the node of the required application select the updates deployment task.
The name of the updates deployment task displayed in the Task type window depends on the application for which you create this task. For detailed information about names of update tasks for the selected Kaspersky applications, see the corresponding Guides.
- In the Schedule wizard window, in the Scheduled start field, select When new updates are downloaded to the repository.
The newly created update distribution task will start for the selected devices every time any updates are downloaded to the Administration Server repository.
If an update distribution task for the required application has already been created for the selected devices, to automatically distribute updates to client devices, in the task properties window, in the Schedule section, select When new updates are downloaded to the repository as the start option in the Scheduled start field.
Distributing updates to secondary Administration Servers automatically
To distribute the updates of the selected application to secondary Administration Servers immediately after the updates are downloaded to the primary Administration Server repository:
- In the console tree, in the primary Administration Server node, select the Tasks folder.
- In the list of tasks in the workspace, select the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task of the Administration Server.
- Open the Settings section of the selected task in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Properties in the context menu of the task.
- By clicking the Edit settings link in the information box for the selected task.
- In the Settings section of the task properties window, select the Other settings subsection, and then click the Configure link.
- In the Other settings window that opens, select the Force update of secondary Administration Servers check box.
- In the settings of the updates download task of the Administration Server, on the Settings tab of the task properties window, select the Force update of secondary Administration Servers check box.
After the primary Administration Server retrieves the updates, the update download tasks automatically start on secondary Administration Servers, regardless of their schedule.
The primary Administration Server updates anti-virus databases, according to the applications installed on secondary Administration Servers. Installation of additional plug-ins and creation of installation packages on the primary Administration Server is not required.
Assigning distribution points automatically
We recommend that you assign distribution points automatically. Kaspersky Security Center will then select on its own which devices must be assigned distribution points.
To assign distribution points automatically:
- Open the main application window.
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the Administration Server for which you want to assign distribution points automatically.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, click Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Sections pane select Distribution points.
- In the right part of the window, select the Automatically assign distribution points option.
If automatic assignment of devices as distribution points is enabled, you cannot configure distribution points manually or edit the list of distribution points.
- Click OK.
Administration Server assigns and configures distribution points automatically.
Assigning a device a distribution point manually
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to assign devices to act as distribution points.
We recommend that you assign distribution points automatically. In this case, Kaspersky Security Center will select on its own which devices must be assigned distribution points. However, if you have to opt out of assigning distribution points automatically for any reason (for example, if you want to use exclusively assigned servers), you can assign distribution points manually after you calculate their number and configuration.
Devices functioning as distribution points must be protected, including physical protection, against any unauthorized access.
To manually assign a device to act as distribution point:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, select the Distribution points section and click the Add button. This button is available if Manually assign distribution points has been selected.
The Add distribution point window opens.
- In the Add distribution point window, perform the following actions:
- Select a device that will act as distribution point (select one in an administration group, or specify the IP address of a device). When selecting a device, keep in mind the operation features of distribution points and the requirements set for the device that acts as distribution point.
- Indicate the specific devices to which the distribution point will distribute updates. You can specify an administration group or a network location description.
- Click OK.
The distribution point that you have added will be displayed in the list of distribution points, in the Distribution points section.
- Select the newly added distribution point in the list and click the Properties button to open its properties window.
- Configure the distribution point in the properties window:
- The General section contains the settings of interaction between the distribution point and client devices.
- In the Scope section, specify the scope to which the distribution point will distribute updates (administration groups and / or network location).
- In the KSN Proxy section, you can configure the application to use the distribution point to forward KSN requests from the managed devices.
- In the Device discovery section, configure the polling of Windows domains, Active Directory, and IP ranges by the distribution point.
- In the Advanced section, specify the folder that the distribution point must use to store distributed data.
The selected devices act as distribution points.
Only devices running a Windows operating system can determine their network location. Network location cannot be determined for devices running other operating systems.
Removing a device from the list of distribution points
To remove a device from the list of distribution points:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Distribution points section, select the device that acts as distribution point, and click the Remove button.
The device will be removed from the list of distribution points and will stop acting as distribution point.
You cannot remove a device from the list of distribution points if it was assigned by the Administration Server automatically.
Downloading updates by distribution points
Kaspersky Security Center allows distribution points to receive updates from the Administration Server, Kaspersky servers, or from a local or network folder.
If you do not need to specify an update source, we recommend that you use the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task for an administration group. Refer to the following topic for details: Creating the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task.
To configure update download for a distribution point:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Distribution points section, select the distribution point through which updates will be delivered to client devices in the group.
- Click the Properties button to open the properties window of the selected distribution point.
- In the distribution point properties window, select the Sources of updates section.
- Select an update source for the distribution point:
- To allow the distribution point to receive updates from the Administration Server, select Retrieve from Administration Server:
- To allow the distribution point to receive updates by using a task, select Use task for forced download of updates:
- Click the Browse button if such a task already exists on the device, and select the task in the list that appears.
- Click the New task button to create a task if no such task yet exists on the device. The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
The Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task is a local task. You have to create a new task for each device that acts as distribution point.
The distribution point will receive updates from the specified source.
Deleting software updates from the repository
To delete software updates from the Administration Server repository:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Software updates subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Software updates folder, select the update that you want to delete.
- In the context menu of the update, select Delete update files.
Software updates will be deleted from the Administration Server repository.
Patch installation for a Kaspersky application in cluster mode
Kaspersky Security Center only supports manual installation of patches for Kaspersky applications in cluster mode.
To install a patch for a Kaspersky application:
- Download the patch to each node of the cluster.
- Run patch installation on the active node.
- Wait for the patch to be successfully installed.
- Run the patch on all subnodes of the cluster consecutively.
If you are running the patch from the command line, use the
-CLUSTER_SECONDARY_NODEkey.The patch is now installed on all nodes of the cluster.
- Run the Kaspersky cluster services manually.
Every node of the cluster is displayed in Administration Console as a device with Network Agent installed.
For information about installed patches, see the Software updates folder or the report on the versions of updates for software modules of Kaspersky applications.
Managing third-party applications on client devices
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to manage applications by Kaspersky and other vendors installed on client devices.
The administrator can perform the following actions:
- Create application categories based on specified criteria.
- Manage application categories using specially created rules.
- Manage applications run on devices.
- Perform inventories and maintain a registry of software installed on devices.
- Fix vulnerabilities in software installed on devices.
- Install updates from Windows Update and other software makers on devices.
- Monitor the use of license keys for licensed applications groups.
Installing third-party software updates
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to manage updates of software installed on client devices and fix vulnerabilities in Microsoft applications and other software makers' products through installing required updates.
Kaspersky Security Center searches for updates through the update search task and downloads them to the updates repository. After completing the search of updates, the application provides the administrator with information about available updates and vulnerabilities in applications that can be fixed using those updates.
Information about available updates for Microsoft Windows is provided by Windows Update service. Administration Server can be used as Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) server. To use Administration Server as WSUS server, you should configure synchronization of updates with Windows Update. After you have configured data synchronization with Windows Update, Administration Server provides updates to Windows Update services on devices in centralized mode and with the set frequency.
You can also manage software updates through a Network Agent policy. To do this, you should create a Network Agent policy and configure software updating in the corresponding windows of the New policy wizard.
The administrator can view a list of available updates in the Software updates subfolder included in the Application management folder. This folder contains a list of updates for Microsoft applications and other software makers' products retrieved by Administration Server that can be distributed to devices. After viewing information about available updates, the administrator can install them to devices.
Kaspersky Security Center updates some applications by removing the previous version of the application and installing the new one.
A user interaction may be required when you update a third-party application or fix a vulnerability in a third-party application on a managed device. For example, the user may be prompted to close the third-party application if it is currently open.
Ensure that the Display Vulnerability and Patch Management option is enabled in the Configure interface window for the primary and secondary Administration Servers. Otherwise, the update search task handles only WSUS updates.
For security reasons, any third-party software updates that you install by using the Vulnerability and patch management feature are automatically scanned for malware by Kaspersky technologies. These technologies are used for automatic file checks and include virus scanning, static analysis, dynamic analysis, behavior analysis in the sandbox environment, and machine learning.
Kaspersky experts do not perform manual analysis of third-party software updates that can be installed by using the Vulnerability and patch management feature. In addition, Kaspersky experts do not search for vulnerabilities (known or unknown) or undocumented features in such updates, nor do they perform other types of analysis of the updates other than those specified in the paragraph above.
Before installing the updates to all of the devices, you can perform a test installation to make sure installed updates will cause no failures to the operation of applications on the devices.
You can find the details of third-party software that can be updated through Kaspersky Security Center by visiting the Technical Support website, on the Kaspersky Security Center page, in the Server Management section.
Scenario: Updating third-party software
This section provides a scenario for updating third-party software installed on the client devices. The third-party software includes applications from Microsoft and other software vendors. Updates for Microsoft applications are provided by the Windows Update service.
Prerequisites
Administration Server must have a connection to the internet to install updates of third-part software other than Microsoft software.
By default, internet connection is not required for Administration Server to install Microsoft software updates on the managed devices. For example, the managed devices can download the Microsoft software updates directly from Microsoft Update servers or from Windows Server with Microsoft Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) deployed in your organization's network. Administration Server must be connected to the internet when you use Administration Server as WSUS server.
Stages
Updating third-party software proceeds in stages:
- Searching for required updates
To find the third-party software updates required for the managed devices, run the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task. When this task is complete, Kaspersky Security Center receives the lists of detected vulnerabilities and required updates for the third-party software installed on the devices that you specified in the task properties.
The Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is created automatically by the Administration Server quick start wizard. If you did not run the wizard, create the task or run the quick start wizard now.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Scanning applications for vulnerabilities, Scheduling the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task, Find vulnerabilities and required updates task settings
- Analyzing the list of found updates
View the Software updates list and decide which updates you want to install. To view detailed information about each update, click the update name in the list. For each update in the list, you can also view the statistics on the update installation on client devices.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Viewing information about available updates
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Viewing information about available third-party software updates
- Configuring installation of updates
When Kaspersky Security Center received the list of the third-party software updates, you can install them on client devices by using the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task or the Install Windows Update updates task. Create one of these tasks. You can create these tasks on the Tasks tab or by using the Software updates list.
The Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is used to install updates for Microsoft applications, including the updates provided by the Windows Update service, and updates of other vendors' software. Note that this task can be created only if you have the license for the Vulnerability and patch management feature.
The Install Windows Update updates task does not require a license, but it can be used to install Windows Update updates only.
To install some software updates you must accept the End User License Agreement (EULA) for the installation software. If you decline the EULA, the software update will not be installed.
You can start an update installation task by schedule. When specifying the task schedule, make sure that the update installation task starts after the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is complete.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Fixing vulnerabilities in applications, Viewing information about available updates
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, Creating the Install Windows Update updates task, Viewing information about available third-party software updates
- Scheduling the tasks
To be sure that the update list is always up-to-date, schedule the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task to run the task automatically from time to time. By default, the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is set to start manually.
If you have created the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, you can schedule it to run with the same frequency as the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task or less often. When scheduling the Install Windows Update updates task, note that for this task you must define the list of updates every time before starting this task.
When scheduling the tasks, make sure that an update installation task starts after the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is complete.
- Approving and declining software updates (optional)
If you have created the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, you can specify rules for update installation in the task properties. If you have created the Install Windows Update updates task, skip this step.
For each rule, you can define the updates to install depending on the update status: Undefined, Approved or Declined. For example, you may want to create a specific task for servers and set a rule for this task to allow installation of only Windows Update updates and only those ones that have Approved status. After that you manually set the Approved status for those updates that you want to install. In this case the Windows Update updates that have the Undefined or Declined status will not be installed on the servers that you specified in the task.
The usage of the Approved status to manage update installation is efficient for a small amount of updates. To install multiple updates, use the rules that you can configure in the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task. We recommend that you set the Approved status for only those specific updates that do not meet the criteria specified in the rules. When you manually approve a large amount of updates, performance of Administration Server decreases and may lead to Administration Server overload.
By default, the downloaded software updates have the Undefined status. You can change the status to Approved or Declined in the Software updates list (Operations → Patch management → Software updates).
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Approving and declining software updates
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Approving and declining third-party software updates
- Configuring Administration Server to work as Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) server (optional)
By default, Windows Update updates are downloaded to the managed devices from Microsoft servers. You can change this setting to use the Administration Server as WSUS server. In this case, the Administration Server synchronizes the update data with Windows Update at the specified frequency and provides updates in centralized mode to Windows Update on networked devices.
To use the Administration Server as WSUS server, create the Perform Windows Update synchronization task and select the Use Administration Server as WSUS server check box in the Network Agent policy.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Synchronizing updates from Windows Update with Administration Server, Configuring Windows updates in a Network Agent policy
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating the Perform Windows Update synchronization task
- Running an update installation task
Start the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task or the Install Windows Update updates task. When you start these tasks, updates are downloaded and installed on managed devices. After the task is complete, make sure that it has the Completed successfully status in the task list.
- Create the report on results of update installation of third-party software (optional)
To view detailed statistics on the update installation, create the Report on results of installation of third-party software updates.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Creating and viewing a report
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Generating and viewing a report
Results
If you have created and configured the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, the updates are installed on the managed devices automatically. When new updates are downloaded to the Administration Server repository, Kaspersky Security Center checks whether they meet the criteria specified in the update rules. All new updates that meet the criteria will be installed automatically at the next task run.
If you have created the Install Windows Update updates task, only those updates specified in the Install Windows Update updates task properties are installed. In future, if you want to install new updates downloaded to the Administration Server repository, you must add the required updates to the list of updates in the existing task or create a new Install Windows Update updates task.
Viewing information about available updates for third-party applications
To view a list of available updates for third-party applications installed on client devices,
In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Software updates subfolder.
In the workspace of the folder, you can view a list of available updates for applications installed on devices.
To view the properties of an update,
In the workspace of the Software updates folder, in the context menu of the update, select Properties.
The following information is available for viewing in the properties window of the update:
- On the General section you can view the Update approval status:
- Undefined—the update is available in the list of updates, but is not approved for installation.
- Approved—the update is available in the list of updates and approved for installation.
- Declined—the update is declined for installation.
- On the Attributes section you can view the values of the Installed automatically field:
- The Automatically value is displayed if the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task can install updates for the application. The task automatically installs new updates from the web address provided by the vendor of third-party software.
- The Manually value is displayed if Kaspersky Security Center cannot install updates for the application automatically. You can install updates manually.
The Installed automatically field is not displayed for Windows application updates.
- List of client devices for which the update is intended.
- List of system components (prerequisites) that have to be installed before the update (if any).
- Software vulnerabilities that the update will fix.
Approving and declining software updates
The settings of an update installation task may require approval of updates that are to be installed. You can approve updates that must be installed and decline updates that must not be installed.
For example, you may want to first check the installation of updates in a test environment and make sure that they do not interfere with the operation of devices, and only then allow the installation of these updates on client devices.
The usage of the Approved status to manage third-party update installation is efficient for a small amount of updates. To install multiple third-party updates, use the rules that you can configure in the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task. We recommend that you set the Approved status for only those specific updates that do not meet the criteria specified in the rules. When you manually approve a large amount of updates, performance of Administration Server decreases and may lead to Administration Server overload.
To approve or decline one or several updates:
- In the console tree, select the Advanced → Application management → Software updates node.
- In the workspace of the Software updates folder, click the Refresh button in the upper right corner. A list of updates appears.
- Select the updates that you want to approve or decline.
The information box for the selected objects appears on the right side of the workspace.
- In the Update approval status drop-down list, select Approved to approve the selected updates or Declined to decline the selected updates.
The default value is Undefined.
The updates for which you set the Approved status are placed in a queue for installation.
The updates for which you set the Declined status are uninstalled (if possible) from all devices on which they were previously installed. Also, they will not be installed on other devices in future.
Some updates for Kaspersky applications cannot be uninstalled. If you set the Declined status for them, Kaspersky Security Center will not uninstall these updates from the devices on which they were previously installed. However, these updates will never be installed on other devices in future. If an update for Kaspersky applications cannot be uninstalled, this property is displayed in the update properties window: in the Sections pane select General, and in the workspace the property will appear under Installation requirements. If you set the Declined status for third-party software updates, these updates will not be installed on devices for which they were planned but have not yet been installed. Updates will still remain on devices on which they were already installed. If you have to delete them, you can manually delete them locally.
Synchronizing updates from Windows Update with Administration Server
If you have selected Use Administration Server as a WSUS server in the Update management settings window of the quick start wizard, the Windows Update synchronization task is created automatically. You can run the task in the Tasks folder. The functionality of a Microsoft software update is only available after the Perform Windows Update synchronization task is successfully completed.
Microsoft software updates may exceed 10 GB. Ensure that the Administration Server database is capable of accommodating such volumes; otherwise, the Perform Windows Update synchronization task will fail. The Microsoft SQL Express database is not supported for the Perform Windows Update synchronization task.
The Perform Windows Update synchronization task only downloads metadata from Microsoft servers. If the network does not use a WSUS server, each client device downloads Microsoft updates from external servers independently.
To create a task for synchronizing Windows Updates with Administration Server:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Software updates subfolder.
- Click the Additional actions button and select Configure Windows Update synchronization in the drop-down list.
The wizard creates the Perform Windows Update synchronization task displayed in the Tasks folder.
The Windows update center data retrieval task creation wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
You can also create the Windows Update synchronization task in the Tasks folder by clicking Create a task.
Microsoft regularly deletes outdated updates from the company's servers so the number of current updates is always between 200,000 and 300,000. To reduce disk space usage and database size, Kaspersky Security Center deletes the outdated updates that are no longer present on Microsoft update servers.
When running the Perform Windows Update synchronization task, the application receives a list of current updates from a Microsoft update server. Next, Kaspersky Security Center compiles a list of updates that have become outdated. At the next start of the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task, Kaspersky Security Center flags all outdated updates and sets the deletion time for them. At the next start of the Perform Windows Update synchronization task, all updates flagged for deletion 30 days ago are deleted. Kaspersky Security Center also checks for outdated updates that were flagged for deletion more than 180 days ago, and then deletes those older updates.
When the Perform Windows Update synchronization task completes and outdated updates are deleted, the database may still have the hash codes pertaining to the files of deleted updates, as well as corresponding files in the %AllUsersProfile%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\.working\wusfiles files (if they were downloaded earlier). You can run the Administration Server maintenance task to delete these outdated records from the database and corresponding files.
Step 1. Defining whether to reduce traffic
When Kaspersky Security Center synchronizes updates with Microsoft Windows Update Servers, information about all files is saved in the Administration Server database. All files required for an update are also downloaded to the drive during interaction with the Windows Update Agent. In particular, Kaspersky Security Center saves information about express update files to the database and downloads them when necessary. Downloading express update files leads to decreased free space on the drive.
To avoid a decrease in disk space volume and to reduce traffic, you can disable the Download express installation files option.
If this option is selected, express update files are downloaded when running the task. By default, this option is not selected.
Step 2. Applications
In this section you can select applications for which updates will be downloaded.
If the All applications check box is selected, updates will be downloaded for all existing applications, and for all applications that may be released in the future.
By default, the All applications check box is selected.
Step 3. Update categories
In this section, you can select categories of updates that will be downloaded to the Administration Server.
If the All categories check box is selected, updates will be downloaded for all existing updates categories, and for all categories that may appear in the future.
By default, the All categories check box is selected.
Step 4. Updates languages
In this window you can select localization languages of updates that will be downloaded to Administration Server. Select one of the following options for downloading localization languages of updates:
Step 5. Selecting the account to start the task
In the Selecting an account to run the task window, you can specify which account to use when running the task. Select one of the following options:
Step 6. Configuring a task start schedule
On the Configure task schedule wizard page, you can create a schedule for task start. If necessary, specify the following settings:
- Scheduled start:
- Run missed tasks
- Use automatically randomized delay for task starts
- Use randomized delay for task starts within an interval of (min)
Step 7. Defining the task name
In the Define the task name window, specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).The default value is Perform Windows Update synchronization.
Step 8. Completing creation of the task
In the Finish task creation window, click the Finish button to finish the wizard.
If you want the task to start as soon as the wizard finishes, select the Run the task after the wizard finishes check box.
The newly created Windows Update synchronization task will appear in the list of tasks in the Tasks folder of the console tree.
Installing updates on devices manually
If you have selected Find and install required updates on the Update management settings page of the quick start wizard, the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is created automatically. You can run or stop the task in the Managed devices folder on the Tasks tab.
If you have selected Search for required updates in the quick start wizard, you can install software updates on client devices through the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
You can do any of the following:
- Create a task for installing updates.
- Add a rule for installing an update to an existing update installation task.
- In the settings of an existing update installation task, configure a test installation of updates.
A user interaction may be required when you update a third-party application or fix a vulnerability in a third-party application on a managed device. For example, the user may be prompted to close the third-party application if it is currently open.
Installing updates by creating an installation task
You can do any of the following:
- Create a task for installing certain updates.
- Select an update and create a task for installing it and similar updates.
To install specific updates:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Software updates subfolder.
- In the workspace, select the updates that you want to install.
- Do any of the following:
- Right-click one of the selected updates in the list, and then select Install update → New task.
- Click the Install update (create task) link in the information box for the selected updates.
- Make your choice in the displayed prompt about installing all previous application updates. Click Yes if you agree to the installation of successive application versions incrementally if this is required for installing the selected updates. Click No if you want to update applications in a straightforward fashion, without installing successive versions. If installing the selected updates is not possible without installing previous versions of applications, the updating of the application fails.
The Updates installation and vulnerabilities fix task creation wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the Selecting an operating system restart option page of the wizard, select the action to perform when the operating system on client devices must be restarted after the operation:
- On the Configure task schedule page of the wizard, you can create a schedule for task start. If necessary, specify the following settings:
- On the Define the task name page of the wizard, specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- On the Finish task creation page of the wizard, click the Finish button to close the wizard.
If you want the task to start as soon as the wizard finishes, select the Run the task after the wizard finishes check box.
After the wizard completes its operation, Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities appears in the Tasks folder.
You can enable automatic installation of system components (prerequisites) prior to installation of an update in the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task properties. When this option is enabled, all required system components are installed before the update. A list of the required components can be found in properties of the update.
In the properties of Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, you can allow installation of updates that upgrade application to a new version.
If the task settings provide rules for installation of third-party updates, the Administration Server downloads all relevant updates from their vendors' websites. Updates are saved to the Administration Server repository and then distributed and installed on devices where they are applicable.
If the task settings provide rules for installation of Microsoft updates and the Administration Server acts as a WSUS server, the Administration Server downloads all relevant updates to the repository and then distributes them to managed devices. If the network does not use a WSUS server, each client device downloads Microsoft updates from external servers independently.
To install a certain update and similar ones:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Software updates subfolder.
- In the workspace, select the update that you want to install.
- Click the Run Update installation wizard button.
The Update installation wizard starts.
The Update installation wizard features are only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the Search for existing update installation tasks page, specify the following settings:
- If you choose to search for existing update installation tasks and if the search retrieves some tasks, you can view properties of these tasks or start them manually. No further actions are required.
Otherwise, click the New update installation task button.
- Select the type of the installation rule to be added to the new task, and then click the Finish button.
- Make your choice in the displayed prompt about installing all previous application updates. Click Yes if you agree to the installation of successive application versions incrementally if this is required for installing the selected updates. Click No if you want to update applications in a straightforward fashion, without installing successive versions. If installing the selected updates is not possible without installing previous versions of applications, the updating of the application fails.
The Updates installation and vulnerabilities fix task creation wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the Selecting an operating system restart option page of the wizard, select the action to perform when the operating system on client devices must be restarted after the operation:
- On the Select devices to which the task will be assigned page of the wizard, select one of the following options:
- On the Configure task schedule page of the wizard, you can create a schedule for task start. If necessary, specify the following settings:
- On the Define the task name page of the wizard, specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- On the Finish task creation page of the wizard, click the Finish button to close the wizard.
If you want the task to start as soon as the wizard finishes, select the Run the task after the wizard finishes check box.
When the wizard finishes, the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is created and displayed in the Tasks folder.
In addition to the settings that you specify during task creation, you can change other properties of a created task.
Upgrading to a new version of the application may cause a malfunction of dependent applications on devices.
Installing an update by adding a rule to an existing installation task
To install an update by adding a rule to an existing installation task:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Software updates subfolder.
- In the workspace, select the update that you want to install.
- Click the Run Update installation wizard button.
The Update installation wizard starts.
The Update installation wizard features are only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the Search for existing update installation tasks page, specify the following settings:
- If you choose to search for existing update installation tasks and if the search retrieves some tasks, you can view properties of these tasks or start them manually. No further actions are required.
Otherwise, click the Add an update installation rule button.
- Select the task to which you want to add a rule, and then click the Add rule button.
Also, you can view properties of the existing tasks, start them manually, or create a new task.
- Select the type of the rule to be added to the selected task, and then click the Finish button.
- Make your choice in the displayed prompt about installing all previous application updates. Click Yes if you agree to the installation of successive application versions incrementally if this is required for installing the selected updates. Click No if you want to update applications in a straightforward fashion, without installing successive versions. If installing the selected updates is not possible without installing previous versions of applications, the updating of the application fails.
A new rule for installing the update is added to the existing Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
Configuring a test installation of updates
To configure a test installation of updates:
- In the console tree, select the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task in the Managed devices folder on the Tasks tab.
- In the context menu of the task, select Properties.
The properties window of the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task opens.
- In the properties window of the task, in the Test installation section select one of the available options for test installation:
- Do not scan. Select this option if you do not want to perform a test installation of updates.
- Run scan on selected devices. Select this option if you want to test updates installation on selected devices. Click the Add button and select devices on which you need to perform test installation of updates.
- Run scan on devices in the specified group. Select this option if you want to test updates installation on a group of devices. In the Specify a test group field, specify a group of devices on which you want to perform a test installation.
- Run scan on specified percentage of devices. Select this option if you want to test updates installation on some portion of devices. In the Percentage of test devices out of all target devices field, specify the percentage of devices on which you want to perform a test installation of updates.
- Upon selecting any option except Do not scan, in the Amount of time to make the decision if the installation is to be continued, in hours field specify the number of hours that must elapse from the test installation of updates until the start of installation of the updates on all devices.
Configuring Windows updates in a Network Agent policy
To configure Windows Updates in a Network Agent policy:
- In the console tree, select Managed devices.
- In the workspace, select the Policies tab.
- Select a Network Agent policy.
- In the context menu of the policy, select Properties.
The properties window for the Network Agent policy opens.
- In the Sections pane, select Software updates and vulnerabilities.
- Select the Use Administration Server as a WSUS server option to download Windows updates to the Administration Server and then distribute them to client devices through Network Agent.
If this option is not selected, Windows updates are not downloaded to the Administration Server. In this case, client devices receive Windows updates directly from Microsoft servers.
- Select the set of updates that the users can install on their devices manually by using Windows Update.
On devices running Windows 10, if Windows Update has already found updates for the device, the new option that you select under Allow users to manage installation of Windows Update updates will be applied only after the updates found are installed.
Select an item in the drop-down list:
- Select the Windows Update search mode:
- Select the Scan executable files for vulnerabilities when running them option if you want to scan executable files for vulnerabilities while the files are being run.
- Make sure that editing is locked for all the settings that you have changed. Otherwise, the changes do not apply.
- Click Apply.
Fixing third-party software vulnerabilities
This section describes the features of Kaspersky Security Center that relate to fixing vulnerabilities in the software installed on managed devices.
Scenario: Finding and fixing third-party software vulnerabilities
This section provides a scenario for finding and fixing vulnerabilities on the managed devices running Windows. You can find and fix software vulnerabilities in the operating system and in third-party software, including Microsoft software.
Prerequisites
- Kaspersky Security Center is deployed in your organization.
- There are managed devices running Windows in your organization.
- Internet connection is required for Administration Server to perform the following tasks:
- To make a list of recommended fixes for vulnerabilities in Microsoft software. The list is created and regularly updated by Kaspersky specialists.
- To fix vulnerabilities in third-part software other than Microsoft software.
Stages
Finding and fixing software vulnerabilities proceeds in stages:
- Scanning for vulnerabilities in the software installed on the managed devices
To find vulnerabilities in the software installed on the managed devices, run the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task. When this task is complete, Kaspersky Security Center receives the lists of detected vulnerabilities and required updates for the third-party software installed on the devices that you specified in the task properties.
The Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is created automatically by Kaspersky Security Center quick start wizard. If you did not run the wizard, start it now or create the task manually.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Scanning applications for vulnerabilities, Scheduling the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task, Find vulnerabilities and required updates task settings
- Analyzing the list of detected software vulnerabilities
View the Software vulnerabilities list and decide which vulnerabilities are to be fixed. To view detailed information about each vulnerability, click the vulnerability name in the list. For each vulnerability in the list, you can also view the statistics on the vulnerability on managed devices.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Viewing information about software vulnerabilities, Viewing statistics of vulnerabilities on managed devices
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Viewing information about software vulnerabilities, Viewing statistics of vulnerabilities on managed devices
- Configuring vulnerabilities fix
When the software vulnerabilities are detected, you can fix the software vulnerabilities on the managed devices by using the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task or the Fix vulnerabilities task.
The Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is used to update and fix vulnerabilities in third-party software, including Microsoft software, installed on the managed devices. This task allows you to install multiple updates and fix multiple vulnerabilities according to certain rules. Note that this task can be created only if you have the license for the Vulnerability and patch management feature. To fix software vulnerabilities the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task uses recommended software updates.
The Fix vulnerabilities task does not require the license option for the Vulnerability and patch management feature. To use this task, you must manually specify user fixes for vulnerabilities in third-party software listed in the task settings. The Fix vulnerabilities task uses recommended fixes for Microsoft software and user fixes for third-party software.
You can start Vulnerability fix wizard that creates one of these tasks automatically, or you can create one of these tasks manually.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Selecting user fixes for vulnerabilities in third-party software, Fixing vulnerabilities in applications
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Selecting user fixes for vulnerabilities in third-party software, Fixing vulnerabilities in third-party software, Creating the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task
- Scheduling the tasks
To be sure that the vulnerabilities list is always up-to-date, schedule the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task to run it automatically from time to time. The recommended average frequency is once a week.
If you have created the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, you can schedule it to run with the same frequency as the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task or less often. When scheduling the Fix vulnerabilities task, note that you have to select fixes for Microsoft software or specify user fixes for third-party software every time before starting the task.
When scheduling the tasks, make sure that a task to fix vulnerability starts after the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is complete.
- Ignoring software vulnerabilities (optional)
If you want, you can ignore software vulnerabilities to be fixed on all managed devices or only on the selected managed devices.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Ignoring software vulnerabilities
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Ignoring software vulnerabilities
- Running a vulnerability fix task
Start the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task or the Fix vulnerability task. When the task is complete, make sure that it has the Completed successfully status in the task list.
- Create the report on results of fixing software vulnerabilities (optional)
To view detailed statistics on the vulnerabilities fix, generate the Report on vulnerabilities. The report displays information about software vulnerabilities that are not fixed. Thus you can have an idea about finding and fixing vulnerabilities in third-party software, including Microsoft software, in your organization.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Creating and viewing a report
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Generating and viewing a report
- Checking configuration of finding and fixing vulnerabilities in third-party software
Be sure that you have done the following:
- Obtained and reviewed the list of software vulnerabilities on managed devices
- Ignored software vulnerabilities if you wanted
- Configured the task to fix vulnerabilities
- Scheduled the tasks to find and to fix software vulnerabilities so that they start sequentially
- Checked that the task to fix software vulnerabilities was run
Results
If you have created and configured the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, the vulnerabilities are fixed on the managed devices automatically. When the task is run, it correlates the list of available software updates to the rules specified in the task settings. All software updates that meet the criteria in the rules will be downloaded to the Administration Server repository and will be installed to fix software vulnerabilities.
If you have created the Fix vulnerabilities task, only software vulnerabilities in Microsoft software are fixed.
Page top
About finding and fixing software vulnerabilities
Kaspersky Security Center detects and fixes software
on managed devices running Microsoft Windows families operating systems. Vulnerabilities are detected in the operating system and in third-party software, including Microsoft software.Updates functionality (including providing anti-virus signature updates and codebase updates), as well as KSN functionality may not be available in the software in the U.S.
Finding software vulnerabilities
To find software vulnerabilities, Kaspersky Security Center uses characteristics from the database of known vulnerabilities. This database is created by Kaspersky specialists. It contains information about vulnerabilities, such as vulnerability description, vulnerability detect date, vulnerability severity level. You can find the details of software vulnerabilities on Kaspersky website.
Kaspersky Security Center uses the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task to find software vulnerabilities.
In certain cases vulnerabilities detected in a Microsoft Windows operating system can be fixed using either of the following methods:
- Installing an update for the OS.
- Upgrading the OS to a newer version (for example, from Windows 10 to Windows 11).
In this scenario KSC displays two entries for the same vulnerability.
Fixing software vulnerabilities
To fix software vulnerabilities Kaspersky Security Center uses software updates issued by the software vendors. The software updates metadata is downloaded to the Administration Server repository as a result of the following tasks run:
- Download updates to the Administration Server repository. This task is intended to download updates metadata for Kaspersky and third-party software. This task is created automatically by the Kaspersky Security Center quick start wizard. You can create the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task manually.
- Perform Windows Update synchronization. This task is intended to download updates metadata for Microsoft software.
Software updates to fix vulnerabilities can be represented as full distribution packages or patches. Software updates that fix software vulnerabilities are named fixes. Recommended fixes are those that are recommended for installation by Kaspersky specialists. User fixes are those that are manually specified for installation by users. To install a user fix, you have to create an installation package containing this fix.
If you have the Kaspersky Security Center license with the Vulnerability and patch management feature, to fix software vulnerabilities you can use Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task. This task automatically fixes multiple vulnerabilities installing recommended fixes. For this task, you can manually configure certain rules to fix multiple vulnerabilities.
If you do not have the Kaspersky Security Center license with the Vulnerability and patch management feature, to fix software vulnerabilities, you can use the Fix vulnerabilities task. By means of this task, you can fix vulnerabilities by installing recommended fixes for Microsoft software and user fixes for other third-party software.
For security reasons, any third-party software updates that you install by using the Vulnerability and patch management feature are automatically scanned for malware by Kaspersky technologies. These technologies are used for automatic file checks and include virus scanning, static analysis, dynamic analysis, behavior analysis in the sandbox environment, and machine learning.
Kaspersky experts do not perform manual analysis of third-party software updates that can be installed by using the Vulnerability and patch management feature. In addition, Kaspersky experts do not search for vulnerabilities (known or unknown) or undocumented features in such updates, nor do they perform other types of analysis of the updates other than those specified in the paragraph above.
A user interaction may be required when you update a third-party application or fix a vulnerability in a third-party application on a managed device. For example, the user may be prompted to close the third-party application if it is currently open.
To fix some software vulnerabilities, you must accept the End User License Agreement (EULA) for installing the software if EULA acceptance is requested. If you decline the EULA, the software vulnerability is not fixed.
Viewing information about software vulnerabilities
To view a list of vulnerabilities detected on client devices,
In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Software vulnerabilities subfolder.
The page displays a list of vulnerabilities in applications detected on managed devices.
To obtain information about a selected vulnerability,
Select Properties from the context menu of the vulnerability.
The properties window of the vulnerability opens, displaying the following information:
- Application in which the vulnerability has been detected.
- List of devices on which the vulnerability has been detected.
- Information on whether the vulnerability has been fixed.
To view the report on all detected vulnerabilities,
In the Software vulnerabilities folder, click the View report on vulnerabilities link.
A report on vulnerabilities in applications installed on devices will be generated. You can view this report in the node with the name of the relevant Administration Server, by opening the Reports tab.
Viewing statistics of vulnerabilities on managed devices
You can view statistics for each software vulnerability on managed devices. Statistics are represented as a diagram. The diagram displays the number of devices with the following statuses:
- Ignored on: <number of devices>. This status is assigned if, in the vulnerability properties, you have manually set the option to ignore the vulnerability.
- Fixed on: <number of devices>. This status is assigned if the task to fix the vulnerability has successfully completed.
- Fix scheduled on: <number of devices>. This status is assigned if you have created the task to fix the vulnerability, but the task is not performed yet.
- Patch applied on: <number of devices>. This status is assigned if you have manually selected a software update to fix the vulnerability, but this software update has not fixed the vulnerability.
- Fix required on: <number of devices>. This status is assigned if the vulnerability was fixed only on some managed devices, and the vulnerability is required to be fixed on more managed devices.
To view the statistics of a vulnerability on managed devices:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Software vulnerabilities subfolder.
The page displays a list of vulnerabilities in applications detected on managed devices.
- Select a vulnerability for which you want to view the statistics.
In the block for working with a selected object, a diagram of the vulnerability statuses is displayed. Clicking a status opens a list of devices on which the vulnerability has the selected status.
Scanning applications for vulnerabilities
If you have configured the application through the quick start wizard, the Vulnerability scan task is created automatically. You can view the task in the Managed devices folder, on the Tasks tab.
To create a task for vulnerability scanning in applications installed on client devices:
- In the console tree, select Advanced → Application management, and then select the Software vulnerabilities subfolder.
- In the workspace, select Additional actions → Configure vulnerability scan.
If a task for vulnerability scanning already exists, the Tasks tab of the Managed devices folder is displayed, with the existing task selected. Otherwise, the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task creation wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- In the Select the task type window, select Find vulnerabilities and required updates.
- On the Settings page of the wizard, specify the task settings as follows:
- On the Configure task schedule page of the wizard, you can create a schedule for task start. If necessary, specify the following settings:
- On the Define the task name page of the wizard, specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- On the Finish task creation page of the wizard, click the Finish button to close the wizard.
If you want the task to start as soon as the wizard finishes, select the Run the task after the wizard finishes check box.
After the wizard completes its operation, the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task appears in the list of tasks in the Managed devices folder, on the Tasks tab.
In addition to the settings that you specify during task creation, you can change other properties of a created task.
When the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is complete, Administration Server displays a list of vulnerabilities found in applications installed on the device; it also displays all software updates required to fix the vulnerabilities detected.
If you encounter the 0x80240033 "Windows Update Agent error 80240033 ("License terms could not be downloaded.")", you can resolve this issue through the Windows Registry.
Administration Server does not display the list of required software updates when you sequentially run two tasks—the Perform Windows Update synchronization task that has the Download express installation files option disabled, and then the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task. In order to view the list of required software updates, you must run the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task again.
Network Agent receives information about any available Windows updates and other Microsoft product updates from Windows Update or the Administration Server, if the Administration Server acts as the WSUS server. Information is transmitted when applications are started (if this is provided for by the policy) and at each routine run of the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task on client devices.
You can find the details of third-party software that can be updated through Kaspersky Security Center by visiting the Technical Support website, on the Kaspersky Security Center page, in the Server Management section.
Fixing vulnerabilities in applications
If you have selected Find and install required updates on the Update management settings page of the quick start wizard, the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is created automatically. The task is displayed in the workspace of the Managed devices folder, on the Tasks tab.
Otherwise, you can do any of the following:
- Create a task for fixing vulnerabilities by installing available updates.
- Add a rule for fixing a vulnerability to an existing vulnerability fix task.
A user interaction may be required when you update a third-party application or fix a vulnerability in a third-party application on a managed device. For example, the user may be prompted to close the third-party application if it is currently open.
Fixing vulnerabilities by creating a vulnerability fix task
You can do any of the following:
- Create a task for fixing multiple vulnerabilities that meet certain rules.
- Select a vulnerability and create a task for fixing it and similar vulnerabilities.
To fix vulnerabilities that meet certain rules:
- In the console tree, select Administration Server on devices for which you want to fix vulnerabilities.
- In the View menu of the main application window, select Configure interface.
- In the window that opens, select the Display Vulnerability and Patch Management check box, and then click OK.
- In the window with the application message, click OK.
- Restart the Administration Console, so the changes take effect.
- In the console tree, select the Managed devices folder.
- In the workspace, select the Tasks tab.
- Click the Create a task button to run the New task wizard. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the Select the task type page of the wizard, select Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities.
If the task is not displayed, check whether your account has the Read, Modify, and Execute rights for the System management: Vulnerability and patch management functional area. You cannot create and configure the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task without these access rights.
- On the Settings page of the wizard, specify the task settings as follows:
- On the Selecting an operating system restart option page of the wizard, select the action to perform when the operating system on client devices must be restarted after the operation:
- On the Configure task schedule page of the wizard, you can create a schedule for task start. If necessary, specify the following settings:
- On the Define the task name page of the wizard, specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- On the Finish task creation page of the wizard, click the Finish button to close the wizard.
If you want the task to start as soon as the wizard finishes, select the Run the task after the wizard finishes check box.
After the wizard completes its operation, the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is created and displayed in the Tasks folder.
In addition to the settings that you specify during task creation, you can change other properties of a created task.
If the task results contain the 0x80240033 "Windows Update Agent error 80240033 ("License terms could not be downloaded.")" error, you can resolve this issue through the Windows Registry.
To fix a specific vulnerability and similar ones:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Software vulnerabilities subfolder.
- Select the vulnerability that you want to fix.
- Click the Run Vulnerability fix wizard button.
The Vulnerability fix wizard starts.
The Vulnerability fix wizard features are only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
Follow the steps of the wizard.
- In the Search for existing vulnerability fix tasks window, specify the following parameters:
- If you choose to search for existing vulnerability fix tasks and if the search retrieves some tasks, you can view properties of these tasks or start them manually. No further actions are required.
Otherwise, click the New vulnerability fix task button.
- Select the type of the vulnerability fix rule to be added to the new task, and then click the Finish button.
- Make your choice in the displayed prompt about installing all previous application updates. Click Yes if you agree to the installation of successive application versions incrementally if this is required for installing the selected updates. Click No if you want to update applications in a straightforward fashion, without installing successive versions. If installing the selected updates is not possible without installing previous versions of applications, the updating of the application fails.
The Updates installation and vulnerabilities fix task creation wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the Selecting an operating system restart option page of the wizard, select the action to perform when the operating system on client devices must be restarted after the operation:
- On the Select devices to which the task will be assigned page of the wizard, select one of the following options:
- On the Configure task schedule page of the wizard, you can create a schedule for task start. If necessary, specify the following settings:
- On the Define the task name page of the wizard, specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- On the Finish task creation page of the wizard, click the Finish button to close the wizard.
If you want the task to start as soon as the wizard finishes, select the Run the task after the wizard finishes check box.
When the wizard completes, the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is created and displayed in the Tasks folder.
In addition to the settings that you specify during task creation, you can change other properties of a created task.
Fixing a vulnerability by adding a rule to an existing vulnerability fix task
To fix a vulnerability by adding a rule to an existing vulnerability fix task:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Software vulnerabilities subfolder.
- Select the vulnerability that you want to fix.
- Click the Run Vulnerability fix wizard button.
The Vulnerability fix wizard starts.
The Vulnerability fix wizard features are only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
Follow the steps of the wizard.
- In the Search for existing vulnerability fix tasks window, specify the following parameters:
- If you choose to search for existing vulnerability fix tasks and if the search retrieves some tasks, you can view properties of these tasks or start them manually. No further actions are required.
Otherwise, click the Add vulnerability fix rule to existing task button.
- Select the task to which you want to add a rule, and then click the Add rule button.
Also, you can view properties of the existing tasks, start them manually, or create a new task.
- Select the type of rule to be added to the selected task, and then click the Finish button.
- Make your choice in the displayed prompt about installing all previous application updates. Click Yes if you agree to the installation of successive application versions incrementally if this is required for installing the selected updates. Click No if you want to update applications in a straightforward fashion, without installing successive versions. If installing the selected updates is not possible without installing previous versions of applications, the updating of the application fails.
A new rule for fixing the vulnerability is added to the existing Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
Fixing vulnerabilities in an isolated network
This section describes the steps that you can take to fix third-party software vulnerabilities on managed devices connected to Administration Servers that do not have internet access.
Scenario: Fixing third-party software vulnerabilities in an isolated network
You can install updates and fix vulnerabilities of the third-party software installed on managed devices in an isolated network. Such networks include Administration Servers and managed devices connected to them that have no internet access. To fix vulnerabilities in this kind of network, you need an Administration Server connected to the internet. Then, you will be able to download patches (required updates) by using the Administration Server with internet access, and then transmit the patches to isolated Administration Servers.
You can download the third-party software updates issued by software vendors, but you cannot download updates for Microsoft software on isolated Administration Servers by using Kaspersky Security Center.
To find out how the process of fixing vulnerabilities in an isolated network works, see the description and scheme of this process.
Prerequisites
Before you start, do the following:
- Allocate one device for connecting to the internet and downloading patches. This device will be counted as the Administration Server with internet access.
- Install Kaspersky Security Center, no earlier than version 14, on the following devices:
- Allocated device, which will act as the Administration Server with internet access
- Isolated devices, which will act as the Administration Servers isolated from the internet (hereinafter referred to as isolated Administration Servers)
- Make sure that every Administration Server has enough disk space for downloading and storing updates and patches.
Stages
Installing updates and fixing third-party software vulnerabilities on managed devices of isolated Administration Servers has the following stages:
- Configuring the Administration Server with internet access
Prepare your Administration Server with internet access to handle requests on required third-party software updates and to download patches.
- Configuring isolated Administration Servers
Prepare your isolated Administration Servers so they can regularly form lists of required updates and handle patches downloaded by the Administration Server with internet access. After configuring, isolated Administration Servers do not try to download patches from the internet anymore. Instead, they get updates through patches.
- Transmitting patches and installing updates on isolated Administration Servers
After you finished configuring Administration Servers, you can transmit the required updates lists and patches between the Administration Server with internet access and isolated Administration Servers. Next, updates from patches will be installed on managed devices by using the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
Results
Thus, the third-party software updates are transmitted to isolated Administration Servers and installed on connected managed devices by using Kaspersky Security Center. It is enough to configure Administration Servers once, and after that you can get updates as often as you need, for example, once or several times per day.
About fixing third-party software vulnerabilities in an isolated network
The process of fixing third-party software vulnerabilities in an isolated network is shown in the figure and described below. You can repeat this process periodically.
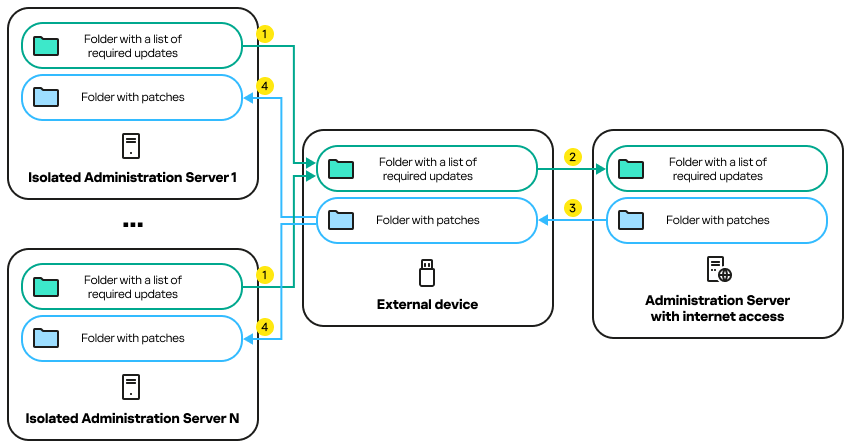
The process of transmitting patches and the list of required updates between the Administration Server with internet access and isolated Administration Servers
Every Administration Server isolated from the internet (hereinafter referred to as an isolated Administration Server) generates a list of updates that are required to be installed on managed devices connected to this Administration Server. The list of required updates is stored in a specific folder and presents a set of binary files. Each file has a name that contains the ID of the patch with the required update. As a result, every file in the list points to a specific patch.
By using an external device, you transfer the list of required updates from the isolated Administration Server to the allocated Administration Server with internet access. After that, the allocated Administration Server downloads patches from the internet and puts them in a separate folder.
When all patches are downloaded and located in the special folder for them, you move the patches to every isolated Administration Server from which you took a list of required updates. You save patches to the folder created especially for them on the isolated Administration Server. As a result, the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task runs patches and installs updates on managed devices of the isolated Administration Servers.
Configuring the Administration Server with internet access to fix vulnerabilities in an isolated network
To prepare for fixing vulnerabilities and transmitting patches in an isolated network, first configure an Administration Server with internet access, and then configure the isolated Administration Servers.
To configure an Administration Server with internet access:
- Create two folders on a disk where Administration Server is installed:
- Folder for the list of required updates
- Folder for patches
You can name these folders whatever you like.
- Grant the Modify access rights to the KLAdmins group in the created folders, by using the standard administrative tools of the operating system.
- Use the klscflag utility to write the paths to the folders in the Administration Server properties.
Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
- Enter the following commands at the Windows command prompt:
- To set the path to the folder for patches:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_DATA_EXPORT_PATH -t s -v "<
path to the folder>" - To set the path to the folder for the list of required updates:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_REQ_IMPORT_PATH -t s -v "<
path to the folder>"
Example:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_DATA_EXPORT_PATH -t s -v "C:\FolderForPatches" - To set the path to the folder for patches:
- If necessary, use the klscflag utility to specify how often the Administration Server should check for new patch requests:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_DATA_EXPORT_PERIOD_SEC -t d -v<value in seconds>The default value is 120 seconds.
Example:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_DATA_EXPORT_PERIOD_SEC -t d -v 150 - Create the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task to obtain information about patches for the third-party software installed on the managed devices, and then set the task schedule.
- Create the Fix vulnerabilities task to specify patches for the third-party software used to fix vulnerabilities, and then set the task schedule.
Run tasks manually if you want them to run earlier than it is specified in the schedule. The order in which tasks are started is important. The Fix vulnerabilities task must be run after finishing the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task.
- Restart the Administration Server service.
Now, the Administration Server with internet access is ready to download and transmit updates to isolated Administration Servers. Before you start fixing vulnerabilities, configure the isolated Administration Servers.
Configuring isolated Administration Servers to fix vulnerabilities in an isolated network
After you finished configuring the Administration Server with internet access, prepare every isolated Administration Server in your network, so you can fix vulnerabilities and install updates on managed devices connected to isolated Administration Servers.
To configure isolated Administration Servers, perform the following actions on every Administration Server:
- Activate a license key for the Vulnerability and patch management (VAPM) feature.
- Create two folders on a disk where Administration Server is installed:
- Folder where the list of required updates will appear
- Folder for patches
You can name these folders whatever you like.
- Grant the Modify permission to the KLAdmins group in the created folders, by using the standard administrative tools of the operating system.
- Use the klscflag utility to write the paths to the folders in the Administration Server properties.
Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
- Enter the following commands at the Windows command prompt:
- To set the path to the folder for patches:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_DATA_IMPORT_PATH -t s -v "<
path to the folder>" - To set the path to the folder for the list of required updates:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_REQ_EXPORT_PATH -t s -v "<
path to the folder>"
Example:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_DATA_IMPORT_PATH -t s -v "C:\FolderForPatches" - To set the path to the folder for patches:
- If necessary, use the klscflag utility to specify how often the isolated Administration Server should check for new patches:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_DATA_IMPORT_PERIOD_SEC -t d -v <
value in seconds>The default value is 120 seconds.
Example:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_DATA_IMPORT_PERIOD_SEC -t d -v 150 - If necessary, use the klscflag utility to calculate the SHA256 hashes of patches:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_DATA_IMPORT_VERIFY_HASH -t d -v 1
If you enter this command, you can make sure that the patches have not been modified during their transfer to the isolated Administration Server and that you have received the correct patches containing the required updates.
By default, Kaspersky Security Center does not calculate the SHA256 hashes of patches. If you enable this option, after the isolated Administration Server receives patches, Kaspersky Security Center computes their hashes and compares the acquired values with the hashes stored in the Administration Server database. If the calculated hash does not match the hash in the database, an error occurs and you have to replace the incorrect patches.
- Create the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task to obtain information about patches for the third-party software installed on the managed devices, and then set the task schedule.
- Create the Fix vulnerabilities task to specify patches for the third-party software used to fix vulnerabilities, and then set the task schedule.
Run tasks manually if you want them to run earlier than it is specified in the schedule. The order in which tasks are started is important. The Fix vulnerabilities task must be run after finishing the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task.
- Restart the Administration Server service.
After configuring all Administration Servers, you can move patches and lists of required updates, and fix third-party software vulnerabilities on managed devices in the isolated network.
Transmitting patches and installing updates in an isolated network
After you have finished configuring Administration Servers, you can transfer patches containing the required updates from the Administration Server with internet access to isolated Administration Servers. You can transmit and install updates as often as you need, for example, once or several times per day.
You need an external device, such as a removable drive, to transfer patches and the list of required updates between Administration Servers. Therefore, make sure that the external device has enough disk space for downloading and storing patches.
The process of transmitting patches and the list of required updates is shown in the figure and described below:

