Merging a client and VFS into one executable file
Let's examine a Client program using Berkeley sockets. Calls made by the Client must be sent to VFS. The normal path consists of starting a separate VFS process and creating an IPC channel. Alternatively, you can integrate VFS functionality directly into the Client executable file. To do so, when building the Client executable file, you need to link it to the vfs_local library that will receive calls, and link it to the implementation libraries vfs_implementation and dnet_implementation.
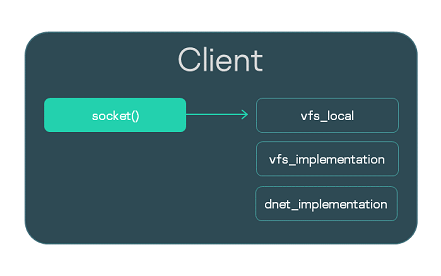
Local linking with VFS is convenient during debugging. In addition, calls for working with the network can be handled much faster due to the exclusion of IPC calls. Nevertheless, insulation of the VFS in a separate process and IPC interaction with it is always recommended as a more secure approach.
Below is a build script for the Client executable file.
CMakeLists.txt
project (client)
include (platform/nk)
# Set compile flags
project_header_default ("STANDARD_GNU_11:YES" "STRICT_WARNINGS:NO")
# Generates the Client.edl.h file
nk_build_edl_files (client_edl_files NK_MODULE "client" EDL "${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/resources/edl/Client.edl")
add_executable (Client "src/client.c")
add_dependencies (Client client_edl_files)
# Linking with VFS libraries
target_link_libraries (Client ${vfs_LOCAL_LIB} ${vfs_IMPLEMENTATION_LIB} ${dnet_IMPLEMENTATION_LIB}
If the Client uses file systems, it must also be linked to the vfs_fs library and to the implementation of the utilized file system in addition to its linking to vfs_local. You also need to add a block device driver to the solution.