The process of transmitting patches and the list of required updates between the Administration Server with internet access and isolated Administration Servers
To install updates and fix vulnerabilities on managed devices connected to isolated Administration Servers:
- Start the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task if it is not yet running.
- Connect an external device to any isolated Administration Server.
- Create two folders on the external device: one for the list of required updates and one for patches. You can name these folders whatever you like.
If you created these folders earlier, clear them.
- Copy the list of required updates from every isolated Administration Server and paste this list into the folder for the list of required updates on the external device.
As a result, you unite all lists acquired from all isolated Administration Servers into one folder. This folder contains binary files with the IDs of patches required for all isolated Administration Servers.
- Connect the external device to the Administration Server with internet access.
- Copy the list of required updates from the external device and paste this list into the folder for the list of required updates on the Administration Server with internet access.
All required patches are automatically downloaded from the internet to the folder for patches on the Administration Server. This can take several hours.
- Make sure that all required patches are downloaded. For this purpose, you can do one of the following:
- Check the folder for patches on the Administration Server with internet access. All patches that were specified in the list of required updates should be downloaded to the necessary folder. This is more convenient if a small number of patches is required.
- Prepare a special script, for example, a shell script. If you get a large number of patches, this will be difficult to check on your own that all patches have been downloaded. In such cases, it is better to automate the check.
- Copy the patches from the Administration Server with internet access and paste them into the corresponding folder on your external device.
- Transfer the patches to every isolated Administration Server. Put the patches into a specific folder for them.
As a result, every isolated Administration Server creates an actual list of updates that are required for managed devices connected to the current Administration Server. After the Administration Server with internet access receives the list of required updates, the Administration Server downloads patches from the internet. When these patches appear on isolated Administration Servers, the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task handles the patches. Thus, updates are installed on managed devices and third-party software vulnerabilities are fixed.
When the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is running, do not reboot the Administration Server device and do not run the Backup of Administration Server data task (it will also cause a reboot). As a result, the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is interrupted, and updates are not installed. In this case, you have to restart this task manually or wait for the task to start according to the configured schedule.
Disabling the option to transmit patches and install updates in an isolated network
You can disable transmitting patches on isolated Administration Servers, for example, if you decided to take one or more Administration Servers out of an isolated network. Thus, you can reduce the number of patches and time to download them.
To disable the option to transmit patches on isolated Administration Servers:
- If you want to take all Administration Servers out of isolation, in the properties of the Administration Server with internet access, delete the paths to the folders for patches and the list of required updates. If you want to keep some Administration Servers in an isolated network, skip this step.
Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
Enter the following commands at the command prompt:
- To delete the path to the folder for patches:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_DATA_EXPORT_PATH -t s -v ""
- To delete the path to the folder for the list of required updates:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_REQ_IMPORT_PATH -t s -v ""
- To delete the path to the folder for patches:
- Restart the Administration Server service if you deleted the paths to the folders on this Administration Server.
- In the properties of every Administration Server that you want to take out of isolation, delete the paths to the folders for patches and the list of required updates.
Enter the following commands at the Windows command prompt, using administrator rights:
- To delete the path to the folder for patches:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_DATA_IMPORT_PATH -t s -v ""
- To delete the path to the folder for the list of required updates:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n VAPM_REQ_EXPORT_PATH -t s -v ""
- To delete the path to the folder for patches:
- Restart the service of every Administration Server on which you deleted the paths to the folders.
As a result, if you reconfigured the Administration Server with internet access, you will no longer receive patches through Kaspersky Security Center. If you reconfigured only some isolated Administration Servers, for example, taking some of them out of the isolated network, you will get patches only for the remaining isolated Administration Servers.
If you want to start fixing vulnerabilities on disabled isolated Administration Servers in the future, you have to configure these Administration Servers and the Administration Server with internet access once again.
Ignoring software vulnerabilities
You can ignore software vulnerabilities to be fixed. The reasons to ignore software vulnerabilities might be, for example, the following:
- You do not consider the software vulnerability to be critical to your organization.
- You understand that the software vulnerability fix can damage data related to the software that required the vulnerability fix.
- You are sure that the software vulnerability is not dangerous for your organization's network because you use other measures to protect your managed devices.
You can ignore a software vulnerability on all managed devices or only on selected managed devices.
To ignore a software vulnerability on all managed devices:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Software vulnerabilities subfolder.
The workspace of the folder displays a list of vulnerabilities in applications detected on devices by the Network Agent installed on them.
- Select the vulnerability you want to ignore.
- Select Properties from the context menu of the vulnerability.
The properties window of the vulnerability opens.
- On the General section, select the Ignore vulnerability option.
- Click OK.
The software vulnerability properties window is closed.
The software vulnerability is ignored on all managed devices.
To ignore a software vulnerability on the selected managed device:
- Open the properties window of the selected managed device and select the Software vulnerabilities section.
- Select a software vulnerability.
- Ignore selected vulnerability.
The software vulnerability is ignored on the selected device.
The ignored software vulnerability will not be fixed after the completion of the Fix vulnerabilities task or Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task. You can exclude ignored software vulnerabilities from the list of vulnerabilities by using a filter.
Selecting user fixes for vulnerabilities in third-party software
To use the Fix vulnerabilities task, you must manually specify the software updates to fix the vulnerabilities in third-party software listed in the task settings. The Fix vulnerabilities task uses recommended fixes for Microsoft software and user fixes for other third-party software. User fixes are software updates to fix vulnerabilities that the administrator manually specifies for installation.
To select user fixes for vulnerabilities in third-party software:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Software vulnerabilities subfolder.
The workspace of the folder displays a list of vulnerabilities in applications detected on devices by the Network Agent installed on them.
- Select the vulnerability for which you want to specify a user fix.
- Select Properties from the context menu of the vulnerability.
The properties window of the vulnerability opens.
- In the User fixes and other fixes section, click the Add button.
The list of available installation packages is displayed. The list of displayed installation packages corresponds to the Remote installation → Installation packages list. If you have not created an installation package containing a user fix for selected vulnerability, you can create the package now by starting the New package wizard.
- Select an installation package (or packages) containing a user fix (or user fixes) for the vulnerability in third-party software.
- Click OK.
The installation packages containing user fixes for the software vulnerability are specified. When the Fix vulnerabilities task is started, the installation package will be installed, and the software vulnerability will be fixed.
Rules for update installation
When fixing vulnerabilities in applications, you must specify rules for update installation. These rules determine updates to install and vulnerabilities to fix.
The exact settings depend on whether you create a rule for updates of Microsoft applications, of third-party applications (applications made by software vendors other than Kaspersky and Microsoft), or of all applications. When creating a rule for Microsoft applications or third-party applications, you can select specific applications and application versions for which you want to install updates. When creating a rule for all applications, you can select specific updates that you want to install and vulnerabilities that you want to fix by means of installing updates.
To create a new rule for updates of all applications:
- On the Settings page of the New task wizard, click the Add button.
The Rule creation wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the Rule type page, select Rule for all updates.
- On the General criteria page, use the drop-down lists to specify the following settings:
- On the Updates page, select the updates to be installed:
- On the Vulnerabilities page, select vulnerabilities that will be fixed by installing the selected updates:
- On the Name page, specify the name for the rule that you are creating. You can later change this name in the Settings section of the properties window of the created task.
After the Rule creation wizard completes its operation, the new rule is created and displayed in the Specify rules for installing updates field of the New task wizard.
To create a new rule for updates of Microsoft applications:
- On the Settings page of the New task wizard, click the Add button.
The Rule creation wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the Rule type page, select Rule for Windows Update.
- On the General criteria page, specify the following settings:
- On the Applications page, select the applications and application versions for which you want to install updates. By default, all applications are selected.
- On the Categories of updates page, select the categories of updates to be installed. These categories are the same as in Microsoft Update Catalog. By default, all categories are selected.
- On the Name page, specify the name for the rule that you are creating. You can later change this name in the Settings section of the properties window of the created task.
After the Rule creation wizard completes its operation, the new rule is created and displayed in the Specify rules for installing updates field of the New task wizard.
To create a new rule for updates of third-party applications:
- On the Settings page of the New task wizard, click the Add button.
The Rule creation wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the Rule type page, select Rule for third-party updates.
- On the General criteria page, specify the following settings:
- On the Applications page, select the applications and application versions for which you want to install updates. By default, all applications are selected.
- On the Name page, specify the name for the rule that you are creating. You can later change this name in the Settings section of the properties window of the created task.
After the Rule creation wizard completes its operation, the new rule is created and displayed in the Specify rules for installing updates field of the New task wizard.
Groups of applications
This section describes how to manage groups of applications installed on devices.
Creating application categories
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to create categories of applications installed on devices.
Application categories can be created in one of the following ways:
- The administrator specifies a folder in which executable files have been included in the selected category.
- The administrator specifies a device from which executable files are to be included in the selected category.
- The administrator sets criteria to be used to include applications in the selected category.
When an application category is created, the administrator can set rules for the application category. Rules define the behavior of applications included in the specified category. For example, you can block or allow startup of applications included in the category.
Managing applications run on devices
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to manage startup of applications on devices in Allowlist mode. For detailed description see Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help. While in Allowlist mode, on selected devices you can only start applications included in the specified categories. The administrator can view results of static analysis applied to rules of applications run on devices for each user.
Inventory of software installed on devices
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to perform inventory of software on devices running Windows and Linux. Network Agent retrieves information about all applications installed on devices. Information retrieved during inventory is displayed in the workspace of the Applications registry folder. The administrator can view detailed information about any application, including its version and manufacturer.
The number of executable files received from a single device cannot exceed 150,000. Having reached this limit, Kaspersky Security Center cannot receive any new files.
Licensed applications group management
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to create licensed applications groups. A licensed applications group includes applications that meet criteria set by the administrator. The administrator can specify the following criteria for licensed applications groups:
- Application name
- Application version
- Manufacturer
- Application tag
Applications that meet one or several criteria are automatically included in a group. To create a licensed applications group, you must set at least one criterion for including applications in this group.
Each licensed applications group has its own license key. The license key of a licensed applications group defines the maximum allowed number of installations for applications included in this group. If the number of installations has exceeded the limit set by the license key, an informational event is logged on Administration Server. The administrator can specify an expiration date for the license key. When this date arrives, an informational event is logged on Administration Server.
Viewing information about executable files
Kaspersky Security Center retrieves all information about executable files that have been run on devices since the operating system was installed on them. Information about executable files is displayed in the main application window, in the workspace of the Executable files folder.
Using Application Control to manage executable files
You can use the Application Control component to allow or block startup of executable files on user devices. The Application Control component supports Windows-based and Linux-based operating systems.
For Linux-based operating systems, the Application Control component is available starting from Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.2 for Linux.Also, the component is available for Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows 3.0 or later.
Prerequisites
- Kaspersky Security Center is deployed in your organization.
- The policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux is created and is active.
- The policy of Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows or Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Linux is created and is active.
Stages
The Application Control usage scenario proceeds in stages:
- Forming and viewing the list of executable files on client devices
This stage helps you find out what executable files are found on managed devices. View the list of executable files and compare it with the lists of allowed and prohibited executable files. The restrictions on executable files usage can be related to the information security polices in your organization.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Inventory of executable files
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Obtaining and viewing a list of executable files stored on client devices
- Creating categories for executable files used in your organization
Analyze the lists of executable files stored on managed devices. Based on the analysis, create categories for executable files. It is recommended to create a "Work applications" category that covers the standard set of executable files that are used at your organization. If different security groups use their own sets of executable files in their work, a separate category can be created for each security group.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Creating an application category with content added manually, Creating an application category that includes executable files from selected devices, Creating application category that includes executable files from a specific folder.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating application category with content added manually, Creating application category that includes executable files from selected devices, Creating application category that includes executable files from a specific folder.
- Configuring Application Control in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy
Configure the Application Control component in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy using the categories you have created on the previous stage.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Configuring application startup management on client devices
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Configuring Application Control in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy
- Configuring Application Control in the Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security application policy
Configure the Application Control component in the Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows policy by using the categories you have created. For more information about Application Control component, refer to Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows Help or Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Linux Help.
If you use a large number of rules, an error may occur when loading the policy. You can increase the maximum request size in bytes by using the following commands:
- For the JSON request:
klscflag -fset -pv ".core/.independent" -s KLLIM -n LP_KLOAPI_MaxSizeOfJsonRequestInBytes -v <max_request_size> -t d - For the HTTP request:
klscflag -fset -pv ".core/.independent" -s KLLIM -n LP_KLOAPI_MaxSizeOfHttpRequestInBytes -v <max_request_size> -t dWhere
<max_request_size>is a maximum request size in bytes (for example,200000000).
- For the JSON request:
- Turning on Application Control component in test mode
To ensure that Application Control rules do not block executable files required for user's work, it is recommended to enable testing of Application Control rules and analyze their operation after creating new rules. When testing is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows or Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security will not block executable files whose startup is forbidden by Application Control rules, but will instead send notifications about their startup to the Administration Server.
When testing Application Control rules, it is recommended to perform the following actions:
- Determine the testing period. Testing period can vary from several days to two months.
- Examine the events resulting from testing the operation of Application Control.
How-to instructions for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Configuring Application Control component in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy. Follow this instruction and enable the Test Mode option in configuration process.
- Changing the categories settings of Application Control component
If necessary, make changes to the Application Control settings. Based on the test results, you can add executable files related to events of the Application Control component to a category with content added manually.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Adding event-related executable files to the application category
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Adding event-related executable files to the application category
- Applying the rules of Application Control in operation mode
After Application Control rules are tested and configuration of categories is complete, you can apply the rules of Application Control in operation mode.
How-to instructions for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Configuring Application Control component in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy. Follow this instruction and disable the Test Mode option in configuration process.
- Verifying Application Control configuration
Be sure that you have done the following:
- Created categories for executable files.
- Configured Application Control using the categories.
- Applied the rules of Application Control in operation mode.
Results
When the scenario is complete, startup of executable files on managed devices is controlled. The users can run only those executable files that are allowed in your organization and cannot run executable files that are prohibited in your organization.
For detailed information about Application Control, refer to the following Help topics:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux Online Help
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows Help
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Linux Help
Obtaining and viewing a list of executable files stored on client devices
You can obtain the list of executable files stored on client devices in one of the following ways:
- Enabling notifications about applications startup in Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
- Creating an inventory task.
Enabling notifications about applications startup in Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy
To enable notifications about applications startup:
- Open the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings, and then go to General settings → Reports and Storage.
- In the Data transfer to Administration Server settings group, select the About started applications check box, and save the changes.
When a user attempts to start executable files, information about these files is added to the list of executable files on a client device. Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends this information to Network Agent, and then Network Agent sends it to Administration Server.
Creating an inventory task
The feature of inventorying executable files is available for the following applications:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux version 11.2 and later
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization 4.0 Light Agent and later versions
You can reduce load on the database while obtaining information about the installed applications. To save a space, run an inventory task on reference devices on which a standard set of software is installed. The preferable number of devices is 1-3.
We strongly do not recommend running the inventory task when using the following databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server Express Edition, MariaDB (all editions).
To create an inventory task for executable files on client devices:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- Click the New task button in the workspace of the Tasks folder.
The New task wizard starts.
- In the Select the task type window of the wizard, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security as the task type, and then select Inventory as the task subtype, and click Next.
- Follow the rest of the wizard instructions.
After the New task wizard has finished, the Inventory task is created and configured. If you want, you can change the settings for the created task. The newly created task is displayed in the list of tasks. If you want, you can change the settings for the created task.
For a detailed description of the inventory task, refer to the following Helps:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux Help
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent
After the Inventory task is performed, the list of executable files stored on managed devices is formed, and you can view the list.
During inventory, executable files in the following formats can be detected (depending on the option that you select in the inventory task properties): MZ, COM, PE, NE, SYS, CMD, BAT, PS1, JS, VBS, REG, MSI, CPL, DLL, JAR, and HTML.
Viewing the list of executable files stored on managed devices
To view the list of executable files stored on client devices:
In the console tree, go to Advanced → Application management → Executable files.
If necessary, you can send an executable file from a managed device to the device with Administration console installed.
To send an executable file:
- In the console tree, go to Advanced → Application management → Executable files.
- Click the link of the executable file that you want to send to the device with Administration console installed.
- In the window that opens, go to the Devices section, and then select the check box of the managed device from which you want to send the executable file.
Before you send the executable file, make sure that the managed device has a direct connection to the Administration Server, by selecting the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server check box.
- Click the Send button, select the destination folder, and then click OK.
The selected executable file is downloaded for further sending to the device with Administration console installed.
Page top
Creating application categories for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policies
You can create application categories for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policies from the Application categories folder and from the Properties window of a Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy.
To create an application category for a Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy from the Application categories folder:
- In the console tree, select Advanced → Application management → Application categories.
- In the workspace of the Application categories folder, click the New category button.
The New category wizard starts.
- On the Category type page, select the type of user category:
- Category with content added manually. Specify the criteria that will be used to assign executable files to the category that is being created.
- Category with content added automatically. Specify the folder from which executable files will be automatically assigned to the created category.
When you create a category with content added automatically, the application inventories the following file types: EXE, COM, DLL, SYS, BAT, PS1, CMD, JS, VBS, REG, MSI, MSC, CPL, HTML, HTM, DRV, OCX, and SCR.
- Category, which includes executable files from the selected devices. Specify a device whose executable files must be automatically assigned to the category.
- Follow the instructions of the wizard.
When the wizard finishes, a custom application category is created. You can view newly created categories by using the list of categories in the workspace of the Application categories folder.
If you want to export an application category to a KLC file, right-click the name of the category, select Export in the menu, and then in the window that opens, specify the file name and click Save.
You can also create an application category from the Policies folder.
To create an application category from the Properties window of a Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy:
- In the console tree, select the Policies folder.
- In the workspace of the Policies folder, select a Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy for which you want to create a category.
- Right-click and select Properties.
- In the Properties window that opens, in the left Sections pane select Security Controls → Application control.
- In the Application control section, in the Control mode and Action drop-down lists make selections for the Allowlist or Denylist, and then click the Add button.
The Application Control rule window containing a list of categories opens.
- Click the Create new button.
- Enter the name of the new category and click OK.
The New category wizard starts.
- On the Category type page, select the type of user category:
- Category with content added manually. Specify the criteria that will be used to assign executable files to the category that is being created.
- Category with content added automatically. Specify the folder from which executable files will be automatically assigned to the created category.
When you create a category with content added automatically, the application inventories the following file types: EXE, COM, DLL, SYS, BAT, PS1, CMD, JS, VBS, REG, MSI, MSC, CPL, HTML, HTM, DRV, OCX, and SCR.
- Category, which includes executable files from the selected devices. Specify a device whose executable files must be automatically assigned to the category.
- Follow the instructions of the wizard.
When the wizard finishes, a custom application category is created. You can view newly created categories in the list of categories.
Application categories are used by the Application Control component included in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. Application Control allows the administrator to impose restrictions on the startup of applications on client devices—for example, restricting the startups to applications in a specified category.
Creating an application category with content added manually
You can specify a set of criteria as a template of executable files for which you want to allow or block a start in your organization. On the basis of executable files corresponding to the criteria, you can create an application category and use it in the Application Control component configuration.
To create an application category with content added manually:
- In the console tree, in the Advanced → Application management folder select the Application categories subfolder.
- Click the New category button.
The New category wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Category type wizard page, select Category with content added manually as the user category type.
- On the Enter the application category name wizard page, enter the new application category name.
- On the Configuring conditions for inclusion of applications in categories page, click the Add button.
- In the drop-down list, specify the relevant settings:
- From the list of executable files
- From file properties
- Metadata from files in folder
- Checksums of the files in the folder
- Certificates for the files from the folder
- MSI installer files metadata
- Checksums of the files from the MSI installer of the application
- From KL category
- Specify path to application (masks supported)
- Select certificate from repository
- Drive type
- On the Creating the application category wizard page, click the Finish button.
Kaspersky Security Center only handles metadata from digitally signed files. No category can be created on the basis of metadata from files that do not contain a digital signature.
When the wizard has completed, a user application category is created, with content added manually. You can view the newly created category using the list of categories in the workspace of the Application categories folder.
If you want to export an application category to a KLC file, right-click the name of the category, select Export in the menu, and then in the window that opens, specify the file name and click Save.
Creating an application category that includes executable files from selected devices
You can use executable files from selected devices as a template of executable files that you want to allow or block. Based on executable files from selected devices, you can create an application category and use it in the Application Control component configuration.
To retrieve the list of executable files from devices:
- Ensure that the policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux is created and is active. Enable the Application Control component in the policy.
- Obtain a list of executable files stored on client devices.
To create application category that includes executable files from selected devices:
- In the console tree, in the Advanced → Application management folder select the Application categories subfolder.
- Click the New category button.
The New category wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Category type wizard page, select Category that includes executable files from selected devices as the user category type.
- On the Enter the application category name wizard page, enter the new application category name.
- On the Settings wizard page, click the Add button.
- Select a device or devices whose executable files will be used to create the application category.
- Specify the following settings:
- On the Filter wizard page, specify the following settings:
- On the Creating the application category wizard page, click the Finish button.
When the wizard has completed, a user application category is created. You can view the newly created category using the list of categories in the workspace of the Application categories folder.
If you want to export an application category to a KLC file, right-click the name of the category, select Export in the menu, and then in the window that opens, specify the file name and click Save.
Page top
Creating an application category that includes executable files from a specific folder
You can use executable files from a selected folder as a standard of executable files that you want to allow or block in your organization. On the basis of executable files from the selected folder, you can create an application category and use it in the Application Control component configuration.
To create an application category that includes executable files from a specific folder:
- In the console tree, in the Advanced → Application management folder select the Application categories subfolder.
- Click the New category button.
The New category wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Category type wizard page, select Category that includes executable files from specific folder as the user category type.
- On the Enter the application category name wizard page, enter the new application category name.
- On the Repository folder wizard page, click the Browse button.
- Specify the folder whose executable files will be used to create the application category.
- Define the following settings:
- Include dynamic-link libraries (DLL) in this category
- Include script data in this category
- Hash value computing algorithm: Calculate SHA256 for files in this category (supported by Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 2 for Windows and later versions) / Calculate MD5 for files in this category (supported by versions earlier than Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 2 for Windows)
- Force folder scan for changes
- On the Creating the application category wizard page, click the Finish button.
When the wizard has completed, a user application category is created. You can view the newly created category using the list of categories in the workspace of the Application categories folder.
If you want to export an application category to a KLC file, right-click the name of the category, select Export in the menu, and then in the window that opens, specify the file name and click Save.
Page top
Adding event-related executable files to the application category
You can add executable files related to the Application startup prohibited and Application startup prohibited in test mode events to an existing application category with content added manually or to a new application category.
To add executable files related to Application Control events to the application category:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Events tab.
- On the Events tab, select the required events.
- In the context menu of one of the selected events, select Add to category.
- In the Action on executable file related to the event window that opens, specify the relevant settings:
Select one of the following:
In the Rule type section, select one of the following settings:
In the File info type section, select one of the following settings:
- Click OK.
Configuring application startup management on client devices
Categorization of applications allows you to optimize management of application runs on devices. You can create an application category and configure Application Control for a policy so only applications from the specified category will be started on devices to which that policy is applied. For example, you have created a category that includes applications named Application_1 and Application_2. After you add this category to a policy, only two applications are allowed to start on devices to which that policy is applied: Application_1 and Application_2. If a user attempts to start an application that has not been included in that category, for example, Application_3, this application is blocked from being started. The user is shown a notification stating that Application_3 is blocked from starting, in accordance with an Application Control rule. You can create a category with content added automatically based on various criteria from a specific folder. In this case, files are automatically added to the category from the specified folder. Executable files of applications are copied to the specified folder and processed automatically; their metrics are added to the category.
To configure the applications run management on client devices:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Application categories subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Application categories folder, create a category of applications that you want to manage while they are being started.
- In the Managed devices folder, on the Policies tab click the New policy button to create a new policy for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, and follow the instructions of the wizard.
If such a policy already exists, you can skip this step. You can configure management of the startup of applications in a specified category through the settings of this policy. The newly created policy is displayed in the Managed devices folder on the Policies tab.
- Select Properties from the context menu of the policy for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The properties window of the policy for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows opens.
- In the properties window of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy, in the Security Controls → Application Control section, select the Application Control check box.
- Click the Add button.
The Application Control rule window opens.
- In the Application Control rule window, in the Category drop-down list select the application category that the startup rule will cover. Configure the startup rule for the selected application category.
For Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 2 and later, no categories are displayed if they were created upon the criterion of the MD5 hash of an executable file.
We do not recommend that you add any categories created according to the criterion of the SHA256 hash of an executable file for versions earlier than Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 2. This may result in application failures.
Detailed instructions on configuring control rules are provided in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help.
- Click OK.
Applications will be run on devices included in the specified category according to the rule that you created. The newly created rule is displayed in the properties window of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy, in the Application Control section.
Viewing the results of static analysis of startup rules applied to executable files
To view information about which executable files are prohibited for users to run:
- In the Managed devices folder in the console tree, select the Policies tab.
- Select Properties from the context menu of the policy for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The properties window of the application policy opens.
- In the Sections pane, select Security Controls and then select the Application Control subsection.
- Click the Static analysis button.
The Analysis of the access rights list window opens. In the left part of the window a user list based on Active Directory data is displayed.
- Select a user from the list.
The right part of the window displays categories of applications assigned to this user.
- To view executable files that the user is not allowed to run, in the Analysis of the access rights list window click the View files button.
A window opens, displaying a list of prohibited executable files.
- To view a list of executable files included in a category, select the application category and click the View files in category button.
A window opens, displaying a list of executable files included in the application category.
Viewing the applications registry
Kaspersky Security Center inventories all software installed on managed devices.
Network Agent compiles a list of applications installed on a Windows or Linux device, and then transmits this list to Administration Server. For Windows-based client devices, Network Agent receives most of the information about installed applications from the Windows registry. For Linux-based client devices, package managers provide information about installed applications to Network Agent.
To view the registry of applications installed on client devices,
In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Applications registry subfolder.
The workspace of the Applications registry folder displays a list of applications installed on client devices and the Administration Server.
You can view the details of any application by opening its context menu and selecting Properties. The application properties window displays the application details and information about its executable files, as well as a list of devices on which the application is installed.
In the context menu of any application in the list you can:
- Add this application to an application category.
- Assign a tag to the application.
- Export the list of applications to a CSV file or TXT file.
- View the application properties, for example, vendor name, version number, list of executable files, list of devices on which the application is installed, list of available software updates, or list of detected software vulnerabilities.
To view applications that meet specific criteria, you can use filtering fields in the workspace of the Applications registry folder.
In the properties window of the selected device, in the Applications registry section, you can view the list of applications installed on the device.
Generating a report on installed applications
In the Applications registry workspace, you can also click the View report on installed applications button to generate a report containing detailed statistics on the installed applications, including the number of devices on which each application is installed. This report, which opens on the Report on Installed applications page, contains information about both the Kaspersky applications and third-party software. If you want information only on Kaspersky applications installed on client devices, in the Summary list, select AO Kaspersky Lab.
Information about Kaspersky applications and third-party software installed on devices that are connected to secondary and virtual Administration Servers is also stored in the applications registry of the primary Administration Server. After you add data from secondary and virtual Administration Servers, click the View report on installed applications button, and on the Report on installed applications page that opens, you can view this information.
To add information from secondary and virtual Administration Servers to the report on installed applications:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Reports tab.
- On the Reports tab, select Report on installed applications.
- Select Properties from the context menu of the report.
The Properties: Report on installed applications window opens.
- In the Hierarchy of Administration Servers section, select the Include data from secondary and virtual Administration Servers check box.
- Click OK.
Information from secondary and virtual Administration Servers will be included in the Report on installed applications.
Changing the software inventory start time
Kaspersky Security Center inventories all software installed on managed client devices running Windows.
Network Agent compiles a list of applications installed on a device, and then transmits this list to Administration Server. Network Agent automatically receives information about installed applications from the Windows registry.
To save the device resources, Network Agent by default starts receiving information about installed applications 10 minutes after the Network Agent service starts.
To change the software inventory start time, which elapses after the Network Agent service runs on a device:
- Open the system registry of the device on which Network Agent is installed (for example, locally, using the regedit command in the Start → Run menu).
- Go to the following hive:
- For 32-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\Components\34\1103\1.0.0.0\NagentFlags
- For 64-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\34\1103\1.0.0.0\NagentFlags
- For 32-bit systems:
- For the KLINV_INV_COLLECTOR_START_DELAY_SEC key, set the required value in seconds.
The default value is 600 seconds.
- Restart the Network Agent service.
The software inventory start time, which elapses after the Network Agent service runs, is changed.
About license key management of third-party applications
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to track license key usage for third-party applications installed on the managed devices. The list of applications for which you can track license key usage is taken from the applications registry. For each license key, you can specify and track violation of the following restrictions:
- Maximum number of devices on which the application using this license key can be installed
- Expiration date of the license key
Kaspersky Security Center does not check whether or not you specify a real license key. You can only track the restrictions that you specify. If one of the restrictions that you impose on a license key is violated, Administration Server registers an informational, warning, or functional failure event.
License keys are bound to applications groups. An applications group is a group of third-party applications that you combine on a basis of a criterion or several criteria. You can define applications by the name of the application, its version, vendor, and tag. An application is added to the group if at least one of the criteria is met. To each applications group, you can bind several license keys, but each license key can be bound to a single applications group only.
One more tool that you can use to track license key usage is Report on status of licensed applications groups. This report provides information about the current status of licensed applications groups, including:
- Number of installations of license keys on each applications group
- Number of license keys in use and vacant license keys
- Detailed list of licensed applications installed on managed devices
The tools for license key management of third-party applications are located in the Third-party licenses usage subfolder (Advanced → Application management → Third-party licenses usage). In this subfolder, you can create applications groups, add license keys, and generate the Report on statuses on licensed application groups.
The tools for license key management of third-party applications are available only if you enabled Vulnerability and patch management option in the Configure interface window.
Page top
Creating licensed applications groups
To create a licensed applications group:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Third-party licenses usage subfolder.
- Click the Add a licensed applications group button to run Licensed application group addition wizard.
Licensed application group addition wizard starts.
- On the Details of licensed applications group step, specify which applications you want to include into the applications group:
- Name of licensed applications group
- Track violated restrictions
- Criteria for adding detected applications to this licensed applications group
- On the Enter data about existing license keys step, specify the license keys that you want to track. Select the Control if license limit is exceeded option, and then add the license keys:
- Click the Add button.
- Select the license key that you want to add, and then click the OK button. If the required license key is not listed, click the Add button, and then specify the license key properties.
- On the Add licensed applications group step, click the Finish button.
A licensed applications group is created and displayed in the Third-party licenses usage folder.
Managing license keys for licensed applications groups
To create a license key for a licensed applications group:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Third-party licenses usage subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Third-party licenses usage folder, click the Manage license keys of licensed applications button.
The License Key Management in licensed applications window opens.
- In the License Key Management in licensed applications window, click the Add button.
The License key window opens.
- In the License key window, specify the properties of the license key and restrictions that the license key imposes on the licensed applications group.
- Name. The name of the license key.
- Comment. Notes on the selected license key.
- Restriction. The number of devices on which the application using this license key can be installed.
- Expires. The expiration date of the license key.
Created license keys are displayed in the License Key Management in licensed applications window.
To apply a license key to a licensed applications group:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Third-party licenses usage subfolder.
- In the Third-party licenses usage folder, select a licensed applications group to which you want to apply a license key.
- Select Properties from the context menu of the licensed applications group.
This opens the properties window of the licensed applications group.
- In the properties window of the licensed applications group, in the License keys section, select Control if license limit is exceeded.
- Click the Add button.
The Selecting a license key window opens.
- In the Selecting a license key window, select a license key that you want to apply to a licensed applications group.
- Click OK.
Restrictions imposed on a licensed applications group and specified in the license key will also apply to the selected licensed applications group.
Inventory of executable files
You can obtain a list of executable files stored on managed devices. To inventory executable files, you must create an inventory task.
The feature of inventorying executable files is available for the following applications:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization 4.0 Light Agent and later versions
The number of executable files received from a single device cannot exceed 150,000. Having reached this limit, Kaspersky Security Center cannot receive any new files.
Before you begin, enable notifications about the applications startup in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy and the Network Agent policy, so you can transfer data to Administration Server.
To enable notifications about applications startup:
- Open the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings and do the following:
- Go to General settings → Reports and Storage.
- In the Data transfer to Administration Server section, select the About started applications check box.
- Save your changes.
- Open the Network Agent policy settings and do the following:
- Go to the Repositories section.
- Select the Details of installed applications check box.
- Save your changes.
To create an inventory task for executable files on client devices:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- Click the New task button in the workspace of the Tasks folder.
The New task wizard starts.
- In the Select the task type window of the wizard, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security as the task type, and then select Inventory as the task subtype, and click Next.
- Follow the rest of the wizard instructions.
After the wizard is done, an inventory task for Kaspersky Endpoint Security is created. The newly created task is displayed in the list of tasks in the workspace of the Tasks folder.
A list of executable files that have been detected on devices during inventory is displayed in the workspace of the Executable files folder.
During inventory, the application detects executable files of the following formats: MZ, COM, PE, NE, SYS, CMD, BAT, PS1, JS, VBS, REG, MSI, CPL, DLL, JAR, and HTML files.
Viewing information about executable files
To view a list of all executable files detected on client devices,
In the Application management folder of the console tree, select the Executable files subfolder.
The workspace of the Executable files folder displays a list of executable files that have been run on devices or have been detected while running the inventory task of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
To view details of executable files that match specific criteria, you can use filtering.
To view the properties of an executable file,
From the context menu of the file, select Properties.
A window opens displaying information about the executable file and a list of devices on which this executable file can be found.
Monitoring and reporting
This section describes the monitoring and reporting capabilities of Kaspersky Security Center. These capabilities give you an overview of your infrastructure, protection statuses, and statistics.
After Kaspersky Security Center deployment or during the operation, you can configure the monitoring and reporting features to best suit your needs.
- Traffic lights
Administration Console allows you to quickly assess the current status of Kaspersky Security Center and managed devices by checking traffic lights.
- Statistics
Statistics on the status of the protection system and managed devices are displayed in information panels that can be customized.
- Reports
The Reports feature allows you to get detailed numerical information about the security of your organization's network, save this information to a file, send it by email, and print it.
- Events
Event selections provide an onscreen view of named sets of events that are selected from the Administration Server database. These sets of events are grouped according to the following categories:
- By importance level—Critical events, Functional failures, Warnings, and Info events
- By time—Recent events
- By type—User requests and Audit events
You can create and view user-defined event selections based on the settings available, in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface, for configuration.
Scenario: Monitoring and reporting
This section provides a scenario for configuring the monitoring and reporting feature in Kaspersky Security Center.
Prerequisites
After you deploy Kaspersky Security Center in an organization's network you can start to monitor it and generate reports on its functioning.
Stages
Monitoring and reporting in an organization's network proceeds in stages:
- Configuring the switching of device statuses
Get acquainted with the settings that define the assignment of device statuses depending on specific conditions. By changing these settings, you can change the number of events with Critical or Warning importance levels.
When configuring the switching of device statuses, be sure that the new settings do not conflict with the information security policies of your organization and that you are able to react to important security events in your organization's network in a timely manner.
- Configuring notifications about events on client devices
Configure notification (by email, by SMS, or by running an executable file) of events on client devices in accordance with your organization's needs.
- Changing the response of your security network to the Virus outbreak event
To adjust the network's response to new events, you can change the specific thresholds in the Administration Server properties. You can also create a stricter policy that will be activated, or create a task that will be run at the occurrence of this event.
- Managing statistics
Configure the display of statistics in accordance with your organization's needs.
- Reviewing the security status of your organization's network
To review the security status of your organization's network, you can do any of the following:
- In the workspace of the Administration Server node, on the Statistics tab open the Protection status second-level tab (page) and review the Real-time protection status information panel
- Generate and review the Report on protection status
- Generate and review the Report on errors
- Locating client devices that are not protected
To locate client devices that are not protected, go the workspace of the Administration Server node, on the Statistics tab open the Protection status second-level tab (page), and review the History of discovery of new networked devices information panel. You can also generate and review the Report on protection deployment.
- Checking protection of client devices
To check protection of client devices, go to the workspace of the Administration Server node, on the Statistics tab open the Deployment or Threat statistics second-level tab (page), and review the relevant information panels. You can also start and review the Critical events event selection.
- Evaluating and limiting the event load on the database
Information about events that occur during operation of managed applications is transferred from a client device and registered in the Administration Server database. To reduce the load on the Administration Server, evaluate and limit the maximum number of events that can be stored in the database.
To evaluate the event load on the database, calculate the database space. You can also limit the maximum number of events to avoid database overflow.
- Reviewing license information
To review license information, go to the workspace of the Administration Server node, on the Statistics tab open the Deployment second-level tab (page), and review the License key usage information panel. You can also generate and review the Report on usage of license keys.
Results
Upon completion of the scenario, you are informed about protection of your organization's network and, thus, can plan actions for further protection.
Page top
Monitoring traffic lights and logged events in Administration Console
Administration Console allows you to quickly assess the current status of Kaspersky Security Center and managed devices by checking traffic lights. The traffic lights are shown in the workspace of the Administration Server node, on the Monitoring tab. The tab provides six information panels with traffic lights and logged events. A traffic light is a colored vertical bar on the left side of a panel. Each panel with a traffic light corresponds to a specific functional scope of Kaspersky Security Center (see the table below).
Scopes covered by traffic lights in Administration Console
Panel name |
Traffic light scope |
|---|---|
Deployment |
Installing Network Agent and security applications on devices on an organization's network |
Management scheme |
Structure of administration groups. Network scanning. Device moving rules |
Protection settings |
Security application functionality: protection status, malware scanning |
Update |
Updates and patches |
Monitoring |
Protection status |
Administration Server |
Administration Server features and properties |
Each traffic light can be any of these five colors (see the table below). The color of a traffic light depends on the current status of Kaspersky Security Center and on events that were logged.
Color codes of traffic lights
Status |
Traffic light color |
Traffic light color meaning |
|---|---|---|
Informational |
Green |
Administrator's intervention is not required. |
Warning |
Yellow |
Administrator's intervention is required. |
Critical |
Red |
Serious problems have been encountered. Administrator's intervention is required to solve them. |
Informational |
Light blue |
Events have been logged that are unrelated to potential or actual threats to the security of managed devices. |
Informational |
Gray |
The details of events are not available or have not yet been retrieved. |
The administrator's goal is to keep traffic lights on all of the information panels on the Monitoring tab green.
The information panels also show logged events that affect traffic lights and the status of Kaspersky Security Center (see the table below).
Name, description, and traffic light colors of logged events
Traffic light color |
Event type display name |
Event type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Red |
License expired on %1 device(s) |
IDS_AK_STATUS_LIC_EXPAIRED |
Events of this type occur when the commercial license has expired. Once a day Kaspersky Security Center checks whether the license has expired on the devices. When the commercial license expires, Kaspersky Security Center provides only basic functionality. To continue using Kaspersky Security Center, renew your commercial license. |
Red |
Security application is not running on: %1 device(s) |
IDS_AK_STATUS_AV_NOT_RUNNING |
Events of this type occur when the security application installed on the device is not running. Make sure that Kaspersky Endpoint Security is running on the device. |
Red |
Protection is disabled on: %1 device(s) |
IDS_AK_STATUS_RTP_NOT_RUNNING |
Events of this type occur when the security application on the device has been disabled for longer than the specified time interval. Check the current status of real-time protection on the device and make sure that all the protection components that you need are enabled. |
Red |
A software vulnerability has been detected on devices |
IDS_AK_STATUS_VULNERABILITIES_FOUND |
Events of this type occur when the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task has detected vulnerabilities with the severity level specified in applications installed on the device. Check the list of available updates in the Software updates subfolder included in the Application management folder. This folder contains a list of updates for Microsoft applications and other software vendors products retrieved by Administration Server, which can be distributed to devices. After viewing information about available updates, install them on the device. |
Red |
Critical events have been registered on the Administration Server |
IDS_AK_STATUS_EVENTS_OCCURED |
Events of this type occur when Administration Server critical events are detected. Check the list of events stored on the Administration Server, and then fix the critical events one by one. |
Red |
Errors have been logged in events on the Administration Server |
IDS_AK_STATUS_ERROR_EVENTS_OCCURED |
Events of this type occur when unexpected errors are logged on the Administration Server side. Check the list of events stored on the Administration Server, and then fix the errors one by one. |
Red |
Lost connection to %1 device(s) |
IDS_AK_STATUS_ADM_LOST_CONTROL1 |
Events of this type occur when the connection between the Administration Server and the device is lost. View the list of disconnected devices and try to reconnect them. |
Red |
%1 device (s) have not connected to the Administration Server in a long time |
IDS_AK_STATUS_ADM_NOT_CONNECTED1 |
Events of this type occur when the device has not connected to the Administration Server within the specified time interval, because the device was turned off. Make sure that the device is turned on and that Network Agent is running. |
Red |
%1 device(s) have a status other than OK |
IDS_AK_STATUS_HOST_NOT_OK |
Events of this type occur when the OK status of the device connected to the Administration Server changes to Critical or Warning. You can troubleshoot the problem by using the Kaspersky Security Center remote diagnostics utility. |
Red |
Databases are outdated on: %1 device(s) |
IDS_AK_STATUS_UPD_HOSTS_NOT_UPDATED |
Events of this type occur when the anti-virus databases have not been updated on the device within the specified time interval. Follow the instructions to update Kaspersky databases. |
Red |
Device(s) where check for Windows Update updates has not been performed in a long time: %1 |
IDS_AK_STATUS_WUA_DATA_OBSOLETE |
Events of this type occur when the Perform Windows Update synchronization task has not been run within the specified time interval. Follow the instructions to synchronize updates from Windows Update with Administration Server. |
Red |
%1 plug-in(s) for Kaspersky Security Center must be installed |
IDS_AK_STATUS_PLUGINS_REQUIRED2 |
Events of this type occur when you need to install additional plug-ins for Kaspersky applications. Download and install the required management plug-ins for the Kaspersky application from the Kaspersky Technical Support webpage. |
Working with reports, statistics, and notifications
This section provides information about how to work with reports, statistics, and selections of events and devices in Kaspersky Security Center, as well as how to configure Administration Server notifications.
Working with reports
Reports in Kaspersky Security Center contain information about the status of managed devices. Reports are generated based on information stored on Administration Server. You can create reports for the following types of objects:
- For device selections created according to specific settings.
- For administration groups.
- For specific devices from different administration groups.
- For all devices on the network (in the deployment report).
The application has a selection of standard report templates. It is also possible to create custom report templates. Reports are displayed in the main application window, in the Administration Server folder in the console tree.
Creating a report template
To create a report template:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Reports tab.
- Click the New report template button.
The New report template wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
After the wizard finishes its operation, the newly created report template is added to the selected Administration Server folder in the console tree. You can use this template for generating and viewing reports.
Page top
Viewing and editing report template properties
You can view and edit basic properties of a report template, for example, the report template name or the fields displayed in the report.
To view and edit properties of a report template:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Reports tab.
- In the list of report templates, select the required report template.
- In the context menu of the selected report template, select Properties.
As an alternative, you can first generate the report, and then click either the Open report template properties button or the Configure report columns button.
- In the window that opens, edit the report template properties. Properties of each report may contain only some of the sections described below.
- General section:
- Report template name
- Maximum number of entries to display
- Print version
- Fields section.
Select the fields that will be displayed in the report, and the order of these fields, and configure whether the information in the report must be sorted and filtered by each of the fields.
- Time interval section.
Modify the report period. Available values are as follows:
- Between the two specified dates
- From the specified date to the report creation date
- From the report creation date, minus the specified number of days, to the report creation date
- Group, Device selection, or Devices section.
Change the set of client devices for which the report creates. Only one of these sections may be present, depending on the settings specified during the report template creation.
- Settings section.
Change the settings of the report. The exact set of settings depends on the specific report.
- Security section. Inherit settings from Administration Server
The Security section is available if the Display security settings sections check box is selected in the interface settings window.
- Hierarchy of Administration Servers section:
- General section:
Extended filter format in report templates
In Kaspersky Security Center 15.1, you can apply the extended filter format to a report template. The extended filter format provides more flexibility in comparison with the default format. You can create complex filtering conditions by using a set of filters, which will be applied to the report by means of the OR logical operator during report creation, as shown below:
Filter[1](Field[1] AND Field[2]... AND Field[n]) OR Filter[2](Field[1] AND Field[2]... AND Field[n]) OR... Filter[n](Field[1] AND Field[2]... AND Field[n])
Additionally, with the extended filter format you can set a time interval value in a relative time format (for example, by using a "For last N days" condition) for specific fields in a filter. The availability and the set of time interval conditions depend on the type of the report template.
Converting the filter into the extended format
The extended filter format for report templates is supported only in Kaspersky Security Center 12 and later versions. After conversion of the default filter into the extended format, the report template becomes incompatible with Administration Servers on your network that have earlier versions of Kaspersky Security Center installed. Information from these Administration Servers will not be received for the report.
To convert the report template default filter into the extended format:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Reports tab.
- In the list of report templates, select the required report template.
- In the context menu of the selected report template, select Properties.
- In the properties window that opens, select the Fields section.
- In the Details fields tab click the Convert filter link.
- In the window that opens, click the OK button.
Conversion into the extended filter format is irreversible for the report template to which it is applied. If you clicked the Convert filter link accidentally, you can cancel the changes by clicking the Cancel button in the report template properties window.
- To apply the changes, close the report template properties window by clicking the OK button.
When the report template properties window opens again, the newly available Filters section is displayed. In this section you can configure the extended filter.
Configuring the extended filter
To configure the extended filter in the report template properties:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Reports tab.
- In the list of report templates, select the report template that was previously converted to extended filter format.
- In the context menu of the selected report template, select Properties.
- In the properties window that opens, select the Filters section.
The Filters section is not displayed if the report template was not previously converted to extended filter format.
In the Filters section of the report template properties window you can review and modify the list of filters applied to the report. Each filter in the list has a unique name and represents a set of filters for corresponding fields in the report.
- Open the filter settings window in one of the following ways:
- To create a new filter, click the Add button.
- To modify the existing filter, select the required filter and click the Modify button.
- In the window that opens, select and specify the values of the required fields of the filter.
- Click the OK button to save changes and close the window.
If you are creating a new filter, the filter name must be specified in the Filter name field before clicking the OK button.
- Close the report template properties window by clicking the OK button.
The extended filter in the report template is configured. Now you can create reports by using this report template.
Creating and viewing a report
To create and view a report:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Reports tab.
- In the list of report templates, double-click the report template that you need.
A report for the selected template is displayed.
The report displays the following data:
- The name and type of report, a brief description and the reporting period, as well as information about the group of devices for which the report is generated.
- Graph chart showing the most representative report data.
- Consolidated table with calculated report indicators.
- Table with detailed report data.
Saving a report
To save a created report:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Reports tab.
- In the list of report templates, select the report template that you need.
- In the context menu of the selected report template, select Save.
The Report saving wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
After the wizard finishes, the folder opens to which you have saved the report file.
When you save a report as an XLS file, all related images, such as the logo and datagram, are saved as separate files.
Page top
Creating a report delivery task
Reports can be emailed. Delivery of reports in Kaspersky Security Center is carried out using the report delivery task.
To create a delivery task for a single report:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Reports tab.
- In the list of report templates, select the report template that you need.
- In the context menu of the selected report template, select Deliver reports.
The Report delivery task creation wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
To create a delivery task for multiple reports:
- In the console tree, under the node with the name of the required Administration Server, select the Tasks folder.
- In the workspace of the Tasks folder, click the Create a task button.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
The newly created report delivery task is displayed in the Tasks folder in the console tree.
The report delivery task is created automatically if the email settings were specified during Kaspersky Security Center installation.
Step 1. Selecting the task type
In the Select the task type window, in the list of tasks select Deliver reports as the task type.
Click Next to proceed to the next step.
Page top
Step 2. Selecting the report type
In the Select report type window, in the list of task creation templates, select the type of report.
Click Next to proceed to the next step.
Page top
Step 3. Actions on a report
In the Action to apply to reports window, specify the following settings:
- Send reports by email
- Save reports to shared folder
- Overwrite older reports of the same type
- Specify account for access to shared folder
When you save or send a report as an XLS file, all related images, such as the logo and datagram, are saved as separate files.
Click Next to proceed to the next step.
Page top
Step 4. Selecting the account to start the task
In the Selecting an account to run the task window, you can specify which account to use when running the task. Select one of the following options:
Click Next to proceed to the next step.
Page top
Step 5. Configuring a task schedule
On the Configure task schedule wizard page, you can create a schedule for task start. If necessary, define the following settings:
- Scheduled start:
- Run missed tasks
- Use automatically randomized delay for task starts
- Use randomized delay for task starts within an interval of (min)
Step 6. Defining the task name
In the Define the task name window, specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
Click Next to proceed to the next step.
Page top
Step 7. Completing creation of the task
In the Finish task creation window, click the Finish button to finish the wizard.
If you want the task to start as soon as the wizard finishes, select the Run the task after the wizard finishes check box.
Page top
Managing statistics
Statistics on the status of the protection system and managed devices are displayed in information panels that can be customized. Statistics are displayed in the workspace of the Administration Server node on the Statistics tab. The tab contains some second-level tabs (pages). Each tabbed page displays information panels with statistics, as well as links to corporate news and other materials from Kaspersky. The statistical information is displayed in information panels as a table or chart (pie or bar). The data in the information panels is updated while the application is running and reflects the current state of the protection application.
You can modify the set of second-level tabs on the Statistics tab, the number of information panels on each tabbed page, and the data display mode in information panels.
To add a new second-level tab with information panels on the Statistics tab:
- Click the Customize view button in the upper right corner of the Statistics tab.
The statistics properties window opens. This window contains a list of tabbed pages that are currently shown on the Statistics tab. In this window, you can change the display order for the pages on the tab, add and remove pages, and proceed to configuration of page properties by clicking the Properties button.
- Click the Add button.
This opens the properties window of a new page.
- Configure the new page:
- In the General section, specify the page name.
- In the Information panels section, click the Add button to add information panels that must be displayed on the page.
Click the Properties button in the Information panels section to set up the properties of information panels that you added: name, type, and appearance of the chart in the panel, as well as data required to plot the chart.
- Click OK.
The tabbed page with information panels that you have added appears on the Statistics tab. Click the settings icon ( ) to proceed instantly to configuration of the page or a selected information panel on that page.
) to proceed instantly to configuration of the page or a selected information panel on that page.
Configuring event notification
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to select a method of notifying the administrator of events on client devices and to configure notification:
- Email. When an event occurs, the application sends a notification to email addresses specified. You can edit the text of the notification.
- SMS. When an event occurs, the application sends a notification to the phone numbers specified. You can configure SMS notifications to be sent through the mail gateway.
- Executable file. When an event occurs on a device, the executable file is started on the administrator's workstation. Using the executable file, the administrator can receive the parameters of any event that has occurred.
To configure notification of events occurring on client devices:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Events tab.
- Click the Configure notifications and event export link and select the Configure notifications value in the drop-down list.
This opens the Properties: Events window.
- In the Notification section, select a notification method (by email, by SMS, or by running an executable file) and define the notification settings:
- In the Notification message field, enter the text that the application will send when an event occurs.
You can use the drop-down list to the right of the text field to add substitution settings with event details (for example, event description, or time of occurrence).
If the notification text contains a percent (%), you must specify it twice in succession to allow message sending. For example, "CPU load is 100%%".
- Click the Send test message button to check whether notification has been configured correctly.
The application sends a test notification to the specified user.
- Click OK to save the changes.
The re-adjusted notification settings are applied to all events that occur on client devices.
You can override notification settings for certain events in the Event configuration section of the Administration Server settings, of a policy settings, or of an application settings.
Creating a certificate for an SMTP server
To create a certificate for an SMTP server:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Events tab.
- Click the Configure notifications and event export link and select the Configure notifications value in the drop-down list.
The event properties window opens.
- On the Email tab, click the Settings link to open the Settings window.
- In the Settings window click the Specify certificate link to open the Certificate for signing window.
- In the Certificate for signing window, click the Browse button.
The Certificate window opens.
- In the Certificate type drop-down list, specify the public or private type of certificate:
- If the private type of certificate (PKCS #12 container) is selected, specify the certificate file and the password.
- If the public type of certificate (X.509 certificate) is selected:
- Specify the private key file (one with the *.prk or *.pem extension).
- Specify the private key password.
- Specify the public key file (one with the *.cer extension).
- Click OK.
The certificate for the SMTP server is issued.
Page top
Event selections
Information about events in the operation of Kaspersky Security Center and managed applications is saved both in the Administration Server database and in the Microsoft Windows system log. You can view information from the Administration Server database in the workspace of the Administration Server node, on the Events tab.
Information on the Events tab is represented as a list of event selections. Each selection includes events of a specific type only. For example, the "Device status is Critical" selection contains only records about changes of device statuses to "Critical". After application installation, the Events tab contains some standard event selections. You can create additional (custom) event selections or export event information to a file.
Viewing an event selection
To view the event selection:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Events tab.
- In the Event selections drop-down list, select the relevant event selection.
If you want events from this selection to be continuously displayed in the workspace, click the star icon (
 ) next to the selection.
) next to the selection.
The workspace will display a list of events, stored on the Administration Server, of the selected type.
You can sort information in the list of events in ascending or descending order in any column.
Customizing an event selection
To customize an event selection:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Events tab.
- Open the relevant event selection on the Events tab.
- Click the Selection properties button.
In the event selection properties window that opens you can configure the event selection.
Creating an event selection
To create an event selection:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Events tab.
- Click the Create a selection button.
- In the New event selection window that opens, enter the name of the new selection and click OK.
A selection with the name that you specified is created in the Event selections drop-down list.
By default, a created event selection contains all events stored on the Administration Server. To cause a selection to display only the events you want, you must customize the selection.
Exporting an event selection to a text file
To export an event selection to a text file:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Events tab.
- Click the Import/Export button.
- In the drop-down list, select Export events to file.
The Events export wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Deleting events from a selection
To delete events from a selection:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the relevant Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Events tab.
- Select the events that you want to delete by using a mouse, the Shift key, or the Ctrl key.
- Delete the selected events in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Delete in the context menu of any of the selected events.
If you select the Delete All item from the context menu, all displayed events will be deleted from the selection, regardless of your choice of events to delete.
- By clicking the Delete event link (if one event is selected) or the Delete events link (if several events are selected) in the information box for these events.
- By selecting Delete in the context menu of any of the selected events.
The selected events are deleted.
Adding applications to exclusions by user requests
When you receive user requests to unblock erroneously blocked applications, you can create an exclusion from the Adaptive Security rules for these applications. Consequently, the applications will no longer be blocked on users' devices. You can track the number of user requests on the Monitoring tab of Administration Server.
To add applications blocked by Kaspersky Endpoint Security to exclusions by user requests:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Events tab.
- In the Event selections drop-down list, select User requests.
- Right-click the user request (or several user requests) containing applications that you want to add to exclusions, and then select Add exclusion.
This starts the Add exclusion wizard. Follow its instructions.
The selected applications will be excluded from the Rule triggers in Smart Training state list (under Repositories in the console tree) after the next synchronization of the client device with the Administration Server, and will no longer appear in the list.
Device selections
Information about the status of devices is displayed in the Device selections folder in the console tree.
Information in the Device selections folder is displayed as a list of device selections. Each selection contains devices that meet specific conditions. For example, the Devices with Critical status selection contains only devices with the Critical status. After application installation, the Device selections folder contains some standard selections. You can create additional (custom) device selections, export selection settings to file, or create selections with settings imported from another file.
Viewing a device selection
To view a device selection:
- In the console tree, select the Device selections folder.
- In the workspace of the folder, in the Devices in this selection list, select the relevant device selection.
- Click the Run selection button.
- Click the Selection results tab.
The workspace will display a list of devices that meet the selection criteria.
You can sort the information in the list of devices in ascending or descending order, in any column.
Page top
Configuring a device selection
To configure a device selection:
- In the console tree, select the Device selections folder.
- In the workspace, click the Selection tab, and then click the relevant device selection in the list of user selections.
- Click the Selection properties button.
- In the properties window that opens, specify the following settings:
- General selection properties.
- Conditions that must be met for including devices in this selection. You can configure the conditions after selecting a condition name and clicking the Properties button.
- Security settings.
- Click OK.
The settings are applied and saved.
Below are descriptions of the conditions for assigning devices to a selection. Conditions are combined by using the OR logical operator: the selection will contain devices that comply with at least one of the listed conditions.
General
In the General section, you can change the name of the selection condition and specify whether that condition must be inverted:
Network
In the Network section, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to their network data:
Tags
In the Tags section, you can configure criteria for including devices into a selection based on key words (tags) that were previously added to the descriptions of managed devices:
Active Directory
In the Active Directory section, you can configure criteria for including devices into a selection based on their Active Directory data:
- Device is in an Active Directory organizational unit
- Include child organizational units
- This device is a member of an Active Directory group
Network activity
In the Network activity section, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to their network activity:
- This device is a distribution point
- Do not disconnect from the Administration Server
- Connection profile switched
- Last connected to Administration Server
- New devices detected by network poll
- Device is visible
Application
In the Application section, you can configure criteria for including devices in a selection based on the selected managed application:
- Application name
- Application version
- Critical update name
- Modules last updated
- Device is managed through Kaspersky Security Center
- Security application is installed
Operating system
In the Operating system section, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to their operating system type.
- Operating system version
- Operating system bit size
- Operating system service pack version
- Operating system build
- Operating system release ID
Device status
In the Device status section, you can configure criteria for including devices into a selection based on the description of the devices status from a managed application:
Protection components
In the Protection components section, you can set up the criteria for including devices in a selection based on their protection status:
Applications registry
In the Applications registry section, you can set up the criteria to search for devices according to applications installed on them:
- Application name
- Application version
- Vendor
- Application status
- Find by update
- Incompatible security application name
- Application tag
- Apply to devices without the specified tags
Hardware registry
In the Hardware registry section, you can configure criteria for including devices into a selection based on their installed hardware:
- Device
- Vendor
- Device name
- Description
- Device vendor
- Serial number
- Inventory number
- User
- Location
- CPU frequency, in MHz
- Virtual CPU cores
- Hard drive volume, in GB
- RAM size, in MB
Virtual machines
In the Virtual machines section, you can set up the criteria to include devices in the selection according to whether these are virtual machines or part of virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI):
Vulnerabilities and updates
In the Vulnerabilities and updates section, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to their Windows Update source:
WUA is switched to Administration Server
Users
In the Users section, you can set up the criteria to include devices in the selection according to the accounts of users who have logged in to the operating system.
Status-affecting problems in managed applications
In the Status-affecting problems in managed applications section, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to the list of possible problems detected by a managed application. If at least one problem that you select exists on a device, the device will be included in the selection. When you select a problem listed for several applications, you have the option to select this problem in all of the lists automatically.
Statuses of components in managed applications
In the Statuses of components in managed applications section, you can configure criteria for including devices in a selection according to the statuses of components in managed applications:
- Data Leakage Prevention status
- Collaboration servers protection status
- Anti-virus protection status of mail servers
- Endpoint Sensor status
Encryption
Cloud segments
In the Cloud segments section, you can configure criteria for including devices in a selection according to their respective cloud segments:
Application components
This section contains the list of components of those applications that have corresponding management plug-ins installed in Administration Console.
In the Application components section, you can specify criteria for including devices in a selection according to the statuses and version numbers of the components that refer to the application that you select:
Page top
Exporting the settings of a device selection to a file
To export the settings of a device selection to a text file:
- In the console tree, select the Device selections folder.
- In the workspace, on the Selection tab, click the relevant device selection in the list of user selections.
Settings can be exported only from the device selections created by a user.
- Click the Run selection button.
- On the Selection results tab, click the Export settings button.
- In the Save as window that opens, specify a name for the selection settings export file, select a folder to save it to, and click the Save button.
The settings of the device selection will be saved to the specified file.
Page top
Creating a device selection
To create a device selection:
- In the console tree, select the Device selections folder.
- In the workspace of the folder, click Advanced and select the Create a selection in the drop-down list.
- In the New device selection window that opens, enter the name of the new selection and click OK.
A new folder with the name you entered will appear in the console tree in the Device selections folder. By default, the new device selection contains all devices included in administration groups of the Administration Server on which the selection was created. To cause a selection to display only the devices you are particularly interested in, configure the selection by clicking the Selection properties button.
Page top
Creating a device selection according to imported settings
To create a device selection according to imported settings:
- In the console tree, select the Device selections folder.
- In the workspace of the folder, click the Advanced button and select Import selection from file in the drop-down list.
- In the window that opens, specify the path to the file from which you want to import the selection settings. Click the Open button.
A New selection entry is created in the Device selections folder. The settings of the new selection are imported from the file that you specified.
If a selection named New selection already exists in the Device selections folder, an index in (<next sequence number>) format is added to the name of the created selection, for example: (1), (2).
Page top
Removing devices from administration groups in a selection
When working with a device selection, you can remove devices from administration groups right in this selection, without switching to the administration groups from which these devices must be removed.
To remove devices from administration groups:
- In the console tree, select the Device selections folder.
- Select the devices that you want to remove by using the Shift or Ctrl keys.
- Remove the selected devices from administration groups in one of the following ways:
- Select Delete in the context menu of any of the selected devices.
- Click the Perform action button and select Remove from group in the drop-down list.
The selected devices are removed from their respective administration groups.
Page top
Monitoring of applications installation and uninstallation
You can monitor installation and uninstallation of specific applications on managed devices (for example, a specific browser). To use this function, you can add applications from the Application registry to the list of monitored applications. When a monitored application is installed or uninstalled, Network Agent publishes respective events: Monitored application has been installed or Monitored application has been uninstalled. You can monitor these events using, for example, event selections or reports.
You can monitor these events only if they are stored in Administration Server database.
To add an application to the list of monitored applications:
- In the Advanced → Application management folder in the console tree, select the Applications registry subfolder.
- Above the list of application, that is displayed, click the Show applications registry properties window button.
- In the Monitored Applications window, that is displayed, click the Add button.
- In the Select application name window, that is displayed, select the applications from the Application registry whose installation or uninstallation you want to monitor.
- In the Select application name window, click the OK button.
After you have configured the list of monitored applications, and a monitored application is installed or uninstalled on managed devices in your organization, you can monitor the respective events, for example using the Recent events event selection.
Page top
Events of Kaspersky Security Center components
Each Kaspersky Security Center component has its own set of event types. This section lists types of events that occur in Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server, Network Agent, and iOS MDM Server. Types of events that occur in Kaspersky applications are not listed in this section.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. For Administration Server, you can additionally view and configure the event list in the Administration Server properties. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
Data structure of event type description
For each event type, its display name, identifier (ID), alphabetic code, description, and the default storage term are provided.
- Event type display name. This text is displayed in Kaspersky Security Center when you configure events and when they occur.
- Event type ID. This numerical code is used when you process events by using third-party tools for event analysis.
- Event type (alphabetic code). This code is used when you browse and process events by using public views that are provided in the Kaspersky Security Center database and when events are exported to a SIEM system.
- Description. This text contains the situations when an event occurs and what you can do in such a case.
- Default storage term. This is the number of days during which the event is stored in the Administration Server database and is displayed in the list of events on Administration Server. After this period elapses, the event is deleted. If the event storage term value is 0, such events are detected but are not displayed in the list of events on Administration Server. If you configured to save such events to the operating system event log, you can find them there.
You can change the storage term for events:
- Administration Console: Setting the storage term for an event
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Setting the storage term for an event
Other data may include the following fields:
- event_id: unique number of the event in the database, generated and assigned automatically; not to be confused with Event type ID.
- task_id: the ID of the task that caused the event (if any)
- severity: one of the following severity levels (in the ascending order of severity):
0) Invalid severity level
1) Info
2) Warning
3) Error
4) Critical
Administration Server events
This section contains information about the events related to the Administration Server.
Administration Server critical events
The table below shows the event types of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server that have the Critical importance level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. For Administration Server, you can additionally view and configure the event list in the Administration Server properties. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
If you specified the port in the Administration Server properties window in the Administration Console, Kaspersky Security Center publishes its metrics and critical events to be obtained by Prometheus, a system for monitoring and alerting. Prometheus obtains the metrics and critical events, and then generates alerts for each event.
Administration Server critical events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Description |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|---|---|
License limit has been exceeded |
4099 |
KLSRV_EV_LICENSE_CHECK_MORE_110 |
Once a day Kaspersky Security Center checks whether a license limit is exceeded. Events of this type occur when Administration Server detects that some licensing limits are exceeded by Kaspersky applications installed on client devices and if the number of currently used licensing units covered by a single license exceeds 110% of the total number of units covered by the license. Even when this event occurs, client devices are protected. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
Kaspersky Security Center determines the rules to generate events when a license limit is exceeded. |
180 days |
Virus outbreak |
26 (for File Threat Protection) |
GNRL_EV_VIRUS_OUTBREAK |
Events of this type occur when the number of malicious objects detected on several managed devices exceeds the threshold within a short period. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
Virus outbreak |
27 (for Mail Threat Protection) |
GNRL_EV_VIRUS_OUTBREAK |
Events of this type occur when the number of malicious objects detected on several managed devices exceeds the threshold within a short period. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
Virus outbreak |
28 (for firewall) |
GNRL_EV_VIRUS_OUTBREAK |
Events of this type occur when the number of malicious objects detected on several managed devices exceeds the threshold within a short period. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
Device has become unmanaged |
4111 |
KLSRV_HOST_OUT_CONTROL |
Events of this type occur if a managed device is visible on the network but has not connected to Administration Server for a specific period. Find out what prevents the proper functioning of Network Agent on the device. Possible causes include network issues and removal of Network Agent from the device. |
180 days |
Device status is Critical |
4113 |
KLSRV_HOST_STATUS_CRITICAL |
Events of this type occur when a managed device is assigned the Critical status. You can configure the conditions under which the device status is changed to Critical. |
180 days |
The key file has been added to the denylist |
4124 |
KLSRV_LICENSE_BLACKLISTED |
Events of this type occur when Kaspersky has added the activation code or key file that you use to the denylist. Contact Technical Support for more details. |
180 days |
Limited functionality mode |
4130 |
KLSRV_EV_LICENSE_SRV_LIMITED_MODE |
Events of this type occur when Kaspersky Security Center starts to operate with basic functionality, without Vulnerability and patch management and without Mobile Device Management features. Following are causes of, and appropriate responses to, the event:
|
180 days |
License expires soon |
4129 |
KLSRV_EV_LICENSE_SRV_EXPIRE_SOON |
Events of this type occur when the commercial license expiration date is approaching. Once a day Kaspersky Security Center checks whether a license expiration date is approaching. Events of this type are published 30 days, 15 days, 5 days and 1 day before the license expiration date. You cannot change the number of days. If the Administration Server is turned off on the specified day before the license expiration date, the event will not be published until the next day. When the commercial license expires, Kaspersky Security Center provides only basic functionality. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
Certificate has expired |
4132 |
KLSRV_CERTIFICATE_EXPIRED |
Events of this type occur when the Administration Server certificate for Mobile Device Management expires. You need to update the expired certificate. |
180 days |
Administration Server certificate has expired. |
6129 |
KLSRV_EV_SRV_CERT_EXPIRED_DN |
Events of this type occur when the Administration Server certificate expires. You need to update the expired certificate. |
180 days |
Updates for Kaspersky application modules have been revoked |
4142 |
KLSRV_SEAMLESS_UPDATE_REVOKED |
Events of this type occur if seamless updates have been revoked (Revoked status is displayed for these updates) by Kaspersky technical specialists; for example, they must be updated to a newer version. The event concerns Kaspersky Security Center patches and does not concern modules of managed Kaspersky applications. The event provides the reason that the seamless updates are not installed. |
180 days |
Audit: Export to SIEM failed |
5130 |
KLAUD_EV_SIEM_EXPORT_ERROR |
Events of this type occur when exporting events to the SIEM system failed due to a connection error with the SIEM system. |
180 days |
Administration Server functional failure events
The table below shows the event types of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server that have the Functional failure importance level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. For Administration Server, you can additionally view and configure the event list in the Administration Server properties. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
Administration Server functional failure events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Description |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Runtime error |
4125 |
KLSRV_RUNTIME_ERROR |
Events of this type occur because of unknown issues. Most often these are DBMS issues, network issues, and other software and hardware issues. Details of the event can be found in the event description. |
180 days |
Limit of installations has been exceeded for one of the licensed applications groups |
4126 |
KLSRV_INVLICPROD_EXCEDED |
Administration Server generates events of this type periodically (every hour). Events of this type occur if in Kaspersky Security Center you manage license keys of third-party applications and if the number of installations has exceeded the limit set by the license key of the third-party application. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
You can manage license keys of third-party applications using the functionality of licensed applications groups. A licensed applications group includes third-party applications that meet criteria set by you. |
180 days |
Failed to poll the cloud segment |
4143 |
KLSRV_KLCLOUD_SCAN_ERROR |
Events of this type occur when Administration Server fails to poll a network segment in a cloud environment. Read the details in the event description and respond accordingly. |
Not stored |
Failed to copy the updates to the specified folder |
4123 |
KLSRV_UPD_REPL_FAIL |
Events of this type occur when software updates are copied to an additional shared folder(s). You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
No free disk space |
4107 |
KLSRV_DISK_FULL |
Events of this type occur when the hard drive of the device on which Administration Server is installed runs out of free space. Free up disk space on the device. |
180 days |
Shared folder is not available |
4108 |
KLSRV_SHARED_FOLDER_UNAVAILABLE |
Events of this type occur if the shared folder of Administration Server is not available. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
The Administration Server database is unavailable |
4109 |
KLSRV_DATABASE_UNAVAILABLE |
Events of this type occur if the Administration Server database becomes unavailable. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
No free space in the Administration Server database |
4110 |
KLSRV_DATABASE_FULL |
Events of this type occur when there is no free space in the Administration Server database. Administration Server does not function when its database has reached its capacity and when further recording to the database is not possible. Following are the causes of this event, depending on the DBMS that you use, and appropriate responses to the event:
|
180 days |
Administration Server warning events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server that have the Warning importance level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. For Administration Server, you can additionally view and configure the event list in the Administration Server properties. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
Administration Server warning events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Description |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|---|---|
A frequent event has been detected |
|
KLSRV_EVENT_SPAM_EVENTS_DETECTED |
Events of this type occur when Administration Server detects a frequent event on a managed device. Refer to the following section for details: Blocking frequent events. |
90 days |
License limit has been exceeded |
4098 |
KLSRV_EV_LICENSE_CHECK_100_110 |
Once a day Kaspersky Security Center checks whether a license limit is exceeded. Events of this type occur when Administration Server detects that some licensing limits are exceeded by Kaspersky applications installed on client devices and if the number of currently used licensing units covered by a single license constitute 100% to 110% of the total number of units covered by the license. Even when this event occurs, client devices are protected. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
Kaspersky Security Center determines the rules to generate events when a license limit is exceeded. |
90 days |
Device has remained inactive on the network for a long time |
4103 |
KLSRV_EVENT_HOSTS_NOT_VISIBLE |
Events of this type occur when a managed device shows inactivity for some time. Most often, this happens when a managed device is decommissioned. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
90 days |
Conflict of device names |
4102 |
KLSRV_EVENT_HOSTS_CONFLICT |
Events of this type occur when Administration Server considers two or more managed devices as a single device. Most often this happens when a cloned hard drive was used for software deployment on managed devices and without switching the Network Agent to the dedicated disk cloning mode on a reference device. To avoid this issue, switch Network Agent to the disk cloning mode on a reference device before cloning the hard drive of this device. |
90 days |
Device status is Warning |
4114 |
KLSRV_HOST_STATUS_WARNING |
Events of this type occur when a managed device is assigned the Warning status. You can configure the conditions under which the device status is changed to Warning. |
90 days |
Limit of installations will soon be exceeded for one of the licensed applications groups |
4127 |
KLSRV_INVLICPROD_FILLED |
Events of this type occur when the number of installations for third-party applications included in a licensed applications group reaches 90% of the maximum allowed value specified in the license key properties. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
You can manage license keys of third-party applications using the functionality of licensed applications groups. |
90 days |
Certificate has been requested |
4133 |
KLSRV_CERTIFICATE_REQUESTED |
Events of this type occur when a certificate for Mobile Device Management fails to be automatically reissued. Following might be the causes and appropriate responses to the event:
|
90 days |
Certificate has been removed |
4134 |
KLSRV_CERTIFICATE_REMOVED |
Events of this type occur when an administrator removes any type of certificate (General, Mail, VPN) for Mobile Device Management. After removing a certificate, mobile devices connected via this certificate will fail to connect to Administration Server. This event might be helpful when investigating malfunctions associated with the management of mobile devices. |
90 days |
Certificate is expiring |
6128 |
KLSRV_EV_SRV_CERT_EXPIRES_SOON |
Events of this type occur when the Administration Server certificate is expiring in 30 days or sooner, and there is no reserve certificate. |
90 days |
APNs certificate has expired |
4135 |
KLSRV_APN_CERTIFICATE_EXPIRED |
Events of this type occur when an APNs certificate expires. You need to manually renew the APNs certificate and install it on an iOS MDM Server. |
Not stored |
APNs certificate expires soon |
4136 |
KLSRV_APN_CERTIFICATE_EXPIRES_SOON |
Events of this type occur when there are fewer than 14 days left before the APNs certificate expires. When the APNs certificate expires, you need to manually renew the APNs certificate and install it on an iOS MDM Server. We recommend that you schedule the APNs certificate renewal in advance of the expiration date. |
Not stored |
Failed to send the FCM message to the mobile device |
4138 |
KLSRV_GCM_DEVICE_ERROR |
Events of this type occur when Mobile Device Management is configured to use Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) for connecting to managed mobile devices with an Android operating system and FCM Server fails to handle some of the requests received from Administration Server. It means that some of the managed mobile devices will not receive a push notification. Read the HTTP code in the details of the event description and respond accordingly. For more information on the HTTP codes received from FCM Server and related errors, please refer to the Firebase service documentation (see chapter "Downstream message error response codes"). |
90 days |
HTTP error sending the FCM message to the FCM server |
4139 |
KLSRV_GCM_HTTP_ERROR |
Events of this type occur when Mobile Device Management is configured to use Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) for connecting managed mobile devices with the Android operating system and FCM Server reverts to the Administration Server a request with a HTTP code other than 200 (OK). Following might be the causes and appropriate responses to the event:
|
90 days |
Failed to send the FCM message to the FCM server |
4140 |
KLSRV_GCM_GENERAL_ERROR |
Events of this type occur due to unexpected errors on the Administration Server side when working with the Firebase Cloud Messaging HTTP protocol. Read the details in the event description and respond accordingly. If you cannot find the solution to an issue on your own, we recommend that you contact Kaspersky Technical Support. |
90 days |
Little free space on the hard drive |
4105 |
KLSRV_NO_SPACE_ON_VOLUMES |
Events of this type occur when the hard drive of the device on which Administration Server is installed almost runs out of free space. Free up disk space on the device. |
90 days |
Little free space in the Administration Server database |
4106 |
KLSRV_NO_SPACE_IN_DATABASE |
Events of this type occur if space in the Administration Server database is too limited. If you do not remedy the situation, soon the Administration Server database will reach its capacity and Administration Server will not function. Following are the causes of this event, depending on the DBMS that you use, and the appropriate responses to the event. You use the SQL Server Express Edition DBMS:
You use a DBMS other than SQL Server Express Edition:
Review the information on DBMS selection. |
90 days |
Connection to the secondary Administration Server has been interrupted |
4116 |
KLSRV_EV_SLAVE_SRV_DISCONNECTED |
Events of this type occur when a connection to the secondary Administration Server is interrupted. Read the Kaspersky Event Log on the device where the secondary Administration Server is installed and respond accordingly. |
90 days |
Connection to the primary Administration Server has been interrupted |
4118 |
KLSRV_EV_MASTER_SRV_DISCONNECTED |
Events of this type occur when a connection to the primary Administration Server is interrupted. Read the Kaspersky Event Log on the device where the primary Administration Server is installed and respond accordingly. |
90 days |
New updates for Kaspersky application modules have been registered |
4141 |
KLSRV_SEAMLESS_UPDATE_REGISTERED |
Events of this type occur when Administration Server registers new updates for the Kaspersky software installed on managed devices that require approval to be installed. Approve or decline the updates by using Administration Console or using Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
90 days |
The limit on the number of events in the database is exceeded, deletion of events has started |
4145 |
KLSRV_EVP_DB_TRUNCATING |
Events of this type occur when deletion of old events from the Administration Server database has started after the Administration Server database capacity is reached. You can respond to the event in the following ways: |
Not stored |
The limit on the number of events in the database is exceeded, the events have been deleted |
4146 |
KLSRV_EVP_DB_TRUNCATED |
Events of this type occur when old events have been deleted from the Administration Server database after the Administration Server database capacity is reached. You can respond to the event in the following ways: |
Not stored |
Audit (Test connection to SIEM server failed) |
5120 |
KLAUD_EV_SIEM_TEST_FAILED |
Events of this type occur when a test connection to the SIEM server failed. |
30 days |
Administration Server informational events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server that have the Info importance level.
Administration Server informational events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Default storage term |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Over 90% of the license key is used up |
4097 |
KLSRV_EV_LICENSE_CHECK_90 |
30 days |
|
New device has been detected |
4100 |
KLSRV_EVENT_HOSTS_NEW_DETECTED |
30 days |
|
Device has been automatically added to the group |
4101 |
KLSRV_EVENT_HOSTS_NEW_REDIRECTED |
30 days |
|
Device has been automatically moved according to a rule |
1074 |
KLSRV_HOST_MOVED_WITH_RULE_EX |
30 days |
|
Device has been removed from the group: inactive on the network for a long time |
4104 |
KLSRV_INVISIBLE_HOSTS_REMOVED |
30 days |
|
Limit of installations will soon be exceeded (more than 95% is used up) for one of the licensed applications groups |
4128 |
KLSRV_INVLICPROD_EXPIRED_SOON |
30 days |
|
Files have been found to send to Kaspersky for analysis |
4131 |
KLSRV_APS_FILE_APPEARED |
30 days |
|
FCM Instance ID has changed on this mobile device |
4137 |
KLSRV_GCM_DEVICE_REGID_CHANGED |
30 days |
|
Updates have been successfully copied to the specified folder |
4122 |
KLSRV_UPD_REPL_OK |
30 days |
|
Connection to the secondary Administration Server has been established |
4115 |
KLSRV_EV_SLAVE_SRV_CONNECTED |
30 days |
|
Connection to the primary Administration Server has been established |
4117 |
KLSRV_EV_MASTER_SRV_CONNECTED |
30 days |
|
Databases have been updated |
4144 |
KLSRV_UPD_BASES_UPDATED |
30 days |
|
Audit: Connection to the Administration Server has been established |
4147 |
KLAUD_EV_SERVERCONNECT |
30 days |
|
Audit: Object has been modified |
4148 |
KLAUD_EV_OBJECTMODIFY |
30 days |
This event tracks changes in the following objects:
|
Audit: Object status has changed |
4150 |
KLAUD_EV_TASK_STATE_CHANGED |
30 days |
For example, this event occurs when a task has failed with an error. |
Audit: Group settings have been modified |
4149 |
KLAUD_EV_ADMGROUP_CHANGED |
30 days |
|
Audit: Connection to Administration Server has been terminated |
4151 |
KLAUD_EV_SERVERDISCONNECT |
30 days |
|
Audit: Object properties have been modified |
4152 |
KLAUD_EV_OBJECTPROPMODIFIED |
30 days |
This event tracks changes in the following properties:
|
Audit: User permissions have been modified |
4153 |
KLAUD_EV_OBJECTACLMODIFIED |
30 days |
|
Audit: Encryption keys have been imported or exported from Administration Server |
5100 |
KLAUD_EV_DPEKEYSEXPORT |
30 days |
|
Audit (Test connection to SIEM server succeeded) |
5110 |
KLAUD_EV_SIEM_TEST_SUCCESS |
30 days |
This event occurs when a test connection to the SIEM server succeeded. |
Network Agent events
This section contains information about the events related to Network Agent.
Network Agent functional failure events
The table below shows the event types of Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent that have the Functional failure severity level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
Network Agent functional failure events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Description |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Update installation error |
7702 |
KLNAG_EV_PATCH_INSTALL_ERROR |
Events of this type occur if automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components was not successful. The event does not concern updates of the managed Kaspersky applications. Read the event description. A Windows issue on the Administration Server might be a reason for this event. If the description mentions any issue of Windows configuration, resolve this issue. |
30 days |
Failed to install the third-party software update |
7697 |
KLNAG_EV_3P_PATCH_INSTALL_ERROR |
Events of this type occur if Vulnerability and patch management and Mobile Device Management features are in use, and if update of third-party software was not successful. Check whether the link to the third-party software is valid. Read the event description. |
30 days |
Failed to install the Windows Update updates |
7717 |
KLNAG_EV_WUA_INSTALL_ERROR |
Events of this type occur if Windows Updates were not successful. Configure Windows Updates in a Network Agent policy. Read the event description. Look for the error in the Microsoft Knowledge Base. Contact Microsoft Technical Support if you cannot resolve the issue yourself. |
30 days |
User management: errors |
7723 |
KLNAG_EV_USR_MNG_ERR |
General warning event. |
30 days |
Failed to restore sudoers file to reference value |
7726 |
KLNAG_EV_SUDOER_RESTORED_ERR |
The event contains the description of the sudoers file replacement error. |
30 days |
Failed to install root certificates |
7728 |
KLNAG_EV_ROOT_CERT_INSTALL_ERR |
The event contains the description of the certificates installation error. |
30 days |
Failed to remove root certificates |
7730 |
KLNAG_EV_ROOT_CERT_REMOVE_ERR |
The event contains the description of the certificates removal error. |
30 days |
Network Agent warning events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent that have the Warning severity level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
Network Agent warning events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|---|
Warning has been returned during installation of the software module update |
7701 |
KLNAG_EV_PATCH_INSTALL_WARNING |
30 days |
Third-party software update installation has completed with a warning |
7696 |
KLNAG_EV_3P_PATCH_INSTALL_WARNING |
30 days |
Third-party software update installation has been postponed |
7698 |
KLNAG_EV_3P_PATCH_INSTALL_SLIPPED |
30 days |
Security issue has occurred |
549 |
GNRL_EV_APP_INCIDENT_OCCURED |
30 days |
KSN Proxy has started. Failed to check KSN for availability |
7718 |
KSNPROXY_STARTED_CON_CHK_FAILED |
30 days |
User management: warnings |
7722 |
KLNAG_EV_USR_MNG_WRN |
30 days |
Sudoers file found doesn't match reference value |
7724 |
KLNAG_EV_SUDOER_DIFFERENT |
30 days |
Network Agent informational events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent that have the Info severity level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
Network Agent informational events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|---|
Update for software modules has been installed successfully |
7699 |
KLNAG_EV_PATCH_INSTALLED_SUCCESSFULLY |
30 days |
Installation of the software module update has started |
7700 |
KLNAG_EV_PATCH_INSTALL_STARTING |
30 days |
Application has been installed |
7703 |
KLNAG_EV_INV_APP_INSTALLED |
30 days |
Application has been uninstalled |
7704 |
KLNAG_EV_INV_APP_UNINSTALLED |
30 days |
Monitored application has been installed |
7705 |
KLNAG_EV_INV_OBS_APP_INSTALLED |
30 days |
Monitored application has been uninstalled |
7706 |
KLNAG_EV_INV_OBS_APP_UNINSTALLED |
30 days |
Third-party application has been installed |
7707 |
KLNAG_EV_INV_CMPTR_APP_INSTALLED |
30 days |
New device has been added |
7708 |
KLNAG_EV_DEVICE_ARRIVAL |
30 days |
Device has been removed |
7709 |
KLNAG_EV_DEVICE_REMOVE |
30 days |
New device has been detected |
7710 |
KLNAG_EV_NAC_DEVICE_DISCOVERED |
30 days |
Device has been authorized |
7711 |
KLNAG_EV_NAC_HOST_AUTHORIZED |
30 days |
Windows Desktop Sharing: File has been read |
7712 |
KLUSRLOG_EV_FILE_READ |
30 days |
Windows Desktop Sharing: File has been modified |
7713 |
KLUSRLOG_EV_FILE_MODIFIED |
30 days |
Windows Desktop Sharing: Application has been started |
7714 |
KLUSRLOG_EV_PROCESS_LAUNCHED |
30 days |
Windows Desktop Sharing: Started |
7715 |
KLUSRLOG_EV_WDS_BEGIN |
30 days |
Windows Desktop Sharing: Stopped |
7716 |
KLUSRLOG_EV_WDS_END |
30 days |
Third-party software update has been installed successfully |
7694 |
KLNAG_EV_3P_PATCH_INSTALLED_SUCCESSFULLY |
30 days |
Third-party software update installation has started |
7695 |
KLNAG_EV_3P_PATCH_INSTALL_STARTING |
30 days |
KSN Proxy has started. KSN availability check has completed successfully |
7719 |
KSNPROXY_STARTED_CON_CHK_OK |
30 days |
KSN Proxy has stopped |
7720 |
KSNPROXY_STOPPED |
30 days |
iOS MDM Server events
This section contains information about the events related to iOS MDM Server.
iOS MDM Server functional failure events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center iOS MDM Server that have the Functional failure severity level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
iOS MDM Server functional failure events
Event type display name |
Event type |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|
Failed to request the list of profile |
PROFILELIST_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to install the profile |
INSTALLPROFILE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to remove the profile |
REMOVEPROFILE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to request the list of provisioning profiles |
PROVISIONINGPROFILELIST_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to install provisioning profile |
INSTALLPROVISIONINGPROFILE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to remove the provisioning profile |
REMOVEPROVISIONINGPROFILE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to request the list of digital certificates |
CERTIFICATELIST_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to request the list of installed applications |
INSTALLEDAPPLICATIONLIST_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to request general information about the mobile device |
DEVICEINFORMATION_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to request security information |
SECURITYINFO_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to lock the mobile device |
DEVICELOCK_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to reset the password |
CLEARPASSCODE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to wipe data from the mobile device |
ERASEDEVICE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to install the app |
INSTALLAPPLICATION_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to set the redemption code for the app |
APPLYREDEMPTIONCODE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to request the list of managed apps |
MANAGEDAPPLICATIONLIST_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to remove the managed app |
REMOVEAPPLICATION_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Roaming settings have been rejected |
SETROAMINGSETTINGS_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Error has occurred in the app operation |
PRODUCT_FAILURE |
30 days |
Command result contains invalid data |
MALFORMED_COMMAND |
30 days |
Failed to send the push notification |
SEND_PUSH_NOTIFICATION_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to send the command |
SEND_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Device not found |
DEVICE_NOT_FOUND |
30 days |
iOS MDM Server warning events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center iOS MDM Server that have the Warning severity level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
iOS MDM Server warning events
Event type display name |
Event type |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|
Attempt to connect a locked mobile device has been detected |
INACTICE_DEVICE_TRY_CONNECTED |
30 days |
Profile has been removed |
MDM_PROFILE_WAS_REMOVED |
30 days |
Attempt to re-use a client certificate has been detected |
CLIENT_CERT_ALREADY_IN_USE |
30 days |
Inactive device has been detected |
FOUND_INACTIVE_DEVICE |
30 days |
Redemption code is required |
NEED_REDEMPTION_CODE |
30 days |
Profile has been included in a policy removed from the device |
UMDM_PROFILE_WAS_REMOVED |
30 days |
iOS MDM Server informational events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center iOS MDM Server that have the Info severity level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
iOS MDM Server informational events
Event type display name |
Event type |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|
New mobile device has been connected |
NEW_DEVICE_CONNECTED |
30 days |
List of profiles has been successfully requested |
PROFILELIST_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Profile has been successfully installed |
INSTALLPROFILE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Profile has been successfully removed |
REMOVEPROFILE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
List of provisioning profiles has been successfully requested |
PROVISIONINGPROFILELIST_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Provisioning profile has been successfully installed |
INSTALLPROVISIONINGPROFILE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Provisioning profile has been successfully removed |
REMOVEPROVISIONINGPROFILE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
List of digital certificates has been successfully requested |
CERTIFICATELIST_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
List of installed applications has been successfully requested |
INSTALLEDAPPLICATIONLIST_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
General information about the mobile device has been successfully requested |
DEVICEINFORMATION_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Security information has been successfully requested |
SECURITYINFO_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Mobile device has been successfully locked |
DEVICELOCK_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
The password has been successfully reset |
CLEARPASSCODE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Data has been wiped from the mobile device |
ERASEDEVICE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
App has been successfully installed |
INSTALLAPPLICATION_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Redemption code has been successfully set for the app |
APPLYREDEMPTIONCODE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
The list of managed apps has been successfully requested |
MANAGEDAPPLICATIONLIST_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Managed app has been removed successfully |
REMOVEAPPLICATION_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Roaming settings have been successfully applied |
SETROAMINGSETTINGS_COMMAND_SUCCESSFUL |
30 days |
Blocking frequent events
This section provides information about managing frequent events blocking, about removing blocking of frequent events, and about exporting the list of frequent events to a file.
About blocking frequent events
A managed application, for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, installed on a single or several managed devices can send a lot of events of the same type to the Administration Server. Receiving frequent events may overload the Administration Server database and overwrite other events. Administration Server starts blocking the most frequent events when the number of all the received events exceeds the specified limit for the database.
Administration Server blocks the frequent events from receiving automatically. You cannot block the frequent events yourself, or choose which events to block.
If you want to find out if an event is blocked, you can check if this event is present in the Blocking frequent events section of the Administration Server properties. If the event is blocked, you can do the following:
- If you want to prevent overwriting the database, you can continue blocking such type of events from receiving.
- If you want, for example, to find the reason of sending the frequent events to the Administration Server, you can unblock frequent events and continue receiving the events of this type anyway.
- If you want to continue receiving the frequent events until they become blocked again, you can remove from blocking the frequent events.
Managing frequent events blocking
Administration Server automatically blocks the receiving of frequent events, but you can stop blocking and continue to receive frequent events. You can also block receiving frequent events that you unblocked before.
To manage frequent events blocking:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, open the context menu of the Administration Server folder, and then select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, go to the Sections pane, and then select Blocking frequent events.
- In the Blocking frequent events section:
- Select the Event type options of the events that you want to block from being received.
- Unselect the Event type options of the events that you want to continue receiving.
- Click the Apply button.
- Click the OK button.
Administration Server receives the frequent events for which you unselected the option Event type and blocks receiving frequent events for which you selected the option Event type.
Removing blocking of frequent events
You can remove blocking for frequent events and start receiving them until Administration Server blocks this type of frequent events again.
To remove blocking of frequent events:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, open the context menu of the Administration Server folder, and then select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, go to the Sections pane, and then select Blocking frequent events.
- In the Blocking frequent events section, click the row of the frequent event for which you want to remove blocking.
- Click the Delete button.
The frequent event is removed from the list of the frequent events. Administration Server will receive events of this type.
Exporting a list of frequent events to a file
To export a list of frequent events to a file:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, open the context menu of the Administration Server folder, and then select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, go to the Sections pane, and then select Blocking frequent events.
- Click the Export to file button.
- In the Save as window that opens, specify the path to the file to which you want to save the list.
- Click the Save button.
All the records on the frequent events list are exported to a file.
Controlling changes in the status of virtual machines
Administration Server stores information about the status of managed devices, such as the hardware registry and the list of installed applications, and the settings of managed applications, tasks and policies. If a virtual machine functions as a managed device, the user can restore its status at any time using a previously created snapshot of the virtual machine. Information about the status of the virtual machine on Administration Server may become outdated.
For example, the administrator had created a protection policy on Administration Server at 12:00 PM, which started to run on virtual machine VM_1 at 12:01 PM. At 12:30 PM, the user of virtual machine VM_1 changed its status by restoring it from a snapshot made at 11:00 AM. The protection policy stops running on the virtual machine. However, outdated information stored on Administration Server states that the protection policy on virtual machine VM_1 continues.
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to monitor changes in the status of virtual machines.
After each synchronization with a device, the Administration Server generates a unique ID that is stored on the device and on the Administration Server. Before starting the next synchronization, Administration Server compares the values of those IDs on both sides. If the values of the IDs do not match, Administration Server recognizes the virtual machine as restored from a snapshot. Administration Server resets all the settings of policies and tasks that are active for the virtual machine and sends it the up-to-date policies and the list of group tasks.
Page top
Monitoring the anti-virus protection status using information from the system registry
To monitor the anti-virus protection status on a client device using information logged by Network Agent, depending on the operating system of the device:
- On the devices running Windows:
- Open the system registry of the client device (for example, locally, using the regedit command in the Start → Run menu).
- Go to the following hive:
- For 32-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\Components\34\1103\1.0.0.0\Statistics\AVState
- For 64-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\34\1103\1.0.0.0\Statistics\AVState
The system registry displays information about the anti-virus protection status of the client device.
- For 32-bit systems:
- On the devices running Linux:
- Information is enclosed in separate text files, one for each type of data, located at /var/opt/kaspersky/klnagent/1103/1.0.0.0/Statistics/AVState/.
- On the devices running macOS:
- Information is enclosed in separate text files, one for each type of data, located at /Library/Application Support/Kaspersky Lab/klnagent/Data/1103/1.0.0.0/Statistics/AVState/.
The anti-virus protection status corresponds to the values of the keys described in the table below.
Registry keys and their possible values
Key (data type) |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
DD-MM-YYYY HH-MM-SS |
Date and time (in UTC format) of the last connection to the Administration Server |
|
IP, DNS name, or NetBIOS name |
Name of the Administration Server that manages the device |
|
a.b.c.d |
Build number of the Network Agent installed on the device |
|
a.b.c.d (patch1; patch2; ...; patchN) |
Full number of the Network Agent version (with patches) installed on the device |
|
Device ID |
ID of the device |
|
0 — no 1 — yes |
The Network Agent is installed in the dynamic VDI mode |
|
0 — no 1 — yes |
A security application is installed on the device |
|
0 — no 1 — yes |
Real-time protection is enabled on the device |
|
0 — no 1 — yes |
A real-time protection component is installed |
|
Real-time protection status: |
|
0 |
Unknown |
|
1 |
Disabled |
|
2 |
Paused |
|
3 |
Starting |
|
4 |
Enabled |
|
5 |
Enabled with the high protection level (maximum protection) |
|
6 |
Enabled with the low protection level (maximum speed) |
|
7 |
Enabled with the default (recommended) settings |
|
8 |
Enabled with custom settings |
|
9 |
Operation failure |
|
|
DD-MM-YYYY HH-MM-SS |
Date and time (in UTC format) of the last full scan |
|
DD-MM-YYYY HH-MM-SS |
Date and time (in UTC format) of the application databases release |
Viewing and configuring the actions when devices show inactivity
If client devices within a group are inactive, you can get notifications about it. You can also automatically delete such devices.
To view or configure the actions when the devices in the group show inactivity:
- In the console tree, right-click the name of the required administration group.
- In the context menu, select Properties.
This opens the administration group properties window.
- In the Properties window, go to the Devices section.
- If needed, enable or disable the following options:
- Click OK.
Your changes are saved and applied.
Page top
Disabling Kaspersky announcements
In Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, the Kaspersky announcements section (Monitoring & reporting → Kaspersky announcements) keeps you informed by providing information related to your version of Kaspersky Security Center and the managed applications installed on managed devices. If you do not want to receive Kaspersky announcements, you can disable this feature.
The Kaspersky announcements include two types of information: security-related announcements and marketing announcements. You can disable the announcements of each type separately.
To disable security-related announcements:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server for which you want to disable security-related announcements.
- Right-click and in the context menu that appears, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window that opens, in the Kaspersky announcements section, disable the Enable the display of Kaspersky announcements in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console option.
- Click OK.
Kaspersky announcements are disabled.
Marketing announcements are disabled by default. You receive marketing announcements only if you enabled Kaspersky Security Network (KSN). You can disable this type of announcement by disabling KSN.
Adjustment of distribution points and connection gateways
A structure of administration groups in Kaspersky Security Center performs the following functions:
- Sets the scope of policies
There is an alternate way of applying relevant settings on devices, by using policy profiles. In this case, you set the scope of policies with tags, device locations in Active Directory organizational units, or membership in Active Directory security groups.
- Sets the scope of group tasks
There is an approach to defining the scope of group tasks that is not based on a hierarchy of administration groups: use of tasks for device selections and tasks for specific devices.
- Sets access rights to devices, virtual Administration Servers, and secondary Administration Servers
- Assigns distribution points
When building the structure of administration groups, you must take into account the topology of the organization's network for the optimum assignment of distribution points. The optimum distribution of distribution points allows you to save traffic on the organization's network.
Depending on the organizational schema and network topology, the following standard configurations can be applied to the structure of administration groups:
- Single office
- Multiple small remote offices
Devices functioning as distribution points must be protected, including physical protection, against any unauthorized access.
Standard configuration of distribution points: Single office
In a standard "single-office" configuration, all devices are on the organization's network so they can "see" each other. The organization's network may consist of a few separate parts (networks or network segments) linked by narrow channels.
The following methods of building the structure of administration groups are possible:
- Building the structure of administration groups taking into account the network topology. The structure of administration groups may not reflect the network topology with absolute precision. A match between the separate parts of the network and certain administration groups would be enough. You can use automatic assignment of distribution points or assign them manually.
- Building the structure of administration groups, without taking the network topology into account. In this case, you must disable automatic assignment of distribution points, and then assign one or several devices to act as distribution points for a root administration group in each of the separate parts of the network, for example, for the Managed devices group. All distribution points will be at the same level and will feature the same scope spanning all devices on the organization's network. In this case, each Network Agent will connect to the distribution point that has the shortest route. The route to a distribution point can be traced with the tracert utility.
Standard configuration of distribution points: Multiple small remote offices
This standard configuration provides for a number of small remote offices, which may communicate with the head office over the internet. Each remote office is located behind the NAT, that is, connection from one remote office to another is not possible because offices are isolated from one another.
The configuration must be reflected in the structure of administration groups: a separate administration group must be created for each remote office (groups Office 1 and Office 2 in the figure below).
Remote offices are included in the administration group structure
One or multiple distribution points must be assigned to each administration group that correspond to an office. Distribution points must be devices at the remote office that have a sufficient amount of free disk space. Devices deployed in the Office 1 group, for example, will access distribution points assigned to the Office 1 administration group.
If some users move between offices physically, with their laptops, you must select two or more devices (in addition to the existing distribution points) in each remote office and assign them to act as distribution points for a top-level administration group (Root group for offices in the figure above).
Example: A laptop is deployed in the Office 1 administration group and then is moved physically to the office that corresponds to the Office 2 administration group. After the laptop is moved, Network Agent attempts to access the distribution points assigned to the Office 1 group, but those distribution points are unavailable. Then, Network Agent starts attempting to access the distribution points that have been assigned to the Root group for offices. Because remote offices are isolated from one another, attempts to access distribution points assigned to the Root group for offices administration group will only be successful when Network Agent attempts to access distribution points in the Office 2 group. That is, the laptop will remain in the administration group that corresponds to the initial office, but the laptop will use the distribution point of the office where it is physically located at the moment.
Assigning a managed device to act as a distribution point
You can manually assign a device to act as a distribution point for an administration group and configure it as a connection gateway in Administration Console.
To assign a device as distribution point of an administration group:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- In the context menu of Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, select the Distribution points section.
- In the right part of the window, select the Manually assign distribution points option.
- Click the Add button.
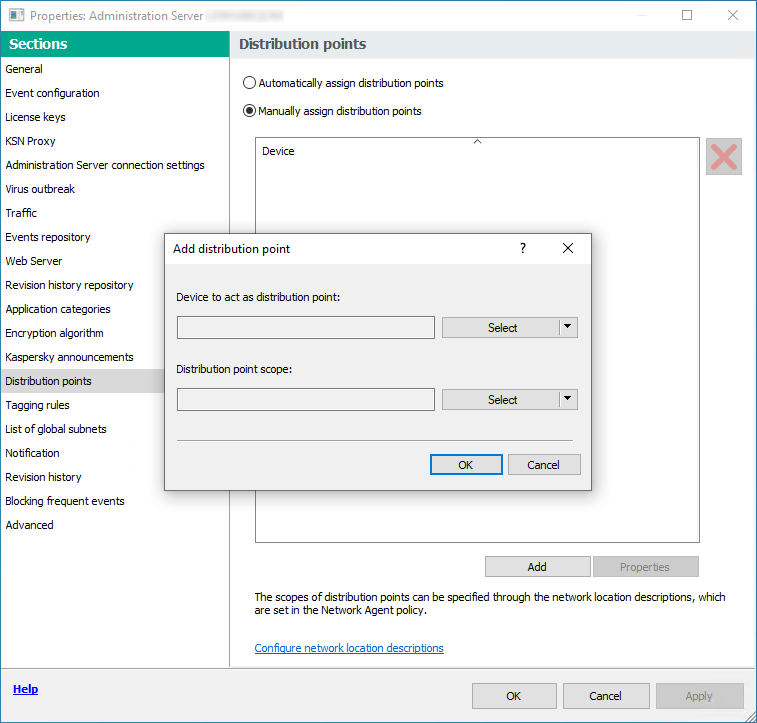
Assign a distribution point manually
This opens the Add distribution point window.
- In the Add distribution point window, perform the following actions:
- Under Device to act as distribution point, click the down arrow (
 ) on the Select split button and select the Add device from group option.
) on the Select split button and select the Add device from group option. - In the Select devices window that opens, select the device to act as a distribution point.
- Under Distribution point scope, click the down arrow (
 ) on the Select split button.
) on the Select split button. - Indicate the specific devices to which the distribution point will distribute updates. You can specify an administration group or a network location description.
- Click OK to close the Add distribution point window.
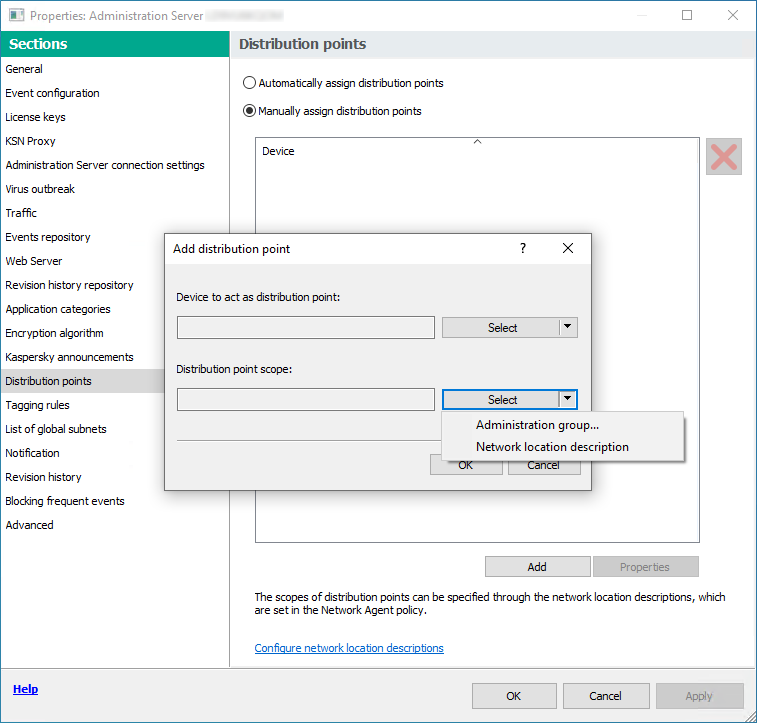
Selecting distribution point scope
- Under Device to act as distribution point, click the down arrow (
The distribution point that you have added will be displayed in the list of distribution points, in the Distribution points section.
The first device with Network Agent installed that connects to the virtual Administration Server will be automatically assigned to act as distribution point and configured as connection gateway.
Connecting a Linux device as a gateway in the demilitarized zone
To connect a Linux device as a gateway in the demilitarized zone (DMZ):
- Download and install Network Agent on the Linux device.
- Run the post-install script and follow the wizard in order to setup the local environment configuration. In the command prompt, run the following command:
$ sudo /opt/kaspersky/klnagent64/lib/bin/setup/postinstall.pl - On the step asking for the Network Agent mode, choose the Use as connection gateway option.
- In MMC-based Administration Console, in the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window that opens, select the Distribution points section.
- In the Distribution points window that opens, in the right part of the window:
- Select the Manually assign distribution points option.
- Click the Add button.
This opens the Add distribution point window.
- In the Add distribution point window, perform the following actions:
- Under Device to act as distribution point, click the down arrow (
 ) on the Select split button, and then select the Add connection gateway in DMZ by address option.
) on the Select split button, and then select the Add connection gateway in DMZ by address option. - Under Distribution point scope, click the down arrow (
 ) on the Select split button.
) on the Select split button. - Indicate the specific devices to which the distribution point will distribute updates. You can specify an administration group.
- Click OK to close the Add distribution point window.
- Under Device to act as distribution point, click the down arrow (
- The distribution point that you have added will be displayed in the list of distribution points, in the Distribution points section.
- Run the klnagchk utility in order to check whether a connection to Kaspersky Security Center has been successfully configured. In the command prompt, run:
$ sudo /opt/kaspersky/klnagent64/bin/klnagchk - In the main menu, go to Kaspersky Security Center and discover the device.
- In the window that opens, click the <Device name>.
- In the drop-down list, select the Move to Group link.
- In the Select group window that opens, click the Distribution points link.
- Click OK.
- Restart the Network Agent service on the Linux client by executing the following command in the command prompt:
$ sudo /opt/kaspersky/klnagent64/bin/klnagchk -restart
Connecting a Linux device as a gateway in the DMZ is completed.
After that, you can connect a Linux device to the Administration Server through the configured connection gateway. Follow these procedures only after you have completed the main installation scenario.
Connecting a Linux device to the Administration Server via a connection gateway
A connection gateway allows you to connect client devices from the demilitarized zone (DMZ) to Administration Server. Windows-based and Linux-based devices can act as a connection gateway. After you have connected and configured the connection gateway, you can use this gateway to connect a Linux device to the Administration Server. Follow the procedure below only after you have completed the main installation scenario.
To connect a Linux device to the Administration Server via a connection gateway, perform the following actions on this device:
- Download and install Network Agent on the Linux device.
- Run the Network Agent post-install script by executing the following command in the command prompt:
$ sudo /opt/kaspersky/klnagent64/lib/bin/setup/postinstall.pl - On the step asking for the Network Agent mode, choose the Connect to server using connection gateway option and enter the address of connection gateway.
- Check the connection with Kaspersky Security Center and the connection gateway, by using the following command in the command prompt:
$ sudo /opt/kaspersky/klnagent64/bin/klnagchkThe address of connection gateway is displayed in the output.
Connecting a Linux device to the Administration Server via a connection gateway is completed. You can use this device to update distribution, for remote installation of applications, and to retrieve information about networked devices.
Adding a connection gateway in the DMZ as a distribution point
A connection gateway waits for connections from Administration Server, rather than establishes connections to Administration Server. It means that right after a connection gateway is installed on a device in the DMZ, Administration Server does not list the device among managed devices. Therefore, you need a special procedure to ensure that Administration Server initiates a connection to the connection gateway.
To add a device with a connection gateway as a distribution point:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- In the context menu of Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, select the Distribution points section.
- In the right part of the window, select the Manually assign distribution points option.
- Click the Add button.
This opens the Add distribution point window.
- In the Add distribution point window, perform the following actions:
- Under Device to act as distribution point, click the down arrow (
 ) on the Select split button, and then select the Add connection gateway in DMZ by address option.
) on the Select split button, and then select the Add connection gateway in DMZ by address option. - In the Enter connection gateway address window that opens, enter the IP address of the connection gateway (or enter the name if the connection gateway is accessible by name).
- Under Distribution point scope, click the down arrow (
 ) on the Select split button.
) on the Select split button. - Indicate the specific devices to which the distribution point will distribute updates. You can specify an administration group or a network location description.
We recommend that you have a separate group for external managed devices.
- Under Device to act as distribution point, click the down arrow (
After you perform these actions, the list of distribution points contains a new entry named Temporary entry for connection gateway.
Administration Server almost immediately attempts to connect to the connection gateway at the address that you specified. If it succeeds, the entry name changes to the name of the connection gateway device. This process takes up to five minutes.
While the temporary entry for the connection gateway is being converted to a named entry, the connection gateway also appears in the Unassigned devices group.
To add a connection gateway to a previously configured network, reinstall the Network Agent on devices that you want to connect to the newly added connection gateway.
Assigning distribution points automatically
We recommend that you assign distribution points automatically. Kaspersky Security Center will then select on its own which devices must be assigned distribution points.
To assign distribution points automatically:
- Open the main application window.
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the Administration Server for which you want to assign distribution points automatically.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, click Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Sections pane select Distribution points.
- In the right part of the window, select the Automatically assign distribution points option.
If automatic assignment of devices as distribution points is enabled, you cannot configure distribution points manually or edit the list of distribution points.
- Click OK.
Administration Server assigns and configures distribution points automatically.
About local installation of Network Agent on a device selected as distribution point
To allow the device selected as the distribution point to directly communicate with the virtual Administration Server in order to act as connection gateway, the Network Agent must be installed locally on this device.
The procedure of local installation of Network Agent on the device defined as distribution point is the same as local installation of Network Agent on any network device.
The following conditions must be met for a device selected as a distribution point:
- During local installation of Network Agent, specify the address of a virtual Administration Server that manages the device in the Server Address field in the Administration Server window of the setup wizard. You can use either the device IP address or device name in the Windows network.
The following format is used for the virtual Administration Server address: <Full address of the physical Administration Server to which the virtual Server is subordinate>/<Name of virtual Administration Server>.
- So that it can act as connection gateway, open all ports of the device that are necessary for communication with the Administration Server.
After Network Agent with specified settings is installed on a device, Kaspersky Security Center performs the following actions automatically:
- Includes this device in the Managed devices group of the virtual Administration Server.
- Assigns this device as the distribution point of the Managed devices group of the virtual Administration Server.
It is necessary and sufficient to install Network Agent locally on the device that is assigned as the distribution point for the Managed devices group on the organization's network. You can install Network Agent remotely on devices that act as distribution points in the nested administration groups. To do this, use the distribution point of the Managed devices group as connection gateway.
About using a distribution point as connection gateway
If the Administration Server is outside the demilitarized zone (DMZ), Network Agents from this zone cannot connect to the Administration Server.
When connecting the Administration Server with Network Agents, you can use a distribution point as the connection gateway. The distribution point opens a port to Administration Server for the connection to be created. When the Administration Server is started, it connects to that distribution point and maintains this connection during the entire session.
Upon receiving a signal from the Administration Server, the distribution point sends a UDP signal to the Network Agents in order to allow connection to the Administration Server. When the Network Agents receive that signal, they connect to the distribution point, which transfers information between the Network Agents and the Administration Server. Information exchange can occur over an IPv4 or IPv6 network.
We recommend that you use a specially assigned device as the connection gateway and cover a maximum of 10,000 client devices (including mobile devices) with this connection gateway.
To add a connection gateway to a previously configured network:
- Install the Network Agent in the connection gateway mode.
- Reinstall the Network Agent on devices that you want to connect to the newly added connection gateway.
Adding IP ranges to the list of ranges polled by a distribution point
You can add an IP range to the list of ranges polled by a distribution point.
To add an IP range to the list of polled ranges:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- In the context menu of the node, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window that opens, select the Distribution points section.
- In the list, select the necessary distribution point, and then click Properties.
- In the distribution point properties window that opens, in the left Sections pane, select Device discovery → IP ranges.
- Select the Enable range polling check box.
- Click the Add button.
The Add button is active only if you select the Enable range polling check box.
The IP range window opens.
- In the IP range window, enter the name of the new IP range (the default name is New range).
- Click the Add button.
- Do one of the following:
- Specify the IP range using the start and end IP addresses.
- Specify the IP range using the address and subnet mask.
- Click Browse and add a subnet from the global list of subnets.
- Click OK.
- Click OK to add the new range with the specified name.
The new range will appear in the list of polled ranges.
Page top
Using a distribution point as a push server
In Kaspersky Security Center, a distribution point can work as a push server for the devices managed through the mobile protocol and for the devices managed by Network Agent. For example, a push server must be enabled if you want to be able to force synchronization of KasperskyOS devices with Administration Server. A push server has the same scope of managed devices as the distribution point on which the push server is enabled. If you have several distribution points assigned for the same administration group, you can enable push server on each of the distribution points. In this case, Administration Server balances the load between the distribution points.
A push server supports the load of up to 50,000 simultaneous connections.
You might want to use distribution points as push servers to make sure that there is continuous connectivity between a managed device and the Administration Server. Continuous connectivity is needed for some operations, such as running and stopping local tasks, receiving statistics for a managed application, or creating a tunnel. If you use a distribution point as a push server, you do not have to use the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option on managed devices or send packets to the UDP port of the Network Agent.
To use a distribution point as a push server:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- In the context menu of the node, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window that opens, select the Distribution points section.
- In the list, select the necessary distribution point, and then click Properties.
- In the distribution point properties window that opens, in the General section of the left Sections pane, select the Use this distribution point as a push server option.
- Specify the push server port number, that is, the port on the distribution point that client devices will use for connection.
By default, port 13295 is used.
- Click the OK button to exit the distribution point properties window.
- Open the Network Agent policy settings window.
- In the Connectivity section, go to the Network subsection.
- In the Network subsection, select the Use distribution point to force connection to the Administration Server option.
- Click the OK button to exit the window.
The distribution point starts acting as a push server. It can now send push notifications to client devices.
If you manage devices with KasperskyOS installed, or plan to do so, you must use a distribution point as a push server. You can also use a distribution point as a push server if you want to send push notifications to client devices.
Other routine work
This section provides recommendations on routine work with Kaspersky Security Center.
Managing Administration Servers
This section provides information about working with Administration Servers and configuring them.
Creating a hierarchy of Administration Servers: adding a secondary Administration Server
You can add an Administration Server as a secondary Administration Server, thus establishing a "primary/secondary" hierarchy. Adding a secondary Administration Server is possible regardless of whether the Administration Server that you intend to use as secondary is available for connection through Administration Console.
When combining two Administration Servers into a hierarchy, make sure that port 13291 is accessible on both Administration Servers. Port 13291 is required to receive connections from Administration Console to the Administration Server.
Connecting an Administration Server as secondary in reference to the primary Administration Server
You can add an Administration Server as secondary by connecting it to the primary Administration Server via port 13000. You will need a device that has Administration Console installed from which TCP ports 13291 can be accessed on both Administration Servers: supposed primary Administration Server and supposed secondary Administration Server.
To add as secondary an Administration Server that is available for connection through Administration Console:
- Make sure that port 13000 of the supposed primary Administration Server is available for receipt of connections from secondary Administration Servers.
- Use Administration Console to connect to the supposed primary Administration Server.
- Select the administration group to which you intend to add the secondary Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the Administration Servers node of the selected group, click the Add secondary Administration Server link.
The Add secondary Administration Server wizard starts.
- At the first step of the wizard (entering the address of the Administration Server being added to the group), enter the network name of the supposed secondary Administration Server.
- Follow the instructions of the wizard.
The "primary/secondary" hierarchy is built. The primary Administration Server will receive connection from the secondary Administration Server.
If you do not have a device that has Administration Console installed from which TCP ports 13291 can be accessed on both Administration Servers (if, for example, the supposed secondary Administration Server is located at a remote office and the system administrator of that office cannot open internet access to port 13291 for security reasons), you will still be able to add a secondary Administration Server.
To add as secondary an Administration Server that is not available for connection through Administration Console:
- Make sure that port 13000 of the supposed primary Administration Server is available for connection from secondary Administration Servers.
- Write the certificate file of the supposed primary Administration Server to an external device, such as a flash drive, or send it to the system administrator of the remote office where the Administration Server is located.
The certificate file of the Administration Server is on the same Administration Server, at %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\cert\klserver.cer.
- Write the certificate file of the supposed secondary Administration Server to an external device, such as a flash drive. If the supposed secondary Administration Server is located at a remote office, contact the system administrator of that office to prompt him or her to send you the certificate.
The certificate file of the Administration Server is on the same Administration Server, at %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\cert\klserver.cer.
- Use Administration Console to connect to the supposed primary Administration Server.
- Select the administration group to which you intend to add the secondary Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the Administration Servers node, click the Add secondary Administration Server link.
The Add secondary Administration Server wizard starts.
- At the first step of the wizard (entering the address), leave the Secondary Administration Server address (optional) field blank.
- In the Secondary Administration Server certificate file window, click the Browse button and select the certificate file of the secondary Administration Server that you saved.
- When the wizard is complete, use a different instance of Administration Console to connect to the supposed secondary Administration Server. If this Administration Server is located at a remote office, contact the system administrator of that office to prompt him or her to connect to the supposed secondary Administration Server and perform further due steps.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server node, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties, proceed to the Advanced section and then to the Hierarchy of Administration Servers subsection.
- Select the This Administration Server is secondary in the hierarchy check box.
The entry fields become available for data input and editing.
- In the Primary Administration Server address field, enter the network name of the supposed primary Administration Server.
- Select the previously saved file with the certificate of the supposed primary Administration Server by clicking the Browse button.
- Click OK.
The "primary/secondary" hierarchy is built. You can connect to the secondary Administration Server through Administration Console. The primary Administration Server will receive connection from the secondary Administration Server.
Connecting the primary Administration Server to a secondary Administration Server
You can add a new Administration Server as secondary so that the primary Administration Server connects to the secondary Administration Server via port 13000. This is advisable if, for example, you place a secondary Administration Server in DMZ.
You will need a device that has Administration Console installed from which TCP ports 13291 can be accessed on both Administration Servers: supposed primary Administration Server and supposed secondary Administration Server.
To add a new Administration Server as secondary and connect the primary Administration Server via port 13000:
- Make sure that port 13000 of the supposed secondary Administration Server is available for receipt of connections from the primary Administration Server.
- Use Administration Console to connect to the supposed primary Administration Server.
- Select the administration group to which you intend to add the secondary Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the Administration Servers node of the relevant administration group, click the Add secondary Administration Server link.
The Add secondary Administration Server wizard starts.
- At the first step of the wizard (entering the address of the Administration Server to be added to the group), enter the network name of the supposed secondary Administration Server and select the Connect primary Administration Server to secondary Administration Server in DMZ check box.
- If you connect to the supposed secondary Administration Server by using a proxy server, at the first step of the wizard select the Use proxy server check box and specify the connection settings.
- Follow the instructions of the wizard.
The hierarchy of Administration Servers is created. The secondary Administration Server will receive connection from the primary Administration Server.
Connecting to an Administration Server and switching between Administration Servers
After Kaspersky Security Center is started, it attempts to connect to an Administration Server. If several Administration Servers are available on the network, the application requests the server to which it was connected during the previous session of Kaspersky Security Center.
When the application is started for the first time after installation, it attempts to connect to the Administration Server that was specified during Kaspersky Security Center installation.
After connection to an Administration Server is established, the folders tree of that Server is displayed in the console tree.
If several Administration Servers have been added to the console tree, you can switch between them.
Administration Console is required for work with each Administration Server. Before the first connection to a new Administration Server, make sure that port 13291, which receives connections from Administration Console, is open, as well as all the remaining ports required for communication between Administration Server and other Kaspersky Security Center components.
To switch to another Administration Server:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the context menu of the node, select Connect to Administration Server.
- In the Connection settings window that opens, in the Administration Server address field specify the name of the Administration Server to which you want to connect. You can specify an IP address or the name of a device on a Windows network as the name of the Administration Server. You can click the Advanced button to configure the connection to the Administration Server (see figure below).
To connect to the Administration Server through a different port than the default port, enter a value in the Administration Server address field in <Administration Server name>:<Port> format.
To connect to a virtual Administration Server, enter a value in the Administration Server address field in <Administration Server address>/<virtual server name> format.
Users who do not have Read rights will be denied access to Administration Server.
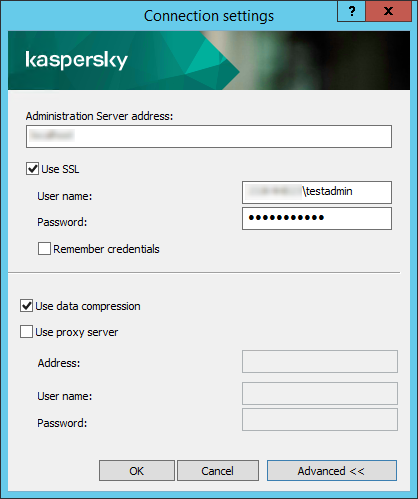
Connecting to Administration Server
- Click OK to complete the switch between Servers.
After the Administration Server is connected, the folders tree of the corresponding node in the console tree is updated.
Access rights to Administration Server and its objects
The KLAdmins and KLOperators groups are created automatically during Kaspersky Security Center installation. These groups are granted permissions to connect to the Administration Server and to process Administration Server objects.
Depending on the type of account that is used for installation of Kaspersky Security Center, the KLAdmins and KLOperators groups are created as follows:
- If the application is installed under a user account included in a domain, the groups are created on the Administration Server and in the domain that includes the Administration Server.
- If the application is installed under a system account, the groups are created on the Administration Server only.
You can view the KLAdmins and KLOperators groups and modify the access privileges of the users that belong to the KLAdmins and KLOperators groups by using the standard administrative tools of the operating system.
The KLAdmins group is granted all access rights; the KLOperators group is granted only Read and Execute rights. The rights granted to the KLAdmins group are locked.
Users that belong to the KLAdmins group are called Kaspersky Security Center administrators, while users from the KLOperators group are called Kaspersky Security Center operators.
In addition to users included in the KLAdmins group, administrator rights for Kaspersky Security Center are also provided to the local administrators of devices on which Administration Server is installed.
You can exclude local administrators from the list of users who have Kaspersky Security Center administrator rights.
All operations started by the administrators of Kaspersky Security Center are performed using the rights of the Administration Server account.
An individual KLAdmins group can be created for each Administration Server from the network; the group will have the necessary rights for that Administration Server only.
If devices belonging to the same domain are included in the administration groups of different Administration Servers, the domain administrator is the Kaspersky Security Center administrator for all the groups. The KLAdmins group is the same for those administration groups; it is created during installation of the first Administration Server. All operations initiated by a Kaspersky Security Center administrator are performed using the account rights of the Administration Server for which these operations have been started.
After the application is installed, an administrator of Kaspersky Security Center can do the following:
- Modify the rights granted to the KLOperators groups.
- Grant rights—to access Kaspersky Security Center functionality—to other security groups and individual users who are registered on the administrator's workstation.
- Assign user access rights within each administration group.
The Kaspersky Security Center administrator can assign access rights to each administration group or to other objects of Administration Server in the Security section in the properties window of the selected object.
You can track user activity by using the records of events in the Administration Server operation. Event records are displayed in the Administration Server node on the Events tab. These events have the importance level Info events and the event types begin with "Audit".
Conditions of connection to an Administration Server over the internet
If an Administration Server is remotely located outside a corporate network, client devices can connect to it over the internet.
For devices to connect to an Administration Server over the internet, the following conditions must be met:
- The remote Administration Server must have an external IP address and the incoming port 13000 must remain open (for connection of Network Agents). We recommend that you also open UDP port 13000 (for receiving notifications of device shut down).
- Network Agents must be installed on the devices.
- When installing Network Agent on devices, you must specify the external IP address of the remote Administration Server. If an installation package is used for installation, specify the external IP address manually in the properties of the installation package, in the Settings section.
- To use the remote Administration Server to manage applications and tasks for a device, in the properties window of the device, in the General section select the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server check box. After the check box is selected, wait until the Administration Server is synchronized with the remote device. The number of client devices maintaining a continuous connection with an Administration Server cannot exceed 300.
To speed up the performance of tasks initiated by a remote Administration Server, you can open port 15000 on a device. In this case, to run a task, the Administration Server sends a special packet to Network Agent over port 15000 without waiting until completion of synchronization with the device.
Page top
Encrypted connection to an Administration Server
Data exchange between client devices and Administration Server, as well as Administration Console connection to Administration Server, can be performed using the TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocol. The TLS protocol can identify the interacting parties, encrypt the data that is transferred, and protect data against modification during transfer. The TLS protocol uses public keys to authenticate the interacting parties and encrypt data.
Authenticating Administration Server when a device is connected
When a client device connects to Administration Server for the first time, Network Agent on the device downloads a copy of the Administration Server certificate and stores it locally.
If you install Network Agent on a device locally, you can select the Administration Server certificate manually.
The downloaded copy of the certificate is used to verify Administration Server rights and permissions during subsequent connections.
During future sessions, Network Agent requests the Administration Server certificate at each connection of the device to Administration Server and compares it with the local copy. If the copies do not match, the device is not allowed access to Administration Server.
Page top
Administration Server authentication during Administration Console connection
At the first connection to Administration Server, Administration Console requests the Administration Server certificate and saves it locally on the administrator's workstation. After that, each time when Administration Console tries to connect to this Administration Server, the Administration Server is identified based on the certificate copy.
If the Administration Server certificate does not match the copy stored on the administrator's workstation, Administration Console prompts you to confirm connection to the Administration Server with the specified name and download a new certificate. After the connection is established, Administration Console saves a copy of the new Administration Server certificate, which will be used to identify the Administration Server in the future.
Page top
Configuring an allowlist of IP addresses to connect to Administration Server
By default, users can log in to Kaspersky Security Center under any device where they can open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console (hereinafter referred to as Web Console) or where MMC-based Administration Console is installed. However, you can configure Administration Server so that users can connect to it only from devices with allowed IP addresses. In this case, even if an intruder steals a Kaspersky Security Center account, he or she will not be able to log in to Kaspersky Security Center because the IP address of the intruder's device is not in the allowlist.
The IP address is verified when a user logs in to Kaspersky Security Center or runs an
that interacts with Administration Server via Kaspersky Security Center OpenAPI. At this moment, a user's device tries to establish a connection with Administration Server. If the IP address of the device is not in the allowlist, an authentication error occurs and the KLAUD_EV_SERVERCONNECT event notifies you that a connection with Administration Server has not been established.Requirements for an allowlist of IP addresses
IP addresses are verified only when the following applications try to connect to Administration Server:
- Web Console Server
If you sign in to Web Console on one device and the Web Console Server is installed on another device, you can configure a firewall on the device where the Web Console Server is installed by using the standard means of the operating system. Then, if someone tries to log in to Web Console, a firewall helps prevent intruders from interfering.
- Administration Console
- Applications interacting with Administration Server via klakaut automation objects
- Applications interacting with Administration Server via OpenAPI, such as Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform or Kaspersky Security for Virtualization
Therefore, specify addresses of the devices on which the applications listed above are installed.
You can set IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. You cannot specify ranges of IP addresses.
How to establish an allowlist of IP addresses
If you have not set an allowlist earlier, follow the instructions below.
To establish an allowlist of IP addresses to log in to Kaspersky Security Center:
- On the Administration Server device, run the command prompt under an account with administrator rights.
- Change your current directory to the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder (usually, <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center).
- Enter the following command, using administrator rights:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_FLAG_ALLOWED_IP_ADDRESSES_FOR_GUI -v "<
IP addresses>" -t sSpecify IP addresses that meet the requirements listed above. Several IP addresses must be separated by a semicolon.
Example of how to allow only one device to connect to Administration Server:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_FLAG_ALLOWED_IP_ADDRESSES_FOR_GUI -v "192.0.2.0" -t s
Example of how to allow multiple devices to connect to Administration Server:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_FLAG_ALLOWED_IP_ADDRESSES_FOR_GUI -v "192.0.2.0; 198.51.100.0; 203.0.113.0" -t s
- Restart the Administration Server service.
You can find out whether you have successfully configured the allowlist of IP addresses in Kaspersky Event Log on the Administration Server.
How to change an allowlist of IP addresses
You can change an allowlist just as you did when you first established it. For this purpose, run the same command and specify a new allowlist:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_FLAG_ALLOWED_IP_ADDRESSES_FOR_GUI -v "<IP addresses>" -t s
If you want to delete some IP addresses from the allowlist, rewrite it. For example, your allowlist includes the following IP addresses: 192.0.2.0; 198.51.100.0; 203.0.113.0. You want to delete the 198.51.100.0 IP address. To do this, enter the following command at the command prompt:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_FLAG_ALLOWED_IP_ADDRESSES_FOR_GUI -v "192.0.2.0; 203.0.113.0" -t s
Do not forget to restart the Administration Server service.
How to reset a configured allowlist of IP addresses
To reset an already configured allowlist of IP addresses:
- Enter the following command at the command prompt, using administrator rights:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_FLAG_ALLOWED_IP_ADDRESSES_FOR_GUI -v "" -t s
- Restart the Administration Server service.
After that, IP addresses are not verified any more.
Page top
Using the klscflag utility to close port 13291
Port 13291 on the Administration Server is used for receiving connections from Administration Consoles. This port is open by default. If you do not want to use the MMC-based Administration Console or the klakaut utility, you can close this port by using the klscflag utility. This utility changes the value of the KLSRV_SP_SERVER_SSL_PORT_GUI_OPEN parameter.
To close port 13291:
- Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
- Execute the following command in the command line:
klscflag -ssvset -pv klserver -s 87 -n KLSRV_SP_SERVER_SSL_PORT_GUI_OPEN -sv false -svt BOOL_T -ss "|ss_type = \"SS_SETTINGS\";"
- Restart the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server service.
Port 13291 is closed.
To check if port 13291 has been successfully closed:
Execute the following command in the command line:
klscflag -ssvget -pv klserver -s 87 -n KLSRV_SP_SERVER_SSL_PORT_GUI_OPEN -svt BOOL_T -ss "|ss_type = \"SS_SETTINGS\";"
This command returns the following result:
+--- (PARAMS_T)
+---KLSRV_SP_SERVER_SSL_PORT_GUI_OPEN = (BOOL_T)false
The false value means that the port is closed. Otherwise, the true value is displayed.
Disconnecting from an Administration Server
To disconnect from an Administration Server:
- In the console tree select the node corresponding to the Administration Server that you want to disconnect.
- In the context menu of the node select Disconnect from Administration Server.
Adding an Administration Server to the console tree
To add an Administration Server to the console tree:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center main window, in the console tree select the Kaspersky Security Center node.
- In the context menu of the node, select New → Administration Server.
A node named Administration Server - <Device name> (Not connected) is created in the console tree from which you will be able to connect to any of the Administration Servers installed on the network.
Page top
Removing an Administration Server from the console tree
To remove an Administration Server from the console tree:
- In the console tree select the node corresponding to the Administration Server that you want to remove.
- In the context menu of the node select Remove.
Adding a virtual Administration Server to the console tree
To add a virtual Administration Server to the console tree:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the Administration Server for which you need to create a virtual Administration Server.
- In the Administration Server node, select the Administration Servers folder.
- In the workspace of the Administration Servers folder, click the Add virtual Administration Server link.
The New virtual Administration Server wizard starts.
- In the Name of virtual Administration Server window, specify the name of the virtual Administration Server to be created.
The name of a virtual Administration Server cannot be more than 255 characters long and cannot include any special characters (such as "*<>?\:|).
- In the Enter address for device connection to virtual Administration Server window, specify the device connection address
The connection address of a virtual Administration Server is the network address through which devices will connect to that Server. The connection address has two parts: the network address of a physical Administration Server and the name of a virtual Administration Server, separated with a slash. The name of the virtual Administration Server will be substituted automatically. The specified address will be used on the virtual Administration Server as the default address in Network Agent installation packages.
- In the Create the virtual Administration Server administrator account window, assign a user from the list to act as virtual Server administrator, or add a new administrator account by clicking the Create button.
You can specify multiple accounts.
A node named Administration Server <Name of virtual Administration Server> is created in the console tree.
Page top
Changing an Administration Server service account. Utility tool klsrvswch
If you have to change the Administration Server service account that was set during installation of Kaspersky Security Center, you can use a utility named klsrvswch that is designed for changing the Administration Server account.
When Kaspersky Security Center is installed, the utility is automatically copied to the application installation folder.
The number of launches of the utility is essentially unlimited.
You must launch the klsrvswch utility on the Administration Server device under the account with administrator rights that was used to install Administration Server.
The klsrvswch utility allows you to change the account type. For example, if you use a local account, you can change it to a domain account or to a managed service account (and vice versa). The klsrvswch utility does not allow you to change the account type to group managed service account (gMSA).
Windows Vista and later Windows versions do not allow the use of a LocalSystem account for the Administration Server. In these Windows versions, the LocalSystem account option is inactive.
To change an Administration Server service account to a domain account:
- Launch the klsrvswch utility from the installation folder of Kaspersky Security Center. The default installation path: <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
This action also launches the wizard for modification of Administration Server service account. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- In the Administration Server service account window, select LocalSystem account.
After the wizard finishes, the Administration Server account is changed. The Administration Server service will start under the LocalSystem Account and use its credentials.
Correct operation of Kaspersky Security Center requires that the account used to start the Administration Server service has administrator rights to the resource where the Administration Server database is hosted.
To change an Administration Server service account to a user account or a managed service account:
- Launch the klsrvswch utility from the installation folder of Kaspersky Security Center. The default installation path: <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
This action also launches the wizard for modification of Administration Server service account. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- In the Administration Server service account window, select Custom account.
- Click the Find now button.
The Select User window opens.
- In the Select User window, click the Object Types button.
- In the object types list, select Users (if you want a user account) or Service Accounts (if you want a managed service account) and click OK.
- In the object name field, enter the name of the account, or a part of the name, and click Check Names.
- In the list of the matching names, select the necessary name, and then click OK.
- If you selected Service Accounts, in the Account password window, leave the Password and Confirm password fields blank. If you selected Users, enter a new password for the user and confirm it.
The Administration Server service account will be changed to the account that you selected.
When Microsoft SQL Server is used in a mode that presupposes authenticating user accounts with Windows tools, access to the database must be granted. The user account must have the status of owner of the Kaspersky Security Center database. The dbo schema is used by default.
Page top
Changing DBMS credentials
You may need to change DBMS credentials, for example, in order to perform a credential rotation for security purposes.
To change DBMS credentials in a Windows environment by using klsrvswch.exe:
- Launch the klsrvswch utility that is located in the installation folder of Kaspersky Security Center. The default installation path: <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
You must launch the klsrvswch utility on the Administration Server device under the account with administrator rights that was used to install Administration Server.
- Click the Next button of the wizard until you reach the Change DBMS access credentials step.
- At the Change DBMS access credentials step of the wizard, perform the following:
The Change DBMS access credentials step of the wizard is skipped if the Windows authentication is used.
- Select the Apply new credentials option.
- Specify a new account name in the Account field.
- Specify a new password for an account in the Password field.
- Specify the new password in the Confirm password field.
You should specify credentials of an account that exists in the DBMS.
- Click the Next button.
After the wizard finishes, the DBMS credentials are changed.
The klsrvswch utility can only be used to change the account's password for SQL authentication. Changing the authorization method is not supported. To change the authorization method, reinstall the Administration Server and specify the desired settings.
Page top
Changing the Administration Server shared folder
The Administration Server shared folder is specified during installation of the Administration Server. You can change the location of the shared folder in the Administration Server properties.
To change the shared folder:
- Create a network share folder and configure permissions for the share and for the folder structure to allow full control rights for the Everyone subgroup.
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, open the context menu of the Administration Server folder and select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Sections pane, select Advanced, and then select Administration Server shared folder.
- In the Administration Server shared folder section, click the Change button.
- Select the folder that you want to use as shared.
- Click the OK button to close the Administration Server properties window.
- Assign read rights for the Everyone subgroup for the folder that you selected as shared.
Resolving issues with Administration Server nodes
The console tree in the left pane of Administration Console contains nodes of Administration Servers. You can add as many Administration Servers as you need to the console tree.
The list of Administration Server nodes in the console tree is stored in a shadow copy of a .msc file by means of Microsoft Management Console. The shadow copy of this file is located in the %USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\MMC\ folder on the device where the Administration Console is installed. For each Administration Server node, the file contains the following information:
- Administration Server address
- Port number
- Whether TLS is in use
This parameter depends on the port number used to connect Administration Console to the Administration Server.
- User name
- Administration Server certificate
Troubleshooting
When Administration Console connects to the Administration Server, the certificate stored locally is compared to the Administration Server certificate. If the certificates do not match, Administration Console generates an error. For example, a certificate mismatch may occur when you replace the Administration Server certificate. In this case, recreate the Administration Server node in the console.
To recreate an Administration Server node:
- Close the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console window.
- Delete the Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 file at %USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\MMC\.
- Run Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
You will be prompted to connect to the Administration Server and accept its existing certificate.
- Do one of the following:
- Accept the existing certificate by clicking the Yes button.
- To specify your certificate, click the No button, and then browse to the certificate file to be used to authenticate the Administration Server.
The certificate issue is resolved. You can use Administration Console to connect to the Administration Server.
Page top
Viewing and modifying the settings of an Administration Server
You can adjust the settings of an Administration Server in the properties window of this Server.
To open the Properties: Administration Server window,
Select Properties in the context menu of the Administration Server node in the console tree.
Adjusting the general settings of Administration Server
You can adjust the general settings of Administration Server in the General, Administration Server connection settings, Events repository, and Security sections of the Administration Server properties window.
The Security section is not displayed in the Administration Server properties window if the display has been disabled in the Administration Console interface.
To enable the display of the Security section in Administration Console:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server that you want.
- In the View menu of the main application window, select Configure interface.
- In the Configure interface window that opens, select the Display security settings sections check box and click OK.
- In the window with the application message, click OK.
The Security section will be displayed in the Administration Server properties window.
Page top
Administration Console interface settings
You can adjust the interface settings of Administration Console to display or hide the user interface controls related to the following features:
- Vulnerability and patch management
- Data encryption and protection
- Endpoint control settings
- Mobile Device Management
- Secondary Administration Servers
- Security Settings sections
To configure the Administration Console interface settings:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server that you want.
- In the View menu of the main application window, select Configure interface.
- In the Configure interface window that opens, select the check boxes next to the features that you want displayed and click OK.
- In the window with the application message, click OK.
The selected features will be displayed in the Administration Console interface.
Page top
Event processing and storage on the Administration Server
Information about events that occur during the operation of the application and managed devices is saved in the Administration Server database. Each event is attributed to a certain type and level of severity (Critical event, Functional failure, Warning, or Info). Depending on the conditions under which an event occurred, the application can assign different levels of severity to events of the same type.
You can view types and levels of severity assigned to events in the Event configuration section of the Administration Server properties window. In the Event configuration section, you can also configure processing of every event by the Administration Server:
- Registration of events on the Administration Server and in event logs of the operating system on a device and on the Administration Server.
- Method used for notifying the administrator of an event (for example, an SMS or email message).
In the Events repository section of the Administration Server properties window, you can edit the settings of events storage in the Administration Server database by limiting the number of event records and record storage term. When you specify the maximum number of events, the application calculates an approximate amount of storage space required for the specified number. You can use this approximate calculation to evaluate whether you have enough free space on the disk to avoid database overflow. The default capacity of the Administration Server database is 400,000 events. The maximum recommended capacity of the database is 45 million events.
The application checks the database every 10 minutes. If the number of events reaches the specified maximum value plus 10,000, the application deletes the oldest events so that only the specified maximum number of events remains.
When the Administration Server deletes old events, it cannot save new events to the database. During this period of time, information about events that were rejected is written to the Kaspersky Event Log. The new events are queued and then saved to the database after the deletion operation is complete.
You can change the settings of any task to save events related to the task progress, or save only task execution results. In doing so, you will reduce the number of events in the database, increase the speed of execution of scenarios associated with analysis of the event table in the database, and lower the risk that critical events will be overwritten by a large number of events.
Page top
Viewing log of connections to the Administration Server
The history of connections and attempts to connect to the Administration Server during its operation can be saved to a log file. The information in the file allows you to track not only connections on your network infrastructure, but unauthorized attempts to access the Administration Server as well.
To log events of connection to the Administration Server:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server for which you want to enable connection event logging.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the properties window that opens, in the Administration Server connection settings section, select the Connection ports subsection.
- Enable the Log Administration Server connection events option.
- Click the OK button to close the Administration Server properties window.
All further events of inbound connections to the Administration Server, authentication results, and SSL errors will be saved to the file %ProgramData%\KasperskyLab\adminkit\logs\sc.syslog.
Page top
Control of virus outbreaks
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to quickly respond to emerging threats of virus outbreaks. Risks of virus outbreaks are assessed by monitoring virus activity on devices.
You can configure assessment rules for threats of virus outbreaks and actions to take in case one emerges; to do this, use the Virus outbreak section of the properties window of Administration Server.
You can specify the notification procedure for the Virus outbreak event in the Event configuration section of the Administration Server properties window, in the Virus outbreak event properties window.
The Virus outbreak event is generated upon detection of Malicious object detected events during the operation of security applications. Therefore, you must save information about all Malicious object detected events on Administration Server in order to recognize virus outbreaks.
You can specify the settings for saving information about any Malicious object detected event in the policies of the security applications.
When Malicious object detected events are counted, only information from the devices of the primary Administration Server is taken into account. The information from secondary Administration Servers is not taken into account. For each secondary Server, the Virus outbreak event is configured individually.
Limiting traffic
To reduce traffic volumes within a network, the application provides the option to limit the speed of data transfer to an Administration Server from specified IP ranges and IP subnets.
You can create and configure traffic-limiting rules in the Traffic section of the Administration Server properties window.
To create a traffic-limiting rule:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the Administration Server for which you want to create a traffic-limiting rule.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, select the Traffic section.
- Click the Add button.
- In the New rule window, specify the following settings:
In the IP range to limit traffic section, select the method that will be used to define the subnet or range for which the data transfer rate will be limited, and then enter the values of the settings for the selected method. Select one of the following methods:
- Specify the range by using address and network mask
- Specify the range by using start and end addresses
In the Traffic limit section, you can adjust the following restrictive settings for the data transfer rate:
Primarily, traffic limiting rules affect the transfer of files. These rules do not apply to the traffic generated by synchronization between Administration Server and Network Agent, or between primary and secondary Administration Servers.
Page top
Configuring Web Server
Web Server is designed for publishing stand-alone installation packages, iOS MDM profiles, and files from a shared folder.
You can define the settings for Web Server connection to the Administration Server and set the Web Server certificate in the Web Server section of the Administration Server properties window.
Page top
Working with internal users
The accounts of internal users are used to work with virtual Administration Servers. Kaspersky Security Center grants the rights of real users to internal users of the application.
The accounts of internal users are created and used only within Kaspersky Security Center. No data on internal users is transferred to the operating system. Kaspersky Security Center authenticates internal users.
You can configure accounts of internal users in the User accounts folder of the console tree.
Page top
Backup and restoration of Administration Server settings
Backup of the settings of Administration Server and its database is performed through the backup task and klbackup utility. A backup copy includes all the main settings and objects pertaining to the Administration Server, such as certificates, primary keys for encryption of drives on managed devices, keys for various licenses, structure of administration groups with all of its contents, tasks, policies, etc. With a backup copy you can recover the operation of an Administration Server as soon as possible, spending from a dozen minutes to a couple of hours on this.
If no backup copy is available, a failure may lead to an irrevocable loss of certificates and all Administration Server settings. This will necessitate reconfiguring Kaspersky Security Center from scratch, and performing initial deployment of Network Agent on the organization's network again. All primary keys for encryption of drives on managed devices will also be lost, risking irrevocable loss of encrypted data on devices with Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Therefore, do not neglect regular backups of Administration Server using the standard backup task.
The quick start wizard creates the backup task for Administration Server settings and sets it to run daily, at 4:00 AM. Backup copies are saved by default in the folder %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskySC.
If an instance of Microsoft SQL Server installed on another device is used as the DBMS, you must modify the backup task by specifying a UNC path, which is available for write by both the Administration Server service and the SQL Server service, as the folder to store backup copies. This requirement derives from a special feature of backup in the Microsoft SQL Server DBMS.
If a local instance of Microsoft SQL Server is used as the DBMS, we also recommend to save backup copies on a dedicated medium in order to secure them against damage together with Administration Server.
Because a backup copy contains important data, the backup task and klbackup utility provide for password protection of backup copies. By default, the backup task is created with a blank password. You must set a password in the properties of the backup task. Neglecting this requirement causes a situation where all keys of Administration Server certificates, keys for licenses, and primary keys for encryption of drives on managed devices remain unencrypted.
In addition to the regular backup, you must also create a backup copy prior to every significant change, including installation of Administration Server upgrades and patches.
If you use Microsoft SQL Server as the DBMS, you can minimize the size of backup copies. To do this, enable the Compress backup option in the SQL Server settings.
Restoration from a backup copy is performed with the utility klbackup on an operable instance of Administration Server that has just been installed and has the same version (or later) for which the backup copy was created.
The instance of Administration Server on which the restoration is to be performed, must use a DBMS of the same type (for example, the same SQL Server or MariaDB) and the same or later version. The version of Administration Server can be the same (with an identical or later patch), or later.
This section describes standard scenarios for restoring settings and objects of Administration Server.
Using a file system snapshot to reduce the backup duration
In Kaspersky Security Center 15.1, the idle time of Administration Server during backup has been reduced as compared to earlier versions. Moreover, the Use file system snapshot for data backup feature has been added to the task settings. This feature provides additional idle reduction by using the klbackup utility, which creates a shadow copy of the disk during backup (this takes a few seconds) and simultaneously copies the database (this takes a few minutes at longest). When klbackup creates a shadow copy of the disk and a copy of the database, the utility makes the Administration Server connectible again.
You can use the file system snapshotting feature only if these two conditions are met:
- The Administration Server shared folder and the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\KasperskyLab folder are located on the same logical disk and are local in reference to the Administration Server.
- The %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\KasperskyLab folder does not contain any symbolic links that have been created manually.
Do not use the feature if either of these conditions cannot be met. In this case, the application would return an error message in response to any attempt to create a file system snapshot.
To use the feature, you must have an account that has been granted the permission to create snapshots of the logical disk storing the %ALLUSERSPROFILE% folder. Note that the Administration Server service account has no such permission.
To use the file system snapshotting feature in order to reduce the backup duration:
- In the Tasks section, select the backup task.
- In the context menu, select Properties.
- In the task properties window that opens, select the Settings section.
- Select the Use file system snapshot for data backup check box.
- In the User name and Password fields, enter the name and password of an account that has the permission to create snapshots of the logical disk storing the %ALLUSERSPROFILE% folder.
- Click Apply.
At any further startup of the backup task, the klbackup utility will create file system snapshots thus reducing the Administration Server idle time during the task run.
Page top
A device with Administration Server is inoperable
If a device with Administration Server is inoperable due to a failure, you are recommended to perform the following actions:
- The new Administration Server must be assigned the same address: NetBIOS name, FQDN, or static IP (depending on which of them was set when Network Agents were deployed).
- Install Administration Server, using a DBMS of the same type, of the same (or later) version. You can install the same version of Server with the same (or later) patch, or a later version. After installation, do not perform the initial setup through the wizard.
- In the Start menu, run the klbackup utility and perform restoration.
The settings of Administration Server or the database are corrupted
If Administration Server is inoperable due to corrupted settings or database (e.g., after a power surge), you are recommended to use the following restoration scenario:
- Scan the file system on the damaged device.
- Uninstall the inoperable version of Administration Server.
- Reinstall Administration Server, using a DBMS of the same type and of the same (or later) version. You can install the same version of Server with the same (or later) patch, or a later version. After installation, do not perform the initial setup through the wizard.
- In the Start menu, run the utility klbackup and perform restoration.
It is prohibited to restore Administration Server in any way other than through the klbackup utility.
Any attempts to restore Administration Server through third-party software will inevitably lead to desynchronization of data on nodes of the distributed application Kaspersky Security Center and, consequently, to improper functioning of the application.
Page top
Backup copying and restoration of Administration Server data
Data backup allows you to move Administration Server from one device to another without data loss. Through backup, you can restore data when moving the Administration Server database to another device, or when upgrading to a newer version of Kaspersky Security Center.Also, you can use data backup to move Administration Server data from Kaspersky Security Center Windows under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux (moving data from Kaspersky Security Center Linux to Kaspersky Security Center Windows is not supported).
Note that the installed management plug-ins are not backed up. After you restore Administration Server data from a backup copy, you need to download and reinstall plug-ins for managed applications.
Before you back up the Administration Server data, check whether a virtual Administration Server is added to the administration group. If a virtual Administration Server is added, make sure that an administrator is assigned to this virtual Administration Server before the backup. You cannot grant the administrator access rights to the virtual Administration Server after the backup. Note that if the administrator account credentials are lost, you will not be able to assign a new administrator to the virtual Administrator Server.
You can create a backup copy of Administration Server data in one of the following ways:
- By creating and running a data backup task through Administration Console.
- By running the klbackup utility on the device that has Administration Server installed. This utility is included in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit. After the installation of Administration Server, the utility is located in the root of the destination folder specified at the application installation.
The following data is saved in the backup copy of Administration Server:
- Database of Administration Server (policies, tasks, application settings, events saved on the Administration Server).
- Configuration details of the structure of administration groups and client devices.
- Repository of distribution packages of applications for remote installation.
- Administration Server certificate.
- Contents of the Updates folder.
By default, the folder path is C:\ProgramData\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\.working\share\Updates\
Recovery of Administration Server data is only possible using the klbackup utility.
Backup of Administration Server data task
Creating a Backup of Administration Server data task
Backup task is an Administration Server task; it is created through the quick start wizard. If a backup task created by the quick start wizard has been deleted, you can create one manually.
To create a Backup of Administration Server data task:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- Start creation of the task in one of the following ways:
- By selecting New → Task in the context menu of the Tasks folder in the console tree.
- By clicking the Create a task button in the workspace.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard. In the Select the task type window of the wizard select the task type named Backup of Administration Server data.
The Backup of Administration Server data task can only be created in a single copy. If the Administration Server data backup task has already been created for the Administration Server, it is not displayed in the task type selection window of the Administration Server backup task creation wizard.
Configuring the Backup of Administration Server data task
After creating a backup task, you can configure the task settings.
To configure the Backup of Administration Server data task:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- In the context menu of the Backup of Administration Server data task, select Properties.
The properties window of the Backup of Administration Server data task opens. The following properties are available:
- General
In the General section, you can specify the task name, view the task creation date, the last command date, the statuses of the task launches, and task results.
- Notification
In the Notification section, you can specify the settings for storing tasks, as well as configure the notifications about the task execution results.
- Schedule
In the Schedule section, you can specify a schedule for task start.
- Destination
In the Destination section, you can specify the path to the folder that will store backup copies of Administration Server data.
- Settings
In the Settings section, you can set the backup protection password and number of backup copies, if needed.
You can also create a shadow copy of the logical disk storing the %ALLUSERSPROFILE% folder and copy the Administration Server database. To do this, you must enable the Use a file system snapshot for data backup option, and then specify the name and password of an account that has the permission to create snapshots.
- Security
In the Security section, you can give users and groups permissions to perform operations on Administration Server. If the Inherit settings from Administration Server option is enabled, the security settings of the task are inherited from the Administration Server.
If this option is disabled, you can configure security settings for the task. You can assign a role to a user or a group of users, or assign permissions to a user or a group of users, as applied to the task.
By default, the Inherit settings from Administration Server option is enabled.
- Revision history
In the Revision history section, you can track the task modification. Every time you save changes made to the task, a revision is created.
Data backup and recovery utility (klbackup)
You can copy Administration Server data for backup and future recovery using the klbackup utility, which is part of the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit.
The klbackup utility can run in either of the two following modes:
Page top
Data backup and recovery in interactive mode
To create a backup copy of Administration Server data in interactive mode:
- Run the klbackup utility located in the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder.
The Backup and restore wizard starts.
- In the first window of the wizard, select Perform backup of Administration Server data.
If you select the Restore or back up Administration Server certificate only option, only a backup copy of the Administration Server certificate and private key will be saved. Backing up of the Administration Server certificate and private key can be useful when you perform the migration from Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Windows to Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Linux. Also, you can migrate managed devices between Kaspersky Security Center Linux Administration Servers, as well as between Kaspersky Security Center Windows Administration Servers. For more information, see Using the klbackup utility to switch managed devices under management of another Administration Server.
Click Next.
- In the next window of the wizard, specify the following options:
- Destination folder for the backup
- Migrate to MySQL/MariaDB format
- Migrate to Azure format
- Include current date and time in the name of the backup destination folder
- Password for the backup
- Click the Next button to start backup.
- If you are working with a database in a cloud environment such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure, in the Sign In to Online Storage window, fill in the following fields:
To recover Administration Server data in interactive mode:
- Run the klbackup utility located in the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder. Start the utility under the same account that you used to install Administration Server. We recommend that you run the utility on a newly installed Administration Server.
The Backup and restore wizard starts.
- In the first window of the wizard, select Restore Administration Server data, and then click Next.
If you select the Restore or back up Administration Server certificate only option, only the Administration Server certificate and private key will be recovered.
When you run the klbackup utility on the inactive failover cluster node, you will be prompted to select one of the options: specify Administration Server certificate or automatically retrieve data from Administration Server.
- In the Restore settings window of the wizard:
- Specify the folder that contains a backup copy of Administration Server data.
If you are working in a cloud environment such as AWS or Azure, specify the address of the storage. Also, make sure that the file is named backup.zip.
- Specify the password that was entered during data backup.
When restoring data, you must specify the same password that was entered during backup. If the path to a shared folder changed after backup, check the operation of tasks that use restored data (restore tasks and remote installation tasks). If necessary, edit the settings of these tasks. While data is being restored from a backup file, no one must access the shared folder of Administration Server. The account under which the klbackup utility is started must have full access to the shared folder.
- Specify the folder that contains a backup copy of Administration Server data.
- Click the Next button to restore data.
Data backup and recovery in silent mode
To create a backup copy or recover Administration Server data in silent mode,
Run klbackup with the required set of keys from the command line of the device that has Administration Server installed.
Network agent flags are not restored when you use the klbackup utility. You need to configure network agent flags manually.
Utility command line syntax:
klbackup -path BACKUP_PATH [-linux_path LINUX_PATH][-node_cert CERT_PATH] [-logfile LOGFILE] [-use_ts]|[-restore] [-password PASSWORD] [-cert_only] [-online]
If no password is specified in the command line of the klbackup utility, the utility prompts you to enter the password interactively.
Descriptions of the keys:
-path BACKUP_PATH—Save information in the BACKUP_PATH folder, or use data from the BACKUP_PATH folder for recovery (mandatory parameter).The database server account and the klbackup utility should be granted permissions for changing data in the folder BACKUP_PATH.
-linux_path LINUX_PATH—Local path to folder with backup data for SQL Server on Linux.The database server account and the klbackup utility should be granted permissions for changing data in the folder LINUX_PATH.
-node_cert CERT_PATH—Server certificate file to configure inactive failover cluster node after recovery. If not set, it will be automatically retrieved from the Server.When you run the klbackup utility on the inactive failover cluster node, use this key to specify the path to the Server certificate.
-logfile LOGFILE—Save a report about Administration Server data backup and recovery.-use_ts—When saving data, copy information to the BACKUP_PATH folder, to the subfolder with a name in theklbackupYYYY-MM-DD # HH-MM-SSformat, which includes the current date and operation time in UTC. If no key is specified, information is saved in the root of the folder BACKUP_PATH.During attempts to save information in a folder that already stores a backup copy, an error message appears. No information will be updated.
Availability of the
-use_tskey allows an Administration Server data archive to be maintained. For example, if the-pathkey indicates the folderC:\KLBackups, the folderklbackup2022/6/19 # 11-30-18then stores information about the status of the Administration Server as of June 19, 2022, at 11:30:18 AM.-restore—Recover Administration Server data. Data recovery is performed based on information contained in the BACKUP_PATH folder. If no key is available, data is backed up in the BACKUP_PATH folder.-password PASSWORD—Password to protect the sensitive data.A forgotten password cannot be recovered. There are no password requirements. The password length is unlimited and zero length (no password) is also possible.
When restoring data, you must specify the same password that was entered during backup. If the path to a shared folder changed after backup, check the operation of tasks that use restored data (restore tasks and remote installation tasks). If necessary, edit the settings of these tasks. While data is being restored from a backup file, no one must access the shared folder of Administration Server. The account under which the klbackup utility is started must have full access to the shared folder. We recommend that you run the utility on a newly installed Administration Server.
-cert_only—Save or recover only the certificate and private key of Administration Server.This flag can be useful when you perform the migration from Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Windows to Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Linux. Also you can migrate managed devices between Kaspersky Security Center Linux Administration Servers as well as between Kaspersky Security Center Windows Administration Servers.
-online—Back up Administration Server data by creating a volume snapshot to minimize the offline time of the Administration Server. When you use the utility to recover data, this option is ignored.
Using the klbackup utility to switch managed devices under management of another Administration Server
The klbackup utility allows you to switch managed devices under management of another Administration Server. You can change the Kaspersky Security Center Windows Administration Server to Kaspersky Security Center Linux Administration Server by using the klbackup utility when you perform the migration. Also, you can migrate managed devices between Kaspersky Security Center Linux Administration Servers, as well as between Kaspersky Security Center Windows Administration Servers.
To switch managed devices under management of another Administration Server by using the klbackup utility:
- On the previous device, create a backup copy of the Administration Server certificate and private key.
You can create a backup copy in one of the following ways:
- By using the klbackup utility interface (only for Kaspersky Security Center Windows Administration Server)
Run the klbackup utility located in the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder, and then create a backup by using the Restore or back up Administration Server certificate only option.
- By using the command prompt (for Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky Security Center Linux Administration Servers version 15.1 or later)
Run the klbackup utility with the
-cert_onlykey from the command line, to create a backup copy of the Administration Server certificate and private key:klbackup -path <path to the backup copy of Administration Server certificate> -cert_only
- By using the klbackup utility interface (only for Kaspersky Security Center Windows Administration Server)
- On the previous device, disconnect Administration Server from the network.
- Assign the same address to the device with another Administration Server.
The new Administration Server can be assigned the NetBIOS name, FQDN, and static IP address. It depends on which Administration Server address was set in the Network Agent installation package when Network Agents were deployed. Alternatively, you can use the connection address that determines the Administration Server to which Network Agent connects (you can obtain this address on managed devices by using the klnagchk utility).
- On a device with another Administration Server, restore the Administration Server certificate and private key from the backup copy.
You can restore a backup copy in one of the following ways:
- By using the klbackup utility interface (only for Kaspersky Security Center Windows Administration Server)
Run the klbackup utility, and then restore a backup by using the Restore or back up Administration Server certificate only option.
- By using the command prompt (for Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky Security Center Linux Administration Servers version 15.1 or later)
Run the klbackup utility with the
-cert_onlykey from the command line, to restore a backup copy of the Administration Server certificate and private key:klbackup -path <path to the backup copy of Administration Server certificate> -restore -cert_only
- By using the klbackup utility interface (only for Kaspersky Security Center Windows Administration Server)
Managed devices are put under the management of another Administration Server. You can go to this Administration Server and ensure that managed devices are visible in the network, and that Network Agent is installed and running on them (the Yes value in the Visible, Network Agent is installed, and Network Agent is running columns).
Page top
Backup and restoring Administration Server data when using MySQL or MariaDB
You can use a data backup to migrate Administration Server data from Kaspersky Security Center Windows under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux. Migration by using Administration Server data backup is supported only for migration to Kaspersky Security Center Linux 15.2 or later from any supported version of Kaspersky Security Center Windows.
If you use MySQL or MariaDB as a DBMS for Kaspersky Security Center Windows and for Kaspersky Security Center Linux, the lower_case_table_names parameter must match for the current and new DBMSs. Otherwise, Administration Server data will be migrated incorrectly.
Before you backup Administration Server data on Kaspersky Security Center Windows, check the lower_case_table_names parameter value. If you do not specify this parameter during the DBMS installation earlier, the default parameter value is used. The default value of the lower_case_table_names parameter for Windows is 1.
When installing MySQL or MariaDB for Kaspersky Security Center Linux, set the lower_case_table_names parameter to the same value as specified for this parameter for Windows by using the instruction from the MySQL website. If you do not specify this parameter, the default parameter value is used. For Linux-based operating systems, the default value of the lower_case_table_names parameter is different from the default value for Windows.
If you want to install MySQL 8.0, specifying the lower_case_table_names parameter according to this instruction may not work. In this case, you must first install MySQL 5.7, specify the lower_case_table_names parameter by using the instruction, and then upgrade MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0. If the lower_case_table_names parameter does not match for the current and new DBMSs, Administration Server data will be restored incorrectly.
Optimizing backup and restoration of Administration Server data
To optimize backup and restoration of Administration Server data to reduce Administration Server downtime, do the following:
- Enable the Use file system snapshot for data backup option.
Refer to the following article for details: Using a file system snapshot to reduce the backup duration.
- Configure the following flags:
Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
- KLSRV_BKP_FILES—Splits the database file into multiple smaller files, from 2 to 32. This can speed up backup and restoration if the DBMS performance is limited by the CPU.
Example:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_BKP_FILES -t d -v 2
- KLSRV_BKP_BACKUP_EXTRA_PARS—Specifies the COMPRESSION and MAXTRANSFERSIZE parameters. This can speed up backup if the DBMS performance is limited by file input/output.
Example:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_BKP_BACKUP_EXTRA_PARS -t s -v "COMPRESSION, MAXTRANSFERSIZE = 4194304"
- KLSRV_BKP_RESTORE_EXTRA_PARS—Specifies the MAXTRANSFERSIZE parameter. This can speed up restoration if the DBMS performance is limited by file input/output.
Example:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_BKP_RESTORE_EXTRA_PARS -t s -v "MAXTRANSFERSIZE = 4194304"
- KLSRV_BKP_ONLINE_DB_BACKUP—removes Administration Server downtime during backup. Only available for the following DBMSs:
- PostgreSQL, Postgres Pro.
- SQL Server with the full recovery model. Refer to the SQL Server documentation for details. When you enable the KLSRV_BKP_ONLINE_DB_BACKUP flag, the SQL Server DBMS is automatically switched to the full recovery model.
Example:
klscflag.exe -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_BKP_ONLINE_DB_BACKUP -t d -v 1
- KLSRV_BKP_FILES—Splits the database file into multiple smaller files, from 2 to 32. This can speed up backup and restoration if the DBMS performance is limited by the CPU.
Migration to Kaspersky Security Center Linux by using Administration Server data backup
You can use a data backup to move the Kaspersky Security Center Windows Administration Server data under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux. Before the migration, make sure that necessary features of Kaspersky Security Center Windows are supported in Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
Limitations:
- Migration by using Administration Server data backup is supported only for migration to Kaspersky Security Center Linux 15.2 or later from any supported version of Kaspersky Security Center Windows.
- The DBMS type used for Kaspersky Security Center Linux must match the DBMS type in the backup from Kaspersky Security Center Windows.
The exception is when you use Microsoft SQL Server as a DBMS for Kaspersky Security Center Windows. Since Kaspersky Security Center Linux does not support Microsoft SQL Server, you can migrate Administration Server data stored in the Microsoft SQL Server database to MySQL or MariaDB.
- If you use MySQL or MariaDB as a DBMS for Kaspersky Security Center Windows and for Kaspersky Security Center Linux, the
lower_case_table_namesparameter must match for the current and new DBMSs.Before you create a data backup, check the
lower_case_table_namesparameter. Then when installing MySQL or MariaDB for Kaspersky Security Center Linux, you must set this parameter to the same value as specified for this parameter for Windows.
To migrate Administration Server data to Kaspersky Security Center Linux:
- Create an up-to-date backup copy of Administration Server data.
- For migration to the same DBMS type: use the klbackup utility or a data backup task on the device that has Administration Server installed.
- For migration of Microsoft SQL Server to MySQL or MariaDB: use the klbackup utility with the Migrate to MySQL/MariaDB format option enabled.
- On a previous device, disconnect Administration Server from the network.
- Select a new device on which to install the Administration Server. This device must meet the hardware and software requirements. Also, check that the ports used on Administration Server are available.
- Assign the same address to the new device.
The new Administration Server can be assigned the NetBIOS name, FQDN, and static IP address. It depends on which Administration Server address was set in the Network Agent installation package when Network Agents were deployed. Alternatively, you can use the connection address that determines the Administration Server to which Network Agent connects (you can obtain this address on managed devices by using the klnagchk utility).
- Select the DBMS type that provides optimum performance. Take into account the number of networked devices, network topology, and workload on the network. You can choose from one of the supported DBMSs.
- Install the DBMS according to the DBMS type selected when creating a backup. For information about how to install the selected DBMS, refer to its documentation.
A new database version must not be lower than the current one.
- Configure the DBMS for working with Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
- Install Kaspersky Security Center Linux on the new device.
- After the installation is complete, recover Administration Server data on the new device by using the klbackup utility.
- Install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
If Kaspersky Security Center Web Console was installed earlier, reinstall it with the same response file.
- Open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and connect to the Administration Server.
The data initialization process usually takes up to 15 minutes after restoring Administration Server data, but the time depends on the hardware performance and the size of Administration Server data. During this time, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console may fail to connect and display the errors.
- Check the functionality of the main Administration Server features when the data initialization in the database is complete. Verify that Administration Server synchronizes with managed devices and Administration Server data is recovered.
- Poll domain controllers to restore information about the domain structure, user accounts, security groups, and DNS names of the devices that are included in the domains.
- If necessary, uninstall the Administration Server and the database server from the previous device.
There must not be multiple Administration Servers on the same network with the same connection address and Administration Server certificate.
The administrator has access to Administration Server data and managed devices that there was access for in Kaspersky Security Center Windows, taking into account the functionality supported in Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
Page top
Moving Administration Server to another device
If you need to use Administration Server on a new device, you can move it in one of the following ways:
- Move Administration Server and the database server to a new device (the database server can be installed on the new device together with Administration Server, or on another device).
- Keep the database server on the previous device and move only Administration Server to a new device.
To move Administration Server to a new device:
- On the previous device, create a backup of Administration Server data.
To do this, you can run the data backup task through Administration Console or run the klbackup utility.
If you use SQL Server as a DBMS for Administration Server, you can migrate the data from SQL Server to MySQL or MariaDB DBMS. To do this, run the klbackup utility in interactive mode to create a data backup. Enable the Migrate to MySQL/MariaDB format option in the Backup settings window of the Backup and restore wizard. Kaspersky Security Center will create a backup compatible with MySQL and MariaDB. After that, you can restore the data from the backup into MySQL or MariaDB.
You can also enable the Migrate to Azure format option to if you want to migrate the data from SQL Server to Azure SQL DBMS.
- On the previous device, disconnect Administration Server from the network.
- Select a new device on which to install the Administration Server. Make sure that the hardware and software on the selected device meet the requirements for Administration Server, Administration Console, and Network Agent. Also, check that ports used on Administration Server are available.
- Assign the same address to the new device.
The new Administration Server can be assigned the NetBIOS name, FQDN, and static IP address. It depends on which Administration Server address was set in the Network Agent installation package when Network Agents were deployed. Alternatively, you can use the connection address that determines the Administration Server to which Network Agent connects (you can obtain this address on managed devices by using the klnagchk utility).
- If needed, on another device, install the database management system (DBMS) that the Administration Server will use.
The database can be installed on the new device together with Administration Server, or on another device. Ensure that this device meets the hardware and software requirements. When you select a DBMS, consider the number of devices covered by the Administration Server.
- Run the installation of the Administration Server on the new device.
- During the Administration Server installation, configure the database server connection settings.
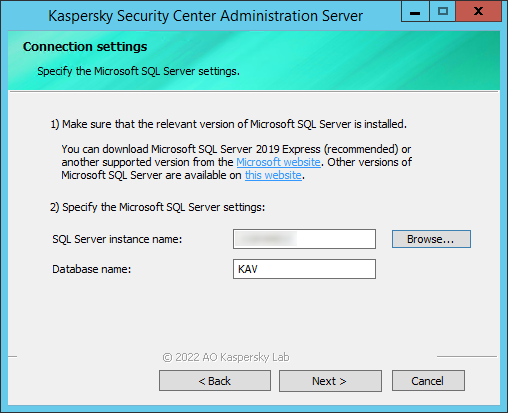
Example of the Connection settings window for Microsoft SQL Server
Depending on where you need to locate the database server, do one of the following:
- After the installation is complete, recover Administration Server data on the new device by using the klbackup utility.
If you use SQL Server as a DBMS on the previous and new devices, note that the version of SQL Server installed on the new device must be the same or later than the version of SQL Server installed on the previous device. Otherwise, you cannot recover Administration Server data on the new device.
- Open Administration Console and connect to the Administration Server.
- Verify that all managed devices are connected to the Administration Server.
- Uninstall the Administration Server and the database server from the previous device.
You can also use Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to move Administration Server and a database server to another device.
Avoiding conflicts between multiple Administration Servers
If you have more than one Administration Server on your network, they can see the same client devices. This may result, for example, in remote installation of the same application to one and the same device from more than one Server and other conflicts. To avoid such a situation, Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 allows you to prevent an application from being installed on a device managed by another Administration Server.
You can also use the Managed by a different Administration Server property as a criterion for the following purposes:
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 uses heuristics to determine whether a client device is managed by the Administration Server you are working with or by a different Administration Server.
Page top
Two-step verification
This section describes how you can use two-step verification to reduce the risk of unauthorized access to Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Scenario: configuring two-step verification for all users
This scenario describes how to enable two-step verification for all users and how to exclude user accounts from two-step verification. If you did not enable two-step verification for your account before you enable it for other users, the application opens the window for enabling two-step verification for your account, first. This scenario also describes how to enable two-step verification for your own account.
If you enabled two-step verification for your account, you may proceed to the stage of enabling of two-step verification for all users.
Prerequisites
Before you start:
- Make sure that your user account has the Modify object ACLs right of the General features: User permissions functional area for modifying security settings for other users' accounts.
- Make sure that the other users of Administration Server install an authenticator app on their devices.
Stages
Enabling two-step verification for all users proceeds in stages:
- Installing an authenticator app on a device
You can install any application that supports the Time-based One-time Password algorithm (TOTP), such as:
- Google Authenticator
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Bitrix24 OTP
- Yandex Key
- Avanpost Authenticator
- Aladdin 2FA
To check if Kaspersky Security Center supports the authenticator app that you want to use, enable two-step verification for all users or for a particular user.
One of the steps suggests that you specify the security code generated by the authenticator app. If it succeeds, then Kaspersky Security Center supports the selected authenticator.
We strongly do not recommend installing the authenticator app on the same device from which the connection to Administration Server is established.
- Synchronizing the authenticator app time with the time of the device on which Administration Server is installed
Ensure that the time on the device with the authenticator app and the time on the device with the Administration Server are synchronized to UTC, by using external time sources. Otherwise, failures may occur during the authentication and activation of two-step verification.
- Enabling two-step verification for your account and receiving the secret key for your account
How-to instructions:
- For MMC-based Administration Console: Enabling two-step verification for your own account
- For Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Enabling two-step verification for your own account
After you enable two-step verification for your account, you can enable two-step verification for all users.
- Enabling two-step verification for all users
Users with two-step verification enabled must use it to log in to Administration Server.
How-to instructions:
- For MMC-based Administration Console: Enabling two-step verification for all users
- For Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Enabling two-step verification for all users
- Editing the name of a security code issuer
If you have several Administration Servers with similar names, you may have to change the security code issuer names for better recognition of different Administration Servers.
How-to instructions:
- For MMC-based Administration Console: Editing the name of a security code issuer
- For Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Editing the name of a security code issuer
- Excluding user accounts for which you do not need to enable two-step verification
If required, you can exclude users from two-step verification. Users with excluded accounts do not have to use two-step verification to log in to Administration Server.
How-to instructions:
- For MMC-based Administration Console: Excluding accounts from two-step verification
- For Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Excluding accounts from two-step verification
- Configuring two-step verification for your own account
If the users are not excluded from two-step verification and two-step verification is not yet configured for their accounts, they need to configure it in the window that opens when they sign-in to Kaspersky Security Center. Otherwise, they will not be able to access the Administration Server in accordance with their rights.
How-to instructions:
- For MMC-based Administration Console: Configuring two-step verification for your own account
- For Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Configuring two-step verification for your own account
Results
Upon completion of this scenario:
- Two-step verification is enabled for your account.
- Two-step verification is enabled for all user accounts of the Administration Server, except for user accounts that were excluded.
About two-step verification
When two-step verification is enabled for an account, a single-use security code is required, in addition to the user name and password, to log in to Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. With domain authentication enabled, the user only needs to enter the single-use security code.
To use two-step verification, install an authenticator app that generates single-use security codes on the mobile device or computer. You can use any application that supports the Time-based One-time Password algorithm (TOTP), such as:
- Google Authenticator
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Bitrix24 OTP
- Yandex Key
- Avanpost Authenticator
- Aladdin 2FA
To check if Kaspersky Security Center supports the authenticator app that you want to use, enable two-step verification for all users or for a particular user.
One of the steps suggests that you specify the security code generated by the authenticator app. If it succeeds, then Kaspersky Security Center supports the selected authenticator.
We highly recommend that you save the secret key or QR code, and keep it in a safe place. This will help you to restore access to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console in case you lose access to the mobile device.
To secure the usage of Kaspersky Security Center, you can enable two-step verification for your own account and enable two-step verification for all users.
You can exclude accounts from two-step verification. This can be necessary for service accounts that cannot receive a security code for authentication.
Rules and Limitations
To be able to activate two-step verification for all users and deactivate two-step verification for particular users:
- Ensure your account has the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area.
- Enable two-step verification for your account.
To be able to deactivate two-step verification for all users:
- Ensure your account has the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area.
- Log in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console by using two-step verification.
If two-step verification is enabled for a user account on Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server version 13 or later, the user will not be able to log in to the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console versions 12, 12.1 or 12.2.
Reissuing the secret key
Any user can reissue the secret key used for two-step verification. When a user logs in to the Administration Server with the reissued secret key, the new secret key is saved for the user account. If the user enters the new secret key incorrectly, the new secret key is not saved, and the current secret key remains valid.
A security code has an identifier referred to as issuer name. The security code issuer name is used as an identifier of the Administration Server in the authenticator app. The security code issuer name has a default value that is the same as the name of the Administration Server. You can change the name of the security code issuer name. If you change the security code issuer name, you must issue a new secret key and pass it to the authenticator app.
Enabling two-step verification for your own account
Before you enable two-step verification for your account, ensure that an authenticator app is installed on the mobile device. Ensure that the time set in the authenticator app is synchronized with the time of Administration Server.
To enable two-step verification for your account:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, open the context menu of the Administration Server folder, and then select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, go to the Sections pane and select Advanced, and then Two-step verification.
- In the Two-step verification section, click the Set up button.
If two-step verification is already enabled for your account, clicking the Set up button resets the secret key so you can re-configure two-step verification.
In the two-step verification properties window that opens, the secret key is displayed.
- Enter the secret key in the authenticator app to receive one-time security code. You can specify the secret key into the authenticator app manually or scan the QR code by the authenticator app on the mobile device.
- Specify the security code generated by the authenticator app, and then click the OK button to exit the two-step verification properties window.
- Click the Apply button.
- Click the OK button.
Two-step verification is enabled for your own account.
Enabling two-step verification for all users
You can enable two-step verification for all users of Administration Server if your account has the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area and if you are authenticated by using two-step verification.
To enable two-step verification for all users:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, open the context menu of the Administration Server folder, and then select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Sections pane, select Advanced, and then Two-step verification.
- Click the Set as required button to enable two-step verification for all users.
- If you did not enable two-step verification for your account, the application opens the window for enabling two-step verification for your own account.
- Enter the secret key in the authenticator app to receive one-time security code. You can specify the secret key into the authenticator app manually or scan the QR code by the authenticator app on the mobile device to receive one-time security code.
- Specify the security code generated by the authenticator app, and then click the OK button to exit the two-step verification properties window.
- In the Two-step verification section, click the Apply button, and then click the OK button.
Two-step verification is enabled for all users. From now on, all users of Administration Server, including the users that were added after enabling this option, have to configure two-step verification for their accounts, except for the users whose accounts are excluded from two-step verification.
Disabling two-step verification for a user account
To disable two-step verification for your own account:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, open the context menu of the Administration Server folder, and then select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Sections pane, select Advanced, and then Two-step verification.
- In the Two-step verification section, click the Disable button.
- Click the Apply button.
- Click the OK button.
Two-step verification is disabled for your account.
You can disable two-step verification of other users' accounts. This provides protection in case, for example, a user loses or breaks a mobile device.
You can disable two-step verification of another user's account only if you have the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area and if you are authenticated by using two-step verification. Following the steps below, you can disable two-step verification for your own account as well.
To disable two-step verification for any user account:
- In the console tree, open the User accounts folder.
The User accounts folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder by default.
- In the workspace, double-click the user account for which you want to disable two-step verification.
For all user accounts for which two-step verification is enabled, the 2FA required column is set to Yes.
- In the Properties: <user name> window that opens, select the Two-step verification section.
- In the Two-step verification section, select the following options:
- If you want to disable two-step verification for a user account, click the Disable button.
- If you want to exclude this user account from two-step verification, select the User can pass authentication by using user name and password only option.
- Click the Apply button.
- Click the OK button.
Two-step verification for a user account is disabled.
If you want to restore access for a user that cannot log in to Administration Console by using two-step verification, disable two-step verification for this user account and select the User can pass authentication by using user name and password only option in the Two-step verification as described above. After that, log in to Administration Console under the user account for which you disabled two-step verification, and then enable verification again.
Disabling required two-step verification for all users
You can disable required two-step verification for all users of the Administration Server if you have Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area and if you are authenticated by using two-step verification.
To disable two-step verification for all users:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, open the context menu of the Administration Server folder, and then select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Sections pane, select Advanced, and then Two-step verification.
- Click the Set as optional button to disable two-step verification for all the users.
- Click the Apply button in the Two-step verification section.
- Click the OK button in the Two-step verification section.
Two-step verification is disabled for all users. Disabling two-step verification for all users does not applied to specific accounts for which two-step verification was previously enabled separately.
Excluding accounts from two-step verification
You can exclude an account from two-step verification if your account has the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area.
If a user account is excluded from two-step verification, that user can log in to Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console without using two-step verification.
Excluding accounts from two-step verification can be necessary for service accounts that cannot pass the security code during authentication.
To exclude a user account from two-step verification:
- If you want to exclude an Active Directory account, perform Active Directory polling to refresh the list of Administration Server users.
- In the console tree, open the User accounts folder.
The User accounts folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder by default.
- In the workspace, double-click the user account that you want to exclude from two-step verification
- In the Properties: <user name> window that opens, select the Two-step verification section.
- In the opened section, select the User can pass authentication by using user name and password only option.
- In the Two-step verification section, click the Apply button, and then click the OK button.
This user account is excluded from two-step verification. You can check the excluded accounts in the list of user accounts.
Editing the name of a security code issuer
You can have several identifiers (they are called issuers) for different Administration Servers. You can change the name of a security code issuer in case, for example, the Administration Server already uses a similar name of security code issuer for another Administration Server. By default, the name of a security code issuer is the same as the name of the Administration Server.
After you change the security code issuer name you have to reissue a new secret key and pass it to the authenticator app.
To specify a new name of a security code issuer:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, open the context menu of the Administration Server folder, and then select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Sections pane, select Advanced, and then Two-step verification.
- Specify a new security code issuer name in the Security code issuer field.
- Click the Apply button in the Two-step verification section.
- Click the OK button in the Two-step verification section.
A new security code issuer name is specified for the Administration Server.
Configuring two-step verification for your own account
The first time you sign in to Kaspersky Security Center after two-step verification is enabled, the window for configuring two-step verification for your own account opens.
Before you configure two-step verification for your account, ensure that an authenticator app is installed on the mobile device. Ensure that the time on the device with the authenticator app and the time on the device with the Administration Server are synchronized to UTC, by using external time sources.
To configure two-step verification for your account:
- Generate a one-time security code by using the authenticator app on the mobile device. To do this, perform one of the following actions:
- Enter the secret key in the authenticator app manually.
- Scan the QR code by using the authenticator app.
A security code will display on the mobile device.
- In the Set up two-step verification window, specify the security code generated by the authenticator app, and then click the OK button.
Two-step verification is configured for your account. You are able to access the Administration Server in accordance with your rights.
Page top
Managing administration groups
This section provides information about how to manage administration groups.
You can perform the following actions on administration groups:
- Add any number of nested groups at any level of hierarchy to administration groups.
- Add devices to administration groups.
- Change the hierarchy of administration groups by moving individual devices and entire groups to other groups.
- Remove nested groups and devices from administration groups.
- Add secondary and virtual Administration Servers to administration groups.
- Move devices from the administration groups of an Administration Server to those of another Server.
- Define which Kaspersky applications will be automatically installed on devices included in a group.
You can perform these actions only if you have the Modify permission in the Management of administration groups area for the administration groups you want to manage (or for the Administration Server to which these groups belong).
Creating administration groups
The hierarchy of administration groups is created in the main application window of Kaspersky Security Center in the Managed devices folder. Administration groups are displayed as folders in the console tree (see the figure below).
Immediately after Kaspersky Security Center installation, the Managed devices folder contains only an empty Administration Servers folder.
The user interface settings determine whether the Administration Servers folder appears in the console tree. To display this folder, on the menu bar select View → Configure interface and in the Configure interface window that opens select the Display secondary Administration Servers check box.
When creating a hierarchy of administration groups, you can add devices and virtual machines to the Managed devices folder, and add nested groups. You can add secondary and virtual Administration Servers to the Administration Servers folder.
Just like the Managed devices folder, each created group initially only contains an empty Administration Servers folder intended to work with secondary and virtual Administration Servers of this group. Information about policies and tasks for this group, and information about devices included into this group, is displayed on the tabs with corresponding names in the workspace of this group.
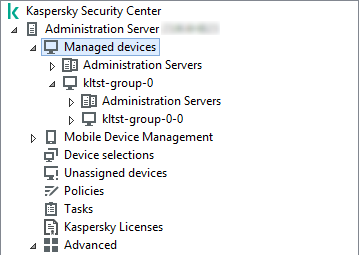
Viewing administration groups hierarchy
To create an administration group:
- In the console tree, expand the Managed devices folder.
- If you want to create a subgroup in an existing administration group, in the Managed devices folder select a subfolder corresponding to the group that is to include the new administration group.
If you create a new top-level administration group, you can skip this step.
- Start the administration group creation in one of the following ways:
- By using the New → Group command in the context menu.
- By clicking the New group button located in the workspace of the main application window, on the Devices tab.
- In the Group name window that opens, enter a name for the group and click OK.
A new administration group folder with the specified name appears in the console tree.
The application allows creating a hierarchy of administration groups based on the structure of Active Directory or the domain network's structure. Also, you can create a structure of groups from a text file.
To create a structure of administration groups:
- In the console tree, select the Managed devices folder.
- In the context menu of the Managed devices folder, select All Tasks → New group structure.
The New administration group structure wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Page top
Moving administration groups
You can move nested administration groups within the groups hierarchy.
An administration group is moved together with all nested groups, secondary Administration Servers, devices, group policies, and tasks. The system will apply to the group all the settings that correspond to its new position in the hierarchy of administration groups.
The name of the group must be unique within one level of the hierarchy. If a group with the same name already exists in the folder into which you move the administration group, you should change the name of the latter. If you have not changed the name of the moved group, an index in (<next sequence number>) format is automatically added to its name when it is moved, for example: (1), (2).
You cannot rename the Managed devices group because it is a built-in element of Administration Console.
To move a group to another folder in the console tree:
- Select a group to move in the console tree.
- Do one of the following:
- Move the group by using the context menu:
- Select Cut from the context menu of the group.
- Select Paste from the context menu of the administration group to which you want to move the selected group.
- Move the group using the main application menu:
- In the main menu, select Action → Cut.
- Select the administration group to which you have to move the selected group in the console tree.
- In the main menu, select Action → Paste.
- Move the group to another in the console tree using the mouse.
- Move the group by using the context menu:
Deleting administration groups
You can delete an administration group if it contains no secondary Administration Servers, nested groups, or client devices, and if no group tasks or policies have been created for it.
Before deleting an administration group, you must delete all secondary Administration Servers, nested groups, and client devices from that group.
To delete a group:
- Select an administration group in the console tree.
- Do one of the following:
- Select Delete from the context menu of the group.
- In the main application menu, select Action → Delete.
- Press the DELETE key.
Automatic creation of a structure of administration groups
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to create a structure of administration groups using the Groups hierarchy creation wizard.
The wizard creates a structure of administration groups based on the following data:
- Structures of Windows domains and workgroups
- Structures of Active Directory groups
- Contents of a text file created by the administrator manually
When the text file is generated, the following requirements must be met:
- The name of each new group must begin with a new line; the delimiter must begin with a line break. Blank lines are ignored.
Example:
Office 1
Office 2
Office 3
Three groups of the first hierarchy level will be created in the target group.
- The name of the nested group must be entered with a slash mark (/).
Example:
Office 1/Division 1/Department 1/Group 1
Four subgroups nested inside each other will be created in the target group.
- To create several nested groups of the same hierarchy level, you must specify the "full path to the group".
Example:
Office 1/Division 1/Department 1
Office 1/Division 2/Department 1
Office 1/Division 3/Department 1
Office 1/Division 4/Department 1
One group of the first hierarchy level Office 1 will be created in the destination group; this group will include four nested groups of the same hierarchy level: "Division 1", "Division 2", "Division 3", and "Division 4". Each of these groups will include the "Department 1" group.
Creating the hierarchy of administration groups through the wizard does not affect the network integrity: instead of existing groups being replaced, new groups are added. A client device cannot be included in an administration group a second time because the device is removed from the Unassigned devices group when it is moved to the administration group.
If, during creation of the administration group structure, a device was not included in the Unassigned devices group for some reason (it was shut down or disconnected from the network), the device will not be automatically moved to the administration group. You can add devices to administration groups manually after the wizard completes.
To launch the automatic creation of a structure of administration groups:
- Select the Managed devices folder in the console tree.
- In the context menu of the Managed devices folder, select All Tasks → New group structure.
The New administration group structure wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Page top
Automatic installation of applications on devices in an administration group
You can specify which installation packages must be used for automatic remote installation of Kaspersky applications to client devices in an administration group.
To configure automatic installation of applications on the devices in an administration group:
- In the console tree, select the required administration group.
- Open the properties window of this administration group.
- In the Sections pane, select Automatic installation, and in the workspace select the installation packages of the applications to be installed on the devices.
- Click OK.
Group tasks are created. These tasks are run on the client devices immediately after they are added to the administration group.
If some installation packages of one application are selected for automatic installation, the installation task is created for the most recent application version only.
Page top
Managing client devices
This section contains information about working with client devices.
Connecting client devices to the Administration Server
The connection of the client device to Administration Server is established by the Network Agent installed on the client device.
When a client device connects to Administration Server, the following operations are performed:
- Automatic data synchronization:
- Synchronization of the list of applications installed on the client device.
- Synchronization of policies, application settings, tasks, and task settings.
- Retrieval of up-to-date information about the condition of applications, execution of tasks, and applications' operation statistics by Administration Server.
- Delivery of the event information to Administration Server that is for processing.
Automatic data synchronization is performed regularly in accordance with the Network Agent settings (for example, every 15 minutes). You can specify the connection interval manually.
Information about an event is delivered to Administration Server as soon as it occurs.
If an Administration Server is remotely located outside a corporate network, client devices can connect to it over the internet.
For devices to connect to an Administration Server over the internet, the following conditions must be met:
- The remote Administration Server must have an external IP address and the incoming port 13000 must remain open (for connection of Network Agents). We recommend that you also open UDP port 13000 (for receiving notifications of device shut down).
- Network Agents must be installed on the devices.
- When installing Network Agent on devices, you must specify the external IP address of the remote Administration Server. If an installation package is used for installation, specify the external IP address manually in the properties of the installation package, in the Settings section.
- To use the remote Administration Server to manage applications and tasks for a device, in the properties window of the device, in the General section select the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server check box. After the check box is selected, wait until the Administration Server is synchronized with the remote device. The number of client devices maintaining a continuous connection with an Administration Server cannot exceed 300.
To speed up the performance of tasks initiated by a remote Administration Server, you can open port 15000 on a device. In this case, to run a task, the Administration Server sends a special packet to Network Agent over port 15000 without waiting until completion of synchronization with the device.
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to configure connection between a client device and Administration Server so that the connection remains active after all operations are completed. Uninterrupted connection is necessary in cases when real-time monitoring of application status is required and Administration Server is unable to establish a connection to the client for some reason (for example, connection is protected by a firewall, opening of ports on the client device is not allowed, or the client device IP address is unknown). You can establish an uninterrupted connection between a client device and Administration Server in the device properties window in the General section.
We recommend that you establish an uninterrupted connection with the most important devices. The total number of connections simultaneously maintained by the Administration Server is limited to 300.
When synchronized manually, the system uses an auxiliary connection method that allows connection initiated by Administration Server. Before establishing the connection on a client device, you must open the UDP port. Administration Server sends a connection request to the UDP port of the client device. In response, the Administration Server's certificate is verified. If the Administration Server certificate matches the certificate copy stored on the client device, the connection is established.
The manual launch of synchronization is also used for obtaining up-to-date information about the condition of applications, execution of tasks, and operation statistics of applications.
Page top
Manually connecting a client device to the Administration Server. Klmover utility
If you have to manually connect a client device to the Administration Server, you can use the klmover utility on the client device.
When Network Agent is installed on a client device, the utility is automatically copied to the Network Agent installation folder.
To manually connect a client device to the Administration Server by using the klmover utility:
On the device, start the klmover utility from the command line.
When started from the command line, the klmover utility can perform the following actions (depending on which keys are in use):
- Connects Network Agent to Administration Server with the specified settings;
- Records the operation results in the event log file or displays them on the screen.
You cannot use the klmover utility for client devices connected to Administration Server through connection gateways. For such devices you have to either reconfigure Network Agent or reinstall Network Agent and specify connection gateway.
Utility command line syntax:
klmover [-logfile <file name>] [-address <server address>] [-pn <port number>] [-ps <SSL port number>] [-nossl] [-cert <path to certificate file>] [-silent] [-dupfix] [-virtserv] [-cloningmode]
The administrator rights are required to run the utility.
Descriptions of the keys:
-logfile <file name>—Record the utility run results in a log file.By default, information is saved in the standard output stream (stdout). If the key is not in use, results and error messages are displayed on the screen.
-address <server address>—Address of the Administration Server for connection.You can specify an IP address, the NetBIOS name, or the DNS name of a device as its address.
-pn <port number>—Number of the port through which non-encrypted connection to the Administration Server is established.The default port number is 14000.
-ps <SSL port number>—Number of the SSL port through which encrypted connection to the Administration Server is established using SSL.The default port number is 13000.
-nossl—Use non-encrypted connection to the Administration Server.If the key is not in use, Network Agent is connected to Administration Server by using encrypted SSL protocol.
-cert <path to certificate file>—Use the specified certificate file for authentication of access to Administration Server.If the key is not in use, Network Agent receives a certificate at the first connection to Administration Server.
-silent—Run the utility in silent mode.Using the key may be useful if, for example, the utility is started from the logon script at the user's registration.
-dupfix—The key is used if Network Agent has been installed using a method that differs from the usual one (with the distribution package)—for example, by recovering it from an ISO disk image.-virtserv—Name of the virtual Administration Server.-cloningmode—Network Agent disk cloning mode.Use one of the following parameters to configure the disk cloning mode:
-cloningmode—Request the status of the disk cloning mode.-cloningmode 1—Enable the disk cloning mode.-cloningmode 0—Disable the disk cloning mode.
For example, to connect Network Agent to Administration Server, run the following command:
klmover -address kscserver.mycompany.com -logfile klmover.log
Tunneling the connection between a client device and the Administration Server
Kaspersky Security Center allows tunneling TCP connections from Administration Console via the Administration Server and then via Network Agent to a specified port on a managed device. Tunneling is designed for connecting a client application on a device with Administration Console installed to a TCP port on a managed device—if no direct connection is possible between Administration Console and the target device.
For example, tunneling is used for connections to a remote desktop, both for connecting to an existing session, and for creating a new remote session.
Tunneling can also be enabled by using external tools. For example, the administrator can run the putty utility, the VNC client, and other tools in this way.
Connection tunneling between a remote client device and Administration Server is required if the port used for connection to Administration Server is not available on the device. The port on the device may be unavailable in the following cases:
- The remote device is connected to a local network that uses the NAT mechanism.
- The remote device is part of the local network of Administration Server, but its port is closed by a firewall.
To tunnel the connection between a client device and Administration Server:
- In the console tree, select the folder of the group that contains the client device.
- On the Devices tab, select the device.
- In the context menu of the device, select All tasks → Connection Tunneling.
- In the Connection Tunneling window that opens, create a tunnel.
Remotely connecting to the desktop of a client device
The administrator can obtain remote access to the desktop of a client device through a Network Agent installed on the device.
Remote connection to a device through the Network Agent is possible even if the TCP and UDP ports of the client device are closed. Upon establishing the connection with the device, the administrator gains full access to information stored on this device and can manage applications installed on it.
This section describes how to establish a connection to a Windows client device and a macOS client device through the Network Agent.
Connecting to Windows client devices
Remote connection with a Windows client device can be established in one of the following ways:
- By using a standard Microsoft Windows component named Remote Desktop Connection.
Connection to a remote desktop is established through the standard Windows utility mstsc.exe in accordance with the utility's settings.
- By using the Windows Desktop Sharing technology.
Connecting to the Windows client device using Remote Desktop Connection
Connection to the current remote desktop session of the user is established without the user's knowledge. Once the administrator connects to the session, the device user is disconnected from the session without an advance notification.
To connect to the desktop of a client device through the Remote Desktop Connection component:
- In the Administration Console tree, select the device to which you need to obtain access.
- In the context menu of the device, select All tasks → Connect to device → New RDP session.
The standard Windows utility mstsc.exe starts, which helps to connect to the remote desktop.
- Follow the instructions shown in the utility's dialog boxes.
When connection to the device is established, the desktop is available in the Remote Desktop Connection window of Microsoft Windows.
Connecting to the Windows client device using Windows Desktop Sharing
When connecting to an existing session of the remote desktop, the session user on the device receives a connection request from the administrator. No information about remote activity on the device and its results will be saved in reports created by Kaspersky Security Center.
The administrator can connect to an existing session on a client device without disconnecting the user in this session. In this case, the administrator and the session user on the device share access to the desktop.
The administrator can configure an audit of user activity on a remote client device. During the audit, the application saves information about files on the client device that have been opened and/or modified by the administrator.
To connect to the desktop of a client device through Windows Desktop Sharing, the following conditions must be met:
- Microsoft Windows Vista or later is installed on the administrator's workstation. The type of operating system of the device hosting Administration Server imposes no restrictions on connection through Windows Desktop Sharing.
To check whether the Windows Desktop Sharing feature is included in your Windows edition, make sure that there is CLSID\{32BE5ED2-5C86-480F-A914-0FF8885A1B3F} key in the Windows Registry.
- Microsoft Windows Vista or later is installed on the client device.
- Kaspersky Security Center uses a license for Vulnerability and patch management.
To connect to the desktop of a client device through Windows Desktop Sharing:
- In the Administration Console tree, select the device to which you need to obtain access.
- In the context menu of the device, select All tasks → Connect to device → Windows Desktop Sharing.
- In the Select remote desktop session window that opens, select the session on the device to which you need to connect.
If connection to the device is established successfully, the desktop of the device will be available in the Kaspersky Remote Desktop Session Viewer window.
- To start interacting with the device, in the main menu of the Kaspersky Remote Desktop Session Viewer window, select Actions → Interactive mode.
The Kaspersky Remote Desktop Session Viewer utility requires a commercial license.
Page top
Connecting to macOS client devices
The administrator can use the Virtual Network Computing (VNC) system to connect to macOS devices.
Connection to a remote desktop is established through a VNC client installed on the Administration Server device. The VNC client switches the keyboard and mouse control from the client device to the administrator.
When the administrator connects to the remote desktop, the user does not receive notifications or connection requests from the administrator. The administrator connects to an existing session on the client device, without disconnecting the user from this session.
To connect to the desktop of a client macOS device through the VNC client, the following conditions must be met:
- VNC client is installed on the Administration Server device.
- Remote login and remote management are allowed on the client device.
- User has allowed the administrator access to the client device in the Sharing settings of the macOS operating system.
To connect to the desktop of a client device through the Virtual Network Computing system:
- In the Administration Console tree, select the device to which you need to obtain access.
- In the context menu of the device, select All tasks → Connection Tunneling.
- In the Connection Tunneling window that opens, do the following:
- In the 1. Network port section, specify the network port number of the device to which you need to connect.
By default, port 5900 is used.
- In the 2. Tunneling section, click the Create tunnel button.
- In the 3. Network settings section, click the Copy button.
- In the 1. Network port section, specify the network port number of the device to which you need to connect.
- Open the VNC client and paste the copied network attributes into the text field. Press Enter.
- In the window that opens, view the certificate details. If you agree to use the certificate, click the Yes button.
- In the Authentication window, specify the credentials of the client device, and then click OK.
Connecting to devices through Windows Desktop Sharing
To connect to a device through Windows Desktop Sharing:
- In the console tree, on the Devices tab, select the Managed devices folder.
The workspace of this folder displays a list of devices.
- In the context menu of the device to which you want to connect, select Connect to device → Windows Desktop Sharing.
The Select remote desktop session window opens.
- In the Select remote desktop session window, select a desktop session for connection to the device.
- Click OK.
The device is connected.
Page top
Configuring the restart of a client device
When using, installing, or removing Kaspersky Security Center, you may have to restart the device. You can specify the restart settings only for devices running Windows.
To configure the restart of a client device:
- In the console tree, select the administration group for which you have to configure the restart.
- In the workspace of the group, select the Policies tab.
- In the workspace, select a policy of Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent in the list of policies, and then select Properties in the context menu of the policy.
- In the policy properties window, select the Restart management section.
- Select the action that must be performed if a restart of the device is required:
- Select Do not restart the operating system to block automatic restart.
- Select Restart the operating system automatically if necessary to allow automatic restart.
- Select Prompt user for action to enable prompting the user to allow the restart.
You can specify the frequency of restart requests, and enable forced restart and forced closure of applications in blocked sessions on the device by selecting the corresponding check boxes and time settings in spin boxes.
- Click OK to save changes and close the policy properties window.
Restart of the device will now be configured.
Page top
Auditing actions on a remote client device
The application enables auditing of the administrator's actions on a remote client devices running Windows. During the audit, the application saves, on the device, information about files that have been opened and/or modified by the administrator. Audit of the administrator's actions is available when the following conditions are met:
- The Vulnerability and patch management license is in use.
- The administrator has the right to start shared access to the desktop of the remote device.
To enable auditing of actions on a remote client device:
- In the console tree, select the administration group for which the audit of the administrator's actions should be configured.
- In the workspace of the group, select the Policies tab.
- Select a policy of Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent, then select Properties in the context menu of the policy.
- In the policy properties window, select the Windows Desktop Sharing section.
- Select the Enable audit check box.
- In the Masks of files to monitor when read and Masks of files to monitor when modified lists, add file masks on which the application must monitor actions during the audit.
By default, the application monitors actions on files with .txt, .rtf, .doc, .xls, .docx, .xlsx, .odt, and .pdf extensions.
- Click OK to save changes and close the policy properties window.
This results in configuration of the audit of the administrator's actions on the user's remote device with shared desktop access.
Records of the administrator's actions on the remote device are logged:
- In the event log on the remote device.
- In a file with the syslog extension located in the Network Agent folder on a remote device (for example, C:\ProgramData\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1103\logs).
- In the events database of Kaspersky Security Center.
Checking the connection between a client device and the Administration Server
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to check connections between a client device and the Administration Server, automatically or manually.
Automatic check of connection is performed on Administration Server. Manual check of the connection is performed on the device.
Automatically checking the connection between a client device and the Administration Server
To start an automatic check of the connection between a client device and Administration Server:
- In the console tree, select the administration group that includes the device.
- In the workspace of the administration group, on the Devices tab, select the device.
- In the context menu of the device, select Check device accessibility.
A window opens that contains information about the accessibility of the device.
Page top
Manually checking the connection between a client device and the Administration Server. Klnagchk utility
You can check the connection, and obtain detailed information about the settings of the connection, between a client device and Administration Server by using the klnagchk utility. The klnagchk utility is located in the Network Agent installation folder.
When started from the command line, the klnagchk utility can perform the following actions (depending on the keys in use):
- Display on the screen or logs the values of the settings used for connecting Network Agent installed on the device to Administration Server.
- Record into an event log file Network Agent statistics (since its last startup) and utility operation results, or displays the information on the screen.
- Attempt to establish a connection between Network Agent and Administration Server.
If the connection attempt fails, the utility sends an ICMP packet to check the status of the device on which Administration Server is installed.
To check the connection between a client device and Administration Server by using the klnagchk utility,
On the device with Network Agent installed, start the klnagchk utility from the command line under a local administrator account.
Utility command line syntax:
klnagchk [-logfile <file name>] [-sp] [-savecert <path to certificate file>] [-restart][-sendhb]
Descriptions of the keys:
-logfile <file name>—Records in a log file with the values of the connection settings between Network Agent and Administration Server, and the utility operation results.By default, information is saved in the standard output stream (stdout). If the key is not in use, settings, results, and error messages are displayed on the screen.
-sp—Shows the password for the user's authentication on the proxy server.The key is in use if connection to the Administration Server is established through a proxy server.
-savecert <file name>—Saves the certificate used to access the Administration Server, in a specified file.-restart—Starts Network Agent after the utility has completed.-sendhb—Starts the synchronization of Network Agent with Administration Server.
After startup, the klnagchk utility accesses the configuration files of Network Agent and displays the connection parameters. These parameters are specified during the Network Agent installation and in the Network Agent policy settings:
Current device—Windows network name of the client device.Network Agent version—Full number of the Network Agent version (with patches) installed on the device.Administration Server address—Address of Administration Server.Use SSL—Parameter that indicates whether a secure connection is used when connecting to the Administration Server.Possible values:
- 0—Secure connection is not used.
- 1—Secure connection is used.
Compress traffic—Parameter that indicates whether the traffic between the client device and Administration Server is compressed.Numbers of the Administration Server SSL ports—Numbers of valid ports for communication with Administration Server when using a secure connection.Numbers of the Administration Server ports—Numbers of valid ports for communication with the Administration Server when using an ordinary connection.Use proxy server—Parameter that indicates whether a proxy server is used.Possible values:
- 0—Proxy server is not used.
- 1—Proxy server is used.
Address—Address and port of the proxy server, separated by a colon. This parameter is displayed only if a proxy server is used.User name—User name for accessing the proxy server. This parameter is displayed only if a proxy server is used.Password—Password for accessing the proxy server. This parameter is displayed only if a proxy server is used. To show the proxy server password, you need to use thespkey in the command.Administration Server certificate—Parameter that indicates whether the client device has an Administration Server certificate. A certificate may not exist, for example, if Network Agent has never successfully connected to Administration Server.Possible values:
not installed—Client device does not have an Administration Server certificate.available—Client device has an Administration Server certificate.
Open UDP port—Parameter that indicates whether Network Agent uses the UDP port to receive synchronization requests from Administration Server.Possible values:
- 0—UDP port is closed for receiving synchronization requests from Administration Server.
- 1—UDP port is opened for receiving synchronization requests from Administration Server.
Numbers of UDP ports—Numbers of UDP ports that can be used by Network Agent.Location name—Network location of the device.State of network location—Parameter that indicates whether the client device can be switched from one Administration Server connection profile to another.Possible values:
Enabled—Administration Server connection profile can be switched for the client device.Disabled—Administration Server connection profile cannot be switched for the client device.
Profile to use—Connection profile for Administration Server.Condition—IP address and subnet mask of the network to which the client device is connected.Synchronization interval (min)—Standard interval between synchronizations.Connection timeout (in seconds)—Connection timeout.Send / receive timeout (in seconds)—Connection timeout of read-write operations.Device ID—Device identifier in the network. TheDevice IDis unique among the client devices managed by a particular Administration Server.Locations of connection gateways—Parameters for connecting the client device to Administration Server through the connection gateway.Location of distribution points—Parameters for connecting the client device to Administration Server through the distribution point.Connection with server—Parameter that indicates whether the connection gateway has a continuous connection to Administration Server. The parameter shows only if the client device acts as a connection gateway.Possible values:
active—The connection gateway has a continuous connection to Administration Server.inactive—The connection gateway does not have a continuous connection to Administration Server.
Connection with server through connection gateway—Parameter that indicates whether the connection to Administration Server through a connection gateway is established correctly. The parameter shows only if the client device acts as a connection gateway.Possible values:
active—The connection to Administration Server through a connection gateway is established correctly.inactive—The connection to Administration Server through a connection gateway is established incorrectly.
Also, the klnagchk utility output can contain one of the following lines:
Administration Server is installed on this device—The klnagchk utility is run on the Administration Server device.This device has been assigned a connection gateway but is not yet registered on Administration Server—The klnagchk utility is run on the device on which Network Agent is installed, in the connection gateway mode. The configured connection gateway is waiting for a connection from Administration Server, but Administration Server does not list the device among managed devices. You need to ensure Administration Server initiates a connection to the connection gateway.This device is a connection gateway—The klnagchk utility is run on the device that acts as a connection gateway.Acts as a distribution point—The klnagchk utility is run on the device that acts as a distribution point.
The klnagchk utility checks the status of the Network Agent service. If the service is not running, the utility stops. If the service is running, the utility displays the following connection statistics:
Total number of synchronization requests—Number of attempts to connect the client device to Administration Server.The number of successful synchronization request—Number of successful attempts to connect the client device to Administration Server.Total number of synchronizations—Number of attempts to synchronize the client device settings with the Administration Server settings.The number of successful synchronizations—Number of successful attempts to synchronize the client device settings with Administration Server.Date/time of the last request for synchronization—Date and time of the last connection.
You need to use the Total number of synchronization requests and The number of successful synchronization request parameters when analyzing the connection between Administration Server and Network Agent. The client device settings synchronize with the Administration Server settings only if the Administration Server settings were changed (for example, if new tasks were added or policy settings were modified). Otherwise, the Total number of synchronizations and The number of successful synchronizations parameter values remain unchanged.
For more information on how to troubleshoot issues with connecting Network Agent to Administration Server, refer to Kaspersky Security Center FAQ.
Page top
About checking the time of connection between a device and the Administration Server
Upon shutting down a device, Network Agent notifies the Administration Server of this event. In Administration Console that device is displayed as shut down. However, Network Agent cannot notify Administration Server of all such events. The Administration Server, therefore, periodically analyzes the Connected to Administration Server attribute (the value of this attribute is displayed in Administration Console, in the device properties, in the General section) for each device and compares it against the synchronization interval from the current settings of Network Agent. If a device has not responded over more than three successive synchronization intervals, that device is marked as shut down.
Page top
Identifying client devices on the Administration Server
Client devices are identified based on their names. A device name is unique among all the names of devices connected to Administration Server.
The name of a device is relayed to Administration Server either when the Windows network is polled and a new device is discovered in it, or at the first connection of Network Agent installed on a device to Administration Server. By default, the name matches the device name in the Windows network (NetBIOS name). If a device with this name is already registered on the Administration Server, an index with the next sequence number will be added to the new device name, for example: <Name>-1, <Name>-2. Under this name, the device is added to the administration group.
Page top
Moving devices to an administration group
You can move devices from one administration group to another only if you have the Modify permission in the Management of administration groups area for both source and target administration groups (or for the Administration Server to which these groups belong).
To include one or several devices in a selected administration group:
- In the console tree, expand the Managed devices folder.
- In the Managed devices folder, select the subfolder that corresponds to the group in which the client devices will be included.
If you want to include the devices in the Managed devices group, you can skip this step.
- In the workspace of the selected administration group, on the Devices tab, start the process of including the devices in the group in one of the following ways:
- By adding the devices to the group by clicking the Move devices to group button in the information box for the list of devices
- By selecting Create → Device in the context menu of the list of devices
The Move devices wizard starts. Following its instructions, select a method for moving the devices to the group and create a list of devices to include in the group.
If you create the list of devices manually, you can use an IP address (or an IP range), a NetBIOS name, or a DNS name as the address of a device. You can manually move to the list only devices for which information has already been added to the Administration Server database upon connection of the device, or after device discovery.
To import a list of devices from a file, specify a TXT file with a list of addresses of the devices to be added. Each address must be specified in a separate line.
After the wizard completes, the selected devices are included in the administration group and are displayed in the list of devices under names generated by Administration Server.
You can move a device to the selected administration group by dragging it from the Unassigned devices folder to the folder of that administration group.
Page top
Changing the Administration Server for client devices
You can change the Administration Server that manages client devices to a different Server using the Change Administration Server task.
To change the Administration Server that manages client devices to a different Server:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- In the workspace of this folder, click the New task button.
The New task wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- At the Select the task type step of the wizard, select the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server node, expand the Advanced folder, and then select the Change Administration Server task.
- In the windows that opens, click the OK button to confirm that you agree to the terms of changing the Administration Server for client devices.
- At the Settings step of the wizard, select the Administration Server that you want to use to manage the selected devices:
- Change to another primary Administration Server
- Change to another virtual Server on this primary Server
If necessary, specify the waiting time before restarting the Network Agent.
- At this step of the wizard, select devices to which the task will be assigned:
- Select networked devices detected by Administration Server. In this case, the task is assigned to specific devices. The specific devices can include devices in administration groups as well as unassigned devices.
- Specify device addresses manually or import addresses from a list. You can specify NetBIOS names, DNS names, IP addresses, and IP subnets of devices to which you want to assign the task.
- Assign task to a device selection. In this case, the task is assigned to devices included in a selection created earlier. You can specify the predefined selection or a custom one that you created.
- Assign task to an administration group. In this case, the task is assigned to devices included in the administration group created earlier.
- At the Selecting an account to run the task step of the wizard, specify the account settings:
- At the Configure task schedule step of the wizard, you can create a schedule for task start. If necessary, specify the following settings:
- At this step of the wizard, specify the name for the task that you are creating.
- At the Finish task creation step of the wizard, click the Finish button to finish the wizard.
If you want the task to start as soon as the wizard finishes, select the Run the task after the wizard finishes check box.
After the task is completed, the client devices for which it was created are put under the management of the Administration Server specified in the task settings.
If the Administration Server supports encryption and data protection and you are creating a Change Administration Server task, a warning is displayed. The warning states that if any encrypted data is stored on devices, after the new Server begins managing the devices, users will be able to access only the encrypted data with which they previously worked. In other cases, no access to encrypted data is provided. For detailed descriptions of scenarios in which access to encrypted data is not provided, refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
Page top
Moving devices connected to Administration Server through connection gateways to another Administration Server
You can move devices connected to the Administration Server through connection gateways to another Administration Server. For example, this may be required if you install another version of Administration Server and do not want to reinstall Network Agent on the devices as it may be time consuming.
The commands described in the instruction must be run on client devices under an account with administrator rights.
To move a device connected through the connection gateway to another Administration Server:
- Run the klmover utility with the
-address <server address>parameter, to switch to the new Administration Server. - Run the
klnagchk -nagwait -tl 4command. - Run the following commands to set a new connection gateway:
klscflag -ssvset -pv klnagent -s FileTransfer -n ft_gateway_mode -sv false -svt BOOL_T -ss "|ss_type = \"SS_SETTINGS\";"klscflag -ssvset -pv klnagent -s FileTransfer -n ft_gateway_loc -sv "gateway_ip_or_name" -svt STRING_T -ss "|ss_type = \"SS_SETTINGS\";"Here
gateway_ip_or_nameis the address of the connection gateway accessible from the internet.klscflag -ssvset -pv klnagent -s FileTransfer -n ft_gateway_ssl_port -sv 13000 -svt INT_T -ss "|ss_type = \"SS_SETTINGS\";"The
13000is the number of the TCP port that the connection gateway is listening to.
- Run the
klnagchk -restart -tl 4command to start the Network Agent service.
The device is moved to the new Administration Server and connected through the new connected gateway.
Page top
Clusters and server arrays
Kaspersky Security Center supports the cluster technology. If Network Agent sends information to Administration Server confirming that an application installed on a client device is part of a server array, this client device becomes a cluster node. The cluster will be added as an individual object in the Managed devices folder of the console tree with the servers icon ( ).
).
A few typical features of a cluster can be distinguished:
- A cluster and any of its nodes are always in the same administration group.
- If the administrator attempts to move a cluster node, the node moves back to its original location.
- If the administrator attempts to move a cluster to a different group, all of its nodes move with it.
Turning on, turning off, and restarting client devices remotely
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to manage client devices remotely by turning on, shutting down, or restarting them.
To remotely manage client devices:
- Connect to the Administration Server that manages the devices.
- Create a device management task in one of the following ways:
- If you need to turn on, turn off or restart devices that are included in the selected administration group, create a task for the selected group.
- If you have to turn on, turn off or restart devices that are included in various administration groups or belong to none of them, create a task for specific devices.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard. In the Select the task type window of the New task wizard, select the Kaspersky Security Center node, open the Advanced folder, and select the Manage devices task.
- Run the created task.
After the task is completed, the command (turn on, turn off, or restart) will be executed on the selected devices.
Page top
About the usage of the continuous connection between a managed device and the Administration Server
By default, Kaspersky Security Center does not feature continuous connectivity between managed devices and the Administration Server. Network Agents on managed devices periodically establish connections and synchronize with the Administration Server. The interval between those synchronization sessions is defined in a policy of Network Agent and is 15 minutes by default. If an early synchronization is required (for example, to force the application of a policy), the Administration Server sends a signed network packet to Network Agent on port UDP 15000. (The Administration Server can send this packet over an IPv4 or IPv6 network.) If no connection through UDP is possible between the Administration Server and a managed device for any reason, synchronization runs at the next routine connection between Network Agent and the Administration Server within the synchronization interval.
However, some operations cannot be performed without an early connection between Network Agent and the Administration Server. These operation include running and stopping local tasks, receiving statistics for a managed application, and creating a tunnel. To make these operations possible, you must enable the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option on the managed device.
About forced synchronization
Although Kaspersky Security Center automatically synchronizes the status, settings, tasks, and policies for managed devices, in some cases the administrator needs to know exactly whether synchronization has already been performed for a specified device at the present moment.
In the context menu of managed devices in Administration Console, the All tasks menu item contains the Force synchronization command. When Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 executes this command, the Administration Server attempts to connect to the device. If this attempt is successful, forced synchronization will be performed. Otherwise, synchronization will be forced only after the next scheduled connection between Network Agent and the Administration Server.
About connection schedule
In the Network Agent properties window, in the Connectivity section, in the Connection schedule subsection, you can specify time intervals during which Network Agent will transmit data to the Administration Server.
Connect when necessary. If this option is selected, the connection is established when Network Agent has to send data to the Administration Server.
Connect at specified time intervals. If this option is selected, Network Agent connects to the Administration Server at a specified time. You can add several connection time periods.
Page top
Sending messages to device users
To send a message to users of devices:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- Create a message sending task for device users in one of the following ways:
- If you want to send a message to the users of devices that belong to the selected administration group, create a task for the selected group.
- If you want to send a message to the users of devices that belong to different administration groups or that do not belong to any administration groups, create a task for specific devices.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- In the task type window of the New task wizard, select the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server node, open the Advanced folder, and select the Send message to user task. The send messages to user task is available only for devices running Windows. You can also send messages in the user's context menu in the User accounts folder.
- Run the created task.
After the task is completed, the created message will be sent to the users of the selected devices. The send messages to user task is available only for devices running Windows. You can also send messages in the user's context menu in the User accounts folder.
Page top
Managing Kaspersky Security for Virtualization
Kaspersky Security Center supports the option of connection of virtual machines to the Administration Server. Virtual machines are protected by Kaspersky Security for Virtualization. For more details, please refer to the documentation for this application.
Page top
Configuring the switching of device statuses
You can change conditions to assign the Critical or Warning status to a device.
To enable changing the device status to Critical:
- Open the properties window in one of the following ways:
- In the Policies folder, in the context menu of an Administration Server policy, select Properties.
- Select Properties in the context menu of an administration group.
- In the Properties window that opens, in the Sections pane, select Device status.
- In the right pane, in the Set to Critical if these are specified section, select the check box next to a condition in the list.
You can change only settings that are not locked in the parent policy.
- Double-click the name of the selected condition, and then, in the window that opens, set the required value for the condition.
You cannot set values for the following conditions: Security application is not installed, Incompatible applications are installed, Software vulnerabilities have been detected, Mobile device settings do not comply with the policy, Unprocessed security issues detected, Device status defined by application, Device has become unmanaged, Security application is not running, License expired.
For the Restart is required condition you can specify the restart reasons. We recommend that you select the check boxes next to all the reasons from the list.
- Click OK.
When specified conditions are met, the managed device is assigned the Critical status.
To enable changing the device status to Warning:
- Open the properties window in one of the following ways:
- In the Policies folder, in the context menu of the Administration Server policy, select Properties.
- Select Properties in the context menu of the administration group.
- In the Properties window that opens, in the Sections pane select Device status.
- In the right pane, in the Set to Warning if these are specified section, select the check box next to a condition in the list.
You can change only settings that are not locked in the parent policy.
- Double-click the name of the selected condition, and then, in the window that opens, set the required value for the condition.
You cannot set values for the following conditions: Security application is not installed, Incompatible applications are installed, Software vulnerabilities have been detected, Mobile device settings do not comply with the policy, Unprocessed security issues detected, Device status defined by application, Device has become unmanaged, Security application is not running, License expired.
For the Restart is required condition you can specify the restart reasons. We recommend that you select the check boxes next to all the reasons from the list.
- Click OK.
When specified conditions are met, the managed device is assigned the Warning status.
Tagging devices and viewing assigned tags
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to tag devices. A tag is the ID of a device that can be used for grouping, describing, or finding devices. Tags assigned to devices can be used for creating selections, for finding devices, and for distributing devices among administration groups.
You can tag devices manually or automatically. Tag a device manually in the device properties; you may use manual tagging when you have to tag an individual device. Auto-tagging is performed by Administration Server in accordance with the specified tagging rules.
In the properties of an Administration Server, you can set up auto-tagging for devices managed by this Administration Server. Devices are tagged automatically when specified rules are met. An individual rule corresponds to each tag. Rules are applied to the network properties of the device, operating system, applications installed on the device, and other device properties. For example, you can set up a rule that will assign the Win tag to all devices running Windows. Then, you can use this tag when creating a device selection; this will help you sort out all devices running Windows, and assign them a task.
You can also use tags as conditions of policy profile activation on a managed device in order to apply specific policy profiles only on devices with specific tags. For example, if a device tagged as Courier appears in the Users administration group and if activation of the corresponding policy profile by the Courier tag has been enabled, then the policy created for the Users group will not be applied to this device—but the profile of the policy profile will be applied. The policy profile can allow this device to start some applications that have been blocked from running by the policy.
You can create multiple tagging rules. A single device can be assigned multiple tags if you have created multiple tagging rules and if the respective conditions of these rules are met simultaneously. You can view the list of all assigned tags in the device properties. Each tagging rule can be enabled or disabled. If a rule is enabled, it is applied to devices managed by Administration Server. If you are not using a rule currently but may need it in the future, you do not have to remove it; you can simply clear the Enable rule check box instead. In this case, the rule is disabled; it will not be executed until the Enable rule check box is selected again. You may need to disable a rule without removing it if you have to exclude the rule from the list of tagging rules temporarily and then include it again.
Automatic device tagging
You can create and edit automatic tagging rules in the Administration Server properties window.
To tag devices automatically:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the Administration Server for which you have to specify tagging rules.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, select the Tagging rules section.
- In the Tagging rules section, click the Add button.
The New rule window opens.
- In the New rule window, configure the general properties of the rule:
- Specify the rule name.
The rule name cannot be more than 255 characters long and cannot include any special characters (such as
"*<>?\:|). - Enable or disable the rule using the Enable rule check box.
By default, the Enable rule check box is selected.
- In the Tag field, enter the tag name.
The tag name cannot be more than 255 characters long and cannot include any special characters (such as
"*<>?\:|).
- Specify the rule name.
- In the Conditions section, click the Add button to add a new condition, or click the Properties button to edit an existing condition.
The New auto-tagging rule condition wizard window opens.
- In the Tag assignment condition window, select the check boxes for the conditions that must affect tagging. You can select multiple conditions.
- Depending on which tagging conditions you selected, the wizard displays the windows for setup of the corresponding conditions. Set up the triggering of the rule by the following conditions:
- Device's use or association with a specific network—Network properties of the device, such as device name in the Windows network, and device inclusion in a domain or an IP subnet.
If case sensitive collation is set for the database that you use for Kaspersky Security Center, keep case when you specify a device DNS name. Otherwise, the auto-tagging rule will not work.
- Use of Active Directory—Presence of the device in an Active Directory organizational unit and membership of the device in an Active Directory group.
- Specific applications—Presence of Network Agent on the device, operating system type, version, and architecture.
- Virtual machines—Inclusion of the device in a specific type of virtual machines.
- Application from the applications registry installed—Presence of applications of different vendors on the device.
- Device's use or association with a specific network—Network properties of the device, such as device name in the Windows network, and device inclusion in a domain or an IP subnet.
- After the condition is set up, enter a name for it, and then close the wizard.
If necessary, you can set multiple conditions for a single rule. In this case, the tag will be assigned to a device if it meets at least one condition. The conditions that you added will be displayed in the rule properties window.
- Click OK in the New rule window, then click OK in the Administration Server properties window.
The newly created rules are enforced on devices managed by the selected Administration Server. If the settings of a device meet the rule conditions, the device is assigned the tag.
Page top
Viewing and configuring tags assigned to a device
You can view the list of all tags that have been assigned to a device, as well as proceed to set up automatic tagging rules in the device properties window.
To view and set up the tags that have been assigned to a device:
- In the console tree, open the Managed devices folder.
- In the workspace of the Managed devices folder, select the device for which you want to view the assigned tags.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Properties.
- In the device properties window, select the Tags section.
A list of tags assigned to the selected device is displayed, as well as the way in which each of the tags were assigned: manually or by a rule.
- If necessary, perform one of the following actions:
- To proceed to setup of tagging rules, click the Set up auto-tagging rules link (only for Windows).
- To rename a tag, select one and click the Rename button.
- To remove a tag, select one and click the Remove button.
- To add a tag manually, enter one in the field in the lower part of the Tags section and click the Add button.
- Click the Apply button, if you have made changes to the Tags section, for your changes to take effect.
- Click OK.
If you removed or renamed a tag in the device properties, this change will not affect the tagging rules that have been set up in the Administration Server properties. The change will only apply to the device whose properties it has been made.
Page top
Remote diagnostics of client devices. Kaspersky Security Center remote diagnostics utility
The utility for remote diagnostics of Kaspersky Security Center (hereinafter referred to as the remote diagnostics utility) is designed for remote execution of the following operations on client devices:
- Enabling and disabling tracing, changing the tracing level, downloading the trace file.
- Downloading system information and application settings.
- Downloading event logs.
- Generating a dump file for an application.
- Starting diagnostics and downloading diagnostics reports.
- Starting and stopping applications.
You can use event logs and diagnostics reports downloaded from a client device to troubleshoot problems on your own. Also, a Kaspersky Technical Support specialist might ask you to download trace files, dump files, event logs, and diagnostics reports from a client device for further analysis at Kaspersky.
The remote diagnostics utility is automatically installed on the device together with Administration Console.
Connecting the remote diagnostics utility to a client device
To connect the remote diagnostics utility to a client device:
- Select any administration group in the console tree.
- In the workspace, on the Devices tab, in the context menu of any device, select Custom tools → Remote diagnostics.
The main window of the remote diagnostics utility opens.
- In the first field of the main window of the remote diagnostics utility, specify which tools you intend to use to connect to the device:
- Access using Microsoft Windows network.
- Access using Administration Server.
- If you have selected Access using Microsoft Windows network in the first field of the main utility window, perform the following actions:
- In the Device field, specify the address of the device to which you need to connect
You can use an IP address, NetBIOS name, or DNS name as the device address.
The default value is the address of the device from whose context menu the utility was started.
- Specify an account for connecting to the device:
- Connect as current user (selected by default). Connect by using the current user account.
- Use provided user name and password to connect. Connect by using a provided user account. Specify the User name and the Password of the required account.
Connection to a device is possible only under the account of the local administrator of the device.
- In the Device field, specify the address of the device to which you need to connect
- If you have selected Access using Administration Server in the first field of the main utility window, perform the following actions:
- In the Administration Server field, specify the address of the Administration Server from which you intend to connect to the device.
You can use an IP address, NetBIOS name, or DNS name as the server address.
The default value is the address of the Administration Server from which the utility has been run.
- If required, select the Use SSL, Compress traffic, and Device belongs to secondary Administration Server check boxes.
If the Device belongs to secondary Administration Server check box is selected, you can fill in the Device belongs to secondary Administration Server field with the name of the secondary Administration Server that manages the device by clicking the Browse button.
- In the Administration Server field, specify the address of the Administration Server from which you intend to connect to the device.
- To connect to the device, click the Sign in button.
You have to authorize by using two-step verification if two-step verification is enabled for your account.
This opens the window intended for remote diagnostics of the device (see the figure below). The left part of the window contains links to operations of device diagnostics. The right part of the window contains the object tree of the device with which the utility can operate. The lower part of the window displays the progress of the utility operations.
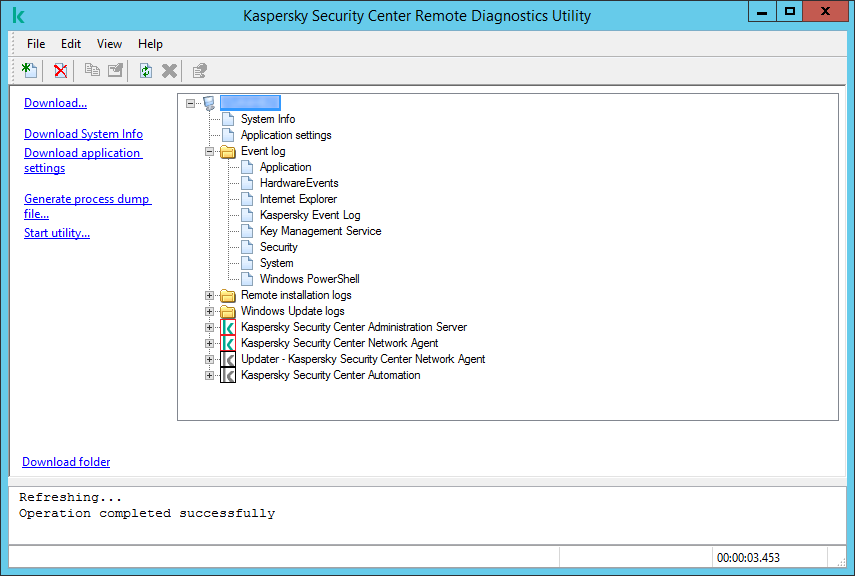
Remote diagnostics utility. Remote device diagnostics window
The remote diagnostics utility saves files downloaded from devices on the desktop of the device from which it was started.
Generating a dump file for an application
An application dump file allows you to view the parameters of the application running on a client device at a point in time. This file also contains information about modules that were loaded for an application.
Obtaining dumps from Linux-based devices is not supported.
To obtain dumps through remote diagnostics, the kldumper utility is used. This utility is designed to obtain the dumps of processes of Kaspersky applications at the request of technical support specialists. Detailed information on the requirements for using the kldumper utility is provided in the Kaspersky Security Center Knowledge Base.
To create a dump file for an application:
- In the workspace of the Managed devices folder, on the Devices tab, open the context menu of the necessary device, and then select Custom tools → Remote diagnostics.
The Kaspersky Security Center Remote Diagnostics Utility window opens.
- Connect the remote diagnostics utility to a client device.
This opens the window intended for remote diagnostics of the device.
- In the left part of the window, click the Generate process dump file link.
- In the Generating the process dump file window that opens, specify the executable file of the application for which you want to generate a dump file.
- Click the OK button.
An archive with the dump file for the specified application is downloaded.
If the specified application is not running on the client device, the "result" folder contained in the downloaded archive will be empty.
If the specified application is running, but the download fails with an error or the "result" folder contained in the downloaded archive is empty, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Knowledge Base.
Page top
Enabling and disabling tracing, downloading the trace file
To enable tracing on a remote device:
- Run the remote diagnostics utility and connect to the necessary device.
- In the objects tree of the device, select the application for which you want to enable tracing.
Tracing can be enabled and disabled for applications with self-defense only if the device is connected using Administration Server tools.
If you want to enable tracing for Network Agent, you can also do it while creating the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task. In this case, Network Agent will write the tracing information even if tracing is disabled for Network Agent in the remote diagnostics utility.
- To enable tracing:
- In the left part of the remote diagnostics utility window, click Enable tracing.
- In the Select tracing level window that opens, we recommend that you keep the default values of the settings. When required, a Technical Support specialist will guide you through the configuration process. The following settings are available:
- Tracing level
- Rotation-based tracing (available for Kaspersky Endpoint Security only)
- Click OK.
- For Kaspersky Endpoint Security, a Technical Support specialist may ask you to enable Xperf tracing for information about the system performance.
To enable Xperf tracing:
- In the left part of the remote diagnostics utility window, click Enable Xperf tracing.
- In the Select tracing level window that opens, depending on the request from the Technical Support specialist, select one of the following tracing levels:
- Select one of the following tracing types:
- You may also be asked to enable the Rotation-based tracing option to prevent excessive increase in the size of the trace file. Then specify the maximum size of the trace file. When the file reaches the maximum size, the oldest tracing information is overwritten with new information.
- Click OK.
In some cases, the security application and its task must be restarted in order to enable tracing.
The remote diagnostics utility enables tracing for the selected application.
To download a trace file of an application:
- Run the remote diagnostics utility and connect to the necessary device, as described in "Connecting the remote diagnostics utility to a client device".
- In the node of the application, in the Trace files folder, select the required file.
- In the left part of the remote diagnostics utility window, click Download entire file.
For large files the most recent trace parts can be downloaded.
You can delete the highlighted trace file. The file can be deleted after tracing is disabled.
The selected file is downloaded to the location specified in the lower part of the window.
To disable tracing on a remote device:
- Run the remote diagnostics utility and connect to the necessary device, as described in "Connecting the remote diagnostics utility to a client device".
- In the device object tree, select the application for which you want to disable tracing.
Tracing can be enabled and disabled for applications with self-defense only if the device is connected using Administration Server tools.
- In the left part of the remote diagnostics utility window, click Disable tracing.
The remote diagnostics utility disables tracing for the selected application.
Page top
Downloading application settings
To download application settings from a remote device:
- Run the remote diagnostics utility and connect to the necessary device, as described in "Connecting the remote diagnostics utility to a client device".
- In the objects tree of the remote diagnostics utility window, select the top node with the name of the device.
- In the left part of the remote diagnostics utility window, select the action you need from the following options:
- Download System Info
- Download application settings
- Generate process dump file
In the window that opens after you click this link, specify the executable file of the application for which you want to generate a dump file.
- Start utility
In the window that opens after you click this link, specify the executable file of the utility that you want to start, and its run settings.
The selected utility is downloaded and launched on the device.
Page top
Downloading event logs
To download an event log from a remote device:
- Run the remote diagnostics utility and connect to the necessary device, as described in "Connecting the remote diagnostics utility to a client device".
- In the System event logs folder of the device object tree, select the relevant log.
- Download the selected log by clicking the Download event log <Event log name> link in the left part of the remote diagnostics utility window.
The selected event log is downloaded to the location specified in the lower pane.
Page top
Downloading multiple diagnostic information items
Kaspersky Security Center remote diagnostics utility allows you to download multiple items of diagnostic information including event logs, system information, trace files, and dump files.
To download diagnostic information from a remote device:
- Run the remote diagnostics utility and connect to the necessary device, as described in "Connecting the remote diagnostics utility to a client device".
- In the left part of the remote diagnostics utility window, click Download.
- Select the check boxes next to the items that you want to download.
- Click Start.
Every selected item is downloaded to the location specified in the lower pane.
Page top
Starting diagnostics and downloading the results
To start diagnostics for an application on a remote device and download the results:
- Run the remote diagnostics utility and connect to the necessary device, as described in "Connecting the remote diagnostics utility to a client device".
- In the object tree of the device, select the necessary application.
- Start diagnostics by clicking the Run diagnostics link in the left part of the remote diagnostics utility window.
A diagnostics report appears in the node of the selected application in the object tree.
- Select the newly generated diagnostics report in the objects tree and download it by clicking the Download folder link.
The selected report is downloaded to the location specified in the lower pane.
Page top
Starting, stopping, and restarting applications
You can start, stop, and restart applications only if you have connected the device using Administration Server tools.
To start, stop, or restart an application:
- Run the remote diagnostics utility and connect to the necessary device, as described in "Connecting the remote diagnostics utility to a client device".
- In the object tree of the device, select the necessary application.
- Select an action in the left part of the remote diagnostics utility window:
- Stop application
- Restart application
- Start application
Depending on the action that you have selected, the application is started, stopped, or restarted.
Page top
UEFI protection devices
A UEFI protection device is a device with a Kaspersky solution or application for UEFI integrated at the BIOS level. Integrated protection ensures device security from the moment the system starts, while protection on devices without integrated software begins functioning only after the security application starts. Kaspersky Security Center supports management of these devices.
To modify the connection settings of UEFI protection devices:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, select Server connection settings → Additional ports.
- In the Additional ports section, modify the relevant settings:
- Click OK.
Settings of a managed device
To view the settings of a managed device:
- In the console tree, select the Managed devices folder.
- In the workspace of the folder, select a device.
- In the context menu of the device, select Properties.
The properties window of the selected device opens, with the General section selected.
General
The General section displays general information about the client device. Information is provided on the basis of data received during the last synchronization of the client device with the Administration Server:
- Name
- Description
- Windows domain
- NetBIOS name
- DNS name
- IP address
- Group
- Last updated
- Last visible
- Connected to Administration Server
- Do not disconnect from the Administration Server
Protection
The Protection section provides information about the current status of anti-virus protection on the client device:
- Device status
- All problems
- Real-time protection
- Last on-demand scan
- Total number of threats detected
- Active threats
- Disk encryption status
Applications
The Applications section lists all Kaspersky applications installed on the client device. This section contains the start button (![]() ) and stop button (
) and stop button (![]() ) that allow you to start and stop the selected Kaspersky application (excluding Network Agent). These buttons are enabled if port 15000 UDP is available on the managed device for receipt push-notifications from Administration Server. If the managed device is unavailable for push-notifications, but the mode of continuous connection to Administration Server is enabled (the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option in the General section is enabled), the start and stop buttons are available too. Also the Applications section contains the following buttons:
) that allow you to start and stop the selected Kaspersky application (excluding Network Agent). These buttons are enabled if port 15000 UDP is available on the managed device for receipt push-notifications from Administration Server. If the managed device is unavailable for push-notifications, but the mode of continuous connection to Administration Server is enabled (the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option in the General section is enabled), the start and stop buttons are available too. Also the Applications section contains the following buttons:
Tasks
In the Tasks tab, you can manage client device tasks: view the list of existing tasks, create new ones, remove, start, and stop tasks, modify their settings, and view execution results. The list of tasks is provided based on data received during the last session of client synchronization with the Administration Server. The Administration Server requests the task status details from the client device.
The start (![]() ), stop (
), stop (![]() ), and remove (
), and remove ( ) buttons are enabled if port 15000 UDP is available on the managed device for receipt push-notifications from Administration Server. If the managed device is unavailable for push-notifications, but the mode of continuous connection to Administration Server is enabled (the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option in the General section is enabled), the start, stop, and remove buttons are available too.
) buttons are enabled if port 15000 UDP is available on the managed device for receipt push-notifications from Administration Server. If the managed device is unavailable for push-notifications, but the mode of continuous connection to Administration Server is enabled (the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option in the General section is enabled), the start, stop, and remove buttons are available too.
If connection is not established, the task status is not displayed and buttons are disabled.
Events
The Events tab displays events logged on the Administration Server for the selected client device.
Tags
In the Tags tab, you can manage the list of keywords that are used for finding client devices: view the list of existing tags, assign tags from the list, configure auto-tagging rules, add new tags and rename old tags, and remove tags.
System Info
The General system info section provides information about the application installed on the client device.
Applications registry
In the Applications registry section, you can view the registry of applications installed on the client device and their updates; you can also set up the display of the applications registry.
Information about installed applications is provided if Network Agent installed on the client device sends required information to the Administration Server. You can configure sending of information to the Administration Server in the properties window of Network Agent or its policy, in the Repositories section.
Executable files
The Executable files section displays executable files found on the client device.
Hardware registry
In the Hardware registry section, you can view information about hardware installed on the client device. You can view this information for Windows devices and Linux devices.
Ensure that the lshw utility is installed on Linux devices from which you want to fetch hardware details. Hardware details fetched from virtual machines may be incomplete depending on the hypervisor used.
If Network Agent is installed on a device running Windows, it sends to the Administration Server the following information about the device hardware:
- RAM
- Mass storage devices
- Motherboard
- CPU
- Network adapters
- Monitors
- Video adapter
- Sound card
If Network Agent is installed on a device running Linux or macOS, it sends to the Administration Server the following information about the device hardware, if this information is provided by the operating system:
- Total RAM volume
- Total volume of mass storage devices
- Motherboard
- CPU
- Network adapters
Sessions
The Sessions section displays only for the Windows devices and contains information about the client device owner, as well as accounts of users who have worked on the selected client device.
Information about domain users is generated based on Active Directory data. The details of local users are provided by Windows Security Account Manager installed on the client device.
The list displays accounts of users that work on the client device.
Security issues
In the Security issues tab, you can view, edit, and create security issues for the client device. Security issues can be created either automatically, through managed Kaspersky applications installed on the client device, or manually by the administrator. For example, if some users regularly move malware from their removable drives to devices, the administrator can create a security issue. The administrator can provide a brief description of the case and recommended actions (such as disciplinary actions to be taken against a user) in the text of the security issue, and can add a link to the user or users.
A security issue for which all of the required actions have been taken is called processed. The presence of unprocessed security issues can be chosen as the condition for a change of the device status to Critical or Warning.
This section contains a list of security issues that have been created for the device. Security issues are classified by severity level and type. The type of a security issue is defined by the Kaspersky application, which creates the security issue. You can highlight processed security issues in the list by selecting the check box in the Processed column.
Software vulnerabilities
The Software vulnerabilities section provides information about vulnerabilities in third-party applications installed on client devices. You can use the search field above the list to look for vulnerabilities by name.
Available updates
This section displays a list of software updates found on this device but not installed yet.
Active policies
This section displays a list of Kaspersky application policies currently assigned to this device.
Active policy profiles
Distribution points
This section provides a list of distribution points with which the device interacts.
General policy settings
General
In the General section, you can modify the policy status and specify the inheritance of policy settings:
- In the Policy status block, you can select one of the policy modes:
- In the Settings inheritance settings group, you can configure the policy inheritance:
Event configuration
The Event configuration section allows you to configure event logging and event notification. Events are distributed by importance level on the following tabs:
- Critical
The Critical tab is not displayed in the Network Agent policy properties.
- Functional failure
- Warning
- Info
On each tab, the list shows the types of events and the default event storage term on the Administration Server (in days). Clicking the Properties button lets you specify the settings of event logging and notifications about events selected in the list. By default, common notification settings specified for the entire Administration Server are used for all event types. However, you can change specific settings for the required event types.
For example, on the Warning tab, you can configure the Security issue has occurred event type. Such events may happen, for instance, when the free disk space of a distribution point is less than 2 GB (at least 4 GB are required to install applications and download updates remotely). To configure the Security issue has occurred event, select it and click the Properties button. After that, you can specify where to store the occurred events and how to notify about them.
If Network Agent detected a security issue, you can manage this issue by using the settings of a managed device.
To select multiple event types, use the Shift or Ctrl key; to select all types, use the Select all button.
Network Agent policy settings
To configure the Network Agent policy:
- In the console tree, select the Policies folder.
- In the workspace of the folder, select the Network Agent policy.
- In the context menu of the policy, select Properties.
The properties window of the Network Agent policy opens.
See the comparison table detailing how the settings below apply, depending on the type of operating system used.
General
In the General section, you can modify the policy status and specify the inheritance of policy settings:
- In the Policy status block, you can select one of the policy modes:
- In the Settings inheritance settings group, you can configure the policy inheritance:
Event configuration
The Event configuration section allows you to configure event logging and event notification. Events are distributed by importance level on the following tabs:
- Critical
The Critical tab is not displayed in the Network Agent policy properties.
- Functional failure
- Warning
- Info
On each tab, the list shows the types of events and the default event storage term on the Administration Server (in days). Clicking the Properties button lets you specify the settings of event logging and notifications about events selected in the list. By default, common notification settings specified for the entire Administration Server are used for all event types. However, you can change specific settings for the required event types.
For example, on the Warning tab, you can configure the Security issue has occurred event type. Such events may happen, for instance, when the free disk space of a distribution point is less than 2 GB (at least 4 GB are required to install applications and download updates remotely). To configure the Security issue has occurred event, select it and click the Properties button. After that, you can specify where to store the occurred events and how to notify about them.
If Network Agent detected a security issue, you can manage this issue by using the settings of a managed device.
To select multiple event types, use the Shift or Ctrl key; to select all types, use the Select all button.
Settings
In the Settings section, you can configure the Network Agent policy:
- Distribute files through distribution points only
- Maximum size of event queue, in MB
- Application is allowed to retrieve policy's extended data on device
- Protect Network Agent service against unauthorized removal or termination, and prevent changes to the settings
- Use uninstallation password
Repositories
In the Repositories section, you can select the types of objects whose details will be sent from Network Agent to Administration Server:
- Details of Windows Update updates
- Details of software vulnerabilities and corresponding updates
- Hardware registry details
- Details of installed applications
- Include information about patches
If modification of some settings in this section is prohibited by the Network Agent policy, you cannot modify these settings.
Software updates and vulnerabilities
In the Software updates and vulnerabilities section, you can configure search and distribution of Windows updates, as well as enable scanning of executable files for vulnerabilities:
- Use Administration Server as a WSUS server
- Under Allow users to manage installation of Windows Update updates, you can limit Windows updates that users can install on their devices manually by using Windows Update.
On devices running Windows 10, if Windows Update has already found updates for the device, the new option that you select under Allow users to manage installation of Windows Update updates will be applied only after the updates found are installed.
Select an item in the drop-down list:
- In the Windows Update search mode settings group, you can select the update search mode:
- Scan executable files for vulnerabilities when running them
Restart management
In the Restart management section, you can specify the action to be performed if the operating system of a managed device has to be restarted for correct use, installation, or uninstallation of an application:
- Do not restart the operating system
- Restart the operating system automatically if necessary
- Prompt user for action
Windows Desktop sharing
In the Windows Desktop Sharing section, you can enable and configure the audit of the administrator's actions performed on a remote device when desktop access is shared:
Manage patches and updates
In the Manage patches and updates section, you can configure download and distribution of updates, as well as installation of patches, on managed devices:
- Automatically install applicable updates and patches for components that have the Undefined status
- Download updates and anti-virus databases from Administration Server in advance (recommended)
Connectivity
The Connectivity section includes three nested subsections:
- Network
- Connection profiles (only for Windows and macOS)
- Connection schedule
In the Network subsection, you can configure the connection to Administration Server, enable the use of a UDP port, and specify its number. The following options are available:
- In the Connection to Administration Server settings group, you can configure connection to the Administration Server and specify the time interval for synchronization between client devices and the Administration Server:
- Use UDP port
- UDP port number
- Use distribution point to force connection to the Administration Server
In the Connection profiles subsection, you can specify the network location settings, configure connection profiles for Administration Server, and enable out-of-office mode when Administration Server is not available.
- Network location settings
- Administration Server connection profiles
- Enable out-of-office mode when Administration Server is not available
In the Connection schedule subsection, you can specify the time intervals during which Network Agent sends data to the Administration Server:
Distribution points
The Distribution points section includes four nested subsections:
- Network polling
- Internet connection settings
- KSN Proxy
- Updates
In the Network polling subsection, you can configure automatic polling of the network. You can enable three types of polling, that is, network polling, IP range polling, and Active Directory polling:
- Enable network polling
- Enable IP range polling
- Use Zeroconf polling (on Linux platforms only; manually specified IP ranges will be ignored)
- Enable Active Directory polling
In the Internet connection settings subsection, you can specify the internet access settings:
- Use proxy server
- Proxy server address
- Port number
- Bypass proxy server for local addresses
- Proxy server authentication
- User name
- Password
In the KSN Proxy subsection, you can configure the application to use the distribution point to forward KSN requests from the managed devices:
- Enable KSN Proxy on the distribution point side
- Forward KSN requests to Administration Server
- Access KSN Cloud/KPSN directly over the internet
- TCP port
- Use UDP port
In the Updates subsection, you can specify whether Network Agent should download diff files by enabling or disabling the Download diff files option. (By default, this option is enabled.)
Revision history
On the Revision history tab, you can view the history of Network Agent policy revisions. You can compare revisions, view revisions, and perform advanced operations, such as save revisions to a file, roll back to a revision, and add and edit revision descriptions.
Managing user accounts
This section provides information about user accounts and roles supported by the application. This section contains instructions on how to create accounts and roles for users of Kaspersky Security Center.
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to manage user accounts and groups of accounts. The application supports two types of accounts:
- Accounts of organization employees. Administration Server retrieves data of the accounts of those users when polling the organization's network.
- Accounts of internal users. These accounts are applied when virtual Administration Servers are used. Accounts of internal users are created and used only within Kaspersky Security Center.
Working with user accounts
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to manage user accounts and groups of accounts. The application supports two types of accounts:
- Accounts of organization employees. Administration Server retrieves data of the accounts of those users when polling the organization's network.
- Accounts of internal users. These accounts are applied when virtual Administration Servers are used. Accounts of internal users are created and used only within Kaspersky Security Center.
You can view the list of user accounts in one of the following ways:
- In the console tree, go to Advanced → User accounts.
- In the console tree, go to the Managed devices → Devices tab → <device name> link → Sessions section.
The Sessions section displays user accounts with active sessions on devices running Windows.
The user account list is displayed correctly if the following requirements are met:
- Use Network Agent of the same version as the Administration Server or later.
- Active Directory polling is enabled to display the accounts of domain users.
- On managed devices running Windows, the Server (LanmanServer) service is running.
You can perform the following actions on user accounts and groups of accounts:
- Configure users' rights of access to the application features by using roles.
- Send messages to users by using email and SMS.
- View the list of the user's mobile devices.
- Issue and install certificates on the user's mobile devices.
- View the list of certificates issued to the user.
- Disable two-step verification for a user account.
Adding an account of an internal user
To add a new internal user account to Kaspersky Security Center:
- In the console tree, open the User accounts folder.
The User accounts folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder by default.
- In the workspace, click the Add user button.
- In the New user window that opens, specify the settings of the new user account:
- A user name (
 )
)Please be careful when entering the user name. You will not be able to change it after saving the changes.
- Description
- Full name
- Main email
- Main phone
- Password for the user connection to Kaspersky Security Center
The password must comply with the following rules:
- The password must be 8 to 256 characters long.
- The password must contain characters from at least three of the groups listed below:
- Uppercase letters (A-Z)
- Lowercase letters (a-z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Special characters (@ # $ % ^ & * - _ ! + = [ ] { } | : ' , . ? / \ ` ~ " ( ) ;)
- The password must not contain any whitespaces, Unicode characters, or the combination of "." and "@", when "." is placed before "@".
To see the entered password, click and hold the Show button.
The number of attempts for entering the password is limited. By default, the maximum number of allowed password entry attempts is 10. You can change the allowed number of attempts to enter a password, as described in "Changing the number of allowed password entry attempts".
If the user enters an invalid password the specified number of times, the user account is blocked for one hour. In the list of user accounts, the user icon (
 ) of a blocked account is dimmed (unavailable). You can unblock the user account only by changing the password.
) of a blocked account is dimmed (unavailable). You can unblock the user account only by changing the password. - If necessary, select the Disable account check box to prohibit the user from connecting to the application. You can disable an account, for example, if you want to create it beforehand but activate it later.
- Select the Request the password when account settings are modified check box if you want to enable an additional option to protect a user account from unauthorized modification. If this option is enabled, modifying user account settings requires authorization of the user with the Modify object ACLs right of the General features: User permissions functional area.
- A user name (
- Click OK.
The newly created user account is displayed in the workspace of the User accounts folder.
Page top
Editing an account of an internal user
To edit an internal user account in Kaspersky Security Center:
- In the console tree, open the User accounts folder.
The User accounts folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder by default.
- In the workspace, double-click the internal user account that you want to edit.
- In the Properties: <user name> window that opens, change the settings of the user account:
- Description
- Full name
- Main email
- Main phone
- Password for the user connection to Kaspersky Security Center
The password must comply with the following rules:
- The password must be 8 to 256 characters long.
- The password must contain characters from at least three of the groups listed below:
- Uppercase letters (A-Z)
- Lowercase letters (a-z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Special characters (@ # $ % ^ & * - _ ! + = [ ] { } | : ' , . ? / \ ` ~ " ( ) ;)
- The password must not contain any whitespaces, Unicode characters, or the combination of "." and "@", when "." is placed before "@".
To see the entered password, click and hold the Show button.
The number of attempts for entering the password is limited. By default, the maximum number of allowed password entry attempts is 10. You can change the allowed number of attempts to enter a password, as described in "Changing the number of allowed password entry attempts".
If the user enters an invalid password the specified number of times, the user account is blocked for one hour. In the list of user accounts, the user icon (
 ) of a blocked account is dimmed (unavailable). You can unblock the user account only by changing the password.
) of a blocked account is dimmed (unavailable). You can unblock the user account only by changing the password. - If necessary, select the Disable account check box to prohibit the user from connecting to the application. You can disable an account, for example, after an employee leaves the company.
- Select the Request the password when account settings are modified option if you want to enable an additional option to protect a user account from unauthorized modification. If this option is enabled, modifying user account settings requires authorization of the user with the Modify object ACLs right of the General features: User permissions functional area.
- Click OK.
The edited user account is displayed in the workspace of the User accounts folder.
Page top
Changing the number of allowed password entry attempts
The Kaspersky Security Center user can enter an invalid password a limited number of times. After the limit is reached, the user account is blocked for one hour.
By default, the maximum number of allowed attempts to enter a password is 10. You can change the number of allowed password entry attempts, as described in this section.
To change the number of allowed password entry attempts:
- Open the system registry of the device on which Administration Server is installed (for example, locally, using the regedit command in the Start → Run menu).
- Go to the following key:
- For 32-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\Components\34\1093\1.0.0.0\ServerFlags
- For 64-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\34\1093\1.0.0.0\ServerFlags
- For 32-bit systems:
- If the SrvSplPpcLogonAttempts value is not present, create it. The value type is DWORD.
By default, after Kaspersky Security Center is installed this value is not created.
- Specify the required number of attempts in the SrvSplPpcLogonAttempts value.
- Click OK to save the changes.
- Restart the Administration Server service.
The maximum number of allowed password entry attempts is changed.
Page top
Configuring the check of the name of an internal user for uniqueness
You can configure the check of the name of an internal user of Kaspersky Security Center for uniqueness when this name is added to the application. The check of the name of an internal user for uniqueness can only be performed on a virtual Administration Server or on the primary Administration Server for which the user account is to be created, or on all virtual Administration Servers and on the primary Administration Server. By default, the name of an internal user is checked for uniqueness on all virtual Administration Servers and on the primary Administration Server.
To enable the check of the name of an internal user for uniqueness on a virtual Administration Server or on the primary Administration Server:
- Open the system registry of the device on which Administration Server is installed (for example, locally, using the regedit command in the Start → Run menu).
- Go to the following hive:
- For 32-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\Components\34\.core\.independent\KLLIM
- For 64-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\34\.core\.independent\KLLIM
- For 32-bit systems:
- For the LP_InterUserUniqVsScope (DWORD) key, set the 00000001 value.
The default value specified for this key is 0.
- Restart the Administration Server service.
The name will only be checked for uniqueness on the virtual Administration Server on which the internal user was created, or on the primary Administration Server if the internal user was created on the primary Administration Server.
To enable the check of the name of an internal user on all virtual Administration Servers and on the primary Administration Server:
- Open the system registry of the device on which Administration Server is installed (for example, locally, using the regedit command in the Start → Run menu).
- Go to the following hive:
- For 64-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\34\.core\.independent\KLLIM
- For 32-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\Components\34\.core\.independent\KLLIM
- For 64-bit systems:
- For the LP_InterUserUniqVsScope (DWORD) key, set the 00000000 value.
The default value specified for this key is 0.
- Restart the Administration Server service.
The check of the name for uniqueness will be performed on all virtual Administration Servers and on the primary Administration Server.
Page top
Adding a security group
You can add security groups (groups of users), perform flexible configuration of groups and security group access to various application features. Security groups can be assigned names that correspond to their respective purposes. For example, the name can correspond to where users are located in the office or to the name of the company's organizational unit to which the users belong.
One user can belong to several security groups. A user account managed by a virtual Administration Server can belong only to security groups of this virtual Server and have access rights only within this virtual Server.
To add a security group:
- In the console tree select the User accounts folder.
The User accounts folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder by default.
- Click the Add security group button.
The Add security group window opens.
- In the Add security group window, in the General section specify the name of the group.
A group name cannot be more than 255 characters long and contain special symbols such as *, <, >, ?, \, :, |. The group name must be unique.
You can enter the group description in the Description entry field. Filling in the Description field is optional.
- Click OK.
The security group that you have added appears in the User accounts folder in the console tree. You can add users to the newly created group.
Page top
Adding a user to a group
To add a user to a group:
- In the console tree, select the User accounts folder.
The User accounts folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder by default.
- In the list of user accounts and groups, select the group to which you want to add the user.
- In the group properties window, select the Group users section and click the Add button.
A window with a list of users opens.
- In the list, select a user that you want to include in the group.
- Click OK.
The user is added to the group and displayed in the list of group users.
Page top
Configuring access rights to application features. Role-based access control
Kaspersky Security Center provides facilities for role-based access to the features of Kaspersky Security Center and managed Kaspersky applications.
You can configure access rights to application features for Kaspersky Security Center users in one of the following ways:
- By configuring the rights for each user or group of users individually.
- By creating standard user roles with a predefined set of rights and assigning those roles to users depending on their scope of duties.
User role (also referred to as a role) is a predefined set of access rights to the features of Kaspersky Security Center or managed Kaspersky applications. A role can be assigned to a user or a group of users.
Application of user roles is intended to simplify and shorten routine procedures of configuring users' access rights to application features. Access rights within a role are configured in accordance with the standard tasks and the users' scope of duties.
User roles can be assigned names that correspond to their respective purposes. You can create an unlimited number of roles in the application.
You can use the predefined user roles with already configured set of rights, or create new roles and configure the required rights yourself.
Access rights to application features
The table below shows the Kaspersky Security Center features with the access rights to manage the associated tasks, reports, settings, and perform the associated user actions.
To perform the user actions listed in the table, a user has to have the right specified next to the action.
Read, Write, and Execute rights are applicable to any task, report, or setting. In addition to these rights, a user has to have the Perform operations on device selections right to manage tasks, reports, or settings on device selections.
All tasks, reports, settings, and installation packages that are missing in the table belong to the General features: Basic functionality functional area.
Access rights to application features
Functional area |
Right |
User action: right required to perform the action |
Task |
Report |
Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
General features: Management of administration groups |
Write |
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Access objects regardless of their ACLs |
Read |
Get read access to all objects: Read |
None |
None |
None |
General features: Basic functionality |
|
|
|
|
None |
General features: Deleted objects |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Event processing |
|
|
None |
None |
Settings:
|
General features: Operations on Administration Server |
|
|
|
None |
None |
General features: Kaspersky software deployment |
|
Approve or decline installation of the patch: Manage Kaspersky patches |
None |
|
Installation package: "Kaspersky" |
General features: Key management |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Enforced report management |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Hierarchy of Administration Servers |
Configure hierarchy of Administration Servers |
Register, update, or delete secondary Administration Servers: Configure hierarchy of Administration Servers |
None |
None |
None |
General features: User permissions |
Modify object ACLs |
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Virtual Administration Servers |
|
|
None |
"Report on results of installation of third-party software updates" |
None |
General features: Encryption Key Management |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
Mobile device management: General |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
System management: Connectivity |
|
|
None |
"Report on device users" |
None |
System management: Hardware inventory |
|
|
None |
|
None |
System management: Network access control |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
System management: Operating system deployment |
|
|
"Create installation package upon reference device OS image" |
None |
Installation package: "OS Image" |
System management: Vulnerability and patch management
|
|
|
|
"Report on software updates" |
None |
System management: Remote installation |
|
|
None |
None |
Installation packages:
|
System management: Software inventory |
|
None |
None |
|
None |
Predefined user roles
User roles assigned to Kaspersky Security Center users provide them with sets of access rights to application features.
Users created on a virtual Server cannot be assigned a role on the Administration Server.
You can use the predefined user roles with already configured set of rights, or create new roles and configure the required rights yourself. Some of the predefined user roles available in Kaspersky Security Center can be associated with specific job positions, for example, Auditor, Security Officer, Supervisor (these roles are present in Kaspersky Security Center starting from the version 11). Access rights of these roles are pre-configured in accordance with the standard tasks and scope of duties of the associated positions. The table below shows how roles can be associated with specific job positions.
Examples of roles for specific job positions
Role |
Comment |
Auditor |
Permits all operations with all types of reports, all viewing operations, including viewing deleted objects (grants the Read and Write permissions in the Deleted objects area). Does not permit other operations. You can assign this role to a person who performs the audit of your organization. |
Supervisor |
Permits all viewing operations; does not permit other operations. You can assign this role to a security officer and other managers in charge of the IT security in your organization. |
Security Officer |
Permits all viewing operations, permits reports management; grants limited permissions in the System management: Connectivity area. You can assign this role to an officer in charge of the IT security in your organization. |
The table below shows the access rights assigned to each predefined user role.
Access rights of predefined user roles
Role |
Description |
|---|---|
Administration Server Administrator |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas:
Grants the Read and Write rights in the General features: Encryption key management functional area. |
Administration Server Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute rights in all of the following functional areas:
|
Auditor |
Permits all operations in the functional areas, in General features:
You can assign this role to a person who performs the audit of your organization. |
Installation Administrator |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas:
Grants the Read and Execute rights in the General features: Virtual Administration Servers functional area. |
Installation Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute rights in all of the following functional areas:
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security Administrator |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas:
Grants the Read and Write rights in the General features: Encryption key management functional area. |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute rights in all of the following functional areas:
|
Main Administrator |
Permits all operations in functional areas, except for the following areas, in General features:
Grants the Read and Write rights in the General features: Encryption key management functional area. |
Main Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute (where applicable) rights in all of the following functional areas:
|
Mobile Device Management Administrator |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas:
|
Mobile Device Management Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute rights in the General features: Basic functionality functional area. Grants Read and Send only information commands to mobile devices in the Mobile Device Management: General functional area. |
Security Officer |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas, in General features:
Grants the Read, Write, Execute, Save files from devices to the administrator's workstation, and Perform operations on device selections rights in the System management: Connectivity functional area. You can assign this role to an officer in charge of the IT security in your organization. |
Self Service Portal User |
Permits all operations in the Mobile Device Management: Self Service Portal functional area. This feature is not supported in Kaspersky Security Center 11 and later version. |
Supervisor |
Grants the Read right in the General features: Access objects regardless of their ACLs and General features: Enforced report management functional areas. You can assign this role to a security officer and other managers in charge of the IT security in your organization. |
Vulnerability and patch management administrator |
Permits all operations in the General features: Basic functionality and System management (including all features) functional areas. |
Vulnerability and patch management operator |
Grants the Read and Execute (where applicable) rights in the General features: Basic functionality and System management (including all features) functional areas. |
Adding a user role
To add a user role:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Sections pane select User roles and click the Add button.
The User roles section is available if the Display security settings sections option is enabled.
- In the New role properties window, configure the role:
- In the Sections, select General and specify the name of the role.
The name of a role cannot be more than 100 characters long.
- Select the Rights section, and configure the set of rights by selecting the Allow and Deny check boxes next to the application features.
If you are operating on the primary Administration Server, you can enable the Relay list of roles to secondary Administration Servers option.
- In the Sections, select General and specify the name of the role.
- Click OK.
The role is added.
User roles that have been created for Administration Server are displayed in the Administration Server properties window, in the User roles section. You can modify and delete user roles, as well as assign roles to security groups or selected users.
Page top
Assigning a role to a user or a security group
To assign a role to a user or a group of users:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, select the Security section.
The Security section is available if the Display security settings sections check box is selected in the interface settings window.
- In the Names of groups or users field, select a user or a group of users to which you want to assign a role.
If the user or the group is not contained in the field, you can add it by clicking the Add button.
When you add a user by clicking the Add button, you can select the type of user authentication (Microsoft Windows or Kaspersky Security Center). Kaspersky Security Center authentication is used for selecting the accounts of internal users that are used for working with virtual Administration Servers.
- Select the Roles tab and click the Add button.
The User roles window opens. This window displays user roles that have been created.
- In the User roles window, select a role for the security group.
- Click OK.
The role with a set of rights for working with Administration Server is assigned to the user or the security group. Roles that have been assigned are displayed on the Roles tab in the Security section of the Administration Server properties window.
Page top
Assigning permissions to users and groups
You can give users and groups permissions to use different features of Administration Server and of the Kaspersky programs for which you have management plug-ins, for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
To assign permissions to a user or a group of users:
- In the console tree, do one of the following:
- Expand the Administration Server node and select the subfolder with the name of the required Administration Server.
- Select the administration group.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server or the administration group, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window (or the administration group properties window) that opens, in the left Sections pane select Security.
The Security section is available if the Display security settings sections check box is selected in the interface settings window.
- In the Security section, in the Names of groups or users list select a user or a group.
- In the permissions list in the lower part of the workspace, on the Rights tab configure the set of rights for the user or group:
- Click the plus signs (+) to expand the nodes in the list and gain access to the permissions.
- Select the Allow and Deny check boxes next to the permissions that you want.
Example 1: Expand the Access objects regardless of their ACLs node or Deleted objects node, and select Read.
Example 2: Expand the Basic functionality node, and select Write.
- When you have configured the set of rights, click Apply.
The set of rights for the user or group of users will be configured.
The permissions of the Administration Server (or the administration group) are divided into the following areas:
- General features:
- Management of administration groups
- Access objects regardless of their ACLs
- Basic functionality
- Deleted objects
- Event processing
- Operations on Administration Server (only in the property window of Administration Server)
- Deploy Kaspersky applications
- License key management
- Enforced report management
- Hierarchy of Servers
- User rights
- Virtual Administration Servers
- Mobile Device Management:
- General
- System Management:
- Connectivity
- Hardware inventory
- Network Access Control
- Deploy operating system
- Manage vulnerabilities and patches
- Remote installation
- Software inventory
If neither Allow nor Deny is selected for a permission, then the permission is considered undefined: it is denied until it is explicitly denied or allowed for the user.
The rights of a user are the sum of the following:
- User's own rights
- Rights of all the roles assigned to this user
- Rights of all the security group to which the user belongs
- Rights of all the roles assigned to the security groups to which the user belongs
If at least one of these sets of rights has Deny for a permission, then the user is denied this permission, even if other sets allow it or leave it undefined.
Page top
Propagating user roles to secondary Administration Servers
By default, the lists of user roles of the primary and secondary Administration Servers are independent. You can configure the application to automatically propagate the user roles created on the primary Administration Server to all of the secondary Administration Servers. The user roles can also be propagated from a secondary Administration Server to its own secondary Administration Servers.
To propagate user roles from the primary Administration Server to the secondary Administration Servers:
- Open the main application window.
- Do one of the following:
- In the console tree, right-click the name of the Administration Server and select Properties in the context menu.
- If you have an active Administration Server policy, in the workspace of the Policies folder, right-click this policy and select Properties in the context menu.
- In the Administration Server properties window, or in the policy settings window, in the Sections pane select User roles.
The User roles section is available if the Display security settings sections option is enabled.
- Enable the Relay list of roles to secondary Administration Servers option.
- Click OK.
The application copies the user roles of the primary Administration Server to the secondary Administration Servers.
When the Relay list of roles to secondary Administration Servers option is enabled and the user roles are propagated, they cannot be edited or deleted on the secondary Administration Servers. When you create a new role or edit an existing one on the primary Administration Server, the changes are automatically copied to the secondary Administration Servers. When you delete a user role on the primary Administration Server, this role remains on the secondary Administration Servers afterward, but it can be edited or deleted.
The roles that are propagated to the secondary Administration Server from the primary Server are displayed with the lock icon ( ). You cannot edit these roles on the secondary Administration Server.
). You cannot edit these roles on the secondary Administration Server.
If you create a role on the primary Administration Server, and there is a role with the same name on its secondary Administration Server, the new role is copied to the secondary Administration Server with the index added to its name, for example, ~~1, ~~2 (the index can be random).
If you disable the Relay list of roles to secondary Administration Servers option, all the user roles remain on the secondary Administration Servers, but they become independent from those on the primary Administration Server. After becoming independent, the user roles on the secondary Administration Servers can be edited or deleted.
Page top
Assigning the user as a device owner
You can assign the user as a device owner to allocate a device to that user. If you have to perform some actions on the device (for example, upgrade hardware), the administrator can notify the device owner to authorize those actions.
To assign a user as the owner of a device:
- In the console tree, select the Managed devices folder.
- In the workspace of the folder, on the Devices tab, select the device for which you need to assign an owner.
- In the context menu of the device, select Properties.
- In the device properties window, select System Info → Sessions.
- Click the Assign button next to the Device owner field.
- In the User selection window, select the user to assign as the device owner and click OK.
- Click OK.
The device owner is assigned. By default, the Device owner field is filled with a value from Active Directory and is updated during every Active Directory poll. You can view the list of device owners in the Report on device owners. You can create a report using the New report template wizard.
Page top
Delivering messages to users
To send a message to a user by email:
- In the console tree, in the User accounts folder, select a user.
The User accounts folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder by default.
- In the user's context menu, select Notify by email.
- Fill in the relevant fields in the Send message to user window and click the OK button.
The message will be sent to the email address that has been specified in the user's properties.
To send an SMS message to a user:
- In the console tree, in the User accounts folder, select a user.
- In the user's context menu, select Send an SMS.
- Fill in the relevant fields in the SMS text window and click the OK button.
The message will be sent to the mobile device with the number that has been specified in the user's properties.
Page top
Viewing the list of user mobile devices
To view a list of a user's mobile devices:
- In the console tree, in the User accounts folder, select a user.
The User accounts folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder by default.
- In the context menu of the user account, select Properties.
- In the properties window of the user account, select the Mobile devices section.
In the Mobile devices section, you can view the list of the user's mobile devices and information about each of them. You can click the Export to file button to save the list of mobile devices to a file.
Page top
Installing a certificate for a user
You can install three types of certificates for a user:
- Shared certificate, which is required to identify the user's mobile device.
- Mail certificate, which is required to set up the corporate mail on the user's mobile device.
- VPN certificate, which is required to set up the virtual private network on the user's mobile device.
To issue a certificate to a user and then install it:
- In the console tree, open the User accounts folder and select a user account.
The User accounts folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder by default.
- In the context menu of the user account, select Install certificate.
The Certificate installation wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
After the Certificate installation wizard has finished, the certificate will be created and installed for the user. You can view the list of installed user certificates and export it to a file.
Page top
Viewing the list of certificates issued to a user
To view a list of all certificates issued to a user:
- In the console tree, in the User accounts folder, select a user.
The User accounts folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder by default.
- In the context menu of the user account, select Properties.
- In the properties window of the user account, select the Certificates section.
In the Certificates section, you can view the list of the user's certificates and information about each of them. You can click the Export to file button to save the list of certificates to a file.
Page top
About the administrator of a virtual Administration Server
An administrator of the enterprise network managed through a virtual Administration Server starts Kaspersky Security Center Web Console under the user account specified in this window to view the details of anti-virus protection.
If necessary, several administrator accounts can be created on a virtual Server.
Users created on a virtual Server cannot be assigned a role on the Administration Server.
The administrator of a virtual Administration Server is an internal user of Kaspersky Security Center. No data on internal users is transferred to the operating system. Kaspersky Security Center authenticates internal users.
Page top
Remote installation of operating systems and applications
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to create operating system images and deploy them on client devices on the network, as well as perform remote installation of applications by Kaspersky or other vendors.
To create images of operating systems, install the Windows ADK's deployment tools and the Windows PE add-on for the Windows ADK tools on the Administration Server. You can create an image of any version of Windows operating system that meets the requirements of the Kaspersky Security Center.
Kaspersky Security Center does not support the 64-bit versions of Windows ADK and Windows PE.
Capturing images of operating systems
Kaspersky Security Center can capture operating system images from devices and transfer those images to the Administration Server. Such images of operating systems are stored on the Administration Server in a dedicated folder. The operating system image of a reference device is captured and then created through an installation package creation task.
The functionality of operating system image capturing has the following features:
- An operating system image cannot be captured on a device on which Administration Server is installed.
- During capture of an operating system image, the sysprep.exe utility resets the settings of the reference device. If you want to restore the settings of the reference device, select the Create backup copy of the device state check box in the OS Imaging task creation wizard.
- The image capturing process provides for a restart of the reference device.
Deploying images of operating systems on new devices
You can use the images received for deployment on new networked devices on which no operating system has been installed yet. A technology named Preboot eXecution Environment (PXE) is used in this case. You select a networked device that will act as PXE server. This device must meet the following requirements:
- Network Agent must be installed on the device.
- A DHCP server cannot be active on the device because a PXE server uses the same ports as a DHCP server.
- The network segment that includes the device must not contain any other PXE servers.
The following conditions must be met to deploy an operating system:
- A network card must be mounted on the device.
- The device must be connected to the network.
- The Network boot option must be selected in BIOS when booting the device.
Deployment of an operating system is performed as follows:
- The client device establishes a connection with the PXE server during the boot up process.
- The client device boots in Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE).
Adding the device to WinPE may require configuration of the set of drivers for WinPE.
- The client device is registered on Administration Server.
- The administrator assigns the client device an installation package with an operating system image.
The administrator can add required drivers to the installation package with the operating system image. The administrator can also specify a configuration file with the operating system settings (answer file) that is to be applied during installation.
- The operating system is deployed on the client device.
The administrator can manually specify the MAC addresses of client devices that have not yet been connected, and assign them the installation package with the operating system image. When the selected client devices connect to the PXE server, the operating system is automatically installed on those devices.
Deploying images of operating systems on devices where another operating system has already been installed
Deployment of images of operating systems on client devices where another operating system has already been installed is performed through the remote installation task for specific devices.
Note that a clean install of the operating system is performed. All data will be deleted.
Installing applications by Kaspersky and other vendors
The administrator can create installation packages of any applications, including those specified by the user, and install the applications on client devices through the remote installation task.
Creating images of operating systems
Images of operating systems are created using the task of removing the operating system image of the reference device.
To create the operating system image making task:
- In the Remote installation folder of the console tree, select the Installation packages subfolder.
- Click the Create installation package button to run the New package wizard.
- In the Select installation package type window of the wizard, click the Create an installation package with the operating system image button.
- Follow the instructions of the wizard.
When the wizard finishes, an Administration Server task is created named Create installation package upon reference device OS image. You can view the task in the Tasks folder.
When the Create installation package upon reference device OS image task is complete, an installation package is created that you can use to deploy the operating system on client devices through a PXE server or the remote installation task. You can view the installation package in the Installation packages folder.
Page top
Installing images of operating systems
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to deploy WIM images of desktop and server-based Windows operating systems on devices within an organization's network.
The following methods can be used to retrieve an operating system image that would be deployable by using Kaspersky Security Center tools:
- Import from the install.wim file included in the Windows distribution package
- Capturing an image from a reference device
Two scenarios are supported for deployment of operating system images:
- Deployment on a "clean" device, that is, without any operating system installed
- Deployment on a device running Windows
Use Windows Preinstallation Environment (Windows PE) for capturing and deploying operating system images. All drivers required for proper functioning of all target devices must be added to WinPE. Generally, network adapter and storage controller drivers must be added.
The following requirements must be met in order to implement scenarios of image deployment and capture:
- Windows Automated Installation Kit (WAIK) version 2.0, or later, or Windows ADK with the Windows PE add-on for the Windows ADK must be installed on the Administration Server. If the scenario allows for installing or capturing images on Windows XP, WAIK must be installed.
- A DHCP server must be available on the network where the target device is located.
- The shared folder of the Administration Server must be open for reading from the network where the target device is located. If the shared folder is located on the Administration Server, access is required for the KlPxeUser account (this account is created automatically while running the Administration Server Installer). If the shared folder is located outside the Administration Server, access must be granted to everyone.
When selecting the operating system image to be installed, the administrator must explicitly specify the CPU architecture of the target device: x86 or x86-64.
Page top
Configuring the KSN proxy server address
By default, the connection name or IP address of the Administration Server coincides with the KSN proxy server address. If you change the connection name or IP address for the Administration Server, you have to specify the correct KSN proxy server address to prevent a loss of connection between host devices and KSN.
To configure the KSN proxy server address:
- In the console tree, go to Advanced → Remote installation → Installation packages.
- In the context menu of Installation packages, select Properties.
- In the window that opens, specify the new KSN proxy server address in the General tab.
- Click the Apply button.
From now on, the specified address is used as the KSN proxy server address. We recommend that you enable the Use KSN Proxy option to optimize traffic on the network.
Adding drivers for Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE)
To add drivers for Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE):
- In the Remote installation folder in the console tree, select the Deploy device images subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Deploy device images folder, click the Additional actions button and select Configure driver set for Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE) in the drop-down list.
The Windows Preinstallation Environment drivers window opens.
- In the Windows Preinstallation Environment drivers window click the Add button.
The Select driver window opens.
- In the Select driver window, select a driver from the list.
If the necessary driver is missing from the list, click the Add button and specify the driver name and folder of the driver distribution package in the Add driver window that opens.
You can select a folder by clicking the Browse button.
In the Add driver window, click OK.
- In the Select driver window, click OK.
The driver will be added to the Administration Server repository. When added to the repository, the driver is displayed in the Select driver window.
- In the Windows Preinstallation Environment drivers window, click OK.
The driver will be added to Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE).
Page top
Adding drivers to an installation package with an operating system image
To add drivers to an installation package with an operating system image:
- In the Remote installation folder of the console tree, select the Installation packages subfolder.
- From the context menu of an installation package with an operating system image, select Properties.
The installation package properties window opens.
- In the installation package properties window, select the Additional drivers section.
- Click the Add button in the Additional drivers section.
The Select driver window opens.
- In the Select driver window, select drivers that you want to add to the installation package with the operating system image.
You can add new drivers to the Administration Server repository by clicking the Add button in the Select driver window.
- Click OK.
Added drivers are displayed in the Additional drivers section of the properties window of the installation package with the operating system image.
Page top
Configuring sysprep.exe utility
The sysprep.exe utility is intended to prepare the device for creation of an operating system image.
To configure sysprep.exe utility:
- In the Remote installation folder of the console tree, select the Installation packages subfolder.
- From the context menu of an installation package with an operating system image, select Properties.
The installation package properties window opens.
- In the installation package properties window, select the sysprep.exe settings section.
- In the sysprep.exe settings section, specify a configuration file to be used during deployment of the operating system on the client device:
- Use default configuration file. Select this option to use the answer file generated by default during capture of the operating system image.
- Specify custom values of main settings. Select this option to specify values for settings through the user interface.
- Specify configuration file. Select this option to use a custom answer file.
- To apply the changes made, click the Apply button.
Deploying operating systems on new networked devices
To deploy an operating system on new devices that have not yet had any operating system installed:
- In the Remote installation folder in the console tree, select the Deploy device images subfolder.
Ensure that the Display Vulnerability and Patch Management option is enabled in the Configure interface window. Otherwise, the Remote installation folder is not displayed.
- Click the Additional actions button and select Manage the list of PXE servers on the network in the drop-down list.
The Properties: Deploy device images window opens, on the PXE servers section.
- In the PXE servers section, click the Add button and, in the PXE servers window that opens, select the device that will be used as PXE server.
The device that you added is displayed in the PXE servers section. The created WinPE files are transferred to the device from the Administration Server. The file transfer process usually takes 10 minutes. Once the transfer is completed, the displayed Status value changes from Getting started to Ready.
- In the PXE servers section select a PXE server and click the Properties button.
- In the properties window of the selected PXE server, on the PXE server connection settings tab configure connection between Administration Server and the PXE server.
- Boot the client device on which you want to deploy the operating system.
- In the BIOS of the client device, select the Network boot installation option.
The client device connects to the PXE server and is then displayed in the workspace of the Deploy device images folder.
- In the Actions section, click the Assign installation package link to select the installation package that will be used for the operating system installation on the selected device.
Use the DiskPart tool on the selected device to check the available disks. At the Windows PE command prompt, type
diskpartto open the DiskPart tool. Typelist diskto list the disks.After you added the device and assigned the installation package to it, the operating system deployment starts automatically on this device.
- To cancel the operating system deployment on the client device, click the Cancel OS image installation link in the Actions section.
To add devices by MAC address:
- In the Deploy device images folder, click Add device MAC address to open the New device window, and specify the MAC address of the device that you want to add.
- In the Deploy device images folder, click Import MAC addresses of devices from file to select the file containing a list of MAC addresses of all devices on which you want to deploy an operating system.
Deploying operating systems on client devices
To deploy an operating system on client devices with another operating system already installed:
- In the console tree, open the Remote installation folder and click the Deploy installation package on managed devices (workstations) link to run the Protection deployment wizard.
- In the Select installation package window of the wizard specify an installation package with an operating system image.
- Follow the instructions of the wizard.
When the wizard completes its operation, a remote installation task is created for installing the operating system on client devices. You can start or stop the task in the Tasks folder.
Page top
Creating installation packages of applications
To create an application installation package:
- In the Remote installation folder of the console tree, select the Installation packages subfolder.
- Click the Create installation package button to run the New package wizard.
- In the Select installation package type window of the wizard, click one of the following buttons:
- Create an installation package for a Kaspersky application. Select this option if you want to create an installation package for a Kaspersky application.
- Create an installation package for the specified executable file. Select this option if you want to create an installation package for a third-party application by using an executable file. Typically, the executable file is a setup file of the application.
- Select an application from the Kaspersky database to create an installation package. Select this option if you want to select the required third-party application from the Kaspersky database to create an installation package. The database is created automatically when you run the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task; the applications are displayed in the list.
- Create an installation package with the operating system image. Select this option if you have to create an installation package with an image of the operating system of a reference device.
When the wizard finishes, an Administration Server task is created with the name Create installation package upon reference device OS image. When this task is completed, an installation package is created that you can use to deploy the operating system image through a PXE server or the remote installation task.
- Follow the instructions of the wizard.
When the wizard finishes, an installation package is created that you can use to install the application on client devices. You can view the installation package by selecting Installation packages in the console tree.
Issuing a certificate for installation packages of applications
To issue a certificate for the installation package of an application:
- In the Remote installation folder of the console tree, select the Installation packages subfolder.
The Remote installation folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder by default.
- In the context menu of the Installation packages folder, select Advanced.
This opens the properties window of the Installation packages folder.
- In the properties window of the Installation packages folder, select the Sign stand-alone packages section.
- In the Sign stand-alone packages section, click the Specify button.
The Certificate window.
- In the Certificate type field, specify the public or private certificate type:
- If the PKCS #12 container value is selected, specify the certificate file and the password.
- If the X.509 certificate value is selected:
- Specify the private key file (one with the *.prk or *.pem extension).
- Specify the private key password.
- Specify the public key file (one with the *.cer extension).
- Click OK.
A certificate for the installation package of the application is issued.
Page top
Installing applications on client devices
To install an application on client devices:
- In the console tree, open the Remote installation folder and click Deploy installation package on managed devices (workstations) to run the Protection deployment wizard.
- In the Select installation package window of the wizard specify the installation package of an application that you want to install.
- Follow the instructions of the wizard.
When the wizard finishes, a remote installation task is created to install the application on client devices. You can start or stop the task in the Tasks folder.
Using the Protection deployment wizard, you can install Network Agent on client devices running Windows, Linux, and macOS.
To manage 64-bit security applications using Kaspersky Security Center on devices running Linux operating systems, you must use the 64-bit Network Agent for Linux. You can download the necessary version of Network Agent from the Technical Support website.
Before remote installation of Network Agent on a device running Linux, you have to prepare the device.
Managing object revisions
This section contains information about object revision management. Kaspersky Security Center allows you to track object modification. Every time you save changes made to an object, a revision is created. Each revision has a number.
Application objects that support revision management include:
- Administration Server properties
- Policies
- Tasks
- Administration groups
- User accounts
- Installation packages
You can perform the following actions on object revisions:
- Compare a selected revision to the current one
- Compare selected revisions
- Compare an object to a selected revision of another object of the same type
- View a selected revision
- Roll back changes made to an object to a selected revision
- Save revisions as a .txt file
In the properties window of any object that supports revision management, the Revision history section displays a list of object revisions with the following details:
- Object revision number
- Date and time the object was modified
- Name of the user who modified the object
- Action performed on the object
- Description of the revision related to the change made to the object settings
About object revisions
You can perform the following actions on object revisions:
- Compare a selected revision to the current one
- Compare selected revisions
- Compare an object to a selected revision of another object of the same type
- View a selected revision
- Roll back changes made to an object to a selected revision
- Save revisions as a .txt file
In the properties window of any object that supports revision management, the Revision history section displays a list of object revisions with the following details:
- Object revision number
- Date and time the object was modified
- Name of the user who modified the object
- Action performed on the object
- Description of the revision related to the change made to the object settings
Viewing the Revision history section
You can compare revisions of an object to the current revision, compare different revisions selected in the list, or compare a revision of an object to a revision of another object of the same type.
To view the Revision history section of an object:
- In the console tree, select one of the following objects:
- Administration Server node
- Policies folder
- Tasks folder
- Folder of an administration group
- User accounts folder
- Deleted objects folder
- Installation packages subfolder, which is nested in the Remote installation folder
- Depending on the location of the relevant object, do one of the following:
- If the object is in the Administration Server node or an administration group node, right-click the node and in the context menu select Properties.
- If the object is in the Policies, Tasks, User accounts, Deleted objects, or Installation packages folder, select the folder, and in the corresponding workspace select the object.
The object properties window opens.
- In the left Sections pane, select Revision history.
The revision history is displayed in the workspace.
Page top
Comparing object revisions
You can compare past revisions of an object to the current revision, compare different revisions selected in the list, or compare a revision of an object to a revision of another object of the same type.
To compare revisions of an object:
- Select an object and proceed to the properties window of the object.
- In the properties window, proceed to the Revision history section.
- In the workspace, in the list of object revisions select the revision for comparison.
To select more than one revision of the object, use the Shift and Ctrl keys.
- Do one of the following:
- Click the Compare split button and select one of the values in the drop-down list:
- Double-click the name of a revision, and in the revision properties window that opens click one of the following buttons:
A report in HTML format about comparison of the revisions is displayed in your default browser.
In this report, you can minimize some of the sections containing revision settings. To minimize a section with object revision settings, click the arrow icon ( ) next to the section name.
) next to the section name.
Administration Server revisions include all details of changes made, except for details from the following areas:
- Traffic section
- Tagging rules section
- Notification section
- Distribution points section
- Virus outbreak section
No information is recorded, from the Virus outbreak section, about the configuration of policy activation that occurs when a Virus outbreak event is triggered.
You can compare revisions of a deleted object to a revision of an existing object, but not the reverse: you cannot compare revisions of an existing object to a revision of a deleted object.
Page top
Setting storage term for object revisions and for deleted object information
The storage term for object revisions and for information about deleted objects is the same. The default storage term is 90 days. This is enough time for the regular audit of the program.
Only users with Modify permission in the Deleted objects area can change the storage period.
To change the storage term for object revisions and for information about deleted objects:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server for which you want to change the storage period.
- Right-click and in the context menu select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window that opens, in the Revision history repository section enter the desired storage term (the number of days).
- Click OK.
The object revisions and information about deleted objects will be stored for the number of days that you entered.
Page top
Viewing an object revision
If you need to know which modifications were made to an object over a certain period of time, you can view the revisions of this object.
To view the revisions of an object:
- Proceed to the Revision history section of the object.
- In the list of object revisions, select the revision whose settings you want to view.
- Do one of the following:
- Click the View revision button.
- Open the revision properties window by double-clicking the revision name, and then clicking the View revision button.
A report in HTML format with the settings of the selected object revision is displayed. In this report, you can minimize some of the sections with object revision settings. To minimize a section with object revision settings, click the arrow icon ( ) next to the section name.
) next to the section name.
Saving an object revision to a file
You can save an object revision as a text file, for example, in order to send it by email.
To save an object revision to a file:
- Proceed to the Revision history section of the object.
- In the list of revisions of an object, select the one whose settings you have to save.
- Click the Advanced button and select the Save to file value in the drop-down list.
The revision is now saved as a .txt file.
Page top
Rolling back changes
You can roll back changes made to an object, if necessary. For example, you may have to revert the settings of a policy to their state on a specific date.
To roll back changes made to an object:
- Proceed to the Revision history section of the object.
- In the list of object revisions, select the number of the revision to which you have to roll back changes.
- Click the Advanced button and select the Roll back value in the drop-down list.
The object is now rolled back to the selected revision. The list of object revisions displays a record of the action that was taken. The revision description displays information about the number of the revision to which you reverted the object.
Page top
Adding a revision description
You can add a description for the revision to simplify the search for revisions in the list.
To add a description for a revision:
- Proceed to the Revision history section of the object.
- In the list of object revisions, select the revision for which you need to add a description.
- Click the Description button.
- In the Object revision description window, enter some text for the revision description.
By default, the object revision description is blank.
- Click OK.
Deletion of objects
This section provides information about deleting objects and viewing information about objects after they are deleted.
You can delete objects, including the following:
- Policies
- Tasks
- Installation packages
- Virtual Administration Servers
- Users
- Security groups
- Administration groups
When you delete an object, information about it remains in the database. The storage term for information about the deleted objects is the same as the storage term for object revisions (the recommended term is 90 days). You can change the storage term only if you have the Modify permission in the Deleted objects area of rights.
About deletion of client devices
When you delete a managed device from an administration group, the application moves the device to the Unassigned devices group. After device deletion, the installed Kaspersky applications—Network Agent and any security application, for example Kaspersky Endpoint Security—remain on the device.
Kaspersky Security Center handles the devices in the Unassigned devices group according to the following rules:
- If you have configured device moving rules and a device meets the criteria of a moving rule, the device is automatically moved to an administration group according to the rule.
- The device is stored in the Unassigned devices group and automatically removed from the group according to the device retention rules.
The device retention rules do not affect the devices that have one or more drives encrypted with full disk encryption. Such devices are not deleted automatically—you can only delete them manually. If you need to delete a device with an encrypted drive, first decrypt the drive, and then delete the device.
When you delete a device with encrypted drive, the data required to decrypt the drive is also deleted. If you select the I understand the risk and want to delete the selected device(s) check box in the confirmation window that opens when you delete such devices (either from the Unassigned devices or the Managed Devices group), it means that you are aware of the subsequent data deletion.
To decrypt the drive, the following conditions must be met:
- The device is reconnected to Administration Server to restore the data required to decrypt the drive.
- The device user remembers the decryption password.
- The security application that was used to encrypt the drive, for example Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, is still installed on the device.
If the drive was encrypted by Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology, you can also try recovering data by using the FDERT Restore Utility.
When you delete a device from the Unassigned devices group manually, the application removes the device from the list. After device deletion, the installed Kaspersky applications (if any) remain on the device. Then, if the device is still visible to Administration Server and you have configured regular network polling, Kaspersky Security Center discovers the device during the network polling and adds it back to the Unassigned devices group. Therefore, it is reasonable to delete a device manually only if the device is invisible to Administration Server.
Deleting an object
You can delete objects such as policies, tasks, installation packages, internal users, and internal security groups if you have Modify permission, which is in the Basic functionality category of rights (see Assigning permissions to users and groups for more information).
To delete an object:
- In the console tree, in the workspace of the required folder select an object.
- Do one of the following:
- Right-click the object and select Delete.
- Press the DELETE key.
The object will be deleted, and the information about it will be stored in the database.
Viewing information about deleted objects
Information about deleted objects is stored in the Deleted objects folder for the same amount of time as object revisions (the recommended period is 90 days).
Only users with Read permission in the Deleted objects area of rights can view the list of deleted objects (see Assigning permissions to users and groups for more information).
To view the list of deleted objects,
In the console tree, select Deleted objects (by default, Deleted objects is a subfolder of the Advanced folder).
If you do not have Read permission in the Deleted objects area of rights, an empty list is displayed in the Deleted objects folder.
The workspace of the Deleted objects folder contains the following information about deleted objects:
- Name. The name of the object.
- Type. Object type, such as policy, task, or installation package.
- Time. Time when the object was deleted.
- User. Account name of the user who deleted the object.
To view more information about an object:
- In the console tree, select Deleted objects (by default, Deleted objects is a subfolder of the Advanced folder).
- In the Deleted objects workspace, select the object that you want.
The box for working with the selected object appears on the right side of the workspace.
- Do one of the following:
- Click the Properties link in the box.
- Right-click the object you selected in the workspace, and in the context menu select Properties.
The properties window of the object opens, displaying the following tabs:
- General
- Revision history
Deleting objects permanently from the list of deleted objects
Only users with Modify permission in the Deleted objects area of rights can delete objects permanently from the list of deleted objects (see Assigning permissions to users and groups for more information).
To delete an object from the list of deleted objects:
- In the console tree, select the node of the required Administration Server and then select the Deleted objects folder.
- In the workspace, select the object(s) that you want to delete.
- Do one of the following:
- Press the DELETE key.
- In the context menu of the object(s) that you selected, select Delete.
- In the confirmation dialog box, click Yes.
The object is deleted permanently from the list of deleted objects. All information about this object (including all its revisions) is permanently removed from the database. You cannot restore this information.
Page top
Mobile Device Management
Management of mobile device protection through Kaspersky Security Center is carried out by using the Mobile Device Management feature, which requires a dedicated license. If you are intending to manage mobile devices owned by employees in your organization, you must enable Mobile Device Management.
This section provides instructions for enabling, configuring and disabling Mobile Device Management. This section also describes how to manage mobile devices connected to Administration Server.
For details about Kaspersky Security for Mobile, see Kaspersky Security for Mobile Help.
Scenario: Mobile Device Management deployment
This section provides a scenario for configuring the Mobile Device Management feature in Kaspersky Security Center.
Prerequisites
Make sure that you have a license that grants access to the Mobile Device Management feature.
Stages
Deployment of the Mobile Device Management feature proceeds in stages:
- Preparing the ports
Make sure that port 13292 is available on the Administration Server. This port is required for connecting mobile devices. Also, you may want to make port 17100 available. This port is only required for the activation proxy server for managed mobile devices; if managed mobile devices have internet access, you do not have to make this port available.
- Enabling Mobile Device Management
You can enable Mobile Device Management when you are running the Administration Server quick start wizard or later.
- Specifying the external address of the Administration Server
You can specify the external address when you run the Administration Server quick start wizard or later. If you did not select Mobile Device Management for installation and did not specify the address in the installation wizard, specify the external address in the installation package properties.
- Adding mobile devices to the Managed devices group
Add the mobile devices to the Managed devices group so that you can manage these devices through policies. You can create a moving rule in one of the steps of the Administration Server quick start wizard. You can also create the moving rule later. If you do not create such a rule, you can add mobile devices to the Managed devices group manually.
You can add mobile devices to the Managed devices group directly, or you can create a subgroup (or multiple subgroups) for them.
At any time afterward, you can connect any new mobile device to the Administration Server using the Mobile device connection wizard.
- Creating a policy for mobile devices
To manage mobile devices, create a policy (or multiple polices) for them in the group where these devices belong. You can change the settings of this policy at any time afterward.
Results
Upon completion of the scenario, you can manage Android and iOS devices using Kaspersky Security Center. You can work with certificates of mobile devices and send commands to mobile devices.
Page top
About group policy for managing iOS MDM devices
To manage iOS MDM devices, you can use the Kaspersky Device Management for iOS management plug-in, which is included in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit. Kaspersky Device Management for iOS allows you to create group policies for specifying the configuration settings of iOS MDM devices without using iPhone Configuration Utility.
A group policy for managing iOS MDM devices provides the administrator with the following options:
- Configuring device password security settings.
- Configuring restrictions on usage of hardware features of the device and restrictions on installation and removal of mobile apps.
- Configuring restrictions on the use of pre-installed mobile apps, such as YouTube, iTunes Store, or Safari.
- Configuring restrictions on media content (such as movies and TV shows) viewed, by the region where the device is located.
- Configuring device connection to the internet through the proxy server (Global HTTP proxy).
- Configuring the account with which the user can access corporate applications and services (Single Sign-On (SSO) technology).
- Monitoring internet usage (visits to websites) on mobile devices.
- Configuring wireless networks (Wi-Fi), access points (APNs), and virtual private networks (VPNs) that use different authentication mechanisms and network protocols.
- Configuring settings of the connection to AirPlay devices for streaming photos, music, and videos.
- Configuring settings of the connection to AirPrint printers for wireless printing of documents from the device.
- Configuring synchronization with the Microsoft Exchange server and user accounts for using corporate email on devices.
- Configuring user credentials for synchronization with the LDAP directory service.
- Configuring user credentials for connecting to CalDAV and CardDAV services that give users access to corporate calendars and contact lists.
- Configuring settings of the iOS interface, such as fonts or icons for favorite websites, on the user's device.
- Adding new security certificates on devices.
- Configuring the Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) server for automatic retrieval of certificates by the device from the Certification Authority.
- Adding custom settings for working with mobile apps.
A policy for managing iOS MDM devices is special in that it is assigned to an administration group that includes iOS MDM Server (referred to as "Mobile Device Server"). All settings specified in this policy are first applied to Mobile Device Server and then to mobile devices managed by such server. In the case of a hierarchical structure of administration groups, secondary Mobile Device Servers receive the policy settings from primary Mobile Device Servers and distribute them to mobile devices.
For more details on how to use the group policy for managing iOS MDM devices in Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console, please refer to the Kaspersky Security for Mobile documentation.
Enabling Mobile Device Management
To manage mobile devices, you must enable Mobile Device Management. If you did not enable this feature in the quick start wizard, you can enable it later. Mobile Device Management requires a license.
Enabling Mobile Device Management is only available on the primary Administration Server.
To enable Mobile Device Management:
- In the console tree, select the Mobile Device Management folder.
- In the workspace of the folder, click the Enable Mobile Device Management button. This button is only available if you have not enabled Mobile Device Management before.
The Additional components page of the Administration Server quick start wizard is displayed.
- Select Enable Mobile Device Management in order to manage mobile devices.
- On the Select application activation method page, activate the application by using a key file or activation code.
Management of mobile devices will not be possible until you activate the Mobile Device Management feature.
- On the Proxy server settings to gain access to the Internet page, select the Use proxy server check box if you want to use a proxy server when connecting to the internet. When this check box is selected, the fields become available for entering settings. Specify the settings for proxy server connection.
- On the Check for updates for plug-ins and installation packages page, select one of the following options:
- Check whether plug-ins and installation packages are up to date
- Skip check
Skipping the check of updates for plug-ins may result in improper functioning of the application.
- On the Latest plug-in versions available page, download and install the latest versions of plug-ins in the language that your application version requires. Updating the plug-ins does not require a license.
After you install the plug-ins and packages, the application checks whether all plug-ins required for proper functioning of mobile devices have been installed. If outdated versions of some plug-ins are detected, the wizard prompts you to download up-to-date versions to replace the outdated ones.
- On the Mobile device connection settings page, set up the Administration Server ports.
When the wizard completes, the following changes will be made:
- The Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android policy will be created.
- The Kaspersky Device Management for iOS policy will be created.
- Ports will be opened on the Administration Server for mobile devices.
Modifying the Mobile Device Management settings
To enable support of mobile devices:
- In the console tree, select the Mobile Device Management folder.
- In the workspace of the folder, click the Connection ports for mobile devices link.
The Additional ports section of the Administration Server properties window is displayed.
- In the Additional ports section, modify the relevant settings:
- Click OK.
Disabling Mobile Device Management
Disabling Mobile Device Management is only available on the primary Administration Server.
To disable Mobile Device Management:
- In the console tree, select the Mobile Device Management folder.
- In the workspace of this folder, click the Configure additional components link.
The Additional components page of the Administration Server quick start wizard is displayed.
- Select Do not enable Mobile Device Management if you do not want to manage mobile devices any longer.
- Click OK.
Previously connected mobile devices will not be able to connect to Administration Server. The port for mobile device connection and the port for mobile device activation will be closed automatically.
Policies that were created for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android and Kaspersky Device Management for iOS will not be deleted. The certificate issuance rules will not be modified. The plug-ins that have been installed will not be removed. The moving rule for mobile devices will not be deleted.
After you re-enable Mobile Device Management on managed mobile devices, you may have to reinstall mobile apps that are required for mobile device management.
Working with commands for mobile devices
This section contains information about commands for managing mobile devices supported by Kaspersky Security Center. The section provides instructions on how to send commands to mobile devices, as well as how to view the execution statuses of commands in the command log.
Commands for mobile device management
Kaspersky Security Center supports commands for mobile device management.
Such commands are used for remote mobile device management. For example, if your mobile device is lost, you can delete corporate data from the device by using a command.
You can use commands for the following types of managed mobile devices:
- iOS MDM devices
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security (KES) devices
Each device type supports a dedicated set of commands.
Special considerations for certain commands
- For all types of devices, if the Reset to factory settings command is successfully executed, all data is deleted from the device, and the device settings are rolled back to their factory values.
- After successful execution of the Wipe corporate data command on an iOS MDM device, all installed configuration profiles, provisioning profiles, the iOS MDM profile, and applications for which the Remove together with iOS MDM profile check box has been selected are removed from the device.
- If the Wipe corporate data command is successfully executed on a KES device, all corporate data, entries in Contacts, the SMS history, the call log, the calendar, the internet connection settings, and the user accounts, except for the Google account, will be deleted from the device. For a KES device, all data from the memory card will also be deleted.
- Before sending the Locate command to a KES device, you will have to confirm that you are using this command for an authorized search for a lost device that belongs to your organization or to one of your employees. A mobile device that receives the Locate command is not locked.
List of commands for mobile devices
The following table shows sets of commands for iOS MDM devices.
Supported commands for mobile device management: iOS MDM devices
Commands |
Command execution result |
|---|---|
Lock |
The mobile device is locked. |
Unlock |
Mobile device locking with a PIN is disabled. The previously specified PIN has been reset. |
Reset to factory settings |
All data is deleted from the mobile device and the settings are rolled back to their default values. |
Wipe corporate data |
All installed configuration profiles, provisioning profiles, the iOS MDM profile, and applications for which the Remove together with iOS MDM profile check box has been selected are removed from the device. |
Synchronize device |
The mobile device data is synchronized with the Administration Server. |
Install profile |
The configuration profile is installed on the mobile device. |
Remove profile |
The configuration profile is deleted from the mobile device. |
Install provisioning profile |
The provisioning profile is installed on the mobile device. |
Remove provisioning profile |
The provisioning profile is deleted from the mobile device. |
Install app |
The app is installed on the mobile device. |
Remove app |
The app is removed from the mobile device. |
Enter redemption code |
Redemption code entered for a paid app. |
Configure roaming |
Data roaming and voice roaming enabled or disabled. |
The following table shows sets of commands for KES devices.
Supported commands for mobile device management: KES devices
Command |
Command execution result |
Lock |
The mobile device is locked. |
Unlock |
Mobile device locking with a PIN is disabled. The previously specified PIN has been reset. |
Reset to factory settings |
All data is deleted from the mobile device and the settings are rolled back to their default values. |
Wipe corporate data |
Corporate data, entries in Contacts, the SMS history, the call log, the calendar, the internet connection settings, and the user accounts (except for the Google account) have been deleted. Memory card data has been wiped. |
Synchronize device |
The mobile device data is synchronized with the Administration Server. |
Locate device |
The mobile device is located and shown on Google Maps. The mobile carrier charges a fee for sending SMS messages and for providing internet connectivity. |
Mugshot |
The mobile device is locked. The photo has been taken by the front camera of the device and saved on Administration Server. Photos can be viewed in the command log. The mobile carrier charges a fee for sending SMS messages and for providing internet connectivity. |
Alarm |
The mobile device sounds an alarm. |
Using Firebase Cloud Messaging
To ensure timely delivery of commands to KES devices managed by the Android operating system, Kaspersky Security Center uses the mechanism of push notifications. Push notifications are exchanged between KES devices and Administration Server through Firebase Cloud Messaging (hereinafter referred to as FCM). In Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console, you can specify the Firebase Cloud Messaging settings to connect KES devices to the service.
To retrieve the settings of Firebase Cloud Messaging, you must have a Google account.
To enable the use of FCM:
- In Administration Console, select the Mobile Device Management node, and the Mobile devices folder.
- In the context menu of the Mobile devices folder, select Properties.
- In the folder properties, select the Firebase Cloud Messaging settings section.
- In the Firebase project number field, specify the FCM Sender ID.
- In the Private key file (in JSON format) field, select the private key file.
At the next synchronization with Administration Server, KES devices managed by Android operating systems will be connected to Firebase Cloud Messaging.
You can edit the Firebase Cloud Messaging settings by clicking the Reset settings button.
Sending commands
To send a command to the user's mobile device:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
The folder workspace displays a list of managed mobile devices.
- Select the user's mobile device to which you need to send a command.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Show command log.
- In the Mobile device management commands window, proceed to the section with the name of the command that you need to send to the mobile device, then click the Send command button.
Depending on the command that you have selected, clicking the Send command button may open the window of advanced settings of the application. For example, when you send the command for deleting a provisioning profile from a mobile device, the application prompts you to select the provisioning profile that must be deleted from the mobile device. Define the advanced settings of the command in that window and confirm your selection. After that, the command will be sent to the mobile device.
You can click the Resend button to send the command to the user's mobile device again.
You can click the Remove from queue button to cancel execution of a command that was sent if the command has not yet been executed.
The Command log section displays commands that have been sent to the mobile device, with the respective execution statuses. Click Refresh to update the list of commands.
- Click OK to close the Mobile device management commands window.
Viewing the statuses of commands in the command log
The application saves to the command log information about all commands that have been sent to mobile devices. The command log contains information about the time and date that each command was sent to the mobile device, their respective statuses, and detailed descriptions of command execution results. For example, in case execution of a command is unsuccessful, the log displays the cause of the error. Records are stored in the command log for 30 days maximum.
Commands sent to mobile devices can have the following statuses:
- Running—The command has been sent to the mobile device.
- Completed—The command execution has successfully completed.
- Completed with error—The command execution has failed.
- Deleting—The command is being removed from the queue of commands sent to the mobile device.
- Deleted—The command has been successfully removed from the queue of commands sent to the mobile device.
- Error deleting—The command could not be removed from the queue of commands sent to the mobile device.
The application maintains a command log for each mobile device.
To view the log of commands sent to a mobile device:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
The folder workspace displays a list of managed mobile devices.
- In the list of mobile devices, select the one for which you want to view the command log.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Show command log.
The Mobile device management commands window opens. The sections of the Mobile device management commands window correspond to the commands that can be sent to the mobile device.
- Select sections containing the necessary commands and view information about how the commands are sent and executed in the Command log section.
In the Command log section, you can view the list of commands that have been sent to the mobile device and details about those commands. The Show commands filter allows you to display in the list only commands with the selected status.
Working with certificates of mobile devices
This section contains information about how to work with certificates of mobile devices.
The root certificate for mobile devices has a fixed expiration term of 700 days after its generation. The reserve certificate is generated 60 days prior to the expiration date. You can modify the time period for generating a reserve certificate with the following command:
klscflag.exe -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_AKLWNGT_MDM_CERT_CHANGE_TIMEOUT -t d -v <timeout in seconds>
The time period for generating a reserve certificate needs to be long enough for all managed mobile devices to synchronize with the Administration Server and retrieve the certificate.
The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
Manual renewal of the root certificate for mobile devices is not supported.
Starting the Certificate installation wizard
You can install the following types of certificates on a user's mobile device:
- Shared certificates for identifying the mobile device
- Mail certificates for configuring the corporate mail on the mobile device
- VPN certificate for configuring access to a virtual private network on the mobile device
To install a certificate on a user's mobile device:
- In the console tree, expand the Mobile Device Management folder and select the Certificates subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Certificates folder, click the Add certificate link to run the Certificate installation wizard.
Follow the instructions of the wizard.
After the wizard finishes, a certificate will be created and added to the list of the user's certificates; in addition, a notification will be sent to the user, providing the user with a link for downloading and installing the certificate on the mobile device. You can view the list of all certificates and export it to a file. You can delete and reissue certificates, as well as view their properties.
Step 1. Selecting certificate type
Specify the type of certificate that must be installed on the user's mobile device:
- Mobile certificate—for identifying the mobile device
- Mail certificate—for configuring the corporate mail on the mobile device
- VPN certificate—for configuring access to a virtual private network on the mobile device
Step 2. Selecting device type
This window is displayed only if you selected Mail certificate or VPN certificate as the certificate type.
Specify the type of the operating system on the device:
- iOS MDM device. Select this option if you have to install a certificate on a mobile device that is connected to the iOS MDM Server by using iOS MDM protocol.
- KES device managed by Kaspersky Security for Mobile. Select this option if you have to install a certificate on a KES device. In this case, the certificate will be used for user identification upon every connection to the Administration Server.
- KES device connected to Administration Server without user certificate authentication. Select this option if you have to install a certificate on a KES device using no certificate authentication. In this case, at the final step of the wizard, in the User notification method window the administrator must select the user authentication type used at every connection to the Administration Server.
Step 3. Selecting a user
In the list, select users, security groups, or Active Directory security groups for which you have to install the certificate.
In the User selection window, you can search for
. You can click Add to add an internal user.
Step 4. Selecting certificate source
In this window, you can select the certificate source that Administration Server will use to identify the mobile device. You can specify a certificate using one of the following methods:
- Create a certificate automatically, by means of Administration Server tools, then deliver the certificate to the device.
- Specify a certificate file that was created earlier. This method is not available if multiple users were selected at the previous step.
Select the Publish certificate check box if you have to send to a user a notification about creation of a certificate for his or her mobile device.
If the user's mobile device has already been previously authenticated using a certificate so there is no need to specify an account name and password to receive a new certificate, clear the Publish certificate check box. In this case, the User notification method window will not be displayed.
Step 5. Assigning a tag to the certificate
The Certificate tag window is displayed if iOS MDM device has been selected in the Device type.
In the drop-down list, you can assign a tag to the certificate of the user's iOS MDM device. The certificate with the assigned tag may have specific parameters set for this tag in the Kaspersky Device Management for iOS policy properties.
The drop-down list prompts you to select the Certificate template 1, Certificate template 2, or Certificate template 3 tag. You can configure the tags in the following sections:
- If Mail certificate has been selected in the Certificate type window, the tags for it can be configured in the properties of the Exchange ActiveSync account for mobile devices (Managed devices → Policies → Kaspersky Device Management for iOS policy properties > Exchange ActiveSync section → Add → Advanced).
- If VPN certificate has been selected in the Certificate type window, the tags for it can be configured in the properties of the VPN for mobile devices (Managed devices → Policies → Kaspersky Device Management for iOS policy properties → VPN section → Add → Advanced). You cannot configure the tags used for VPN certificates if the L2TP, PPTP, or IPSec (Cisco) connection type is selected for your VPN.
Step 6. Specifying certificate publishing settings
In this window, you can specify the following certificate publishing settings:
- Do not notify the user about a new certificate
- Allow the device to have multiple receipts of a single certificate (only for devices with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android installed)
Step 7. Selecting user notification method
This window is not displayed if you selected iOS MDM device as the device type or if you selected the Do not notify the user about a new certificate option.
In the User notification method window, you can configure the user notification about certificate installation on the mobile device.
In the Authentication method field, specify the user authentication type:
This field is displayed if you selected Mobile certificate in the Certificate type window or if you selected KES device connected to Administration Server without user certificate authentication as the device type.
Select the user notification option:
Step 8. Generating the certificate
At this step, the certificate is created.
You can click Finish to exit the wizard.
The certificate is generated and displayed in the list of certificates in the workspace of the Certificates folder.
Configuring certificate issuance rules
The certificates are used for the device authentication on the Administration Server. All managed mobile devices must have certificates. You can configure how the certificates are issued.
To configure certificate issuance rules:
- In the console tree, expand the Mobile Device Management folder and select the Certificates subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Certificates folder, click the Configure certificate issuance rules button to open the Certificate issuance rules window.
- Proceed to the section with the name of a certificate type:
Issuance of mobile certificates—To configure the issuance of certificates for the mobile devices.
Issuance of mail certificates—To configure the issuance of mail certificates.
Issuance of VPN certificates—To configure the issuance of VPN certificates.
- In the Issuance settings section, configure the issuance of the certificate:
- Specify the certificate term in days.
Certificates for mobile devices are limited by the root certificate's expiration date. If you specify the certificate term longer than the root certificate's expiration date, the certificate term will be automatically adjusted on generation.
- Select a certificate source (Administration Server or Certificates are specified manually).
Administration Server is selected as the default source of certificates.
- Specify a certificate template (Default template, Other template).
Configuration of templates is available if the Integration with PKI section features the integration with Public Key Infrastructure enabled.
- Specify the certificate term in days.
- In the Automatic Updates settings section, configure automatic updates of the certificate:
- In the Renew when certificate is to expire in (days) field, specify how many days before expiration the certificate must be renewed.
- To enable automatic updates of certificates, select the Reissue certificate automatically if possible check box.
- In the Password protection section, enable and configure the use of a password when decrypting certificates.
Password protection is only available for mobile certificates.
- Select the Prompt for password during certificate installation check box.
- Use the slider to define the maximum number of symbols in the password for encryption.
- Click OK.
Integration with public key infrastructure
Integration of the application with the public key infrastructure (PKI) is required to simplify the issuance of domain certificates to users. Following integration, certificates are issued automatically.
The minimum supported PKI server version is Windows Server 2008.
You have to configure the account for integration with PKI. The account must meet the following requirements:
- Be a domain user and administrator on a device that has Administration Server installed.
- Be granted the SeServiceLogonRight privilege on the device with Administration Server installed.
To create a permanent user profile, log on at least once under the configured user account on the device with Administration Server installed. In this user's certificate repository on the Administration Server device, install the Enrollment Agent certificate provided by domain administrators.
To configure integration with the public keys infrastructure:
- In the console tree, expand the Mobile Device Management folder and select the Certificates subfolder.
- In the workspace, click the Integrate with public key infrastructure button to open the Integration with PKI section of the Certificate issuance rules window.
The Integration with PKI section of the Certificate issuance rules window opens.
- Select the Integrate issuance of certificates with PKI check box.
- In the Account field, specify the name of the user account to be used for integration with the public key infrastructure.
- In the Password field, enter the domain password for the account.
- In the Certificate template name in PKI system list, select the certificate template that will be used for the issuance of certificates to domain users.
A dedicated service is run in Kaspersky Security Center under the specified user account. This service is responsible for issuing users' domain certificates. The service is run when the list of certificate templates is loaded by clicking the Refresh list button or when a certificate is generated.
- Click OK to save the settings.
Following integration, certificates are issued automatically.
Enabling support of Kerberos Constrained Delegation
The application supports usage of Kerberos Constrained Delegation.
To enable support of Kerberos Constrained Delegation:
- In the console tree, open the Mobile Device Management folder.
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile Device Servers subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Mobile Device Servers folder, select an iOS MDM Server.
- In the context menu of the iOS MDM Server, select Properties.
- In the properties window of the iOS MDM Server, select the Settings section.
- In the Settings section, select the Ensure compatibility with Kerberos constrained delegation check box.
- Click OK.
Adding iOS mobile devices to the list of managed devices
To add an iOS mobile device to the list of managed devices, a shared certificate must be delivered and installed on the device. Shared certificates are used by Administration Server for identifying mobile devices. A shared certificate for an iOS mobile device is delivered within an iOS MDM profile. After a shared certificate is delivered and installed on a mobile device, the device appears in the list of managed devices.
Kaspersky no longer supports Kaspersky Safe Browser.
You can add mobile devices of users to the list of managed devices by means of the Mobile device connection wizard.
To connect an iOS device to the Administration Server by using a shared certificate:
- Start the Mobile device connection wizard in one of the following ways:
- Use the context menu in the User accounts folder:
- In the console tree, expand the Advanced folder and select the User accounts subfolder.
- In the workspace of the User accounts folder, select the users, security groups, or Active Directory security groups whose mobile devices you want to add to the list of managed devices.
- Right-click and in the context menu of the user account, select Add mobile device.
The Mobile device connection wizard starts.
- In the workspace of the Mobile devices folder click the Add mobile device button:
- In the console tree, expand the Mobile Device Management folder and select the Mobile devices subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Mobile devices subfolder, click the Add mobile device button.
The Mobile device connection wizard starts.
- Use the context menu in the User accounts folder:
- On the Operating system page of the wizard, select iOS as the mobile device operating system type.
- On the Selecting iOS MDM Server page, select the iOS MDM Server.
- On the Select users whose mobile devices you want to manage page, select the users, security groups, or Active Directory security groups whose mobile devices you want to add to the list of managed devices.
This step is skipped if you start the wizard by selecting Add mobile device in the context menu of the User accounts folder.
If you want to add a new user account into the list, click the Add button and enter the user account properties in the window that opens. If you want to modify or review the user account properties, select the user account from the list and click the Properties button.
- On the Certificate source page of the wizard, specify the method for creating the shared certificate that Administration Server will use to identify the mobile device. You can specify a shared certificate in one of the following ways:
- On the User notification method page of the wizard, define the settings for notifying the mobile device user by SMS or email about certificate creation:
- On the Result page, click Finish to close the wizard.
The iOS MDM profile is automatically published on the Kaspersky Security Center Web Server. The mobile device user receives a notification with a link for downloading the iOS MDM profile from the Web Server. The user clicks the link. Next, the mobile device's operating system prompts the user to accept the iOS MDM profile installation. The user must agree to install the iOS MDM profile before the iOS MDM profile can be downloaded to the mobile device. After the iOS MDM profile is downloaded and the mobile device is synchronized with the Administration Server, the device is displayed in the Mobile devices folder, which is a subfolder of the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree.
For the user to proceed to the Kaspersky Security Center Web Server by using the link, connection with the Administration Server over port 8061 must be available on the mobile device.
Adding Android mobile devices to the list of managed devices
To add an Android mobile device to the list of managed devices, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android and a shared certificate must be delivered and installed on the mobile device. Shared certificates are used by Administration Server for identifying mobile devices. After a shared certificate is delivered and installed on a mobile device, the device appears in the list of managed devices.
You can add mobile devices of users to the list of managed devices by means of the Mobile device connection wizard. The wizard provides two options for delivery and installation of a shared certificate and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android:
- By using a Google Play link
- By using a link from Kaspersky Security Center Web Server
The Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android installation package stored for distribution on Administration Server is used for installation
Starting the Mobile device connection wizard
To start the Mobile device connection wizard, do one of the following:
- Use the context menu in the User accounts folder:
- In the console tree, expand the Advanced folder and select the User accounts subfolder.
- In the workspace of the User accounts folder, select the users, security groups, or Active Directory security groups whose mobile devices you want to add to the list of managed devices.
- Right-click and in the context menu of the user account, select Add mobile device.
The Mobile device connection wizard starts.
- In the workspace of the Mobile devices folder click the Add mobile device button:
- In the console tree, expand the Mobile Device Management folder and select the Mobile devices subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Mobile devices subfolder, click the Add mobile device button.
The Mobile device connection wizard starts.
Adding an Android mobile device by using a Google Play link
To install Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android and a shared certificate on a mobile device using a Google Play link:
- Start the Mobile device connection wizard.
- On the Operating system page of the wizard, select Android as the mobile device operating system type.
- On the Method to install Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android on devices page of the wizard, select Download the app from Google Play.
- On the Select users whose mobile devices you want to manage page of the wizard, select the users, security groups, or Active Directory security groups whose mobile devices you want to add to the list of managed devices.
This step is skipped if the wizard is started by selecting Add mobile device in the context menu of User accounts folder.
If you want to add a new user account into the list, click the Add button and enter the user account properties in the window that opens. If you want to modify or review the user account properties, select the user account from the list and click the Properties button.
- On the Certificate source page of the wizard, specify the method for creating the shared certificate that Administration Server will use to identify the mobile device. You can specify a shared certificate in one of the following ways:
- On the User notification method page of the wizard, define the settings for notifying the mobile device user by SMS or email about certificate creation:
- On the Result page, click Finish to close the wizard.
After the wizard finishes, a link and a QR code will be sent to the user's mobile device, allowing download of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android. The user clicks the link or scans the QR code. Next, the mobile device's operating system prompts the user to accept installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android installation. After Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android is downloaded and installed, the mobile device connects to the Administration Server and downloads a shared certificate. After the certificate is installed on the mobile device, the device is displayed in the Mobile devices folder, which is a subfolder of the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree.
Adding an Android mobile device using a link from Kaspersky Security Center Web Server
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android installation package published on the Administration Server is used for installation.
To install Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android and a shared certificate on a mobile device using a link from Web Server:
- Start the Mobile device connection wizard.
- On the Operating system page of the wizard, select Android as the mobile device operating system type.
- On the Method to install Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android on devices page of the wizard, select Download the app installation package from Kaspersky Security Center.
In the field that appears below, select an installation package or create a new one by clicking New.
- On the Select users whose mobile devices you want to manage page of the wizard, select the users, security groups, or Active Directory security groups whose mobile devices you want to add to the list of managed devices.
This step is skipped if the wizard is started by selecting Add mobile device in the context menu of User accounts folder.
If you want to add a new user account into the list, click the Add button and enter the user account properties in the window that opens. If you want to modify or review the user account properties, select the user account from the list and click the Properties button.
- On the Certificate source page of the wizard, specify the method for creating the shared certificate that Administration Server will use to identify the mobile device. You can specify a shared certificate in one of the following ways:
- On the User notification method page of the wizard, define the settings for notifying the mobile device user by SMS or email about certificate creation:
- On the Result page, click Finish to close the wizard.
The mobile app package of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android is automatically published on the Kaspersky Security Center Web Server. The mobile app package contains the app, the settings for connecting the mobile device to the Administration Server, and a certificate. The mobile device user will receive a notification containing a link for downloading the package from the Web Server. The user clicks the link. The operating system of the device then prompts the user to accept installation of the mobile app package. If the user agrees, the package will be downloaded to the mobile device. After the package is downloaded and the mobile device is synchronized with the Administration Server, the device is displayed in the Mobile devices folder, which is a subfolder of the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree.
Managing iOS MDM devices
This section describes advanced features for management of iOS MDM devices through Kaspersky Security Center. The application supports the following features for management of iOS MDM devices:
- Define the settings of managed iOS MDM devices in centralized mode and restrict features of devices through configuration profiles. You can add or modify configuration profiles and install them on mobile devices.
- Install apps on mobile devices by means of provisioning profiles, bypassing App Store. For example, you can use provisioning profiles for installation of in-house corporate apps on users' mobile devices. A provisioning profile contains information about an app and a mobile device.
- Install apps on an iOS MDM device through the App Store. Before installing an app on an iOS MDM device, you must add that app to an iOS MDM Server.
Every 24 hours, a push notification is sent to all connected iOS MDM devices in order to synchronize data with the iOS MDM Server.
For information about the configuration profile and the provisioning profile, as well as apps installed on an iOS MDM device, please refer to the properties window of the device.
Signing an iOS MDM profile by a certificate
You can sign an iOS MDM profile by a certificate. You can use a certificate that you issued yourself or you can receive a certificate from trusted certification authorities.
iOS devices display a disclaimer for non-signed profiles and prompt the user to trust the signer when installing the profile.
To sign an iOS MDM profile by a certificate:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
- In the context menu of the Mobile devices folder, select Properties.
- In the properties window of the folder, select the Connection settings for iOS devices section.
- Click the Browse button under the Select certificate file field.
The Certificate window.
- In the Certificate type field, specify the public or private certificate type:
- If the PKCS #12 container value is selected, specify the certificate file and the password.
- If the X.509 certificate value is selected:
- Specify the private key file (one with the *.prk or *.pem extension).
- Specify the private key password.
- Specify the public key file (one with the *.cer extension).
- Click OK.
The iOS MDM profile is signed by a certificate.
Adding a configuration profile
To create a configuration profile, you can use Apple Configurator 2, which is available at the Apple Inc. website. Apple Configurator 2 works only on devices running macOS; if you do not have such devices at your disposal, you can use iPhone Configuration Utility on the device with Administration Console instead. However, Apple Inc. does not support iPhone Configuration Utility any longer.
To create a configuration profile using iPhone Configuration Utility and to add it to an iOS MDM Server:
- In the console tree, select the Mobile Device Management folder.
- In the workspace of the Mobile Device Management folder, select the Mobile Device Servers subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Mobile Device Servers folder, select an iOS MDM Server.
- In the context menu of the iOS MDM Server, select Properties.
The Mobile Device Server properties window opens.
- In the properties window of the iOS MDM Server, select the Configuration profiles section.
- In the Configuration profiles section, click the Create button.
The New configuration profile window opens.
- In the New configuration profile window, specify a name and ID for the profile.
The configuration profile ID should be unique; the value should be specified in Reverse-DNS format, for example, com.companyname.identifier.
- Click OK.
iPhone Configuration Utility then starts if you have it installed.
- Reconfigure the profile in iPhone Configuration Utility.
For a description of the profile settings and instructions on how to configure the profile, please refer to the documentation enclosed with iPhone Configuration Utility.
After you configure the profile with iPhone Configuration Utility, the new configuration profile is displayed in the Configuration profiles section in the properties window of the iOS MDM Server.
You can click the Modify button to modify the configuration profile.
You can click the Import button to load the configuration profile to a program.
You can click the Export button to save the configuration profile to a file.
The profile that you have created must be installed on iOS MDM devices.
Installing a configuration profile on a device
To install a configuration profile to a mobile device:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
The folder workspace displays a list of managed mobile devices.
- In the workspace, filter iOS MDM devices by protocol type (iOS MDM).
- Select the user mobile device on which you have to install a configuration profile.
You can select multiple mobile devices to install the profile on them simultaneously.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Show command log.
- In the Mobile device management commands window, proceed to the Install profile section and click the Send command button.
You can also send the command to the mobile device by selecting All commands in the context menu of that mobile device, and then selecting Install profile.
The Select profiles window opens showing a list of profiles. Select from the list the profile that you have to install on the mobile device. You can select multiple profiles to install them on the mobile device simultaneously. To select the range of profiles, use the Shift key. To combine profiles into a group, use the CTRL key.
- Click OK to send the command to the mobile device.
When the command is executed, the selected configuration profile will be installed on the user's mobile device. If the command is successfully executed, the current status of the command in the command log will be shown as Done.
You can click the Resend button to send the command to the user's mobile device again.
You can click the Remove from queue button to cancel execution of a command that was sent if the command has not yet been executed.
The Command log section displays commands that have been sent to the mobile device, with the respective execution statuses. Click Refresh to update the list of commands.
- Click OK to close the Mobile device management commands window.
You can view the profile that you installed and remove it, if necessary.
Removing the configuration profile from a device
To remove a configuration profile from a mobile device:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
The folder workspace displays a list of managed mobile devices.
- In the workspace, filter iOS MDM devices by clicking the iOS MDM link.
- Select the user's mobile device from which you have to remove the configuration profile.
You can select multiple mobile devices to remove the profile from them simultaneously.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Show command log.
- In the Mobile device management commands window, proceed to the Remove profile section and click the Send command button.
You can also send the command to the mobile device by selecting All commands from the context menu of the device, and then selecting Remove profile.
The Remove profiles window opens showing a list of profiles.
- Select from the list the profile that you have to remove from the mobile device. You can select multiple profiles to remove them from the mobile device simultaneously. To select the range of profiles, use the Shift key. To combine profiles into a group, use the CTRL key.
- Click OK to send the command to the mobile device.
When the command is executed, the selected configuration profile will be removed from the user's mobile device. If the command is executed successfully, the current status of the command will be shown as Completed.
You can click the Resend button to send the command to the user's mobile device again.
You can click the Remove from queue button to cancel execution of a command that was sent if the command has not yet been executed.
The Command log section displays commands that have been sent to the mobile device, with the respective execution statuses. Click Refresh to update the list of commands.
- Click OK to close the Mobile device management commands window.
Adding a new device by publishing a link to a profile
In Administration Console, the administrator creates a new iOS MDM profile, using the Certificate installation wizard. The wizard performs the following actions:
- The iOS MDM profile is automatically published on the Web Server.
- The user is sent a link to the iOS MDM profile by SMS or by email. Upon receiving the link, the user installs the iOS MDM profile on the mobile device.
- The mobile device connects to the iOS MDM Server.
Due to a stricter security policy introduced by Apple, you have to set up TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2 protocol versions when connecting a mobile device running iOS 11 to an Administration Server that has integration with Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) enabled.
Adding a new device through profile installation by the administrator
To connect a mobile device to an iOS MDM Server by installing an iOS MDM profile on that mobile device, the administrator must perform the following actions:
- In Administration Console, open the Certificate installation wizard.
- Create a new iOS MDM profile by selecting the Show certificate after the wizard finishes check box in the wizard window.
- Save the iOS MDM profile.
- Install the iOS MDM profile on the user's mobile device through the Apple Configurator utility.
The mobile device connects to the iOS MDM Server.
Due to a stricter security policy introduced by Apple, you have to set up TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2 protocol versions when connecting a mobile device running iOS 11 to an Administration Server that has integration with Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) enabled.
Adding a provisioning profile
To add a provisioning profile to an iOS MDM Server:
- In the console tree, open the Mobile Device Management folder.
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile Device Servers subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Mobile Device Servers folder, select an iOS MDM Server.
- In the context menu of the iOS MDM Server, select Properties.
The Mobile Device Server properties window opens.
- In the properties window of the iOS MDM Server, go to the Provisioning profiles section.
- In the Provisioning profiles section, click the Import button and specify the path to a provisioning profile file.
The profile will be added to the iOS MDM Server settings.
You can click the Export button to save the provisioning profile to a file.
You can install the provisioning profile that you imported on iOS MDM devices.
Installing a provisioning profile to a device
To install a provisioning profile on a mobile device:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
The folder workspace displays a list of managed mobile devices.
- In the workspace, filter iOS MDM devices by protocol type (iOS MDM).
- Select the user's mobile device on which you have to install the provisioning profile.
You can select multiple mobile devices to install the provisioning profile simultaneously.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Show command log.
- In the Mobile device management commands window, proceed to the Install provisioning profile section and click the Send command button.
You can also send the command to the mobile device by selecting All commands from the context menu of that mobile device, and then selecting Install provisioning profile.
The Select provisioning profiles window opens showing a list of provisioning profiles. Select from the list the provisioning profile that you have to install on the mobile device. You can select multiple provisioning profiles to install them on the mobile device simultaneously. To select the range of provisioning profiles, use the Shift key. To combine provisioning profiles into a group, use the Ctrl key.
- Click OK to send the command to the mobile device.
When the command is executed, the selected provisioning profile will be installed on the user's mobile device. If the command is successfully executed, its current status in the command log is shown as Completed.
You can click the Resend button to send the command to the user's mobile device again.
You can click the Remove from queue button to cancel execution of a command that was sent if the command has not yet been executed.
The Command log section displays commands that have been sent to the mobile device, with the respective execution statuses. Click Refresh to update the list of commands.
- Click OK to close the Mobile device management commands window.
You can view the profile that you installed and remove it, if necessary.
Removing a provisioning profile from a device
To remove a provisioning profile from a mobile device:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
The folder workspace displays a list of managed mobile devices.
- In the workspace, filter iOS MDM devices by protocol type (iOS MDM).
- Select the user's mobile device from which you have to remove the provisioning profile.
You can select multiple mobile devices to remove the provisioning profile from them simultaneously.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Show command log.
- In the Mobile device management commands window, proceed to the Remove provisioning profile section and click the Send command button.
You can also send the command to the mobile device by selecting All commands from the context menu and then selecting Remove provisioning profile.
The Remove provisioning profiles window opens showing a list of profiles.
- Select from the list the provisioning profile that you need to remove from the mobile device. You can select multiple provisioning profiles to remove them from the mobile device simultaneously. To select the range of provisioning profiles, use the Shift key. To combine provisioning profiles into a group, use the Ctrl key.
- Click OK to send the command to the mobile device.
When the command is executed, the selected provisioning profile will be removed from the user's mobile device. Applications that are related to the deleted provisioning profile will not be operable. If the command is executed successfully, the current status of the command will be shown as Completed.
You can click the Resend button to send the command to the user's mobile device again.
You can click the Remove from queue button to cancel execution of a command that was sent if the command has not yet been executed.
The Command log section displays commands that have been sent to the mobile device, with the respective execution statuses. Click Refresh to update the list of commands.
- Click OK to close the Mobile device management commands window.
Adding a managed application
Before installing an app on an iOS MDM device, you must add that app to an iOS MDM Server. An application is considered managed if it has been installed on a device through Kaspersky Security Center. A managed application can be managed remotely by means of Kaspersky Security Center.
To add a managed application to an iOS MDM Server:
- In the console tree, open the Mobile Device Management folder.
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile Device Servers subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Mobile Device Servers folder, select an iOS MDM Server.
- In the context menu of the iOS MDM Server, select Properties.
This opens the properties window of the iOS MDM Server.
- In the properties window of the iOS MDM Server, select the Managed applications section.
- Click the Add button in the Managed applications section.
The Add an application window opens.
- In the Add an application window, in the App name field, specify the name of the application to be added.
- In the Apple ID or link to manifest file field, specify the Apple ID of the application to be added, or specify a link to a manifest file that can be used to download the application.
- If you want a managed application to be removed from the user's mobile device along with the iOS MDM profile when removing the latter, select the Remove together with iOS MDM profile check box.
- If you want to block the application data backup through iTunes, select the Block data backup check box.
- Click OK.
The added application is displayed in the Managed applications section of the properties window of the iOS MDM Server.
Installing an app on a mobile device
To install an app on an iOS MDM mobile device:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
The folder workspace displays a list of managed mobile devices.
- Select the iOS MDM device on which you want to install an app.
You can select multiple mobile devices to install the application on them simultaneously.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Show command log.
- In the Mobile device management commands window, proceed to the Install app section and click the Send command button.
You can also send the command to the mobile device by selecting All commands in the context menu of that mobile device, and then selecting Install app.
The Select apps window opens showing a list of profiles. Select from the list the application that you have to install on the mobile device. You can select multiple applications to install them on the mobile device simultaneously. To select a range of apps, use the Shift key. To combine apps into a group, use the Ctrl key.
- Click OK to send the command to the mobile device.
When the command is executed, the selected application will be installed on the user's mobile device. If the command is successfully executed, its current status in the command log will be shown as Completed.
You can click the Resend button to send the command to the user's mobile device again. You can click the Remove from queue button to cancel execution of a command that was sent if the command has not yet been executed.
The Command log section displays commands that have been sent to the mobile device, with the respective execution statuses. Click Refresh to update the list of commands.
- Click OK to close the Mobile device management commands window.
Information about the application installed is displayed in the properties of the iOS MDM mobile device. You can remove the application from the mobile device through the command log or the context menu of the mobile device.
Removing an app from a device
To remove an app from a mobile device:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
The folder workspace displays a list of managed mobile devices.
- In the workspace, filter iOS MDM devices by protocol type (iOS MDM).
- Select the user's mobile device from which you have to remove the app.
You can select multiple mobile devices to remove the app from them simultaneously.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Show command log.
- In the Mobile device management commands window, proceed to the Remove app section and click the Send command button.
You can also send the command to the mobile device by selecting All commands in the context menu of that mobile device, and then selecting Remove app.
The Remove apps window opens showing a list of applications.
- Select from the list the app that you need to remove from the mobile device. You can select multiple apps to remove them simultaneously. To select a range of apps, use the Shift key. To combine apps into a group, use the Ctrl key.
- Click OK to send the command to the mobile device.
When the command is executed, the selected app will be removed from the user's mobile device. If the command is executed successfully, the current status of the command will be shown as Completed.
You can click the Resend button to send the command to the user's mobile device again.
You can click the Remove from queue button to cancel execution of a command that was sent if the command has not yet been executed.
The Command log section displays commands that have been sent to the mobile device, with the respective execution statuses. Click Refresh to update the list of commands.
- Click OK to close the Mobile device management commands window.
Configuring roaming on an iOS MDM mobile device
To configure roaming:
- In the console tree, open the Mobile Device Management folder.
- In the Mobile Device Management folder, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
The folder workspace displays a list of managed mobile devices.
- Select the iOS MDM device owned by the user for whom you have to configure roaming.
You can select multiple mobile devices to configure roaming on them simultaneously.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Show command log.
- In the Mobile device management commands window, proceed to the Configure roaming section and click the Send command button.
You can also send the command to the mobile device by selecting All commands → Configure roaming from the context menu of the device.
- In the Roaming settings window, specify the relevant settings:
Roaming is configured for the selected devices.
Viewing information about an iOS MDM device
To view information about an iOS MDM device:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
The folder workspace displays a list of managed mobile devices.
- In the workspace, filter iOS MDM devices by clicking the iOS MDM link.
- Select the mobile device for which you want to view the information.
- From the context menu of the mobile device select Properties.
The properties window of the iOS MDM device opens.
The properties window of the mobile device displays information about the connected iOS MDM device.
Disconnecting an iOS MDM device from management
To disconnect an iOS MDM device from the iOS MDM Server:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
The folder workspace displays a list of managed mobile devices.
- In the workspace, filter iOS MDM devices by clicking the iOS MDM link.
- Select the mobile device that you have to disconnect.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Delete.
The iOS MDM device will be marked in the list for removal. The mobile device will be automatically removed from the list of managed devices after it is removed from the iOS MDM Server database. The mobile device will be removed from the iOS MDM Server database within one minute.
After the iOS MDM device is disconnected from management, all installed configuration profiles, the iOS MDM profile, and applications for which the Remove together with iOS MDM profile option has been enabled, will be removed from the mobile device.
Sending commands to a device
To send a command to an iOS MDM device:
- In Administration Console, open the Mobile Device Management node.
- Select the Mobile devices folder.
- In the Mobile devices folder, select the mobile device to which the commands need to be sent.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Show command log.
- In the list that appears, select the command to be sent to the mobile device.
Checking the execution status of commands sent
To check the execution status of a command that has been sent to a mobile device:
- In Administration Console, open the Mobile Device Management node.
- Select the Mobile devices folder.
- In the Mobile devices folder, select the mobile device on which the execution status needs to be checked for the selected commands.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Show command log.
Managing KES devices
In Kaspersky Security Center, you can manage KES mobile devices in the following ways:
- Centrally manage KES devices by using commands.
- View information about the settings for management of KES devices.
- Install applications by using mobile app packages.
- Disconnect KES devices from management.
Creating a mobile applications package for KES devices
A Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android license is required to create a mobile applications package for KES devices.
To create a mobile applications package:
- In the Remote installation folder of the console tree, select the Installation packages subfolder.
The Remote installation folder is a subfolder of the Advanced folder by default.
- Click the Additional actions button and select Manage mobile apps packages in the drop-down list.
- In the Mobile apps package management window, click the New button.
- The New package wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
The newly created mobile applications package is displayed in the Mobile apps package management window.
Enabling certificate-based authentication of KES devices
To enable certificate-based authentication of a KES device:
- Open the system registry of the client device that has Administration Server installed (for example, locally, using the regedit command in the Start → Run menu).
- Go to the following hive:
- For 32-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\Components\34\.core\.independent\KLLIM
- For 64-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\34\.core\.independent\KLLIM
- For 32-bit systems:
- Create a key with the LP_MobileMustUseTwoWayAuthOnPort13292 name.
- Specify REG_DWORD as the key type.
- Set the key value on 1.
- Restart the Administration Server service.
Mandatory certificate-based authentication of the KES device using a shared certificate will be enabled after you run the Administration Server service.
The first connection of the KES device to the Administration Server does not require a certificate.
By default, certificate-based authentication of KES devices is disabled.
Viewing information about a KES device
To view information about a KES device:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
The folder workspace displays a list of managed mobile devices.
- In the workspace, filter KES devices by protocol type (KES).
- Select the mobile device for which you want to view the information.
- From the context menu of the mobile device select Properties.
The properties window of the KES device opens.
The properties window of the mobile device displays information about the connected KES device.
Disconnecting a KES device from management
To disconnect a KES device from management, the user has to remove Network Agent from the mobile device. After the user has removed Network Agent, the mobile device details are removed from the Administration Server database, and the administrator can remove the mobile device from the list of managed devices.
To remove a KES device from the list of managed devices:
- In the Mobile Device Management folder in the console tree, select the Mobile devices subfolder.
The folder workspace displays a list of managed mobile devices.
- In the workspace, filter KES devices by protocol type (KES).
- Select the mobile device that you must disconnect from management.
- In the context menu of the mobile device, select Delete.
The mobile device is removed from the list of managed devices.
If Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android has not been removed from the mobile device, that mobile device reappears in the list of managed devices after synchronization with the Administration Server.
Data encryption and protection
Data encryption reduces the risk of unintentional leakage in case your notebook, removable drive, or hard drive is stolen or lost, or upon access by unauthorized users and applications.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows provides encryption functionality. Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows allows you to encrypt files stored on local drives of devices and removable drives, as well as encrypt removable drives and hard drives entirely.
Encryption rules are configured through Kaspersky Security Center by defining policies. Encryption and decryption according to the existing rules are performed when applying a policy.
Availability of the encryption management feature is determined by the user interface settings.
The administrator can perform the following actions:
- Configure and perform file encryption or decryption on local drives of the device.
- Configure and perform file encryption on removable drives.
- Create rules of access to encrypted files by applications.
- Create and deliver to the user a key file for access to encrypted files if file encryption is restricted on the user's device.
- Configure and perform hard drive encryption.
- Manage user access to encrypted hard drives and removable drives (manage authentication agent accounts, create and deliver to users information on request for account name and password restoration, as well as access keys for encrypted devices).
- View encryption statuses and reports about encryption of files.
These operations are performed using tools integrated into Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. For detailed instructions on how to perform operations and a description of encryption features please refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help.
Kaspersky Security Center supports encryption management functionality for devices running macOS operating systems. Encryption is configured using Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac tools for those application versions that support encryption functionality. For detailed instructions on how to perform operations and a description of encryption features, refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac Administrator's Guide.
Viewing the list of encrypted devices
To view the list of devices storing encrypted information:
- In the console tree of Administration Server, select the Data encryption and protection folder.
- Open the list of encrypted devices in one of the following ways:
- By clicking the Go to list of encrypted drives link in the Manage encrypted drives section.
- By selecting the Encrypted drives folder in the console tree.
The workspace displays information about devices on the network storing encrypted files, and about devices encrypted at the drive level. After the information on a device is decrypted, the device is automatically removed from the list.
You can sort the information in the list of devices either in ascending or descending order in any column.
The user interface settings determine whether the Data encryption and protection folder appears in the console tree.
Page top
Viewing the list of encryption events
When running data encryption or decryption tasks on devices, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows sends Kaspersky Security Center information about events of the following types:
- Cannot encrypt or decrypt a file, or create an encrypted archive due to a lack of free disk space.
- Cannot encrypt or decrypt a file, or create an encrypted archive due to license issues.
- Cannot encrypt or decrypt a file, or create an encrypted archive due to missing access rights.
- The application has been prohibited to access an encrypted file.
- Unknown errors.
To view a list of events that have occurred during data encryption on devices:
- In the console tree of Administration Server, select the Data encryption and protection folder.
- Open the list of events that occurred during encryption in one of the following ways:
- By clicking the Go to error list link in the Data encryption errors section.
- By selecting the Encrypted drives folder in the console tree.
The workspace displays information about problems that have occurred during data encryption on devices.
You can take the following actions in the list of encryption events:
- Sort data records in ascending or descending order in any of the columns.
- Perform a quick search for records (by text match with a substring in any of the list fields).
- Export the list of events to a text file.
The user interface settings determine whether the Data encryption and protection folder appears in the console tree.
Page top
Exporting the list of encryption events to a text file
To export the list of encryption events to a text file:
- Create a list of encryption events.
- From the context menu of the events list select Export list.
The Export list window opens.
- In the Export list window, specify the name of the text file with the list of events, select a folder to save it and click the Save button.
The list of encryption events will be saved to the file that you have specified.
Creating and viewing encryption reports
You can generate the following reports:
- Report on encryption status of managed devices. This report provides details about the data encryption of various managed devices. For example, the report shows the number of devices to which the policy with configured encryption rules applies. Also, you can find out, for instance, how many devices need to be rebooted. The report also contains information about the encryption technology and algorithm for every device.
- Report on encryption status of mass storage devices. This report contains similar information as the report on the encryption status of managed devices, but it provides data only for mass storage devices and removable drives.
- Report on rights to access encrypted drives. This report shows which user accounts have access to encrypted drives.
- Report on file encryption errors. This report contains information about errors that occurred when the data encryption or decryption tasks were run on devices.
- Report on blockage of access to encrypted files. This report contains information about blocking application access to encrypted files. This report is helpful if an unauthorized user or application tries to access encrypted files or drives.
To generate the report on encryption of devices:
- In the console tree, select the Data encryption and protection folder.
- Do one of the following:
- To generate the report on the encryption status of managed devices, click the View report on encryption status of mass storage devices link.
If you have not configured this report yet, the New report template wizard will start. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- To generate the report on encryption status of mass storage devices, in the console tree select the Encrypted drives subfolder, and then click the View report on encryption status of mass storage devices button.
- To generate the report on the encryption status of managed devices, click the View report on encryption status of mass storage devices link.
The report generation starts. The report appears on the Reports tab of the Administration Server node.
To generate the report on rights of access to encrypted devices:
- In the console tree, select the Data encryption and protection folder.
- Do one of the following:
- Click the Report on rights to access encrypted drives link in the Manage encrypted drives section to start the New report template wizard.
- Select the Encrypted drives subfolder, then click the Report on rights to access encrypted drives button to start the New report template wizard.
- Follow the steps of the New report template wizard.
The report generation starts. The report appears on the Reports tab of the Administration Server node.
To generate the report on file encryption errors:
- In the console tree, select the Data encryption and protection folder.
- Do one of the following:
- Click the View report on file encryption errors link in the Data encryption errors section to start the New report template wizard.
- Select the Encryption events subfolder, then click the Report on file encryption errors link to start the New report template wizard.
- Follow the steps of the New report template wizard.
The report generation starts. The report appears on the Reports tab of the Administration Server node.
To generate the report on the status of encryption of managed devices:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Reports tab.
- Click the New report template button to start the New report template wizard.
- Follow the instructions of the New report template wizard. In the Selecting the report template type window, in the Other section select Report on encryption status of managed devices.
After you have finished with the New report template wizard, a new report template appears in the Administration Server node, on the Reports tab.
- In the node of the relevant Administration Server on the Reports tab, select the report template that was created during the previous steps of the instructions.
The report generation starts. The report appears on the Reports tab of the Administration Server node.
You can also obtain information about whether the encryption statuses of devices and removable drives conform to the encryption policy by viewing information panes on the Statistics tab of the Administration Server node.
To generate the report on blockage of access to encrypted files:
- In the console tree, select the node with the name of the required Administration Server.
- In the workspace of the node, select the Reports tab.
- Click the New report template button to start the New report template wizard.
- Follow the instructions of the New report template wizard. In the Selecting the report template type window, in the Other section, select Report on blockage of access to encrypted files.
After the New report template wizard finishes, a new report template appears in the Administration Server node, on the Reports tab.
- In the node of the Administration Server on the Reports tab, select the report template that was created during the previous steps of the instructions.
The report generation starts. The report appears on the Reports tab of the Administration Server node.
Page top
Transmitting encryption keys between Administration Servers
If the data encryption feature is enabled on a managed device, the encryption key is stored on the Administration Server. The encryption key is used to access encrypted data and to manage the encryption policy.
The encryption key must be transmitted to another Administration Server in the following cases:
- You reconfigure Network Agent on a managed device to assign the device to another Administration Server. If this device contains encrypted data, the encryption key must be transmitted to the target Administration Server. Otherwise, the data cannot be decrypted.
- You encrypt a removable drive connected to a device D1 that is managed by the Administration Server S1, and then you connect this removable drive to a device D2 managed by the Administration Server S2. To access to the data on the removable drive, the encryption key must be transmitted from the Administration Server S1 to the Administration Server S2.
- You encrypt a file on a device D1 managed by the Administration Server S1, and then you try to access the file on a device D2 managed by the Administration Server S2. To access the file, the encryption key must be transmitted from the Administration Server S1 to the Administration Server S2.
You can transmit encryption keys the following ways:
- Automatically, by enabling the Use hierarchy of Administration Servers to obtain encryption keys option in the properties of two Administration Servers between which an encryption key must be transmitted. If this option is disabled for one of the Administration Servers, the automatic transmission of encryption keys is not possible.
When you enable the Use hierarchy of Administration Servers to obtain encryption keys option in an Administration Server properties, the Administration Server sends all of the encryption keys stored in its repository to the primary Administration Server (if any) one level up in the hierarchy.
When you try to access encrypted data, the Administration Server first searches the encryption key in its own repository. If the Use hierarchy of Administration Servers to obtain encryption keys option is enabled and the required encryption key has not been found in the repository, the Administration Server additionally sends a request to the primary Administration Servers (if any) to provide the required encryption key. The request will be sent to all of the primary Administration Servers up to the server on the highest level of the hierarchy.
The Use hierarchy of Administration Servers to obtain encryption keys option is currently not available in the Web Console interface. If you don't have access to the MMC-based Administration Console, use the primary Administration Server to manage encrypted devices.
- Manually from one Administration Server to another by exporting and importing the file containing the encryption keys.
The export and import of encryption keys are actions that are included in the Encryption key management feature. To perform these actions, configure the access rights to the feature for users of Kaspersky Security Center as follows:
- Grant the Read access right to the Encryption key management feature for a user that exports encryption keys from the secondary Administration Server.
- Grant the Write access right to the Encryption key management feature for a user that imports encryption keys to the target Administration Server.
To enable automatic transmission of encryption keys between Administration Servers within the hierarchy:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server for which you want to enable automatic transmission of encryption keys.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the properties window, select the Encryption algorithm section.
- Enable the Use hierarchy of Administration Servers to obtain encryption keys option.
- Click OK to apply the changes.
The encryption keys will be transmitted to primary Administration Servers (if any) at the next synchronization (the heartbeat). This Administration Server will also provide, upon request, an encryption key from its repository to a secondary Administration Server.
To transmit encryption keys between Administration Servers manually:
- In the console tree of Administration Server, select the secondary Administration Server from which you want to transmit encryption keys.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the properties window, select the Encryption algorithm section.
- Click the Export encryption keys from Administration Server.
Make sure that a user that exports encryption keys from the Server is granted the Read access right to the Encryption key management feature.
- In the Export encryption keys window:
- Click the Browse button, and then specify where to save the file.
- Specify a password to protect the file from unauthorized access.
Remember the password. A lost password cannot be retrieved. If the password is lost, you have to repeat the export procedure. Therefore, make a note of the password and keep it handy.
- Transmit the file to another Administration Server, for example, through a shared folder or removable drive.
- On the target Administration Server, make sure that Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console is running.
- In the console tree of Administration Server, select the target Administration Server where you want to transmit encryption keys.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the properties window, select the Encryption algorithm section.
- Click Import encryption keys to Administration Server.
Make sure that a user that imports encryption keys to the Server is granted the Write access right to the Encryption key management feature.
- In the Import encryption keys window:
- Click the Browse button, and then select the file containing encryption keys.
- Specify the password.
- Click OK.
The encryption keys are transmitted to the target Administration Server.
Data repositories
This section provides information about data stored on the Administration Server and used for tracking the condition of client devices and for servicing them.
The Repositories folder of the console tree displays the data used for tracking the statuses of client devices.
The Repositories folder contains the following objects:
- Updates downloaded by the Administration Server that are distributed to client devices
- List of equipment detected on the network
- License keys detected on client devices
- Files placed in Quarantine folders on devices by security applications
- Files placed in Backup on client devices
- Files postponed for a later scan by security applications
Exporting a list of repository objects to a text file
You can export the list of objects from the repository to a text file.
To export the list of objects from the repository to a text file:
- In the console tree, in the Repositories folder select the subfolder of the relevant repository.
- In the repository subfolder, select Export list in the context menu.
This will open the Export list window, in which you can specify the name of text file and path to the folder where it was placed.
Installation packages
Kaspersky Security Center places the installation packages for applications of Kaspersky and third-party vendors in data repositories.
An installation package is a set of files required to install an application. An installation package contains the setup settings and initial configuration of the application being installed.
If you want to install an application on a client device, create an installation package for that application, or use an existing one. The list of created installation packages is stored in the Remote installation folder of the console tree, the Installation packages subfolder.
Main statuses of files in the repository
Security applications scan files on devices for known viruses and other programs that may pose a threat, assign statuses to files, and place some of them in the repository.
For example, security applications can do the following:
- Save a copy of a file to the repository before deletion
- Isolate probably infected files in the repository
The main statuses of files are presented in the table below. You can obtain more detailed information about actions to take on files in respective Help systems of security applications.
Statuses of files in the repository
Status name |
Status description |
|---|---|
Infected |
The file has a section of code of a known virus or other malware whose information is found in Kaspersky anti-virus databases. |
Not infected |
No known viruses or other malware were detected in the file. |
Warning |
The file contains a fragment of code that partially matches a snippet of code of a known threat. |
Probably infected |
The file contains either modified code of a known virus or code resembling a virus that is not yet known to Kaspersky. |
Placed to folder by user |
The user manually placed the file in the repository because the file's behavior gave rise to suspicion that it contains some threats. The user can scan the file for threats by using up-to-date databases. |
False positive |
A Kaspersky application assigned Infected status to a non-infected file because its code is similar to that of a virus. After a scan with up-to-date databases, the file is identified as non-infected. |
Disinfected |
The file was successfully disinfected. |
Deleted |
The file was deleted during processing. |
Password-protected |
The file cannot be processed because it is protected with a password. |
Triggering of rules in Smart Training mode
This section provides information about the detections performed by the Adaptive Anomaly Control rules in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows on client devices.
The rules detect anomalous behavior on client devices and may block it. If the rules work in Smart Training mode, they detect anomalous behavior and send reports about every such occurrence to Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server. This information is stored as a list in the Rule triggers in Smart Training state subfolder of the Repositories folder. You can confirm detections as correct or add them as exclusions, so that this type of behavior is not considered anomalous anymore.
Information about detections is stored in the event log on the Administration Server (along with other events) and in the Adaptive Anomaly Control report.
For more information about Adaptive Anomaly Control, the rules, their modes and statuses, refer to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
Viewing the list of detections performed using Adaptive Anomaly Control rules
To view the list of detections performed by Adaptive Anomaly Control rules:
- In the console tree, select the node of the Administration Server that you require.
- Select the Rule triggers in Smart Training state subfolder (by default, this is a subfolder of Advanced → Repositories).
The list displays the following information about detections performed using Adaptive Anomaly Control rules:
To view properties of each information element:
- In the console tree, select the node of the Administration Server that you require.
- Select the Rule triggers in Smart Training state subfolder (by default, this is a subfolder of Advanced → Repositories).
- In the Rule triggers in Smart Training state workspace, select the object that you want.
- Do one of the following:
- Click the Properties link in the information box that appears on the right side of the screen.
- Right-click and in the context menu select Properties.
The properties window of the object opens, displaying information about the selected element.
You can confirm or add to exclusions any element in the list of detections of Adaptive Anomaly Control rules.
To confirm an element,
Select an element (or several elements) in the list of detections and click the Confirm button.
The status of the element(s) will be changed to Confirming.
Your confirmation will contribute to the statistics used by the rules (for more information, refer to Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11 for Windows Help).
To add an element as an exclusion,
Right-click an element (or several elements) in the list of detections and select Add to exclusions in the context menu.
The Add exclusion wizard starts. Follow the wizard instructions.
If you reject or confirm an element, it will be excluded from the list of detections after the next synchronization of the client device with the Administration Server, and will no longer appear in the list.
Page top
Adding exclusions from the Adaptive Anomaly Control rules
The Add exclusion wizard allows you to add exclusions from the Adaptive Anomaly Control rules for Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
You can start the wizard through one of the three procedures below.
To start the Add exclusion wizard through the Adaptive Anomaly Control node:
- In the console tree, select the node of the required Administration Server.
- Select Rule triggers in Smart Training state (by default, this is a subfolder of Advanced → Repositories).
- In the workspace, right-click an element (or several elements) in the list of detections and select Add to exclusions.
You can add up to 1000 exclusions at a time. If you select more elements and try to add them to exclusions, an error message is displayed.
The Add exclusion wizard starts.
You can start the Add exclusion wizard from other nodes in the console tree:
- Events tab of the main window of the Administration Server (then the User requests option or Recent events option).
- Report on Adaptive Anomaly Control rules state, Detections count column.
Step 1. Selecting the application
This step can be skipped if you have only one Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows version and do not have other applications that support the Adaptive Anomaly Control rules.
The Add exclusion wizard shows the list of Kaspersky applications whose management plug-ins allow you to add exclusions to the policies for these applications. Select an application from this list and click Next to proceed to selecting the policy to which the exclusion will be added.
Page top
Step 2. Selecting the policy (policies)
The wizard shows the list of policies (with policy profiles) for Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
Select all the policies and profiles to which you want to add exclusions and click Next.
Page top
Step 3. Processing of the policy (policies)
The wizard displays a progress bar as the policies are processed. You can interrupt the processing of policies by clicking Cancel.
Inherited policies cannot be updated. If you do not have the rights to modify a policy, this policy will not be updated either.
When all the policies are processed (or if you interrupt the processing), a report appears. It shows which policies were updated successfully (green icon) and which policies were not updated (red icon).
This is the last step of the wizard. Click Finish to close the wizard.
Page top
Quarantine and Backup
Kaspersky anti-virus applications installed on client devices may place files in Quarantine or Backup during device scan.
Quarantine is a special repository for storing files that are probably infected with viruses and files that cannot be disinfected at the time when they are detected.
Backup is designed for storing backup copies of files that have been deleted or modified during the disinfection process.
Kaspersky Security Center creates a summarized list of files placed in Quarantine or Backup by Kaspersky applications on the devices. Network Agents on client devices transmit information about the files in Quarantine and Backup to the Administration Server. You can use Administration Console to view the properties of files stored in repositories on devices, run malware scans of those repositories, and delete files from them. The icons of the file statuses are described in the appendix.
Operations with Quarantine and Backup are supported for versions 6.0 or later of Kaspersky Anti-Virus for Windows Workstations and Kaspersky Anti-Virus for Windows Servers, as well as for Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 for Windows, or later versions.
Kaspersky Security Center does not copy files from repositories to Administration Server. All files are stored in repositories on the devices. You can restore a file only on the device with the anti-virus application, which placed that file in the repository.
Enabling remote management for files in the repositories
By default, you cannot manage files placed in repositories on client devices.
To enable remote management of files stored in repositories on client devices:
- In the console tree, select an administration group, for which you want to enable remote management for files in the repository.
- In the group workspace, open the Policies tab.
- On the Policies tab, select the policy of the security application that has placed the files in the repositories on the devices.
- In the policy settings window in the Data transfer to Administration Server group of settings, select the check boxes corresponding to the repositories for which you want to enable the remote management.
The location of the Data transfer to Administration Server settings group in the policy properties window and the names of check boxes depend on the currently used security application.
Viewing properties of a file placed in repository
To view properties of a file in Quarantine or Backup:
- In the console tree, select the Repositories folder, the Quarantine or Backup subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Quarantine (Backup) folder, select a file whose properties you want to view.
- By selecting Properties in the context menu of the file.
Deleting files from repositories
To delete a file from Quarantine or Backup:
- In the console tree, in the Repositories folder, select the Quarantine or Backup subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Quarantine (or Backup) folder select the files that you want to delete by using the Shift and Ctrl keys.
- Delete the files in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Delete in the context menu of the files.
- By clicking the Delete (Delete) if you want to delete one file) link in the information box for the selected files.
The security applications that placed files in repositories on client devices will delete the same files from those repositories.
Page top
Restoring files from repositories
To restore a file from Quarantine or Backup:
- In the console tree, select the Repositories folder, the Quarantine or Backup subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Quarantine (Backup) folder select the files that you want to restore by using the Shift and Ctrl keys.
- Start restoration of the files in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Restore in the context menu of the files.
- By clicking the Restore link in the information box for the selected files.
The security applications that placed files in repositories on client devices will restore the same files to their original folders.
Page top
Saving a file from repositories to disk
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to save on a disk copies of files that a security application placed in Quarantine or Backup on a client device. Files are copied to the device with Kaspersky Security Center installed, to the specified folder.
To save a copy of file from Quarantine or Backup to a hard drive:
- In the console tree, select the Repositories folder, the Quarantine or Backup subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Quarantine (Backup) folder, select a file that you want to copy to the hard drive.
- Start copying in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Save to Disk in the context menu of the file.
- By clicking the Save to Disk link in the information box for the selected file.
The security application that placed the file in Quarantine on the client device will save a copy of that file to the specified folder.
Page top
Scanning files in Quarantine
To scan quarantined files:
- In the console tree, select the Repositories folder, the Quarantine subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Quarantine folder, select the files that you want to scan by using the Shift and Ctrl keys.
- Start the file scan in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Scan in the context menu of the file.
- By clicking the Scan link in the information box for the selected files.
The application runs the on-demand scan task for security applications that have placed the selected files in Quarantine on the devices where those files are stored.
Page top
Active threats
Information about unprocessed files that have been detected on client devices is stored in the Repositories folder, Active threats subfolder.
Postponed processing and disinfection are performed by the security application upon request or after a specified event occurs. You can configure the postponed processing.
Disinfecting an unprocessed file
To start disinfection of an unprocessed file:
- In the console tree, in the Repositories folder select the Active threats subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Active threats folder, select the file that you have to disinfect.
- Start disinfection of the file in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Disinfect in the context menu of the file.
- By clicking the Disinfect link in the information box for the selected file.
The attempt to disinfect this file is then performed.
If the file is disinfected, the security application installed on the client device restores it to its original folder. The record of the file is removed from the list in the Active threats folder. If the file cannot be disinfected, the security application installed on the device deletes it from that device. The record of the file is removed from the list in the Active threats folder.
File disinfection and deletion capability may vary depending on which security application is installed, its version and settings.
Page top
Saving an unprocessed file to disk
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to save to disk copies of unprocessed files found on client devices. Files are copied to the device with Kaspersky Security Center installed, to the specified folder.
You can save copies of files in the following cases:
- Files were deleted or modified during disinfection and their copies are stored in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows storage on the managed device.
- Log only option is selected for the Action on threat detection parameter (Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection) in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
To save a copy of an unprocessed file to disk:
- In the console tree, in the Repositories folder select the Active threats subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Active threats folder, select the files that you have to copy to disk.
- Start copying in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Save to Disk in the context menu of the file.
- By clicking the Save to Disk link in the information box for the selected file.
The security application installed on the client device on which the unprocessed file has been found saves a copy of that file to the specified folder.
Page top
Deleting files from the "Active threats" folder
To delete a file from the Active threats folder:
- In the console tree, in the Repositories folder select the Active threats subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Active threats folder, select the files that you have to delete by using the Shift and Ctrl keys.
- Delete the files in one of the following ways:
- By selecting Delete in the context menu of the files.
- By clicking the Delete (Delete if you want to delete one file) link in the information box for the selected files.
The security applications that placed the files in repositories on client devices, will delete the same files from those repositories. The records of the files are removed from the list in the Active threats folder.
Page top
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN)
This section describes how to use an online service infrastructure named Kaspersky Security Network (KSN). The section provides the details on KSN, as well as instructions on how to enable KSN, configure access to KSN, and view the statistics of the use of KSN proxy server.
Updates functionality (including providing anti-virus signature updates and codebase updates), as well as KSN functionality may not be available in the software in the U.S.
About KSN
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is an online service infrastructure that provides access to the online Knowledge Base of Kaspersky, which contains information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software. The use of data from Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky applications to threats, improves the effectiveness of some protection components, and reduces the risk of false positives. KSN allows you to use Kaspersky reputation databases to retrieve information about applications installed on managed devices.
Kaspersky Security Center supports the following infrastructure solutions:
- KSN is a solution that allows you to exchange information with Kaspersky Security Network. If you participate in KSN, you agree to send to Kaspersky, in automatic mode, information about the operation of Kaspersky applications installed on client devices that are managed through Kaspersky Security Center. Information is transferred in accordance with the current KSN access settings. Kaspersky analysts additionally analyze received information and include it in the reputation and statistical databases of Kaspersky Security Network. Kaspersky Security Center uses this solution by default.
- Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN) is a solution that allows users of devices with Kaspersky applications installed to obtain access to reputation databases of Kaspersky Security Network, and other statistical data, without sending data to Global KSN from their own devices. KPSN is designed for corporate customers who are unable to participate in Kaspersky Security Network for any of the following reasons:
- User devices are not connected to the internet.
- Transmission of any data outside the country or outside the corporate LAN is prohibited by law or restricted by corporate security policies.
You can set up access settings of Kaspersky Private Security Network in the KSN Proxy settings section of the Administration Server properties window.
The application prompts you to join KSN while running the quick start wizard. You can start or stop using KSN at any moment when using the application.
You use KSN in accordance with the KSN Statement that you read and accept when you enable KSN. If the KSN Statement is updated, it is displayed to you when you upgrade a version of Administration Server. You can accept the updated KSN Statement or decline it. If you decline it, you keep using KSN in accordance with the previous version of KSN Statement that you accepted before.
When KSN is enabled, Kaspersky Security Center checks if the KSN servers are accessible. If access to the servers using system DNS is not possible, the application uses public DNS servers. This is necessary to make sure the level of security is maintained for the managed devices.
Client devices managed by the Administration Server interact with KSN through KSN proxy server. KSN proxy server provides the following features:
- Client devices can send requests to KSN, obtain information from KSN, and transfer information to KSN even if they do not have direct access to the internet.
- The KSN proxy server caches processed data, thus reducing the load on the outbound channel and the time period spent for waiting for information requested by a client device.
You can configure the KSN proxy server in the KSN Proxy settings section of the Administration Server properties window.
Page top
Setting up access to Kaspersky Security Network
You can set up access to Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) on the Administration Server and on a distribution point.
To set up Administration Server access to Kaspersky Security Network (KSN):
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server for which you want to configure access to KSN.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Sections pane, select KSN Proxy → KSN Proxy settings.
- In the workspace, enable the Use Administration Server as proxy server option to use the KSN proxy service.
Data is sent from client devices to KSN in accordance with the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy, which is active on those client devices. If this check box is cleared, no data will be sent to KSN from the Administration Server and client devices through Kaspersky Security Center. However, client devices can send data to KSN directly (bypassing Kaspersky Security Center), in accordance with their respective settings. The Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy, which is active on client devices, determines which data will be sent directly (bypassing Kaspersky Security Center) from those devices to KSN.
- Enable the I agree to use Kaspersky Security Network option.
If this option is enabled, client devices send patch installation results to Kaspersky. When enabling this option, make sure to read and accept the terms of the KSN Statement.
If you are using Kaspersky Private Security Network, enable the Configure KPSN option and click the Select file with KSN Proxy settings button to download the settings of KPSN (files with the extensions pkcs7 and pem). After the settings are downloaded, the interface displays the provider's name and contacts, as well as the creation date of the file with the settings of KPSN.
When you enable KPSN, pay attention to the distribution points configured to send KSN requests directly to the Cloud KSN. The distribution points that have Network Agent version 11 (or earlier) installed will continue to send KSN requests to the Cloud KSN. To reconfigure the distribution points to send KSN requests to KPSN, enable the Forward KSN requests to Administration Server option for each distribution point. You can enable this option in the distribution point properties or in the Network Agent policy.
When you select the Configure KPSN check box, a message appears with details about KPSN.
If you enable the Configure KPSN option in Kaspersky Security Center, these applications receive information about supporting KPSN. In the settings window of the application, in the Kaspersky Security Network subsection of the Advanced Threat Protection section, the information about selected KSN provider is displayed — KSN or KPSN.
If you use application versions earlier than Kaspersky Security for Virtualization 3.0 Agentless Service Pack 2 or earlier than Kaspersky Security for Virtualization 3.0 Service Pack 1 Light Agent when running KPSN, we recommend that you use secondary Administration Servers for which the use of KPSN has not been enabled.
Kaspersky Security Center does not send any statistical data to Kaspersky Security Network if KPSN is configured in the KSN Proxy → KSN Proxy settings section of the Administration Server properties window.
If you have the proxy server settings configured in the Administration Server properties, but your network architecture requires that you use KPSN directly, enable the Ignore proxy server settings when connecting to KPSN option. Otherwise, requests from the managed applications cannot reach KPSN.
- Configure the Administration Server connection to the KSN proxy service:
- Under Connection settings, for the TCP port, specify the number of the TCP port that will be used for connecting to the KSN proxy server. The default port to connect to the KSN proxy server is 13111.
- If you want the Administration Server to connect to the KSN proxy server through a UDP port, enable the Use UDP port option and specify a port number for the UDP port. By default, this option is disabled, and TCP port is used. If this option is enabled, the default UDP port to connect to the KSN proxy server is 15111.
- If you want the Administration Server to connect to the KSN proxy server through an HTTPS port, enable the Use HTTPS through port option and specify a port number. By default, this option is disabled, and TCP port is used. If this option is enabled, the default HTTPS port to connect to the KSN proxy server is 17111.
- Enable the Connect secondary Administration Servers to KSN through primary Administration Server option.
If this option is enabled, secondary Administration Servers of any hierarchy level use the primary Administration Server as the KSN proxy server. If this option is disabled, secondary Administration Servers connect to KSN on their own. In this case, managed devices use secondary Administration Servers as KSN proxy servers.
Secondary Administration Servers use the primary Administration Server as a proxy server if in the right pane of the KSN Proxy settings section, in the properties of secondary Administration Servers the Use Administration Server as a proxy server check box is selected.
- Click OK.
The KSN access settings will be saved.
You can also set up distribution point access to KSN, for example, if you want to reduce the load on the Administration Server. The distribution point that acts as a KSN proxy server sends KSN requests from managed devices to Kaspersky directly, without using the Administration Server.
To set up distribution point access to Kaspersky Security Network (KSN):
- Make sure that the distribution point is assigned manually.
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, select the Distribution points section.
- Select the distribution point in the list and click the Properties button to open its properties window.
- In the distribution point properties window, in the KSN Proxy section, select Access KSN Cloud/KPSN directly over the internet.
- Click OK.
The distribution point will act as a KSN proxy server.
Page top
Enabling and disabling KSN
To enable KSN:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server for which you need to enable KSN.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the KSN Proxy section, select the KSN Proxy settings subsection.
- Select the Use Administration Server as a proxy server.
The KSN proxy server is enabled.
- Select the I agree to use Kaspersky Security Network check box.
KSN will be enabled.
If this check box is selected, client devices send patch installation results to Kaspersky. When selecting this check box, you should read and accept the terms of the KSN Statement.
- Click OK.
To disable KSN:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server for which you need to enable KSN.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the KSN Proxy section, select the KSN Proxy settings subsection.
- Clear the Use Administration Server as proxy server check box to disable the KSN proxy service, or clear the I agree to use Kaspersky Security Network check box.
If this check box is cleared, client devices will send no patch installation results to Kaspersky.
If you are using KPSN, clear the Configure KPSN check box.
KSN will be disabled.
- Click OK.
Viewing the accepted KSN Statement
When you enable Kaspersky Security Network (KSN), you must read and accept the KSN Statement. You can view the accepted KSN Statement at any time.
To view the accepted KSN Statement:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server for which you enabled KSN.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the KSN Proxy section, select the KSN Proxy settings subsection.
- Click the View accepted KSN Statement link.
In the window that opens, you can view the text of the accepted KSN Statement.
Page top
Viewing the KSN proxy server statistics
KSN proxy server is a service that ensures interaction between the
infrastructure and client devices that are managed through the Administration Server.Using a KSN proxy server provides you the following features:
- Client devices can send requests to KSN and transfer information to KSN even if they do not have direct access to the internet.
- The KSN proxy server caches processed data, thus reducing the load on the outbound channel and the time period spent for waiting for information requested by a client device.
In the Administration Server properties window, you can configure the KSN proxy server and view statistics on the KSN proxy server usage.
To view the statistics of KSN proxy server:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server for which you need to view the KSN statistics.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the KSN Proxy section, select the KSN Proxy statistics subsection.
This section displays the actual statistics of the operation of KSN proxy server (the number of cache records, packages processed in cache, and received packages). Also, if Administration Server is connected to KSN, the corresponding informational message displays.
If necessary, perform these additional actions:
- Click Refresh to update the statistics on the KSN proxy server usage.
- Click the Export to file button to export the statistics to a CSV file.
- Click the Check KSN connection button to check if the Administration Server is currently connected to KSN.
- Click the OK button to close the Administration Server properties window.
Accepting an updated KSN Statement
You use KSN in accordance with the KSN Statement that you read and accept when you enable KSN. If the KSN Statement is updated, it is displayed to you when you update or upgrade Administration Server. You can accept the updated KSN Statement or decline it. If you decline it, you keep using KSN in accordance with the version of the KSN Statement that you previously accepted.
After updating or upgrading Administration Server, the updated KSN Statement is displayed automatically. If you decline the updated KSN Statement, you still can view and accept it later.
To view and then accept or decline an updated KSN Statement:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- On the Monitoring tab, in the Monitoring section, click the The accepted Kaspersky Security Network Statement is obsolete link.
The KSN Statement window opens.
- Carefully read the KSN Statement, and then make your decision. If you accept the updated KSN Statement, click the I accept the terms of the License Agreement button. If you decline the updated KSN Statement, click the Cancel button.
Depending on your choice, KSN keeps working in accordance with the terms of the current or updated KSN Statement. You can view the text of the accepted KSN Statement in the properties of Administration Server at any time.
Page top
Enhanced protection with Kaspersky Security Network
Kaspersky offers an extra layer of protection to users through the Kaspersky Security Network. This protection method is designed to combat advanced persistent threats and zero-day attacks. Integrated cloud technologies and the expertise of Kaspersky virus analysts make Kaspersky Endpoint Security the unsurpassed choice for protection against the most sophisticated network threats.
Details on enhanced protection in Kaspersky Endpoint Security are available on the Kaspersky website.
Page top
Checking whether the distribution point works as KSN proxy server
On a managed device assigned to work as a distribution point, you can enable KSN proxy server. A managed device works as KSN proxy server when the ksnproxy service is running on the device. You can check, turn on, or turn off this service on the device locally.
You can assign a Windows-based or a Linux-based device as a distribution point. The method of distribution point checking depends on the operating system of this distribution point.
To check whether the Windows-based distribution point works as KSN proxy server:
- On the distribution point device, in Windows, open Services (All Programs → Administrative Tools → Services).
- In the list of services, check whether the ksnproxy service is running.
If the ksnproxy service is running, then Network Agent on the device participates in Kaspersky Security Network and works as KSN proxy server for the managed devices included in the scope of the distribution point.
If you want, you may turn off the ksnproxy service. In this case, Network Agent on the distribution point stops participating in Kaspersky Security Network. This requires local administrator rights.
To check whether the Linux-based distribution point works as KSN proxy server:
- On the distribution point device, display the list of running processes.
- In the list of running processes, check whether the
/opt/kaspersky/ksc64/sbin/ksnproxyprocess is running.
If /opt/kaspersky/ksc64/sbin/ksnproxy process is running, then Network Agent on the device participates in Kaspersky Security Network and works as the KSN proxy server for the managed devices included in the scope of the distribution point.
Switching between Online Help and Offline Help
If you do not have internet access, you can use the Offline Help.
To switch between Online Help and Offline Help:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center main window, in the console tree select the Kaspersky Security Center 15.1.
- Click the Global interface settings link.
The settings window opens.
- In the settings window, click Use Offline Help.
- Click OK.
The settings are applied and saved. If you want, you can change the settings back at any time and start using Online Help at any time.
Page top
Export of events to SIEM systems
This section explains how to export events registered by Kaspersky Security Center to external Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems.
Configuring event export to SIEM systems
Kaspersky Security Center allows configuring by one of the following methods: export to any SIEM system that use Syslog format, export to QRadar, Splunk, ArcSight SIEM systems that use LEEF and CEF formats or export of events to SIEM systems directly from the Kaspersky Security Center database. When you complete this scenario, Administration Server sends events to SIEM system automatically.
Prerequisites
Before you start configuration export of events in the Kaspersky Security Center:
- Learn more about the methods of event export.
- Make sure that you have the values of system settings.
You can perform the steps of this scenario in any order.
The process of export of events to SIEM system consists of the following steps:
- Configuring SIEM system to receive events from Kaspersky Security Center
How-to instructions: Configuring event export in a SIEM system
- Selecting events you want to export to SIEM system:
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Marking events of a Kaspersky application for export in Syslog format, Marking general events for export in Syslog format
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Marking events of a Kaspersky application for export in Syslog format, Marking general events for export in Syslog format
- Configuring export of events to SIEM system using one of the following methods:
- Using TCP/IP, UDP or TLS over TCP protocols.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Configuring export of events to SIEM systems
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Configuring export of events to SIEM systems
- Using export of events directly from the Kaspersky Security Center database (a set of public views is provided in the Kaspersky Security Center database; you can find the description of these public views in the klakdb.chm document).
- Using TCP/IP, UDP or TLS over TCP protocols.
Results
After configuring export of events to SIEM system you can view export results if you selected events which you want to export.
Before you begin
When setting up automatic export of events in the Kaspersky Security Center, you must specify some of the SIEM system settings. It is recommended that you check these settings in advance in order to prepare for setting up Kaspersky Security Center.
To successfully configure automatic sending of events to a SIEM system, you must know the following settings:
About events in Kaspersky Security Center
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to receive information about events that occur during the operation of Administration Server and Kaspersky applications installed on managed devices. Information about events is saved in the Administration Server database. You can export this information to external SIEM systems. Exporting event information to external SIEM systems enables administrators of SIEM systems to promptly respond to security system events that occur on managed devices or administration groups.
Event types
In Kaspersky Security Center, there are the following types of events:
- General events. These events occur in all managed Kaspersky applications. An example of a general event is Virus outbreak. General events have strictly defined syntax and semantics. General events are used, for instance, in reports and dashboards.
- Managed Kaspersky applications-specific events. Each managed Kaspersky application has its own set of events.
Event sources
Events can be generated by the following applications:
- Kaspersky Security Center components:
- Managed Kaspersky applications
For details about the events generated by Kaspersky managed applications, refer to the documentation of the corresponding application.
You can view the full list of events that can be generated by an application on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. For Administration Server, you can additionally view the event list in the Administration Server properties.
Importance level of events
Each event has its own importance level. Depending on the conditions of its occurrence, an event can be assigned various importance levels. There are four importance levels of events:
- A critical event is an event that indicates the occurrence of a critical problem that may lead to data loss, an operational malfunction, or a critical error.
- A functional failure is an event that indicates the occurrence of a serious problem, error or malfunction that occurred during operation of the application or while performing a procedure.
- A warning is an event that is not necessarily serious, but nevertheless indicates a potential problem in the future. Most events are designated as warnings if the application can be restored without loss of data or functional capabilities after such events occur.
- An info event is an event that occurs for the purpose of informing about successful completion of an operation, proper functioning of the application, or completion of a procedure.
Each event has a defined storage term, during which you can view or modify it in Kaspersky Security Center. Some events are not saved in the Administration Server database by default because their defined storage term is zero. Only events that will be stored in the Administration Server database for at least one day can be exported to external systems.
About event export
You can use event export within centralized systems that deal with security issues on an organizational and technical level, provide security monitoring services, and consolidate information from different solutions. These are SIEM systems, which provide real-time analysis of security alerts and events generated by network hardware and applications, or Security Operation Centers (SOCs).
These systems receive data from many sources, including networks, security, servers, databases, and applications. SIEM systems also provide functionality to consolidate monitored data in order to help you avoid missing critical events. In addition, the systems perform automated analysis of correlated events and alerts in order to notify the administrators of immediate security issues. Alerting can be implemented through a dashboard or can be sent through third-party channels such as email.
The process of exporting events from Kaspersky Security Center to external SIEM systems involves two parties: an event sender—Kaspersky Security Center and an event receiver—SIEM system. To successfully export events, you must configure this in your SIEM system and in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console. It does not matter which side you configure first. You can configure the transmission of events in the Kaspersky Security Center and then configure the receipt of events by the SIEM system, or vice versa.
Methods for sending events from Kaspersky Security Center
There are three methods for sending events from Kaspersky Security Center to external systems:
- Sending events over the Syslog protocol to any SIEM system
Using the Syslog protocol, you can relay any events that occur on the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and in Kaspersky applications that are installed on managed devices. The Syslog protocol is a standard message-logging protocol. You can use it to export events to any SIEM system.
For this purpose, you need to mark the events that you want to relay to the SIEM system. You can mark the events in Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. Only marked events will be relayed to the SIEM system. If you marked nothing, no events will be relayed.
- Sending events over the CEF and LEEF protocols to QRadar, Splunk, and ArcSight systems
You can use the CEF and LEEF protocols to export general events. When exporting events over the CEF and LEEF protocols, you do not have the capability to select specific events to export. Instead, all general events are exported. To convert Kaspersky Security Center events to events in the CEF and LEEF format, you can use the siem_conversion_rules.xml file. This file contains the list of Kaspersky Security Center event attributes and corresponding attributes of events in the CEF and LEEF format. Also, the siem_conversion_rules.xml file contains the rules for generating messages corresponding to events. This file is included in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit.
Unlike the Syslog protocol, the CEF and LEEF protocols are not universal. CEF and LEEF are intended for the appropriate SIEM systems (QRadar, Splunk, and ArcSight). Therefore, when you choose to export events over one of these protocols, you use the required parser in the SIEM system.
- Directly from the Kaspersky Security Center database to any SIEM system
This method of exporting events can be used to receive events directly from public views of the database by means of SQL queries. The results of a query are saved to an XML file that can be used as input data for an external system. Only events available in public views can be exported directly from the database.
Receipt of events by the SIEM system
The SIEM system must receive and correctly parse events received from Kaspersky Security Center. For these purposes, you must properly configure the SIEM system. The configuration depends on the specific SIEM system utilized. However, there are a number of general steps in the configuration of all SIEM systems, such as configuring the receiver and the parser.
About configuring event export in a SIEM system
The process of exporting events from Kaspersky Security Center to external SIEM systems involves two parties: an event sender—Kaspersky Security Center and an event receiver—SIEM system. You must configure the export of events in your SIEM system and in the Kaspersky Security Center.
The settings that you specify in the SIEM system depend on the particular system that you are using. Generally, for all SIEM systems you must set up a receiver and, optionally, a message parser to parse received events.
Setting up the receiver
To receive events sent by Kaspersky Security Center, you must set up the receiver in your SIEM system. In general, the following settings must be specified in the SIEM system:
Depending on the SIEM system that you use, you may have to specify some additional receiver settings.
The figure below shows the receiver setup screen in ArcSight.
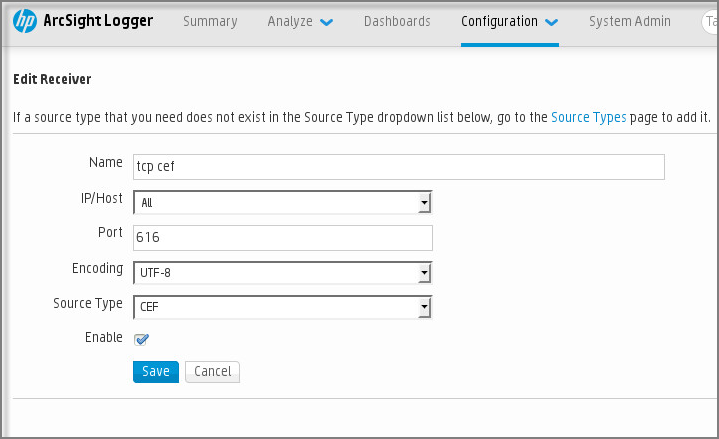
Receiver setup in ArcSight
Message parser
Exported events are passed to SIEM systems as messages. These messages must be properly parsed so that information on the events can be used by the SIEM system. Message parsers are part of the SIEM system; they are used to split the contents of the message into the relevant fields, such as event ID, severity, description, parameters. This enables the SIEM system to process events received from Kaspersky Security Center so that they can be stored in the SIEM system database.
Marking of events for export to SIEM systems in Syslog format
After enabling automatic export of events, you must select which events will be exported to the external SIEM system.
You can configure export of events in the Syslog format to an external system based on one of the following conditions:
- Marking general events. If you mark events to export in a policy, in the settings of an event, or in the Administration Server settings, the SIEM system will receive the marked events that occurred in all applications managed by the specific policy. If exported events were selected in the policy, you will not be able to redefine them for an individual application managed by this policy.
- Marking events for a managed application. If you mark events to export for a managed application installed on a managed device, the SIEM system will receive only the events that occurred in this application.
Marking events of a Kaspersky application for export in Syslog format
If you want to export events that occurred in an individual managed application installed on a managed device, mark the events for export for the application. If previously exported events were marked in the policy, you will not be able to redefine the marked events for an individual application managed by this policy.
To mark the events for export for an individual managed application:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, select the Managed devices node and go to the Devices tab.
- Right-click to open the context menu of the relevant device and select Properties.
- In the device properties window that opens, select the Applications section.
- In the list of applications that appears, select the application whose events you need to export and click the Properties button.
- In the application properties window, select the Event configuration section.
- In the list of events that appears, select one or several events that need to be exported to the SIEM system, and click the Properties button.
- In the event properties window that appears, select the Export to SIEM system using Syslog check box to mark the selected events for export in Syslog format. Clear the Export to SIEM system using Syslog check box to unmark the selected events for export in Syslog format.
If event properties are defined in a policy, the fields of this window cannot be edited.
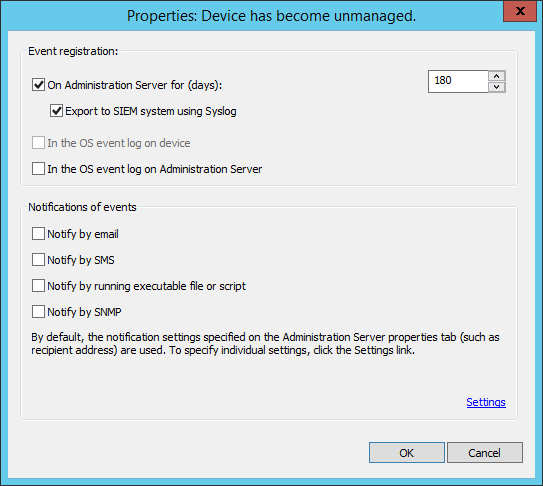
Event properties window
- Click OK to save the changes.
- Click OK in the application properties window and in the device properties window.
The marked events will be sent to the SIEM system over the Syslog format. The events for which you unselected the Export to SIEM system using Syslog check box, will not be exported to a SIEM system. The export will start immediately after you enable automatic export and select the events to export. Configure the SIEM system to ensure that it can receive events from Kaspersky Security Center.
Marking general events for export in Syslog format
If you want to export events that occurred in all applications managed by a specific policy, mark the events to export in the policy. In this case, you cannot mark events for an individual managed application.
To mark general events for export to a SIEM system:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, select the Policies node.
- Right-click to open the context menu of the relevant policy and select Properties.
- In the policy properties window that opens, select the Event configuration section.
- In the list of events that appears, select one or several events that need to be exported to the SIEM system, and click the Properties button.
If you need to select all events, click the Select all button.
- In the event properties window that appears, select the Export to SIEM system using Syslog check box to mark the selected events for export in Syslog format. Unselect the Export to SIEM system using Syslog check box to unmark the selected events for export in Syslog format.

Administration Server event properties window
- Click OK to save the changes.
- In the policy properties window, click OK.
The marked events will be sent to the SIEM system over the Syslog format. The events for which you unselected the Export to SIEM system using Syslog check box, will not be exported to a SIEM system. The export will start immediately after you enable automatic export and select the events to export. Configure the SIEM system to ensure that it can receive events from Kaspersky Security Center.
About exporting events using Syslog format
You can use the Syslog format to export to SIEM systems the events that occur in Administration Server and other Kaspersky applications installed on managed devices.
Syslog is a standard for message logging protocol. It permits separation of the software that generates messages, the system that stores them, and the software that reports and analyzes them. Each message is labeled with a facility code, indicating the software type that generates the message, and is assigned a severity level.
The Syslog format is defined by Request for Comments (RFC) documents published by the Internet Engineering Task Force (internet standards). The RFC 5424 standard is used to export the events from Kaspersky Security Center to external systems.
In Kaspersky Security Center, you can configure export of the events to the external systems using the Syslog format.
The export process consists of two steps:
- Enabling automatic event export. At this step, Kaspersky Security Center is configured so that it sends events to the SIEM system. Kaspersky Security Center starts sending events immediately after you enable automatic export.
- Selecting the events to be exported to the external system. At this step, you select which event to export to the SIEM system.
About exporting events using CEF and LEEF formats
You can use the CEF and LEEF formats to export to SIEM systems general events, as well as the events transferred by Kaspersky applications to the Administration Server. The set of export events is predefined, and you cannot select the events to be exported. Before sending events to the SIEM system (QRadar, ArcSight, or Splunk), it is necessary to interpret Kaspersky Security Center events to events in the CEF and LEEF format by using the rules specified in the siem_conversion_rules.xml file.
Select the format of export on the basis of the SIEM system used. The table below shows SIEM systems and the corresponding formats of export.
Formats of event export to a SIEM system
SIEM system |
Format of export |
|---|---|
QRadar |
LEEF |
ArcSight |
CEF |
Splunk |
CEF |
- LEEF (Log Event Extended Format)—A customized event format for IBM Security QRadar SIEM. QRadar can integrate, identify, and process LEEF events. LEEF events must use UTF-8 character encoding. You can find detailed information on LEEF protocol in IBM Knowledge Center.
- CEF (Common Event Format)—An open log management standard that improves the interoperability of security-related information from different security and network devices and applications. CEF enables you to use a common event log format so that data can easily be integrated and aggregated for analysis by an enterprise management system. CEF events must use UTF-8 character encoding.
Automatic export means that Kaspersky Security Center sends general events to the SIEM system. Automatic export of events starts immediately after you enable it. This section explains in detail how to enable automatic event export.
Configuring Kaspersky Security Center for export of events to a SIEM system
You can enable automatic event export in Kaspersky Security Center.
Only general events can be exported from managed applications over the CEF and LEEF formats. Interpretation rules used to convert events to the CEF and LEEF formats are specified in the siem_conversion_rules.xml file that is included in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit. Application-specific events cannot be exported from managed applications over the CEF and LEEF formats. If you need to export events of managed applications or a custom set of events that has been configured using the policies of managed applications, you have to export the events in the Syslog format.
To enable automatic export of events:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, select the Administration Server whose events you want to export.
- In the workspace of the selected Administration Server, select the Events tab.
- Click the drop-down arrow next to the Configure notifications and event export link, and then select Configure export to SIEM system in the drop-down list.
The events properties window opens, displaying the Event export section.
- In the Event export section, specify the following export settings:
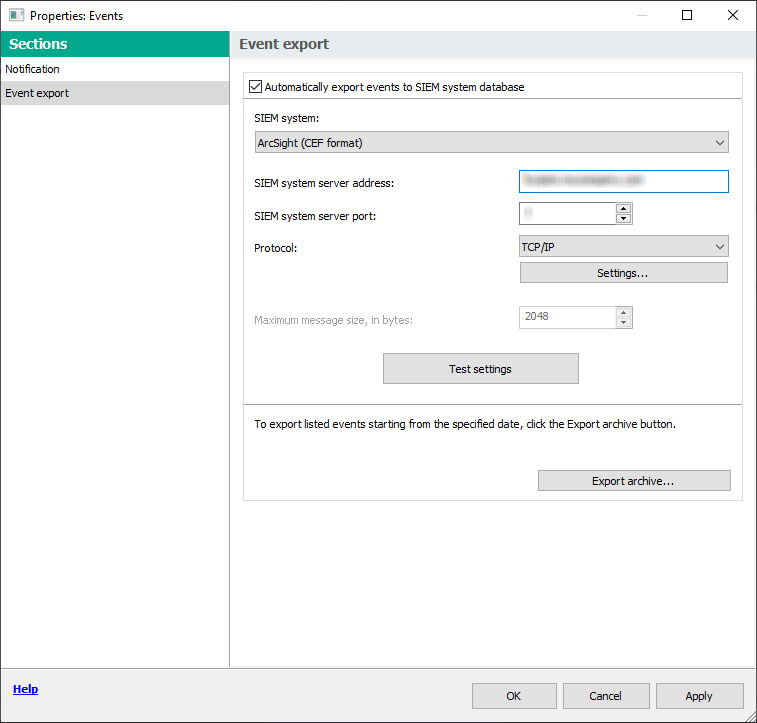
Event export section of the event properties window
- Automatically export events to SIEM system database
- SIEM system
If you select the Syslog format, you must specify:
- SIEM system server address
- SIEM system server port
- Protocol
- If you want to export to the SIEM system database the events that occurred after a specified date in the past, click the Export archive button, and then specify the start date for event export. By default, the event export starts immediately after you enable it.
- To check that the SIEM system connection is successfully configured, click the Test settings button.
The application tries to establish connection with the SIEM system server and send a test event. The connection status is displayed.
- Click OK.
Automatic export of events is enabled.
After enabling automatic export of events, you must select which events will be exported to the SIEM system.
Exporting events directly from the database
You can retrieve events directly from the Kaspersky Security Center database without having to use the Kaspersky Security Center interface. You can either query the public views directly and retrieve the event data, or create your own views on the basis of existing public views and address them to get the data you need.
Public views
For your convenience, a set of public views is provided in the Kaspersky Security Center database. You can find the description of these public views in the klakdb.chm document.
The v_akpub_ev_event public view contains a set of fields that represent the event parameters in the database. In the klakdb.chm document you can also find information on public views corresponding to other Kaspersky Security Center entities, for example, devices, applications, or users. You can use this information in your queries.
This section contains instructions for executing an SQL query by means of the klsql2 utility and a query example.
To create SQL queries or database views, you can also use any other program for working with databases. Information on how to view the parameters for connecting to the Kaspersky Security Center database, such as instance name and database name, is given in the corresponding section.
Executing an SQL query using the klsql2 utility
This article describes how to download and use the klsql2 utility, and how to execute an SQL query by using this utility.
To use the klsql2 utility:
- Locate the klsql2 utility in the installation folder of Kaspersky Security Center. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center. Do not use klsql2 utility versions intended for older Kaspersky Security Center versions.
- Create a file with the .sql extension in any text editor and place the file in the same folder with the utility.
- In the created .sql file, type the SQL query that you want, and then save the file.
- On the device with Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server installed, in the command line, type the following command to execute the SQL query from the .sql file and save the results to the result.xml file:
klsql2 -i src.sql -u <username> -p <password> -o result.xmlwhere
<username>and<password>are credentials of the user account that has access to the database. - If required, enter the login and password of the user account that has access to the database.
- Open the newly created result.xml files to view the SQL query results.
You can edit the .sql file and create any SQL query to the public views. Then, from the command line, execute your SQL query and save the results to a file.
Example of an SQL query in the klsql2 utility
This section shows an example of an SQL query, executed by means of the klsql2 utility.
The following examples illustrate retrieval of the events that occurred on devices during the last seven days, and display of the events ordered by the time they occur, the most recent events are displayed first.
Example for Microsoft SQL Server: SELECT e.nId, /* event identifier */ e.tmRiseTime, /* time, when the event occurred */ e.strEventType, /* internal name of the event type */ e.wstrEventTypeDisplayName, /* displayed name of the event */ e.wstrDescription, /* displayed description of the event */ e.wstrGroupName, /* name of the group, where the device is located */ h.wstrDisplayName, /* displayed name of the device, on which the event occurred */ CAST(((h.nIp / 16777216) & 255) AS varchar(4)) + '.' + CAST(((h.nIp / 65536) & 255) AS varchar(4)) + '.' + CAST(((h.nIp / 256) & 255) AS varchar(4)) + '.' + CAST(((h.nIp) & 255) AS varchar(4)) as strIp /* IP address of the device, on which the event occurred */ FROM v_akpub_ev_event e INNER JOIN v_akpub_host h ON h.nId=e.nHostId WHERE e.tmRiseTime>=DATEADD(Day, -7, GETUTCDATE()) ORDER BY e.tmRiseTime DESC |
Example for PostgreSQL: SELECT "e"."nId", /* event identifier */ "e"."tmRiseTime", /* time, when the event occurred */ "e"."strEventType", /* internal name of the event type */ "e"."wstrEventTypeDisplayName", /* displayed name of the event */ "e"."wstrDescription", /* displayed description of the event */ "e"."wstrGroupName", /* displayed description of the event */ "h"."wstrDisplayName", /* displayed name of the device, on which the event occurred */ ( CAST((("h"."nIp" / 16777216 )& 255 ) AS VARCHAR(4)) || '.' || CAST((("h"."nIp" / 65536 )& 255 ) AS VARCHAR(4)) || '.' || CAST((("h"."nIp" / 256 )& 255 ) AS VARCHAR(4)) || '.' || CAST((("h"."nIp" )& 255 ) AS VARCHAR(4)) ) AS "strIp" /* IP address of the device, on which the event occurred */ FROM "v_akpub_ev_event" AS "e" INNER JOIN "v_akpub_host" AS "h" ON "h"."nId" = "e"."nHostId" WHERE "e"."tmRiseTime" >= NOW() AT TIME ZONE 'utc' + make_interval(days => CAST(-7 AS INT)) ORDER BY "e"."tmRiseTime" DESC ; |
Example for MySQL or MariaDB: SELECT `e`.`nId`, /* event identifier */ `e`.`tmRiseTime`, /* time, when the event occurred */ `e`.`strEventType`, /* internal name of the event type */ `e`.`wstrEventTypeDisplayName`, /* displayed name of the event */ `e`.`wstrDescription`, /* displayed description of the event */ `e`.`wstrGroupName`, /* device group name */ `h`.`wstrDisplayName`, /* displayed name of the device, on which the event occurred */ CONCAT( LEFT(CAST(((`h`.`nIp` DIV 1677721) & 255) AS CHAR), 4), '.', LEFT(CAST(((`h`.`nIp` DIV 65536) & 255) AS CHAR), 4), '.', LEFT(CAST(((`h`.`nIp` DIV 256) & 255) AS CHAR), 4), '.', LEFT(CAST(((`h`.`nIp`) & 255) AS CHAR), 4) ) AS `strIp` /* IP address of the device, on which the event occurred */ FROM `v_akpub_ev_event` AS `e` INNER JOIN `v_akpub_host` AS `h` ON `h`.`nId` = `e`.`nHostId` WHERE `e`.`tmRiseTime` >= ADDDATE( UTC_TIMESTAMP( ) , INTERVAL -7 DAY) ORDER BY `e`.`tmRiseTime` DESC ; |
Viewing the Kaspersky Security Center database name
It can be helpful to know a database name if you need, for example, send an SQL query and connect to the database from your SQL script editor.
To view the name of the Kaspersky Security Center database:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center console tree, open the context menu of the Administration Server folder and select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Sections pane select Advanced and then Details of current database.
- In the Details of current database section, note the following database properties (see figure below):
- Instance name
- Database name
- Space allocated for the Kaspersky Security Center database
- Size of data in the entire database
- Number of events stored in the database
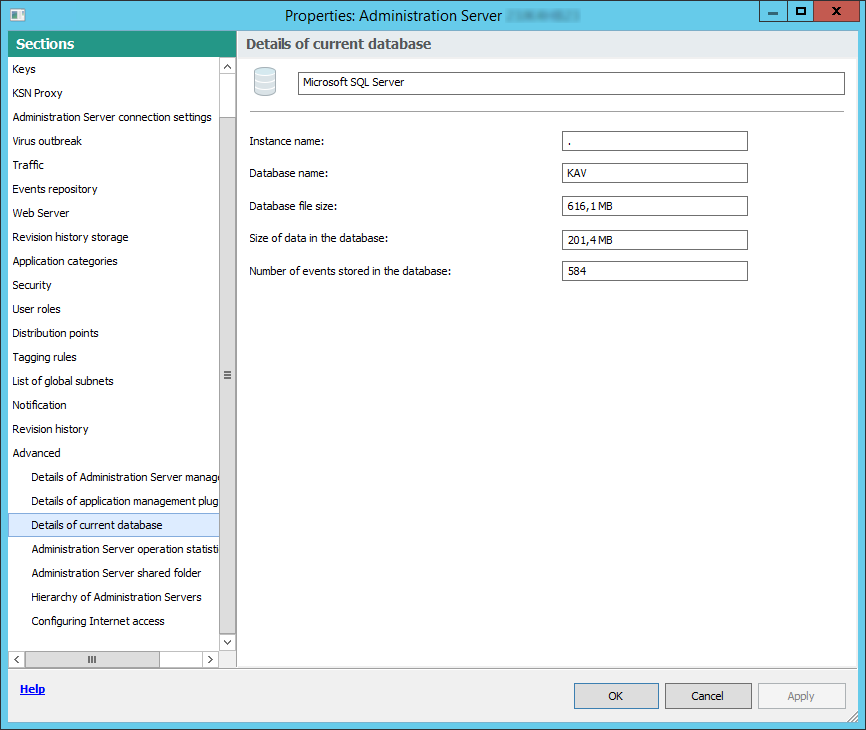
Section with information about the current Administration Server database
- Click the OK button to close the Administration Server properties window.
Use the database name to address the database in your SQL queries.
Viewing export results
You can control for successful completion of the event export procedure. To do this, check whether messages with export events are received by your SIEM system.
If the events sent from Kaspersky Security Center are received and properly parsed by your SIEM system, configuration on both sides is done properly. Otherwise, check the settings you specified in Kaspersky Security Center against the configuration in your SIEM system.
The figure below shows the events exported to ArcSight. For example, the first event is a critical Administration Server event: "Device status is Critical".
The representation of export events in the SIEM system varies according to the SIEM system you use.
Example of events
Using SNMP for sending statistics to third-party applications
This section describes how to get information from Administration Server by using Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) in Windows. Kaspersky Security Center contains SNMP agent, which transfers statistics of Administration Server performance to side applications using OIDs.
This section also contains information on resolving problems that you might encounter while using SNMP for Kaspersky Security Center.
Configuring the SNMP service for use with Kaspersky Security Center
This section describes how to configure the SNMP service on Windows to get information from Administration Server by using Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
SNMP support is disabled by default on Windows.
To enable SNMP support in Windows:
- Navigate to Control Panel.
- Open the Add or Remove Programs menu.
- Click Turn Windows features on or off.
- In the Windows features list, navigate to the SNMP feature, and then click OK.
- Navigate to Control Panel → Administrative Tools → Services.
- Choose the SNMP service and run it.
- Check if listening works by testing it with
netstatfor a standard UDP-port.
SNMP support is enabled on Windows.
To configure SNMP services in Windows:
- Make sure that the SNMP agent component of Kaspersky Security Center was installed during regular or silent installation.
- Make sure that the SNMP Service and SNMP Trap Windows services are running.
- Make sure that ManageEngine MIB Browser is installed on your system.
- In the SNMP Service service properties, on the Security tab, add two communities with the following rights:
Community
Rights
kasperskyNOTIFYpublicREAD WRITE - In the Accept SNMP packets from these hosts field, add the IP address of the device where ManageEngine MIB Browser is installed, for example, 10.10.10.105.
- On the Traps tab, type
kasperskyin the Community name field. - Click OK to save changes and close the service properties window.
- In ManageEngine MIB Browser, load adminkit.mib file from the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder. By default, the adminkit.mib file is in <Disk>:\Program Files\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center\snmp folder.
- In the Host field of ManageEngine MIB Browser window, add IP address of the device where Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server is installed.
The SNMP service is configured to get information from Administration Server by using Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
Page top
SNMP agent and object identifiers
For Kaspersky Security Center, SNMP agent is implemented as a dynamic library klsnmpag.dll, which is registered by the installer during Administration Server installation. SNMP agent works inside the snmp.exe process (that is a Windows service). Third-party applications use SNMP to receive statistics, which comes in the form of counters, on Administration Server performance.
Each counter has a unique object identifier (also referred to as OID). An object identifier is a sequence of numbers divided by dots. The object identifiers of Administration Server start with the 1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093 prefix. The OID of the counter is a concatenation of that prefix with a suffix describing the counter. For example, the counter with the OID value of 1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.4 has the suffix with value of 1.1.4.
You can use an SNMP client (such as Zabbix) to monitor the state of your system. In order to get the information, you can search for a value of OID that corresponds to the information and enter that value into your SNMP client. Then your SNMP client will return you another value that characterizes the status of your system.
The list of counters and counter types is in the adminkit.mib file on the Administration Server. MIB stands for Management Information Base. You can import and parse .mib files via the MIB Viewer application that is designed for requesting and displaying the counter values.
Getting a string counter name from an object identifier
In order to use an object identifier (OID) for transferring information to third-party applications, you may need to get a string counter name from that OID.
To get a string counter name from an OID:
- Open the
adminkit.mibfile, that is located on the Administration Server, in a text editor. - Locate the namespace describing the first value (from left to right).
For example, for 1.1.4 OID suffix would be
"counters" (::= { kladminkit 1 }). - Locate the namespace describing the second value.
For example, for 1.1.4 OID suffix would be
counters 1, which stands fordeployment. - Locate the namespace describing the third value.
For example, for 1.1.4 OID suffix would be
deployment 4, which stands forhostsWithAntivirus.
The string counter name is the concatenation of these values, for example, <MIB base namespace>.counters.deployment.hostsWithAntivirus, and it corresponds to the OID with the value of 1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.4.
Values of object identifiers for SNMP
The table below shows the values and descriptions of the objects identifiers (also referred to as OIDs), that are used for transferring information on Administration Server performance to third-party applications.
Values and descriptions of object identifiers for SNMP
Value of object identifier |
Numeric data type |
OID |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.1 |
Deployment status. The status can be one of the following:
|
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.2.1 |
The reason Value equals 1 in case a few devices were found without managed applications, and 0 otherwise. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.2.2 |
The reason |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.2.3 |
The reason |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.2.4 |
The reason |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.3 |
Number of devices in Administration Server groups. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.4 |
Number of devices in Administration Server groups with managed applications installed. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.5 |
Number of devices on which the task of the remote installation failed. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.6 |
ID of a license key that expires soon (in less than 7 days). |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.7 |
ID of the expired license key. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.8 |
Number of days before the license expires. For this parameter, the license period is considered expired if there are less than 7 days left until the expiration date. If there are more than 7 days left until the expiration date, the value is 0. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.9 |
Number of devices with a license that expires soon (in less than 7 days). |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.1.10 |
Number of devices with an expired license. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.2.1 |
Current status of Anti-virus bases update. The status can be one of the following:
|
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.2.2.1 |
This reason shows that Administration Server was not updated for a log time. The amount of time considered long is specified in |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.2.2.2 |
This reason shows that some devices were not updated for a long time (by default, 7 days or more for Critical and 3 days for Warning). You can obtain the number of those devices via |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.2.3 |
Last time when Anti-virus bases were updated on Administration Server. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.2.4 |
Number of devices containing Anti-virus bases that are not updated for a long time (by default, 7 days or more for Critical and 3 days for Warning). If there are devices with the Critical update status, only these devices are counted. You can obtain the update status via |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.3.1 |
Status of real-time protection. One of the following:
|
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.3.2.1 |
This reason shows that a security application is not running on some devices. You can obtain the number of those devices via |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.3.2.2 |
This reason shows that real-time protection is not running on some devices. You can obtain the number of those devices via |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.3.2.4 |
This reason shows that there are devices containing non-disinfected objects. You can obtain the number of those devices via |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.3.2.5 |
This reason shows that there are threats found on some devices. You can obtain the number of those devices via |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.3.2.6 |
This reason shows the virus outbreak status of the system. Value equals 1 if a certain amount of viruses were found during a certain amount of time, and 0 otherwise. Amount of viruses and amount of time are specified on Administration Server, by using the |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.3.3 |
Number of devices with security applications not running. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.3.4 |
Number of devices with real-time protection not running. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.3.5 |
Number of devices with real-time protection level not acceptable. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.3.6 |
Number of devices containing non-disinfected objects. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.3.7 |
Number of devices containing threats. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.4.1 |
Status of Anti-virus full scan. One of the following:
|
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.4.2.1 |
This reason shows that some devices have not been scanned for a certain amount of time. You can obtain the number of those devices via |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.4.3 |
Number of devices that have not been scanned for a certain amount of time. The amount of time is specified in |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.5.1 |
Status of the logical network of Administration Server. One of the following:
|
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.5.2.1 |
This reason shows that some devices have not been connected to Administration Server for a long time (7 days or more for a device of Warning status and 4 days for a device of Critical status). You can obtain the number of those devices via |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.5.2.2 |
This reason shows that there are devices whose control has been lost by Administration Server. You can obtain the number of those devices via |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.5.3 |
Number of devices found by Administration Server that do not belong to any Administration Server groups. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.5.4 |
Number of groups at Administration Server. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.5.5 |
Number of devices that have not been connected to Administration Server for a long time. The amount of time considered long is specified in |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.5.6 |
Number of devices that are not controlled by Administration Server. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.6.1 |
Status of events subsystem. One of the following:
|
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.6.2.1 |
The reason Value equals 1 if there is at least one critical event on any device, and 0 otherwise. |
|
|
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23668.1093.1.6.3 |
Number of critical events on Administration Server. |
Troubleshooting
This section lists solutions for a few typical issues that you might encounter while using the SNMP service.
Third-party application can not connect to the SNMP service
Make sure that SNMP service is installed and configured as described in Configuring SNMP service for using with Kaspersky Security Center section.
SNMP service is working, yet the third-party application cannot get any values
Allow SNMP agent tracing and make sure that a non-empty file is created. This means that the SNMP agent is properly registered and functioning. After this, allow connections from the SNMP service in the side service settings. If a side service operates on the same host as the SNMP agent, the list of IP addresses should contain either the IP address of that host or loopback 127.0.0.1.
An SNMP service that communicates with agents should be running in Windows. You can specify the paths to SNMP agents in the Windows Registry via regedit.
- For Windows 10:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SNMP\Parameters\ExtensionAgents
- For Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\SNMP\Parameters\ExtensionAgents
You can allow SNMP agent tracing via regedit as well.
- For 32-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\Components\34\1093\1.0.0.0\SNMP\Debug
- For 64-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\34\1093\1.0.0.0\SNMP\Debug
"TraceLevel"=dword:00000004
"TraceDir"="C:\\"
Values do not match the statuses of Administration Console
In order to reduce the load at Administration Server, the caching of values is implemented for the SNMP agent. The latency between the cache being actualized and the values being changed on the Administration Server may cause mismatches between the values returned by the SNMP agent and the actual ones. When working with third-party applications, you should consider that possible latency.
Page top
Working in a cloud environment
This section provides information about Kaspersky Security Center deployment and maintenance in cloud environments, such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Updates functionality (including providing anti-virus signature updates and codebase updates), as well as KSN functionality may not be available in the software in the U.S.
About work in a cloud environment
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 not only works with on-premises devices, but also provides special features for working in a cloud environment. Kaspersky Security Center works with the following virtual machines:
- Amazon EC2 instances (hereinafter, also referred to as instances). An Amazon EC2 instance is a virtual machine that is created on the basis of the Amazon Web Services (AWS) platform. Kaspersky Security Center uses AWS API (Application Programming Interface).
- Microsoft Azure virtual machines. Kaspersky Security Center uses Azure API.
- Google Cloud virtual machines instances. Kaspersky Security Center uses Google API.
You can deploy Kaspersky Security Center on an instance or a virtual machine to manage protection of devices in a cloud environment and to use special features of Kaspersky Security Center for work in a cloud environment. These features include:
- Using API tools to poll devices in a cloud environment
- Using API tools to install Network Agent and security applications on devices in a cloud environment
- Searching devices based on whether they belong to a specific cloud segment
You can also use an instance or a virtual machine on which a Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server is deployed to protect on-premises devices (for example, if a cloud server turns out to be easier for you to service and maintain than a physical one). If this is the case, you work with the Administration Server in the same way that you would if the Administration Server were installed on an on-premises device.
In a Kaspersky Security Center that has been deployed from a paid Amazon Machine Image (AMI) (in AWS) or a usage-based monthly billed SKU (in Azure), Vulnerability and patch management (including integration with SIEM systems) is automatically activated; Mobile Device Management cannot be activated.
The Administration Server is installed together with Administration Console. Kaspersky Security for Windows Server is also automatically installed on the device on which the Administration Server is installed.
You can configure Kaspersky Security Center with the Configure cloud environment wizard, taking into account the specifics of working in a cloud environment.
Scenario: Deployment for a cloud environment
This section describes the deployment of Kaspersky Security Center for working in cloud environments such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
After you finish the deployment scenario, Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and Administration Console are started and configured with the default parameters. Anti-Virus protection managed by Kaspersky Security Center is deployed on the selected Amazon EC2 instances or Microsoft Azure virtual machines. You can then fine-tune the configuration of Kaspersky Security Center, create a complex structure of administration groups, and create various policies and tasks for groups.
The deployment of Kaspersky Security Center for working in cloud environments consists of the following parts:
- Preparation work
- Deploying Administration Server
- Installing Kaspersky anti-virus applications on virtual devices that need to be protected
- Configuring the update download settings
- Configuring the settings for managing reports about the protection status of devices
The Configure cloud environment wizard is intended for performing the initial configuration. It starts automatically the first time that Kaspersky Security Center is deployed from a ready-to-use image. You can manually start the wizard at any time. In addition, you can manually perform all of the actions that it performs.
We recommend that you plan for a minimum of one hour for deploying Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server in the cloud environment and at least one working day for protection deployment in the cloud environment.
Deployment of Kaspersky Security Center in the cloud environment proceeds in stages:
- Planning the configuration of cloud segments
Learn how Kaspersky Security Center works in a cloud environment. Plan where Administration Server will be deployed (inside or outside of the cloud environment); and determine how many cloud segments you plan to protect. If you are planning to deploy Administration Server outside of the cloud environment or if you are planning to protect more than 5000 devices, you will need to install Administration Server manually.
To work with Google Cloud, you can only install Administration Server manually.
- Planning the resources
Make sure that you have everything that is required for deployment.
- Subscribing to Kaspersky Security Center as a ready-to-use image
Select one of the ready-to-use AMIs at AWS Marketplace or select a Usage-based monthly billed SKU at Azure Marketplace, pay for it according to marketplace rules if necessary (or use the BYOL model), and then use the image to deploy an Amazon EC2 instance or Microsoft Azure virtual machine with Kaspersky Security Center installed.
This stage is necessary only if you plan to deploy Administration Server on an instance or a virtual machine within a cloud environment and you are also planning to deploy protection for no more than 5000 devices. Otherwise, this stage is not necessary and instead you manually have to install Administration Server, Administration Console, and the DBMS.
This step is unavailable for Google Cloud.
- Determining the location of the DBMS
Determine where your DBMS will be.
If you plan to use a database outside the cloud environment, make sure that you have a working database.
If you plan to use Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS), create a database with RDS in the AWS cloud environment.
If you plan to use Microsoft Azure SQL DBMS, create a database with the Azure Database service in the Microsoft Azure cloud environment.
If you plan to use Google MySQL, create a database in the Google Cloud (Please refer to https://cloud.google.com/sql/docs/mysql for details).
- Installing Administration Server and Administration Console (Microsoft Management Console based and/or web-based Console) on selected devices manually
Install Administration Server, Administration Console, and the DBMS on the selected devices, as described in the main installation scenario for Kaspersky Security Center.
This stage is necessary if you plan to place Administration Server outside of a cloud environment or if you plan to deploy protection for more than 5000 devices. Then make sure that your Administration Server meets hardware requirements. Otherwise, this stage is not necessary and a subscription to Kaspersky Security Center as a ready-to-use image in AWS Marketplace, Azure Marketplace, or Google Cloud is sufficient.
- Ensuring that Administration Server has the permissions to work with cloud APIs
In AWS, go to the AWS Management Console and create an IAM role or an IAM user account. The created IAM role (or IAM user account) will allow Kaspersky Security Center to work with the AWS API: Poll cloud segments and deploy protection.
In Azure, create a subscription and an Application ID with password. Kaspersky Security Center uses these credentials to work with the Azure API: Poll cloud segments and deploy protection.
In Google Cloud, register a project, get your project ID and a private key. Kaspersky Security Center uses these credentials to poll cloud segments by using the Google API.
- Creating an IAM role for protected instances (for AWS only)
In the AWS Management Console, create an IAM role that defines the set of permissions for executing requests to AWS. This newly created role will be subsequently assigned to new instances. The IAM role is required in order to use Kaspersky Security Center to install applications on instances.
- Preparing a database by using Amazon Relational Database Service or Microsoft Azure SQL
If you plan to use Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS), create an Amazon RDS database instance and an S3 bucket on which the database backup will be stored. You can skip this stage if you want a database on the same EC2 instance where Administration Server is installed or if you want your database to be located somewhere else.
If you plan to use Microsoft Azure SQL, create a storage account and a database in Microsoft Azure.
If you plan to use Google MySQL, configure your database in the Google Cloud. (Please refer to https://cloud.google.com/sql/docs/mysql for details.)
- Licensing Kaspersky Security Center for working in the cloud environment
Make sure that you have licensed Kaspersky Security Center to work in the cloud environment and provide an activation code or key file so that the application can add it to license storage. This stage can be completed during the configuration of the cloud environment.
This stage is required if you are using Kaspersky Security Center installed from a free ready-to-use AMI based on the BYOL model or if you are manually installing Kaspersky Security Center without the use of AMIs. In each of these cases, you will need a license for Kaspersky Security for Virtualization or a license for Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security, to activate Kaspersky Security Center.
If you are using Kaspersky Security Center installed from a ready-to-use image, this stage is not necessary and the corresponding window of the Configure cloud environment wizard is not displayed.
- Authorization in the cloud environment
Provide Kaspersky Security Center with your AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud credentials so that Kaspersky Security Center can operate with the necessary permissions. This stage can be completed during the authorization in the cloud environment.
- Polling a cloud segment so that Administration Server can receive information about devices in the cloud segment
Start cloud segment polling. In the AWS environment, Kaspersky Security Center will receive the addresses and names of all instances that can be accessed, based on the permissions of the IAM role or IAM user. In the Microsoft Azure environment, Kaspersky Security Center will receive the addresses and names of all virtual machines that can be accessed, based on the permissions of the Reader role.
You can then use Kaspersky Security Center to install Kaspersky applications and software from other vendors on the detected instances or virtual machines.
Kaspersky Security Center regularly starts a poll, which means that new instances or virtual machines are automatically detected.
- Combining all network devices into the Cloud administration group
Move the discovered instances or virtual machines into the Managed devices\Cloud administration group so that they can become available for centralized management. If you want to assign devices to subgroups, for example, depending on which operating system is installed on them, you can create several administration groups within the Managed devices\Cloud group. You can enable automatic moving of all devices that will be detected during routine polls to the Managed devices\Cloud group.
- Using Network Agent to connect networked devices to Administration Server
Install Network Agent on devices in the cloud environment. Network Agent is the Kaspersky Security Center component that provides for communication between devices and Administration Server. Network Agent settings are configured automatically by default.
You can install Network Agent on each device locally. You can also install Network Agent on devices remotely using Kaspersky Security Center. Or, you can skip this stage and install Network Agent together with the latest versions of the security applications.
- Installing the latest versions of security applications on networked devices
Select the devices on which you want to install security applications, and then install the latest versions of security applications on those devices. You can perform the installation either remotely using Kaspersky Security Center on Administration Server or locally.
You may have to create installation packages for these programs manually.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux is intended for instances and virtual machines running Linux.
Kaspersky Security for Windows Server is intended for instances and virtual machines running Windows.
- Configuring update settings
The Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is created automatically when you start configuring the cloud environment. You can also create the task manually. This task automatically finds and downloads required application updates for subsequent installation to network devices using Kaspersky Security Center tools.
It is recommended to complete the following stage after the cloud environment configuration is complete:
- Configuring report management
You can view reports on the Monitoring tab in the workspace of the Administration Server node. You can also receive reports by email. Reports on the Monitoring tab are available by default. To configure the receipt of reports by email, specify the email addresses that should receive reports, and then configure the format of reports.
Results
Upon completion of the scenario, you can make sure that the initial configuration was successful:
- You can connect to Administration Server through Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- The latest versions of Kaspersky security applications are installed and running on managed devices.
- Kaspersky Security Center has created the default policies and tasks for all managed devices.
Prerequisites for deploying Kaspersky Security Center in a cloud environment
Before starting deployment of Kaspersky Security Center in the Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure cloud environment, make sure that you have the following:
- Internet access
- One of the following accounts:
- Amazon Web Services account (for work with AWS)
- Microsoft account (for work with Azure)
- Google account (for work with Google Cloud)
- One of the following:
- License for Kaspersky Security for Virtualization
- License for Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security
- Funds to purchase such a license (Kaspersky Security for Virtualization or Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security)
- Funds to pay for a ready-to-use image at the Azure Marketplace
- Guides for the latest versions of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux and Kaspersky Security for Windows Server
Hardware requirements for the Administration Server in a cloud environment
For deployment in cloud environments, the requirements for Administration Server and database server are the same as the requirements for physical Administration Server (depending on how many devices you want to manage). Please refer to the documentation of the cloud environment for details.
Licensing options in a cloud environment
Work in a cloud environment is outside the basic functionality of Kaspersky Security Center and therefore requires a dedicated license.
Two Kaspersky Security Center licensing options are available for working in a cloud environment:
- Paid AMI (in Amazon Web Services) or Usage-based monthly billed SKU (in Microsoft Azure).
This grants a license for Kaspersky Security Center as well as licenses for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux and Kaspersky Security for Windows Server. You have to pay according to the rules of the cloud environment that you use.
This model lets you have not more than 200 client devices for one Administration Server.
- A free-of-charge, ready-to-use image using a proprietary license, according to the Bring Your Own License (BYOL) model.
For Kaspersky Security Center licensing in AWS or Azure, you must have a license for one of the following applications:
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization
- Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security
The BYOL model lets you have up to 100,000 client devices for one Administration Server. This model also lets you manage devices outside the AWS, Azure, or Google environment.
You can choose the BYOL model in any of the following cases:
- You already own a valid license for Kaspersky Security for Virtualization.
- You already own a valid license for Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security.
- You are willing to purchase a license immediately before deployment of Kaspersky Security Center.
At the stage of initial setup, Kaspersky Security Center prompts you for an activation code or key file.
If you choose BYOL, you will not have to pay for Kaspersky Security Center through Azure Marketplace or AWS Marketplace.
In both cases, Vulnerability and patch management is automatically activated, and Mobile Device Management cannot be activated.
You may encounter an error when trying to activate the feature Support of the cloud environment using the license for Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security.
Upon subscribing to Kaspersky Security Center, you get an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance or a Microsoft Azure virtual machine with Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server. The installation packages for Kaspersky Security for Windows Server and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux are available on the Administration Server. You can install these applications on devices in the cloud environment. You do not have to license these applications.
If a managed device is not visible to the Administration Server for more than a week, the application (Kaspersky Security for Windows Server or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux) on the device will shift to limited functionality mode. To activate the application again, you have to make the device on which the application is installed visible to the Administration Server again.
Database options for work in a cloud environment
You must have a database to work with Kaspersky Security Center. When deploying Kaspersky Security Center in AWS, in Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud, you have three options:
- Create a local database on the same device with the Administration Server. Kaspersky Security Center comes with a SQL Server Express database that can support up to 5000 managed devices. Choose this option if SQL Server Express Edition is enough for your needs.
- Create a database with the Relational Database Service (RDS) in the AWS cloud environment, or with the Azure Database service in the Microsoft Azure cloud environment. Choose this option if you want a DBMS other than SQL Express. Your data will be transferred inside the cloud environment, where it will remain, and you will not have any extra expenses. If you already work with Kaspersky Security Center on premises and have some data in your database, you can transfer your data to the new database.
For work on Google Cloud Platform, you can only use Cloud SQL for MySQL.
- Use an existing database server. Choose this option if you already have a database server and want to use it for Kaspersky Security Center. If this server is outside the cloud environment, your data will be transferred over the internet, which might result in extra expenses.
The procedure of Kaspersky Security Center deployment in the cloud environment has a special step for creating (choosing) a database.
Working in Amazon Web Services cloud environment
This section tells you how to prepare for working with Kaspersky Security Center in Amazon Web Services.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
About work in Amazon Web Services cloud environment
You can purchase Kaspersky Security Center at AWS Marketplace in the form of an Amazon Machine Image (AMI), which is a ready-to-use image of a preconfigured virtual machine. You can subscribe to a paid AMI or BYOL AMI and, based on that image, create an Amazon EC2 instance with Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server installed.
To work with the AWS platform and, in particular, to purchase apps at AWS Marketplace and create instances, you need an Amazon Web Services account. You can create a free account at https://aws.amazon.com. You can also use an existing Amazon account.
If you subscribed to an AMI available at AWS Marketplace, you receive an instance with your ready-to-use Kaspersky Security Center. You do not have to install the application yourself. In this case, Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server is installed on the instance without your involvement. After installation, you can start Administration Console and connect to Administration Server to begin working with Kaspersky Security Center.
To learn more about an AMI and how AWS Marketplace works, please visit the AWS Marketplace Help page. For more information about working with the AWS platform, using instances, and related concepts, please refer to the Amazon Web Services documentation.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Creating IAM roles and IAM user accounts for Amazon EC2 instances
This section describes the actions that must be performed to ensure correct operation of the Administration Server. These actions include work with the AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles and user accounts. Also described are the actions that must be taken on client devices to install Network Agent on them and then install Kaspersky Security for Windows Server and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux.
Ensuring that the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server has the permissions to work with AWS
The standards for operating in the Amazon Web Services cloud environment prescribe that a special IAM role be assigned to the Administration Server instance for working with AWS services. An IAM role is an IAM entity that defines the set of permissions for execution of requests to AWS services. The IAM role provides the permissions for cloud segment polling and installation of applications on instances.
After you create an IAM role and assign it to the Administration Server, you will be able to deploy protection of instances by using this role, without providing any additional information to Kaspersky Security Center.
However, it may be advisable to not create an IAM role for the Administration Server in the following cases:
- The devices whose protection you plan to manage are EC2 instances within the Amazon Web Services cloud environment but the Administration Server is outside of the environment.
- You plan to manage the protection of instances not only within your cloud segment but also within other cloud segments that were created under a different account in AWS. In this case, you will need an IAM role only for the protection of your cloud segment. An IAM role will not be needed to protect another cloud segment.
In these cases, instead of creating an IAM role you will need to create an IAM user account, that will be used by Kaspersky Security Center to work with AWS services. Before starting to work with the Administration Server, create an IAM user account with an AWS IAM access key (hereinafter also referred to as IAM access key).
Creation of an IAM role or IAM user account requires the AWS Management Console. To work with the AWS Management Console, you will need a user name and password from an account in AWS.
Creating an IAM role for the Administration Server
Before you deploy the Administration Server, in the AWS Management Console create an IAM role with permissions required for installation of applications on instances. For more details, see AWS Help sections about IAM roles.
To create an IAM role for the Administration Server:
- Open the AWS Management Console and log in under your AWS account.
- In the Roles section, create a role with the following permissions:
- AmazonEC2ReadOnlyAccess, if you plan to only run cloud segment polling and do not plan to install applications on EC2 instances using AWS API.
- AmazonEC2ReadOnlyAccess and AmazonSSMFullAccess, if you plan to run cloud segment polling and install applications on EC2 instances using AWS API. In this case, you will also need to assign an IAM role with the AmazonEC2RoleforSSM permission to the protected EC2 instances.
You will need to assign this role to the EC2 instance that you will use as the Administration Server.
The newly created role is available for all applications on the Administration Server. Therefore, any application running on the Administration Server has the capability to poll cloud segments or install applications on EC2 instances within a cloud segment.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Creating an IAM user account for work with Kaspersky Security Center
An IAM user account is required for working with Kaspersky Security Center if the Administration Server has not been assigned an IAM role with permissions for device discovery and installation of applications on instances. The same account, or a different account, is also required for backing up the Administration Server data task if you use an S3 bucket. You can create one IAM user account with all the necessary permissions, or you can create two separate user accounts.
An IAM access key that you will need to provide to Kaspersky Security Center during initial configuration is automatically created for the IAM user. An IAM access key consists of an access key ID and a secret key. For more details about the IAM service, please refer to the following AWS reference pages:
- http://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/introduction.html.
- http://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/IAM_UseCases.html#UseCase_EC2.
To create an IAM user account with the necessary permissions:
- Open the AWS Management Console and sign in under your account.
- In the list of AWS services, select IAM (as shown in the figure below).
List of services in the AWS Management Console
A window opens containing a list of user names and a menu that lets you work with the tool.
- Navigate through the areas of the console dealing with user accounts, and add a new user name or names.
- For the user(s) you add, specify the following AWS properties:
- Access type: Programmatic Access.
- Permissions boundary not set.
- Permissions:
- ReadOnlyAccess—If you plan to run only cloud segment polling and do not plan to install applications on EC2 instances using AWS API.
- ReadOnlyAccess and AmazonSSMFullAccess—If you plan to run cloud segment polling and install applications on EC2 instances using AWS API. In this case, you must assign an IAM role with the AmazonEC2RoleforSSM permission to the protected EC2 instances.
After you add permissions, view them for accuracy. In case of a mistaken selection, go back to the previous screen and make the selection again.
- After you create the user account, a table appears containing the IAM access key of the new IAM user. The access key ID is displayed in the Access key ID column. The secret key is displayed as asterisks in the Secret access key column. To view the secret key, click Show.
The newly created account is displayed in the list of IAM user accounts that corresponds to your account in AWS.
When deploying Kaspersky Security Center in a cloud segment, you must specify that you are using an IAM user account and provide the access key ID and secret access key to Kaspersky Security Center.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Creating an IAM role for installation of applications on Amazon EC2 instances
Before you start protection deployment on EC2 instances by using Kaspersky Security Center, create in the AWS Management Console an IAM role with permissions required for installation of applications on instances. For more details, see AWS Help sections AWS Help about IAM roles.
The IAM role is required so that you can assign it to all EC2 instances on which you plan to install security applications by using Kaspersky Security Center. If you do not assign an instance the IAM role with the necessary permissions, installation of applications on this instance using AWS API tools will result in an error.
To work with the AWS Management Console, you will need a user name and password from an account in AWS.
To create an IAM role for installing applications on instances:
- Open the AWS Management Console and log in under your AWS account.
- In the menu on the left, select Roles.
- Click the Create Role button.
- In the list of services that appears, select EC2 and then in the Select Your Use Case list select EC2 again.
- Click the Next: Permissions button.
- In the list that opens, select the check box next to AmazonEC2RoleforSSM.
- Click the Next: Review button.
- Enter a name and a description for the IAM role and click the Create role button.
The role that you created appears in the list of roles with the name and description that you entered.
Hereinafter, you can use the newly created IAM role to create new EC2 instances that you intend to protect through Kaspersky Security Center, as well as associate it with existing instances.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Working with Amazon RDS
This section describes which actions must be taken to prepare a database of Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) for Kaspersky Security Center, place it in an option group, create an IAM role for working with an RDS database, prepare an S3 bucket for storage, and migrate an existing database to RDS.
Amazon RDS is a web service that helps AWS users to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the AWS cloud environment. If you want, you can use an Amazon RDS database to work with Kaspersky Security Center.
You can work with the following databases:
- Microsoft SQL Server
- SQL Express Edition
- Aurora MySQL 5.7
- Standard MySQL 5.7
Creating an Amazon RDS instance
If you want to use Amazon RDS as the DBMS, you have to create an Amazon RDS database instance. This section describes how to select SQL Express Edition; if you want to work with Aurora MySQL or Standard MySQL (versions 5.7, 8.0), you must select one of those engines.
To create an Amazon RDS database instance:
- Open the AWS Management Console at https://console.aws.amazon.com and sign in under your account.
- Using the AWS interface, create a database with the following settings:
- Engine: Microsoft SQL Server, SQL Express Edition
- DB engine version: SQL Server 2014 12.00.5546.0v1
- DB instance class: db.t2.medium
- Storage type: General purpose
- Allocated storage: minimum 50 GiB
- Security group: the same group where the EC2 instance with Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server will be located
Create an identifier, username and password for your RDS instance.
You may leave default settings in all the other fields. Or, change the default settings if you want to customize your Amazon RDS instance. To get help, refer to the AWS information pages.
- At the last step, AWS displays the results of the process. If you want to view the details of your Amazon RDS instance, click View DB instance details. If you want to proceed to the next action, start creating an option group for your Amazon RDS instance.
The creation of a new Amazon RDS instance may take up to several minutes. After the instance is created, you can use it for work with Kaspersky Security Center data.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Creating option group for Amazon RDS instance
You need to place your Amazon RDS instance into an option group.
To create an option group for your Amazon RDS instance:
- Make sure that you are in the AWS Management Console (https://console.aws.amazon.com) and signed in under your account.
- In the menu line, click Services.
The list of available services appears (see figure below).

List of services in the AWS Management Console
- In the list, click RDS.
- In the left pane, click Option groups.
- Click the Create group button.
- Create an option group with the following settings, if you chose SQL Server at the stage of creating the Amazon RDS instance:
- Engine: SQLserver-ex
- Major engine version: 12.00
If you chose a different SQL database at the stage of creating the Amazon RDS instance, then choose a corresponding engine.
The group is created and displayed in the list of your groups.
After creating the option group, place your Amazon RDS instance into this option group.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Modifying the option group
The default configuration of the option group in which you placed the Amazon RDS instance is not enough for working with the Kaspersky Security Center database. You have to add options to the option group and create a new IAM role for working with the database.
To modify the option group and create a new IAM role:
- Make sure that you are in the AWS Management Console (https://console.aws.amazon.com) and signed in under your account.
- In the menu line, click Services.
The list of available services appears (see figure below).

List of services in the AWS Management Console
- In the list, select RDS.
- In the left pane, click Option groups.
The list of option groups is displayed.
- Select the option group in which you placed your Amazon RDS instance and click the Add option button.
The Add option window opens.
- In the IAM role section, select the Create a new role / Yes option and enter a name for the new IAM role.
The role is created with a default set of permissions. Later, you will have to change its permissions.
- In the S3 bucket section, do one of the following:
- If you haven't created an Amazon S3 bucket instance for the data backup, select the Create a new S3 bucket link and create a new S3 bucket, using the AWS interface.
- If you already have created an Amazon S3 bucket instance for the Administration Server data backup task, select your S3 bucket from the drop-down list.
- Finish adding options by clicking the Add option button at the bottom of the page.
You have modified the option group and created a new IAM role for working with the RDS database.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Modifying permissions for IAM role for Amazon RDS database instance
After you add options to the option group, you must assign required permissions to the IAM role that you created for working with the Amazon RDS database instance.
To assign required permissions to the IAM role that you created for work with the Amazon RDS database instance:
- Make sure that you are in the AWS Management Console (https://console.aws.amazon.com) and signed in under your account.
- In the list of services, select IAM.
A window opens containing a list of user names and a menu that lets you work with the tool.
- In the menu, select Roles.
- In the list of IAM roles displayed in the workspace, select the role that you created when adding option to the option group.
- Using the AWS interface, delete the sqlNativeBackup-<date> policy.
- Using the AWS interface, attach the AmazonS3FullAccess policy to the role.
The IAM role is assigned the required permissions to work with Amazon RDS.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Preparing Amazon S3 bucket for database
If you plan to use Amazon Relational Database System (Amazon RDS) database, you have to create an Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket instance where the regular Backup of the database will be stored. For information about Amazon S3 and about S3 buckets, refer to the Amazon help pages. For more information about creating an Amazon S3 instance, refer to Amazon S3 help page.
To create an Amazon S3 bucket:
- Make sure that the AWS Management Console is open and you are signed in under your account.
- In the list of AWS services, select S3.
- Navigate the console to create a bucket, following the instructions of the wizard.
- Select the same region where your Administration Server is located (or will be located).
- When the wizard finishes, make sure that the new bucket appears in the list of buckets.
A new S3 bucket is created and appears in your list of buckets. You have to specify this bucket when adding options to the option group. You will also have to specify the address of your S3 bucket to Kaspersky Security Center when the Kaspersky Security Center creates the Backup of Administration Server data task.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Migrating the database to Amazon RDS
You can migrate your Kaspersky Security Center database from an on-premises device to an Amazon S3 instance that supports Amazon RDS. To do this, you need an S3 bucket for an RDS database and an IAM user account with AmazonS3FullAccess permission for this S3 bucket.
To perform the migration of the database:
- Make sure that you have created an RDS instance (refer to Amazon RDS reference pages for more information).
- On your physical Administration Server (on-premises), run the Kaspersky Backup utility to back up Administration Server data.
You must make sure that the file is named backup.zip.
- Copy the backup.zip file to the EC2 instance on which Administration Server is installed.
Make sure that you have enough disk space on the EC2 instance on which Administration Server is installed. In the AWS environment, you can add disk space to your instance to accommodate the process of database migration.
- On the AWS Administration Server, start the Kaspersky Backup utility again in interactive mode.
The Backup and restore wizard starts.
- At the Select action step, select Restore Administration Server data and click Next.
- At the Restore settings step, click the Browse button next to the Folder for storage of backup copies.
- In the Sign In to Online Storage window that opens, fill in the following fields and then click OK:
- Select the Migrate from local backup option. The Browse button becomes available.
- Click the Browse button to choose the folder on the AWS Administration Server where you copied the backup.zip file.
- Click Next and complete the procedure.
Your data will be restored to the RDS database using your S3 bucket. You can use this database for further work with Kaspersky Security Center in the AWS environment.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Working in Microsoft Azure cloud environment
This section provides information about Kaspersky Security Center deployment and maintenance in a cloud environment provided by Microsoft Azure, as well as details of protection deployment on virtual machines in this cloud environment.
In a Kaspersky Security Center that has been deployed from a Usage-based monthly billed SKU, Vulnerability and patch management is automatically activated, and Mobile Device Management cannot be activated.
About work in Microsoft Azure
To work with the Microsoft Azure platform and, in particular, to purchase apps at the Azure Marketplace and create virtual machines, you will need an Azure subscription. Before you deploy Administration Server, create an Azure Application ID with permissions required for installation of applications on virtual machines.
If you purchase a Kaspersky Security Center image at the Azure Marketplace, you can deploy a virtual machine with your ready-to-use Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server. You must select settings of the virtual machine, but you do not have to install the application yourself. After installation, you can start Administration Console and connect to Administration Server to begin working with Kaspersky Security Center.
You can also use an Azure virtual machine with Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server deployed on it to protect on-premises devices (for example, if a cloud server turns out to be easier to service and maintain than a physical one). If this is the case, you work with the Administration Server in the same way that you would if the Administration Server were installed on an on-premises device. If you do not plan to use Azure API tools, you do not need an Azure Application ID. In this case, an Azure subscription is enough.
Creating a subscription, Application ID, and password
To work with Kaspersky Security Center in the Microsoft Azure environment, you need an Azure subscription, Azure Application ID, and Azure Application password. You can use an existing subscription, if you already have one.
An Azure subscription grants its owner access to the Microsoft Azure Platform Management Portal and to Microsoft Azure services. The owner can use the Microsoft Azure Platform to manage services such as Azure SQL and Azure Storage.
To create a Microsoft Azure subscription,
Go to https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cost-management-billing/manage/create-subscription and follow the instructions there.
More information about creating a subscription is available on the Microsoft website. You will get a subscription ID, which you will later provide to Kaspersky Security Center together with Application ID and password.
To create and save Azure Application ID and password:
- Go to https://portal.azure.com and make sure that you are logged in.
- Following the instructions on the reference page, create your Application ID.
- Go to the Keys section of the application settings.
- In the Keys section, fill in the Description and Expires fields and leave the Value field empty.
- Click Save.
When you click Save, the system automatically fills the Value field with a long sequence of characters. This sequence is your Azure Application password (for example, yXyPOy6Tre9PYgP/j4XVyJCvepPHk2M/UYJ+QlfFvdU=). The description is displayed as you entered it.
- Copy the password and save it, so that you can later provide the Application ID and password to Kaspersky Security Center.
You can copy the password only when it has been created. Later, the password will no longer be displayed and you cannot restore it.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Assigning a role to the Azure Application ID
If you only want to detect virtual machines using device discovery, your Azure Application ID must have the Reader role. If you want not only to detect virtual machines, but also to deploy protection on the virtual machines, your Azure Application ID must have the Virtual Machine Contributor role.
Follow the instructions on the Microsoft website to assign a role to your Azure Application ID.
Deploying Administration Server in Microsoft Azure and selecting database
To deploy Administration Server in the Microsoft Azure environment:
- Sign in to Microsoft Azure using your account.
- Go to the Azure portal.
- In the left pane, click the green plus sign.
- Type "Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security" in the search field in the menu.
Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security is a combination of Kaspersky Security Center and two security applications for protection of instances: Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux and Kaspersky Security for Windows Server.
- In the list of results, select Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security or Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security (BYOL).
In the right part of the screen, an information window appears.
- Read information and click the Create button in the end of the information window.
- Fill all the necessary fields. Use the tooltips to get information and assistance.
- When selecting the size, select one of the three starred options.
In most cases, 8 gigabytes (GB) of RAM is enough. However, in Azure, you can increase the size of RAM and other resources of the virtual machine at any time.
- When selecting a database, select one of the following, according to your plan:
- Local—If you want a database on the same virtual machine where the Administration Server will be deployed. Kaspersky Security Center comes with an SQL Server Express database. Choose this option if SQL Server Express is enough for your needs.
- New—If you want a new RDS database in the Azure environment. Choose this option if you want a DBMS other than SQL Server Express. Your data will be transferred to the cloud environment, where it will remain, and you will not have any extra expenses.
- Existing—If you want to use an existing database server. In this case, you will have to specify its location. If this server is outside the Azure environment, your data will be transferred over the internet, which might result in extra expenses.
- When entering the subscription ID, use the subscription that you created earlier.
After deployment, you can connect to the Administration Server using RDP. You can use the Administration Console to work with the Administration Server.
Working with Azure SQL
This section describes which actions must be taken to prepare a Microsoft Azure database for Kaspersky Security Center, prepare an Azure storage account, and migrate an existing database to Azure SQL.
SQL Database is a general-purpose relational database managed service in Microsoft Azure.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Creating Azure storage account
You have to create a storage account in Microsoft Azure for working with Azure SQL database and for deployment scripts.
To create a storage account:
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- In the left pane, select Storage accounts to proceed to the Storage accounts window.
- In the Storage accounts window, click the Add button to proceed to the Create storage account window.
- Fill in all the necessary fields to create a storage account:
- Location: must be the same as the location of the Administration Server.
- Other fields: you may leave the default values.
Use the tooltips to get information about each field.
After the storage account is created, the list of your storage accounts is displayed.
- In the list of your storage accounts, click the name of the newly created account to see information about this account.
- Make sure you know the account name, the resource group, and access keys for this storage account. You will need this information for working with Kaspersky Security Center.
You can refer to Azure website for help.
If you already have a storage account, you can use it for working with Kaspersky Security Center.
Creating Azure SQL database and SQL Server
You need an SQL database and SQL Server in the Azure environment.
To create an Azure SQL database and SQL Server:
- Follow the instructions on the Azure website.
You can create a new server when Microsoft Azure prompts you to do so; if you already have an Azure SQL Server, you can use it for Kaspersky Security Center rather than creating a new one.
- After creating the SQL database and SQL Server, make sure that you know its resource name and resource group:
- Go to https://portal.azure.com and make sure that you are logged in.
- In the left pane, select SQL databases.
- Click the name of a database from the list of your databases.
The properties window opens.
- The name of the database is the resource name. The name of the resource group is displayed in the Overview section of the properties window.
You need the resource name and resource group of the database for migrating the database to Azure SQL.
Migrating the database to Azure SQL
After Administration Server is deployed in the Azure environment, you can migrate your Kaspersky Security Center database from an on-premises device to Azure SQL. You need an Azure storage account for an Azure SQL database. You also must have Microsoft SQL Server Data-Tier Application Framework (DacFx) and SQLSysCLRTypes on your Administration Server.
To perform the migration of the database:
- Make sure that you have created an Azure storage account.
- Make sure that you have SQLSysCLRTypes and DacFx on your Administration Server.
You can download Microsoft SQL Server Data-Tier Application Framework (17.0.1 DacFx) and SQLSysCLRTypes (choose the version corresponding to the version of your SQL Server) from the official Microsoft website.
- On your physical Administration Server (on-premises), run the Kaspersky Backup utility to back up Administration Server data with the Migrate to Azure format option enabled.
- Copy the backup file to the Azure Administration Server.
Make sure that you have enough disk space on the Azure virtual machine where the Administration Server is installed. In the Azure environment, you can add disk space to your virtual machines to accommodate the process of database migration.
- On the Administration Server located in the Microsoft Azure environment, start the Kaspersky Backup utility again in interactive mode.
The Backup and restore wizard starts.
- At the Select action step, select Restore Administration Server data and click Next.
- At the Restore settings step, click the Browse button next to the Folder for storage of backup copies.
- In the Sign In to Online Storage window that opens, fill in the following fields and then click OK:
- Select the Migrate from local backup option.
The Browse button becomes available.
- Click the Browse button to choose the folder on the Azure Administration Server where you copied the backup file.
- Click Next and complete the procedure.
Your data will be restored to the Azure SQL database by using your Azure storage. You can use this database for further work with Kaspersky Security Center in the Azure environment.
The addresses of web pages cited in this document are correct as of the Kaspersky Security Center release date.
Working in Google Cloud
This section provides information about work with Kaspersky Security Center in a cloud environment provided by Google.
Creating client email, project ID, and private key
You can use the Google API to work with Kaspersky Security Center in Google Cloud Platform. A Google account is required. Please refer to the Google documentation at https://cloud.google.com for more information.
You will need to create and provide Kaspersky Security Center with the following credentials:
Working with Google Cloud SQL for MySQL instance
You can create a database in Google Cloud and use this database for Kaspersky Security Center.
Kaspersky Security Center works with MySQL 5.7 and 5.6. Other versions of MySQL have not been tested.
To create and configure a MySQL database:
In your browser, go to https://cloud.google.com/sql/docs/mysql/create-instance#create-2nd-gen and follow the instructions provided.
When configuring a MySQL database, use the following flags:
- sort_buffer_size 10000000
- join_buffer_size 20000000
- innodb_lock_wait_timeout 300
- max_allowed_packet 32000000
- innodb_thread_concurrency 20
- max_connections 151
- tmp_table_size 67108864
- max_heap_table_size 67108864
- lower_case_table_names 1
Prerequisites for client devices in a cloud environment necessary for work with Kaspersky Security Center
The devices on which you intend to install Administration Server, Network Agent, and Kaspersky security applications must meet the following conditions:
- The configuration of security groups makes available the following ports on the Administration Server (minimum set of ports required for deployment):
- 8060 HTTP—For transfer of Network Agent installation packages and security application installation packages from the Administration Server to protected instances
- 8061 HTTPS—For transfer of Network Agent installation packages and security application installation packages from the Administration Server to protected instances
- 13000 TCP—For transfers from protected instances and secondary Administration Servers to the primary Administration Server using SSL
- 13000 UDP—For transfer of information about shutdown of instances to the Administration Server
- 14000 TCP—For transfers from protected instances and secondary Administration Servers to the primary Administration Server without using SSL
- 13291—For connecting Administration Console to the Administration Server
- 40080—For the operation of deployment scripts
You can configure security groups in AWS Management Console or at the Azure portal. If you intend to use Kaspersky Security Center in a non-default configuration, please refer to the Knowledge Base. Examples of non-default configurations include not installing Administration Console on the Administration Server device but installing it on your workstation instead, or using a KSN proxy server.
- Port 15000 UDP is available on the client devices (for receipt of requests for communication with the Administration Server).
- In the AWS cloud environment:
- If you plan to use AWS API, the IAM role is set under which the applications will be installed on the instances.
- On each Amazon EC2 instance, Systems Manager Agent (SSM Agent) is installed and running.
- SSM Agent enables Kaspersky Security Center to automatically install applications on devices and groups of devices without requesting confirmation by an administrator each time.
- On instances that are running a Windows operating system and were deployed from AMIs later than November 2016, SSM Agent is installed and running. You will have to manually install SSM Agent on all other devices. For details about installing SSM Agent on devices running Windows and Linux operating systems, please refer to the AWS Help page.
- In the Microsoft Azure cloud environment:
- On each Azure virtual machine, Azure VM Agent is installed and running.
By default, a new virtual machine is created with Azure VM Agent, and you do not have to install or enable it manually. Please refer to Microsoft Help pages for details about Azure VM Agent on Windows devices and on Linux devices.
- Your Azure Application ID has the following roles:
- Reader (to discover virtual machines by using polling)
- Virtual Machine Contributor (to deploy protection on the virtual machines)
- SQL Server Contributor (to use an SQL database in the Microsoft Azure environment)
If you want to perform all these operations, assign all the three roles to your Azure Application ID.
- On each Azure virtual machine, Azure VM Agent is installed and running.
Creating installation packages required to configure cloud environment
The Configure cloud environment wizard in Kaspersky Security Center is available if you have the installation packages and management plug-ins for the following programs:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
Deployment of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows in a cloud environment will be available after the upcoming release of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.0 for Windows.
- Kaspersky Security for Windows Server
These installation packages are required for installing the applications on the instances or virtual machines that you want to protect. If you do not have these installation packages, you must create them. Otherwise, the Configure cloud environment wizard cannot work.
To create installation packages:
- Download the latest versions of the applications and plug-ins at the Kaspersky website:
- The installer and the management plug-in for Kaspersky Security for Windows Server.
- The installer, files for remote installation via Kaspersky Security Center, and the management plug-in for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux.
- Save all files on the instance (or virtual machine) where the Administration Server is installed.
- Extract the files from all the packages.
- Start Kaspersky Security Center.
- In the console tree, go to Advanced → Remote installation → Installation packages and click Create installation package.
- Select Create Kaspersky installation package.
- Specify the name for the package and the path to the application installer: <folder>\<file name>.kud, and then click Next.
- Read the End User License Agreement and select the check box confirming that you accept its terms, and then click Next.
The installation package will be uploaded to the Administration Server and will be available in the list of installation packages.
Configuration of a cloud environment becomes available as soon as you create the installation packages and install the management plug-ins on the Administration Server.
Configuring cloud environment
To configure Kaspersky Security Center by using the Configure cloud environment wizard, you must have the following:
- Specific credentials for a cloud environment:
- An IAM role that has been granted the right to poll the cloud segment or an IAM user account that has been granted the right to poll the cloud segment (for work with Amazon Web Services)
- Azure Application ID, password, and subscription (for work with Microsoft Azure)
- Google client email, Project ID, and private key (for work with Google Cloud)
- Installation packages:
- Network Agent for Windows
- Network Agent for Linux
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- Web plug-in for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- At least one of the following:
- Installation package and web plug-in for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (recommended)
- Installation package and web plug-in for Kaspersky Security for Windows Server
If you do not want to use cloud environment capabilities (if, for example, you want to manage protection of physical client devices only), you can close the Configure cloud environment wizard and run the standard Administration Server quick start wizard manually.
The Configure cloud environment operation starts automatically at the first connection to Administration Server through Administration Console if you are deploying Kaspersky Security Center from a ready-to-use image. You can also start the Configure cloud environment wizard manually at any time.
To start the Configure cloud environment wizard manually:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server node.
- In the context menu of the node, select All Tasks → Configure cloud environment.
The average work session lasts about 15 minutes.
About the Configure cloud environment wizard
The Configure cloud environment wizard allows you to configure Kaspersky Security Center while taking into account the specifics of working in a cloud environment.
The wizard creates the following objects:
- Network Agent policy with default settings
- Policy for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- Policy for Kaspersky Security for Windows Server
- Administration group for instances and a rule for automatically moving instances to this administration group
- Administration Server data backup task
- Tasks for installing protection on devices running Linux and Windows
- Tasks for each managed device:
- Quick Malware Scan
- Update download
If you selected the BYOL licensing option, configuring cloud environment also activates Kaspersky Security Center with a key file or activation code and places the key file or activation code in the license storage.
Step 1. Selecting the application activation method
This step is not displayed if you signed up for one of the ready-to-use AMIs (at the AWS Marketplace), or for a Usage-based monthly billed SKU (at the Azure Marketplace). In this case, the wizard immediately proceeds to the next step. However, you cannot purchase a ready-to-use AMI for Google Cloud.
If you selected BYOL licensing option for Kaspersky Security Center, the wizard prompts you to select the application activation method.
Activate the application with an activation code (or a key file) for Kaspersky Security for Virtualization or for Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security.
You can activate the application in one of the following ways:
- By entering an activation code.
Online activation will start. This process involves verification of the specified activation code, as well as issuance and activation of a key file.
- By specifying a key file.
The application will check the key file and either activate it if it contains the correct information, or prompt you to specify another key file.
Kaspersky Security Center places the license key in the license storage and marks it as automatically distributed on managed devices.
If you connect to an instance using standard Remote Desktop Connection in Microsoft Windows or a similar application, in the remote connection properties you must specify the drive of the physical device that you are using to connect. This ensures access from the instance to the files on your physical device, and lets you select and specify the key file.
When working with Kaspersky Security Center deployed from a paid AMI or for a Usage-based monthly billed SKU, you cannot add key files or activation codes to the license storage.
Step 2. Selecting the cloud environment
Select the cloud environment in which you are deploying Kaspersky Security Center: AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
Step 3. Authorization in the cloud environment
AWS
If you selected AWS, either specify that you have an IAM role with the required rights, or provide Kaspersky Security Center with an AWS IAM access key. Cloud segment polling is not possible without an IAM role or an AWS IAM access key.
Specify the following settings for the connection that will be used for further polling of the cloud segment:
This connection is saved in the application settings. You can create only a single AWS IAM access key with the Configure cloud environment. Subsequently, you can specify more connections to manage other cloud segments.
If you want to install applications on instances through Kaspersky Security Center, you must make sure that your IAM role (or the IAM user whose account is associated with the key that you are entering) has all the necessary permissions.
Azure
If you selected Azure, specify the following settings for the connection that will be used for further polling the cloud segment:
- Connection name
- Azure Application ID
- Azure Subscription ID
- Azure Application password
- Azure storage account name
- Azure storage access key
This connection is saved in the application settings.
Google Cloud
If you selected Google Cloud, specify the following settings for the connection that will be used for further polling the cloud segment:
This connection is saved in the application settings.
Step 4. Configuring synchronization with Cloud and choosing further actions
At this step, cloud segment polling starts and a special administration group for instances is created. The instances found during polling are placed into this group. The cloud segment polling schedule is configured (every 5 minutes by default).
A Synchronize with Cloud automatic moving rule is also created. For each subsequent scan of the cloud network, virtual devices detected will be moved to the corresponding subgroup within the Managed devices\Cloud group.
On the Synchronization with the cloud segment page, you can define the following settings:
For Google Cloud, you can only perform the deployment with Kaspersky Security Center native tools. If you selected Google Cloud, the Deploy protection option is not available.
Step 5. Configuring Kaspersky Security Network in the cloud environment
Specify the settings for relaying information about Kaspersky Security Center operations to the Kaspersky Security Network knowledge base. Select one of the following options:
Kaspersky recommends participation in Kaspersky Security Network.
Step 6. Configuring email notifications in the cloud environment
Configure the delivery of notifications about events registered during the operation of Kaspersky applications on virtual client devices. These settings will be used as the default settings for application policies.
To configure the delivery of notifications about events occurring in Kaspersky applications, use the following settings:
You can test the new email notification settings by clicking the Send test message button. If the test message was successfully received at the addresses specified in the Recipients (email addresses) field, the settings have been correctly configured.
Step 7. Creating an initial configuration of the protection of the cloud environment
At this step, Kaspersky Security Center automatically creates policies and tasks. The Configure initial protection window displays a list of policies and tasks created by the application.
If you use an RDS database in the AWS cloud environment, you have to provide IAM access key pair to Kaspersky Security Center when the Administration Server backup task is being created. In this case, fill in the following fields:
If you use an Azure SQL database in the Azure cloud environment, you have to provide information about your Azure SQL Server to Kaspersky Security Center when the Administration Server backup task is being created. In this case, fill in the following fields:
- Azure storage account name
- Azure Subscription ID
- Azure Application password
- Azure Application ID
- Azure SQL server name
- Azure SQL server resource group
- Azure storage access key
If you are deploying the Administration Server in the Google Cloud, you have to select a folder where the backup copies will be stored. Select a folder on your local device or a folder on a virtual machine instance.
The Next button becomes available after the creation of all policies and tasks that are necessary for minimum configuration of protection.
If a device on which the tasks are supposed to run is not visible to the Administration Server, then the tasks start only when the device becomes visible. If you create a new EC2 instance or a new Azure virtual machine, it might take some time before it becomes visible to the Administration Server. If you want Network Agent and the security applications to be installed on all the newly created devices as soon as possible, make sure that the Run missed tasks option is enabled for the Install application remotely tasks. Otherwise, a newly created instance/virtual machine will not get Network Agent and the security applications until the task starts according to its schedule.
Step 8. Selecting the action when the operating system must be restarted during installation (for the cloud environment)
If you previously selected Deploy protection, you must choose what to do when the operating system of a target device has to be restarted. If you did not select the Deploy protection option, this step is skipped.
Select whether to restart instances if the device operating system has to be restarted during installation of applications:
If you want to force the closing of all applications in blocked sessions on the instances before the restart, select the Force closure of applications in blocked sessions check box. If this check box is cleared, you will have to close manually all applications that are running on blocked instances.
Step 9. Receiving updates by the Administration Server
At this step, you can view the progress of downloading updates necessary for correct operation of the Administration Server. You can click the Next button, without waiting for download completion, to proceed to the final page of the wizard.
The wizard finishes.
Checking configuration
To check whether Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 is properly configured for working in a cloud environment:
- Start Kaspersky Security Center and make sure that you can connect to the Administration Server via the Administration Console.
- In the console tree, select Managed devices\Cloud.
- When viewing any of the subgroups in the Managed devices\Cloud group, make sure that the Devices tab displays all devices of that subgroup.
If the devices are not displayed, you can poll the corresponding cloud segments manually to find them.
- Make sure that the Policies tab has active policies for the following applications:
- Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent
- Kaspersky Security for Windows Server
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
If they are not listed, you can create them manually.
- Make sure that the Tasks tab lists the following tasks:
- Backup of Administration Server data
- Update task for Windows Server
- Administration Server maintenance
- Download updates to the Administration Server repository
- Find vulnerabilities and required updates
- Install protection for Windows
- Install protection for Linux
- Quick scan task for Windows Server
- Quick Scan
- Install updates for Linux
If they are not listed, you can create them manually.
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 is properly configured for work in a cloud environment.
Cloud device group
You can manage cloud devices by combining them into groups. At the stage of initially configuring Kaspersky Security Center, the Managed devices\Cloud administration group is created by default, and cloud devices detected during polling are placed into this group.
If you selected the Synchronize administration group structure with the cloud segment option when you configured synchronization, the structure of subgroups in this administration group is identical to the structure of your cloud segments. (However, in AWS, availability zones and placement groups are not represented in the structure; in Microsoft Azure, subnets are not represented in the structure.) Empty subgroups within the group that are detected during polling are automatically deleted.
You can also manually create administration groups by combining all or specific devices.
By default, the Managed devices\Cloud group inherits the policies and tasks from the Managed devices group. You can change the settings if the Editing allowed check boxes are selected in the properties of the settings of the corresponding policies and tasks.
Network segment polling
Information about the structure of the network and devices in this network is received by the Administration Server through regular polling of cloud segments by using AWS API, Azure API, or Google API tools. Kaspersky Security Center uses this information to update the contents of the Unassigned devices and Managed devices folders. If you have configured devices to be moved to administration groups automatically, the detected devices are included in administration groups.
To allow the Administration Server to poll cloud segments, you must have the rights provided with an IAM role or IAM user account (in AWS), or with Application ID and password (in Azure), or with a Google client email, Google project ID, and private key.
You can add and delete connections, as well as set the polling schedule for each cloud segment.
Adding connections for cloud segment polling
To add a connection for cloud segment polling to the list of available connections:
- In the console tree, select the Device discovery → Cloud node.
- In the workspace of the window, click Configure polling.
A properties window opens containing a list of connections available for cloud segment polling.
- Click the Add button.
The Connection window opens.
- Specify the name of the cloud environment for the connection that will be used for further polling of the cloud segment:
If you selected AWS, specify the following settings:
The Configure cloud environment wizard allows you to specify only a single AWS IAM access key. Subsequently, you can specify more connections to manage other cloud segments.
If you selected Azure, specify the following settings:
- Connection name
- Azure Application ID
- Azure Subscription ID
- Azure Application password
- Azure storage account name
- Azure storage access key
If you selected Google Cloud, specify the following settings:
- If you want, select Set polling schedule and change the default settings.
The connection is saved in the application settings.
After the new cloud segment is polled for the first time, the subgroup corresponding to that segment appears in the Managed devices\Cloud administration group.
If you specify incorrect credentials, no instances will be found during cloud segment polling and a new subgroup will not appear in the Managed devices\Cloud administration group.
Deleting connections for cloud segment polling
If you no longer have to poll a specific cloud segment, you can delete the connection corresponding to that segment from the list of available connections. You can also delete a connection if, for example, permissions to poll a cloud segment have been transferred to another AWS IAM user with a different key.
To delete a connection:
- In the console tree, select the Device discovery → Cloud node.
- In the workspace of the window, select Configure polling.
A window opens containing a list of connections available for cloud segment polling.
- Select the connection that you want to delete and click the Delete button in the right part of the window.
- In the window that opens, click the OK button to confirm your selection.
If you are deleting connections from the list of available connections, the devices that are in the corresponding segments are automatically deleted from the corresponding administration groups.
Configuring the polling schedule
Cloud segment polling is performed according to schedule. You can set the polling frequency.
The polling frequency is automatically set at 5 minutes in the Configure cloud environment settings. You can change this value at any time and set a different schedule. However, it is not recommended to configure polling to run more frequently than every 5 minutes, because this could lead to errors in the API operation.
To configure a cloud segment polling schedule:
- In the console tree, select the Device discovery → Cloud node.
- In the workspace, click Configure polling.
The cloud properties window opens.
- In the list, select the connection you want and click the Properties button.
The connection properties window opens.
- In the properties window, click the Set polling schedule link.
The Schedule window opens.
- Define the following settings:
- Scheduled start
Polling schedule options:
- Run missed tasks
- Scheduled start
- Click OK to save the changes.
The polling schedule is configured and saved.
Installing applications on devices in a cloud environment
You can install the following Kaspersky applications on the devices in a cloud environment: Kaspersky Security for Windows Server (for Windows devices) and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux (for Linux devices).
Client devices on which you intend to install protection must meet the requirements for Kaspersky Security Center operation in a cloud environment. You must have a valid license to install applications on AWS instances, Microsoft Azure virtual machines or Google virtual machine instances.
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 supports the following scenarios:
- A client device is discovered by means of an API; the installation is also performed by means of an API. For AWS and Azure cloud environments, this scenario is supported.
- A client device is discovered by means of Active Directory polling, Windows domains polling, or IP range polling; the installation is performed by means of Kaspersky Security Center.
- A client device is discovered by means of Google API; the installation is performed by means of Kaspersky Security Center. For Google Cloud, only this scenario is supported.
Other ways of installation of the applications are not supported.
To install applications on virtual devices, use installation packages.
To create a task for remote installation of the application on instances by using AWS API or Azure API:
- In the console tree, select the Tasks folder.
- Click the New task button.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- On the Select the task type page, select Install application remotely as the task type.
- On the Select devices page, select the relevant devices from the Managed devices\Cloud group.
- If Network Agent has not yet been installed on the devices on which you are intending to install the application, on the Selecting an account to run the task page select Account required (Network Agent is not used) and click the Add button in the right part of the window. In the menu that appears, select one of the following:
You can provide multiple credentials by clicking the Add button for each new one. If different cloud segments require different credentials, provide the credentials for all the segments.
After the wizard finishes, the task for remote installation of the application appears in the list of tasks in the workspace of the Tasks folder.
In Microsoft Azure, remote installation of security applications on a virtual machine may result in deleting Custom Script Extension installed on this virtual machine.
Viewing the properties of cloud devices
To view the properties of a cloud device:
- In the console tree, in the Device discovery → Cloud node, select the subnode that corresponds to the group where the relevant instance is located.
If you are unaware of the group where the relevant virtual device is located, use the search function:
- Right-click the name of the Managed devices → Cloud node, and then select Search in the context menu.
- In the window that opens, perform a search.
If a device exists that meets the criteria that you set, its name and details will be displayed in the lower part of the window.
- Right-click the name of the relevant node. In the context menu, select Properties.
In the window that opens, the object properties are displayed.
The System Info → General system info section contains the properties that are specific for devices in cloud environment:
- Device discovered using API (AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud; if the device cannot be detected by using API tools, the No value is displayed).
- Cloud Region.
- Cloud VPC (for AWS and Google Cloud devices only).
- Cloud availability zone (for AWS and Google Cloud devices only).
- Cloud subnet.
- Cloud placement group (this unit is only displayed if the instance belongs to a placement group; otherwise, it is not displayed).
You can click the Export to file button to export this information to a .csv or .txt file.
Synchronization with cloud
During the Configure cloud environment operation, the Synchronize with Cloud rule is created automatically. This rule allows you to automatically move instances detected in each poll, from the Unassigned devices group to the Managed devices\Cloud group, to make these instances available for centralized management. By default, the rule is active after it is created. You can disable, modify, or enforce the rule at any time.
To edit the properties of the Synchronize with Cloud rule and/or enforce the rule:
- In the console tree, right-click the name of the Device discovery node.
- In the context menu, select Properties.
- In the Properties window that opens, in the Sections pane, select Move devices.
- In the list of device moving rules in the workspace, select Synchronize with Cloud and then click the Properties button in the lower part of the window.
The rule properties window opens.
- If necessary, specify the following settings in the Cloud segments settings group:
- Device is in cloud segment
- Include child objects
- Move devices from nested objects to corresponding subgroups
- Create subgroups corresponding to containers of newly detected devices
- Delete subgroups for which no match is found in the cloud segments
If you enabled the Synchronize with Cloud option when running the Configure cloud environment, the Synchronize with Cloud rule is created with the Create subgroups corresponding to containers of newly detected devices and Delete subgroups for which no match is found in the cloud segments check boxes selected.
If you did not enable Synchronize with Cloud option, the Synchronize with Cloud rule is created with these options disabled (cleared). If your work with Kaspersky Security Center requires that the structure of subgroups in the Managed devices\Cloud subgroup matches the structure of cloud segments, enable the Create subgroups corresponding to containers of newly detected devices and Delete subgroups for which no match is found in the cloud segments options in the rule properties, and then enforce the rule.
- Device is in cloud segment
- In the Device discovered using API drop-down list, select one of the following values:
- AWS. The device is discovered by using the AWS API, that is, the device is definitely in the AWS cloud environment.
- Azure. The device is discovered by using the Azure API, that is, the device is definitely in the Azure cloud environment.
- Google Cloud. The device is discovered by using the Google API, that is, the device is definitely in the Google Cloud environment.
- No. The device cannot be detected by using the AWS, Azure, or Google API, that is, it is either outside the cloud environment or it is in the cloud environment but it cannot be detected by using an API.
- No value. This condition does not apply. If necessary, set up other rule properties in other sections.
- If necessary, enforce the rule by clicking the Force button in the lower part of the window.
The Rule execution wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard. When the wizard finishes, the rule will be run and the structure of subgroups in the Managed devices\Cloud subgroup will match the structure of your cloud segments.
- Click the OK button.
The properties are set up and saved.
To disable the Synchronize with Cloud rule:
- In the console tree, right-click the name of the Device discovery node.
- In the context menu, select Properties.
- In the Properties window that opens, in the Sections pane, select Move devices.
- In the list of device moving rules in the workspace, disable (clear) the Synchronize with Cloud option and click OK.
The rule is disabled and will no longer be applied.
Using deployment scripts for deploying security applications
When Kaspersky Security Center is deployed in a cloud environment, you can use deployment scripts for automating the deployment of security applications. The deployment scripts for the Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud are available as ZIP files at the Kaspersky Support page.
You can deploy the latest versions of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux and Kaspersky Security for Windows Server by using deployment scripts only if you already have created installation packages and management plug-ins for these programs. To deploy the latest versions of the security applications by using deployment scripts, perform the following on the Administration Server in the cloud environment:
- Start the Configure cloud environment operation.
- Follow the instructions provided at https://support.kaspersky.com/14713.
Deployment of Kaspersky Security Center in Yandex.Cloud
You can deploy Kaspersky Security Center in Yandex.Cloud. Only the pay-per-use mode is available; cloud databases are not supported.
In Yandex.Cloud, the following deployment methods for the security applications are available:
- By native means of Kaspersky Security Center, that is, via the Remote installation task (the deployment of the security programs is only possible if Administration Server and the virtual machines to be protected are on the same network segment)
- Via deployments scripts
For deployment of Kaspersky Security Center in Yandex.Cloud, you must have a service account in Yandex.Cloud. You must give this account the marketplace.meteringAgent permission and associate this account with the virtual machine (please refer to https://cloud.yandex.com/en for details).
Page top
Appendices
This section provides reference information and additional facts regarding the use of Kaspersky Security Center.
Advanced features
This section describes a range of additional options of Kaspersky Security Center designed for expanding the functionality of centralized management of applications on devices.
Kaspersky Security Center operation automation. klakaut utility
You can automate the Kaspersky Security Center operation using the klakaut utility. The klakaut utility and a Help system for it are located in the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder.
Page top
Custom tools
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to create a list of custom tools (hereinafter also referred to simply as tools), that is, applications activated for a client device in Administration Console, through the Custom tools group of the context menu. Each tool in the list will be associated with a separate menu command, which Administration Console uses to start the application corresponding to that tool.
The applications starts on the administrator's workstation. The application can accept the attributes of a remote client device as command-line arguments (NetBIOS name, DNS name, or IP address). Connection to the remote device can be established through tunneling.
By default, the list of custom tools contains the following service programs for each client device:
- Remote diagnostics is a utility for remote diagnostics of Kaspersky Security Center.
- Remote Desktop is a standard Microsoft Windows component named Remote Desktop Connection.
- Computer Management is a standard Microsoft Windows component.
To add or remove custom tools, or to edit their settings,
In the context menu of the client device, select Custom tools → Configure custom tools.
The Custom tools window opens. In this window, you can add custom tools or edit their settings by using the Add and Modify buttons. To remove a custom tool, click the remove button with the red cross icon ( ).
).
Network Agent disk cloning mode
Cloning the hard drive of a reference device is a popular method of software installation on new devices. If Network Agent is running in standard mode on the hard drive of the reference device, the following problem arises:
After the reference disk image with Network Agent is deployed on new devices, they are displayed in Administration Console under a single icon. This problem arises because the cloning procedure causes new devices to keep identical internal data, which allows the Administration Server to associate a device with an icon in Administration Console.
The special Network Agent disk cloning mode allows you to avoid problems with an incorrect display of new devices in Administration Console after cloning. Use this mode when you deploy software (with Network Agent) on new devices by cloning the disk.
In disk cloning mode, Network Agent keeps running but does not connect to the Administration Server. When exiting the cloning mode, Network Agent deletes the internal data, which causes Administration Server to associate multiple devices with a single icon in Administration Console. Upon completing the cloning of the reference device image, new devices are displayed in Administration Console properly (under individual icons).
Network Agent disk cloning mode use scenario
- The administrator installs Network Agent on the reference device.
- The administrator checks the Network Agent connection to the Administration Server using the klnagchk utility.
- The administrator enables the Network Agent disk cloning mode.
- The administrator installs software and patches on the device, and restarts it as many times as needed.
- The administrator clones the hard drive of the reference device on any number of devices.
- Each cloned copy must meet the following conditions:
- The device name must be changed.
- The device must be restarted.
- The disk cloning mode must be disabled.
Enabling and disabling the disk cloning mode using the klmover utility
To enable or disable the Network Agent disk cloning mode:
- Run the klmover utility on the device with Network Agent installed that you have to clone.
The klmover utility is located in the Network Agent installation folder.
- To enable the disk cloning mode, enter the following command at the Windows command prompt:
klmover -cloningmode 1.Network Agent switches to disk cloning mode.
- To request the current status of the disk cloning mode, enter the following command at the command prompt:
klmover -cloningmode.The utility window shows whether the disk cloning mode is enabled or disabled.
- To disable the disk cloning mode, enter the following command in the utility command line:
klmover -cloningmode 0.
Preparing a reference device with Network Agent installed for creating an image of operating system
You may want to create an operating system image of a reference device with Network Agent installed and then to deploy the image on the networked devices. In this case, you create an operating system image of a reference device on which the Network Agent has not yet been started. If you start the Network Agent on a reference device before creating an operating system image, Administration Server's identification of devices deployed from an operating system image of the reference device will be problematic.
To prepare the reference device for creating an image of the operating system:
- Make sure that the Windows operating system is installed on the reference device and install the other software that you need on that device.
- On the reference device, in the Windows Network Connections settings, disconnect the reference device from the network where Kaspersky Security Center is installed.
- On the reference device, start the local installation of Network Agent by using the setup.exe file.
The Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent setup wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- On the Administration Server page of the wizard, specify the Administration Server IP address.
If you do not know the exact address of the Administration Server, enter localhost. You can change the IP address later by using the klmover utility with the
-addresskey. - On the Start application page of the wizard, disable the Start application during installation option.
- When the Network Agent installation is complete, do not restart the device before creating an operating system image.
If you restart the device, you will have to repeat the whole process of preparing a reference device for creation of an operating system image.
- On the reference device, in the command line, start the sysprep utility and execute the following command:
sysprep.exe /generalize /oobe /shutdown.
The reference device is ready for creating an operating system image.
Configuring receipt of messages from File Integrity Monitor
Managed applications such as Kaspersky Security for Windows Server or Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent send messages from File Integrity Monitor to Kaspersky Security Center. Kaspersky Security Center also allows you to monitor any changes to critically important components of systems (such as web servers and ATMs) and promptly respond to breaches of the integrity of such systems. For these purposes, you can receive messages from the File Integrity Monitor component. The File Integrity Monitor component lets you monitor not only the file system of a device, but also its registry hives, firewall status, and the status of connected hardware.
You must configure Kaspersky Security Center to receive messages from the File Integrity Monitor component without using Kaspersky Security for Windows Server or Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent.
To configure receipt of messages from File Integrity Monitor:
- Open the system registry of the device on which Administration Server is installed (for example, locally, using the regedit command in the Start → Run menu).
- Go to the following hive:
- For 32-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\KasperskyLab\Components\34\1093\1.0.0.0\ServerFlags
- For 64-bit systems:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\34\1093\1.0.0.0\ServerFlags
- For 32-bit systems:
- Create keys:
- Create the key KLSRV_EVP_FIM_PERIOD_SEC to specify the time period for counting the number of processed events. Specify the following settings:
- Specify KLSRV_EVP_FIM_PERIOD_SEC as the key name.
- Specify DWORD as the key type.
- Specify a range of values for the time interval from 43 200 to 172 800 seconds. By default, the time interval is 86 400 seconds.
- Create the key KLSRV_EVP_FIM_LIMIT to limit the number of received events for the specified time interval. Specify the following settings:
- Specify KLSRV_EVP_FIM_LIMIT as the key name.
- Specify DWORD as the key type.
- Specify a range of values for received events from 2 000 to 50 000. The default number of events is 20 000.
- Create the key KLSRV_EVP_FIM_PERIOD_ACCURACY_SEC to count events with accuracy up to a specific time interval. Specify the following settings:
- Specify KLSRV_EVP_FIM_PERIOD_ACCURACY_SEC as the key name.
- Specify DWORD as the key type.
- Specify a range of values from 120 to 600 seconds. The default time interval is 300 seconds.
- Create the key KLSRV_EVP_FIM_OVERFLOW_LATENCY_SEC so that, after the specified amount of time, the application can check whether the number of events processed over the time interval is turning out to be less than the specified limit. This check is performed upon reaching the limit for receiving events. If this condition is met, the application resumes saving events to the database. Specify the following settings:
- Specify KLSRV_EVP_FIM_OVERFLOW_LATENCY_SEC as the key name.
- Specify DWORD as the key type.
- Specify a range of values from 600 to 3 600 seconds. The default time interval is 1 800 seconds.
If the keys are not created, the default values are used.
- Create the key KLSRV_EVP_FIM_PERIOD_SEC to specify the time period for counting the number of processed events. Specify the following settings:
- Restart the Administration Server service.
The limits on receiving events from the File Integrity Monitor component will be configured. You can view the results of the File Integrity Monitor component in the reports named Top 10 rules of File Integrity Monitor / System Integrity Monitoring that were triggered on devices most frequently and Top 10 devices with File Integrity Monitor / System Integrity Monitoring rules most frequently triggered.
Page top
Administration Server maintenance
The Administration Server maintenance allows you to free up space in the folder of the Administration Server and reduce the database volume by deleting objects that are no longer needed. This helps you to improve the performance and operational reliability of the application. We recommend that you perform maintenance on the Administration Server at least weekly.
Administration Server maintenance is performed by using the dedicated task. The application performs the following actions when maintaining the Administration Server:
- Deletes unnecessary folders and files from the storage folder.
- Deletes unnecessary records from tables (also known as "dangling pointers").
- Clears the cache.
- Maintains the database (if you use SQL Server or PostgreSQL as a DBMS):
- Checks the database for errors (available only for SQL Server).
- Re-organizes database indexes.
- Updates the database statistics.
- Shrinks the database (if necessary).
The Administration Server maintenance task supports MariaDB versions 10.3 and later. If you use MariaDB versions 10.2 or earlier, administrators have to maintain this DBMS on their own.
To create the Administration Server maintenance task:
- In the console tree, select the node of the Administration Server for which you want to create the Administration Server maintenance task.
- Select the Tasks folder.
- Click the New task button in the workspace of the Tasks folder.
The New task wizard starts.
- In the Select the task type window of the wizard, select Administration Server maintenance as the task type, and then click Next.
- If you have to shrink the Administration Server database during maintenance, in the Settings window of the wizard, select the Shrink database check box.
- Follow the rest of the wizard instructions.
The newly created task is displayed in the list of tasks in the workspace of the Tasks folder. Only one Administration Server maintenance task can be running for a single Administration Server. If an Administration Server maintenance task has already been created for an Administration Server, no new Administration Server maintenance task can be created.
Page top
Access to public DNS servers
If access to Kaspersky servers by using the system DNS is not possible, Kaspersky Security Center can use the following public DNS servers, in the following order:
- Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8)
- Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1)
- Alibaba Cloud DNS (223.6.6.6)
- Quad9 DNS (9.9.9.9)
- CleanBrowsing (185.228.168.168)
Requests to these DNS servers may contain domain addresses and the public IP address of the Administration Server, because the application establishes a TCP/UDP connection to the DNS server. If Kaspersky Security Center is using a public DNS server, data processing is governed by the privacy policy of the relevant service.
To configure the use of public DNS by using the klscflag utility:
- Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
- To disable the use of public DNS, run the following command:
klscflag -fset -pv ".core/.independent" -s Transport -n ForceUseSystemDNS -t d -v 1 - To enable the use of public DNS, run the following command:
klscflag -fset -pv ".core/.independent" -s Transport -n ForceUseSystemDNS -t d -v 0
User notification method window
In the User notification method window, you can configure the user notification about certificate installation on the mobile device:
- Show QR code in wizard. If you select this option, a link to the installation package will be shown at the final step of the Mobile device connection wizard.
- Send QR code to user. If you select this option, you can specify the settings for notifying the user about connection of a device.
In the By email group of settings, you can configure user notification about installation of a new certificate on his or her mobile device using email messages. This notification method is only available if the SMTP Server is enabled.
In the By SMS group of settings, you can configure the user notification about installation of a certificate on his or her mobile device by using SMS. This notification method is only available if SMS notification is enabled.
Click the Edit message link in the By email and By SMS groups of settings to view and edit the notification message, if necessary.
Device selection window
Choose a selection from the Device selection list. The list contains the predefined selections and the selections created by the user.
You can view the details of device selections in the workspace of the Device selections section.
Page top
Define the name of the new object window
In the window, specify the name of the newly created object. A name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
Page top
Application categories section
In this section, you can configure the distribution of information about application categories on client devices.
Full data transmission (for Network Agents 10 Service Pack 2 and earlier)
Transmission of modified data only (for Network Agents 10 Service Pack 2 and later)
Features of using the management interface
This section describes actions that you can perform in the main window of Kaspersky Security Center.
Console tree
The console tree (see the figure below) is designed to display the hierarchy of Administration Servers on the corporate network, the structure of their administration groups, and other objects of the application, such as the Repositories or Application management folders. The name space of Kaspersky Security Center can contain several nodes including the names of servers corresponding to the installed Administration Servers included in the hierarchy.

Console tree
Administration Server node
The Administration Server – <Device name> node is a container that shows the structural organization of the selected Administration Server.
The workspace of the Administration Server node contains summary information about the current status of the application and devices managed through the Administration Server. Information in the workspace is distributed between various tabs:
- Monitoring. Displays information about the application operation and the current status of client devices in real-time mode. Important messages for the administrator (such as messages on vulnerabilities, errors, or viruses detected) are highlighted in a specific color. You can use links on the Monitoring tab to perform the standard administrator tasks (for example, install and configure the security application on client devices), as well as to go to other folders in the console tree.
- Statistics. Contains a set of charts grouped by topics (protection status, Anti-Virus statistics, updates, etc.). These charts visualize current information about the application operation and the status of client devices.
- Reports. Contains templates for reports generated by the application. On this tab, you can create reports using preset templates, as well as create custom report templates.
- Events window. Contains records on events that have been registered during the application operation. Those records are distributed between topics for ease of reading and filtering. On this tab, you can view selections of events that have been generated automatically, as well as create custom selections.
Folders in the Administration Server node
The Administration Server – <Device name> node includes the following folders:
- Managed devices. This folder is intended for storage, display, configuration, and modification of the structure of administration groups, group policies, and group tasks.
- Mobile Device Management. This folder is intended for managing mobile devices. The Mobile Device Management folder contains the following subfolders:
- Mobile Device Servers. Intended for managing iOS MDM Servers.
- Mobile Devices. It is intended for managing mobile devices, KES, and iOS MDM.
- Certificates. It is intended for managing certificates of mobile devices.
- Device selections. This folder is intended for quick selection of devices that meet specified criteria (a device selection) among all managed devices. For example, you can quickly select devices on which no security application is installed, and proceed to these devices (view the list). You can perform specific actions on these selected devices, for example, assign them some tasks. You can use preset selections or create your own custom selections.
- Unassigned devices. This folder contains a list of devices that have not been included in any of the administration groups. You can perform some actions on unassigned devices, for example, move them into administration groups or install applications on them.
- Policies. This folder is intended for viewing and creating policies.
- Tasks. This folder is intended for viewing and creating tasks.
- Kaspersky Licenses. Contains a list of license keys available for Kaspersky applications. In the workspace of this folder, you can add new license keys to the license key repository, deploy license keys to managed devices, and view the license key usage report.
- Advanced. This folder contains a set of subfolders that correspond to various groups of application features.
Advanced folder. Moving folders in the console tree
The Advanced folder includes the following subfolders:
- User accounts. Contains a list of network user accounts.
- Application management. Intended for managing applications installed on devices on the network. The Application management folder contains the following subfolders:
- Application categories. Intended for managing custom application categories.
- Applications registry. Contains a list of applications on devices with Network Agent installed.
- Executable files. Contains the list of executable files stored on client devices with Network Agent installed.
- Software vulnerabilities. Contains a list of vulnerabilities in applications on devices with Network Agent installed.
- Software updates. Contains a list of application updates received by Administration Server that can be distributed on devices.
- Third-party licenses usage. Contains a list of licensed applications groups. You can use licensed applications groups to monitor the usage of licenses for third-party software (non-Kaspersky applications) and possible violations of license limit.
- Remote installation. This folder is intended for managing remote installation of operating systems and applications. The Remote installation folder contains the following subfolders:
- Deploy device images. Intended for deploying images of operating systems on devices.
- Installation packages. Contains a list of installation packages that can be used for remote installation of applications on devices.
- Data encryption and protection. This folder is intended for managing the process of data encryption on hard drives and removable drives.
- Network poll. This folder displays the network in which Administration Server is installed. Administration Server receives information about the structure of the network and its devices, through regular polls of the Windows network, IP subnets, and Active Directory on the corporate network. Poll results are displayed in the workspaces of the corresponding folders: Domains, IP ranges, and Active Directory.
- Repositories. This folder is intended for operations with objects used to monitor the status of devices and perform maintenance. The Repositories folder contains the following subfolders:
- Adaptive anomaly detection. Contains a list of detects performed by the Kaspersky Endpoint Security rules working in the SMART Training mode on client devices.
- Kaspersky software updates and patches. Contains a list of updates received by Administration Server that can be distributed to devices.
- Hardware. Contains a list of hardware connected to the organization's network.
- Quarantine. Contains a list of objects moved to Quarantine by anti-virus applications on devices.
- Backup. Contains a list of backup copies of files that were deleted or modified during disinfection on devices.
- Unprocessed files. Contains a list of files assigned for later scanning by anti-virus applications.
You can change the set of subfolders included in the Advanced folder. Frequently used subfolders can be moved up one level from the Advanced folder. Subfolders that are used rarely can be moved to the Advanced folder.
To move a subfolder out of the Advanced folder:
- In the console tree, select the subfolder that you want to move out of the Advanced folder.
- In the context menu of the subfolder, select View → Move from Advanced folder.
You can also move a subfolder out of the Advanced folder in the workspace of the Advanced folder by clicking the Move from Advanced folder link in the section with the name of that subfolder.
To move a subfolder to the Advanced folder:
- In the console tree, select the subfolder that you need to move to the Advanced folder.
- In the context menu of the subfolder, select View → Move to Advanced folder.
How to update data in the workspace
In Kaspersky Security Center, the workspace data (such as device statuses, statistics, and reports) are never updated automatically.
To update data in the workspace:
- Press the F5 key.
- In the context menu of the object in the console tree, select Refresh.
- Click the refresh icon (
 ) in the workspace.
) in the workspace.
How to navigate the console tree
To navigate the console tree, you can use the following toolbar buttons:
 —One step back.
—One step back. —One step forward.
—One step forward. —One level up.
—One level up.
You can also use a navigation chain located in the upper-right corner of the workspace. The navigation chain contains the full path to the folder of the console tree in which you are currently located. All elements of the chain, except for the last one, are links to the objects in the console tree.
Page top
How to open the object properties window in the workspace
You can change the properties of the most Administration Console objects in the object properties window.
To open the properties window of an object located in the workspace:
- From the context menu of the object, select Properties.
- Select an object and press ALT+ENTER.
How to select a group of objects in the workspace
You can select a group of objects in the workspace. You can select a group of objects, for example, to create a set of devices for which you may create tasks later.
To select an objects range:
- Select the first object in the range and press Shift.
- Hold down the Shift key and select the last object in the range.
The range will be selected.
To group separate objects:
- Select the first object in the group and press Ctrl.
- Hold down the Ctrl key and select other objects that you want to include in the group.
The objects will be grouped.
Page top
How to change the set of columns in the workspace
Administration Console allows you to change a set of columns displayed in the workspace.
To change a set of columns displayed in the workspace:
- In the console tree, click the object for which you wish to change the set of columns.
- In the workspace of the folder, open the window intended for configuration of the set of columns by clicking the Add/Remove columns link.
- In the Add/Remove columns window, specify the set of columns to be displayed.
Reference information
Tables of this section provide summary information about the context menu of Administration Console objects, as well as about the statuses of console tree objects and workspace objects.
Context menu commands
This section lists Administration Console objects and corresponding context menu items (see table below).
Items of the context menu of Administration Console objects
Object |
Menu item |
Menu item purpose |
|---|---|---|
General items of context menu |
Search |
Opens the devices search window. |
Refresh |
Refreshes the display of the selected object. |
|
Export list |
Exports the current list to a file. |
|
Properties |
Opens the properties window of the selected object. |
|
View → Add/Remove columns |
Adds or removes columns to/from the table of objects in the workspace. |
|
View → Large icons |
Shows objects in the workspace as large icons. |
|
View → Small icons |
Shows objects in the workspace as small icons. |
|
View → List |
Shows objects in the workspace as a list. |
|
View → Table |
Shows objects in the workspace as a table. |
|
View → Configure |
Configures the display of Administration Console elements. |
|
Kaspersky Security Center |
New → Administration Server |
Adds an Administration Server to the console tree. |
<Administration Server name> |
Connect to Administration Server |
Connects to the Administration Server. |
Disconnect from Administration Server |
Disconnects from the Administration Server. |
|
Managed devices |
Install application |
Starts the Remote installation wizard. |
View → Configure interface |
Configures the display of interface elements. |
|
Remove |
Removes the Administration Server from the console tree. |
|
Install application |
Starts the Remote installation wizard for the administration group. |
|
Reset Virus Counter |
Resets the virus counters for devices included in the administration group. |
|
View report on threats |
Creates a report on threats and virus activity on devices included in the administration group. |
|
New → Group |
Creates an administration group. |
|
All Tasks → New group structure |
Creates a structure of administration groups based on the structure of domains or Active Directory. |
|
All Tasks → Show Message |
Starts the New message for user wizard intended for the users of devices included in the administration group. |
|
Managed devices → Administration Servers |
New → Secondary Administration Server |
Starts the Add secondary Administration Server wizard. |
New → Virtual Administration Server |
Starts the New virtual Administration Server wizard. |
|
Mobile Device Management → Mobile devices |
New → Mobile device |
Connects a new mobile device of the user. |
Mobile Device Management → Certificates |
New → Certificate |
Creates a certificate. |
Create → Mobile device |
Connects a new mobile device of the user. |
|
Device selections |
New → New selection |
Creates a device selection. |
All Tasks → Import |
Imports a selection from a file. |
|
Kaspersky Licenses |
Add activation code or key file |
Adds a license key to the Administration Server repository. |
Activate Application |
Starts the Application activation task creation wizard. |
|
Report on usage of license keys |
Creates and shows a report on license keys on client devices. |
|
Application management → Application categories |
New → Category |
Creates an application category. |
Application management → Applications registry |
Filter |
Sets up a filter for the list of applications. |
Monitored Applications |
Configures the publishing of events related to installation of applications. |
|
Remove applications that are not installed |
Clears the list of all details of applications that are no longer installed on networked devices. |
|
Application management → Software updates |
Accept License Agreements for updates |
Accepts the License Agreements of software updates. |
Application management → Third-party licenses usage |
New → Licensed applications group |
Creates a licensed applications group. |
Remote installation → Installation packages |
Show current application versions |
Shows the list of up-to-date versions of Kaspersky applications available on web servers. |
New → Installation package |
Creates an installation package. |
|
All Tasks → Update databases |
Updates application databases in installation packages. |
|
All Tasks → Show the general list of stand-alone packages |
Shows the list of stand-alone packages created for installation packages. |
|
Device discovery → Domains |
All Tasks → Device Activity |
Sets up the Administration Server's response to inactivity of networked devices. |
Device discovery → IP ranges |
New → IP range |
Creates an IP range. |
Repositories → Updates for Kaspersky databases and software modules |
Download updates |
Opens the properties window of the Download updates to the repository task of the Administration Server. |
Updates Download Settings |
Configures the Download updates to the repository task of the Administration Server. |
|
Report on usage of anti-virus databases |
Creates and shows a report on versions of databases. |
|
All Tasks → Clear updates repository |
Clears the repository of updates on the Administration Server. |
|
Repositories → Hardware |
New → Device |
Creates a new device. |
List of managed devices. Description of columns
The following table displays the names and respective descriptions of columns in the list of managed devices.
Descriptions of columns in the list of managed devices
Column name |
Value |
|---|---|
Name |
NetBIOS name of the client device. The descriptions of the icons of device names are given in the appendix. |
Operating system type |
Type of operating system installed on the client device. |
Windows domain |
Name of the Windows domain in which the client device is located. |
Network Agent is installed |
Result of Network Agent installation on the client device: Yes, No, Unknown. |
Network Agent is running |
The result of Network Agent operation: Yes, No, Unknown. |
Real-time protection |
Security application is installed: Yes, No, Unknown. |
Last connected to Administration Server |
Time period that has elapsed since the client device was connected to the Administration Server. |
Last update of anti-virus databases |
The time period that has elapsed since the last update of managed devices. |
Status |
Current status of the client device: OK, Critical, or Warning. |
Status description |
Conditions for change of the client device status to Critical or Warning. The device status changes to Warning or Critical under the following conditions:
The device status only changes to Critical by the following reasons:
Managed Kaspersky applications on client devices can add status descriptions to the list. Kaspersky Security Center can receive the description of a client device status from managed Kaspersky applications installed on that device. If the status that has been assigned to the device by a managed application is other than that assigned by Kaspersky Security Center, Administration Console displays the status that is the most critical to the device security. For example, if a managed application has assigned the Critical status to the device while Kaspersky Security Center has assigned it the Warning status, Administration Console displays the Critical status for that device with the corresponding description provided by the managed application. |
Information updated |
Time period that has elapsed since the client device was last synchronized successfully with the Administration Server (that is, since the last network scan). |
DNS name |
DNS domain name of the client device. |
DNS domain |
The main DNS suffix. |
IP address |
IP address of the client device. It is recommended to use the IPv4 address. |
Last visible |
Time period during which the client device has remained visible on the network. |
Last full scan |
Date and time of the last scan of the client device performed by the security application upon the user's request. |
Total number of threats detected |
Number of threats found. |
Real-time protection status |
Real-time protection status: Starting, Running, Running (maximum protection), Running (maximum speed), Running (recommended settings), Running (custom settings), Stopped, Paused, Failed. |
Connection IP address |
The IP address that is used for connection to Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server. |
Network Agent version |
Version of Network Agent. |
Application version |
Version of the security application installed on the client device. |
Anti-virus databases released |
The version of the anti-virus databases. |
System last started |
Date and time when the client device was last turned on. |
Restart is required |
Restart of the client device is required. |
Distribution point |
Name of the device that acts as distribution point for this client device. |
Description |
Description of the client device received after a network scan. |
Encryption status |
Data encryption status of the client device. |
WUA status |
Status of Windows Update Agent on the client device. Yes corresponds to client devices that receive updates through Windows Update from the Administration Server. No corresponds to client devices that receive updates through Windows Update from other sources. |
Operating system bit size |
Bit size of the operating system installed on the client device. |
Spam protection status |
Status of Spam protection component: Running, Starting, Stopped, Paused, Failed, Unknown |
Data Leakage Prevention status |
Status of Data Leakage Prevention component: Running, Starting, Stopped, Paused, Failed, Unknown |
Collaboration servers protection status |
Status of Content Filtering component: Running, Starting, Stopped, Paused, Failed, Unknown |
Anti-virus protection status of mail servers |
Status of Mail Server anti-virus protection component: Running, Starting, Stopped, Paused, Failed, Unknown |
Endpoint Sensor status |
Status of Endpoint Detection and Response component (KATA): Running, Starting, Stopped, Paused, Failed, Unknown |
Created
|
Time when the <Device Name> icon was created. This attribute is used to compare various events with each other.
|
Name of virtual or secondary Administration Server
|
Name of virtual or secondary Administration Server. This column is only available in lists that contain devices from different Administration Servers. |
Parent group
|
Name of the administration group where the < Device Name> icon is located. This column is only available in lists that contain devices from different Administration Servers. |
Managed by a different Administration Server
|
The parameter can take one of these values:
|
Operating system build
|
The build number of the operating system. You can specify whether the selected operating system must have an equal, earlier, or later build number. You can also configure searching for all build numbers except the specified one.
|
Operating system release ID
|
The release identifier (ID) of the operating system. You can specify whether the selected operating system must have an equal, earlier, or later release ID. You can also configure searching for all release ID numbers except the specified one.
|
Statuses of devices, tasks, and policies
The table below contains a list of icons displayed in the console tree and in the Administration Console workspace, next to the names of devices, tasks, and policies. Those icons define the statuses of objects.
Statuses of devices, tasks, and policies
Icon |
Status |
|
Device with an operating system for workstations detected in the system but not yet included in any of the administration groups. |
|
Device with an operating system for workstations included in an administration group, with the OK status. |
|
Device with an operating system for workstations included in an administration group, with the Warning status. |
|
Device with an operating system for workstations included in an administration group, with the Critical status. |
|
Device with an operating system for workstations included in an administration group, which has lost connection with the Administration Server. |
|
Device with an operating system for servers detected in the system but not yet included in any of the administration groups. |
|
Device with an operating system for servers included in an administration group, with the OK status. |
|
Device with an operating system for servers included in an administration group, with the Warning status. |
|
Device with an operating system for servers included in an administration group, with the Critical status. |
|
Device with an operating system for servers included in an administration group, which has lost connection with the Administration Server. |
|
Mobile device detected on the network and included in none of the administration groups. |
|
Mobile device included in an administration group, with the OK status. |
|
Mobile device included in an administration group, with the Warning status. |
|
Mobile device included in an administration group, with the Critical status. |
|
Mobile device included in an administration group, having lost its connection with the Administration Server. |
|
UEFI protection device detected on the network but not included in any administration group. UEFI protection device is on the network. |
|
UEFI protection device detected on the network but not included in any administration group. UEFI protection device is not on the network. |
|
UEFI protection device included in an administration group, with OK status. UEFI protection device is on the network. |
|
UEFI protection device included in an administration group, with OK status. UEFI protection device is not on the network. |
|
UEFI protection device included in an administration group, with Warning status. UEFI protection device is on the network. |
|
UEFI protection device included in an administration group, with Warning status. UEFI protection device is not on the network. |
|
UEFI protection device included in an administration group, with Critical status. UEFI protection device is on the network. |
|
UEFI protection device included in an administration group, with Critical status. UEFI protection device is not on the network. |
|
Active policy. |
|
Inactive policy. |
|
Active policy inherited from a group that was created on the primary Administration Server. |
|
Active policy inherited from a top-level group. |
|
Task (group task, Administration Server task, or task for specific devices) with the Scheduled or Completed successfully status. |
|
Task (group task, Administration Server task, or task for specific devices) with the Running status. |
|
Task (group task, Administration Server task, or task for specific devices) with the Failed status. |
|
Task inherited from a group that was created on the primary Administration Server. |
|
Task inherited from a top-level group. |
File status icons in Administration Console
For ease of file management in Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console, icons are displayed next to the names of files (see table below). Icons indicate statuses assigned to files by managed Kaspersky applications on client devices. Icons are shown in the workspaces of the Quarantine, Backup, and Active threats folders.
Statuses are assigned to objects by Kaspersky Endpoint Security installed on the client device on which the object is located.
Correspondence between icons and file statuses
Icon |
Status |
|
File with the Infected status. |
|
File with the Warning or Probably infected status. |
|
File with the Added by user status. |
|
File with the False positive status. |
|
File with the Disinfected status. |
|
File with the Deleted status. |
|
File in the Quarantine folder with the Not infected, Password-protected or Must be sent to Kaspersky status. If there is no status description next to an icon, this means that the managed Kaspersky application on the client device has reported an unknown status to Kaspersky Security Center. |
|
File in the Backup folder with the Not infected, Password-protected or Must be sent to Kaspersky status. If there is no status description next to an icon, this means that the managed Kaspersky application on the client device has reported an unknown status to Kaspersky Security Center. |
|
File in the Active threats folder with Not infected, Password-protected or Must be sent to Kaspersky status. If there is no status description next to an icon, this means that the managed Kaspersky application on the client device has reported an unknown status to Kaspersky Security Center. |
Searching and exporting data
This section contains information about data search methods and about exporting data.
Finding devices
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to find devices on the basis of specified criteria. Search results can be saved to a text file.
The search feature allows you to find the following devices:
- Client devices in administration groups of an Administration Server and its secondary Servers.
- Unassigned devices managed by an Administration Server and its secondary Servers.
To find client devices included in an administration group:
- In the console tree, select an administration group folder.
- Select Search from the context menu of the administration group folder.
- On the tabs of the Search window, specify the criteria for the search of devices, and click the Find now button.
Devices that meet the specified search criteria are now displayed in a table in the lower part of the Search window.
To find unassigned devices:
- In the console tree, select the Unassigned devices folder.
- Select Search from the context menu of the Unassigned devices folder.
- On the tabs of the Search window, specify the criteria for the search of devices, and click the Find now button.
Devices that meet the specified search criteria are now displayed in a table in the lower part of the Search window.
To find devices regardless of whether they are included in an administration group:
- In the console tree, select the Administration Server %s node.
- In the context menu of the node, select Search.
- On the tabs of the Search window, specify the criteria for the search of devices, and click the Find now button.
Devices that meet the specified search criteria are now displayed in a table in the lower part of the Search window.
In the Search window you can also search for administration groups and secondary Administration Servers using a drop-down list in the top right corner of the window. Search functionality for administration groups and secondary Administration Servers is not available if you opened the Search window from the Unassigned devices folder.
To find devices, you can use regular expressions in the fields of the Search window.
Full text search in the Search window is available:
- On the Network tab, in the Description field
- On the Hardware tab, in the Device, Vendor, and Description fields
Device search settings
Below are descriptions of the settings used for searching managed devices. Search results are displayed in the lower part of the window.
Network
On the Network tab, you can specify the criteria that will be used to search for devices according to their network data:
- Device name or IP address
- Windows domain
- Administration group
- Description
- IP range
- Managed by a different Administration Server
Tags
On the Tags tab, you can configure a device search based on key words (tags) that were previously added to the descriptions of managed devices:
Active Directory
On the Active Directory tab, you can specify that devices should be searched for in the Active Directory organizational unit (OU) or group. You can also include devices from all child OUs of the specified Active Directory OU in the selection. To select devices, define the following settings:
- Device is in an Active Directory organizational unit
- Include child organizational units
- This device is a member of an Active Directory group
Network activity
On the Network activity tab, you can specify the criteria that will be used to search for devices according to their network activity:
- This device is a distribution point
- Do not disconnect from the Administration Server
- Connection profile switched
- Last connected to Administration Server
- New devices detected by network poll
- Device is visible
Application
On the Application tab, you can specify the criteria that will be used to search for devices according to the selected managed application:
- Application name
- Application version
- Critical update name
- Modules last updated
- Device is managed through Kaspersky Security Center
- Security application is installed
Operating system
On the Operating system tab, you can set up the following criteria to find devices by their operating system (OS) type:
- Operating system version
- Operating system bit size
- Operating system service pack version
- Operating system build
- Operating system release ID
Device status
On the Device status tab, you can specify criteria for searching devices based on the device status from the managed application:
- Device status
- Real-time protection status
- Device status description
- Device status defined by application
Protection components
On the Protection components tab, you can set up the criteria to search for client devices by their protection status.
Applications registry
On the Applications registry tab, you can configure the search for devices according to applications installed on them:
- Application name
- Application version
- Vendor
- Application status
- Find by update
- Incompatible security application name
- Application tag
Hierarchy of Administration Servers
On the Hierarchy of Administration Servers tab, check the Include data from secondary Administration Servers (down to level) box if you want the information stored on secondary Administration Servers to be considered while searching for devices, and in the entry field, you can specify the nesting level of secondary Administration Server from which information is considered while searching for devices. By default, this check box is cleared.
Virtual machines
On the Virtual machines tab, you can configure the search for devices according to whether these are virtual machines or part of virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI):
Hardware
On the Hardware tab, you can configure search for client devices according to their hardware:
- Device
- Vendor
- Description
- Inventory number
- CPU frequency, in MHz
- Virtual CPU cores
- Hard drive volume, in GB
- RAM size, in MB
Vulnerabilities and updates
On the Vulnerabilities and updates tab, you can set up the criterion to search for devices according to their Windows Update source:
Users
On the Users tab, you can set up the criteria to search for devices according to the accounts of users who have logged in to the operating system.
Status-affecting problems in managed applications
On the Status-affecting problems in managed applications tab, you can set up search for devices according to descriptions of their statuses provided by the managed application:
Statuses of components in managed applications
On the Statuses of components in managed applications tab, you can set up the criteria to search for devices according to the statuses of components in managed applications:
- Data Leakage Prevention status
- Collaboration servers protection status
- Anti-virus protection status of mail servers
- Endpoint Sensor status
Encryption
Cloud segments
On the Cloud segments tab, you can configure a search based on whether a device belongs to specific cloud segments:
Application components
This section contains the list of components of those applications that have corresponding management plug-ins installed in Administration Console.
In the Application components section, you can specify criteria for including devices in a selection according to the statuses and version numbers of the components that refer to the application that you select:
Using masks in string variables
Using masks for string variables is allowed. When creating masks, you can use the following regular expressions:
- Wildcard character (*)—Any string of 0 or more characters.
- Question mark (?)—Any single character.
- [<range>]—Any single character from a specified range or set.
For example: [0–9]—Any digit. [abcdef]—Any of the characters a, b, c, d, e, or f.
Using regular expressions in the search field
You can use the following regular expressions in the search field to search for specific words and characters:
- *. Replaces any sequence of characters. To search for such words as Server, Servers, or Server room, enter the
Server*expression in the search field. - ?. Replaces any single character. To search for such words as Word or Ward, enter the
W?rdexpression in the search field.Text in the search field cannot begin with a question mark (?).
- [<range>]. Replaces any single character from a specified range or set. To search for any numeral, enter the
[0-9]expression in the search field. To search for one of the characters—a, b, c, d, e, or f—enter the[abcdef]expression in the search field.
Use the following regular expressions in the search field to run a full-text search:
- Space. The result is all devices whose descriptions contain any of the listed words. For example, to search for a phrase that contains the word "Secondary" or "Virtual" (or both these words), enter the
Secondary Virtualexpression in the search field. - Plus sign (+), AND, or &&. When a plus sign precedes a word, all search results will contain this word. For example, to search for a phrase that contains both the word "Secondary" and the word "Virtual", you can enter any of the following expressions in the search field:
+Secondary+Virtual,Secondary AND Virtual,Secondary && Virtual. - OR or ||. When placed between two words, it indicates that one word or the other can be found in the text. To search for a phrase that contains either the word "Secondary" or the word "Virtual", you can enter any of the following expressions in the search field:
Secondary OR Virtual,Secondary || Virtual. - Minus sign (-). When a minus sign precedes a word, no search results will contain this word. To search for a phrase that must contain such word as Secondary and must not contain such word as Virtual, you must enter the
+Secondary-Virtualexpression in the search field. "<some text>". Text enclosed in quotation marks must be present in the text. To search for a phrase that contains such word combination as Secondary Server, you must enter the"Secondary Server"expression in the search field.
Full-text search is available in the following filtering blocks:
- In the event list filtering block, by the Event and Description columns.
- In the user account filtering block, by the Name column.
- In the applications registry filtering block, by the Name column, if the Show in list section has no grouping selected as the filtering criterion.
Exporting lists from dialog boxes
In dialog boxes of the application you can export lists of objects to text files.
Export of a list of objects is possible for dialog box sections that contain the Export to file button.
Page top
General task settings
This section contains the settings that you can view and configure for most of your tasks. The list of settings available depends on the task you are configuring.
Settings specified during task creation
You can specify the following settings when creating a task. Some of these settings can also be modified in the properties of the created task.
- Operating system restart settings:
- Task scheduling settings:
- Devices to which the task will be assigned:
- Account settings:
Settings specified after task creation
You can specify the following settings only after a task is created.
- Group task settings:
- Advanced scheduling settings:
- Notification settings:
- Security settings
- Task scope settings
Depending on how the task scope is determined, the following settings are present:
- Revision history
Download updates to the Administration Server repository task settings
Settings specified during task creation
You can specify the following settings when creating a task. Some of these settings can also be modified in the properties of the created task.
- Sources of updates
- Other settings
Force update of secondary Administration Servers
Copy downloaded updates to additional folders
Do not force updating of devices and secondary Administration Servers unless copying is complete
Settings specified after task creation
You can specify the following settings only after a task is created.
- Settings section, Content of updates block
- Update verification section
Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task settings
Settings specified during task creation
You can specify the following settings when creating a task. Some of these settings can also be modified in the properties of the created task.
- Sources of updates
- Other settings → Folder for storing updates
Settings specified after task creation
You can specify the following setting in the Settings section, in the Content of updates block only after a task is created.
Find vulnerabilities and required updates task settings
Settings specified during task creation
You can specify the following settings when creating a task. Some of these settings can also be modified in the properties of the created task.
- Search for vulnerabilities and updates listed by Microsoft
- Search for third-party vulnerabilities and updates listed by Kaspersky
- Enable advanced diagnostics
Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task settings
Settings specified during task creation
You can specify the following settings when creating a task. Some of these settings can also be modified in the properties of the created task.
- Specify rules for installing updates
- Start installation at device restart or shutdown
- Install required general system components
- Allow installation of new application versions during updates
- Download updates to the device without installing them
- Enable advanced diagnostics
Settings specified after task creation
You can specify settings in the sections listed below only after a task is created. For a full description of the task settings, see General task settings.
- General. In this section, general information about the task is displayed. Also, you can specify to which devices the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task should apply:
- Updates to install
In the Updates to install section, you can view the list of updates that the task installs. Only updates that match the applied task settings are shown.
- Test installation of updates:
- Do not scan. Select this option if you do not want to perform a test installation of updates.
- Run scan on selected devices. Select this option if you want to test updates installation on selected devices. Click the Add button and select devices on which you need to perform test installation of updates.
- Run scan on devices in the specified group. Select this option if you want to test updates installation on a group of devices. In the Specify a test group field, specify a group of devices on which you want to perform a test installation.
- Run scan on specified percentage of devices. Select this option if you want to test updates installation on some portion of devices. In the Percentage of test devices out of all target devices field, specify the percentage of devices on which you want to perform a test installation of updates.
Global list of subnets
This section provides information about the global list of subnets that you can use in the rules.
To store the information about subnets of your network, you can set up a global list of subnets for each Administration Server you use. This list helps you match pairs {IP address, mask} and physical units such as branch offices. You can use subnets from this list in the networking rules and settings.
Adding subnets to the global list of subnets
You can add subnets with their descriptions to the global list of subnets.
To add a subnet to the global list of subnets:
- In the console tree, select the node of the Administration Server that you require.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Properties window that opens, in the Sections pane select List of global subnets.
- Click the Add button.
The New subnet window opens.
- Fill in the following fields:
- Click OK.
The subnet appears in the list of subnets.
Page top
Viewing and modifying subnet properties in the global list of subnets
You can view and modify the properties of subnets in the global list of subnets.
To view or modify properties of a subnet in the global list of subnets:
- In the console tree, select the node of the Administration Server that you require.
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Properties window that opens, in the left Sections pane, select List of global subnets.
- In the list, select the subnet that you want.
- Click the Properties button.
The New subnet window opens.
- If necessary, change the settings of the subnet.
- Click OK.
If you have made changes, they will be stored.
Page top
Usage of Network Agent for Windows, Linux, and macOS: Comparison
The Network Agent usage varies depending on the operating system of the device. The Network Agent policy and installation package settings also differ depending on the operating system. The table below compares Network Agent features and usage scenarios available for Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems.
Network Agent feature comparison
Network Agent feature |
Windows |
Linux |
macOS |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Installing with third-party tools for remote installation of applications |
|
|
|
Installing manually, by running application installers on devices |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Manually connecting a client device to the Administration Server. klmover utility |
|
|
|
Automatic installing of updates and patches for Kaspersky Security Center components |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Without using Network Location Awareness (NLA). |
Without using Network Location Awareness (NLA). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(If one or more devices running Linux or macOS are within the scope of the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task, the task completes with the Failed status, even if it has successfully completed on all Windows devices.) |
|
Push installation of applications |
|
Restricted: it is not possible to perform push installation on Windows devices by using Linux distribution points. |
Restricted: it is not possible to perform push installation on Windows devices by using macOS distribution points. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring operating system updates in a Network Agent policy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Optimization settings for virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Auditing actions on a remote client device by using Windows Desktop Sharing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Checking the connection between a client device and the Administration Server. klnagchk utility |
|
|
|
|
|
By using the Virtual Network Computing (VNC) system. |
|
Downloading a stand-alone installation package through the Migration wizard |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Viewing information about the hardware of client devices |
|
Information about the hardware of Linux devices sent to the Administration Server by Network Agent installed on these devices is limited to the information specified in the description of the managed device settings for Administration Console and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
Information about the hardware of macOS devices sent to the Administration Server by Network Agent installed on these devices is limited to the information specified in the description of the managed device settings for Administration Console and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console (hereinafter also referred to as Kaspersky Security Center Web Console) is a web application designed to manage the status of the security system of a network protected by Kaspersky applications.
Using the application, you can do the following:
- Manage the status of the organization's security system.
- Install Kaspersky applications on devices on your network and manage installed applications.
- Manage policies created for devices on your network.
- Manage user accounts.
- Manage tasks for applications installed on your network devices.
- View reports on the security system status.
- Manage the delivery of reports to system administrators and other IT experts.
For information about hardware and software requirements, refer to Web Console requirements.
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console provides a web interface that ensures interaction between your device and Administration Server over a browser. Administration Server is an application designed for managing Kaspersky applications installed on your network devices. Administration Server connects to devices on your network over channels protected with Secure Socket Layer (SSL). When you connect to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console by using your browser, the browser establishes a connection with Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server.
You operate Kaspersky Security Center Web Console as follows:
- Use a browser to connect to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, where the web portal interface is displayed.
- Use web portal controls to choose a command that you want to run. Kaspersky Security Center Web Console performs the following operations:
- If you select a command used for receiving information (for example, to view a list of devices), Kaspersky Security Center Web Console generates a request for information to Administration Server, receives the necessary data, and sends it to the browser in an easy-to-view format.
- If you have chosen a command used for management (for example, remote installation of an application), Kaspersky Security Center Web Console receives the command from the browser and sends it to Administration Server. Then the application receives the result from Administration Server and sends it to the browser in an easy-to-view format.
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is a multi-language application. You can change the interface language at any time, without reopening the application. When you install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console together with Kaspersky Security Center, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console has the same interface language as the installation file. When you install only Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, the application has the same interface language as your operating system. If Kaspersky Security Center Web Console does not support the language of the installation file or operating system, English is set by default.
Mobile Device Management is not supported in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. However, if you added mobile devices to an administration group by using Microsoft Management Console, these devices are also displayed in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Deployment diagram of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
The figure below shows the deployment diagram of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
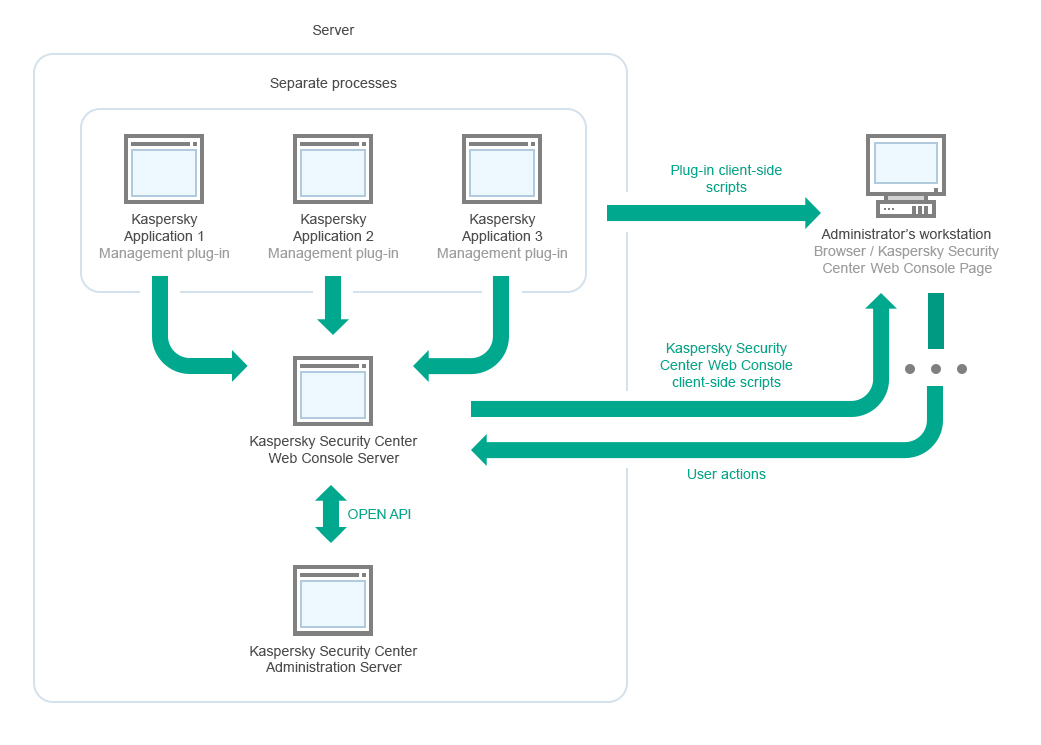
Deployment diagram of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
Management plug-ins for Kaspersky applications installed on protected devices (one plug-in for each application) are deployed together with Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server.
As an administrator, you access Kaspersky Security Center Web Console by using a browser on your workstation.
When you perform specific actions in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server communicates with Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server through OpenAPI. Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server requests the required information from Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and displays the results of your operations in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Page top
Ports used by Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
The table below lists the ports that must be open on the device where Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server (also referred to as Kaspersky Security Center Web Console) is installed.
Ports used by Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
Port number |
Service name |
Protocol |
Port purpose |
Scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
2001 |
Kaspersky Security Center Product Plugins Server
|
HTTPS |
API port that is used by the management plug-in processes to receive requests from the "Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Management Service" |
Running node.exe processes of management plug-ins
|
1329, 2003 |
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Management Service
|
HTTPS |
API ports that are used to receive requests from the "Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Management Service" running on the same device |
Updating Kaspersky Security Center Web Console components
|
2005 |
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
|
HTTPS |
API port that is used to receive requests from the "Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Management Service" running on the same device |
Running node.exe processes of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
|
3333 |
Kaspersky OSMP KAS Service |
HTTPS |
OAuth2.0 authorization endpoint port |
Identity and Access Manager |
4004 |
Kaspersky OSMP Facade Service |
HTTPS |
OAuth2.0 identity provider port |
Identity and Access Manager |
4444 |
Kaspersky OSMP KAS Service |
HTTPS |
OAuth2.0 Token introspection endpoint port |
Identity and Access Manager |
8200 |
|
HTTP |
API port that is used to generate certificates by means of HashiCorp Vault (for more details, see the HashiCorp Vault website) |
Installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and updating Kaspersky Security Center Web Console components |
4150, 4151, 4152 |
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Message Queue |
HTTPS |
API ports of the Message Broker that are used for communication between processes of both Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and management plug-ins |
Interaction between Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and management plug-ins |
The table below lists the ports that do not have to be open on the device where Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server is installed. However, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console uses these ports for Identity and Access Manager.
Ports used by Kaspersky Security Center Web Console for Identity and Access Manager
Port number |
Service name |
Protocol |
Port purpose |
Scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
4445 |
Kaspersky OSMP KAS Service |
HTTPS |
Main Identity and Access Manager port that receives configuration from Kaspersky Security Center Web Console for OAuth2.0 authorization endpoint port (for more information about OAuth 2.0, see the OAuth website) |
Identity and Access Manager |
2444 |
Kaspersky OSMP Facade Service |
HTTPS |
Port for the configuration of Identity and Access Manager |
Identity and Access Manager |
2445 |
Kaspersky OSMP Facade Service |
HTTPS |
Port for the connection of "Kaspersky OSMP KAS Service" to "Kaspersky OSMP Facade Service" |
Identity and Access Manager |
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface
Kaspersky Security Center is managed through the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
The Kaspersky Security Center Web Console window contains the following items:
- Main menu in the left part of the window
- Work area in the right part of the window
Main menu
The main menu contains the following sections:
- Administration Server. Displays the name of the Administration Server that you are currently connected to. Click the settings icon (
 ) to open the Administration Server properties.
) to open the Administration Server properties. - Monitoring & Reporting. Provides an overview of your infrastructure, protection statuses, and statistics.
- Assets (Devices). Contains tools for assets, as well as tasks and Kaspersky application policies.
- Users & Roles. Allows you to manage users and roles, configure user rights by assigning roles to the users, and associate policy profiles with roles.
- Operations. Contains a variety of operations, including application licensing, viewing and managing encrypted drives and encryption events, and third-party application management. This also provides you access to application repositories.
- Discovery & Deployment. Allows you to poll the network to discover client devices, and distribute the devices to administration groups manually or automatically. This section also contains the quick start wizard and Protection deployment wizard.
- Marketplace. Contains information about the entire range of Kaspersky business solutions and allows you to select the ones you need, and then proceed to purchase those solutions at the Kaspersky website.
- Settings. Allows you to back up the current state of a web plug-in to be able to restore the saved state later. Contains your personal settings related to the interface appearance, such as interface language or theme.
- Your account menu. Contains a link to Kaspersky Security Center Help. It also allows you to sign out of Kaspersky Security Center, and view the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console version and the list of installed management web plug-ins.
Work area
The work area displays the information you choose to view in the sections of the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface window. It also contains control elements that you can use to configure how the information is displayed.
Page top
Pinning and unpinning sections of the main menu
You can pin sections of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to add them to favorites and access them quickly from the Pinned section in the main menu.
If there are no pinned elements, the Pinned section is not displayed in the main menu.
You can pin sections that display pages only. For example, if you go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices, a page with the table of devices opens, which means you can pin the Managed devices section. If a window or no element is displayed after you select the section in the main menu, then you cannot pin such a section.
To pin a section:
- In the main menu, hover the mouse cursor over the section you want to pin.
The pin icon (
 ) is displayed.
) is displayed. - Click the pin icon (
 ).
).
The section is pinned and displayed in the Pinned section.
The maximum number of elements that you can pin is five.
You can also remove elements from favorites by unpinning them.
To unpin a section:
- In the main menu, go to the Pinned section.
- Hover the mouse cursor over the section you want to unpin, and then click the unpin icon (
 ).
).
The section is removed from favorites.
Page top
Scenario: Installation and initial setup of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
This scenario describes how to install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, perform initial setup of the Administration Server by using the quick start wizard, and install Kaspersky applications on managed devices by using the Protection deployment wizard.
Installation and initial setup of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console proceeds in stages:
- Installing a database management system (DBMS)
Install the DBMS that will be used by Kaspersky Security Center or use an existing one.
For information about how to install the selected DBMS, refer to its documentation.
- Installing Administration Server, Administration Console, Network Agent
Administration Console and the server version of Network Agent are installed together with Administration Server.
During the installation of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server, specify whether you want to install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console on the same device. If you choose to install both components on the same device, you do not have to install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console separately, because it is installed automatically. If you want to install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console on a different device, then, after installing Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server, proceed to installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
If you did not choose to install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console together with the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server on the previous step, install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console separately. You can install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console on a different device or the same device where Administration Server is installed.
- Performing initial setup
When Administration Server installation is complete, at the first connection to the Administration Server the quick start wizard starts automatically. Perform initial configuration of Administration Server according to the existing requirements. During the initial configuration stage, the wizard uses the default settings to create the policies and tasks that are required for protection deployment. However, the default settings may be less than optimal for the needs of your organization. If necessary, you can edit the settings of policies and tasks.
- Licensing of Kaspersky Security Center (optional)
Kaspersky Security Center with support of Administration Console basic functionality does not require a license. You need a commercial license if you want to use one or several of the additional features, including Vulnerability and patch management, Mobile Device Management, and Integration with the SIEM systems. You can add a key file or activation code for these features at the corresponding step of the quick start wizard or manually.
- Discovery of networked devices
This stage is handled by the quick start wizard. You can also discover the devices manually. Kaspersky Security Center receives the addresses and names of all devices detected on the network. You can then use Kaspersky Security Center to install Kaspersky applications and software from other vendors on the detected devices. Kaspersky Security Center regularly starts device discovery, which means that if any new instances appear on the network, they will be detected automatically.
- Arranging devices into administration groups
This stage is handled by the quick start wizard, but you can also move the detected devices into groups manually.
- Installing Network Agent and security applications on networked devices
Deployment of protection on an enterprise network entails installation of Network Agent and security applications (for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows) on devices that have been detected by Administration Server during the device discovery.
To install the applications remotely, run the Protection deployment wizard.
Security applications protect devices against viruses and other programs that pose a threat. Network Agent ensures communication between the device and Administration Server. Network Agent settings are configured automatically by default.
Before you start installing Network Agent and the security applications on networked devices, make sure that these devices are accessible (turned on).
- Deploying license keys to client devices
Deploy license keys to client devices to activate managed security applications on those devices.
- Installing Kaspersky Security for Mobile (optional)
If you plan to manage corporate mobile devices, follow the instructions provided in the Kaspersky Security for Mobile Help for information about deployment of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android.
- Configuring Kaspersky application policies
To apply different application settings to different devices you can use device-centric security management and/or user-centric security management. Device-centric security management can be implemented by using policies and tasks. You can apply tasks only to those devices that meet specific conditions. To set the conditions for filtering devices, use device selections and tags.
- Monitoring the network protection status
You can monitor your network by using widgets on the dashboard, generate reports from Kaspersky applications, configure and view selections of events received from the applications on the managed devices, and view notification lists.
Installation
This section describes installation of Kaspersky Security Center and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Installing Kaspersky Security Center (Standard installation)
This procedure describes how to install Kaspersky Security Center. Before installation, you must install a database management system.
To install Kaspersky Security Center:
- Under an account with administrative privileges, run the ksc_<build number>_full_<localization language>.exe executable file.
- In the application selection window that opens, click Install Kaspersky Security Center.
The Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server setup wizard starts.
- Beginning with the Welcome page, proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- If Microsoft .NET Framework is not installed, install it.
- Accept the terms of the License Agreement and the Privacy Policy.
- Select the installation type. For evaluation purposes, we recommend that you keep the default Standard value.
- If you want to install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console on the same device, select the Install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console check box.
If you clear the check box, you can later install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console separately on the same or another device.
- Select the size of your network. For evaluation purposes, we recommend that you keep the default Fewer than 100 networked devices value.
- Select the type of database server that you installed earlier.
- Specify the connection parameters for the database server that you installed earlier.
- Specify the authentication parameters for the database server that you installed earlier.
- Click the Install button to start the installation.
- After the installation successfully completes, choose whether or not you want to start Administration Console right after you close the wizard.
If you choose to open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, the login screen will open. Then you will be able to perform the initial configuration of the Administration Server by using the quick start wizard.
You can open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console only if it is already installed. You cannot open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console if you did not install it during the installation of Kaspersky Security Center or separately.
- In the Administration Console window that opens, click the installed Administration Server.
- In the Administration Server certificate window that opens, click the Yes button to continue.
The Administration Server quick start wizard starts if you did not run it in the web-based Administration Console.
Troubleshooting
If the Administration Server certificate window does not open and connection errors are displayed, try the following:
- In Windows, open Services (Control Panel → Administrative Tools → Services). Check that Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent and Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server services are running.
- In Windows, open Event Viewer (Control Panel → Administrative Tools → Event Viewer), and then select Applications and Services Logs → Kaspersky Event Log. Make sure that the log does not contain errors and contains events like Administration Server <version number> is running.
Installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
This section describes how to install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server (also referred to as Kaspersky Security Center Web Console) separately. Before installation, you must install a DBMS and the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server. You can install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console either on the same device where Kaspersky Security Center is installed, or on a different one.
To install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
- Under an account with administrative privileges, run the ksc-web-console-<version number>.<build number>.exe installation file.
This starts the setup wizard.
- Select a language for the setup wizard.
- In the welcome window, click Next.
- In the License Agreement window, read and accept the terms of the End User License Agreement. The installation continues after you accept the EULA, otherwise, the Next button is unavailable.
- In the Destination folder window, select a folder where Kaspersky Security Center Web Console will be installed (by default, %ProgramFiles%\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center Web Console). If such a folder does not exist, it is created automatically during the installation.
You can change the destination folder by using the Browse button.
- In the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console connection settings window, specify the following information:
- The address of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console (by default, 127.0.0.1).
- The port that Kaspersky Security Center Web Console will use for incoming connections, that is, the port that gives access to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console from a browser (by default, 8080).
We recommend that you leave the address and the port number as they are.
If you want, you can click Test to make sure that the selected port is available.
If you want to enable logging of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console activities, select the appropriate option. If you do not select this option, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console log files will not be created.
- In the Account settings window, specify the account names and passwords.
We recommend that you use default accounts.
- In the Client certificate window, select one of the following:
- Generate new certificate. This option is recommended if you do not have a browser certificate.
- Choose existing certificate. You can select this option if you already have a browser certificate; in this case, specify the path to it.
- If you choose to generate a new certificate, when you open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, the browser may inform you that the connection to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is not private and the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console certificate is invalid. This warning appears because the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console certificate is self-signed and automatically generated by Kaspersky Security Center. To remove this warning, create a certificate that is trusted in your infrastructure and that meets the requirements for custom certificates. Next, select the Choose existing certificate option in the Client certificate window, and then specify the path to your custom certificate.
Certificates in the PFX format are not supported by Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. To use such a certificate, you must first convert it to the supported PEM format by using an OpenSSL-based cross-platform utility, such as OpenSSL for Windows.
- In the Trusted Administration Servers window, make sure that your Administration Server is on the list and click Next to proceed to the last window of the installer.
If you need to add a new Administration Server to the list, click the Add button. In the opened window, specify the properties of a new trusted Administration Server:
- Administration Server name
The Administration Server name that will be displayed in the login window of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Administration Server address
The IP address of the device where you install Administration Server.
- Administration Server port
The OpenAPI port that Kaspersky Security Center Web Console uses to connect to Administration Server (default value is 13299).
- Administration Server certificate
The certificate file is stored on the device where Administration Server is installed. The default path to the Administration Server certificate:
- For Windows—%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\cert
- For Linux—/var/opt/kaspersky/klnagent_srv/1093/cert/
If you install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console on the same device where Administration Server is installed, use one of the paths given above. Otherwise, copy the certificate file from device where Administration Server is installed to the device where you install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, and then specify the local path to the certificate.
- Administration Server name
- In the Identity and Access Manager (IAM) window, specify whether you want to install Identity and Access Manager (also referred to as IAM). If you choose to install Identity and Access Manager, specify the following port numbers:
- KAS administrator port. By default, port 4445 is used to receive configuration from the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console for OAuth2.0 authorization endpoint port.
- Facade administrator port. By default, port 2444 is used for the configuration of Identity and Access Manager.
- Facade interaction port. By default, port 2445 is used for the connection of Kaspersky OSMP KAS Service to Kaspersky OSMP Facade Service.
If you want, you can change the default port numbers. You will not be able to change them in the future via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- In the last window of the installer, click Install to begin the installation.
After the installation successfully completes, a shortcut appears on your desktop, and you can log in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
The Administration Server quick start wizard starts if you did not run it in the Microsoft Management Console based Administration Console.
Troubleshooting
If Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is not displayed in your browser at the URL you typed, try the following:
- Check that you specified the correct host name or IP address of the device on which Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is installed.
- Check that the device that you want to operate has access to the device on which Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is installed.
- Check that firewall settings on the device on which Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is installed allow incoming connections through port 8080 and for application node.exe.
- In Windows, open Services. Check that the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console service is running.
- Check that you can access Kaspersky Security Center by using Administration Console.
- In Windows, open Event Viewer, and then select Applications and Services Logs → Kaspersky Event Log. Make sure that the log does not contain errors.
Installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console connected to Administration Server installed on failover cluster nodes
This section describes how to install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server (hereinafter also referred to as Kaspersky Security Center Web Console), that connects to Administration Server installed on Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster nodes or Windows Server failover cluster nodes. Prior to installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, install a DBMS and Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server on Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster nodes or on Windows Server failover cluster nodes.
If you use a Windows Server failover cluster, we do not recommend installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console on a failover cluster node. In case of node failure, you will lose access to Administration Server.
To install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console that connects to Administration Server installed on failover cluster nodes:
- Perform the steps of the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console installation, starting from step 1 to step 8.
- At step 9, in the Trusted Administration Servers window, click the Add button to add a failover cluster as a trusted Administration Server.
In the opened window, specify the following properties:
- Administration Server name
The cluster name that will be displayed in the login window of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Administration Server address
Depending on the failover cluster type, specify the cluster address:
- Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster. Specify the IP address of the secondary network adapter as the cluster address if you created the adapter when preparing the cluster nodes. Otherwise, specify the IP address of the third-party load balancer that you use.
- Windows Server failover cluster. Specify the cluster address that you obtained when creating the Windows Server failover cluster.
- Administration Server port
The OpenAPI port that Kaspersky Security Center Web Console uses to connect to Administration Server (default value is 13299).
- Administration Server certificate
The Administration Server certificate is located in the shared data storage of the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster or the Windows Server failover cluster. The default path to the certificate file: <shared data folder>\1093\cert\klserver.cer. Copy the certificate file from the shared data storage to the device where you install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. Specify the local path to the Administration Server certificate.
- Administration Server name
- Continue with the standard installation of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
After the installation is complete, a shortcut appears on your desktop and you can log in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
If you use a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster, you can go to Discovery & deployment → Unassigned devices to view the information about the cluster nodes and the file server.
Page top
Upgrading Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
If you want to use a newer version of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console without removing your currently installed instance, you can use the standard upgrade procedure provided in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console installer.
To upgrade Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
- Under an account with administrator rights, run the ksc-web-console-<version number>.<build number>.exe installation file, where <build number> stands for a Kaspersky Security Center Web Console build whose number is later than that of your currently installed instance.
- In the setup wizard window that opens, select a language, and then click OK.
- In the welcome window, select the Upgrade option, and then click Next.
- In the License Agreement window, read and accept the terms of the End User License Agreement. The installation continues after you accept the EULA; otherwise, the Next button is unavailable.
- Progress through the steps of the setup wizard until you finish the installation. When progressing, you can also modify the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console settings that you specified during the previous installation. When you reach the Ready for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console modification step, click the Upgrade button. Wait until the new settings are applied and on the next step of the setup wizard, click Finish. You can also click the Start Kaspersky Security Center Web Console in your browser link to start the upgraded instance of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console immediately.
Modifying the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console settings during the upgrade is only available in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console version 12.2 or later.
Your Kaspersky Security Center Web Console instance is upgraded.
Certificates for work with Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
The section describes how to issue and replace certificates for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and how to renew a certificate for Administration Server if the Server interacts with Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Reissuing the certificate for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
Most browsers impose a limit on the validity term of a certificate. To fall within this limit, the validity term of the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console certificate is limited to 397 days. You can replace an existing certificate received from a certification authority (CA) by issuing a new self-signed certificate manually. Alternatively, you can reissue your expired Kaspersky Security Center Web Console certificate.
Automatically reissuing the certificate for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is not supported. You have to manually reissue the expired certificate.
If you already use a self-signed certificate, you can also reissue it by upgrading Kaspersky Security Center Web Console through the standard procedure in the installer (Upgrade option).
When you open the Web Console, the browser may inform you that the connection to the Web Console is not private and the Web Console certificate is invalid. This warning appears because the Web Console certificate is self-signed and automatically generated by Kaspersky Security Center. To remove or prevent this warning, you can do one of the following:
- Specify a custom certificate when you reissue it (recommended option). Create a certificate that is trusted in your infrastructure and that meets the requirements for custom certificates.
- Add the Web Console certificate to the list of trusted browser certificates after you reissue the certificate. We recommend that you use this option only if you cannot create a custom certificate.
To issue a new certificate when you install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console for the first time:
- Run the routine installation of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- When you reach the Client certificate step of the setup wizard, select the Generate new certificate option, and then click the Next button.
- Progress through the remaining steps of the setup wizard until you finish the installation.
A new certificate for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is issued with a validity term of 397 days.
To reissue the expired Kaspersky Security Center Web Console certificate:
- Under an account with administrator rights, run the ksc-web-console-<version number>.<build number>.exe installation file.
- In the setup wizard window that opens, select a language, and then click OK.
- In the welcome window, select the Reissue certificate option, and then click Next.
- On the next step, wait until the reconfiguration of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is complete, and then click Finish.
The Kaspersky Security Center Web Console certificate is reissued for another validity term of 397 days.
If you use Identity and Access Manager, you must also reissue all the TLS certificates for the ports that Identity and Access Manager uses. Kaspersky Security Center Web Console displays a notification when a certificate expires. You must follow the notification instructions.
Page top
Replacing certificate for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
By default, when you install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server, a browser certificate for the application is generated automatically. You can replace the automatically generated certificate with a custom one.
To replace the certificate for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server with a custom one:
- On the device where Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server is installed, run the ksc-web-console-<version number>.<build number>.exe installation file under an account with administrative privileges.
This starts the setup wizard.
- On the first page of the wizard, select the Upgrade option.
- On the Client certificate page, select the Choose existing certificate option and specify the path to the custom certificate.
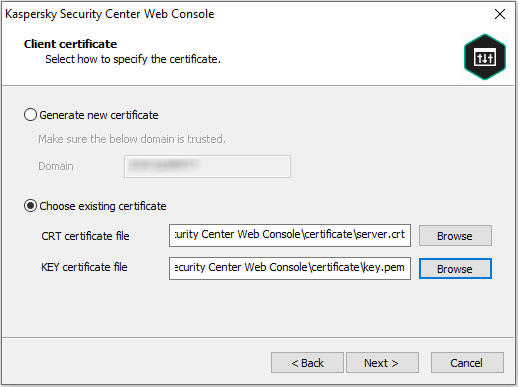
Specifying client certificate
- On the last page of the wizard, click Modify to apply the new settings.
- After the application reconfiguration successfully completes, click the Finish button.
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console works with the specified certificate.
Page top
Specifying certificates for trusted Administration Servers in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
The existing Administration Server certificate is automatically replaced with a new one before the certificate expiration date. You can also replace the existing Administration Server certificate with a custom one. Every time the certificate is changed, the new certificate must be specified in the settings of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. Otherwise, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console will not be able to connect to the Administration Server.
To specify a new certificate for the Administration Server:
- On the device where the Administration Server is installed, copy the certificate file, for example, to a mass storage device.
By default, the certificate file is stored in the following folder:
- For Windows—%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\cert
- For Linux—/var/opt/kaspersky/klnagent_srv/1093/cert/
- On the device where Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is installed, place the certificate file in a local folder.
- Run the ksc-web-console-<version number>.<build number>.exe installation file under an account with administrative privileges.
This starts the setup wizard.
- On the first wizard page, select the Upgrade option.
Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- On the Trusted Administration Servers page of the wizard, select the required Administration Server and click the Edit button.
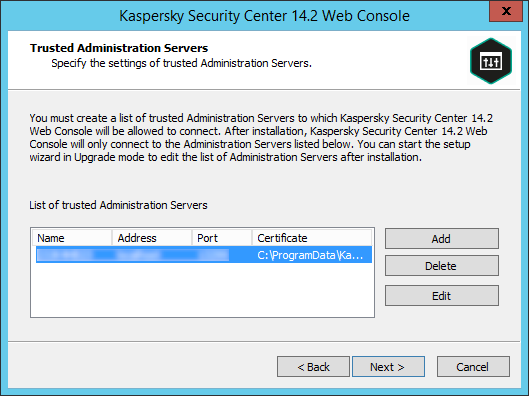
Specifying trusted Administration Servers
- In the Edit Administration Server window that opens, click the Browse button, specify the path to the new certificate file, and then click the Update button to apply changes.
- On the Ready for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console modification page of the wizard, click the Upgrade button to start the upgrade.
- After the application reconfiguration successfully completes, click the Finish button.
- Log in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console works with the specified certificate.
Converting a PFX certificate to the PEM format
To use a PFX certificate in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you must first convert it to the PEM format by using any convenient OpenSSL-based cross-platform utility.
To convert a PFX certificate to the PEM format in the Windows operating system:
- In an OpenSSL-based cross-platform utility, execute the following commands:
openssl pkcs12 -in <filename.pfx> -clcerts -nokeys -out server.crtopenssl pkcs12 -in <filename.pfx> -nocerts -nodes -out key.pemAs a result, you get a public key as a .crt file and a private key as a passphrase-protected .pem file.
- Make sure that the .crt and .pem files are generated to the same folder where the .pfx file is stored.
- If the .crt or .pem file contains the "Bag Attributes", delete these attributes by using any convenient text editor, and then save the file.
- Restart the Windows service.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console does not support passphrase-protected certificates. Therefore, run the following command in an OpenSSL-based cross-platform utility to remove a passphrase from the .pem file:
openssl rsa -in key.pem -out key-without-passphrase.pemDo not use the same name for the input and output .pem files.
As a result, the new .pem file is unencrypted. You do not have to enter a passphrase to use it.
The .crt and .pem files are ready to use, so you can specify them in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console installer.
To convert a PFX certificate to the PEM format in the Linux operating system:
- In an OpenSSL-based cross-platform utility, execute the following commands:
openssl pkcs12 -in <filename.pfx> -clcerts -nokeys | sed -ne '/-BEGIN CERTIFICATE-/,/-END CERTIFICATE-/p' > server.crtopenssl pkcs12 -in <filename.pfx> -nocerts -nodes | sed -ne '/-BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-/,/-END PRIVATE KEY-/p' > key.pem - Make sure that the certificate file and the private key are generated to the same directory where the .pfx file is stored.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console does not support passphrase-protected certificates. Therefore, run the following command in an OpenSSL-based cross-platform utility to remove a passphrase from the .pem file:
openssl rsa -in key.pem -out key-without-passphrase.pemDo not use the same name for the input and output .pem files.
As a result, the new .pem file is unencrypted. You do not have to enter a passphrase to use it.
The .crt and .pem files are ready to use, so you can specify them in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console installer.
Page top
Migration from Kaspersky Security Center Windows
This section describes the migration of managed devices and related objects (policies, tasks, groups, tags, and other objects) from Kaspersky Security Center Windows to:
About migration to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console
You can perform migration from Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. After that, you get access to Administration Server and database management system (DBMS), which are hosted in the Kaspersky infrastructure. You do not need a physical server or a DBMS—both are maintained for you by Kaspersky experts.
You can migrate your managed devices running a Windows, Linux, or macOS operating system under the control of Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. If your network includes a hierarchy of Administration Servers, you can save it in Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. In addition, you can transfer:
- Tasks and policies of managed applications
- Global tasks
- Custom device selections
- Administration group structure and included devices
- Tags that have been assigned to migrating devices
After you finish the migration, you can manage the devices by using Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. At the same time, the transferred objects are preserved and Network Agent is re-installed on all managed devices.
For information on how to perform the migration and a list of the prerequisites, see the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console Help.
Page top
About migration to Kaspersky Security Center Linux
Following this scenario, you can transfer the administration group structure, included managed devices and other group objects (policies, tasks, global tasks, tags, and device selections), from Kaspersky Security Center Windows under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
Limitations:
- Migration is only possible from Kaspersky Security Center Windows version 14.2 or later to Kaspersky Security Center Linux version 15 or later.
- You can perform this scenario only by using Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Before you begin, learn more about the features and limitations of Kaspersky Security Center Linux:
- Functional differences between Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky Security Center Linux
- List of Kaspersky applications supported by Kaspersky Security Center Linux
Stages
The migration scenario proceeds in stages:
- Choose a migration method
You migrate to Kaspersky Security Center Linux through the Migration wizard. The Migration wizard steps depend on whether or not Administration Servers of Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky Security Center Linux are arranged into a hierarchy:
- Migration by using a hierarchy of Administration Servers
Choose this option if Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Windows acts as secondary to Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Linux. You manage the migration process and switch between Servers within a single instance of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. If you prefer this option, you can arrange Administration Servers into a hierarchy to simplify the migration procedure. To do this, create the hierarchy before starting the migration.
- Migration by using an export file (ZIP archive)
Choose this option if Administration Servers of Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky Security Center Linux are not arranged into a hierarchy. You manage the migration process with two instances of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console—an instance for Kaspersky Security Center Windows and another one for Kaspersky Security Center Linux. In this case, you will use the export file that you created and downloaded during the export from Kaspersky Security Center Windows and import this file to Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
- Migration by using a hierarchy of Administration Servers
- Back up the certificate and private key of Kaspersky Security Center Windows Administration Server (optional step)
You might want to put the managed devices under the management of the Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Linux by restoring the certificate and private key of Administration Server from a backup copy. In this case, back up the certificate and private key of Kaspersky Security Center Windows Administration Server. Then at stage 6, restore the certificate and private key.
- Export data from Kaspersky Security Center Windows
Open Kaspersky Security Center Windows, and then run the Migration wizard.
- Import data to Kaspersky Security Center Linux
Continue the Migration wizard to import the exported data to Kaspersky Security Center Linux. If the Servers are arranged into a hierarchy, the import starts automatically after a successful export within the same wizard. If the Servers are not arranged into a hierarchy, you continue the Migration wizard after switching to Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
- Perform additional actions to transfer objects and settings from Kaspersky Security Center Windows to Kaspersky Security Center Linux manually (optional step)
You might also want to transfer the objects and settings that cannot be transferred through the Migration wizard. For example, you could additionally do the following:
- Transfer the license keys used by Administration Server and managed applications
- Configure global tasks of Administration Server
- Configure Network Agent policy settings
- Create installation packages of applications
- Create virtual Servers
- Assign and configure distribution points
- Configure device moving rules
- Configure rules for auto-tagging devices
- Create application categories
- Move the imported managed devices under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux
To complete the migration, move the imported managed devices under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux. You can do it by one of the following methods:
- Through the klmover utility
Use the klmover utility and specify the connection settings for the new Administration Server.
- Through the Change Administration Server task
Create a Change Administration Server task, specify the imported managed devices, new Administration Server, and other task settings. Then run the task to put the managed devices under the management of the Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
- Through removal (if already installed) and further installation of Network Agent on the managed devices
Create a new Network Agent installation package and specify the connection settings for the new Administration Server in the installation package properties. Remove Network Agent on the imported managed devices, and then use the installation package to install Network Agent on the imported managed devices through a remote installation task. You can also create and use a stand-alone installation package to install Network Agent locally. For more information, see Switching managed devices under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
- Through restoring the certificate and private key of Administration Server from a backup copy (only for migration to Kaspersky Security Center Linux 15.1 or later)
Assign the same network address to the device with Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Linux as on Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Windows. Run the klbackup utility with the
-cert_onlyparameter, to restore the Administration Server certificate and private key from the backup copy that you saved at stage 2. In the command line, execute the following command:/opt/kaspersky/ksc64/sbin/klbackup -path <path to the backup copy of Administration Server certificate> -restore -cert_only. For more information, see Using the klbackup utility to switch managed devices under management of another Administration Server.
- Through the klmover utility
- Update Network Agent to the latest version
We recommend that you upgrade the Network Agent for Linux to the same version as Kaspersky Security Center.
- Make sure the managed devices are visible on the new Administration Server
On Kaspersky Security Center Linux Administration Server, open the managed devices list (Assets (Devices) → Managed devices), and check the values in the Visible, Network Agent is installed, and Last connected to Administration Server columns.
Other methods of data migration
Besides the Migration wizard, you can also transfer specific tasks and policies:
- Export the tasks from Kaspersky Security Center Windows, and then import the tasks to Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
- Export specific policies from Kaspersky Security Center Windows, and then import the policies to Kaspersky Security Center Linux. The related policy profiles are exported and imported together with the selected policies.
About migration to Kaspersky XDR Expert
Following this scenario, you can transfer the administration group structure, included managed devices and other group objects (policies, tasks, global tasks, tags, and device selections) from Kaspersky Security Center Windows under management of Kaspersky XDR Expert.
Limitations:
- Migration is only possible from Kaspersky Security Center 14.2 Windows to Kaspersky XDR Expert starting from version 1.0.
- You can perform this scenario only by using Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Stages
The migration scenario proceeds in stages:
- Choose a migration method
You migrate to Kaspersky XDR Expert through the Migration wizard. The Migration wizard steps depend on whether or not Administration Servers of Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky XDR Expert are arranged into a hierarchy:
- Migration by using a hierarchy of Administration Servers
Choose this option if Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Windows acts as secondary to Administration Server of Kaspersky XDR Expert. You manage the migration process and switch between Servers within OSMP Console. If you prefer this option, you can arrange Administration Servers into a hierarchy to simplify the migration procedure. To do this, create the hierarchy before starting the migration.
- Migration by using an export file (ZIP archive)
Choose this option if Administration Servers of Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky XDR Expert are not arranged into a hierarchy. You manage the migration process with two Consoles—an instance for Kaspersky Security Center Windows and OSMP Console. In this case, you will use the export file that you created and downloaded during the export from Kaspersky Security Center Windows and import this file to Kaspersky XDR Expert.
- Migration by using a hierarchy of Administration Servers
- Export data from Kaspersky Security Center Windows
Open Kaspersky Security Center Windows, and then run the Migration wizard.
- Import data to Kaspersky XDR Expert
Continue the Migration wizard to import the exported data to Kaspersky XDR Expert.
If the Servers are arranged into a hierarchy, the import starts automatically after a successful export within the same wizard. If the Servers are not arranged into a hierarchy, you continue the Migration wizard after switching to Kaspersky XDR Expert.
- Perform additional actions to transfer objects and settings from Kaspersky Security Center Windows to Kaspersky XDR Expert manually (optional step)
You might also want to transfer the objects and settings that cannot be transferred through the Migration wizard. For example, you could additionally do the following:
- Configure global tasks of Administration Server
- Configure Network Agent policy settings
- Create installation packages of applications
- Create virtual Servers
- Assign and configure distribution points
- Configure device moving rules
- Configure rules for auto-tagging devices
- Create application categories
- Move the imported managed devices under management of Kaspersky XDR Expert
To complete the migration, move the imported managed devices under management of Kaspersky XDR Expert. You can do it by one of the following methods:
- Through Kaspersky Security Center group task
Use the Change Administration Server task to change the Administration Server to a different one for specific client devices.
- Through the klmover utility
Use the klmover utility and specify the connection settings for the new Administration Server.
- Through installation or re-installation of Network Agent on the managed devices
Create a new Network Agent installation package and specify the connection settings for the new Administration Server in the installation package properties. Use the installation package to install Network Agent on the imported managed devices through a remote installation task.
You can also create and use a stand-alone installation package to install Network Agent locally.
- Through Kaspersky Security Center group task
- Update Network Agent to the latest version
We recommend that you upgrade the Network Agent to the same version as OSMP Console.
- Make sure the managed devices are visible on the new Administration Server
On Kaspersky XDR Expert Administration Server, open the managed devices list (Assets (Devices) → Managed devices), and check the values in the Visible, Network Agent is installed, and Last connected to Administration Server columns.
Other methods of data migration
Besides the Migration wizard, you can also transfer specific tasks and policies:
- Export the tasks from Kaspersky Security Center Windows, and then import the tasks to Kaspersky XDR Expert.
- Export the policies from Kaspersky Security Center Windows, and then import the policies to Kaspersky XDR Expert. The related policy profiles are exported and imported together with the selected policies.
Exporting group objects from Kaspersky Security Center Windows
Migration administration group structure, included managed devices and other group objects from Kaspersky Security Center Windows to Kaspersky Security Center Linux requires that you first select data for exporting and create an export file. The export file contains information about all group objects that you want to migrate. The export file will be used for subsequent import to Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
You can export the following objects:
- Tasks and policies of managed applications
- Global tasks
- Custom device selections
- Administration group structure and included devices
- Tags that have been assigned to migrating devices
Before you start exporting, read general information about migration to Kaspersky Security Center Linux. Choose the migration method—by using or not using the hierarchy of Administration Servers of Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
To export managed devices and related group objects through the Migration wizard:
- Depending on whether or not the Administration Servers of Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky Security Center Linux are arranged into a hierarchy, do one of the following:
- If the Servers are arranged into a hierarchy, open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, and then switch to the Server of Kaspersky Security Center Windows.
- If the Servers are not arranged into a hierarchy, open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console connected to Kaspersky Security Center Windows.
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Migration.
- To start the wizard and follow its steps, select where you want to transfer your data and settings.
- If you want to transfer your data and settings to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, select Migrate to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
- If you want to transfer your data and settings to Kaspersky Security Center Linux or Kaspersky XDR Expert, select Migrate to Kaspersky Security Center Linux or Open Single Management Platform.
- Select the administration group or subgroup to export. Please make sure that the selected administration group or subgroup contains no more than 10,000 devices.
- Select the managed applications whose tasks and policies will be exported. Select only applications that are supported by Kaspersky Security Center Linux. The objects of unsupported applications will still be exported, but they will not be operable.
- Use the links on the left to select the global tasks, device selections, and reports to export. The Group objects link allows you to exclude custom roles, internal users and security groups, and custom application categories from the export.
The export file (ZIP archive) is created. Depending on whether or not you perform migration with Administration Server hierarchy support, the export file is saved as follows:
- If the Servers are arranged into a hierarchy, the export file is saved to the temporary folder on Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server.
- If the Servers are not arranged into a hierarchy, the export file is downloaded to your device.
For migration with Administration Server hierarchy support, the import starts automatically after a successful export. For migration without Administration Server hierarchy support, you can import the saved export file to Kaspersky Security Center Linux manually.
Page top
Importing the export file to Kaspersky Security Center Linux
To transfer information about managed devices, objects, and their settings that you exported from Kaspersky Security Center Windows, you must import it to Kaspersky Security Center Linux or Kaspersky XDR Expert.
To import managed devices and related group objects through the Migration wizard:
- Depending on whether or not the Administration Servers of Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky Security Center Linux are arranged into a hierarchy, do one of the following:
- If the Servers are arranged into a hierarchy, proceed to the next step of the Migration wizard after the export is completed. The import starts automatically after a successful export within this wizard (see step 2 of this instruction).
- If the Servers are not arranged into a hierarchy:
- Open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console connected to Kaspersky Security Center Linux or Kaspersky XDR Expert.
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Migration.
- Select the export file (ZIP archive) that you created and downloaded during the export from Kaspersky Security Center Windows. The upload of the export file starts.
- After the export file is uploaded successfully, you can continue importing. If you want to specify another export file, click the Change link, and then select the required file.
- The entire hierarchy of administration groups of Kaspersky Security Center Linux is displayed.
Select the check box next to the target administration group to which the objects of the exported administration group (managed devices, policies, tasks, and other group objects) must be restored.
- The import of group objects starts. You cannot minimize the Migration wizard and perform any concurrent operations during the import. Wait until the refresh icons (
 ) next to all items in the list of objects are replaced with green check marks (
) next to all items in the list of objects are replaced with green check marks ( ) and the import finishes.
) and the import finishes. - When the import completes, the exported structure of administration groups, including device details, appears under the target administration group that you selected. If the name of the object that you restore is identical to the name of an existing object, the restored object has an incremental suffix added.
If in a migrated task the details of the account under which the task is run are specified, you have to open the task and enter the password again after the import is completed.
If the import has completed with an error, you can do one of the following:
- For migration with Administration Server hierarchy support, you can start to import the export file again.
- For migration without Administration Server hierarchy support, you can start the Migration wizard to select another export file, and then import it again.
You can check whether the group objects included in the export scope have been successfully imported to Kaspersky Security Center Linux. To do this, go to the Assets (Devices) section and ensure whether the imported objects appear in the corresponding subsections.
Note that the imported managed devices are displayed in the Managed devices subsection, but they are invisible in the network and Network Agent is not installed and running on them (the No value in the Visible, Network Agent is installed, and Network Agent is running columns).
To complete the migration, you need to switch the managed devices to be under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
Page top
Switching managed devices to be under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux
After a successful import of information about managed devices, objects, and their settings to Kaspersky Security Center Linux, you need to switch the managed devices to be under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux to complete the migration.
You can move the managed devices to be under Kaspersky Security Center Linux by one of the following methods:
- Using the klmover utility.
- Using the Change Administration Server task.
- Restoring the certificate and private key of Administration Server from a backup copy (only for migration to Kaspersky Security Center Linux 15.1 or later).
For details, refer to stage 6 of the main migration scenario.
- Installing Network Agent on the managed devices through a remote installation task.
To switch managed devices to be under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux by installing Network Agent:
- Remove Network Agent on the imported managed devices that will be switched under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
- Switch to Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Windows.
- Go to Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Installation packages, and then open the properties of an existing installation package of Network Agent.
If the installation package of Network Agent is absent in the package list, download a new one.
You can also create and use a stand-alone installation package to install Network Agent locally.
- On the Settings tab, select the Connection section. Specify the connection settings of Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
- Create a remote installation task for the imported managed devices, and then specify the reconfigured Network Agent installation package.
You can install Network Agent through Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Windows or through a Windows-based device that acts as a distribution point. If you use Administration Server, enable the Using operating system resources through Administration Server option. If you use a distribution point, enable the Using operating system resources through distribution points option.
- Run the remote installation task.
After the remote installation task finishes successfully, go to Administration Server of Kaspersky Security Center Linux and ensure that managed devices are visible in the network, and that Network Agent is installed and running on them (the Yes value in the Visible, Network Agent is installed, and Network Agent is running columns).
Page top
Signing in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and signing out
You can sign in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console after you install the Administration Server and Web Console Server. You must know the web address of the Administration Server and the port number specified during installation (by default, the port is 8080). In your browser, JavaScript must be enabled.
You can sign in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console by using the following methods:
- By using domain authentication
If you choose this method, make sure that domain controller polling has been activated and the domain users are added to the Administration Server.
- By specifying the administrator's user name and password
Signing in by using domain authentication
To sign in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console by using domain authentication:
- In your browser, go to <Administration Server web address>:<Port number>.
The sign-in page is displayed.
- If you added several trusted servers, in the Administration Servers list select the Administration Server that you want to connect to.
If you only added a single Administration Server, the Administration Servers list is not displayed.
- Do one of the following:
- Click the Use domain authentication button.
- If one or more virtual Administration Servers are created on the Server and you want to sign in to a virtual Server by using domain authentication:
- Click Show virtual Server options.
- Type the virtual Administration Server name that you specified while creating the virtual Server.
- Click the Use domain authentication button.
- If two-step verification is enabled for your account, specify the security code generated by the authenticator app on the mobile device.
You can go back to the sign-in page, if necessary.
After sign-in, the dashboard is displayed, containing the language and theme that you used last time. You can navigate through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and use it to work with Kaspersky Security Center.
Signing in by specifying the administrator's user name and password
To sign in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console by specifying the administrator's user name and password:
- In your browser, go to <Administration Server web address>:<Port number>.
The sign-in page is displayed.
- If you added several trusted servers, in the Administration Servers list select the Administration Server that you want to connect to.
If you only added a single Administration Server, the Administration Servers list is not displayed.
- Do one of the following:
- To sign in to the Administration Server:
- Enter the user name and password of the local Administrator.
- Click the Sign in button.
- If one or more virtual Administration Servers are created on the Server and you want to sign in to a virtual Server:
- Click Show virtual Server options.
- Type the virtual Administration Server name that you specified while creating the virtual Server.
- Enter the user name and password of the administrator who has rights on the virtual Administration Server.
- Click the Sign in button.
- To sign in to the Administration Server:
- If two-step verification is enabled for your account, specify the security code generated by the authenticator app on the mobile device.
You can go back to the sign-in page, if necessary.
- If forced password change is enabled for your account or your password has expired, the password change window will be displayed. Set a new password to sign-in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
After sign-in, the dashboard is displayed, containing the language and theme that you used last time. You can navigate through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and use it to work with Kaspersky Security Center.
Signing out
To sign out of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console,
In the main menu, go to your account settings, and then select Sign out.
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is closed, and the sign-in page is displayed.
Page top
Identity and Access Manager in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
This section provides information about Identity and Access Manager (also referred to as IAM).
About Identity and Access Manager
Identity and Access Manager (also referred to as IAM) is a Kaspersky Security Center Web Console component that enables you to use a single sign-on (SSO) between Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks web interface. IAM uses the OAuth 2.0 protocol to ensure authorization of Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
In this case, the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks, which you get access to via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, is referred to as a resource server, and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks web interface are referred to as OAuth 2.0 clients. A resource server is a program that works with multiple users and requires authorization. The client uses a token for authorization on the resource server. A token is a unique sequence of bytes. When a token expires, it is automatically reissued. IAM acts a single authorization server for multiple OAuth 2.0 clients.
You can install IAM when installing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. You can enable it later at any time in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console settings. If a Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity Server or a Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity web interface is installed on a device that is managed by the same Administration Server, IAM detects this program and a notification is displayed in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console informing you about this. You can register Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks and later use SSO for both Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks web interface.
If you sign out of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, your session in Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks web interface will end and you will have to log in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console again.
Enabling Identity and Access Manager: scenario
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that you have access to Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks version 3.1 or later.
Stages
Enabling Identity and Access Manager (also referred to as IAM) proceeds in stages:
- Checking the necessary ports
Make sure that ports 3333, 4004, and 4444 are opened on the device where Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is installed. These ports are needed for using OAuth 2.0. If you want, you can change the default port numbers in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console settings window.
Besides the ports 3333, 4004, and 4444, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console also uses ports 4445, 2444, and 2445 for various purposes.
- Installing Identity and Access Manager
During the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console installation, specify that you want to install Identity and Access Manager. If you did not do so, run the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console setup wizard again.
- Configuring Identity and Access Manager
In the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console settings window, make sure that the Identity and Access Manager (IAM) toggle button is enabled. Also, specify DNS name of the device where Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is installed: the client applications will connect to this device.
- Specifying the token settings
In the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console settings window, specify lifetime of tokens and authorization timeout that Identity and Access Manager will use. You can use the default values, or you can specify your own values according to your needs.
- Granting certificates
If you prefer to use the certificates generated by the Administration Server, then in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console settings window, download the root certificates for the ports used by IAM and distribute them to the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console users' workstations. Otherwise, the users' browsers will display error messages when trying to connect to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Registering the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Servers and Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks web interfaces
When IAM is installed, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console displays a message saying that an Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Server (or multiple Servers) and one or more Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks web interfaces are waiting to be registered. Click this message to register your Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Server (or multiple Servers) and web interface (or multiple web interfaces).
Results
After you complete this scenario, you will be able to use SSO and IAM for Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Page top
Configuring Identity and Access Manager in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
To configure Identity and Access Manager according to your needs:
- In the main menu, go to Settings → Identity and Access Manager.
- In the Identity and Access Manager section, make sure that Identity and Access Manager is enabled.
- Click the Settings link under the Network name of the Identity and Access Manager device line.
- Specify DNS name of the device on which you installed Identity and Access Manager. Client applications will connect to this device.
- If you want, change the default token settings, certificate settings, and port numbers by clicking the Settings link under the relevant group of settings.
Identity and Access Manager is enabled and working according to your needs.
Registering Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks application in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
To start working with Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks application via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you must first register it in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
To register Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks application:
- Make sure that the following is done:
- You have downloaded and installed the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks web plug-in.
However, you can do it later while waiting for the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Server to synchronize with the Administration Server.
- You have completed the Single Sign-On (SSO) technology usage preparations scenario.
- The necessary settings in the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks web interface are specified on Kaspersky Security Center page. For details, please refer to the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Online Help.
- You are logged in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console under an administrator account.
- IAM is configured.
- You have downloaded and installed the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks web plug-in.
- Move the device where Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Server is installed from the Unassigned devices group to the Managed devices group:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Unassigned devices.
- Select the check box next to the device where Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Server is installed.
- Click the Move to group button.
- In the hierarchy of administration groups, select the check box next to the Managed devices group.
- Click the Move button.
- Proceed to the properties of the device where the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Server is installed.
- On the device properties page, in the General section, select the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option, and then click the Save button.
- On the device properties page, select the Applications section.
- In the Applications section, select Kaspersky Network Agent.
- If the current status of the application is Stopped, wait until it changes to Running.
This may take up to 15 minutes. If you have not yet install the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks web plug-in, you can do it now, while you are waiting.
- In the main menu, go to Settings → Identity and Access Manager.
In the Registration requests field, one pending request is displayed.
- Click the Settings link under the Registration requests field.
- In the list of registered clients that opens, select the check box next to the name of the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Server, that has the Pending status, and then click the Approve button.
If you do not want to register the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Server, you can click the Decline button and get back to this list later.
After you click the Approve button, the status changes to Approved, and then to Ready. If the status does not change, you can click the Refresh button.
- Close the list of registered clients and make sure that the value in the Registered clients field has increased.
- To add the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks widget on the dashboard:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Dashboard.
- On the dashboard, click the Add or restore web widget button.
- In the widget menu that opens, select Other.
- Select the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks widget.
You can now proceed to the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks web interface using the link in the widget.
After you complete the registration procedure, a new button, Kaspersky Security Center, appears on the login page of the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks web interface. You can click this button to log in to Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks web interface under your Kaspersky Security Center credentials.
Page top
Lifetime of tokens and authorization timeout for Identity and Access Manager
When configuring Identity and Access Manager (also referred to as IAM), you must specify the settings for the token lifetime and authorization timeout. The default settings are designed to reflect both the security standards and the server load. However, you can change these settings according to your organization's policies.
IAM automatically re-issues a token when it is about to expire.
The table below lists the default token lifetime settings.
Token lifetime settings
Token |
Default lifetime (in seconds) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Identity token (id_token) |
86400 |
Identity token used by the OAuth 2.0 client (that is, either Kaspersky Security Center Web Console or Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity Console). IAM sends the ID token containing information about the user (that is, the user profile) to the client. |
Access token (access_token) |
86400 |
Access token used by the OAuth 2.0 client to access to the resource server on behalf of the resource owner identified by IAM. |
Refresh token (refresh_token) |
172800 |
The OAuth 2.0 client uses this token for re-issuing the Identity token and the Access token. |
The table below lists the timeouts for auth_code and login_consent_request.
Authorization timeout settings
Setting |
Default timeout (in seconds) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Authorization code (auth_code) |
3600 |
Timeout for exchanging code for the token. The OAuth 2.0 client sends this code to the resource server and gets the access token in exchange. |
Login consent request timeout (login_consent_request) |
3600 |
Timeout for delegating user rights to the OAuth 2.0 client. |
For more information about tokens, see the OAuth website.
To configure timeout for clients with no detected mouse or keyboard activity:
- In the installation folder of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, find and open the config.json file. The file contains the parameters to configure the timeout for idle clients.
- Use the
clientIdleTimeoutparameter to specify time, in milliseconds, after which an inactive client displays a warning popup. - Use the
clientLogoutTimeoutparameter to specify time, in milliseconds, after which IAM authorization for the inactive client is terminated. TheclientLogoutTimeoutcounts down sequentially after theclientIdleTimeout.
Downloading and distributing the IAM certificates
By default, Identity and Access Manager uses the certificates generated by the Administration Server to grant browsers access to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. However, If you want, you can use custom certificates. Whatever certificate you use, you must make sure that all workstations from which Kaspersky Security Center Web Console users access Kaspersky Security Center Web Console trust this certificate.
To download and distribute certificates:
- In the main menu, go to Settings → Identity and Access Manager.
- For each certificate, click the Settings link under the relevant group of settings, and then do one of the following:
- If you want to use the certificate that the Administration Server generated during the installation of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
- Select Certificate generated by Administration Server in the certificate properties window that opens.
- Click the Download button to download the certificate.
- Distribute the downloaded certificate to all workstations from which Kaspersky Security Center Web Console users access Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- If you have a certificate that you want to use:
- Select Custom TLS certificate in the certificate properties window that opens.
- Select the certificate file and the private key.
- Click the OK button.
- Distribute the certificate to all workstations from which users access Kaspersky Security Center Web Console or Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity Console.
- If you want to use the certificate that the Administration Server generated during the installation of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
The certificates grant users access to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity Console.
You have to re-issue all the certificates timely. The certificates generated by the Administration Server must be re-generated manually. The certificates generated by the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console installer must be re-generated by using the installer.
Disabling Identity and Access Manager
If you want, you can disable Identity and Access Manager (also referred to as IAM).
To disable IAM,
- In the main menu, go to Settings → Integration.
- In the Identity and Access Manager section, switch the Identity and Access Manager toggle button to disabled.
You can enable IAM any time later.
If you update Kaspersky Security Center Web Console via the installer and specify that you do not want to install IAM, then Kaspersky Security Center Web Console will be upgraded and IAM will not be installed. All the information about integration with Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks will be deleted from your device, as well as IAM configuration files and log files.
Configuring domain authentication by using the NTLM and Kerberos protocols
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 enables you to use domain authentication in OpenAPI by using the NTLM and Kerberos protocols. Using domain authentication allows a Windows user to enable secure authentication in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console without having to re-enter the password on the corporate network (single sign-on).
Domain authentication in OpenAPI over the Kerberos protocol has the following restrictions:
- The user of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console must be authenticated in Active Directory by using the Kerberos protocol. The user must have a valid Kerberos Ticket Granting Ticket (also referred to as a TGT). A TGT is issued automatically when you authenticate to the domain.
- You must configure Kerberos authentication in the browser. For details, refer to the documentation of the browser you are using.
If you want to use domain authentication by using Kerberos protocols, your network must meet the following conditions:
- Administration Server must be run under the domain account name.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server must be installed on the same device where the Administration Server is installed.
- You must specify the following Service Principal Names (SPN) for the Administration Server account:
- "http/<server.fqnd.name>"
- "http/<server>"
Here, <server> is the network name of the Administration Server device, and <server.fqnd.name> is the FQDN name of the Administration Server device.
- When connecting to the Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, the Administration Server address must be specified exactly as the address for which the Service Principal Name (SPN) is registered. You can specify either <server.fqnd.name> or <server>.
- For a password-free login, the browser process in which the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is open as browser must run under a domain account.
Kerberos and NTLM protocols are only supported in OpenAPI for Kaspersky Security Center 15.1. They are not supported in OpenAPI for Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
Page top
Configuring Administration Server
This section describes the configuration process and properties of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
Configuring the connection of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to Administration Server
To set the connection ports of Administration Server:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Connection ports section.
The application displays the main connection settings of the selected Server.
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is connected to Administration Server through SSL port TCP 13299. The same port can be used by klakaut automation objects.
Port TCP 14000 can be used for connecting Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, distribution points, secondary Administration Servers, and klakaut automation objects, as well as for receiving data from client devices.
Normally, SSL port TCP 13000 can only be used by Network Agent, a secondary Administration Server, and the primary Administration Server in DMZ. In some cases, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console may have to be connected through SSL port 13000:
- If a single SSL port is likely to be used both for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and for other activities (receiving data from client devices, connecting distribution points, connecting secondary Administration Servers).
- If a klakaut automation object is not connected to Administration Server directly but through a distribution point in the DMZ.
Configuring Administration Server connection events logging
The history of connections and attempts to connect to the Administration Server during its operation can be saved to a log file. The information in the file allows you to track not only connections inside your network infrastructure, but unauthorized attempts to access the server as well.
To log events of connection to the Administration Server:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Connection ports section.
- Enable the Log Administration Server connection events option.
All further events of inbound connections to the Administration Server, authentication results, and SSL errors will be saved to the file %ProgramData%\KasperskyLab\adminkit\logs\sc.syslog.
Page top
Configuring internet access settings for Administration Server
You must configure internet access to use Kaspersky Security Network, and to download updates of anti-virus databases for Kaspersky Security Center and managed Kaspersky applications.
To specify the internet access settings for Administration Server:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the Administration Server name.
) next to the Administration Server name.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Configuring internet access section.
- Enable the Use proxy server option if you want to use a proxy server when connecting to the internet. If this option is enabled, the fields are available for entering settings. Specify the following settings for a proxy server connection:
You can also configure internet access by using the quick start wizard.
Page top
Setting the maximum number of events in the event repository
In the Events repository section of the Administration Server properties window, you can edit the settings of events storage in the Administration Server database by limiting the number of event records and record storage term. When you specify the maximum number of events, the application calculates an approximate amount of storage space required for the specified number. You can use this approximate calculation to evaluate whether you have enough free space on the disk to avoid database overflow. The default capacity of the Administration Server database is 400,000 events. The maximum recommended capacity of the database is 45 million events.
The application checks the database every 10 minutes. If the number of events reaches the specified maximum value plus 10,000, the application deletes the oldest events so that only the specified maximum number of events remains.
When the Administration Server deletes old events, it cannot save new events to the database. During this period of time, information about events that were rejected is written to the Kaspersky Event Log. The new events are queued and then saved to the database after the deletion operation is complete.
To limit the number of events that can be stored in the events repository on the Administration Server:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Events repository section. Specify the maximum number of events stored in the database.
- Click the Save button.
Additionally, you can change the settings of any task to save events related to the task progress, or save only task execution results. In doing so, you will reduce the number of events in the database, increase the speed of execution of scenarios associated with analysis of the event table in the database, and lower the risk that critical events will be overwritten by a large number of events.
Connection settings of UEFI protection devices
A UEFI protection device is a device with a Kaspersky solution or application for UEFI integrated at the BIOS level. Integrated protection ensures device security from the moment the system starts, while protection on devices without integrated software begins functioning only after the security application starts. Kaspersky Security Center supports management of these devices.
To modify the connection settings of UEFI protection devices:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Additional ports section.
- Modify the relevant settings:
- Click the Save button.
The UEFI protection devices can now connect to the Administration Server.
Page top
Creating a hierarchy of Administration Servers: adding a secondary Administration Server
Adding secondary Administration Server (performed on the future primary Administration Server)
You can add an Administration Server as a secondary Administration Server, thus establishing a "primary/secondary" hierarchy.
To add a secondary Administration Server that is available for connection through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
- Make sure that port 13000 of the future primary Administration Server is available for receipt of connections from secondary Administration Servers.
- On the future primary Administration Server, click the settings icon (
 ).
). - On the properties page that opens, select the Administration Servers tab.
- Select the check box next to the name of th administration group to which you want to add the Administration Server.
- On the menu line, click Connect secondary Administration Server.
The Add secondary Administration Server wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- Fill in the following fields:
- Specify the certificate for the secondary Administration Server. If you specified the Secondary Server address parameter, you can click the Get from secondary Administration Server button to obtain the certificate. Otherwise, click the Browse for the certificate file button and locate the certificate file.
- Specify the connection settings:
- Enter the address of the future primary Administration Server.
- If the future secondary Administration Server uses a proxy server, enter the proxy server address and user credentials to connect to the proxy server.
- Enter the credentials of the user that has access rights on the future secondary Administration Server.
- If two-step verification is enabled and configured, specify the security code generated by the authenticator app.
If two-step verification is enabled, but not configured for the account that you specify, create the hierarchy from the future secondary Server (see instructions below).
If the connection settings are correct, the connection with the future secondary Server is established and the "primary/secondary" hierarchy is built. If the connection has failed, check the connection settings or specify the certificate of the future secondary Server manually.
The connection between the primary and secondary Administration Servers is established through port 13000. The tasks and policies from the primary Administration Server are received and applied. The secondary Administration Server is displayed on the primary Administration Server, in the administration group to which it was added.
Adding secondary Administration Server (performed on the future secondary Administration Server)
If you could not connect to the future secondary Administration Server (for example, because it was temporarily disconnected or unavailable), you are still able to add a secondary Administration Server.
To add as secondary an Administration Server that is not available for connection through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
- Send the certificate file of the future primary Administration Server to the system administrator of the office where the future secondary Administration Server is located. (You can, for example, write the file to an external device, such as a flash drive, or send it by email.)
The certificate file is located on the future primary Administration Server, at %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\cert\klserver.cer.
- Prompt the system administrator in charge of the future secondary Administration Server to do the following:
- Click the settings icon (
 ).
). - On the properties page that opens, proceed to the Hierarchy of Administration Servers section of the General tab.
- Select the This Administration Server is secondary in the hierarchy option.
- In the Primary Administration Server address field, enter the network name of the future primary Administration Server.
- Select the previously saved file with the certificate of the future primary Administration Server by clicking Browse.
- If necessary, select the Connect primary Administration Server to secondary Administration Server in DMZ check box.
- If the connection to the future secondary Administration Server is performed through a proxy server, select the Use proxy server option and specify the connection settings.
- Click Save.
- Click the settings icon (
The "primary/secondary" hierarchy is built. The primary Administration Server starts receiving connection from the secondary Administration Server using port 13000. The tasks and policies from the primary Administration Server are received and applied. The secondary Administration Server is displayed on the primary Administration Server, in the administration group where it was added.
Viewing the list of secondary Administration Servers
To view the list of the secondary (including virtual) Administration Servers:
In the main menu, click the name of the Administration Server, which is next to the settings icon (![]() ).
).
The drop-down list of the secondary (including virtual) Administration Servers is displayed.
You can proceed to any of these Administration Servers by clicking its name.
The administration groups are shown, too, but they are grayed and not available for management in this menu.
If you are connected to your primary Administration Server in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, and can not connect to a virtual Administration Server that is managed by a secondary Administration Server, you can use one of the following ways:
- Modify the existing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console installation to add the secondary Server to the list of trusted Administration Servers. Then you will be able to connect to the virtual Administration Server in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Use Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to connect directly to the secondary Administration Server where the virtual Server was created. Then you will be able to switch to the virtual Administration Server in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Use MMC-based Administration Console to connect directly to the virtual Server.
Deleting a hierarchy of Administration Servers
If you no longer want to have a hierarchy of Administration Servers, you can disconnect them from this hierarchy.
To delete a hierarchy of Administration Servers:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the primary Administration Server.
) next to the name of the primary Administration Server. - On the page that opens, proceed to the Administration Servers tab.
- In the administration group from which you want to delete the secondary Administration Server, select the secondary Administration Server.
- On the menu line, click Delete.
- In the window that opens, click OK to confirm that you want to delete the secondary Administration Server.
The former primary Administration Server and the former secondary Administration Server are now independent of each other. The hierarchy no longer exists.
Page top
Administration Server maintenance
The Administration Server maintenance allows you to free up space in the folder of the Administration Server and reduce the database volume by deleting objects that are no longer needed. This helps you to improve the performance and operation reliability of the application. We recommend that you maintain the Administration Server at least every week.
The Administration Server maintenance is performed using the dedicated task. The application performs the following actions when maintaining the Administration Server:
- Deletes unnecessary folders and files from the storage folder.
- Deletes unnecessary records from tables (also known as "dangling pointers").
- Clears the cache.
- Maintains the database (if you use SQL Server or PostgreSQL as a DBMS):
- Checks the database for errors (available only for SQL Server).
- Re-organizes database indexes.
- Updates the database statistics.
- Shrinks the database (if necessary).
The Administration Server maintenance task supports MariaDB versions 10.3 and later. If you use MariaDB versions 10.2 or earlier, administrators have to maintain this DBMS on their own.
The Administration Server maintenance task is created automatically when you install Kaspersky Security Center. If the Administration Server maintenance task is deleted, you can create it manually.
To create the Administration Server maintenance task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click the Add button.
The New task wizard starts.
- In the New task settings window of the wizard, select Administration Server maintenance as the task type and click the Next button.
- Follow the rest of the wizard instructions.
The newly created task is displayed in the list of tasks. Only one Administration Server maintenance task can be running for a single Administration Server. If an Administration Server maintenance task has already been created for an Administration Server, no new Administration Server maintenance task can be created.
Page top
Configuring the interface
You can configure the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface to display and hide sections and interface elements, depending on the features being used.
To configure the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface in accordance with the currently used set of features:
- In the main menu, go to your account settings, and then select Interface options.
- In the Interface options window that opens, enable or disable the required options.
- Click Save.
After that, the console displays sections in the main menu in accordance with enabled options. For example, if you enable Show EDR alerts, the Monitoring & reporting → Alerts section appears in the main menu.
Page top
Managing virtual Administration Servers
This section describes the following actions to manage virtual Administration Servers:
- Create virtual Administration Servers
- Enable and disable virtual Administration Servers
- Assign an administrator for a virtual Administration Server
- Change the Administration Server for client devices
- Delete virtual Administration Servers
Creating a virtual Administration Server
You can create virtual Administration Servers and add them to administration groups.
To create and add a virtual Administration Server:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. - On the page that opens, proceed to the Administration Servers tab.
- Select the administration group to which you want to add a virtual Administration Server.
The virtual Administration Server will manage devices from the selected group (including the subgroups). - On the menu line, click New virtual Administration Server.
- On the page that opens, define the properties of the new virtual Administration Server:
- Name of virtual Administration Server.
- Administration Server connection address
You can specify the name or the IP address of your Administration Server.
- From the list of users, select the virtual Administration Server administrator. If you want, you can edit one of the existing accounts before assigning it the administrator's role, or create a new user account.
- Click Save.
The new virtual Administration Server is created, added to the administration group and displayed on the Administration Servers tab.
If you are connected to your primary Administration Server in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, and can not connect to a virtual Administration Server that is managed by a secondary Administration Server, you can use one of the following ways:
- Modify the existing Kaspersky Security Center Web Console installation to add the secondary Server to the list of trusted Administration Servers. Then you will be able to connect to the virtual Administration Server in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Use Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to connect directly to the secondary Administration Server where the virtual Server was created. Then you will be able to switch to the virtual Administration Server in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Use MMC-based Administration Console to connect directly to the virtual Server.
Enabling and disabling a virtual Administration Server
When you create a new virtual Administration Server, it is enabled by default. You can disable or enable it again at any time. Disabling or enabling a virtual Administration Server is equal to switching off or on a physical Administration Server.
To enable or disable a virtual Administration Server:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. - On the page that opens, proceed to the Administration Servers tab.
- Select the virtual Administration Server that you want to enable or disable.
- On the menu line, click the Enable / disable virtual Administration Server button.
The virtual Administration Server state is changed to enabled or disabled, depending on its previous state. The updated state is displayed next to the Administration Server name.
Assigning an administrator for a virtual Administration Server
When you use virtual Administration Servers in your organization, you might want to assign a dedicated administrator for each virtual Administration Server. For example, this might be useful when you create virtual Administration Servers to manage separate offices or departments of your organization, or if you are an MSP provider and you manage your tenants through virtual Administration Servers.
When you create a virtual Administration Server, it inherits the user list and all of the user rights of the primary Administration Server. If a user has access rights to the primary Server, this user has access rights to the virtual Server as well. After creation, you configure the access rights to the Servers independently. If you want to assign an administrator for a virtual Administration Server only, make sure that the administrator does not have access rights on the primary Administration Server.
You assign an administrator for a virtual Administration Server by granting the administrator access rights to the virtual Administration Server. You can grant the required access rights in one of the following ways:
- Configure access rights for the administrator manually
- Assign one or more user roles for the administrator
To sign in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, an administrator of a virtual Administration Server specifies the virtual Administration Server name, user name, and password. Kaspersky Security Center Web Console authenticates the administrator and opens the virtual Administration Server to which the administrator has access rights. The administrator cannot switch between Administration Servers.
Prerequisites
Before you start, ensure that the following conditions are met:
- The virtual Administration Server is created.
- On the primary Administration Server, you have created an account for the administrator that you want to assign for the virtual Administration Server.
- You have the Modify object ACLs right in the General features → User permissions functional area.
Configuring access rights manually
To assign an administrator for a virtual Administration Server:
- In the main menu, switch to the required virtual Administration Server:
- Click the chevron icon (
 ) to the right of the current Administration Server name.
) to the right of the current Administration Server name. - Select the required Administration Server.
- Click the chevron icon (
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the Administration Server.
) next to the name of the Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the Access rights tab, click the Add button.
A unified list of users of the primary Administration Server and the current virtual Administration Server opens.
- From the list of users, select the account of the administrator that you want to assign for the virtual Administration Server, and then click the OK button.
The application adds the selected user to the user list on the Access rights tab.
- Select the check box next to the added account, and then click the Access rights button.
- Configure the rights that the administrator will have on the virtual Administration Server.
For successful authentication, at minimum, the administrator must have the following rights:
- Read right in the General features → Basic functionality functional area
- Read right in the General features → Virtual Administration Servers functional area
The application saves the modified user rights to the administrator account.
Configuring access rights by assigning user roles
Alternatively, you can grant the access rights to a virtual Administration Server administrator through user roles. For example, this might be useful if you want to assign several administrators on the same virtual Administration Server. If this is the case, you can assign the administrators' accounts the same one or more user roles instead of configuring the same user rights for several administrators.
To assign an administrator for a virtual Administration Server by assigning user roles:
- On the primary Administration Server, create a new user role, and then specify all of the required access rights that an administrator must have on the virtual Administration Server. You can create several roles, for example, if you want to separate access to different functional areas.
- In the main menu, switch to the required virtual Administration Server:
- Click the chevron icon (
 ) to the right of the current Administration Server name.
) to the right of the current Administration Server name. - Select the required Administration Server.
- Click the chevron icon (
- Assign the new role or several roles to the administrator account.
The application assigns the roles to the administrator account.
Configuring access rights at the object level
In addition to assigning access rights at the functional area level, you can configure access to specific objects on the virtual Administration Server, for example, to a specific administration group or a task. To do this, switch to the virtual Administration Server, and then configure the access rights in the object's properties.
Changing the Administration Server for client devices
You can change the Administration Server that manages client devices to a different Server using the Change Administration Server task. After the task completion, the selected client devices will be put under the management of the Administration Server that you specify.
You cannot use the Change Administration Server task for client devices connected to Administration Server through connection gateways. For such devices you have to either reconfigure Network Agent or reinstall Network Agent and specify connection gateway.
To change the Administration Server that manages client devices to a different Server:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- At the New task settings step of the wizard, specify the following settings:
- In the Application drop-down list, select Kaspersky Security Center.
- In the Task type field, select Change Administration Server.
- In the Task name field, specify the name for the task that you are creating.
A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- Select devices to which the task will be assigned:
- At the Task scope step of the wizard, specify an administration group, devices with specific addresses, or a device selection.
- At this step of the wizard, confirm that you agree to the terms of changing the Administration Server for client devices.
- At this step of the wizard, select the Administration Server that you want to use to manage the selected devices:
- At the Selecting an account to run the task step of the wizard, specify the account settings:
- If you want to change the default task settings, at the Finish task creation step of the wizard, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option.
If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can change the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Finish button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the name of the created task to open the task properties window.
- If you want to change the default task settings, in the task properties window, specify the general task settings according to your needs.
- Click the Save button.
The task is created and configured.
- Run the created task.
After the task is completed, the client devices for which it was created are put under the management of the Administration Server specified in the task settings.
Deleting a virtual Administration Server
When you delete a virtual Administration Server, all of the objects created on the Administration Server, including policies and tasks, will be deleted as well. The managed devices from the administration groups that were managed by the virtual Administration Server will be removed from the administration groups. To return the devices under management of Kaspersky Security Center, run the network polling, and then move the found devices from the Unassigned devices group to the administration groups.
To delete a virtual Administration Server:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the Administration Server.
) next to the name of the Administration Server. - On the page that opens, proceed to the Administration Servers tab.
- Select the virtual Administration Server that you want to delete.
- On the menu line, click the Delete button.
The virtual Administration Server is deleted.
Enabling account protection from unauthorized modification
You can enable an additional option to protect a user account from unauthorized modification. If this option is enabled, modifying user account settings requires authorization of the user with the rights for modification.
To enable or disable account protection from unauthorized modification:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users.
- Click the name of the internal user account for which you want to specify account protection from unauthorized modification.
- In the user settings window that opens, select the Account protection tab.
- On the Account protection tab, select the Request authentication to check the permission to modify user accounts option, if you want to request credentials every time when account settings are changed or modified. Otherwise, select the Allow users to modify this account without additional authentication option.
- Click the Save button.
Account protection from unauthorized modification is enabled for a user account.
Page top
Two-step verification
This section describes how you can use two-step verification to reduce the risk of unauthorized access to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Scenario: Configuring two-step verification for all users
This scenario describes how to enable two-step verification for all users and how to exclude user accounts from two-step verification. If you did not enable two-step verification for your account before you enable it for other users, the application opens the window for enabling two-step verification for your account, first. This scenario also describes how to enable two-step verification for your own account.
If you enabled two-step verification for your account, you may proceed to the stage of enabling of two-step verification for all users.
Prerequisites
Before you start:
- Make sure that your user account has the Modify object ACLs right of the General features: User permissions functional area for modifying security settings for other users' accounts.
- Make sure that the other users of Administration Server install an authenticator app on their devices.
Stages
Enabling two-step verification for all users proceeds in stages:
- Installing an authenticator app on a device
You can install any application that supports the Time-based One-time Password algorithm (TOTP), such as:
- Google Authenticator
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Bitrix24 OTP
- Yandex Key
- Avanpost Authenticator
- Aladdin 2FA
To check if Kaspersky Security Center supports the authenticator app that you want to use, enable two-step verification for all users or for a particular user.
One of the steps suggests that you specify the security code generated by the authenticator app. If it succeeds, then Kaspersky Security Center supports the selected authenticator.
We strongly do not recommend installing the authenticator app on the same device from which the connection to Administration Server is established.
- Synchronizing the authenticator app time with the time of the device on which Administration Server is installed
Ensure that the time on the device with the authenticator app and the time on the device with the Administration Server are synchronized to UTC, by using external time sources. Otherwise, failures may occur during the authentication and activation of two-step verification.
- Enabling two-step verification for your account and receiving the secret key for your account
How-to instructions:
- For MMC-based Administration Console: Enabling two-step verification for your own account
- For Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Enabling two-step verification for your own account
After you enable two-step verification for your account, you can enable two-step verification for all users.
- Enabling two-step verification for all users
Users with two-step verification enabled must use it to log in to Administration Server.
How-to instructions:
- For MMC-based Administration Console: Enabling two-step verification for all users
- For Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Enabling two-step verification for all users
- Editing the name of a security code issuer
If you have several Administration Servers with similar names, you may have to change the security code issuer names for better recognition of different Administration Servers.
How-to instructions:
- For MMC-based Administration Console: Editing the name of a security code issuer
- For Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Editing the name of a security code issuer
- Excluding user accounts for which you do not need to enable two-step verification
If required, you can exclude users from two-step verification. Users with excluded accounts do not have to use two-step verification to log in to Administration Server.
How-to instructions:
- For MMC-based Administration Console: Excluding accounts from two-step verification
- For Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Excluding accounts from two-step verification
- Configuring two-step verification for your own account
If the users are not excluded from two-step verification and two-step verification is not yet configured for their accounts, they need to configure it in the window that opens when they sign-in to Kaspersky Security Center. Otherwise, they will not be able to access the Administration Server in accordance with their rights.
How-to instructions:
- For MMC-based Administration Console: Configuring two-step verification for your own account
- For Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Configuring two-step verification for your own account
Results
Upon completion of this scenario:
- Two-step verification is enabled for your account.
- Two-step verification is enabled for all user accounts of the Administration Server, except for user accounts that were excluded.
About two-step verification
When two-step verification is enabled for an account, a single-use security code is required, in addition to the user name and password, to log in to Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. With domain authentication enabled, the user only needs to enter the single-use security code.
To use two-step verification, install an authenticator app that generates single-use security codes on the mobile device or computer. You can use any application that supports the Time-based One-time Password algorithm (TOTP), such as:
- Google Authenticator
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Bitrix24 OTP
- Yandex Key
- Avanpost Authenticator
- Aladdin 2FA
To check if Kaspersky Security Center supports the authenticator app that you want to use, enable two-step verification for all users or for a particular user.
One of the steps suggests that you specify the security code generated by the authenticator app. If it succeeds, then Kaspersky Security Center supports the selected authenticator.
We highly recommend that you save the secret key or QR code and keep it in a safe place. This will help you to restore access to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console in case you lose access to the mobile device.
To secure the usage of Kaspersky Security Center, you can enable two-step verification for your own account and enable two-step verification for all users.
You can exclude accounts from two-step verification. This can be necessary for service accounts that cannot receive a security code for authentication.
Rules and Limitations
To be able to activate two-step verification for all users and deactivate two-step verification for particular users:
- Ensure your account has the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area.
- Enable two-step verification for your account.
To be able to deactivate two-step verification for all users:
- Ensure your account has the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area.
- Log in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console by using two-step verification.
If two-step verification is enabled for a user account on Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server version 13 or later, the user will not be able to log in to the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console versions 12, 12.1 or 12.2.
Reissuing the secret key
Any user can reissue the secret key used for two-step verification. When a user logs in to the Administration Server with the reissued secret key, the new secret key is saved for the user account. If the user enters the new secret key incorrectly, the new secret key is not saved, and the current secret key remains valid.
A security code has an identifier referred to as issuer name. The security code issuer name is used as an identifier of the Administration Server in the authenticator app. The security code issuer name has a default value that is the same as the name of the Administration Server. You can change the name of the security code issuer name. If you change the security code issuer name, you must issue a new secret key and pass it to the authenticator app.
Enabling two-step verification for your own account
You can enable two-step verification only for your own account.
Before you enable two-step verification for your account, ensure that an authenticator app is installed on the mobile device. Ensure that the time set in the authenticator app is synchronized with the time set of the device on which Administration Server is installed.
To enable two-step verification for a user account:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users.
- Click the name of your account.
- In the user settings window that opens, select the Authentication security tab.
- On the Authentication security tab:
- Select the Request user name, password, and security code (two-step verification) option. Click the Save button.
- In the two-step verification window that opens, click View how to set up two-step verification.
Enter the secret key in the authenticator app or click View QR code and scan the QR code by the authenticator app on the mobile device to receive one-time security code.
- In the two-step verification window, specify the security code generated by the authenticator app, and then click the Check and apply button.
- Click the Save button.
Two-step verification is enabled for your account.
Enabling required two-step verification for all users
You can enable two-step verification for all users of Administration Server if your account has the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area and if you are authenticated by using two-step verification.
To enable two-step verification for all users:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the Authentication security tab of the properties window, switch the toggle button of the two-step verification for all users option to the enabled position.
- If you did not enable two-step verification for your account, the application opens the window for enabling two-step verification for your own account.
- In the two-step verification window, click View how to set up two-step verification.
- Enter the secret key in the authenticator app manually or click View QR code and scan the QR code by the authenticator app on the mobile device to receive one-time security code.
- In the two-step verification window, specify the security code generated by the authenticator app, and then click the Check and apply button.
Two-step verification is enabled for all users. From now on, users of the Administration Server, including the users that were added after enabling two-step verification for all users, have to configure two-step verification for their accounts, except for users that are excluded from two-step verification.
Disabling two-step verification for a user account
You can disable two-step verification for your own account, as well as for an account of any other user.
You can disable two-step verification of another user's account if your account has the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area and if you are authenticated by using two-step verification.
To disable two-step verification for a user account:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users.
- Click the name of the internal user account for whom you want to disable two-step verification. This may be your own account or an account of any other user.
- In the user settings window that opens, select the Account protection tab.
- On the Account protection tab, select the Request only user name and password option if you want to disable two-step verification for a user account.
- Click the Save button.
Two-step verification is disabled for the user account.
If you want to restore access for a user that cannot log in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console by using two-step verification, disable two-step verification for this user account, and then select the Request only user name and password option as described above. After that, log in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console under the user account for which you disabled two-step verification, and then enable verification again.
Disabling required two-step verification for all users
You can disable required two-step verification for all users if two-step verification is enabled for your account and your account has the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area. If two-step verification is not enabled for your account, you must enable two-step verification for your account before disabling it for all users.
To disable two-step verification for all users:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the Authentication security tab of the properties window, switch the toggle button of the two-step verification for all users option to disabled position.
- Enter the credentials of your account in the authentication window.
Two-step verification is disabled for all users. Disabling two-step verification for all users does not applied to specific accounts for which two-step verification was previously enabled separately.
Excluding accounts from two-step verification
You can exclude user accounts from two-step verification if you have the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area.
If a user account is excluded from the list of two-step verification for all users, this user does not have to use two-step verification.
Excluding accounts from two-step verification can be necessary for service accounts that cannot pass the security code during authentication.
If you want to exclude some user accounts from two-step verification:
- You must perform Microsoft Active Directory domain controller polling in order to refresh the list of Administration Server users, if you want to exclude Active Directory accounts.
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the Authentication security tab of the properties window, in the two-step verification exclusions table click the Add button.
- In the window that opens:
- Select the user accounts that you want to exclude.
- Click the OK button.
The selected user accounts are excluded from two-step verification.
Generating a new secret key
You can generate a new secret key for a two-step verification for your account only if you are authorized by using two-step verification.
To generate a new secret key for a user account:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users.
- Click the name of the user account for whom you want to generate a new secret key for two-step verification.
- In the user settings window that opens, select the Account protection tab.
- In the Account protection tab, click the Generate a new secret key link.
- In the two-step verification window that opens, specify a new security key generated by the authenticator app.
- Click the Check and apply button.
A new secret key is generated for the user.
If you lose the mobile device, you can install an authenticator app on another mobile device and generate a new secret key to restore access to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Page top
Editing the name of a security code issuer
You can have several identifiers (they are called issuers) for different Administration Servers. You can change the name of a security code issuer in case, for example, if the Administration Server already uses a similar name of security code issuer for another Administration Server. By default, the name of a security code issuer is the same as the name of the Administration Server.
After you change the security code issuer name you have to reissue a new secret key and pass it to the authenticator app.
To specify a new name of security code issuer:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- In the user settings window that opens, select the Account protection tab.
- On the Account protection tab, click the Edit link.
The Edit Security code issuer section opens.
- Specify a new security code issuer name.
- Click the OK button.
A new security code issuer name is specified for the Administration Server.
Configuring two-step verification for your own account
The first time you sign in to Kaspersky Security Center after two-step verification is enabled, the window for configuring two-step verification for your own account opens.
Before you configure two-step verification for your account, ensure that an authenticator app is installed on the mobile device.
Ensure that the time on the device with the authenticator app and the time on the device with the Administration Server are synchronized to UTC, by using external time sources.
To configure two-step verification for your account:
- Generate a one-time security code by using the authenticator app on the mobile device. To do this, perform one of the following actions:
- Enter the secret key in the authenticator app manually.
- Click View QR code and scan the QR code by using the authenticator app.
A security code will display on the mobile device.
- In the configure two-step verification window, specify the security code generated by the authenticator app, and then click the Check and apply button.
Two-step verification is configured for your account. You are able to access the Administration Server in accordance with your rights.
Page top
Prohibit new users from setting up two-step verification for themselves
In order to further improve Kaspersky Security Center Web Console access security, you can prohibit new users from setting up two-step verification for themselves.
If this option is enabled, a user with disabled two-step verification, for example new domain administrator, cannot configure two-step verification for themselves. Therefore, such user cannot be authenticated on Administration Server and cannot sign in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console without approval from another Kaspersky Security Center administrator who already has two-step verification enabled.
This option is available if two-step verification is enabled for all users.
To prohibit new users from setting up two-step verification for themselves:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the Authentication security tab of the properties window, switch the toggle button Prohibit new users from setting up two-step verification for themselves to the enabled position.
This option does not affect the user accounts added to the two-step verification exclusions.
In order to grant Kaspersky Security Center Web Console access to a user with disabled two-step verification, temporary turn off the Prohibit new users from setting up two-step verification for themselves option, ask the user to enable two-step verification, and then turn on the option back.
Page top
Backup copying and restoration of Administration Server data
Data backup allows you to move Administration Server from one device to another without data loss. Through backup, you can restore data when moving the Administration Server database to another device, or when upgrading to a newer version of Kaspersky Security Center.Also, you can use data backup to move Administration Server data from Kaspersky Security Center Windows under management of Kaspersky Security Center Linux (moving data from Kaspersky Security Center Linux to Kaspersky Security Center Windows is not supported).
Note that the installed management plug-ins are not backed up. After you restore Administration Server data from a backup copy, you need to download and reinstall plug-ins for managed applications.
Before you back up the Administration Server data, check whether a virtual Administration Server is added to the administration group. If a virtual Administration Server is added, make sure that an administrator is assigned to this virtual Administration Server before the backup. You cannot grant the administrator access rights to the virtual Administration Server after the backup. Note that if the administrator account credentials are lost, you will not be able to assign a new administrator to the virtual Administrator Server.
You can create a backup copy of Administration Server data in one of the following ways:
- By creating and running a data backup task through Administration Console.
- By running the klbackup utility on the device that has Administration Server installed. This utility is included in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit. After the installation of Administration Server, the utility is located in the root of the destination folder specified at the application installation.
The following data is saved in the backup copy of Administration Server:
- Database of Administration Server (policies, tasks, application settings, events saved on the Administration Server).
- Configuration details of the structure of administration groups and client devices.
- Repository of distribution packages of applications for remote installation.
- Administration Server certificate.
- Contents of the Updates folder.
By default, the folder path is C:\ProgramData\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\.working\share\Updates\
Recovery of Administration Server data is only possible using the klbackup utility.
Creating a data backup task
Backup tasks are Administration Server tasks; they are created through the quick start wizard. If a backup task created by the quick start wizard has been deleted, you can create one manually.
To create an Administration Server data backup task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click the Add button.
The New task wizard starts.
- In the New task settings window of the wizard, select the task type named Backup of Administration Server data.
- Follow the rest of the wizard instructions.
The Backup of Administration Server data task can only be created in a single copy. If the Administration Server data backup task has already been created for the Administration Server, it is not displayed in the task type selection window of the Administration Server backup task creation wizard.
To configure the Backup of Administration Server data task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks, and then select the Backup of Administration Server data task.
- Click the Backup of Administration Server data task.
The task properties window opens.
- If necessary, specify the general task settings according to your needs.
- In the Application settings section, specify the path to the folder for storage backup copies of Administration Server data, set the backup protection password, and number of backup copies if needed.
- Click Save to apply changes.
The Backup of Administration Server data task is configured.
Page top
Moving Administration Server to another device
If you need to use Administration Server on a new device, you can move it in one of the following ways:
- Move Administration Server and the database server to a new device (the database server can be installed on the new device together with Administration Server, or on another device).
- Keep the database server on the previous device and move only Administration Server to a new device.
To move Administration Server and the database server to a new device:
- On the previous device, create a backup of Administration Server data.
To do this, you can run the data backup task through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console or run the klbackup utility.
If you use SQL Server as a DBMS for Administration Server, you can migrate the data from SQL Server to MySQL or MariaDB DBMS. To do this, run the klbackup utility in interactive mode to create a data backup. Enable the Migrate to MySQL/MariaDB format option in the Backup settings window of the Backup and restore wizard. Kaspersky Security Center will create a backup compatible with MySQL and MariaDB. After that, you can restore the data from the backup into MySQL or MariaDB.
You can also enable the Migrate to Azure format option to if you want to migrate the data from SQL Server to Azure SQL DBMS.
- On the previous device, disconnect Administration Server from the network.
- Select a new device on which to install the Administration Server. Make sure that the hardware and software on the selected device meet the requirements for Administration Server, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, and Network Agent. Also, check that ports used on Administration Server are available.
- Assign the same address to the new device.
The new Administration Server can be assigned the NetBIOS name, FQDN, and static IP address. It depends on which Administration Server address was set in the Network Agent installation package when Network Agents were deployed. Alternatively, you can use the connection address that determines the Administration Server to which Network Agent connects (you can obtain this address on managed devices by using the klnagchk utility).
- If needed, on another device, install the database management system (DBMS) that the Administration Server will use.
The database can be installed on the new device together with Administration Server, or on another device. Ensure that this device meets the hardware and software requirements. When you select a DBMS, consider the number of devices covered by the Administration Server.
- Run the installation of the Administration Server on the new device.
- During the Administration Server installation, configure the database server connection settings.

Example of the Connection settings window for Microsoft SQL Server
Depending on where you need to locate the database server, do one of the following:
- After the installation is complete, recover Administration Server data on the new device by using the klbackup utility.
If you use SQL Server as a DBMS on the previous and new devices, note that the version of SQL Server installed on the new device must be the same or later than the version of SQL Server installed on the previous device. Otherwise, you cannot recover Administration Server data on the new device.
- Open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and connect to the Administration Server.
- Verify that all manage devices are connected to the Administration Server.
- Uninstall the Administration Server and the database server from the previous device.
You can also use Administration Console to move Administration Server and a database server to another device.
Initial setup of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
This section describes steps you must take after the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console installation to perform its initial setup.
Quick start wizard (Kaspersky Security Center Web Console)
This section provides information about the Administration Server quick start wizard.
The wizard requires internet access. If your Administration Server does not have internet access, we recommend that you perform all the steps of the wizard manually through the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to adjust a minimum selection of settings required to build a centralized management system for protecting your network against security threats. This configuration is performed through the quick start wizard. When the wizard is running, you can make the following changes to the application:
- Add key files or enter activation codes that can be automatically distributed to devices within administration groups.
- Configure interaction with Kaspersky Security Network (KSN). If you have allowed the use of KSN, the wizard enables the KSN proxy server service, which ensures connection between KSN and devices.
- Set up email delivery of notifications of events that occur during operation of Administration Server and managed applications (successful notification delivery requires that the Messenger service run on the Administration Server and all recipient devices).
- Create a protection policy for workstations and servers, as well as malware scan tasks, update download tasks, and data backup tasks, for the top level of the hierarchy of managed devices.
The quick start wizard creates policies only for those applications whose Managed devices folder does not contain policies. The quick start wizard does not create tasks if tasks with the same names have already been created for the top level in the hierarchy of managed devices.
The application automatically prompts you to run the quick start wizard after Administration Server installation, at the first connection to it. You can also start the quick start wizard manually at any time.
To start the quick start wizard manually:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the Administration Server.
) next to the name of the Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the General section.
Administration Server properties window
- Click Start quick start wizard.
The wizard prompts you to perform initial configuration of the Administration Server. Follow the instructions of the wizard. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
Step 1. Specifying the internet connection settings
Specify the internet access settings for Administration Server. You must configure internet access to use Kaspersky Security Network and to download updates of anti-virus databases for Kaspersky Security Center and managed Kaspersky applications.
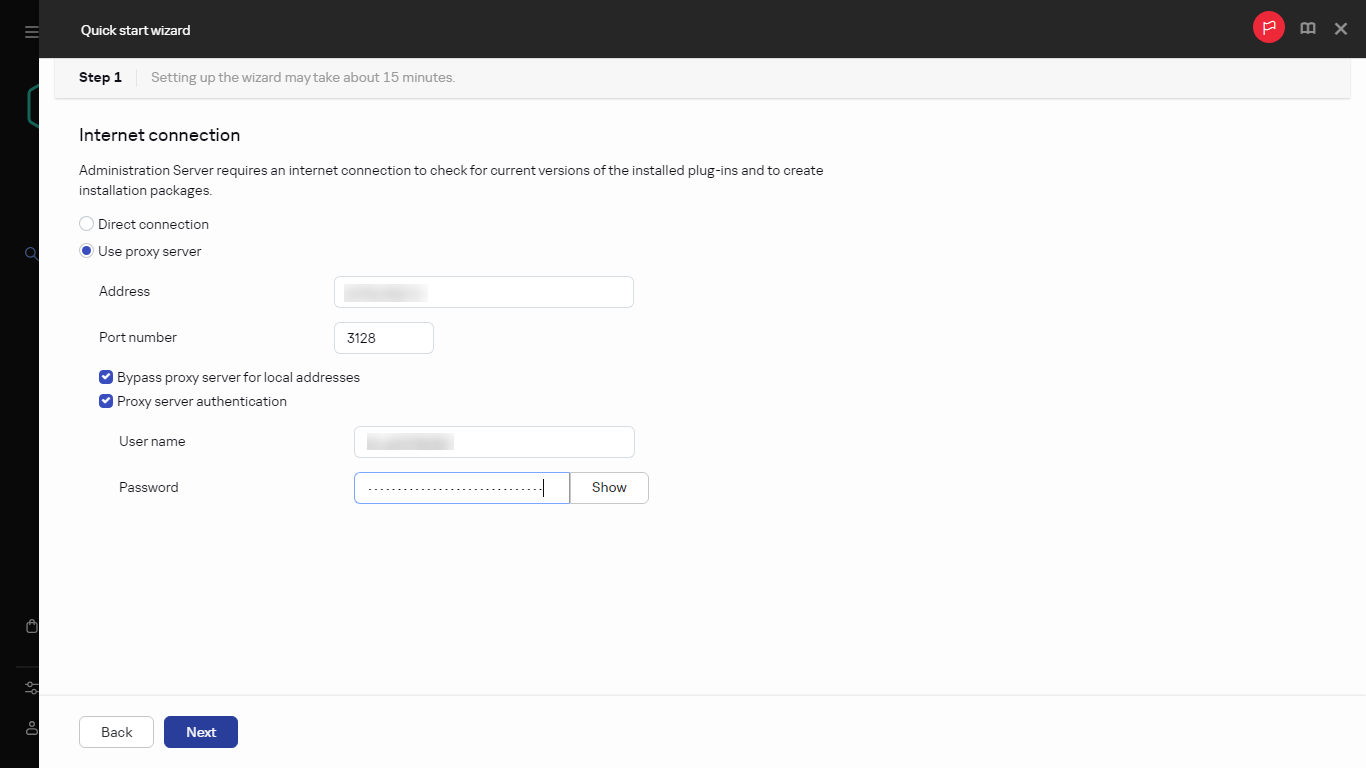
Internet connection settings
Enable the Use proxy server option if you want to use a proxy server when connecting to the internet. If this option is enabled, the fields are available for entering settings. Specify the following settings for a proxy server connection:
- Address
- Port number
- Bypass proxy server for local addresses
- Proxy server authentication
- User name
- Password
You can configure internet access later, separately from the quick start wizard.
Page top
Step 2. Downloading required updates
The required updates are downloaded from the Kaspersky servers automatically.
Downloading required updates
Page top
Step 3. Selecting the assets to secure
Select the protection areas and operating systems that are in use on your network. When you select these options, you specify the filters for application management plug-ins and distribution packages on Kaspersky servers that you can download to install on client devices on your network.
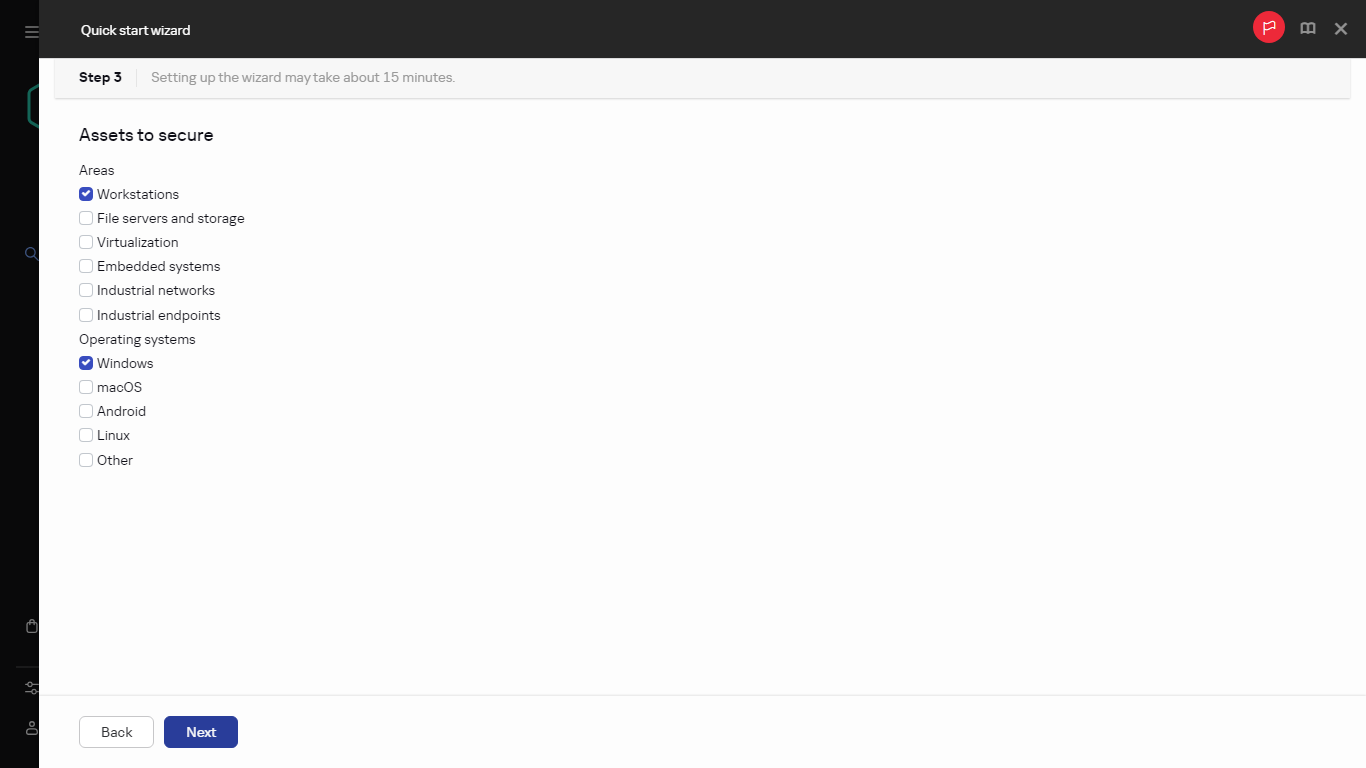
Selecting the assets to secure
Select the options:
You can select the Kaspersky application packages from the list of available packages later, separately from the quick start wizard. To simplify the search for the required packages, you can filter the list of available packages by various criteria.
Page top
Step 4. Selecting encryption in solutions
The Encryption in solutions window is displayed only if you have selected Workstations as a protection scope.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows includes encryption tools for information stored on Windows-based client devices. These encryption tools have the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) implemented with a 256-bit or 56-bit key length.
Download and usage of the distribution package with a 256-bit key length must be performed in compliance with applicable laws and regulations. To download a distribution package of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows that is valid for the needs of your organization, consult the legislation of the country where the client devices of your organization are located.
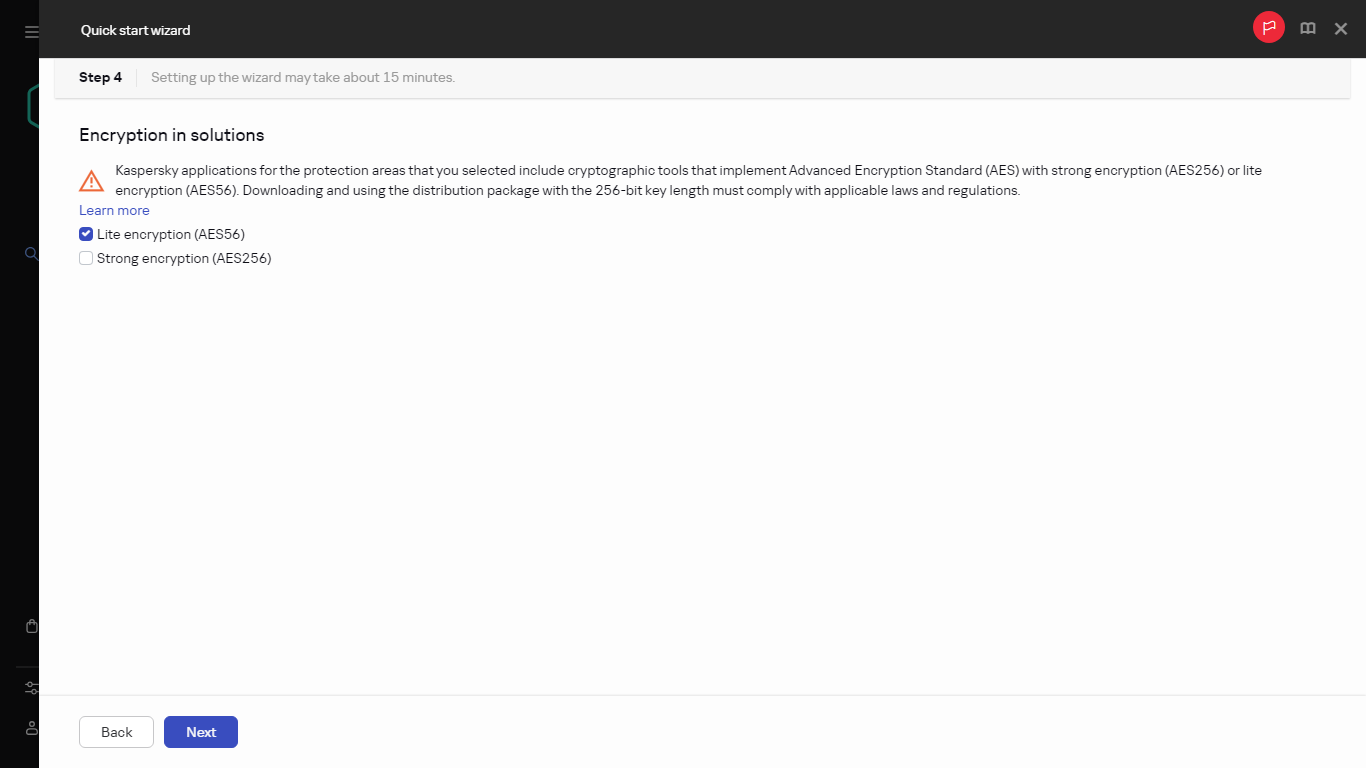
Selecting encryption in solutions
In the Encryption in solutions window, select one of the following encryption types:
- Lite encryption. This encryption type uses a 56-bit key length.
- Strong encryption. This encryption type uses a 256-bit key length.
You can select the distribution package for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows with the required encryption type later, separately from the quick start wizard.
Page top
Step 5. Configuring installation of plug-ins for managed applications
Select plug-ins for managed applications to install. A list of plug-ins located on Kaspersky servers is displayed. The list is filtered according to the options selected on the previous step of the wizard. By default, a full list includes plug-ins of all languages. To display only plug-in of specific language, use filter.
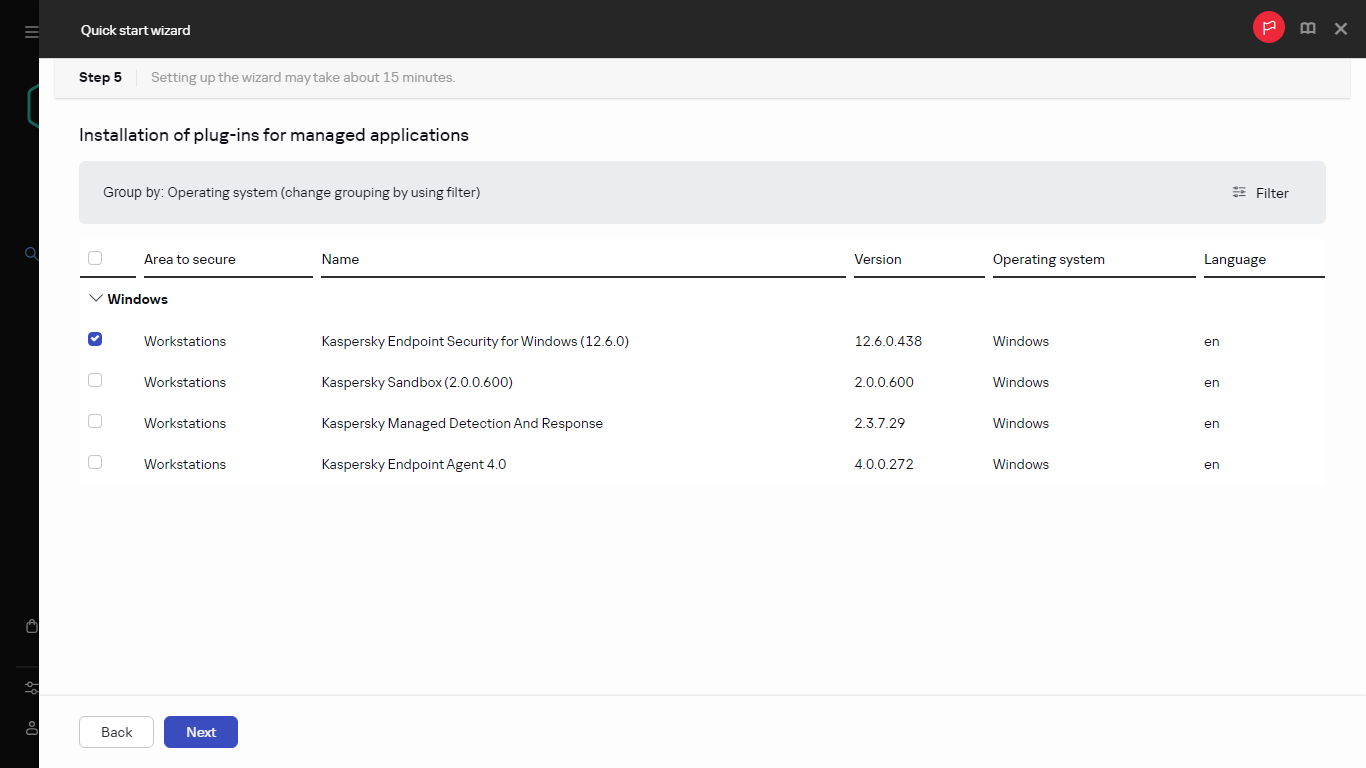
Installation of plug-ins for managed applications
The list of plug-ins includes the following columns:
After the plug-ins are selected, click Next to start installation.
You can install management plug-ins for Kaspersky applications manually, separately from the quick start wizard.
The quick start wizard automatically installs the selected plug-ins. To install some plug-ins, you must accept the terms of the EULA. Read the text of EULA displayed, select the I agree to use Kaspersky Security Network check box and click the Install button. If you do not accept the terms of the EULA, the plug-in is not installed.
When all the selected plug-ins are installed, the quick start wizard automatically takes you to the next step.
Step 6. Installing the selected plug-ins
The quick start wizard automatically installs the plug-ins that you selected in the previous step. To install some plug-ins, you must accept the terms of the EULA. Read the text of EULA displayed, select the I agree to use Kaspersky Security Network check box and click the Install button. If you do not accept the terms of the EULA, the plug-in is not installed.
When all the selected plug-ins are installed, the quick start wizard automatically takes you to the next step.
Page top
Step 7. Downloading distribution packages and creating installation packages
Select the distribution packages to download.
Distributives of managed applications may require a specific minimum version of Kaspersky Security Center to be installed.
After you have selected an encryption type for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, a list of distribution packages of both encryption types is displayed. A distribution package with the selected encryption type is selected in the list. You can select distribution packages of any encryption type. The distribution package language corresponds to the Kaspersky Security Center language. If a distribution package of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows for the Kaspersky Security Center language does not exist, the English distribution package is selected.
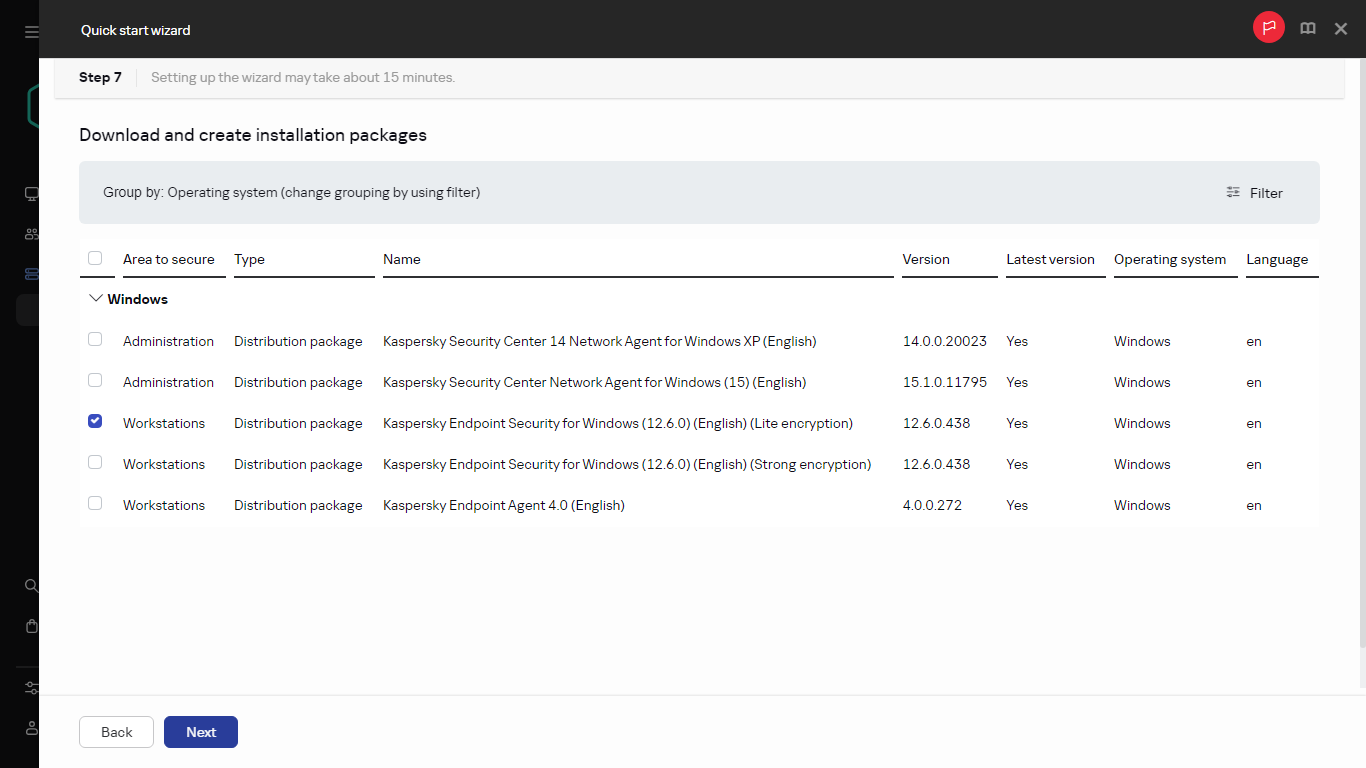
Downloading distribution packages and creating installation packages
To finish downloading of some distribution packages you must accept EULA. When you click the Accept button, the text of EULA is displayed. To proceed to the next step of the wizard, you must accept the terms and conditions of the EULA and the terms and conditions of Kaspersky Privacy Policy. If you do not accept the terms and conditions, the downloading of the package is canceled.
After you have accepted the terms and conditions of the EULA and the terms and conditions of Kaspersky Privacy Policy, the downloading of the distribution packages continues. Later, you can use installation packages to deploy Kaspersky applications on client devices.
You can download distribution packages and create installation packages later, separately from the quick start wizard.
Page top
Step 8. Configuring Kaspersky Security Network
Specify the settings for relaying information about Kaspersky Security Center operations to the Kaspersky Security Network knowledge base.
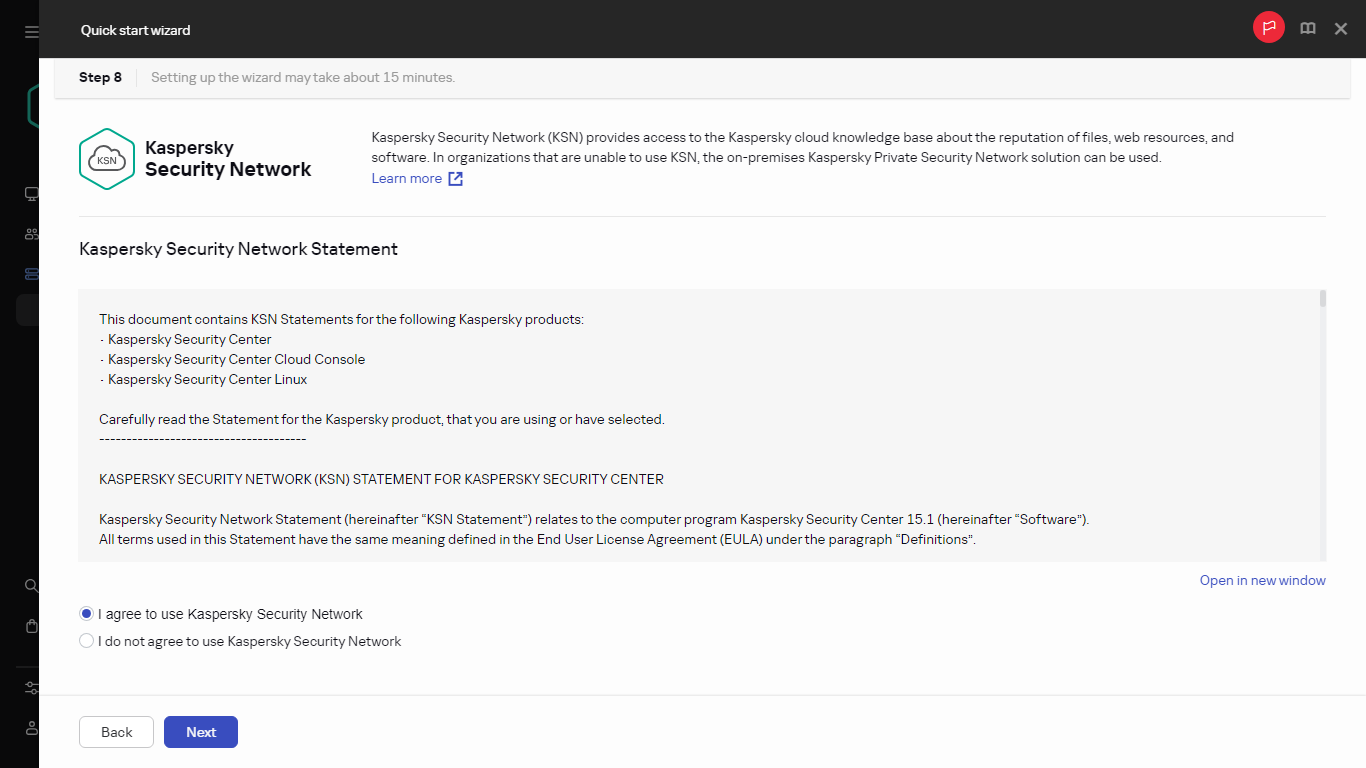
Configuring Kaspersky Security Network
Select one of the following options:
You can set up access to Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) later, separately from the quick start wizard.
Page top
Step 9. Selecting the application activation method
Select one of the following Kaspersky Security Center activation options:
- By entering your activation code
- By specifying a key file
- By postponing the application activation
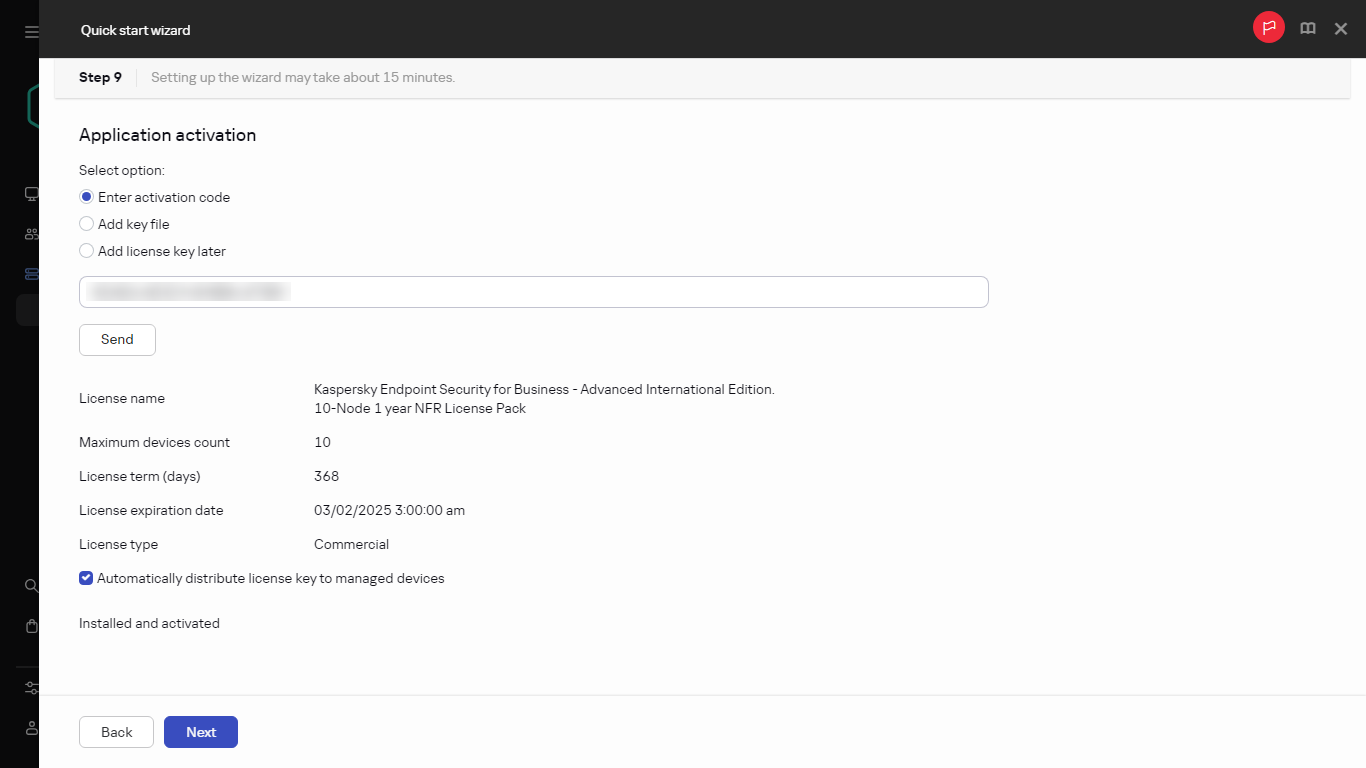
Selecting the application activation method
If you chose to postpone application activation, you can add a license key later at any time by selecting Operations → Licensing.
When working with Kaspersky Security Center deployed from a paid AMI or for a Usage-based monthly billed SKU, you cannot specify a key file or enter a code.
Step 10. Specifying the third-party update management settings
This step is not displayed if you do not have the Vulnerability and patch management license and the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task already exists.
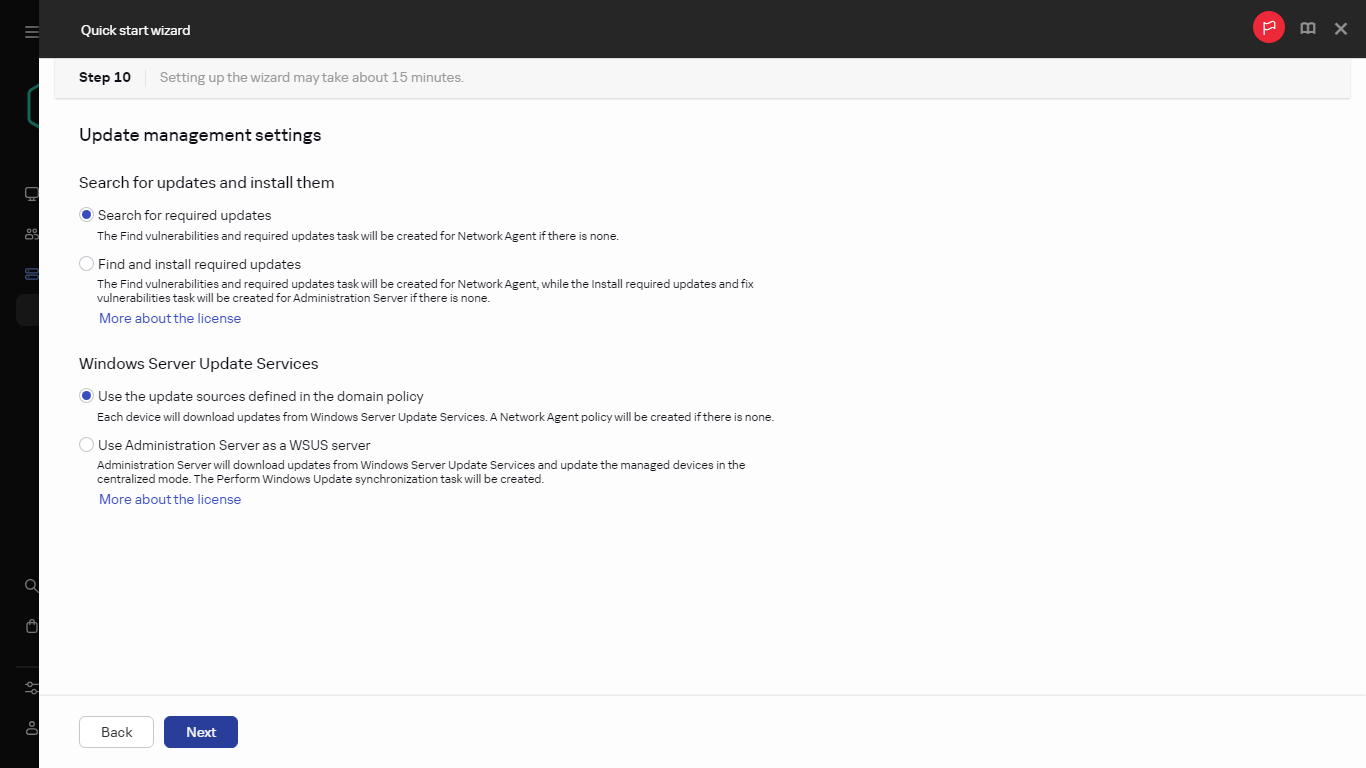
Third-party update management settings
For third-party software updates, select one of the following options:
- Search for required updates
- Find and install required updates
This option is only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
For Windows Update updates, select one of the following options:
- Use the update sources defined in the domain policy
- Use Administration Server as a WSUS server
This option is only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
You can create the Find vulnerabilities and required updates and Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities tasks separately from the quick start wizard. To use Administration Server as the WSUS server, create the Perform Windows Update synchronization task, and then select the Use Administration Server as a WSUS server option in the Network Agent policy.
Step 11. Creating a basic network protection configuration
You can check a list of policies and tasks that are created.
Wait for the creation of policies and tasks to complete before proceeding to the next step of the wizard.
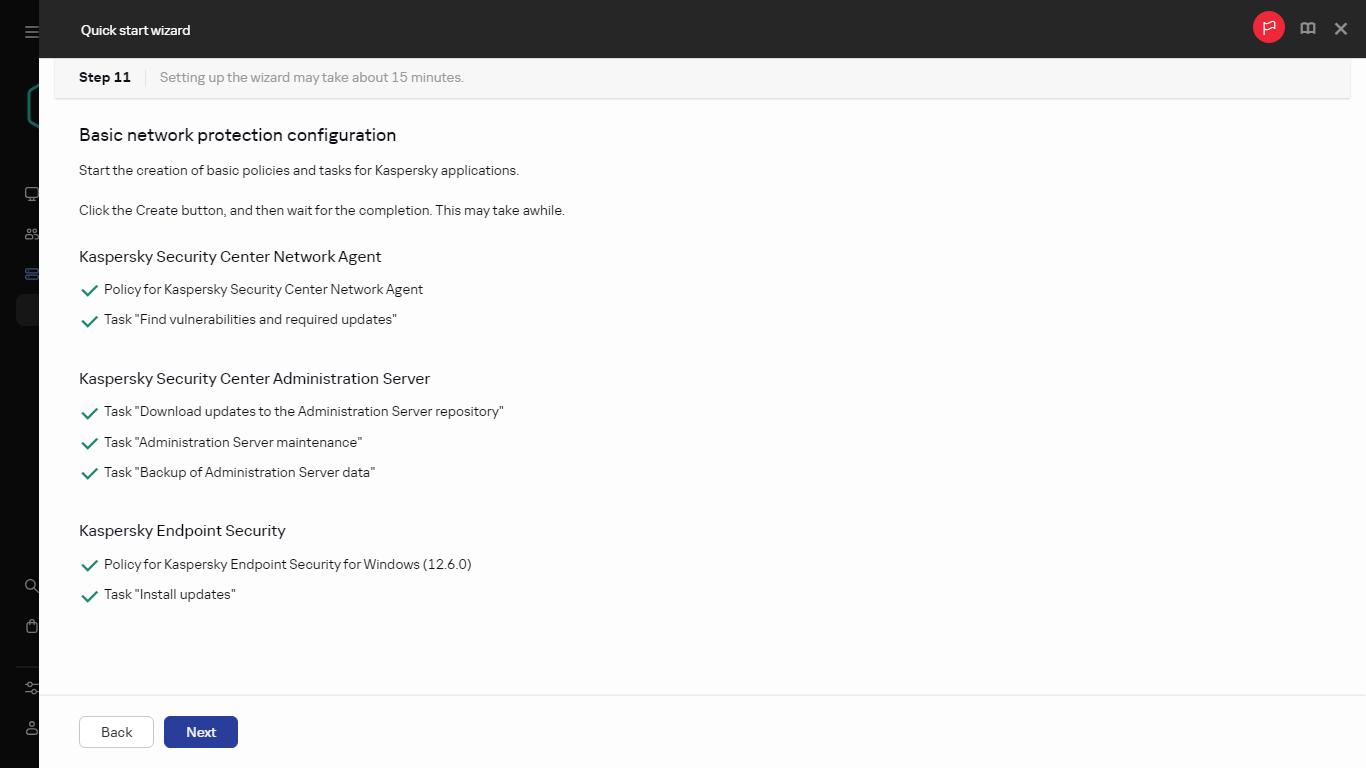
Creating a basic network protection configuration
You can create the required tasks and policies later, separately from the quick start wizard.
Page top
Step 12. Configuring email notifications
Configure the delivery of notifications about events registered during the operation of Kaspersky applications on client devices. These settings will be used as the default settings for application policies.
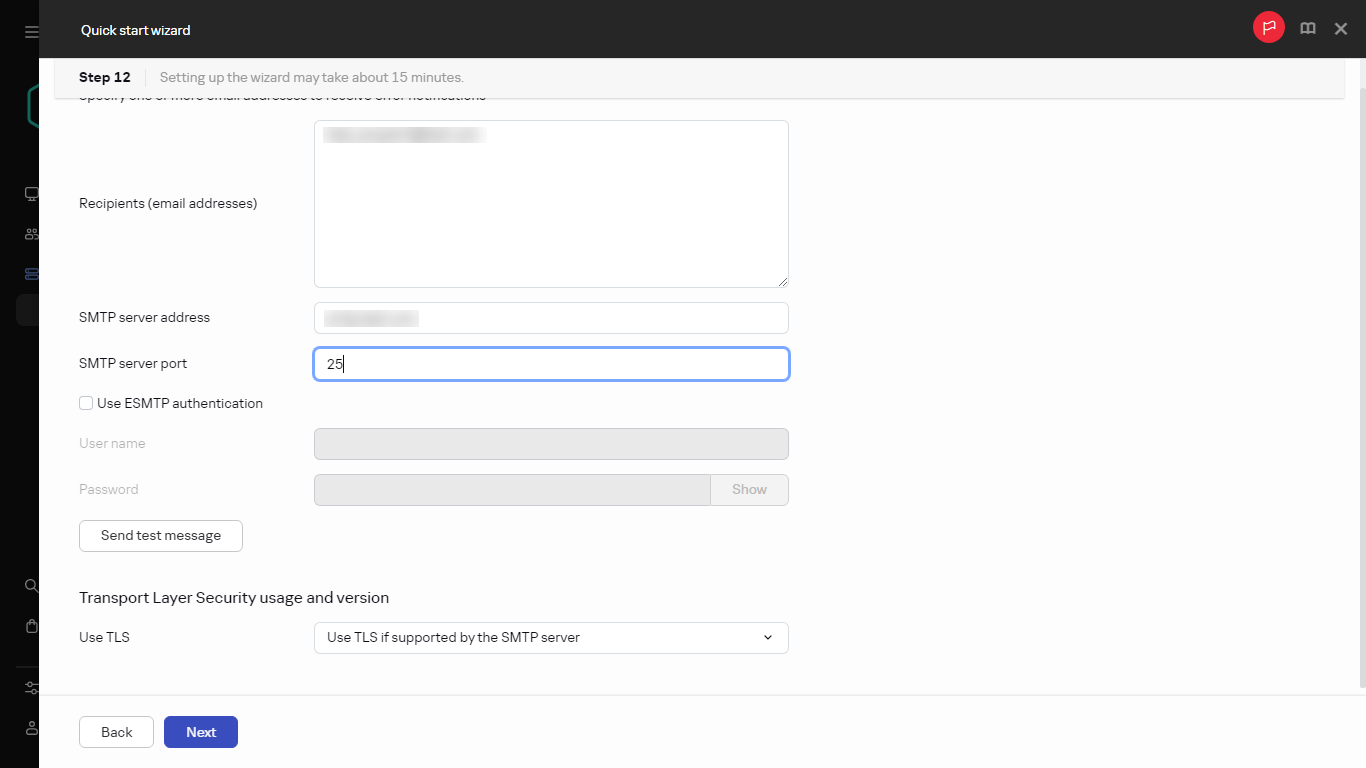
Configuring email notifications
To configure the delivery of notifications about events occurring in Kaspersky applications, use the following settings:
You can test the new email notification settings by clicking the Send test message button.
You can configure event notifications later, separately from the quick start wizard.
Page top
Step 13. Performing a network poll
Administration Server performs an initial poll. During the poll, a progress bar is displayed. When the poll is complete, the View detected devices link becomes available. You can click this link to view network devices detected by Administration Server. To return to the quick start wizard, press the Escape key.
You can poll your network later, separately from the quick start wizard. Use Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to configure the polling of a domain controller, Windows domains, IP ranges, and IPv6 networks.
Step 14. Closing the quick start wizard
On the quick start wizard completion page, select the Run Protection deployment wizard check box if you want to start automatic installation of anti-virus applications or Network Agent on devices on your network.
Final step of Quick start wizard
To close the wizard, click the Finish button.
Page top
Connecting out-of-office devices
This section describes how to connect out-of-office devices (that is, managed devices that are located outside of the main network) to Administration Server.
Scenario: Connecting out-of-office devices through a connection gateway
This scenario describes how to connect managed devices that are located outside of the main network to Administration Server.
Prerequisites
The scenario has the following prerequisites:
- A demilitarized zone (DMZ) is organized in your organization's network.
- Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server is deployed on the corporate network.
Stages
This scenario proceeds in stages:
- Selecting a client device in the DMZ
This device will be used as a connection gateway. The device that you select must meet the requirements for connection gateways.
- Installing Network Agent in the connection gateway role
We recommend that you use a local installation to install Network Agent on the selected device.
By default, the installation file is located at: \\<server name>\KLSHARE\PkgInst\NetAgent_<version number>
In the Connection gateway window of the Network Agent setup wizard, select Use Network Agent as a connection gateway in DMZ. This mode simultaneously activates the connection gateway role and tells Network Agent to wait for connections from Administration Server, rather than establish connections to Administration Server.
Alternatively, you can install Network Agent on a Linux device and configure Network Agent to work as a connection gateway, but pay attention to the list of limitations of Network Agent running on Linux devices.
- Allowing connections in firewalls on the connection gateway
To make sure that Administration Server can actually connect to the connection gateway in the DMZ, allow connections to TCP port 13000 in all firewalls between Administration Server and the connection gateway.
If the connection gateway has no real IP address on the internet, but instead is located behind Network Address Translation (NAT), configure a rule to forward connections through NAT.
- Creating an administration group for external devices
Create a new group under the Managed devices group. This new group will contain external managed devices.
- Connecting the connection gateway to Administration Server
The connection gateway that you have configured is waiting for a connection from Administration Server. However, Administration Server does not list the device with the connection gateway among managed devices. This is because the connection gateway has not tried to establish a connection to Administration Server. Therefore, you need a special procedure to ensure that Administration Server initiates a connection to the connection gateway.
Do the following:
- Add the connection gateway as a distribution point.
- Move the connection gateway from the Unassigned devices group to the group that you have created for external devices.
The connection gateway is connected and configured.
- Connecting external desktop devices to Administration Server
Usually, external desktop devices are not moved inside the perimeter. Therefore, you need to configure them to connect to Administration Server through the gateway when installing Network Agent.
- Setting up updates for external desktop devices
If updates of security applications are configured to be downloaded from Administration Server, external devices download updates through the connection gateway. This has two disadvantages:
- This is unnecessary traffic, which takes up bandwidth of the company's internet communication channel.
- This is not necessarily the quickest way to get updates. It is very likely that it would be cheaper and faster for external devices to receive updates from Kaspersky update servers.
Do the following:
- Connecting traveling laptops to Administration Server
Traveling laptops are within the network sometimes and outside the network at other times. For effective management, you need them to connect to Administration Server differently depending on their location. For efficient use of traffic, they also need to receive updates from different sources, depending on their location.
You need to configure rules for out-of-office users: connection profiles and network location descriptions. Each rule defines the Administration Server instance to which traveling laptops must connect, depending on their location and the Administration Server instance from which they must receive updates.
Scenario: Connecting out-of-office devices through a secondary Administration Server in DMZ
If you want to connect managed devices that are located outside of the main network to Administration Server, you can do it by using a secondary Administration Server located in the demilitarized zone (DMZ).
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that you have done the following:
- A DMZ is organized in your organization's network.
- Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server is deployed on the internal network of the organization.
Stages
This scenario proceeds in stages:
- Selecting a client device in the DMZ
In the DMZ, select a client device that will be used as a secondary Administration Server.
- Installing Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server
Install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server on this client device.
- Creating a hierarchy of Administration Servers
If you place a secondary Administration Server in the DMZ, the secondary Administration Server must receive a connection from the primary Administration Server. To do this, add a new Administration Server as secondary so that the primary Administration Server connects to the secondary Administration Server through port 13000. When combining two Administration Servers into a hierarchy, make sure that port 13299 is accessible on both Administration Servers. Kaspersky Security Center Web Console connects to an Administration Server through port 13299.
- Connecting out-of-office managed devices to the secondary Administration Server
You can connect out-of-office devices to the Administration Server in the DMZ in the same way that the connection is established between Administration Server and managed devices that are located in the main network. Out-of-office managed devices initiate the connection through port 13000.
About connecting out-of-office devices
Some managed devices are always located outside of the main network (for example, devices in a company's regional branches; kiosks, ATMs, and terminals installed at various points of sale; devices in the home offices of employees). Some devices travel outside the perimeter from time to time (for example, laptops of users who visit regional branches or a customer's office).
You still need to monitor and manage the protection of out-of-office devices—receive actual information about their protection status and keep the security applications on them in the up-to-date state. This is necessary because, for example, if such a device is compromised while being away from the main network, it could become a platform for propagating threats as soon as it connects to the main network. To connect out-of-office devices to Administration Server, you can use two methods:
- Connection gateway in the demilitarized zone (DMZ)
See the data traffic scheme: Administration Server on LAN, managed devices on the Internet, connection gateway in use
- Administration Server in DMZ
See the data traffic scheme: Administration Server in DMZ, managed devices on Internet
A connection gateway in the DMZ
A recommended method for connecting out-of-office devices to Administration Server is organizing a DMZ in the organization's network and installing a connection gateway in the DMZ. External devices will connect to the connection gateway, and Administration Server inside the network will initiate a connection to the devices via the connection gateway.
As compared to the other method, this one is more secure:
- You do not need to open access to Administration Server from outside the network.
- A compromised connection gateway does not pose a high risk to the safety of the network devices. A connection gateway does not actually manage anything itself and does not establish any connections.
Also, a connection gateway does not require many hardware resources.
However, this method has a more complicated configuration process:
- To act a device as a connection gateway in the DMZ, you need to install Network Agent and connect it to Administration Server in a specific way.
- You will not be able to use the same address for connecting to Administration Server for all situations. From outside the perimeter, you will need to use not just a different address (connection gateway address), but also a different connection mode: through a connection gateway.
- You also need to define different connection settings for laptops in different locations.
To add a connection gateway to a previously configured network:
- Install the Network Agent in the connection gateway mode.
- Reinstall the Network Agent on devices that you want to connect to the newly added connection gateway.
Administration Server in the DMZ
Another method is installing a single Administration Server in the DMZ.
This configuration is less secure than the other method. To manage external laptops in this case, Administration Server must accept connections from any address on the internet. It will still manage all devices in the internal network, but from the DMZ. Therefore, a compromised Server could cause an enormous amount of damage, despite the low likelihood of such an event.
The risk gets significantly lower if Administration Server in the DMZ does not manage devices in the internal network. Such a configuration can be used, for example, by a service provider to manage the devices of customers.
You might want to use this method in the following cases:
- If you are familiar with installing and configuring Administration Server, and do not want to perform another procedure to install and configure a connection gateway.
- If you need to manage more devices. The maximum capacity of Administration Server is 100,000 devices, while a connection gateway can support up to 10,000 devices.
This solution also has possible difficulties:
- Administration Server requires more hardware resources and one more database.
- Information about devices will be stored in two unrelated databases (for Administration Server inside the network and another one in the DMZ), which complicates monitoring.
- To manage all devices, Administration Server needs to be joined into a hierarchy, which complicates not only monitoring but also management. A secondary Administration Server instance imposes limitations on the possible structures of administration groups. You have to decide how and which tasks and policies to distribute to a secondary Administration Server instance.
- Configuring external devices to use Administration Server in the DMZ from the outside and to use the primary Administration Server from the inside is not simpler than to just configure them to use a conditional connection through a gateway.
- High security risks. A compromised Administration Server instance makes it easier to compromise its managed laptops. If this happens, the hackers just need to wait for one of the laptops to return to the corporate network so that they can continue their attack on the local area network.
Connecting external desktop devices to Administration Server
Desktop devices that are always outside of the main network (for example, devices in the company's regional branches; kiosks, ATMs, and terminals installed at various points of sale; devices in the home offices of employees) cannot be connected to Administration Server directly. They must be connected to Administration Server via a connection gateway that is installed in the demilitarized zone (DMZ). This configuration is made when installing Network Agent on those devices.
To connect external desktop devices to Administration Server:
- Create a new installation package for Network Agent.
- Open the properties of the created installation package and go to Settings → Advanced, and then select the Connect to Administration Server by using a connection gateway option.
The Connect to Administration Server by using a connection gateway setting is incompatible with the Use Network Agent as a connection gateway in DMZ setting. You cannot enable both of these settings at the same time.
- In the Connection gateway address field, specify the public address of the connection gateway.
If the connection gateway is located behind Network Address Translation (NAT) and does not have its own public address, configure a NAT gateway rule for forwarding connections from the public address to the internal address of the connection gateway.
- Create a stand-alone installation package based on the created installation package.
- Deliver the stand-alone installation package to the target devices, either electronically or on a removable drive.
- Install Network Agent from the stand-alone package.
External desktop devices are connected to Administration Server.
Page top
About connection profiles for out-of-office users
Out-of-office users of laptops (hereinafter also referred to as "devices") may need to change the method of connecting to an Administration Server or switch between Administration Servers depending on the current location of the device on the enterprise network.
Connection profiles are supported only for devices running Windows and macOS.
Using different addresses of a single Administration Server
Devices with Network Agent installed can connect to the Administration Server either from the organization's intranet or from the internet. This situation may require Network Agent to use different addresses for connection to Administration Server: the external Administration Server address for the internet connection and the internal Administration Server address for the internal network connection.
To do this, add a profile for connection to Administration Server from the internet in the Network Agent policy properties (in the Application settings → Connectivity → Connection profiles → Administration Server connection profiles section). In the profile creation window, disable the Use to receive updates only option and make sure that the Synchronize connection settings with the Administration Server settings specified in this profile option is selected. If you use a connection gateway to access Administration Server (for example, in a Kaspersky Security Center configuration as that described in Internet access: Network Agent as connection gateway in DMZ), you must specify the address of the connection gateway in the corresponding field of the connection profile.
Switching between Administration Servers depending on the current network
If the organization has multiple offices with different Administration Servers and some of the devices with Network Agent installed move between them, you need Network Agent to connect to the Administration Server of the local network in the office where the device is currently located.
In this case, create a profile for connection to Administration Server in the Network Agent policy properties for each of the offices, except for the home office where the original home Administration Server is located. Specify the addresses of Administration Servers in connection profiles and enable or disable the Use to receive updates only option:
- Select the option if you need Network Agent to be synchronized with the home Administration Server, while using the local Server for downloading updates only.
- Disable this option if it is necessary for Network Agent to be managed completely by the local Administration Server.
After that, you must set up the conditions of switching to the newly created profiles: at least one condition for each of the offices, except for the home office. Every condition's purpose consists in detection of items that are specific for an office's network environment. If a condition is true, the corresponding profile gets activated. If none of the conditions is true, Network Agent switches to the home Administration Server.
Creating a connection profile for out-of-office users
An Administration Server connection profile is available only on devices running Windows and macOS.
To create a profile for connecting Network Agent to Administration Server for out-of-office users:
- If you want to create a connection profile for a group of managed devices, open the Network Agent policy of this group. To do this, do the following:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the current path link.
- In the window that opens, select a required administration group.
After that, the current path is changed.
- Add the Network Agent policy for the group of managed devices. If you have already created it, click the Network Agent policy name to open the policy properties.
- If you want to create a connection profile for a specific managed device, do the following:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click the name of the managed device.
- In the managed device properties window that opens, go to the Applications tab.
- Click the name of the Network Agent policy to which only the selected managed device applies.
- In the properties window that opens, go to Application settings → Connectivity → Connection profiles.
- In the Administration Server connection profiles section, click the Add button.
By default, the list of connection profiles contains the <Offline mode> and <Home Administration Server> profiles. Profiles cannot be edited or removed.
The <Offline mode> profile does not specify any Server for connection. Therefore, Network Agent, when switched to that profile, does not attempt to connect to any Administration Server while applications installed on client devices run under out-of-office policies. The <Offline mode> profile can be used if devices are disconnected from the network.
The <Home Administration Server> profile specifies the connection for the Administration Server that was selected during Network Agent installation. The <Home Administration Server> profile is applied when a device is reconnected to the home Administration Server after it was running on an external network for some time.
- In the Configure profile window that opens, configure the connection profile:
- Profile name
- Administration Server address
- Port number
- SSL port
- Use SSL connection
- Select the Use proxy server option if you want to use a proxy server when connecting to the internet. If this option is selected, fields are available for entering settings. Specify the following settings for a proxy server connection:
- Connection gateway address
- Enable out-of-office mode when Administration Server is not available
- Use to receive updates only
- Synchronize connection settings with the Administration Server settings specified in this profile
A profile for connecting Network Agent to Administration Server is created for out-of-office users. When Network Agent connects to Administration Server by using this profile, applications installed on the client device will use policies for devices in out-of-office mode or out-of-office policies.
About switching Network Agent to other Administration Servers
Kaspersky Security Center provides the option of switching Network Agent on a client device to other Administration Servers if the following settings of the network have been changed:
- Condition for DHCP server address—The IP address of the network Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server has changed.
- Condition for default connection gateway address—The address of the main network gateway has changed.
- Condition for DNS domain—The DNS suffix of the subnet has changed.
- Condition for DNS server address—The IP address of the network DNS server has changed.
- Condition for WINS server address—The IP address of the network WINS server has changed. This setting is available only for devices running Windows.
- Condition for name resolvability—The DNS or NetBIOS name of the client device has changed.
- Condition for subnet—Changes the subnet address and mask.
- Condition for Windows domain accessibility—Changes the status of the Windows domain to which the client device is connected. This setting is available only for devices running Windows.
- Condition for SSL connection address accessibility—The client device can or cannot (depending on the option that you select) establish an SSL connection with a specified Server (name:port). For each server, you can additionally specify an SSL certificate. In this case, the Network Agent verifies the Server certificate in addition to checking the capability of an SSL connection. If the certificate does not match, the connection fails.
This feature is supported only for Network Agents installed on devices running Windows or macOS.
The initial settings of the Network Agent connection to Administration Server are defined when installing the Network Agent. Afterwards, if rules for switching the Network Agent to other Administration Servers have been created, the Network Agent responds to changes in the network settings as follows:
- If the network settings comply with one of the rules created, Network Agent connects to the Administration Server specified in this rule. Applications installed on client devices switch to out-of-office policies, provided such behavior is enabled by a rule.
- If none of the rules apply, Network Agent reverts to the default settings of connection to the Administration Server specified during the installation. Applications installed on client devices switch back to active policies.
- If the Administration Server is not accessible, Network Agent uses out-of-office policies.
Network Agent switches to the out-of-office policy only if the Enable out-of-office mode when Administration Server is not available option is enabled in the Network Agent policy settings.
The settings of Network Agent connection to Administration Server are saved in a connection profile. In the connection profile, you can create rules for switching client devices to out-of-office policies, and you can configure the profile so that it could only be used for downloading updates.
Creating a Network Agent switching rule by network location
Network Agent-switching by network location is available only on devices running Windows and macOS.
To create a rule for Network Agent switching from one Administration Server to another if network settings change:
- If you want to create a rule for a group of managed devices, open the Network Agent policy of this group. To do this, do the following:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the current path link.
- In the window that opens, select a required administration group.
After that, the current path is changed.
- Add the Network Agent policy for the group of managed devices. If you have already created it, click the Network Agent policy name to open the policy properties.
- If you want to create a rule for a specific managed device, do the following:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click the name of the managed device.
- In the managed device properties window that opens, go to the Applications tab.
- Click the name of the Network Agent policy to which only the selected managed device applies.
- In the properties window that opens, go to Application settings → Connectivity → Connection profiles.
- In the Network location settings section, click the Add button.
- In the properties window that opens, configure the network location description and switching rule. Specify the following network location description settings:
- Select conditions for the Network Agent switching rule:
- Condition for DHCP server address—The IP address of the network Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server has changed.
- Condition for default connection gateway address—The address of the main network gateway has changed.
- Condition for DNS domain—The DNS suffix of the subnet has changed.
- Condition for DNS server address—The IP address of the network DNS server has changed.
- Condition for WINS server address—The IP address of the network WINS server has changed. This setting is available only for devices running Windows.
- Condition for name resolvability—The DNS or NetBIOS name of the client device has changed.
- Condition for subnet—Changes the subnet address and mask.
- Condition for Windows domain accessibility—Changes the status of the Windows domain to which the client device is connected. This setting is available only for devices running Windows.
- Condition for SSL connection address accessibility—The client device can or cannot (depending on the option that you select) establish an SSL connection with a specified Server (name:port). For each server, you can additionally specify an SSL certificate. In this case, the Network Agent verifies the Server certificate in addition to checking the capability of an SSL connection. If the certificate does not match, the connection fails.
The conditions in a rule are combined by using the logical AND operator. To trigger a switching rule by the network location description, all of the rule switching conditions must be met.
- In the condition section, specify when Network Agent should be switched to another Administration Server. For this purpose, click the Add button, and then set the condition value.
Also, the Matches at least one value from the list option is enabled by default. You can disable this option if you want the condition to be met with all specified values.
- Save your changes.
A new switching rule by the network location description is created; any time its conditions are met, the Network Agent uses the connection profile specified in the rule to connect to the Administration Server.
Protection deployment wizard
To install Kaspersky applications, you can use the Protection deployment wizard. The Protection deployment wizard enables remote installation of applications either through specially created installation packages or directly from a distribution package.
The Protection deployment wizard performs the following actions:
- Downloads an installation package for application installation (if it was not created earlier). The installation package is located at Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Installation packages. You can use this installation package for the application installation in the future.
- Creates and runs a remote installation task for specific devices or for an administration group. The newly created remote installation task is stored in the Tasks section. You can later start this task manually. The task type is Install application remotely.
If you want to install Network Agent on devices with the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 operating system, install the insserv-compat package first to configure Network Agent.
Starting Protection deployment wizard
To start the Protection deployment wizard manually,
In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Protection deployment wizard.
The Protection deployment wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
Selecting the installation package
Select the installation package of the application that you want to install.
If the installation package of the required application is not listed, click the Add button and then select the application from the list.
Selecting a method for distribution of key file or activation code
Select a method for the distribution of the key file or the activation code:
If the installation package already includes a key file or an activation code, this window is displayed, but it only contains the license key information.
Selecting Network Agent version
If you selected the installation package of an application other than Network Agent, you also have to install Network Agent, which connects the application with Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
Select the latest version of Network Agent.
Page top
Step 5. Specifying the remote installation task settings
On the Remote installation task settings page, specify the settings for remote installation of the application.
In the Force installation package download settings group, specify how files that are required for the application installation are distributed to client devices:
- Using Network Agent
- Using operating system resources through distribution points
- Using operating system resources through Administration Server
Define the additional settings:
- Do not re-install application if it is already installed
- Assign package installation in Active Directory group policies
Step 6. Restart management
Specify the action to be performed if the operating system must be restarted when you install the application:
- Do not restart the device
- Restart the device
- Prompt user for action
- Force closure of applications in blocked sessions
Step 7. Removing incompatible applications before installation
This step is only present if the application that you deploy is known to be incompatible with some other applications.
Select the option if you want Kaspersky Security Center to automatically remove applications that are incompatible with the application you deploy.
The list of incompatible applications is also displayed.
If you do not select this option, the application will only be installed on devices that have no incompatible applications.
Step 8. Moving devices to Managed devices
Specify whether devices must be moved to an administration group after Network Agent installation.
The Do not move devices option is selected by default. For security reasons, you might want to move the devices manually.
Step 9. Selecting accounts to access devices
If necessary, add the accounts that will be used to start the remote installation task:
Step 10. Starting installation
This page is the final step of the wizard. At this step, the Remote installation task has been successfully created and configured.
By default, the Run the task after the wizard finishes option is not selected. If you select this option, the Remote installation task will start immediately after you complete the wizard. If you do not select this option, the Remote installation task will not start. You can later start this task manually.
Click OK to complete the final step of the Protection deployment wizard.
Kaspersky applications deployment through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
This section describes Kaspersky applications deployment on client devices in your organization by means of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Scenario: Kaspersky applications deployment through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
This scenario explains how to deploy Kaspersky applications through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. You can use the quick start wizard and Protection deployment wizard, or you can complete all necessary steps manually.
The following applications are available for deployment by using Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
Stages
Kaspersky applications deployment proceeds in stages:
- Downloading management plug-in for the application
This stage is handled by the quick start wizard. If you choose not to run the wizard, download the plug-in for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows manually.
If you plan to manage corporate mobile devices, follow the instructions provided in the Kaspersky Security for Mobile Help to download and install the management plug-ins for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android.
- Downloading and creating installation packages
This stage is handled by the quick start wizard.
The quick start wizard allows you to download the installation package with the management plug-in. If you did not select this option when running the wizard, or if you did not run the wizard at all, you must download the package manually.
If you cannot install Kaspersky applications by means of Kaspersky Security Center on some devices, for example, on remote employees' devices, you can create stand-alone installation packages for applications. If you use stand-alone packages to install Kaspersky applications, you do not have to create and run a remote installation task, nor create and configure tasks for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- Creating, configuring, and running the remote installation task
For Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, this stage is part of the Protection deployment wizard, which starts automatically after the quick start wizard has finished. If you choose not to run the Protection deployment wizard, you must create this task manually and configure it manually.
You also can manually create several remote installation tasks for different administration groups or different device selections. You can deploy different versions of one application in these tasks.
Make sure that all the devices on your network are discovered; then run the remote installation task (or tasks).
If you want to install Network Agent on devices with the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 operating system, install the insserv-compat package first to configure Network Agent.
If you want to install Network Agent on devices that use the operating system RED OS 7.3.4 or later or MSVSPHERE 9.2 or later, install the libxcrypt-compat package for the correct function of Network Agent.
- Creating and configuring tasks for the managed application
The Install update task of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows must be configured.
This stage is part of the quick start wizard: the task is created and configured automatically with the default settings. If you did not run the wizard, you must create this task manually and configure it manually. If you use the quick start wizard, make sure that the schedule for the task meets your requirements. (By default, the scheduled start for the task is set to Manually, but you might want to choose another option.)
Other Kaspersky applications might have other default tasks. Please refer to the documentation of the corresponding applications for details.
Make sure that the schedule for each task that you create meets your requirements.
- Installing Kaspersky Security for Mobile (optional)
If you plan to manage corporate mobile devices, follow the instructions provided in the Kaspersky Security for Mobile Help for information about deployment of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android.
- Creating policies
Create the policy for each application manually or (in case of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows) through the quick start wizard. You can use the default settings of the policy; you can also modify the default settings of the policy according to your needs at any time.
- Verifying the results
Make sure that deployment was completed successfully: you have policies and tasks for each application, and these applications are installed on the managed devices.
Results
Completion of the scenario yields the following:
- All required policies and tasks for the selected applications are created.
- The schedules of tasks are configured according to your needs.
- The selected applications are deployed, or scheduled to be deployed, on the selected client devices.
Getting plug-ins for Kaspersky applications
To deploy a Kaspersky application, such as Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, you must download the management plug-in for the application.
To download a management plug-in for a Kaspersky application:
- In the main menu, go to Settings → Web plug-ins.
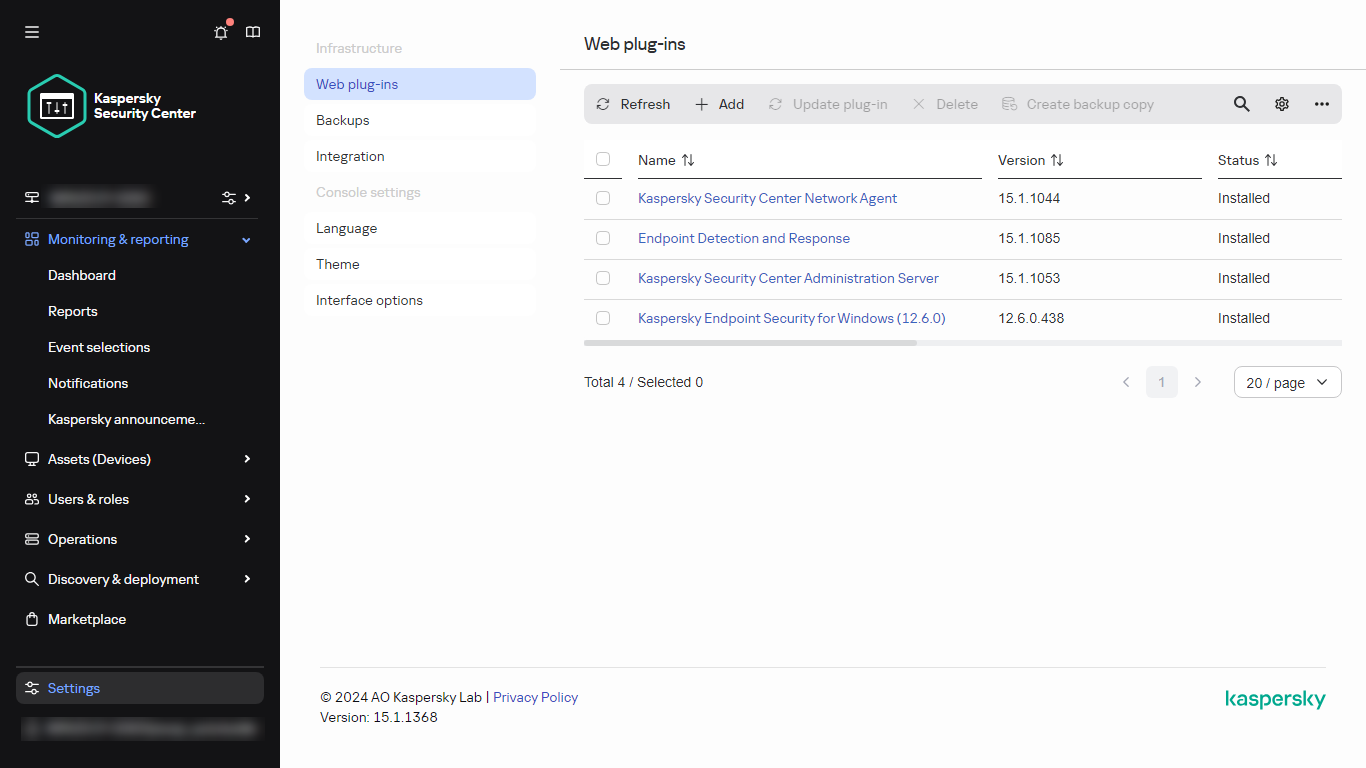
The list of installed web plug-ins
- In the window that opens, click the Add button.
The list of available plug-ins is displayed.
- In the list of available plug-ins, select the plug-in you want to download (for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11 for Windows) by clicking on its name.
A plug-in description page is displayed.
- On the plug-in description page, click Install plug-in.
- When the installation is complete, click OK.
The management plug-in is downloaded with the default configuration and displayed in the list of management plug-ins.
You can add plug-ins and update downloaded plug-ins from a file. You can download management plug-ins and web management plug-ins from the Kaspersky Technical Support webpage.
To download or update plug-in from a file:
- In the main menu, go to Settings → Web plug-ins.
- Do one of the following:
- Click Add from file to download a plug-in from a file.
- Click Update from file to download an update of a plug-in from a file.
- Specify the file and signature of the file.
- Download the specified files.
The management plug-in is downloaded from the file and displayed in the list of management plug-ins.
Downloading and creating installation packages for Kaspersky applications
You can create installation packages for Kaspersky applications from Kaspersky web servers if your Administration Server has access to the internet.
To download and create installation package for Kaspersky application:
- Do one of the following:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Installation packages.
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories → Installation packages.
You can also view notifications about new packages for Kaspersky applications in the list of onscreen notifications. If there are notifications about a new package, you can click the link next to the notification and proceed to the list of available installation packages.
A list of installation packages available on Administration Server is displayed.
- Click Add.
The New package wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- Select Create an installation package for a Kaspersky application.
A list of available installation packages on Kaspersky web servers appears. The list contains installation packages only for those applications that are compatible with the current version of Kaspersky Security Center.
- Click the name of an installation package, for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (11.1.0).
A window opens with information about the installation package.
You can download and use an installation package which includes cryptographic tools that implement strong encryption, if it complies with applicable laws and regulations. To download the installation package of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows valid for the needs of your organization, consult the legislation of the country where the client devices of your organization are located.
- Read the information and click the Download and create installation package button.
If a distribution package can not be converted to an installation package, the Download distribution package button instead of the Download and create installation package is displayed.
The downloading of the installation package to Administration Server starts. You can close the wizard's window or proceed to the next step of the instruction. If you close the wizard's window, the download process will continue in background mode.
If you want to track an installation package download process:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories → Installation packages → In progress ().
- Track the operation progress in the Download progress column and the Download status column of the table.
When the process is complete, the installation package is added to the list on the Downloaded tab. If the download process stops and the download status switches to Accept EULA, then click the installation package name, and then proceed to the next step of the instruction.
If the size of data contained in the selected distribution package exceeds the current limit, an error message is displayed. You can change the limit value and then proceed with the installation package creation.
- For some Kaspersky applications, during the download process the Show EULA button is displayed. If it is displayed, do the following:
- Click the Show EULA button to read the End User License Agreement (EULA).
- Read the EULA that is displayed on the screen, and click Accept.
The downloading continues after you accept the EULA. If you click Decline, the download is stopped.
- When the downloading is complete, click the Close button.
The selected installation package is downloaded to the Administration Server shared folder, to the Packages subfolder. After downloading, the installation package is displayed in the list of installation packages.
Changing the limit on the size of custom installation package data
The total size of data unpacked during creation of a custom installation package is limited. The default limit is 1 GB.
If you attempt to upload an archive file that contains data exceeding the current limit, an error message is displayed. You might have to increase this limit value when creating installation packages from large distribution packages.
To change the limit value for the custom installation package size:
- On the Administration Server device, run the command prompt under the account that was used to install Administration Server.
- Change your current directory to the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder (usually, <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center).
- Depending on the type of Administration Server installation, enter one of the following commands, using administrator rights:
- Normal local installation:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n MaxArchivePkgSize -t d -v <number of bytes> - Installation on the Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n MaxArchivePkgSize -t d -v <number of bytes> --stp klfoc - Installation on a Windows Server failover cluster:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n MaxArchivePkgSize -t d -v <number of bytes> --stp cluster
Where <number of bytes> is a number of bytes in hexadecimal or decimal format.
For example, if the required limit is 2 GB, you can specify the decimal value 2147483648 or the hexadecimal value 0x80000000. In this case, for a local installation of Administration Server, you can use the following command:
klscflag -fset -pv klserver -n MaxArchivePkgSize -t d -v 2147483648 - Normal local installation:
The limit on the size of custom installation package data is changed.
Page top
Downloading distribution packages for Kaspersky applications
In Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you can download and save distribution packages for Kaspersky applications. You can use the distribution packages to install the applications manually, without using Kaspersky Security Center.
To download and save distribution packages for Kaspersky applications:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Kaspersky applications → Current application versions.
A list of available distribution packages, plug-ins, and patches opens. Kaspersky Security Center displays only those items that are compatible with its current version.
- In the list, click the name of the package that you want to download.
The description of the package opens.
- Read the description and click the Download and create installation package button.
If a distribution package cannot be converted to an installation package, the Download distribution package button is displayed instead of the Download and create installation package.
The download of the installation package to Administration Server starts.
The selected installation or distribution package is downloaded to the Administration Server shared folder, to the Packages subfolder. After it is downloaded, the installation package is displayed in the list of installation packages.
Page top
Checking that Kaspersky Endpoint Security is deployed successfully
To ensure that you have correctly deployed Kaspersky applications, such as Kaspersky Endpoint Security:
- Using Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, make sure that you have the following:
- A policy for Kaspersky Endpoint Security and/or other security applications that you use.
- Tasks for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows: Quick Scan task and Install update task (if you use Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows).
- Tasks for other security applications that you use.
- On one of the managed devices, selected for installation, make sure of the following:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security or another Kaspersky security application is installed.
- In Kaspersky Endpoint Security, the File Threat Protection, Web Threat Protection, and Mail Threat Protection settings match the policy that you created for this device.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security service can be stopped and started manually.
- Group tasks can be stopped and started manually.
Creating stand-alone installation packages
You and device users in your organization can use stand-alone installation packages to install applications on devices manually.
A stand-alone installation package is an executable file (installer.exe) that you can store on Web Server, in a shared folder, send by email, or transfer to a client device by another method. On the client device, the user can run the received file locally to install an application without involving Kaspersky Security Center. You can create stand-alone installation packages for Kaspersky applications and for third-party applications for Windows, macOS, and Linux platforms. To create a stand-alone installation package for a third-party application, you must create a custom installation package.
Be sure that the stand-alone installation package is not available for unauthorized persons.
To create a stand-alone installation package:
- Do one of the following:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Installation packages.
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories → Installation packages.
A list of installation packages available on Administration Server is displayed.
- In the list of installation packages, select an installation package and, above the list, click the Deploy button.
- Select the Using a stand-alone package option.
The Stand-alone installation package creation wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- Make sure that the Install Network Agent together with this application option is enabled if you want to install Network Agent together with the selected application.
By default, this option is enabled. We recommend enabling this option if you are not sure whether Network Agent is installed on the device. If Network Agent is already installed on the device, after the stand-alone installation package with Network Agent is installed, Network Agent will be updated to the newer version.
If you disable this option, Network Agent will not be installed on the device and the device will be unmanaged.
If a stand-alone installation package for the selected application already exists on Administration Server, the wizard informs you about this fact. In this case, you must select one of the following actions:
- Create stand-alone installation package. Select this option if, for example, you want to create a stand-alone installation package for a new application version and also want to retain a stand-alone installation package that you created for a previous application version. The new stand-alone installation package is placed in another folder.
- Use existing stand-alone installation package. Select this option if you want to use an existing stand-alone installation package. The process of package creation will not be started.
- Rebuild existing stand-alone installation package. Select this option if you want to create a stand-alone installation package for the same application again. The stand-alone installation package is placed in the same folder.
- On the Move to list of managed devices step, the Do not move devices option is enabled by default. If you do not want to move the client device to any administration group after Network Agent installation, leave this option enabled.
If you want to move the client device after Network Agent installation, select the Move unassigned devices to this group option and specify an administration group to which you want to move the client device. By default, the device is moved to the Managed devices group.
- When the process of the stand-alone installation package creation is finished, click the FINISH button.
The Stand-alone Installation Package Creation Wizard closes.
The stand-alone installation package is created and placed in the PkgInst subfolder of the Administration Server shared folder. You can view the list of stand-alone packages by clicking the View the list of stand-alone packages button above the list of installation packages.
Viewing the list of stand-alone installation packages
You can view the list of stand-alone installation packages and properties of each stand-alone installation package.
To view the list of stand-alone installation packages for all installation packages:
Above the list, click the View the list of stand-alone packages button.
In the list of stand-alone installation packages, their properties are displayed as follows:
- Package name. Stand-alone installation package name that is automatically formed as the application name included in the package and the application version.
- Application name. Application name included in the stand-alone installation package.
- Application version.
- Network Agent installation package name. The property is displayed only if Network Agent is included in the stand-alone installation package.
- Network Agent version. The property is displayed only if Network Agent is included in the stand-alone installation package.
- Size. File size in MB.
- Group. Name of the group to which the client device is moved after Network Agent installation.
- Created. Date and time of the stand-alone installation package creation.
- Modified. Date and time of the stand-alone installation package modification.
- Path. Full path to the folder where the stand-alone installation package is located.
- Web address. Web address of the stand-alone installation package location.
- File hash. The property is used to certify that the stand-alone installation package was not changed by third-party persons and a user has the same file you have created and transferred to the user.
To view the list of stand-alone installation packages for specific installation package:
Select the installation package in the list and, above the list, click the View the list of stand-alone packages button.
In the list of stand-alone installation packages, you can do the following:
- Publish a stand-alone installation package on the Web Server by clicking the Publish button. Published stand-alone installation package is available for downloading for users whom you sent the link to the stand-alone installation package.
- Cancel publication of a stand-alone installation package on the Web Server by clicking the Unpublish button. Unpublished stand-alone installation package is available for downloading only for you and other administrators.
- Download a stand-alone installation package to your device by clicking the Download button.
- Send email with the link to a stand-alone installation package by clicking the Send by email button.
- Remove a stand-alone installation package by clicking the Remove button.
Creating custom installation packages
You can use custom installation packages to do the following:
- To install any application (such as a text editor) on a client device, for example, by means of a task.
- To create a stand-alone installation package.
A custom installation package is a folder with a set of files. The source to create a custom installation package is an archive file. The archive file contains a file or files that must be included in the custom installation package. While creating a custom installation package, you can specify command-line parameters, for example, to install the application in silent mode.
If you have an active license key for the Vulnerability and patch management (VAPM) feature, you can convert your default installation settings for the relevant custom installation package and use the values recommended by Kaspersky experts. The settings are automatically converted during the creation of the custom installation package only if the corresponding executable file is included in the Kaspersky database of third-party applications.
To create a custom installation package:
- Do one of the following:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Installation packages.
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories → Installation packages.
A list of installation packages available on Administration Server is displayed.
- Click Add.
The New package wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- Select Create an installation package from a file.
- Specify the package name and click the Browse button.
A standard Windows Open window in your browser opens to let you choose a file to create the installation package.
- Choose an archive file located on the available disks.
You can upload a ZIP, CAB, TAR, or TAR.GZ archive file. It is not possible to create an installation package from an SFX (self-extracting archive) file.
If you want the settings to be converted during the package installation, make sure the Convert settings to recommended values for applications recognized by Kaspersky Security Center after the wizard finishes check box is selected, and then click Next.
File upload to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server starts.
If you enabled the use of the recommended installation settings, Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 checks whether the executable file is included in the Kaspersky database of third-party applications. If the check is successful, you get a notification informing you that the file is recognized. The settings are converted and the custom installation package is created. No further actions are required. Click the Finish button to close the wizard.
- Select a file (from the list of files that are extracted from the chosen archive file) and specify the command-line parameters of an executable file.
You can specify command-line parameters to install the application from the installation package in a silent mode. Specifying command-line parameters is optional.
The process to create the installation package is started.
The wizard informs you when the process is finished.
If the installation package is not created, an appropriate message is displayed.
- Click the Finish button to close the wizard.
The installation package that you created is downloaded to the Packages subfolder of the Administration Server shared folder. After downloading, the installation package appears in the list of installation packages.
In the list of installation packages available on Administration Server, by clicking the link with the name of a custom installation package, you can:
- View the following properties of an installation package:
- Name. Custom installation package name.
- Source. Application vendor name.
- Application. Application name packed into the custom installation package.
- Version. Application version.
- Language. Language of the application packed into the custom installation package.
- Size (MB). Size of the installation package.
- Operating system. Type of the operating system for which the installation package is intended.
- Created. Installation package creation date.
- Modified. Installation package modification date.
- Type. Type of the installation package.
- Change the package name and command-line parameters. This feature is available only for packages that are not created on the basis of Kaspersky applications.
If you have converted the package installation settings to the recommended values for the custom package creation process, two additional sections may appear on the Settings tab of the custom installation package properties: Settings and Installation procedure.
The Settings section contains the following properties, shown in a table:
- Name. This column shows the name assigned to an installation parameter.
- Type. This column shows the type of an installation parameter.
- Value. This column shows the type of data defined by an installation parameter (Bool, Filepath, Numeric, Path, or String).
The Installation procedure section contains a table that describes the following properties of the update included in the custom installation package:
- Name. The name of the update.
- Description. The description of the update.
- Source. The source of the update, that is, whether it was released by Microsoft or by a different third-party developer.
- Type. The type of the update, that is, whether it is intended for a driver or an application.
- Category. The Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) category displayed for Microsoft updates (Critical Updates, Definition Updates, Drivers, Feature Packs, Security Updates, Service Packs, Tools, Update Rollups, Updates, or Upgrade).
- Importance level according to MSRC. The importance level of the update defined by Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC).
- Importance level. The importance level of the update defined by Kaspersky.
- Patch importance level (for patches intended for Kaspersky applications). The importance level of the patch if it is intended for a Kaspersky application.
- Article. The identifier (ID) of the article in the Knowledge Base describing the update.
- Bulletin. The ID of the security bulletin describing the update.
- Not assigned for installation. Displays whether the update has the Not assigned for installation status.
- To be installed. Displays whether the update has the To be installed status.
- Installing. Displays whether the update has the Installing status.
- Installed. Displays whether the update has the Installed status.
- Failed. Displays whether the update has the Failed status.
- Restart is required. Displays whether the update has the Restart is required status.
- Registered. Displays the date and time when the update was registered.
- Installed in interactive mode. Displays whether the update requires interaction with the user during installation.
- Revoked. Displays the date and time when the update was revoked.
- Update approval status. Displays whether the update is approved for installation.
- Revision. Displays the current revision number of the update.
- Update ID. Displays the ID of the update.
- Application version. Displays the version number that the application will be updated to.
- Superseded. Displays other update(s) that can supersede the update.
- Superseding. Displays other update(s) that can be superseded by the update.
- You must accept the terms of the License Agreement. Displays whether the update requires acceptance of the terms of an End User License Agreement (EULA).
- Vendor. Displays the name of the update vendor.
- Application family. Displays the name of the family of applications to which the update belongs.
- Application. Displays the name of the application to which the update belongs.
- Language. Displays the language of the update localization.
- Not assigned for installation (new version). Displays whether the update has the Not assigned for installation (new version) status.
- Requires prerequisites installation. Displays whether the update has the Requires prerequisites installation status.
- Download mode. Displays the mode of the update download.
- Is a patch. Displays whether the update is a patch.
- Not installed. Displays whether the update has the Not installed status.
Distributing installation packages to secondary Administration Servers
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to create installation packages for Kaspersky applications and for third-party applications, as well as distribute installation packages to client devices and install applications from the packages. To optimize the load on the primary Administration Server, you can distribute installation packages to secondary Administration Servers. After that, the secondary Servers transmit the packages to client devices, and then you can perform the remote installation of the applications on your client devices.
To distribute installation packages to secondary Administration Servers:
- Make sure that the secondary Administration Servers are connected to the primary Administration Server.
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
The list of tasks is displayed.
- Click the Add button.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the New task settings page, from the Application drop-down list, select Kaspersky Security Center. Then, from the Task type drop-down list, select Distribute installation package, and then specify the task name.
- On the Task scope page, select the devices to which the task is assigned in one of the following ways:
- If you want to create a task for all secondary Administration Servers in a specific administration group, select this group, and then create a group task for it.
- If you want to create a task for specific secondary Administration Servers, select these Servers, and then create a task for them.
- On the Distributed installation packages page, select the installation packages that are to be copied to the secondary Administration Servers.
- Specify an account to run the Distribute installation package task under this account. You can use your account and keep the Default account option enabled. Alternatively, you can specify that the task should be run under another account that has the necessary access rights. To do this, select the Specify account option, and then enter the credentials of that account.
- On the Finish task creation page, you can enable the Open task details when creation is complete option to open the task properties window, and then modify the default task settings. Otherwise, you can configure the task settings later, at any time.
- Click the Finish button.
The task created for distributing installation packages to the secondary Administration Servers is displayed in the task list.
- You can run the task manually or wait for it to launch according to the schedule that you specified in the task settings.
After the task is complete, the selected installation packages are copied to the specified secondary Administration Servers.
Page top
Installing applications using a remote installation task
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to install applications on devices remotely, using remote installation tasks. Those tasks are created and assigned to devices through a dedicated wizard. To assign a task more quickly and easily, you can specify devices (up to 1000 devices) in the wizard window in one of the following ways:
- Select networked devices detected by Administration Server. In this case, the task is assigned to specific devices. The specific devices can include devices in administration groups as well as unassigned devices.
- Specify device addresses manually or import addresses from a list. You can specify NetBIOS names, DNS names, IP addresses, and IP subnets of devices to which you want to assign the task.
- Assign task to a device selection. In this case, the task is assigned to devices included in a selection created earlier. You can specify the predefined selection or a custom one that you created.
- Assign task to an administration group. In this case, the task is assigned to devices included in an administration group created earlier.
For correct remote installation on a device with no Network Agent installed, the following ports must be opened: a) TCP 139 and 445; b) UDP 137 and 138. By default, these ports are opened on all devices included in the domain. They are opened automatically by the remote installation preparation utility.
Installing an application remotely
This section contains information on how to install an application remotely on an administration group, devices with specific IP addresses, or a selection of managed devices.
To install an application on specific devices:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts.
- In the Task type field, select Install application remotely.
- Select one of the following options:
- Assign task to an administration group
- Specify device addresses manually or import addresses from a list
- Assign task to a device selection
The Install application remotely task is created for the specified devices. If you selected the Assign task to an administration group option, the task is a group one.
- At the Task scope step, specify an administration group, devices with specific addresses, or a device selection.
The available settings depend on the option selected at the previous step.
- At the Installation packages step, specify the following settings:
- In the Select installation package field, select the installation package of an application that you want to install.
- In the Force installation package download settings group, specify how files that are required for the application installation are distributed to client devices:
- In the Maximum number of concurrent downloads field, specify the maximum allowed number of client devices to which Administration Server can simultaneously transmit the files.
- In the Maximum number of installation attempts field, specify the maximum allowed number of installer runs.
If the number of attempts specified in the parameter is exceeded, Kaspersky Security Center does not start the installer on the device anymore. To restart the Install application remotely task, increase the value of the Maximum number of installation attempts parameter and start the task. Alternatively, you can create a new Install application remotely task.
- If you migrate from one Kaspersky application to another and your current application is password-protected, enter the password in the Password to uninstall the current Kaspersky application field. Note that during the migration, your current Kaspersky application will be uninstalled.
The Password to uninstall the current Kaspersky application field is only available if you have selected the Using Network Agent option in the Force installation package download settings group.
You can use the uninstall password only for the Kaspersky Security for Windows Server to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows migration scenario when installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows by using the Install application remotely task. Using the uninstall password when installing other components may cause installation errors.
To complete the migration scenario successfully, make sure that the following prerequisites are met:
- You are using Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent 14.2 for Windows or later.
- You are installing the application on devices running Windows.
- Define the additional setting:
- Select on which devices you want to install the application:
- Specify whether devices must be moved to an administration group after installation:
- Do not move devices
- Move unassigned devices to the selected group (only a single group can be selected)
Note that the Do not move devices option is selected by default. For security reasons, you might want to move the devices manually.
- At the this step of the wizard, specify whether the devices must be restarted during installation of applications:
- If necessary, at the Select accounts to access devices step, add the accounts that will be used to start the Install application remotely task:
- At the Finish task creation step, click the Finish button to create the task and close the wizard.
If you enabled the Open task details when creation is complete option, the task settings window opens. In this window, you can check the task parameters, modify them, or configure a task start schedule, if necessary.
- In the task list, select the task you created, and then click Start.
Alternatively, wait for the task to launch according to the schedule that you specified in the task settings.
When the remote installation task is completed, the selected application is installed on the specified devices.
Installing an application through Active Directory group policies
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to install Kaspersky applications on managed devices by using Active Directory group policies.
You can install applications by using Active Directory group policies only from installation packages that include Network Agent.
To install an application by using Active Directory group policies:
- Run the Protection deployment wizard. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
- On the Remote installation task settings page of the Protection deployment wizard, enable the Assign package installation in Active Directory group policies option.
- On the Select accounts to access devices page, select the Account required (Network Agent is not used) option.
- Add the account with administrator privileges on the device where Kaspersky Security Center is installed or the account included in the Group Policy Creator Owners domain group.
- Grant the permissions to the selected account:
- Go to Control Panel → Administrative Tools and open Group Policy Management.
- Click the node with the required domain.
- Click the Delegation section.
- In the Permission drop-down list, select Link GPOs.
- Click Add.
- In the Select User, Computer, or Group window that opens, select the necessary account.
- Click OK to close the Select User, Computer, or Group window.
- In the Groups and users list, select the account that you have just added, and then click Advanced → Advanced.
- In the Permission entries list, double-click the account that you have just added.
- Grant the following permissions:
- Create Group objects
- Delete Group objects
- Create group Policy Container objects
- Delete group Policy Container objects
- Click OK to save the changes.
- Define other settings by following the instructions of the wizard.
- Run the created remote installation task manually or wait for its scheduled start.
The following remote installation sequence starts:
- When the task is running, the following objects are created in each domain that includes any client devices from the specified set:
- Group policy object (GPO) under the name Kaspersky_AK{GUID}.
- A security group that corresponds to the GPO. This security group includes client devices covered by the task. The content of the security group defines the scope of the GPO.
- Kaspersky Security Center installs the selected Kaspersky applications on client devices directly from Share, that is, the shared network folder of the application. In the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder, an auxiliary subfolder will be created that contains the .msi file for the application to be installed.
- When new devices are added to the task scope, they are added to the security group after the next start of the task. If the Run missed tasks option is selected in the task schedule, devices are added to the security group immediately.
- When devices are deleted from the task scope, they are deleted from the security group after the next start of the task.
- When a task is deleted from Active Directory, the GPO, the link to the GPO, and the corresponding security group are deleted, too.
If you want to apply another installation schema using Active Directory, you can configure the required settings manually. For example, this may be required in the following cases:
- When the anti-virus protection administrator does not have rights to make changes to the Active Directory of certain domains
- When the original installation package has to be stored on a separate network resource
- When it is necessary to link a GPO to specific Active Directory units
The following options for using an alternative installation scheme through Active Directory are available:
- If installation is to be performed directly from the Kaspersky Security Center shared folder, in the GPO properties you must specify the .msi file located in the exec subfolder of the installation package folder for the required application.
- If the installation package has to be located on another network resource, you must copy the whole exec folder content to it, because in addition to the file with .msi extension the folder contains configuration files generated when the package was created. To install the license key with the application, copy the key file to this folder as well.
Installing applications on secondary Administration Servers
To install an application on secondary Administration Servers:
- Establish a connection with the Administration Server that controls the relevant secondary Administration Servers.
- Make sure that the installation package corresponding to the application being installed is available on each of the selected secondary Administration Servers. If you cannot find the installation package on any of the secondary Servers, distribute it. For this purpose, create a task with the Distribute installation package task type.
- Create a task for a remote application installation on secondary Administration Servers. Select the Install application on secondary Administration Server remotely task type.
The New task wizard creates a task for remote installation of the application selected in the wizard on specific secondary Administration Servers.
- Run the task manually or wait for it to launch according to the schedule that you specified in the task settings.
When the remote installation task is complete, the selected application is installed on the secondary Administration Servers.
Page top
Specifying settings for remote installation on Unix devices
When you install an application on a Unix device by using a remote installation task, you can specify Unix-specific settings for the task. These settings are available in the task properties after the task is created.
To specify Unix-specific settings for a remote installation task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click the name of the remote installation task for which you want to specify the Unix-specific settings.
The task properties window opens.
- Go to Application settings → Unix-specific settings.
- Specify the following settings:
- Click the Save button.
The specified task settings are saved.
Starting and stopping Kaspersky applications
You can use the Start or stop application task for starting and stopping Kaspersky applications on managed devices.
To create the Start or stop application task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- In the Application drop-down list, select the application for which you want to create the task.
Kaspersky applications are displayed in the list if you have previously added management web plug-ins for these applications.
- In the Task type list, select the Application activation task.
- In the Task name field, specify the name of the new task.
The task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- Select the devices to which the task will be assigned.
- In the Applications window, do the following:
- Select the check boxes next to the names of applications for which you want to create the task.
- Select the Start application or the Stop application option.
- If you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option at the Finish task creation step. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Finish button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the name of the created task to open the task properties window.
- In the task properties window, specify the general task settings according to your needs, and then save the settings.
The task is created and configured.
If you want to run the task, select it in the task list, and then click the Start button.
Page top
Mobile Device Management
Management of mobile device protection through Kaspersky Security Center is carried out by using the Mobile Device Management feature, which requires a dedicated license. If you are intending to manage mobile devices owned by employees in your organization, enable and configure Mobile Device Management.
Mobile Device Management enables you to manage Android devices of the employees. The protection is provided by the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android mobile app installed on the devices. This mobile app ensures protection of mobile devices against web threats, viruses and other programs that pose threats. For centralized management through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you must install the following web management plug-ins on the device where Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is installed:
- Kaspersky Security for Mobile Plug-in
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android Plug-in
For information about protection deployment and management of mobile devices, see Kaspersky Security for Mobile Help.
Modifying the Mobile Device Management settings in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
To modify the Mobile Device Management settings:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Additional ports section.
- Modify the relevant settings:
- Click the Save button.
The mobile devices can now connect to the Administration Server.
Replacing third-party security applications
Installation of Kaspersky security applications through Kaspersky Security Center may require removal of third-party software incompatible with the application being installed. Kaspersky Security Center provides several ways of removing the third-party applications.
Removing incompatible applications by using the installer
This option is available in Microsoft Management Console-based Administration Console only.
The installer method of removing incompatible applications is supported by various types of installation. Before the security application installation, all incompatible applications are removed automatically if the properties window of the installation package of this security application (Incompatible applications section) has the Uninstall incompatible applications automatically option selected.
Removing incompatible applications when configuring remote installation of an application
You can enable the Uninstall incompatible applications automatically option when you configure remote installation of a security application. In Microsoft Management Console (MMC) based Administration Console, this option is available in the Remote installation wizard. In Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you can find this option in the Protection deployment wizard. When this option is enabled, Kaspersky Security Center removes incompatible applications before installing a security application on a managed device.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Removing incompatible applications using Remote Installation Wizard
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Removing incompatible applications before installation
Removing incompatible applications through a dedicated task
To remove incompatible applications, use the Uninstall application remotely task. This task should be run on devices before the security application installation task. For example, in the installation task you can select On completing another task as the schedule type where the other task is Uninstall application remotely.
This method of uninstallation is useful when the security application installer cannot properly remove an incompatible application.
How-to instructions for Administration Console: Creating a task.
Page top
Discovering networked devices
This section describes search and discovery of networked devices.
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to find devices on the basis of specified criteria. You can save search results to a text file.
The search and discovery feature allows you to find the following devices:
- Managed devices in administration groups of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and its secondary Administration Servers.
- Unassigned devices managed by Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and its secondary Administration Servers.
Scenario: Discovering networked devices
You must perform device discovery before installation of the security applications. The Administration Server receives information about discovered devices and allows you to manage the devices through policies. Regular network polls are needed to update the list of devices available in the network.
Before you start network polling, make sure that the SMB protocol is enabled. Otherwise, Kaspersky Security Center cannot discover devices in the polled network. To enable the SMB protocol, follow the instructions for your operating system.
Discovery of networked devices proceeds in the following stages:
- Discover devices
The quick start wizard guides you through initial device discovery, and helps you find networked devices such as computers, tablets, and mobile phones. You can also perform device discovery manually.
- Configure scheduled polls
Decide which polling type(s) you want to use regularly. Enable the desired types and configure the poll schedule as you see fit. You can refer to the recommendations for network polling frequency.
- Set up rules for adding discovered devices to administration groups (Optional)
If new devices appear on your network, they are discovered during regular polls and are automatically included in the Unassigned devices group. You can set up device moving rules to automate the allocation of devices to the Managed devices group. You can also configure retention rules.
If you skip the step 3, the newly discovered devices are allocated to the Unassigned devices group. If you want, you can move these devices to the Managed devices group manually. If you move the devices to the Managed devices group manually, you can analyze information about each device and decide whether you want to move it to an administration group, and, if so, to which exact group.
Results
Completion of the scenario yields the following:
- Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server discovers the devices that are on the network and provides you with information about them.
- Future polls are set up and are conducted according to the specified schedule.
- The newly discovered devices are arranged according to the configured rules. (Or, if no rules are configured, the devices stay in the Unassigned devices group).
Device discovery
This section describes the types of device discovery available in Kaspersky Security Center and provides information using each type.
The Administration Server receives information about the structure of the network and devices on this network through regular polling. The information is recorded to the Administration Server database. Administration Server can use the following types of polling:
- Windows network polling. The Administration Server can perform two kinds of Windows network poll: quick and full. During a quick poll, the Administration Server only retrieves information from the list of the NetBIOS names of devices in all network domains and workgroups. During a full poll, more information is requested from each client device, such as operating system name, IP address, DNS name, and NetBIOS name. By default, both quick poll and full poll are enabled. Windows network polling may fail to discover devices, for example, if the ports UDP 137, UDP 138, TCP 139 are closed on the router or by the firewall.
- Domain controller polling. The Administration Server or a distribution point retrieves information about the domain structure and about DNS names of the devices that are included in the domain. By default, this type of polling is enabled. We recommend that you use domain controller polling if all networked devices are members of a domain. If some of the networked devices are not included in the domain, these devices cannot be discovered by domain controller polling.
- IP range polling. The Administration Server polls the specified IP ranges using ICMP packets or the NBNS protocol and compiles a complete set of data on devices within those IP ranges. By default, this type of polling is disabled. It is not recommended to use this type of polling if you use Windows network polling and/or Active Directory polling.
- Zeroconf polling. A distribution point that polls the IPv6 network by using zero-configuration networking (also referred to as Zeroconf). By default, this type of polling is disabled. You can use Zeroconf polling if the distribution point runs Linux.
If you set up and enabled device moving rules, the newly discovered devices are automatically included in the Managed devices group. If no moving rules have been enabled, the newly discovered devices are automatically included in the Unassigned devices group.
You can modify device discovery settings for each type. For example, you may want to modify the polling schedule or to set whether to poll the entire domain forest or only a specific domain.
Before you start network polling, make sure that the SMB protocol is enabled. Otherwise, Kaspersky Security Center cannot discover devices in the polled network. To enable the SMB protocol, follow the instructions for your operating system.
Windows network polling
About Windows network polling
During a quick poll, the Administration Server only retrieves information from the list of the NetBIOS names of devices in all network domains and workgroups. During a full poll, the following information is requested from each client device:
- Operating system name
- IP address
- DNS name
- NetBIOS name
Both quick polls and full polls require the following:
- Ports UDP 137/138, TCP 139, UDP 445, TCP 445 must be available in the network.
- The SMB protocol is enabled.
- The Microsoft Computer Browser service must be used, and the primary browser computer must be enabled on the Administration Server.
- The Microsoft Computer Browser service must be used, and the primary browser computer must be enabled on the client devices:
- On at least one device, if the number of networked devices does not exceed 32.
- On at least one device for each 32 networked devices.
The full poll can run only if the quick poll has run at least once.
Viewing and modifying the settings for Windows network polling
To modify the properties of Windows network polling:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Discovery → Windows domains.
- Click the Properties button.
The Windows domain properties window opens.
- Enable or disable Windows network polling by using the Enable Windows network polling toggle button.
- Configure the poll schedule. By default, the quick polling runs every 15 minutes and the full polling runs every 60 minutes.
Polling schedule options:
- Save the properties of Windows network polling.
The properties are saved and applied to all of the discovered Windows domains and workgroups.
Running the poll manually
To run the poll immediately,
Click Start quick poll or Start full poll.
When the polling is complete, you can view the list of discovered devices on the Windows domains page by selecting the check box next to a domain name, and then clicking the Devices button.
IP range polling
Initially, Kaspersky Security Center gets IP ranges for polling from the network settings of the device on which it is installed. If the device address is 192.168.0.1 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, Kaspersky Security Center includes the network 192.168.0.0/24 in the list of polling address automatically. Kaspersky Security Center polls all addresses from 192.168.0.1 to 192.168.0.254.
It is not recommended to use IP range polling if you use Windows network polling and/or Active Directory polling.
Kaspersky Security Center can poll IP ranges by reverse DNS lookup or by using the NBNS protocol:
- Reverse DNS lookup
Kaspersky Security Center attempts to perform reverse name resolution for every IP address from the specified range to a DNS name using standard DNS requests. If this operation succeeds, the server sends an
ICMP ECHO REQUEST(the same as the ping command) to the received name. If the device responds, the information about it is added to the Kaspersky Security Center database. The reverse name resolution is necessary to exclude the network devices that can have an IP address but are not computers, for example, network printers or routers.This polling method relies upon a correctly configured local DNS service. It must have a reverse lookup zone. In the networks where Active Directory is used, such a zone is maintained automatically. But in these networks, IP subnet polling does not provide more information than Active Directory polling. Moreover, administrators of small networks often do not configure the reverse lookup zone because it is not necessary for the work of many network services. For these reasons, IP subnet polling is disabled by default.
- NBNS protocol
If the reverse name resolution is not possible in your network for some reason, Kaspersky Security Center uses the NBNS protocol to poll the IP ranges. If a request to an IP address returns a NetBIOS name, the information about this device is added to the Kaspersky Security Center database.
Before you start network polling, make sure that the SMB protocol is enabled. Otherwise, Kaspersky Security Center cannot discover devices in the polled network. To enable the SMB protocol, follow the instructions for your operating system.
Viewing and modifying the settings for IP range polling
To view and modify the properties of IP range polling:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Discovery → IP ranges.
- Click the Properties button.
The IP polling properties window opens.
- Enable or disable IP polling by using the Allow polling toggle button.
- Configure the poll schedule. By default, IP polling runs every 420 minutes (seven hours).
When specifying the polling interval, make sure that this setting does not exceed the value of the IP address lifetime parameter. If an IP address is not verified by polling during the IP address lifetime, this IP address is automatically removed from the polling results. By default, the life span of the polling results is 24 hours, because dynamic IP addresses (assigned using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)) change every 24 hours.
Polling schedule options:
- Click the Save button.
The properties are saved and applied to all IP ranges.
Running the poll manually
To run the poll immediately,
click Start poll.
Adding and modifying an IP range
Initially, Kaspersky Security Center gets IP ranges for polling from the network settings of the device on which it is installed. If the device address is 192.168.0.1 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, Kaspersky Security Center includes the network 192.168.0.0/24 in the list of polling address automatically. Kaspersky Security Center polls all addresses from 192.168.0.1 to 192.168.0.254. You can modify the automatically defined IP ranges or add custom IP ranges.
You can create a range only for IPv4 addresses. If you enable Zeroconf polling, Kaspersky Security Center will poll the whole network.
To add a new IP range:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Discovery → IP ranges.
- To add a new IP range, click the Add button.
- In the window that opens, specify the following settings:
- Select Enable IP range polling if you want to poll the subnet or interval that you have added. Otherwise, the subnet or interval that you have added will not be polled.
- Click the Save button.
The new IP range is added to the list of IP ranges.
You can run polling of each IP range separately by using the Start poll button. When the polling is complete, you can view the list of discovered devices by using the Devices button. By default, the life span of the polling results is 24 hours and it is equal to the IP address lifetime setting.
To add a subnet to an existing IP range:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Discovery → IP ranges.
- Click the name of the IP range to which you want to add a subnet.
- In the window that opens, click the Add button.
- Specify a subnet by using either its address and mask, or by using the first and last IP address in the IP range. Or, add an existing subnet by clicking the Browse button.
- Click the Save button.
The new subnet is added to the IP range.
- Click the Save button.
The new settings of the IP range are saved.
You can add as many subnets as you need. Named IP ranges are not allowed to overlap, but unnamed subnets inside an IP range have no such restrictions. You can enable and disable polling independently for every IP range.
Zeroconf polling
This polling type is supported only for Linux-based distribution points.
A distribution point can poll networks that have devices with IPv6 addresses. In this case, IP ranges are not specified and the distribution point polls the whole network by using zero-configuration networking (referred to as Zeroconf). To start using Zeroconf, you must install the avahi-browse utility on the distribution point.
To enable IPv6 network polling:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Discovery → IP ranges.
- Click the Properties button.
- In the window that opens, switch on the Use Zeroconf to poll IPv6 networks toggle button.
After that, the distribution point starts to poll your network. In this case, the specified IP ranges are ignored.
Page top
Domain controller polling
Kaspersky Security Center supports polling of a Microsoft Active Directory domain controller and a Samba domain controller.
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to poll a Samba domain controller only by using a Linux distribution point. For a Samba domain controller, Samba 4 is used as an Active Directory domain controller.
When you poll a domain controller, Administration Server or a distribution point retrieves information about the domain structure, user accounts, security groups, and DNS names of the devices that are included in the domain.
We recommend using domain controller polling if all networked devices are members of a domain. If some of the networked devices are not included in the domain, these devices cannot be discovered by domain controller polling.
Prerequisites
Before you poll a domain controller, ensure that you allow connections to the domain controller through a firewall or a proxy server. Also ensure that the following protocols are enabled on the domain controller:
- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
- Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL)
This protocol is used if connection to the domain controller is established by using the SASL authentication. Administration Server and distribution points supports only the DIGEST-MD5 mechanism.
- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol over Secure Sockets Layer (LDAPS)
This protocol is used if you need to connect to the domain controller over an encrypted connection.
Ensure that the following ports are available on the domain controller device:
- 389 for the LDAP protocol and Simple Authentication (including SASL)
- 636 for the LDAPS protocol
Domain controller polling by using Administration Server
You can use Administration Server to poll only a Microsoft Active Directory domain controller.
To poll a domain controller by using Administration Server:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Discovery → Domain controllers.
- Click Polling settings.
The Domain controller polling settings window opens.
- Select the Enable domain controller polling option.
- In the Advanced settings section, specify the polling scope:
- Poll current domain
Select this option to poll a domain to which the Kaspersky Security Center belongs.
- Poll entire domain forest
Select this option to poll a domain forest to which the Kaspersky Security Center belongs.
- Poll specified domains
Select this option to poll a domain with specified address and user credentials.
- Poll current domain
- If necessary, specify the polling schedule. The default period is one hour. The data received at the next polling completely replaces old data.
The following polling schedule options are available:
- Every N days
- Every N minutes
- By days of week
- Every month on specified days of selected weeks
- Run missed tasks
If you change user accounts in a security group of the domain, these changes will be displayed in Kaspersky Security Center an hour after you poll the domain controller.
- Click Save to apply changes.
- If you want to perform the poll immediately, click the Start poll button.
Domain controller polling by using a distribution point
You can also poll a Microsoft Active Directory domain controller and a Samba domain controller by using a distribution point. A Windows- or Linux-based managed device can act as a distribution point.
For a Linux distribution point, polling of a Microsoft Active Directory domain controller and a Samba domain controller are supported.
For a Windows distribution point, only polling of a Microsoft Active Directory domain controller is supported.
Polling with a Mac distribution point is not supported.
To configure domain controller polling by using the distribution point:
- Open the distribution point properties.
- Select the Domain controller polling section.
- Select the Enable domain controller polling option.
- Select the domain controller that you want to poll.
If you use a Linux distribution point, in the Poll specified domains section, click Add, and then specify the address and user credentials of the domain controller.
If you use a Windows distribution point, you can select one of the following options:
- Poll current domain
- Poll entire domain forest
- Poll specified domains
- Click the Set polling schedule button to specify the polling schedule options if needed.
Polling starts only according to the specified schedule. Manual start of polling is not available.
After the polling is completed, the domain structure will be displayed in the Domain controllers section.
If you set up and enabled device moving rules, the newly discovered devices are automatically included in the Managed devices group. If no moving rules have been enabled, the newly discovered devices are automatically included in the Unassigned devices group.
The discovered user accounts can be used for domain authentication in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Authentication and connection to a domain controller
Authentication and connection to a domain controller when polling a domain
When polling a domain controller by using a Linux distribution point, the distribution point identifies the connection protocol to establish the initial connection to the domain controller. This protocol is used for all future connections to the domain controller. When establishing the initial connection to the domain controller, you can change connection options by using the Network Agent flags KLNAG_LDAP_TLS_REQCERT and KLNAG_LDAP_SSL_CACERT. You can configure the Network Agent flags by using klscflag, as described in this article.
The initial connection to a domain controller proceeds as follows:
- A Linux distribution point attempts to connect to the domain controller over LDAPS.
By default, certificate verification is not required. Set the
KLNAG_LDAP_TLS_REQCERTflag to 1 to enforce certificate verification.Possible values of the
KLNAG_LDAP_TLS_REQCERTflag:0—The certificate is requested, but if it is not provided or the certificate verification failed, then the TLS connection is still considered successfully created (default value).1—Strict verification of the LDAP server certificate is required.
By default, when the
KLNAG_LDAP_SSL_CACERTflag is not specified, the OS-dependent path to the certificate authority (CA) is used to access the certificate chain. Use theKLNAG_LDAP_SSL_CACERTflag to specify a custom path. - If the LDAPS connection fails, a Linux distribution point attempts to connect to the domain controller over a non-encrypted TCP connection by using SASL (DIGEST-MD5).
Configuring flags
You can use the klscflag utility to configure flags.
On a Linux distribution point, run the command line, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. By default, on the Linux distribution point, the klscflag utility is located in /opt/kaspersky/ksc64/sbin.
For example, the following command enforces certificate verification:
klscflag -fset -pv klnagent -n KLNAG_LDAP_TLS_REQCERT -t d -v 1
Configuring a Samba domain controller
Kaspersky Security Center supports a Linux domain controller running only on Samba 4.
A Samba domain controller supports the same schema extensions as a Microsoft Active Directory domain controller. You can enable full compatibility of a Samba domain controller with a Microsoft Active Directory domain controller by using the Samba 4 schema extension. This is an optional action.
We recommend enabling full compatibility of a Samba domain controller with a Microsoft Active Directory domain controller. This will ensure the correct interaction between Kaspersky Security Center and the Samba domain controller.
To enable full compatibility of a Samba domain controller with a Microsoft Active Directory domain controller:
- Execute the following command to use the RFC2307 schema extension:
samba-tool domain provision --use-rfc2307 --interactive - Enable the schema update in a Samba domain controller. To do this, add the following line to the
/etc/samba/smb.conffile:dsdb:schema update allowed = trueIf the schema update completes with an error, you need to perform a full restore of the domain controller that acts as a schema master.
If you want to poll a Samba domain controller correctly, you have to specify the netbios name and workgroup parameters in the /etc/samba/smb.conf file.
Configuring retention rules for unassigned devices
After Windows network polling is complete, the found devices are placed into subgroups of the Unassigned devices administration group. This administration group can be found at Discovery & deployment → Discovery → Windows domains. The Windows domains folder is the parent group. It contains child groups named after the corresponding domains and workgroups that have been found during the poll. The parent group may also contain the administration group of mobile devices. You can configure the retention rules of the unassigned devices for the parent group and for each of the child groups. The retention rules do not depend on the device discovery settings and work even if the device discovery is disabled.
The device retention rules do not affect the devices that have one or more drives encrypted with full disk encryption. Such devices are not deleted automatically—you can only delete them manually. If you need to delete a device with an encrypted drive, first decrypt the drive, and then delete the device.
To configure retention rules for unassigned devices:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Discovery → Windows domains.
- Do one of the following:
- To configure settings of the parent group, click the Properties button.
The Windows domain properties window opens.
- To configure settings of a child group, click its name.
The child group properties window opens.
- To configure settings of the parent group, click the Properties button.
- Define the following settings:
- Click the Accept button.
Your changes are saved and applied.
Kaspersky applications: licensing and activation
This section describes the features of Kaspersky Security Center related to working with the license keys of managed Kaspersky applications.
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to perform centralized distribution of license keys for Kaspersky applications on client devices, monitor their use, and renew licenses.
When adding a license key using Kaspersky Security Center, the settings of the license key are saved on the Administration Server. Based on this information, the application generates a license key usage report and notifies the administrator of license expirations and violation of license restrictions that are set in the properties of license keys. You can configure notifications of the use of license keys within the Administration Server settings.
Licensing of managed applications
The Kaspersky applications installed on managed devices must be licensed by applying a key file or activation code to each of the applications. A key file or activation code can be deployed in the following ways:
- Automatic deployment
- The installation package of a managed application
- The Add license key task for a managed application
- Manual activation of a managed application
You can add a new active or reserve license key by any of the methods listed above. A Kaspersky application uses an active key at the current moment and stores a reserve key to apply after the active key expires. The application for which you add a license key defines whether the key is active or reserve. The key definition does not depend on the method that you use to add a new license key.
Automatic deployment
If you use different managed applications and you have to deploy a specific key file or activation code to devices, opt for other ways of deploying that activation code or key file.
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to automatically deploy available license keys to devices. For example, three license keys are stored in the Administration Server repository. You have selected the Automatically distribute license key to managed devices check box for all three license keys. A Kaspersky security application—for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows—is installed on the organization's devices. A new device is discovered to which a license key must be deployed. The application determines, for instance, that two of the license keys from the repository can be deployed to the device: license key named Key_1 and license key named Key_2. One of these license keys is deployed to the device. In this case, it cannot be predicted which of the two license keys will be deployed to the device because automatic deployment of license keys does not provide for any administrator activity.
When a license key is deployed, the devices are recounted for that license key. You must make sure that the number of devices to which the license key was deployed does not exceed the license limit. If the number of devices exceeds the license limit, all devices that were not covered by the license will be assigned Critical status.
Before deployment, the key file or activation code must be added to the Administration Server repository.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console:
or
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
Note that an automatically distributed license key may not be displayed in the virtual Administration Server repository in the following cases:
- The license key is not valid for the application.
- The virtual Administration Server does not have managed devices.
- The license key has already been used for devices managed by another virtual Administration Server and the limit on the number of devices has been reached.
Adding a key file or activation code to the installation package of a managed application
For security reasons, this option is not recommended. A key file or activation code added to an installation package may be compromised.
If you install a managed application using an installation package, you can specify an activation code or key file in this installation package or in the policy of the application. The license key will be deployed to managed devices at the next synchronization of the device with the Administration Server.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console:
or
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Adding a license key to an installation package
Deployment through the Add license key task for a managed application
If you opt for using the Add license key task for a managed application, you can select the license key that must be deployed to devices and select the devices in any convenient way—for example, by selecting an administration group or a device selection.
Before deployment, the key file or activation code must be added to the Administration Server repository.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console:
- Adding a license key to the Administration Server repository
- Deploying a license key to client devices
or
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
Adding an activation code or a key file manually to the devices
You can activate the installed Kaspersky application locally, by using the tools provided in the application interface. Please refer to the documentation of the installed application.
Adding a license key to the Administration Server repository
To add a license key to the Administration Server repository:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Licensing → Kaspersky licenses.
- Click the Add button.
- Choose what you want to add:
- Add key file
Click the Select key file button and browse to the .key file that you want to add.
- Enter activation code
Specify the activation code in the text field and click the Send button.
- Add key file
- Click the Close button.
The license key or several license keys are added to the Administration Server repository.
Adding an Administration Server license key
To add an Administration Server license key:
- In the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window that opens, select the License keys section.
- In the Active license key section, click the Edit button.
- In the window that opens, add a license key by clicking the Add button.
The Add license key wizard starts.
After the wizard is finished, you can check if the features are displayed in the Administration Console according to the corresponding license.
Page top
Deploying a license key to client devices
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console allows you to distribute a license key to client devices automatically or through the Application activation task. You can use the task to distribute keys to a specific device group. During distribution of a license key via the task, the licensing limit on the number of devices is not taken into account. Use the automatic key distribution to cease distribution of a license key automatically when the licensing limit is reached.
If you enable automatic distribution of a license key, do not create an Application activation task to distribute that key to client devices. Otherwise, the load on the Administration Server will increase due to frequent synchronization.
Before deployment, add the license key to the Administration Server repository.
To distribute a license key to client devices through the Application activation task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- In the Application drop-down list, select the application for which you want to add a license key.
- In the Task type list, select the Application activation task.
- In the Task name field, specify the name of the new task.
- Select the devices to which the task will be assigned.
- At the Selecting a license key step of the wizard, click the Add key link to add the license key.
- On the key adding pane, add the license key by using one of the following options:
You need to add the license key only if you did not add it to the Administration Server repository prior to creating the Application activation task.
- Select the Enter activation code option to enter an activation code, and then do the following:
- Specify the activation code, and then click the Send button.
Information about the license key appears in the key adding pane.
- Click the Save button.
If you want to distribute the license key to managed devices automatically, enable the Automatically distribute license key to managed devices option.
The key adding pane closes.
- Specify the activation code, and then click the Send button.
- Select the Add key file option to add a key file, and then do the following:
- Click the Select key file button.
- In the window that opens, select a key file, and then click the Open button.
Information about the license key appears in the license key adding pane.
- Click the Save button.
If you want to distribute the license key to managed devices automatically, enable the Automatically distribute license key to managed devices option.
The key adding pane closes.
- Select the Enter activation code option to enter an activation code, and then do the following:
- Select the license key in the table of keys.
- At the License information step of the wizard, clear the default Use as a reserve key check box if you want to replace the active license key.
For example, this is needed when the organization changes, and another organization's key is required on the device; or if the key was reissued, and a new license expires earlier than the current license. To avoid errors, you have to clear the Use as a reserve key check box.
If you want to find out more information about the issues that may occur when adding a license key to Kaspersky Security Center and the ways to resolve them, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Knowledge Base.
- At the Finish task creation step of the wizard, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option to modify the default task settings.
If you do not enable this option, the task will be created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later.
- Click the Finish button.
The wizard creates the task. If you enabled the Open task details when creation is complete option, the task properties window automatically opens. In this window, you can specify the general task settings and, if required, change the settings specified during task creation.
You can also open the task properties window by clicking the name of the created task in the list of tasks.
The task is created, configured, and displayed in the list of tasks.
- To run the task, select it in the task list, and then click the Start button.
You can also set a task start schedule on the Schedule tab of the task properties window.
For a detailed description of scheduled start settings, refer to the general task settings.
After the task is completed, the license key is deployed to the selected devices.
Automatic distribution of a license key
Kaspersky Security Center allows automatic distribution of license keys to managed devices if they are located in the license keys repository on the Administration Server.
To distribute a license key to managed devices automatically:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Licensing → Kaspersky licenses.
- Click the name of the license key that you want to distribute to devices automatically.
- In the license key properties window that opens, select the Automatically distribute license key to managed devices check box.
- Click the Save button.
The license key is automatically distributed to all compatible devices.
License key distribution is performed by means of Network Agent. No license key distribution tasks are created for the application.
During automatic distribution of a license key, the licensing limit on the number of devices is taken into account. The licensing limit is set in the properties of the license key. If the licensing limit is reached, distribution of this license key on devices ceases automatically.
Note that an automatically distributed license key may not be displayed in the virtual Administration Server repository in the following cases:
- The license key is not valid for the application.
- The virtual Administration Server does not have managed devices.
- The license key has already been used for devices managed by another virtual Administration Server and the limit on the number of devices has been reached.
The virtual Administration Server automatically distributes license keys from its repository and from the repository of the Administration Server. We recommend that you:
- Use the Add license key task to select the license key that must be deployed to devices.
- Avoid disabling the Allow automatic deployment of license keys from this virtual Administration Server to its devices option in the virtual Administration Server settings. Otherwise, the virtual Administration Server will not distribute license keys to devices, including the license keys from the Administration Server repository.
If you select the Automatically distribute license key to managed devices check box in the license key properties window, a license key is distributed on your network immediately. If you do not select this option, you can use a task to distribute a license key later.
Automatic distribution of license keys configured on the primary Administration Server does not extend to devices managed by non-virtual secondary Administration Servers.
Viewing information about license keys in use
To view the list of the license keys added to the Administration Server repository:
In the main menu, go to Operations → Licensing → Kaspersky licenses.
The displayed list contains the key files and activation codes added to the Administration Server repository.
To view detailed information about a license key:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Licensing → Kaspersky licenses.
- Click the name of the required license key.
In the license key properties window that opens, you can view:
- On the General tab—The main information about the license key
- On the Devices tab—The list of client devices where the license key was used for activation of the installed Kaspersky application
To view which license keys are deployed to a specific client device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click the name of the required device.
- In the device properties window that opens, select the Applications tab.
- Click the name of the application for which you want to view the information about the license key.
- In the application properties window that opens, select the General tab, and then open the License section.
The main information about the active and reserve license keys is displayed.
To define the up-to-date settings of virtual Administration Server license keys, the Administration Server sends a request to Kaspersky activation servers at least once per day. If access to the servers using system DNS is not possible, the application uses public DNS servers.
Deleting a license key from the repository
When you delete the active license key for an additional feature of Administration Server, for example Vulnerability and patch management or Mobile Device Management, the corresponding feature becomes unavailable. If a reserve license key has been added, the reserve license key automatically becomes the active license key after the former active license key is deleted.
When you delete the active license key deployed to a managed device, the application will continue working on the managed device.
To delete a key file or activation code from the Administration Server repository:
- Check that Administration Server does not use a key file or activation code that you want to delete. If the Administration Server does, you cannot delete the key. To perform the check:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the License keys section.
- If the required key file or activation code is displayed in the section that opens, click the Remove active license key button, and then confirm the operation. After that, the Administration Server does not use the deleted license key, but the key remains in the Administration Server repository. If the required key file or activation code is not displayed, the Administration Server does not use it.
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Licensing → Kaspersky licenses.
- Select the required key file or activation code, and then click the Delete button.
The selected key file or activation code is deleted from the repository.
You can add a deleted license key again or add a new license key.
Revoking consent with an End User License Agreement
If you decide to stop protecting some of your client devices, you can revoke the End User License Agreement (EULA) for any managed Kaspersky application. You must uninstall the selected application before revoking its EULA.
The EULAs that were accepted on a virtual Administration Server can be revoked on the virtual Administration Server or on the primary Administration Server. The EULAs that were accepted on a primary Administration Server can be revoked only on the primary Administration Server.
To revoke a EULA for managed Kaspersky applications:
- Open the Administration Server properties window and on the General tab select the End User License Agreements section.
A list of EULAs—accepted upon creation of installation packages, at the seamless installation of updates, or upon deployment of Kaspersky Security for Mobile—is displayed.
- In the list, select the EULA that you want to revoke.
You can view the following properties of the EULA:
- Date when the EULA was accepted
- Name of the user who accepted the EULA
- Click the acceptance date of any EULA to open its properties window that displays the following data:
- Name of the user who accepted the EULA
- Date when the EULA was accepted
- Unique identifier (UID) of the EULA
- Full text of the EULA
- List of objects (installation packages, seamless updates, mobile apps) linked to the EULA, and their respective names and types
- In the lower part of the EULA properties window, click the Revoke License Agreement button.
If there exist any objects (installation packages and their respective tasks) that prevent the EULA from being revoked, the corresponding notification is displayed. You cannot proceed with revocation until you delete these objects.
In the window that opens, you are informed that you must first uninstall the Kaspersky application corresponding to the EULA.
- Click the button to confirm revocation.
The EULA is revoked. It is no longer displayed in the list of License Agreements in the End User License Agreements section. The EULA properties window closes; the application is no longer installed.
Renewing licenses for Kaspersky applications
You can renew a Kaspersky application license that has expired or is about to expire (in less than 30 days).
To renew an expired license or a license that is about to expire:
- Do either of the following:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Licensing → Kaspersky licenses.
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Dashboard, and then click the View expiring licenses link next to a notification.
The Kaspersky licenses window opens, where you can view and renew licenses.
- Click the Renew license link next to the required license.
By clicking a license renewal link, you agree to transfer to Kaspersky the following information about Kaspersky Security Center: its version, the localization you are using, the software license ID (that is, the ID of the license you are renewing), and whether you purchased the license via a partner company or not.
- In the window of the license renewal service that opens follow the instructions to renew a license.
The license is renewed.
In Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, the notifications are displayed when a license is about to expire, according to the following schedule:
- 30 days before the expiration
- 7 days before the expiration
- 3 days before the expiration
- 24 hours before the expiration
- When a license has expired
Using Kaspersky Marketplace to choose Kaspersky business solutions
Marketplace is a section in the main menu that enables you to view the entire range of Kaspersky business solutions, select the ones you need, and proceed to the purchase at the Kaspersky website. You can use filters to view only those solutions that fit your organization and the requirements for your information security system. When you select a solution, Kaspersky Security Center redirects you to the related webpage at the Kaspersky website to learn more about that solution. Each webpage enables you to proceed to the purchase or contains instructions on the purchase process.
In the Marketplace section, you can filter Kaspersky solutions by using the following criteria:
- Number of devices (endpoints, servers, and other types of assets) that you want to protect:
- 50–250
- 250–1000
- More than 1000
- Maturity level of your organization's information security team:
- Foundations
This level is typical for enterprises that only have an IT team. The maximum possible number of threats is blocked automatically.
- Optimum
This level is typical for enterprises that have a specific IT security function within the IT team. At this level, companies require solutions that enable them to counter commodity threats and threats that circumvent existing preventive mechanisms.
- Expert
This level is typical for enterprises with complex and distributed IT environments. The IT security team is mature or the company has an SOC (Security Operations Center) team. The required solutions enable the companies to counter complex threats and targeted attacks.
- Foundations
- Types of assets that you want to protect:
- Endpoints: workstations of employees, physical and virtual machines, embedded systems
- Servers: physical and virtual servers
- Cloud: public, private, or hybrid cloud environments; cloud services
- Network: local area network, IT infrastructure
- Service: security-related services provided by Kaspersky
To find and purchase a Kaspersky business solution:
- In the main menu, go to Marketplace.
By default, the section displays all available Kaspersky business solutions.
- To view only those solutions that suit your organization, select the required values in the filters.
- Click the solution that you want to purchase or you want to learn more about.
You will be redirected to the solution webpage. You can follow the on-screen instructions to proceed to the purchase.
Configuring network protection
This section contains information about manual configuration of policies and tasks, about user roles, about building an administration group structure and hierarchy of tasks.
Scenario: Configuring network protection
The quick start wizard creates policies and tasks with the default settings. These settings may turn out to be sub-optimal or even disallowed by the organization. Therefore, we recommend that you fine-tune these policies and tasks and create other policies and tasks, if they are necessary for your network.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that you have done the following:
- Installed Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server
- Installed Kaspersky Security Center Web Console (optional)
- Completed the Kaspersky Security Center main installation scenario
- Completed the quick start wizard or manually created the following policies and tasks in the Managed devices administration group:
- Policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Group task for updating Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Policy of Network Agent
- Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
Configuring network protection proceeds in stages:
- Setup and propagation of Kaspersky application policies and policy profiles
To configure and propagate settings for Kaspersky applications installed on the managed devices, you can use two different security management approaches—device-centric or user-centric. These two approaches can also be combined. To implement device-centric security management, you can use tools provided in Microsoft Management Console-based Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. User-centric security management can be implemented through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console only.
- Configuring tasks for remote management of Kaspersky applications
Check the tasks created with the quick start wizard and fine-tune them, if necessary.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console:
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
If necessary, create additional tasks to manage the Kaspersky applications installed on the client devices.
- Evaluating and limiting the event load on the database
Information about events that occur during the operation of managed applications is transferred from a client device and registered in the Administration Server database. To reduce the load on the Administration Server, evaluate and limit the maximum number of events that can be stored in the database.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Setting the maximum number of events
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Setting the maximum number of events
Results
Upon completion of this scenario, your network will be protected by configuration of Kaspersky applications, tasks, and events received by the Administration Server:
- The Kaspersky applications are configured according to the policies and policy profiles.
- The applications are managed through a set of tasks.
- The maximum number of events that can be stored in the database is set.
When the network protection configuration is complete, you can proceed to configuring regular updates to Kaspersky databases and applications.
For details about how to configure automatic responses to threats detected by Kaspersky Sandbox, please refer to the Kaspersky Sandbox 2.0 Online Help.
About device-centric and user-centric security management approaches
You can manage security settings from the standpoint of device features and from the standpoint of user roles. The first approach is called device-centric security management and the second is called user-centric security management. To apply different application settings to different devices you can use either or both types of management in combination. To implement device-centric security management, you can use tools provided in Microsoft Management Console-based Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. User-centric security management can be implemented through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console only.
Device-centric security management enables you to apply different security application settings to managed devices depending on device-specific features. For example, you can apply different settings to devices allocated in different administration groups. You can also differentiate the devices by usage of those devices in Active Directory, or their hardware specifications.
User-centric security management enables you to apply different security application settings to different user roles. You can create several user roles, assign an appropriate user role to each user, and define different application settings to the devices owned by users with different roles. For example, you may want to apply different application settings to devices of accountants and human resources (HR) specialists. As a result, when user-centric security management is implemented, each department—accounts department and HR department—has its own settings configuration for Kaspersky applications. A settings configuration defines which application settings can be changed by users and which are forcibly set and locked by the administrator.
By using user-centric security management you can apply specific application settings to individual users. This may be required when an employee has a unique role in the company or when you want to monitor security issues related to devices of a specific person. Depending on the role of this employee in the company, you can expand or limit the rights of this person to change application settings. For example, you might want to expand the rights of a system administrator who manages client devices in a local office.
You can also combine the device-centric and user-centric security management approaches. For example, you can configure a specific application policy for each administration group, and then create policy profiles for one or several user roles of your enterprise. In this case the policies and policy profiles are applied in the following order:
- The policies created for device-centric security management are applied.
- They are modified by the policy profiles according to the policy profile priorities.
- The policies are modified by the policy profiles associated with user roles.
Policy setup and propagation: Device-centric approach
When you complete this scenario, the applications will be configured on all of the managed devices in accordance with the application policies and policy profiles that you define.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that you have installed Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console (optional). If you installed Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you might also want to consider user-centric security management as an alternative or additional option to the device-centric approach.
Stages
The scenario of device-centric management of Kaspersky applications consists of the following steps:
- Configuring application policies
Configure settings for Kaspersky applications installed on the managed devices by creating a policy for each application. The set of policies will be propagated to the client devices.
When you configure the protection of your network in the quick start wizard, Kaspersky Security Center creates the default policy for the following applications:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows—for Windows-based client devices
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux—for Linux-based client devices
If you completed the configuration process by using this wizard, you do not have to create a new policy for this application. Proceed to the manual setup of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
If you have a hierarchical structure of several Administration Servers and/or administration groups, the secondary Administration Servers and child administration groups inherit the policies from the primary Administration Server by default. You can force the inheritance by the child groups and secondary Administration Servers to prohibit any modifications of the settings configured in the upstream policy. If you want only part of the settings to be forcibly inherited, you can lock them in the upstream policy. The rest unlocked settings will be available for modification in the downstream policies. The created hierarchy of policies will allow you to effectively manage devices in the administration groups.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Creating a policy
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating a policy
- Creating policy profiles (optional)
If you want devices within a single administration group to run under different policy settings, create policy profiles for those devices. A policy profile is a named subset of policy settings. This subset is distributed on target devices together with the policy, supplementing it under a specific condition called the profile activation condition. Profiles only contain settings that differ from the "basic" policy, which is active on the managed device.
By using profile activation conditions, you can apply different policy profiles, for example, to the devices located in a specific unit or security group of Active Directory, having a specific hardware configuration, or marked with specific tags. Use tags to filter devices that meet specific criteria. For example, you can create a tag called Windows, mark all devices running Windows operating system with this tag, and then specify this tag as an activation condition for a policy profile. As a result, Kaspersky applications installed on all devices running Windows will be managed by their own policy profile.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console:
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
- Propagating policies and policy profiles to the managed devices
By default, the Administration Server automatically synchronizes with managed devices every 15 minutes. You can circumvent auto-synchronization and run the synchronization manually by using the Force synchronization command. Also the synchronization is forced after you create or change a policy or a policy profile. During the synchronization, the new or changed policies and policy profiles are propagated to the managed devices.
If you use Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you can check whether the policies and policy profiles were delivered to a device. Kaspersky Security Center specifies the delivery date and time in the properties of the device.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Forced synchronization
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Forced synchronization
Results
When the device-centric scenario is complete, the Kaspersky applications are configured according to the settings specified and propagated through the hierarchy of policies.
The configured application policies and policy profiles will be applied automatically to the new devices added to the administration groups.
Policy setup and propagation: User-centric approach
This section describes the scenario of user-centric approach to the centralized configuration of Kaspersky applications installed on the managed devices. When you complete this scenario, the applications will be configured on all of the managed devices in accordance with the application policies and policy profiles that you define.
This scenario can be implemented through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console version 13 or later.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that you have successfully installed Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, and completed the main installation scenario. You might also want to consider device-centric security management as an alternative or additional option to the user-centric approach. Learn more about two management approaches.
Process
The scenario of user-centric management of Kaspersky applications consists of the following steps:
- Configuring application policies
Configure settings for Kaspersky applications installed on the managed devices by creating a policy for each application. The set of policies will be propagated to the client devices.
When you configure the protection of your network in quick start wizard, Kaspersky Security Center creates the default policy for Kaspersky Endpoint Security. If you completed the configuration process by using this wizard, you do not have to create a new policy for this application. Proceed to the manual setup of Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
If you have a hierarchical structure of several Administration Servers and/or administration groups, the secondary Administration Servers and child administration groups inherit the policies from the primary Administration Server by default. You can force the inheritance by the child groups and secondary Administration Servers to prohibit any modifications of the settings configured in the upstream policy. If you want only part of the settings to be forcibly inherited, you can lock them in the upstream policy. The rest unlocked settings will be available for modification in the downstream policies. The created hierarchy of policies will allow you to effectively manage devices in the administration groups.
How-to instructions: Creating a policy
- Specifying owners of the devices
Assign the managed devices to the corresponding users.
How-to instructions: Assigning a user as a device owner
- Defining user roles typical for your enterprise
Think about different kinds of work that the employees of your enterprise typically perform. You must divide all employees in accordance with their roles. For example, you can divide them by departments, professions, or positions. After that you will need to create a user role for each group. Keep in mind that each user role will have its own policy profile containing application settings specific for this role.
- Creating user roles
Create and configure a user role for each group of employees that you defined on the previous step or use the predefined user roles. The user roles will contain set of rights of access to the application features.
How-to instructions: Creating a user role
- Defining the scope of each user role
For each of the created user roles, define users and/or security groups and administration groups. Settings associated with a user role apply only to devices that belong to users who have this role, and only if these devices belong to groups associated with this role, including child groups.
How-to instructions: Editing the scope of a user role
- Creating policy profiles
Create a policy profile for each user role in your enterprise. The policy profiles define which settings will be applied to the applications installed on users' devices depending on the role of each user.
How-to instructions: Creating a policy profile
- Associating policy profiles with the user roles
Associate the created policy profiles with the user roles. After that: the policy profile becomes active for a user that has the specified role. The settings configured in the policy profile will be applied to the Kaspersky applications installed on the user's devices.
How-to instructions: Associating policy profiles with roles
- Propagating policies and policy profiles to the managed devices
By default, the Administration Server automatically synchronizes with managed devices every 15 minutes. During the synchronization, the new or changed policies and policy profiles are propagated to the managed devices. You can circumvent auto-synchronization and run the synchronization manually by using the Force synchronization command. When synchronization is complete, the policies and policy profiles are delivered and applied to the installed Kaspersky applications.
You can check whether the policies and policy profiles were delivered to a device. Kaspersky Security Center specifies the delivery date and time in the properties of the device.
How-to instructions: Forced synchronization
Results
When the user-centric scenario is complete, the Kaspersky applications are configured according to the settings specified and propagated through the hierarchy of policies and policy profiles.
For a new user, you will have to create a new account, assign the user one of the created user roles, and assign the devices to the user. The configured application policies and policy profiles will be automatically applied to the devices of this user.
Network Agent policy settings
To configure the Network Agent policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the name of the Network Agent policy.
The properties window of the Network Agent policy opens.
See the comparison table detailing how the settings below apply, depending on the type of operating system used.
General
On this tab, you can modify the policy status and specify the inheritance of policy settings:
- Under Policy status, you can select one of the policy modes:
- In the Settings inheritance settings group, you can configure the policy inheritance:
Event configuration
On this tab, you can configure event logging and event notification. Events are distributed according to importance level in the following sections on the Event configuration tab:
- Functional failure
- Warning
- Info
In each section, the event type list shows the types of events and the default event storage term on the Administration Server (in days). After you click the event type, you can specify the settings of event logging and notifications about events selected in the list. By default, common notification settings specified for the entire Administration Server are used for all event types. However, you can change specific settings for required event types.
For example, in the Warning section, you can configure the Security issue has occurred event type. Such events may happen, for instance, when the free disk space of a distribution point is less than 2 GB (at least 4 GB are required to install applications and download updates remotely). To configure the Security issue has occurred event, click it and specify where to store the occurred events and how to notify about them.
If Network Agent detected a security issue, you can manage this issue by using the settings of a managed device.
Application settings
Settings
In the Settings section, you can configure the Network Agent policy:
- Distribute files through distribution points only
- Maximum size of event queue, in MB
- Application is allowed to retrieve policy's extended data on device
- Protect the Network Agent service against unauthorized removal or termination, and prevent changes to the settings
- Use uninstallation password
Repositories
In the Repositories section, you can select the types of objects whose details will be sent from Network Agent to Administration Server. If modification of some settings in this section is prohibited by the Network Agent policy, you cannot modify these settings.
- Details of installed applications
- Include information about patches
- Details of Windows Update updates
- Details of software vulnerabilities and corresponding updates
- Hardware registry details
Software updates and vulnerabilities
In the Software updates and vulnerabilities section, you can configure search and distribution of Windows updates, as well as enable scanning of executable files for vulnerabilities:
- Use Administration Server as a WSUS server
- You can limit Windows updates that users can install on their devices manually by using Windows Update.
On devices running Windows 10, if Windows Update has already found updates for the device, the new option that you select under Allow users to manage installation of Windows Update updates will be applied only after the updates found are installed.
Select an item in the drop-down list:
- In the Windows Update search mode settings group, you can select the update search mode:
- Scan executable files for vulnerabilities when running them
Restart management
In the Restart management section, you can specify the action to be performed if the operating system of a managed device has to be restarted for correct use, installation, or uninstallation of an application:
- Do not restart the operating system
- Restart the operating system automatically if necessary
- Prompt user for action
Windows Desktop Sharing
In the Windows Desktop Sharing section, you can enable and configure the audit of the administrator's actions performed on a remote device when desktop access is shared:
Manage patches and updates
In the Manage patches and updates section, you can configure download and distribution of updates, as well as installation of patches, on managed devices:
- Automatically install applicable updates and patches for components that have the Undefined status
- Download updates and anti-virus databases from Administration Server in advance (recommended)
Connectivity
The Connectivity section includes three subsections:
- Network
- Connection profiles
- Connection schedule
In the Network subsection, you can configure the connection to Administration Server, enable the use of a UDP port, and specify the UDP port number.
- In the Connect to Administration Server settings group, you can configure connection to the Administration Server and specify the time interval for synchronization between client devices and the Administration Server:
- Use UDP port
- UDP port number
- Use the distribution point to force a connection to Administration Server
In the Connection profiles subsection, you can specify the network location settings and enable out-of-office mode when Administration Server is not available:
- Network location settings
- Administration Server connection profiles
- Enable out-of-office mode when Administration Server is not available
In the Connection schedule subsection, you can specify the time intervals during which Network Agent sends data to the Administration Server:
Network polling by distribution points
In the Network polling by distribution points section, you can configure automatic polling of the network. You can use the following options to enable the polling and set its frequency:
Network settings for distribution points
In the Network settings for distribution points section, you can specify the internet access settings:
- Use proxy server
- Address
- Port number
- Bypass proxy server for local addresses
- Proxy server authentication
- User name
- Password
KSN Proxy (distribution points)
In the KSN Proxy (distribution points) section, you can configure the application to use the distribution point to forward Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) requests from the managed devices:
- Enable KSN Proxy on the distribution point side
- Forward KSN requests to Administration Server
- Access KSN Cloud/KPSN directly over the internet
- Port
- UDP port
Updates (distribution points)
In the Updates (distribution points) section, you can enable the downloading diff files feature, so distribution points take updates in the form of diff files from Kaspersky update servers.
Local account management (Linux only)
The Local account management (Linux only) section includes three subsections:
- User certificates management
- Add or edit applicable local administrator groups
- Upload a reference file to protect the sudoers file on the user's device from changes
In the User certificates management subsection, you can specify which root certificates to install. These certificates can be used, for example, to verify the authenticity of websites or web servers.
In the Add or edit applicable local administrator groups subsection, you can manage local administrator groups. These groups are used, for example, when revoking local administrator rights. You can also check the list of privileged user accounts using the Report on privileged device users (Linux only).
In the Upload a reference file to protect the sudoers file on the user's device from changes subsection, you can configure control of the sudoers file. Privileged groups and device users are defined by the sudoers file on the device. The sudoers file is located at /etc/sudoers. You can upload a reference sudoers file to protect the sudoers file from changes. This will prevent unwanted changes to the sudoers file.
An invalid reference sudoers file may cause the user's device to malfunction.
Revision history
On this tab, you can view the list of the policy revisions and roll back changes made to the policy, if necessary.
Comparison of Network Agent policy settings by operating systems
The table below shows which Network Agent policy settings you can use in Administration Console and <WC-NAME> to configure Network Agent with a specific operating system.
Network Agent policy settings: comparison by operating systems
Policy section |
Windows |
macOS |
Linux |
|---|---|---|---|
General |
|
|
|
Event configuration |
|
|
|
Settings |
|
|
The following options are available:
|
Repositories |
|
The Hardware registry details option is available. |
The following options are available:
|
Software updates and vulnerabilities |
|
|
|
Restart management |
|
|
|
Windows Desktop Sharing |
|
|
|
Manage patches and updates |
|
|
|
Connectivity → Network |
|
|
Except the Open Network Agent ports in Microsoft Windows Firewall option. |
Connectivity → Connection profiles |
|
|
|
Connectivity → Connection schedule |
|
|
|
Network polling by distribution points |
Only the Windows network, IP ranges, and Domain controllers options are available. |
|
The following options are available:
|
Network settings for distribution points |
|
|
|
KSN Proxy (distribution points) |
|
|
|
Updates (distribution points) |
|
|
|
Revision history |
|
|
|
Enabling and disabling the low resource consumption mode for Network Agent
The low resource consumption mode allows you to limit the RAM usage of the Network Agent installed on the client device. By default, the low resource consumption mode is disabled.
In the low resource consumption mode, the following functions are not performed:
- Network Agent cannot be assigned to act as a distribution point (either manually or automatically).
- Network Agent does not log information about the status of the Network Agent in a separate text file.
- Network Agent does not support the offline model of update download.
- The following components and processes are disabled:
- Obtaining information about third-party updates and vulnerabilities.
- Running the KSN Proxy on the distribution point side.
- Uploading updates to the distribution point repository.
- Bypassing the DNS server block.
- Obtaining information about free disk space.
Components and processes resume operation after disabling the low resource consumption mode.
To enable the low resource consumption mode:
- Execute the following command in the command line on the client device:
C:\Program files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\NetworkAgent>klscflag -fset -pv klnagent -n KLNAG_FLAG_TEST_VM_PERF -t d -v 1 - Restart the Network Agent.
- To check that the low resource consumption mode is enabled, in Windows, open Event Viewer, and then select Applications and Services Logs → Kaspersky Event Log.
Make sure that the log contains events like Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent is working in low resource consumption mode.
The low resource consumption mode is enabled.
To disable the low resource consumption mode:
- Execute the following command in the command line on the client device:
C:\Program files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\NetworkAgent>klscflag -fset -pv klnagent -n KLNAG_FLAG_TEST_VM_PERF -t d -v 0 - Restart the Network Agent.
- To check that the low resource consumption mode is disabled, in Windows, open Event Viewer, and then select Applications and Services Logs → Kaspersky Event Log.
Make sure that the last klnagent event does not contain the message Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent is working in low resource consumption mode.
The low resource consumption mode is disabled.
You can also enable the low resource consumption mode remotely by using an Execute scripts remotely task.
Page top
Manual setup of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy
This section provides recommendations on how to configure the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy. You can perform setup in the policy properties window. When you edit a setting, click the lock icon to the right of the relevant group of settings to apply the specified values to a workstation.
Configuring Kaspersky Security Network
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is the infrastructure of cloud services that contains information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software. Kaspersky Security Network enables Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows to respond faster to different kinds of threats, enhances the performance of the protection components, and decreases the likelihood of false positives. For more information about Kaspersky Security Network, see the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
To specify recommended KSN settings:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The properties window of the selected policy opens.
- In the policy properties, go to Application settings → Advanced Threat Protection → Kaspersky Security Network.
- Make sure that the Kaspersky Security Network option is enabled. Using this option helps to redistribute and optimize traffic on the network.
If you use Managed Detection and Response, you must enable Kaspersky Security Network option for the distribution point and enable extended KSN mode.
- Enable use of KSN servers if the KSN proxy service is not available. KSN servers may be located either on the side of Kaspersky (when KSN is used) or on the side of third parties (when KPSN is used).
- Click OK.
The recommended KSN settings are specified.
Checking the list of the networks protected by Firewall
Make sure that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Firewall protects all your networks. By default, Firewall protects networks with the following types of connection:
- Public network. Security applications, firewalls, or filters do not protect devices in such a network.
- Local network. Access to files and printers is restricted for devices in this network.
- Trusted network. Devices in such a network are protected from attacks and unauthorized access to files and data.
If you configured a custom network, make sure that Firewall protects it. For this purpose, check the list of the networks in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy properties. The list may not contain all the networks.
For more information about Firewall, see the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
To check the list of networks:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The properties window of the selected policy opens.
- In the policy properties, go to Application settings → Essential Threat Protection → Firewall.
- Under Available networks, click the Network settings link.
The Network connections window opens. This window displays the list of networks.
- If the list has a missing network, add it.
Disabling the scan of network drives
When Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows scans network drives, this can place a significant load on them. It is more convenient to perform indirect scanning on file servers.
You can disable scanning of network drives in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy properties. For a description of these policy properties, see the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
To disable scanning of network drives:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The properties window of the selected policy opens.
- In the policy properties, go to Application settings → Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection.
- Under Protection scope, disable the All network drives option.
- Click OK.
Scanning of network drives is disabled.
Excluding software details from the Administration Server memory
We recommend that Administration Server does not save information about software modules that are started on the network devices. As a result, the Administration Server memory does not overrun.
You can disable saving this information in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy properties.
To disable saving information about installed software modules:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The properties window of the selected policy opens.
- In the policy properties, go to Application settings → General Settings → Reports and Storage.
- Under Data transfer to Administration Server, disable the About started applications check box if it is still enabled in the top-level policy.
When this check box is selected, the Administration Server database saves information about all versions of all software modules on the networked devices. This information may require a significant amount of disk space in the Kaspersky Security Center database (dozens of gigabytes).
The information about installed software modules is no longer saved to the Administration Server database.
Configuring access to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows interface on workstations
If the threat protection on the organization's network must be managed in centralized mode through Kaspersky Security Center, specify the interface settings in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy properties, as described below. As a result, you will prevent unauthorized access to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows on workstations and the changing of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows settings.
For a description of these policy properties, see the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
To specify recommended interface settings:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The properties window of the selected policy opens.
- In the policy properties, go to Application settings → General settings → Interface.
- Under Interaction with user, select the Do not display user interface option. This disables the display of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows user interface on workstations, so their users cannot change the settings of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- Under Password protection, enable the toggle switch. This reduces the risk of unauthorized or unintended changes in the settings of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows on workstations.
The recommended settings for the interface of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows are specified.
Saving important policy events in the Administration Server database
To avoid the Administration Server database overflow, we recommend that you save only important events to the database.
To configure registration of important events in the Administration Server database:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The properties window of the selected policy opens.
- In the policy properties, open the Event configuration tab.
- In the Critical section, click Add event and select check boxes next to the following events only:
- End User License Agreement violated
- Application autorun is disabled
- Activation error
- Active threat detected. Advanced Disinfection should be started
- Disinfection impossible
- Previously opened dangerous link detected
- Process terminated
- Network activity blocked
- Network attack detected
- Application startup prohibited
- Access denied (local bases)
- Access denied (KSN)
- Local update error
- Cannot start two tasks at the same time
- Error in interaction with Kaspersky Security Center
- Not all components were updated
- Error applying file encryption / decryption rules
- Error enabling portable mode
- Error disabling portable mode
- Could not load encryption module
- Policy cannot be applied
- Error changing application components
- Click OK.
- In the Functional failure section, click Add event and select check box next to the event Invalid task settings. Settings not applied.
- Click OK.
- In the Warning section, click Add event and select check boxes next to the following events only:
- Self-Defense is disabled
- Protection components are disabled
- Incorrect reserve key
- Legitimate software that can be used by intruders to damage your computer or personal data was detected (local bases)
- Legitimate software that can be used by intruders to damage your computer or personal data was detected (KSN)
- Object deleted
- Object disinfected
- User has opted out of the encryption policy
- File was restored from quarantine on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server by the administrator
- File was quarantined on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server by the administrator
- Application startup blockage message to administrator
- Device access blockage message to administrator
- Web page access blockage message to administrator
- Click OK.
- In the Info section, click Add event and select check boxes next to the following events only:
- A backup copy of the object was created
- Application startup prohibited in test mode
- Click OK.
Registration of important events in the Administration Server database is configured.
Manual setup of the group update task for Kaspersky Endpoint Security
The optimal and recommended schedule option for Kaspersky Endpoint Security is When new updates are downloaded to the repository when the Use automatically randomized delay for task starts check box is selected.
Granting offline access to the external device blocked by Device Control
In Device Control component of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy, you can manage user access to external devices that are installed on or connected to the client device (for example, hard drives, cameras, or Wi-Fi modules). This lets you protect the client device from infection when such external devices are connected, and prevent loss or leaks of data.
If you need to grant temporary access to the external device blocked by Device Control but it is not possible to add the device to the list of trusted devices, you can grant temporary offline access to the external device. Offline access means that the client device has no access to the network.
You can grant offline access to the external device blocked by Device Control only if the Allow requests for temporary access option is enabled in the settings of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy, in the Application settings → Security Controls → Device Control section.
Granting offline access to the external device blocked by Device Control includes the following stages:
- In the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows dialog window, device user who wants to have access to the blocked external device, generates a request access file and sends it to the Kaspersky Security Center administrator.
- Getting this request, the Kaspersky Security Center administrator creates an access key file and send it to the device user.
- In the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows dialog window, the device user activates the access key file and obtains temporary access to the external device.
To grant temporary access to the external device blocked by Device Control:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
The list of managed devices is displayed.
- In this list, select the user's device that requests access to the external device blocked by Device Control.
You can select only one device.
- Above the list of managed devices, click the ellipsis button (
 ), and then click the Grant access to the device in offline mode button.
), and then click the Grant access to the device in offline mode button. - In the Application settings window that opens, in the Device Control section, click the Browse button.
- Select the request access file that you have received from the user, and then click the Open button. The file should have the AKEY format.
The details of the locked device to which the user has requested access is displayed.
- Specify the value of the Access duration setting.
This setting defines the length of time for which you grant the user access to the locked device. The default value is the value that was specified by the user when creating the request access file.
- Specify the time period during which the access key can be activated on the device.
This setting defines the time period during which the user can activate access to the blocked device by using the provided access key.
- Click the Save button.
This opens the standard Save access key window of Microsoft Windows.
- Select the destination folder in which you want to save the file containing the access key for the blocked device.
- Click the Save button.
As a result, when you send the user the access key file and the user activates it in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows dialog window, the user has temporary access to the blocked device for the specific period.
Removing applications or software updates remotely
To remove applications or software updates remotely from selected devices:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- For the Kaspersky Security Center application, select the Uninstall application remotely task type.
- Specify the name for the task that you are creating.
A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- Select devices to which the task will be assigned.
- Select what kind of software you want to remove, and then select specific applications, updates, or patches that you want to remove:
- Specify how client devices will download the Uninstallation utility:
- Specify the operating system restart settings:
- If necessary, add the accounts that will be used to start the remote uninstallation task:
- If you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option on the Finish task creation page. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Finish button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the name of the created task to open the task properties window.
- In the task properties window, specify the general task settings.
- Click the Save button.
- Run the task manually or wait for it to launch according to the schedule you specified in the task settings.
Upon completion of the remote uninstallation task, the selected application will be removed from the selected devices.
Remote uninstallation issues
Sometimes remote uninstallation of third-party applications may finish with the following warning: "Remote uninstallation has finished on this device with warnings: Application for removal is not installed." This issue occurs when the application to be uninstalled has already been uninstalled or was installed only for an individual user. Applications installed for an individual user (also referred to as per-user applications) become invisible and cannot be uninstalled remotely if the user is not logged in.
This behavior differs from applications intended for use by multiple users on the same device (also referred to as per-device applications). Per-device applications are visible and accessible to all users of the device.
Therefore, per-user applications must be uninstalled only when the user is logged in.
Source of information about installed applications
Network Agent retrieves information about software installed on Windows devices from the following registry keys:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
Contains information about applications installed for all users.
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
Contains information about applications installed for all users.
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
Contains information about applications installed for the current user.
- HKEY_USER<...>\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
Contains information about applications installed for specific users.
About tasks
Kaspersky Security Center manages Kaspersky security applications installed on devices by creating and running tasks. Tasks are required for installing, launching, and stopping applications, scanning files, updating databases and software modules, and performing other actions on applications.
Tasks for a specific application can be created using Kaspersky Security Center Web Console only if the management plug-in for that application is installed on Kaspersky Security Center Web Console Server.
Tasks can be performed on the Administration Server and on devices.
The tasks that are performed on the Administration Server include the following:
- Automatic distribution of reports
- Downloading of updates to the repository
- Backup of Administration Server data
- Maintenance of the database
The following types of tasks are performed on devices:
- Local tasks—Tasks that are performed on a specific device
Local tasks can be modified either by the administrator, using Administration Console tools, or by the user of a remote device (for example, through the security application interface). If a local task has been modified simultaneously by the administrator and the user of a managed device, the changes made by the administrator will take effect because they have a higher priority.
- Group tasks—Tasks that are performed on all devices of a specific group
Unless otherwise specified in the task properties, a group task also affects all subgroups of the selected group. A group task also affects (optionally) devices that have been connected to secondary and virtual Administration Servers deployed in the group or any of its subgroups.
- Global tasks—Tasks that are performed on a set of devices, regardless of whether they are included in any group.
For each application, you can create any number of group tasks, global tasks, or local tasks.
You can make changes to the settings of tasks, view the progress of tasks, and copy, export, import, and delete tasks.
A task is started on a device only if the application for which the task was created is running.
Execution results of tasks are saved in the operating system event log on each device, in the operating system event log on the Administration Server, and in the Administration Server database.
Do not include private data in task settings. For example, avoid specifying the domain administrator password.
About task scope
The scope of a task is the set of devices on which the task is performed. The types of scope are as follows:
- For a local task, the scope is the device itself.
- For an Administration Server task, the scope is the Administration Server.
- For a group task, the scope is the list of devices included in the group.
When creating a global task, you can use the following methods to specify its scope:
- Specifying certain devices manually.
You can use an IP address (or IP range), NetBIOS name, or DNS name as the device address.
- Importing a list of devices from a TXT file with the device addresses to be added (each address must be placed on an individual line).
If you import a list of devices from a file or create a list manually, and if devices are identified by their names, the list can only contain devices for which information has already been entered into the Administration Server database. Moreover, the information must have been entered when those devices were connected or during device discovery.
- Specifying a device selection.
Over time, the scope of a task changes as the set of devices included in the selection change. A selection of devices can be made on the basis of device attributes, including software installed on a device, and on the basis of tags assigned to devices. Device selection is the most flexible way to specify the scope of a task.
Tasks for device selections are always run on a schedule by the Administration Server. These tasks cannot be run on devices that lack connection to the Administration Server. Tasks whose scope is specified by using other methods are run directly on devices and therefore do not depend on the device connection to the Administration Server.
Tasks for device selections are not run on the local time of a device; instead, they are run on the local time of the Administration Server. Tasks whose scope is specified by using other methods are run on the local time of a device.
Creating a task
To create a task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Follow its instructions.
- If you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option on the Finish task creation page. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Finish button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
To create a new task assigned to the selected devices:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
The list of managed devices is displayed.
- In the list of managed devices, select check boxes next to the devices to run the task for them. You can use the search and filter functions to find the devices you're looking for.
- Click the Run task button, and then select Add a new task.
The New task wizard starts.
On the first step of the wizard, you can remove the devices selected to include in the task scope. Follow the wizard instructions.
- Click the Finish button.
The task is created for the selected devices.
Starting a task manually
The application starts tasks according to the schedule settings specified in the properties of each task. You can start a task manually at any time from the task list. Alternatively, you can select devices in the Managed devices list, and then start an existing task for them.
To start a task manually:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- In the task list, select the check box next to the task that you want to start.
- Click the Start button.
The task starts. You can check the task status in the Status column or by clicking the Result button.
Viewing the task list
You can view the list of tasks that are created in Kaspersky Security Center.
To view the list of tasks,
In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
The list of tasks is displayed. The tasks are grouped by the names of applications to which they are related. For example, the Uninstall application remotely task is related to the Administration Server, and the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task refers to the Network Agent.
To view properties of a task,
Click the name of the task.
The task properties window is displayed with several named tabs. For example, the Task type is displayed on the General tab, and the task schedule—on the Schedule tab.
General task settings
This section contains the settings that you can view and configure for most of your tasks. The list of settings available depends on the task you are configuring.
Settings specified during task creation
You can specify the following settings when creating a task. Some of these settings can also be modified in the properties of the created task.
- Operating system restart settings:
- Task scheduling settings:
The types of schedule may vary depending on the task.
- Devices to which the task will be assigned:
- Account settings:
Settings specified after task creation
You can specify the following settings only after a task is created.
- Group task settings:
- Advanced scheduling settings:
- Notification settings:
- Store task history block:
- Notify administrator of task execution results
- Notify of errors only
- Security settings.
- Task scope settings.
Depending on how the task scope is determined, the following settings are present:
- Revision history.
Exporting a task
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to save a task and its settings to a KLT file. You can use this KLT file to import the saved task both to Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
To export a task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Select the check box next to the task that you want to export.
You cannot export multiple tasks at the same time. If you select more than one task, the Export button will be disabled. Administration Server tasks are also unavailable for export.
- Click the Export button.
- In the opened Save as window, specify the task file name and path. Click the Save button.
The Save as window is displayed only if you use Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, or Opera. If you use another browser, the task file is automatically saved in the Downloads folder.
Importing a task
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to import a task from a KLT file. The KLT file contains the exported task and its settings.
To import a task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click the Import button.
- Click the Browse button to choose a task file that you want to import.
- In the opened window, specify the path to the KLT task file, and then click the Open button. Note that you can select only one task file.
The task processing starts.
- After the task is processed successfully, select the devices to which you want to assign the task. To do this, select one of the following options:
- Specify the task scope.
- Click the Complete button to finish the task import.
The notification with the import results appears. If the task is imported successfully, you can click the Details link to view the task properties.
After a successful import, the task is displayed in the task list. The task settings and schedule are also imported. The task will be started according to its schedule.
If the newly imported task has an identical name to an existing task, the name of the imported task is expanded with the (<next sequence number>) index, for example: (1), (2).
Page top
Starting the Change tasks password wizard
For a non-local task, you can specify an account under which the task must be run. You can specify the account during task creation or in the properties of an existing task. If the specified account is used in accordance with security instructions of the organization, these instructions might require changing the account password from time to time. When the account password expires and you set a new one, the tasks will not start until you specify the new valid password in the task properties.
The Change tasks password wizard enables you to automatically replace the old password with the new one in all tasks in which the account is specified. Alternatively, you can change this password manually in the properties of each task.
To start the Change tasks password wizard:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Manage credentials of accounts for starting tasks.
Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Step 1. Specifying credentials
Specify new credentials that are currently valid in your system (for example, in Active Directory). When you switch to the next step of the wizard, Kaspersky Security Center checks if the specified account name matches the account name in the properties of each non-local task. If the account names match, the password in the task properties will be automatically replaced with the new one.
To specify the new account, select an option:
If you fill in the Previous password (optional; if you want to replace it with the current one) field, Kaspersky Security Center replaces the password only for those tasks in which both the account name and the old password are found. The replacement is performed automatically. In all other cases you have to choose an action to take in the next step of the wizard.
Step 2. Selecting an action to take
If you did not specify the previous password in the first step of the wizard or if the specified old password has not matched the passwords in the task properties, you must choose an action to take for the tasks found.
To choose an action for a task:
- Select the check box next to the task for which you want to choose an action.
- Perform one of the following:
- To remove the password in the task properties, click Delete credentials.
The task is switched to run under the default account.
- To replace the password with a new one, click Enforce the password change even if the old password is wrong or not provided.
- To cancel the password change, click No action is selected.
- To remove the password in the task properties, click Delete credentials.
The chosen actions are applied after you move to the next step of the wizard.
Step 3. Viewing the results
On the last step of the wizard, view the results for each of the found tasks. To complete the wizard, click the Finish button.
Creating Execute scripts remotely task
You can create an Execute scripts remotely task to execute an installation package on a client device and to remotely install an application.
An installation package contains a ZIP archive with a set of scripts for execution on client devices as well as a manifest.json file. Learn more about creating this type of installation package this article.
This task must be started only on devices with Network Agent for Linux.
To start an Execute scripts remotely task:
- Go to the New task wizard and select the Execute scripts remotely task type.
- Enter the task name and select the devices the task will be assigned to. Click the Next button.
- Select an installation package based on a ZIP archive with a manifest.json file for remote execution.
If you do not want to rerun the task on devices where it has already completed, turn on the Do not start this task on devices on which it has already been completed option.
- Select an account to run the task.
If you select the default account, the task will be performed by the Network Agent (root account).
When the Execute scripts remotely task starts, you cannot change the account it is assigned to. To change the account the task is assigned to, stop the task in the task settings and create it again with the correct account details.
- If you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option on the Finish task creation page. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings at any later time.
- Click the Finish button.
The Execute scripts remotely task is created and appears in the list of tasks.
After receiving data from the Execute scripts remotely task, Network Agent restricts access to the received data for all users, except the administrator and the user specified in the task settings.
Remotely installing applications on devices using the Execute scripts remotely task
The Execute scripts remotely task can be used to remotely install an application on a client device by creating a custom installation package.
Learn how to prepare an archive for this task in this article.
To create an installation package for remote installation of an application on a client device, the following files must be included in the archive you want to upload for this task:
- <
package_name>.deb - install.sh
- manifest.json
When the Execute scripts remotely task starts, the Network Agent will upload the installation package with the application to the client device. When the client device receives the installation package, Network Agent on this device parses the manifest.json file and defines the execution order of scripts and actions depending on the result and then starts execution.
When the Execute scripts remotely task is completed, the application will be installed on the client device.
Page top
Configuring notifications and monitoring for the Execute scripts remotely task
You can configure monitoring, event-saving behavior, and notifications for the Execute scripts remotely task.
To view the status of the Execute scripts remotely:
- In the main menu, go to Devices → Tasks.
The list of tasks is displayed.
- Select the task and click Device history.
The progress of the task is shown.
To configure the event-saving behavior:
- In the list of tasks, click on the task and go to the Settings tab.
- In the Notifications section, click the Settings button.
- Select one of the following options for how the application behaves after the task is complete:
- Save all events.
- Save events related to task progress.
- Save only task execution results.
The events are saved in the Device history and Events repository.
By default, only the task execution results are saved.
If you select Save all events, only the task execution results will be saved.
- If you want to keep the events in the Administration Server database, in the event log on the Administration Server, or on the device, turn on the corresponding option.
Learn more about configuring notifications in this article.
Page top
Preparing an archive for Execute scripts remotely task
An archive for the Execute scripts remotely task based on a manifest.json file must meet the following requirements:
- Archive format: ZIP.
- Total size: no more than 1 GB.
- The number of files and folders in the archive is unlimited.
- The manifest file for the archive must match the schema below and must be named manifest.json. The schema is validated only during task execution on a device.
- The archive must be structured as follows:
manifest.json<file1><file2><folder1>/<file3><folder2>/<folder3>/<file4>...<fileX>manifest.json is the manifest file for the task.
<file1>, ...., <fileX>is the set of files with scripts to be executed.
Creating an installation package based on a manifest file
To create an installation package based on a manifest file:
- Do one of the following:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Installation packages.
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories → Installation packages.
A list of installation packages available on Administration Server is displayed.
- Click Add.
The New package wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- Select Create an installation package for the Execute scripts remotely task based on a ZIP archive with the manifest.json file.
- Specify the package name and click the Browse button.
A standard Windows Open window opens in your browser to let you choose a file to create the installation package.
- Choose an archive file located on the available disks. Learn how to prepare an archive for this task in this article.
The file begins to upload to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
The process to create the installation package is started.
The wizard informs you when the process is finished.
If the installation package is not created, an appropriate message is displayed.
- Click the Finish button to close the wizard.
The installation package that you created is downloaded to the Packages subfolder of the Administration Server shared folder. After downloading, the installation package appears in the list of installation packages.
In the list of installation packages available on the Administration Server, you can click the link with the name of a custom installation package to:
- View the following properties of an installation package:
- Name. Custom installation package name.
- Source. Application vendor name.
- Version. Application version.
- Created. Installation package creation date.
- Modified. Installation package modification date.
- Path. Path to the custom installation package on the Administration Server.
- Change the package name and command-line parameters. This feature is available only for packages that are not created based on Kaspersky applications.
Managing client devices
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to manage client devices:
- View settings and statuses of managed devices, including clusters and server arrays.
- Configure distribution points.
- Manage tasks.
You can use administration groups to combine client devices in a set that can be managed as a single unit. A client device can be included in only one administration group. Devices can be allocated to a group automatically based on Rule conditions:
You can use device selections to filter devices based on a condition. You can also tag devices for creating selections, for finding devices, and for distributing devices among administration groups.
Settings of a managed device
To view the settings of a managed device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
The list of managed devices is displayed.
- In the list of managed devices, click the link with the name of the required device.
The properties window of the selected device is displayed.
The following tabs are displayed in the upper part of the properties window representing the main groups of the settings:
If you use a PostgreSQL, MariaDB or MySQL DBMS, the Events tab may display an incomplete list of events for the selected client device. This occurs when the DBMS stores a very large amount of events. You can increase the number of displayed events by doing either of the following:
To see a full list of events logged on the Administration Server for the device, use Reports.
Creating administration groups
Immediately after Kaspersky Security Center installation, the hierarchy of administration groups contains only one administration group, called Managed devices. When creating a hierarchy of administration groups, you can add devices, including virtual machines, to the Managed devices group, and add nested groups (see the figure below).
Viewing administration groups hierarchy
To create an administration group:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- In the administration group structure, select the administration group that is to include the new administration group.
- Click the Add button.
- In the Name of the new administration group window that opens, enter a name for the group, and then click the Add button.
A new administration group with the specified name appears in the hierarchy of administration groups.
The application allows creating a hierarchy of administration groups based on the structure of Active Directory or the domain network's structure. Also, you can create a structure of groups from a text file.
To create a structure of administration groups:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- Click the Import button.
The New administration group structure wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Page top
Adding devices to an administration group manually
You can move devices to administration groups automatically by creating device moving rules or manually by moving devices from one administration group to another or by adding devices to a selected administration group. This section describes how to manually add devices to an administration group.
To add manually one or more devices to a selected administration group:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click the Current path:
<current path>link above the list. - In the window that opens, select the administration group to which you want to add the devices.
- Click the Add devices button.
The Move devices wizard starts.
- Make a list of the devices that you want to add to the administration group.
You can add only devices for which information has already been added to the Administration Server database either upon connection of the device or after device discovery.
Select how you want to add devices to the list:
- Click the Add devices button, and then specify the devices in one of the following ways:
- Select devices from the list of devices detected by the Administration Server.
- Specify a device IP address or an IP range.
- Specify the NetBIOS name or DNS name of a device.
The device name field must not contain space characters or the following prohibited characters: \ / * ; : ` ~ ! @ # $ ^ & ( ) = + [ ] { } | , < > %
- Click the Import devices from file button to import a list of devices from a .txt file. Each device address or name must be specified on a separate line.
The file must not contain space characters or the following prohibited characters: \ / * ; : ` ~ ! @ # $ ^ & ( ) = + [ ] { } | , < > %
- Click the Add devices button, and then specify the devices in one of the following ways:
- View the list of devices to be added to the administration group. You can edit the list by adding or removing devices.
- After making sure that the list is correct, click the Next button.
The wizard processes the device list and displays the result. The successfully processed devices are added to the administration group and are displayed in the list of devices under names generated by Administration Server.
Moving devices or clusters to an administration group manually
You can move devices from one administration group to another, or from the group of unassigned devices to an administration group.
You can also move clusters or server arrays from one administration group to another. When you move a cluster or server array to another group, all of its nodes move with it, because a cluster and any of its nodes always belong to the same administration group. When you select a single cluster node on the Devices tab, the Move to group button becomes unavailable.
To move one or several devices or clusters to a selected administration group:
- Open the administration group from which you want to move the devices. To do this, perform one of the following:
- To open an administration group, in the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices, click the path link in the Current path field, and select an administration group in the left-side pane that opens.
- To open the Unassigned devices group, in the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Unassigned devices.
- If the administration group contains clusters or server arrays, the Managed devices section is divided into two tabs—the Devices tab and the Clusters and server arrays tab. Open the tab for the object that you want to move.
- Select the check boxes next to the devices or clusters that you want to move to a different group.
- Click the Move to group button.
- In the hierarchy of administration groups, select the check box next to the administration group to which you want to move the selected devices or clusters.
- Click the Move button.
The selected devices or clusters are moved to the selected administration group.
Page top
Creating device moving rules
You can set up device moving rules, that is, rules that automatically allocate devices to administration groups.
To create a moving rule:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Moving rules.
- Click Add.
- In the window that opens, specify the following information on the General tab:
- On the Rule conditions tab, specify at least one criterion by which the devices are moved to an administration group.
- Click Save.
The moving rule is created. It is displayed in the list of moving rules.
The higher the position is on the list, the higher the priority of the rule. To increase or decrease the priority of a moving rule, move the rule up or down in the list, respectively, using the mouse.
If the Apply rule continuously option is selected, the moving rule is applied regardless of the priority settings. Such rules are applied according to the schedule which the Administration Server sets up automatically.
If the device attributes meet the conditions of multiple rules, the device is moved to the target group of the rule with the highest priority (that is, has the highest rank in the list of rules).
Copying device moving rules
You can copy moving rules, for example, if you want to have several identical rules for different target administration groups.
To copy an existing a moving rule:
- Do one of the following:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Moving rules.
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Moving rules.
The list of moving rules is displayed.
- Select the check box next to the rule you want to copy.
- Click Copy.
- In the window that opens, change the following information on the General tab—or make no changes if you only want to copy the rule without changing its settings:
- On the Rule conditions tab, specify at least one criterion for the devices that you want to be moved automatically.
- Click Save.
The new moving rule is created. It is displayed in the list of moving rules.
Conditions for a device moving rule
When you create or copy a rule to move client devices to administration groups, on the Rule conditions tab you set conditions for moving the devices. To determine which devices to move, you can use the following criteria:
- Tags assigned to client devices.
- Network parameters. For example, you can move devices with IP addresses from a specified range.
- Managed applications installed on client devices, for instance, Network Agent or Administration Server.
- Virtual machines, which are the client devices.
- Information about the Active Directory organizational unit (OU) with the client devices.
- Information about a cloud segment with the client devices.
Below, you can find the description on how to specify this information in a device moving rule.
If you specify several conditions in the rule, the AND logical operator works and all the conditions apply at the same time. If you do not select any options or keep some fields blank, such conditions do not apply.
Tags tab
On this tab, you can configure a device moving rule based on device tags that were previously added to the descriptions of client devices. To do this, select the required tags. Also, you can enable the following options:
Network tab
On this tab, you can specify the network data of devices that a device moving rule considers:
- Device name on the Windows network
- Windows domain
- DNS name of the device
- DNS domain
- IP range
- IP address for connection to Administration Server
- Device is in IP range
- Connection profile changed
- Managed by a different Administration Server
Applications tab
On this tab, you can configure a device moving rule based on the managed applications and operating systems installed on client devices:
- Network Agent is installed
- Applications
- Operating system version
- Operating system bit size
- Operating system service pack version
- User certificate
- Operating system build
- Operating system release number
Virtual machines tab
On this tab, you can configure a device moving rule according to whether client devices are virtual machines or part of a virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI):
- This is a virtual machine
- Virtual machine type
- Part of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure
Domain controller tab
On this tab, you can specify that it is necessary to move devices included in the domain organizational unit. You can also move devices from all child organizational units of the specified domain organizational unit:
- Device is included in the following organizational unit
- Include child organizational units
- Move devices from child units to corresponding subgroups
- Create subgroups corresponding to containers of newly detected devices
- Delete subgroups that are not present in the domain
- Device is included in the following domain security group
Cloud segments tab
On this tab, you can specify that it is necessary to move devices that belong to specific cloud segments:
- Device is in a cloud segment
- Include child objects
- Move devices from nested objects to corresponding subgroups
- Create subgroups corresponding to containers of newly detected devices
- Delete subgroups for which no match is found in the cloud segments
- Device discovered by using the API
About clusters and server arrays
Kaspersky Security Center supports cluster technology. If Network Agent sends information to Administration Server confirming that an application installed on a client device is part of a server array, this client device becomes a cluster node.
If an administration group contains clusters or server arrays, the Managed devices page displays two tabs—one for individual devices, and one for clusters and server arrays. After the managed devices are detected as cluster nodes, the cluster is added as an individual object to the Clusters and server arrays tab.
The cluster or server array nodes are listed on the Devices tab, along with other managed devices. You can view properties of the nodes as individual devices and perform other operations, but you cannot delete a cluster node or move it to another administration group separately from its cluster. You can only delete or move an entire cluster.
You can perform the following operations with clusters or server arrays:
- View properties
- Move the cluster or server array to another administration group
When you move a cluster or server array to another group, all of its nodes move with it, because a cluster and any of its nodes always belong to the same administration group.
- Delete
It is reasonable to delete a cluster or server array only when the cluster or server array does not exist in the organization network any longer. If a cluster is still visible on your network and Network Agent and the Kaspersky security application are still installed on the cluster nodes, Kaspersky Security Center returns the deleted cluster and its nodes back to the list of managed devices automatically.
Properties of a cluster or server array
To view the settings of a cluster or server array:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices → Clusters and server arrays.
The list of clusters and server arrays is displayed.
- Click the name of the required cluster or server array.
The properties window of the selected cluster or server array is displayed.
General
The General section displays general information about the cluster or server array. Information is provided on the basis of data received during the last synchronization of the cluster nodes with the Administration Server:
- Name
- Description
- Windows domain
- NetBIOS name
- DNS name
Tasks
In the Tasks tab, you can manage the tasks assigned to the cluster or server array: view the list of existing tasks; create new ones; remove, start, and stop tasks; modify task settings; and view execution results. The listed tasks relate to the Kaspersky security application installed on the cluster nodes. Kaspersky Security Center receives the task list and the task status details from the cluster nodes. If a connection is not established, the status is not displayed.
Nodes
This tab displays a list of nodes included into the cluster or server array. You can click a node name to view the device properties window.
Kaspersky application
The properties window may also contain additional tabs with the information and settings related to the Kaspersky security application installed on the cluster nodes.
Viewing and configuring the actions when devices show inactivity
If client devices within a group are inactive, you can get notifications about it. You can also automatically delete such devices.
To view or configure the actions when the devices in the group show inactivity:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- Click the name of the required administration group.
The administration group properties window opens.
- In the properties window, go to the Settings tab.
- In the Inheritance section, enable or disable the following options:
- In the Device activity section, enable or disable the following options:
- Click Save.
Your changes are saved and applied.
Page top
About device statuses
Kaspersky Security Center assigns a status to each managed device. The particular status depends on whether the conditions defined by the user are met. In some cases, when assigning a status to a device, Kaspersky Security Center takes into consideration the device's visibility flag on the network (see the table below). If Kaspersky Security Center does not find a device on the network within two hours, the visibility flag of the device is set to Not Visible.
The statuses are the following:
- Critical or Critical / Visible
- Warning or Warning / Visible
- OK or OK / Visible
The table below lists the default conditions that must be met to assign the Critical or Warning status to a device, with all possible values.
Conditions for assigning a status to a device
Condition |
Condition description |
Available values |
|---|---|---|
Security application is not installed |
Network Agent is installed on the device, but a security application is not installed. |
|
Too many viruses detected |
Some viruses have been found on the device by a task for virus detection, for example, the Malware scan task, and the number of viruses found exceeds the specified value. |
More than 0. |
Real-time protection level differs from the level set by the Administrator |
The device is visible on the network, but the real-time protection level differs from the level set (in the condition) by the administrator for the device status. |
|
Malware scan has not been performed in a long time |
The device is visible on the network and a security application is installed on the device, but neither the Malware scan task nor a local scan task has been run within the specified time interval. The condition is applicable only to devices that were added to the Administration Server database 7 days ago or earlier. |
More than 1 day. |
Databases are outdated |
The device is visible on the network and a security application is installed on the device, but the anti-virus databases have not been updated on this device within the specified time interval. The condition is applicable only to devices that were added to the Administration Server database 1 day ago or earlier. |
More than 1 day. |
Not connected in a long time |
Network Agent is installed on the device, but the device has not connected to an Administration Server within the specified time interval, because the device was turned off. |
More than 1 day. |
Active threats are detected |
The number of unprocessed objects in the Active threats folder exceeds the specified value. |
More than 0 items. |
Restart is required |
The device is visible on the network, but an application requires the device restart longer than the specified time interval and for one of the selected reasons. |
More than 0 minutes. |
Incompatible applications are installed |
The device is visible on the network, but software inventory performed through Network Agent has detected incompatible applications installed on the device. |
|
Software vulnerabilities have been detected |
The device is visible on the network and Network Agent is installed on the device, but the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task has detected vulnerabilities with the specified severity level in applications installed on the device. |
|
License expired |
The device is visible on the network, but the license has expired. |
|
License expires soon |
The device is visible on the network, but the license will expire on the device in less than the specified number of days. |
More than 0 days. |
Check for Windows Update updates has not been performed in a long time |
The device is visible on the network, but the Perform Windows Update synchronization task has not been run within the specified time interval. |
More than 1 day. |
Invalid encryption status |
Network Agent is installed on the device, but the device encryption result is equal to the specified value. |
|
Mobile device settings do not comply with the policy |
The mobile device settings are other than the settings that were specified in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android policy during the check of compliance rules. |
|
Unprocessed security issues detected |
Some unprocessed security issues have been found on the device. Security issues can be created either automatically, through managed Kaspersky applications installed on the client device, or manually by the administrator. |
|
Device status defined by application |
The status of the device is defined by the managed application. |
|
Device is out of disk space |
Free disk space on the device is less than the specified value or the device could not be synchronized with the Administration Server. The Critical or Warning status is changed to the OK status when the device is successfully synchronized with the Administration Server and free space on the device is greater than or equal to the specified value. |
More than 0 MB. |
Device has become unmanaged |
During device discovery, the device was recognized as visible on the network, but more than three attempts to synchronize with the Administration Server failed. |
|
Protection is disabled |
The device is visible on the network, but the security application on the device has been disabled for longer than the specified time interval. In this case, the state of the security application is stopped or failure, and differs from the following: starting, running, or suspended. |
More than 0 minutes. |
Security application is not running |
The device is visible on the network and a security application is installed on the device but is not running. |
|
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to set up automatic switching of the status of a device in an administration group when specified conditions are met. When specified conditions are met, the client device is assigned one of the following statuses: Critical or Warning. When specified conditions are not met, the client device is assigned the OK status.
Different statuses may correspond to different values of one condition. For example, by default, if the Databases are outdated condition has the More than 3 days value, the client device is assigned the Warning status; if the value is More than 7 days, the Critical status is assigned.
If you upgrade the Kaspersky Security Center from the previous version, the values of the Databases are outdated condition for assigning the status to Critical or Warning do not change.
When Kaspersky Security Center assigns a status to a device, for some conditions (see the Condition description column) the visibility flag is taken into consideration. For example, if a managed device was assigned the Critical status because the Databases are outdated condition was met, and later the visibility flag was set for the device, then the device is assigned the OK status.
Configuring the switching of device statuses
You can change conditions to assign the Critical or Warning status to a device.
To enable changing the device status to Critical:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- In the list of groups that opens, click the link with the name of a group for which you want to change switching the device statuses.
- In the properties window that opens, select the Device status tab.
- In the left pane, select Critical.
- In the right pane, in the Set to Critical if these are specified section, enable the condition to switch a device to the Critical status.
You can change only settings that are not locked in the parent policy.
- Select the radio button next to the condition in the list.
- In the upper-left corner of the list, click the Edit button.
- Set the required value for the selected condition.
Values cannot be set for every condition.
- Click OK.
When specified conditions are met, the managed device is assigned the Critical status.
To enable changing the device status to Warning:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- In the list of groups that opens, click the link with the name of a group for which you want to change switching the device statuses.
- In the properties window that opens, select the Device status tab.
- In the left pane, select Warning.
- In the right pane, in the Set to Warning if these are specified section, enable the condition to switch a device to the Warning status.
You can change only settings that are not locked in the parent policy.
- Select the radio button next to the condition in the list.
- In the upper-left corner of the list, click the Edit button.
- Set the required value for the selected condition.
Values cannot be set for every condition.
- Click OK.
When specified conditions are met, the managed device is assigned the Warning status.
Remotely connecting to the desktop of a client device
The administrator can obtain remote access to the desktop of a client device through a Network Agent installed on the device. Remote connection to a device through the Network Agent is possible even if the TCP and UDP ports of the client device are closed.
Upon establishing the connection with the device, the administrator gains full access to information stored on this device and can manage applications installed on it.
Remote connection must be allowed in the operating system settings of the target managed device. For example, in Windows 10, this option is called Allow Remote Assistance connections to this computer (you can find this option at Control Panel → System and Security → System → Remote settings). If you have a license for the Vulnerability and patch management feature, you can enable this option forcibly when you establish connection to a managed device. If you do not have the license, enable this option locally on the target managed device. If this option is disabled, remote connection is not possible.
To establish remote connection to a device, you must have two utilities:
- Kaspersky utility named klsctunnel. This utility must be stored on the administrator's workstation. You use this utility for tunneling the connection between a client device and the Administration Server.
Kaspersky Security Center allows tunneling TCP connections from Administration Console via the Administration Server and then via Network Agent to a specified port on a managed device. Tunneling is designed for connecting a client application on a device with Administration Console installed to a TCP port on a managed device—if no direct connection is possible between Administration Console and the target device.
Connection tunneling between a remote client device and Administration Server is required if the port used for connection to Administration Server is not available on the device. The port on the device may be unavailable in the following cases:
- The remote device is connected to a local network that uses the NAT mechanism.
- The remote device is part of the local network of Administration Server, but its port is closed by a firewall.
- Standard Microsoft Windows component named Remote Desktop Connection. Connection to a remote desktop is established through the standard Windows utility mstsc.exe in accordance with the utility's settings.
Connection to the current remote desktop session of the user is established without the user's knowledge. Once the administrator connects to the session, the device user is disconnected from the session without an advance notification.
To connect to the desktop of a client device:
- In MMC-based Administration Console, in the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window that opens, go to Administration Server connection settings → Connection ports.
- Make sure that the Open RDP port for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console option is enabled.
- In Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- In the Current path field above the list of managed devices, click the path link.
- In the left-side pane that opens, select the administration group that contains the device to which you want to obtain access.
- Select the check box next to the name of the device to which you want to obtain access.
- Click the Connect to Remote Desktop button.
The Remote Desktop (Windows only) window opens.
- Enable the Allow remote desktop connection on managed device option. In this case, the connection will be established even if remote connections are currently prohibited in the operating system settings on the managed device.
This option is only available if you have a license for the Vulnerability and patch management feature.
- Click the Download button to download the klsctunnel utility.
- Click the Copy to clipboard button to copy the text from the text field. This text is a Binary Large Object (BLOB) that contains settings required to establish connection between the Administration Server and the managed device.
A BLOB is valid for 3 minutes. If it has expired, reopen the Remote Desktop (Windows only) window to generate a new BLOB.
- Run the klsctunnel utility.
The utility window opens.
- Paste the copied text into the text field.
- If you use a proxy server, select the Use proxy server check box, and then specify the proxy server connection settings.
- Click the Open port button.
The Remote Desktop Connection login window opens.
- Specify the credentials of the account under which you are currently logged in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Click the Connect button.
When connection to the device is established, the desktop is available in the Remote Desktop Connection window of Microsoft Windows.
Page top
Connecting to devices through Windows Desktop Sharing
The administrator can obtain remote access to the desktop of a client device through a Network Agent installed on the device. Remote connection to a device through the Network Agent is possible even if the TCP and UDP ports of the client device are closed.
The administrator can connect to an existing session on a client device without disconnecting the user in this session. In this case, the administrator and the session user on the device share access to the desktop.
To establish remote connection to a device, you must have two utilities:
- Kaspersky utility named klsctunnel. This utility must be stored on the administrator's workstation. You use this utility for tunneling the connection between a client device and the Administration Server.
Kaspersky Security Center allows tunneling TCP connections from Administration Console via the Administration Server and then via Network Agent to a specified port on a managed device. Tunneling is designed for connecting a client application on a device with Administration Console installed to a TCP port on a managed device—if no direct connection is possible between Administration Console and the target device.
Connection tunneling between a remote client device and Administration Server is required if the port used for connection to Administration Server is not available on the device. The port on the device may be unavailable in the following cases:
- The remote device is connected to a local network that uses the NAT mechanism.
- The remote device is part of the local network of Administration Server, but its port is closed by a firewall.
- Windows Desktop Sharing. When connecting to an existing session of the remote desktop, the session user on the device receives a connection request from the administrator. No information about remote activity on the device and its results will be saved in reports created by Kaspersky Security Center.
The administrator can configure an audit of user activity on a remote client device. During the audit, the application saves information about files on the client device that have been opened and/or modified by the administrator.
To connect to the desktop of a client device through Windows Desktop Sharing, the following conditions must be met:
- Microsoft Windows Vista or later is installed on the administrator's workstation. The type of operating system of the device hosting Administration Server imposes no restrictions on connection through Windows Desktop Sharing.
To check whether the Windows Desktop Sharing feature is included in your Windows edition, make sure that there is CLSID\{32BE5ED2-5C86-480F-A914-0FF8885A1B3F} key in the Windows Registry.
- Microsoft Windows Vista or later is installed on the client device.
- Kaspersky Security Center uses a license for Vulnerability and patch management.
To connect to the desktop of a client device through Windows Desktop Sharing:
- In MMC-based Administration Console, in the context menu of the Administration Server, select Properties.
- In the Administration Server properties window that opens, go to Administration Server connection settings → Connection ports.
- Make sure that the Open RDP port for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console option is enabled.
- In Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- In the Current path field above the list of managed devices, click the path link.
- In the left-side pane that opens, select the administration group that contains the device to which you want to obtain access.
- Select the check box next to the name of the device to which you want to obtain access.
- Click the Windows Desktop Sharing button.
The Windows Desktop Sharing wizard opens.
- Click the Download button to download the klsctunnel utility, and wait for the download process to complete.
If you already have the klsctunnel utility, skip this step.
- Click the Next button.
- Select the session on the device to which you want to connect, and then click the Next button.
- On the target device, in the dialog box that opens, the user must allow a desktop sharing session. Otherwise, the session is not possible.
After the device user confirms the desktop sharing session, the next page of the wizard opens.
- Click the Copy to clipboard button to copy the text from the text field. This text is a Binary Large OBject (BLOB) that contains settings required to establish connection between the Administration Server and the managed device.
A BLOB is valid for 3 minutes. If it has expired, generate a new BLOB.
- Run the klsctunnel utility.
The utility window opens.
- Paste the copied text into the text field.
- If you use a proxy server, select the Use proxy server check box, and then specify the proxy server connection settings.
- Click the Open port button.
Desktop sharing starts in a new window. If you want to interact with the device, click the menu icon (![]() ) in the upper-left corner of the window, and then select Interactive mode.
) in the upper-left corner of the window, and then select Interactive mode.
Device selections
Device selections are a tool for filtering devices according to specific conditions. You can use device selections to manage several devices: for example, to view a report about only these devices or to move all of these devices to another group.
Kaspersky Security Center provides a broad range of predefined selections (for example, Devices with Critical status, Protection is disabled, Active threats are detected). Predefined selections cannot be deleted. You can also create and configure additional user-defined selections.
In user-defined selections, you can set the search scope and select all devices, managed devices, or unassigned devices. Search parameters are specified in the conditions. In the device selection you can create several conditions with different search parameters. For example, you can create two conditions and specify different IP ranges in each of them. If several conditions are specified, a selection displays the devices that meet any of the conditions. By contrast, search parameters within a condition are superimposed. If both an IP range and the name of an installed application are specified in a condition, only those devices will be displayed where both the application is installed and the IP address belongs to the specified range.
Viewing the device list from a device selection
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to view the list of devices from a device selection.
To view the device list from the device selection:
- In the main menu, go to the Assets (Devices) → Device selections or Discovery & deployment → Device selections section.
- In the selection list, click the name of the device selection.
The page displays a table with information about the devices included in the device selection.
- You can group and filter the data of the device table as follows:
- Click the settings icon (
 ), and then select the columns to be displayed in the table.
), and then select the columns to be displayed in the table. - Click the filter icon (
 ), and then specify and apply the filter criterion in the invoked menu.
), and then specify and apply the filter criterion in the invoked menu. The filtered table of devices is displayed.
- Click the settings icon (
You can select one or several devices in the device selection and click the New task button to create a task that will be applied to these devices.
To move the selected devices of the device selection to another administration group, click the Move to group button, and then select the target administration group.
Page top
Creating a device selection
To create a device selection:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Device selections.
A page with a list of device selections is displayed.
- Click the Add button.
The Device selection settings window opens.
- Enter the name of the new selection.
- Specify the group that contains the devices to be included in the device selection:
- Find any devices—Searching for devices that meet the selection criteria and included in the Managed Devices or Unassigned devices group.
- Find managed devices—Searching for devices that meet the selection criteria and included in the Managed Devices group.
- Find unassigned devices—Searching for devices that meet the selection criteria and included in the Unassigned devices group.
You can enable the Include data from secondary Administration Servers check box to enable searching for devices that meet the selection criteria and managed by secondary Administration Servers.
- Click the Add button.
- In the window that opens, specify conditions that must be met for including devices in this selection, and then click the OK button.
- Click the Save button.
The device selection is created and added to the list of device selections.
Page top
Configuring a device selection
To configure a device selection:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Device selections.
A page with a list of device selections is displayed.
- Select the relevant user-defined device selection, and click the Properties button.
The Device selection settings window opens.
- On the General tab, click the New condition link.
- Specify conditions that must be met for including devices in this selection.
- Click the Save button.
The settings are applied and saved.
Below are descriptions of the conditions for assigning devices to a selection. Conditions are combined by using the OR logical operator: the selection will contain devices that comply with at least one of the listed conditions.
General
In the General section, you can change the name of the selection condition and specify whether that condition must be inverted:
Network infrastructure
In the Network subsection, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to their network data:
- Device name
- Domain
- Administration group
- Description
- IP range
- Managed by a different Administration Server
In the Domain controller subsection, you can configure criteria for including devices into a selection based on domain membership:
In the Network activity subsection, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to their network activity:
- Acts as a distribution point
- Do not disconnect from the Administration Server
- Connection profile switched
- Last connected to Administration Server
- New devices detected by network poll
- Device is visible
In the Cloud segments subsection, you can configure criteria for including devices in a selection according to their respective cloud segments:
Device statuses
In the Managed device status subsection, you can configure criteria for including devices into a selection based on the description of the devices status from a managed application:
In the Status of components in managed applications subsection, you can configure criteria for including devices in a selection according to the statuses of components in managed applications:
- Data Leakage Prevention status
- Collaboration servers protection status
- Anti-virus protection status of mail servers
- Endpoint Sensor status
In the Status-affecting problems in managed applications subsection, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to the list of possible problems detected by a managed application. If at least one problem that you select exists on a device, the device will be included in the selection. When you select a problem listed for several applications, you have the option to select this problem in all of the lists automatically.
You can select check boxes for descriptions of statuses from the managed application; upon receipt of these statuses, the devices will be included in the selection. When you select a status listed for several applications, you have the option to select this status in all of the lists automatically.
System details
In the Operating system section, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to their operating system type.
- Platform type
- Operating system service pack version
- Operating system bit size
- Operating system build
- Operating system release number
In the Virtual machines section, you can set up the criteria to include devices in the selection according to whether these are virtual machines or part of virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI):
In the Hardware registry subsection, you can configure criteria for including devices into a selection based on their installed hardware:
Ensure that the lshw utility is installed on Linux devices from which you want to fetch hardware details. Hardware details fetched from virtual machines may be incomplete depending on the hypervisor used.
- Device
- Vendor
- Device name
- Description
- Device vendor
- Serial number
- Inventory number
- User
- Location
- CPU clock rate, in MHz, from
- CPU clock rate, in MHz, to
- Number of virtual CPU cores, from
- Number of virtual CPU cores, to
- Hard drive volume, in GB, from
- Hard drive volume, in GB, to
- RAM size, in MB, from
- RAM size, in MB, to
Third-party software details
In the Applications registry subsection, you can set up the criteria to search for devices according to applications installed on them:
- Application name
- Application version
- Vendor
- Application status
- Find by update
- Name of incompatible security application
- Application tag
- Apply to devices without the specified tags
In the Vulnerabilities and updates subsection, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to their Windows Update source:
WUA is switched to Administration Server
Details of Kaspersky applications
In the Kaspersky applications subsection, you can configure criteria for including devices in a selection based on the selected managed application:
- Application name
- Application version
- Critical update name
- Select the period of the last update of modules
- Device is managed through Administration Server
- Security application is installed
In the Anti-virus protection subsection, you can set up the criteria for including devices in a selection based on their protection status:
In the Encryption subsection, you can configure the criterion for including devices in a selection based on the selected encryption algorithm:
The Application components subsection contains the list of components of those applications that have corresponding management plug-ins installed in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
In the Application components subsection, you can specify criteria for including devices in a selection according to the statuses and version numbers of the components that refer to the application that you select:
Tags
In the Tags section, you can configure criteria for including devices into a selection based on key words (tags) that were previously added to the descriptions of managed devices:
Apply if at least one specified tag matches
To add tags to the criterion, click the Add button, and select tags by clicking the Tag entry field. Specify whether to include or exclude the devices with the selected tags in the device selection.
Users
In the Users section, you can set up the criteria to include devices in the selection according to the accounts of users who have logged in to the operating system.
Page top
Exporting the device list from a device selection
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to save information about devices from a device selection and export it as a CSV or a TXT file.
To export the device list from the device selection:
- Open the table with the devices from the device selection.
- Use one of the following ways to select the devices that you want to export:
- To select particular devices, select the check boxes next to them.
- To select all devices from the current table page, select the check box in the device table header, and then select the Select all on current page check box.
- To select all devices from the table, select the check box in the device table header, and then select the Select all check box.
- Click the Export to CSV or Export to TXT button. All information about the selected devices included in the table will be exported.
Note that if you applied a filter criterion to the device table, only the filtered data from the displayed columns will be exported.
Page top
Removing devices from administration groups in a selection
When working with a device selection, you can remove devices from administration groups right in this selection, without switching to the administration groups from which these devices must be removed.
To remove devices from administration groups:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Device selections or Discovery & deployment → Device selections.
- In the selection list, click the name of the device selection.
The page displays a table with information about the devices included in the device selection.
- Select the devices that you want to remove, and then click Delete.
The selected devices are removed from their respective administration groups.
Device tags
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to tag devices. A tag is the label of a device and it can be used for grouping, describing, or finding devices. Tags assigned to devices can be used for creating selections, for finding devices, and for distributing devices among administration groups.
You can tag devices manually or automatically. You may use manual tagging when you want to tag an individual device. Auto-tagging is performed by Kaspersky Security Center in accordance with the specified tagging rules.
Devices are tagged automatically when specified rules are met. An individual rule corresponds to each tag. Rules are applied to the network properties of the device, operating system, applications installed on the device, and other device properties. For example, if you have a hybrid infrastructure of physical machines, Amazon EC2 instances, and Microsoft Azure virtual machines, you can set up a rule that will assign the [Azure] tag to all Microsoft Azure virtual machines. Then, you can use this tag when creating a device selection; and this will help you sort all Microsoft Azure virtual machines and assign them a task.
A tag is automatically removed from a device in the following cases:
- When the device stops meeting conditions of the rule that assigns the tag.
- When the rule that assigns the tag is disabled or deleted.
The list of tags and the list of rules on each Administration Server are independent of all other Administration Servers, including a primary Administration Server or subordinate virtual Administration Servers. A rule is applied only to devices from the same Administration Server on which the rule is created.
Creating a device tag
To create a device tag:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tags → Device tags.
- Click Add.
A new tag window opens.
- In the Tag field, enter the tag name.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The new tag appears in the list of device tags.
Renaming a device tag
To rename a device tag:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tags → Device tags.
- Click the name of the tag that you want to rename.
A tag properties window opens.
- In the Tag field, change the tag name.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The updated tag appears in the list of device tags.
Deleting a device tag
To delete a device tag:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tags → Device tags.
- In the list, select the device tag that you want to delete.
- Click the Delete button.
- In the window that opens, click Yes.
The device tag is deleted. The deleted tag is automatically removed from all of the devices to which it was assigned.
The tag that you have deleted is not removed automatically from auto-tagging rules. After the tag is deleted, it will be assigned to a new device only when the device first meets the conditions of a rule that assigns the tag.
The deleted tag is not removed automatically from the device if this tag is assigned to the device by an application or Network Agent. To remove the tag from your device, use the klscflag utility.
Viewing devices to which a tag is assigned
To view devices to which a tag is assigned:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tags → Device tags.
- Click the View devices link next to the tag for which you want to view assigned devices.
You will be redirected to the Managed devices section of the main menu, with the devices filtered by the tag for which you clicked the View devices link.
- If you want to return to the list of device tags, click the Back button of your browser.
After you view the devices to which the tag is assigned, you can either create and assign a new tag or assign the existing tag to other devices. In this case, you have to remove the filter by tag, select the devices, and then assign the tag.
Viewing tags assigned to a device
To view tags assigned to a device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click the name of the device whose tags you want to view.
- In the device properties window that opens, select the Tags tab.
The list of tags assigned to the selected device is displayed. In the Tag assigned column you can view how the tag was assigned.
You can assign another tag to the device or remove an already assigned tag. You can also view all device tags that exist on the Administration Server.
You can also view tags assigned to a device in the command line using the klscflag utility.
To view tags assigned to a device in the command line, run the following command:
klscflag -ssvget -pv 1103/1.0.0.0 -s KLNAG_SECTION_TAGS_INFO -n KLCONN_HOST_TAGS -svt ARRAY_T -ss "|ss_type = \"SS_PRODINFO\";"
Tagging a device manually
To assign a tag to a device manually:
- View tags assigned to the device to which you want to assign another tag.
- Click Add.
- In the window that opens, do one of the following:
- To create and assign a new tag, select Create new tag, and then specify the name of the new tag.
- To select an existing tag, select Assign existing tag, and then select the necessary tag in the drop-down list.
- Click OK to apply the changes.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The selected tag is assigned to the device.
Removing an assigned tag from a device
To remove a tag from a device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click the name of the device whose tags you want to view.
- In the device properties window that opens, select the Tags tab.
- Select the check box next to the tag that you want to remove.
- At the top of the list, click the Unassign tag? button.
- In the window that opens, click Yes.
The tag is removed from the device.
The unassigned device tag is not deleted. If you want, you can delete it manually.
You cannot manually remove tags assigned to the device by applications or Network Agent. To remove these tags, use the klscflag utility.
Viewing rules for tagging devices automatically
To view rules for tagging devices automatically,
Do any of the following:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tags → Auto-tagging rules.
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tags → Device tags, and then click the Set up auto-tagging rules link.
- View tags assigned to a device and then click the Settings button.
The list of rules for auto-tagging devices appears.
Editing a rule for tagging devices automatically
To edit a rule for tagging devices automatically:
- View rules for tagging devices automatically.
- Click the name of the rule that you want to edit.
A rule settings window opens.
- Edit the general properties of the rule:
- In the Rule name field, change the rule name.
The name cannot be more than 256 characters long.
- Do any of the following:
- Enable the rule by switching the toggle button to Rule enabled.
- Disable the rule by switching the toggle button to Rule disabled.
- In the Rule name field, change the rule name.
- Do any of the following:
- If you want to add a new condition, click the Add button, and specify the settings of the new condition in the window that opens.
- If you want to edit an existing condition, click the name of the condition that you want to edit, and then edit the condition settings.
- If you want to delete a condition, select the check box next to the name of the condition that you want to delete, and then click Delete.
- Click OK in the conditions settings window.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The edited rule is shown in the list.
Creating a rule for tagging devices automatically
To create a rule for tagging devices automatically:
- View rules for tagging devices automatically.
- Click Add.
A new rule settings window opens.
- Configure the general properties of the rule:
- In the Rule name field, enter the rule name.
The name cannot be more than 256 characters long.
- Do one of the following:
- Enable the rule by switching the toggle button to Rule enabled.
- Disable the rule by switching the toggle button to Rule disabled.
- In the Tag field, enter the new device tag name or select one of the existing device tags from the list.
The name cannot be more than 256 characters long.
- In the Rule name field, enter the rule name.
- In the conditions section, click the Add button to add a new condition.
A new condition settings window open.
- Enter the condition name.
The name cannot be more than 256 characters long. The name must be unique within a rule.
- Set up the triggering of the rule according to the following conditions. You can select multiple conditions.
- Network—Network properties of the device, such as the device name on the Windows network, or device inclusion in a domain or an IP subnet.
If case sensitive collation is set for the database that you use for Kaspersky Security Center, keep case when you specify a device DNS name. Otherwise, the auto-tagging rule will not work.
- Applications—Presence of Network Agent on the device, operating system type, version, and architecture.
- Virtual machines—Device belongs to a specific type of virtual machine.
- Domain controller—Presence of the device in an Active Directory organizational unit and membership of the device in an Active Directory group.
- Applications registry—Presence of applications of different vendors on the device.
- Network—Network properties of the device, such as the device name on the Windows network, or device inclusion in a domain or an IP subnet.
- Click OK to save the changes.
If necessary, you can set multiple conditions for a single rule. In this case, the tag will be assigned to a device if it meets at least one condition.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The newly created rule is enforced on devices managed by the selected Administration Server. If the settings of a device meet the rule conditions, the device is assigned the tag.
Later, the rule is applied in the following cases:
- Automatically and periodically, depending on the server workload
- After you edit the rule
- When you run the rule manually
- After the Administration Server detects a change in the settings of a device that meets the rule conditions or the settings of a group that contains such device
You can create multiple tagging rules. A single device can be assigned multiple tags if you have created multiple tagging rules and if the respective conditions of these rules are met simultaneously. You can view the list of all assigned tags in the device properties.
Running rules for auto-tagging devices
When a rule is run, the tag specified in properties of this rule is assigned to devices that meet conditions specified in properties of the same rule. You can run only active rules.
To run rules for auto-tagging devices:
- View rules for tagging devices automatically.
- Select check boxes next to active rules that you want to run.
- Click the Run rule button.
The selected rules are run.
Deleting a rule for tagging devices automatically
To delete a rule for tagging devices automatically:
- View rules for tagging devices automatically.
- Select the check box next to the rule that you want to delete.
- Click Delete.
- In the window that opens, click Delete again.
The selected rule is deleted. The tag that was specified in properties of this rule is unassigned from all of the devices that it was assigned to.
The unassigned device tag is not deleted. If you want, you can delete it manually.
Managing device tags by using the klscflag utility
To assign a set of tags to a device, you need to run the klscflag utility on the client device to which you want to assign tags.
The klscflag utility overwrites the existing set of tags assigned to the device. This means, that you can add new tags, or remove specific tags by specifying the desired set of tags in the command. The utility does not have separate commands for adding or removing individual tags. Instead, you modify the entire set of tags.
When specifying tag names in commands like klscflag, it is recommended to use a consistent case approach, such as all caps. Using all caps can help avoid potential issues with tags that differ only in case, depending on the DBMS configuration.
To assign tags to your device by using the klscflag utility:
- Run the Windows command prompt by using administrator rights, and then change your current directory to the directory with the klscflag utility. The klscflag utility is located in the folder where Network Agent is installed. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\NetworkAgent.
- Enter one of the following commands:
- To assign a set of tags:
klscflag -ssvset -pv 1103/1.0.0.0 -s KLNAG_SECTION_TAGS_INFO -n KLCONN_HOST_TAGS -sv "[\"TAG NAME 1\",\"TAG NAME 2\",\"TAG NAME 3\"]" -svt ARRAY_T -ss "|ss_type = \"SS_PRODINFO\";"where
[\"TAG NAME 1\",\"TAG NAME 2\",\"TAG NAME 3\"]is the list of tags you that want to assign to your device.If you leave the square brackets empty, this will remove all tags from the device:
klscflag -ssvset -pv 1103/1.0.0.0 -s KLNAG_SECTION_TAGS_INFO -n KLCONN_HOST_TAGS -sv "[]" -svt ARRAY_T -ss "|ss_type = \"SS_PRODINFO\";" - To assign a new tag to an existing set of tags:
klscflag -ssvset -pv 1103/1.0.0.0 -s KLNAG_SECTION_TAGS_INFO -n KLCONN_HOST_TAGS -sv "[\"NEW TAG NAME\",\"TAG NAME 1\",\"TAG NAME 2\",\"TAG NAME 3\"]" -svt ARRAY_T -ss "|ss_type = \"SS_PRODINFO\";"where
NEW TAG NAMEis the name of the tag that you want to assign to your device andTAG NAME 1,TAG NAME 2,TAG NAME 3are the names of the tags already assigned to the device. - To remove a specific tag without removing other tags already assigned to the device, run the command with the updated set of tags.
For example, if your current tags are
TAG NAME 1,TAG NAME 2,TAG NAME 3and you want to removeTAG NAME 2, run the following command:klscflag -ssvset -pv 1103/1.0.0.0 -s KLNAG_SECTION_TAGS_INFO -n KLCONN_HOST_TAGS -sv "[\"TAG NAME 1\",\"TAG NAME 3\"]" -svt ARRAY_T -ss "|ss_type = \"SS_PRODINFO\";"
- To assign a set of tags:
- Restart the Network Agent service.
The klscflag utility assigns the specified tags to your device. To make sure that the klscflag utility has assigned the specified tags successfully, view tags assigned to the device.
Alternatively, you can assign device tags manually.
Page top
Policies and policy profiles
In Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you can create policies for Kaspersky applications. This section describes policies and policy profiles, and provides instructions for creating and modifying them.
About policies and policy profiles
A policy is a set of Kaspersky application settings that are applied to an administration group and its subgroups. You can install several Kaspersky applications on the devices of an administration group. Kaspersky Security Center provides a single policy for each Kaspersky application in an administration group. A policy has one of the following statuses (see the table below):
The status of the policy
Status |
Description |
|---|---|
Active |
The current policy that is applied to the device. Only one policy may be active for a Kaspersky application in each administration group. Devices apply the settings values of an active policy for a Kaspersky application. |
Inactive |
A policy that is not currently applied to a device. |
Out-of-office |
If this option is selected, the policy becomes active when the device leaves the corporate network. |
Policies function according to the following rules:
- Multiple policies with different values can be configured for a single application.
- Only one policy can be active for the current application.
- You can activate an inactive policy when a specific event occurs. For example, you can enforce stricter anti-virus protection settings during virus outbreaks.
- A policy can have child policies.
Generally, you can use policies as preparations for emergency situations, such as a virus attack. For example, if there is an attack via flash drives, you can activate a policy that blocks access to flash drives. In this case, the current active policy automatically becomes inactive.
In order to prevent maintaining multiple policies, for example, when different occasions assume changing of several settings only, you may use policy profiles.
A policy profile is a named subset of policy settings values that replaces the settings values of a policy. A policy profile affects the effective settings formation on a managed device. Effective settings are a set of policy settings, policy profile settings, and local application settings that are currently applied for the device.
Policy profiles function according to the following rules:
- A policy profile takes an effect when a specific activation condition occurs.
- Policy profiles contain values of settings that differ from the policy settings.
- Activation of a policy profile changes the effective settings of the managed device.
- A policy can include a maximum of 100 policy profiles.
About lock and locked settings
Each policy setting has a lock button icon ( ). The table below shows lock button statuses:
). The table below shows lock button statuses:
Lock button statuses
Status |
Description |
|---|---|
|
If an open lock is displayed next to a setting and the toggle button is disabled, the setting is not specified in the policy. A user can change these settings in the managed application interface. These type of settings are called unlocked. |
|
If a closed lock is displayed next to a setting and the toggle button is enabled, the setting is applied to the devices where the policy is enforced. A user cannot modify the values of these settings in the managed application interface. These type of settings are called locked. |
We highly recommend that you close locks for the policy settings that you want to apply on the managed devices. The unlocked policy settings can be reassigned by Kaspersky application settings on a managed device.
You can use a lock button for performing the following actions:
- Locking settings for an administration subgroup policy
- Locking settings of a Kaspersky application on a managed device
Thus, a locked setting is used for implementing effective settings on a managed device.
A process of effective settings implementation includes the following actions:
- Managed device applies settings values of Kaspersky application.
- Managed device applies locked settings values of a policy.
A policy and managed Kaspersky application contain the same set of settings. When you configure policy settings, the Kaspersky application settings change values on a managed device. You cannot adjust locked settings on a managed device (see the figure below):
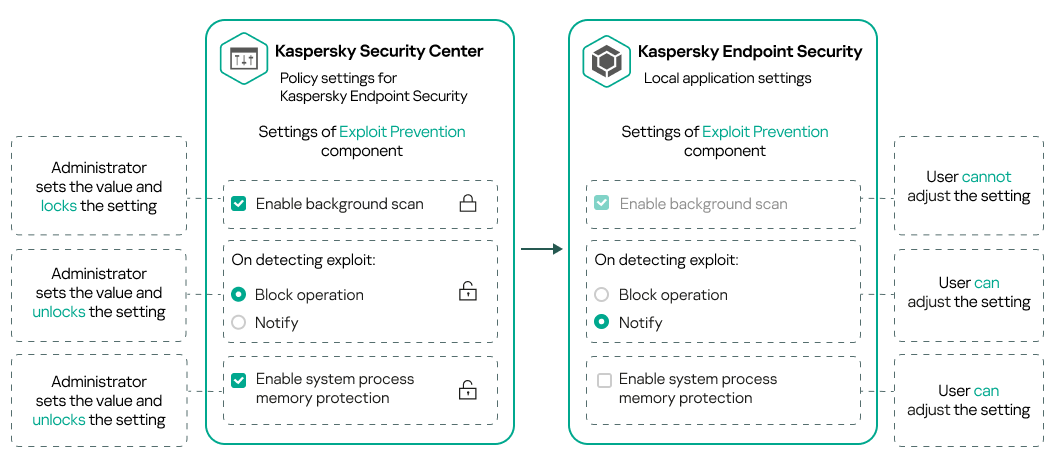
Locks and Kaspersky application settings
Inheritance of policies and policy profiles
This section provides information about the hierarchy and inheritance of policies and policy profiles.
Hierarchy of policies
If different devices need different settings, you can organize devices into administration groups.
You can specify a policy for a single administration group. Policy settings can be inherited. Inheritance means receiving policy settings values in subgroups (child groups) from a policy of a higher-level (parent) administration group.
Hereinafter, a policy for a parent group is also referred to as a parent policy. A policy for a subgroup (child group) is also referred to as a child policy.
By default, at least one managed devices group exists on Administration Server. If you want to create custom groups, they are created as subgroups (child groups) within the managed devices group.
Policies of the same application act on each other, according to a hierarchy of administration groups. Locked settings from a policy of a higher-level (parent) administration group will reassign policy settings values of a subgroup (see the figure below).
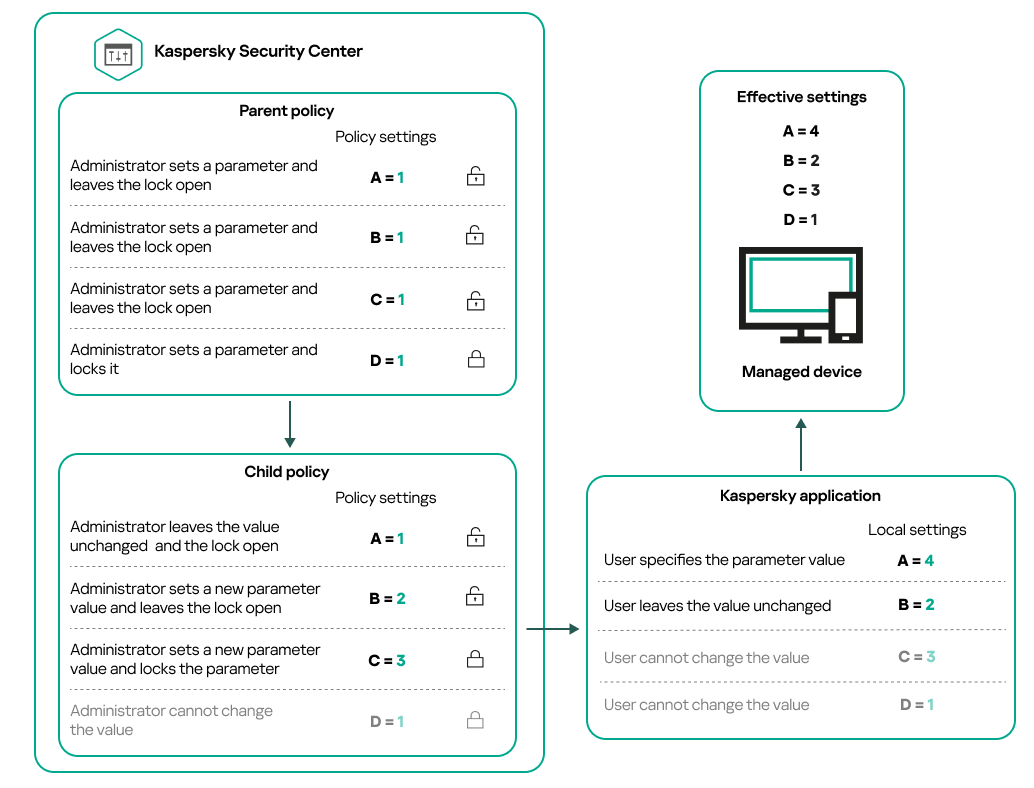
Hierarchy of policies
Page top
Policy profiles in a hierarchy of policies
Policy profiles have the following priority assignment conditions:
- A profile's position in a policy profile list indicates its priority. You can change a policy profile priority. The highest position in a list indicates the highest priority (see the figure below).
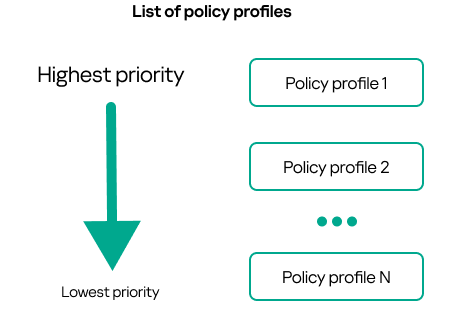
Priority definition of a policy profile
- Activation conditions of policy profiles do not depend on each other. Several policy profiles can be activated simultaneously. If several policy profiles affect the same setting, the device takes the setting value from the policy profile with the highest priority (see the figure below).
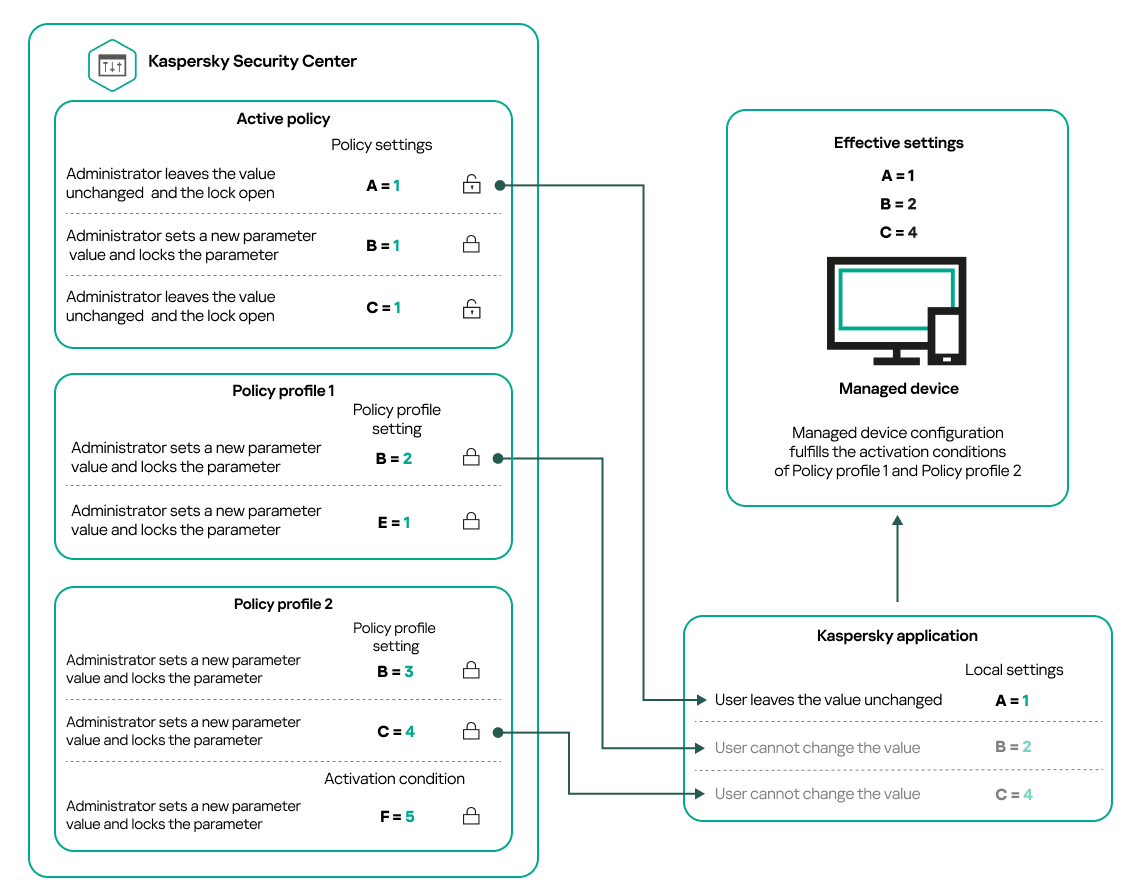
Managed device configuration fulfills activation conditions of several policy profiles
Policy profiles in a hierarchy of inheritance
Policy profiles from different hierarchy level policies comply with the following conditions:
- A lower-level policy inherits policy profiles from a higher-level policy. A policy profile inherited from a higher-level policy obtains higher priority than the original policy profile's level.
- You cannot change a priority of an inherited policy profile (see the figure below).
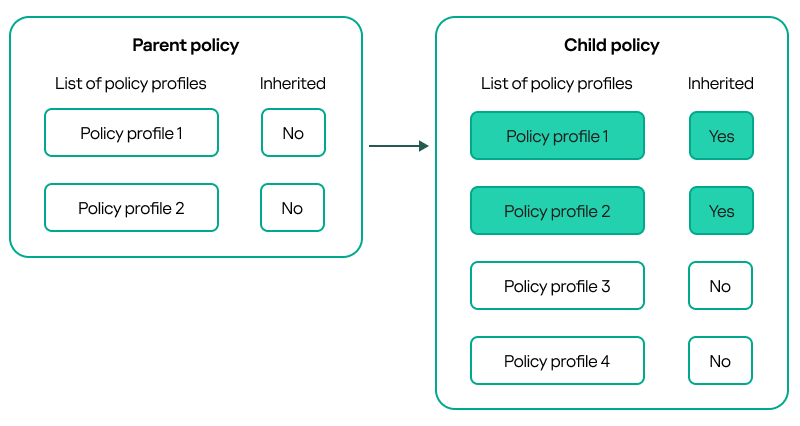
Inheritance of policy profiles
Policy profiles with the same name
If there are two policies with the same names in different hierarchy levels, these policies function according to the following rules:
- Locked settings and the profile activation condition of a higher-level policy profile changes the settings and profile activation condition of a lower-level policy profile (see the figure below).
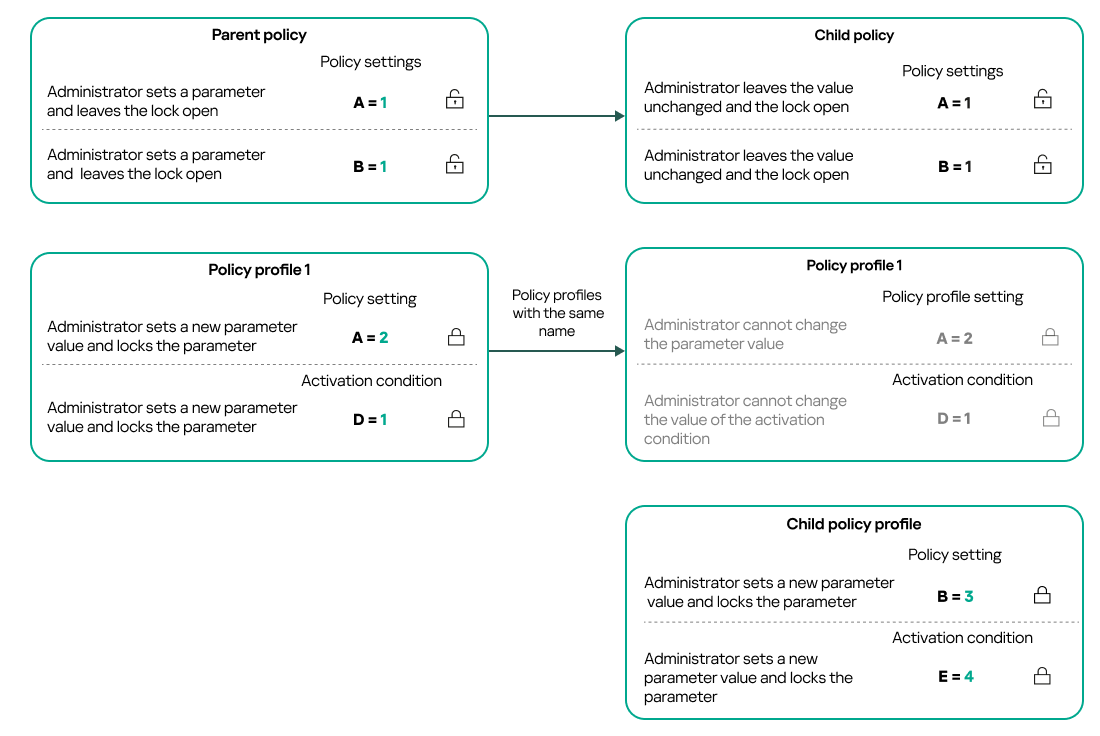
Child profile inherits settings values from a parent policy profile
- Unlocked settings and the profile activation condition of a higher-level policy profile do not change the settings and profile activation condition of a lower-level policy profile.
How settings are implemented on a managed device
Implementation of effective settings on a managed device can be described as follows:
- The values of all settings that have not been locked are taken from the policy.
- Then they are overwritten with the values of managed application settings.
- And then the locked settings values from the effective policy are applied. Locked settings values change the values of unlocked effective settings.
Managing policies
This section describes managing policies and provides information about viewing the list of policies, creating a policy, modifying a policy, copying a policy, moving a policy, forced synchronization, viewing the policy distribution status chart, and deleting a policy.
Viewing the list of policies
You can view lists of policies created for the Administration Server or for any administration group.
To view a list of policies:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- In the administration group structure, select the administration group for which you want to view the list of policies.
The list of policies appears in tabular format. If there are no policies, the table is empty. You can show or hide the columns of the table, change their order, view only lines that contain a value that you specify, or use search.
Creating a policy
You can create policies; you can also modify and delete existing policies.
To create a policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Select the administration group for which the policy is to be created:
- For the root group.
In this case you can proceed to the next step.
- For a subgroup:
- Click the current path link at the top of the window.
- In the panel that opens, click the link with the name of the required subgroup.
The current path changes to reflect the selected subgroup.
- For the root group.
- Click Add.
The Select application window opens.
- Select the application for which you want to create a policy.
- Click Next.
The new policy settings window opens with the General tab selected.
- If you want, change the default name, default status, and default inheritance settings of the policy.
- Select the Application settings tab.
Or, you can click Save and exit. The policy will appear in the list of policies, and you can edit its settings later.
- On the Application settings tab, in the left pane, select the category that you want and in the results pane on the right, edit the settings of the policy. You can edit policy settings in each category (section).
The set of settings depends on the application for which you create a policy. For details, refer to the following:
- Administration Server configuration
- Network Agent policy settings
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows documentation
For details about settings of other security applications, refer to the documentation for the corresponding application.
When editing the settings, you can click Cancel to cancel the last operation.
- Click Save to save the policy.
The policy will appear in the list of policies.
Modifying a policy
To modify a policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy that you want to modify.
The policy settings window opens.
- Specify the general settings and settings of the application for which you create a policy. For details, refer to the following:
- Administration Server configuration
- Network Agent policy settings
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows documentation
For details about settings of other security applications, refer to the documentation for that application.
- Click Save.
The changes made to the policy will be saved in the policy properties, and will appear in the Revision history section.
General policy settings
General
In the General tab, you can modify the policy status and specify the inheritance of policy settings:
- In the Policy status block, you can select one of the policy modes:
- In the Settings inheritance settings group, you can configure the policy inheritance:
Event configuration
The Event configuration tab allows you to configure event logging and event notification. Events are distributed by importance level on the following tabs:
- Critical
The Critical section is not displayed in the Network Agent policy properties.
- Functional failure
- Warning
- Info
In each section, the list shows the types of events and the default event storage term on the Administration Server (in days). Clicking an event type lets you specify the following settings:
- Event registration
You can specify how many days to store the event and select where to store the event:
- Export to SIEM system by using Syslog
- Store in the OS event log on device
- Store in the OS event log on Administration Server
- Event notifications
You can select if you want to be notified about the event in one of the following ways:
- Notify by email
- Notify by SMS
- Notify by running an executable file or script
- Notify by SNMP
By default, the notification settings specified on the Administration Server properties tab (such as recipient address) are used. If you want, you can change these settings in the Email, SMS, and Executable file to be run tabs.
Revision history
The Revision history tab allows you to view the list of the policy revisions and roll back changes made to the policy, if necessary.
Enabling and disabling a policy inheritance option
To enable or disable the inheritance option in a policy:
- Open the required policy.
- Open the General tab.
- Enable or disable policy inheritance:
- If you enable Inherit settings from parent policy in a child policy and an administrator locks some settings in the parent policy, then you cannot change these settings in the child policy.
- If you disable Inherit settings from parent policy in a child policy, then you can change all of the settings in the child policy, even if some settings are locked in the parent policy.
- If you enable Force inheritance of settings in child policies in the parent group, this enables the Inherit settings from parent policy option for each child policy. In this case, you cannot disable this option for any child policy. All of the settings that are locked in the parent policy are forcibly inherited in the child groups, and you cannot change these settings in the child groups.
- Click the Save button to save changes or click the Cancel button to reject changes.
By default, the Inherit settings from parent policy option is enabled for a new policy.
If a policy has profiles, all of the child policies inherit these profiles.
Copying a policy
You can copy policies from one administration group to another.
To copy a policy to another administration group:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Select the check box next to the policy (or policies) that you want to copy.
- Click the Copy button.
On the right side of the screen, the tree of the administration groups appears.
- In the tree, select the target group, that is, the group to which you want to copy the policy (or policies).
- Click the Copy button at the bottom of the screen.
- Click OK to confirm the operation.
The policy (policies) will be copied to the target group with all its profiles. The status of each copied policy in the target group will be Inactive. You can change the status to Active at any time.
If a policy with the name identical to that of the newly moved policy already exists in the target group, the name of the newly moved policy is expanded with the (<next sequence number>) index, for example: (1).
Moving a policy
You can move policies from one administration group to another. For example, you want to delete a group, but you want to use its policies for another group. In this case, you may want move the policy from the old group to the new one before deleting the old group.
To move a policy to another administration group:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Select the check box next to the policy (or policies) that you want to move.
- Click the Move button.
On the right side of the screen, the tree of the administration groups appears.
- In the tree, select the target group, that is, the group to which you want to move the policy (or policies).
- Click the Move button at the bottom of the screen.
- Click OK to confirm the operation.
If a policy is not inherited from the source group, it is moved to the target group with all its profiles. The status of the policy in the target group is Inactive. You can change the status to Active at any time.
If a policy is inherited from the source group, it remains in the source group. It is copied to the target group with all its profiles. The status of the policy in the target group is Inactive. You can change the status to Active at any time.
If a policy with the name identical to that of the newly moved policy already exists in the target group, the name of the newly moved policy is expanded with the (<next sequence number>) index, for example: (1).
Exporting a policy
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to save a policy, its settings, and the policy profiles to a KLP file. You can use this KLP file to import the saved policy both to Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
To export a policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Select the check box next to the policy that you want to export.
You cannot export multiple policies at the same time. If you select more than one policy, the Export button will be disabled.
- Click the Export button.
- In the opened Save as window, specify the policy file name and path. Click the Save button.
The Save as window is displayed only if you use Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, or Opera. If you use another browser, the policy file is automatically saved in the Downloads folder.
Importing a policy
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to import a policy from a KLP file. The KLP file contains the exported policy, its settings, and the policy profiles.
To import a policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the Import button.
- Click the Browse button to choose a policy file that you want to import.
- In the opened window, specify the path to the KLP policy file, and then click the Open button. Note that you can select only one policy file.
The policy processing starts.
- After the policy is processed successfully, select the administration group to which you want to apply the policy.
- Click the Complete button to finish the policy import.
The notification with the import results appears. If the policy is imported successfully, you can click the Details link to view the policy properties.
After a successful import, the policy is displayed in the policy list. The settings and profiles of the policy are also imported. Regardless of the policy status that was selected during the export, the imported policy is inactive. You can change the policy status in the policy properties.
If the newly imported policy has a name identical to that of an existing policy, the name of the imported policy is expanded with the (<next sequence number>) index, for example: (1), (2).
Page top
Viewing the policy distribution status chart
In Kaspersky Security Center, you can view the status of policy application on each device in a policy distribution status chart.
To view the policy distribution status on each device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Select check box next to the name of the policy for which you want to view the distribution status on devices.
- In the menu that appears, select the Distribution link.
The <Policy name> distribution results window opens.
- In the <Policy name> distribution results window that opens, the Status description of the policy is displayed.
You can change number of results displayed in the list with policy distribution. The maximum number of devices is 100,000.
To change the number of devices displayed in the list with policy distribution results:
- In the main menu, go to your account settings, and then select Interface options.
- In the Limit of devices displayed in policy distribution results, enter the number of devices (up to 100,000).
By default, the number is 5000.
- Click Save.
The settings are saved and applied.
Activating a policy automatically at the Virus outbreak event
To make a policy perform automatic activation at a Virus outbreak event:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens, with the General tab selected.
- Select the Virus outbreak section.
- In the right pane, click the Configure policies to activate when a virus outbreak event occurs link.
The Policy activation window opens.
- In the section relating to the component that detects a virus outbreak—Anti-Virus for workstations and file servers, Anti-Virus for mail servers, or Anti-Virus for perimeter defense—select the option button next to the entry you want, and then click Add.
A window opens with the Managed devices administration group.
- Click the chevron icon (
 ) next to Managed devices.
) next to Managed devices.A hierarchy of administration groups and their policies is displayed.
- In the hierarchy of administration groups and their policies, click the name of a policy or policies that are activated when a virus outbreak is detected.
To select all policies in the list or in a group, select the check box next to the required name.
- Click the Save button.
The window with the hierarchy of administration groups and their policies is closed.
The selected policies are added to the list of policies that are activated when a virus outbreak is detected. The selected policies are activated at the virus outbreak, independent whether they are active or inactive.
If a policy has been activated on the Virus outbreak event, you can return to the previous policy only by using the manual mode.
Deleting a policy
You can delete a policy if you do not need it anymore. You can delete only a policy that is not inherited in the specified administration group. If a policy is inherited, you can only delete it in the upper-level group for which it was created.
To delete a policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Select the check box next to the policy that you want to delete, and click Delete.
The Delete button becomes unavailable (dimmed) if you select an inherited policy.
- Click OK to confirm the operation.
The policy is deleted together with all its profiles.
Managing policy profiles
This section describes managing policy profiles and provides information about viewing the profiles of a policy, changing a policy profile priority, creating a policy profile, modifying a policy profile, copying a policy profile, creating a policy profile activation rule, and deleting a policy profile.
Viewing the profiles of a policy
To view profiles of a policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the name of the policy whose profiles you want to view.
The policy properties window opens with the General tab selected.
- Open the Policy profiles tab.
The list of policy profiles appears in tabular format. If the policy does not have profiles, an empty table appears.
Changing a policy profile priority
To change a policy profile priority:
- Proceed to the list of profiles of a policy that you want.
The list of policy profiles appears.
- On the Policy profiles tab, select the check box next to the policy profile for which you want to change priority.
- Set a new position of the policy profile in the list by clicking Prioritize or Deprioritize.
The higher a policy profile is located in the list, the higher its priority.
- Click the Save button.
Priority of the selected policy profile is changed and applied.
Creating a policy profile
To create a policy profile:
- Proceed to the list of profiles of the policy that you want.
The list of policy profiles appears. If the policy does not have profiles, an empty table appears.
- Click Add.
- If you want, change the default name and default inheritance settings of the profile.
- Select the Application settings tab.
Alternatively, you can click Save and exit. The profile that you have created appears in the list of policy profiles, and you can edit its settings later.
- On the Application settings tab, in the left pane, select the category that you want and in the results pane on the right, edit the settings for the profile. You can edit policy profile settings in each category (section).
When editing the settings, you can click Cancel to cancel the last operation.
- Click Save to save the profile.
The profile will appear in the list of policy profiles.
Modifying a policy profile
The capability to edit a policy profile is only available for policies of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
To modify a policy profile:
- Proceed to the list of profiles of a policy that you want.
The list of policy profiles appears.
- On the Policy profiles tab, click the policy profile that you want to modify.
The policy profile properties window opens.
- Configure the profile in the properties window:
- If necessary, on the General tab, change the profile name and enable or disable the profile.
- Edit the profile activation rules.
- Edit the application settings.
For details about settings of security applications, please see the documentation of the corresponding application.
- Click Save.
The modified settings will take effect either after the device is synchronized with the Administration Server (if the policy profile is active), or after an activation rule is triggered (if the policy profile is inactive).
Copying a policy profile
You can copy a policy profile to the current policy or to another, for example, if you want to have identical profiles for different policies. You can also use copying if you want to have two or more profiles that differ in only a small number of settings.
To copy a policy profile:
- Proceed to the list of profiles of a policy that you want.
The list of policy profiles appears. If the policy does not have profiles, an empty table appears.
- On the Policy profiles tab, select the policy profile that you want to copy.
- Click Copy.
- In the window that opens, select the policy to which you want to copy the profile.
You can copy a policy profile to the same policy or to a policy that you specify.
- Click Copy.
The policy profile is copied to the policy that you selected. The newly copied profile gets the lowest priority. If you copy the profile to the same policy, the name of the newly copied profile will be expanded with the () index, for example: (1), (2).
Later, you can change the settings of the profile, including its name and its priority; the original policy profile will not be changed in this case.
Creating a policy profile activation rule
To create a policy profile activation rule:
- Proceed to the list of profiles of a policy that you want.
The list of policy profiles appears.
- On the Policy profiles tab, click the policy profile for which you need to create an activation rule.
If the list of policy profiles is empty, you can create a policy profile.
- On the Activation rules tab, click the Add button.
The window with policy profile activation rules opens.
- Specify a name for the rule.
- Select the check boxes next to the conditions that must affect activation of the policy profile that you are creating:
- General rules for policy profile activation
For this option, specify at the next step:
- Rules for specific device owner
For this option, specify at the next step:
- Rules for hardware specifications
For this option, specify at the next step:
- Rules for role assignment
For this option, specify at the next step:
- Rules for tag usage
For this option, specify at the next step:
- Rules for Active Directory usage
For this option, specify at the next step:
The number of additional pages of the wizard depends on the settings that you select at the first step. You can modify policy profile activation rules later.
- General rules for policy profile activation
- Check the list of the configured parameters. If the list is correct, click Create.
The profile will be saved. The profile will be activated on the device when activation rules are triggered.
Policy profile activation rules created for the profile are displayed in the policy profile properties on the Activation rules tab. You can modify or remove any policy profile activation rule.
Multiple activation rules can be triggered simultaneously.
Deleting a policy profile
To delete a policy profile:
- Proceed to the list of profiles of a policy that you want.
The list of policy profiles appears.
- On the Policy profiles tab, select the check box next to the policy profile that you want to delete, and click Delete.
- In the window that opens, click Delete again.
The policy profile is deleted. If the policy is inherited by a lower-level group, the profile remains in that group, but becomes the policy profile of that group. This is done to eliminate significant change in settings of the managed applications installed on the devices of lower-level groups.
Data encryption and protection
Data encryption reduces the risk of unintentional leakage in case your laptop or hard drive is stolen or lost, or upon access by unauthorized users and applications.
The following Kaspersky applications support encryption:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac
You can show or hide some of the interface elements related to the encryption management feature by using the user interface settings.
Encryption of data in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
You can manage the following types of encryption:
- BitLocker Drive Encryption on devices running a Windows operating system for servers
- Kaspersky Disk Encryption on devices running a Windows operating system for workstation
By using these components of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, you can, for example, enable or disable encryption, view the list of encrypted drives, or generate and view reports about encryption.
You configure encryption by defining policies of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows in Kaspersky Security Center. Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows performs encryption and decryption according to the active policy. For detailed instructions on how to configure rules and a description of encryption features, see the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
Encryption of data in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac
You can use FileVault encryption on devices running macOS. While working with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, you can enable or disable this encryption.
You configure encryption by defining policies of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac in Kaspersky Security Center. Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac performs encryption and decryption according to the active policy. For a detailed description of encryption features, see the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac Help.
Viewing the list of encrypted drives
In Kaspersky Security Center, you can view details about encrypted drives and devices that are encrypted at the drive level. After the information on a drive is decrypted, the drive is automatically removed from the list.
To view the list of encrypted drives,
In the main menu, go to Operations → Data encryption and protection → Encrypted drives.
If the section is not on the menu, this means that it is hidden. In the user interface settings, enable the Show data encryption and protection option to display the section.
You can export the list of encrypted drives to a CSV or TXT file. To do this, click the Export to CSV or Export to TXT button.
Viewing the list of encryption events
When running data encryption or decryption tasks on devices, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows sends Kaspersky Security Center information about events of the following types:
- Cannot encrypt or decrypt a file, or create an encrypted archive, due to a lack of free disk space.
- Cannot encrypt or decrypt a file, or create an encrypted archive, due to license issues.
- Cannot encrypt or decrypt a file, or create an encrypted archive, due to missing access rights.
- The application has been prohibited from accessing an encrypted file.
- Unknown errors.
To view a list of events that occurred during data encryption on devices,
In the main menu, go to Operations → Data encryption and protection → Encryption events.
If the section is not on the menu, this means that it is hidden. In the user interface settings, enable the Show data encryption and protection option to display the section.
You can export the list of encrypted drives to a CSV or TXT file. To do this, click the Export to CSV or Export to TXT button.
Alternatively, you can examine the list of encryption events for every managed device.
To view the encryption events for a managed device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click on the name of a managed device.
- On the General tab, go to the Protection section.
- Click the View data encryption errors link.
Creating and viewing encryption reports
You can generate the following reports:
- Report on encryption status of managed devices. This report provides details about the data encryption of various managed devices. For example, the report shows the number of devices to which the policy with configured encryption rules applies. Also, you can find out, for instance, how many devices need to be rebooted. The report also contains information about the encryption technology and algorithm for every device.
- Report on encryption status of mass storage devices. This report contains similar information as the report on the encryption status of managed devices, but it provides data only for mass storage devices and removable drives.
- Report on rights to access encrypted drives. This report shows which user accounts have access to encrypted drives.
- Report on file encryption errors. This report contains information about errors that occurred when the data encryption or decryption tasks were run on devices.
- Report on blockage of access to encrypted files. This report contains information about blocking application access to encrypted files. This report is helpful if an unauthorized user or application tries to access encrypted files or drives.
You can generate any report in the Monitoring & reporting → Reports section. Alternatively, in the Operations → Data encryption and protection section, you can generate the following encryption reports:
- Report on encryption status of mass storage devices
- Report on rights to access encrypted drives
- Report on file encryption errors
To generate an encryption report in the Data encryption and protection section:
- Make sure that you enabled the Show data encryption and protection option in the Interface options.
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Data encryption and protection.
- Open one of the following sections:
- Encrypted drives generates the report on encryption status of mass storage devices or the report on rights to access encrypted drives.
- Encryption events generates the report on file encryption errors.
- Click the name of the report that you want to generate.
The report generation starts.
Granting access to an encrypted drive in offline mode
A user can request access to an encrypted device, for example, when Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows is not installed on the managed device. After you receive the request, you can create an access key file and send it to the user. All of the use cases and detailed instructions are provided in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
To grant access to an encrypted drive in offline mode:
- Get a request access file from a user (a file with the FDERTC extension). Follow the instructions in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help to generate the file in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Data encryption and protection → Encrypted drives.
A list of encrypted drives appears.
- Select the drive to which the user requested access.
- Click the Grant access to the device in offline mode button.
- In the window that opens, select the plug-in corresponding to the Kaspersky application that was used to encrypt the selected drive.
If a drive is encrypted with a Kaspersky application that is not supported by Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, use Microsoft Management Console-based Administration Console to grant the offline access.
- Follow the instructions provided in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help (see expanding blocks at the end of the section).
After that, the user applies the received file to access the encrypted drive and read data stored on the drive.
Users and user roles
This section describes users and user roles, and provides instructions for creating and modifying them, for assigning roles and groups to users, and for associating policy profiles with roles.
About user roles
A user role (also referred to as a role) is an object containing a set of rights and privileges. A role can be associated with settings of Kaspersky applications installed on a user device. You can assign a role to a set of users or to a set of security groups at any level in the hierarchy of administration groups, Administration Servers, or at the level of specific objects.
If you manage devices through a hierarchy of Administration Servers that includes virtual Administration Servers, note that you can create, modify, or delete user roles only from a physical Administration Server. Then, you can propagate the user roles to secondary Administration Servers, including virtual ones.
You can associate user roles with policy profiles. If a user is assigned a role, this user gets security settings necessary to perform job functions.
A user role can be associated with users of devices in a specific administration group.
User role scope
A user role scope is a combination of users and administration groups. Settings associated with a user role apply only to devices that belong to users who have this role, and only if these devices belong to groups associated with this role, including child groups.
Advantage of using roles
An advantage of using roles is that you do not have to specify security settings for each of the managed devices or for each of the users separately. The number of users and devices in a company may be quite large, but the number of different job functions that require different security settings is considerably smaller.
Differences from using policy profiles
Policy profiles are properties of a policy that is created for each Kaspersky application separately. A role is associated with many policy profiles created for different applications. Therefore, a role is a method of uniting settings for a certain user type in one place.
Viewing user accounts and sessions
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to manage user accounts and groups of accounts. The application supports two types of accounts:
- Accounts of organization employees. Administration Server retrieves data of the accounts of those users when polling the organization's network.
- Accounts of internal users. These accounts are applied when virtual Administration Servers are used. Accounts of internal users are created and used only within Kaspersky Security Center.
You can view the list of user accounts and sessions in one of the following ways:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups.
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices → <device name> link → General tab → General section → Sessions block.
The Sessions section displays user accounts with active sessions on devices running Windows.
The list of user accounts and sessions is displayed correctly if the following requirements are met:
- Use Network Agent of the same version as Administration Server or later.
- Active Directory polling is enabled to display the accounts of domain users.
- On managed devices running Windows, the Server (LanmanServer) service is running.
Configuring access rights to application features. Role-based access control
Kaspersky Security Center provides facilities for role-based access to the features of Kaspersky Security Center and managed Kaspersky applications.
You can configure access rights to application features for Kaspersky Security Center users in one of the following ways:
- By configuring the rights for each user or group of users individually.
- By creating standard user roles with a predefined set of rights and assigning those roles to users depending on their scope of duties.
Application of user roles is intended to simplify and shorten routine procedures of configuring users' access rights to application features. Access rights within a role are configured in accordance with the standard tasks and the users' scope of duties.
User roles can be assigned names that correspond to their respective purposes. You can create an unlimited number of roles in the application.
You can use the predefined user roles with already configured set of rights, or create new roles and configure the required rights yourself.
Access rights to application features
The table below shows the Kaspersky Security Center features with the access rights to manage the associated tasks, reports, settings, and perform the associated user actions.
To perform the user actions listed in the table, a user has to have the right specified next to the action.
Read, Write, and Execute rights are applicable to any task, report, or setting. In addition to these rights, a user has to have the Perform operations on device selections right to manage tasks, reports, or settings on device selections.
The General features: Access objects regardless of their ACLs functional area is intended for audit purposes. When users are granted Read rights in this functional area, they get full Read access to all objects and are able to execute any created tasks on selections of devices connected to the Administration Server via Network Agent with local administrator rights (root for Linux). We recommend granting these rights carefully and to a limited set of users who need them to perform their official duties.
All tasks, reports, settings, and installation packages that are missing in the table belong to the General features: Basic functionality functional area.
Access rights to application features
Functional area |
Right |
User action: right required to perform the action |
Task |
Report |
Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
General features: Management of administration groups |
Write |
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Access objects regardless of their ACLs |
Read |
Get read access to all objects: Read |
None |
None |
Access is granted regardless of other rights, even if they prohibit read access to specific objects. |
General features: Basic functionality |
|
|
|
|
None |
General features: Deleted objects |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Event processing |
|
|
None |
None |
Settings:
|
General features: Operations on Administration Server |
|
|
|
None |
None |
General features: Kaspersky software deployment |
|
Approve or decline installation of the patch: Manage Kaspersky patches |
None |
|
Installation package: "Kaspersky" |
General features: Key management |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Enforced report management |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Hierarchy of Administration Servers |
Configure hierarchy of Administration Servers |
Register, update, or delete secondary Administration Servers: Configure hierarchy of Administration Servers |
None |
None |
None |
General features: User permissions |
Modify object ACLs |
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Virtual Administration Servers |
|
|
None |
"Report on results of installation of third-party software updates" |
None |
General features: Encryption Key Management |
Write |
Import the encryption keys: Write |
None |
None |
None |
Mobile device management: General |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
System management: Connectivity |
|
|
None |
"Report on device users" |
None |
System management: Hardware inventory |
|
|
None |
|
None |
System management: Network access control |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
System management: Operating system deployment |
|
|
"Create installation package upon reference device OS image" |
None |
Installation package: "OS Image" |
System management: Vulnerability and patch management
|
|
|
|
"Report on software updates" |
None |
System management: Remote installation |
|
|
None |
None |
Installation packages:
|
System management: Software inventory |
|
None |
None |
|
None |
System management: Execute scripts remotely |
|
User can view the task properties: Read User can create, delete, or modify an installation package: Write User can run a task: Write. On client Linux devices scripts are executed with root privileges. User can run a task or schedule it to run: Execute User can run a task on a selection of devices: Perform operations on device selections |
"Execute scripts remotely" |
None |
None |
Predefined user roles
User roles assigned to Kaspersky Security Center users provide them with sets of access rights to application features.
Users created on a virtual Server cannot be assigned a role on the Administration Server.
You can use the predefined user roles with already configured set of rights, or create new roles and configure the required rights yourself. Some of the predefined user roles available in Kaspersky Security Center can be associated with specific job positions, for example, Auditor, Security Officer, Supervisor (these roles are present in Kaspersky Security Center starting from the version 11). Access rights of these roles are pre-configured in accordance with the standard tasks and scope of duties of the associated positions. The table below shows how roles can be associated with specific job positions.
Examples of roles for specific job positions
Role |
Comment |
Auditor |
Permits all operations with all types of reports, all viewing operations, including viewing deleted objects (grants the Read and Write permissions in the Deleted objects area). Does not permit other operations. You can assign this role to a person who performs the audit of your organization. |
Supervisor |
Permits all viewing operations; does not permit other operations. You can assign this role to a security officer and other managers in charge of the IT security in your organization. |
Security Officer |
Permits all viewing operations, permits reports management; grants limited permissions in the System management: Connectivity area. You can assign this role to an officer in charge of the IT security in your organization. |
The table below shows the access rights assigned to each predefined user role.
Access rights of predefined user roles
Role |
Description |
|---|---|
Administration Server Administrator |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas:
Grants the Read and Write rights in the General features: Encryption key management functional area. |
Administration Server Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute rights in all of the following functional areas:
|
Auditor |
Permits all operations in the functional areas, in General features:
You can assign this role to a person who performs the audit of your organization. |
Installation Administrator |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas:
Grants the Read and Execute rights in the General features: Virtual Administration Servers functional area. |
Installation Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute rights in all of the following functional areas:
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security Administrator |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas:
Grants the Read and Write rights in the General features: Encryption key management functional area. |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute rights in all of the following functional areas:
|
Main Administrator |
Permits all operations in functional areas, except for the following areas, in General features:
Grants the Read and Write rights in the General features: Encryption key management functional area. |
Main Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute (where applicable) rights in all of the following functional areas:
|
Mobile Device Management Administrator |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas:
|
Mobile Device Management Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute rights in the General features: Basic functionality functional area. Grants Read and Send only information commands to mobile devices in the Mobile Device Management: General functional area. |
Security Officer |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas, in General features:
Grants the Read, Write, Execute, Save files from devices to the administrator's workstation, and Perform operations on device selections rights in the System management: Connectivity functional area. You can assign this role to an officer in charge of the IT security in your organization. |
Self Service Portal User |
Permits all operations in the Mobile Device Management: Self Service Portal functional area. This feature is not supported in Kaspersky Security Center 11 and later version. |
Supervisor |
Grants the Read right in the General features: Access objects regardless of their ACLs and General features: Enforced report management functional areas. You can assign this role to a security officer and other managers in charge of the IT security in your organization. |
Vulnerability and patch management administrator |
Permits all operations in the General features: Basic functionality and System management (including all features) functional areas. |
Vulnerability and patch management operator |
Grants the Read and Execute (where applicable) rights in the General features: Basic functionality and System management (including all features) functional areas. |
Assigning access rights to specific objects
In addition to assigning access rights at the server level, you can configure access to specific objects, for example, to a specific task. The application allows you to specify access rights to the following object types:
- Administration groups
- Tasks
- Reports
- Device selections
- Event selections
To assign access rights to a specific object:
- Depending on the object type, in the main menu, go to the corresponding section:
- Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups
- Assets (Devices) → Tasks
- Monitoring & reporting → Reports
- Assets (Devices) → Device selections
- Monitoring & reporting → Event selections
- Open the properties of the object to which you want to configure access rights.
To open the properties window of an administration group or a task, click the object name. Properties of other objects can be opened by using the button on the toolbar.
- In the properties window, open the Access rights section.
The user list opens. The listed users and security groups have access rights to the object. By default, if you use a hierarchy of administration groups or Servers, the list and access rights are inherited from the parent administration group or primary Server.
- To be able to modify the list, enable the Use custom permissions option.
- Configure access rights:
- Use the Add and Delete buttons to modify the list.
- Specify access rights for a user or security group. Do one of the following:
- If you want to specify access rights manually, select the user or security group, click the Access rights button, and then specify the access rights.
- If you want to assign a user role to the user or security group, select the user or security group, click the Roles button, and then select the role to assign.
- Click the Save button.
The access rights to the object are configured.
Assigning access rights to users and security groups
You can give users and security groups access rights to use different features of Administration Server, for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux.
To assign access rights to a user or a security group:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the Access rights tab, select the check box next to the name of the user or the security group to whom to assign rights, and then click the Access rights button.
You cannot select multiple users or security groups at the same time. If you select more than one item, the Access rights button will be disabled.
- Configure the set of rights for the user or group:
- Expand the node with features of Administration Server or other Kaspersky application.
- Select the Allow or Deny check box next to the feature or the access right that you want.
Example 1: Select the Allow check box next to the Application integration node to grant all available access rights to the Application integration feature (Read, Write, and Execute) for a user or group.
Example 2: Expand the Encryption key management node, and then select the Allow check box next to the Write permission to grant the Write access right to the Encryption key management feature for a user or group.
- After you configure the set of access rights, click OK.
The set of rights for the user or group of users will be configured.
The permissions of the Administration Server (or the administration group) are divided into the following areas:
- General features:
- Management of administration groups
- Access objects regardless of their ACLs
- Basic functionality
- Deleted objects
- Encryption Key Management
- Event processing
- Operations on Administration Server (only in the property window of Administration Server)
- Device tags
- Kaspersky application deployment
- License key management
- Application integration
- Enforced report management
- Hierarchy of Administration Servers
- User permissions
- Virtual Administration Servers
- Mobile Device Management:
- General
- Self Service Portal
- System Management:
- Connectivity
- Execute scripts remotely
- Hardware inventory
- Network Access Control
- Operating system deployment
- Vulnerability and patch management
- Remote installation
- Software inventory
If neither Allow nor Deny is selected for an access right, then the access right is considered undefined: it is denied until it is explicitly denied or allowed for the user.
The rights of a user are the sum of the following:
- User's own rights
- Rights of all the roles assigned to this user
- Rights of all the security group to which the user belongs
- Rights of all the roles assigned to the security groups to which the user belongs
If at least one of these sets of rights has Deny for a permission, then the user is denied this permission, even if other sets allow it or leave it undefined.
You can also add users and security groups to the scope of a user role to use different features of Administration Server. Settings associated with a user role will only apply only to devices that belong to users who have this role, and only if these devices belong to groups associated with this role, including child groups.
Page top
Adding an account of an internal user
If you want to add a user account, ensure that your account has the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area.
To add a new internal user account to Kaspersky Security Center:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users tab.
- Click Add.
- In the Add user window that opens, specify the settings of the new user account:
- Name
- Password
The password must comply with the following rules:
- The password must be 8 to 256 characters long.
- The password must contain characters from at least three of the groups listed below:
- Uppercase letters (A-Z)
- Lowercase letters (a-z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Special characters (@ # $ % ^ & * - _ ! + = [ ] { } | : ' , . ? / \ ` ~ " ( ) ;)
- The password must not contain any whitespaces, Unicode characters, or the combination of "." and "@", when "." is placed before "@".
To see the entered password, click
 .
. You can enable the User must change password at first sign-in option to force the password change at the first user authentication.
- Save the changes to complete the creation of the new user account.
A new user account is added to the user list.
Creating a security group
To create a security group:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Groups tab.
- Click Add.
- In the Create security group window that opens, specify the following settings for the new security group:
- Group name
- Description
- Click Save to save the changes.
A new security group is added to the group list.
Editing an account of an internal user
If you want to edit a user account, ensure that your account has the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area.
To edit an internal user account in Kaspersky Security Center:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users tab.
- Click the name of the user account that you want to edit.
- In the user settings window that opens, on the General tab, change the settings of the user account:
- User status
- Name
- Full name
- Description
- Email address
- Main phone
- Password
- On the Authentication security tab, you can specify the security settings for this account.
- On the Groups tab, you can add the user to security groups.
- On the Devices tab, you can assign devices to the user.
- On the Roles tab, you can assign roles to the user.
- Save the changes to complete the editing of the user account.
The updated user account appears in the list of users.
Editing a security group
To edit a security group:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Groups tab.
- Click the name of the security group that you want to edit.
- In the group settings window that opens, change the settings of the security group:
- On the General tab, you can change the Name and Description settings. These settings are available only for internal security groups.
- On the Users tab, you can add users to the security group. This setting is available only for internal users and internal security groups.
- On the Roles tab, you can assign a role to the security group.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The changes are applied to the security group.
Assigning a role to a user or a security group
To assign a role to a user or a security group:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users or the Groups tab.
- Select the name of the user or the security group to whom to assign a role.
You can select multiple names.
- On the menu line, click the Assign role button.
The Role assignment wizard starts.
- Follow the instructions of the wizard: select the role that you want to assign to the selected users or security groups, and then select the scope of role.
A user role scope is a combination of users and administration groups. Settings associated with a user role apply only to devices that belong to users who have this role, and only if these devices belong to groups associated with this role, including child groups.
The role with a set of rights for working with Administration Server is assigned to the user (or users, or the security group). In the list of users or security groups, a check box appears in the Has assigned roles column.
Users created on a virtual Server cannot be assigned a role on the Administration Server.
Page top
Adding user accounts to an internal security group
You can add only accounts of internal users to an internal security group.
To add user accounts to an internal security group:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users tab.
- Select check boxes next to user accounts that you want to add to a security group.
- Click the Assign group button.
- In the Assign group window that opens, select the security group to which you want to add user accounts.
- Click the Save button.
The user accounts are added to the security group. You can also add internal users to a security group by using the group settings.
Assigning a user as a device owner
For information about assigning a user as a mobile device owner, see Kaspersky Security for Mobile Help.
To assign a user as a device owner:
- If you want to assign an owner of a device connected to a virtual Administration Server, first switch to the virtual Administration Server:
- In the main menu, click the chevron icon (
 ) to the right of the current Administration Server name.
) to the right of the current Administration Server name. - Select the required Administration Server.
- In the main menu, click the chevron icon (
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users tab.
A user list opens. If you are currently connected to a virtual Administration Server, the list includes users from the current virtual Administration Server and the primary Administration Server.
- Click the name of the user account that you want to assign as a device owner.
- In the user settings window that opens, select the Devices tab.
- Click Add.
- From the device list, select the device that you want to assign to the user.
- Click OK.
The selected device is added to the list of devices assigned to the user.
You can perform the same operation at Assets (Devices) → Managed devices, by clicking the name of the device that you want to assign, and then clicking the Manage device owner link.
Assigning a user as a Linux device owner after installation of Network Agent
To allow the user to register as a Linux device owner:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, go to Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Installation packages.
The list of installation packages opens.
- Click on the installation package of Network Agent.
The properties window of the installation package opens.
- In the installation package properties window, click Settings → Advanced.
- In the User registration as a device owner (Linux only) section, turn on the Allow running the user registration utility after Network Agent installation option and click Save.
The utility for registering the user as a device owner can be run via the command line on the client device.
To register a user as a Linux device owner on the client device:
- Execute the following command in the command line on the client device:
$ /opt/kaspersky/klnagent64/bin/nagregister -set_owner - Enter the login and password, if prompted.
If the login and the password are included in the answer file or installation package of Network Agent, execute the following command in the command line on the client device:
$ /opt/kaspersky/klnagent64/bin/nagregister -set_owner -unattended
If the user is included in an internal security group, the login must contain the user name.
If the user is included in an Active Directory security group, the login must contain the user name and domain name.
If two-step verification is turned on for the user, you have to enter the time-based one-time password (TOTP) from the app.
The user will be registered as a device owner.
Page top
Deleting a user or a security group
You can delete only internal users or internal security groups.
To delete a user or a security group:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users or the Groups tab.
- Select the check box next to the user or the security group that you want to delete.
- Click Delete.
- In the window that opens, click OK.
The user or the security group is deleted.
Changing the password for a user account
You may need to change the password for your own account or for another user account if the current password is about to expire or you want to change it to a more secure one.
The password must comply with the following rules:
- The password must be 8 to 256 characters long.
- The password must contain characters from at least three of the groups listed below:
- Uppercase letters (A-Z)
- Lowercase letters (a-z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Special characters (@ # $ % ^ & * - _ ! + = [ ] { } | : ' , . ? / \ ` ~ " ( ) ;)
- The password must not contain any whitespaces, Unicode characters, or the combination of "." and "@", when "." is placed before "@".
Changing the password for your own account
To edit the password for your account:
- In the main menu, go to your account settings, and then select Change password.
- Enter the current password, and then specify the new password for the connection to Kaspersky Security Center.
To see the entered password, click
 .
. - If your account is protected against unauthorized modification, you must confirm that you have the permissions to change this account. In the Account protection window, specify the credentials of your own account or the account that has the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area.
- If two-step verification is enabled for the account that you used in the previous step, enter the security code generated by the authenticator app on the mobile device.
Changing the password for an internal user account
To edit the password for an internal user account:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users tab.
- Click the name of the user account that you want to edit.
- In the user settings window that opens, on the General tab, click the Change password button.
- Set a new password for the user connection to Kaspersky Security Center.
To see the entered password, click
 .
. - If necessary, enable the User must change password at first sign-in option, to force the password change at the next user authentication.
- If the user account is protected against unauthorized modification, you must confirm that you have the permissions to change this account. In the Account protection window, specify the credentials of the account that has the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area.
Configuring the options for changing a password by using server flags
You can use the klscflag utility to configure changing password by using the following commands:
- Configuring the password rotation period (the
LP_SplPwdChangePeriodDaysflag)klscflag.exe -fset -pv .core/.independent -s KLLIM -n LP_SplPwdChangePeriodDays -t d -v <rotation_period>Where
<rotation_period>is a period of time in days after which the user password expires. Possible values: 0–730. If the parameter value is 0, the password rotation is disabled. - Configuring the time of the previous warning about the need to change the password (the
LP_SplPwdChangeNotificationHoursflag)klscflag.exe -fset -pv .core/.independent -s KLLIM -n LP_SplPwdChangeNotificationHours -t d -v <warning_time>Where
<warning_time>is a period of time in hours before the user password expires. During this time, the notification about the need for the password change is displayed. Possible values: 0–17520. If the parameter value is 0, the warning time is 25 percent of the password rotation period. - Specifying the default value of the User must change password at first sign-in option (the
LP_SplPwdForceChangeflag)klscflag.exe -fset -pv .core/.independent -s KLLIM -n LP_SplPwdForceChange -t d -v <value>Where the possible values of the
<value>flag:1—The User must change password at first sign-in option is enabled.0—The User must change password at first sign-in option is disabled.
To view the current flag value, run the following command:
klscflag.exe -fget -pv .core/.independent -s KLLIM -n <flag> -t d
Where <flag> is the LP_SplPwdChangePeriodDays, LP_SplPwdChangeNotificationHours, or LP_SplPwdForceChange flag.
Creating a user role
To create a user role:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Roles.
- Click Add.
- In the New role name window that opens, enter the name of the new role.
- Click OK to apply the changes.
- In the role properties window that opens, change the settings of the role:
- On the General tab, edit the role name.
You cannot edit the name of a predefined role.
- On the Settings tab, edit the role scope and policies and profiles associated with the role.
- On the Access rights tab, edit the rights for access to Kaspersky applications.
- On the General tab, edit the role name.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The new role appears in the list of user roles.
Editing a user role
To edit a user role:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Roles.
- Click the name of the role that you want to edit.
- In the role properties window that opens, change the settings of the role:
- On the General tab, edit the role name.
You cannot edit the name of a predefined role.
- On the Settings tab, edit the role scope and policies and profiles associated with the role.
- On the Access rights tab, edit the rights for access to Kaspersky applications.
- On the General tab, edit the role name.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The updated role appears in the list of user roles.
Editing the scope of a user role
A user role scope is a combination of users and administration groups. Settings associated with a user role apply only to devices that belong to users who have this role, and only if these devices belong to groups associated with this role, including child groups.
To add users, security groups, and administration groups to the scope of a user role, you can use either of the following methods:
Method 1:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users or the Groups tab.
- Select check boxes next to the users or security groups that you want to add to the user role scope.
- Click the Assign role button.
The Role assignment wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Select role step, select the user role that you want to assign.
- On the Define scope step, select the administration group that you want to add to the user role scope.
- Click the Assign role button to close the window.
The selected users or security groups and the selected administration group are added to the scope of the user role.
Method 2:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Roles.
- Click the name of the role for which you want to define the scope.
- In the role properties window that opens, select the Settings tab.
- In the Role scope section, click Add.
The Role assignment wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Define scope step, select the administration group that you want to add to the user role scope.
- On the Select users step, select users and security groups that you want to add to the user role scope.
- Click the Assign role button to close the window.
- Click the Close button (
 ) to close the role properties window.
) to close the role properties window.
The selected users or security groups and the selected administration group are added to the scope of the user role.
Method 3:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the Access rights tab, select the check box next to the name of the user or the security group that you want to add to the user role scope, and then click the Roles button.
You cannot select multiple users or security groups at the same time. If you select more than one item, the Roles button will be disabled.
- In the Roles window, select the user role that you want to assign, and then apply and save changes.
The selected users or security groups are added to the scope of the user role.
Deleting a user role
To delete a user role:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Roles.
- Select the check box next to the name of the role that you want to delete.
- Click Delete.
- In the window that opens, click OK.
The user role is deleted.
Associating policy profiles with roles
You can associate user roles with policy profiles. In this case, the activation rule for this policy profile is based on the role: the policy profile becomes active for a user that has the specified role.
For example, the policy bars any GPS navigation software on all devices in an administration group. GPS navigation software is necessary only on a single device in the Users administration group—the device owned by a courier. In this case, you can assign a "Courier" role to its owner, and then create a policy profile allowing GPS navigation software to run only on the devices whose owners are assigned the "Courier" role. All the other policy settings are preserved. Only the user with the role "Courier" will be allowed to run GPS navigation software. Later, if another worker is assigned the "Courier" role, the new worker also can run navigation software on your organization's device. Running GPS navigation software will still be prohibited on other devices in the same administration group.
To associate a role with a policy profile:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Roles.
- Click the name of the role that you want to associate with a policy profile.
The role properties window opens with the General tab selected.
- Select the Settings tab, and scroll down to the Policies & profiles section.
- Click Edit.
- To associate the role with:
- An existing policy profile—Click the chevron icon (
 ) next to the required policy name, and then select the check box next to the profile with which you want to associate the role.
) next to the required policy name, and then select the check box next to the profile with which you want to associate the role. - A new policy profile:
- Select the check box next to the policy for which you want to create a profile.
- Click New policy profile.
- Specify a name for the new profile and configure the profile settings.
- Click the Save button.
- Select the check box next to the new profile.
- An existing policy profile—Click the chevron icon (
- Click Assign to role.
The profile is associated with the role and appears in the role properties. The profile applies automatically to any device whose owner is assigned the role.
Changing account password
You can change the local account password, for example, when the user forgets the local account password or to perform a scheduled password change.
The password change will apply even if the user has not signed in to the account. You can also change the password for the local root account.
This task may be performed only on Linux devices.
To change the local account password on specific devices:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts.
- In the Task type field, select Change account password (Linux only).
- Select one of the following options:
- Assign task to an administration group
- Specify device addresses manually or import addresses from a list
- Assign task to a device selection
The Change account password (Linux only) task is created for the specified devices. If you selected the Assign task to an administration group option, the task is a group one.
- At the Task scope step, specify an administration group, devices with specific addresses, or a device selection.
The available settings depend on the option selected at the previous step.
- At the Enter account name and new password step, specify the following settings:
- In the Account name field, specify the name of the account for which you want to change the password.
- In the New password field, specify the password, that will be set for the account specified in the previous field.
To see the characters that you entered, click and hold the Show button.
- If necessary, select the Set as a one-time password (the user must change the password after the first login) check box.
- At the Finish task creation step, click the Finish button to create the task and close the wizard.
If you enabled the Open task details when creation is complete option, the task settings window opens. In this window, you can check the task parameters, modify them, or configure a task start schedule, if necessary.
- In the task list, select the task you created, and then click Start.
Alternatively, wait for the task to launch according to the schedule that you specified in the task settings.
When the change account password task completes, the password is changed for the specified local account on the specified devices.
To ensure correct operation of the change account password tasks,
must be disabled on the user device. Page top
Revoking local administrator rights
You can revoke local administrator rights from accounts. This provides you with an extra layer of control of user accounts. For example, you can revoke local administrator rights after a one-time assignment is complete.
When this task is run, the specified local account is checked to see whether it belongs to local administrator groups.These groups are defined in the Network Agent policy settings. You may customize the list of local administrator groups in the Network Agent policy settings. You can also check the list of privileged user accounts using the Report on privileged device users (Linux only).
This task may be performed only on Linux devices.
To revoke local administrator rights on specific devices:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts.
- In the Task type field, select Revoke local administrator rights (Linux only).
- Select one of the following options:
- Assign task to an administration group
- Specify device addresses manually or import addresses from a list
- Assign task to a device selection
The Revoke local administrator rights(Linux only) task is created for the specified devices. If you selected the Assign task to an administration group option, the task is a group one.
- At the Task scope step, specify an administration group, devices with specific addresses, or a device selection.
The available settings depend on the option selected at the previous step.
- At this step of the wizard, specify the following settings:
- In the Operating mode settings group, select the operating mode:
- Specify the local accounts:
- Click Add.
- In the window that opens, do the following:
- In the Account name field, specify the name of the local account.
- In the Account action settings group (available only if the Revoke local administrator rights from listed accounts option is selected), select the action.
- Keep account
- Delete account
- At the Finish task creation step, click the Finish button to create the task and close the wizard.
If you enabled the Open task details when creation is complete option, the task settings window opens. In this window, you can check the task parameters, modify them, or configure a task start schedule, if necessary.
- In the task list, select the task you created, and then click Start.
Alternatively, wait for the task to launch according to the schedule that you specified in the task settings.
When the revoke local administrator rights task is completed, the local administrator rights are revoked from the specified local accounts on the specified devices.
Page top
Managing object revisions
This section contains information about object revision management. Kaspersky Security Center allows you to track object modification. Every time you save changes made to an object, a revision is created. Each revision has a number.
Application objects that support revision management include:
- Administration Server properties
- Policies
- Tasks
- Administration groups
- User accounts
- Installation packages
You can perform the following actions on object revisions:
- View a selected revision (available only for policies)
- Roll back changes made to an object to a selected revision
- Save revisions as a JSON file (available only for policies)
In the properties window of any object that supports revision management, the Revision history section displays a list of object revisions with the following details:
- Revision—Object revision number.
- Time—Date and time the object was modified.
- User—Name of the user who modified the object.
- User device IP address—IP address of the device from which the object was modified.
- Web Console IP address—IP address of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console with which the object was modified.
- Action—Action performed on the object.
- Description—Description of the revision related to the change made to the object settings.
By default, the object revision description is blank. To add a description to a revision, select the relevant revision and click the Edit description button. In the opened window, enter some text for the revision description.
Rolling back an object to a previous revision
You can roll back changes made to an object, if necessary. For example, you may have to revert the settings of a policy to their state on a specific date.
To roll back changes made to an object:
- In the object's properties window, open the Revision history tab.
- In the list of object revisions, select the revision that you want to roll back changes for.
- Click the Roll back button.
- Click OK to confirm the operation.
The object is now rolled back to the selected revision. The list of object revisions displays a record of the action that was taken. The revision description displays information about the number of the revision to which you reverted the object.
Rolling back operation is available only for policy and task objects.
Adding a revision description
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to track object modification. Every time you save changes made to an object, a revision is created. Each revision has a number.
You can add a description for the revision to simplify the search for revisions in the list.
To add a description for a revision:
- In the object's properties window, open the Revision history tab.
- In the list of object revisions, select the revision for which you need to add a description.
- Click the Edit description button.
The Description window opens.
- In the Description window, enter some text for the revision description.
By default, the object revision description is blank.
- Save the revision description.
The description is added for the revision of the object.
Page top
Viewing and saving a policy revision
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to view which modifications were made to a policy over a certain period, as well as save information about these modifications in a file.
Viewing and saving a policy revision are available if the corresponding management web plug-in supports this functionality.
To view a policy revision:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy for the revision that you want to view, and then go to the Revision history section.
- In the list of policy revisions, click the number of the revision that you want to view.
If the revision size is more than 10 MB, you will not be able to view it by using Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. You will be prompted to save the selected revision to a JSON file.
If the revision size does not exceed 10 MB, a report in the HTML format with the settings of the selected policy revision is displayed. Since the report is displayed in a pop-up window, ensure that pop-ups are allowed in your browser.
To save a policy revision to a JSON file,
In the list of policy revisions, select the revision that you want to save, and then click Save to file.
The revision is saved to a JSON file.
Page top
Deletion of objects
This section provides information about deleting objects and viewing information about objects after they are deleted.
You can delete objects, including the following:
- Policies
- Tasks
- Installation packages
- Virtual Administration Servers
- Users
- Security groups
- Administration groups
When you delete an object, information about it remains in the database. The storage term for information about the deleted objects is the same as the storage term for object revisions (the recommended term is 90 days). You can change the storage term only if you have the Modify permission in the Deleted objects area of rights.
About deletion of client devices
When you delete a managed device from an administration group, the application moves the device to the Unassigned devices group. After device deletion, the installed Kaspersky applications—Network Agent and any security application, for example Kaspersky Endpoint Security—remain on the device.
Kaspersky Security Center handles the devices in the Unassigned devices group according to the following rules:
- If you have configured device moving rules and a device meets the criteria of a moving rule, the device is automatically moved to an administration group according to the rule.
- The device is stored in the Unassigned devices group and automatically removed from the group according to the device retention rules.
The device retention rules do not affect the devices that have one or more drives encrypted with full disk encryption. Such devices are not deleted automatically—you can only delete them manually. If you need to delete a device with an encrypted drive, first decrypt the drive, and then delete the device.
When you delete a device with encrypted drive, the data required to decrypt the drive is also deleted. If you select the I understand the risk and want to delete the selected device(s) check box in the confirmation window that opens when you delete such devices (either from the Unassigned devices or the Managed Devices group), it means that you are aware of the subsequent data deletion.
To decrypt the drive, the following conditions must be met:
- The device is reconnected to Administration Server to restore the data required to decrypt the drive.
- The device user remembers the decryption password.
- The security application that was used to encrypt the drive, for example Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, is still installed on the device.
If the drive was encrypted by Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology, you can also try recovering data by using the FDERT Restore Utility.
When you delete a device from the Unassigned devices group manually, the application removes the device from the list. After device deletion, the installed Kaspersky applications (if any) remain on the device. Then, if the device is still visible to Administration Server and you have configured regular network polling, Kaspersky Security Center discovers the device during the network polling and adds it back to the Unassigned devices group. Therefore, it is reasonable to delete a device manually only if the device is invisible to Administration Server.
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN)
This section describes how to use an online service infrastructure named Kaspersky Security Network (KSN). The section provides the details on KSN, as well as instructions on how to enable KSN, configure access to KSN, and view the statistics of the use of KSN proxy server.
Updates functionality (including providing anti-virus signature updates and codebase updates), as well as KSN functionality may not be available in the software in the U.S.
About KSN
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is an online service infrastructure that provides access to the online Knowledge Base of Kaspersky, which contains information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software. The use of data from Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky applications to threats, improves the effectiveness of some protection components, and reduces the risk of false positives. KSN allows you to use Kaspersky reputation databases to retrieve information about applications installed on managed devices.
Kaspersky Security Center supports the following infrastructure solutions:
- KSN is a solution that allows you to exchange information with Kaspersky Security Network. If you participate in KSN, you agree to send to Kaspersky, in automatic mode, information about the operation of Kaspersky applications installed on client devices that are managed through Kaspersky Security Center. Information is transferred in accordance with the current KSN access settings. Kaspersky analysts additionally analyze received information and include it in the reputation and statistical databases of Kaspersky Security Network. Kaspersky Security Center uses this solution by default.
- Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN) is a solution that allows users of devices with Kaspersky applications installed to obtain access to reputation databases of Kaspersky Security Network, and other statistical data, without sending data to Global KSN from their own devices. KPSN is designed for corporate customers who are unable to participate in Kaspersky Security Network for any of the following reasons:
- User devices are not connected to the internet.
- Transmission of any data outside the country or outside the corporate LAN is prohibited by law or restricted by corporate security policies.
You can set up access settings of Kaspersky Private Security Network in the KSN Proxy settings section of the Administration Server properties window.
The application prompts you to join KSN while running the quick start wizard. You can start or stop using KSN at any moment when using the application.
You use KSN in accordance with the KSN Statement that you read and accept when you enable KSN. If the KSN Statement is updated, it is displayed to you when you upgrade a version of Administration Server. You can accept the updated KSN Statement or decline it. If you decline it, you keep using KSN in accordance with the previous version of KSN Statement that you accepted before.
When KSN is enabled, Kaspersky Security Center checks if the KSN servers are accessible. If access to the servers using system DNS is not possible, the application uses public DNS servers. This is necessary to make sure the level of security is maintained for the managed devices.
Client devices managed by the Administration Server interact with KSN through KSN proxy server. KSN proxy server provides the following features:
- Client devices can send requests to KSN, obtain information from KSN, and transfer information to KSN even if they do not have direct access to the internet.
- The KSN proxy server caches processed data, thus reducing the load on the outbound channel and the time period spent for waiting for information requested by a client device.
You can configure the KSN proxy server in the KSN Proxy settings section of the Administration Server properties window.
Page top
Setting up access to KSN
You can set up access to Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) on Administration Server and on a distribution point.
To set up Administration Server access to KSN:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the KSN Proxy settings section.
- Switch the toggle button to the Enable KSN Proxy on Administration Server Enabled position.
If this option is enabled, KSN proxy server sends data to KSN to increase the efficiency of Kaspersky Security Center components and improve the performance of the Kaspersky applications. Data is sent from client devices to KSN in accordance with the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy, which is active on those client devices. If this toggle button is disabled, no data will be sent to KSN from the Administration Server and client devices through Kaspersky Security Center. However, client devices can send data to KSN directly (bypassing Kaspersky Security Center), in accordance with their respective settings. The Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy, which is active on client devices, determines which data will be sent directly (bypassing Kaspersky Security Center) from those devices to KSN.
- Switch the toggle button to the Use Kaspersky Security Network Enabled position.
If this option is enabled, client devices send patch installation results to Kaspersky. When enabling this option, make sure to read and accept the terms of the KSN Statement.
If you are using
, switch the toggle button to the Use Kaspersky Private Security Network Enabled position and click the Select file with KSN Proxy settings button to download the settings of KPSN (files with the extensions pkcs7 and pem). After the settings are downloaded, the interface displays the provider's name and contacts, as well as the creation date of the file with the settings of KPSN.When you enable KPSN, pay attention to the distribution points configured to send KSN requests directly to the Cloud KSN. The distribution points that have Network Agent version 11 (or earlier) installed will continue to send KSN requests to the Cloud KSN. To reconfigure the distribution points to send KSN requests to KPSN, enable the Forward KSN requests to Administration Server option for each distribution point. You can enable this option in the distribution point properties or in the Network Agent policy.
When you switch the toggle button to the Use Kaspersky Private Security Network Enabled position, a message appears with details about KPSN.
The following Kaspersky applications support KPSN:
- Kaspersky Security Center
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization 3.0 Agentless Service Pack 2
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization 3.0 Service Pack 1 Light Agent
If you enable KPSN in Kaspersky Security Center, these applications receive information about supporting KPSN. In the settings window of the application, in the Kaspersky Security Network subsection of the Advanced Threat Protection section, the information about selected KSN provider is displayed — KSN or KPSN.
If you use application versions earlier than Kaspersky Security for Virtualization 3.0 Agentless Service Pack 2 or earlier than Kaspersky Security for Virtualization 3.0 Service Pack 1 Light Agent when running KPSN, we recommend that you use secondary Administration Servers for which the use of KPSN has not been enabled.
Kaspersky Security Center does not send any statistical data to Kaspersky Security Network if KPSN is configured in the KSN Proxy settings section of the Administration Server properties window.
- If you have the proxy server settings configured in the Administration Server properties, but your network architecture requires that you use KPSN directly, enable the Ignore proxy server settings when connecting to KPSN option. Otherwise, requests from the managed applications cannot reach KPSN.
- Configure the Administration Server connection to the KSN proxy service:
- Under Connection settings, for the TCP port, specify the number of the TCP port that will be used for connecting to the KSN proxy server. The default port to connect to the KSN proxy server is 13111.
- If you want the Administration Server to connect to the KSN proxy server through a UDP port, enable the Use UDP port option and specify a port number for the UDP port. By default, this option is disabled, and TCP port is used. If this option is enabled, the default UDP port to connect to the KSN proxy server is 15111.
- If you want the Administration Server to connect to the KSN proxy server through an HTTPS port, enable the Use HTTPS option and specify a port number for the HTTPS through port. By default, this option is disabled, and TCP port is used. If this option is enabled, the default HTTPS port to connect to the KSN proxy server is 17111.
- Switch the toggle button to the Connect secondary Administration Servers to KSN through the primary Administration Server Enabled position.
If this option is enabled, secondary Administration Servers use the primary Administration Server as the KSN proxy server. If this option is disabled, secondary Administration Servers connect to KSN on their own. In this case, managed devices use secondary Administration Servers as KSN proxy servers.
Secondary Administration Servers use the primary Administration Server as a proxy server if in the right pane of the KSN Proxy settings section, in the properties of secondary Administration Servers the toggle button is switched to the Enable KSN Proxy on Administration Server Enabled position.
- Click the Save button.
The KSN access settings will be saved.
You can also set up distribution point access to KSN, for example, if you want to reduce the load on the Administration Server. The distribution point that acts as a KSN proxy server sends KSN requests from managed devices to Kaspersky directly, without using the Administration Server.
To set up distribution point access to Kaspersky Security Network (KSN):
- Make sure that the distribution point is assigned manually.
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Distribution points section.
- Click the name of the distribution point to open its properties window.
- In the distribution point properties window, in the KSN Proxy section, enable the Enable KSN Proxy on the distribution point side option, and then enable the Access KSN Cloud/KPSN directly over the internet option.
- Click OK.
The distribution point will act as a KSN proxy server.
Page top
Enabling and disabling the usage of KSN
To enable the usage of KSN:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the KSN Proxy settings section.
- Switch the toggle button to the Enable KSN Proxy on Administration Server Enabled position.
The KSN proxy server is enabled and sends data to KSN to increase the efficiency of Kaspersky Security Center components and improve the performance of Kaspersky applications.
- Depending on the KSN infrastructure solution that you are using, enable the corresponding toggle buttons.
- If you are using Global KSN, switch the toggle button to the Use Kaspersky Security Network Enabled position.
Sending data to KSN is now available. When enabling this option, you have to read and accept the terms of the KSN Statement.
- If you are using KPSN, switch the toggle button to the Use Kaspersky Private Security Network Enabled position, and then click the Select file with KSN Proxy settings button to download the settings of KPSN (files with the extensions pkcs7 and pem). After the settings are downloaded, the interface displays the provider's name and contacts, as well as the creation date of the file with the settings of KPSN.
When you switch the toggle button to the Use Kaspersky Private Security Network Enabled position, a message appears with details about KPSN.
- If you are using Global KSN, switch the toggle button to the Use Kaspersky Security Network Enabled position.
- Click the Save button.
To disable the usage of KSN:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the KSN Proxy settings section.
- Switch the toggle button to the Enable KSN Proxy on Administration Server Disabled position to disable the KSN proxy service.
- Click the Save button.
Viewing the accepted KSN Statement
When you enable Kaspersky Security Network (KSN), you must read and accept the KSN Statement. You can view the accepted KSN Statement at any time.
To view the accepted KSN Statement:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the KSN Proxy settings section.
- Click the View Kaspersky Security Network Statement link.
In the window that opens, you can view the text of the accepted KSN Statement.
Page top
Accepting an updated KSN Statement
You use KSN in accordance with the KSN Statement that you read and accept when you enable KSN. If the KSN Statement is updated, it is displayed to you when you upgrade a version of Administration Server. You can accept the updated KSN Statement or decline it. If you decline it, you will continue using KSN in accordance with the version of the KSN Statement that you previously accepted.
After upgrading a version of Administration Server, the updated KSN Statement is displayed automatically. If you decline the updated KSN Statement, you can still view and accept it later.
To view and then accept or decline an updated KSN Statement:
- Click the View notifications link in the upper-right corner of the main application window.
The Notifications window opens.
- Click the View the updated KSN Statement link.
The Kaspersky Security Network Statement update window opens.
- Read the KSN Statement, and then make your decision by clicking one of the following buttons:
- I accept the updated KSN Statement
- Use KSN under the old Statement
Depending on your choice, KSN keeps working in accordance with the terms of the current or updated KSN Statement. You can view the text of the accepted KSN Statement in the properties of Administration Server at any time.
Page top
Checking whether the distribution point works as KSN proxy server
On a managed device assigned to work as a distribution point, you can enable KSN proxy server. A managed device works as KSN proxy server when the ksnproxy service is running on the device. You can check, turn on, or turn off this service on the device locally.
You can assign a Windows-based or a Linux-based device as a distribution point. The method of distribution point checking depends on the operating system of this distribution point.
To check whether the Windows-based distribution point works as KSN proxy server:
- On the distribution point device, in Windows, open Services (All Programs → Administrative Tools → Services).
- In the list of services, check whether the ksnproxy service is running.
If the ksnproxy service is running, then Network Agent on the device participates in Kaspersky Security Network and works as KSN proxy server for the managed devices included in the scope of the distribution point.
If you want, you may turn off the ksnproxy service. In this case, Network Agent on the distribution point stops participating in Kaspersky Security Network. This requires local administrator rights.
To check whether the Linux-based distribution point works as KSN proxy server:
- On the distribution point device, display the list of running processes.
- In the list of running processes, check whether the
/opt/kaspersky/ksc64/sbin/ksnproxyprocess is running.
If /opt/kaspersky/ksc64/sbin/ksnproxy process is running, then Network Agent on the device participates in Kaspersky Security Network and works as the KSN proxy server for the managed devices included in the scope of the distribution point.
Scenario: Upgrading Kaspersky Security Center and managed security applications
This section describes the main brief scenario for Kaspersky Security Center and managed security applications upgrade.
The Kaspersky Security Center and managed security applications upgrade proceeds in stages:
- Checking the hardware and software requirements
Ensure your hardware meets the requirements and install the required updates.
- Planning the resources
Assess how much disk space your database occupies. Make sure that you have enough disk space to store the backup copy of the Administration Server settings and the database.
- Getting the installer file for Kaspersky Security Center
Get the executable file for the current version of Kaspersky Security Center and save it on the device that will work as the Administration Server. Read the Release Notes of the version of Kaspersky Security Center that you want to use.
- Creating a backup copy of the previous version
Use the data backup and recovery utility to create a backup copy of the Administration Server data. You can also create a backup task.
It is recommended to export the list of installed plug-ins.
- Running the installer
Run the executable file for the latest version of Kaspersky Security Center. When running the file, specify that you have a backup copy and specify its location. Your data will be restored from the backup.
- Upgrading the managed applications
You can upgrade the application if there is a newer version available. Read the list of supported Kaspersky applications and make sure that your version of Kaspersky Security Center is compatible with this application. Then perform the upgrade of the application as described in its release notes.
Results
Upon completion of the upgrade scenario, make sure that new version of Administration Server is successfully installed in Microsoft Management Console. Click Help → About Kaspersky Security Center. The version is displayed.
To make sure that you are using the new version of Administration Server in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, at the top of the screen click the settings icon (![]() ) next to the name of the Administration Server. In the Administration Server properties window that opens, on the General tab, select the General section. The version is displayed.
) next to the name of the Administration Server. In the Administration Server properties window that opens, on the General tab, select the General section. The version is displayed.
If you need to recover Administration Server data, follow the steps described in the following topic: Data backup and recovery in interactive mode.
If you upgraded a managed security application, make sure that it is correctly installed on the managed device(s). For more information, please refer to the documentation of this application.
Page top
Updating Kaspersky databases and applications
This section describes steps you must take to regularly update the following:
- Kaspersky databases and software modules
- Installed Kaspersky applications, including Kaspersky Security Center components and security applications
Updates functionality (including providing anti-virus signature updates and codebase updates), as well as KSN functionality may not be available in the software in the U.S.
Scenario: Regular updating Kaspersky databases and applications
This section provides a scenario for regular updating of Kaspersky databases, software modules, and applications. After you complete the Configuring network protection scenario, you must maintain the reliability of the protection system to make sure that the Administration Servers and managed devices are kept protected against various threats, including viruses, network attacks, and phishing attacks.
Network protection is kept up-to-date by regular updates of the following:
- Kaspersky databases and software modules
- Installed Kaspersky applications, including Kaspersky Security Center components and security applications
When you complete this scenario, you can be sure of the following:
- Your network is protected by the most recent Kaspersky software, including Kaspersky Security Center components and security applications.
- The anti-virus databases and other Kaspersky databases critical for the network safety are always up-to-date.
Prerequisites
The managed devices must have a connection to the Administration Server. If they do not have a connection, consider updating Kaspersky databases, software modules, and applications manually or directly from the Kaspersky update servers.
Administration Server must have a connection to the internet.
Before you start, make sure that you have done the following:
- Deployed the Kaspersky security applications to the managed devices according to the scenario of deploying Kaspersky applications through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
- Created and configured all required policies, policy profiles, and tasks according to the scenario of configuring network protection.
- Assigned an appropriate amount of distribution points in accordance with the number of managed devices and the network topology.
Updating Kaspersky databases and applications proceeds in stages:
- Choosing an update scheme
There are several schemes that you can use to install updates to Kaspersky Security Center components and security applications. Choose the scheme or several schemes that meet the requirements of your network best.
- Creating the task for downloading updates to the repository of the Administration Server
This task is created automatically by the Kaspersky Security Center quick start wizard. If you did not run the wizard, create the task now.
This task is required to download updates from Kaspersky update servers to the repository of the Administration Server, as well as to update Kaspersky databases and software modules for Kaspersky Security Center. After the updates are downloaded, they can be propagated to the managed devices.
If your network has assigned distribution points, the updates are automatically downloaded from the Administration Server repository to the repositories of the distribution points. In this case the managed devices included in the scope of a distribution point download the updates from the repository of the distribution point instead of the Administration Server repository.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Creating the task for downloading updates to the repository of the Administration Server
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating the task for downloading updates to the repository of the Administration Server
- Creating the task for downloading updates to the repositories of distribution points (optional)
By default, the updates are downloaded to the distribution points from the Administration server. You can configure Kaspersky Security Center to download the updates to the distribution points directly from Kaspersky update servers. Download to the repositories of distribution points is preferable if the traffic between the Administration Server and the distribution points is more expensive than the traffic between the distribution points and Kaspersky update servers, or if your Administration Server does not have internet access.
When your network has assigned distribution points and the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task is created, the distribution points download updates from Kaspersky update servers, and not from the Administration Server repository.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Creating the task for downloading updates to the repositories of distribution points
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating the task for downloading updates to the repositories of distribution points
- Configuring distribution points
When your network has assigned distribution points, make sure that the Deploy updates option is enabled in the properties of all required distribution points. When this option is disabled for a distribution point, the devices included in the scope of the distribution point download updates from the repository of the Administration Server.
If you want the managed devices to receive updates only from the distribution points, enable the Distribute files through distribution points only option in the Network Agent policy.
- Optimizing the update process by using the offline model of update download or diff files (optional)
You can optimize the update process by using the offline model of update download (enabled by default) or by using diff files. For each network segment, you have to choose which of these two features to enable, because they cannot work simultaneously.
When the offline model of update download is enabled, Network Agent downloads the required updates to the managed device once the updates are downloaded to the Administration Server repository, before the security application requests the updates. This enhances the reliability of the update process. To use this feature, enable the Download updates and anti-virus databases from Administration Server in advance (recommended) option in the Network Agent policy.
If you do not use the offline model of update download, you can optimize traffic between the Administration Server and the managed devices by using diff files. When this feature is enabled, the Administration Server or a distribution point downloads diff files instead of entire files of Kaspersky databases or software modules. A diff file describes the differences between two versions of a file of a database or software module. Therefore, a diff file occupies less space than an entire file. This results in decrease in the traffic between the Administration Server or distribution points and the managed devices. To use this feature, enable the Download diff files option in the properties of the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task and/or the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task.
How-to instructions:
- Using diff files for updating Kaspersky databases and software modules
- Administration Console: Enabling and disabling the offline model of update download
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Enabling and disabling the offline model of update download
- Verifying downloaded updates (optional)
Before installing the downloaded updates, you can verify the updates through the Update verification task. This task sequentially runs the device update tasks and malware scan tasks configured through settings for the specified collection of test devices. Upon obtaining the task results, the Administration Server starts or blocks the update propagation to the remaining devices.
The Update verification task can be performed as part of the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task. In the properties of the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task, enable the Verify updates before distributing option in the Administration Console or the Run update verification option in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Verifying downloaded updates
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Verifying downloaded updates
- Approving and declining software updates
By default, the downloaded software updates have the Undefined status. You can change the status to Approved or Declined. The approved updates are always installed. If an update requires reviewing and accepting the terms of the End User License Agreement, then you first need to accept the terms. After that the update can be propagated to the managed devices. The undefined updates can only be installed on Network Agent and other Kaspersky Security Center components in accordance with the Network Agent policy settings. The updates for which you set Declined status will not be installed on devices. If a declined update for a security application was previously installed, Kaspersky Security Center will try to uninstall the update from all devices. Updates for Kaspersky Security Center components cannot be uninstalled.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Approving and declining software updates
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Approving and declining software updates
- Configuring automatic installation of updates and patches for Kaspersky Security Center components
The downloaded updates and patches for Network Agent and other Kaspersky Security Center components are installed automatically. If you have left the Automatically install applicable updates and patches for components that have the Undefined status option enabled in the Network Agent properties, then all updates will be installed automatically after they are downloaded to the repository (or several repositories). If this option is disabled, Kaspersky patches that have been downloaded and tagged with the Undefined status will be installed only after you change their status to Approved.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Enabling and disabling automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Enabling and disabling automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components
- Installation of updates for the Administration Server
Software updates for the Administration Server do not depend on the update statuses. They are not installed automatically and must be preliminarily approved by the administrator on the Monitoring tab in the Administration Console (Administration Server
<server name>→ Monitoring) or on the Notifications section in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console (Monitoring & reporting → Notifications). After that, the administrator must explicitly run installation of the updates. - Configuring automatic installation of updates for the security applications
Create the Update tasks for the managed applications to provide timely updates to the applications, software modules and Kaspersky databases, including anti-virus databases. To ensure timely updates, we recommend that you select the When new updates are downloaded to the repository option when configuring the task schedule.
If your network includes IPv6-only devices and you want to regularly update the security applications installed on these devices, make sure that the Administration Server (version no earlier than 13.2) and the Network Agent (version no earlier than 13.2) are installed on managed devices.
By default, updates for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux are installed only after you change the update status to Approved. You can change the update settings in the Update task.
If an update requires reviewing and accepting the terms of the End User License Agreement, then you first need to accept the terms. After that the update can be propagated to the managed devices.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Automatic installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security updates on devices
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Automatic installation of Kaspersky Endpoint Security updates on devices
Results
Upon completion of the scenario, Kaspersky Security Center is configured to update Kaspersky databases and installed Kaspersky applications after the updates are downloaded to the repository of the Administration Server or to the repositories of distribution points. You can then proceed to monitoring the network status.
About updating Kaspersky databases, software modules, and applications
To be sure that the protection of your Administration Servers and managed devices is up-to-date, you must provide timely updates of the following:
- Kaspersky databases and software modules
Before downloading Kaspersky databases and software modules, Kaspersky Security Center checks if Kaspersky servers are accessible. If access to the servers using system DNS is not possible, the application uses public DNS servers. This is necessary to make sure anti-virus databases are updated and the level of security is maintained for the managed devices.
- Installed Kaspersky applications, including Kaspersky Security Center components and security applications
Depending on the configuration of your network, you can use the following schemes of downloading and distributing the required updates to the managed devices:
- By using a single task: Download updates to the Administration Server repository
- By using two tasks:
- The Download updates to the Administration Server repository task
- The Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task
- Manually through a local folder, a shared folder, or an FTP server
- Directly from Kaspersky update servers to Kaspersky Endpoint Security on the managed devices
- Through a local or network folder if Administration Server has no internet connection
Using the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task
In this scheme, Kaspersky Security Center downloads updates through the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task. In small networks that contain less than 300 managed devices in a single network segment or less than 10 managed devices in each network segment, the updates are distributed to the managed devices directly from the Administration Server repository (see figure below).

Updating by using the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task without distribution points
By default, the Administration Server communicates with Kaspersky update servers and downloads updates by using the HTTPS protocol. You can configure the Administration Server to use the HTTP protocol instead of HTTPS.
If your network contains more than 300 managed devices in a single network segment or if your network consists of several network segments with more than 9 managed devices in each network segment, we recommend that you use distribution points to propagate the updates to the managed devices (see figure below). Distribution points reduce the load on the Administration Server and optimize traffic between the Administration Server and the managed devices. You can calculate the number and configuration of distribution points required for your network.
In this scheme, the updates are automatically downloaded from the Administration Server repository to the repositories of the distribution points. The managed devices included in the scope of a distribution point download the updates from the repository of the distribution point instead of the Administration Server repository.

Updating by using the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task with distribution points
When the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task is complete, the following updates are downloaded to the Administration Server repository:
- Kaspersky databases and software modules for Kaspersky Security Center
These updates are installed automatically.
- Kaspersky databases and software modules for the security applications on the managed devices
These updates are installed through the Update task for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- Updates for the Administration Server
These updates are not installed automatically. The administrator must explicitly approve and run installation of the updates.
Local administrator rights are required for installing patches on the Administration Server.
- Updates for the components of Kaspersky Security Center
By default, these updates are installed automatically. You can change the settings in the Network Agent policy.
- Updates for the security applications
By default, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows installs only those updates that you approve. (You can approve updates via the Administration Console or via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console). The updates are installed through the Update task and can be configured in the properties of this task.
The Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task is not available on virtual Administration Servers. The repository of the virtual Administration Server displays updates downloaded to the primary Administration Server.
You can configure the updates to be verified for operability and errors on a set of test devices. If the verification is successful, the updates are distributed to other managed devices.
Each Kaspersky application requests required updates from Administration Server. Administration Server aggregates these requests and downloads only those updates that are requested by any application. This ensures that the same updates are not downloaded multiple times and that unnecessary updates are not downloaded at all. When running the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task, Administration Server sends the following information to Kaspersky update servers automatically in order to ensure the downloading of relevant versions of Kaspersky databases and software modules:
- Application ID and version
- Application installation ID
- Active key ID
- Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task run ID
None of the transmitted information contains personal or other confidential data. AO Kaspersky Lab protects information in accordance with requirements established by law.
Using two tasks: the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task and the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task
You can download updates to the repositories of distribution points directly from the Kaspersky update servers instead of the Administration Server repository, and then distribute the updates to the managed devices (see figure below). Download to the repositories of distribution points is preferable if the traffic between the Administration Server and the distribution points is more expensive than the traffic between the distribution points and Kaspersky update servers, or if your Administration Server does not have internet access.

Updating by using the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task and the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task
By default, the Administration Server and distribution points communicate with Kaspersky update servers and download updates by using the HTTPS protocol. You can configure the Administration Server and/or distribution points to use the HTTP protocol instead of HTTPS.
To implement this scheme, create the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task in addition to the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task. After that the distribution points will download updates from Kaspersky update servers, and not from the Administration Server repository.
Distribution point devices running macOS cannot download updates from Kaspersky update servers.
If one or more devices running macOS are within the scope of the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task, the task completes with the Failed status, even if it has successfully completed on all Windows devices.
The Download updates to the Administration Server repository task is also required for this scheme, because this task is used to download Kaspersky databases and software modules for Kaspersky Security Center.
Manually through a local folder, a shared folder, or an FTP server
If the client devices do not have a connection to the Administration Server, you can use a local folder or a shared resource as a source for updating Kaspersky databases, software modules, and applications. In this scheme, you need to copy required updates from the Administration Server repository to a removable drive, then copy the updates to the local folder or the shared resource specified as an update source in the settings of Kaspersky Endpoint Security (see figure below).

Updating through a local folder, a shared folder, or an FTP server
For more information about sources of updates in Kaspersky Endpoint Security, see the following Helps:
Directly from Kaspersky update servers to Kaspersky Endpoint Security on the managed devices
On the managed devices, you can configure Kaspersky Endpoint Security to receive updates directly from Kaspersky update servers (see figure below).

Updating security applications directly from Kaspersky update servers
In this scheme, the security application does not use the repositories provided by Kaspersky Security Center. To receive updates directly from Kaspersky update servers, specify Kaspersky update servers as an update source in the interface of the security application. For more information about these settings, see the following Helps:
Through a local or network folder if Administration Server has no internet connection
If Administration Server has no internet connection, you can configure the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task to download updates from a local or network folder. In this case, you must copy the required update files to the specified folder from time to time. For example, you can copy the required update files from one of the following sources:
- Administration Server that has an internet connection (see the figure below)
Because an Administration Server downloads only the updates that are requested by the security applications, the sets of security applications managed by the Administration Servers—the one that has an internet connection and the one that does not—must match.
If the Administration Server that you use to download updates has version 13.2 or earlier, open properties of the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task, and then enable the Download updates by using the old scheme option.

Updating through a local or network folder if Administration Server has no internet connection
- Kaspersky Update Utility
Because this utility uses the old scheme to download updates, open properties of the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task, and then enable the Download updates by using the old scheme option.
Creating the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task
The Download updates to the Administration Server repository task of the Administration Server is created automatically by the Kaspersky Security Center quick start wizard. You can create only one Download updates to the Administration Server repository task. Therefore, you can create a Download updates to the Administration Server repository task only if this task was removed from the Administration Server tasks list.
This task is required to download updates from Kaspersky update servers to the repository of the Administration Server. The list of updates includes:
- Updates to databases and software modules for Administration Server
- Updates to databases and software modules for Kaspersky security applications
- Updates to Kaspersky Security Center components
- Updates to Kaspersky security applications
After the updates are downloaded, they can be propagated to the managed devices.
Before distributing updates to the managed devices, you can run the Update verification task. This allows you to make sure that Administration Server will install the downloaded updates properly and a security level will not decrease because of the updates. To verify them before distributing, configure the Run update verification option in the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task settings.
To create the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- For the Kaspersky Security Center application, select the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task type.
- Specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- If you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option on the Finish task creation page. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Create button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the name of the created task to open the task properties window.
- In the task properties window, on the Application settings tab, specify the following settings:
- Sources of updates
- Folder for storing updates
- Other settings:
- Content of updates:
- Download updates by using the old scheme
- Run update verification
- In the task properties window, on the Schedule tab, create a schedule for task start. If necessary, specify the following settings:
- Click the Save button.
The task is created and configured.
When Administration Server performs the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task, updates to databases and software modules are downloaded from the updates source and stored in the shared folder of Administration Server. If you create this task for an administration group, it will only be applied to Network Agents included in the specified administration group.
Updates are distributed to client devices and secondary Administration Servers from the shared folder of Administration Server.
Verifying downloaded updates
Before installing updates to the managed devices, you can first check the updates for operability and errors through the Update verification task. The Update verification task is performed automatically as part of the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task. The Administration Server downloads updates from the source, saves them in the temporary repository, and runs the Update verification task. If the task completes successfully, the updates are copied from the temporary repository to the Administration Server shared folder. They are distributed to all client devices for which the Administration Server is the source of updates.
If, as a result of the Update verification task, updates located in the temporary repository are incorrect or if the Update verification task completes with an error, such updates are not copied to the shared folder. The Administration Server retains the previous set of updates. Also, the tasks that have the When new updates are downloaded to the repository schedule type are not started then. These operations are performed at the next start of the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task if scanning of the new updates completes successfully.
A set of updates is considered invalid if any of the following conditions is met on at least one test device:
- An update task error occurred.
- The real-time protection status of the security application changed after the updates were applied.
- An infected object was detected during running of the on-demand scan task.
- A runtime error of a Kaspersky application occurred.
If none of the listed conditions is true for any test device, the set of updates is considered valid, and the Update verification task is considered to have completed successfully.
Before you start to create the Update verification task, perform the prerequisites:
- Create an administration group with several test devices. You will need this group to verify the updates.
We recommend using devices with the most reliable protection and the most popular application configuration across the network. This approach increases the quality and probability of virus detection during scans, and minimizes the risk of false positives. If viruses are detected on test devices, the Update verification task is considered unsuccessful.
- Create the update and malware scan tasks for an application supported by Kaspersky Security Center, for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows or Kaspersky Security for Windows Server. When creating the update and malware scan tasks, specify the administration group with the test devices.
The Update verification task sequentially runs the update and malware scan tasks on test devices to check that all updates are valid. In addition, when creating the Update verification task, you need to specify the update and malware scan tasks.
- Create the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task.
To make Kaspersky Security Center verify downloaded updates before distributing them to client devices:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task.
- In the task properties window that opens, go to the Application settings tab, and then enable the Run update verification option.
- If the Update verification task exists, click the Select task button. In the window that opens, select the Update verification task in the administration group with test devices.
- If you did not create the Update verification task earlier, do the following:
- Click the New task button.
- In the New task wizard that opens, specify the task name if you want to change the preset name.
- Select the administration group with test devices, which you created earlier.
- First, select the update task of a required application supported by Kaspersky Security Center, and then select the malware scan task.
After that, the following options appear. We recommend leaving them enabled:
- Specify an account from which the Update verification task will be run. You can use your account and leave the Default account option enabled. Alternatively, you can specify that the task should be run under another account that has the necessary access rights. To do this, select the Specify account option, and then enter the credentials of that account.
- Click Save to close the properties window of the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task.
The automatic update verification is enabled. Now, you can run the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task, and it will start from update verification.
Creating the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task
The Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task works only on distribution point devices running Windows. Distribution point devices running Linux or macOS cannot download updates from Kaspersky update servers.If at least one device running Linux or macOS is within the task scope, the task will have the Failed status. Even if the task is completed successfully on all Windows devices, it will return an error on the remaining devices.
You can create the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task for an administration group. This task will run for distribution points included in the specified administration group.
You can use this task, for example, if traffic between the Administration Server and the distribution point(s) is more expensive than traffic between the distribution point(s) and Kaspersky update servers, or if your Administration Server does not have internet access.
This task is required to download updates from Kaspersky update servers to the repositories of distribution points. The list of updates includes:
- Updates to databases and software modules for Kaspersky security applications
- Updates to Kaspersky Security Center components
- Updates to Kaspersky security applications
After the updates are downloaded, they can be propagated to the managed devices.
To create the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task, for a selected administration group:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click the Add button.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- For the Kaspersky Security Center application, in the Task type field select Download updates to the repositories of distribution points.
- Specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- Select an option button to specify the administration group, the device selection, or the devices to which the task applies.
- At the Finish task creation step, if you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Create button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the name of the created task to open the task properties window.
- On the Application settings tab of the task properties window, specify the following settings:
- Create a schedule for task start. If necessary, specify the following settings:
- Click the Save button.
The task is created and configured.
In addition to the settings that you specify during task creation, you can change other properties of a created task.
When the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task is performed, updates for databases and software modules are downloaded from the update source and stored in the shared folder. Downloaded updates will only be used by distribution points that are included in the specified administration group and that have no update download task explicitly set for them.
Enabling and disabling automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components
Updates and patches for the Administration Server can be installed only manually, after obtaining explicit approval from the administrator.
Automatic installation of updates and patches for Kaspersky Security Center components is enabled by default during Network Agent installation on the device. You can disable it during Network Agent installation, or disable it later by using a policy.
To disable automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components during local installation of Network Agent on a device:
- Start local installation of Network Agent on the device.
- At the Advanced settings step, clear the Automatically install applicable updates and patches for components that have Undefined status check box.
- Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Network Agent with disabled automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components will be installed on the device. You can enable automatic updating and patching later by using a policy.
To disable automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components during Network Agent installation on the device through an installation package:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories → Installation packages.
- Click the Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent <version number> package.
- In the properties window, open the Settings tab.
- Turn off the Automatically install applicable updates and patches for components that have the Undefined status toggle button.
Network Agent with disabled automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components will be installed from this package. You can enable automatic updating and patching later by using a policy.
If this check box was selected (or cleared) during Network Agent installation on the device, you can subsequently enable (or disable) automatic updating by using the Network Agent policy.
To enable or disable automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components by using the Network Agent policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the Network Agent policy.
- In the policy properties window, open the Application settings tab.
- In the Manage patches and updates section, turn on or off the Automatically install applicable updates and patches for components that have the Undefined status toggle button to enable or disable, respectively, automatic updating and patching.
- Set the lock (
 ) for this toggle button.
) for this toggle button.
The policy will be applied to the selected devices, and automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components will be enabled (or disabled) on these devices.
Automatic installation of updates for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
You can configure automatic updates of databases and software modules of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows on client devices.
To configure download and automatic installation of updates of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows on devices:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click the Add button.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- For the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows application, select Update as the task subtype.
- Specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- Choose the task scope.
- Specify the administration group, the device selection, or the devices to which the task applies.
- At the Finish task creation step, if you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Create button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the name of the created task to open the task properties window.
- On the Application settings tab of the task properties window, define the update task settings in local or mobile mode:
- Local mode: Connection is established between the device and the Administration Server.
- Mobile mode: No connection is established between Kaspersky Security Center and the device (for example, when the device is not connected to the internet).
- Enable the update sources that you want to use to update databases and application modules for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. If required, change positions of the sources in the list by using the Move up and Move down buttons. If several update sources are enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows tries to connect to them one after another, starting from the top of the list, and performs the update task by retrieving the update package from the first available source.
- Enable the Install approved application module updates option to download and install software module updates together with the application databases.
If the option is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows notifies the user about available software module updates and includes software module updates in the update package when running the update task. Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows installs only those updates for which you have set the Approved status; they will be installed locally through the application interface or through Kaspersky Security Center.
You can also enable the Automatically install critical application module updates option. If any updates are available for software modules, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows automatically installs those that have Critical status; the remaining updates will be installed after you approve them.
If updating the software module requires reviewing and accepting the terms of the License Agreement and Privacy Policy, the application installs updates after the terms of the License Agreement and Privacy Policy have been accepted by the user.
- Select the Copy updates to folder check box in order for the application to save downloaded updates to a folder, and then specify the folder path.
- Schedule the task. To ensure timely updates, we recommend that you select the When new updates are downloaded to the repository option.
- Click Save.
When the Update task is running, the application sends requests to Kaspersky update servers.
Some updates require installation of the latest versions of management plug-ins.
Approving and declining software updates
The settings of an update installation task may require approval of updates that are to be installed. You can approve updates that must be installed and decline updates that must not be installed.
For example, you may want to first check the installation of updates in a test environment and make sure that they do not interfere with the operation of devices, and only then allow the installation of these updates on client devices.
To approve or decline one or several updates:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Kaspersky applications → Seamless updates.
A list of available updates appears.
Updates of managed applications may require a specific minimum version of Kaspersky Security Center to be installed. If this version is later than your current version, these updates are displayed but cannot be approved. Also, no installation packages can be created from such updates until you upgrade Kaspersky Security Center. You are prompted to upgrade your Kaspersky Security Center instance to the required minimum version.
- Select the updates that you want to approve or decline.
- Click Approve to approve the selected updates or Decline to decline the selected updates.
The default value is Undefined.
The updates to which you assign Approved status are placed in a queue for installation.
The updates to which you assign Declined status are uninstalled (if possible) from all devices on which they were previously installed. Also, they will not be installed on other devices in future.
Some updates for Kaspersky applications cannot be uninstalled. If you set Declined status for them, Kaspersky Security Center will not uninstall these updates from the devices on which they were previously installed. However, these updates will never be installed on other devices in future.
If you set Declined status for third-party software updates, these updates will not be installed on devices for which they were planned but have not yet been installed. Updates will remain on devices on which they were already installed. If you have to delete the updates, you can manually delete them locally.
Updating Administration Server
You can install Administration Server updates by using Update Administration Server wizard.
To install an Administration Server update:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Kaspersky applications → Seamless updates.
- Run the Update Administration Server wizard in one of the following ways:
- Click the name of an Administration Server update in the list of updates, and in the window that opens, click the Run Update Administration Server wizard link.
- Click the Run Update Administration Server wizard link in the notification field at the top of the window.
- In the Update Administration Server wizard window, select one of the following to specify when to install an update:
- Install now. Select this option if you want to install the update now.
- Postpone installation. Select this option if you want to install the update later. In this case, a notification about this update will be displayed.
- Ignore update. Select this option if you do not want to install an update and do not want to receive notifications about this update.
- Select the Create backup copy of Administration Server before update installation option if you want to create a backup of Administration Server before installing the update.
- Click the OK button to finish the wizard.
In the backup process is interrupted, the update installation process is also interrupted.
Enabling and disabling the offline model of update download
We recommend that you avoid disabling the offline model of update download. Disabling it may cause failures in update delivery to devices. In certain cases, a Kaspersky Technical Support specialist may recommend that you disable the Download updates and anti-virus databases from Administration Server in advance option. Then, you will have to make sure that the task for receiving updates for Kaspersky applications has been set up.
To enable or disable the offline model of update download for an administration group:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click Groups.
- In the administration group structure, select the administration group for which you need to enable the offline model of update download.
- Click the Network Agent policy.
The properties window of the Network Agent policy opens.
By default, settings of child policies are inherited from parent policies and cannot be modified. If the policy that you want to modify is inherited, you first need to create a new policy for Network Agent in the required administration group. In the newly created policy, you can modify the settings that are not locked in the parent policy.
- In the Application settings tab, select the Manage patches and updates section.
- Enable or disable the Download updates and anti-virus databases from Administration Server in advance (recommended) option to enable or disable, respectively, the offline model of update download.
By default, the offline model of update download is enabled.
The offline model of update download will be enabled or disabled.
Updating Kaspersky databases and software modules on offline devices
Updating Kaspersky databases and software modules on managed devices is an important task for maintaining protection of the devices against viruses and other threats. Administrators usually configure regular updates through usage of the Administration Server repository or repositories of distribution points.
When you need to update databases and software modules on a device (or a group of devices) that is not connected to the Administration Server (primary or secondary), a distribution point or the internet, you have to use alternative sources of updates, such as an FTP server or a local folder. In this case you have to deliver the files of the required updates by using a mass storage device, such as a flash drive or an external hard drive.
You can copy the required updates from:
- The Administration Server.
To be sure the Administration Server repository contains the updates required for the security application installed on an offline device, at least one of the managed online devices must have the same security application installed. This application must be configured to receive the updates from the Administration Server repository through the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task.
- Any device that has the same security application installed and configured to receive the updates from the Administration Server repository, a distribution point repository, or directly from the Kaspersky update servers.
Below is an example of configuring updates of databases and software modules by copying them from the Administration Server repository.
To update Kaspersky databases and software modules on offline devices:
- Connect the removable drive to the device where the Administration Server is installed.
- Copy the updates files to the removable drive.
By default, the updates are located at: \\<server name>\KLSHARE\Updates.
Alternatively, you can configure Kaspersky Security Center to regularly copy the updates to the folder that you select. For this purpose, use the Copy downloaded updates to additional folders option in the properties of the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task. If you specify a folder located on a flash drive or an external hard drive as a destination folder for this option, this mass storage device will always contain the latest version of the updates.
- On offline devices, configure the security application (for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows) to receive updates from a local folder or a shared resource, such as an FTP server or a shared folder.
- Copy the updates files from the removable drive to the local folder or the shared resource that you want to use as an update source.
- On the offline device that requires update installation, start the update task of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
After the update task is complete, the Kaspersky databases and software modules are up-to-date on the device.
Backing up and restoring web plug-ins
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console allows you to back up the current state of a web plug-in to be able to restore the saved state later. For example, you can back up a web plug-in before updating it to a newer version. After the update, if the newer version does not meet your requirements or expectations, you can restore the previous version of the web plug-in from the backup.
To back up web plug-ins:
- In the main menu, go to Settings → Web plug-ins.
- In the Web plug-ins section, select the web plug-ins that you want to back up, and then click the Create backup copy button.
The selected web plug-ins are backed up. You can view the created backups in the Backups section.
To restore a web plug-in from a backup:
- In the main menu, go to Settings → Backups.
- In the Backups section, select the backup of the web plug-in that you want to restore, and then click the Restore from backup button.
The web plug-in is restored from the selected backup.
Adjustment of distribution points and connection gateways
A structure of administration groups in Kaspersky Security Center performs the following functions:
- Sets the scope of policies
There is an alternate way of applying relevant settings on devices, by using policy profiles. In this case, you set the scope of policies with tags, device locations in Active Directory organizational units, or membership in Active Directory security groups.
- Sets the scope of group tasks
There is an approach to defining the scope of group tasks that is not based on a hierarchy of administration groups: use of tasks for device selections and tasks for specific devices.
- Sets access rights to devices, virtual Administration Servers, and secondary Administration Servers
- Assigns distribution points
When building the structure of administration groups, you must take into account the topology of the organization's network for the optimum assignment of distribution points. The optimum distribution of distribution points allows you to save traffic on the organization's network.
Depending on the organizational schema and network topology, the following standard configurations can be applied to the structure of administration groups:
- Single office
- Multiple small remote offices
Devices functioning as distribution points must be protected, including physical protection, against any unauthorized access.
Standard configuration of distribution points: Single office
In a standard "single-office" configuration, all devices are on the organization's network so they can "see" each other. The organization's network may consist of a few separate parts (networks or network segments) linked by narrow channels.
The following methods of building the structure of administration groups are possible:
- Building the structure of administration groups taking into account the network topology. The structure of administration groups may not reflect the network topology with absolute precision. A match between the separate parts of the network and certain administration groups would be enough. You can use automatic assignment of distribution points or assign them manually.
- Building the structure of administration groups, without taking the network topology into account. In this case, you must disable automatic assignment of distribution points, and then assign one or several devices to act as distribution points for a root administration group in each of the separate parts of the network, for example, for the Managed devices group. All distribution points will be at the same level and will feature the same scope spanning all devices on the organization's network. In this case, each Network Agent will connect to the distribution point that has the shortest route. The route to a distribution point can be traced with the tracert utility.
Standard configuration of distribution points: Multiple small remote offices
This standard configuration provides for a number of small remote offices, which may communicate with the head office over the internet. Each remote office is located behind the NAT, that is, connection from one remote office to another is not possible because offices are isolated from one another.
The configuration must be reflected in the structure of administration groups: a separate administration group must be created for each remote office (groups Office 1 and Office 2 in the figure below).

Remote offices are included in the administration group structure
One or multiple distribution points must be assigned to each administration group that correspond to an office. Distribution points must be devices at the remote office that have a sufficient amount of free disk space. Devices deployed in the Office 1 group, for example, will access distribution points assigned to the Office 1 administration group.
If some users move between offices physically, with their laptops, you must select two or more devices (in addition to the existing distribution points) in each remote office and assign them to act as distribution points for a top-level administration group (Root group for offices in the figure above).
Example: A laptop is deployed in the Office 1 administration group and then is moved physically to the office that corresponds to the Office 2 administration group. After the laptop is moved, Network Agent attempts to access the distribution points assigned to the Office 1 group, but those distribution points are unavailable. Then, Network Agent starts attempting to access the distribution points that have been assigned to the Root group for offices. Because remote offices are isolated from one another, attempts to access distribution points assigned to the Root group for offices administration group will only be successful when Network Agent attempts to access distribution points in the Office 2 group. That is, the laptop will remain in the administration group that corresponds to the initial office, but the laptop will use the distribution point of the office where it is physically located at the moment.
About assigning distribution points
You can assign a managed device as a distribution point manually or automatically.
If you assign managed device as a distribution point manually, you can select any device in your network.
If you assign distribution points automatically, Kaspersky Security Center can select only the managed device that meets the following conditions:
- The device has at least 50 GB of free disk space.
- The managed device is connected with Kaspersky Security Center directly (not through the gateway).
- The managed device is not a laptop.
If your network does not have devices that meet the specified conditions, Kaspersky Security Center will not assign any device as a distribution point automatically.
Assigning distribution points automatically
We recommend that you assign distribution points automatically. In this case, Kaspersky Security Center will select on its own which devices must be assigned distribution points.
To assign distribution points automatically:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Distribution points section.
- Select the Automatically assign distribution points option.
If automatic assignment of devices as distribution points is enabled, you cannot configure distribution points manually or edit the list of distribution points.
- Click the Save button.
Administration Server assigns and configures distribution points automatically.
Assigning distribution points manually
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to manually assign devices to act as distribution points.
We recommend that you assign distribution points automatically. In this case, Kaspersky Security Center will select on its own which devices must be assigned distribution points. However, if you have to opt out of assigning distribution points automatically for any reason (for example, if you want to use exclusively assigned servers), you can assign distribution points manually after you calculate their number and configuration.
Devices functioning as distribution points must be protected, including physical protection, against any unauthorized access.
To manually assign a device to act as distribution point:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Distribution points section.
- Select the Manually assign distribution points option.
- Click the Assign button.
- Select the device that you want to make a distribution point.
When selecting a device, keep in mind the operation features of distribution points and the requirements set for the device that acts as distribution point.
- Select the administration group that you want to include in the scope of the selected distribution point.
- Click the OK button.
The distribution point that you have added will be displayed in the list of distribution points, in the Distribution points section.
- Click the newly added distribution point in the list to open its properties window.
- Configure the distribution point in the properties window:
- The General section contains the setting of interaction between the distribution point and client devices:
- In the Scope section, specify the scope to which the distribution point will distribute updates (administration groups and/or network location).
Only devices running a Windows operating system can determine their network location. Network location cannot be determined for devices running other operating systems.
- If the distribution point works on a machine other than Administration Server, in the Source of updates section, you can select a source of updates for the distribution point:
- In the Internet connection settings subsection, you can specify the internet access settings:
- In the KSN Proxy section, you can configure the application to use the distribution point to forward KSN requests from the managed devices:
- If the distribution point works on a machine other than Administration Server, in the Connection gateway section, you can configure the distribution point to act as a gateway for connection between Network Agent instances and Administration Server:
- Connection gateway
- Establish connection to gateway from Administration Server (if gateway is in DMZ)
- Open local port for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
When connecting mobile devices to Administration Server via the distribution point that acts as a connection gateway, you can enable the following options:
- Open port for mobile devices (SSL authentication of the Administration Server only)
- Open port for mobile devices (two-way SSL authentication)
In both cases, the certificates are checked while the TLS session is being established on the distribution point only. The certificates are not forwarded to be checked by the Administration Server. After a TLS session with the mobile device is established, the distribution point uses the Administration Server certificate to create a tunnel for synchronization between the mobile device and Administration Server. If you open the port for two-way SSL authentication, the only way to distribute the mobile device certificate is via an installation package.
- Configure the polling of Windows domains, Active Directory, and IP ranges by the distribution point:
- In the Advanced section, specify the folder that the distribution point must use to store distributed data:
- Click the OK button.
The selected devices act as distribution points.
Modifying the list of distribution points for an administration group
You can view the list of distribution points assigned to a specific administration group and modify the list by adding or removing distribution points.
To view and modify the list of distribution points assigned to an administration group:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- In the Current path field above the list of managed devices, click the path link.
- In the left-side pane that opens, select an administration group for which you want to view the assigned distribution points.
This enables the Distribution points menu item.
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Distribution points.
- To add new distribution points for the administration group, click the Assign button above the list of managed devices and select devices from the pane that opens.
- To remove the assigned distribution points, select devices from the list and click the Unassign button.
Depending on your modifications, the new distribution points are added to the list or existing distribution points are removed from the list.
Forced synchronization
Although Kaspersky Security Center automatically synchronizes the status, settings, tasks, and policies for managed devices, in some cases you might want to run the synchronization for a specified device forcibly. You can run forced synchronization for the following devices:
- Devices that have Network Agent installed
- Devices running KasperskyOS
Before running forced synchronization for a KasperskyOS device, ensure that the device is included in a distribution point scope and that a push server is enabled on the distribution point.
- iOS devices
- Android devices
Before running forced synchronization for an Android device, you must configure Firebase Cloud Messaging.
Synchronizing a single device
To force synchronization between the Administration Server and a managed device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click the name of the device that you want to synchronize with the Administration Server.
A property window opens with the General section selected.
- Click the Force synchronization button.
The application synchronizes the selected device with the Administration Server.
Synchronizing multiple devices
To force synchronization between the Administration Server and multiple managed devices:
- Open the device list of an administration group or a device selection:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices, click the path link in the Current path field above the list of managed devices, then select the administration group that contains devices to synchronize.
- Run a device selection to view the device list.
- Select the check boxes next to the devices that you want to synchronize with the Administration Server.
- Above the list of managed devices, click the ellipsis button (
 ), and then click the Force synchronization button.
), and then click the Force synchronization button.The application synchronizes the selected devices with the Administration Server.
- In the device list, check that the time of last connection to the Administration Server has changed, for the selected devices, to the current time. If the time has not changed, update the page content by clicking the Refresh button.
The selected devices are synchronized with the Administration Server.
Viewing the time of a policy delivery
After changing a policy for a Kaspersky application on the Administration Server, the administrator can check whether the changed policy has been delivered to a specific managed device. A policy can be delivered during a regular synchronization or a forced synchronization.
To view the date and time that an application policy was delivered to a managed device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click the name of the device that you want to synchronize with the Administration Server.
A property window opens with the General section selected.
- Select the Applications tab.
- Select the application for which you want to view the policy synchronization date.
The application policy window opens with the General section selected and the policy delivery date and time displayed.
Enabling a push server
In Kaspersky Security Center, a distribution point can work as a push server for the devices managed through the mobile protocol and for the devices managed by Network Agent. For example, a push server must be enabled if you want to be able to force synchronization of KasperskyOS devices with Administration Server. A push server has the same scope of managed devices as the distribution point on which the push server is enabled. If you have several distribution points assigned for the same administration group, you can enable push server on each of the distribution points. In this case, Administration Server balances the load between the distribution points.
You might want to use distribution points as push servers to make sure that there is continuous connectivity between a managed device and the Administration Server. Continuous connectivity is needed for some operations, such as running and stopping local tasks, receiving statistics for a managed application, or creating a tunnel. If you use a distribution point as a push server, you do not have to use the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option on managed devices or send packets to the UDP port of the Network Agent.
A push server supports the load of up to 50,000 simultaneous connections.
To enable push server on a distribution point:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Distribution points section.
- Click the name of the distribution point on which you want to enable the push server.
The distribution point properties window opens.
- On the General section, enable the Run push server option.
- In the Push server port field, type the port number. You can specify number of any unoccupied port.
- In the Address for remote hosts field, specify the IP address or the name of the distribution point device.
- Click the OK button.
The push server is enabled on the selected distribution point.
Managing third-party applications on client devices
This section describes the features of Kaspersky Security Center that are related to the management of third-party applications installed on client devices.
Installing third-party software updates
Kaspersky Security Center enables you to manage updates of third-party software installed on managed devices and fix vulnerabilities in Microsoft applications and other software makers' products through installation of required updates.
Kaspersky Security Center can update third-party software from the current version to the latest version only.
The list of third-party software can be updated and extended with new applications. You can check whether you can update the third-party software (installed on users' devices) with Kaspersky Security Center by viewing the list of available updates in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Kaspersky Security Center searches for updates through the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task. When this task is complete, Administration Server receives the lists of detected vulnerabilities and required updates for the third-party software installed on the devices that you specified in the task properties. After viewing information about available updates, you can install them on devices.
Kaspersky Security Center updates some applications by removing the previous version of the application and installing the new one.
A user interaction may be required when you update a third-party application or fix a vulnerability in a third-party application on a managed device. For example, the user may be prompted to close the third-party application if it is currently open.
For security reasons, any third-party software updates that you install by using the Vulnerability and patch management feature are automatically scanned for malware by Kaspersky technologies. These technologies are used for automatic file checks and include virus scanning, static analysis, dynamic analysis, behavior analysis in the sandbox environment, and machine learning.
Kaspersky experts do not perform manual analysis of third-party software updates that can be installed by using the Vulnerability and patch management feature. In addition, Kaspersky experts do not search for vulnerabilities (known or unknown) or undocumented features in such updates, nor do they perform other types of analysis of the updates other than those specified in the paragraph above.
Tasks for installing third-party software updates
When metadata of the third-party software updates is downloaded to the repository, you can install the updates on client devices by using the following tasks:
- The Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task
The Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is used to install updates for Microsoft applications, including the updates provided by the Windows Update service, and updates of other vendors' software. Note that this task can be created only if you have the license for the Vulnerability and patch management feature.
When this task is complete, the updates are installed on the managed devices automatically. When metadata of new updates is downloaded to the Administration Server repository, Kaspersky Security Center checks whether the updates meet the criteria specified in the update rules. All new updates that meet the criteria will be downloaded and installed automatically at the next task run.
- The Install Windows Update updates task
The Install Windows Update updates task does not require a license, but it can be used to install Windows Update updates only.
When this task is complete, only those updates that are specified in the task properties are installed. In future, if you want to install new updates downloaded to the Administration Server repository, you must add the required updates to the list of updates in the existing task or create a new Install Windows Update updates task.
Using Administration Server as WSUS server
Information about available updates for Microsoft Windows is provided by the Windows Update service. The Administration Server can be used as the Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) server. To use Administration Server as the WSUS server, you create the Perform Windows Update synchronization task and select the Use Administration Server as WSUS server option in the Network Agent policy. After you have configured data synchronization with Windows Update, Administration Server provides updates to Windows Update services on devices in centralized mode and with the set frequency.
Scenario: Updating third-party software
This section provides a scenario for updating third-party software installed on the client devices. The third-party software includes applications from Microsoft and other software vendors. Updates for Microsoft applications are provided by the Windows Update service.
Prerequisites
Administration Server must have a connection to the internet to install updates of third-part software other than Microsoft software.
By default, internet connection is not required for Administration Server to install Microsoft software updates on the managed devices. For example, the managed devices can download the Microsoft software updates directly from Microsoft Update servers or from Windows Server with Microsoft Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) deployed in your organization's network. Administration Server must be connected to the internet when you use Administration Server as WSUS server.
Stages
Updating third-party software proceeds in stages:
- Searching for required updates
To find the third-party software updates required for the managed devices, run the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task. When this task is complete, Kaspersky Security Center receives the lists of detected vulnerabilities and required updates for the third-party software installed on the devices that you specified in the task properties.
The Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is created automatically by the Administration Server quick start wizard. If you did not run the wizard, create the task or run the quick start wizard now.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Scanning applications for vulnerabilities, Scheduling the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task, Find vulnerabilities and required updates task settings
- Analyzing the list of found updates
View the Software updates list and decide which updates you want to install. To view detailed information about each update, click the update name in the list. For each update in the list, you can also view the statistics on the update installation on client devices.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Viewing information about available updates
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Viewing information about available third-party software updates
- Configuring installation of updates
When Kaspersky Security Center received the list of the third-party software updates, you can install them on client devices by using the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task or the Install Windows Update updates task. Create one of these tasks. You can create these tasks on the Tasks tab or by using the Software updates list.
The Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is used to install updates for Microsoft applications, including the updates provided by the Windows Update service, and updates of other vendors' software. Note that this task can be created only if you have the license for the Vulnerability and patch management feature.
The Install Windows Update updates task does not require a license, but it can be used to install Windows Update updates only.
To install some software updates you must accept the End User License Agreement (EULA) for the installation software. If you decline the EULA, the software update will not be installed.
You can start an update installation task by schedule. When specifying the task schedule, make sure that the update installation task starts after the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is complete.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Fixing vulnerabilities in applications, Viewing information about available updates
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, Creating the Install Windows Update updates task, Viewing information about available third-party software updates
- Scheduling the tasks
To be sure that the update list is always up-to-date, schedule the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task to run the task automatically from time to time. By default, the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is set to start manually.
If you have created the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, you can schedule it to run with the same frequency as the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task or less often. When scheduling the Install Windows Update updates task, note that for this task you must define the list of updates every time before starting this task.
When scheduling the tasks, make sure that an update installation task starts after the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is complete.
- Approving and declining software updates (optional)
If you have created the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, you can specify rules for update installation in the task properties. If you have created the Install Windows Update updates task, skip this step.
For each rule, you can define the updates to install depending on the update status: Undefined, Approved or Declined. For example, you may want to create a specific task for servers and set a rule for this task to allow installation of only Windows Update updates and only those ones that have Approved status. After that you manually set the Approved status for those updates that you want to install. In this case the Windows Update updates that have the Undefined or Declined status will not be installed on the servers that you specified in the task.
The usage of the Approved status to manage update installation is efficient for a small amount of updates. To install multiple updates, use the rules that you can configure in the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task. We recommend that you set the Approved status for only those specific updates that do not meet the criteria specified in the rules. When you manually approve a large amount of updates, performance of Administration Server decreases and may lead to Administration Server overload.
By default, the downloaded software updates have the Undefined status. You can change the status to Approved or Declined in the Software updates list (Operations → Patch management → Software updates).
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Approving and declining software updates
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Approving and declining third-party software updates
- Configuring Administration Server to work as Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) server (optional)
By default, Windows Update updates are downloaded to the managed devices from Microsoft servers. You can change this setting to use the Administration Server as WSUS server. In this case, the Administration Server synchronizes the update data with Windows Update at the specified frequency and provides updates in centralized mode to Windows Update on networked devices.
To use the Administration Server as WSUS server, create the Perform Windows Update synchronization task and select the Use Administration Server as WSUS server check box in the Network Agent policy.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Synchronizing updates from Windows Update with Administration Server, Configuring Windows updates in a Network Agent policy
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating the Perform Windows Update synchronization task
- Running an update installation task
Start the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task or the Install Windows Update updates task. When you start these tasks, updates are downloaded and installed on managed devices. After the task is complete, make sure that it has the Completed successfully status in the task list.
- Create the report on results of update installation of third-party software (optional)
To view detailed statistics on the update installation, create the Report on results of installation of third-party software updates.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Creating and viewing a report
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Generating and viewing a report
Results
If you have created and configured the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, the updates are installed on the managed devices automatically. When new updates are downloaded to the Administration Server repository, Kaspersky Security Center checks whether they meet the criteria specified in the update rules. All new updates that meet the criteria will be installed automatically at the next task run.
If you have created the Install Windows Update updates task, only those updates specified in the Install Windows Update updates task properties are installed. In future, if you want to install new updates downloaded to the Administration Server repository, you must add the required updates to the list of updates in the existing task or create a new Install Windows Update updates task.
Installing third-party software updates
You can install third-party software updates on managed devices by creating and running one of the following tasks:
- Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities
The Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task can be created only if you have a license for the Vulnerability and patch management feature. You can use this task to install both Windows Update updates provided by Microsoft and updates of other vendors' software.
- Install Windows Update updates
You can use the Install Windows Update updates task to install Windows Update updates only.
A user interaction may be required when you update a third-party application or fix a vulnerability in a third-party application on a managed device. For example, the user may be prompted to close the third-party application if it is currently open.
As an option, you can create a task to install the required updates in the following ways:
- By opening the update list and specifying which updates to install.
As a result, a new task to install the selected updates is created. As an option, you can add the selected updates to an existing task.
- By running the Update installation wizard.
The Update installation wizard is only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
The wizard simplifies creation and configuration of an update installation task, and allows you to eliminate the creation of redundant tasks that contain the same updates to install.
Installing third-party software updates by using the update list
To install third-party software updates by using the list of updates:
- Open one of the lists of updates:
- To open the general update list, in the main menu, go to Operations → Patch management → Software updates.
- To open the update list for a managed device, in the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices → <device name> → Advanced → Available updates.
- To open the update list for a specific application, in the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Applications registry → <application name> → Available updates.
A list of available updates appears.
- Select the check boxes next to the updates that you want to install.
- Click the Install updates button.
To install some software updates, you must accept the End User License Agreement (EULA). If you decline the EULA, the software update is not installed.
- Select one of the following options:
- New task
The New task wizard starts. If you have the Vulnerability and patch management license, the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is preselected. If you do not have the license, the Install Windows Update updates task is preselected. Follow the steps of the wizard to complete the task creation.
- Install update (add rule to specified task)
Select a task to which you want to add the selected updates. If you have the Vulnerability and patch management license, select the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task. A new rule to install the selected updates will be automatically added to the selected task. If you do not have the license, select the Install Windows Update updates task. The selected updates will be added to the task properties.
The task properties window opens. Click the Save button to save the changes.
- New task
If you have chosen to create a task, the task is created and displayed in the task list at Assets (Devices) → Tasks. If you have chosen to add the updates to an existing task, the updates are saved in the task properties.
To install third-party software updates, start the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task or the Install Windows Update updates task. You can start any of these tasks manually or specify schedule settings in the properties of the task that you start. When specifying the task schedule, make sure that the update installation task starts after the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is complete.
Installing third-party software updates by using the Update installation wizard
The Update installation wizard is only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
To create a task to install third-party software updates by using the Update installation wizard:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Patch management → Software updates.
A list of available updates appears.
- Select the check box next to the update that you want to install.
- Click the Run Update installation wizard button.
The Update installation wizard starts. The Select the update installation task page displays the list of all existing tasks of the following types:
- Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities
- Install Windows Update updates
- Fix vulnerabilities
You cannot modify the tasks of the last two types to install new updates. To install new updates, you can only use the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities tasks.
- If you want the wizard to display only those tasks that install the update that you selected, then enable the Show only tasks that install this update option.
- Choose what you want to do:
- To start a task, select the check box next to the task name, and then click the Start button.
- To add a new rule to an existing task:
- Select the check box next to the task name, and then click the Add rule button.
- On the page that opens, configure the new rule:
- Installation rule for updates of this importance level
- Installation rule for updates of this importance level according to MSRC
- Installation rule for updates by this vendor
- Installation rule for updates of the type
- Installation rule for the selected update
- Approve selected updates
- Automatically install all previous application updates that are required to install the selected updates
- Click the Add button.
- To create a task:
- Click the New task button.
- On the page that opens, configure the new rule:
- Installation rule for updates of this importance level
- Installation rule for updates of this importance level according to MSRC
- Installation rule for updates by this vendor
- Installation rule for updates of the type
- Installation rule for the selected update
- Approve selected updates
- Automatically install all previous application updates that are required to install the selected updates
- Click the Add button.
If you have chosen to start a task, you can close the wizard. The task will complete in background mode. No further actions are required.
If you have chosen to add a rule to an existing task, the task properties window opens. The new rule is already added to the task properties. You can view or modify the rule or other task settings. Click the Save button to save the changes.
If you have chosen to create a task, you continue to create the task in the New task wizard. The new rule that you added in the Update installation wizard is displayed in the New task wizard. When you complete the wizard, the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is added to the task list.
Creating the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
Through the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task, Kaspersky Security Center receives the lists of detected vulnerabilities and required updates for the third-party software installed on the managed devices.
The Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is created automatically when the quick start wizard is running. If you did not run the wizard, you can create the task manually.
To create the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- For the Kaspersky Security Center application, select the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task type.
- Specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- Select devices to which the task will be assigned.
- If you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option on the Finish task creation page. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Create button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the name of the created task to open the task properties window.
- In the task properties window, specify the general task settings.
- On the Application settings tab, specify the following settings:
- Search for vulnerabilities and updates listed by Microsoft
- Connect to the update server to update data
- Search for third-party vulnerabilities and updates listed by Kaspersky
- Specify paths for advanced search of applications across the file system
- Enable advanced diagnostics
- Maximum size, in MB, of advanced diagnostics files
- Click the Save button.
The task is created and configured.
If the task results contain a warning of the 0x80240033 "Windows Update Agent error 80240033 ("License terms could not be downloaded.")" error, you can resolve this issue through the Windows Registry.
Find vulnerabilities and required updates task settings
The Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is created automatically when the quick start wizard is running. If you did not run the wizard, you can create the task manually.
In addition to the general task settings, you can specify the following settings when creating the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task or later, when configuring the properties of the created task:
- Search for vulnerabilities and updates listed by Microsoft
- Connect to the update server to update data
- Search for third-party vulnerabilities and updates listed by Kaspersky
- Specify paths for advanced search of applications across the file system
- Enable advanced diagnostics
- Maximum size, in MB, of advanced diagnostics files
Recommendations on the task schedule
When scheduling the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task, make sure that two options—Run missed tasks and Use automatically randomized delay for task starts—are enabled.
By default, the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is set to start manually. If the organization's workplace rules provide for shutting down all devices at this time, the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task will run after the devices are turned on again, that is, in the morning of the next day. Such activity may be undesirable because a vulnerability scan may increase the load on CPUs and disk subsystems. You must set up the most convenient schedule for the task based on the workplace rules adopted in the organization.
Creating the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task
The Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
The Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is used to update and fix vulnerabilities in third-party software, including Microsoft software, installed on the managed devices. This task allows you to install multiple updates and fix multiple vulnerabilities according to certain rules.
To install updates or fix vulnerabilities by using the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, you can do one of the following:
- Run the Update installation wizard or the Vulnerability fix wizard.
- Create an Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
- Add a rule for update installation to an existing Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
To create the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- For the Kaspersky Security Center application, select the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task type.
If the task is not displayed, check whether your account has the Read, Modify, and Execute rights for the System management: Vulnerability and patch management functional area. You cannot create and configure the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task without these access rights.
- Specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- Select devices to which the task will be assigned.
- Specify the rules for update installation, and then specify the following settings:
- Start installation at device restart or shutdown
- Install the required general system components
- Allow installation of new application versions during updates
- Download updates to the device without installing them
- Download updates to
- Enable advanced diagnostics
- Maximum size, in MB, of advanced diagnostics files
- Specify the operating system restart settings:
- If you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option on the Finish task creation page. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Finish button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the name of the created task to open the task properties window.
- In the task properties window, specify the general task settings according to your needs.
- Click the Save button.
The task is created and configured.
If the task results contain a warning of the 0x80240033 "Windows Update Agent error 80240033 ("License terms could not be downloaded.")" error, you can resolve this issue through the Windows Registry.
Adding rules for update installation
This feature is only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
When installing software updates or fixing software vulnerabilities by using the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, you must specify rules for the update installation. These rules determine the updates to install and the vulnerabilities to fix.
The exact settings depend on whether you add a rule for all updates, for Windows Update updates, or for updates of third-party applications (applications made by software vendors other than Kaspersky and Microsoft). When adding a rule for Windows Update updates or updates of third-party applications, you can select specific applications and application versions for which you want to install updates. When adding a rule for all updates, you can select specific updates that you want to install and vulnerabilities that you want to fix by means of installing updates.
You can add a rule for update installation in the following ways:
- By adding a rule while creating a new Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
- By adding a rule on the Application Settings tab in the properties window of an existing Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
- Through the Update installation wizard or the Vulnerability fix wizard.
To add a new rule for all updates:
- Click the Add button.
The Rule creation wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Rule type page, select Rule for all updates.
- On the General criteria page, use the drop-down lists to specify the following settings:
- On the Updates page, select the updates to be installed:
- On the Vulnerabilities page, select vulnerabilities that will be fixed by installing the selected updates:
- On the Name page, specify the name for the rule that you are adding. You can later change this name in the Settings section of the properties window of the created task.
After the Rule creation wizard completes its operation, the new rule is added and displayed in the rule list in the New task wizard or in the task properties.
To add a new rule for Windows Update updates:
- Click the Add button.
The Rule creation wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Rule type page, select Rule for Windows Update.
- On the General criteria page, specify the following settings:
- On the Applications page, select the applications and application versions for which you want to install updates. By default, all applications are selected.
- On the Categories of updates page, select the categories of updates to be installed. These categories are the same as in Microsoft Update Catalog. By default, all categories are selected.
- On the Name page, specify the name for the rule that you are adding. You can later change this name in the Settings section of the properties window of the created task.
After the Rule creation wizard completes its operation, the new rule is added and displayed in the rule list in the New task wizard or in the task properties.
To add a new rule for updates of third-party applications:
- Click the Add button.
The Rule creation wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Rule type page, select Rule for third-party updates.
- On the General criteria page, specify the following settings:
- On the Applications page, select the applications and application versions for which you want to install updates. By default, all applications are selected.
- On the Name page, specify the name for the rule that you are adding. You can later change this name in the Settings section of the properties window of the created task.
After the Rule creation wizard completes its operation, the new rule is added and displayed in the rule list in the New task wizard or in the task properties.
Creating the Install Windows Update updates task
The Install Windows Update updates task allows you to install software updates provided by the Windows Update service on managed devices.
If you do not have the Vulnerability and patch management license, you cannot create new tasks of the Install Windows Update updates type. To install new updates, you can add them to an existing Install Windows Update updates task. We recommend that you use the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task instead of the Install Windows Update updates task. The Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task enables you to install multiple updates and fix multiple vulnerabilities automatically, according to the rules that you define. In addition, this task enables you to install updates from software vendors other than Microsoft.
A user interaction may be required when you update a third-party application or fix a vulnerability in a third-party application on a managed device. For example, the user may be prompted to close the third-party application if it is currently open.
To create the Install Windows Update updates task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- For the Kaspersky Security Center application, select the Install Windows Update updates task type.
- Specify the name for the task that you are creating.
A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- Select devices to which the task will be assigned.
- Click the Add button.
The list of updates opens.
- Select the Windows Update updates that you want to install, and then click OK.
- Specify the operating system restart settings:
- Specify the account settings:
- If you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option on the Finish task creation page. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Finish button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the name of the created task to open the task properties window.
- In the task properties window, specify the general task settings according to your needs.
- Click the Save button.
The task is created and configured.
Viewing information about available third-party software updates
You can view the list of available updates for third-party software, including Microsoft software, installed on client devices.
To view a list of available updates for third-party applications installed on client devices,
In the main menu, go to Operations → Patch management → Software updates.
A list of available updates appears.
You can specify a filter to view the list of software updates. Click the Filter icon (![]() ) in the upper right corner of the software updates list to manage the filter. You can also select one of preset filters from the Preset filters drop-down list above the software vulnerabilities list.
) in the upper right corner of the software updates list to manage the filter. You can also select one of preset filters from the Preset filters drop-down list above the software vulnerabilities list.
To view the properties of an update:
- Click the name of the required software update.
- The properties window of the update opens, displaying information grouped on the following tabs:
To view the statistics of an update installation:
- Select the check box next to the required software update.
- Click the Statistics of update installation statuses button.
The diagram of the update installation statuses is displayed. Clicking a status opens a list of devices on which the update has the selected status.
You can view information about available software updates for third-party software, including Microsoft software, installed on the selected managed device running Windows.
To view a list of available updates for third-party software installed on the selected managed device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
The list of managed devices is displayed.
- In the list of managed devices, click the link with the name of the device for which you want to view third-party software updates.
The properties window of the selected device is displayed.
- In the properties window of the selected device, select the Advanced tab.
- In the left pane, select the Available updates section. If you want to view only installed updates, enable the Show installed updates option.
The list of available third-party software updates for the selected device is displayed.
Exporting the list of available software updates to a file
You can export the list of updates for third-party software, including Microsoft software, that is displayed at the moment to the CSV or TXT files. You can use these files, for example, to send them to your information security manager or to store them for purposes of statistics.
To export to a text file the list of available updates for third-party software installed on all managed devices:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Patch management → Software updates.
The page displays a list of available updates for third-party software installed on all managed devices.
- Click the Export to TXT or Export to CSV button, depending on the format you prefer for export.
The file containing the list of available updates for third-party software, including Microsoft software, is downloaded to the device that you use at the moment.
To export to a text file the list of available updates for third-party software installed on the selected managed device:
- Open the list of available third-party software updates on the selected managed device.
- Select the software updates you want to export.
Skip this step if you want to export a complete list of software updates.
If you want to export a complete list of software updates, only updates displaying on the current page will be exported.
If you want to export only installed updates, select the Show installed updates check box.
- Click the Export to TXT or Export to CSV button, depending on the format you prefer for export.
The file containing the list of updates for third-party software, including Microsoft software, installed on the selected managed device is downloaded to the device you are using at the moment.
Approving and declining third-party software updates
When you configure the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, you can create a rule that requires a specific status of updates that are to be installed. For example, an update rule can allow installation of the following:
- Only approved updates
- Only approved and undefined updates
- All updates irrespective of the update statuses
You can approve updates that must be installed and decline updates that must not be installed.
The usage of the Approved status to manage update installation is efficient for a small amount of updates. To install multiple updates, use the rules that you can configure in the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task. We recommend that you set the Approved status for only those specific updates that do not meet the criteria specified in the rules. When you manually approve a large amount of updates, performance of Administration Server decreases and may lead to Administration Server overload.
To approve or decline one or several updates:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Patch management → Software updates.
A list of available updates appears.
- Select the updates that you want to approve or decline.
- Click Approve to approve the selected updates or Decline to decline the selected updates.
The default value is Undefined.
The selected updates have the statuses that you defined.
As an option, you can change the approval status in the properties of a specific update.
To approve or decline an update in its properties:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Patch management → Software updates.
A list of available updates appears.
- Click the name of the update that you want to approve or decline.
The update properties window opens.
- In the General section, select a status for the update by changing the Update approval status option. You can select the Approved, Declined, or Undefined status.
- Click the Save button to save the changes.
The selected update has the status that you defined.
If you set Declined status for third-party software updates, these updates will not be installed on devices for which they were planned but have not yet been installed. Updates will remain on devices on which they were already installed. If you have to delete them, you can manually delete them locally.
Creating the Perform Windows Update synchronization task
The Perform Windows Update synchronization task is only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
The Perform Windows Update synchronization task is required if you want to use the Administration Server as a WSUS server. In this case, the Administration Server downloads Windows updates to the database, and provides the updates to Windows Update on client devices, in the centralized mode through Network Agents. If the network does not use a WSUS server, each client device downloads Microsoft updates from external servers independently.
The Perform Windows Update synchronization task only downloads metadata from Microsoft servers. Kaspersky Security Center downloads the updates when you run an update installation task and only those updates that you select for installation.
When running the Perform Windows Update synchronization task, the application receives a list of current updates from a Microsoft update server. Next, Kaspersky Security Center compiles a list of updates that have become outdated. At the next start of the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task, Kaspersky Security Center flags all outdated updates and sets the deletion time for them. At the next start of the Perform Windows Update synchronization task, all updates flagged for deletion 30 days ago are deleted. Kaspersky Security Center also checks for outdated updates that were flagged for deletion more than 180 days ago, and then deletes those older updates.
When the Perform Windows Update synchronization task completes and outdated updates are deleted, the database may still have the hash codes pertaining to the files of deleted updates, as well as corresponding files in the %AllUsersProfile%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\.working\wusfiles files (if they were downloaded earlier). You can run the Administration Server maintenance task to delete these outdated records from the database and corresponding files.
To create the Perform Windows Update synchronization task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- For the Kaspersky Security Center application, select the Perform Windows Update synchronization task type.
- Specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- Enable the Download express installation files option if you want the express update files to be downloaded when running the task.
When Kaspersky Security Center synchronizes updates with Microsoft Windows Update Servers, information about all files is saved in the Administration Server database. All files required for an update are also downloaded to the drive during interaction with the Windows Update Agent. In particular, Kaspersky Security Center saves information about express update files to the database and downloads them when necessary. Downloading express update files leads to decreased free space on the drive.
To avoid a decrease in disk space volume and to reduce traffic, disable the Download express installation files option.
- Select the applications for which you want to download updates.
If the All applications check box is selected, updates will be downloaded for all existing applications, and for all applications that may be released in the future.
- Select the categories of updates that you want to download to the Administration Server.
If the All categories check box is selected, updates will be downloaded for all existing updates categories, and for all categories that may appear in the future.
- Select the localization languages for the updates that you want to download to the Administration Server. Select one of the following options:
- Specify which account to use when running the task. Select one of the following options:
- If you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option on the Finish task creation page. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Finish button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the name of the created task to open the task properties window.
- In the task properties window, specify the general task settings according to your needs.
- Click the Save button.
The task is created and configured.
Updating third-party applications automatically
Some third-party applications can be updated automatically. The application vendor defines whether or not the application supports the auto-update feature. If a third-party application installed on a managed device supports auto-update, you can specify the auto-update setting in the application properties. After you change the auto-update setting, Network Agents apply the new setting on each managed device on which the application is installed.
The auto-update setting is independent of the other objects and settings of the Vulnerability and patch management feature. For example, this setting does not depend on an update approval status or the update installation tasks, such as Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities, Install Windows Update updates, and Fix vulnerabilities.
To configure the auto-update setting for a third-party application:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Applications registry.
- Click the name of the application for which you want to change the auto-update setting.
To simplify the search, you can filter the list by the Automatic Updates status column.
The application properties window opens.
- In the General section, select a value for the following setting:
- Click the Save button to save the changes.
The auto-update setting is applied to the selected application.
Fixing third-party software vulnerabilities
This section describes the features of Kaspersky Security Center that relate to fixing vulnerabilities in the software installed on managed devices.
Scenario: Finding and fixing third-party software vulnerabilities
This section provides a scenario for finding and fixing vulnerabilities on the managed devices running Windows. You can find and fix software vulnerabilities in the operating system and in third-party software, including Microsoft software.
Prerequisites
- Kaspersky Security Center is deployed in your organization.
- There are managed devices running Windows in your organization.
- Internet connection is required for Administration Server to perform the following tasks:
- To make a list of recommended fixes for vulnerabilities in Microsoft software. The list is created and regularly updated by Kaspersky specialists.
- To fix vulnerabilities in third-part software other than Microsoft software.
Stages
Finding and fixing software vulnerabilities proceeds in stages:
- Scanning for vulnerabilities in the software installed on the managed devices
To find vulnerabilities in the software installed on the managed devices, run the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task. When this task is complete, Kaspersky Security Center receives the lists of detected vulnerabilities and required updates for the third-party software installed on the devices that you specified in the task properties.
The Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is created automatically by Kaspersky Security Center quick start wizard. If you did not run the wizard, start it now or create the task manually.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Scanning applications for vulnerabilities, Scheduling the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task, Find vulnerabilities and required updates task settings
- Analyzing the list of detected software vulnerabilities
View the Software vulnerabilities list and decide which vulnerabilities are to be fixed. To view detailed information about each vulnerability, click the vulnerability name in the list. For each vulnerability in the list, you can also view the statistics on the vulnerability on managed devices.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Viewing information about software vulnerabilities, Viewing statistics of vulnerabilities on managed devices
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Viewing information about software vulnerabilities, Viewing statistics of vulnerabilities on managed devices
- Configuring vulnerabilities fix
When the software vulnerabilities are detected, you can fix the software vulnerabilities on the managed devices by using the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task or the Fix vulnerabilities task.
The Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is used to update and fix vulnerabilities in third-party software, including Microsoft software, installed on the managed devices. This task allows you to install multiple updates and fix multiple vulnerabilities according to certain rules. Note that this task can be created only if you have the license for the Vulnerability and patch management feature. To fix software vulnerabilities the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task uses recommended software updates.
The Fix vulnerabilities task does not require the license option for the Vulnerability and patch management feature. To use this task, you must manually specify user fixes for vulnerabilities in third-party software listed in the task settings. The Fix vulnerabilities task uses recommended fixes for Microsoft software and user fixes for third-party software.
You can start Vulnerability fix wizard that creates one of these tasks automatically, or you can create one of these tasks manually.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Selecting user fixes for vulnerabilities in third-party software, Fixing vulnerabilities in applications
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Selecting user fixes for vulnerabilities in third-party software, Fixing vulnerabilities in third-party software, Creating the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task
- Scheduling the tasks
To be sure that the vulnerabilities list is always up-to-date, schedule the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task to run it automatically from time to time. The recommended average frequency is once a week.
If you have created the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, you can schedule it to run with the same frequency as the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task or less often. When scheduling the Fix vulnerabilities task, note that you have to select fixes for Microsoft software or specify user fixes for third-party software every time before starting the task.
When scheduling the tasks, make sure that a task to fix vulnerability starts after the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task is complete.
- Ignoring software vulnerabilities (optional)
If you want, you can ignore software vulnerabilities to be fixed on all managed devices or only on the selected managed devices.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Ignoring software vulnerabilities
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Ignoring software vulnerabilities
- Running a vulnerability fix task
Start the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task or the Fix vulnerability task. When the task is complete, make sure that it has the Completed successfully status in the task list.
- Create the report on results of fixing software vulnerabilities (optional)
To view detailed statistics on the vulnerabilities fix, generate the Report on vulnerabilities. The report displays information about software vulnerabilities that are not fixed. Thus you can have an idea about finding and fixing vulnerabilities in third-party software, including Microsoft software, in your organization.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Creating and viewing a report
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Generating and viewing a report
- Checking configuration of finding and fixing vulnerabilities in third-party software
Be sure that you have done the following:
- Obtained and reviewed the list of software vulnerabilities on managed devices
- Ignored software vulnerabilities if you wanted
- Configured the task to fix vulnerabilities
- Scheduled the tasks to find and to fix software vulnerabilities so that they start sequentially
- Checked that the task to fix software vulnerabilities was run
Results
If you have created and configured the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, the vulnerabilities are fixed on the managed devices automatically. When the task is run, it correlates the list of available software updates to the rules specified in the task settings. All software updates that meet the criteria in the rules will be downloaded to the Administration Server repository and will be installed to fix software vulnerabilities.
If you have created the Fix vulnerabilities task, only software vulnerabilities in Microsoft software are fixed.
Page top
About finding and fixing software vulnerabilities
Kaspersky Security Center detects and fixes software vulnerabilities on managed devices running Microsoft Windows families operating systems. Vulnerabilities are detected in the operating system and in third-party software, including Microsoft software.
Updates functionality (including providing anti-virus signature updates and codebase updates), as well as KSN functionality may not be available in the software in the U.S.
Finding software vulnerabilities
To find software vulnerabilities, Kaspersky Security Center uses characteristics from the database of known vulnerabilities. This database is created by Kaspersky specialists. It contains information about vulnerabilities, such as vulnerability description, vulnerability detect date, vulnerability severity level. You can find the details of software vulnerabilities on Kaspersky website.
Kaspersky Security Center uses the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task to find software vulnerabilities.
In certain cases vulnerabilities detected in a Microsoft Windows operating system can be fixed using either of the following methods:
- Installing an update for the OS.
- Upgrading the OS to a newer version (for example, from Windows 10 to Windows 11).
In this scenario KSC displays two entries for the same vulnerability.
Fixing software vulnerabilities
To fix software vulnerabilities Kaspersky Security Center uses software updates issued by the software vendors. The software updates metadata is downloaded to the Administration Server repository as a result of the following tasks run:
- Download updates to the Administration Server repository. This task is intended to download updates metadata for Kaspersky and third-party software. This task is created automatically by the Kaspersky Security Center quick start wizard. You can create the Download updates to the Administration Server repository task manually.
- Perform Windows Update synchronization. This task is intended to download updates metadata for Microsoft software.
Software updates to fix vulnerabilities can be represented as full distribution packages or patches. Software updates that fix software vulnerabilities are named fixes. Recommended fixes are those that are recommended for installation by Kaspersky specialists. User fixes are those that are manually specified for installation by users. To install a user fix, you have to create an installation package containing this fix.
If you have the Kaspersky Security Center license with the Vulnerability and patch management feature, to fix software vulnerabilities you can use Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task. This task automatically fixes multiple vulnerabilities installing recommended fixes. For this task, you can manually configure certain rules to fix multiple vulnerabilities.
If you do not have the Kaspersky Security Center license with the Vulnerability and patch management feature, to fix software vulnerabilities, you can use the Fix vulnerabilities task. By means of this task, you can fix vulnerabilities by installing recommended fixes for Microsoft software and user fixes for other third-party software.
For security reasons, any third-party software updates that you install by using the Vulnerability and patch management feature are automatically scanned for malware by Kaspersky technologies. These technologies are used for automatic file checks and include virus scanning, static analysis, dynamic analysis, behavior analysis in the sandbox environment, and machine learning.
Kaspersky experts do not perform manual analysis of third-party software updates that can be installed by using the Vulnerability and patch management feature. In addition, Kaspersky experts do not search for vulnerabilities (known or unknown) or undocumented features in such updates, nor do they perform other types of analysis of the updates other than those specified in the paragraph above.
A user interaction may be required when you update a third-party application or fix a vulnerability in a third-party application on a managed device. For example, the user may be prompted to close the third-party application if it is currently open.
To fix some software vulnerabilities, you must accept the End User License Agreement (EULA) for installing the software if EULA acceptance is requested. If you decline the EULA, the software vulnerability is not fixed.
Fixing third-party software vulnerabilities
After you obtain the software vulnerabilities list, you can fix software vulnerabilities on managed devices that are running Windows. You can fix software vulnerabilities in the operating system and in third-party software, including Microsoft software, by creating and running the Fix vulnerabilities task or the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
A user interaction may be required when you update a third-party application or fix a vulnerability in a third-party application on a managed device. For example, the user may be prompted to close the third-party application if it is currently open.
As an option, you can create a task to fix software vulnerabilities in the following ways:
- By opening the vulnerability list and specifying which vulnerabilities to fix.
As a result, a new task to fix software vulnerabilities is created. As an option, you can add the selected vulnerabilities to an existing task.
- By running the Vulnerability fix wizard.
The Vulnerability fix wizard is only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
The wizard simplifies creation and configuration of a vulnerability fix task and allows you to eliminate the creation of redundant tasks that contain the same updates to install.
Fixing software vulnerabilities by using the vulnerability list
To fix software vulnerabilities:
- Open one of the lists of vulnerabilities:
- To open the general vulnerability list, in the main menu, go to Operations → Patch management → Software vulnerabilities.
- To open the vulnerability list for a managed device, in the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices → <device name> → Advanced → Software vulnerabilities.
- To open the vulnerability list for a specific application, in the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Applications registry → <application name> → Vulnerabilities.
A page with a list of vulnerabilities in the third-party software is displayed.
- Select one or more vulnerabilities in the list, and then click the Fix vulnerability button.
If a recommended software update to fix one of the selected vulnerabilities is absent, an informative message is displayed.
To fix some software vulnerabilities, you must accept the End User License Agreement (EULA) for installing the software, if EULA acceptance is requested. If you decline the EULA, the software vulnerability is not fixed.
- Select one of the following options:
- New task
The New task wizard starts. If you have the Vulnerability and patch management license, the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is preselected. If you do not have the license, the Fix vulnerabilities task is preselected. Follow the steps of the wizard to complete the task creation.
- Fix vulnerability (add rule to specified task)
Select a task to which you want to add the selected vulnerabilities. If you have the Vulnerability and patch management license, select the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task. A new rule to fix the selected vulnerabilities will be automatically added to the selected task. If you do not have the license, select the Fix vulnerabilities task. The selected vulnerabilities will be added to the task properties.
The task properties window opens. Click the Save button to save the changes.
- New task
If you have chosen to create a task, the task is created and displayed in the task list at Assets (Devices) → Tasks. If you have chosen to add the vulnerabilities to an existing task, the vulnerabilities are saved in the task properties.
To fix the third-party software vulnerabilities, start the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task or the Fix vulnerabilities task. If you have created the Fix vulnerabilities task, you must manually specify the software updates to fix the software vulnerabilities listed in the task settings.
Fixing software vulnerabilities by using the Vulnerability fix wizard
The Vulnerability fix wizard is only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
To fix software vulnerabilities by using the Vulnerability fix wizard:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Patch management → Software vulnerabilities.
A page with a list of vulnerabilities in the third-party software installed on managed devices is displayed.
- Select the check box next to the vulnerability that you want to fix.
- Click the Run Vulnerability fix wizard button.
The Vulnerability fix wizard starts. The Select the vulnerability fix task page displays the list of all existing tasks of the following types:
- Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities
- Install Windows Update updates
- Fix vulnerabilities
You cannot modify the last two types of tasks to install new updates. To install new updates, you can only use the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
- If you want the wizard to display only those tasks that fix the vulnerability that you selected, then enable the Show only tasks that fix this vulnerability option.
- Choose what you want to do:
- To start a task, select the check box next to the task name, and then click the Start button.
- To add a new rule to an existing task:
- Select the check box next to the task name, and then click the Add rule button.
- On the page that opens, configure the new rule:
- Rule for fixing vulnerabilities of this severity level
- Rule for fixing vulnerabilities by means of updates of the same type as the update defined as recommended for the selected vulnerability (available only for Microsoft software vulnerabilities)
- Rule for fixing vulnerabilities in applications from the selected vendor (available only for third-party software vulnerabilities)
- Rule for fixing a vulnerability in all versions of the selected application (available only for third-party software vulnerabilities)
- Rule for fixing the selected vulnerability
- Approve updates that fix this vulnerability
- Click the Add button.
- To create a task:
- Click the New task button.
- On the page that opens, configure the new rule:
- Rule for fixing vulnerabilities of this severity level
- Rule for fixing vulnerabilities by means of updates of the same type as the update defined as recommended for the selected vulnerability (available only for Microsoft software vulnerabilities)
- Rule for fixing vulnerabilities in applications from the selected vendor (available only for third-party software vulnerabilities)
- Rule for fixing a vulnerability in all versions of the selected application (available only for third-party software vulnerabilities)
- Rule for fixing the selected vulnerability
- Approve updates that fix this vulnerability
- Click the Add button.
If you have chosen to start a task, you can close the wizard. The task will complete in background mode. No further actions are required.
If you have chosen to add a rule to an existing task, the task properties window opens. The new rule is already added to the task properties. You can view or modify the rule or other task settings. Click the Save button to save the changes.
If you have chosen to create a task, you continue to create the task in the New task wizard. The new rule that you added in the Vulnerability fix wizard is displayed in the New task wizard. When you complete the wizard, the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is added to the task list.
Creating the Fix vulnerabilities task
The Fix vulnerabilities task allows you fix software vulnerabilities on managed devices that are running Windows. You can fix software vulnerabilities in third-party software, including Microsoft software.
If you do not have the Vulnerability and patch management license, you cannot create new tasks of the Fix vulnerabilities type. To fix new vulnerabilities, you can add them to an existing Fix vulnerabilities task. We recommend that you use the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task instead of the Fix vulnerabilities task. The Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task enables you to install multiple updates and fix multiple vulnerabilities automatically, according to the rules that you define.
A user interaction may be required when you update a third-party application or fix a vulnerability in a third-party application on a managed device. For example, the user may be prompted to close the third-party application if it is currently open.
To create the Fix vulnerabilities task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- For the Kaspersky Security Center application, select the Fix vulnerabilities task type.
- Specify the name for the task that you are creating.
A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- Select devices to which the task will be assigned.
- Click the Add button.
The list of vulnerabilities opens.
- Select the vulnerabilities that you want to fix, and then click OK.
Microsoft software vulnerabilities usually have recommended fixes. No additional actions are required for them. For vulnerabilities in software from other vendors, you first need to specify a user fix for each vulnerability that you want to fix. After that, you will be able to add those vulnerabilities into the Fix vulnerabilities task.
- Specify the operating system restart settings:
- Specify the account settings:
- If you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option on the Finish task creation page. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Finish button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the name of the created task to open the task properties window.
- In the task properties window, specify the general task settings according to your needs.
- Click the Save button.
The task is created and configured.
Creating the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task
The Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
The Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task is used to update and fix vulnerabilities in third-party software, including Microsoft software, installed on the managed devices. This task allows you to install multiple updates and fix multiple vulnerabilities according to certain rules.
To install updates or fix vulnerabilities by using the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, you can do one of the following:
- Run the Update installation wizard or the Vulnerability fix wizard.
- Create an Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
- Add a rule for update installation to an existing Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
To create the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- For the Kaspersky Security Center application, select the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task type.
If the task is not displayed, check whether your account has the Read, Modify, and Execute rights for the System management: Vulnerability and patch management functional area. You cannot create and configure the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task without these access rights.
- Specify the name for the task that you are creating. A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- Select devices to which the task will be assigned.
- Specify the rules for update installation, and then specify the following settings:
- Start installation at device restart or shutdown
- Install the required general system components
- Allow installation of new application versions during updates
- Download updates to the device without installing them
- Download updates to
- Enable advanced diagnostics
- Maximum size, in MB, of advanced diagnostics files
- Specify the operating system restart settings:
- If you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option on the Finish task creation page. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Finish button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the name of the created task to open the task properties window.
- In the task properties window, specify the general task settings according to your needs.
- Click the Save button.
The task is created and configured.
If the task results contain a warning of the 0x80240033 "Windows Update Agent error 80240033 ("License terms could not be downloaded.")" error, you can resolve this issue through the Windows Registry.
Adding rules for update installation
This feature is only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
When installing software updates or fixing software vulnerabilities by using the Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task, you must specify rules for the update installation. These rules determine the updates to install and the vulnerabilities to fix.
The exact settings depend on whether you add a rule for all updates, for Windows Update updates, or for updates of third-party applications (applications made by software vendors other than Kaspersky and Microsoft). When adding a rule for Windows Update updates or updates of third-party applications, you can select specific applications and application versions for which you want to install updates. When adding a rule for all updates, you can select specific updates that you want to install and vulnerabilities that you want to fix by means of installing updates.
You can add a rule for update installation in the following ways:
- By adding a rule while creating a new Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
- By adding a rule on the Application Settings tab in the properties window of an existing Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task.
- Through the Update installation wizard or the Vulnerability fix wizard.
To add a new rule for all updates:
- Click the Add button.
The Rule creation wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Rule type page, select Rule for all updates.
- On the General criteria page, use the drop-down lists to specify the following settings:
- On the Updates page, select the updates to be installed:
- On the Vulnerabilities page, select vulnerabilities that will be fixed by installing the selected updates:
- On the Name page, specify the name for the rule that you are adding. You can later change this name in the Settings section of the properties window of the created task.
After the Rule creation wizard completes its operation, the new rule is added and displayed in the rule list in the New task wizard or in the task properties.
To add a new rule for Windows Update updates:
- Click the Add button.
The Rule creation wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Rule type page, select Rule for Windows Update.
- On the General criteria page, specify the following settings:
- On the Applications page, select the applications and application versions for which you want to install updates. By default, all applications are selected.
- On the Categories of updates page, select the categories of updates to be installed. These categories are the same as in Microsoft Update Catalog. By default, all categories are selected.
- On the Name page, specify the name for the rule that you are adding. You can later change this name in the Settings section of the properties window of the created task.
After the Rule creation wizard completes its operation, the new rule is added and displayed in the rule list in the New task wizard or in the task properties.
To add a new rule for updates of third-party applications:
- Click the Add button.
The Rule creation wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Rule type page, select Rule for third-party updates.
- On the General criteria page, specify the following settings:
- On the Applications page, select the applications and application versions for which you want to install updates. By default, all applications are selected.
- On the Name page, specify the name for the rule that you are adding. You can later change this name in the Settings section of the properties window of the created task.
After the Rule creation wizard completes its operation, the new rule is added and displayed in the rule list in the New task wizard or in the task properties.
Selecting user fixes for vulnerabilities in third-party software
To use the Fix vulnerabilities task, you must manually specify the software updates to fix the vulnerabilities in third-party software listed in the task settings. The Fix vulnerabilities task uses recommended fixes for Microsoft software and user fixes for other third-party software. User fixes are software updates to fix vulnerabilities that the administrator manually specifies for installation.
To select user fixes for vulnerabilities in third-party software:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Patch management → Software vulnerabilities.
The page displays the list of software vulnerabilities detected on client devices.
- In the list of software vulnerabilities, click the link with the name of the software vulnerability for which you want to specify a user fix.
The properties window of the vulnerability opens.
- In the left pane, select the User fixes and other fixes section.
The list of user fixes for the selected software vulnerability is displayed.
- Click Add.
The list of available installation packages is displayed. The list of displayed installation packages corresponds to the Operations → Repositories → Installation packages list. If you have not created an installation package containing a user fix for selected vulnerability, you can create the package now by starting the New package wizard.
- Select an installation package (or packages) containing a user fix (or user fixes) for the vulnerability in third-party software.
- Click Save.
The installation packages containing user fixes for the software vulnerability are specified. When the Fix vulnerabilities task is started, the installation package will be installed, and the software vulnerability will be fixed.
Viewing information about software vulnerabilities detected on all managed devices
After you have scanned software on managed devices for vulnerabilities, you can view the list of software vulnerabilities detected on all managed devices. If you run the task for the hierarchy of Administration Servers, you can view the list of managed devices with detected vulnerabilities only for the selected Administration Server.
To view the list of software vulnerabilities detected on all managed devices,
In the main menu, go to Operations → Patch management → Software vulnerabilities.
The page displays the list of software vulnerabilities detected on client devices.
You can also generate and view a Report on vulnerabilities.
You can specify a filter to view the list of software vulnerabilities. Click the Filter icon (![]() ) in the upper right corner of the software vulnerabilities list to manage the filter. You can also select one of preset filters from the Preset filters drop-down list above the software vulnerabilities list.
) in the upper right corner of the software vulnerabilities list to manage the filter. You can also select one of preset filters from the Preset filters drop-down list above the software vulnerabilities list.
You can obtain detailed information about any vulnerability from the list.
To obtain information about a software vulnerability:
In the list of software vulnerabilities, click the link with the name of the vulnerability.
The properties window of the software vulnerability opens.
Viewing information about software vulnerabilities detected on the selected managed device
You can view information about software vulnerabilities detected on the selected managed device running Windows.
To view the list of software vulnerabilities detected on the selected managed device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
The list of managed devices is displayed.
- In the list of managed devices, click the link with the name of the device for which you want to view detected software vulnerabilities.
The properties window of the selected device is displayed.
- In the properties window of the selected device, select the Advanced tab.
- In the left pane, select the Software vulnerabilities section.
The list of software vulnerabilities detected on the selected managed device is displayed.
To view the properties of the selected software vulnerability,
Click the link with the name of the software vulnerability in the list of software vulnerabilities.
The properties window of the selected software vulnerability is displayed.
Viewing statistics of vulnerabilities on managed devices
You can view statistics for each software vulnerability on managed devices. Statistics are represented as a diagram. The diagram displays the number of devices with the following statuses:
- Ignored on: <number of devices>. This status is assigned if, in the vulnerability properties, you have manually set the option to ignore the vulnerability.
- Fixed on: <number of devices>. This status is assigned if the task to fix the vulnerability has successfully completed.
- Fix scheduled on: <number of devices>. This status is assigned if you have created the task to fix the vulnerability, but the task is not performed yet.
- Patch applied on: <number of devices>. This status is assigned if you have manually selected a software update to fix the vulnerability, but this software update has not fixed the vulnerability.
- Fix required on: <number of devices>. This status is assigned if the vulnerability was fixed only on some managed devices, and the vulnerability is required to be fixed on more managed devices.
To view the statistics of a vulnerability on managed devices:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Patch management → Software vulnerabilities.
The page displays a list of vulnerabilities in applications detected on managed devices.
- Select the check box next to the required vulnerability.
- Click the Statistics of vulnerability on devices button.
A diagram of the vulnerability statuses is displayed. Clicking a status opens a list of devices on which the vulnerability has the selected status.
Exporting the list of software vulnerabilities to a file
You can export the displayed list of vulnerabilities to the CSV or TXT files. You can use these files, for example, to send them to your information security manager or to store them for purposes of statistics.
To export the list of software vulnerabilities detected on all managed devices to a text file:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Patch management → Software vulnerabilities.
The page displays a list of vulnerabilities in applications detected on managed devices.
- Click the Export to TXT or Export to CSV button, depending on the format you prefer for export.
The file containing the list of software vulnerabilities is downloaded to the device that you use at the moment.
To export the list of software vulnerabilities detected on selected managed device to a text file:
- Open the list of software vulnerabilities detected on selected managed device.
- Select the software vulnerabilities you want to export.
Skip this step if you want to export a complete list of software vulnerabilities detected on the managed device.
If you want to export complete list of software vulnerabilities detected on the managed device, only vulnerabilities displaying on the current page will be exported.
- Click the Export to TXT or Export to CSV button, depending on the format you prefer for export.
The file containing the list of software vulnerabilities detected on the selected managed device is downloaded to the device you are using at the moment.
Ignoring software vulnerabilities
You can ignore software vulnerabilities to be fixed. The reasons to ignore software vulnerabilities might be, for example, the following:
- You do not consider the software vulnerability to be critical to your organization.
- You understand that the software vulnerability fix can damage data related to the software that required the vulnerability fix.
- You are sure that the software vulnerability is not dangerous for your organization's network because you use other measures to protect your managed devices.
You can ignore a software vulnerability on all managed devices or only on selected managed devices.
To ignore a software vulnerability on all managed devices:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Patch management → Software vulnerabilities.
The page displays the list of software vulnerabilities detected on managed devices.
- In the list of software vulnerabilities, click the link with the name of the software vulnerability you want to ignore.
The software vulnerability properties window opens.
- On the General tab, enable the Ignore vulnerability option.
- Click the Save button.
The software vulnerability properties window closes.
The software vulnerability is ignored on all managed devices.
To ignore a software vulnerability on the selected managed device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
The list of managed devices is displayed.
- In the list of managed devices, click the link with the name of the device on which you want to ignore a software vulnerability.
The device properties window is opened.
- In the device properties window, select the Advanced tab.
- In the left pane, select the Software vulnerabilities section.
The list of software vulnerabilities detected on the device is displayed.
- In the list of software vulnerabilities, select the vulnerability you want to ignore on the selected device.
The software vulnerability properties window opens.
- In the software vulnerability properties window, on the General tab, enable the Ignore vulnerability option.
- Click the Save button.
The software vulnerability properties window closes.
- Close the device properties window.
The software vulnerability is ignored on the selected device.
The ignored software vulnerability will not be fixed after the completion of the Fix vulnerabilities task or Install required updates and fix vulnerabilities task. You can exclude ignored software vulnerabilities from the list of vulnerabilities by using a filter.
Managing applications run on client devices
This section describes the features of Kaspersky Security Center related to the management of applications run on client devices.
Using Application Control to manage executable files
You can use the Application Control component to allow or block startup of executable files on user devices. The Application Control component supports Windows-based and Linux-based operating systems.
For Linux-based operating systems, the Application Control component is available starting from Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.2 for Linux.Also, the component is available for Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows 3.0 or later.
Prerequisites
- Kaspersky Security Center is deployed in your organization.
- The policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux is created and is active.
- The policy of Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows or Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Linux is created and is active.
Stages
The Application Control usage scenario proceeds in stages:
- Forming and viewing the list of executable files on client devices
This stage helps you find out what executable files are found on managed devices. View the list of executable files and compare it with the lists of allowed and prohibited executable files. The restrictions on executable files usage can be related to the information security polices in your organization.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Inventory of executable files
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Obtaining and viewing a list of executable files stored on client devices
- Creating categories for executable files used in your organization
Analyze the lists of executable files stored on managed devices. Based on the analysis, create categories for executable files. It is recommended to create a "Work applications" category that covers the standard set of executable files that are used at your organization. If different security groups use their own sets of executable files in their work, a separate category can be created for each security group.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Creating an application category with content added manually, Creating an application category that includes executable files from selected devices, Creating application category that includes executable files from a specific folder.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Creating application category with content added manually, Creating application category that includes executable files from selected devices, Creating application category that includes executable files from a specific folder.
- Configuring Application Control in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy
Configure the Application Control component in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy using the categories you have created on the previous stage.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Configuring application startup management on client devices
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Configuring Application Control in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy
- Configuring Application Control in the Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security application policy
Configure the Application Control component in the Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows policy by using the categories you have created. For more information about Application Control component, refer to Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows Help or Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Linux Help.
If you use a large number of rules, an error may occur when loading the policy. You can increase the maximum request size in bytes by using the following commands:
- For the JSON request:
klscflag -fset -pv ".core/.independent" -s KLLIM -n LP_KLOAPI_MaxSizeOfJsonRequestInBytes -v <max_request_size> -t d - For the HTTP request:
klscflag -fset -pv ".core/.independent" -s KLLIM -n LP_KLOAPI_MaxSizeOfHttpRequestInBytes -v <max_request_size> -t dWhere
<max_request_size>is a maximum request size in bytes (for example,200000000).
- For the JSON request:
- Turning on Application Control component in test mode
To ensure that Application Control rules do not block executable files required for user's work, it is recommended to enable testing of Application Control rules and analyze their operation after creating new rules. When testing is enabled, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows or Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security will not block executable files whose startup is forbidden by Application Control rules, but will instead send notifications about their startup to the Administration Server.
When testing Application Control rules, it is recommended to perform the following actions:
- Determine the testing period. Testing period can vary from several days to two months.
- Examine the events resulting from testing the operation of Application Control.
How-to instructions for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Configuring Application Control component in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy. Follow this instruction and enable the Test Mode option in configuration process.
- Changing the categories settings of Application Control component
If necessary, make changes to the Application Control settings. Based on the test results, you can add executable files related to events of the Application Control component to a category with content added manually.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Adding event-related executable files to the application category
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Adding event-related executable files to the application category
- Applying the rules of Application Control in operation mode
After Application Control rules are tested and configuration of categories is complete, you can apply the rules of Application Control in operation mode.
How-to instructions for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Configuring Application Control component in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy. Follow this instruction and disable the Test Mode option in configuration process.
- Verifying Application Control configuration
Be sure that you have done the following:
- Created categories for executable files.
- Configured Application Control using the categories.
- Applied the rules of Application Control in operation mode.
Results
When the scenario is complete, startup of executable files on managed devices is controlled. The users can run only those executable files that are allowed in your organization and cannot run executable files that are prohibited in your organization.
For detailed information about Application Control, refer to the following Help topics:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux Online Help
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows Help
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Linux Help
Application Control modes and categories
The Application Control component monitors users' attempts to start executable files. You can use Application Control rules to control the startup of executable files.
Application Control component is available for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.2 for Linux and later versions, and for Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent. All the instructions in this section describe configuration of Application Control for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
Startup of executable files whose settings do not match any of the Application Control rules is regulated by the selected operating mode of the component:
- Denylist. The mode is used if you want to allow the startup of all executable files except those specified in block rules. This mode is selected by default.
- Allowlist. The mode is used if you want to block the startup of all executable files except those specified in allow rules.
The Application Control rules are implemented through categories for executable files. In Kaspersky Security Center there are three types of categories:
- Category with content added manually. You define conditions, for example, file metadata, file hashcode, file certificate, KL category, file path, to include executable files in the category.
- Category that includes executable files from selected devices. You specify a device whose executable files are automatically included in the category.
- Category that includes executable files from selected folder. You specify a folder from which executable files are automatically included in the category.
For detailed information about Application Control, refer to the following Help topics:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux Online Help
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows Help
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Linux Help
Obtaining and viewing a list of executable files stored on client devices
You can obtain the list of executable files stored on client devices in one of the following ways:
- Enabling notifications about applications startup in Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
- Creating an inventory task.
Enabling notifications about applications startup in Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy
To enable notifications about applications startup:
- Open the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings, and then go to General settings → Reports and Storage.
- In the Data transfer to Administration Server settings group, select the About started applications check box, and save the changes.
When a user attempts to start executable files, information about these files is added to the list of executable files on a client device. Kaspersky Endpoint Security sends this information to Network Agent, and then Network Agent sends it to Administration Server.
Creating an inventory task
The feature of inventorying executable files is available for the following applications:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux version 11.2 and later
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization 4.0 Light Agent and later versions
You can reduce load on the database while obtaining information about the installed applications. To save database space, run an inventory task on reference devices on which a standard set of software is installed. The preferable number of devices is 1-3.
We strongly do not recommend running the inventory task when using the following databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server Express Edition, MariaDB (all editions).
To create an inventory task for executable files on client devices:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
The list of tasks is displayed.
- Click the Add button.
The New task wizard starts. Follow the steps of the wizard.
- On the New task settings page, in the Application drop-down list, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux, depending on the operating system type of the client devices.
- In the Task type drop-down list, select Inventory.
- On the Finish task creation page, click the Finish button.
After the New task wizard has finished, the Inventory task is created and configured. If you want, you can change the settings for the created task. The newly created task is displayed in the list of tasks.
For a detailed description of the inventory task, refer to the following Helps:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux Help
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent
After the Inventory task is performed, the list of executable files stored on managed devices is formed, and you can view the list.
During inventory, executable files in the following formats can be detected (depending on the option that you select in the inventory task properties): MZ, COM, PE, NE, SYS, CMD, BAT, PS1, JS, VBS, REG, MSI, CPL, DLL, JAR, and HTML.
Viewing the list of executable files stored on managed devices
To view the list of executable files stored on client devices:
In the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Executable files.
The page displays the list of executable files stored on client devices.
If necessary, you can send the executable file of the managed device to the device where your Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is open.
To send an executable file:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Executable files.
- Click the link of the executable file that you want to send.
- In the window that opens, go to the Devices section, and then select the check box of the managed device from which you want to send the executable file.
Before you send the executable file, make sure that the managed device has a direct connection to the Administration Server, by selecting the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server check box.
- Click the Send button.
The selected executable file is downloaded for further sending to the device where your Kaspersky Security Center Web Console is open.
Creating application category with content added manually
You can specify a set of criteria as a template of executable files for which you want to allow or block a start in your organization. On the basis of executable files corresponding to the criteria, you can create an application category and use it in the Application Control component configuration.
To create an application category with content added manually:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Application categories.
The page with a list of application categories is displayed.
- Click the Add button.
The New category wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Select category creation method step, select the Category with content added manually. Data of executable files is manually added to the category option.
- On the Conditions step, click the Add button to add a condition criterion to include files in the creating category.
- On the Condition criteria step, select a rule type for the creation of category from the list:
- From KL category
- Select certificate from repository
- Specify path to application (masks supported)
- Removable drive
- Hash, metadata, or certificate:
The selected criterion is added to the list of conditions.
You can add as many criteria for the creating application category as you need.
- On the Exclusions step, click the Add button to add an exclusive condition criterion to exclude files from the category that is being created.
- On the Condition criteria step, select a rule type from the list, in the same way that you selected a rule type for category creation.
When the wizard finishes, the application category is created. It is displayed in the list of application categories. You can use the created application category when you configure Application Control.
For detailed information about Application Control, refer to the following Help topics:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux Online Help
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows Help
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Linux Help
Creating an application category that includes executable files from selected devices
You can use executable files from selected devices as a template of executable files that you want to allow or block. Based on executable files from selected devices, you can create a category and use it in the Application Control component configuration.
To retrieve the list of executable files from devices:
- Ensure that the policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux is created and is active. Enable the Application Control component in the policy.
- Obtain a list of executable files stored on client devices.
To create a category that includes executable files from selected devices:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Application categories.
The page with a list of categories is displayed.
- Click the Add button.
The New category wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Select category creation method step, specify the category name and select the Category that includes executable files from selected devices. These executable files are processed automatically and their metrics are added to the category option.
- Click Add.
- In the window that opens, select a device or devices whose executable files will be used to create the category.
- Specify the following settings:
When the wizard finishes, the category for executable files is created. It is displayed in the list of categories. You can use the created category when you configure Application Control.
Creating an application category that includes executable files from selected folder
You can use executable files from a selected folder as a standard of executable files that you want to allow or block in your organization. On the basis of executable files from the selected folder, you can create an application category and use it in the Application Control component configuration.
To create a category that includes executable files from the selected folder:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Application categories.
The page with a list of categories is displayed.
- Click the Add button.
The New category wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Select category creation method step, specify the category name and select the Category that includes executable files from a specific folder. Executable files of applications copied to the specified folder are automatically processed and their metrics are added to the category option.
- Specify the folder whose executable files will be used to create the category.
- Define the following settings:
- Include dynamic-link libraries (DLL) in this category
- Include script data in this category
- Hash value computing algorithm: Calculate SHA256 for files in this category (supported by Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 2 for Windows and later versions) / Calculate MD5 for files in this category (supported by versions earlier than Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 Service Pack 2 for Windows)
- Force folder scan for changes
When the wizard finishes, the category of executable files is created. It is displayed in the list of categories. You can use the category at Application Control configuration.
For detailed information about Application Control, refer to the following Help topics:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux Online Help
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows Help
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Linux Help
Viewing the list of application categories
You can view the list of configured categories of executable files and the settings of each category.
To view the list of application categories,
In the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Application categories.
The page with a list of categories is displayed.
To view properties of an application category,
Click the name of the category.
The properties window of the category is displayed. The properties are grouped on several tabs.
Adding event-related executable files to the application category
After you configure Application Control in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policies, the following events will be displayed in the list of events:
- Application startup prohibited (Critical event). This event is displayed if you have configured Application Control to apply rules.
- Application startup prohibited in test mode (Info event). This event is displayed if you have configured Application Control to test rules.
- Message to administrator about application startup prohibition (Warning event). This event is displayed if you have configured Application Control to apply rules and a user has requested access to the application that is blocked at startup.
It is recommended to create event selections to view events related to Application Control operation.
You can add executable files related to Application Control events to an existing application category or to a new application category. You can add executable files only to an application category with content added manually.
To add executable files related to Application Control events to an application category:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Event selections.
The list of event selections is displayed.
- Select the event selection to view events related to Application Control and start this event selection.
If you have not created event selection related to Application Control, you can select and start a predefined selection, for example, Recent events.
The list of events is displayed.
- Select the events whose associated executable files you want to add to the application category, and then click the Assign to category button.
The New category wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the wizard page, specify the relevant settings:
- In the Action on executable file related to the event section, select one of the following options:
- In the Rule type section, select one of the following options:
- Rules for adding to inclusions
- Rules for adding to exclusions
- In the Parameter used as a condition section, select one of the following options:
- Click OK.
When the wizard finishes, executable files related to the Application Control events are added to the existing application category or to a new application category. You can view settings of the application category that you have modified or created.
For detailed information about Application Control, refer to the following Help topics:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux Online Help
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows Help
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Linux Help
Configuring Application Control in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy
After you create Application Control categories, you can use them for configuring Application Control in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policies.
To configure Application Control in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
A page with a list of policies is displayed.
- Click the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy.
The policy settings window opens.
- Go to Application settings → Security Controls → Application Control.
The Application Control window with the Application Control settings is displayed.
- The Application Control option is enabled by default. Ensure that the Application Control DISABLED toggle button is switched to the disabled position.
- In the Application Control Settings block settings, enable the operation mode to apply the Application Control rules and allow Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows to block startup of applications.
If you want to test the Application Control rules, in the Application Control Settings section, enable test mode. In test mode, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows does not block startup of applications, but logs information about triggered rules in the report. Click the View report link to view this information.
- Enable the Control DLL modules load option if you want Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows to monitor the loading of DLL modules when applications are started by users.
Information about the module and the application that loaded the module will be saved to a report.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows monitors only the DLL modules and drivers loaded after the Control DLL modules load option is selected. Restart the device after selecting the Control DLL modules load option if you want Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows to monitor all DLL modules and drivers, including those loaded before Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows is started.
- (Optional) In the Message templates block, change the template of the message that is displayed when an application is blocked from starting and the template of the email message that is sent to you.
- In the Application Control Mode block settings, select the Denylist or Allowlist mode.
By default, the Denylist mode is selected.
- Click the Rules Lists Settings link.
The Denylists and allowlists window opens to let you add an application category. By default, the Denylist tab is selected if the Denylist mode is selected, and the Allowlist tab is selected if the Allowlist mode is selected.
- In the Denylists and allowlists window, click the Add button.
The Application Control rule window opens.
- Click the Please choose a category link.
The Application Category window opens.
- Add the application category (or categories) that you created earlier.
You can edit the settings of a created category by clicking the Edit button.
You can create a new category by clicking the Add button.
You can delete a category from the list by clicking the Delete button.
- After the list of application categories is complete, click the OK button.
The Application Category window closes.
- In the Application Control rule window, in the Subjects and their rights section, create a list of users and groups of users to apply the Application Control rule.
- Click the OK button to save the settings and to close the Application Control rule window.
- Click the OK button to save the settings and to close the Denylists and allowlists window.
- Click the OK button to save the settings and to close the Application Control window.
- Close the window with the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy settings.
Application Control is configured. After the policy is propagated to the client devices, the startup of executable files is managed.
For detailed information about Application Control, refer to the following Help topics:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux Online Help
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows Help
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Linux Help
Obtaining and viewing a list of applications installed on client devices
Kaspersky Security Center inventories all software installed on managed client devices running Linux and Windows.
Network Agent compiles a list of applications installed on a device, and then transmits this list to Administration Server. It takes about 10-15 minutes for the Network Agent to update the application list.
For Windows-based client devices, Network Agent receives most of the information about installed applications from the Windows registry. For Linux-based client devices, package managers provide information about installed applications to Network Agent.
If an application from the Applications registry section was detected on a Linux device, the application properties do not contain information about related executable files.
To view the list of applications installed on managed devices:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Applications registry.
The page displays a table with the applications that are installed on managed devices. Select the application to view its properties, for example, vendor name, version number, list of executable files, list of devices on which the application is installed, list of available software updates, and list of detected software vulnerabilities.
- You can group and filter the data of the table with installed applications as follows:
- Click the settings icon (
 ) in the upper-right corner of the table.
) in the upper-right corner of the table.In the invoked Columns settings menu, select the columns to be displayed in the table. To view the operating system type of the client devices on which the application is installed, select the Operating system type column.
- Click the filter icon (
 ) in the upper-right corner of the table, and then specify and apply the filter criterion in the invoked menu.
) in the upper-right corner of the table, and then specify and apply the filter criterion in the invoked menu. The filtered table of installed applications is displayed.
- Click the settings icon (
To view the list of applications installed on a specific managed device,
In the main menu, go to Devices → Managed devices → <device name> → Advanced → Applications registry. In this menu, you can export the list of applications to a CSV file or TXT file.
For detailed information about Application Control, refer to the following Help topics:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux Online Help
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Windows Help
- Kaspersky Embedded Systems Security for Linux Help
Creating an installation package of a third-party application from the Kaspersky database
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console allows you to perform remote installation of third-party applications by using installation packages. Such third-party applications are included in a dedicated Kaspersky database. This database is created automatically when you run the Download updates to the repository of the Administration Server task for the first time.
To create an installation package of a third-party application from the Kaspersky database:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Installation packages.
- Click the Add button.
- On the New package wizard page that opens, select the Select an application from the Kaspersky database to create an installation package option, and then click Next.
- In the list of applications that opens, select the relevant application, and then click Next.
- Select the relevant localization language in the drop-down list, and then click Next.
This step is only displayed if the application offers multiple language options.
- If you are prompted to accept a License Agreement for the installation, on the End User License Agreement page that opens, click the link to read the License Agreement on the vendor's website, and then select the I confirm that I have fully read, understand, and accept the terms and conditions of this End User License Agreement check box.
- On the Name of the new installation package page that opens, in the Package name field, enter the name for the installation package, and then click Next.
Wait until the newly created installation package is uploaded to Administration Server. When the New package wizard displays the message informing you the package creation process was successful, click Finish.
The newly created installation package appears on the list of installation packages. You can select this package when creating or reconfiguring the Install application remotely task.
Viewing and modifying the settings of an installation package of a third-party application from the Kaspersky database
If you have previously created any installation packages of third-party applications listed in the Kaspersky database, you can subsequently view and modify the settings of these packages.
Modifying the settings of an installation package of a third-party application from the Kaspersky database is only available under the Vulnerability and patch management license.
To view and modify the settings of an installation package of a third-party application from the Kaspersky database:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Installation packages.
- In the list of installation packages that opens, click the name of the relevant package.
- On the properties page that opens, modify the settings, if necessary.
- Click the Save button.
The settings that you modified are saved.
Settings of an installation package of a third-party application from the Kaspersky database
The settings of an installation package of a third-party application are grouped on the following tabs:
Only a part of the settings listed below are displayed by default so you can add the corresponding columns by clicking the Filter button and selecting relevant column names from the list.
- General tab:
- Entry field that contains the name of the installation package that can be edited manually
- Application
- Version
- Size
- Created
- Path
- Installation procedure tab:
- Install the required general system components
- Table that displays the update properties and containing the following columns:
- Name
- Description
- Source
- Type
- Category
- Importance level according to MSRC
- Importance level
- Patch importance level
- Article
- Bulletin
- Not assigned for installation (new version)
- To be installed
- Installing
- Installed
- Failed
- Restart is required
- Registered
- Installed in interactive mode
- Revoked
- Update approval status
- Revision
- Update ID
- Application version
- Superseded
- Superseding
- You must accept the terms of the License Agreement
- Description URL
- Application family
- Application
- Localization language
- Not assigned for installation (new version)
- Requires prerequisites installation
- Download mode
- Is a patch
- Not installed
- Settings tab that displays the installation package settings—with their names, descriptions, and values—used as command-line parameters during installation. If the package provides no such settings, the corresponding message is displayed. You can modify the values of these settings.
- Revision history tab that displays the installation package revisions and containing the following columns:
- Revision—The revision number of the installation packages.
- Time—Date and time the installation package settings were modified.
- User—Name of the user who modified the installation package settings.
- Action—Action performed on the installation package within the revision.
- Description—Description of the revision related to the change made to the installation package settings.
By default, the revision description is blank. To add a description to a revision, select the relevant revision, and then click the Edit description button. In the opened window, enter some text for the revision description.
Application tags
Kaspersky Security Center enables you to tag the applications from applications registry. A tag is the label of an application that can be used for grouping or finding applications. A tag assigned to applications can serve as a condition in device selections.
For example, you can create the [Browsers] tag and assign it to all browsers such as Microsoft Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox.
Creating an application tag
To create an application tag:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Application tags.
- Click Add.
A new tag window opens.
- Enter the tag name.
- Click OK to save the changes.
The new tag appears in the list of application tags.
Renaming an application tag
To rename an application tag:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Application tags.
- Select the check box next to the tag that you want to rename, and then click Edit.
A tag properties window opens.
- Change the tag name.
- Click OK to save the changes.
The updated tag appears in the list of application tags.
Assigning tags to an application
To assign one or several tags to an application:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Applications registry.
- Click the name of the application to which you want to assign tags.
- Select the Tags tab.
The tab displays all application tags that exist on the Administration Server. For tags assigned to the selected application, the check box in the Tag assigned column is selected.
- For tags that you want to assign, select check boxes in the Tag assigned column.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The tags are assigned to the application.
Removing assigned tags from an application
To remove one or several tags from an application:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Applications registry.
- Click the name of the application from which you want to remove tags.
- Select the Tags tab.
The tab displays all application tags that exist on the Administration Server. For tags assigned to the selected application, the check box in the Tag assigned column is selected.
- For tags that you want to remove, clear check boxes in the Tag assigned column.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The tags are removed from the application.
The removed application tags are not deleted. If you want, you can delete them manually.
Deleting an application tag
To delete an application tag:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Third-party applications → Application tags.
- In the list, select the application tag that you want to delete.
- Click the Delete button.
- In the window that opens, click OK.
The application tag is deleted. The deleted tag is automatically removed from all of the applications to which it was assigned.
Monitoring and reporting
This section describes the monitoring and reporting capabilities of Kaspersky Security Center. These capabilities give you an overview of your infrastructure, protection statuses, and statistics.
After Kaspersky Security Center deployment or during the operation, you can configure the monitoring and reporting features to best suit your needs.
Scenario: Monitoring and reporting
This section provides a scenario for configuring the monitoring and reporting feature in Kaspersky Security Center.
Prerequisites
After you deploy Kaspersky Security Center in an organization's network you can start to monitor it and generate reports on its functioning.
Monitoring and reporting in an organization's network proceeds in stages:
- Configuring the switching of device statuses
Get acquainted with the settings for device statuses depending on specific conditions. By changing these settings, you can change the number of events with Critical or Warning importance levels. When configuring the switching of device statuses, be sure of the following:
- New settings do not conflict with the information security policies of your organization.
- You are able to react to important security events in your organization's network in a timely manner.
- Configuring notifications about events on client devices
How-to instructions:
- Changing the response of your security network to the Virus outbreak event
You can change the specific thresholds in the Administration Server properties. You can also create a stricter policy that will be activated or create a task that will be run at the occurrence of this event.
- Performing recommended actions for Critical and Warning notifications
How-to instructions:
- Reviewing the security status of your organization's network
How-to instructions:
- Locating client devices that are not protected
How-to instructions:
- Checking protection of client devices
How-to instructions:
- Evaluating and limiting the event load on the database
Information about events that occur during operation of managed applications is transferred from a client device and registered in the Administration Server database. To reduce the load on the Administration Server, evaluate and limit the maximum number of events that can be stored in the database.
How-to instructions:
- Reviewing license information
How-to instructions:
Results
Upon completion of the scenario, you are informed about protection of your organization's network and, thus, can plan actions for further protection.
About types of monitoring and reporting
Information on security events in an organization's network is stored in the Administration Server database. Based on the events, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console provides the following types of monitoring and reporting in your organization's network:
- Dashboard
- Reports
- Event selections
- Notifications
Dashboard
The dashboard allows you to monitor security trends on your organization's network by providing you with a graphical display of information.
Reports
The Reports feature allows you to get detailed numerical information about the security of your organization's network, save this information to a file, send it by email, and print it.
Event selections
Event selections provide an onscreen view of named sets of events that are selected from the Administration Server database. These sets of events are grouped according to the following categories:
- By importance level—Critical events, Functional failures, Warnings, and Info events
- By time—Recent events
- By type—User requests and Audit events
You can create and view user-defined event selections based on the settings available, in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface, for configuration.
Notifications
Notifications alert you about events and help you to speed up your responses to these events by performing recommended actions or actions you consider as appropriate.
Page top
Dashboard and widgets
This section contains information about the dashboard and the widgets that the dashboard provides. The section includes instructions on how to manage widgets and configure widget settings.
Using the dashboard
The dashboard allows you to monitor security trends on your organization's network by providing you with a graphical display of information.
The dashboard is available in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, in the Monitoring & reporting section, by clicking Dashboard.
The dashboard provides widgets that can be customized. You can choose a large number of different widgets, presented as pie charts or donut charts, tables, graphs, bar charts, and lists. The information displayed in widgets is automatically updated, the update period is one to two minutes. The interval between updates varies for different widgets. You can refresh data on a widget manually at any time by means of the settings menu.
By default, widgets include information about all events stored in the database of Administration Server.
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console has a default set of widgets for the following categories:
- Protection status
- Deployment
- Updating
- Threat statistics
- Other
Some widgets have text information with links. You can view detailed information by clicking a link.
When configuring the dashboard, you can add widgets that you need, hide widgets that you do not need, change the size or appearance of widgets, move widgets, and change their settings.
Adding widgets to the dashboard
To add widgets to the dashboard:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Dashboard.
- Click the Add or restore web widget button.
- In the list of available widgets, select the widgets that you want to add to the dashboard.
Widgets are grouped by category. To view the list of widgets included in a category, click the chevron icon (
 ) next to the category name.
) next to the category name. - Click the Add button.
The selected widgets are added at the end of the dashboard.
You can now edit the representation and parameters of the added widgets.
Hiding a widget from the dashboard
To hide a displayed widget from the dashboard:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Dashboard.
- Click the settings icon (
 ) next to the widget that you want to hide.
) next to the widget that you want to hide. - Select Hide web widget.
- In the Warning window that opens, click OK.
The selected widget is hidden. Later, you can add this widget to the dashboard again.
Moving a widget on the dashboard
To move a widget on the dashboard:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Dashboard.
- Click the settings icon (
 ) next to the widget that you want to move.
) next to the widget that you want to move. - Select Move.
- Click the place to which you want to move the widget. You can select only another widget.
The places of the selected widgets are swapped.
Changing the widget size or appearance
For widgets that display a graph, you can change its representation—a bar chart or a line chart. For some widgets, you can change their size: compact, medium, or maximum.
To change the widget representation:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Dashboard.
- Click the settings icon (
 ) next to the widget that you want to edit.
) next to the widget that you want to edit. - Do one of the following:
- To display the widget as a bar chart, select Chart type: Bars.
- To display the widget as a line chart, select Chart type: Lines.
- To change the area occupied by the widget, select one of the values:
- Compact
- Compact (bar only)
- Medium (donut chart)
- Medium (bar chart)
- Maximum
The representation of the selected widget is changed.
Changing widget settings
To change settings of a widget:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Dashboard.
- Click the settings icon (
 ) next to the widget that you want to change.
) next to the widget that you want to change. - Select Show settings.
- In the widget settings window that opens, change the widget settings as required.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The settings of the selected widget are changed.
The set of settings depends on the specific widget. Below are some of the common settings:
- Web widget scope (the set of objects for which the widget displays information)—for example, an administration group or device selection.
- Select task (the task for which the widget displays information).
- Time interval (the time interval during which the information is displayed in the widget)—between the two specified dates; from the specified date to the current day; or from the current day minus the specified number of days to the current day.
- Set to Critical if these are specified and Set to Warning if these are specified (the rules that determine the color of a traffic light).
After you change the widget settings, you can refresh data on the widget manually.
To refresh data on a widget:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Dashboard.
- Click the settings icon (
 ) next to the widget that you want to move.
) next to the widget that you want to move. - Select Refresh.
The data on the widget is refreshed.
About the Dashboard-only mode
You can configure the Dashboard-only mode for employees who do not manage the network but who want to view the network protection statistics in Kaspersky Security Center (for example, a top manager). When a user has this mode enabled, only a dashboard with a predefined set of widgets is displayed to the user. Thus, he or she can monitor the statistics specified in the widgets, for example, the protection status of all managed devices, the number of recently detected threats, or the list of the most frequent threats in the network.
When a user works in the Dashboard-only mode, the following restrictions are applied:
- The main menu is not displayed to the user, so he or she cannot change the network protection settings.
- The user cannot perform any actions with widgets, for example, add or hide them. Therefore, you need to put all widgets required for the user on the dashboard and configure them, for instance, set the rule of counting objects or specify the time interval.
You cannot assign the Dashboard-only mode to yourself. If you want to work in this mode, contact a system administrator, Managed Service Provider (MSP), or a user with the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area.
Configuring the Dashboard-only mode
Before you begin to configure the Dashboard-only mode, make sure that the following prerequisites are met:
- You have the Modify object ACLs right in the General features: User permissions functional area. If you do not have this right, the tab for configuring the mode will be missing.
- The user has the Read right in the General features: Basic functionality functional area.
If a hierarchy of Administration Servers is arranged in your network, for configuring the Dashboard-only mode go to the Server where the user account is available on the Users tab of the Users & roles → Users & groups section. It can be a primary server or physical secondary server. It is not possible to adjust the mode on a virtual server.
To configure the Dashboard-only mode:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users tab.
- Click the user account name for which you want to adjust the dashboard with widgets.
- In the account settings window that opens, select the Dashboard tab.
On the tab that opens, the same dashboard is displayed for you as for the user.
- If the Display the console in Dashboard-only mode option is enabled, switch the toggle button to disable it.
When this option is enabled, you are also unable to change the dashboard. After you disable the option, you can manage widgets.
- Configure the dashboard appearance. The set of widgets prepared on the Dashboard tab is available for the user with the customizable account. He or she cannot change any settings or size of the widgets, add, or remove any widgets from the dashboard. Therefore, adjust them for the user, so he or she can view the network protection statistics. For this purpose, on the Dashboard tab you can perform the same actions with widgets as in the Monitoring & reporting → Dashboard section:
- Add new widgets to the dashboard.
- Hide widgets that the user doesn't need.
- Move widgets into a specific order.
- Change the size or appearance of widgets.
- Change the widget settings.
- Switch the toggle button to enable the Display the console in Dashboard-only mode option.
After that, only the dashboard is available for the user. He or she can monitor statistics but cannot change the network protection settings and dashboard appearance. As the same dashboard is displayed for you as for the user, you are also unable to change the dashboard.
If you keep the option disabled, the main menu is displayed for the user, so he or she can perform various actions in Kaspersky Security Center, including changing security settings and widgets.
- Click the Save button when you finish configuring the Dashboard-only mode. Only after that will the prepared dashboard be displayed to the user.
- If the user wants to view statistics of supported Kaspersky applications and needs access rights to do so, configure the rights for the user. After that, Kaspersky applications data is displayed for the user in the widgets of these applications.
Now the user can log in to Kaspersky Security Center under the customized account and monitor the network protection statistics in the Dashboard-only mode.
Page top
Reports
This section describes how to use reports, manage custom report templates, use report templates to generate new reports, and create report delivery tasks.
Using reports
The Reports feature allows you to get detailed numerical information about the security of your organization's network, save this information to a file, send it by email, and print it.
Reports are available in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, in the Monitoring & reporting section, by clicking Reports.
By default, reports include information for the last 30 days.
Kaspersky Security Center has a default set of reports for the following categories:
- Protection status
- Deployment
- Updating
- Threat statistics
- Other
You can create custom report templates, edit report templates, and delete them.
You can create reports that are based on existing templates, export reports to files, and create tasks for report delivery.
Creating a report template
To create a report template:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Reports
- Click Add.
The New report template wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- Enter the report name and select the report type.
- On the Scope step of the wizard, select the set of client devices (administration group, device selection, selected devices, or all networked devices) whose data will be displayed in reports that are based on this report template.
- On the Reporting period step of the wizard, specify the report period. Available values are as follows:
- Between the two specified dates
- From the specified date to the report creation date
- From the report creation date, minus the specified number of days, to the report creation date
This page may not appear for some reports.
- Click OK to close the wizard.
- Do one of the following:
- Click the Save and run button to save the new report template and to run a report based on it.
The report template is saved. The report is generated.
- Click the Save button to save the new report template.
The report template is saved.
- Click the Save and run button to save the new report template and to run a report based on it.
You can use the new template for generating and viewing reports.
Viewing and editing report template properties
You can view and edit basic properties of a report template, for example, the report template name or the fields displayed in the report.
To view and edit properties of a report template:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Reports.
- Select the check box next to the report template whose properties you want to view and edit.
As an alternative, you can first generate the report, and then click the Edit button.
- Click the Open report template properties button.
The Editing report <Report name> window opens with the General tab selected.
- Edit the report template properties:
- General tab:
- Report template name
- Maximum number of entries to display
- Group
Click the Settings button to change the set of client devices for which the report is created. For some types of the reports, the button may be unavailable. The actual settings depend on the settings specified during creation of the report template.
- Time interval
Click the Settings button to modify the report period. For some types of the reports, the button may be unavailable. Available values are as follows:
- Between the two specified dates
- From the specified date to the report creation date
- From the report creation date, minus the specified number of days, to the report creation date
- Include data from secondary and virtual Administration Servers
- Up to nesting level
- Data wait interval (min)
- Cache data from secondary Administration Servers
- Cache update frequency (h)
- Transfer detailed information from secondary Administration Servers
- Fields tab
Select the fields that will be displayed in the report, and use the Move up button and Move down button to change the order of these fields. Use the Add button or Edit button to specify whether the information in the report must be sorted and filtered by each of the fields.
In the Filters of Details fields section, you can also click the Convert filters button to start using the extended filtering format. This format enables you to combine filtering conditions specified in various fields by using the logical OR operation. After you click the button, the Convert filters panel opens on the right. Click the Convert filters button to confirm conversion. You can now define a converted filter with conditions from the Details fields section that are applied by using the logical OR operation.
Conversion of a report to the format supporting complex filtering conditions will make the report incompatible with the previous versions of Kaspersky Security Center (11 and earlier). Also, the converted report will not contain any data from secondary Administration Servers running such incompatible versions.
- General tab:
- Click Save to save the changes.
- Close the Editing report <Report name> window.
The updated report template appears in the list of report templates.
Page top
Exporting a report to a file
You can export a report to an XML, HTML, or PDF file.
To export a report to a file:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Reports.
- Select the check box next to the report that you want to export to a file.
- Click the Export report button.
- In the window that opens, change the report file name in the Name field. By default, the file name coincides with the name of the selected report template.
- Select the report file type: XML, HTML, or PDF.
- Click the Export report button.
The report in selected format will be downloaded to your device—to the default folder of your device—or a standard Save as window in your browser will open to let you save the file where you want.
The report is saved to the file.
Generating and viewing a report
To create and view a report:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Reports.
- Click the name of the report template that you want to use to create a report.
A report using the selected template is generated and displayed.
Report data is displayed according to the localization set for the Administration Server.
The report displays the following data:
- On the Summary tab:
- The name and type of report, a brief description and the reporting period, as well as information about the group of devices for which the report is generated.
- Graph chart showing the most representative report data.
- Consolidated table with calculated report indicators.
- On the Details tab, a table with detailed report data is displayed.
Creating a report delivery task
You can create a task that will deliver selected reports.
To create a report delivery task:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Reports.
- Select the check boxes next to the report templates for which you want to create a report delivery task.
- Click the Create delivery task button.
The New task wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- At the New task settings step of the wizard, enter the task name.
The default name is Deliver reports. If a task with this name already exists, a sequence number (<N>) is added to the task name.
- At the Report configuration step of the wizard, specify the following settings:
- Report templates to be delivered by the task.
- The report format: HTML, XLS, or PDF.
The wkhtmltopdf tool is required to convert a report to PDF. When you select the PDF option, Administration Server checks whether the wkhtmltopdf tool is installed on the device. If the tool is not installed, the application displays a message about the necessity to install the tool on the Administration Server device. Install the tool manually, and then proceed to the next step.
- Whether the reports are to be sent by email, together with email notification settings.
You can specify up to 20 email addresses. To separate email addresses, press Enter. You can also paste a comma-separated list of email addresses, and then press Enter.
- Whether the reports are to be saved to a folder, whether previously saved reports in this folder are to be overwritten, and whether a specific account is to be used to access the folder (for a shared folder).
- At the Configure task schedule step of the wizard, select the task start schedule.
The following task schedule options are available:
- At this step of the wizard, configure other task schedule settings:
- In the Task schedule section, check or reconfigure the previously selected schedule and set the time interval, days of the month or week, set the virus outbreak condition or completing another task as a trigger to start the task. A start time can also be specified in this section if an applicable schedule is selected.
- In the Additional settings section, specify the following settings:
- At the Selecting an account to run the task step of the wizard, specify the credentials of the user account that is used to run the task.
- If you want to modify other task settings after the task is created, at the Finish task creation step of the wizard, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option (by default, this option is enabled).
- Click the Finish button to create the task and close the wizard.
The report delivery task is created. If the Open task details when creation is complete option is enabled, the task settings window opens.
Deleting report templates
To delete one or several report templates:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Reports.
- Select check boxes next to the report templates that you want to delete.
- Click the Delete button.
- In the window that opens, click OK to confirm your selection.
The selected report templates are deleted. If these report templates were included in the report delivery tasks, they are also removed from the tasks.
Events and event selections
This section provides information about events and event selections, about the types of events that occur in Kaspersky Security Center components, and about managing frequent events blocking.
About Kaspersky Security Center events
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to receive information about events that occur during the operation of Administration Server and Kaspersky applications installed on managed devices. Information about events is saved in the Administration Server database.
Event types
In Kaspersky Security Center, there are the following types of events:
- General events. These events occur in all managed Kaspersky applications. An example of a general event is Virus outbreak. General events have strictly defined syntax and semantics. General events are used, for instance, in reports and dashboards.
- Managed Kaspersky applications-specific events. Each managed Kaspersky application has its own set of events.
Event sources
Events can be generated by the following applications:
- Kaspersky Security Center components:
- Administration Server
- Network Agent
- iOS MDM Server
- Exchange Mobile Device Server
- Managed Kaspersky applications
For details about the events generated by Kaspersky managed applications, refer to the documentation of the corresponding application.
You can view the full list of events that can be generated by an application on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. For Administration Server, you can additionally view the event list in the Administration Server properties.
Importance level of events
Each event has its own importance level. Depending on the conditions of its occurrence, an event can be assigned various importance levels. There are four importance levels of events:
- A critical event is an event that indicates the occurrence of a critical problem that may lead to data loss, an operational malfunction, or a critical error.
- A functional failure is an event that indicates the occurrence of a serious problem, error or malfunction that occurred during operation of the application or while performing a procedure.
- A warning is an event that is not necessarily serious, but nevertheless indicates a potential problem in the future. Most events are designated as warnings if the application can be restored without loss of data or functional capabilities after such events occur.
- An info event is an event that occurs for the purpose of informing about successful completion of an operation, proper functioning of the application, or completion of a procedure.
Each event has a defined storage term, during which you can view or modify it in Kaspersky Security Center. Some events are not saved in the Administration Server database by default because their defined storage term is zero. Only events that will be stored in the Administration Server database for at least one day can be exported to external systems.
Page top
Using event selections
Event selections provide an onscreen view of named sets of events that are selected from the Administration Server database. These sets of events are grouped according to the following categories:
- By importance level—Critical events, Functional failures, Warnings, and Info events
- By time—Recent events
- By type—User requests and Audit events
You can create and view user-defined event selections based on the settings available, in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface, for configuration.
Event selections are available in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, in the Monitoring & reporting section, by clicking Event selections.
By default, event selections include information for the last seven days.
Kaspersky Security Center has a default set of event (predefined) selections:
- Events with different importance levels:
- Critical events
- Functional failures
- Warnings
- Informational messages
- User requests (events of managed applications)
- Recent events (over the last week)
- Audit events.
You can also create and configure additional user-defined selections. In user-defined selections, you can filter events by the properties of the devices they originated from (device names, IP ranges, and administration groups), by event types and severity levels, by application and component name, and by time interval. It is also possible to include task results in the search scope. You can also use a simple search field where a word or several words can be typed. All events that contain any of the typed words anywhere in their attributes (such as event name, description, component name) are displayed.
Both for predefined and user-defined selections, you can limit the number of displayed events or the number of records to search. Both options affect the time it takes Kaspersky Security Center to display the events. The larger the database is, the more time-consuming the process can be.
You can do the following:
- Edit properties of event selections
- Generate event selections
- View details of event selections
- Delete event selections
- Delete events from the Administration Server database
Creating an event selection
To create an event selection:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Event selections.
- Click Add.
- In the New event selection window that opens, specify the settings of the new event selection. Do this in one or more of the sections in the window.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The confirmation window opens.
- To view the event selection result, keep the Go to selection result check box selected.
- Click Save to confirm the event selection creation.
If you kept the Go to selection result check box selected, the event selection result is displayed. Otherwise, the new event selection appears in the list of event selections.
Editing an event selection
To edit an event selection:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Event selections.
- Select the check box next to the event selection that you want to edit.
- Click the Properties button.
An event selection settings window opens.
- Edit the properties of the event selection.
For predefined event selections, you can edit only the properties on the following tabs: General (except for the selection name), Time, and Access rights.
For user-defined selections, you can edit all properties.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The edited event selection is shown in the list.
Viewing a list of an event selection
To view an event selection:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Event selections.
- Select the check box next to the event selection that you want to start.
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to configure sorting in the event selection result, do the following:
- Click the Reconfigure sorting and start button.
- In the displayed Reconfigure sorting for event selection window, specify the sorting settings.
- Click the name of the selection.
- Otherwise, if you want to view the list of events as they are sorted on the Administration Server, click the name of the selection.
- If you want to configure sorting in the event selection result, do the following:
The event selection result is displayed.
Exporting an event selection
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to save an event selection and its settings to a KLO file. You can use this KLO file to import the saved event selection both to Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
Note that you can export only user-defined event selections. Event selections from the default set of Kaspersky Security Center (predefined selections) cannot be saved to a file.
To export an event selection:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Event selections.
- Select the check box next to the event selection that you want to export.
You cannot export multiple event selections at the same time. If you select more than one selection, the Export button will be disabled.
- Click the Export button.
- In the opened Save as window, specify the event selection file name and path, and then click the Save button.
The Save as window is displayed only if you use Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, or Opera. If you use another browser, the event selection file is automatically saved in the Downloads folder.
Importing an event selection
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to import an event selection from a KLO file. The KLO file contains the exported event selection and its settings.
To import an event selection:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Event selections.
- Click the Import button, and then choose an event selection file that you want to import.
- In the opened window, specify the path to the KLO file, and then click the Open button. Note that you can select only one event selection file.
The event selection processing starts.
The notification with the import results appears. If the event selection is imported successfully, you can click the View import details link to view the event selection properties.
After a successful import, the event selection is displayed in the selection list. The settings of the event selection are also imported.
If the newly imported event selection has a name identical to that of an existing event selection, the name of the imported selection is expanded with the (<next sequence number>) index, for example: (1), (2).
Page top
Viewing details of an event
To view details of an event:
- Start an event selection.
- Click the time of the required event.
The Event properties window opens.
- In the displayed window, you can do the following:
- View the information about the selected event
- Go to the next event and the previous event in the event selection result
- Go to the device on which the event occurred
- Go to the administration group that includes the device on which the event occurred
- For an event related to a task, go to the task properties
Exporting events to a file
To export events to a file:
- Start an event selection.
- Select the check box next to the required event.
- Click the Export to file button.
The selected event is exported to a file.
Viewing an object history from an event
From an event of creation or modification of an object that supports revision management, you can switch to the revision history of the object.
To view an object history from an event:
- Start an event selection.
- Select the check box next to the required event.
- Click the Revision history button.
The revision history of the object is opened.
Deleting events
To delete one or several events:
- Start an event selection.
- Select the check boxes next to the required events.
- Click the Delete button.
The selected events are deleted and cannot be restored.
Deleting event selections
You can delete only user-defined event selections. Predefined event selections cannot be deleted.
To delete one or several event selections:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Event selections.
- Select the check boxes next to the event selections that you want to delete.
- Click Delete.
- In the window that opens, click OK.
The event selection is deleted.
Setting the storage term for an event
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to receive information about events that occur during the operation of Administration Server and Kaspersky applications installed on managed devices. Information about events is saved in the Administration Server database. You might need to store some events for a longer or shorter period than specified by default values. You can change the default settings of the storage term for an event.
If you are not interested in storing some events in the database of Administration Server, you can disable the appropriate setting in the Administration Server policy and Kaspersky application policy, or in the Administration Server properties (only for Administration Server events). This will reduce the number of event types in the database.
The longer the storage term for an event, the faster the database reaches its maximum capacity. However, a longer storage term for an event lets you perform monitoring and reporting tasks for a longer period.
To set the storage term for an event in the database of Administration Server:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Do one of the following:
- To configure the storage term of the events of Network Agent or of a managed Kaspersky application, click the name of the corresponding policy.
The policy properties page opens.
- To configure Administration Server events, in the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. If you have a policy for the Administration Server, you can click the name of this policy instead.
The Administration Server properties page (or the Administration Server policy properties page) opens.
- To configure the storage term of the events of Network Agent or of a managed Kaspersky application, click the name of the corresponding policy.
- Select the Event configuration tab.
A list of event types related to the Critical section is displayed.
- Select the Functional failure, Warning, or Info section.
- In the list of event types in the right pane, click the link for the event whose storage term you want to change.
In the Event registration section of the window that opens, the Store in the Administration Server database for (days) option is enabled.
- In the edit box below this toggle button, enter the number of days to store the event.
- If you do not want to store an event in the Administration Server database, disable the Store in the Administration Server database for (days) option.
If you configure Administration Server events in Administration Server properties window and if event settings are locked in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server policy, you cannot redefine the storage term value for an event.
- Click OK.
The properties window of the policy is closed.
From now on, when Administration Server receives and stores the events of the selected type, they will have the changed storage term. Administration Server does not change the storage term of previously received events.
Page top
Events of Kaspersky Security Center components
Each Kaspersky Security Center component has its own set of event types. This section lists types of events that occur in Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server, Network Agent, and iOS MDM Server. Types of events that occur in Kaspersky applications are not listed in this section.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. For Administration Server, you can additionally view and configure the event list in the Administration Server properties. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
Data structure of event type description
For each event type, its display name, identifier (ID), alphabetic code, description, and the default storage term are provided.
- Event type display name. This text is displayed in Kaspersky Security Center when you configure events and when they occur.
- Event type ID. This numerical code is used when you process events by using third-party tools for event analysis.
- Event type (alphabetic code). This code is used when you browse and process events by using public views that are provided in the Kaspersky Security Center database and when events are exported to a SIEM system.
- Description. This text contains the situations when an event occurs and what you can do in such a case.
- Default storage term. This is the number of days during which the event is stored in the Administration Server database and is displayed in the list of events on Administration Server. After this period elapses, the event is deleted. If the event storage term value is 0, such events are detected but are not displayed in the list of events on Administration Server. If you configured to save such events to the operating system event log, you can find them there.
You can change the storage term for events:
- Administration Console: Setting the storage term for an event
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Setting the storage term for an event
Other data may include the following fields:
- event_id: unique number of the event in the database, generated and assigned automatically; not to be confused with Event type ID.
- task_id: the ID of the task that caused the event (if any)
- severity: one of the following severity levels (in the ascending order of severity):
0) Invalid severity level
1) Info
2) Warning
3) Error
4) Critical
Administration Server events
This section contains information about the events related to the Administration Server.
Administration Server critical events
The table below shows the event types of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server that have the Critical importance level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. For Administration Server, you can additionally view and configure the event list in the Administration Server properties. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
If you specified the port in the Administration Server properties window in the Administration Console, Kaspersky Security Center publishes its metrics and critical events to be obtained by Prometheus, a system for monitoring and alerting. Prometheus obtains the metrics and critical events, and then generates alerts for each event.
Administration Server critical events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Description |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|---|---|
License limit has been exceeded |
4099 |
KLSRV_EV_LICENSE_CHECK_MORE_110 |
Once a day Kaspersky Security Center checks whether a license limit is exceeded. Events of this type occur when Administration Server detects that some licensing limits are exceeded by Kaspersky applications installed on client devices and if the number of currently used licensing units covered by a single license exceeds 110% of the total number of units covered by the license. Even when this event occurs, client devices are protected. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
Kaspersky Security Center determines the rules to generate events when a license limit is exceeded. |
180 days |
Virus outbreak |
26 (for File Threat Protection) |
GNRL_EV_VIRUS_OUTBREAK |
Events of this type occur when the number of malicious objects detected on several managed devices exceeds the threshold within a short period. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
Virus outbreak |
27 (for Mail Threat Protection) |
GNRL_EV_VIRUS_OUTBREAK |
Events of this type occur when the number of malicious objects detected on several managed devices exceeds the threshold within a short period. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
Virus outbreak |
28 (for firewall) |
GNRL_EV_VIRUS_OUTBREAK |
Events of this type occur when the number of malicious objects detected on several managed devices exceeds the threshold within a short period. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
Device has become unmanaged |
4111 |
KLSRV_HOST_OUT_CONTROL |
Events of this type occur if a managed device is visible on the network but has not connected to Administration Server for a specific period. Find out what prevents the proper functioning of Network Agent on the device. Possible causes include network issues and removal of Network Agent from the device. |
180 days |
Device status is Critical |
4113 |
KLSRV_HOST_STATUS_CRITICAL |
Events of this type occur when a managed device is assigned the Critical status. You can configure the conditions under which the device status is changed to Critical. |
180 days |
The key file has been added to the denylist |
4124 |
KLSRV_LICENSE_BLACKLISTED |
Events of this type occur when Kaspersky has added the activation code or key file that you use to the denylist. Contact Technical Support for more details. |
180 days |
Limited functionality mode |
4130 |
KLSRV_EV_LICENSE_SRV_LIMITED_MODE |
Events of this type occur when Kaspersky Security Center starts to operate with basic functionality, without Vulnerability and patch management and without Mobile Device Management features. Following are causes of, and appropriate responses to, the event:
|
180 days |
License expires soon |
4129 |
KLSRV_EV_LICENSE_SRV_EXPIRE_SOON |
Events of this type occur when the commercial license expiration date is approaching. Once a day Kaspersky Security Center checks whether a license expiration date is approaching. Events of this type are published 30 days, 15 days, 5 days and 1 day before the license expiration date. You cannot change the number of days. If the Administration Server is turned off on the specified day before the license expiration date, the event will not be published until the next day. When the commercial license expires, Kaspersky Security Center provides only basic functionality. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
Certificate has expired |
4132 |
KLSRV_CERTIFICATE_EXPIRED |
Events of this type occur when the Administration Server certificate for Mobile Device Management expires. You need to update the expired certificate. |
180 days |
Administration Server certificate has expired. |
6129 |
KLSRV_EV_SRV_CERT_EXPIRED_DN |
Events of this type occur when the Administration Server certificate expires. You need to update the expired certificate. |
180 days |
Updates for Kaspersky application modules have been revoked |
4142 |
KLSRV_SEAMLESS_UPDATE_REVOKED |
Events of this type occur if seamless updates have been revoked (Revoked status is displayed for these updates) by Kaspersky technical specialists; for example, they must be updated to a newer version. The event concerns Kaspersky Security Center patches and does not concern modules of managed Kaspersky applications. The event provides the reason that the seamless updates are not installed. |
180 days |
Audit: Export to SIEM failed |
5130 |
KLAUD_EV_SIEM_EXPORT_ERROR |
Events of this type occur when exporting events to the SIEM system failed due to a connection error with the SIEM system. |
180 days |
Administration Server functional failure events
The table below shows the event types of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server that have the Functional failure importance level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. For Administration Server, you can additionally view and configure the event list in the Administration Server properties. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
Administration Server functional failure events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Description |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Runtime error |
4125 |
KLSRV_RUNTIME_ERROR |
Events of this type occur because of unknown issues. Most often these are DBMS issues, network issues, and other software and hardware issues. Details of the event can be found in the event description. |
180 days |
Limit of installations has been exceeded for one of the licensed applications groups |
4126 |
KLSRV_INVLICPROD_EXCEDED |
Administration Server generates events of this type periodically (every hour). Events of this type occur if in Kaspersky Security Center you manage license keys of third-party applications and if the number of installations has exceeded the limit set by the license key of the third-party application. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
You can manage license keys of third-party applications using the functionality of licensed applications groups. A licensed applications group includes third-party applications that meet criteria set by you. |
180 days |
Failed to poll the cloud segment |
4143 |
KLSRV_KLCLOUD_SCAN_ERROR |
Events of this type occur when Administration Server fails to poll a network segment in a cloud environment. Read the details in the event description and respond accordingly. |
Not stored |
Failed to copy the updates to the specified folder |
4123 |
KLSRV_UPD_REPL_FAIL |
Events of this type occur when software updates are copied to an additional shared folder(s). You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
No free disk space |
4107 |
KLSRV_DISK_FULL |
Events of this type occur when the hard drive of the device on which Administration Server is installed runs out of free space. Free up disk space on the device. |
180 days |
Shared folder is not available |
4108 |
KLSRV_SHARED_FOLDER_UNAVAILABLE |
Events of this type occur if the shared folder of Administration Server is not available. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
The Administration Server database is unavailable |
4109 |
KLSRV_DATABASE_UNAVAILABLE |
Events of this type occur if the Administration Server database becomes unavailable. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
180 days |
No free space in the Administration Server database |
4110 |
KLSRV_DATABASE_FULL |
Events of this type occur when there is no free space in the Administration Server database. Administration Server does not function when its database has reached its capacity and when further recording to the database is not possible. Following are the causes of this event, depending on the DBMS that you use, and appropriate responses to the event:
|
180 days |
Administration Server warning events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server that have the Warning importance level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. For Administration Server, you can additionally view and configure the event list in the Administration Server properties. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
Administration Server warning events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Description |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|---|---|
A frequent event has been detected |
|
KLSRV_EVENT_SPAM_EVENTS_DETECTED |
Events of this type occur when Administration Server detects a frequent event on a managed device. Refer to the following section for details: Blocking frequent events. |
90 days |
License limit has been exceeded |
4098 |
KLSRV_EV_LICENSE_CHECK_100_110 |
Once a day Kaspersky Security Center checks whether a license limit is exceeded. Events of this type occur when Administration Server detects that some licensing limits are exceeded by Kaspersky applications installed on client devices and if the number of currently used licensing units covered by a single license constitute 100% to 110% of the total number of units covered by the license. Even when this event occurs, client devices are protected. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
Kaspersky Security Center determines the rules to generate events when a license limit is exceeded. |
90 days |
Device has remained inactive on the network for a long time |
4103 |
KLSRV_EVENT_HOSTS_NOT_VISIBLE |
Events of this type occur when a managed device shows inactivity for some time. Most often, this happens when a managed device is decommissioned. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
|
90 days |
Conflict of device names |
4102 |
KLSRV_EVENT_HOSTS_CONFLICT |
Events of this type occur when Administration Server considers two or more managed devices as a single device. Most often this happens when a cloned hard drive was used for software deployment on managed devices and without switching the Network Agent to the dedicated disk cloning mode on a reference device. To avoid this issue, switch Network Agent to the disk cloning mode on a reference device before cloning the hard drive of this device. |
90 days |
Device status is Warning |
4114 |
KLSRV_HOST_STATUS_WARNING |
Events of this type occur when a managed device is assigned the Warning status. You can configure the conditions under which the device status is changed to Warning. |
90 days |
Limit of installations will soon be exceeded for one of the licensed applications groups |
4127 |
KLSRV_INVLICPROD_FILLED |
Events of this type occur when the number of installations for third-party applications included in a licensed applications group reaches 90% of the maximum allowed value specified in the license key properties. You can respond to the event in the following ways:
You can manage license keys of third-party applications using the functionality of licensed applications groups. |
90 days |
Certificate has been requested |
4133 |
KLSRV_CERTIFICATE_REQUESTED |
Events of this type occur when a certificate for Mobile Device Management fails to be automatically reissued. Following might be the causes and appropriate responses to the event:
|
90 days |
Certificate has been removed |
4134 |
KLSRV_CERTIFICATE_REMOVED |
Events of this type occur when an administrator removes any type of certificate (General, Mail, VPN) for Mobile Device Management. After removing a certificate, mobile devices connected via this certificate will fail to connect to Administration Server. This event might be helpful when investigating malfunctions associated with the management of mobile devices. |
90 days |
Certificate is expiring |
6128 |
KLSRV_EV_SRV_CERT_EXPIRES_SOON |
Events of this type occur when the Administration Server certificate is expiring in 30 days or sooner, and there is no reserve certificate. |
90 days |
APNs certificate has expired |
4135 |
KLSRV_APN_CERTIFICATE_EXPIRED |
Events of this type occur when an APNs certificate expires. You need to manually renew the APNs certificate and install it on an iOS MDM Server. |
Not stored |
APNs certificate expires soon |
4136 |
KLSRV_APN_CERTIFICATE_EXPIRES_SOON |
Events of this type occur when there are fewer than 14 days left before the APNs certificate expires. When the APNs certificate expires, you need to manually renew the APNs certificate and install it on an iOS MDM Server. We recommend that you schedule the APNs certificate renewal in advance of the expiration date. |
Not stored |
Failed to send the FCM message to the mobile device |
4138 |
KLSRV_GCM_DEVICE_ERROR |
Events of this type occur when Mobile Device Management is configured to use Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) for connecting to managed mobile devices with an Android operating system and FCM Server fails to handle some of the requests received from Administration Server. It means that some of the managed mobile devices will not receive a push notification. Read the HTTP code in the details of the event description and respond accordingly. For more information on the HTTP codes received from FCM Server and related errors, please refer to the Firebase service documentation (see chapter "Downstream message error response codes"). |
90 days |
HTTP error sending the FCM message to the FCM server |
4139 |
KLSRV_GCM_HTTP_ERROR |
Events of this type occur when Mobile Device Management is configured to use Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) for connecting managed mobile devices with the Android operating system and FCM Server reverts to the Administration Server a request with a HTTP code other than 200 (OK). Following might be the causes and appropriate responses to the event:
|
90 days |
Failed to send the FCM message to the FCM server |
4140 |
KLSRV_GCM_GENERAL_ERROR |
Events of this type occur due to unexpected errors on the Administration Server side when working with the Firebase Cloud Messaging HTTP protocol. Read the details in the event description and respond accordingly. If you cannot find the solution to an issue on your own, we recommend that you contact Kaspersky Technical Support. |
90 days |
Little free space on the hard drive |
4105 |
KLSRV_NO_SPACE_ON_VOLUMES |
Events of this type occur when the hard drive of the device on which Administration Server is installed almost runs out of free space. Free up disk space on the device. |
90 days |
Little free space in the Administration Server database |
4106 |
KLSRV_NO_SPACE_IN_DATABASE |
Events of this type occur if space in the Administration Server database is too limited. If you do not remedy the situation, soon the Administration Server database will reach its capacity and Administration Server will not function. Following are the causes of this event, depending on the DBMS that you use, and the appropriate responses to the event. You use the SQL Server Express Edition DBMS:
You use a DBMS other than SQL Server Express Edition:
Review the information on DBMS selection. |
90 days |
Connection to the secondary Administration Server has been interrupted |
4116 |
KLSRV_EV_SLAVE_SRV_DISCONNECTED |
Events of this type occur when a connection to the secondary Administration Server is interrupted. Read the Kaspersky Event Log on the device where the secondary Administration Server is installed and respond accordingly. |
90 days |
Connection to the primary Administration Server has been interrupted |
4118 |
KLSRV_EV_MASTER_SRV_DISCONNECTED |
Events of this type occur when a connection to the primary Administration Server is interrupted. Read the Kaspersky Event Log on the device where the primary Administration Server is installed and respond accordingly. |
90 days |
New updates for Kaspersky application modules have been registered |
4141 |
KLSRV_SEAMLESS_UPDATE_REGISTERED |
Events of this type occur when Administration Server registers new updates for the Kaspersky software installed on managed devices that require approval to be installed. Approve or decline the updates by using Administration Console or using Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. |
90 days |
The limit on the number of events in the database is exceeded, deletion of events has started |
4145 |
KLSRV_EVP_DB_TRUNCATING |
Events of this type occur when deletion of old events from the Administration Server database has started after the Administration Server database capacity is reached. You can respond to the event in the following ways: |
Not stored |
The limit on the number of events in the database is exceeded, the events have been deleted |
4146 |
KLSRV_EVP_DB_TRUNCATED |
Events of this type occur when old events have been deleted from the Administration Server database after the Administration Server database capacity is reached. You can respond to the event in the following ways: |
Not stored |
Audit (Test connection to SIEM server failed) |
5120 |
KLAUD_EV_SIEM_TEST_FAILED |
Events of this type occur when a test connection to the SIEM server failed. |
30 days |
Administration Server informational events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server that have the Info importance level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. For Administration Server, you can additionally view and configure the event list in the Administration Server properties. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
Administration Server informational events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Default storage term |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Over 90% of the license key is used up |
4097 |
KLSRV_EV_LICENSE_CHECK_90 |
30 days |
|
New device has been detected |
4100 |
KLSRV_EVENT_HOSTS_NEW_DETECTED |
30 days |
|
Device has been automatically added to the group |
4101 |
KLSRV_EVENT_HOSTS_NEW_REDIRECTED |
30 days |
|
Device has been automatically moved according to a rule |
1074 |
KLSRV_HOST_MOVED_WITH_RULE_EX |
30 days |
|
Device has been removed from the group: inactive on the network for a long time |
4104 |
KLSRV_INVISIBLE_HOSTS_REMOVED |
30 days |
|
Limit of installations will soon be exceeded (more than 95% is used up) for one of the licensed applications groups |
4128 |
KLSRV_INVLICPROD_EXPIRED_SOON |
30 days |
|
Files have been found to send to Kaspersky for analysis |
4131 |
KLSRV_APS_FILE_APPEARED |
30 days |
|
FCM Instance ID has changed on this mobile device |
4137 |
KLSRV_GCM_DEVICE_REGID_CHANGED |
30 days |
|
Updates have been successfully copied to the specified folder |
4122 |
KLSRV_UPD_REPL_OK |
30 days |
|
Connection to the secondary Administration Server has been established |
4115 |
KLSRV_EV_SLAVE_SRV_CONNECTED |
30 days |
|
Connection to the primary Administration Server has been established |
4117 |
KLSRV_EV_MASTER_SRV_CONNECTED |
30 days |
|
Databases have been updated |
4144 |
KLSRV_UPD_BASES_UPDATED |
30 days |
|
Audit: Connection to the Administration Server has been established |
4147 |
KLAUD_EV_SERVERCONNECT |
30 days |
|
Audit: Object has been modified |
4148 |
KLAUD_EV_OBJECTMODIFY |
30 days |
This event tracks changes in the following objects:
|
Audit: Object status has changed |
4150 |
KLAUD_EV_TASK_STATE_CHANGED |
30 days |
For example, this event occurs when a task has failed with an error. |
Audit: Group settings have been modified |
4149 |
KLAUD_EV_ADMGROUP_CHANGED |
30 days |
|
Audit: Connection to Administration Server has been terminated |
4151 |
KLAUD_EV_SERVERDISCONNECT |
30 days |
|
Audit: Object properties have been modified |
4152 |
KLAUD_EV_OBJECTPROPMODIFIED |
30 days |
This event tracks changes in the following properties:
|
Audit: User permissions have been modified |
4153 |
KLAUD_EV_OBJECTACLMODIFIED |
30 days |
|
Audit: Encryption keys have been imported or exported from Administration Server |
5100 |
KLAUD_EV_DPEKEYSEXPORT |
30 days |
|
Audit: Test connection to SIEM server succeeded |
5110 |
KLAUD_EV_SIEM_TEST_SUCCESS |
30 days |
This event occurs when a test connection to the SIEM server succeeded. |
Reserve certificate created |
6126 |
KLSRV_EV_SRV_CERT_RESERVE_CREATED |
30 days |
This event occurs when an Administration Server certificate has been created. |
Certificate renewing |
6127 |
KLSRV_EV_SRV_CERT_RENEWED |
30 days |
This event occurs when the Administration Server certificate has been renewed. |
Network Agent events
This section contains information about the events related to Network Agent.
Network Agent functional failure events
The table below shows the event types of Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent that have the Functional failure severity level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
Network Agent functional failure events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Description |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Update installation error |
7702 |
KLNAG_EV_PATCH_INSTALL_ERROR |
Events of this type occur if automatic updating and patching for Kaspersky Security Center components was not successful. The event does not concern updates of the managed Kaspersky applications. Read the event description. A Windows issue on the Administration Server might be a reason for this event. If the description mentions any issue of Windows configuration, resolve this issue. |
30 days |
Failed to install the third-party software update |
7697 |
KLNAG_EV_3P_PATCH_INSTALL_ERROR |
Events of this type occur if Vulnerability and patch management and Mobile Device Management features are in use, and if update of third-party software was not successful. Check whether the link to the third-party software is valid. Read the event description. |
30 days |
Failed to install the Windows Update updates |
7717 |
KLNAG_EV_WUA_INSTALL_ERROR |
Events of this type occur if Windows Updates were not successful. Configure Windows Updates in a Network Agent policy. Read the event description. Look for the error in the Microsoft Knowledge Base. Contact Microsoft Technical Support if you cannot resolve the issue yourself. |
30 days |
User management: errors |
7723 |
KLNAG_EV_USR_MNG_ERR |
General warning event. |
30 days |
Failed to restore sudoers file to reference value |
7726 |
KLNAG_EV_SUDOER_RESTORED_ERR |
The event contains the description of the sudoers file replacement error. |
30 days |
Failed to install root certificates |
7728 |
KLNAG_EV_ROOT_CERT_INSTALL_ERR |
The event contains the description of the certificates installation error. |
30 days |
Failed to remove root certificates |
7730 |
KLNAG_EV_ROOT_CERT_REMOVE_ERR |
The event contains the description of the certificates removal error. |
30 days |
Network Agent warning events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent that have the Warning severity level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
Network Agent warning events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|---|
Warning has been returned during installation of the software module update |
7701 |
KLNAG_EV_PATCH_INSTALL_WARNING |
30 days |
Third-party software update installation has completed with a warning |
7696 |
KLNAG_EV_3P_PATCH_INSTALL_WARNING |
30 days |
Third-party software update installation has been postponed |
7698 |
KLNAG_EV_3P_PATCH_INSTALL_SLIPPED |
30 days |
Security issue has occurred |
549 |
GNRL_EV_APP_INCIDENT_OCCURED |
30 days |
KSN Proxy has started. Failed to check KSN for availability |
7718 |
KSNPROXY_STARTED_CON_CHK_FAILED |
30 days |
User management: warnings |
7722 |
KLNAG_EV_USR_MNG_WRN |
30 days |
Sudoers file found doesn't match reference value |
7724 |
KLNAG_EV_SUDOER_DIFFERENT |
30 days |
Network Agent informational events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent that have the Info severity level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
Network Agent informational events
Event type display name |
Event type ID |
Event type |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|---|
Update for software modules has been installed successfully |
7699 |
KLNAG_EV_PATCH_INSTALLED_SUCCESSFULLY |
30 days |
Installation of the software module update has started |
7700 |
KLNAG_EV_PATCH_INSTALL_STARTING |
30 days |
Application has been installed |
7703 |
KLNAG_EV_INV_APP_INSTALLED |
30 days |
Application has been uninstalled |
7704 |
KLNAG_EV_INV_APP_UNINSTALLED |
30 days |
Monitored application has been installed |
7705 |
KLNAG_EV_INV_OBS_APP_INSTALLED |
30 days |
Monitored application has been uninstalled |
7706 |
KLNAG_EV_INV_OBS_APP_UNINSTALLED |
30 days |
Third-party application has been installed |
7707 |
KLNAG_EV_INV_CMPTR_APP_INSTALLED |
30 days |
New device has been added |
7708 |
KLNAG_EV_DEVICE_ARRIVAL |
30 days |
Device has been removed |
7709 |
KLNAG_EV_DEVICE_REMOVE |
30 days |
New device has been detected |
7710 |
KLNAG_EV_NAC_DEVICE_DISCOVERED |
30 days |
Device has been authorized |
7711 |
KLNAG_EV_NAC_HOST_AUTHORIZED |
30 days |
Windows Desktop Sharing: File has been read |
7712 |
KLUSRLOG_EV_FILE_READ |
30 days |
Windows Desktop Sharing: File has been modified |
7713 |
KLUSRLOG_EV_FILE_MODIFIED |
30 days |
Windows Desktop Sharing: Application has been started |
7714 |
KLUSRLOG_EV_PROCESS_LAUNCHED |
30 days |
Windows Desktop Sharing: Started |
7715 |
KLUSRLOG_EV_WDS_BEGIN |
30 days |
Windows Desktop Sharing: Stopped |
7716 |
KLUSRLOG_EV_WDS_END |
30 days |
Third-party software update has been installed successfully |
7694 |
KLNAG_EV_3P_PATCH_INSTALLED_SUCCESSFULLY |
30 days |
Third-party software update installation has started |
7695 |
KLNAG_EV_3P_PATCH_INSTALL_STARTING |
30 days |
KSN Proxy has started. KSN availability check has completed successfully |
7719 |
KSNPROXY_STARTED_CON_CHK_OK |
30 days |
KSN Proxy has stopped |
7720 |
KSNPROXY_STOPPED |
30 days |
iOS MDM Server events
This section contains information about the events related to iOS MDM Server.
iOS MDM Server functional failure events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center iOS MDM Server that have the Functional failure severity level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
iOS MDM Server functional failure events
Event type display name |
Event type |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|
Failed to request the list of profile |
PROFILELIST_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to install the profile |
INSTALLPROFILE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to remove the profile |
REMOVEPROFILE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to request the list of provisioning profiles |
PROVISIONINGPROFILELIST_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to install provisioning profile |
INSTALLPROVISIONINGPROFILE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to remove the provisioning profile |
REMOVEPROVISIONINGPROFILE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to request the list of digital certificates |
CERTIFICATELIST_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to request the list of installed applications |
INSTALLEDAPPLICATIONLIST_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to request general information about the mobile device |
DEVICEINFORMATION_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to request security information |
SECURITYINFO_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to lock the mobile device |
DEVICELOCK_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to reset the password |
CLEARPASSCODE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to wipe data from the mobile device |
ERASEDEVICE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to install the app |
INSTALLAPPLICATION_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to set the redemption code for the app |
APPLYREDEMPTIONCODE_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to request the list of managed apps |
MANAGEDAPPLICATIONLIST_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to remove the managed app |
REMOVEAPPLICATION_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Roaming settings have been rejected |
SETROAMINGSETTINGS_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Error has occurred in the app operation |
PRODUCT_FAILURE |
30 days |
Command result contains invalid data |
MALFORMED_COMMAND |
30 days |
Failed to send the push notification |
SEND_PUSH_NOTIFICATION_FAILED |
30 days |
Failed to send the command |
SEND_COMMAND_FAILED |
30 days |
Device not found |
DEVICE_NOT_FOUND |
30 days |
iOS MDM Server warning events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center iOS MDM Server that have the Warning severity level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
iOS MDM Server warning events
Event type display name |
Event type |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|
Attempt to connect a locked mobile device has been detected |
INACTICE_DEVICE_TRY_CONNECTED |
30 days |
Profile has been removed |
MDM_PROFILE_WAS_REMOVED |
30 days |
Attempt to re-use a client certificate has been detected |
CLIENT_CERT_ALREADY_IN_USE |
30 days |
Inactive device has been detected |
FOUND_INACTIVE_DEVICE |
30 days |
Redemption code is required |
NEED_REDEMPTION_CODE |
30 days |
Profile has been included in a policy removed from the device |
UMDM_PROFILE_WAS_REMOVED |
30 days |
iOS MDM Server informational events
The table below shows the events of Kaspersky Security Center iOS MDM Server that have the Info severity level.
For each event that can be generated by an application, you can specify notification settings and storage settings on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. If you want to configure notification settings for all the events at once, configure general notification settings in the Administration Server properties.
iOS MDM Server informational events
Event type display name |
Event type |
Default storage term |
|---|---|---|
New mobile device has been connected |
NEW_DEVICE_CONNECTED |
30 days |
List of profiles has been successfully requested |
PROFILELIST_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Profile has been successfully installed |
INSTALLPROFILE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Profile has been successfully removed |
REMOVEPROFILE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
List of provisioning profiles has been successfully requested |
PROVISIONINGPROFILELIST_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Provisioning profile has been successfully installed |
INSTALLPROVISIONINGPROFILE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Provisioning profile has been successfully removed |
REMOVEPROVISIONINGPROFILE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
List of digital certificates has been successfully requested |
CERTIFICATELIST_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
List of installed applications has been successfully requested |
INSTALLEDAPPLICATIONLIST_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
General information about the mobile device has been successfully requested |
DEVICEINFORMATION_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Security information has been successfully requested |
SECURITYINFO_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Mobile device has been successfully locked |
DEVICELOCK_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
The password has been successfully reset |
CLEARPASSCODE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Data has been wiped from the mobile device |
ERASEDEVICE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
App has been successfully installed |
INSTALLAPPLICATION_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Redemption code has been successfully set for the app |
APPLYREDEMPTIONCODE_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
The list of managed apps has been successfully requested |
MANAGEDAPPLICATIONLIST_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Managed app has been removed successfully |
REMOVEAPPLICATION_COMMAND_SUCCESSFULL |
30 days |
Roaming settings have been successfully applied |
SETROAMINGSETTINGS_COMMAND_SUCCESSFUL |
30 days |
Blocking frequent events
This section provides information about managing frequent events blocking and about removing blocking of frequent events.
About blocking frequent events
A managed application, for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, installed on a single or several managed devices can send a lot of events of the same type to the Administration Server. Receiving frequent events may overload the Administration Server database and overwrite other events. Administration Server starts blocking the most frequent events when the number of all the received events exceeds the specified limit for the database.
Administration Server blocks the frequent events from receiving automatically. You cannot block the frequent events yourself, or choose which events to block.
If you want to find out if an event is blocked, you can view the notification list or you can check if this event is present in the Blocking frequent events section of the Administration Server properties. If the event is blocked, you can do the following:
- If you want to prevent overwriting the database, you can continue blocking such type of events from receiving.
- If you want, for example, to find the reason of sending the frequent events to the Administration Server, you can unblock frequent events and continue receiving the events of this type anyway.
- If you want to continue receiving the frequent events until they become blocked again, you can remove from blocking the frequent events.
Managing frequent events blocking
Administration Server blocks the automatic receiving of frequent events, but you can unblock and continue to receive frequent events. You can also block receiving frequent events that you unblocked before.
To manage frequent events blocking:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Blocking frequent events section.
- In the Blocking frequent events section:
- If you want to unblock the receiving of frequent events:
- Select the frequent events you want to unblock, and then click the Exclude button.
- Click the Save button.
- If you want to block receiving frequent events:
- Select the frequent events you want to block, and then click the Block button.
- Click the Save button.
- If you want to unblock the receiving of frequent events:
Administration Server receives the unblocked frequent events and does not receive the blocked frequent events.
Removing blocking of frequent events
You can remove blocking for frequent events and start receiving them until Administration Server blocks these frequent events again.
To remove blocking for frequent events:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Blocking frequent events section.
- In the Blocking frequent events section, select the frequent event types for which you want to remove blocking.
- Click the Remove from blocking button.
The frequent event is removed from the list of frequent events. Administration Server will receive events of this type.
Receiving events from Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers
Information about events during the operation of managed applications, such as Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, is transferred from managed devices and registered in the Administration Server database. By default, the events from Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers version 9.0 MR6 and earlier are not registered in the Administration Server database. If Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers version 9.0 MR6 and earlier is installed on the managed devices in your organization and you want to receive events from this application, enable the event registration for this application by using the klscflag utility.
To enable the event registration for Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers:
- On the Administration Server device, run the Windows command prompt under an account with administrator rights.
- Change your current directory to the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder (usually, C:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center).
- Run one of the following commands:
- For the Administration Server installed on a Windows Server failover cluster:
klscflag.exe --stp cluster -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_EVP_ENABLE_HOST_EVENT_BODY_VALIDATION -t d -v 0 - For the Administration Server installed on a Kaspersky Security Center failover cluster node:
klscflag.exe --stp klfoc -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_EVP_ENABLE_HOST_EVENT_BODY_VALIDATION -t d -v 0 - For the Administration Server that is not working on a cluster:
klscflag.exe -fset -pv klserver -n KLSRV_EVP_ENABLE_HOST_EVENT_BODY_VALIDATION -t d -v 0
- For the Administration Server installed on a Windows Server failover cluster:
The event registration for Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers is enabled.
For Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers, you cannot set the storage term for the events or select which events must be saved in the Administration Server repository. You can set the maximum number of events that can be saved in the repository. This setting is applied to the events received from all of the Kaspersky applications.
Notifications and device statuses
This section contains information on how to view notifications, configure notification delivery, use device statuses, and enable changing device statuses.
Using notifications
Notifications alert you about events and help you to speed up your responses to these events by performing recommended actions or actions you consider as appropriate.
Depending on the notification method chosen, the following types of notifications are available:
- Onscreen notifications
- Notifications by SMS
- Notifications by email
- Notifications by executable file or script
Onscreen notifications
Onscreen notifications alert you to events grouped by importance levels (Critical, Warning, and Informational).
Onscreen notification can have one of two statuses:
- Reviewed. It means you have performed recommended action for the notification, or you have assigned this status for the notification manually.
- Not Reviewed. It means you have not performed recommended action for the notification, or you have not assigned this status for the notification manually.
By default, the list of notifications include notifications in the Not Reviewed status.
You can monitor your organization's network viewing onscreen notifications and responding to them in a real time.
Notifications by email, by SMS, and by executable file or a script
Kaspersky Security Center provides the capability to monitor your organization's network by sending notifications about any event that you consider important. For any event, you can configure notifications by email, by SMS, or by running an executable file or a script.
Upon receiving notifications by email or by SMS, you can decide on your response to an event. This response should be the most appropriate for your organization's network. By running an executable file or a script, you predefine a response to an event. You can also consider running an executable file or a script as a primary response to an event. After the executable file runs, you can take other steps to respond to the event.
Page top
Viewing onscreen notifications
You can view notifications onscreen in three ways:
- In the Monitoring & reporting → Notifications section. Here you can view notifications relating to predefined categories.
- In a separate window that can be opened no matter which section you are using at the moment. In this case, you can mark notifications as reviewed.
- In the Notifications by selected severity level widget on the Monitoring & reporting → Dashboard section. In the widget, you can view only notifications of events that are at the Critical and Warning importance levels.
You can perform actions, for example, you can response to an event.
To view notifications from predefined categories:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Notifications.
The All notifications category is selected in the left pane, and in the right pane, all the notifications are displayed.
- In the left pane, select one of the categories:
- Deployment
- Devices
- Protection
- Updates (this includes notifications about Kaspersky applications available for download and notifications about anti-virus database updates that have been downloaded)
- Exploit Prevention
- Administration Server (this includes events concerning only Administration Server)
- Useful links (this includes links to Kaspersky resources, for example, Kaspersky Technical Support, Kaspersky forum, license renewal page, or the Kaspersky IT Encyclopedia)
- Kaspersky news (this includes information about releases of Kaspersky applications)
A list of notifications of the selected category is displayed. The list contains the following:
- Icon related to the topic of the notification: deployment (
 ), protection (
), protection ( ), updates (
), updates ( ), device management (
), device management ( ), Exploit Prevention (
), Exploit Prevention ( ), Administration Server (
), Administration Server ( ).
). - Notification importance level. Notifications of the following importance levels are displayed: Critical notifications (
 ), Warning notifications (
), Warning notifications ( ), Info notifications. Notifications in the list are grouped by importance levels.
), Info notifications. Notifications in the list are grouped by importance levels. - Notification. This contains a description of the notification.
- Action. This contains a link to a quick action that we recommend you perform. For example, by clicking this link, you can proceed to the repository and install security applications on devices, or view a list of devices or a list of events. After you perform the recommended action for the notification, this notification is assigned the Reviewed status.
- Status registered. This contains the number of days or hours that have passed from the moment when the notification was registered on the Administration Server.
To view onscreen notifications in a separate window by importance level:
- In the upper-right corner of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, click the flag icon (
 ).
).If the flag icon has a red dot, there are notifications that have not been reviewed.
A window opens listing the notifications. By default, the All notifications tab is selected and the notifications are grouped by importance level: Critical, Warning, and Info.
- Select the System tab.
The list of Critical (
 ) and Warning (
) and Warning ( ) importance levels notifications is displayed. The notification list includes the following:
) importance levels notifications is displayed. The notification list includes the following:- Color marker. Critical notifications are marked in red. Warning notifications are marked in yellow.
- Icon indicating the topic of the notification: deployment (
 ), protection (
), protection ( ), updates (
), updates ( ), device management (
), device management ( ), Exploit Prevention (
), Exploit Prevention ( ), Administration Server (
), Administration Server ( ).
). - Description of the notification.
- Flag icon. The flag icon is gray if notifications have been assigned the Not Reviewed status. When you select the gray flag icon and assign the Reviewed status to a notification, the icon changes color to white.
- Link to the recommended action. When you perform the recommended action after clicking the link, the notification gets the Reviewed status.
- Number of days that have passed since the date when the notification was registered on the Administration Server.
- Select the More tab.
The list of Info importance level notifications is displayed.
The organization of the list is the same as for the list on the System tab (see the description above). The only difference is the absence of a color marker.
You can filter notifications by the date interval when they were registered on Administration Server. Use the Show filter check box to manage the filter.
To view onscreen notifications in the widget:
- In the Dashboard section, select Add or restore web widget.
- In the window that opens, click the Other category, select the Notifications by selected severity level widget, and click Add.
The widget now appears on the Dashboard tab. By default, the notifications of Critical importance level are displayed on the widget.
You can click the Settings button on the widget and change the widget settings to view notifications of the Warning importance level. Or, you can add another widget: Notifications by selected severity level, with a Warning importance level.
The list of notifications on the widget is limited by its size and includes two notifications. These two notifications relate to the latest events.
The notification list in the widget includes the following:
- Icon related to the topic of the notification: deployment (
 ), protection (
), protection ( ), updates (
), updates ( ), device management (
), device management ( ), Exploit Prevention (
), Exploit Prevention ( ), Administration Server (
), Administration Server ( ).
). - Description of the notification with a link to the recommended action. When you perform a recommended action after clicking the link, the notification gets the Reviewed status.
- Number of days or number of hours that have passed since the date when the notification was registered on the Administration Server.
- Link to other notifications. Upon clicking this link, you are transferred to the view of notifications in the Notifications section of the Monitoring & reporting section.
About device statuses
Kaspersky Security Center assigns a status to each managed device. The particular status depends on whether the conditions defined by the user are met. In some cases, when assigning a status to a device, Kaspersky Security Center takes into consideration the device's visibility flag on the network (see the table below). If Kaspersky Security Center does not find a device on the network within two hours, the visibility flag of the device is set to Not Visible.
The statuses are the following:
- Critical or Critical / Visible
- Warning or Warning / Visible
- OK or OK / Visible
The table below lists the default conditions that must be met to assign the Critical or Warning status to a device, with all possible values.
Conditions for assigning a status to a device
Condition |
Condition description |
Available values |
|---|---|---|
Security application is not installed |
Network Agent is installed on the device, but a security application is not installed. |
|
Too many viruses detected |
Some viruses have been found on the device by a task for virus detection, for example, the Malware scan task, and the number of viruses found exceeds the specified value. |
More than 0. |
Real-time protection level differs from the level set by the Administrator |
The device is visible on the network, but the real-time protection level differs from the level set (in the condition) by the administrator for the device status. |
|
Malware scan has not been performed in a long time |
The device is visible on the network and a security application is installed on the device, but neither the Malware scan task nor a local scan task has been run within the specified time interval. The condition is applicable only to devices that were added to the Administration Server database 7 days ago or earlier. |
More than 1 day. |
Databases are outdated |
The device is visible on the network and a security application is installed on the device, but the anti-virus databases have not been updated on this device within the specified time interval. The condition is applicable only to devices that were added to the Administration Server database 1 day ago or earlier. |
More than 1 day. |
Not connected in a long time |
Network Agent is installed on the device, but the device has not connected to an Administration Server within the specified time interval, because the device was turned off. |
More than 1 day. |
Active threats are detected |
The number of unprocessed objects in the Active threats folder exceeds the specified value. |
More than 0 items. |
Restart is required |
The device is visible on the network, but an application requires the device restart longer than the specified time interval and for one of the selected reasons. |
More than 0 minutes. |
Incompatible applications are installed |
The device is visible on the network, but software inventory performed through Network Agent has detected incompatible applications installed on the device. |
|
Software vulnerabilities have been detected |
The device is visible on the network and Network Agent is installed on the device, but the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task has detected vulnerabilities with the specified severity level in applications installed on the device. |
|
License expired |
The device is visible on the network, but the license has expired. |
|
License expires soon |
The device is visible on the network, but the license will expire on the device in less than the specified number of days. |
More than 0 days. |
Check for Windows Update updates has not been performed in a long time |
The device is visible on the network, but the Perform Windows Update synchronization task has not been run within the specified time interval. |
More than 1 day. |
Invalid encryption status |
Network Agent is installed on the device, but the device encryption result is equal to the specified value. |
|
Mobile device settings do not comply with the policy |
The mobile device settings are other than the settings that were specified in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android policy during the check of compliance rules. |
|
Unprocessed security issues detected |
Some unprocessed security issues have been found on the device. Security issues can be created either automatically, through managed Kaspersky applications installed on the client device, or manually by the administrator. |
|
Device status defined by application |
The status of the device is defined by the managed application. |
|
Device is out of disk space |
Free disk space on the device is less than the specified value or the device could not be synchronized with the Administration Server. The Critical or Warning status is changed to the OK status when the device is successfully synchronized with the Administration Server and free space on the device is greater than or equal to the specified value. |
More than 0 MB. |
Device has become unmanaged |
During device discovery, the device was recognized as visible on the network, but more than three attempts to synchronize with the Administration Server failed. |
|
Protection is disabled |
The device is visible on the network, but the security application on the device has been disabled for longer than the specified time interval. In this case, the state of the security application is stopped or failure, and differs from the following: starting, running, or suspended. |
More than 0 minutes. |
Security application is not running |
The device is visible on the network and a security application is installed on the device but is not running. |
|
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to set up automatic switching of the status of a device in an administration group when specified conditions are met. When specified conditions are met, the client device is assigned one of the following statuses: Critical or Warning. When specified conditions are not met, the client device is assigned the OK status.
Different statuses may correspond to different values of one condition. For example, by default, if the Databases are outdated condition has the More than 3 days value, the client device is assigned the Warning status; if the value is More than 7 days, the Critical status is assigned.
If you upgrade the Kaspersky Security Center from the previous version, the values of the Databases are outdated condition for assigning the status to Critical or Warning do not change.
When Kaspersky Security Center assigns a status to a device, for some conditions (see the Condition description column) the visibility flag is taken into consideration. For example, if a managed device was assigned the Critical status because the Databases are outdated condition was met, and later the visibility flag was set for the device, then the device is assigned the OK status.
Configuring the switching of device statuses
You can change conditions to assign the Critical or Warning status to a device.
To enable changing the device status to Critical:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- In the list of groups that opens, click the link with the name of a group for which you want to change switching the device statuses.
- In the properties window that opens, select the Device status tab.
- In the left pane, select Critical.
- In the right pane, in the Set to Critical if these are specified section, enable the condition to switch a device to the Critical status.
You can change only settings that are not locked in the parent policy.
- Select the radio button next to the condition in the list.
- In the upper-left corner of the list, click the Edit button.
- Set the required value for the selected condition.
Values cannot be set for every condition.
- Click OK.
When specified conditions are met, the managed device is assigned the Critical status.
To enable changing the device status to Warning:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- In the list of groups that opens, click the link with the name of a group for which you want to change switching the device statuses.
- In the properties window that opens, select the Device status tab.
- In the left pane, select Warning.
- In the right pane, in the Set to Warning if these are specified section, enable the condition to switch a device to the Warning status.
You can change only settings that are not locked in the parent policy.
- Select the radio button next to the condition in the list.
- In the upper-left corner of the list, click the Edit button.
- Set the required value for the selected condition.
Values cannot be set for every condition.
- Click OK.
When specified conditions are met, the managed device is assigned the Warning status.
Configuring notification delivery
You can configure notification about events occurring in Kaspersky Security Center. Depending on the notification method chosen, the following types of notifications are available:
- Email—When an event occurs, Kaspersky Security Center sends a notification to the email addresses specified.
- SMS—When an event occurs, Kaspersky Security Center sends a notification to the phone numbers specified.
- Executable file—When an event occurs, the executable file is run on the Administration Server.
To configure notification delivery of events occurring in Kaspersky Security Center:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens with the General tab selected.
- Click the Notification section, and in the right pane select the tab for the notification method you want:
- On the tab, define the notification settings.
- Click the OK button to close the Administration Server properties window.
The saved notification delivery settings are applied to all events that occur in Kaspersky Security Center.
You can override notification delivery settings for certain events in the Event configuration section of the Administration Server settings, of a policy's settings, or of an application's settings.
Event notifications displayed by running an executable file
Kaspersky Security Center can notify the administrator about events on client devices by running an executable file. The executable file must contain another executable file with placeholders of the event to be relayed to the administrator (see the table below).
Placeholders for describing an event
Placeholder |
Placeholder description |
|---|---|
%SEVERITY% |
Event severity. Possible values:
|
%COMPUTER% |
Name of the device where the event occurred. Maximum length of the device name is 256 characters. |
%DOMAIN% |
Domain name of the device where the event occurred. |
%EVENT% |
Name of the event type. Maximum length of the event type name is 50 characters. |
%DESCR% |
Event description. Maximum length of the description is 1000 characters. |
%RISE_TIME% |
Event creation time. |
%KLCSAK_EVENT_TASK_DISPLAY_NAME% |
Task name. Maximum length of the task name is 100 characters. |
%KL_PRODUCT% |
Product name. |
%KL_VERSION% |
Product version number. |
%KLCSAK_EVENT_SEVERITY_NUM% |
Event severity number. Possible values:
|
%HOST_IP% |
IP address of the device where the event occurred. |
%HOST_CONN_IP% |
Connection IP address of the device where the event occurred. |
Example: Event notifications are sent by an executable file (such as script1.bat) inside which another executable file (such as script2.bat) with the %COMPUTER% placeholder is launched. When an event occurs, the script1.bat file is run on the administrator's device, which, in turn, runs the script2.bat file with the %COMPUTER% placeholder. The administrator then receives the name of the device where the event occurred. |
Kaspersky announcements
This section describes how to use, configure, and disable Kaspersky announcements.
About Kaspersky announcements
The Kaspersky announcements section (Monitoring & reporting → Kaspersky announcements) keeps you informed by providing information related to your version of Kaspersky Security Center and the managed applications installed on the managed devices. Kaspersky Security Center periodically updates the information in the section by removing outdated announcements and adding new information.
Kaspersky Security Center shows only those Kaspersky announcements that relate to the currently connected Administration Server and the Kaspersky applications installed on the managed devices of this Administration Server. The announcements are shown individually for any type of Administration Server—primary, secondary, or virtual.
Administration Server must have an internet connection to receive Kaspersky announcements.
The announcements include information of the following types:
- Security-related announcements
Security-related announcements are intended to keep the Kaspersky applications installed in your network up-to-date and fully functional. The announcements may include information about critical updates for Kaspersky applications, fixes for found vulnerabilities, and ways to fix other issues in Kaspersky applications. Security-related announcements are enabled by default. If you do not want to receive the announcements, you can disable this feature.
To show you the information that corresponds to your network protection configuration, Kaspersky Security Center sends data to Kaspersky cloud servers and receives only those announcements that relate to the Kaspersky applications installed in your network. The data set that can be sent to the servers is described in the End User License Agreement that you accept when you install Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
- Marketing announcements
Marketing announcements include information about special offers for your Kaspersky applications, advertisements, and news from Kaspersky. Marketing announcements are disabled by default. You receive this type of announcements only if you enabled Kaspersky Security Network (KSN). You can disable marketing announcements by disabling KSN.
To show you only relevant information that might be helpful in protecting your network devices and in your everyday tasks, Kaspersky Security Center sends data to Kaspersky cloud servers and receives the appropriate announcements. The data set that can be sent to the servers is described in the Processed Data section of the KSN Statement.
New information is divided into the following categories, according to importance:
- Critical info
- Important news
- Warning
- Info
When new information appears in the Kaspersky announcements section, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console displays a notification label that corresponds to the importance level of the announcements. You can click the label to view this announcement in the Kaspersky announcements section.
You can specify the Kaspersky announcements settings, including the announcement categories that you want to view and where to display the notification label.
Specifying Kaspersky announcements settings
In the Kaspersky announcements section, you can specify the Kaspersky announcements settings, including the categories of the announcements that you want to view and where to display the notification label.
To configure Kaspersky announcements:
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Kaspersky announcements.
- Click the Settings link.
The Kaspersky announcement settings window opens.
- Specify the following settings:
- Select the importance level of the announcements that you want to view. The announcements of other categories will not be displayed.
- Select where you want to see the notification label. The label can be displayed in all console sections, or in the Monitoring & reporting section and its subsections.
- Click the OK button.
The Kaspersky announcement settings are specified.
Disabling Kaspersky announcements
The Kaspersky announcements section (Monitoring & reporting → Kaspersky announcements) keeps you informed by providing information related to your version of Kaspersky Security Center and managed applications installed on the managed devices. If you do not want to receive Kaspersky announcements, you can disable this feature.
The Kaspersky announcements include two types of information: security-related announcements and marketing announcements. You can disable the announcements of each type separately.
To disable security-related announcements:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Kaspersky announcements section.
- Switch the toggle button to the Security-related announcements Disabled position.
- Click the Save button.
Kaspersky announcements are disabled.
Marketing announcements are disabled by default. You receive marketing announcements only if you enabled Kaspersky Security Network (KSN). You can disable this type of announcement by disabling KSN.
To disable marketing announcements:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the KSN Proxy settings section.
- Disable the Use Kaspersky Security Network Enabled option.
- Click the Save button.
Marketing announcements are disabled.
Viewing information about the detects of threats
You can enable or disable displaying information about alerts.
To enable or disable displaying the Alerts section in the main menu:
- In the main menu, go to your account settings, and then select Interface options.
- In the Interface options window that opens, enable or disable the Show EDR alerts option.
- Click Save.
The console displays the Alerts subsection in the Monitoring & reporting section of the main menu. In the Alerts subsection, you can view information about the detects of threats on the endpoint devices. If you add a license key for EDR Optimum, then Kaspersky Security Center Web Console automatically displays Alerts subsection in the Monitoring & reporting section of the main menu. Also, you can add a widget that displays information about alerts.
The Alerts subsection is displayed automatically only if you added the license key for EDR Optimum before enabling the Show EDR alerts option. If you added the license key after enabling the Show EDR alerts option, the Alerts subsection will be displayed only after you re-enable this option.
To display detailed information about detected threats in the alert card correctly, you have to install the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent plug-in and the compatible version of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security plug-in (Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux 12.1 or later, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac 12.1 or later, or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows 12.6 or later).
Use the Filter menu to filter alerts by date and field values.
The Object type field contains the following values:
- Unknown
- Phishing link
- Virus
- Trojan
- Malicious tool
- Backdoor
- Worm
- Other application
- Adware
- Pornware
- Dangerous packed program
- Dangerous behavior
The Automatic response field contains the following values:
- Malicious object detected
- Object deleted
- Object disinfected
- Object failed to disinfect
- Object moved to Quarantine
- Password-protected archive detected
- Virus detected
Cloud Discovery
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to monitor the use of cloud services on managed devices running Windows and to block access to cloud services that you consider unwanted. Cloud Discovery tracks user attempts to gain access to these services through both browsers and desktop applications. It also tracks user attempts to gain access to cloud services over unencrypted connections (for example, using the HTTP protocol). This feature helps you to detect and halt the use of cloud services by shadow IT.
The blocking capability is available only if you activated Kaspersky Security Center under a Kaspersky Next EDR Optimum or Kaspersky Next XDR Expert license.
The blocking capability is available only if you use Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.2 for Windows or later. Earlier versions of the security application only allow you to monitor the use of cloud services.
You can enable the Cloud Discovery feature and select the security policies or profiles for which you want to enable the feature. You can also enable or disable the feature separately in each security policy or profile. You can block access to cloud services that you do not want users to access.
To be able to block access to unwanted cloud services, make sure that the following prerequisites are met:
- You use Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.2 for Windows or later. Earlier versions of the security application only allow you to monitor the use of cloud services.
- You have purchased a Kaspersky Next license tier that includes the ability to block access to unwanted cloud services. For details, refer to Kaspersky Next Help.
The Cloud Discovery widget and the Cloud Discovery reports display information about successful and blocked attempts to gain access to cloud services. The widget also displays the risk level of each cloud service. Kaspersky Security Center gets information about the use of cloud services from all of the managed devices that are protected only by the security policies or profiles that have the feature enabled.
Enabling Cloud Discovery by using the widget
The Cloud Discovery feature allows you to get information about the use of cloud services from all of the managed devices that are protected only by the security policies that have the feature enabled. You can enable or disable Cloud Discovery for the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy only.
There are two ways to enable the Cloud Discovery feature:
- By using the Cloud Discovery widget.
- In the properties of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy.
For details on how to enable the Cloud Discovery feature in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy properties, refer to the Cloud Discovery section of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
Note that you can disable the Cloud Discovery feature in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy parameters only.
To enable Cloud Discovery, you must have the Write right in the General features: Basic functionality functional area.
To enable the Cloud Discovery feature by using the Cloud Discovery widget:
- Go to Kaspersky Security Center.
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Dashboard.
- On the Cloud Discovery widget, click the Enable button.
If you have Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows version 12.4 installed, enable the Cloud Discovery feature in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy properties. For details, refer to the Cloud Discovery section of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
If you have Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows earlier than version 12.4, update the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows plug-in to version 12.5.
- In the Enable Cloud Discovery window that opens, select the security policies for which you want to enable the feature, and then click the Enable button.
The following policy settings will be enabled automatically: Inject script into web traffic to interact with web pages, Web Session monitor, and Encrypted connections scan.
The Cloud Discovery feature is enabled and the widget is added to the dashboard.
Page top
Adding the Cloud Discovery widget to the dashboard
You can add the Cloud Discovery widget to the dashboard to monitor the use of cloud services on managed devices.
To add the Cloud Discovery widget to the dashboard, you must have the Write right in the General features: Basic functionality functional area.
To add the Cloud Discovery widget to the dashboard:
- Go to Kaspersky Security Center.
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Dashboard.
- Click the Add or restore web widget button.
- In the list of available widgets, click the chevron icon (
 ) next to the Other category.
) next to the Other category. - Select the Cloud Discovery widget, and then click the Add button.
If the Cloud Discovery feature is disabled, follow the instructions in the Enabling Cloud Discovery by using the widget section.
The selected widget is added at the end of the dashboard.
Page top
Viewing information about the use of cloud services
You can view the Cloud Discovery widget that shows information about attempts to gain access to cloud services. The widget also displays the risk level of each cloud service. Kaspersky Security Center gets information about the use of cloud services from all of the managed devices that are protected only by the security profiles that have the feature enabled.
Before viewing, make sure that:
- The Cloud Discovery widget is added to the dashboard.
- The Cloud Discovery feature is enabled.
- You have the Read right in the General features: Basic functionality functional area.
To view the Cloud Discovery widget:
- Go to Kaspersky Security Center.
- In the main menu, go to Monitoring & reporting → Dashboard.
The Cloud Discovery widget is displayed on the dashboard.
- On the left side of the Cloud Discovery widget, select a category of cloud services.
The table on the right side of the widget displays up to five services from the selected category, to which users most often try to gain access. Both successful and blocked attempts are counted.
- On the right side of the widget, select a specific service.
The table below displays up to ten devices that most often attempt to gain access to the service. In this table, you can generate two types of reports: report on successful access attempts and report on blocked access attempts.
In addition, in this table you can block access to the cloud service for a specific device.
The widget displays the requested information.
From the displayed widget, you can do the following:
- Proceed to the Monitoring & reporting → Reports section, to view the Cloud Discovery reports.
- Block or allow access to the selected cloud service.
The blocking capability is available only if you activated Kaspersky Security Center under a Kaspersky Next EDR Optimum or Kaspersky Next XDR Expert license.
The blocking capability is available only if you use Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.2 for Windows or later. Earlier versions of the security application only allow you to monitor the use of cloud services.
Page top
Risk level of a cloud service
For each cloud service, Cloud Discovery provides you with a risk level. The risk level helps you determine which services do not fit the security requirements of your organization. For example, you may want to take the risk level into account when deciding whether to block access to a certain service.
The risk level is an estimated index and does not say anything about the quality of a cloud service or about the service manufacturer. The risk level is simply a recommendation from Kaspersky experts.
Risk levels of cloud services are displayed in the Cloud Discovery widget and in the list of all monitored cloud services.
Page top
Blocking access to unwanted cloud services
You can block access to cloud services that you do not want users to access. You can also allow access to cloud services that were previously blocked.
Among other considerations, you may want to take the risk level into account when deciding whether to block access to a certain service.
You can block or allow access to cloud services for a security policy or profile.
There are two ways to block access to unwanted cloud services:
- By using the Cloud Discovery widget.
In this case, you can block access to the services one by one.
- In the properties of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy.
In this case, you can block access to the services one by one or block an entire category at once.
For details on how to enable the Cloud Discovery feature in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy properties, refer to the Cloud Discovery section of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
To block or allow access to a cloud service by using the widget:
- Open the Cloud Discovery widget, and then select the required cloud service.
- In the Top 10 devices that use the service pane, find the security policy or profile for which you want to block or allow the service.
- On the required line, in the Access status in policy or profile column, do any of the following:
- To block the service, select Blocked in the drop-down list.
- To allow the service, select Allowed in the drop-down list.
- Click the Save button.
Access to the selected service is blocked or allowed for the security policy or profile.
Page top
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console activity logging
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console activity logging can help to investigate the causes of a software malfunction. When you contact Kaspersky Technical Support about a Kaspersky Security Center Web Console malfunction, Kaspersky Technical Support specialists can request Kaspersky Security Center Web Console log files from you. Kaspersky Security Center Web Console log files are stored in the <Kaspersky Security Center Web Console installation folder>/logs folder the entire time you use the application. Log files are not sent to Kaspersky Technical Support specialists automatically.
To enable Kaspersky Security Center Web Console activity logging,
Select the Enable logging of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console activities check box in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console connection settings window of the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console setup wizard.
The log files are in text format.
The log file names are in the format logs-<component name>.<device name>-<file revision number>.YYYY-MM-DD, where:
- <component name> is the name of the Kaspersky Security Center component or is the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console management plug-in name.
- <device name> is the name of the device on which the <component name> is running.
- <file revision number> is the number of the log file created for the <component name> that is in operation on the <device name>. Within one day, several log files for the same <component name> and <device name> can be created. The maximum size of a log file is 50 megabytes (MB). When the maximum file size is reached, a new log file is created. A new log file <file revision number> is incremented by 1.
- YYYY, MM, and DD are the year, month, and day when the log was first created. When a new day starts a new log file is created.
Integration between Kaspersky Security Center and other solutions
This section describes how to configure access from Kaspersky Security Center Web Console to another Kaspersky application, such as Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response. Also this section describes how to configure export to SIEM systems.
Establishing a background connection
To enable Kaspersky Security Center Web Console perform its background tasks, you have to establish a background connection between Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and Administration Server. You can establish this connection only if your account has the Modify object ACLs right of the General features: User permissions functional area.
If you install plug-in of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows 12.6, or if you update the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows plug-in from the version earlier than 11.7 and a background connection is not established yet, a notification is displayed that you have to establish a background connection. Also, you will have to grant the service account with the rights of the General features: Operations on Administration Server functional area.
To establish a background connection:
- In the main menu, go to Settings → Integration.
- In the Integration section, switch the toggle button for establishing a background connection to the position: Background connection for integration Enabled.
- In the opened Enable a background connection section, click the OK button.
The background connection between Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and Administration Server is established. Administration Server creates an account for the background connection and this account is used as a service account to maintain interaction between Kaspersky Security Center and another Kaspersky application or solution. The name of this service account contains the NWCSvcUser prefix.
Administration Server automatically changes the password of the service account once every 30 days, for security reasons. You cannot delete the service account manually. Administration Server deletes this account automatically when you disable a cross-service connection. Administration Server creates a single service account for each Administration Console and assigns all the service accounts to the security group with the name ServiceNwcGroup. Administration Server creates this security group automatically during the Kaspersky Security Center installation process. You cannot delete this security group manually.
Exporting events to SIEM systems
This section describes how to configure export of events to the SIEM systems.
Configuring event export to SIEM systems
Kaspersky Security Center allows configuring by one of the following methods: export to any SIEM system that use Syslog format, export to QRadar, Splunk, ArcSight SIEM systems that use LEEF and CEF formats or export of events to SIEM systems directly from the Kaspersky Security Center database. When you complete this scenario, Administration Server sends events to SIEM system automatically.
Prerequisites
Before you start configuration export of events in the Kaspersky Security Center:
- Learn more about the methods of event export.
- Make sure that you have the values of system settings.
You can perform the steps of this scenario in any order.
The process of export of events to SIEM system consists of the following steps:
- Configuring SIEM system to receive events from Kaspersky Security Center
How-to instructions: Configuring event export in a SIEM system
- Selecting events you want to export to SIEM system:
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Marking events of a Kaspersky application for export in Syslog format, Marking general events for export in Syslog format
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Marking events of a Kaspersky application for export in Syslog format, Marking general events for export in Syslog format
- Configuring export of events to SIEM system using one of the following methods:
- Using TCP/IP, UDP or TLS over TCP protocols.
How-to instructions:
- Administration Console: Configuring export of events to SIEM systems
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console: Configuring export of events to SIEM systems
- Using export of events directly from the Kaspersky Security Center database (a set of public views is provided in the Kaspersky Security Center database; you can find the description of these public views in the klakdb.chm document).
- Using TCP/IP, UDP or TLS over TCP protocols.
Results
After configuring export of events to SIEM system you can view export results if you selected events which you want to export.
Before you begin
When setting up automatic export of events in the Kaspersky Security Center, you must specify some of the SIEM system settings. It is recommended that you check these settings in advance in order to prepare for setting up Kaspersky Security Center.
To successfully configure automatic sending of events to a SIEM system, you must know the following settings:
About events in Kaspersky Security Center
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to receive information about events that occur during the operation of Administration Server and Kaspersky applications installed on managed devices. Information about events is saved in the Administration Server database. You can export this information to external SIEM systems. Exporting event information to external SIEM systems enables administrators of SIEM systems to promptly respond to security system events that occur on managed devices or administration groups.
Event types
In Kaspersky Security Center, there are the following types of events:
- General events. These events occur in all managed Kaspersky applications. An example of a general event is Virus outbreak. General events have strictly defined syntax and semantics. General events are used, for instance, in reports and dashboards.
- Managed Kaspersky applications-specific events. Each managed Kaspersky application has its own set of events.
Event sources
Events can be generated by the following applications:
- Kaspersky Security Center components:
- Managed Kaspersky applications
For details about the events generated by Kaspersky managed applications, refer to the documentation of the corresponding application.
You can view the full list of events that can be generated by an application on the Event configuration tab in the application policy. For Administration Server, you can additionally view the event list in the Administration Server properties.
Importance level of events
Each event has its own importance level. Depending on the conditions of its occurrence, an event can be assigned various importance levels. There are four importance levels of events:
- A critical event is an event that indicates the occurrence of a critical problem that may lead to data loss, an operational malfunction, or a critical error.
- A functional failure is an event that indicates the occurrence of a serious problem, error or malfunction that occurred during operation of the application or while performing a procedure.
- A warning is an event that is not necessarily serious, but nevertheless indicates a potential problem in the future. Most events are designated as warnings if the application can be restored without loss of data or functional capabilities after such events occur.
- An info event is an event that occurs for the purpose of informing about successful completion of an operation, proper functioning of the application, or completion of a procedure.
Each event has a defined storage term, during which you can view or modify it in Kaspersky Security Center. Some events are not saved in the Administration Server database by default because their defined storage term is zero. Only events that will be stored in the Administration Server database for at least one day can be exported to external systems.
About event export
You can use event export within centralized systems that deal with security issues on an organizational and technical level, provide security monitoring services, and consolidate information from different solutions. These are SIEM systems, which provide real-time analysis of security alerts and events generated by network hardware and applications, or Security Operation Centers (SOCs).
These systems receive data from many sources, including networks, security, servers, databases, and applications. SIEM systems also provide functionality to consolidate monitored data in order to help you avoid missing critical events. In addition, the systems perform automated analysis of correlated events and alerts in order to notify the administrators of immediate security issues. Alerting can be implemented through a dashboard or can be sent through third-party channels such as email.
The process of exporting events from Kaspersky Security Center to external SIEM systems involves two parties: an event sender—Kaspersky Security Center and an event receiver—SIEM system. To successfully export events, you must configure this in your SIEM system and in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console. It does not matter which side you configure first. You can configure the transmission of events in the Kaspersky Security Center and then configure the receipt of events by the SIEM system, or vice versa.
Methods for sending events from Kaspersky Security Center
There are three methods for sending events from Kaspersky Security Center to external systems:
- Sending events over the Syslog protocol to any SIEM system
Using the Syslog protocol, you can relay any events that occur on the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and in Kaspersky applications that are installed on managed devices. The Syslog protocol is a standard message-logging protocol. You can use it to export events to any SIEM system.
For this purpose, you need to mark the events that you want to relay to the SIEM system. You can mark the events in Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. Only marked events will be relayed to the SIEM system. If you marked nothing, no events will be relayed.
- Sending events over the CEF and LEEF protocols to QRadar, Splunk, and ArcSight systems
You can use the CEF and LEEF protocols to export general events. When exporting events over the CEF and LEEF protocols, you do not have the capability to select specific events to export. Instead, all general events are exported. To convert Kaspersky Security Center events to events in the CEF and LEEF format, you can use the siem_conversion_rules.xml file. This file contains the list of Kaspersky Security Center event attributes and corresponding attributes of events in the CEF and LEEF format. Also, the siem_conversion_rules.xml file contains the rules for generating messages corresponding to events. This file is included in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit.
Unlike the Syslog protocol, the CEF and LEEF protocols are not universal. CEF and LEEF are intended for the appropriate SIEM systems (QRadar, Splunk, and ArcSight). Therefore, when you choose to export events over one of these protocols, you use the required parser in the SIEM system.
- Directly from the Kaspersky Security Center database to any SIEM system
This method of exporting events can be used to receive events directly from public views of the database by means of SQL queries. The results of a query are saved to an XML file that can be used as input data for an external system. Only events available in public views can be exported directly from the database.
Receipt of events by the SIEM system
The SIEM system must receive and correctly parse events received from Kaspersky Security Center. For these purposes, you must properly configure the SIEM system. The configuration depends on the specific SIEM system utilized. However, there are a number of general steps in the configuration of all SIEM systems, such as configuring the receiver and the parser.
About configuring event export in a SIEM system
The process of exporting events from Kaspersky Security Center to external SIEM systems involves two parties: an event sender—Kaspersky Security Center and an event receiver—SIEM system. You must configure the export of events in your SIEM system and in the Kaspersky Security Center.
The settings that you specify in the SIEM system depend on the particular system that you are using. Generally, for all SIEM systems you must set up a receiver and, optionally, a message parser to parse received events.
Setting up the receiver
To receive events sent by Kaspersky Security Center, you must set up the receiver in your SIEM system. In general, the following settings must be specified in the SIEM system:
Depending on the SIEM system that you use, you may have to specify some additional receiver settings.
The figure below shows the receiver setup screen in ArcSight.

Receiver setup in ArcSight
Message parser
Exported events are passed to SIEM systems as messages. These messages must be properly parsed so that information on the events can be used by the SIEM system. Message parsers are part of the SIEM system; they are used to split the contents of the message into the relevant fields, such as event ID, severity, description, parameters. This enables the SIEM system to process events received from Kaspersky Security Center so that they can be stored in the SIEM system database.
Marking of events for export to SIEM systems in Syslog format
After enabling automatic export of events, you must select which events will be exported to the external SIEM system.
You can configure export of events in the Syslog format to an external system based on one of the following conditions:
- Marking general events. If you mark events to export in a policy, in the settings of an event, or in the Administration Server settings, the SIEM system will receive the marked events that occurred in all applications managed by the specific policy. If exported events were selected in the policy, you will not be able to redefine them for an individual application managed by this policy.
- Marking events for a managed application. If you mark events to export for a managed application installed on a managed device, the SIEM system will receive only the events that occurred in this application.
About marking events for export to SIEM system in the Syslog format
After enabling automatic export of events, you must select which events will be exported to the external SIEM system.
You can configure export of events in the Syslog format to an external system based on one of the following conditions:
- Marking general events. If you mark events to export in a policy, in the settings of an event, or in the Administration Server settings, the SIEM system will receive the marked events that occurred in all applications managed by the specific policy. If exported events were selected in the policy, you will not be able to redefine them for an individual application managed by this policy.
- Marking events for a managed application. If you mark events to export for a managed application installed on a managed device, the SIEM system will receive only the events that occurred in this application.
Marking events of a Kaspersky application for export in the Syslog format
If you want to export events that occurred in a specific managed application installed on the managed devices, mark the events for export in the application policy. In this case, the marked events are exported from all of the devices included in the policy scope.
To mark events for export for a specific managed application:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy of the application for which you want to mark events.
The policy settings window opens.
- Go to the Event configuration section.
- Select the check boxes next to the events that you want to export to a SIEM system.
- Click the Mark for export to SIEM system by using Syslog button.
You can also mark an event for export to a SIEM system in the Event registration section, which opens by clicking the link of the event.
- A check mark (
 ) appears in the Syslog column of the event or events that you marked for export to the SIEM system.
) appears in the Syslog column of the event or events that you marked for export to the SIEM system. - Click the Save button.
The marked events from the managed application are ready to be exported to a SIEM system.
You can mark which events to export to a SIEM system for a specific managed device. If previously exported events were marked in an application policy, you will not be able to redefine the marked events for a managed device.
To mark events for export for a managed device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
The list of managed devices is displayed.
- Click the link with the name of the required device in the list of managed devices.
The properties window of the selected device is displayed.
- Go to the Applications section.
- Click the link with the name of the required application in the list of applications.
- Go to the Event configuration section.
- Select the check boxes next to the events that you want to export to SIEM.
- Click the Mark for export to SIEM system by using Syslog button.
Also, you can mark an event for export to a SIEM system in the Event registration section, that opens by clicking the link of the event.
- A check mark (
 ) appears in the Syslog column of the event or events that you marked for export to the SIEM system.
) appears in the Syslog column of the event or events that you marked for export to the SIEM system.
From now on, Administration Server sends the marked events to the SIEM system if export to the SIEM system is configured.
Marking general events for export in Syslog format
You can mark general events that Administration Server will export to SIEM systems by using the Syslog format.
To mark general events for export to a SIEM system:
- Do one of the following:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. - In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles, and then click a link of a policy.
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
- In the window that opens, go to the Event configuration tab.
- Click Mark for export to SIEM system by using Syslog.
Also, you can mark an event for export to SIEM system in the Event registration section, that opens by clicking the link of the event.
- A check mark (
 ) appears in the Syslog column of the event or events that you marked for export to the SIEM system.
) appears in the Syslog column of the event or events that you marked for export to the SIEM system.
From now on, Administration Server sends the marked events to the SIEM system if export to the SIEM system is configured.
About exporting events using CEF and LEEF formats
You can use the CEF and LEEF formats to export to SIEM systems general events, as well as the events transferred by Kaspersky applications to the Administration Server. The set of export events is predefined, and you cannot select the events to be exported. Before sending events to the SIEM system (QRadar, ArcSight, or Splunk), it is necessary to interpret Kaspersky Security Center events to events in the CEF and LEEF format by using the rules specified in the siem_conversion_rules.xml file.
Select the format of export on the basis of the SIEM system used. The table below shows SIEM systems and the corresponding formats of export.
Formats of event export to a SIEM system
SIEM system |
Format of export |
|---|---|
QRadar |
LEEF |
ArcSight |
CEF |
Splunk |
CEF |
- LEEF (Log Event Extended Format)—A customized event format for IBM Security QRadar SIEM. QRadar can integrate, identify, and process LEEF events. LEEF events must use UTF-8 character encoding. You can find detailed information on LEEF protocol in IBM Knowledge Center.
- CEF (Common Event Format)—An open log management standard that improves the interoperability of security-related information from different security and network devices and applications. CEF enables you to use a common event log format so that data can easily be integrated and aggregated for analysis by an enterprise management system. CEF events must use UTF-8 character encoding.
Automatic export means that Kaspersky Security Center sends general events to the SIEM system. Automatic export of events starts immediately after you enable it. This section explains in detail how to enable automatic event export.
Converting events to the CEF or LEEF format
Before sending events to the SIEM system (QRadar, ArcSight, or Splunk), it is necessary to interpret Kaspersky Security Center events to events in the CEF and LEEF format by using the rules specified in the siem_conversion_rules.xml file. This file is included in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit.
The siem_conversion_rules.xml file contains the predefined interpretation rules to convert events to the CEF and LEEF format. If you want to use additional event interpretation rules, you can add them to the file manually.
The siem_conversion_rules.xml file includes the <product name="SP_QRADAR" vendor="IBM"> and <product name="SP_QRADAR" vendor="IBM"> sections. The <product name="SP_QRADAR" vendor="IBM"> section contains rules for generating events in the LEEF format, which can be exported to the QRadar SIEM system. The <product name="SP_ARCSIGHT" vendor="HP"> section contains rules for generating events in the CEF format, which can be exported to the ArcSight or Splunk SIEM system.
Each section has the <common> subsection, in which Kaspersky Security Center event attributes and corresponding attributes of events in the LEEF format are located. These common attributes are used for all types of events that can be exported.
Also, each section has the <event> subsections. Each <event> subsection contains additional attributes that are added to those listed in the <common> section.
You can add a new event generation rule to the siem_conversion_rules.xml file manually.
To add a new event generation rule,
Add a new <event> subsection to the <product name="SP_QRADAR" vendor="IBM"> or <product name="SP_QRADAR" vendor="IBM"> section, and then specify the additional event attributes, if needed.
If an event consist only of common attributes, the <event> subsection will be empty.
siem_conversion_rules.xml
About exporting events using Syslog format
You can use the Syslog format to export to SIEM systems the events that occur in Administration Server and other Kaspersky applications installed on managed devices.
Syslog is a standard for message logging protocol. It permits separation of the software that generates messages, the system that stores them, and the software that reports and analyzes them. Each message is labeled with a facility code, indicating the software type that generates the message, and is assigned a severity level.
The Syslog format is defined by Request for Comments (RFC) documents published by the Internet Engineering Task Force (internet standards). The RFC 5424 standard is used to export the events from Kaspersky Security Center to external systems.
In Kaspersky Security Center, you can configure export of the events to the external systems using the Syslog format.
The export process consists of two steps:
- Enabling automatic event export. At this step, Kaspersky Security Center is configured so that it sends events to the SIEM system. Kaspersky Security Center starts sending events immediately after you enable automatic export.
- Selecting the events to be exported to the external system. At this step, you select which event to export to the SIEM system.
Configuring Kaspersky Security Center for export of events to a SIEM system
To export events to a SIEM system, you have to configure the process of export in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Before sending events to the SIEM system (QRadar, ArcSight, or Splunk), it is necessary to interpret Kaspersky Security Center events to events in the CEF and LEEF format by using the rules specified in the siem_conversion_rules.xml file.
To configure export to SIEM systems in the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Export to SIEM section.
- Click the Settings link.
The Export settings section opens.
- Specify the settings in the Export settings section:
If you select the System log data format, you must specify:
- If you want, you can export archived events from the Administration Server database and set the start date from which you want to start the export of archived events:
- Click the Set the export start date link.
- In the section that opens, specify the start date in the Start date of system events export field.
- Click the OK button.
- Switch the option to the Automatically export events to SIEM system database Enabled position.
- To check that the SIEM system connection is successfully configured, click the Check connection button.
The connection with the SIEM system server is established, and a test event is sent. The connection status will be displayed.
- Click the Save button.
Export to SIEM system is configured.
Exporting events directly from the database
You can retrieve events directly from the Kaspersky Security Center database without having to use the Kaspersky Security Center interface. You can either query the public views directly and retrieve the event data, or create your own views on the basis of existing public views and address them to get the data you need.
Public views
For your convenience, a set of public views is provided in the Kaspersky Security Center database. You can find the description of these public views in the klakdb.chm document.
The v_akpub_ev_event public view contains a set of fields that represent the event parameters in the database. In the klakdb.chm document you can also find information on public views corresponding to other Kaspersky Security Center entities, for example, devices, applications, or users. You can use this information in your queries.
This section contains instructions for executing an SQL query by means of the klsql2 utility and a query example.
To create SQL queries or database views, you can also use any other program for working with databases. Information on how to view the parameters for connecting to the Kaspersky Security Center database, such as instance name and database name, is given in the corresponding section.
Executing an SQL query using the klsql2 utility
This article describes how to download and use the klsql2 utility, and how to execute an SQL query by using this utility.
To use the klsql2 utility:
- Locate the klsql2 utility in the installation folder of Kaspersky Security Center. The default installation path is <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center. Do not use klsql2 utility versions intended for older Kaspersky Security Center versions.
- Create a file with the .sql extension in any text editor and place the file in the same folder with the utility.
- In the created .sql file, type the SQL query that you want, and then save the file.
- On the device with Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server installed, in the command line, type the following command to execute the SQL query from the .sql file and save the results to the result.xml file:
klsql2 -i src.sql -u <username> -p <password> -o result.xmlwhere
<username>and<password>are credentials of the user account that has access to the database. - If required, enter the login and password of the user account that has access to the database.
- Open the newly created result.xml files to view the SQL query results.
You can edit the .sql file and create any SQL query to the public views. Then, from the command line, execute your SQL query and save the results to a file.
Example of an SQL query in the klsql2 utility
This section shows an example of an SQL query, executed by means of the klsql2 utility.
The following examples illustrate retrieval of the events that occurred on devices during the last seven days, and display of the events ordered by the time they occur, the most recent events are displayed first.
Example for Microsoft SQL Server: SELECT e.nId, /* event identifier */ e.tmRiseTime, /* time, when the event occurred */ e.strEventType, /* internal name of the event type */ e.wstrEventTypeDisplayName, /* displayed name of the event */ e.wstrDescription, /* displayed description of the event */ e.wstrGroupName, /* name of the group, where the device is located */ h.wstrDisplayName, /* displayed name of the device, on which the event occurred */ CAST(((h.nIp / 16777216) & 255) AS varchar(4)) + '.' + CAST(((h.nIp / 65536) & 255) AS varchar(4)) + '.' + CAST(((h.nIp / 256) & 255) AS varchar(4)) + '.' + CAST(((h.nIp) & 255) AS varchar(4)) as strIp /* IP address of the device, on which the event occurred */ FROM v_akpub_ev_event e INNER JOIN v_akpub_host h ON h.nId=e.nHostId WHERE e.tmRiseTime>=DATEADD(Day, -7, GETUTCDATE()) ORDER BY e.tmRiseTime DESC |
Example for PostgreSQL: SELECT "e"."nId", /* event identifier */ "e"."tmRiseTime", /* time, when the event occurred */ "e"."strEventType", /* internal name of the event type */ "e"."wstrEventTypeDisplayName", /* displayed name of the event */ "e"."wstrDescription", /* displayed description of the event */ "e"."wstrGroupName", /* displayed description of the event */ "h"."wstrDisplayName", /* displayed name of the device, on which the event occurred */ ( CAST((("h"."nIp" / 16777216 )& 255 ) AS VARCHAR(4)) || '.' || CAST((("h"."nIp" / 65536 )& 255 ) AS VARCHAR(4)) || '.' || CAST((("h"."nIp" / 256 )& 255 ) AS VARCHAR(4)) || '.' || CAST((("h"."nIp" )& 255 ) AS VARCHAR(4)) ) AS "strIp" /* IP address of the device, on which the event occurred */ FROM "v_akpub_ev_event" AS "e" INNER JOIN "v_akpub_host" AS "h" ON "h"."nId" = "e"."nHostId" WHERE "e"."tmRiseTime" >= NOW() AT TIME ZONE 'utc' + make_interval(days => CAST(-7 AS INT)) ORDER BY "e"."tmRiseTime" DESC ; |
Example for MySQL or MariaDB: SELECT `e`.`nId`, /* event identifier */ `e`.`tmRiseTime`, /* time, when the event occurred */ `e`.`strEventType`, /* internal name of the event type */ `e`.`wstrEventTypeDisplayName`, /* displayed name of the event */ `e`.`wstrDescription`, /* displayed description of the event */ `e`.`wstrGroupName`, /* device group name */ `h`.`wstrDisplayName`, /* displayed name of the device, on which the event occurred */ CONCAT( LEFT(CAST(((`h`.`nIp` DIV 1677721) & 255) AS CHAR), 4), '.', LEFT(CAST(((`h`.`nIp` DIV 65536) & 255) AS CHAR), 4), '.', LEFT(CAST(((`h`.`nIp` DIV 256) & 255) AS CHAR), 4), '.', LEFT(CAST(((`h`.`nIp`) & 255) AS CHAR), 4) ) AS `strIp` /* IP address of the device, on which the event occurred */ FROM `v_akpub_ev_event` AS `e` INNER JOIN `v_akpub_host` AS `h` ON `h`.`nId` = `e`.`nHostId` WHERE `e`.`tmRiseTime` >= ADDDATE( UTC_TIMESTAMP( ) , INTERVAL -7 DAY) ORDER BY `e`.`tmRiseTime` DESC ; |
Viewing the Kaspersky Security Center database name
If you want to access Kaspersky Security Center database by means of the SQL Server, MySQL, or MariaDB database management tools, you must know the name of the database in order to connect to it from your SQL script editor.
To view the name of the Kaspersky Security Center database:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Details of current database section.
The database name is specified in the Database name field. Use the database name to address the database in your SQL queries.
Viewing export results
You can control for successful completion of the event export procedure. To do this, check whether messages with export events are received by your SIEM system.
If the events sent from Kaspersky Security Center are received and properly parsed by your SIEM system, configuration on both sides is done properly. Otherwise, check the settings you specified in Kaspersky Security Center against the configuration in your SIEM system.
The figure below shows the events exported to ArcSight. For example, the first event is a critical Administration Server event: "Device status is Critical".
The representation of export events in the SIEM system varies according to the SIEM system you use.

Example of events
Working with Kaspersky Security Center Web Console in a cloud environment
This section provides information about Kaspersky Security Center Web Console features related to deployment and maintenance of Kaspersky Security Center in cloud environments, such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
To work within a cloud environment, you need a special license. If you do not have such a license, the interface elements related to cloud devices are not displayed.
Cloud environment configuration in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
To configure Kaspersky Security Center by using the Configure cloud environment wizard, you must have the following:
- Specific credentials for a cloud environment:
- An IAM role that has been granted the right to poll the cloud segment or an IAM user account that has been granted the right to poll the cloud segment (for work with Amazon Web Services)
- Azure Application ID, password, and subscription (for work with Microsoft Azure)
- Google client email, Project ID, and private key (for work with Google Cloud)
- Installation packages:
- Network Agent for Windows
- Network Agent for Linux
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- Web plug-in for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- At least one of the following:
- Installation package and web plug-in for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (recommended)
- Installation package and web plug-in for Kaspersky Security for Windows Server
The Configure cloud environment wizard starts automatically at the first connection to Administration Server through Administration Console if you deploy Kaspersky Security Center from a ready-to-use image. You can also start the wizard manually at any time.
To start the Configure cloud environment wizard manually,
In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Configure cloud environment.
The wizard starts.
An average work session for cloud environment configuration lasts about 15 minutes.
Step 1. Checking the required plug-ins and installation packages
This step is not displayed if you have all of the required web plug-ins and installation packages listed below.
To configure a cloud environment, you must have the following components:
- Installation packages:
- Network Agent for Windows
- Network Agent for Linux
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- Web plug-in for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- At least one of the following:
- Installation package and web plug-in for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (recommended)
- Installation package and web plug-in for Kaspersky Security for Windows Server
We recommend that you use Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows instead of Kaspersky Security for Windows Server.
Kaspersky Security Center automatically detects the components that you already have and lists only ones that are missing. Download the listed components by clicking the Select applications to download button, and then selecting the required plug-ins and installation packages. After you download a component, you can use the Refresh button to update the list of missing components.
Step 2. Licensing the application
This step is displayed only if you are using a BYOL AMI and you have not activated the application with a Kaspersky Security for Virtualization license or a Kaspersky Hybrid Cloud Security license.
Specify the license key and click Next to proceed.
The license key is added to the Administration Server storage.
If you run the wizard again, this step is not displayed.
Page top
Step 3. Selecting the cloud environment and authorization
This section describes features applicable only to Kaspersky Security Center 12.1 or a later version.
Specify the following settings:
Enter your credentials to receive authorization in the cloud environment that you specified.
AWS
If you selected AWS as the cloud segment type, you need an IAM role or an AWS IAM access key for further polling of the cloud segment.
- AWS IAM role assigned to an EC2 instance
Select this option if you have an IAM role with the required rights for the Administration Server.
- AWS IAM user
Select this option if you have an AWS IAM access key. Enter your key data:
- Access key ID
- Secret key
To see the characters that you entered, click and hold the Show button.
Azure
If you selected Azure as the cloud segment type, specify the following settings for the connection that will be used for further polling of the cloud segment:
- Azure Application ID
- Azure Subscription ID
- Azure Application password
To see the characters that you entered, click and hold the Show button.
- Azure storage account name
- Azure storage access key
To see the characters that you entered, click and hold the Show button.
Google Cloud
If you selected Google Cloud as the cloud segment type, specify the following settings for the connection that will be used for further polling the cloud segment:
- Client email address
- Project ID
- Private key
To see the characters that you entered, click and hold the Show button.
The connection that you specified is saved in the application settings.
The Configure cloud environment wizard allows you to specify only one segment. Later, you can specify more connections to manage other cloud segments.
Click Next to proceed.
Step 4. Segment polling, configuring synchronization with Cloud and choosing further actions
At this step, cloud segment polling starts, and a special administration group for cloud devices is automatically created. The devices found during polling are placed into this group. The cloud segment polling schedule is configured (every 5 minutes by default; you can change this setting later).
A Synchronize with Cloud automatic moving rule is also created. For each subsequent scan of the cloud network, virtual devices detected will be moved to the corresponding subgroup within the Managed devices\Cloud group.
Define the following settings:
If you select the Deploy protection option, the Restarting devices section becomes available. In this section, you must choose what to do when the operating system of a target device has to be restarted. Select whether to restart instances if the device operating system has to be restarted during installation of applications:
Click Next to proceed.
For Google Cloud, you can only perform deployment with Kaspersky Security Center native tools. If you selected Google Cloud, the Deploy protection option is not available.
Step 5. Selecting an application to create a policy and tasks for
This step is only displayed if you have installation packages and plug-ins for both Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows and Kaspersky Security for Windows Server. If you have a plug-in and an installation package for only one of those applications, this step is skipped and Kaspersky Security Center creates a policy and tasks for the existing application.
Select an application for which you want to create a policy and tasks:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Kaspersky Security for Windows Server
Step 6. Configuring Kaspersky Security Network for Kaspersky Security Center
Specify the settings for relaying information about Kaspersky Security Center operations to the Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) knowledge base. Select one of the following options:
Kaspersky recommends participation in Kaspersky Security Network.
KSN agreements for managed applications may also be displayed. If you agree to use Kaspersky Security Network, the managed application will send data to Kaspersky. If you do not agree to participate in Kaspersky Security Network, the managed application will not send data to Kaspersky. (You can change this setting later in the application policy.)
Click Next to proceed.
Page top
Step 7. Creating an initial configuration of protection
You can check a list of policies and tasks that are created.
Wait for the creation of policies and tasks to complete, and then click Next to proceed. On the last page of the wizard, click the Finish button to exit.
Page top
Network segment polling via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
Information about the structure of the network (and devices in it) is received by Administration Server through regular polling of cloud segments by using AWS API, Azure API, or Google API tools. Kaspersky Security Center uses this information to update the contents of the Unassigned devices and Managed devices folders. If you have configured devices to be moved to administration groups automatically, detected devices are included in administration groups.
To allow the Administration Server to poll cloud segments, you must have the corresponding rights that are provided with an IAM role or IAM user account (in AWS), or with Application ID and password (in Azure), or with a Google client email, Google project ID, and private key (in Google Cloud).
You can add and delete connections, as well as set the polling schedule, for each cloud segment.
Adding connections for cloud segment polling
To add a connection for cloud segment polling to the list of available connections:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Discovery → Cloud.
- In the window that opens, click Properties.
- In the Settings window that opens, click Add.
The Cloud segment settings window opens.
- Specify the name of the cloud environment for the connection that will be used for further polling of the cloud segment:
- Enter your credentials to receive authorization in the cloud environment that you specified.
- If you selected AWS, specify the following settings:
- Use AWS IAM role
- AWS IAM user account credentials
If you specified that you have AWS IAM user account credentials, specify the following:
To see the characters that you entered, click and hold the Show button.
- If you selected Azure, specify the following settings:
- Azure Application ID
- Azure Subscription ID
- Azure Application password
To see the characters that you entered, click and hold the Show button.
- Azure storage account name
- Azure storage access key
To see the characters that you entered, click and hold the Show button.
If you selected Google Cloud, specify the following settings:
- Client email address
- Project ID
- Private key
To see the characters that you entered, click and hold the Show button.
- If you selected AWS, specify the following settings:
- If you want, click Set polling schedule and change the default settings.
The connection is saved in the application settings.
After the new cloud segment is polled for the first time, the subgroup corresponding to that segment appears in the Managed devices\Cloud administration group.
If you specify incorrect credentials, no instances will be found during cloud segment polling and a new subgroup will not appear in the Managed devices\Cloud administration group.
Page top
Deleting a connection for cloud segment polling
If you no longer have to poll a specific cloud segment, you can delete the connection corresponding to it from the list of available connections. You can also delete a connection if, for example, permissions to poll a cloud segment have been transferred to another user who has different credentials.
To delete a connection:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Discovery → Cloud.
- In the window that opens, click Properties.
- In the Settings window that opens, click the name of the segment that you want to delete.
- Click Delete.
- In the window that opens, click the OK button to confirm your selection.
The connection is deleted. The devices in the cloud segment corresponding to this connection are automatically deleted from the administration groups.
Page top
Configuring the polling schedule via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
Cloud segment polling is performed according to schedule. You can set the polling frequency.
The polling frequency is automatically set at 5 minutes in the Configure cloud environment settings. You can change this value at any time and set a different schedule. However, it is not recommended to configure polling to run more frequently than every 5 minutes, because this could lead to errors in the API operation.
To configure a cloud segment polling schedule:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Discovery → Cloud.
- In the window that opens, click Properties.
- In the Settings window that opens, click the name of the segment for which you want to configure a polling schedule.
This opens the Cloud segment settings window.
- In the Cloud segment settings window, click the Set polling schedule button.
This opens the Schedule window.
- In the Schedule window, define the following settings:
- Scheduled start
Polling schedule options:
- Every N days
- Every N minutes
- By days of week
- Every month on specified days of selected weeks
- Start interval
- Starting from
- Run missed tasks
- Scheduled start
- Save the changes.
The polling schedule for the segment is configured and saved.
Page top
Viewing the results of cloud segment polling via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
You can view the results of cloud segment polling, that is, view the list of cloud devices managed by the Administration Server.
To view the results of cloud segment polling,
In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Discovery → Cloud.
This displays the cloud segments available for polling.
Page top
Viewing the properties of cloud devices via Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
You can view the properties of each cloud device.
To view the properties of a cloud device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click the name of the device whose properties you want to view.
A properties window opens with the General section selected.
- If you want to view the properties specific for cloud devices, select the System section in the properties window.
The properties are displayed depending on the cloud platform of the device.
For the devices in AWS, the following properties are displayed:
- Device discovered using API (value: AWS)
- Cloud Region
- Cloud VPC
- Cloud availability zone
- Cloud subnet
- Cloud placement group (this unit is only displayed if the instance belongs to a placement group; otherwise, it is not displayed)
For the devices in Azure, the following properties are displayed:
- Device discovered using API (value: Microsoft Azure)
- Cloud Region
- Cloud subnet
For the devices in Google Cloud, the following properties are displayed:
- Device discovered using API (value: Google Cloud)
- Cloud Region
- Cloud VPC
- Cloud availability zone
- Cloud subnet
Synchronization with Cloud: Configuring the moving rule
During the Configure cloud environment operation, the Synchronize with Cloud rule is created automatically. This rule allows you to automatically move devices detected in each poll from the Unassigned devices group to the Managed devices\Cloud group, to make these devices available for centralized management. By default, the rule is active after it is created. You can disable, modify, or enforce the rule at any time.
To edit the properties of the Synchronize with Cloud rule and/or enforce the rule:
- In the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Moving rules.
This opens a list of moving rules.
- In the list of moving rules, select Synchronize with cloud.
This opens the rule properties window.
- If necessary, specify the following settings in the Rule conditions tab, in the Cloud segments tab:
- Device is in a cloud segment
- Include child objects
- Move devices from nested objects to corresponding subgroups
- Create subgroups corresponding to containers of newly detected devices
- Delete subgroups for which no match is found in the cloud segments
If you enabled the Synchronize administration groups with cloud structure option when using the Configure cloud environment, the Synchronize with cloud rule is created with the Create subgroups corresponding to containers of newly detected devices and Delete subgroups for which no match is found in the cloud segments options enabled.
If you did not enable the Synchronize administration groups with cloud structure option, the Synchronize with cloud rule is created with these options disabled (cleared). If your work with Kaspersky Security Center requires that the structure of subgroups in the Managed devices\Cloud subgroup matches the structure of cloud segments, enable the Create subgroups corresponding to containers of newly detected devices and Delete subgroups for which no match is found in the cloud segments options in the rule properties, and then enforce the rule.
- In the Device discovered by using the API drop-down list, select one of the following values:
- No. The device cannot be detected by using AWS, Azure, or Google API, that is, it is either outside the cloud environment, or it is in the cloud environment but it cannot be detected by using an API for some reason.
- AWS. The device is discovered by using AWS API, that is, the device definitely is in the AWS cloud environment.
- Azure. The device is discovered by using Azure API, that is, the device definitely is in the Azure cloud environment.
- Google Cloud. The device is discovered by using Google API, that is, the device definitely is in the Google cloud environment.
- No value. This criterion cannot be applied.
- If necessary, set up other rule properties in the other sections.
The moving rule is configured.
Remote installation of applications to the Azure virtual machines
You must have a valid license to install applications on Microsoft Azure virtual machines.
Kaspersky Security Center supports the following scenarios:
- A client device is discovered by means of Azure API; the installation is also performed by means of an API. Using the Azure API means that you can only install the following applications:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Kaspersky Security for Windows Server
- A client device is discovered by means of Azure API; the installation is performed by means of a distribution point or, if there are no distribution points, manually by using standalone installation packages. You can install any application supported by Kaspersky Security Center in this way.
To create a task for remote installation of an application on Azure virtual machines:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts.
- Follow the instructions of the wizard:
- Select Install application remotely as the task type.
- On the Installation packages page, select Remote installation by Microsoft Azure API.
- When selecting the account to access devices, use an existing Azure account, or click Add and enter the credentials of your Azure account:
- Select the relevant devices from the Managed devices\Cloud group.
After the wizard finishes, the task for remote installation of the application appears in the list of tasks.
Creating Backup of the Administration Server data task by using a cloud DBMS
Backup tasks are Administration Server tasks. You create a backup task if you want to use a DBMS located in a cloud environment (AWS or Azure).
To create an Administration Server data backup task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts.
- On the first page of the wizard, in the Application list, select Kaspersky Security Center 15.1, and in the Task type list, select Backup of Administration Server data.
- On the corresponding page of the wizard, specify the following information:
- If you are working with a database in AWS:
- If you are working with a database in Microsoft Azure:
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks. If you enable the Open task details when creation is complete option, you can modify the default task settings immediately after the task is created. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
Page top
Remote diagnostics of client devices
You can use remote diagnostics for remote execution of the following operations on Windows-based and Linux-based client devices:
- Enabling and disabling tracing, changing the tracing level, and downloading the trace file
- Downloading system information and application settings
- Downloading event logs
- Generating a dump file for an application
- Starting diagnostics and downloading diagnostics reports
- Starting, stopping, and restarting applications
You can use event logs and diagnostics reports downloaded from a client device to troubleshoot problems on your own. Also, if you contact Kaspersky Technical Support, a Technical Support specialist might ask you to download trace files, dump files, event logs, and diagnostics reports from a client device for further analysis at Kaspersky.
Opening the remote diagnostics window
To perform remote diagnostics on Windows-based and Linux-based client devices, you first have to open the remote diagnostics window.
To open the remote diagnostics window:
- To select the device for which you want to open the remote diagnostics window, perform one of the following:
- If the device belongs to an administration group, in the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- If the device belongs to the Unassigned devices group, in the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Unassigned devices.
- Click the name of the required device.
- In the device properties window that opens, select the Advanced tab.
- In the window that opens, click Remote diagnostics.
This opens the Remote diagnostics window of a client device. If connection between Administration Server and the client device is not established, the error message displays.
Alternatively, if you need to obtain all diagnostic information about a Linux-based client device at once, you can run the collect.sh script on this device.
Enabling and disabling tracing for applications
You can enable and disable tracing for applications, including Xperf tracing.
Enabling and disabling tracing
To enable or disable tracing on a remote device:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Kaspersky applications tab.
In the Application management section, the list of Kaspersky applications installed on the device displays.
- In the list of applications, select the application for which you want to enable or disable tracing.
The list of remote diagnostics options opens.
- If you want to enable tracing:
- In the Tracing section, click Enable tracing.
- In the Modify tracing level window that opens, we recommend that you keep the default values of the settings. When required, a Technical Support specialist will guide you through the configuration process. The following settings are available:
- Tracing level
- Rotation-based tracing
This setting is available for Kaspersky Endpoint Security only.
- Click Save.
The tracing is enabled for the selected application. In some cases, the security application and its task must be restarted in order to enable tracing.
On Linux-based client devices, tracing for the Updater of Network Agent component is regulated by the Network Agent settings. Therefore, the Enable tracing and Modify tracing level options are disabled for this component on client devices running Linux.
- If you want to disable tracing for the selected application, click the Disable tracing button.
The tracing is disabled for the selected application.
Enabling Xperf tracing
For Kaspersky Endpoint Security, a Technical Support specialist may ask you to enable Xperf tracing for information about the system performance.
To enable and configure Xperf tracing or disable it:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Kaspersky applications tab.
In the Application management section, the list of Kaspersky applications installed on the device displays.
- In the list of applications, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The list of remote diagnostics options for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows displays.
- In the Xperf tracing section, click Enable Xperf tracing.
If Xperf tracing is already enabled, the Disable Xperf tracing button is displayed instead. Click this button if you want to disable Xperf tracing for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- In the Change Xperf tracing level window that opens, depending on the request from the Technical Support specialist, do the following:
- Select one of the following tracing levels:
- Select one of the following Xperf tracing types:
You may also be asked to enable the Rotation file size, in MB option to prevent excessive increase in the size of the trace file. Then specify the maximum size of the trace file. When the file reaches the maximum size, the oldest tracing information is overwritten with new information.
- Define the rotation file size.
- Click Save.
Xperf tracing is enabled and configured.
- If you want to disable Xperf tracing for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, click Disable Xperf tracing in the Xperf tracing section.
Xperf tracing is disabled.
Downloading trace files of an application
To download a trace file of an application:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Kaspersky applications tab.
In the Application management section, the list of Kaspersky applications installed on the device displays.
- In the list of applications, select the application for which you want to download a trace file.
- In the Tracing section, click the Trace files button.
This opens the Device tracing logs window, where a list of trace files is displayed.
- In the list of trace files, select the file that you want to download.
- Do one of the following:
- Download the selected file by clicking Download. You can select one or several files for downloading.
- Download a portion of the selected file:
- Click Download a portion.
You cannot download portions of several files at the same time. If you select more than one trace file, the Download a portion button will be disabled.
- In the window that opens, specify the name and the file portion to download, according to your needs.
For Linux-based devices, editing the file portion name is not available.
- Click Download.
- Click Download a portion.
The selected file, or its portion, is downloaded to the location that you specify.
Page top
Deleting trace files
You can delete trace files that are no longer needed.
To delete a trace file:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window that opens, select the Event logs tab.
- In the Trace files section, click Windows Update logs or Remote installation logs, depending on which trace files you want to delete.
The Windows Update logs link is available only for Windows-based client devices.
This opens the Device tracing logs window, where a list of trace files is displayed.
- In the list of trace files, select one or several files that you want to delete.
- Click the Remove button.
The selected trace files are deleted.
Page top
Downloading application settings
To download application settings from a client device:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Kaspersky applications tab.
- In the Application settings section, click the Download button to download information about the settings of the applications installed on the client device.
The ZIP archive with information is downloaded to the specified location.
Page top
Downloading event logs
To download an event log from a remote device:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, on the Event logs tab, click All device logs.
- In the All device logs window, select one or several relevant logs.
- Do one of the following:
- Download the selected log by clicking Download entire file.
- Download a portion of the selected log:
- Click Download a portion.
You cannot download portions of several logs at the same time. If you select more than one event log, the Download a portion button will be disabled.
- In the window that opens, specify the name and the log portion to download, according to your needs.
For Linux-based devices, editing the log portion name is not available.
- Click Download.
- Click Download a portion.
The selected event log, or a portion of it, is downloaded to the specified location.
Page top
Starting, stopping, restarting the application
You can start, stop, and restart applications on a client device.
To start, stop, or restart an application:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Kaspersky applications tab.
In the Application management section, the list of Kaspersky applications installed on the device displays.
- In the list of applications, select the application that you want to start, stop, or restart.
- Select an action by clicking one of the following buttons:
- Stop application
This button is available only if the application is currently running.
- Restart application
This button is available only if the application is currently running.
- Start application
This button is available only if the application is not currently running.
Depending on the action that you have selected, the required application is started, stopped, or restarted on the client device.
- Stop application
If you restart the Network Agent, a message is displayed stating that the current connection of the device to the Administration Server will be lost.
Page top
Running the remote diagnostics of Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent and downloading the results
To start diagnostics for Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent on a remote device and download the results:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Kaspersky applications tab.
In the Application management section, the list of Kaspersky applications installed on the device displays.
- In the list of applications, select Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent.
The list of remote diagnostics options opens.
- In the Diagnostics report section, click the Run diagnostics button.
This starts the remote diagnostics process and generates a diagnostics report. When the diagnostics process is complete, the Download diagnostics report button becomes available.
- Click the Download diagnostics report button to download the report.
The report is downloaded to the specified location.
Page top
Running an application on a client device
You may have to run an application on the client device, if a Kaspersky support specialist requests it. You do not have to install the application on that device.
To run an application on the client device:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Running a remote application tab.
- In the Application files section, click the Browse button to select a ZIP archive containing the application that you want to run on the client device.
The ZIP archive must include the utility folder. This folder contains the executable file to be run on a remote device.
You can specify the executable file name and the command-line arguments, if necessary. To do this, fill in the Executable file in an archive to be run on a remote device and Command-line arguments fields.
- Click the Upload and run button to run the specified application on a client device.
- Follow the instructions of the Kaspersky support specialist.
Generating a dump file for an application
An application dump file allows you to view the parameters of the application running on a client device at a point in time. This file also contains information about modules that were loaded for an application.
Obtaining dump files from Linux-based devices is not supported.
To obtain dump files through remote diagnostics, the kldumper utility is used. This utility is designed to obtain the dump files of processes of Kaspersky applications at the request of technical support specialists. Detailed information on the requirements for using the kldumper utility is provided in the Kaspersky Security Center Knowledge Base.
To create a dump file for an application:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Running a remote application tab.
- In the Generating the process dump file section, specify the executable file of the application for which you want to generate a dump file.
- Click the Download dump file button.
An archive with the dump file for the specified application is downloaded.
If the specified application is not running on the client device, the "result" folder contained in the downloaded archive will be empty.
If the specified application is running, but the downloading fails with an error or the "result" folder contained in the downloaded archive is empty, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Knowledge Base.
Running remote diagnostics on a Linux-based client device
Kaspersky Security Center allows you to download the basic diagnostic information from a client device. Alternatively, you can obtain the diagnostic information about a Linux-based device by using the collect.sh script by Kaspersky. This script is run on the Linux-based client device that needs to be diagnosed, and then it generates a file with the diagnostic information, the system information about this device, trace files of applications, device logs, and a dump file for emergency-terminated applications.
We recommend that you use the collect.sh script to obtain all diagnostic information about the Linux-based client device at once. If you download the diagnostic information remotely through Kaspersky Security Center, you will need to go through all sections of the remote diagnostics interface. Also the diagnostic information for a Linux-based device will probably not be obtained completely.
If you need to send the generated file with the diagnostic information to the Kaspersky Technical Support, delete all confidential information before sending the file.
To download the diagnostic information from a Linux-based client device by using the collect.sh script:
- Download the collect.sh script packed in the collect.tar.gz archive.
- Copy the downloaded archive to the Linux-based client device that needs to be diagnosed.
- Run the following command to unpack the collect.tar.gz archive:
# tar -xzf collect.tar.gz - Run the following command to specify the script execution rights:
# chmod +x collect.sh - Run the collect.sh script by using an account with administrator rights:
# ./collect.sh
A file with the diagnostic information is generated and saved to the /tmp/$HOST_NAME-collect.tar.gz folder.
Page top
Downloading and deleting files from Quarantine and Backup
This section gives information on how to download and how to delete files from Quarantine and Backup in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Downloading files from Quarantine and Backup
You can download files from Quarantine and Backup only if one of the two conditions is met: either the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option is enabled in the settings of the device, or a connection gateway is in use. Otherwise, the downloading is not possible.
To save a copy of file from Quarantine or Backup to a hard drive:
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to save a copy of file from Quarantine, in the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories → Quarantine.
- If you want to save a copy of file from Backup, in the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories → Backup.
- In the window that opens, select a file that you want to download and click Download.
The download starts. A copy of the file that had been placed in Quarantine on the client device is saved to the specified folder.
About removing objects from the Quarantine, Backup, or Active threats repositories
When Kaspersky security applications installed on client devices place objects to the Quarantine, Backup, or Active threats repositories, they send the information about the added objects to the Quarantine, Backup, or Active threats sections in Kaspersky Security Center. When you open one of these sections, select an object from the list and click the Remove button, Kaspersky Security Center performs one of the following actions or both actions:
- Removes the selected object from the list
- Deletes the selected object from the repository
The action to perform is defined by the Kaspersky application that placed the selected object to the repository. The Kaspersky application is specified in the Entry added by field. Refer to the documentation of the Kaspersky application for details about which action is to be performed.
Changing the language of the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface
You can select the language of the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console interface.
To change the interface language:
- In the main menu, go to Settings → Language.
- Select one of the supported localization languages.
API Reference Guide
This Kaspersky Security Center OpenAPI reference guide is designed to assist in the following tasks:
- Automation and customization. You can automate tasks that you might not want to handle manually by using Administration Console. You can also implement custom scenarios that are not yet supported in Administration Console. For example, as an administrator, you can use Kaspersky Security Center OpenAPI to create and run scripts that will facilitate developing the structure of administration groups and keep that structure up-to-date.
- Custom development. For example, you can develop an alternative MMC-based Administration Console for your clients, which permits a limited set of actions.
In the OpenAPI reference guide, you can use the search field in the right part of the screen to locate the information you need.
Samples of scripts
The OpenAPI reference guide contains samples of the Python scripts listed in the table below. The samples show how you can call OpenAPI methods and automatically accomplish various tasks for protecting your network, for instance, create a "primary/secondary" hierarchy, run tasks in Kaspersky Security Center, or assign distribution points. You can run the samples as is or create your own scripts based on the samples.
To call the OpenAPI methods and run scripts:
- Download the KlAkOAPI.tar.gz archive. This archive includes the KlAkOAPI package and samples (you can copy them from the archive or the OpenAPI reference guide). The KlAkOAPI.tar.gz archive is also located in the Kaspersky Security Center installation folder.
- Install the KlAkOAPI package from the KlAkOAPI.tar.gz archive on a device where Administration Server is installed.
You can call the OpenAPI methods, run the samples and your own scripts only on devices where Administration Server and the KlAkOAPI package are installed.
Matching between user scenarios and samples of Kaspersky Security Center OpenAPI methods
Sample
Purpose of the sample
Scenario
You can extract and process data by using the
KlAkParamsdata structure. The sample shows how to work with this data structure.The sample output may be present in different ways. You can get the data to send an HTTP method or to use it in your code.
You can add a secondary Administration Server and establish a "primary/secondary" hierarchy. Alternately, you can disconnect the secondary Administration Server from the hierarchy.
Create the group hierarchy with a structure based on the Active Directory unit
You can poll the Active Directory unit and form a hierarchy of discovered device groups.
Create the group hierarchy with a structure based on the cached Active Directory unit
You can form a hierarchy of the managed device groups based on the Active Directory unit polled earlier. If new devices appear in the Active Directory after the last polling, they are not added into the group because they are not in the saved polling results.
Download network list files via connection gateway to the specified device
You can connect to Network Agent on the needed device by using a connection gateway, and then download a file with the network list to your device.
You can connect to the primary Administration Server, download a required license key from it, and transmit this key to all the secondary Administration Servers included in a hierarchy.
You can create different reports. For instance, you can generate the report of effective user rights by using this sample. This report describes the rights that a user has, depending on his or her group and role.
You can download the report in the HTML, PDF, or Excel format.
You can connect to Network Agent on the needed device by using a connection gateway, and then run the necessary task.
Create IP subnets based on Active Directory Site and Services
You can create an IP subnet based on the Active Directory unit that you use.
The sample launches polling of the specified IP range and deletes discovered subnets to avoid their conflict with a new subnet. Therefore, do not run this sample in the network where it is important to keep subnets.
After polling, the sample refers to the Active Directory, examines every device in it, and creates the IP subnet. To do this, the sample uses masks and IP addresses of all devices.
You can assign managed devices as distribution points (previously known as update agents).
You can perform various actions with administration groups. The sample shows how to do the following:
- Get an identifier of the "Managed devices" root group
- Move through the group hierarchy
- Retrieve the full, expanded hierarchy of groups, along with their names and nesting
You can find out the following information:
- Task progress history
- Current task status
- Number of tasks in different statuses
You can also run a task. By default, the sample runs a task after it outputs statistics.
You can create a task. Specify the following task parameters in the sample:
- Type
- Method of run
- Name
- Device group for which the task will be used
By default, the sample creates a task with the "Show message" type. You can run this task for all managed devices of Administration Server. If necessary, you can specify your own task parameters.
You can get a list of all the active license keys for Kaspersky applications installed on managed devices of Administration Server. The list contains detailed data about every license key, such as a name, type, or expiration date.
You can create an account for further work.
You can create the application category with the needed parameters.
Creating an application category with content added manually
You can use the SrvView class to request detailed information from the Administration Server. For instance, you can get a list of users by using this sample.
Applications interacting with Kaspersky Security Center via OpenAPI
Some applications interact with Kaspersky Security Center via OpenAPI. Such applications include, for example, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform or Kaspersky Security for Virtualization. This can also be a custom client application developed by you based on OpenAPI.
Applications interacting with Kaspersky Security Center via OpenAPI connect to Administration Server. If you have configured an allowlist of IP addresses for connecting to the Administration Server, add IP addresses of devices where applications using Kaspersky Security Center OpenAPI are installed. To find out whether the application that you use works by OpenAPI, see Help of this application.
Page top
Best Practices for Service Providers
This section provides information about how to configure and use Kaspersky Security Center.
This section contains recommendations on how to deploy, configure, and use the application, as well as describes ways of resolving typical issues in the application operation.
Planning Kaspersky Security Center deployment
When planning the deployment of Kaspersky Security Center components on an organization's network, you must take into account the size and scope of the project; specifically, the following factors:
- Total number of devices
- Number of MSP clients
One Administration Server can support a maximum of 100,000 devices. If the total number of devices on an organization's network exceeds 100,000, multiple Administration Servers must be deployed on the service provider side and combined into a hierarchy for convenient centralized management.
Up to 500 virtual Servers can be created on a single Administration Server, so an individual Administration Server is required for each 500 MSP clients.
At the stage of deployment planning, the assignment of the special certificate X.509 to the Administration Server must be considered. Assignment of the X.509 certificate to the Administration Server may be useful in the following cases (partial list):
- Inspecting secure socket layer (SSL) traffic by means of an SSL termination proxy
- Specifying required values in certificate fields
- Providing the required encryption strength of a certificate
Providing internet access to Administration Server
To allow devices on the client network to access Administration Server over the internet, you have to make available the following Administration Server ports:
- 13000 TCP—Administration Server TLS port for connecting Network Agents deployed on the client network
- 8061 TCP—HTTPS port for publishing stand-alone packages using Administration Console tools
- 8060 TCP—HTTP port for publishing stand-alone packages using Administration Console tools
- 13292 TCP—TLS port required only if there are mobile devices that need to be managed
If you need to provide clients with basic options of network administration through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, you also have to open the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console port 8080 TCP (HTTPS port).
Page top
Kaspersky Security Center standard configuration
One or several Administration Servers are deployed on the MSPs' servers. The number of Administration Servers can be selected either based on available hardware, or on the total number of MSP clients served or total number of managed devices.
One Administration Server can support up to 100,000 devices. You must consider the possibility of increasing the number of managed devices in the near future: it may be useful to connect a slightly smaller number of devices to a single Administration Server.
Up to 500 virtual Servers can be created on a single Administration Server, so an individual Administration Server is required for each 500 MSP clients.
If multiple Servers are used, it is recommended that you combine them into a hierarchy. Using a hierarchy of Administration Servers allows you to avoid dubbed policies and tasks, handle the whole set of managed devices, as if they are managed by a single Administration Server: i.e., search for devices, build selections of devices, and create reports.
On each virtual Server that corresponds to an MSP client, you must assign one or several distribution point(s). If MSP clients and the Administration Server are linked through the internet, it may be useful to create a Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task for the distribution points, so that they will download updates directly from Kaspersky servers, not from the Administration Server.
If some devices in the MSP client network have no direct internet access, you have to switch the distribution points to the connection gateway mode. In this case, Network Agents on devices on the MSP client network will be connected, for further synchronization, to the Administration Server—but through the gateway, not directly.
As the Administration Server, most probably, will not be able to poll the on the MSP client network, it may be useful to turn this function over to a distribution point.
The Administration Server will not be able to send notifications to port 15000 UDP to managed devices located behind the NAT on the MSP client network. To resolve this issue, it may be useful to enable the mode of continuous connection to the Administration Server in the properties of devices acting as distribution points and running in connection gateway mode (Do not disconnect from the Administration Server check box). The continuous connection mode is available if the total number of distribution points does not exceed 300.
Page top
About distribution points
Device with Network Agent installed can be used as distribution point. In this mode, Network Agent can perform the following functions:
- Transfer files to client devices, including:
- Updates of Kaspersky databases and software modules
The updates can be retrieved either from the Administration Server or from Kaspersky servers. In the latter case, the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points task must be created for the device serving as the distribution point.
- Third-party software updates
- Installation packages
- Windows updates when you use Administration Server as a WSUS server
- Updates of Kaspersky databases and software modules
- Install software (including initial deployment of Network Agents) on other devices.
- Poll the network to detect new devices and update information about existing ones. A distribution point can apply the same device discovery methods as the Administration Server.
Deployment of distribution points on an organization's network pursues the following objectives:
- Reduce the load on the Administration Server if it functions as the update source.
- Optimize internet traffic since, in this case, each device on the MSP client network does not have to access Kaspersky servers or the Administration Server for updates.
- Provide the Administration Server access to devices behind the NAT (relative to the Administration Server) of the MSP client network, which allows the Administration Server to perform the following actions:
- Send notifications to devices over UDP on the IPv4 or IPv6 network
- Poll the IPv4 or IPv6 network
- Perform initial deployment
- Act as a push server
A distribution point is assigned for an administration group. In this case, the distribution point's scope includes all devices within the administration group and all of its subgroups. However, the device acting as the distribution point does not have to be included in the administration group to which it has been assigned.
You can make a distribution point function as a connection gateway. In this case, devices in the scope of this distribution point will be connected to the Administration Server through the gateway, not directly. You can use this mode in scenarios that do not allow the establishment of a direct connection between devices with Network Agent and an Administration Server.
Devices functioning as distribution points must be protected, including physical protection, against any unauthorized access.
Hierarchy of Administration Servers
An MSP may run multiple Administration Servers. It can be inconvenient to administer several separate Administration Servers, so a hierarchy can be applied. A "primary/secondary" configuration for two Administration Servers provides the following options:
- A secondary Administration Server inherits policies and tasks from the primary Administration Server, thus preventing duplication of settings.
- Selections of devices on the primary Administration Server can include devices from secondary Administration Servers.
- Reports on the primary Administration Server can contain data (including detailed information) from secondary Administration Servers.
The primary Administration Server only receives data from non-virtual secondary Administration Servers within the scope of the options listed above. This limitation does not apply to virtual Administration Servers, which share the database with their primary Administration Server.
Page top
Virtual Administration Servers
On the basis of a physical Administration Server, multiple virtual Administration Servers can be created, which will be similar to secondary Administration Servers. Compared to the discretionary access model, which is based on access control lists (ACLs), the virtual Administration Server model is more functional and provides a larger degree of isolation. In addition to a dedicated structure of administration groups for assigned devices with policies and tasks, each virtual Administration Server features its own group of unassigned devices, own sets of reports, selected devices and events, installation packages, moving rules, etc. For maximum mutual isolation of MSP clients, we recommend that you choose virtual Administration Servers as the functionality to be used. In addition, creating a virtual Administration Server for each MSP client allows you to provide clients basic options of network administration through Kaspersky Security Center Web Console.
Virtual Administration Servers are very similar to secondary Administration Servers, but with the following distinctions:
- A virtual Administration Server lacks most global settings and its own TCP ports.
- A virtual Administration Server has no secondary Administration Servers.
- A virtual Administration Server has no other virtual Administration Servers.
- A physical Administration Server views devices, groups, events, and objects on managed devices (items in Quarantine, applications registry, etc.) of all its virtual Administration Servers.
- A virtual Administration Server can only scan the network with distribution points connected.
Managing mobile devices with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android
Mobile devices with installed Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android (hereinafter referred to as KES devices) are managed by means of the Administration Server. Kaspersky Security Center supports the following features for managing KES devices:
- Handling mobile devices as client devices:
- Membership in administration groups
- Monitoring, such as viewing statuses, events, and reports
- Modifying local settings and assigning policies for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android
- Sending commands in centralized mode
- Installing mobile apps packages remotely
Administration Server manages KES devices through TLS, TCP port 13292.
Deployment and initial setup
Kaspersky Security Center is a distributed application. Kaspersky Security Center includes the following applications:
- Administration Server—The core component, designed for managing devices of an organization and storing data in a DBMS.
- Administration Console—The basic tool for the administrator. Administration Console is shipped together with Administration Server, but it can also be installed individually on one or several devices run by the administrator.
- Kaspersky Security Center Web Console—A web interface for Administration Server designed for basic operations. You can install this component on any device that meets the hardware and software requirements.
- Network Agent—Designed for managing the security application installed on a device, as well as getting information about that device. Network Agents are installed on devices of an organization.
Deployment of Kaspersky Security Center on an organization's network is performed as follows:
- Installation of Administration Server
- Installation of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Installation of Administration Console on the administrator's device
- Installation of Network Agent and the security application on devices of the enterprise
Recommendations on Administration Server installation
This section contains recommendations on how to install Administration Server. This section also provides scenarios for using a shared folder on the Administration Server device in order to deploy Network Agent on client devices.
Creating accounts for the Administration Server services on a failover cluster
By default, the installer automatically creates non-privileged accounts for services of Administration Server. This behavior is the most convenient for Administration Server installation on an ordinary device.
However, installation of Administration Server on a failover cluster requires a different scenario:
- Create non-privileged domain accounts for services of Administration Server and make them members of a global domain security group named KLAdmins.
- In the Administration Server Installer, specify the domain accounts that have been created for the services.
Selecting a DBMS
When selecting the database management system (DBMS) to be used by an Administration Server, you must take into account the number of devices covered by the Administration Server.
The following table lists the valid DBMS options, as well as the recommendations and restrictions on their use.
Recommendations and restrictions on DBMS
DBMS |
Recommendations and restrictions |
|---|---|
SQL Server Express Edition 2016 or later |
Use this DBMS if you intend to run a single Administration Server for less than 10,000 devices. It is recommended to disable the Software inventory task and disable (in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings) notifications of Administration Server on started applications. You can limit the maximum number of events in the event repository to prevent database overflow. Refer to the following topic for details: Calculation of database space. Concurrent use of the SQL Server Express Edition DBMS by Administration Server and another application is strictly forbidden. The Microsoft SQL Express database is not supported for the Perform Windows Update synchronization task. |
Local SQL Server edition, other than Express, 2016 or later |
No limitations. |
Remote SQL Server edition, other than Express, 2016 or later |
Only valid if both devices are in the same Windows domain; if the domains differ, a two-way trust relationship must be established between them. |
Local or remote MySQL 5.5, 5.6, or 5.7 (MySQL versions 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, and 5.5.5 are no longer supported) |
Use this DBMS if you intend to run a single Administration Server for less than 10,000 devices. It is recommended to disable the Software inventory task and disable (in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings) notifications of Administration Server on started applications. Refer to the following topic for details: Calculation of database space. |
Local or remote MySQL 8.0.20 or later |
Use this DBMS if you intend to run a single Administration Server for less than 50,000 devices. It is recommended to disable the Software inventory task and disable (in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings) notifications of Administration Server on started applications. Refer to the following topic for details: Calculation of database space. |
Local or remote MariaDB (see supported versions) |
Use this DBMS if you intend to run a single Administration Server for less than 20,000 devices. It is recommended to disable the Software inventory task and disable (in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings) notifications of Administration Server on started applications. Refer to the following topic for details: Calculation of database space. |
PostgreSQL, Postgres Pro (see supported versions) |
Use one of these DBMS if you intend to run a single Administration Server for less than 50,000 devices. It is recommended to disable the Software inventory task and disable (in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings) notifications of Administration Server on started applications. Refer to the following topic for details: Calculation of database space. |
If you use a PostgreSQL, MariaDB or MySQL DBMS, the Events tab may display an incomplete list of events for the selected client device. This occurs when the DBMS stores a very large amount of events. You can increase the number of displayed events by doing either of the following:
To see a full list of events logged on the Administration Server for the device, use Reports.
If you are using SQL Server 2019 as a DBMS and you do not have cumulative patch CU12 or later, you have to perform the following after installing Kaspersky Security Center:
- Connect to SQL Server using SQL Management Studio.
- Run the following commands (if you chose a different name for the database, use that name instead of KAV):
USE KAVGOALTER DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION SET TSQL_SCALAR_UDF_INLINING = OFFGO - Restart the SQL Server 2019 service.
Otherwise, using SQL Server 2019 may result in errors, such as "There is insufficient system memory in resource pool 'internal' to run this query."
Specifying the address of the Administration Server
When installing Administration Server, you must specify the external address of the Administration Server. This address will be used as the default address when creating installation packages of Network Agent. After that, you will be able to change the address of the Administration Server host by using Administration Console tools; the address will not change automatically in Network Agent installation packages that have been already created.
Configuring protection on a client organization's network
After Administration Server installation is complete, Administration Console launches and prompts you to perform the initial setup through the relevant wizard. When the quick start wizard is running, the following policies and tasks are created in the root administration group:
- Policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Group task for updating Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Group task for scanning a device with Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Policy of Network Agent
- Vulnerability scan task (task of Network Agent)
- Updates installation and vulnerabilities fix task (task of Network Agent)
Policies and tasks are created with the default settings, which may turn out to be sub-optimal or even inadmissible for the organization. Therefore, you must check the properties of objects that have been created and modify them manually, if necessary.
This section contains information about manual configuration of policies, tasks, and other settings of Administration Server, and information about the distribution point, building an administration group structure and hierarchy of tasks, and other settings.
Manual setup of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy
This section provides recommendations on how to configure the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy, which is created by the quick start wizard. You can perform the setup in the policy properties window.
When editing a setting, keep in mind that you must click the lock icon above the relevant setting in order to allow using its value on a workstation.
Configuring the policy in the Advanced Threat Protection section
For a full description of the settings in this section, please refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows documentation.
In the Advanced Threat Protection section, you can configure the use of Kaspersky Security Network for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. You can also configure Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows modules, such as Behavior Detection, Exploit Prevention, Host Intrusion Prevention, and Remediation Engine.
In the Kaspersky Security Network subsection, we recommend that you enable the Kaspersky Security Network option. Using this option helps to redistribute and optimize traffic on the network. If the Kaspersky Security Network option is disabled, you can enable direct use of KSN servers.
Configuring the policy in the Essential Threat Protection section
For a full description of the settings in this section, please refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows documentation.
In the Essential Threat Protection section of the policy properties window, we recommend that you specify additional settings in the Firewall and File Threat Protection subsections.
The Firewall subsection contains settings that allow you to control the network activity of applications on the client devices. A client device uses a network to which one of the following statuses is assigned: public, local, or trusted. Depending on the network status, Kaspersky Endpoint Security can allow or deny network activity on a device. When you add a new network to your organization, you must assign an appropriate network status to it. For example, if the client device is a laptop, we recommend that this device use the public or trusted network, because the laptop is not always connected to the local network. In the Firewall subsection, you can check whether you correctly assigned statuses to the networks used in your organization.
To check the list of networks:
- In the policy properties, go to Essential Threat Protection → Firewall.
- In the Available networks section, click the Settings button.
- In the Firewall window that opens, go to the Networks tab to view the list of networks.
In the File Threat Protection subsection, you can disable the scanning of network drives. Scanning network drives can place a significant load on network drives. It is more convenient to perform indirect scanning, on file servers.
To disable scanning of network drives:
- In the policy properties, go to Essential Threat Protection → File Threat Protection.
- In the Security level section, click the Settings button.
- In the File Threat Protection window that opens, on the General tab clear the All network drives check box.
Configuring the policy in the General Settings section
For the full description of the settings in this section, please refer to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security documentation.
Described below are advanced setup actions, which we recommend that you perform in the policy properties window of Kaspersky Endpoint Security, in the General Settings section.
General Settings section, Reports and Storage subsection
In the Data transfer to Administration Server section, please note the About started applications check box. If this check box is selected, the Administration Server database saves information about all versions of all software modules on the networked devices. This information may require a significant amount of disk space in the Kaspersky Security Center database (dozens of gigabytes). Therefore, if the About started applications check box is still selected in the top-level policy, it must be cleared.
General Settings section, Interface subsection
If the threat protection in the organization's network must be managed in centralized mode through Administration Console, you must disable the display of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security user interface on workstations (by clearing the Display application interface check box in the Interaction with user section), and enable password protection (by selecting the Enable password protection check box in the Password protection section).
Page top
Configuring the policy in the Event configuration section
In the Event configuration section, you should disable the saving of any events on Administration Server, except for the following ones:
- On the Critical tab:
- Application autorun is disabled
- Access denied
- Application startup prohibited
- Disinfection impossible
- End User License Agreement violated
- Could not load encryption module
- Cannot start two tasks at the same time
- Active threat detected. Advanced Disinfection should be started
- Network attack detected
- Not all components were updated
- Activation error
- Error enabling portable mode
- Error in interaction with Kaspersky Security Center
- Error disabling portable mode
- Error changing application components
- Error applying file encryption / decryption rules
- Policy cannot be applied
- Process terminated
- Network activity blocked
- On the Functional failure tab: Invalid task settings. Settings not applied
- On the Warning tab:
- Self-Defense is disabled
- Incorrect reserve key
- User has opted out of the encryption policy
- On the Info tab: Application startup prohibited in test mode
Manual setup of the group update task for Kaspersky Endpoint Security
If the Administration Server acts as the update source, the optimal and recommended schedule option for Kaspersky Endpoint Security is When new updates are downloaded to the repository with the Use automatically randomized delay for task starts check box selected.
If a local task for downloading updates from Kaspersky servers to the repository is created on each distribution point, periodic scheduling will be optimal and recommended for the Kaspersky Endpoint Security group update task. In this case, the randomization interval value should be set on 1 hour.
Page top
Manual setup of the group task for scanning a device with Kaspersky Endpoint Security
The quick start wizard creates a group task for scanning a device. By default, the task is assigned a Run on Fridays at 7:00 PM schedule with automatic randomization, and the Run missed tasks check box is cleared.
This means that if devices in an organization are shut down on Fridays, for example, at 6:30 PM, the device scan task will never run. You must set up the most convenient schedule for this task based on the workplace rules adopted in the organization.
Scheduling the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
The quick start wizard creates the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task for Network Agent. By default, the task is assigned a Run on Tuesdays at 7:00 PM schedule with automatic randomization, and the Run missed tasks check box is selected.
If the organization's workplace rules provide for shutting down all devices at this time, the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task will run after the devices are turned on again, that is, on Wednesday morning. Such activity may be undesirable because a vulnerability scan may increase the load on CPUs and disk subsystems. You must set up the most convenient schedule for the task based on the workplace rules adopted in the organization.
Manual setup of the group task for updates installation and vulnerabilities fix
The quick start wizard creates a group task for updates installation and vulnerabilities fix for Network Agent. By default, the task is set up to run every day at 01:00 AM, with automatic randomization, and the Run missed tasks option is not enabled.
If the organization's workplace rules provide for shutting down devices overnight, the update installation will never run. You must set up the most convenient schedule for the vulnerability scan task based on the workplace rules adopted in the organization. It is also important to keep in mind that installation of updates may require restarting the device.
Building a structure of administration groups and assigning distribution points
A structure of administration groups in Kaspersky Security Center performs the following functions:
- Sets the scope of policies.
There is an alternate way of applying relevant settings on devices, by using policy profiles. In this case, the scope of policies is set, for example, with tags, device locations in Active Directory organizational units and membership in Active Directory security groups.
- Sets the scope of group tasks.
There is an approach to defining the scope of group tasks that is not based on a hierarchy of administration groups: use of tasks for device selections and tasks for specific devices.
- Sets access rights to devices, virtual Administration Servers, and secondary Administration Servers.
- Assigns distribution points.
When building the structure of administration groups, you must take into account the topology of the organization's network for the optimum assignment of distribution points. The optimum distribution of distribution points allows you to save traffic on the organization's network.
Depending on the organizational schema and network topology adopted by the MSP client, the following standard configurations can be applied to the structure of administration groups:
- Single office
- Multiple small detached offices
Standard MSP client configuration: Single office
In a standard "single-office" configuration, all devices are on the organization's network so they can "see" each other. The organization's network may consist of a few separate parts (networks or network segments) linked by narrow channels.
The following methods of building the structure of administration groups are possible:
- Building the structure of administration groups taking into account the network topology. The structure of administration groups may not reflect the network topology with absolute precision. A match between the separate parts of the network and certain administration groups would be enough. You can use automatic assignment of distribution points or assign them manually.
- Building the structure of administration groups, without taking the network topology into account. In this case, you must disable automatic assignment of distribution points and then assign one or several devices to act as distribution points for a root administration group in each of the separate parts of the network, for example, for the Managed devices group. All distribution points will be at the same level and will feature the same scope spanning all devices on the organization's network. In this case, each of Network Agents will connect to the distribution point that has the shortest route. The route to a distribution point can be traced with the tracert utility.
Standard MSP client configuration: Multiple small remote offices
This standard configuration provides for a number of small remote offices, which may be communicated with the head office via the internet. Each remote office is located behind the NAT, that is, connection from one remote office to another is not possible because offices are isolated from one another.
The configuration must be reflected in the structure of administration groups: a separate administration group must be created for each remote office (groups Office 1 and Office 2 in the figure below).

Remote offices are included in the administration group structure
One or multiple distribution points must be assigned to each administration group corresponding to an office. Distribution points must be devices at the remote office that have a sufficient amount of free disk space. Devices deployed in the Office 1 group, for example, will access distribution points assigned to the Office 1 administration group.
If some users move between offices physically, with their laptops, you must select two or more devices (in addition to the existing distribution points) in each remote office and assign them to act as distribution points for a top-level administration group (Root group for offices in the figure above).
Example: A laptop is deployed in the Office 1 administration group and then is moved physically to the office that corresponds to the Office 2 administration group. After the laptop is moved, Network Agent attempts to access the distribution points assigned to the Office 1 group, but those distribution points are unavailable. Then, Network Agent starts attempting to access the distribution points that have been assigned to the Root group for offices. Because remote offices are isolated from one another, attempts to access distribution points assigned to the Root group for offices administration group will only be successful when Network Agent attempts to access distribution points in the Office 2 group. That is, the laptop will remain in the administration group that corresponds to the initial office, but the laptop will use the distribution point of the office where it is physically located at the moment.
Hierarchy of policies, using policy profiles
This section provides information about how to apply policies to devices in administration groups. This section also provides information about policy profiles.
Hierarchy of policies
In Kaspersky Security Center, you use policies for defining a single collection of settings to multiple devices. For example, the policy scope of application P defined for administration group G includes managed devices with application P installed that have been deployed in group G and all of its subgroups, except for subgroups where the Inherit from parent group check box is cleared in the properties.
A policy differs from any local setting by lock icons ( ) next to its settings. If a setting (or a group of settings) is locked in the policy properties, you must, first, use this setting (or group of settings) when creating effective settings and, second, you must write the settings or group of settings to the downstream policy.
) next to its settings. If a setting (or a group of settings) is locked in the policy properties, you must, first, use this setting (or group of settings) when creating effective settings and, second, you must write the settings or group of settings to the downstream policy.
Creation of the effective settings on a device can be described as follows: the values of all settings that have not been locked are taken from the policy, then they are overwritten with the values of local settings, and then the resulting collection is overwritten with the values of locked settings taken from the policy.
Policies of the same application affect each other through the hierarchy of administration groups: Locked settings from the upstream policy overwrite the same settings from the downstream policy.
There is a special policy for out-of-office users. This policy takes effect on a device when the device switches into out-of-office mode. Out-of-office policies do not affect other policies through the hierarchy of administration groups.
Page top
Policy profiles
Applying policies to devices only through the hierarchy of administration groups may be inconvenient in many circumstances. It may be necessary to create several instances of a single policy that differ in one or two settings for different administration groups, and synchronize the contents of those policies in the future.
To help you avoid such problems, Kaspersky Security Center supports policy profiles. A policy profile is a named subset of policy settings. This subset is distributed on target devices together with the policy, supplementing it under a specific condition called the profile activation condition. Profiles only contain settings that differ from the "basic" policy, which is active on the client device (computer or mobile device). Activation of a profile modifies the policy settings that were active on the device before the profile was activated. Those settings take values that have been specified in the profile.
The following restrictions are currently imposed on policy profiles:
- A policy can include a maximum 100 profiles.
- A policy profile cannot contain other profiles.
- A policy profile cannot contain notification settings.
Contents of a profile
A policy profile contains the following constituent parts:
- Name. Profiles with identical names affect each other through the hierarchy of administration groups with common rules.
- Subset of policy settings. Unlike the policy, which contains all the settings, a profile only contains settings that are actually required (locked settings).
- Activation condition is a logical expression with the device properties. A profile is active (supplements the policy) only when the profile activation condition becomes true. In all other cases, the profile is inactive and ignored. The following device properties can be included in that logical expression:
- Status of out-of-office mode.
- Properties of network environment—Name of the active rule for Network Agent connection.
- Presence or absence of specified tags on the device.
- Device location in Active Directory unit: explicit (the device is right in the specified OU), or implicit (the device is in an OU, which is within the specified OU at any nesting level).
- Device's membership in an Active Directory security group (explicit or implicit).
- Device owner's membership in an Active Directory security group (explicit or implicit).
- Profile disabling check box. Disabled profiles are always ignored and their respective activation conditions are not verified.
- Profile priority. The activation conditions of different profiles are independent, so several profiles can be activated simultaneously. If active profiles contain non-overlapping collections of settings, no problems will arise. However, if two active profiles contain different values of the same setting, an ambiguity will occur. This ambiguity is to be avoided through profile priorities: The value of the ambiguous variable will be taken from the profile that has the higher priority (the one that is rated higher in the list of profiles).
Behavior of profiles when policies affect each other through the hierarchy
Profiles with the same name are merged according to the policy merge rules. Profiles of an upstream policy have a higher priority than profiles of a downstream policy. If editing settings is prohibited in the upstream policy (it is locked), the downstream policy uses the profile activation conditions from the upstream one. If editing settings is allowed in the upstream policy, the profile activation conditions from the downstream policy are used.
Since a policy profile may contain the Device is offline property in its activation condition, profiles completely replace the feature of policies for out-of-office users, which will no longer be supported.
A policy for out-of-office users may contain profiles, but its profiles can only be activated after the device switches into out-of-office mode.
Page top
Tasks
Kaspersky Security Center manages Kaspersky security applications installed on devices by creating and running tasks. Tasks are required for installing, launching, and stopping applications, scanning files, updating databases and software modules, and performing other actions on applications.
Tasks for a specific application can be created only if the management plug-in for that application is installed.
Tasks can be performed on the Administration Server and on devices.
The following tasks are performed on the Administration Server:
- Automatic distribution of reports
- Downloading of updates to the repository of the Administration Server
- Backup of Administration Server data
- Maintenance of the database
- Windows Update synchronization
- Creation of an installation package based on the operating system (OS) image of a reference device
The following types of tasks are performed on devices:
- Local tasks—Tasks that are performed on a specific device
Local tasks can be modified either by the administrator, by using Administration Console tools, or by the user of a remote device (for example, through the security application interface). If a local task has been modified simultaneously by the administrator and the user of a managed device, the changes made by the administrator will take effect because they have a higher priority.
- Group tasks—Tasks that are performed on all devices of a specific group
Unless otherwise specified in the task properties, a group task also affects all subgroups of the selected group. A group task also affects (optionally) devices that have been connected to secondary and virtual Administration Servers deployed in the group or any of its subgroups.
- Global tasks—Tasks that are performed on a set of devices, regardless of whether they are included in any group
For each application, you can create any number of group tasks, global tasks, or local tasks.
You can make changes to the settings of tasks, view the progress of tasks, and copy, export, import, and delete tasks.
A task is started on a device only if the application for which the task was created is running.
Results of tasks are saved in the Microsoft Windows event log and the Kaspersky Security Center event log, both centrally on the Administration Server and locally on each device.
Do not include private data in task settings. For example, avoid specifying the domain administrator password.
Device moving rules
We recommend that you automate the allocation of devices to administration groups on the virtual server that corresponds to an MSP client, using device moving rules. A device moving rule consists of three main parts: a name, an execution condition (logical expression with the device attributes), and a target administration group. A rule moves a device to the target administration group if the device attributes meet the rule execution condition.
All device moving rules have priorities. The Administration Server checks the device attributes as to whether they meet the execution condition of each rule, in ascending order of priority. If the device attributes meet the execution condition of a rule, the device is moved to the target group, so the rule processing is complete for this device. If the device attributes meet the conditions of multiple rules, the device is moved to the target group of the rule with the highest priority (that is, has the highest rank in the list of rules).
Device moving rules can be created implicitly. For example, in the properties of an installation package or a remote installation task, you can specify the administration group to which the device must be moved after Network Agent is installed on it. Also, device moving rules can be created explicitly by the administrator of Kaspersky Security Center, in the list of moving rules. The list is located in Administration Console, in the properties of the Unassigned devices group.
By default, a device moving rule is intended for one-time initial allocation of devices to administration groups. The rule moves devices from the Unassigned devices group only once. If a device once was moved by this rule, the rule will never move it again, even if you return the device to the Unassigned devices group manually. This is the recommended way of applying moving rules.
You can move devices that have already been allocated to some of the administration groups. To do this, in the properties of a rule, clear the Move only devices that do not belong to an administration group check box.
Applying moving rules to devices that have already been allocated to some of the administration groups, significantly increases the load on the Administration Server.
You can create a moving rule that would affect a single device repeatedly.
We strongly recommend that you avoid moving a single device from one group to another repeatedly (for example, in order to apply a special policy to that device, run a special group task, or update the device through a specific distribution point).
Such scenarios are not supported, because they increase the load on Administration Server and network traffic to an extreme degree. These scenarios also conflict with the operating principles of Kaspersky Security Center (particularly in the area of access rights, events, and reports). Another solution must be found, for example, through the use of policy profiles, tasks for device selections, assignment of Network Agents according to the standard scenario, and so on.
Page top
Software categorization
The main tool for monitoring the running of applications are Kaspersky categories (hereinafter also referred to as KL categories). KL categories help Kaspersky Security Center administrators to simplify the support of software categorization and minimize traffic going to managed devices.
User categories must only be created for applications that cannot be classified in any of the existing KL categories (for example, for custom-made software). User categories are created on the basis of an application installation package (MSI) or a folder with installation packages.
If a large collection of software is available, which has not been categorized through KL categories, it may be useful to create an automatically updated category. The checksums of executable files will be automatically added to this category on every modification of the folder containing distribution packages.
Do not create automatically updated categories of software for the folders My Documents, %windir%, %ProgramFiles%, and %ProgramFiles(x86)%. The pool of files in these folders is subject to frequent changes, which leads to an increased load on Administration Server and increased network traffic. You must create a dedicated folder with the collection of software and periodically add new items to it.
Page top
About multi-tenant applications
Kaspersky Security Center enables administrators of service providers and tenant administrators to use Kaspersky applications with multitenancy support. After a multi-tenant Kaspersky application is installed in the infrastructure of a service provider, tenants can start using the application.
To separate tasks and policies related to different tenants, you must create a dedicated virtual Administration Server in Kaspersky Security Center for each tenant. All tasks and policies for multi-tenant applications running for a tenant must be created for the Managed devices administration group of the virtual Administration Server corresponding to that tenant. The tasks created for the administration groups related to the primary Administration Server do not affect the devices of tenants.
Unlike service provider administrators, a tenant administrator can create and view tasks and application policies only for the devices of the corresponding tenant. The sets of tasks and policy settings available to service provider administrators and tenant administrators are different. Some of the tasks and policy settings are not available to tenant administrators.
Within a hierarchical structure of a tenant, the policies created for multi-tenant applications are inherited to lower-level administration groups as well as to upper-level administration groups: the policy is propagated to all client devices that belong to the tenant.
Backup and restoration of Administration Server settings
Backup of the settings of Administration Server and its database is performed through the backup task and klbackup utility. A backup copy includes all the main settings and objects pertaining to the Administration Server, such as certificates, primary keys for encryption of drives on managed devices, keys for various licenses, structure of administration groups with all of its contents, tasks, policies, etc. With a backup copy you can recover the operation of an Administration Server as soon as possible, spending from a dozen minutes to a couple of hours on this.
If no backup copy is available, a failure may lead to an irrevocable loss of certificates and all Administration Server settings. This will necessitate reconfiguring Kaspersky Security Center from scratch, and performing initial deployment of Network Agent on the organization's network again. All primary keys for encryption of drives on managed devices will also be lost, risking irrevocable loss of encrypted data on devices with Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Therefore, do not neglect regular backups of Administration Server using the standard backup task.
The quick start wizard creates the backup task for Administration Server settings and sets it to run daily, at 4:00 AM. Backup copies are saved by default in the folder %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskySC.
If an instance of Microsoft SQL Server installed on another device is used as the DBMS, you must modify the backup task by specifying a UNC path, which is available for write by both the Administration Server service and the SQL Server service, as the folder to store backup copies. This requirement derives from a special feature of backup in the Microsoft SQL Server DBMS.
If a local instance of Microsoft SQL Server is used as the DBMS, we also recommend to save backup copies on a dedicated medium in order to secure them against damage together with Administration Server.
Because a backup copy contains important data, the backup task and klbackup utility provide for password protection of backup copies. By default, the backup task is created with a blank password. You must set a password in the properties of the backup task. Neglecting this requirement causes a situation where all keys of Administration Server certificates, keys for licenses, and primary keys for encryption of drives on managed devices remain unencrypted.
In addition to the regular backup, you must also create a backup copy prior to every significant change, including installation of Administration Server upgrades and patches.
If you use Microsoft SQL Server as the DBMS, you can minimize the size of backup copies. To do this, enable the Compress backup option in the SQL Server settings.
Restoration from a backup copy is performed with the utility klbackup on an operable instance of Administration Server that has just been installed and has the same version (or later) for which the backup copy was created.
The instance of Administration Server on which the restoration is to be performed, must use a DBMS of the same type (for example, the same SQL Server or MariaDB) and the same or later version. The version of Administration Server can be the same (with an identical or later patch), or later.
This section describes standard scenarios for restoring settings and objects of Administration Server.
A device with Administration Server is inoperable
If a device with Administration Server is inoperable due to a failure, you are recommended to perform the following actions:
- The new Administration Server must be assigned the same address: NetBIOS name, FQDN, or static IP (depending on which of them was set when Network Agents were deployed).
- Install Administration Server, using a DBMS of the same type, of the same (or later) version. You can install the same version of Server with the same (or later) patch, or a later version. After installation, do not perform the initial setup through the wizard.
- In the Start menu, run the klbackup utility and perform restoration.
The settings of Administration Server or the database are corrupted
If Administration Server is inoperable due to corrupted settings or database (e.g., after a power surge), you are recommended to use the following restoration scenario:
- Scan the file system on the damaged device.
- Uninstall the inoperable version of Administration Server.
- Reinstall Administration Server, using a DBMS of the same type and of the same (or later) version. You can install the same version of Server with the same (or later) patch, or a later version. After installation, do not perform the initial setup through the wizard.
- In the Start menu, run the utility klbackup and perform restoration.
It is prohibited to restore Administration Server in any way other than through the klbackup utility.
Any attempts to restore Administration Server through third-party software will inevitably lead to desynchronization of data on nodes of the distributed application Kaspersky Security Center and, consequently, to improper functioning of the application.
Page top
Deploying Network Agent and the security application
To manage devices in an organization, you have to install Network Agent on each of them. Deployment of distributed Kaspersky Security Center on corporate devices normally begins with installation of Network Agent on them.
In Microsoft Windows XP, Network Agent might not perform the following operations correctly: downloading updates directly from Kaspersky servers (as a distribution point); functioning as a KSN proxy server (as a distribution point); and detecting third-party vulnerabilities (if Vulnerability and patch management is used).
Initial deployment
If a Network Agent has already been installed on a device, remote installation of applications on that device is performed through this Network Agent. The distribution package of an application to be installed is transferred over communication channels between Network Agents and Administration Server, along with the installation settings defined by the administrator. To transfer the distribution package, you can use relay distribution nodes, that is, distribution points, multicast delivery, etc. For more details on how to install applications on managed devices with Network Agent already installed, see below in this section.
You can perform initial installation of Network Agent on devices running Windows, using one of the following methods:
- With third-party tools for remote installation of applications.
- With Windows group policies: using standard Windows management tools for group policies.
- In forced mode, using special options in the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center.
- By sending device users links to stand-alone packages generated by Kaspersky Security Center. Stand-alone packages are executable modules that contain the distribution packages of selected applications with their settings defined.
- Manually, by running application installers on devices.
On platforms other than Microsoft Windows, you have to perform initial installation of Network Agent on managed devices either through the existing third-party tools, or manually, by sending users an archive with a pre-configured distribution package. You can upgrade Network Agent to a new version or install other Kaspersky applications on non-Windows platforms, using Network Agents (already installed on devices) to perform remote installation tasks. In this case, installation is identical to that on devices running Microsoft Windows.
When selecting a method and a strategy for deployment of applications on a managed network, you must consider a number of factors (partial list):
- Configuration of the corporate network
- Total number of devices
- Presence of Windows domains on the managed network, possibility to modify Active Directory group policies in those domains
- Awareness of the user account(s) with local administrator rights on devices on which initial deployment of Kaspersky applications has been planned (i.e., availability of a domain user account with local administrator rights, or presence of unified local user accounts with administrator rights on those devices)
- Connection type and bandwidth of network channels between the Administration Server and MSP client networks, as well as the bandwidth of channels inside those networks
- Security settings applied on remote devices at the start of deployment (such as use of UAC and Simple File Sharing mode)
Configuring installers
Before starting deployment of Kaspersky applications on a network, you must specify the installation settings, that is, those defined during the application installation. When installing Network Agent, you should specify, at a minimum, an address for connection to the Administration Server and the proxy settings; some advanced settings may also be required. Depending on the installation method that you have selected, you can define settings in different ways. In the simplest case (manual interactive installation on a selected device), all relevant settings can be defined through the user interface of the Installer, so, in some cases, initial deployment can even be performed by sending users a link to the Network Agent distribution package together with the settings (Administration Server address, etc.) that the user must enter in the Installer interface.
This method is not recommended for use since it is inconvenient for users, entailing a high risk of errors when defining settings manually; it is also non-usable with silent installation of applications on device groups. In general, the administrator must specify values for settings in centralized mode; those values can subsequently be used for creation of stand-alone packages. Stand-alone packages are self-extracting archives that contain distribution packages with settings defined by the administrator. Stand-alone packages can be located on resources that allow both downloading by end users (for example, on Kaspersky Security Center Web Server) and silent installation on selected networked devices.
Page top
Installation packages
The first and main method of defining the installation settings of applications is all-purpose and thus suitable for all installation methods, both with Kaspersky Security Center tools, and with most third-party tools. This method consists of creating installation packages of applications in Kaspersky Security Center.
Installation packages are generated using the following methods:
- Automatically, from specified distribution packages, on the basis of included descriptors (files with the kud extension that contain rules for installation and results analysis, and other information)
- From the executable files of installers or from installers in Microsoft Windows Installer (MSI) format, for standard or supported applications
Generated installation packages are organized hierarchically as folders with subfolders and files. In addition to the original distribution package, an installation package contains editable settings (including the installer's settings and rules for processing such cases as necessity of restarting the operating system in order to complete installation), as well as minor auxiliary modules.
Values of installation settings that are specific for a selected application to be supported can be specified in the Administration Console user interface when creating an installation package (more settings can be found in the properties of an installation package that has already been created). When performing remote installation of applications through Kaspersky Security Center tools, installation packages are delivered to target devices so that running the installer of an application makes all administrator-defined settings available for it. When using third-party tools for installation of Kaspersky applications, you only have to ensure the availability of the entire installation package on the target device, that is, the availability of the distribution package and its settings. Installation packages are created and stored by Kaspersky Security Center in a dedicated subfolder of the shared data folder.
Do not specify any details of privileged accounts in the parameters of installation packages.
For instructions about using this configuration method for Kaspersky applications before deployment through third-party tools, see section "Deployment using group policies of Microsoft Windows."
Immediately after Kaspersky Security Center installation, a few installation packages are automatically generated; they are ready for installation and include Network Agent packages and security application packages for Microsoft Windows.
In some cases, using installation packages for deployment of applications on an MSP client network implies the need to create installation packages on virtual Servers that correspond to MSP clients. Creating installation packages on virtual Servers allows you to use different installation settings for different MSP clients. In the first instance, this is useful when handling Network Agent installation packages since Network Agents deployed on the networks of different MSP clients use different addresses to connect to the Administration Server. Actually, the connection address determines the Server to which Network Agent connects.
In addition to the possibility to create new installation packages immediately on a virtual Administration Server, the main operation mode for installation packages on virtual Administration Servers is the "distribution" of installation packages from the primary Administration Server to virtual ones. You can distribute selected (or all) installation packages to selected virtual Administration Servers (including all Servers within a selected administration group) using the corresponding Administration Server task. Also, you can select the list of installation packages of the primary Administration Server when creating a new virtual Administration Server. The packages that you have selected will be immediately distributed to a newly created virtual Administration Server.
When distributing an installation package, its contents are not copied entirely. The file repository on a virtual Administration Server, which corresponds to the installation package being distributed, only stores files of settings that are specific for that virtual Server. The main part of the installation package (including the distribution package of the application being installed) remains unchanged; it is stored only in the primary Administration Server repository. This allows you to increase the system performance dramatically and reduce the required disk volume. When handling installation packages distributed to virtual Administration Servers (i.e., when running remote installation tasks or creating stand-alone installation packages), the data from the original installation package of the primary Administration Server is "merged" with the settings files, which correspond to the distributed package on the virtual Administration Server.
Although the license key for an application can be set in the installation package properties, it is advisable to avoid this license distribution method because it is easy to accidentally obtain read access to files in the folder. You should use automatically distributed license keys or installation tasks for license keys.
Page top
MSI properties and transform files
Another way of configuring installation on Windows platform is to define MSI properties and transform files. This method can be used when performing installation through third-party tools intended for installers in Microsoft Installer format, as well as when performing installation through Windows group policies using standard Microsoft tools or other third-party tools designed for handling Windows group policies.
Page top
Deployment with third-party tools for remote installation of applications
When any tools for remote installation of applications (such as Microsoft System Center) are available in an organization, it is convenient to perform initial deployment by using those tools.
The following actions must be performed:
- Select the method for configuring installation that best suits the deployment tool to be used.
- Define the mechanism for synchronization between the modification of the settings of installation packages (through the Administration Console interface) and the operation of selected third-party tools used for deployment of applications from installation package data.
General information about the remote installation tasks in Kaspersky Security Center
Kaspersky Security Center provides a broad range of methods for remote installation of applications, which are implemented as remote installation tasks. You can create a remote installation task both for a specified administration group and for specific devices or a selection of devices (such tasks are displayed in Administration Console, in the Tasks folder). When creating a task, you can select installation packages (those of Network Agent and / or another application) to be installed within this task, as well as specify certain settings that define the method of remote installation.
Tasks for administration groups affect both devices included in a specified group and all devices in all subgroups within that administration group. A task covers devices of secondary Administration Servers included in a group or any of its subgroups if the corresponding setting is enabled in the task.
Tasks for specific devices refresh the list of client devices at each run in accordance with the selection contents at the moment the task starts. If a selection includes devices that have been connected to secondary Administration Servers, the task will run on those devices, too.
To ensure a successful operation of a remote installation task on devices connected to secondary Administration Servers, you must use the distribution task to distribute installation packages used by your task to corresponding secondary Administration Servers in advance.
Page top
Deployment using group policies of Microsoft Windows
It is recommended that you perform the initial deployment of Network Agents through Microsoft Windows group policies if the following conditions are met:
- This device is member of an Active Directory domain.
- Access to the domain controller is granted with the administrator rights, which allow you to create and modify Active Directory group policies.
- Configured installation packages can be moved to the network hosting target managed devices (to a shared folder that is available for reading by all target devices).
- The deployment scheme allows you to wait for the next routine restart of target devices before starting deployment of Network Agents on them (or you can force a Windows group policy to be applied to those devices).
This deployment scheme consists of the following:
- The application distribution package in Microsoft Installer format (MSI package) is located in a shared folder (a folder where the LocalSystem accounts of target devices have read permissions).
- In the Active Directory group policy, an installation object is created for the distribution package.
- The installation scope is set by specifying the organizational unit (OU) and / or the security group, which includes the target devices.
- The next time a target device logs in to the domain (before device users log in to the system), all installed applications are checked for the presence of the required application. If the application is not found, the distribution package is downloaded from the resource specified in the policy and is then installed.
An advantage of this deployment scheme is that assigned applications are installed on target devices while the operating system is loading, that is, even before the user logs in to the system. Even if a user with sufficient rights removes the application, it will be reinstalled at the next launch of the operating system. This deployment scheme's shortcoming is that changes made by the administrator to the group policy will not take effect until the devices are restarted (if no additional tools are involved).
You can use group policies to install both Network Agent and other applications if their respective installers are in Windows Installer format.
Installation of Network Agent from the MSI package is possible only in silent mode, interactive installation from the MSI package is not supported.
Besides, when you select this deployment method, you have to assess the load on the file resource from which files will be copied to target devices after you apply the Windows group policy. You also have to choose the method of delivering the configured installation package to that resource, as well as the method of synchronizing the relevant changes in its settings.
Handling Microsoft Windows policies through the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center
This deployment method is only available if access to the controller of the domain, which contains the target devices, is possible from the Administration Server device, while the shared folder of the Administration Server (the one storing installation packages) is accessible for reading from target devices. Owing to the above reasons, this deployment method is not viewed as applicable to MSP.
Unassisted installation of applications through policies of Microsoft Windows
The administrator can create objects required for installation in a Windows group policy on his or her own behalf. In this case, you have to upload the packages to a stand-alone file server and provide a link to them.
The following installation scenarios are possible:
- The administrator creates an installation package and sets up its properties in Administration Console. Then the administrator copies the entire EXEC subfolder of this package from the shared folder of Kaspersky Security Center to a folder on a dedicated file resource of the organization. The group policy object provides a link to the MSI file of this package stored in a subfolder on the dedicated file resource of the organization.
- The administrator downloads the application distribution package (including that of Network Agent) from the internet and uploads it to the dedicated file resource of the organization. The group policy object provides a link to the MSI file of this package stored in a subfolder on the dedicated file resource of the organization. The installation settings are defined by configuring the MSI properties or by configuring MST transform files.
Forced deployment through the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center
To perform the initial deployment of Network Agent or other applications, you can force installation of selected installation packages by using the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center—provided that each device has a user account(s) with local administrator rights.
Forced installation can also be applied if devices cannot be directly accessed by Administration Server: for example, devices are on isolated networks, or they are on a local network while the Administration Server item is in DMZ.
In case of initial deployment, Network Agent is not installed. Therefore, in the settings of the remote installation task, you cannot select distribution of files required for application installation by using Network Agent. You can only choose to distribute files by using operating system resources through Administration Server or distribution points.
The Administration Server service must run under an account that has administrative privileges on the target devices. Alternatively, you can specify an account that has access to the admin$ share in the settings of the remote installation task.
By default, the remote installation task connects to devices by using the credentials of the account under which the Administration Server is running. It is important to clarify that this is the account used for accessing the admin$ share, rather than the account under which the remote installation task runs. Installation is carried out under the LocalSystem account.
You can specify target devices either explicitly (with a list), by selecting the Kaspersky Security Center administration group to which they belong; or by creating a selection of devices based upon a specific criterion. The installation start time is defined by the task schedule. If the Run missed tasks setting is enabled in the task properties, the task can be run either immediately after target devices are turned on or when they are moved to the target administration group.
Forced installation consists of delivering installation packages to target devices, subsequent copying of files to the admin$ resource on each of the target devices, and remote registration of supporting services on those devices. Delivery of installation packages to target devices is performed through a Kaspersky Security Center feature that ensures network interaction. The following conditions must be met in this case:
- Target devices are accessible from the Administration Server side or from the distribution point side.
- Name resolution for target devices functions properly on the network.
- The administrative shares (admin$) remain enabled on target devices.
- The following system services are running on target devices:
- Server (LanmanServer)
By default, this service is running.
- DCOM Server Process Launcher (DcomLaunch)
- RPC Endpoint Mapper (RpcEptMapper)
- Remote Procedure Call (RpcSs)
- Server (LanmanServer)
- Port TCP 445 is open on target devices to enable remote access through Windows tools.
TCP 139, UDP 137, and UDP 138 are used by older protocols and are no longer necessary for current applications.
Dynamic outbound access ports must be allowed on the firewall for connections from the Administration Server and distribution points to target devices.
- The Active Directory domain policy security settings are allowed to provide the operation of the NTLM protocol during the deployment of Network Agent.
- On target devices running Microsoft Windows XP, Simple File Sharing mode is disabled.
- On target devices, the access sharing and security model are set as Classic – local users authenticate as themselves. It can in no way be Guest only – local users authenticate as Guest.
- Target devices are members of the domain, or uniform accounts with administrator rights are created on target devices in advance.
To successfully deploy Network Agent or other applications to a device that is not joined to a Windows Server 2003 or later Active Directory domain, you must disable remote UAC on that device. Remote UAC is one of the reasons that prevent local administrative accounts from accessing admin$, which is necessary for forced deployment of Network Agent or other applications. Disabling remote UAC does not affect local UAC.
During installation on new devices that have not yet been allocated to any of the Kaspersky Security Center administration groups, you can open the remote installation task properties and specify the administration group to which devices will be moved after Network Agent installation.
When creating a group task, keep in mind that each group task affects all devices in all nested groups within a selected group. Therefore, you must avoid duplicating installation tasks in subgroups.
A simplified way to create tasks for forced installation of applications is automatic installation. To do this, you must open the administration group properties, open the list of installation packages, and then select the ones that must be installed on devices in this group. As a result, the selected installation packages will be automatically installed on all devices in this group and all of its subgroups. The time interval over which the packages will be installed depends on the network throughput and the total number of networked devices.
To reduce the load on Administration Server during the delivery of installation packages to target devices, you can select installation via distribution points in the installation task. Note that this installation method places a significant load on devices acting as distribution points. Therefore, it is recommended that you select devices that meet the requirements for distribution points. If you use distribution points, you have to make sure that they are present in each of the isolated subnets hosting target devices.
Using distribution points as local installation centers may also be useful when performing installation on devices in subnets communicated with Administration Server via a low-capacity channel while a broader channel is available between devices in the same subnet.
The free disk space in the partition with the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit folder must exceed, by many times, the total size of the distribution packages of installed applications.
Page top
Running stand-alone packages created by Kaspersky Security Center
The above-described methods of initial deployment of Network Agent and other applications cannot always be implemented because it is not possible to meet all of the applicable conditions. In such cases, you can create a common executable file called a stand-alone installation package through Kaspersky Security Center, using installation packages with the relevant installation settings that have been prepared by the administrator. A stand-alone installation package can be published either on an internal Web Server (included in Kaspersky Security Center) if this is deemed reasonable (outside access to that Web Server has been configured for target device users), or on an exclusively deployed Web Server included in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. You can also copy stand-alone packages to another Web Server.
You can use Kaspersky Security Center to send selected users an email message containing a link to the stand-alone package file on the currently used Web Server, prompting them to run the file (either in interactive mode, or with the "-s" key for silent installation). You can attach the stand-alone installation package to an email message and then send it to the users of devices that have no access to the Web Server. The administrator can also copy the stand-alone package to an external device, deliver it to a relevant device, and then run it later.
You can create a stand-alone package from a Network Agent package, a package of another application (for example, the security application), or both. If the stand-alone package has been created from Network Agent and another application, installation starts with Network Agent.
When creating a stand-alone package with Network Agent, you can specify the administration group to which new devices (those that have not been allocated to any of the administration groups) will be automatically moved when Network Agent installation completes on them.
Stand-alone packages can run in interactive mode (by default), displaying the result for installation of applications they contain, or they can run in silent mode (when run with the key "-s"). Silent mode can be used for installation from scripts, for example, from scripts configured to run after an operating system image is deployed. The result of installation in silent mode is determined by the return code of the process.
Page top
Options for manual installation of applications
Administrators or experienced users can install applications manually in interactive mode. They can use either original distribution packages or installation packages generated from them and stored in the shared folder of Kaspersky Security Center. By default, installers run in interactive mode and prompt users for all required values. However, when running the process setup.exe from the root of an installation package with the key "-s", the installer will be running in silent mode and with the settings that have been defined when configuring the installation package.
When running setup.exe from the root of an installation package, the package will first be copied to a temporary local folder, and then the application installer will be run from the local folder.
Page top
Remote installation of applications on devices with Network Agent installed
If an operable Network Agent connected to the primary Administration Server (or to any of its secondary Servers) is installed on a device, you can upgrade Network Agent on this device, as well as install, upgrade, or remove any supported applications through Network Agent.
You can enable this option by selecting the Using Network Agent check box in the properties of the remote installation task.
If this check box is selected, installation packages with installation settings defined by the administrator will be transferred to target devices over communication channels between Network Agent and the Administration Server.
To optimize the load on the Administration Server and minimize traffic between the Administration Server and the devices, it is useful to assign distribution points on every remote network or in every broadcasting domain (see sections About distribution points and Building a structure of administration groups and assigning distribution points). In this case, installation packages and the installer settings are distributed from the Administration Server to target devices through distribution points.
Moreover, you can use distribution points for broadcasting (multicast) delivery of installation packages, which allows reducing network traffic significantly when deploying applications.
When transferring installation packages to target devices over communication channels between Network Agents and the Administration Server, all installation packages that have been prepared for transfer will also be cached in the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\.working\FTServer folder. When using multiple large installation packages of various types and involving a large number of distribution points, the size of this folder may increase dramatically.
Files cannot be deleted from the FTServer folder manually. When original installation packages are deleted, the corresponding data will be automatically deleted from the FTServer folder.
All data received on the distribution points side are saved to the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1103\$FTClTmp folder.
Files cannot be deleted from the $FTClTmp folder manually. As tasks using data from this folder complete, the contents of this folder will be deleted automatically.
Because installation packages are distributed over communication channels between Administration Server and Network Agents from an intermediate repository in a format optimized for network transfers, no changes are allowed in installation packages stored in the original folder of each installation package. Those changes will not be automatically registered by Administration Server. If you need to modify the files of installation packages manually (although you are recommended to avoid this scenario), you must edit any of the settings of an installation package in Administration Console. Editing the settings of an installation package in Administration Console causes Administration Server to update the package image in the cache that has been prepared for transfer to target devices.
Page top
Managing device restarts in the remote installation task
Devices often need a restart to complete the remote installation of applications (particularly on Windows).
If you use the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center, in the New task wizard or in the properties window of the task that has been created (Operating system restart section), you can select the action to perform when the Windows device requires a restart:
- Do not restart the device. In this case, no automatic restart will be performed. To complete the installation, you must restart the device (for example, manually or through the device management task). Information about the required restart will be saved in the task results and in the device status. This option is suitable for installation tasks on servers and other devices where continuous operation is critical.
- Restart the device. In this case, the device is always restarted automatically if a restart is required for completion of the installation. This option is useful for installation tasks on devices that provide for regular pauses in their operation (shutdown or restart).
- Prompt user for action. In this case, the restart reminder is displayed on the screen of the client device, prompting the user to restart it manually. Some advanced settings can be defined for this option: text of the message for the user, the message display frequency, and the time interval after which a restart will be forced (without the user's confirmation). The Prompt user for action is the most suitable for workstations where users need a possibility of selecting the most convenient time for a restart.
Suitability of databases updating in an installation package of an anti-virus application
Before starting the protection deployment, you must keep in mind the possibility of updating anti-virus databases (including modules of automatic patches) shipped together with the distribution package of the security application. It is useful to update the databases in the installation package of the application before starting the deployment (for example, by using the corresponding command in the context menu of a selected installation package). This will reduce the number of restarts required for completion of protection deployment on target devices. If your remote installation involves installation packages that have been relayed to virtual Servers from the primary Administration Server, you only have to update databases in the original package on the primary Server. In this case, you do not have to update databases in relayed packages on virtual Servers.
Page top
Removing incompatible third-party security applications
Installation of Kaspersky security applications through Kaspersky Security Center may require removal of third-party software incompatible with the application being installed. There are two main ways of removing the third-party applications.
Automatic removal of incompatible applications by using the installer
When you run the installer, it shows a list of applications that are incompatible with a Kaspersky application:
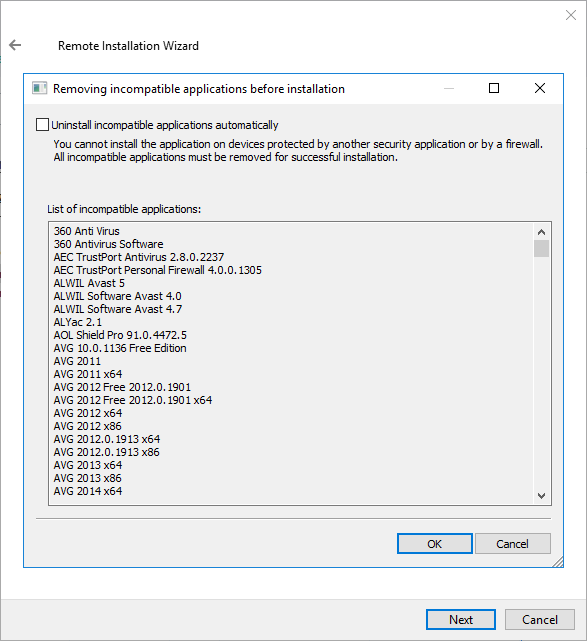
The list of incompatible applications that is displayed in the Remote installation wizard
Kaspersky Security Center detects incompatible software. Accordingly, you can select the Uninstall incompatible applications automatically check box to continue installation. If you clear this check box and do not uninstall the incompatible software, the error occurs and the Kaspersky application is not installed.
Automatic removal of incompatible applications is supported by various types of installation.
Removing incompatible applications through a dedicated task
To remove incompatible applications, use the Uninstall application remotely task. This task should be run on devices before the security application installation task. For example, in the installation task you can select On completing another task as the schedule type where the other task is Uninstall application remotely.
This method of uninstallation is useful when the security application installer cannot properly remove an incompatible application.
Page top
Removing password-protected Network Agent by using the command prompt
To remotely uninstall the Network Agent for which you set an uninstallation password, you can use the command prompt.
If you lose or forgot the password from the password-protected Network Agent installed on the device that is no longer under the management of Kaspersky Security Center, you cannot remove Network Agent by using the klmover utility, the Cleaner tool (cleaner.exe), or the command prompt. In this case, you have to reinstall the operating system on the device with the installed password-protected Network Agent.
To uninstall Network Agent via the command prompt:
- Convert your uninstallation password into a hex code.
Use an internet resource, programming environment, text editor, or other suitable tool to convert your password into hex code.
Make sure that the output delimiter used to separate the generated hex code into parts is set to
00. For example, the hex code51 77 65 72 74 79is incorrect, and the hex code510077006500720074007900is correct. - Enter the following command in the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
msiexec.exe /x{<product code>} /qn KLUNINSTPASSWD=<hex code of your uninstallation password>You can find the product code of your Network Agent in the table below.
Network Agent product codes
Localization
Product code
Arabic
{FA7BF140-F356-404A-BDA3-3EF0878D7C63}
Bulgarian
{4DBF6741-FA51-4C14-AFD2-B7D9246995F6}
Czech
{478A6A0B-D177-4402-B703-808C05C56B13}
English
{BCF4CF24-88AB-45E1-A6E6-40C8278A70C5}
French
{2924BEDA-E0D7-4DAF-A224-50D2E0B12F5B}
German
{2F383CB3-6D7C-449D-9874-164E49E1E0F5}
Hungarian
{8899A4D4-D678-49F8-AD96-0B784F58D355}
Italian
{DC3A3164-36B3-4FB4-B7BF-16A41C35A728}
Japanese
{790C176F-7780-4C84-8B9C-455F5C0E61C5}
Korean
{70812A40-973B-4DA1-96B9-C2011280CD99}
Polish
{1A7B331A-ABBE-4230-995E-BCD99C5A18CF}
Portuguese
{0F05E4E5-5A89-482C-9A62-47CC58643788}
Romanian
{FF802D76-E241-41D3-AAB4-DC7FBD659446}
Russian
{ED1C2D7E-5C7A-48D8-A697-57D1C080ABA7}
Simplified Chinese
{FBD7C01E-49CB-4182-8714-9DB1EAE255CB}
Spanish
{F03982CF-1C5C-4E12-9F9E-D36C35E62402}
Spanish-mx
{29748B5F-D88A-4933-B614-1CCCD6EFB0B7}
Traditional Chinese
{F6AD731A-36B4-4739-B1D4-70D6EDA35147}
Turkish
{2475A66D-698B-4050-93FF-9B48EE82E2BA}
Using tools for remote installation of applications in Kaspersky Security Center for running relevant executable files on managed devices
Using the New package wizard, you can select any executable file and define the settings of the command line for it. For this you can add to the installation package either the selected file itself or the entire folder in which this file is stored. Then you must create the remote installation task and select the installation package that has been created.
While the task is running, the specified executable file with the defined settings of the command prompt will be run on target devices.
If you use installers in Microsoft Windows Installer (MSI) format, Kaspersky Security Center analyzes the installation results by means of standard tools.
If the Vulnerability and patch management license is available, Kaspersky Security Center (when creating an installation package for any supported application in the corporate environment) also uses rules for installation and analysis of installation results that are in its updatable database.
Otherwise, the default task for executable files waits for the completion of the running process, and of all its child processes. After completion of all of the running processes, the task will be completed successfully regardless of the return code of the initial process. To change such behavior of this task, before creating the task, you have to manually modify the .kpd files that were generated by Kaspersky Security Center in the folder of the newly created installation package and its subfolders.
.kpd files use ASCII encoding. .kud files use Unicode encoding.
For the task not to wait for the completion of the running process, set the value of the Wait setting to 0 in the [SetupProcessResult] section:
Example: [SetupProcessResult] Wait=0 |
For the task to wait only for the completion of the running process on Windows, not for the completion of all child processes, set the value of the WaitJob setting to 0 in the [SetupProcessResult], section, for example:
Example: [SetupProcessResult] WaitJob=0 |
For the task to complete successfully or return an error depending on the return code of the running process, create an executable .bat file that saves the error code to a file, for example:
Example: echo [ResponseResult] > setup.log echo ResultCode=2 >> setup.log exit 0 |
And then modify the .kud files that were generated by Kaspersky Security Center in the folder of the newly created installation package:
Example: [SetupMainResult] File=setup.log Section=ResponseResult Value=ResultCode [SetupMainResult_SuccessCodes] 0=Installation completed successfully. [SetupMainResult_ErrorCodes] 1=Installation script error 2=Custom error |
In this case, any code other than those listed will result in an error returned.
To display a string with a comment on the successful completion of the task or an error in the task results, enter brief descriptions of errors corresponding to return codes of the process in the [SetupProcessResult_SuccessCodes] and [SetupProcessResult_ErrorCodes] sections, for example:
Example: [SetupProcessResult_SuccessCodes] 0= Installation completed successfully 3010=A restart is required to complete the installation [SetupProcessResult_ErrorCodes] 1602=Installation canceled by the user 1603=Fatal error during installation |
To use Kaspersky Security Center tools for managing the device restart (if a restart is required to complete an operation), list the return codes of the process that indicate that a restart must be performed, in the [SetupProcessResult_NeedReboot] section:
Example: [SetupProcessResult_NeedReboot] 3010= |
Monitoring the deployment
To monitor the Kaspersky Security Center deployment and make sure that a security application and Network Agent are installed on managed devices, you have to check the traffic light in the Deployment section. This traffic light is located in the workspace of the Administration Server node in the main window of Administration Console. The traffic light reflects the current deployment status. The number of devices with Network Agent and security applications installed is displayed next to the traffic light. When any installation tasks are running, you can monitor their progress here. If any installation errors occur, the number of errors is displayed here. You can view the details of any error by clicking the link.
You can also use the deployment schema in the workspace of the Managed devices folder on the Groups tab. The chart reflects the deployment process, showing the number of devices without Network Agent, with Network Agent, or with Network Agent and a security application.
For more details on the progress of the deployment (or the operation of a specific installation task) open the results window of the relevant remote installation task: Right-click the task and select Results in the context menu. The window displays two lists: the upper one contains the task statuses on devices, while the lower one contains task events on the device that is currently selected in the upper list.
Information about deployment errors are added to the Kaspersky Event Log on Administration Server. Information about errors is also available in the corresponding selection of events in the Reports and notifications folder, the Events subfolder.
Page top
Configuring installers
This section provides information about the files of Kaspersky Security Center installers and the installation settings, as well as recommendations on how to install Administration Server and Network Agent in silent mode.
General information
Installers of Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 components (Administration Server, Network Agent, and Administration Console) are built on Windows Installer technology. An MSI package is the core of an installer. This format of packaging allows using all of the advantages provided by Windows Installer: scalability, availability of a patching system, transformation system, centralized installation through third-party solutions, and transparent registration with the operating system.
Installation in silent mode (with a response file)
The installers of Administration Server and Network Agent have the feature of working with the response file (ss_install.xml), where the parameters for installation in silent mode without user participation are integrated. The ss_install.xml file is located in the same folder as the MSI package; it is used automatically during installation in silent mode. You can enable the silent installation mode with the command line key "/s".
An overview of an example run follows:
setup.exe /s |
Before you start the installer in silent mode, read the End User License Agreement (EULA). If the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit does not include a TXT file with the text of the EULA, you can download the file from the Kaspersky website.
The ss_install.xml file is an instance of the internal format of parameters of the Kaspersky Security Center installer. Distribution packages contain the ss_install.xml file with the default parameters.
Please do not modify the ss_install.xml file manually. This file can be modified through the tools of Kaspersky Security Center, when editing the parameters of the installation packages in Administration Console.
To modify the response file for Administration Server installation:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center distribution package. If you use a full package EXE file, unpack it.
- From the Server folder, open the command line, and then run the following command:
setup.exe /r ss_install.xml
The Kaspersky Security Center installer starts.
- Follow the wizard's steps to configure the Kaspersky Security Center installation.
When you complete the wizard, the response file is automatically modified according to the new settings that you specified.
Installation of Network Agent in silent mode (without a response file)
You can install Network Agent with a single .msi package, specifying the values of MSI properties in the standard way. This scenario allows Network Agent to be installed by using group policies.
Do not rename the installation package Kaspersky Network Agent.msi. Renaming this package may cause installation errors during future updates of Network Agent.
To avoid conflicts between parameters defined through MSI properties and parameters defined in the response file, you can disable the response file by setting the property DONT_USE_ANSWER_FILE=1. The MSI file is located in the Kaspersky Security Center distribution package, in the Packages\NetAgent\exec folder. An example of a run of the Network Agent installer with an .msi package is as follows.
Installation of Network Agent in silent mode requires acceptance of the terms of the End User License Agreement. Use the EULA=1 parameter only if you have fully read, understand and accept the terms of the End User License Agreement.
Example:
|
You can also define the installation parameters for an .msi package by preparing the response file in advance (one with an .mst extension). This command appears as follows:
Example:
|
You can specify several response files in a single command.
Partial installation configuration through setup.exe
When running installation of applications through setup.exe, you can add the values of any properties of MSI to the MSI package.
This command appears as follows:
Example: /v"PROPERTY_NAME1=PROPERTY_VALUE1 PROPERTYNAME2=PROPERTYVALUE2" |
Administration Server installation parameters
The table below describes the MSI properties that you can configure when installing Administration Server. All of the parameters are optional, except for EULA and PRIVACYPOLICY.
Parameters of Administration Server installation in silent mode
MSI property |
Description |
Available values |
|---|---|---|
EULA |
Acceptance of the terms of the License Agreement (required) |
|
PRIVACYPOLICY |
Acceptance of the terms of the Privacy Policy (required) |
|
INSTALLATIONMODETYPE |
Type of Administration Server installation |
|
INSTALLDIR |
Application installation folder |
String value. |
ADDLOCAL |
List of components to install (separated by commas) |
CSAdminKitServer, NAgent, CSAdminKitConsole, NSAC, MobileSupport, KSNProxy, SNMPAgent, GdiPlusRedist, Microsoft_VC90_CRT_x86, Microsoft_VC100_CRT_x86. Minimum list of components sufficient for proper Administration Server installation:
|
NETRANGETYPE |
Network size |
|
SRV_ACCOUNT_TYPE |
Way of specifying the user for the operation of the Administration Server service |
|
SERVERACCOUNTNAME |
User name for the service |
String value. |
SERVERACCOUNTPWD |
User password for the service |
String value. |
DBTYPE |
Database type |
|
MYSQLSERVERNAME |
Full name of MySQL or MariaDB server |
String value. |
MYSQLSERVERPORT |
Number of port for connection to MySQL or MariaDB server |
Numerical value. |
MYSQLDBNAME |
Name of MySQL or MariaDB server database |
String value. |
MYSQLACCOUNTNAME |
User name for connection to MySQL or MariaDB server database |
String value. |
MYSQLACCOUNTPWD |
User password for connection to MySQL or MariaDB server database |
String value. |
MSSQLCONNECTIONTYPE |
Type of use of MSSQL database |
|
MSSQLSERVERNAME |
Full name of SQL Server instance |
String value. |
MSSQLDBNAME |
Name of SQL Server database |
String value. |
MSSQLAUTHTYPE |
Method of authentication for connection to SQL Server |
|
MSSQLACCOUNTNAME |
User name for connection to SQL Server in SQLServer mode |
String value. |
MSSQLACCOUNTPWD |
User password for connection to SQL Server in SQLServer mode |
String value. |
CREATE_SHARE_TYPE |
Method of specifying the shared folder |
|
EXISTSHAREFOLDERNAME |
Full path to an existing shared folder |
String value. |
SERVERPORT |
Port number to connect to Administration Server |
Numerical value. |
SERVERSSLPORT |
Number of port for establishing SSL connection to Administration Server |
Numerical value. |
SERVERADDRESS |
Administration Server address |
String value. |
SERVERCERT2048BITS |
Size of the key for the Administration Server certificate (bits) |
|
MOBILESERVERADDRESS |
Address of the Administration Server for connection of mobile devices; ignored if the MobileSupport component has not been selected |
String value. |
Network Agent installation settings
The table below describes the MSI properties that you can configure when installing Network Agent. All of the parameters are optional, except for SERVERADDRESS.
Properties of MSI
MSI property |
Description |
Available values |
|---|---|---|
DONT_USE_ANSWER_FILE |
Read installation parameters from response file |
|
INSTALLDIR |
Installation folder |
|
SERVERADDRESS |
Administration Server address (required) |
|
SERVERPORT |
Number of port for connection to Administration Server |
|
SERVERSSLPORT |
Number of port for SSL connection |
|
USESSL |
Whether to use SSL connection |
|
OPENUDPPORT |
Whether to open a UDP port |
|
UDPPORT |
UDP port number |
|
USEPROXY |
Whether to use a proxy server |
|
PROXYADDRESS |
Proxy address |
|
PROXYPORT |
Number of port for connection to Administration Server |
|
PROXYLOGIN |
Account for connection to proxy server |
|
PROXYPASSWORD |
Password of account for connection to proxy server. Do not specify any details of privileged accounts in the parameters of installation packages. |
|
GATEWAYMODE |
Connection gateway use mode |
|
GATEWAYADDRESS |
Connection gateway address |
|
CERTSELECTION |
Method of receiving a certificate |
|
CERTFILE |
Path to the certificate file |
|
VMVDI |
Enable dynamic mode for VDI |
|
LAUNCHPROGRAM |
Whether to run Network Agent service after installation |
|
Virtual infrastructure
Kaspersky Security Center supports the use of virtual machines. You can install Network Agent and the security application on each virtual machine, and you can protect virtual machines at the hypervisor level. In the first case, you can use either a standard security application or Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent to protect your virtual machines. In the second case, you can use Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Agentless.
Kaspersky Security Center supports rollbacks of virtual machines to their previous state.
Tips on reducing the load on virtual machines
When installing Network Agent on a virtual machine, you are advised to consider disabling some Kaspersky Security Center features that seem to be of little use for virtual machines.
When installing Network Agent on a virtual machine or on a template intended for generation of virtual machines, we recommend the following actions:
- If you are running a remote installation, in the properties window of the Network Agent installation package, in the Advanced section, select the Optimize settings for VDI option.
- If you are running an interactive installation through a wizard, in the wizard window, select the Optimize the Network Agent settings for the virtual infrastructure option.
Selecting those options alters the settings of Network Agent so that the following features remain disabled by default (before a policy is applied):
- Retrieving information about software installed
- Retrieving information about hardware
- Retrieving information about vulnerabilities detected
- Retrieving information about updates required
Usually, those features are not necessary on virtual machines because they use uniform software and virtual hardware.
Disabling the features is invertible. If any of the disabled features is required, you can enable it through the policy of Network Agent, or through the local settings of Network Agent. The local settings of Network Agent are available through the context menu of the relevant device in Administration Console.
Support of dynamic virtual machines
Kaspersky Security Center supports dynamic virtual machines. If a virtual infrastructure has been deployed on the organization's network, dynamic (temporary) virtual machines can be used in certain cases. The dynamic VMs are created under unique names based on a template that has been prepared by the administrator. The user works on a VM for a while and then, after being turned off, this virtual machine will be removed from the virtual infrastructure. If Kaspersky Security Center has been deployed on the organization's network, a virtual machine with installed Network Agent will be added to the Administration Server database. After you turn off a virtual machine, the corresponding entry must also be removed from the database of Administration Server.
To make functional the feature of automatic removal of entries on virtual machines, when installing Network Agent on a template for dynamic virtual machines, select the Enable dynamic mode for VDI option:
- For remote installation—In the properties window of the installation package of Network Agent (Advanced section)
- For interactive installation—In the Network Agent installation wizard
Avoid selecting the Enable dynamic mode for VDI option when installing Network Agent on physical devices.
If you want events from dynamic virtual machines to be stored on the Administration Server for a while after you remove those virtual machines, then, in the Administration Server properties window, in the Events repository section, select the Store events after devices are deleted option and specify the maximum storage term for events (in days).
Support of virtual machines copying
Copying a virtual machine with installed Network Agent or creating one from a template with installed Network Agent is identical to the deployment of Network Agents by capturing and copying a hard drive image. So, in general case, when copying virtual machines, you need to perform the same actions as when deploying Network Agent by copying a disk image.
However, the two cases described below showcase Network Agent, which detects the copying automatically. Owing to the above reasons, you do not have to perform the sophisticated operations described under "Deployment by capturing and copying the hard drive of a device":
- The Enable dynamic mode for VDI option was selected when Network Agent was installed—After each restart of the operating system, this virtual machine will be recognized as a new device, regardless of whether it has been copied or not.
- One of the following hypervisors is in use: VMware, HyperV, or Xen: Network Agent detects the copying of the virtual machine by the changed IDs of the virtual hardware.
Analysis of changes in virtual hardware is not absolutely reliable. Before applying this method widely, you must test it on a small pool of virtual machines for the version of the hypervisor currently used in your organization.
Support of file system rollback for devices with Network Agent
Kaspersky Security Center is a distributed application. Rolling back the file system to a previous state on a device with Network Agent installed will lead to data desynchronization and improper functioning of Kaspersky Security Center.
The file system (or a part of it) can be rolled back in the following cases:
- When copying an image of the hard drive.
- When restoring a state of the virtual machine by means of the virtual infrastructure.
- When restoring data from a backup copy or a recovery point.
Scenarios under which third-party software on devices with Network Agent installed affects the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\ folder are only critical scenarios for Kaspersky Security Center. Therefore, you must always exclude this folder from the recovery procedure, if possible.
Because the workplace rules of some organizations provide for rollbacks of the file system on devices, support for the file system rollback on devices with Network Agent installed has been added to Kaspersky Security Center, starting with version 10 Maintenance Release 1 (Administration Server and Network Agents must be of version 10 Maintenance Release 1 or later). When detected, those devices are automatically reconnected to the Administration Server with full data cleansing and full synchronization.
By default, support of file system rollback detection is enabled in Kaspersky Security Center 15.1.
As much as possible, avoid rolling back the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\ folder on devices with Network Agent installed, because full resynchronization of data requires a large amount of resources.
A rollback of the system state is absolutely not allowed on a device with Administration Server installed. Nor is a rollback of the database used by Administration Server.
You can restore a state of Administration Server from a backup copy only with the standard klbackup utility.
Page top
About connection profiles for out-of-office users
Out-of-office users of laptops (hereinafter also referred to as "devices") may need to change the method of connecting to an Administration Server or switch between Administration Servers depending on the current location of the device on the enterprise network.
Connection profiles are supported only for devices running Windows and macOS.
Using different addresses of a single Administration Server
Devices with Network Agent installed can connect to the Administration Server either from the organization's intranet or from the internet. This situation may require Network Agent to use different addresses for connection to Administration Server: the external Administration Server address for the Internet connection and the internal Administration Server address for the internal network connection.
To do this, you must add a profile (for connection to Administration Server from the Internet) to the Network Agent policy. Add the profile in the policy properties (Connectivity section, Connection profiles subsection). In the profile creation window, you must disable the Use to receive updates only option and select the Synchronize connection settings with the Administration Server settings specified in this profile option. If you use a connection gateway to access Administration Server (for example, in a Kaspersky Security Center configuration as that described in Internet access: Network Agent as connection gateway in DMZ), you must specify the address of the connection gateway in the corresponding field of the connection profile.
Switching between Administration Servers depending on the current network
If the organization has multiple offices with different Administration Servers and some of the devices with Network Agent installed move between them, you need Network Agent to connect to the Administration Server of the local network in the office where the device is currently located.
In this case, you must create a profile for connection to Administration Server in the properties of the policy of Network Agent for each of the offices, except for the home office where the original home Administration Server is located. You must specify the addresses of Administration Servers in connection profiles and enable or disable the Use to receive updates only option:
- Select the option if you need Network Agent to be synchronized with the home Administration Server, while using the local Server for downloading updates only.
- Disable this option if it is necessary for Network Agent to be managed completely by the local Administration Server.
After that, you must set up the conditions of switching to the newly created profiles: at least one condition for each of the offices, except for the home office. Every condition's purpose consists in detection of items that are specific for an office's network environment. If a condition is true, the corresponding profile gets activated. If none of the conditions is true, Network Agent switches to the home Administration Server.
Deploying the Mobile Device Management feature
This section provides information about initial deployment of the Mobile Device Management feature.
Connecting KES devices to the Administration Server
Depending on the method used for connection of devices to the Administration Server, two deployment schemes are possible for Kaspersky Device Management for iOS for KES devices:
- Scheme of deployment with direct connection of devices to the Administration Server
- Scheme of deployment involving a reverse proxy that supports Kerberos constrained delegation
Direct connection of devices to the Administration Server
KES devices can connect directly to port 13292 of the Administration Server.
Depending on the method used for authentication, two options are possible for connection of KES devices to the Administration Server:
- Connecting devices with a user certificate
- Connecting devices without a user certificate
Connecting a device with a user certificate
When connecting a device with a user certificate, that device is associated with the user account to which the corresponding certificate has been assigned through Administration Server tools.
In this case, two-way SSL authentication (mutual authentication) will be used. Both the Administration Server and the device will be authenticated with certificates.
Connecting a device without a user certificate
When connecting a device without a user certificate, that device is associated with none of the user's accounts on the Administration Server. However, when the device receives any certificate, the device will be associated with the user to which the corresponding certificate has been assigned through Administration Server tools.
When connecting that device to the Administration Server, one-way SSL authentication will be applied, which means that only the Administration Server is authenticated with the certificate. After the device retrieves the user certificate, the type of authentication will change to two-way SSL authentication (2-way SSL authentication, mutual authentication).
Page top
Scheme for connecting KES devices to the Server involving Kerberos constrained delegation (KCD)
The scheme for connecting KES devices to the Administration Server involving Kerberos constrained delegation (KCD) provides for the following:
- Integration with a reverse proxy that supports KCD.
- Use of Kerberos Constrained Delegation (hereinafter referred to as KCD) for authentication of mobile devices.
- Integration with Public Key Infrastructure (hereinafter referred to as PKI) for applying user certificates.
When using this connection scheme, please note the following:
- The type of connection of KES devices to the reverse proxy must be "two-way SSL authentication", that is, a device must connect to the reverse proxy through its proprietary user certificate. To do this, you need to integrate the user certificate into the installation package of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android, which has been installed on the device. This KES package must be created by the Administration Server specifically for this device (user).
- You must specify the special (customized) certificate instead of the default server certificate for the mobile protocol:
- In the Administration Server properties window, in the Settings section, select the Open port for mobile devices check box and select Add certificate in the drop-down list.
- In the window that opens, specify the same certificate that was set on the reverse proxy when the point of access to the mobile protocol was published on the Administration Server.
- User certificates for KES devices must be issued by the Certificate Authority (CA) of the domain. Keep in mind that if the domain includes multiple root CAs, user certificates must be issued by the CA, which has been set in the publication on the reverse proxy.
You can make sure the user certificate is in compliance with the above-described requirement, using one of the following methods:
- Specify the special user certificate in the New package wizard and in the Certificate installation wizard.
- Integrate the Administration Server with the domain's PKI and define the corresponding setting in the rules for issuance of certificates:
- In the console tree, expand the Mobile Device Management folder and select the Certificates subfolder.
- In the workspace of the Certificates folder, click the Configure certificate issuance rules button to open the Certificate issuance rules window.
- In the Integration with PKI section, configure integration with the Public Key Infrastructure.
- In the Issuance of mobile certificates section, specify the source of certificates.
Below is an example of setup of Kerberos Constrained Delegation (KCD) with the following assumptions:
- Point of access to the mobile protocol on the Administration Server is set up on port 13292.
- The name of the device with the reverse proxy is firewall.mydom.local.
- The name of the device with Administration Server is ksc.mydom.local.
- Name of the external publishing of the point of access to the mobile protocol is kes4mob.mydom.global.
Domain account for Administration Server
You must create a domain account (for example, KSCMobileSrvcUsr) under which the Administration Server service will run. You can specify an account for the Administration Server service when installing the Administration Server or through the klsrvswch utility. The klsrvswch utility is located in the installation folder of Administration Server. The default installation path: <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
A domain account must be specified by the following reasons:
- The feature for management of KES devices is an integral part of Administration Server.
- To ensure a proper functioning of Kerberos Constrained Delegation (KCD), the receive side (i.e., the Administration Server) must run under a domain account.
Service Principal Name for http/kes4mob.mydom.local
In the domain, under the KSCMobileSrvcUsr account, add an SPN for publishing the mobile protocol service on port 13292 of the device with Administration Server. For the kes4mob.mydom.local device with Administration Server, this will appear as follows:
setspn -a http/kes4mob.mydom.local:13292 mydom\KSCMobileSrvcUsr
Configuring the domain properties of the device with the reverse proxy (firewall.mydom.local)
To delegate traffic, you must trust the device with the reverse proxy (firewall.mydom.local) to the service defined by the SPN (http/kes4mob.mydom.local:13292).
To trust the device with the reverse proxy to the service defined by the SPN (http/kes4mob.mydom.local:13292), the administrator must perform the following actions:
- In the Microsoft Management Console snap-in named "Active Directory Users and Computers", select the device with the reverse proxy installed (firewall.mydom.local).
- In the device properties, on the Delegation tab, set the Trust this computer for delegation to specified service only toggle to Use any authentication protocol.
- In the Services to which this account can present delegated credentials list, add the SPN http/kes4mob.mydom.local:13292.
Special (customized) certificate for the publishing (kes4mob.mydom.global)
To publish the mobile protocol of Administration Server, you must issue a special (customized) certificate for the FQDN kes4mob.mydom.global and specify it instead of the default server certificate in the settings of the mobile protocol of Administration Server in Administration Console. To do this, in the properties window of the Administration Server, in the Settings section select the Open port for mobile devices check box and then select Add certificate in the drop-down list.
Please note that the server certificate container (file with the p12 or pfx extension) must also contain a chain of root certificates (public keys).
Configuring publication on the reverse proxy
On the reverse proxy, for traffic that goes from the mobile device side to port 13292 of kes4mob.mydom.global, you have to configure KCD on the SPN (http/kes4mob.mydom.local:13292), using the server certificate issued for the FQND kes4mob.mydom.global. Please note that publishing and the published access point (port 13292 of the Administration Server) must share the same server certificate.
Using Firebase Cloud Messaging
To ensure timely delivery of commands to KES devices managed by the Android operating system, Kaspersky Security Center uses the mechanism of push notifications. Push notifications are exchanged between KES devices and Administration Server through Firebase Cloud Messaging (hereinafter referred to as FCM). In Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console, you can specify the Firebase Cloud Messaging settings to connect KES devices to the service.
To retrieve the settings of Firebase Cloud Messaging, you must have a Google account.
To enable the use of FCM:
- In Administration Console, select the Mobile Device Management node, and the Mobile devices folder.
- In the context menu of the Mobile devices folder, select Properties.
- In the folder properties, select the Firebase Cloud Messaging settings section.
- In the Firebase project number field, specify the FCM Sender ID.
- In the Private key file (in JSON format) field, select the private key file.
At the next synchronization with Administration Server, KES devices managed by Android operating systems will be connected to Firebase Cloud Messaging.
You can edit the Firebase Cloud Messaging settings by clicking the Reset settings button.
When you switch to a different Firebase project, you need to wait 10 minutes for FCM to resume.
FCM service runs in the following address ranges:
- From the KES device's side, access is required to ports 443 (HTTPS), 5228 (HTTPS), 5229 (HTTPS), and 5230 (HTTPS) of the following addresses:
- google.com
- fcm.googleapis.com
- android.apis.google.com
- All of the IP addresses listed in Google's ASN of 15169
- From the Administration Server side, access is required to port 443 (HTTPS) of the following addresses:
- fcm.googleapis.com
- All of the IP addresses listed in Google's ASN of 15169
If the proxy server settings (Advanced / Configuring Internet access) have been specified in the Administration Server properties in Administration Console, they will be used for interaction with FCM.
Configuring FCM: getting the Sender ID and private key file
To configure FCM:
- Register on the Google portal.
- Go to the Firebase console.
- Do one of the following:
- To create a new project, click Create a project and follow the instructions on the screen.
- Open an existing project.
- Click the gear icon and choose Project settings.
The Project settings window opens.
- Select the Cloud Messaging tab.
- Retrieve the relevant Sender ID from the Sender ID field in the Firebase Cloud Messaging API (V1) section.
- Select the Service accounts tab and click Generate new private key.
- In the window that opens, click Generate key to generate and download a private key file.
Firebase Cloud Messaging is now configured.
Page top
Integration with Public Key Infrastructure
Integration with Public Key Infrastructure (hereinafter referred to as PKI) is primarily intended for simplifying the issuance of domain user certificates by Administration Server.
The administrator can assign a domain certificate for a user in Administration Console. This can be done using one of the following methods:
- Assign the user a special (customized) certificate from a file in the Certificate installation wizard.
- Perform integration with PKI and assign PKI to act as the source of certificates for a specific type of certificates or for all types of certificates.
The settings of integration with PKI are available in the workspace of the Mobile Device Management / Certificates folder by clicking the Integrate with public key infrastructure link.
General principle of integration with PKI for issuance of domain user certificates
In Administration Console, click the Integrate with public key infrastructure link in the workspace of the Mobile Device Management / Certificates folder to specify a domain account that will be used by Administration Server to issue domain user certificates through the domain's CA (hereinafter referred to as the account under which integration with PKI is performed).
Please note the following:
- The settings of integration with PKI provide you the possibility to specify the default template for all types of certificates. Note that the rules for issuance of certificates (available in the workspace of the Mobile Device Management / Certificates folder by clicking the Configure certificate issuance rules button) allow you to specify an individual template for every type of certificates.
- A special Enrollment Agent (EA) certificate must be installed on the device with Administration Server, in the certificates repository of the account under which integration with PKI is performed. The Enrollment Agent (EA) certificate is issued by the administrator of the domain's CA (Certificate Authority).
The account under which integration with PKI is performed must meet the following criteria:
- It is a domain user.
- It is a local administrator of the device with Administration Server from which integration with PKI is initiated.
- It has the right to Log On As Service.
- The device with Administration Server installed must be run at least once under this account to create a permanent user profile.
Kaspersky Security Center Web Server
Kaspersky Security Center Web Server (hereinafter referred to as Web Server) is a component of Kaspersky Security Center. Web Server is designed for publishing stand-alone installation packages, stand-alone installation packages for mobile devices, and files from the shared folder.
Installation packages that have been created are published on Web Server automatically and then removed after the first download. The administrator can send the new link to the user in any convenient way, such as by email.
By clicking the link, the user can download the required information to a mobile device.
Web Server settings
If fine-tuning of Web Server is required, its properties allow you to change ports for HTTP (8060) and HTTPS (8061). In addition to changing ports, you can replace the server certificate for HTTPS and change the FQDN of Web Server for HTTP.
Page top
Other routine work
This section provides recommendations on routine work with Kaspersky Security Center.
Monitoring traffic lights and logged events in Administration Console
Administration Console allows you to quickly assess the current status of Kaspersky Security Center and managed devices by checking traffic lights. The traffic lights are shown in the workspace of the Administration Server node, on the Monitoring tab. The tab provides six information panels with traffic lights and logged events. A traffic light is a colored vertical bar on the left side of a panel. Each panel with a traffic light corresponds to a specific functional scope of Kaspersky Security Center (see the table below).
Scopes covered by traffic lights in Administration Console
Panel name |
Traffic light scope |
|---|---|
Deployment |
Installing Network Agent and security applications on devices on an organization's network |
Management scheme |
Structure of administration groups. Network scanning. Device moving rules |
Protection settings |
Security application functionality: protection status, malware scanning |
Update |
Updates and patches |
Monitoring |
Protection status |
Administration Server |
Administration Server features and properties |
Each traffic light can be any of these five colors (see the table below). The color of a traffic light depends on the current status of Kaspersky Security Center and on events that were logged.
Color codes of traffic lights
Status |
Traffic light color |
Traffic light color meaning |
|---|---|---|
Informational |
Green |
Administrator's intervention is not required. |
Warning |
Yellow |
Administrator's intervention is required. |
Critical |
Red |
Serious problems have been encountered. Administrator's intervention is required to solve them. |
Informational |
Light blue |
Events have been logged that are unrelated to potential or actual threats to the security of managed devices. |
Informational |
Gray |
The details of events are not available or have not yet been retrieved. |
The administrator's goal is to keep traffic lights on all of the information panels on the Monitoring tab green.
The information panels also show logged events that affect traffic lights and the status of Kaspersky Security Center (see the table below).
Name, description, and traffic light colors of logged events
Traffic light color |
Event type display name |
Event type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Red |
License expired on %1 device(s) |
IDS_AK_STATUS_LIC_EXPAIRED |
Events of this type occur when the commercial license has expired. Once a day Kaspersky Security Center checks whether the license has expired on the devices. When the commercial license expires, Kaspersky Security Center provides only basic functionality. To continue using Kaspersky Security Center, renew your commercial license. |
Red |
Security application is not running on: %1 device(s) |
IDS_AK_STATUS_AV_NOT_RUNNING |
Events of this type occur when the security application installed on the device is not running. Make sure that Kaspersky Endpoint Security is running on the device. |
Red |
Protection is disabled on: %1 device(s) |
IDS_AK_STATUS_RTP_NOT_RUNNING |
Events of this type occur when the security application on the device has been disabled for longer than the specified time interval. Check the current status of real-time protection on the device and make sure that all the protection components that you need are enabled. |
Red |
A software vulnerability has been detected on devices |
IDS_AK_STATUS_VULNERABILITIES_FOUND |
Events of this type occur when the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task has detected vulnerabilities with the severity level specified in applications installed on the device. Check the list of available updates in the Software updates subfolder included in the Application management folder. This folder contains a list of updates for Microsoft applications and other software vendors products retrieved by Administration Server, which can be distributed to devices. After viewing information about available updates, install them on the device. |
Red |
Critical events have been registered on the Administration Server |
IDS_AK_STATUS_EVENTS_OCCURED |
Events of this type occur when Administration Server critical events are detected. Check the list of events stored on the Administration Server, and then fix the critical events one by one. |
Red |
Errors have been logged in events on the Administration Server |
IDS_AK_STATUS_ERROR_EVENTS_OCCURED |
Events of this type occur when unexpected errors are logged on the Administration Server side. Check the list of events stored on the Administration Server, and then fix the errors one by one. |
Red |
Lost connection to %1 device(s) |
IDS_AK_STATUS_ADM_LOST_CONTROL1 |
Events of this type occur when the connection between the Administration Server and the device is lost. View the list of disconnected devices and try to reconnect them. |
Red |
%1 device (s) have not connected to the Administration Server in a long time |
IDS_AK_STATUS_ADM_NOT_CONNECTED1 |
Events of this type occur when the device has not connected to the Administration Server within the specified time interval, because the device was turned off. Make sure that the device is turned on and that Network Agent is running. |
Red |
%1 device(s) have a status other than OK |
IDS_AK_STATUS_HOST_NOT_OK |
Events of this type occur when the OK status of the device connected to the Administration Server changes to Critical or Warning. You can troubleshoot the problem by using the Kaspersky Security Center remote diagnostics utility. |
Red |
Databases are outdated on: %1 device(s) |
IDS_AK_STATUS_UPD_HOSTS_NOT_UPDATED |
Events of this type occur when the anti-virus databases have not been updated on the device within the specified time interval. Follow the instructions to update Kaspersky databases. |
Red |
Device(s) where check for Windows Update updates has not been performed in a long time: %1 |
IDS_AK_STATUS_WUA_DATA_OBSOLETE |
Events of this type occur when the Perform Windows Update synchronization task has not been run within the specified time interval. Follow the instructions to synchronize updates from Windows Update with Administration Server. |
Red |
%1 plug-in(s) for Kaspersky Security Center must be installed |
IDS_AK_STATUS_PLUGINS_REQUIRED2 |
Events of this type occur when you need to install additional plug-ins for Kaspersky applications. Download and install the required management plug-ins for the Kaspersky application from the Kaspersky Technical Support webpage. |
Remote access to managed devices
This section provides information about remote access to managed devices.
Using the "Do not disconnect from the Administration Server" option to provide continuous connectivity between a managed device and the Administration Server
If you do not use push servers, Kaspersky Security Center does not provide continuous connectivity between managed devices and the Administration Server. Network Agents on managed devices periodically establish connections and synchronize with the Administration Server. The interval between those synchronization sessions is defined in a policy of Network Agent. If an early synchronization is required, the Administration Server (or a distribution point, if it is in use) sends a signed network packet over an IPv4 or IPv6 network to the UDP port of the Network Agent. By default, the port number is 15000. If no connection through UDP is possible between the Administration Server and a managed device, synchronization will run at the next regular connection of Network Agent to the Administration Server within the synchronization interval.
Some operations cannot be performed without an early connection between Network Agent and the Administration Server, such as running and stopping local tasks, receiving statistics for a managed application, or creating a tunnel. To resolve this issue, if you are not using push servers, you can use the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option to make sure that there is continuous connectivity between a managed device and the Administration Server.
To provide continuous connectivity between a managed device and the Administration Server:
- In the console tree, select the Managed devices folder.
- In the workspace of the folder, select the managed device with which you want to provide continuous connectivity.
- In the context menu of the device, select Properties.
The properties window of the selected device opens.
- In the General section of the displayed window, select the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option.
Continuous connectivity is established between the managed device and the Administration Server.
The maximum total number of devices with the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option selected is 300.
About checking the time of connection between a device and the Administration Server
Upon shutting down a device, Network Agent notifies the Administration Server of this event. In Administration Console that device is displayed as shut down. However, Network Agent cannot notify Administration Server of all such events. The Administration Server, therefore, periodically analyzes the Connected to Administration Server attribute (the value of this attribute is displayed in Administration Console, in the device properties, in the General section) for each device and compares it against the synchronization interval from the current settings of Network Agent. If a device has not responded over more than three successive synchronization intervals, that device is marked as shut down.
Page top
About forced synchronization
Although Kaspersky Security Center automatically synchronizes the status, settings, tasks, and policies for managed devices, in some cases the administrator needs to know exactly whether synchronization has already been performed for a specified device at the present moment.
In the context menu of managed devices in Administration Console, the All tasks menu item contains the Force synchronization command. When Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 executes this command, the Administration Server attempts to connect to the device. If this attempt is successful, forced synchronization will be performed. Otherwise, synchronization will be forced only after the next scheduled connection between Network Agent and the Administration Server.
About tunneling
Kaspersky Security Center allows tunneling TCP connections from Administration Console via the Administration Server and then via Network Agent to a specified port on a managed device. Tunneling is designed for connecting a client application on a device with Administration Console installed to a TCP port on a managed device—if no direct connection is possible between Administration Console and the target device.
For example, tunneling is used for connections to a remote desktop, both for connecting to an existing session, and for creating a new remote session.
Tunneling can also be enabled by using external tools. For example, the administrator can run the putty utility, the VNC client, and other tools in this way.
Page top
About this Guide
Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 (also referred to as Kaspersky Security Center) Sizing Guide is intended for professionals who install and administer Kaspersky Security Center, as well as for those who provide technical support to organizations that use Kaspersky Security Center.
All recommendations and calculations are given for networks on which Kaspersky Security Center manages the protection of devices with Kaspersky software installed, including mobile devices. If mobile devices, or any other managed devices, are to be considered separately, this is stated specifically.
To obtain and maintain optimum performance under varying operational conditions, you must take into account the number of networked devices, network topology, and set of Kaspersky Security Center features that you require.
This Guide provides the following information:
- Limitations of Kaspersky Security Center
- Calculations for the key nodes of Kaspersky Security Center (Administration Servers and distribution points):
- Hardware requirements for Administration Servers and distribution points
- Calculation of the number and hierarchy of Administration Servers
- Calculation of the number and configuration of distribution points
- Configuration of event logging in the database depending on the number of networked devices
- Common best practices for performance optimization
- Configuration of specific tasks aimed at optimal performance of Kaspersky Security Center
- Traffic rate (network load) between Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and every protected device
Consulting this guide is recommended in the following cases:
- When planning resources prior to Kaspersky Security Center installation
- When planning significant changes to the scale of the network on which Kaspersky Security Center is deployed
- When switching from using Kaspersky Security Center within a limited network segment (a test environment) to full-scale deployment of Kaspersky Security Center on the corporate network
- When making changes to the set of Kaspersky Security Center features used
Information about limitations of Kaspersky Security Center
The following table displays the limitations of the current version of Kaspersky Security Center.
Limitations of Kaspersky Security Center
Type of limitation |
Value |
|---|---|
Maximum number of managed devices per Administration Server |
100,000 |
Maximum number of devices with the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option selected |
300 |
Maximum number of administration groups |
10,000 |
Maximum number of events to store |
45,000,000 |
Maximum number of policies |
2000 |
Maximum number of tasks |
2000 |
Maximum total number of Active Directory objects (organizational units, OUs) and accounts of users, devices, and security groups) |
1,000,000 |
Maximum number of profiles in a policy |
100 |
Maximum number of secondary Administration Servers on a single primary Administration Server |
500 |
Maximum number of virtual Administration Servers |
500 |
Maximum number of devices that a single distribution point can cover (distribution points can cover non-mobile devices only) |
10,000 |
Maximum number of devices that may use a single connection gateway |
10,000, including mobile devices |
Maximum number of mobile devices per Administration Server |
100,000 minus the number of stationary managed devices |
Calculations for Administration Servers
This section provides the software and hardware requirements for devices used as Administration Servers. Also provided are recommendations for calculating the number and hierarchy of Administration Servers depending on the configuration of the organization's network.
Calculation of hardware resources for the Administration Server
This section contains calculations that provide guidance for planning hardware resources for the Administration Server. A recommendation on calculating disk space when the Vulnerability and patch management feature is used is provided separately.
Hardware requirements for the DBMS and the Administration Server
The following tables give the recommended minimum hardware requirements to a DBMS and Administration Server obtained during tests. For a complete list of operating systems and DBMSs supported, please refer to the list of hardware and software requirements.
Administration Server and DBMS are on different devices, the network includes 50 000 devices
Configuration of the device that has Administration Server installed
Hardware |
Value |
CPU |
4 cores, 2500 MHz |
RAM |
8 GB |
Hard drive |
300 GB, RAID recommended |
Network adapter |
1 Gbit |
Configuration of the device that has DBMS installed
Hardware |
Value |
|---|---|
CPU |
4 cores, 2500 MHz |
RAM |
16 GB |
Hard drive |
200 GB, SATA RAID |
Network adapter |
1 Gbit |
Administration Server and DBMS are on the same device, the network includes 50 000 devices
Configuration of the device that has Administration Server and DBMS installed
Hardware |
Value |
|---|---|
CPU |
8 cores, 2500 MHz |
RAM |
16 GB |
Hard drive |
500 GB, SATA RAID |
Network adapter |
1 Gbit |
Administration Server and DBMS are on different devices, the network includes 100 000 devices
Configuration of the device that has Administration Server installed
Hardware |
Value |
|---|---|
CPU |
8 cores, 2.13 GHz |
RAM |
8 GB |
Hard drive |
1 TB, with RAID |
Network adapter |
1 Gbit |
Configuration of the device with DBMS installed
Hardware |
Value |
|---|---|
CPU |
8 cores, 2.53 GHz |
RAM |
26 GB |
Hard drive |
500 GB, SATA RAID |
Network adapter |
1 Gbit |
The tests were run under the following settings:
- Automatic assignment of distribution points is enabled on the Administration Server, or distribution points are assigned manually in accordance with the recommended table.
- The backup task saves backup copies to a file resource located on a dedicated server.
- The synchronization interval for Network Agents is set as specified in the table below.
Synchronization interval for Network Agents
Synchronization interval (minutes)
Number of managed devices
15
10,000
30
20,000
45
30,000
60
40,000
75
50,000
150
100,000
Calculation of database space
The approximate amount of space that must be reserved in the database can be calculated using the following formula:
(600 * C + 2.3 * E + 2.5 * A + 1.2 * N * F), KB
where:
- C is the number of devices.
- E is the number of events to store.
- A is the total number of Active Directory objects:
- Device accounts
- User accounts
- Accounts of security groups
- Active Directory organizational units
If scanning of Active Directory is disabled, A is considered to equal zero.
- N is the average number of inventoried executable files on an endpoint device.
- F is the number of endpoint devices, where executable files were inventoried.
If you plan to enable (in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy settings) notification of Administration Server on applications that you run, you will need additional (0.03 * C) gigabytes to store in the database the information about applications that you run.
If Administration Server distributes Windows updates (thus acting as the Windows Server Update Services server), the database will require an additional 2.5 GB.
During operation, a certain unallocated space is always present in the database. Therefore, the actual size of the database file (by default, the KAV.MDF file, if you use SQL Server as the DBMS) often turns out to be approximately twice as large as the amount of space occupied in the database.
It is not recommended to limit explicitly the size of the transaction log (by default, the file KAV_log.LDF, if you use SQL Server as the DBMS). It is recommended to leave the default value of th MAXSIZE parameter. However, if you have to limit the size of this file, take into consideration that the typical necessary value of the MAXSIZE parameter for KAV_log.LDF is 20480 MB.
Calculation of disk space (with and without the use of the Vulnerability and patch management feature)
Calculation of disk space without the use of the Vulnerability and patch management feature
The Administration Server disk space required for the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit folder can be estimated approximately using the formula:
(724 * C + 0.15 * E + 0.17 * A), KB
where:
- C is the number of devices.
- E is the number of events to store.
- A is the total number of Active Directory objects:
- Device accounts
- User accounts
- Accounts of security groups
- Active Directory organizational units
If scanning of Active Directory is disabled, A is considered to equal zero.
Calculation of additional disk space with the use of the Vulnerability and patch management feature
- Updates. The shared folder additionally requires at least 4 GB to store updates.
- Installation packages. If some installation packages are stored on the Administration Server, the shared folder will require an additional amount of free disk space equal to the total size of all of the available installation packages to be installed.
- Remote installation tasks. If remote installation tasks are present on the Administration Server, an additional amount of free disk space (in the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit folder) equal to the total size of all installation packages to be installed will be required.
- Patches. If Administration Server is involved in installation of patches, an additional amount of disk space will be required:
- The patches folder should have the amount of disk space equal to the total size of all patches that have been downloaded. By default, patches are stored in the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\.working\wusfiles folder.
You can use the klsrvswch utility to specify a different folder for storing patches. The klsrvswch utility is located in the folder where Administration Server is installed. The default installation path: <Disk>:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security Center.
If Administration Server is used as the WSUS server, you are advised to allocate at least 100 GB to this folder.
- The %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit folder must have an amount of disk space equal to the total size of those patches that are referenced by existing instances of update (patch) installation and vulnerability fix tasks.
- The patches folder should have the amount of disk space equal to the total size of all patches that have been downloaded. By default, patches are stored in the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\.working\wusfiles folder.
Calculation of the number and configuration of Administration Servers
To reduce the load on the primary Administration Server, you can assign a separate Administration Server to each administration group. The number of secondary Administration Servers cannot exceed 500 for a single primary Administration Server.
We recommend that you create the configuration of Administration Servers in correspondence to the configuration of your organization's network.
Page top
Recommendations for connecting dynamic virtual machines to Kaspersky Security Center
Dynamic virtual machines (also referred to as dynamic VMs) consume more resources than static virtual machines.
For more information on dynamic virtual machines, see Support of dynamic virtual machines.
When a new dynamic VM is connected, Kaspersky Security Center creates an icon for this dynamic VM in Administration Console and moves the dynamic VM to the administration group. After that, the dynamic VM is added to the Administration Server database. The Administration Server is fully synchronized with Network Agent installed on this dynamic VM.
In an organization's network, Network Agent creates the following network lists for each dynamic VM:
- Hardware
- Installed software
- Detected vulnerabilities
- Events and lists of executable files of the Application control component
The Network Agent transfers these network lists to the Administration Server. The size of the network lists depends on components installed on the dynamic VM, and may affect the performance of Kaspersky Security Center and database management system (DBMS). Note that the load can grow non-linearly.
After the user finishes working with the dynamic VM and turns it off, this machine is then removed from the virtual infrastructure and entries about this machine are removed from the Administration Server database.
All these actions consume a lot of Kaspersky Security Center and Administration Server database resources, and can reduce the performance of Kaspersky Security Center and DBMS. We recommend that you connect up to 20,000 dynamic VMs to Kaspersky Security Center.
You can connect more than 20,000 dynamic VMs to Kaspersky Security Center if the connected dynamic VMs perform standard operations (for example, database updates) and consume no more than 80 percent of memory and 75–80 percent of available cores.
Changing policy settings, software or operating system on the dynamic VM can reduce or increase resource consumption. The consumption of 80–95 percent of resources is considered optimal.
Page top
Calculations for distribution points and connection gateways
This section provides the hardware requirements for devices used as distribution points together with recommendations for calculating the number of distribution points and connection gateways depending on the configuration of the corporate network.
Requirements for a distribution point
To handle up to 10,000 client devices, a distribution point must meet, at a minimum, the following requirements (a configuration for a test stand is provided):
- CPU: Intel Core i7-7700 CPU, 3.60 GHz 4 cores.
- RAM: 8 GB.
- Free storage space: 120 GB.
It is not recommended to assign the Administration Server as a distribution point, as this will increase the load on the Administration Server.
If any remote installation tasks are pending on the Administration Server, the device with the distribution point will also require an amount of free disk space that is equal to the total size of the installation packages to be installed.
If one or multiple instances of the task for update (patch) installation and vulnerability fix are pending on the Administration Server, the device with the distribution point will also require additional free disk space, equal to twice the total size of all patches to be installed.
If you use the scheme where distribution points receive database updates and application software modules directly from Kaspersky update servers, the distribution points must be connected to the internet.
Calculating the number and configuration of distribution points
The more client devices a network contains, the more distribution points it requires. We recommend that you not disable automatic assignment of distribution points. When automatic assignment of distribution points is enabled, Administration Server assigns distribution points if the number of client devices is quite large and defines their configuration.
Using exclusively assigned distribution points
If you plan to use certain specific devices as distribution points (that is, exclusively assigned servers), you can opt out of using automatic assignment of distribution points. In this case, make sure that the devices that you intend to make distribution points have sufficient volume of free disk space, are not shut down regularly, and have Sleep mode disabled.
Number of exclusively assigned distribution points on a network that contains a single network segment, based on the number of networked devices
Number of client devices in the network segment |
Number of distribution points |
|---|---|
Less than 300 |
0 (Do not assign distribution points) |
More than 300 |
Acceptable: (N/10,000 + 1), recommended: (N/5000 + 2), where N is the number of networked devices |
Number of exclusively assigned distribution points on a network that contains multiple network segments, based on the number of networked devices
Number of client devices per network segment |
Number of distribution points |
|---|---|
Less than 10 |
0 (Do not assign distribution points) |
10–100 |
1 |
More than 100 |
Acceptable: (N/10,000 + 1), recommended: (N/5000 + 2), where N is the number of networked devices |
Using standard client devices (workstations) as distribution points
If you plan to use standard client devices (that is, workstations) as distribution points, we recommend that you assign distribution points as shown in the tables below in order to avoid excessive load on the communication channels and on Administration Server:
Number of workstations functioning as distribution points on a network that contains a single network segment, based on the number of networked devices
Number of client devices in the network segment |
Number of distribution points |
|---|---|
Less than 300 |
0 (Do not assign distribution points) |
More than 300 |
(N/300 + 1), where N is the number of networked devices; there must be at least 3 distribution points |
Number of workstations functioning as distribution points on a network that contains multiple network segments, based on the number of networked devices
Number of client devices per network segment |
Number of distribution points |
|---|---|
Less than 10 |
0 (Do not assign distribution points) |
10–30 |
1 |
31–300 |
2 |
More than 300 |
(N/300 + 1), where N is the number of networked devices; there must be at least 3 distribution points |
If a distribution point is shut down (or not available for some other reason), the managed devices in its scope can access the Administration Server for updates.
Calculation of the number of connection gateways
If you plan to use a connection gateway, we recommend that you designate a special device for this function.
A connection gateway can cover a maximum 10,000 managed devices, including mobile devices.
Page top
Logging of information about events for tasks and policies
This section provides calculations associated with event storage in the database of the Administration Server and offers recommendations on how to minimize the number of events, thereby reducing the load on the Administration Server.
By default, the properties of each task and policy provide for storing all events related to task execution and policy enforcement.
However, if a task is run quite frequently (for example, more than once per week) and on a fairly large number of devices (for example, more than 10,000), the number of events may turn out to be too large and the events may flood the database. In this case, it is recommended to select one of two options in the task settings:
- Save events related to task progress. In this case, the database receives only information about task launch, progress, and completion (successful, with a warning or error) from each device on which the task is run.
- Save only task execution results. In this case, the database receives only information about task completion (successful, with a warning or error) from each device on which the task is run.
If a policy has been defined for a fairly large number of devices (for example, more than 10,000), the number of events may also turn out to be large and the events may flood the database. In this case, it is recommended to choose only the most critical events in the policy settings and enable their logging. You are advised to disable the logging of all other events.
In doing so, you will reduce the number of events in the database, increase the speed of execution of scenarios associated with analysis of the event table in the database, and lower the risk that critical events will be overwritten by a large number of events.
You can also reduce the storage term for events associated with a task or a policy. The default period is 7 days for task-related events and 30 days for policy-related events. When changing the event storage term, consider the work procedures in place at your organization and the amount of time that the system administrator can devote to analyzing each event.
It is advisable to modify the event storage settings in any of the following cases:
- Events about changes in the intermediate states of group tasks and events about applying policies occupy a large share of all events in the Kaspersky Security Center database.
- The Kaspersky Event Log begins showing entries about automatic removal of events when the established limit on the total number of events stored in the database is exceeded.
Choose event logging options based on the assumption that the optimal number of events coming from a single device per day must not exceed 20. You can increase this limit slightly, if necessary, but only if the number of devices on your network is relatively small (fewer than 10,000).
Page top
Specific considerations and optimal settings of certain tasks
Certain tasks are subject to specific considerations related to the number of networked devices. This section offers recommendations on the optimal configuration of settings for such tasks.
Device discovery, the data backup task, Administration Server maintenance task, and group tasks for updating Kaspersky Endpoint Security are part of the basic functionality of Kaspersky Security Center.
Device discovery frequency
It is not advisable to increase the default frequency of device discovery because this can create an excessive load on domain controllers. Instead, it is recommended to schedule polling at the minimum possible frequency permitted by the needs of your organization. Recommendations for calculating the optimal schedule are provided in the table below.
Device discovery schedule
Number of networked devices |
Recommended device discovery frequency |
|---|---|
Less than 10,000 |
Default frequency or less |
10,000 or greater |
Once per day or less |
Administration Server data backup task and Administration Server maintenance task
The Administration Server stops working when the following tasks are running:
- Backup of Administration Server data
- Administration Server maintenance
When these tasks are running, the database cannot receive any data.
You may have to reschedule these tasks so that they are not executed at the same time as other Administration Server tasks.
Page top
Group tasks for updating Kaspersky Endpoint Security
If the Administration Server acts as the update source, the recommended schedule option for group update tasks of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 and later versions is When new updates are downloaded to the repository with the Use automatically randomized delay for task starts check box selected.
If a local task for downloading updates from Kaspersky servers to the repository is created on each distribution point, periodic scheduling is recommended for the Kaspersky Endpoint Security group update task. The value of the randomization period must be one hour in this case.
Page top
Inventory task
You can reduce load on the database while obtaining information about the executable files. To do this, we recommend that you run an inventory task for Kaspersky Endpoint Security on reference devices on which a standard set of software is installed.
The number of executable files received by the Administration Server from a single device cannot exceed 150,000. When Kaspersky Security Center reaches this limit, it cannot receive any new files.
Typically, the number of files on a common client device does not exceed 60,000. The number of executable files on a file server can be greater than and even exceed the 150,000 threshold.
Test measurements have shown that the inventory task has the following results on a device running the Windows 7 operating system with Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11 installed and no third-party applications installed:
- With the DLL modules inventory and Script files inventory check boxes cleared: approximately 3000 files.
- With the DLL modules inventory and Script files inventory check boxes selected: from 10,000 to 20,000 files depending on the number of operating system service packs installed.
- With only the Script files inventory check box selected: approximately 10,000 files.
Details of network load spread among Administration Server and protected devices
This section provides the results of test measurements of network traffic with a description of the conditions under which the measurements were performed. You can refer to this information when planning the network infrastructure and the throughput capacity of network channels within your organization (or between the Administration Server and another organization with devices to protect). Knowing the throughput capacity of the network, you can also estimate approximately how much time different data transmission operations will take.
Traffic consumption under various scenarios
The table below shows the results of measuring tests conducted on traffic between the Administration Server and a managed device in different scenarios.
By default, devices are synchronized with the Administration Server every 15 minutes or at a longer interval. However, if you modify the settings of a policy or a task on the Administration Server, early synchronization occurs on devices to which the policy (or task) is applicable so the new settings are transmitted to the devices.
Traffic rate between the Administration Server and managed device
Scenario |
Traffic from the Administration Server to each managed device |
Traffic from each managed device to the Administration Server |
|---|---|---|
Installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.7 for Windows with updated databases |
390 MB |
3.3 MB |
Network Agent installation |
75 MB |
397 KB |
Concurrent installation of Network Agent and Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.7 for Windows |
459 MB |
3.6 MB |
Initial update of anti-virus databases without updating the databases in the package (if participation in Kaspersky Security Network is disabled) |
113 MB |
1,8 MB |
Daily update of anti-virus databases (if participation in Kaspersky Security Network is enabled) |
22 MB |
373 MB |
Initial synchronization before update of databases on a device (transfer of policies and tasks) |
382 KB |
446 KB |
Initial synchronization after updating databases on a device |
20 KB |
157 KB |
Synchronization with no changes on the Administration Server (according to schedule) |
18 KB |
23 KB |
Synchronization when a single setting in a group policy is changed (as soon as the setting is altered) |
19 KB |
20 KB |
Synchronization when a single setting in a group task is changed (as soon as the setting is altered) |
14 KB |
11 KB |
Forced synchronization |
110 KB |
109 KB |
Virus detected event (1 virus) |
44 KB |
50 KB |
Virus detected event (10 viruses) |
58 KB |
77 KB |
One-time traffic after enabling the Application Registry list |
up to 10 KB |
up to 12 KB |
Everyday traffic when the Application Registry list is enabled |
up to 840 KB |
up to 1 MB |
Average traffic usage per 24 hours
The average 24-hour traffic usage between the Administration Server and a managed device is as follows:
- Traffic from the Administration Server to the managed device is 840 KB.
- Traffic from the managed device to the Administration Server is 1 MB.
The traffic was measured under the following conditions:
- The managed device had Network Agent and Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.6 for Windows installed.
- The device was not assigned a distribution point.
- Vulnerability and patch management was not enabled.
- The frequency of synchronization with the Administration Server was 15 minutes.
Contact Technical Support
This section describes how to get technical support and the terms on which it is available.
How to get technical support
If you can't find a solution to your issue in the Kaspersky Security Center documentation or in any of the sources of information about Kaspersky Security Center, contact Kaspersky Technical Support. Technical Support specialists will answer all your questions about installing and using Kaspersky Security Center.
Kaspersky provides support of Kaspersky Security Center during its lifecycle (see the application support lifecycle page). Before contacting Technical Support, please read the support rules.
You can contact Technical Support in one of the following ways:
- By visiting the Technical Support website
- By sending a request to Technical Support from the Kaspersky CompanyAccount portal
Technical support via Kaspersky CompanyAccount
Kaspersky CompanyAccount is a portal for companies that use Kaspersky applications. The Kaspersky CompanyAccount portal is designed to facilitate interaction between users and Kaspersky specialists through online requests. You can use Kaspersky CompanyAccount to track the status of your online requests and store a history of them as well.
You can register all of your organization's employees under a single account on Kaspersky CompanyAccount. A single account lets you centrally manage electronic requests from registered employees to Kaspersky and also manage the privileges of these employees via Kaspersky CompanyAccount.
The Kaspersky CompanyAccount portal is available in the following languages:
- English
- Spanish
- Italian
- German
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Russian
- French
- Japanese
To learn more about Kaspersky CompanyAccount, visit the Technical Support website.
Page top
Obtaining dump files of Administration Server
Dump files of Administration Server contain all information about the Administration Server processes at a point in time. Dump files of Administration Server are stored in the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\~dumps folder. Dump files are stored as long as Kaspersky Security Center is in use, and are deleted permanently when it is removed. Dump files are not sent to Kaspersky automatically.
If Administration Server crashes, you can contact Kaspersky Technical Support. A Technical Support specialist may ask you to send the dump files of Administration Server for further analysis at Kaspersky.
Dump files may contain personal data. We recommend protecting information from unauthorized access before sending it to Kaspersky.
Page top
Sources of information about the application
Kaspersky Security Center page on the Kaspersky website
On the Kaspersky Security Center page on the Kaspersky website, you can view general information about the application, its functions, and features.
Kaspersky Security Center page in the Knowledge Base
The Knowledge Base is a section on the Kaspersky Technical Support website.
On the Kaspersky Security Center page in the Knowledge Base, you can read articles that provide useful information, recommendations, and answers to frequently asked questions on how to buy, install, and use the application.
Articles in the Knowledge Base may provide answers to questions that relate both to Kaspersky Security Center as well as to other Kaspersky applications. Articles in the Knowledge Base may also contain Technical Support news.
Discuss Kaspersky applications with the community
If your question does not require an immediate answer, you can discuss it with Kaspersky experts and other users on our Forum.
On the Forum, you can view discussion topics, post your comments, and create new discussion topics.
An internet connection is required to access website resources.
If you cannot find a solution to your problem, contact Technical Support.
Page topGlossary
Active key
A key that is currently used by the application.
Additional (or reserve) license key
A key that certifies the right to use the application but is not currently being used.
Administration Console
A component of Windows-based Kaspersky Security Center (also called MMC-based Administration Console). This component provides a user interface for the administrative services of Administration Server and Network Agent.
Administration group
A set of devices grouped by function and by installed Kaspersky applications. Devices are grouped as a single entity for the convenience of management. A group can include other groups. Group policies and group tasks can be created for each installed application in the group.
Administration Server
A component of Kaspersky Security Center that centrally stores information about all Kaspersky applications that are installed on the corporate network. It can also be used to manage these applications.
Administration Server certificate
The certificate that the Administration Server uses for the following purposes:
- Authentication of Administration Server when connecting to MMC-based Administration Console or Kaspersky Security Center Web Console
- Secure interaction between Administration Server and Network Agents on managed devices
- Authentication of Administration Servers when connecting a primary Administration Server to a secondary Administration Server
The certificate is created automatically when you install the Administration Server, and then stored on the Administration Server.
Administration Server client (Client device)
A device, server, or workstation on which Network Agent is installed and managed Kaspersky applications are running.
Administration Server data backup
Copying of the Administration Server data for backup and subsequent restoration performed by using the backup utility. The utility can save:
- Database of the Administration Server (policies, tasks, application settings, events saved on the Administration Server)
- Configuration information about the structure of administration groups and client devices
- Repository of the installation files for remote installation of applications (content of the folders: Packages, Uninstall Updates)
- Administration Server certificate
Administrator rights
The level of the user's rights and privileges required for administration of Exchange objects within an Exchange organization.
Administrator's workstation
A device where Administration Console is installed or that you use to open Kaspersky Security Center Web Console. This component provides a Kaspersky Security Center management interface.
The administrator's workstation is used to configure and manage the server side of Kaspersky Security Center. Using the administrator's workstation, the administrator builds and manages a centralized anti-virus protection system for a corporate LAN based on Kaspersky applications.
Amazon EC2 instance
A virtual machine created based on an AMI image using Amazon Web Services.
Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
The template containing the software configuration necessary for running the virtual machine. Multiple instances can be created based on a single AMI.
Anti-virus databases
Databases that contain information about computer security threats known to Kaspersky as of when the anti-virus databases are released. Entries in anti-virus databases allow malicious code to be detected in scanned objects. Anti-virus databases are created by Kaspersky specialists and updated hourly.
Anti-virus protection service provider
An organization that provides a client organization with anti-virus protection services based on Kaspersky solutions.
Application Shop
Component of Kaspersky Security Center. Application Shop is used for installing applications on Android devices owned by users. Application Shop allows you to publish the APK files of applications and links to applications in Google Play.
Authentication Agent
Interface that lets you complete authentication to access encrypted hard drives and load the operating system after the bootable hard drive has been encrypted.
Available update
A set of updates for Kaspersky application modules, including critical updates accumulated over a certain period of time and changes to the application's architecture.
AWS Application Program Interface (AWS API)
The application programming interface of the AWS platform that is used by Kaspersky Security Center. Specifically, AWS API tools are used for cloud segment polling and installing Network Agent on instances.
AWS IAM access key
A combination consisting of the key ID (which looks like "AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE") and secret key (which looks like "wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY"). This pair belongs to the IAM user and is used to obtain access to AWS services.
AWS Management Console
The web interface for viewing and managing AWS resources. AWS Management Console is available on the web at https://aws.amazon.com/console/.
Backup folder
Special folder for storage of Administration Server data copies created using the backup utility.
Broadcast domain
A logical area of a network in which all nodes can exchange data using a broadcasting channel at the level of OSI (Open Systems Interconnection Basic Reference Model).
Centralized application management
Remote application management using the administration services provided in Kaspersky Security Center.
Client administrator
A staff member of a client organization who is responsible for monitoring the anti-virus protection status.
Cloud Discovery
Cloud Discovery is a component of the Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) solution that protects the cloud infrastructure of an organization. Cloud Discovery manages user access to cloud services. Cloud services include, for example, Microsoft Teams, Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365. Cloud services are grouped in categories, for example, Data exchange, Messengers, Email.
Cloud environment
Virtual machines and other virtual resources that are based on a cloud platform and are combined into networks.
Configuration profile
Policy that contains a collection of settings and restrictions for an iOS MDM mobile device.
Connection gateway
A connection gateway is a Network Agent acting in a special mode. A connection gateway accepts connections from other Network Agents and tunnels them to the Administration Server through its own connection with the Server. Unlike an ordinary Network Agent, a connection gateway waits for connections from the Administration Server rather than establishes connections to the Administration Server.
Demilitarized zone (DMZ)
Demilitarized zone is a segment of a local network that contains servers, which respond to requests from the global Web. In order to ensure the security of an organization's local network, access to the LAN from the demilitarized zone is protected with a firewall.
Device owner
Device owner is a user whom the administrator can contact when the need arises to perform certain operations on a device.
Direct application management
Application management through a local interface.
Distribution point
Computer that has Network Agent installed and is used for update distribution, remote installation of applications, getting information about computers in an administration group and/or broadcasting domain. Distribution points are designed to reduce the load on the Administration Server during update distribution and to optimize network traffic. Distribution points can be assigned automatically, by the Administration Server, or manually, by the administrator. Distribution point was previously known as update agent.
Event repository
A part of the Administration Server database dedicated to storage of information about events that occur in Kaspersky Security Center.
Event severity
Property of an event encountered during the operation of a Kaspersky application. There are the following severity levels:
- Critical event
- Functional failure
- Warning
- Info
Events of the same type can have different severity levels depending on the situation in which the event occurred.
Forced installation
Method for remote installation of Kaspersky applications that allows you to install software on specific client devices. For successful forced installation, the account used for the task must have sufficient rights to start applications remotely on client devices. This method is recommended for installing applications on devices that are running Microsoft Windows operating systems and that support this functionality.
Group task
A task defined for an administration group and performed on all client devices included in that administration group.
Hardening Guide
A set of recommendations and features for configuring Kaspersky Security Center and its components, aimed to reduce the risks of its compromise.
Home Administration Server
Home Administration Server is the Administration Server that was specified during Network Agent installation. The home Administration Server can be used in settings of Network Agent connection profiles.
HTTPS
Secure protocol for data transfer, using encryption, between a browser and a web server. HTTPS is used to gain access to restricted information, such as corporate or financial data.
IAM role
Set of rights for making requests to AWS-based services. IAM roles are not linked to a specific user or group; they provide access rights without AWS IAM access keys. You can assign an IAM role to IAM users, EC2 instances, and AWS-based applications or services.
IAM user
The user of AWS services. An IAM user may have the rights to perform cloud segment polling.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
The AWS service that enables management of user access to other AWS services and resources.
Incompatible application
An anti-virus application from a third-party developer or a Kaspersky application that does not support management through Kaspersky Security Center.
Installation package
A set of files created for remote installation of a Kaspersky application by using the Kaspersky Security Center remote administration system. The installation package contains a range of settings needed to install the application and get it running immediately after installation. Settings correspond to application defaults. The installation package is created using files with the .kpd and .kud extensions included in the application distribution kit.
Internal users
The accounts of internal users are used to work with virtual Administration Servers. Kaspersky Security Center grants the rights of real users to internal users of the application.
The accounts of internal users are created and used only within Kaspersky Security Center. No data on internal users is transferred to the operating system. Kaspersky Security Center authenticates internal users.
iOS MDM device
A mobile device that is connected to the iOS MDM Server by using the iOS MDM protocol. Devices running the iOS operating system can be connected and managed by means of the iOS MDM protocol.
iOS MDM profile
Collection of settings for connecting iOS mobile devices to Administration Server. The user installs an iOS MDM profile to a mobile device, after which this mobile device connects to Administration Server.
iOS MDM Server
A component of Kaspersky Security Center that is installed on a client device, allowing connection of iOS mobile devices to the Administration Server and management of iOS mobile devices through Apple Push Notifications (APNs).
JavaScript
A programming language that expands the performance of web pages. Web pages created using JavaScript can perform functions (for example, change the view of interface elements or open additional windows) without refreshing the web page with new data from a web server. To view pages created by using JavaScript, enable JavaScript support in the configuration of your browser.
Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN)
Kaspersky Private Security Network is a solution that gives users of devices with Kaspersky applications installed access to reputation databases of Kaspersky Security Network and other statistical data—without sending data from their devices to Kaspersky Security Network. Kaspersky Private Security Network is designed for corporate customers who are unable to participate in Kaspersky Security Network for any of the following reasons:
- Devices are not connected to the internet.
- Transmission of any data outside the country or the corporate LAN is prohibited by law or corporate security policies.
Kaspersky Security Center Administrator
The person managing application operations through the Kaspersky Security Center remote centralized administration system.
Kaspersky Security Center Operator
A user who monitors the status and operation of a protection system managed with Kaspersky Security Center.
Kaspersky Security Center System Health Validator (SHV)
A component of Kaspersky Security Center designed for checking the operating system's operability in case of concurrent operation of Kaspersky Security Center and Microsoft NAP.
Kaspersky Security Center Web Server
A component of Kaspersky Security Center that is installed together with Administration Server. Web Server is designed for transmission, over a network, of stand-alone installation packages, iOS MDM profiles, and files from a shared folder.
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN)
An infrastructure of cloud services that provides access to the Kaspersky database with constantly updated information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software. Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky applications to threats, improves the performance of some protection components, and reduces the likelihood of false positives.
Kaspersky update servers
HTTP(S) servers at Kaspersky from which Kaspersky applications download database and application module updates.
KES device
A mobile device that is connected to Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server and managed through the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android app.
Key file
A file in xxxxxxxx.key format that makes it possible to use a Kaspersky application under a trial or commercial license.
License term
A time period during which you have access to the application features and rights to use additional services. The services you can use depend on the type of the license.
Licensed applications group
A group of applications created on the basis of criteria set by the administrator (for example, by vendor), for which statistics of installations on client devices are maintained.
Local installation
Installation of a security application on a device on a corporate network that presumes manual installation startup from the distribution package of the security application or manual startup of a published installation package that was pre-downloaded to the device.
Local task
A task defined and running on a single client computer.
Managed devices
Corporate networked devices that are included in an administration group.
Management plug-in
A specialized component that provides the interface for application management through Administration Console. Each application has its own plug-in. It is included in all Kaspersky applications that can be managed by using Kaspersky Security Center.
Manual installation
Installation of a security application on a device in the corporate network from the distribution package. Manual installation requires the involvement of an administrator or another IT specialist. Usually manual installation is done if remote installation has completed with an error.
MITM attack
Man in The Middle. An attack on the IT infrastructure of an organization in which a hacker hijacks the communication link between two access points, relays it, and modifies the connection between these access points if necessary.
Mobile Device Server
A component of Kaspersky Security Center that provides access to mobile devices and allows you to manage them through Administration Console.
Network Agent
A Kaspersky Security Center component that enables interaction between the Administration Server and Kaspersky applications that are installed on a specific network node (workstation or server). This component is common to all of the company's applications for Microsoft Windows. Separate versions of Network Agent exist for Kaspersky applications developed for Unix-like OS and macOS.
Network anti-virus protection
A set of technical and organizational measures that lower the risk of allowing viruses and spam to penetrate the network of an organization, and that prevent network attacks, phishing, and other threats. Network security increases when you use security applications and services and when you apply and adhere to the corporate data security policy.
Network protection status
Current protection status, which defines the safety of corporate networked devices. The network protection status includes such factors as installed security applications, usage of license keys, and number and types of threats detected.
Patch importance level
Attribute of the patch. There are five importance levels for Microsoft patches and third-party patches:
- Critical
- High
- Medium
- Low
- Unknown
The importance level of a third-party patch or Microsoft patch is determined by the least favorable severity level among the vulnerabilities that the patches should fix.
Policy
A policy determines an application's settings and manages the ability to configure that application on computers within an administration group. An individual policy must be created for each application. You can create multiple policies for applications installed on computers in each administration group, but only one policy can be applied at a time to each application within an administration group.
Program settings
Application settings that are common to all types of tasks and govern the overall operation of the application, such as application performance settings, report settings, and backup settings.
Protection status
Current protection status, which reflects the level of computer security.
Provisioning profile
Collection of settings for applications' operation on iOS mobile devices. A provisioning profile contains information about the license; it is linked to a specific application.
Remote installation
Installation of Kaspersky applications by using the services provided by Kaspersky Security Center.
Restoration
Relocation of the original object from Quarantine or Backup to its original folder where the object had been stored before it was quarantined, disinfected or deleted, or to a user-defined folder.
Restoration of Administration Server data
Restoration of Administration Server data from the information saved in Backup by using the backup utility. The utility can restore:
- Database of the Administration Server (policies, tasks, application settings, events saved on the Administration Server)
- Configuration information about the structure of administration groups and client devices
- Repository of the installation files for remote installation of applications (content of the folders: Packages, Uninstall Updates)
- Administration Server certificate
Service provider's administrator
A staff member at an anti-virus protection service provider. This administrator performs installation and maintenance jobs for anti-virus protection systems based on Kaspersky anti-virus products and also provides technical support to customers.
Shared certificate
A certificate intended for identifying the user's mobile device.
SSL
A data encryption protocol used on the internet and local networks. The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol is used in web applications to create a secure connection between a client and server.
Task
Functions performed by the Kaspersky application are implemented as tasks, such as: Real-time file protection, Full computer scan, and Database update.
Task for specific devices
A task assigned to a set of client devices from arbitrary administration groups and performed on those devices.
Task settings
Application settings that are specific for each task type.
UEFI protection device
Device with a Kaspersky solution or application for UEFI integrated at the BIOS level. Integrated protection ensures device security from the moment the system starts, while protection on devices without integrated software begins functioning only after the security application starts.
Update
The procedure of replacing or adding new files (databases or application modules) retrieved from the Kaspersky update servers.
Upgrade of Kaspersky Security Center
The procedure of installing a newer version of Kaspersky Security Center on a device that has an earlier version of this application installed.
Virtual Administration Server
A component of Kaspersky Security Center, designed for management of the protection system of a client organization's network.
Virtual Administration Server is a particular case of a secondary Administration Server and has the following restrictions as compared with a physical Administration Server:
- Virtual Administration Server can be created only on a primary Administration Server.
- Virtual Administration Server uses the primary Administration Server database in its operation. Data backup and restoration tasks, as well as update scan and download tasks, are not supported on a virtual Administration Server.
- Virtual Server does not support creation of secondary Administration Servers (including virtual Servers).
Virus activity threshold
Maximum allowed number of events of the specified type within a limited time; when this number is exceeded, it is interpreted as increased virus activity and as a threat of a virus outbreak. This feature is important during periods of virus outbreaks because it enables administrators to respond in a timely manner to virus attack threats.
Virus outbreak
A series of deliberate attempts to infect a device with a virus.
Vulnerability
A flaw in an operating system or an application that may be exploited by malware makers to penetrate the operating system or application, and corrupt its integrity. The presence of a large number of vulnerabilities in an operating system makes it unreliable, because viruses that penetrate the operating system may cause disruptions in the operating system itself and in installed applications.
Windows Server Update Services (WSUS)
An application used for distribution of updates for Microsoft applications on users' computers in an organization's network.
Page top
Information about third-party code
Information about third-party code is contained in the file legal_notices.txt, in the application installation folder.
Page top
Trademark notices
Registered trademarks and service marks are the property of their respective owners.
Adobe, Acrobat, Flash, Shockwave and PostScript are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Adobe in the United States and/or other countries.
AMD, AMD64 are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Amazon, Amazon Web Services, AWS, Amazon EC2, AWS Marketplace are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates.
Apache is either a registered trademark or a trademark of the Apache Software Foundation.
Apple, AirPlay, AirDrop, AirPrint, App Store, Apple Configurator, AppleScript, FaceTime, FileVault, iBook, iBooks, iCloud, iPad, iPhone, iTunes, Leopard, macOS, Mac, Mac OS, OS X, Safari, Snow Leopard, Tiger, QuickTime, and Touch ID are trademarks of Apple Inc.
Arm is a registered trademark of Arm Limited (or its subsidiaries) in the US and/or elsewhere.
The Bluetooth word, mark and logos are owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc.
Ubuntu, LTS are registered trademarks of Canonical Ltd.
Cisco Systems, Cisco, Cisco Jabber, IOS are registered trademarks or trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
Citrix, XenServer are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Cloud Software Group, Inc., and/or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries.
Corel is a trademark or registered trademark of Corel Corporation and/or its subsidiaries in Canada, the United States and/or other countries.
Cloudflare, the Cloudflare logo, and Cloudflare Workers are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of Cloudflare, Inc. in the United States and other jurisdictions.
Dropbox is a trademark of Dropbox, Inc.
Radmin is a registered trademark of Famatech.
Firebird is a registered trademark of the Firebird Foundation.
Foxit is a registered trademark of Foxit Corporation.
FreeBSD is a registered trademark of The FreeBSD Foundation.
Google, Android, Chrome, Chromium, Dalvik, Firebase, Google Chrome, Google Earth, Google Play, Google Maps, Hangouts, Google Public DNS, and YouTube are trademarks of Google LLC.
EulerOS, FusionCompute, FusionSphere are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Intel, Core, Xeon are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries.
IBM, QRadar are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation, registered in many jurisdictions worldwide.
Node.js is a trademark of Joyent, Inc.
Linux is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries.
Logitech is either a registered trademark or trademark of Logitech in the United States and/or other countries.
Microsoft, Active Directory, ActiveSync, BitLocker, Excel, Forefront, Internet Explorer, InfoPath, Hyper-V, Microsoft Edge, MultiPoint, MS-DOS, Office 365, PowerShell, PowerPoint, SharePoint, SQL Server, OneNote, Outlook, Skype, Tahoma, Visio, Win32, Windows, Windows PowerShell, Windows Media, Windows Mobile, Windows Server, Windows Phone, Windows Vista, and Windows Azure are trademarks of the Microsoft group of companies.
CVE is a registered trademark of The MITRE Corporation.
Mozilla, Firefox, Thunderbird are trademarks of the Mozilla Foundation in the U.S. and other countries.
Novell is a registered trademark of Novell Enterprises Inc. in the United States and other countries.
NetWare is a registered trademark of Novell Inc. in the United States and other countries.
OpenVPN is a registered trademark of OpenVPN, Inc.
OpenSSL is a trademark owned by the OpenSSL Software Foundation.
Oracle, Java, JavaScript, and TouchDown are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Parallels, the Parallels logo, and Coherence are trademarks or registered trademarks of Parallels International GmbH.
Chef is a trademark or registered trademark of Progress Software Corporation and/or one of its subsidiaries or affiliates in the U.S. and/or other countries.
Puppet is a trademark or registered trademark of Puppet, Inc.
Python is a trademark or registered trademark of the Python Software Foundation.
Red Hat, Fedora, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux are trademarks or registered trademarks of Red Hat, Inc. or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
Ansible is a registered trademark of Red Hat, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
CentOS is a trademark or registered trademark of Red Hat, Inc. or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
BlackBerry is owned by Research In Motion Limited and is registered in the United States and may be pending or registered in other countries.
Rocky Linux is a trademark of The Rocky Enterprise Software Foundation.
SAMSUNG is a trademark of SAMSUNG in the United States or other countries.
Debian is a registered trademark of Software in the Public Interest, Inc.
Splunk, SPL are trademarks and registered trademarks of Splunk Inc. in the United States and other countries.
SUSE is a registered trademark of SUSE LLC in the United States and other countries.
Symbian trademark is owned by the Symbian Foundation Ltd.
OpenAPI is a trademark of The Linux Foundation.
UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively through X/Open Company Limited.
Zabbix is a registered trademark of Zabbix SIA.
Page top
Known issues
Kaspersky Security Center Web Console has a number of limitations that are not critical to operation of the application:
- The console displays the Alerts subsection in the Monitoring & reporting section of the main menu only if you added a license key for EDR Optimum to the Administration Server repository by entering the activation code.
- To ensure encryption strength, the Administration Server certificate must be signed using SHA-2 and have a minimum key length 2048. If you need to reissue the certificate, refer to the Kaspersky Security Center Knowledge Base.
- If you create a task with the Every N days and By days of week scheduling settings in Kaspersky Security Center 15.1 Web Console, and then open the task in earlier versions of Kaspersky Security Center Web Console or Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console (for example, when the task is also applied on the secondary Administration Servers which can be both Linux-based and Windows-based), the scheduling settings may be displayed incorrectly, or an error may occur.
- When you configure export to SIEM systems in Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, and select the UDP protocol, an error is returned after you click the Check connection button, since UDP does not establish a connection and the data delivery cannot be guaranteed.
- When you run a task to remove Network Agent from a device based on Arm architecture and running Astra Linux Special Edition RUSB.10015-01 (operational update 1.7), Network Agent is successfully removed, but the task status for the current progress in the task list is frozen.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy displays a protection level that does not match the protection level displayed in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- The properties window of the Kaspersky Device Management for iOS policy still contains the Settings of EAS devices section, even though Exchange ActiveSync is no longer supported.
- Connection to KSN through HTTPS fails if Kaspersky Security Center is installed on a device with Cyrillic symbols in the device name and KSN Proxy is enabled on the Administration Server.
- When you try to change the properties of a user account that has the Request authentication to check for permission to modify user accounts option enabled, and then click Cancel in the Account protection window, an unexpected error occurs.
- After successful completion of a local IOC Scan task, the task status is displayed as Scheduled in the task list.
- If you change the time or time zone on your device, you must restart the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console service.
- If a proxy is used on the device, and the proxy environment variables are set, the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console installer may freeze.
- When you import the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points or Update verification task, the Select devices to which the task will be assigned option is enabled. These tasks cannot be assigned to a device selection or specific devices. If you assign the Download updates to the repositories of distribution points or Update verification task to specific devices, the task will be imported incorrectly.
- If you perform Active Directory polling by using a Linux distribution point with Network Agent version 15 installed, you can poll only Active Directory domains for which you specify the address and user credentials. Polling of the current Active Directory domain and the Active Directory domain forest is not available.
- Client devices might not be found after running Windows network polling.
- In the Add secondary Administration Server wizard, if you specify an account with enabled two-step verification for authentication on the future secondary Server, the wizard finishes with an error. To resolve this issue, specify an account for which two-step verification is disabled or create the hierarchy from the future secondary Server.
- While signing in to Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, if you use domain authentication and specify a virtual Administration Server to connect to, then you sign out, and then try to sign in to the primary Administration Server, Kaspersky Security Center Web Console connects to the virtual Administration Server. To connect to the primary Administration Server, reopen the browser.
- The Quick/Full Windows network polling returns an empty result.
- If you install Kaspersky Security Center Web Console with Identity and Access Manager, and then change the Administration Server for Kaspersky Security Center Web Console, Identity and Access Manager does not get the information about the new Administration Server.
- A managed device that has more than one network adapter sends Administration Server information about the MAC address of the network adapter that is not the one that is used to connect to Administration Server.
- If you start an Execute scripts remotely task for a specified account and change an account it is assigned for in the task settings, the changes will not be saved. To change the account the task is assigned to, stop the task in the task settings and restart it.
- Test connection to SIEM fails when the CEF data format is selected.


















































 ) on the right.
) on the right.
